User login
Negative home COVID test no ‘free pass’ for kids, study finds
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
With the country looking increasingly to rapid testing as an off-ramp from the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study shows that the performance of the tests in children falls below standards set by regulatory agencies in the United States and elsewhere for diagnostic accuracy.
Experts said the findings, from a meta-analysis by researchers in the United Kingdom and Germany, underscore that, while a positive result on a rapid test is almost certainly an indicator of infection, negative results often are unreliable and can lead to a false sense of security.
“Real-life performance of current antigen tests for professional use in pediatric populations is below the minimum performance criteria set by WHO, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (U.K.),” according to Naomi Fujita-Rohwerder, PhD, a research associate at the Cologne-based German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG), and her colleagues, whose study appears in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
The researchers said that the study suggests that performance of rapid testing in a pediatric population is comparable to that in adults. However, they said they could not identify any studies investigating self-testing in children, which also could affect test performance.
Egon Ozer, MD, PhD, director of the center for pathogen genomics and microbial evolution at Northwestern University in Chicago, said the finding that specificity was high but sensitivity was middling “suggests that we should be very careful about interpreting negative antigen test results in children and recognize that there is a fair amount of uncertainty in the tests in this situation.”
Researchers from IQWiG, which examines the advantages and disadvantages of medical interventions, and the University of Manchester (England), conducted the systematic review and meta-analysis, which they described as the first of its kind to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of rapid point-of-care tests for current SARS-CoV-2 infections in children.
They compiled information from 17 studies with a total 6,355 participants. They compared all antigen tests to reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The studies compared eight antigen tests from six different brands. The rapid antigen tests, available from pharmacies and online stores, are widely used for self-testing in schools and testing toddlers before kindergarten.
The pooled diagnostic sensitivity of antigen tests was 64.2% and specificity was 99.1%.
Dr. Ozer noted that the analysis “was not able to address important outstanding questions such as the likelihood of transmitting infection with a false-negative antigen test versus a true-negative antigen test or how much repeated testing can increase the sensitivity.”
“In Europe, we don’t know how most tests perform in real life,” Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said. “And even in countries like the United States, where market access is more stringent, we don’t know whether self-testing performed by children or sample collection in toddlers by laypersons has a significant impact on the diagnostic accuracy. Also, diagnostic accuracy estimates reported in our study may not apply to the current omicron or future variants of SARS-CoV-2 or vaccinated children. Hopefully, these essential gaps in the evidence will get addressed soon.”
Dr. Ozer said one takeaway from this study is negative antigen tests should not be considered a “free pass” in children, especially if the child is symptomatic, has been recently exposed to COVID-19, or is planning to spend time with individuals with conditions that place them at high risk for complications of COVID-19 infection. “In such cases, consider getting PCR testing or at least performing a repeat antigen test 36-48 hours after the first negative,” he said.
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder said the low diagnostic sensitivity may affect the use of the tests. The gaps in evidence her group found in their study point to research needed to support evidence-based decision-making. “In particular, evidence is needed on real-life performance of tests in schools, self-testing performed by children, and kindergarten, [particularly] sample collection in toddlers by laypersons,” she said.
However, she stressed, testing is only a single measure. “Effectively reducing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 during the current pandemic requires multilayered mitigation measures,” she said. “Rapid testing represents one single layer. It can have its use at the population level, even though the sensitivity of antigen tests is lower than expected. However, antigen-based rapid testing is not a magic bullet: If your kid tests negative, do not disregard other mitigation measures.”
Edward Campbell, PhD, a virologist at Loyola University of Chicago, who serves on the board of LaGrange Elementary School District 102 outside Chicago, said the findings were unsurprising.
“This study generally looks consistent with what is known for adults. These rapid antigen tests are less sensitive than other tests,” said Dr. Campbell, who also runs a testing company for private schools in the Chicago area using reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. Even so, he said, “These tests are still effective at identifying people who are infectious to some degree. Never miss an opportunity to test.”
Dr. Fujita-Rohwerder disclosed no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Campbell owns Safeguard Surveillance.
BMJ EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE
Feds’ website for free at-home COVID tests launches day early
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Biden administration’s new no-cost, at-home testing program launched Jan. 18, a day ahead of schedule.
The administration said 500 million tests are available to be delivered to homes across the country. This accounts for half of the president’s recent pledge to purchase 1 billion free at-home COVID-19 tests to distribute to the American public.
On a Jan. 14 call with reporters, senior White House officials offered some details about the new program.
Here’s what we know so far.
How do I order my free tests?
Americans can visit COVIDtests.gov to order their rapid at-home tests. You can also order directly from the U.S. Postal Service website. After you order, you’ll receive a confirmation email that promises to send tracking information once your order ships.
What information do I need to order the tests?
You only need your name and home mailing address.
There is also an option to provide your email address to get updates on the status of your order.
What if someone needs help ordering the tests?
There will be a free call-in line for people needing more help, including those having trouble accessing the internet, according to White House officials.
What tests will be available?
There are nine at-home tests available through FDA emergency use authorization. According to the Frequently Asked Questions section of COVIDtests.gov, "You will not be able to choose the brand you order as part of this program.”
How long will it take to get the tests once I order them?
Tests are expected to ship 7 to 12 days after you order them.
But White House officials say that the time frame will likely shorten as the program gains steam.
How many can I order?
There’s a limit of four tests per residential mailing address.
For larger families, White House officials suggest trying other free testing options, like visiting COVID-19 testing sites or your local health center.
Is this a one-time opportunity?
The White House doesn’t say, but officials did mention that if you run out of your four free tests, there are many other ways to access free at-home tests, such as COVID-19 testing sites, pharmacies, and community health centers.
The free tests available through COVIDtests.gov are in addition to an estimated 375 million at-home rapid tests on the market in the U.S. this month.
When should people use a rapid at-home test?
