User login
Children and COVID: New cases and hospital admissions skyrocket
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.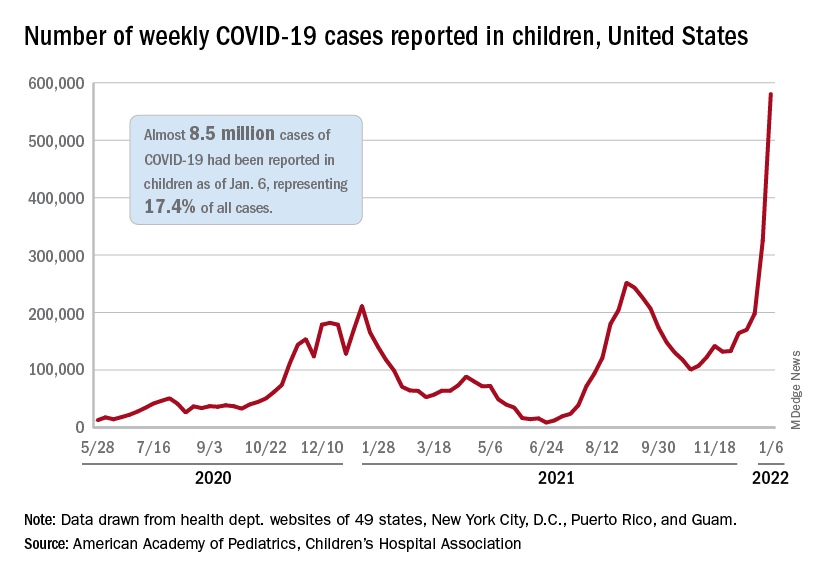
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
U.S. reports record-breaking 1.35 million new COVID cases in a day
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC: More kids hospitalized with COVID since pandemic began
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-vaccine myocarditis: Rare, mild, and usually in young men
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
At-risk Americans become eligible for fourth COVID shot this week
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
COVID-19 linked to increased diabetes risk in youth
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with an increased risk for diabetes among youth, whereas other acute respiratory infections were not, new data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate.
The results from two large U.S. health claims databases were published in an early release in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report by Catherine E. Barrett, PhD, and colleagues of the CDC’s COVID-19 Emergency Response Team and Division of Diabetes Translation.
Clinicians should monitor individuals younger than 18 years in the months following a SARS-CoV-2 infection for new diabetes onset, they advise.
The findings, which are supported by independent studies in adults, “underscore the importance of COVID-19 prevention among all age groups, including vaccination for all eligible children and adolescents, and chronic disease prevention and treatment,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
Diabetes type couldn’t be reliably distinguished from the databases, which is noted as an important study limitation.
“SARS-CoV-2 infection might lead to type 1 or type 2 diabetes through complex and differing mechanisms,” they say.
Emerging evidence began to suggest, in mid-2020, that COVID-19 may trigger the onset of diabetes in healthy people. A new global registry was subsequently established to collect data on patients with COVID-19–related diabetes, called the CoviDiab registry.
Not clear if diabetes after COVID-19 is transient or permanent
From one of the databases used in the new study, known as IQVIA, 80,893 individuals aged younger than 18 years diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 2020 to February 26, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched people during that period who did not have COVID-19 and to prepandemic groups with and without a diagnosis of acute respiratory illness during March 1, 2017, to February 26, 2018.
From the second database, HealthVerity, 439,439 youth diagnosed with COVID-19 during March 1, 2020, to June 28, 2021, were compared with age- and sex-matched youth without COVID-19. Here, there was no prepandemic comparison group.
Diabetes diagnoses were coded in 0.08% with COVID-19 vs. 0.03% without COVID-19 in IQVIA and in 0.25% vs. 0.19% in HealthVerity.
Thus, new diabetes diagnoses were 166% and 31% more likely to occur in those with COVID-19 in IQVIA and HealthVerity, respectively. And in IQVIA, those with COVID-19 were 116% more likely to develop diabetes than were those with prepandemic acute respiratory illnesses. Those differences were all significant, whereas non–SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections were not associated with diabetes, Dr. Barrett and colleagues say.
