User login
Antithrombotic therapy not warranted in COVID-19 outpatients
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapy in clinically stable, nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients does not offer protection against adverse cardiovascular or pulmonary events, new randomized clinical trial results suggest.
Antithrombotic therapy has proven useful in acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19, but in this study, treatment with aspirin or apixaban (Eliquis) did not reduce the rate of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary causes in patients ill with COVID-19 but who were not hospitalized.
“Among symptomatic, clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19, treatment with aspirin or apixaban compared with placebo did not reduce the rate of a composite clinical outcome,” the authors conclude. “However, the study was terminated after enrollment of 9% of participants because of a primary event rate lower than anticipated.”
The study, which was led by Jean M. Connors, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, was published online October 11 in JAMA.
The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was a randomized, adaptive, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that sought to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7,000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
The trial was conducted at 52 sites in the U.S. between Sept. 2020 and June 2021, with final follow-up this past August 5, and involved minimal face-to-face interactions with study participants.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164 patients), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
The primary endpoint was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause.
The trial was terminated early this past June by the independent data monitoring committee because of lower than anticipated event rates. At the time, just 657 symptomatic outpatients with COVID-19 had been enrolled.
The median age of the study participants was 54 years (Interquartile Range [IQR] 46-59); 59% were women.
The median time from diagnosis to randomization was 7 days, and the median time from randomization to initiation of study medications was 3 days.
The trial’s primary efficacy and safety analyses were restricted to patients who received at least one dose of trial medication, for a final number of 558 patients.
Among these patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5 mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group.
The researchers found that the absolute risk reductions compared with placebo for the primary outcome were 0.0% (95% confidence interval not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% confidence interval, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
No major bleeding events were reported.
The absolute risk differences compared with placebo for clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding events were 2% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%) in the aspirin group, 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%) in the prophylactic-dose apixaban group, and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) in the therapeutic-dose apixaban group.
Safety and efficacy results were similar in all randomly assigned patients.
The researchers speculated that a combination of two demographic shifts over time may have led to the lower than anticipated rate of events in ACTIV-4B.
“First, the threshold for hospital admission has markedly declined since the beginning of the pandemic, such that hospitalization is no longer limited almost exclusively to those with severe pulmonary distress likely to require mechanical ventilation,” they write. “As a result, the severity of illness among individuals with COVID-19 and destined for outpatient care has declined.”
“Second, at least within the U.S., where the trial was conducted, individuals currently being infected with SARS-CoV-2 tend to be younger and have fewer comorbidities when compared with individuals with incident infection at the onset of the pandemic,” they add.
Further, COVID-19 testing was quite limited early in the pandemic, they note, “and it is possible that the anticipated event rates based on data from registries available at that time were overestimated because the denominator (that is, the number of infected individuals overall) was essentially unknown.”
Robust evidence
“The ACTIV-4B trial is the first randomized trial to generate robust evidence about the effects of antithrombotic therapy in outpatients with COVID-19,” Otavio Berwanger, MD, PhD, director of the Academic Research Organization, Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paulo-SP, Brazil, told this news organization.
“It should be noted that this was a well-designed trial with low risk of bias. On the other hand, the main limitation is the low number of events and, consequently, the limited statistical power,” said Dr. Berwanger, who wrote an accompanying editorial.
The ACTIV-4B trial has immediate implications for clinical practice, he added.
“In this sense, considering the neutral results for major cardiopulmonary outcomes, the use of aspirin or apixaban for the management of outpatients with COVID-19 should not be recommended.”
ACTIV-4B also provides useful information for the steering committees of other ongoing trials of antithrombotic therapy for patients with COVID-19 who are not hospitalized, Dr. Berwanger added.
“In this sense, probably issues like statistical power, outcome choices, recruitment feasibility, and even futility would need to be revisited. And finally, lessons learned from the implementation of an innovative, pragmatic, and decentralized trial design represent an important legacy for future trials in cardiovascular diseases and other common conditions,” he said.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Connors reports financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Abbott, Alnylam, Takeda, Roche, and Sanofi. Dr. Berwanger reports financial relationships with AstraZeneca, Amgen, Servier, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Novartis, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccination rates vary by zodiac sign
COVID-19 vaccination rates vary dramatically by astrological sign, with Leos at the top of the list and Scorpios at the bottom, according to The Salt Lake Tribune.
The Salt Lake County Health Department calculated the rates based on anonymous birth dates from the county’s vaccination data and then compared those figures to national estimates for the overall population represented by each sign.
“Now that Mercury is not in retrograde, we’re just going to leave this here … (and yes, this is based on data),” the Health Department wrote in a Twitter post on Tuesday.
“The COVID-19 vaccine is backed by science and is no way influenced by horoscopes,” the department continued. “But come on Scorpios!”
According to the graphic, 70% of those with the Leo sign are fully vaccinated, followed by Aquarius at 67%, and Aries and Sagittarius both at 59%. The other signs range from 58% to 50%, in descending order: Cancer, Taurus, Gemini, Libra, Pisces, Capricorn, and Virgo. Scorpio sits at the bottom of the list, with 46% fully vaccinated.
Notably, three of the top four signs are elemental fire signs, The Salt Lake Tribune noted.
“We are overachievers,” Jeff Eason, an Aries and the department’s bureau manager of population health and informatics, who did the analysis, told the newspaper.
The Health Department’s post sparked positive and negative feedback across social media, with some musing about their own sign’s inclinations and others scoffing at astrology altogether.
“What we’re really doing is finding new and different ways to keep our community talking about vaccination when there is significant message fatigue around this topic,” the department wrote in the comments.
The range of vaccination rates was startlingly wide, Mr. Eason told The Salt Lake Tribune. But he noted that the difference “could all come down to denominators.”
Each sign’s vaccination rate was ranked almost exactly inverse to its share of the overall population, the newspaper reported. Scorpios and Virgos make up 9.4% and 9.3% of the U.S. population, respectively, as compared with 7.1% for Leos and 6.3% for Aquarians.
If the 12 astrological signs were more evenly distributed in Salt Lake County than nationally, Mr. Eason said, the range of vaccinations rates wouldn’t be as wide as the analysis shows.
“Obviously, it’s not super scientific because we are talking astrology,” Nicholas Rupp, a spokesman for the health department and a vaccinated Scorpio, told the newspaper.
Still, health department officials wanted to do the analysis as a fun way to start conversations and promote vaccinations. About 59% of Salt Lake County residents are fully vaccinated, and about 54% of Utah residents are fully vaccinated.
“We do have message fatigue around vaccines,” Mr. Rupp said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 vaccination rates vary dramatically by astrological sign, with Leos at the top of the list and Scorpios at the bottom, according to The Salt Lake Tribune.
The Salt Lake County Health Department calculated the rates based on anonymous birth dates from the county’s vaccination data and then compared those figures to national estimates for the overall population represented by each sign.
“Now that Mercury is not in retrograde, we’re just going to leave this here … (and yes, this is based on data),” the Health Department wrote in a Twitter post on Tuesday.
“The COVID-19 vaccine is backed by science and is no way influenced by horoscopes,” the department continued. “But come on Scorpios!”
According to the graphic, 70% of those with the Leo sign are fully vaccinated, followed by Aquarius at 67%, and Aries and Sagittarius both at 59%. The other signs range from 58% to 50%, in descending order: Cancer, Taurus, Gemini, Libra, Pisces, Capricorn, and Virgo. Scorpio sits at the bottom of the list, with 46% fully vaccinated.
Notably, three of the top four signs are elemental fire signs, The Salt Lake Tribune noted.
“We are overachievers,” Jeff Eason, an Aries and the department’s bureau manager of population health and informatics, who did the analysis, told the newspaper.
The Health Department’s post sparked positive and negative feedback across social media, with some musing about their own sign’s inclinations and others scoffing at astrology altogether.
“What we’re really doing is finding new and different ways to keep our community talking about vaccination when there is significant message fatigue around this topic,” the department wrote in the comments.
The range of vaccination rates was startlingly wide, Mr. Eason told The Salt Lake Tribune. But he noted that the difference “could all come down to denominators.”
Each sign’s vaccination rate was ranked almost exactly inverse to its share of the overall population, the newspaper reported. Scorpios and Virgos make up 9.4% and 9.3% of the U.S. population, respectively, as compared with 7.1% for Leos and 6.3% for Aquarians.
If the 12 astrological signs were more evenly distributed in Salt Lake County than nationally, Mr. Eason said, the range of vaccinations rates wouldn’t be as wide as the analysis shows.
“Obviously, it’s not super scientific because we are talking astrology,” Nicholas Rupp, a spokesman for the health department and a vaccinated Scorpio, told the newspaper.
Still, health department officials wanted to do the analysis as a fun way to start conversations and promote vaccinations. About 59% of Salt Lake County residents are fully vaccinated, and about 54% of Utah residents are fully vaccinated.
“We do have message fatigue around vaccines,” Mr. Rupp said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 vaccination rates vary dramatically by astrological sign, with Leos at the top of the list and Scorpios at the bottom, according to The Salt Lake Tribune.
The Salt Lake County Health Department calculated the rates based on anonymous birth dates from the county’s vaccination data and then compared those figures to national estimates for the overall population represented by each sign.
“Now that Mercury is not in retrograde, we’re just going to leave this here … (and yes, this is based on data),” the Health Department wrote in a Twitter post on Tuesday.
“The COVID-19 vaccine is backed by science and is no way influenced by horoscopes,” the department continued. “But come on Scorpios!”
According to the graphic, 70% of those with the Leo sign are fully vaccinated, followed by Aquarius at 67%, and Aries and Sagittarius both at 59%. The other signs range from 58% to 50%, in descending order: Cancer, Taurus, Gemini, Libra, Pisces, Capricorn, and Virgo. Scorpio sits at the bottom of the list, with 46% fully vaccinated.
Notably, three of the top four signs are elemental fire signs, The Salt Lake Tribune noted.
“We are overachievers,” Jeff Eason, an Aries and the department’s bureau manager of population health and informatics, who did the analysis, told the newspaper.
The Health Department’s post sparked positive and negative feedback across social media, with some musing about their own sign’s inclinations and others scoffing at astrology altogether.
“What we’re really doing is finding new and different ways to keep our community talking about vaccination when there is significant message fatigue around this topic,” the department wrote in the comments.
The range of vaccination rates was startlingly wide, Mr. Eason told The Salt Lake Tribune. But he noted that the difference “could all come down to denominators.”
Each sign’s vaccination rate was ranked almost exactly inverse to its share of the overall population, the newspaper reported. Scorpios and Virgos make up 9.4% and 9.3% of the U.S. population, respectively, as compared with 7.1% for Leos and 6.3% for Aquarians.
