User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Powered by CHEST Physician, Clinician Reviews, MDedge Family Medicine, Internal Medicine News, and The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management.
G-CSF safe, but antibiotics are more concerning in SCLC
GENEVA – In patients with limited stage–small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) treated with concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, the use of antibiotics to prevent febrile neutropenia was associated with worse outcomes, but granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) prescribed for the same purposes appeared to be safe, reported investigators.
In a subanalysis of data on patients with early SCLC enrolled in the phase III CONVERT trial comparing chemotherapy with concurrent once-daily vs. twice-daily radiation, the use of antibiotic prophylaxis of neutropenia was associated with worse overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival, (PFS) compared with no antibiotics, reported Fabio Gomes, MD, from the Christie NHS Foundation Trust Hospital in Manchester, England.
The use of G-CSF was, however, associated with higher rates of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and anemia, requiring supportive measures, he acknowledged.
The role of G-CSF with concurrent thoracic radiotherapy is controversial because of safety concerns, but data are scarce, Dr. Gomes said. He noted that the American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines on the use of white blood cell growth factors recommend against their routine use.
However, some of those concerns arose in the mid-1990s when granulocyt macrophage–stimulating colony factor (GM-CSF) was used, rather than G-CSF, which acts on only a single blood lineage, namely neutrophils. Additionally, modern radiology techniques are more precise than they were 20 years ago, reducing the risk of toxicity, he noted.
In the CONVERT trial, 547 patients with LS-SCLC were randomly assigned to receive four to six cycles of cisplatin and etoposide chemotherapy concurrently with either once daily thoracic radiation for a total dose of 66 Gy divided into 33 fractions delivered over 45 days or to twice-daily radiation at a total dose of 45 Gy divided into 30 fractions delivered over 19 days.
There was no difference between the groups in the primary endpoint of overall survival.
In the subanalysis reported here, Gomes et al. looked at the use of G-CSF, delivered at the investigator’s discretion, in 487 patients. Approximately 40% of patients in the subanalysis received G-CSF during at least one treatment cycle.
Prophylactic antibiotics were recommended by the investigators for use in association with at least one chemotherapy cycle, and 49% of patients in the subanalysis received them during at least one cycle.
Hematological toxicities included grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia occurring in 29.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 13.3% of those who did not (P less than .001). The rates were similar between the once-daily and twice-daily radiation groups.
Grade 3 or 4 anemia occurred in 16.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 10.7% of those who didn’t (P = .027). The difference was significant only among patients in the twice-daily radiation arm (20.9% vs. 8.3%, respectively; P = .004).
Patients in the twice-daily radiation arms who received G-CSF also required more platelet transfusion, compared with the once-daily arm (P less than .001), and, in both arms, G-CSF was associated with more red-cell transfusions (P = .007 for once-daily and .001 for twice daily).
G-CSF was not associated with either pneumonitis or esophagitis, and there were no differences in treatment-related deaths with either G-CSF or antibiotics.
Median OS by G-CSF use was 29 months with and 27 months without, a difference that was not significant (P = .08). Median PFS also did not differ by G-CSF use or nonuse.
When it came to antibiotic prophylaxis, however, both median OS and PFS were significant worse with antibiotic use (OS, 24 months with vs. 33 months without; P = .016; PFS, P = .03).
“We are very reassured that there are no significant additional toxicities [with G-CSF] from radiation in the acute setting,” commented Sanjay Popat, FRCP, PhD, from the Royal Marsden Hospital in London, the invited discussant.
“However, we have no data as yet on the impact of G-CSF usage on febrile neutropenia, which is of course the fundamental that we’re aiming to improve in the hope that this will contribute to [lowering] costs,” he added.
The study was sponsored by the Christie Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, Cancer Research UK, EORTC, GECP, GFPC, and IFCT. Dr. Gomes reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Popat reported consultation, honoraria, travel expenses, and institutional research from multiple entities.
GENEVA – In patients with limited stage–small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) treated with concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, the use of antibiotics to prevent febrile neutropenia was associated with worse outcomes, but granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) prescribed for the same purposes appeared to be safe, reported investigators.
In a subanalysis of data on patients with early SCLC enrolled in the phase III CONVERT trial comparing chemotherapy with concurrent once-daily vs. twice-daily radiation, the use of antibiotic prophylaxis of neutropenia was associated with worse overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival, (PFS) compared with no antibiotics, reported Fabio Gomes, MD, from the Christie NHS Foundation Trust Hospital in Manchester, England.
The use of G-CSF was, however, associated with higher rates of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and anemia, requiring supportive measures, he acknowledged.
The role of G-CSF with concurrent thoracic radiotherapy is controversial because of safety concerns, but data are scarce, Dr. Gomes said. He noted that the American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines on the use of white blood cell growth factors recommend against their routine use.