In both databases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common at diabetes onset among those with, vs. without, COVID-19: 48.5% vs. 13.6% in IQVIA and 40.2% vs. 29.7% in HealthVerity. In IQVIA, 22.0% with prepandemic acute respiratory illness presented with DKA.
Dr. Barrett and colleagues offer several potential explanations for the observed association between COVID-19 and diabetes, including a direct attack on pancreatic beta cells expressing angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, or via stress hyperglycemia resulting from cytokine storm and alterations in glucose metabolism.
Another possibility is the precipitation to diabetes from prediabetes; the latter is a condition present in one in five U.S. adolescents.
Steroid treatment during hospitalization might have led to transient hyperglycemia, but only 1.5% to 2.2% of diabetes codes were for drug- or chemical-induced diabetes. The majority were for type 1 or 2.
Alternatively, pandemic-associated weight gain might have also contributed to risks for both severe COVID-19 and type 2 diabetes.
“Although this study can provide information on the risk for diabetes following SARS-CoV-2 infection, additional data are needed to understand underlying pathogenic mechanisms, either those caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection itself or resulting from treatments, and whether a COVID-19–associated diabetes diagnosis is transient or leads to a chronic condition,” Dr. Barrett and colleagues conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MMWR
As pandemic regs expire, states get tougher on telehealth: report
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among the most important restrictions that have been reinstated in some states are those barring requirements for insurers to cover telehealth and regulations that prohibit telehealth visits across state lines, unless the physician is licensed in both states.
“Only three states – Arizona, Florida, and Indiana – allow all health care providers to easily practice telehealth across state lines,” says a news release on the think tanks’ report. “Forty-seven others have arbitrary barriers in place that limit patients’ access to specialists and available appointments based purely on residency.”
“Once the [state-based] public health emergency declarations started to end or executive orders were withdrawn, many of the new flexibilities for providers, insurers, and patients were lost overnight,” Vittorio Nastasi, a policy analyst at Reason Foundation and a co-author of the report, says in the news release. “States need to adopt a number of telehealth reforms to provide their residents better access to this safe and effective virtual care.”
On a positive note, the report says, most states have removed the requirement that a patient must first see a provider in person before they can use telehealth services. The exceptions are Tennessee, Alaska, and West Virginia, which require an in-person visit before certain telehealth services can be provided.
In addition, 20 states allow nurse practitioners to conduct telehealth visits without being under the supervision of a physician. Prior to the pandemic, some states allowed only doctors to use telehealth, the report says, but, during the COVID crisis, “the acute shortage of providers in many counties adds to the need for more kinds of providers to be able to use it.”
A number of states place restrictions on the telehealth modalities that can be utilized. Under the definition by the American Telemedicine Association, telehealth includes audio-video visits, remote patient monitoring, and “store and forward” telemedicine, which entails collecting clinical information and sending it to another site for evaluation. The latter method is particularly useful for consultations with specialists, the report notes.
Coverage mandates and payment parity
The report also examines other parameters of telehealth regulations in each state, including whether they have telehealth coverage mandates and whether they require physicians to be paid the same amount for similar types of in-person and telehealth visits.
The report views insurance mandates as beneficial, but not if they require coverage of all virtual services. While telehealth can be a game changer for post-stroke care and for other “treatment-intensive conditions,” the report says, the evidence of better outcomes for other conditions treated through telehealth is far less certain. Therefore, it advises states to “protect flexibility so that new innovative models can emerge.”
Ateev Mehrotra, MD, a professor at Harvard Medical School who studies telehealth, agrees that it offers more value in some clinical situations than in others. “High value is improving quality or outcomes at a reasonable cost,” he told this news organization. “If a telemedicine visit for stroke can save a person’s life and prevent disability, let’s pay for it. A telemedicine visit for a cold may not be necessary. Mom’s chicken soup is fine.”