If the 12 astrological signs were more evenly distributed in Salt Lake County than nationally, Mr. Eason said, the range of vaccinations rates wouldn’t be as wide as the analysis shows.
“Obviously, it’s not super scientific because we are talking astrology,” Nicholas Rupp, a spokesman for the health department and a vaccinated Scorpio, told the newspaper.
Still, health department officials wanted to do the analysis as a fun way to start conversations and promote vaccinations. About 59% of Salt Lake County residents are fully vaccinated, and about 54% of Utah residents are fully vaccinated.
“We do have message fatigue around vaccines,” Mr. Rupp said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Better COVID-19 outcomes confirmed in TNF inhibitor users
Among patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) who get COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization and death is lower if they are receiving tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor monotherapy, compared with receiving most other common drugs for these conditions, with or without TNF inhibitors, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open The only combination not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization or death was TNF inhibitor therapy with methotrexate.
“These findings support the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy during the pandemic and warrant further research investigating the association of other biologic therapies with COVID-19 outcomes,” write Zara Izadi, MPharm, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues. “Treatment with TNF inhibitor combination therapy was associated with a more favorable safety profile when methotrexate rather than azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine was used, suggesting that clinicians would benefit from weighing the risks versus benefits of deescalating treatment or changing medications when a patient is receiving concomitant TNF inhibitors and azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine,” they write.
Findings mirror those seen in other settings
These findings are in line with what has been found in other settings, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center, vice chair of clinical research, and medical director of the dermatology clinical studies unit at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In the beginning of the pandemic, there was concern about use of immune-modulating treatments, and many patients self-discontinued treatments like TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “This has ultimately proved unnecessary and unfortunately resulted in harm to many patients due to flaring of their underlying disease.”
Dr. Gelfand emphasized the importance of vaccinating patients against COVID-19 as soon as possible and of getting a third dose for those who are already fully vaccinated with the Pfizer or Moderna shots, as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“I typically recommend this third dose be taken 6 months after the second dose,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The good news is that TNF inhibitors do not seem to meaningfully impact response to mRNA vaccines.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed data from three international registries of adults with rheumatic diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis who had COVID-19 between March 12, 2020, and Feb. 1, 2021. The registries included the Secure Epidemiology of Coronavirus Under Research Exclusion for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SECURE-IBD) registry, the Psoriasis Patient Registry for Outcomes, Therapy and Epidemiology of COVID-19 Infection (PsoProtect), and the physician-reported registry from the Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA).
The population included 6,077 patients from 74 countries. About half of the cohort (52.9%) were from Europe; more than half were women (58.6%). The average age was 48 years. A little over one-third of the patients (35.3%) had rheumatoid arthritis, 25.3% had Crohn’s disease, 12.5% had ulcerative colitis, 10.3% had spondyloarthritis, and 9.3% had psoriatic arthritis. Smaller percentages had psoriasis (4.9%), another type of arthritis or multiple types (1.7%), or another inflammatory bowel disease (0.6%).
One in five patients (21.3%) were hospitalized, and 3.1% died. The researchers compared outcomes for those who were receiving TNF inhibitor therapy alone to outcomes for those who were taking azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine therapy (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), methotrexate (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. They adjusted their analysis to account for active disease and common comorbidities, as well as geography and the period during the pandemic in which the person was admitted, because treatment regimens and hospitalization indications have varied over time.
All of the therapies except the combination of TNF inhibitors and methotrexate were associated with higher odds of hospitalization and death than TNF inhibitor monotherapy.
The researchers explored several possible explanations for the findings, including the possibility that high serum TNF concentrations may have been associated with more organ damage at the time of COVID-19 admission, owing to interaction with SARS-CoV-2–associated hyperinflammation.
“Therefore, blocking TNF could inhibit this detrimental immune response,” the authors write. “Multiple case series reporting favorable outcomes among patients receiving TNF inhibitor therapy support this assertion.”
Another possibility relates to the effects of taking non–TNF inhibitor medications for immunosuppression. The authors note that thiopurine medications are linked to a greater risk for opportunistic viral infections and that JAK inhibitors may reduce the body’s ability to clear the virus because of its suppression of innate immune response.
The authors also postulate that methotrexate may lower the likelihood of cytokine storm linked to COVID-19, even though methotrexate monotherapy was associated with poorer outcomes. “This association could mean that TNF inhibitor therapy is exerting a protective benefit or that methotrexate therapy is exerting a harmful consequence,” the authors write.
Caution needed in interpreting uncontrolled, registry-based data
The findings were not surprising to Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the research.
“We’ve been monitoring IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] patients through the Secure registry similar to the rheumatologic and dermatologic societies and have not identified a signal of harm from any international groups,” Dr. Hanauer told this news organization. He noted that these registries also have not shown an increased risk for COVID-19 complications among patients receiving TNF inhibitors, antiadhesion therapies, or anti–IL12/23 inhibitors, compared with the general population not taking these therapies.
The study’s size and the diversity of patients strengthen its findings. However, the registries’ use of convenience sampling increases the potential for reporting bias, although the results remained similar after a sensitivity analysis. The study also lacked a control group, and the registries did not collect data uniformly.
“These are databases that rely on reporting from investigators and are not comprehensive prospective studies,” Dr. Hanauer noted as another study limitation.
Dr. Gelfand similarly advised caution in interpreting these findings, inasmuch as the study is a “collection of spontaneous reports” that should be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than testing.
“Fortunately, more rigorous studies have been conducted, typically in large medical record systems, and have confirmed the hypothesis that TNF inhibitors are associated with a lower risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, compared to other treatments,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Previous smaller studies similarly found better outcomes among patients taking TNF inhibitors, compared with other therapies, but their participants were predominantly from North America and Europe, noted Licio A. Velloso, MD, PhD, of the University of Campinas, in São Paulo, in an accompanying commentary.
On the basis of the findings of this study, “which included a much larger sample comprising distinct diseases and patients with a multitude of genetic backgrounds, the evidence in favor of the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy for patients with IMIDs during the COVID-19 pandemic has become more substantial,” Dr. Velloso writes. “The finding that maintenance of TNF inhibitor monotherapy is associated with reductions in the risk of severe COVID-19 among patients with IMIDs offers new perspective that may guide health care professionals in the difficult decisions regarding therapeutic approaches among this specific group of patients.”
The research was funded by the American College of Rheumatology, the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Center, and the Psoriasis Association. Many authors reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Velloso has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant to companies that market TNF inhibitors. Dr. Gelfand has consulted for and received research grants from companies that market TNF inhibitors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) who get COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization and death is lower if they are receiving tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor monotherapy, compared with receiving most other common drugs for these conditions, with or without TNF inhibitors, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open The only combination not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization or death was TNF inhibitor therapy with methotrexate.
“These findings support the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy during the pandemic and warrant further research investigating the association of other biologic therapies with COVID-19 outcomes,” write Zara Izadi, MPharm, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues. “Treatment with TNF inhibitor combination therapy was associated with a more favorable safety profile when methotrexate rather than azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine was used, suggesting that clinicians would benefit from weighing the risks versus benefits of deescalating treatment or changing medications when a patient is receiving concomitant TNF inhibitors and azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine,” they write.
Findings mirror those seen in other settings
These findings are in line with what has been found in other settings, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center, vice chair of clinical research, and medical director of the dermatology clinical studies unit at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In the beginning of the pandemic, there was concern about use of immune-modulating treatments, and many patients self-discontinued treatments like TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “This has ultimately proved unnecessary and unfortunately resulted in harm to many patients due to flaring of their underlying disease.”
Dr. Gelfand emphasized the importance of vaccinating patients against COVID-19 as soon as possible and of getting a third dose for those who are already fully vaccinated with the Pfizer or Moderna shots, as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“I typically recommend this third dose be taken 6 months after the second dose,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The good news is that TNF inhibitors do not seem to meaningfully impact response to mRNA vaccines.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed data from three international registries of adults with rheumatic diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis who had COVID-19 between March 12, 2020, and Feb. 1, 2021. The registries included the Secure Epidemiology of Coronavirus Under Research Exclusion for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SECURE-IBD) registry, the Psoriasis Patient Registry for Outcomes, Therapy and Epidemiology of COVID-19 Infection (PsoProtect), and the physician-reported registry from the Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA).
The population included 6,077 patients from 74 countries. About half of the cohort (52.9%) were from Europe; more than half were women (58.6%). The average age was 48 years. A little over one-third of the patients (35.3%) had rheumatoid arthritis, 25.3% had Crohn’s disease, 12.5% had ulcerative colitis, 10.3% had spondyloarthritis, and 9.3% had psoriatic arthritis. Smaller percentages had psoriasis (4.9%), another type of arthritis or multiple types (1.7%), or another inflammatory bowel disease (0.6%).
One in five patients (21.3%) were hospitalized, and 3.1% died. The researchers compared outcomes for those who were receiving TNF inhibitor therapy alone to outcomes for those who were taking azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine therapy (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), methotrexate (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. They adjusted their analysis to account for active disease and common comorbidities, as well as geography and the period during the pandemic in which the person was admitted, because treatment regimens and hospitalization indications have varied over time.
All of the therapies except the combination of TNF inhibitors and methotrexate were associated with higher odds of hospitalization and death than TNF inhibitor monotherapy.
The researchers explored several possible explanations for the findings, including the possibility that high serum TNF concentrations may have been associated with more organ damage at the time of COVID-19 admission, owing to interaction with SARS-CoV-2–associated hyperinflammation.
“Therefore, blocking TNF could inhibit this detrimental immune response,” the authors write. “Multiple case series reporting favorable outcomes among patients receiving TNF inhibitor therapy support this assertion.”
Another possibility relates to the effects of taking non–TNF inhibitor medications for immunosuppression. The authors note that thiopurine medications are linked to a greater risk for opportunistic viral infections and that JAK inhibitors may reduce the body’s ability to clear the virus because of its suppression of innate immune response.
The authors also postulate that methotrexate may lower the likelihood of cytokine storm linked to COVID-19, even though methotrexate monotherapy was associated with poorer outcomes. “This association could mean that TNF inhibitor therapy is exerting a protective benefit or that methotrexate therapy is exerting a harmful consequence,” the authors write.
Caution needed in interpreting uncontrolled, registry-based data
The findings were not surprising to Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the research.
“We’ve been monitoring IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] patients through the Secure registry similar to the rheumatologic and dermatologic societies and have not identified a signal of harm from any international groups,” Dr. Hanauer told this news organization. He noted that these registries also have not shown an increased risk for COVID-19 complications among patients receiving TNF inhibitors, antiadhesion therapies, or anti–IL12/23 inhibitors, compared with the general population not taking these therapies.
The study’s size and the diversity of patients strengthen its findings. However, the registries’ use of convenience sampling increases the potential for reporting bias, although the results remained similar after a sensitivity analysis. The study also lacked a control group, and the registries did not collect data uniformly.