The CDC and experts with other public health groups agree that Americans should consider using at-home rapid tests in the following situations:
- If they begin to have symptoms consistent with COVID-19;
- At least 5 days after close contact with someone who has COVID;
- If someone is indoors with a group of people who are at risk of severe disease or are unvaccinated.
Are at-home rapid tests accurate?
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal officials confirmed through studies that all tests distributed through this program can detect the Omicron variant. These agencies also confirmed that their performance is consistent with the FDA’s emergency use authorization.
Is the website designed to handle high demand?
After the original website to sign up for health insurance under the Affordable Care Act crashed repeatedly at launch, the government says it has prepared for high demand for ordering at-home rapid tests.
The U.S. Digital Service (USDS), an organization founded after Healthcare.gov, has partnered with the Postal Service to plan for the launch.
The Postal Service has expanded its staffing, similar to what’s done during the holidays.
All orders in the continental United States will be shipped through first-class mail, with shipments to Alaska, Hawaii, U.S. territories, and military and overseas addresses sent through priority mail.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Federal website for free COVID-19 tests opens Jan. 19
The tests will ship within 7 to 12 days after being ordered, senior officials from President Joe Biden’s administration said Jan. 14. The U.S. Postal Service will handle the shipping and delivery through first-class mail.
People will input their name and mailing address on the website and can share an email address to receive updates on the order, according to NPR. People won’t need to pay shipping costs or enter a credit card number to order tests, according to the website’s homepage.
The website will be offered in both English and Spanish. The Biden administration will also set up a phone number so those without internet access can place orders.
Officials didn’t share a specific time that the website will open, according to he New York Times — simply that it will go live sometime on Jan. 19. Each household will be limited to ordering four tests.
Starting Jan. 15, people with private insurance were able to seek reimbursement for tests they purchase on their own. At the same time, some insurers have said it could take weeks to set up a system for smooth reimbursement, the newspaper reported.
Last week’s announcement is the latest step in the president’s pledge to get coronavirus tests to Americans. In December, Biden said his administration would purchase 500 million tests and distribute them to Americans for free. On Jan. 13, he announced that the administration would buy another 500 million tests, bringing the total to 1 billion.
So far, the administration has signed contracts to produce 420 million tests, the newspaper reported. With the website opening this week and the lag in shipping, the tests will likely arrive by the end of January at the earliest, which could be after the peak of the current coronavirus surge in some parts of the country.
At-home tests have been in high demand, with some pharmacies, retailers, and websites reporting no stock in recent weeks. People have lined up at community testing sites for hours to get tested as the national average of daily cases has climbed above 800,000 last week.
Some consumers have also been confused about how or when to use at-home tests. On Jan. 14, Biden administration officials said that people should use rapid tests for three reasons:
- If they begin to experience COVID-19 symptoms;
- When it has been five or more days after being exposed to someone who tests positive;
- If they are gathering indoors with a high-risk person and want to check if they are negative.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The tests will ship within 7 to 12 days after being ordered, senior officials from President Joe Biden’s administration said Jan. 14. The U.S. Postal Service will handle the shipping and delivery through first-class mail.
People will input their name and mailing address on the website and can share an email address to receive updates on the order, according to NPR. People won’t need to pay shipping costs or enter a credit card number to order tests, according to the website’s homepage.
The website will be offered in both English and Spanish. The Biden administration will also set up a phone number so those without internet access can place orders.
Officials didn’t share a specific time that the website will open, according to he New York Times — simply that it will go live sometime on Jan. 19. Each household will be limited to ordering four tests.
Starting Jan. 15, people with private insurance were able to seek reimbursement for tests they purchase on their own. At the same time, some insurers have said it could take weeks to set up a system for smooth reimbursement, the newspaper reported.
Last week’s announcement is the latest step in the president’s pledge to get coronavirus tests to Americans. In December, Biden said his administration would purchase 500 million tests and distribute them to Americans for free. On Jan. 13, he announced that the administration would buy another 500 million tests, bringing the total to 1 billion.
So far, the administration has signed contracts to produce 420 million tests, the newspaper reported. With the website opening this week and the lag in shipping, the tests will likely arrive by the end of January at the earliest, which could be after the peak of the current coronavirus surge in some parts of the country.
At-home tests have been in high demand, with some pharmacies, retailers, and websites reporting no stock in recent weeks. People have lined up at community testing sites for hours to get tested as the national average of daily cases has climbed above 800,000 last week.
Some consumers have also been confused about how or when to use at-home tests. On Jan. 14, Biden administration officials said that people should use rapid tests for three reasons:
- If they begin to experience COVID-19 symptoms;
- When it has been five or more days after being exposed to someone who tests positive;
- If they are gathering indoors with a high-risk person and want to check if they are negative.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The tests will ship within 7 to 12 days after being ordered, senior officials from President Joe Biden’s administration said Jan. 14. The U.S. Postal Service will handle the shipping and delivery through first-class mail.
People will input their name and mailing address on the website and can share an email address to receive updates on the order, according to NPR. People won’t need to pay shipping costs or enter a credit card number to order tests, according to the website’s homepage.
The website will be offered in both English and Spanish. The Biden administration will also set up a phone number so those without internet access can place orders.
Officials didn’t share a specific time that the website will open, according to he New York Times — simply that it will go live sometime on Jan. 19. Each household will be limited to ordering four tests.
Starting Jan. 15, people with private insurance were able to seek reimbursement for tests they purchase on their own. At the same time, some insurers have said it could take weeks to set up a system for smooth reimbursement, the newspaper reported.
Last week’s announcement is the latest step in the president’s pledge to get coronavirus tests to Americans. In December, Biden said his administration would purchase 500 million tests and distribute them to Americans for free. On Jan. 13, he announced that the administration would buy another 500 million tests, bringing the total to 1 billion.
So far, the administration has signed contracts to produce 420 million tests, the newspaper reported. With the website opening this week and the lag in shipping, the tests will likely arrive by the end of January at the earliest, which could be after the peak of the current coronavirus surge in some parts of the country.