A little over half of the states still require payment parity, according to the report. While these regulations are intended to promote the use of telehealth, the authors note, they can increase the growth of health care costs. Moreover, they argue, it’s hard to defend equal payments for virtual visits when the overhead required to deliver them – such as office rental, utility, and labor costs – is much lower than that for in-person visits. Also, it makes no sense for health systems to charge facility fees for telehealth visits when these visits can be initiated from anywhere, they say.
Dr. Mehrotra concurs with this view. “If you see someone in your office, your fee includes all the overhead for your office, and it’s a substantial cost,” he says. “For many procedures, it’s more than half of the cost. If you have a telemedicine visit and you’re at home, why would you pay the same amount? The visit may take the same amount of time, but all the money that goes for overhead is not accounted for.”
Telemedicine across state lines
The report’s contention about the difficulty of conducting telehealth encounters across most state lines seems to be at odds with the growth in the Interstate Medical Licensure Compact, which makes it easier for physicians in one compact member state to get licensed in others. Currently, 35 states belong to the compact, Joe Knickrehm, vice president of communications for the Federation of State Medical Boards, told this news organization.
In addition, he says, “12 state boards issue a special purpose license, telemedicine license or certificate, or license to practice medicine across state lines to allow for the practice of telemedicine.”
The catch, Dr. Mehrotra says, is that, despite the streamlining of license applications in compact member states, the fees charged by the state boards are still very high – a point that the report also makes. “If I want to have broad scope of practice, I’d have to pay thousands of dollars to many states. The license fees start to add up. Also, I have to keep track of each state’s CME requirements, which are all different. Keeping up with all of that is an administration burden, and it’s a pain.”
Mr. Knickrehm contends that obtaining multiple licenses via the compact “is generally less expensive for physicians than the cost of requesting transcripts, fingerprints, and other necessary paperwork each time they apply for licensure in a new state. Physicians are seeing the benefits of an expedited process that allows them to begin practicing more quickly [in other states].”
Dr. Mehrotra says he has seen the same retrenchment in state telehealth regulations that the report references. However, he says, “CMS [the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services] has signaled that at least through 2022 and maybe into 2023, they’ll continue their extensions of telemedicine [pandemic regulations].” After that, Congress would have to decide whether to make the changes permanent.
“Right now, it’s hard for me to see how a payer is going to pull back on telehealth, unless there’s ample evidence of overuse of telehealth,” he argues. “With the public and providers liking telehealth, it’s hard to say on theoretical grounds that we should stop using it. That’s why Medicare and others have extended it and why Congress will too.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccination has little impact on menstrual cycle
Women may rest a bit easier thanks to results from a study showing that vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 virus has almost no impact on a woman’s menstrual cycle. The issue is significant, as regular menstruation is a sign of health and fertility, and fears of disturbances might increase vaccination hesitancy as COVID-19 cases continue to surge.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, led a group studying prospective data on almost 24,000 menstrual cycles reported by almost 4,000 U.S. women.
The investigators found that COVID-19 vaccination was associated with a less than 1-day change in cycle length for the menstrual cycles after the first and second inoculations, compared with prevaccine cycles. Vaccination had no effect on the actual number of days menstrual bleeding lasted.
The study looked at the menstrual patterns of women aged 18-45 years with normal cycle lengths of 24-38 days for the three consecutive cycles before the first vaccine dose and for three consecutive postvaccine cycles. The final sample included 2,403 vaccinated and 1,556 unvaccinated individuals.
In vaccinated women, the study initially found a slight average increase in cycle length after dose one of 71% of a day and 91% of a day after dose two. Following adjustments, those increases dropped to 64% of a day after the first dose and 79% of a day after the second dose.
In unvaccinated women, the study looked at six cycles over a similar time period and found no significant changes from baseline.
“Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination is associated with a small change in cycle length but not menses length,” Dr. Edelman’s group concluded in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
In the rare instance that a woman received two vaccine doses within the same menstrual cycle, the change in length could increase to 2 days. These variations appear to resolve quickly, possibly as soon as the next cycle after vaccination and do not indicate any cause for long-term physical or reproductive health concern, according to the authors.
Reports by women on social media, however, have suggested that postvaccine menstrual disruptions are more common with, for example, heavier and breakthrough bleeding. But it appears such changes are temporary and resolve quickly.
“These findings are reassuring and validating,” Dr. Edelman said in an interview. On a population level, the changes indicate no cause for concern for long-term physical or reproductive health and no reason to avoid vaccination. “On a personal level, people want this information so they know what to expect when they get vaccinated, and not worry about a pregnancy scare or be disappointed if they were trying for pregnancy.”
According to the International Federation of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, variations in cycle length of fewer than 8 days are considered normal, said Christine Metz, PhD, a research biologist and a professor of molecular medicine at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y. “Thus, the extra 17 hours added to the menstrual cycle length in the vaccination group in this study is well within the ‘normal’ range.”
In a group of about 1,600 menstruating women being studied at Dr. Metz’s center, some have anecdotally reported transient cycle changes post vaccination for COVID-19, including delays in menstruation onset and changes in bleeding patterns.
Exactly how vaccination might alter menstrual cycle length is not known and has not been studied with vaccination against other infections such as influenza and meningococcal disease.
“Many factors are known to affect menstrual cycle length including changes in diet, sleep, and exercise, as well as sickness, travel, and stress,” Dr. Metz said. The COVID-19 vaccines have affected people in different ways, with side effects ranging from injection-site pain to nausea, aches, fever, and fatigue. “Vaccination side effects, particularly if severe, could lead to changes in diet, exercise, and sleep, and feelings of sickness and/or stress.”
These stressors can alter hormone production and stability, as well as the body’s response to hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and other hormones associated with female reproduction. “Because these hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, variations in these hormones can either shorten or lengthen the cycle,” Dr. Metz explained.
More research needs to be done at the global level, according to the authors. “Questions remain about other possible changes in menstrual cycles, such as menstrual symptoms, unscheduled bleeding, and changes in the quality and quantity of menstrual bleeding.”
This research was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Edelman reported support from the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the World Health Organization, Gynuity, and the Karolinska Institute as well as royalties from UpToDate. Other study authors reported similar relationships with not-for-profit and private-sector companies. Three coauthors are employees of Natural Cycles, a fertility tracking device that was used in the study. Dr. Metz disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to her comments.
Women may rest a bit easier thanks to results from a study showing that vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 virus has almost no impact on a woman’s menstrual cycle. The issue is significant, as regular menstruation is a sign of health and fertility, and fears of disturbances might increase vaccination hesitancy as COVID-19 cases continue to surge.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, led a group studying prospective data on almost 24,000 menstrual cycles reported by almost 4,000 U.S. women.
The investigators found that COVID-19 vaccination was associated with a less than 1-day change in cycle length for the menstrual cycles after the first and second inoculations, compared with prevaccine cycles. Vaccination had no effect on the actual number of days menstrual bleeding lasted.
The study looked at the menstrual patterns of women aged 18-45 years with normal cycle lengths of 24-38 days for the three consecutive cycles before the first vaccine dose and for three consecutive postvaccine cycles. The final sample included 2,403 vaccinated and 1,556 unvaccinated individuals.
In vaccinated women, the study initially found a slight average increase in cycle length after dose one of 71% of a day and 91% of a day after dose two. Following adjustments, those increases dropped to 64% of a day after the first dose and 79% of a day after the second dose.
In unvaccinated women, the study looked at six cycles over a similar time period and found no significant changes from baseline.
“Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination is associated with a small change in cycle length but not menses length,” Dr. Edelman’s group concluded in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
In the rare instance that a woman received two vaccine doses within the same menstrual cycle, the change in length could increase to 2 days. These variations appear to resolve quickly, possibly as soon as the next cycle after vaccination and do not indicate any cause for long-term physical or reproductive health concern, according to the authors.