However, some of those concerns arose in the mid-1990s when granulocyt macrophage–stimulating colony factor (GM-CSF) was used, rather than G-CSF, which acts on only a single blood lineage, namely neutrophils. Additionally, modern radiology techniques are more precise than they were 20 years ago, reducing the risk of toxicity, he noted.
In the CONVERT trial, 547 patients with LS-SCLC were randomly assigned to receive four to six cycles of cisplatin and etoposide chemotherapy concurrently with either once daily thoracic radiation for a total dose of 66 Gy divided into 33 fractions delivered over 45 days or to twice-daily radiation at a total dose of 45 Gy divided into 30 fractions delivered over 19 days.
There was no difference between the groups in the primary endpoint of overall survival.
In the subanalysis reported here, Gomes et al. looked at the use of G-CSF, delivered at the investigator’s discretion, in 487 patients. Approximately 40% of patients in the subanalysis received G-CSF during at least one treatment cycle.
Prophylactic antibiotics were recommended by the investigators for use in association with at least one chemotherapy cycle, and 49% of patients in the subanalysis received them during at least one cycle.
Hematological toxicities included grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia occurring in 29.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 13.3% of those who did not (P less than .001). The rates were similar between the once-daily and twice-daily radiation groups.
Grade 3 or 4 anemia occurred in 16.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 10.7% of those who didn’t (P = .027). The difference was significant only among patients in the twice-daily radiation arm (20.9% vs. 8.3%, respectively; P = .004).
Patients in the twice-daily radiation arms who received G-CSF also required more platelet transfusion, compared with the once-daily arm (P less than .001), and, in both arms, G-CSF was associated with more red-cell transfusions (P = .007 for once-daily and .001 for twice daily).
G-CSF was not associated with either pneumonitis or esophagitis, and there were no differences in treatment-related deaths with either G-CSF or antibiotics.
Median OS by G-CSF use was 29 months with and 27 months without, a difference that was not significant (P = .08). Median PFS also did not differ by G-CSF use or nonuse.
When it came to antibiotic prophylaxis, however, both median OS and PFS were significant worse with antibiotic use (OS, 24 months with vs. 33 months without; P = .016; PFS, P = .03).
“We are very reassured that there are no significant additional toxicities [with G-CSF] from radiation in the acute setting,” commented Sanjay Popat, FRCP, PhD, from the Royal Marsden Hospital in London, the invited discussant.
“However, we have no data as yet on the impact of G-CSF usage on febrile neutropenia, which is of course the fundamental that we’re aiming to improve in the hope that this will contribute to [lowering] costs,” he added.
The study was sponsored by the Christie Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, Cancer Research UK, EORTC, GECP, GFPC, and IFCT. Dr. Gomes reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Popat reported consultation, honoraria, travel expenses, and institutional research from multiple entities.
GENEVA – In patients with limited stage–small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) treated with concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, the use of antibiotics to prevent febrile neutropenia was associated with worse outcomes, but granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) prescribed for the same purposes appeared to be safe, reported investigators.
In a subanalysis of data on patients with early SCLC enrolled in the phase III CONVERT trial comparing chemotherapy with concurrent once-daily vs. twice-daily radiation, the use of antibiotic prophylaxis of neutropenia was associated with worse overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival, (PFS) compared with no antibiotics, reported Fabio Gomes, MD, from the Christie NHS Foundation Trust Hospital in Manchester, England.
The use of G-CSF was, however, associated with higher rates of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia and anemia, requiring supportive measures, he acknowledged.
The role of G-CSF with concurrent thoracic radiotherapy is controversial because of safety concerns, but data are scarce, Dr. Gomes said. He noted that the American Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines on the use of white blood cell growth factors recommend against their routine use.
However, some of those concerns arose in the mid-1990s when granulocyt macrophage–stimulating colony factor (GM-CSF) was used, rather than G-CSF, which acts on only a single blood lineage, namely neutrophils. Additionally, modern radiology techniques are more precise than they were 20 years ago, reducing the risk of toxicity, he noted.
In the CONVERT trial, 547 patients with LS-SCLC were randomly assigned to receive four to six cycles of cisplatin and etoposide chemotherapy concurrently with either once daily thoracic radiation for a total dose of 66 Gy divided into 33 fractions delivered over 45 days or to twice-daily radiation at a total dose of 45 Gy divided into 30 fractions delivered over 19 days.
There was no difference between the groups in the primary endpoint of overall survival.
In the subanalysis reported here, Gomes et al. looked at the use of G-CSF, delivered at the investigator’s discretion, in 487 patients. Approximately 40% of patients in the subanalysis received G-CSF during at least one treatment cycle.
Prophylactic antibiotics were recommended by the investigators for use in association with at least one chemotherapy cycle, and 49% of patients in the subanalysis received them during at least one cycle.
Hematological toxicities included grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia occurring in 29.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 13.3% of those who did not (P less than .001). The rates were similar between the once-daily and twice-daily radiation groups.