At-home tests have been in high demand, with some pharmacies, retailers, and websites reporting no stock in recent weeks. People have lined up at community testing sites for hours to get tested as the national average of daily cases has climbed above 800,000 last week.
Some consumers have also been confused about how or when to use at-home tests. On Jan. 14, Biden administration officials said that people should use rapid tests for three reasons:
- If they begin to experience COVID-19 symptoms;
- When it has been five or more days after being exposed to someone who tests positive;
- If they are gathering indoors with a high-risk person and want to check if they are negative.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Docs pen open letter to support Fauci against partisan ‘attacks’
“We deplore the personal attacks on Dr. Fauci. The criticism is inaccurate, unscientific, ill-founded in the facts and, increasingly, motivated by partisan politics,” reads the letter of support, initiated by Ezekiel Emanuel, MD, and signed by almost 300 scientists and public health and medical professionals, including Nobel Laureates, a former Republican senator, and leadership of medical societies and institutions.
Dr. Fauci has led the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases since 1984 and serves as President Biden’s top medical advisor on the pandemic.
“Dr. Anthony Fauci has served the U.S.A. with wisdom and integrity for nearly 40 years. Through HIV, Ebola, and now COVID, he has unswervingly served the United States guiding the country to very successful outcomes. He has our unreserved respect and trust as a scientist and a national leader,” the letter reads.
Dr. Fauci has repeatedly faced harsh criticism from congressional Republicans, especially Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) and Sen. Roger Marshall (R-Kan.).
At a particularly contentious congressional hearing earlier this week on the federal government’s response to Omicron, Dr. Fauci fought back, telling Sen. Marshall, “You’re so misinformed, it’s extraordinary.”
Dr. Fauci, who has received death threats and harassment of his family, told Sen. Rand that his “completely untrue” statements and rhetoric “kindles the crazies out there.”
‘Sagacious counsel’
The personal attacks on Dr. Fauci are a “distraction from what should be the national focus – working together to finally overcome a pandemic that is killing about 500,000 people a year. We are grateful for Dr. Fauci’s dedication and tireless efforts to help the country through this pandemic and other health crises,” the letter reads.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci has provided the American political leadership and the public with sagacious counsel in these most difficult of times. His advice has been as well informed as data and the rapidly evolving circumstances allowed,” it states.
“Importantly,” Dr. Fauci has given his advice with “humility, being clear about what we know and what is unknown, but requires judgment. He has consistently emphasized the importance of mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination. These are standard and necessary public health measures that we all support,” the letter states.
“We are grateful that Dr. Fauci has consistently stated the science in a way that represents the facts as they emerge, without unwarranted speculation.”
“Sadly, in these politically polarized times where misinformation contaminates the United States’ response to the pandemic, routine public health measures have become unnecessarily controversial, undermining the effectiveness of our country’s response,” the letter reads.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We deplore the personal attacks on Dr. Fauci. The criticism is inaccurate, unscientific, ill-founded in the facts and, increasingly, motivated by partisan politics,” reads the letter of support, initiated by Ezekiel Emanuel, MD, and signed by almost 300 scientists and public health and medical professionals, including Nobel Laureates, a former Republican senator, and leadership of medical societies and institutions.
Dr. Fauci has led the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases since 1984 and serves as President Biden’s top medical advisor on the pandemic.
“Dr. Anthony Fauci has served the U.S.A. with wisdom and integrity for nearly 40 years. Through HIV, Ebola, and now COVID, he has unswervingly served the United States guiding the country to very successful outcomes. He has our unreserved respect and trust as a scientist and a national leader,” the letter reads.
Dr. Fauci has repeatedly faced harsh criticism from congressional Republicans, especially Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) and Sen. Roger Marshall (R-Kan.).
At a particularly contentious congressional hearing earlier this week on the federal government’s response to Omicron, Dr. Fauci fought back, telling Sen. Marshall, “You’re so misinformed, it’s extraordinary.”
Dr. Fauci, who has received death threats and harassment of his family, told Sen. Rand that his “completely untrue” statements and rhetoric “kindles the crazies out there.”
‘Sagacious counsel’
The personal attacks on Dr. Fauci are a “distraction from what should be the national focus – working together to finally overcome a pandemic that is killing about 500,000 people a year. We are grateful for Dr. Fauci’s dedication and tireless efforts to help the country through this pandemic and other health crises,” the letter reads.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci has provided the American political leadership and the public with sagacious counsel in these most difficult of times. His advice has been as well informed as data and the rapidly evolving circumstances allowed,” it states.
“Importantly,” Dr. Fauci has given his advice with “humility, being clear about what we know and what is unknown, but requires judgment. He has consistently emphasized the importance of mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination. These are standard and necessary public health measures that we all support,” the letter states.
“We are grateful that Dr. Fauci has consistently stated the science in a way that represents the facts as they emerge, without unwarranted speculation.”
“Sadly, in these politically polarized times where misinformation contaminates the United States’ response to the pandemic, routine public health measures have become unnecessarily controversial, undermining the effectiveness of our country’s response,” the letter reads.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“We deplore the personal attacks on Dr. Fauci. The criticism is inaccurate, unscientific, ill-founded in the facts and, increasingly, motivated by partisan politics,” reads the letter of support, initiated by Ezekiel Emanuel, MD, and signed by almost 300 scientists and public health and medical professionals, including Nobel Laureates, a former Republican senator, and leadership of medical societies and institutions.
Dr. Fauci has led the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases since 1984 and serves as President Biden’s top medical advisor on the pandemic.
“Dr. Anthony Fauci has served the U.S.A. with wisdom and integrity for nearly 40 years. Through HIV, Ebola, and now COVID, he has unswervingly served the United States guiding the country to very successful outcomes. He has our unreserved respect and trust as a scientist and a national leader,” the letter reads.
Dr. Fauci has repeatedly faced harsh criticism from congressional Republicans, especially Sen. Rand Paul (R-Ky.) and Sen. Roger Marshall (R-Kan.).