Reports by women on social media, however, have suggested that postvaccine menstrual disruptions are more common with, for example, heavier and breakthrough bleeding. But it appears such changes are temporary and resolve quickly.
“These findings are reassuring and validating,” Dr. Edelman said in an interview. On a population level, the changes indicate no cause for concern for long-term physical or reproductive health and no reason to avoid vaccination. “On a personal level, people want this information so they know what to expect when they get vaccinated, and not worry about a pregnancy scare or be disappointed if they were trying for pregnancy.”
According to the International Federation of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, variations in cycle length of fewer than 8 days are considered normal, said Christine Metz, PhD, a research biologist and a professor of molecular medicine at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y. “Thus, the extra 17 hours added to the menstrual cycle length in the vaccination group in this study is well within the ‘normal’ range.”
In a group of about 1,600 menstruating women being studied at Dr. Metz’s center, some have anecdotally reported transient cycle changes post vaccination for COVID-19, including delays in menstruation onset and changes in bleeding patterns.
Exactly how vaccination might alter menstrual cycle length is not known and has not been studied with vaccination against other infections such as influenza and meningococcal disease.
“Many factors are known to affect menstrual cycle length including changes in diet, sleep, and exercise, as well as sickness, travel, and stress,” Dr. Metz said. The COVID-19 vaccines have affected people in different ways, with side effects ranging from injection-site pain to nausea, aches, fever, and fatigue. “Vaccination side effects, particularly if severe, could lead to changes in diet, exercise, and sleep, and feelings of sickness and/or stress.”
These stressors can alter hormone production and stability, as well as the body’s response to hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and other hormones associated with female reproduction. “Because these hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, variations in these hormones can either shorten or lengthen the cycle,” Dr. Metz explained.
More research needs to be done at the global level, according to the authors. “Questions remain about other possible changes in menstrual cycles, such as menstrual symptoms, unscheduled bleeding, and changes in the quality and quantity of menstrual bleeding.”
This research was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Edelman reported support from the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the World Health Organization, Gynuity, and the Karolinska Institute as well as royalties from UpToDate. Other study authors reported similar relationships with not-for-profit and private-sector companies. Three coauthors are employees of Natural Cycles, a fertility tracking device that was used in the study. Dr. Metz disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to her comments.
Women may rest a bit easier thanks to results from a study showing that vaccination against the SARS-CoV-2 virus has almost no impact on a woman’s menstrual cycle. The issue is significant, as regular menstruation is a sign of health and fertility, and fears of disturbances might increase vaccination hesitancy as COVID-19 cases continue to surge.
Alison Edelman, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, led a group studying prospective data on almost 24,000 menstrual cycles reported by almost 4,000 U.S. women.
The investigators found that COVID-19 vaccination was associated with a less than 1-day change in cycle length for the menstrual cycles after the first and second inoculations, compared with prevaccine cycles. Vaccination had no effect on the actual number of days menstrual bleeding lasted.
The study looked at the menstrual patterns of women aged 18-45 years with normal cycle lengths of 24-38 days for the three consecutive cycles before the first vaccine dose and for three consecutive postvaccine cycles. The final sample included 2,403 vaccinated and 1,556 unvaccinated individuals.
In vaccinated women, the study initially found a slight average increase in cycle length after dose one of 71% of a day and 91% of a day after dose two. Following adjustments, those increases dropped to 64% of a day after the first dose and 79% of a day after the second dose.
In unvaccinated women, the study looked at six cycles over a similar time period and found no significant changes from baseline.
“Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination is associated with a small change in cycle length but not menses length,” Dr. Edelman’s group concluded in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
In the rare instance that a woman received two vaccine doses within the same menstrual cycle, the change in length could increase to 2 days. These variations appear to resolve quickly, possibly as soon as the next cycle after vaccination and do not indicate any cause for long-term physical or reproductive health concern, according to the authors.