“These are databases that rely on reporting from investigators and are not comprehensive prospective studies,” Dr. Hanauer noted as another study limitation.
Dr. Gelfand similarly advised caution in interpreting these findings, inasmuch as the study is a “collection of spontaneous reports” that should be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than testing.
“Fortunately, more rigorous studies have been conducted, typically in large medical record systems, and have confirmed the hypothesis that TNF inhibitors are associated with a lower risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, compared to other treatments,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Previous smaller studies similarly found better outcomes among patients taking TNF inhibitors, compared with other therapies, but their participants were predominantly from North America and Europe, noted Licio A. Velloso, MD, PhD, of the University of Campinas, in São Paulo, in an accompanying commentary.
On the basis of the findings of this study, “which included a much larger sample comprising distinct diseases and patients with a multitude of genetic backgrounds, the evidence in favor of the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy for patients with IMIDs during the COVID-19 pandemic has become more substantial,” Dr. Velloso writes. “The finding that maintenance of TNF inhibitor monotherapy is associated with reductions in the risk of severe COVID-19 among patients with IMIDs offers new perspective that may guide health care professionals in the difficult decisions regarding therapeutic approaches among this specific group of patients.”
The research was funded by the American College of Rheumatology, the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Center, and the Psoriasis Association. Many authors reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Velloso has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant to companies that market TNF inhibitors. Dr. Gelfand has consulted for and received research grants from companies that market TNF inhibitors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) who get COVID-19, the risk for hospitalization and death is lower if they are receiving tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor monotherapy, compared with receiving most other common drugs for these conditions, with or without TNF inhibitors, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open The only combination not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization or death was TNF inhibitor therapy with methotrexate.
“These findings support the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy during the pandemic and warrant further research investigating the association of other biologic therapies with COVID-19 outcomes,” write Zara Izadi, MPharm, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues. “Treatment with TNF inhibitor combination therapy was associated with a more favorable safety profile when methotrexate rather than azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine was used, suggesting that clinicians would benefit from weighing the risks versus benefits of deescalating treatment or changing medications when a patient is receiving concomitant TNF inhibitors and azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine,” they write.
Findings mirror those seen in other settings
These findings are in line with what has been found in other settings, according to Joel M. Gelfand, MD, director of the psoriasis and phototherapy treatment center, vice chair of clinical research, and medical director of the dermatology clinical studies unit at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In the beginning of the pandemic, there was concern about use of immune-modulating treatments, and many patients self-discontinued treatments like TNF inhibitors,” Dr. Gelfand, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization. “This has ultimately proved unnecessary and unfortunately resulted in harm to many patients due to flaring of their underlying disease.”
Dr. Gelfand emphasized the importance of vaccinating patients against COVID-19 as soon as possible and of getting a third dose for those who are already fully vaccinated with the Pfizer or Moderna shots, as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“I typically recommend this third dose be taken 6 months after the second dose,” Dr. Gelfand said. “The good news is that TNF inhibitors do not seem to meaningfully impact response to mRNA vaccines.”
Study details
The researchers analyzed data from three international registries of adults with rheumatic diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis who had COVID-19 between March 12, 2020, and Feb. 1, 2021. The registries included the Secure Epidemiology of Coronavirus Under Research Exclusion for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SECURE-IBD) registry, the Psoriasis Patient Registry for Outcomes, Therapy and Epidemiology of COVID-19 Infection (PsoProtect), and the physician-reported registry from the Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA).
The population included 6,077 patients from 74 countries. About half of the cohort (52.9%) were from Europe; more than half were women (58.6%). The average age was 48 years. A little over one-third of the patients (35.3%) had rheumatoid arthritis, 25.3% had Crohn’s disease, 12.5% had ulcerative colitis, 10.3% had spondyloarthritis, and 9.3% had psoriatic arthritis. Smaller percentages had psoriasis (4.9%), another type of arthritis or multiple types (1.7%), or another inflammatory bowel disease (0.6%).
One in five patients (21.3%) were hospitalized, and 3.1% died. The researchers compared outcomes for those who were receiving TNF inhibitor therapy alone to outcomes for those who were taking azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine therapy (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), methotrexate (alone or with a TNF inhibitor), and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors. They adjusted their analysis to account for active disease and common comorbidities, as well as geography and the period during the pandemic in which the person was admitted, because treatment regimens and hospitalization indications have varied over time.
All of the therapies except the combination of TNF inhibitors and methotrexate were associated with higher odds of hospitalization and death than TNF inhibitor monotherapy.
The researchers explored several possible explanations for the findings, including the possibility that high serum TNF concentrations may have been associated with more organ damage at the time of COVID-19 admission, owing to interaction with SARS-CoV-2–associated hyperinflammation.
“Therefore, blocking TNF could inhibit this detrimental immune response,” the authors write. “Multiple case series reporting favorable outcomes among patients receiving TNF inhibitor therapy support this assertion.”
Another possibility relates to the effects of taking non–TNF inhibitor medications for immunosuppression. The authors note that thiopurine medications are linked to a greater risk for opportunistic viral infections and that JAK inhibitors may reduce the body’s ability to clear the virus because of its suppression of innate immune response.
The authors also postulate that methotrexate may lower the likelihood of cytokine storm linked to COVID-19, even though methotrexate monotherapy was associated with poorer outcomes. “This association could mean that TNF inhibitor therapy is exerting a protective benefit or that methotrexate therapy is exerting a harmful consequence,” the authors write.
Caution needed in interpreting uncontrolled, registry-based data
The findings were not surprising to Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, medical director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the research.
“We’ve been monitoring IBD [inflammatory bowel disease] patients through the Secure registry similar to the rheumatologic and dermatologic societies and have not identified a signal of harm from any international groups,” Dr. Hanauer told this news organization. He noted that these registries also have not shown an increased risk for COVID-19 complications among patients receiving TNF inhibitors, antiadhesion therapies, or anti–IL12/23 inhibitors, compared with the general population not taking these therapies.
The study’s size and the diversity of patients strengthen its findings. However, the registries’ use of convenience sampling increases the potential for reporting bias, although the results remained similar after a sensitivity analysis. The study also lacked a control group, and the registries did not collect data uniformly.
“These are databases that rely on reporting from investigators and are not comprehensive prospective studies,” Dr. Hanauer noted as another study limitation.
Dr. Gelfand similarly advised caution in interpreting these findings, inasmuch as the study is a “collection of spontaneous reports” that should be viewed as hypothesis-generating rather than testing.
“Fortunately, more rigorous studies have been conducted, typically in large medical record systems, and have confirmed the hypothesis that TNF inhibitors are associated with a lower risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes, compared to other treatments,” Dr. Gelfand said.
Previous smaller studies similarly found better outcomes among patients taking TNF inhibitors, compared with other therapies, but their participants were predominantly from North America and Europe, noted Licio A. Velloso, MD, PhD, of the University of Campinas, in São Paulo, in an accompanying commentary.
On the basis of the findings of this study, “which included a much larger sample comprising distinct diseases and patients with a multitude of genetic backgrounds, the evidence in favor of the continued use of TNF inhibitor monotherapy for patients with IMIDs during the COVID-19 pandemic has become more substantial,” Dr. Velloso writes. “The finding that maintenance of TNF inhibitor monotherapy is associated with reductions in the risk of severe COVID-19 among patients with IMIDs offers new perspective that may guide health care professionals in the difficult decisions regarding therapeutic approaches among this specific group of patients.”
The research was funded by the American College of Rheumatology, the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, the United Kingdom’s National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Center, and the Psoriasis Association. Many authors reported receiving grants and/or personal fees from a variety of pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Velloso has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer has served as a consultant to companies that market TNF inhibitors. Dr. Gelfand has consulted for and received research grants from companies that market TNF inhibitors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel backs COVID-19 boosters for nearly all adults
Editor’s note: This story was updated with the CDC director’s endorsement.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, has signed off on an advisory panel’s earlier unanimous vote to recommend boosters for the Moderna and Johnson and Johnson COVID vaccines.
The decision now means that millions of Americans are eligible to get a booster shot for either the Pfizer, Moderna, or J&J COVID vaccines.
“The evidence shows that all three COVID-19 vaccines authorized in the United States are safe – as demonstrated by the over 400 million vaccine doses already given. And, they are all highly effective in reducing the risk of severe disease, hospitalization, and death, even in the midst of the widely circulating Delta variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a CDC news release.
She also signed off on the panel’s suggestion that individuals can mix or match the booster from any one of the three available COVID-19 vaccines.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended in a late afternoon 15-0 vote that everyone over age 18 who are at least 2 months past their Johnson & Johnson vaccine should get a booster, an endorsement that affects an estimated 13 million Americans.
Those eligible for a booster at least 6 months after their last Moderna shot are the same groups who can get a Pfizer booster.
They are:
- Anyone over age 65.
- Those over age 18 with an underlying health condition that puts them at risk of severe COVID-19.
- Those over age 18 who may be at higher risk of a COVID-19 infection because they live or work in a risky setting.
These recommendations are in line with the Food and Drug Administration’s Oct. 20 authorization of the boosters, along with the ability to mix-and-match vaccines.
There are an estimated 47 million Pfizer recipients and 39 million people vaccinated with Moderna who are now eligible for a booster dose, according to data presented by the CDC.
Questions, concerns
Before voting, some committee members expressed discomfort in broadly recommending boosters, stressing that there is very little evidence supporting the need for boosters in people younger than age 50.
“I can’t say that I am comfortable that anybody under 50 – an otherwise healthy individual – needs a booster vaccine at this time with either Moderna or Pfizer,” said ACIP member Sarah Long, MD, professor of pediatrics at Drexel University in Philadelphia.
She said she would try to mitigate any potential harm by having some kind of age restriction on the otherwise worried well.
“We don’t usually have the vaccines [for] the worried well. We give it because we have a need that’s worth the risk, and there’s a burden of severity of disease,” Dr. Long said.
The evidence to date shows that all the vaccines authorized for use in the U.S. continue to protect people well against severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
But breakthrough infections are on the rise, especially for people who initially received the Johnson and Johnson one-dose vaccine.
On Oct. 21, Pfizer released data from a study of more than 10,000 fully vaccinated people. Half were randomly assigned to get a booster of their Comirnaty vaccine, the other half were given a placebo.
Over the ensuing 2.5 months, there were 5 COVID-19 cases in the boosted group, and 109 in the group that got a placebo.
The data were posted in a press release and have not yet been peer reviewed, but are the first to show clinical effectiveness of boosters at preventing COVID-19 infections.
Data recently considered by the FDA and CDC for booster doses come from studies that were mostly shorter and smaller. These studies looked at biomarkers of immunity like the concentration of antibodies in a person’s blood and the percentage of study participants who saw a boost to those antibodies.