At a particularly contentious congressional hearing earlier this week on the federal government’s response to Omicron, Dr. Fauci fought back, telling Sen. Marshall, “You’re so misinformed, it’s extraordinary.”
Dr. Fauci, who has received death threats and harassment of his family, told Sen. Rand that his “completely untrue” statements and rhetoric “kindles the crazies out there.”
‘Sagacious counsel’
The personal attacks on Dr. Fauci are a “distraction from what should be the national focus – working together to finally overcome a pandemic that is killing about 500,000 people a year. We are grateful for Dr. Fauci’s dedication and tireless efforts to help the country through this pandemic and other health crises,” the letter reads.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fauci has provided the American political leadership and the public with sagacious counsel in these most difficult of times. His advice has been as well informed as data and the rapidly evolving circumstances allowed,” it states.
“Importantly,” Dr. Fauci has given his advice with “humility, being clear about what we know and what is unknown, but requires judgment. He has consistently emphasized the importance of mask-wearing, social distancing, and vaccination. These are standard and necessary public health measures that we all support,” the letter states.
“We are grateful that Dr. Fauci has consistently stated the science in a way that represents the facts as they emerge, without unwarranted speculation.”
“Sadly, in these politically polarized times where misinformation contaminates the United States’ response to the pandemic, routine public health measures have become unnecessarily controversial, undermining the effectiveness of our country’s response,” the letter reads.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac inflammation can be present after mild COVID infection
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Myocardial inflammation is present in a small proportion of patients who have recovered from relatively mild cases of COVID-19 infection, a new study shows.
“Our findings suggest that even in patients who have had relatively mild cases of COVID-19, some will have inflammatory changes to the heart, and these changes can be present without any cardiac symptoms,” senior author, Paaladinesh Thavendiranathan, MD, University of Toronto, told this news organization.
“While our data suggest that this inflammation improves over time, and the outcomes seem positive, we don’t know if there will be any long-term consequences,” he added.
Noting that even a short period of inflammation in the heart may be associated with symptoms or arrhythmias in the longer term, Dr. Thavendiranathan said: “I would recommend that it is best to avoid getting the infection if there is any chance of heart inflammation.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology on Jan. 12.
The authors explain that among patients hospitalized with COVID, early studies suggested that approximately one in four experience cardiovascular injury, defined as an elevation in troponin levels, which was associated with a 5- to 10-fold increase in the risk for death. But there is limited information on cardiac injury in patients who do not require hospitalization.
Although a broad range of abnormal myocardial tissue has been reported in several cardiac MRI studies of patients recovered from COVID infection, there is little understanding of persistent changes in myocardial metabolism in recovered patients, which is a potential concern, given that COVID-19 is associated with systemic inflammation during the acute illness, they say.
For the current study, the researchers examined myocardial inflammation measured using two different methods – cardiac MRI and fluorodeoxyglucose–positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) – in individuals who had recovered from COVID-19 infection and looked at how this related to changes in inflammatory blood markers.
Lead author Kate Hanneman, MD, also from the University of Toronto, explained that FDG-PET imaging is more sensitive than MRI in detecting active inflammation. “Inflammatory cells have a higher uptake of glucose, and FDG-PET imaging is used to look for metabolically active inflammatory tissue that takes up glucose. It gives complementary information to MRI. Cardiac MRI shows structural or functional changes, such as scarring or edema, whereas FDG-PET imaging directly measures metabolic activity related to inflammatory cells.”
The study involved 47 individuals, 51% female, with a mean age of 43 years, who had recently recovered from COVID-19 infection. Of these, the majority had had relatively mild COVID disease, with 85% not requiring hospitalization.
Cardiac imaging was performed a mean of 67 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. At the time of imaging, 19 participants (40%) reported at least one cardiac symptom, including palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
Results showed that eight patients (17%) had focal FDG uptake on PET consistent with myocardial inflammation. Compared with those without FDG uptake, patients with focal FDG uptake had higher regional T2, T1, and extracellular volume (colocalizing with focal FDG uptake), higher prevalence of late gadolinium enhancement indicating fibrosis, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, worse global longitudinal and circumferential strain, and higher systemic inflammatory blood markers, including interleukin (IL)-6, IL- 8, an high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Of the 47 patients in the study, 13 had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine. There was no significant difference in the proportion of patients who were PET-positive among those who had received a COVID-19 vaccine and those who had not.
There was also no difference in inflammation in patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19 and those who had managed their infection at home.
Among patients with focal FDG uptake, PET, MRI, and inflammatory blood markers improved at follow-up imaging performed a mean of 52 days after the first imaging. The authors say this suggests that these abnormalities were not related to pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Of the eight patients with positive FDG-PET results, two did not show any MRI abnormalities. These two patients also had elevated inflammatory biomarkers. “PET is a more sensitive method of measuring cardiac inflammation, and our results show that these changes may not always translate into functional changes seen on MRI,” Dr. Thavendiranathan noted.
The only cardiac risk factor that was more common in participants with FDG uptake was hypertension. Although cardiac symptoms were nearly twice as common in participants with focal FDG uptake, this difference was not statistically significant.
“Given the growing number of survivors with similar symptoms, these interesting findings warrant further investigation,” the authors say.
Noting that FDG uptake correlated with elevations in systemic inflammatory biomarkers, the researchers suggest that “a more intense systemic inflammatory process may be contributing to cardiac inflammation and the consequential alteration to regional and global myocardial function in PET-positive participants.”
On repeat imaging 2 months later, all eight patients who showed FDG uptake showed improvement or resolution of inflammation without any treatment, although two patients still had some signs of inflammation. Blood biomarkers also improved on follow-up.
“This is encouraging information, but we need longer-term data to see if there are any long-term repercussions of this inflammation,” Dr. Hanneman said.
“Overall, the study findings suggest an imaging phenotype that is expected to have good prognosis. However, longer-term follow-up studies are required to understand the need for ongoing cardiac surveillance, relationship to cardiac symptoms, guidance for safe return to exercise and sports participation, and long-term cardiovascular disease risk,” the researchers state.