Grade 3 or 4 anemia occurred in 16.9% of patients who received G-CSF, vs. 10.7% of those who didn’t (P = .027). The difference was significant only among patients in the twice-daily radiation arm (20.9% vs. 8.3%, respectively; P = .004).
Patients in the twice-daily radiation arms who received G-CSF also required more platelet transfusion, compared with the once-daily arm (P less than .001), and, in both arms, G-CSF was associated with more red-cell transfusions (P = .007 for once-daily and .001 for twice daily).
G-CSF was not associated with either pneumonitis or esophagitis, and there were no differences in treatment-related deaths with either G-CSF or antibiotics.
Median OS by G-CSF use was 29 months with and 27 months without, a difference that was not significant (P = .08). Median PFS also did not differ by G-CSF use or nonuse.
When it came to antibiotic prophylaxis, however, both median OS and PFS were significant worse with antibiotic use (OS, 24 months with vs. 33 months without; P = .016; PFS, P = .03).
“We are very reassured that there are no significant additional toxicities [with G-CSF] from radiation in the acute setting,” commented Sanjay Popat, FRCP, PhD, from the Royal Marsden Hospital in London, the invited discussant.
“However, we have no data as yet on the impact of G-CSF usage on febrile neutropenia, which is of course the fundamental that we’re aiming to improve in the hope that this will contribute to [lowering] costs,” he added.
The study was sponsored by the Christie Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, Cancer Research UK, EORTC, GECP, GFPC, and IFCT. Dr. Gomes reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Popat reported consultation, honoraria, travel expenses, and institutional research from multiple entities.
FROM ELCC
Key clinical point: Febrile neutropenia prophylaxis with G-CSF was safe, but prophylactic antibiotics were associated with worse overall survival in patients with limited stage–small cell lung cancer.
Major finding: Both median overall and progression-free survival were lower among patients who received prophylactic antibiotics. There were no differences in survival by G-CSF use.
Data source: Subanalysis of data on 487 patients in the phase III CONVERT trial comparing once-daily and twice daily radiation concurrent with chemotherapy in LS-SCLC.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by the Christie Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, Cancer Research UK, EORTC, GECP, GFPC, and IFCT. Dr. Gomes reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Popat reported consultation, honoraria, travel expenses, and institutional research from multiple entities.
Noncardiovascular comorbidities spike in acute heart failure
PARIS – Patients hospitalized for heart failure increasingly present with a growing number of noncardiovascular comorbidities, according to registry data from more than 300 U.S. hospitals.
During the decade of 2005-2014, the percentage of patients hospitalized for heart failure diagnosed with three or more noncardiovascular comorbidities (NCCs) jumped from abut 17% of these patients in 2005 to about 28% in 2015, Abhinav Sharma, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the ESC. This increase occurred as the percentages of hospitalized heart failure patients with none or one NCC showed clear decreases.
U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure “appear to now be sicker and more medically complex. Probably, a large number of the noncardiovascular comorbidities are not being recognized when the focus is on treating the patient’s heart failure,” he said in an interview. “If we can identify the noncardiovascular comorbidities and target appropriate treatment, it may potentially decrease the risk of readmissions.”
He included five NCCs in his analysis: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity.
His analysis showed that a higher rate of readmissions, as well as increased mortality both in hospital and during the 30 days following discharge, are outcomes that all connect with increased numbers of NCCs. Patients with three or more NCCs at the time of their heart failure admission were about 50% more likely to die in hospital, about 65% more likely to die during the 30 days following admission, about 35% more likely to be readmitted, and about half as likely to be discharged home following hospitalization, when compared with patients with no NCC in multivariate analyses that adjusted for demographic and other clinical variables. Patients with three or more NCCs were also about 67% more likely to have an index hospitalization of at least 4 days, compared with patients with no NCC.
Dr. Sharma speculated that the increased prevalence of multiple NCCs in acute heart failure patients may result, in part, from secular trends in the rates of diabetes and obesity and the noncardiovascular comorbidities associated with these conditions. All five of the NCCs included in his analysis showed increased prevalence rates from 2005 to 2014 in the patients he studied. The biggest jump occurred in the prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which rose from about 27% in 2005 to about 35% in 2014.
His study used data collected in the Get With the Guidelines–Heart Failure Registry, which began in 2005, and included just under 208,000 total patients. He acknowledged that it is hard to know how representative these patients are of the entire population of U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure during the study period, because the patients he studied came from a self-selected group of more than 300 hospitals that opted to participate in the registry. “We need to see if this can be extrapolated to all U.S. hospitals,” Dr. Sharma said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
PARIS – Patients hospitalized for heart failure increasingly present with a growing number of noncardiovascular comorbidities, according to registry data from more than 300 U.S. hospitals.
During the decade of 2005-2014, the percentage of patients hospitalized for heart failure diagnosed with three or more noncardiovascular comorbidities (NCCs) jumped from abut 17% of these patients in 2005 to about 28% in 2015, Abhinav Sharma, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the ESC. This increase occurred as the percentages of hospitalized heart failure patients with none or one NCC showed clear decreases.