The studies demonstrated that boosters indeed restore high levels of antibodies, but unlike the newest Pfizer data they were not able to show that these antibodies prevented COVID-19.
These studies also weren’t powered to pick up on any less common safety problems that might arise after another dose of the shots.
“Real world” recommendations
In the end, however, the panel felt it was more important to be permissive in allowing boosters so that individuals and their doctors could be free to make their own decisions.
“The decision made by the FDA and the ACIP recommendations, I think, reflects the real world. The public is going to do what they feel driven to do. This at least adds a scientific review of the currently available data,” said Jay Varkey, MD, an infectious disease physician and associate professor at Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved in the ACIP’s deliberations.
Dr. Varkey said he would recommend that anyone who is younger than 65, and who has no underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or obesity, speak with their doctor about their individual benefits and risks before getting a booster.
The CDC is planning to release a detailed suite of clinical considerations to help people weigh the risks and benefits of getting a booster.
Safety updates presented at the meeting show that serious adverse events after vaccination are extremely rare, but in some cases, they may rise above the risk for those problems generally seen in the population.
Those rare events include the disabling autoimmune condition Guillain-Barré syndrome and the platelet disorder thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS), which causes blood clots along with the risk of excess bleeding because of a low platelet count.
Both can occur after the J&J vaccine. Out of 15.3 million doses of the vaccine given to date, there have been 47 cases of TTS and five deaths. These events are more common in younger women.
The mRNA vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, can cause heart inflammation called myocarditis or pericarditis. This side effect is more common in men 18-24 years old. The reported rate of myocarditis after vaccination is 39 cases for every 1 million doses.
In voting to permit boosters, committee member Wilbur Chen, MD, professor at the University of Maryland’s Center for Vaccine Development, said he hoped boosters wouldn’t give Americans false confidence.
Dr. Chen stressed that ending the pandemic would depend on “a multilayered approach” that includes masking, social distancing, avoiding large crowds indoors, and convincing more Americans to take their first doses of the vaccines.
“We’re not just going to vaccinate ourselves out of this situation,” Dr. Chen said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Editor’s note: This story was updated with the CDC director’s endorsement.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, has signed off on an advisory panel’s earlier unanimous vote to recommend boosters for the Moderna and Johnson and Johnson COVID vaccines.
The decision now means that millions of Americans are eligible to get a booster shot for either the Pfizer, Moderna, or J&J COVID vaccines.
“The evidence shows that all three COVID-19 vaccines authorized in the United States are safe – as demonstrated by the over 400 million vaccine doses already given. And, they are all highly effective in reducing the risk of severe disease, hospitalization, and death, even in the midst of the widely circulating Delta variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a CDC news release.
She also signed off on the panel’s suggestion that individuals can mix or match the booster from any one of the three available COVID-19 vaccines.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended in a late afternoon 15-0 vote that everyone over age 18 who are at least 2 months past their Johnson & Johnson vaccine should get a booster, an endorsement that affects an estimated 13 million Americans.
Those eligible for a booster at least 6 months after their last Moderna shot are the same groups who can get a Pfizer booster.
They are:
- Anyone over age 65.
- Those over age 18 with an underlying health condition that puts them at risk of severe COVID-19.
- Those over age 18 who may be at higher risk of a COVID-19 infection because they live or work in a risky setting.
These recommendations are in line with the Food and Drug Administration’s Oct. 20 authorization of the boosters, along with the ability to mix-and-match vaccines.
There are an estimated 47 million Pfizer recipients and 39 million people vaccinated with Moderna who are now eligible for a booster dose, according to data presented by the CDC.
Questions, concerns
Before voting, some committee members expressed discomfort in broadly recommending boosters, stressing that there is very little evidence supporting the need for boosters in people younger than age 50.
“I can’t say that I am comfortable that anybody under 50 – an otherwise healthy individual – needs a booster vaccine at this time with either Moderna or Pfizer,” said ACIP member Sarah Long, MD, professor of pediatrics at Drexel University in Philadelphia.
She said she would try to mitigate any potential harm by having some kind of age restriction on the otherwise worried well.
“We don’t usually have the vaccines [for] the worried well. We give it because we have a need that’s worth the risk, and there’s a burden of severity of disease,” Dr. Long said.
The evidence to date shows that all the vaccines authorized for use in the U.S. continue to protect people well against severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
But breakthrough infections are on the rise, especially for people who initially received the Johnson and Johnson one-dose vaccine.
On Oct. 21, Pfizer released data from a study of more than 10,000 fully vaccinated people. Half were randomly assigned to get a booster of their Comirnaty vaccine, the other half were given a placebo.
Over the ensuing 2.5 months, there were 5 COVID-19 cases in the boosted group, and 109 in the group that got a placebo.
The data were posted in a press release and have not yet been peer reviewed, but are the first to show clinical effectiveness of boosters at preventing COVID-19 infections.
Data recently considered by the FDA and CDC for booster doses come from studies that were mostly shorter and smaller. These studies looked at biomarkers of immunity like the concentration of antibodies in a person’s blood and the percentage of study participants who saw a boost to those antibodies.
The studies demonstrated that boosters indeed restore high levels of antibodies, but unlike the newest Pfizer data they were not able to show that these antibodies prevented COVID-19.
These studies also weren’t powered to pick up on any less common safety problems that might arise after another dose of the shots.
“Real world” recommendations
In the end, however, the panel felt it was more important to be permissive in allowing boosters so that individuals and their doctors could be free to make their own decisions.
“The decision made by the FDA and the ACIP recommendations, I think, reflects the real world. The public is going to do what they feel driven to do. This at least adds a scientific review of the currently available data,” said Jay Varkey, MD, an infectious disease physician and associate professor at Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved in the ACIP’s deliberations.
Dr. Varkey said he would recommend that anyone who is younger than 65, and who has no underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or obesity, speak with their doctor about their individual benefits and risks before getting a booster.
The CDC is planning to release a detailed suite of clinical considerations to help people weigh the risks and benefits of getting a booster.
Safety updates presented at the meeting show that serious adverse events after vaccination are extremely rare, but in some cases, they may rise above the risk for those problems generally seen in the population.
Those rare events include the disabling autoimmune condition Guillain-Barré syndrome and the platelet disorder thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS), which causes blood clots along with the risk of excess bleeding because of a low platelet count.
Both can occur after the J&J vaccine. Out of 15.3 million doses of the vaccine given to date, there have been 47 cases of TTS and five deaths. These events are more common in younger women.
The mRNA vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, can cause heart inflammation called myocarditis or pericarditis. This side effect is more common in men 18-24 years old. The reported rate of myocarditis after vaccination is 39 cases for every 1 million doses.
In voting to permit boosters, committee member Wilbur Chen, MD, professor at the University of Maryland’s Center for Vaccine Development, said he hoped boosters wouldn’t give Americans false confidence.
Dr. Chen stressed that ending the pandemic would depend on “a multilayered approach” that includes masking, social distancing, avoiding large crowds indoors, and convincing more Americans to take their first doses of the vaccines.
“We’re not just going to vaccinate ourselves out of this situation,” Dr. Chen said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Editor’s note: This story was updated with the CDC director’s endorsement.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, has signed off on an advisory panel’s earlier unanimous vote to recommend boosters for the Moderna and Johnson and Johnson COVID vaccines.
The decision now means that millions of Americans are eligible to get a booster shot for either the Pfizer, Moderna, or J&J COVID vaccines.
“The evidence shows that all three COVID-19 vaccines authorized in the United States are safe – as demonstrated by the over 400 million vaccine doses already given. And, they are all highly effective in reducing the risk of severe disease, hospitalization, and death, even in the midst of the widely circulating Delta variant,” Dr. Walensky said in a CDC news release.
She also signed off on the panel’s suggestion that individuals can mix or match the booster from any one of the three available COVID-19 vaccines.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended in a late afternoon 15-0 vote that everyone over age 18 who are at least 2 months past their Johnson & Johnson vaccine should get a booster, an endorsement that affects an estimated 13 million Americans.
Those eligible for a booster at least 6 months after their last Moderna shot are the same groups who can get a Pfizer booster.
They are:
- Anyone over age 65.
- Those over age 18 with an underlying health condition that puts them at risk of severe COVID-19.
- Those over age 18 who may be at higher risk of a COVID-19 infection because they live or work in a risky setting.
These recommendations are in line with the Food and Drug Administration’s Oct. 20 authorization of the boosters, along with the ability to mix-and-match vaccines.
There are an estimated 47 million Pfizer recipients and 39 million people vaccinated with Moderna who are now eligible for a booster dose, according to data presented by the CDC.
Questions, concerns
Before voting, some committee members expressed discomfort in broadly recommending boosters, stressing that there is very little evidence supporting the need for boosters in people younger than age 50.
“I can’t say that I am comfortable that anybody under 50 – an otherwise healthy individual – needs a booster vaccine at this time with either Moderna or Pfizer,” said ACIP member Sarah Long, MD, professor of pediatrics at Drexel University in Philadelphia.
She said she would try to mitigate any potential harm by having some kind of age restriction on the otherwise worried well.
“We don’t usually have the vaccines [for] the worried well. We give it because we have a need that’s worth the risk, and there’s a burden of severity of disease,” Dr. Long said.
The evidence to date shows that all the vaccines authorized for use in the U.S. continue to protect people well against severe COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
But breakthrough infections are on the rise, especially for people who initially received the Johnson and Johnson one-dose vaccine.
On Oct. 21, Pfizer released data from a study of more than 10,000 fully vaccinated people. Half were randomly assigned to get a booster of their Comirnaty vaccine, the other half were given a placebo.
Over the ensuing 2.5 months, there were 5 COVID-19 cases in the boosted group, and 109 in the group that got a placebo.
The data were posted in a press release and have not yet been peer reviewed, but are the first to show clinical effectiveness of boosters at preventing COVID-19 infections.
Data recently considered by the FDA and CDC for booster doses come from studies that were mostly shorter and smaller. These studies looked at biomarkers of immunity like the concentration of antibodies in a person’s blood and the percentage of study participants who saw a boost to those antibodies.
The studies demonstrated that boosters indeed restore high levels of antibodies, but unlike the newest Pfizer data they were not able to show that these antibodies prevented COVID-19.
These studies also weren’t powered to pick up on any less common safety problems that might arise after another dose of the shots.
“Real world” recommendations
In the end, however, the panel felt it was more important to be permissive in allowing boosters so that individuals and their doctors could be free to make their own decisions.
“The decision made by the FDA and the ACIP recommendations, I think, reflects the real world. The public is going to do what they feel driven to do. This at least adds a scientific review of the currently available data,” said Jay Varkey, MD, an infectious disease physician and associate professor at Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved in the ACIP’s deliberations.