This study was funded by grants from the Joint Department of Medical Imaging Academic Incentive Fund, Peter Munk Cardiac Center Innovation Committee, and Ted Rogers Center for Heart Research. Dr. Hanneman reports personal fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Amicus, and Medscape outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Quebec plans to fine unvaccinated adults
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The amount hasn’t been decided yet, but it will be “significant” and more than $100. More details will be released at a later date, The Associated Press reported.
“Those who refuse to get their first doses in the coming weeks will have to pay a new health contribution,” Premier Francois Legault said during a news conference.
Not getting vaccinated burdens the health care system, and not all residents should pay for it, he said. About 10% of adults in Quebec are unvaccinated, but they represent about 50% of intensive care patients.
“I think it’s reasonable a majority of the population is asking that there be consequences,” he said. “It’s a question of fairness for the 90% of the population that have made some sacrifices. We owe them.”
The fine will apply to those who don’t qualify for a medical exemption, Mr. Legault said.
Provinces across Canada have reported a surge in COVID-19 cases due to the Omicron variant, with Quebec being one of the hardest-hit, according to Reuters. The province is regularly recording the highest daily case count across the country.
Quebec also has announced a 10 p.m. to 5 a.m. curfew, the AP reported. Starting Jan. 18, liquor and cannabis stores in the province will require proof of vaccination, and shopping malls and hair salons could soon require them as well.
About a quarter of all Canadians live in Quebec, according to CNN. The province was one of the first in Canada to require proof of vaccination for residents to eat in restaurants, go to the gym, or attend sporting events.
Some European countries have announced fees for unvaccinated residents, the AP reported, but Quebec is the first in Canada to announce a financial penalty for those who don’t get a shot.
In Greece, people older than 60 have until Jan. 16 to receive the first dose, or they will be fined 100 euros for every month they remain unvaccinated, the AP reported.
Austria will impose fines up to 3,600 euros for those who don’t follow the vaccine mandate for ages 14 and older, which is slated to start in February.
In Italy, residents who are 50 and older are required to be vaccinated. In mid-February, those who are unvaccinated could be fined up to 1,600 euros if they enter their workplaces, the AP reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC to update mask recommendations as Omicron spreads
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said on Jan. 12.
“We are preparing an update to the info on our mask website to best reflect the options that are available to people and the different levels of protection different masks provide, and we want to provide Americans the best and most updated information to choose what mask is going to be right for them,” she said at a White House news briefing.
While the higher-quality masks provide better protection, they can be uncomfortable to wear, expensive, and harder to find. That’s why Dr. Walensky added an important caveat.
“Any mask is better than no mask, and we do encourage all Americans to wear a well-fitting mask to protect themselves and prevent the spread of COVID-19. That recommendation is not going to change,” she said.
“Most importantly, the best mask that you wear is the one you will wear and the one you can keep on all day long and tolerate in public indoor settings.”
Meanwhile, the World Health Organization was more focused on vaccines.
WHO officials stressed on Jan. 12 that global vaccine distribution is first priority in defeating the highly contagious Omicron variant, as well as other variants that may evolve.
The WHO’s Technical Advisory Group on COVID-19 Vaccine Composition – a group of experts assessing how COVID-19 vaccines perform against Omicron and other emerging variants – says there is an “urgent need” for broader access to vaccines, along with reviewing and updating current vaccines as needed to ensure protection.
The WHO also disputed the idea that COVID-19 could become endemic in one largely vaccinated nation, while the rest of the world remains unprotected.
“It is up to us how this pandemic unfolds,” Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, the WHO’s technical lead on COVID-19 response, said at a news briefing.
The WHO has a goal of vaccinating 70% of the population of every country by the middle of the year.
But right now, 90 countries have yet to reach 40% vaccination rates, and 36 of those countries have less than 10% of their populations vaccinated, according to WHO Director General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD.
A staggering 85% of the African population has not received a first dose.
But progress is being made, Dr. Ghebreyesus said at the briefing.
The WHO said there were over 15 million COVID-19 cases reported last week – the most ever in a single week – and this is likely an underestimate.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa 2 months ago and now found on all seven continents, is “rapidly replacing Delta in almost all countries,” Dr. Ghebreyesus said.
Dr. Walensky said this week’s U.S. daily average COVID-19 case count was 751,000, an increase of 47% from last week. The average daily hospital admissions this week is 19,800, an increase of 33%. Deaths are up 40%, reaching 1,600 per day.
But she also reported new data that supports other research showing Omicron may produce less severe disease. Kaiser Permanente Southern California released a study on Jan. 11 showing that, compared with Delta infections, Omicron was associated with a 53% reduction in hospitalizations, a 74% reduction in intensive care unit admissions, and a 91% lower risk of death.
In the study, no patients with Omicron required mechanical ventilation. The strain now accounts for 98% of cases nationwide.
But Dr. Walensky warned the lower disease severity is not enough to make up for the sheer number of cases that continue to overwhelm hospital systems.
“While we are seeing early evidence that Omicron is less severe than Delta and that those infected are less likely to require hospitalization, it’s important to note that Omicron continues to be much more transmissible than Delta,” she said. “The sudden rise in cases due to Omicron is resulting in unprecedented daily case counts, sickness, absenteeism, and strains on our health care system.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Common cold could protect against COVID-19, study says
, according to a small study published Jan. 10 in Nature Communications.
Previous studies have shown that T cells created from other coronaviruses can recognize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. In the new study, researchers at Imperial College London found that the presence of these T cells at the time of COVID-19 exposure could reduce the chance of getting infected.
The findings could provide a blueprint for a second-generation, universal vaccine to prevent infection from COVID-19 variants, including Omicron and ones that crop up later.
“Being exposed to SARS-CoV-2 virus doesn’t always result in infection, and we’ve been keen to understand why,” Rhia Kundu, PhD, the lead study author from Imperial’s National Heart and Lung Institute, said in a statement.