U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure “appear to now be sicker and more medically complex. Probably, a large number of the noncardiovascular comorbidities are not being recognized when the focus is on treating the patient’s heart failure,” he said in an interview. “If we can identify the noncardiovascular comorbidities and target appropriate treatment, it may potentially decrease the risk of readmissions.”
He included five NCCs in his analysis: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity.
His analysis showed that a higher rate of readmissions, as well as increased mortality both in hospital and during the 30 days following discharge, are outcomes that all connect with increased numbers of NCCs. Patients with three or more NCCs at the time of their heart failure admission were about 50% more likely to die in hospital, about 65% more likely to die during the 30 days following admission, about 35% more likely to be readmitted, and about half as likely to be discharged home following hospitalization, when compared with patients with no NCC in multivariate analyses that adjusted for demographic and other clinical variables. Patients with three or more NCCs were also about 67% more likely to have an index hospitalization of at least 4 days, compared with patients with no NCC.
Dr. Sharma speculated that the increased prevalence of multiple NCCs in acute heart failure patients may result, in part, from secular trends in the rates of diabetes and obesity and the noncardiovascular comorbidities associated with these conditions. All five of the NCCs included in his analysis showed increased prevalence rates from 2005 to 2014 in the patients he studied. The biggest jump occurred in the prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which rose from about 27% in 2005 to about 35% in 2014.
His study used data collected in the Get With the Guidelines–Heart Failure Registry, which began in 2005, and included just under 208,000 total patients. He acknowledged that it is hard to know how representative these patients are of the entire population of U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure during the study period, because the patients he studied came from a self-selected group of more than 300 hospitals that opted to participate in the registry. “We need to see if this can be extrapolated to all U.S. hospitals,” Dr. Sharma said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
PARIS – Patients hospitalized for heart failure increasingly present with a growing number of noncardiovascular comorbidities, according to registry data from more than 300 U.S. hospitals.
During the decade of 2005-2014, the percentage of patients hospitalized for heart failure diagnosed with three or more noncardiovascular comorbidities (NCCs) jumped from abut 17% of these patients in 2005 to about 28% in 2015, Abhinav Sharma, MD, said at a meeting held by the Heart Failure Association of the ESC. This increase occurred as the percentages of hospitalized heart failure patients with none or one NCC showed clear decreases.
U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure “appear to now be sicker and more medically complex. Probably, a large number of the noncardiovascular comorbidities are not being recognized when the focus is on treating the patient’s heart failure,” he said in an interview. “If we can identify the noncardiovascular comorbidities and target appropriate treatment, it may potentially decrease the risk of readmissions.”
He included five NCCs in his analysis: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, anemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity.
His analysis showed that a higher rate of readmissions, as well as increased mortality both in hospital and during the 30 days following discharge, are outcomes that all connect with increased numbers of NCCs. Patients with three or more NCCs at the time of their heart failure admission were about 50% more likely to die in hospital, about 65% more likely to die during the 30 days following admission, about 35% more likely to be readmitted, and about half as likely to be discharged home following hospitalization, when compared with patients with no NCC in multivariate analyses that adjusted for demographic and other clinical variables. Patients with three or more NCCs were also about 67% more likely to have an index hospitalization of at least 4 days, compared with patients with no NCC.
Dr. Sharma speculated that the increased prevalence of multiple NCCs in acute heart failure patients may result, in part, from secular trends in the rates of diabetes and obesity and the noncardiovascular comorbidities associated with these conditions. All five of the NCCs included in his analysis showed increased prevalence rates from 2005 to 2014 in the patients he studied. The biggest jump occurred in the prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which rose from about 27% in 2005 to about 35% in 2014.
His study used data collected in the Get With the Guidelines–Heart Failure Registry, which began in 2005, and included just under 208,000 total patients. He acknowledged that it is hard to know how representative these patients are of the entire population of U.S. patients hospitalized for heart failure during the study period, because the patients he studied came from a self-selected group of more than 300 hospitals that opted to participate in the registry. “We need to see if this can be extrapolated to all U.S. hospitals,” Dr. Sharma said.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
AT HEART FAILURE 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The prevalence of three or more noncardiovascular comorbidities jumped from about 17% in 2005 to about 28% in 2014.
Data source: Review of 207,984 U.S. hospitalized heart failure patients included in the Get With the Guidelines–Heart Failure Registry during 2005-2014.
Disclosures: Dr. Sharma has received research support from Roche Diagnostics and Takeda.
ASCO updates NSCLC guidelines for adjuvant therapy
Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy is recommended for routine use in non–small cell lung cancer patients with stage IIA, IIB, or IIIA disease who have undergone complete surgical resections, according to updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
In patients with stage IA disease, the guidelines recommend against cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The new guidelines are based on a systematic review current to January 2016 and an American Society for Radiation Oncology guideline and systematic review, which ASCO had already endorsed, which formed the basis for recommendations on adjuvant radiation therapy, Mark G. Kris, MD, and panel authors said (J Clin Oncol. 2017 April 26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.4401).