Dr. Varkey said he would recommend that anyone who is younger than 65, and who has no underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or obesity, speak with their doctor about their individual benefits and risks before getting a booster.
The CDC is planning to release a detailed suite of clinical considerations to help people weigh the risks and benefits of getting a booster.
Safety updates presented at the meeting show that serious adverse events after vaccination are extremely rare, but in some cases, they may rise above the risk for those problems generally seen in the population.
Those rare events include the disabling autoimmune condition Guillain-Barré syndrome and the platelet disorder thrombosis with thrombocytopenia (TTS), which causes blood clots along with the risk of excess bleeding because of a low platelet count.
Both can occur after the J&J vaccine. Out of 15.3 million doses of the vaccine given to date, there have been 47 cases of TTS and five deaths. These events are more common in younger women.
The mRNA vaccines, such as those from Pfizer and Moderna, can cause heart inflammation called myocarditis or pericarditis. This side effect is more common in men 18-24 years old. The reported rate of myocarditis after vaccination is 39 cases for every 1 million doses.
In voting to permit boosters, committee member Wilbur Chen, MD, professor at the University of Maryland’s Center for Vaccine Development, said he hoped boosters wouldn’t give Americans false confidence.
Dr. Chen stressed that ending the pandemic would depend on “a multilayered approach” that includes masking, social distancing, avoiding large crowds indoors, and convincing more Americans to take their first doses of the vaccines.
“We’re not just going to vaccinate ourselves out of this situation,” Dr. Chen said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Comorbidities larger factor than race in COVID ICU deaths?
Racial/ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortality rates may be related more to comorbidities than to demographics, suggest authors of a new study.
Researchers compared the length of stay in intensive care units in two suburban hospitals for patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infections. Their study shows that although the incidence of comorbidities and rates of use of mechanical ventilation and death were higher among Black patients than among patients of other races, length of stay in the ICU was generally similar for patients of all races. The study was conducted by Tripti Kumar, DO, from Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, Pennsylvania, and colleagues.
“Racial disparities are observed in the United States concerning COVID-19, and studies have discovered that minority populations are at ongoing risk for health inequity,” Dr. Kumar said in a narrated e-poster presented during the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2021 Annual Meeting.
“Primary prevention initiatives should take precedence in mitigating the effect that comorbidities have on these vulnerable populations to help reduce necessity for mechanical ventilation, hospital length of stay, and overall mortality,” she said.
Higher death rates for Black patients
At the time the study was conducted, the COVID-19 death rate in the United States had topped 500,000 (as of this writing, it stands at 726,000). Of those who died, 22.4% were Black, 18.1% were Hispanic, and 3.6% were of Asian descent. The numbers of COVID-19 diagnoses and deaths were significantly higher in U.S. counties where the proportions of Black residents were higher, the authors note.
To see whether differences in COVID-19 outcomes were reflected in ICU length of stay, the researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of data on 162 patients admitted to ICUs at Paoli Hospital and Lankenau Medical Center, both in the suburban Philadelphia town of Wynnewood.
All patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 from March through June 2020.
In all, 60% of the study population were Black, 35% were White, 3% were Asian, and 2% were Hispanic. Women composed 46% of the sample.
The average length of ICU stay, which was the primary endpoint, was similar among Black patients (15.4 days), White patients (15.5 days), and Asians (16 days). The shortest average hospital stay was among Hispanic patients, at 11.3 days.
The investigators determined that among all races, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and smoking was highest among Black patients.
Overall, nearly 85% of patients required mechanical ventilation. Among the patients who required it, 86% were Black, 84% were White, 66% were Hispanic, and 75% were Asian.
Overall mortality was 62%. It was higher among Black patients, at 60%, than among White patients, at 33%. The investigators did not report mortality rates for Hispanic or Asian patients.
Missing data
Demondes Haynes, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care and associate dean for admissions at the University of Mississippi Medical Center and School of Medicine, Jackson, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization that there are some gaps in the study that make it difficult to draw strong conclusions about the findings.
“For sure, comorbidities contribute a great deal to mortality, but is there something else going on? I think this poster is incomplete in that it cannot answer that question,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the use of retrospective rather than prospective data makes it hard to account for potential confounders.
“I agree that these findings show the potential contribution of comorbidities, but to me, this is a little incomplete to make that a definitive statement,” he said.
“I can’t argue with their recommendation for primary prevention – we definitely want to do primary prevention to decrease comorbidities. Would it decrease overall mortality? It might, it sure might, for just COVID-19 I’d say no, we need more information.”
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Kumar and colleagues and Dr. Haynes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Racial/ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortality rates may be related more to comorbidities than to demographics, suggest authors of a new study.
Researchers compared the length of stay in intensive care units in two suburban hospitals for patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infections. Their study shows that although the incidence of comorbidities and rates of use of mechanical ventilation and death were higher among Black patients than among patients of other races, length of stay in the ICU was generally similar for patients of all races. The study was conducted by Tripti Kumar, DO, from Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, Pennsylvania, and colleagues.
“Racial disparities are observed in the United States concerning COVID-19, and studies have discovered that minority populations are at ongoing risk for health inequity,” Dr. Kumar said in a narrated e-poster presented during the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2021 Annual Meeting.
“Primary prevention initiatives should take precedence in mitigating the effect that comorbidities have on these vulnerable populations to help reduce necessity for mechanical ventilation, hospital length of stay, and overall mortality,” she said.
Higher death rates for Black patients
At the time the study was conducted, the COVID-19 death rate in the United States had topped 500,000 (as of this writing, it stands at 726,000). Of those who died, 22.4% were Black, 18.1% were Hispanic, and 3.6% were of Asian descent. The numbers of COVID-19 diagnoses and deaths were significantly higher in U.S. counties where the proportions of Black residents were higher, the authors note.
To see whether differences in COVID-19 outcomes were reflected in ICU length of stay, the researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of data on 162 patients admitted to ICUs at Paoli Hospital and Lankenau Medical Center, both in the suburban Philadelphia town of Wynnewood.
All patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 from March through June 2020.
In all, 60% of the study population were Black, 35% were White, 3% were Asian, and 2% were Hispanic. Women composed 46% of the sample.
The average length of ICU stay, which was the primary endpoint, was similar among Black patients (15.4 days), White patients (15.5 days), and Asians (16 days). The shortest average hospital stay was among Hispanic patients, at 11.3 days.
The investigators determined that among all races, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and smoking was highest among Black patients.
Overall, nearly 85% of patients required mechanical ventilation. Among the patients who required it, 86% were Black, 84% were White, 66% were Hispanic, and 75% were Asian.
Overall mortality was 62%. It was higher among Black patients, at 60%, than among White patients, at 33%. The investigators did not report mortality rates for Hispanic or Asian patients.
Missing data
Demondes Haynes, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care and associate dean for admissions at the University of Mississippi Medical Center and School of Medicine, Jackson, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization that there are some gaps in the study that make it difficult to draw strong conclusions about the findings.
“For sure, comorbidities contribute a great deal to mortality, but is there something else going on? I think this poster is incomplete in that it cannot answer that question,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the use of retrospective rather than prospective data makes it hard to account for potential confounders.
“I agree that these findings show the potential contribution of comorbidities, but to me, this is a little incomplete to make that a definitive statement,” he said.
“I can’t argue with their recommendation for primary prevention – we definitely want to do primary prevention to decrease comorbidities. Would it decrease overall mortality? It might, it sure might, for just COVID-19 I’d say no, we need more information.”
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Kumar and colleagues and Dr. Haynes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Racial/ethnic disparities in COVID-19 mortality rates may be related more to comorbidities than to demographics, suggest authors of a new study.
Researchers compared the length of stay in intensive care units in two suburban hospitals for patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infections. Their study shows that although the incidence of comorbidities and rates of use of mechanical ventilation and death were higher among Black patients than among patients of other races, length of stay in the ICU was generally similar for patients of all races. The study was conducted by Tripti Kumar, DO, from Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, Pennsylvania, and colleagues.
“Racial disparities are observed in the United States concerning COVID-19, and studies have discovered that minority populations are at ongoing risk for health inequity,” Dr. Kumar said in a narrated e-poster presented during the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2021 Annual Meeting.
“Primary prevention initiatives should take precedence in mitigating the effect that comorbidities have on these vulnerable populations to help reduce necessity for mechanical ventilation, hospital length of stay, and overall mortality,” she said.
Higher death rates for Black patients
At the time the study was conducted, the COVID-19 death rate in the United States had topped 500,000 (as of this writing, it stands at 726,000). Of those who died, 22.4% were Black, 18.1% were Hispanic, and 3.6% were of Asian descent. The numbers of COVID-19 diagnoses and deaths were significantly higher in U.S. counties where the proportions of Black residents were higher, the authors note.
To see whether differences in COVID-19 outcomes were reflected in ICU length of stay, the researchers conducted a retrospective chart review of data on 162 patients admitted to ICUs at Paoli Hospital and Lankenau Medical Center, both in the suburban Philadelphia town of Wynnewood.
All patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 from March through June 2020.
In all, 60% of the study population were Black, 35% were White, 3% were Asian, and 2% were Hispanic. Women composed 46% of the sample.
The average length of ICU stay, which was the primary endpoint, was similar among Black patients (15.4 days), White patients (15.5 days), and Asians (16 days). The shortest average hospital stay was among Hispanic patients, at 11.3 days.
The investigators determined that among all races, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and smoking was highest among Black patients.
Overall, nearly 85% of patients required mechanical ventilation. Among the patients who required it, 86% were Black, 84% were White, 66% were Hispanic, and 75% were Asian.
Overall mortality was 62%. It was higher among Black patients, at 60%, than among White patients, at 33%. The investigators did not report mortality rates for Hispanic or Asian patients.
Missing data
Demondes Haynes, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care and associate dean for admissions at the University of Mississippi Medical Center and School of Medicine, Jackson, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization that there are some gaps in the study that make it difficult to draw strong conclusions about the findings.
“For sure, comorbidities contribute a great deal to mortality, but is there something else going on? I think this poster is incomplete in that it cannot answer that question,” he said in an interview.
He noted that the use of retrospective rather than prospective data makes it hard to account for potential confounders.
“I agree that these findings show the potential contribution of comorbidities, but to me, this is a little incomplete to make that a definitive statement,” he said.
“I can’t argue with their recommendation for primary prevention – we definitely want to do primary prevention to decrease comorbidities. Would it decrease overall mortality? It might, it sure might, for just COVID-19 I’d say no, we need more information.”
No funding source for the study was reported. Dr. Kumar and colleagues and Dr. Haynes reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA authorizes boosters for Moderna, J&J, allows mix-and-match
in people who are eligible to get them.