People with higher levels of T cells from the common cold were less likely to become infected with COVID-19, the researchers found.
“While this is an important discovery, it is only one form of protection, and I would stress that no one should rely on this alone,” Dr. Kundu said. “Instead, the best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is to be fully vaccinated, including getting your booster dose.”
For the study, Dr. Kundu and colleagues analyzed blood samples from 52 people who lived with someone with confirmed COVID-19 in September 2020. Among the 26 people who didn’t contract COVID-19, there were “significantly higher levels” of preexisting T cells from common cold coronaviruses, as compared with the 26 people who did become infected.
The T cells researched in the study are considered “cross-reactive” and can recognize the proteins of SARS-CoV-2. They offer protection by targeting proteins inside the SARS-CoV-2 virus, rather than the spike proteins on the surface that allow the virus to invade cells.
The current COVID-19 vaccines target the spike proteins, which are more likely to mutate than internal proteins, the researchers wrote. The Omicron variant, for instance, has numerous mutations on spike proteins that may allow it to evade vaccines.
The data suggest that the next step of COVID-19 vaccine development could focus on internal proteins, the researchers said, which could provide lasting protection because T-cell responses persist longer than antibody responses that fade within a few months of vaccination.
“New vaccines that include these conserved, internal proteins would therefore induce broadly protective T-cell responses that should protect against current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants,” Ajit Lalvani, MD, the senior study author and director of Imperial’s respiratory infections health protection research unit, said in the statement.
But more research is needed, the authors said, noting that the study had a small sample size and lacked ethnic diversity, which puts limits on the research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com
, according to a small study published Jan. 10 in Nature Communications.
Previous studies have shown that T cells created from other coronaviruses can recognize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. In the new study, researchers at Imperial College London found that the presence of these T cells at the time of COVID-19 exposure could reduce the chance of getting infected.
The findings could provide a blueprint for a second-generation, universal vaccine to prevent infection from COVID-19 variants, including Omicron and ones that crop up later.
“Being exposed to SARS-CoV-2 virus doesn’t always result in infection, and we’ve been keen to understand why,” Rhia Kundu, PhD, the lead study author from Imperial’s National Heart and Lung Institute, said in a statement.
People with higher levels of T cells from the common cold were less likely to become infected with COVID-19, the researchers found.
“While this is an important discovery, it is only one form of protection, and I would stress that no one should rely on this alone,” Dr. Kundu said. “Instead, the best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is to be fully vaccinated, including getting your booster dose.”
For the study, Dr. Kundu and colleagues analyzed blood samples from 52 people who lived with someone with confirmed COVID-19 in September 2020. Among the 26 people who didn’t contract COVID-19, there were “significantly higher levels” of preexisting T cells from common cold coronaviruses, as compared with the 26 people who did become infected.
The T cells researched in the study are considered “cross-reactive” and can recognize the proteins of SARS-CoV-2. They offer protection by targeting proteins inside the SARS-CoV-2 virus, rather than the spike proteins on the surface that allow the virus to invade cells.
The current COVID-19 vaccines target the spike proteins, which are more likely to mutate than internal proteins, the researchers wrote. The Omicron variant, for instance, has numerous mutations on spike proteins that may allow it to evade vaccines.
The data suggest that the next step of COVID-19 vaccine development could focus on internal proteins, the researchers said, which could provide lasting protection because T-cell responses persist longer than antibody responses that fade within a few months of vaccination.
“New vaccines that include these conserved, internal proteins would therefore induce broadly protective T-cell responses that should protect against current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants,” Ajit Lalvani, MD, the senior study author and director of Imperial’s respiratory infections health protection research unit, said in the statement.
But more research is needed, the authors said, noting that the study had a small sample size and lacked ethnic diversity, which puts limits on the research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com
, according to a small study published Jan. 10 in Nature Communications.
Previous studies have shown that T cells created from other coronaviruses can recognize SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. In the new study, researchers at Imperial College London found that the presence of these T cells at the time of COVID-19 exposure could reduce the chance of getting infected.
The findings could provide a blueprint for a second-generation, universal vaccine to prevent infection from COVID-19 variants, including Omicron and ones that crop up later.
“Being exposed to SARS-CoV-2 virus doesn’t always result in infection, and we’ve been keen to understand why,” Rhia Kundu, PhD, the lead study author from Imperial’s National Heart and Lung Institute, said in a statement.
People with higher levels of T cells from the common cold were less likely to become infected with COVID-19, the researchers found.
“While this is an important discovery, it is only one form of protection, and I would stress that no one should rely on this alone,” Dr. Kundu said. “Instead, the best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is to be fully vaccinated, including getting your booster dose.”
For the study, Dr. Kundu and colleagues analyzed blood samples from 52 people who lived with someone with confirmed COVID-19 in September 2020. Among the 26 people who didn’t contract COVID-19, there were “significantly higher levels” of preexisting T cells from common cold coronaviruses, as compared with the 26 people who did become infected.
The T cells researched in the study are considered “cross-reactive” and can recognize the proteins of SARS-CoV-2. They offer protection by targeting proteins inside the SARS-CoV-2 virus, rather than the spike proteins on the surface that allow the virus to invade cells.
The current COVID-19 vaccines target the spike proteins, which are more likely to mutate than internal proteins, the researchers wrote. The Omicron variant, for instance, has numerous mutations on spike proteins that may allow it to evade vaccines.
The data suggest that the next step of COVID-19 vaccine development could focus on internal proteins, the researchers said, which could provide lasting protection because T-cell responses persist longer than antibody responses that fade within a few months of vaccination.
“New vaccines that include these conserved, internal proteins would therefore induce broadly protective T-cell responses that should protect against current and future SARS-CoV-2 variants,” Ajit Lalvani, MD, the senior study author and director of Imperial’s respiratory infections health protection research unit, said in the statement.