The guidelines, available online, also recommend against routine cisplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with stage IB disease, but they suggest an evaluation of these patients to explore the pros and cons of adjuvant chemotherapy.
With respect to radiation, the authors recommend against it for patients with resected stage I or stage II disease, and they recommend against it for routine use in patients with stage IIIA. However, in patients with IIIA N2 disease, patients should be evaluated postoperatively, in consultation with a medical oncologist, for the potential risks and benefits of adjuvant radiation.
The authors also provide some recommendations for communicating with patients regarding treatment decisions. There are few studies examining this question, so the recommendations are based on low-quality evidence.
Non–small cell lung cancer patients may have complex social, psychological, and medical issues, and discussions should be carried out with this in mind. Pain, impaired breathing, and fatigue are common after surgery, and smoking cessation can lead to short-term stress as a result of nicotine withdrawal. Older patients may have a range of comorbidities.
Studies show that patients are most satisfied if they feel that physicians allow them to share in the decision making, and if they are given sufficient time to choose. To that end, the authors recommend a session dedicated to discussion of adjuvant therapy.
Communicating risk of death is challenging for many reasons. Patients should be asked how they would like to hear about their risks: some prefer general terms, while others may opt for numbers, charts, or graphs. The guidelines include a risk chart that can help patients understand the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy.
The study authors report financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy is recommended for routine use in non–small cell lung cancer patients with stage IIA, IIB, or IIIA disease who have undergone complete surgical resections, according to updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
In patients with stage IA disease, the guidelines recommend against cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The new guidelines are based on a systematic review current to January 2016 and an American Society for Radiation Oncology guideline and systematic review, which ASCO had already endorsed, which formed the basis for recommendations on adjuvant radiation therapy, Mark G. Kris, MD, and panel authors said (J Clin Oncol. 2017 April 26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.4401).
The guidelines, available online, also recommend against routine cisplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with stage IB disease, but they suggest an evaluation of these patients to explore the pros and cons of adjuvant chemotherapy.
With respect to radiation, the authors recommend against it for patients with resected stage I or stage II disease, and they recommend against it for routine use in patients with stage IIIA. However, in patients with IIIA N2 disease, patients should be evaluated postoperatively, in consultation with a medical oncologist, for the potential risks and benefits of adjuvant radiation.
The authors also provide some recommendations for communicating with patients regarding treatment decisions. There are few studies examining this question, so the recommendations are based on low-quality evidence.
Non–small cell lung cancer patients may have complex social, psychological, and medical issues, and discussions should be carried out with this in mind. Pain, impaired breathing, and fatigue are common after surgery, and smoking cessation can lead to short-term stress as a result of nicotine withdrawal. Older patients may have a range of comorbidities.
Studies show that patients are most satisfied if they feel that physicians allow them to share in the decision making, and if they are given sufficient time to choose. To that end, the authors recommend a session dedicated to discussion of adjuvant therapy.
Communicating risk of death is challenging for many reasons. Patients should be asked how they would like to hear about their risks: some prefer general terms, while others may opt for numbers, charts, or graphs. The guidelines include a risk chart that can help patients understand the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy.
The study authors report financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy is recommended for routine use in non–small cell lung cancer patients with stage IIA, IIB, or IIIA disease who have undergone complete surgical resections, according to updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
In patients with stage IA disease, the guidelines recommend against cisplatin-based chemotherapy. The new guidelines are based on a systematic review current to January 2016 and an American Society for Radiation Oncology guideline and systematic review, which ASCO had already endorsed, which formed the basis for recommendations on adjuvant radiation therapy, Mark G. Kris, MD, and panel authors said (J Clin Oncol. 2017 April 26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.4401).
The guidelines, available online, also recommend against routine cisplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with stage IB disease, but they suggest an evaluation of these patients to explore the pros and cons of adjuvant chemotherapy.
With respect to radiation, the authors recommend against it for patients with resected stage I or stage II disease, and they recommend against it for routine use in patients with stage IIIA. However, in patients with IIIA N2 disease, patients should be evaluated postoperatively, in consultation with a medical oncologist, for the potential risks and benefits of adjuvant radiation.
The authors also provide some recommendations for communicating with patients regarding treatment decisions. There are few studies examining this question, so the recommendations are based on low-quality evidence.
Non–small cell lung cancer patients may have complex social, psychological, and medical issues, and discussions should be carried out with this in mind. Pain, impaired breathing, and fatigue are common after surgery, and smoking cessation can lead to short-term stress as a result of nicotine withdrawal. Older patients may have a range of comorbidities.