The move to amend the Emergency Use Authorization for these vaccines gives the vaccine experts on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices latitude to recommend a mix-and-match strategy if they feel the science supports it.
The committee convenes Oct. 21 for a day-long meeting to make its recommendations for additional doses.
People who’ve previously received two doses of the Moderna mRNA vaccine, which is now called Spikevax, are eligible for a third dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are 6 months past their second dose and are:
- 65 years of age or older
- 18 to 64 years of age, but at high risk for severe COVID-19 because of an underlying health condition
- 18 to 64 years of age and at high risk for exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus because they live in a group setting, such as a prison or care home, or work in a risky occupation, such as healthcare
People who’ve previously received a dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are eligible for a second dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are over the age of 18 and at least 2 months past their vaccination.
“Today’s actions demonstrate our commitment to public health in proactively fighting against the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in a news release. “As the pandemic continues to impact the country, science has shown that vaccination continues to be the safest and most effective way to prevent COVID-19, including the most serious consequences of the disease, such as hospitalization and death.
“The available data suggest waning immunity in some populations who are fully vaccinated. The availability of these authorized boosters is important for continued protection against COVID-19 disease.”
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
in people who are eligible to get them.
The move to amend the Emergency Use Authorization for these vaccines gives the vaccine experts on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices latitude to recommend a mix-and-match strategy if they feel the science supports it.
The committee convenes Oct. 21 for a day-long meeting to make its recommendations for additional doses.
People who’ve previously received two doses of the Moderna mRNA vaccine, which is now called Spikevax, are eligible for a third dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are 6 months past their second dose and are:
- 65 years of age or older
- 18 to 64 years of age, but at high risk for severe COVID-19 because of an underlying health condition
- 18 to 64 years of age and at high risk for exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus because they live in a group setting, such as a prison or care home, or work in a risky occupation, such as healthcare
People who’ve previously received a dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are eligible for a second dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are over the age of 18 and at least 2 months past their vaccination.
“Today’s actions demonstrate our commitment to public health in proactively fighting against the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in a news release. “As the pandemic continues to impact the country, science has shown that vaccination continues to be the safest and most effective way to prevent COVID-19, including the most serious consequences of the disease, such as hospitalization and death.
“The available data suggest waning immunity in some populations who are fully vaccinated. The availability of these authorized boosters is important for continued protection against COVID-19 disease.”
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
in people who are eligible to get them.
The move to amend the Emergency Use Authorization for these vaccines gives the vaccine experts on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices latitude to recommend a mix-and-match strategy if they feel the science supports it.
The committee convenes Oct. 21 for a day-long meeting to make its recommendations for additional doses.
People who’ve previously received two doses of the Moderna mRNA vaccine, which is now called Spikevax, are eligible for a third dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are 6 months past their second dose and are:
- 65 years of age or older
- 18 to 64 years of age, but at high risk for severe COVID-19 because of an underlying health condition
- 18 to 64 years of age and at high risk for exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus because they live in a group setting, such as a prison or care home, or work in a risky occupation, such as healthcare
People who’ve previously received a dose of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine are eligible for a second dose of any COVID-19 vaccine if they are over the age of 18 and at least 2 months past their vaccination.
“Today’s actions demonstrate our commitment to public health in proactively fighting against the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, in a news release. “As the pandemic continues to impact the country, science has shown that vaccination continues to be the safest and most effective way to prevent COVID-19, including the most serious consequences of the disease, such as hospitalization and death.
“The available data suggest waning immunity in some populations who are fully vaccinated. The availability of these authorized boosters is important for continued protection against COVID-19 disease.”
A version of this article was first published on Medscape.com.
White House announces vaccination plans for younger children
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
States were allowed to begin preordering the shots this week. But they can’t be delivered into kids’ arms until the FDA and CDC sign off. The shots could be available in early November.
“We know millions of parents have been waiting for COVID-19 vaccine for kids in this age group, and should the FDA and CDC authorize the vaccine, we will be ready to get shots in arms,” Jeff Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said at a briefing Oct. 20.
Asked whether announcing plans to deliver a vaccine to children might put pressure on the agencies considering the evidence for their use, Mr. Zients defended the Biden administration’s plans.
“This is the right way to do things: To be operationally ready,” he said. Mr. Zients said they had learned a lesson from the prior administration.
“The decision was made by the FDA and CDC, and the operations weren’t ready. And that meant that adults at the time were not able to receive their vaccines as efficiently, equitably as possible. And this will enable us to be ready for kids,” he said.
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late September from its test of the vaccine in 2,200 children. The company said the shots had a favorable safety profile and generated “robust” antibody responses.
An FDA panel is scheduled to meet on Oct. 26 to consider Pfizer’s application. The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will meet the following week, on Nov. 2 and 3.
Laying the groundwork
Doctors applauded the advance planning.
“Laying this advance groundwork, ensuring supply is available at physician practices, and that a patient’s own physician is available to answer questions, is critical to the continued success of this rollout,” Gerald Harmon, MD, president of the American Medical Association, said in a written statement.
The shots planned for children are 10 micrograms, a smaller dose than is given to adults. To be fully immunized, kids get two doses, spaced about 21 days apart. Vaccines for younger children are packaged in smaller vials and injected through smaller needles, too.
The vaccine for younger children will roll out slightly differently than it has for adults and teens. While adults mostly got their COVID-19 vaccines through pop-up mass vaccination sites, health departments, and other community locations, the strategy to get children immunized against COVID is centered on the offices of pediatricians and primary care doctors.
The White House says 25,000 doctors have already signed up to give the vaccines.
The vaccination campaign will get underway at a tough moment for pediatricians.
The voicemail message at Roswell Pediatrics Center in the suburbs north of Atlanta, for instance, warns parents to be patient.
“Due to the current, new COVID-19 surge, we are experiencing extremely high call volume, as well as suffering from the same staffing shortages that most businesses are having,” the message says, adding that they’re working around the clock to answer questions and return phone calls.
Jesse Hackell, MD, says he knows the feeling. He’s the chief operating officer of Pomona Pediatrics in Pomona, N.Y., and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“We’re swamped now by kids who get sent home from school because they sneezed once and they have to be cleared before they can go back to school,” he said. “We’re seeing kids who we don’t need to see in terms of the degree of illness because the school requires them to be cleared [of COVID-19].”
Dr. Hackell has been offering the vaccines to kids ages 12 and up since May. He’s planning to offer it to younger children too.
“Adding the vaccines to it is going to be a challenge, but you know we’ll get up to speed and we’ll make it happen,” he said, adding that pediatricians have done many large-scale vaccination campaigns, like those for the H1N1 influenza vaccine in 2009.
Dr. Hackell helped to draft a new policy in New York that will require COVID-19 vaccines for schoolchildren once they are granted full approval from the FDA. Other states may follow with their own vaccination requirements.
He said ultimately, vaccinating school-age children is going to make them safer, will help prevent the virus from mutating and spreading, and will help society as a whole get back to normal.
“We’re the vaccine experts in pediatrics. This is what we do. It’s a huge part of our practice like no other specialty. If we can’t get it right, how can anyone else be expected to?” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: Vaccinations lower than ever as cases continue to drop
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
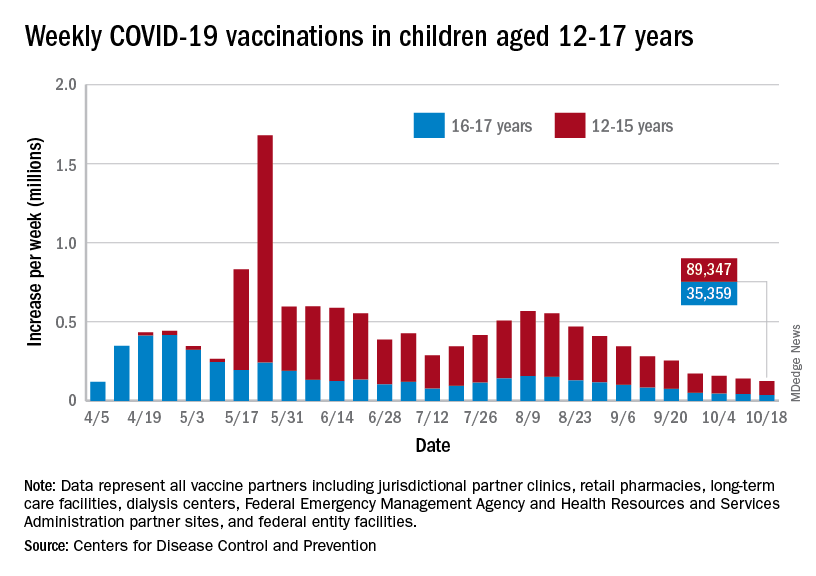
Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
As the COVID-19 vaccine heads toward approval for children under age 12 years, the number of older children receiving it dropped for the 10th consecutive week, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Over 47% of all children aged 12-17 years – that’s close to 12 million eligible individuals – have not received even one dose of COVID-19 vaccine, and less than 44% (about 11.1 million) were fully vaccinated as of Oct. 18, the CDC reported on its COVID Data Tracker.
, when eligibility expanded to include 12- to 15-year-olds, according to the CDC data, which also show that weekly vaccinations have never been lower.
Fortunately, the decline in new cases also continued, as the national total fell for a 6th straight week. There were more than 130,000 child cases reported during the week of Oct. 8-14, compared with 148,000 the previous week and the high of almost 252,000 in late August/early September, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
That brings the cumulative count to 6.18 million, with children accounting for 16.4% of all cases reported since the start of the pandemic. For the week of Oct. 8-14, children represented 25.5% of all COVID-19 cases in the 46 states with up-to-date online dashboards, the AAP and CHA said, noting that New York has never reported age ranges for cases and that Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas stopped reporting over the summer.
Current data indicate that child cases in California now exceed 671,000, more than any other state, followed by Florida with 439,000 (the state defines a child as someone aged 0-14 years) and Illinois with 301,000. Vermont has the highest proportion of COVID-19 cases occurring in children (24.3%), with Alaska (24.1%) and South Carolina (23.2%) just behind. The highest rate of cases – 15,569 per 100,000 children – can be found in South Carolina, while the lowest is in Hawaii (4,838 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA reported.
The total number of COVID-related deaths in children is 681 as of Oct. 18, according to the CDC, with the AAP/CHA reporting 558 as of Oct. 14, based on data from 45 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam. The CDC reports 65,655 admissions since Aug. 1, 2020, in children aged 0-17 years, and the AAP/CHA tally 23,582 since May 5, 2020, among children in 24 states and New York City.
National Academies issue guidance for childhood COVID-19 vaccines
While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has yet to give the green light to COVID-19 vaccination for children who are under age 12, it is expected that approval will be granted. In anticipation of the FDA’s go-ahead, which is expected in the coming weeks, a new “rapid expert consultation” has identified “actionable guidance” that state and local decision-makers can use to communicate with the public. The goal is to build confidence in and promote the uptake of COVID-19 vaccines, especially for parents who are contemplating vaccinating their children.