Reports by women on social media, however, have suggested that postvaccine menstrual disruptions are more common with, for example, heavier and breakthrough bleeding. But it appears such changes are temporary and resolve quickly.
“These findings are reassuring and validating,” Dr. Edelman said in an interview. On a population level, the changes indicate no cause for concern for long-term physical or reproductive health and no reason to avoid vaccination. “On a personal level, people want this information so they know what to expect when they get vaccinated, and not worry about a pregnancy scare or be disappointed if they were trying for pregnancy.”
According to the International Federation of Gynecologists and Obstetricians, variations in cycle length of fewer than 8 days are considered normal, said Christine Metz, PhD, a research biologist and a professor of molecular medicine at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, N.Y. “Thus, the extra 17 hours added to the menstrual cycle length in the vaccination group in this study is well within the ‘normal’ range.”
In a group of about 1,600 menstruating women being studied at Dr. Metz’s center, some have anecdotally reported transient cycle changes post vaccination for COVID-19, including delays in menstruation onset and changes in bleeding patterns.
Exactly how vaccination might alter menstrual cycle length is not known and has not been studied with vaccination against other infections such as influenza and meningococcal disease.
“Many factors are known to affect menstrual cycle length including changes in diet, sleep, and exercise, as well as sickness, travel, and stress,” Dr. Metz said. The COVID-19 vaccines have affected people in different ways, with side effects ranging from injection-site pain to nausea, aches, fever, and fatigue. “Vaccination side effects, particularly if severe, could lead to changes in diet, exercise, and sleep, and feelings of sickness and/or stress.”
These stressors can alter hormone production and stability, as well as the body’s response to hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, and other hormones associated with female reproduction. “Because these hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, variations in these hormones can either shorten or lengthen the cycle,” Dr. Metz explained.
More research needs to be done at the global level, according to the authors. “Questions remain about other possible changes in menstrual cycles, such as menstrual symptoms, unscheduled bleeding, and changes in the quality and quantity of menstrual bleeding.”
This research was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Edelman reported support from the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the World Health Organization, Gynuity, and the Karolinska Institute as well as royalties from UpToDate. Other study authors reported similar relationships with not-for-profit and private-sector companies. Three coauthors are employees of Natural Cycles, a fertility tracking device that was used in the study. Dr. Metz disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to her comments.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
First ‘flurona’ cases reported in the U.S.
The first known case was detected in Israel, but until the first week of January no cases had been reported in the United States.
In Los Angeles, a teenaged boy tested positive for both illnesses at a COVID testing site in Brentwood, the Los Angeles Times reported. The child’s mother tested positive for COVID the next day.
“This is the first one that we’re aware of,” Steve Farzam, chief operating officer of 911 COVID Testing, told the LA Times. “In and of itself, it’s not overly concerning; however, it is concerning and can be problematic for someone who has pre-existing medical conditions, anyone who is immunocompromised.”
The teen and his family of five had just returned from vacation in Cabo San Lucas, Mexico. All said they tested negative before the trip, but they tested again when they got home because one of the children had a runny nose, Mr. Farzam said.
The boy, who had not been vaccinated for COVID or the flu, doesn’t have serious symptoms and is recovering at home.
In Houston, a 17-year-old boy, his siblings, and his father felt sick a few days before Christmas and went in for testing, TV station KTRK reported. The teen tested positive for both the flu and COVID.
“I ended up getting tested the day before Christmas for strep throat, flu and COVID,” the teenager, Alec Zierlein, told KTRK. “I didn’t think I had any of the three. It felt like a mild cold.”
Health officials reported Jan. 5 that a flurona case was detected in Hays, Kan., TV station WIBW reported. The patient was being treated in the ICU. No other details were provided. In Israel, flurona was first found in an unvaccinated pregnant woman at Rabin Medical Center in Petach Tikva, according to the Times of Israel. She tested positive for both viruses when she arrived at the medical center, and doctors double-checked to confirm her diagnosis. The woman had mild symptoms and was released in good condition, the news outlet reported.