Studies show that patients are most satisfied if they feel that physicians allow them to share in the decision making, and if they are given sufficient time to choose. To that end, the authors recommend a session dedicated to discussion of adjuvant therapy.
Communicating risk of death is challenging for many reasons. Patients should be asked how they would like to hear about their risks: some prefer general terms, while others may opt for numbers, charts, or graphs. The guidelines include a risk chart that can help patients understand the potential benefits and risks of chemotherapy.
The study authors report financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
Hospital infections top WHO’s list of priority pathogens
The World Health Organization is urging governments to focus antibiotic research efforts on a list of urgent bacterial threats, topped by several increasingly powerful superbugs that cause hospital-based infections and other potentially deadly conditions.
The WHO listed the top 20 bacteria that it believes are most harmful to human health, other than mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis. The germ was not included in the list because it’s generally accepted to be the most urgent priority for new antibiotic research and development, Marie-Paule Kieny, PhD, a WHO assistant director, said at a press conference.
The priority list is needed because the antibiotic pipeline is “practically dry,” thanks to scientific research challenges and a lack of financial incentives, according to Dr. Kieny. “Antibiotics are generally used for the short term, unlike therapies for chronic diseases, which bring in much higher returns on investment,” she said. The list “is intended to signal to the scientific community and the pharmaceutical industry the areas they should focus on to address urgent public health threats.”
The WHO list begins with Priority 1/“Critical” pathogens that it believes most urgently need to be targeted through antibiotic research and development: Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant; Pseudomonas aeruginosa, carbapenem-resistant; and Enterobacteriaceae (including Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Proteus spp., Providencia spp., and Morganella spp.), carbapenem-resistant, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing.
“These bacteria are responsible for severe infections and high mortality rates, mostly in hospitalized patients, transplant recipients, those receiving chemotherapy, or patients in intensive care units,” Dr. Kieny said. “While these bacteria are not widespread and do not generally affect healthy individuals, the burden for patients and society is now alarming – and new, effective therapies are imperative.”
Priority 2/”High” pathogens are Enterococcus faecium, vancomycin-resistant; Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin intermediate and resistant; Helicobacter pylori, clarithromycin-resistant; Campylobacter, fluoroquinolone-resistant; Salmonella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant; Neisseria gonorrhoeae, third-generation cephalosporin-resistant and fluoroquinolone-resistant.
Pathogens in this category can infect healthy individuals, Dr. Kieny noted. “These infections, although not associated with significant mortality, have a dramatic health and economic impact on communities and, in particular, in low-income countries.”
Priority 3/”Medium” pathogens are Streptococcus pneumoniae, penicillin–non-susceptible; Haemophilus influenzae, ampicillin-resistant; and Shigella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant.
These pathogens “represent a threat because of increasing resistance but still have some effective antibiotic options available,” Dr. Kieny said.
According to a statement provided by the WHO, the priority list doesn’t include streptococcus A and B or chlamydia, because resistance hasn’t reached the level of a public health threat.
One goal of the list is to focus attention on the development of small-market, gram-negative drugs that combat hospital-based infections, explained Nicola Magrini, MD, a WHO scientist who also spoke at the press conference.
Over the last decade, he said, the pipeline has instead focused more on gram-positive agents – mostly linked to beta-lactamase – that have wider market potential and generate less resistance.
“From a clinical point of view, these multidrug-resistant gram-negative clinical trials are very difficult and expensive to do, more than for gram-positive,” noted Evelina Tacconelli, MD, PhD, a contributor to the WHO report. “Because when we talk about gram-negative, we need to cover multiple pathogens and not just one or two, as in the case of gram-positive.”
Dr. Magrini said he couldn’t provide estimates about how many people worldwide are affected by the listed pathogens. However, he said a full report with numbers will be released by June.
It does appear that patients with severe infection from antibiotic-resistant germs face a mortality rate of up to 60%, while extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–positive E. coli accounts for up to 70% of urinary tract infections in many countries, explained Dr. Tacconelli, head of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Tübingen, Germany.
“Even if we don’t know exactly how many,” she said, “we are talking about millions of people affected.”
The World Health Organization is urging governments to focus antibiotic research efforts on a list of urgent bacterial threats, topped by several increasingly powerful superbugs that cause hospital-based infections and other potentially deadly conditions.
The WHO listed the top 20 bacteria that it believes are most harmful to human health, other than mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis. The germ was not included in the list because it’s generally accepted to be the most urgent priority for new antibiotic research and development, Marie-Paule Kieny, PhD, a WHO assistant director, said at a press conference.
The priority list is needed because the antibiotic pipeline is “practically dry,” thanks to scientific research challenges and a lack of financial incentives, according to Dr. Kieny. “Antibiotics are generally used for the short term, unlike therapies for chronic diseases, which bring in much higher returns on investment,” she said. The list “is intended to signal to the scientific community and the pharmaceutical industry the areas they should focus on to address urgent public health threats.”