They note that key factors in decision-making concern vaccine side effects, the efficacy of the vaccine in children, availability of research in their child’s age group, research conducted by the parents themselves, and recommendations by the child’s health care provider.
“One of the reasons that the COVID vaccine only became available for children 12 and over months after it was approved for adults is that it takes time and many, many trial participants who are closely monitored before the vaccine ever reaches the general public,” said Nusheen Ameenuddin, MD, MPH, MPA, an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “We continue to talk to parents about the fact that the vaccines have been very safe and effective in this group, and even though people are concerned about side effects, they are much milder and less frequent than the effects of the disease itself.”
Dr. Ameenuddin noted that the lack of data in this age group can be concerning for parents. “It’s not like other vaccines which have been available for a long time, and the clinical trial data are still limited for this age group,” she said. “But I think the main point that practitioners need to emphasize is that, even though the vaccine is new, the science for this vaccine has been around for about a decade.”
The unique circumstances of a pandemic, she pointed out, allowed for important information about effectiveness, safety, and side effects to be obtained more quickly from clinical trial data.
“We have really good evidence for kids 12 and over, about safety and effectiveness, and even though children are not small adults and have their own unique physiology, this has provided a good starting point to suggest that kids slightly younger will also respond well to the vaccines,” said Dr. Ameenuddin, who is also chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Communications and Media. “As we learn more, we can start gathering more information about even younger kids to ensure that the right dosage and spacing of vaccines can provide maximum vaccine effectiveness and protection from disease.”
The guidance was published Oct. 13 by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
The rapid expert consultation was produced through the Societal Experts Action Network, an activity of the National Academies that is sponsored by the NASEM and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation. The goal of SEAN is to connect researchers in the social, behavioral, and economic sciences with decision-makers to respond to policy questions related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In their expert consultation, the authors emphasize that vaccination is critical for decreasing transmission and controlling infection, as well as limiting the emergence of future serious variants. As of Oct. 3, 2021, about 65% of the U.S. population had received at least one dose of the vaccine, and the rate has begun to lag in many areas of the country. There are a variety of reasons for vaccine hesitancy, they note, including perception of low risks from COVID-19 or of high risks from COVID-19 vaccines, exposure to media, political agendas, lack of confidence in science, and distrust of the medical establishment. The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine is currently authorized for emergency use for individuals 12 years of age and older and fully approved for those aged 16 and older, while the Moderna and the Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for emergency use for those 18 years of age and older.
Many children between the ages of 12 and 17 have not been vaccinated, and the major concerns reported by parents include not knowing enough about the long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccine in children (88%), concerns about children experiencing serious side effects (79%), and concerns that the COVID-19 vaccine might negatively affect future fertility (73%).
The National Academies have previously released two other “rapid expert consultations” which have addressed building vaccine confidence, and both reports provide key strategies for communicating information about COVID-19 vaccines. In this paper, the focus was on communicating with parents to gain confidence in the vaccine and address concerns.
Key points
The key strategies highlighted for communicating with parents include the following:
- Emphasizing safety and efficacy: Parents should be informed about the ongoing research and clinical trials that will answer more questions about the vaccine and that there is continued monitoring for any safety risks. Pointing to the safety data from the clinical trials for 12- to 17-year-olds, and the lack of serious adverse events from the vaccine in this age group may help alleviate concerns.
- CalibriEncouraging parents to talk with a primary care provider: Research shows that parents trust family physicians and other health care practitioners to provide them with accurate information about vaccines. Local, state, and national leaders can provide messaging templates and other resources to health care professionals who are engaged in these conversations.
- Leveraging social networks to influence parents’ vaccination decisions: Parents are influenced by their social network connections. It is important to engage these networks, especially with members of their community who are considered trustworthy and influential. Social networks may also be very diverse, and include family members, friends, coworkers, social media, and members of their religious community.
While the guidance states that different groups of parents will require different messaging, they suggest that communication can begin with a focus on the things that vaccination can accomplish. In addition to preventing infection with COVID-19, it will allow children to attend school in person and participate in extracurricular activities such as sports, without risking their health. “One thing I’ve learned over several years of working with vaccine-hesitant parents is that you have to tailor each approach to the individual,” said Dr. Ameenuddin. “Different people have different concerns, and first and foremost, it’s important to listen.”
For some parents, emphasizing that the more people that can be vaccinated and the sooner it can be done, the sooner everyone can return to a normal life is a good approach, she added. “I think it’s important to emphasize both the individual and communal benefits of vaccines, but that won’t necessarily reach every person with concerns. I think it’s important to find out what is most important to individuals and work from there to find a way to connect with that family to encourage vaccination.”
Dr. Ameenuddin has no disclosures.
While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has yet to give the green light to COVID-19 vaccination for children who are under age 12, it is expected that approval will be granted. In anticipation of the FDA’s go-ahead, which is expected in the coming weeks, a new “rapid expert consultation” has identified “actionable guidance” that state and local decision-makers can use to communicate with the public. The goal is to build confidence in and promote the uptake of COVID-19 vaccines, especially for parents who are contemplating vaccinating their children.
They note that key factors in decision-making concern vaccine side effects, the efficacy of the vaccine in children, availability of research in their child’s age group, research conducted by the parents themselves, and recommendations by the child’s health care provider.
“One of the reasons that the COVID vaccine only became available for children 12 and over months after it was approved for adults is that it takes time and many, many trial participants who are closely monitored before the vaccine ever reaches the general public,” said Nusheen Ameenuddin, MD, MPH, MPA, an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “We continue to talk to parents about the fact that the vaccines have been very safe and effective in this group, and even though people are concerned about side effects, they are much milder and less frequent than the effects of the disease itself.”
Dr. Ameenuddin noted that the lack of data in this age group can be concerning for parents. “It’s not like other vaccines which have been available for a long time, and the clinical trial data are still limited for this age group,” she said. “But I think the main point that practitioners need to emphasize is that, even though the vaccine is new, the science for this vaccine has been around for about a decade.”
The unique circumstances of a pandemic, she pointed out, allowed for important information about effectiveness, safety, and side effects to be obtained more quickly from clinical trial data.
“We have really good evidence for kids 12 and over, about safety and effectiveness, and even though children are not small adults and have their own unique physiology, this has provided a good starting point to suggest that kids slightly younger will also respond well to the vaccines,” said Dr. Ameenuddin, who is also chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Communications and Media. “As we learn more, we can start gathering more information about even younger kids to ensure that the right dosage and spacing of vaccines can provide maximum vaccine effectiveness and protection from disease.”
The guidance was published Oct. 13 by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
The rapid expert consultation was produced through the Societal Experts Action Network, an activity of the National Academies that is sponsored by the NASEM and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation. The goal of SEAN is to connect researchers in the social, behavioral, and economic sciences with decision-makers to respond to policy questions related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In their expert consultation, the authors emphasize that vaccination is critical for decreasing transmission and controlling infection, as well as limiting the emergence of future serious variants. As of Oct. 3, 2021, about 65% of the U.S. population had received at least one dose of the vaccine, and the rate has begun to lag in many areas of the country. There are a variety of reasons for vaccine hesitancy, they note, including perception of low risks from COVID-19 or of high risks from COVID-19 vaccines, exposure to media, political agendas, lack of confidence in science, and distrust of the medical establishment. The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine is currently authorized for emergency use for individuals 12 years of age and older and fully approved for those aged 16 and older, while the Moderna and the Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for emergency use for those 18 years of age and older.
Many children between the ages of 12 and 17 have not been vaccinated, and the major concerns reported by parents include not knowing enough about the long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccine in children (88%), concerns about children experiencing serious side effects (79%), and concerns that the COVID-19 vaccine might negatively affect future fertility (73%).
The National Academies have previously released two other “rapid expert consultations” which have addressed building vaccine confidence, and both reports provide key strategies for communicating information about COVID-19 vaccines. In this paper, the focus was on communicating with parents to gain confidence in the vaccine and address concerns.
Key points
The key strategies highlighted for communicating with parents include the following:
- Emphasizing safety and efficacy: Parents should be informed about the ongoing research and clinical trials that will answer more questions about the vaccine and that there is continued monitoring for any safety risks. Pointing to the safety data from the clinical trials for 12- to 17-year-olds, and the lack of serious adverse events from the vaccine in this age group may help alleviate concerns.
- CalibriEncouraging parents to talk with a primary care provider: Research shows that parents trust family physicians and other health care practitioners to provide them with accurate information about vaccines. Local, state, and national leaders can provide messaging templates and other resources to health care professionals who are engaged in these conversations.
- Leveraging social networks to influence parents’ vaccination decisions: Parents are influenced by their social network connections. It is important to engage these networks, especially with members of their community who are considered trustworthy and influential. Social networks may also be very diverse, and include family members, friends, coworkers, social media, and members of their religious community.
While the guidance states that different groups of parents will require different messaging, they suggest that communication can begin with a focus on the things that vaccination can accomplish. In addition to preventing infection with COVID-19, it will allow children to attend school in person and participate in extracurricular activities such as sports, without risking their health. “One thing I’ve learned over several years of working with vaccine-hesitant parents is that you have to tailor each approach to the individual,” said Dr. Ameenuddin. “Different people have different concerns, and first and foremost, it’s important to listen.”
For some parents, emphasizing that the more people that can be vaccinated and the sooner it can be done, the sooner everyone can return to a normal life is a good approach, she added. “I think it’s important to emphasize both the individual and communal benefits of vaccines, but that won’t necessarily reach every person with concerns. I think it’s important to find out what is most important to individuals and work from there to find a way to connect with that family to encourage vaccination.”
Dr. Ameenuddin has no disclosures.
While the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has yet to give the green light to COVID-19 vaccination for children who are under age 12, it is expected that approval will be granted. In anticipation of the FDA’s go-ahead, which is expected in the coming weeks, a new “rapid expert consultation” has identified “actionable guidance” that state and local decision-makers can use to communicate with the public. The goal is to build confidence in and promote the uptake of COVID-19 vaccines, especially for parents who are contemplating vaccinating their children.
They note that key factors in decision-making concern vaccine side effects, the efficacy of the vaccine in children, availability of research in their child’s age group, research conducted by the parents themselves, and recommendations by the child’s health care provider.
“One of the reasons that the COVID vaccine only became available for children 12 and over months after it was approved for adults is that it takes time and many, many trial participants who are closely monitored before the vaccine ever reaches the general public,” said Nusheen Ameenuddin, MD, MPH, MPA, an assistant professor of pediatrics at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “We continue to talk to parents about the fact that the vaccines have been very safe and effective in this group, and even though people are concerned about side effects, they are much milder and less frequent than the effects of the disease itself.”