Public health officials in Israel said they are concerned that an increase in both viruses at the same time could lead to many hospitalizations.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first known case was detected in Israel, but until the first week of January no cases had been reported in the United States.
In Los Angeles, a teenaged boy tested positive for both illnesses at a COVID testing site in Brentwood, the Los Angeles Times reported. The child’s mother tested positive for COVID the next day.
“This is the first one that we’re aware of,” Steve Farzam, chief operating officer of 911 COVID Testing, told the LA Times. “In and of itself, it’s not overly concerning; however, it is concerning and can be problematic for someone who has pre-existing medical conditions, anyone who is immunocompromised.”
The teen and his family of five had just returned from vacation in Cabo San Lucas, Mexico. All said they tested negative before the trip, but they tested again when they got home because one of the children had a runny nose, Mr. Farzam said.
The boy, who had not been vaccinated for COVID or the flu, doesn’t have serious symptoms and is recovering at home.
In Houston, a 17-year-old boy, his siblings, and his father felt sick a few days before Christmas and went in for testing, TV station KTRK reported. The teen tested positive for both the flu and COVID.
“I ended up getting tested the day before Christmas for strep throat, flu and COVID,” the teenager, Alec Zierlein, told KTRK. “I didn’t think I had any of the three. It felt like a mild cold.”
Health officials reported Jan. 5 that a flurona case was detected in Hays, Kan., TV station WIBW reported. The patient was being treated in the ICU. No other details were provided. In Israel, flurona was first found in an unvaccinated pregnant woman at Rabin Medical Center in Petach Tikva, according to the Times of Israel. She tested positive for both viruses when she arrived at the medical center, and doctors double-checked to confirm her diagnosis. The woman had mild symptoms and was released in good condition, the news outlet reported.
Public health officials in Israel said they are concerned that an increase in both viruses at the same time could lead to many hospitalizations.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first known case was detected in Israel, but until the first week of January no cases had been reported in the United States.
In Los Angeles, a teenaged boy tested positive for both illnesses at a COVID testing site in Brentwood, the Los Angeles Times reported. The child’s mother tested positive for COVID the next day.
“This is the first one that we’re aware of,” Steve Farzam, chief operating officer of 911 COVID Testing, told the LA Times. “In and of itself, it’s not overly concerning; however, it is concerning and can be problematic for someone who has pre-existing medical conditions, anyone who is immunocompromised.”
The teen and his family of five had just returned from vacation in Cabo San Lucas, Mexico. All said they tested negative before the trip, but they tested again when they got home because one of the children had a runny nose, Mr. Farzam said.
The boy, who had not been vaccinated for COVID or the flu, doesn’t have serious symptoms and is recovering at home.
In Houston, a 17-year-old boy, his siblings, and his father felt sick a few days before Christmas and went in for testing, TV station KTRK reported. The teen tested positive for both the flu and COVID.
“I ended up getting tested the day before Christmas for strep throat, flu and COVID,” the teenager, Alec Zierlein, told KTRK. “I didn’t think I had any of the three. It felt like a mild cold.”
Health officials reported Jan. 5 that a flurona case was detected in Hays, Kan., TV station WIBW reported. The patient was being treated in the ICU. No other details were provided. In Israel, flurona was first found in an unvaccinated pregnant woman at Rabin Medical Center in Petach Tikva, according to the Times of Israel. She tested positive for both viruses when she arrived at the medical center, and doctors double-checked to confirm her diagnosis. The woman had mild symptoms and was released in good condition, the news outlet reported.
Public health officials in Israel said they are concerned that an increase in both viruses at the same time could lead to many hospitalizations.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Could the Omicron surge hasten the transition from pandemic to endemic?
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The record-setting surge in COVID-19 cases nationwide – including more than one million new infections reported on Jan. 3 – raises questions about whether the higher Omicron variant transmissibility will accelerate a transition from pandemic to endemic disease.