The WHO list begins with Priority 1/“Critical” pathogens that it believes most urgently need to be targeted through antibiotic research and development: Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant; Pseudomonas aeruginosa, carbapenem-resistant; and Enterobacteriaceae (including Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Proteus spp., Providencia spp., and Morganella spp.), carbapenem-resistant, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing.
“These bacteria are responsible for severe infections and high mortality rates, mostly in hospitalized patients, transplant recipients, those receiving chemotherapy, or patients in intensive care units,” Dr. Kieny said. “While these bacteria are not widespread and do not generally affect healthy individuals, the burden for patients and society is now alarming – and new, effective therapies are imperative.”
Priority 2/”High” pathogens are Enterococcus faecium, vancomycin-resistant; Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin intermediate and resistant; Helicobacter pylori, clarithromycin-resistant; Campylobacter, fluoroquinolone-resistant; Salmonella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant; Neisseria gonorrhoeae, third-generation cephalosporin-resistant and fluoroquinolone-resistant.
Pathogens in this category can infect healthy individuals, Dr. Kieny noted. “These infections, although not associated with significant mortality, have a dramatic health and economic impact on communities and, in particular, in low-income countries.”
Priority 3/”Medium” pathogens are Streptococcus pneumoniae, penicillin–non-susceptible; Haemophilus influenzae, ampicillin-resistant; and Shigella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant.
These pathogens “represent a threat because of increasing resistance but still have some effective antibiotic options available,” Dr. Kieny said.
According to a statement provided by the WHO, the priority list doesn’t include streptococcus A and B or chlamydia, because resistance hasn’t reached the level of a public health threat.
One goal of the list is to focus attention on the development of small-market, gram-negative drugs that combat hospital-based infections, explained Nicola Magrini, MD, a WHO scientist who also spoke at the press conference.
Over the last decade, he said, the pipeline has instead focused more on gram-positive agents – mostly linked to beta-lactamase – that have wider market potential and generate less resistance.
“From a clinical point of view, these multidrug-resistant gram-negative clinical trials are very difficult and expensive to do, more than for gram-positive,” noted Evelina Tacconelli, MD, PhD, a contributor to the WHO report. “Because when we talk about gram-negative, we need to cover multiple pathogens and not just one or two, as in the case of gram-positive.”
Dr. Magrini said he couldn’t provide estimates about how many people worldwide are affected by the listed pathogens. However, he said a full report with numbers will be released by June.
It does appear that patients with severe infection from antibiotic-resistant germs face a mortality rate of up to 60%, while extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–positive E. coli accounts for up to 70% of urinary tract infections in many countries, explained Dr. Tacconelli, head of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Tübingen, Germany.
“Even if we don’t know exactly how many,” she said, “we are talking about millions of people affected.”
The World Health Organization is urging governments to focus antibiotic research efforts on a list of urgent bacterial threats, topped by several increasingly powerful superbugs that cause hospital-based infections and other potentially deadly conditions.
The WHO listed the top 20 bacteria that it believes are most harmful to human health, other than mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes tuberculosis. The germ was not included in the list because it’s generally accepted to be the most urgent priority for new antibiotic research and development, Marie-Paule Kieny, PhD, a WHO assistant director, said at a press conference.
The priority list is needed because the antibiotic pipeline is “practically dry,” thanks to scientific research challenges and a lack of financial incentives, according to Dr. Kieny. “Antibiotics are generally used for the short term, unlike therapies for chronic diseases, which bring in much higher returns on investment,” she said. The list “is intended to signal to the scientific community and the pharmaceutical industry the areas they should focus on to address urgent public health threats.”
The WHO list begins with Priority 1/“Critical” pathogens that it believes most urgently need to be targeted through antibiotic research and development: Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant; Pseudomonas aeruginosa, carbapenem-resistant; and Enterobacteriaceae (including Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Serratia spp., Proteus spp., Providencia spp., and Morganella spp.), carbapenem-resistant, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing.
“These bacteria are responsible for severe infections and high mortality rates, mostly in hospitalized patients, transplant recipients, those receiving chemotherapy, or patients in intensive care units,” Dr. Kieny said. “While these bacteria are not widespread and do not generally affect healthy individuals, the burden for patients and society is now alarming – and new, effective therapies are imperative.”
Priority 2/”High” pathogens are Enterococcus faecium, vancomycin-resistant; Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin intermediate and resistant; Helicobacter pylori, clarithromycin-resistant; Campylobacter, fluoroquinolone-resistant; Salmonella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant; Neisseria gonorrhoeae, third-generation cephalosporin-resistant and fluoroquinolone-resistant.
Pathogens in this category can infect healthy individuals, Dr. Kieny noted. “These infections, although not associated with significant mortality, have a dramatic health and economic impact on communities and, in particular, in low-income countries.”
Priority 3/”Medium” pathogens are Streptococcus pneumoniae, penicillin–non-susceptible; Haemophilus influenzae, ampicillin-resistant; and Shigella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant.