Dr. Ameenuddin noted that the lack of data in this age group can be concerning for parents. “It’s not like other vaccines which have been available for a long time, and the clinical trial data are still limited for this age group,” she said. “But I think the main point that practitioners need to emphasize is that, even though the vaccine is new, the science for this vaccine has been around for about a decade.”
The unique circumstances of a pandemic, she pointed out, allowed for important information about effectiveness, safety, and side effects to be obtained more quickly from clinical trial data.
“We have really good evidence for kids 12 and over, about safety and effectiveness, and even though children are not small adults and have their own unique physiology, this has provided a good starting point to suggest that kids slightly younger will also respond well to the vaccines,” said Dr. Ameenuddin, who is also chair of the American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Communications and Media. “As we learn more, we can start gathering more information about even younger kids to ensure that the right dosage and spacing of vaccines can provide maximum vaccine effectiveness and protection from disease.”
The guidance was published Oct. 13 by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
The rapid expert consultation was produced through the Societal Experts Action Network, an activity of the National Academies that is sponsored by the NASEM and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation. The goal of SEAN is to connect researchers in the social, behavioral, and economic sciences with decision-makers to respond to policy questions related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In their expert consultation, the authors emphasize that vaccination is critical for decreasing transmission and controlling infection, as well as limiting the emergence of future serious variants. As of Oct. 3, 2021, about 65% of the U.S. population had received at least one dose of the vaccine, and the rate has begun to lag in many areas of the country. There are a variety of reasons for vaccine hesitancy, they note, including perception of low risks from COVID-19 or of high risks from COVID-19 vaccines, exposure to media, political agendas, lack of confidence in science, and distrust of the medical establishment. The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine is currently authorized for emergency use for individuals 12 years of age and older and fully approved for those aged 16 and older, while the Moderna and the Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for emergency use for those 18 years of age and older.
Many children between the ages of 12 and 17 have not been vaccinated, and the major concerns reported by parents include not knowing enough about the long-term effects of the COVID-19 vaccine in children (88%), concerns about children experiencing serious side effects (79%), and concerns that the COVID-19 vaccine might negatively affect future fertility (73%).
The National Academies have previously released two other “rapid expert consultations” which have addressed building vaccine confidence, and both reports provide key strategies for communicating information about COVID-19 vaccines. In this paper, the focus was on communicating with parents to gain confidence in the vaccine and address concerns.
Key points
The key strategies highlighted for communicating with parents include the following:
- Emphasizing safety and efficacy: Parents should be informed about the ongoing research and clinical trials that will answer more questions about the vaccine and that there is continued monitoring for any safety risks. Pointing to the safety data from the clinical trials for 12- to 17-year-olds, and the lack of serious adverse events from the vaccine in this age group may help alleviate concerns.
- CalibriEncouraging parents to talk with a primary care provider: Research shows that parents trust family physicians and other health care practitioners to provide them with accurate information about vaccines. Local, state, and national leaders can provide messaging templates and other resources to health care professionals who are engaged in these conversations.
- Leveraging social networks to influence parents’ vaccination decisions: Parents are influenced by their social network connections. It is important to engage these networks, especially with members of their community who are considered trustworthy and influential. Social networks may also be very diverse, and include family members, friends, coworkers, social media, and members of their religious community.
While the guidance states that different groups of parents will require different messaging, they suggest that communication can begin with a focus on the things that vaccination can accomplish. In addition to preventing infection with COVID-19, it will allow children to attend school in person and participate in extracurricular activities such as sports, without risking their health. “One thing I’ve learned over several years of working with vaccine-hesitant parents is that you have to tailor each approach to the individual,” said Dr. Ameenuddin. “Different people have different concerns, and first and foremost, it’s important to listen.”
For some parents, emphasizing that the more people that can be vaccinated and the sooner it can be done, the sooner everyone can return to a normal life is a good approach, she added. “I think it’s important to emphasize both the individual and communal benefits of vaccines, but that won’t necessarily reach every person with concerns. I think it’s important to find out what is most important to individuals and work from there to find a way to connect with that family to encourage vaccination.”
Dr. Ameenuddin has no disclosures.
PA defends against license suspension for COVID treatment
The suspension stemmed from allegations against Scott C. Miller, PA-C, by at least six COVID patients, including some who weren’t his patients or whom he never examined and a few who later died from the virus, according to the Washington Medical Commission.
“Miller’s treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care,” the suspension report states. “Miller began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative for COVID-19, and prescribing it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.”
Mr. Miller has until early November to respond to the allegations. On his clinic’s website, Mr. Miller stated, “In response to the charges, I want to reassure all of you that the initial attacks against me have been brought on by a small handful of people that have no ties to our medical practice, and by pharmacies and hospitals that have a zero tolerance policy on family members asking that I help them advocate for loved ones that have been admitted and written off in our current system of dismissiveness and neglect.”
Mr. Miller also expressed gratitude for the support he has received recently. A GoFundMe campaign to raise money for Mr. Miller’s legal fund had raised more than $59,000 at press time. His GoFundMe page had been shared 2,400 times. He has more than 550 followers and more than 400 donors.
“I don’t know that I have the words to adequately describe the deep sense of love and connection I have received from you, the families I serve, and those that have reached out to me in this deeply challenging time,” he wrote on the clinic website.
Mr. Miller has spoken publicly about his anti-mask views and his support for ivermectin, according to the commission report. As part of the suspension, he was charged with making “misleading representations regarding the efficacy of non-FDA approved treatment and mask use.”
In one case that was cited in the report, a 39-year-old patient contacted the pediatric clinic, and Mr. Miller spoke with the patient by phone. The patient reported that he had tested positive for COVID. Mr. Miller advised the patient to take supplements, including vitamin D and C, zinc, and melatonin, and he prescribed ivermectin, dexamethasone, and azithromycin. He did not perform an exam, verify the information that the patient had provided, advise the patient regarding interactions, or order follow-up testing, the report states.
Other charges against Mr. Miller include harassing hospital staff by making threatening statements about hospitals and doctors who treat COVID-19 patients and misrepresenting his original 2013 license application. He denied on the application that he was being investigated by another licensing board. At the time, the California Physician Assistant Board was investigating him for providing medical care and prescribing without a supervising doctor’s authorization and without conducting physical exams, among other charges.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The suspension stemmed from allegations against Scott C. Miller, PA-C, by at least six COVID patients, including some who weren’t his patients or whom he never examined and a few who later died from the virus, according to the Washington Medical Commission.
“Miller’s treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care,” the suspension report states. “Miller began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative for COVID-19, and prescribing it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.”
Mr. Miller has until early November to respond to the allegations. On his clinic’s website, Mr. Miller stated, “In response to the charges, I want to reassure all of you that the initial attacks against me have been brought on by a small handful of people that have no ties to our medical practice, and by pharmacies and hospitals that have a zero tolerance policy on family members asking that I help them advocate for loved ones that have been admitted and written off in our current system of dismissiveness and neglect.”
Mr. Miller also expressed gratitude for the support he has received recently. A GoFundMe campaign to raise money for Mr. Miller’s legal fund had raised more than $59,000 at press time. His GoFundMe page had been shared 2,400 times. He has more than 550 followers and more than 400 donors.
“I don’t know that I have the words to adequately describe the deep sense of love and connection I have received from you, the families I serve, and those that have reached out to me in this deeply challenging time,” he wrote on the clinic website.
Mr. Miller has spoken publicly about his anti-mask views and his support for ivermectin, according to the commission report. As part of the suspension, he was charged with making “misleading representations regarding the efficacy of non-FDA approved treatment and mask use.”
In one case that was cited in the report, a 39-year-old patient contacted the pediatric clinic, and Mr. Miller spoke with the patient by phone. The patient reported that he had tested positive for COVID. Mr. Miller advised the patient to take supplements, including vitamin D and C, zinc, and melatonin, and he prescribed ivermectin, dexamethasone, and azithromycin. He did not perform an exam, verify the information that the patient had provided, advise the patient regarding interactions, or order follow-up testing, the report states.
Other charges against Mr. Miller include harassing hospital staff by making threatening statements about hospitals and doctors who treat COVID-19 patients and misrepresenting his original 2013 license application. He denied on the application that he was being investigated by another licensing board. At the time, the California Physician Assistant Board was investigating him for providing medical care and prescribing without a supervising doctor’s authorization and without conducting physical exams, among other charges.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The suspension stemmed from allegations against Scott C. Miller, PA-C, by at least six COVID patients, including some who weren’t his patients or whom he never examined and a few who later died from the virus, according to the Washington Medical Commission.
“Miller’s treatment of COVID-19 patients fell below the standard of care,” the suspension report states. “Miller began a public campaign promoting ivermectin as a curative for COVID-19, and prescribing it without adequate examination to at least one person, with no reliable clinical studies that establish its efficacy in preventing or treating COVID-19.”
Mr. Miller has until early November to respond to the allegations. On his clinic’s website, Mr. Miller stated, “In response to the charges, I want to reassure all of you that the initial attacks against me have been brought on by a small handful of people that have no ties to our medical practice, and by pharmacies and hospitals that have a zero tolerance policy on family members asking that I help them advocate for loved ones that have been admitted and written off in our current system of dismissiveness and neglect.”
Mr. Miller also expressed gratitude for the support he has received recently. A GoFundMe campaign to raise money for Mr. Miller’s legal fund had raised more than $59,000 at press time. His GoFundMe page had been shared 2,400 times. He has more than 550 followers and more than 400 donors.
“I don’t know that I have the words to adequately describe the deep sense of love and connection I have received from you, the families I serve, and those that have reached out to me in this deeply challenging time,” he wrote on the clinic website.
Mr. Miller has spoken publicly about his anti-mask views and his support for ivermectin, according to the commission report. As part of the suspension, he was charged with making “misleading representations regarding the efficacy of non-FDA approved treatment and mask use.”
In one case that was cited in the report, a 39-year-old patient contacted the pediatric clinic, and Mr. Miller spoke with the patient by phone. The patient reported that he had tested positive for COVID. Mr. Miller advised the patient to take supplements, including vitamin D and C, zinc, and melatonin, and he prescribed ivermectin, dexamethasone, and azithromycin. He did not perform an exam, verify the information that the patient had provided, advise the patient regarding interactions, or order follow-up testing, the report states.
Other charges against Mr. Miller include harassing hospital staff by making threatening statements about hospitals and doctors who treat COVID-19 patients and misrepresenting his original 2013 license application. He denied on the application that he was being investigated by another licensing board. At the time, the California Physician Assistant Board was investigating him for providing medical care and prescribing without a supervising doctor’s authorization and without conducting physical exams, among other charges.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.