Furthermore,
Infectious disease experts weigh in on these possibilities.
An endemic eventuality?
Whether the current surge will mean the predicted switch to endemic COVID-19 will come sooner “is very hard to predict,” Michael Lin, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“It’s an open question,” he said, “if another highly transmissible variant will emerge.”
On a positive note, “at this point many more people have received their vaccinations or been infected. And over time, repeated infections have led to milder symptoms,” added Dr. Lin, hospital epidemiologist at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
“It could end up being a seasonal variant,” he said.
COVID-19 going endemic is “a real possibility, but unfortunately ... it doesn’t seem necessarily that we’re going to have the same predictable pattern we have with the flu,” said Eleftherios Mylonakis, MD, PhD, chief of infectious diseases for Lifespan and its affiliates at Rhode Island Hospital and Miriam Hospital in Providence.
“We have a number of other viruses that don’t follow the same annual pattern,” he said.
Unknowns include how long individuals’ immune responses, including T-cell defenses, will last going forward.
A transition from pandemic to endemic is “not a light switch, and there are no metrics associated with what endemic means for COVID-19,” said Syra Madad, DHSc., MSc, MCP, an infectious disease epidemiologist at Harvard’s Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs, Boston.
“Instead, we should continue to focus on decreasing transmission rates and preventing our hospitals from getting overwhelmed,” she said.
A hastening to herd immunity?
“The short answer is yes,” Dr. Lin said when asked if the increased transmissibility and increased cases linked to the Omicron surge could get the U.S. closer to herd immunity.
“The twist in this whole story,” he said, “is the virus mutated enough to escape first-line immune defenses, specifically antibodies. That is why we are seeing breakthrough infections, even in highly vaccinated populations.”
Dr. Mylonakis was more skeptical regarding herd immunity.
“The concept of herd immunity with a rapidly evolving virus is very difficult” to address, he said.
One reason is the number of unknown factors, Dr. Mylonakis said. He predicted a clearer picture will emerge after the Omicrons surge subsides. Also, with so many people infected by the Omicron variant, immune protection should peak.
“People will have boosted immunity. Not everybody, unfortunately, because there are people who cannot really mount [a full immune response] because of age, because of immunosuppression, etc.,” said Dr. Mylonakis, who is also professor of infectious diseases at Brown University.
“But the majority of the population will be exposed and will mount some degree of immunity.”
Dr. Madad agreed. “The omicron variant will add much more immunity into our population by both the preferred pathway – which is through vaccination – as well as through those that are unvaccinated and get infected with omicron,” she said.
“The pathway to gain immunity from vaccination is the safest option, and already over 1 million doses of the COVID-19 vaccine are going into arms per day – this includes first, second, and additional doses like boosters,” added Dr. Madad, who is also senior director of the System-wide Special Pathogens Program at New York City Health and Hospitals.
A shorter, more intense surge?
The United Kingdom’s experience with COVID-19 has often served as a bellwether of what is likely to happen in the U.S. If that is the case with the Omicron surge, the peak should last about 4 weeks, Dr. Mylonakis said.
In other words, the accelerated spread of Omicron could mean this surge passes more quickly than Delta.
Furthermore, some evidence suggests neutralizing antibodies produced by Omicron infection remain effective against the Delta variant – thereby reducing the risk of Delta reinfections over time.
The ability to neutralize the Delta variant increased more than fourfold after a median 14 days, according to data from a preprint study posted Dec. 27 on MedRxiv.
At the same time, neutralization of the Omicron variant increased 14-fold as participants mounted an antibody response. The study was conducted in vaccinated and unvaccinated people infected by Omicron in South Africa shortly after symptoms started. It has yet to be peer reviewed.
Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, described the results as “especially good news” in a tweet.
The current surge could also mean enhanced protection in the future.
“As we look at getting to the other side of this Omicron wave, we will end up with more immunity,” Dr. Madad said. “And with more immunity means we’ll be better guarded against the next emerging variant.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.