But more research is needed, the authors said, noting that the study had a small sample size and lacked ethnic diversity, which puts limits on the research.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com
Ranking seven COVID-19 antigen tests by ease of use: Report
Some COVID-19 rapid antigen home test kits are much easier to use than others, according to an analysis by ECRI, an independent, nonprofit patient safety organization.
None of the tests were rated as “excellent” in terms of usability and some had “noteworthy” usability concerns, the company said.
If a test is hard to use, “chances are that you may miss a step or not follow the right order, or contaminate the testing area and that can definitely influence the accuracy of the test and lead to a wrong test result,” Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, president and CEO of ECRI, told this news organization.
To gauge usability, ECRI used the “industry-standard” system usability scale (SUS), which rates products on a scale of 0 to 100 with 100 being the easiest to use.
More than 30 points separated the top and bottom tests analyzed. The top performer was On/Go, followed by CareStart and Flowflex.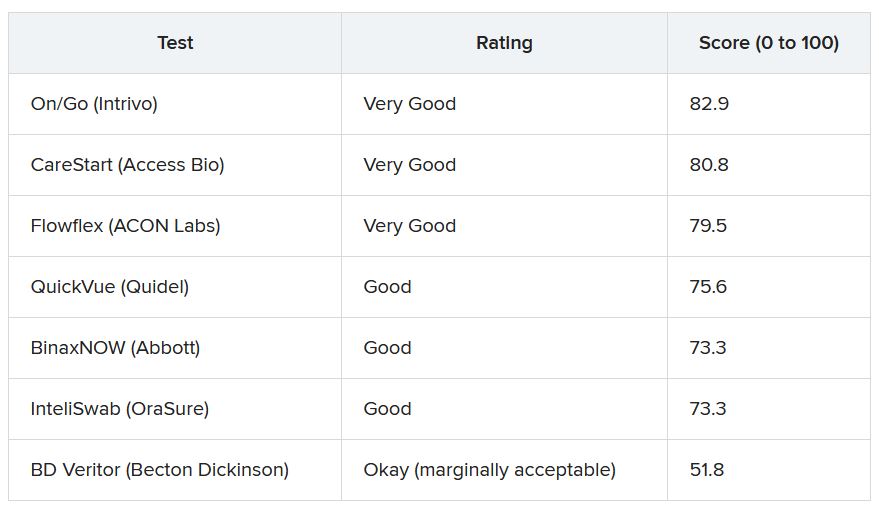
ECRI analysts found that some tests require particularly fine motor skills or have instructions with extremely small font size that may make it hard for older adults or people with complex health conditions to use the tests correctly.
“If you have a tremor from Parkinson’s, for example, or anything which won’t allow you to handle small items, you will have difficulties to do that test by yourself. That is the No. 1 concern we have,” Dr. Schabacker said.
“The second concern is readability, as all of these tests have relatively small instructions. One of them actually has doesn’t even have instructions – you have to download an app,” he noted.
Given demand and supply issues, Dr. Schabacker acknowledged that consumers might not have a choice in which test to use and may have to rely on whatever is available.
These tests are a “hot commodity right now,” he said. “If you have a choice, people should use the ones which are easiest to use, which is the On/Go, the CareStart, or the Flowflex.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some COVID-19 rapid antigen home test kits are much easier to use than others, according to an analysis by ECRI, an independent, nonprofit patient safety organization.
None of the tests were rated as “excellent” in terms of usability and some had “noteworthy” usability concerns, the company said.
If a test is hard to use, “chances are that you may miss a step or not follow the right order, or contaminate the testing area and that can definitely influence the accuracy of the test and lead to a wrong test result,” Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, president and CEO of ECRI, told this news organization.
To gauge usability, ECRI used the “industry-standard” system usability scale (SUS), which rates products on a scale of 0 to 100 with 100 being the easiest to use.
More than 30 points separated the top and bottom tests analyzed. The top performer was On/Go, followed by CareStart and Flowflex.
ECRI analysts found that some tests require particularly fine motor skills or have instructions with extremely small font size that may make it hard for older adults or people with complex health conditions to use the tests correctly.
“If you have a tremor from Parkinson’s, for example, or anything which won’t allow you to handle small items, you will have difficulties to do that test by yourself. That is the No. 1 concern we have,” Dr. Schabacker said.
“The second concern is readability, as all of these tests have relatively small instructions. One of them actually has doesn’t even have instructions – you have to download an app,” he noted.
Given demand and supply issues, Dr. Schabacker acknowledged that consumers might not have a choice in which test to use and may have to rely on whatever is available.
These tests are a “hot commodity right now,” he said. “If you have a choice, people should use the ones which are easiest to use, which is the On/Go, the CareStart, or the Flowflex.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some COVID-19 rapid antigen home test kits are much easier to use than others, according to an analysis by ECRI, an independent, nonprofit patient safety organization.
None of the tests were rated as “excellent” in terms of usability and some had “noteworthy” usability concerns, the company said.
If a test is hard to use, “chances are that you may miss a step or not follow the right order, or contaminate the testing area and that can definitely influence the accuracy of the test and lead to a wrong test result,” Marcus Schabacker, MD, PhD, president and CEO of ECRI, told this news organization.
To gauge usability, ECRI used the “industry-standard” system usability scale (SUS), which rates products on a scale of 0 to 100 with 100 being the easiest to use.
More than 30 points separated the top and bottom tests analyzed. The top performer was On/Go, followed by CareStart and Flowflex.
ECRI analysts found that some tests require particularly fine motor skills or have instructions with extremely small font size that may make it hard for older adults or people with complex health conditions to use the tests correctly.
“If you have a tremor from Parkinson’s, for example, or anything which won’t allow you to handle small items, you will have difficulties to do that test by yourself. That is the No. 1 concern we have,” Dr. Schabacker said.
“The second concern is readability, as all of these tests have relatively small instructions. One of them actually has doesn’t even have instructions – you have to download an app,” he noted.
Given demand and supply issues, Dr. Schabacker acknowledged that consumers might not have a choice in which test to use and may have to rely on whatever is available.
These tests are a “hot commodity right now,” he said. “If you have a choice, people should use the ones which are easiest to use, which is the On/Go, the CareStart, or the Flowflex.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians react: Should docs lose their licenses for spreading false COVID information?
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors providing “fraudulent” COVID-19 information became a hot-button issue for physicians responding to Medscape’s recent article, "Shouldn’t Doctors Who Spread False COVID-19 Information Lose Their Licenses?”
COVID-19 safety recommendations are set by mainstream medical organizations as new information becomes available, but some doctors consistently oppose advice from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other medical authorities. These physicians often promote off-label, unapproved use of medications for COVID-19 and/or contradict mainstream safety guidelines such as vaccines, masks, and social distancing.
Some medical organizations are concerned that these doctors are hampering efforts to control the highly contagious coronavirus and are, at worst, placing lives in danger with their contrarian views that can spread like wildfire on social media sites. Their words are often used by those who refuse to be vaccinated or wear masks.
State licensing boards have mostly refused to discipline these doctors for making false and/or misleading claims, but as the virus spreads, there are calls to take action against them. However, others worry that such actions would violate free speech and critical thought.
Yes, those doctors are doing wrong
Several physicians took a strong stand against their fellow doctors who are spreading misinformation about COVID-19.
One doctor endorsed the idea of removing licenses for spreading misinformation and called for criminal prosecution: “It should certainly be grounds for cancellation of all licensing (after appropriate examination to rule out acute psychotic episodes, dementia, tumor, etc.) and very likely [include] a charge of manslaughter.”
Another health care provider said, “A person who does not accept science should not, of course, be allowed to practice medicine. One who argues publicly that vaccines and masks don’t work should be prosecuted for crimes ranging from reckless endangerment to attempted murder.”
One reader framed COVID-19 misinformers in stark terms: “These men and women are medical prostitutes. Their medical and surgical colleges [should] have a panel to track in-court testimony and the disinformation they spread ...”
“This is malpractice of the worst kind,” said a clinician. “Public health officials and science are quite clear on [the] best practices for safety during a pandemic, which is killing millions. This is a standard of care.”
“Medical Boards should suspend licenses and give the physician a chance to testify [about] the scientific basis for his comments,” added a health care provider. “Boards involve themselves in all kinds of perceived disciplinary infractions. We are in the midst of a lethal pandemic. I would think that would take precedence over many other issues?”
“I do believe that physicians have the responsibility to speak the truth and have scientifically displayed minds,” said a reader. “Not [to] promulgate misleading, false, and/or unverified information.”
“Any physician, who holds a license, should abide [by] government and state regulation,” asserted a doctor. “He should be disciplined by the board for spreading medical/public misinformation since he is creating potential harm to the population.”
One specialist insisted that “state boards do not do enough to restrict/limit the practice of physicians touting questionable therapies.”
“Any doctor who spreads false information about Covid is hurting our country, our individuals, and our economy and leading to needless deaths,” asserted a physician. “However, there are uncertainties, and where those exist, physicians [should] simply say ‘it is unknown.’”
No, those physicians have a right to speak their beliefs
However, many physicians worried that science and controversial thought were being muzzled.
“Absolutely no,” a doctor stated. “Who judges what is misinformation in this age where debate is canceled? Science advances with challenge, and it’s not about an authority dictating the allowable opinion.”
Another clinician claimed the “truth is very difficult to discern from less-than-truth in a country running on a profit-oriented economic ideology.”
One specialist warned that if disinformation doctors are held responsible, then “that means a lot of doctors” will be “gone” because “almost anything that is written or said about COVID can be contested.”
Another physician warned his colleagues about suppressing new ideas: “To condemn what we didn’t try, or purposefully ignore a different approach because [it] doesn’t agree with our opinion is suppression of information.”
Some doctors insisted the issue extended beyond medicine and into Constitutional freedoms. They also expressed their mistrust in the government to regulate physicians.
“There is a First Amendment in this country,” said one reader. “What you think is false may not be so. The people can listen to whoever they want to and make their own medical decisions. We do not need one iota more of politicizing medicine. Having an MD or DO does not mean you relinquish your First Amendment rights.”
“One of the fundamental problems with a system that allows government to ‘license’ physicians, or any other profession, is that politics inevitably turn to cronyism, and big businesses and wealthy people start controlling the government,” argued a doctor.
One clinician suggested enforcement against health food, drug company commercials, and talk shows: “What about all the [misinformation] at the health food stores and the like. Doctors of natural-whatever? Those info-commercials on tv. How many faxes do I get to ‘approve’ because ‘patients request’ braces and pain-treating expensive compounds advertised on TV? We tolerate those ... What about Dr. Oz and the docs on talk shows claiming BS?”
And the debate goes even further
Some physicians questioned the very notion of claiming “truth.”
“Nobody should be certain that they have the ‘absolute truth,’” said one reader. “In fact, the best clinical insights exceed so-called knowledge by at least one step.”
“Who can determine exactly what is truth?” asked another clinician. “For sure, the ‘Federal Government,’ who ‘is here to help you,’ is not qualified to make such determinations, and who are you to make such a suggestion as to remove someone’s license because they disagree with you? Give me a break!”
Another physician echoed that sentiment: “What’s true and false is often and certainly currently debatable. There are well-qualified physicians (with credentials such as the development of mRNA technology), virologists, and biostatisticians that have valid thoughts on this but do not necessarily agree with the drug company-sponsored journals and news channels (most of them). Their voices should be heard, and they should not lose their licenses. They are doing their work in good conscience.”
One reader commented that he wanted his “freedom of speech,” and offered this defiant advice: “You can take this license and shove it.”
Finally, a physician noted that the political climate has influenced medical directives: “If someone in a leadership role knowingly, and with intent, spread false information, that is wrong. However, during this global pandemic the active and the politics have combined. Red state no mandate, blue state mandate – what does that tell you about American leadership?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.