These pathogens “represent a threat because of increasing resistance but still have some effective antibiotic options available,” Dr. Kieny said.
According to a statement provided by the WHO, the priority list doesn’t include streptococcus A and B or chlamydia, because resistance hasn’t reached the level of a public health threat.
One goal of the list is to focus attention on the development of small-market, gram-negative drugs that combat hospital-based infections, explained Nicola Magrini, MD, a WHO scientist who also spoke at the press conference.
Over the last decade, he said, the pipeline has instead focused more on gram-positive agents – mostly linked to beta-lactamase – that have wider market potential and generate less resistance.
“From a clinical point of view, these multidrug-resistant gram-negative clinical trials are very difficult and expensive to do, more than for gram-positive,” noted Evelina Tacconelli, MD, PhD, a contributor to the WHO report. “Because when we talk about gram-negative, we need to cover multiple pathogens and not just one or two, as in the case of gram-positive.”
Dr. Magrini said he couldn’t provide estimates about how many people worldwide are affected by the listed pathogens. However, he said a full report with numbers will be released by June.
It does appear that patients with severe infection from antibiotic-resistant germs face a mortality rate of up to 60%, while extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–positive E. coli accounts for up to 70% of urinary tract infections in many countries, explained Dr. Tacconelli, head of the division of infectious diseases at the University of Tübingen, Germany.
“Even if we don’t know exactly how many,” she said, “we are talking about millions of people affected.”
FDA warns against use of codeine, tramadol in children
The Food and Drug Administration is restricting the use of two opiates – codeine and tramadol – in children, and also warns they are potentially dangerous to infants of breastfeeding women.
Codeine is approved to treat pain and cough; tramadol is approved to treat pain.
“We understand that there are limited options when it comes to treating pain or cough in children, and that these changes may raise some questions for health care providers and parents. However, please know that our decision today was made based on the latest evidence and with this goal in mind: keeping our kids safe,” Douglas Throckmorton, MD, the deputy center director for regulatory programs at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
In 2013, the FDA updated prescription codeine labeling to contain a boxed warning and contraindication for children up to age 18 years regarding the risk of slowed breathing from codeine prescribed after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. And in 2015, the agency issued warnings about the risk of serious breathing problems in children who had ultrarapid metabolism of codeine and tramadol.
In the current safety statement, the FDA said it will require additional labeling changes, including contraindications for use of codeine or tramadol in all children younger than 12 years of age and a new contraindication for tramadol in children younger than 18 years being treated for pain after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, warnings about their use in children 12-18 years of age with certain medical conditions, and a stronger warning recommending against their use in nursing mothers.
Single-ingredient codeine and all tramadol-containing products are FDA-approved only for use in adults, the agency noted.
The agency cited particular concerns over those who are “ultra-rapid metabolizers” of substrates of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype. These people more quickly convert codeine into potentially dangerously high levels of morphine, which can lead to fatal respiratory depression.
Supporting the restrictions and warning were data on 64 cases of respiratory depression that occurred worldwide between 1969 and 2015, when a codeine-based medicine was used in children younger than 18 years. Twenty-four of these children died.
The most frequently cited medicines in the cases were acetaminophen with codeine and promethazine with codeine with or without phenylephrine, either given to soothe postoperative pain, general pain, sore or strep throat pain, or cough and cold.
Ten of the 64 cases implicated the CYP2D6 genotype. Seven of the patients were “ultrarapid metabolizers,” five of whom died.
Data cited on tramadol included nine worldwide cases of tramadol-related respiratory depression occurring between 1969 and 2016, resulting in the deaths of three children, all under the age of 6 years, and all of whom were taking the drug for postoperative pain or fever.
All but one case of respiratory depression occurred within the first 24 hours of taking the drug. One of the patients was genotyped for CYP2D6, and found to have three functional alleles consistent with ultrarapid metabolism.
Mothers who are ultrarapid metabolizers of codeine can have high levels of morphine in their breast milk that are dangerous to their breastfed infants, whereas there is less of a threat posed by women with normal codeine metabolism because the amount of codeine secreted into the breast milk is low and dose dependent.
The FDA stated that data reveal numerous reports of respiratory depression and at least one death in infants of breastfeeding mothers taking these medicines, particularly mothers with the CYP2D6 genotype. Although there are FDA-cleared tests for ultrarapid metabolism, they are not commonly used.
The agency stated that breastfeeding women taking any opioid pain medicine, including codeine or tramadol should contact their health care provider if they notice the infant is sleeping more than 4 hours at a time, or if the infant is having difficulty breastfeeding or seems limp.
Clinicians are urged to report side effects that occur while using codeine or tramadol to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
The Food and Drug Administration is restricting the use of two opiates – codeine and tramadol – in children, and also warns they are potentially dangerous to infants of breastfeeding women.
Codeine is approved to treat pain and cough; tramadol is approved to treat pain.
“We understand that there are limited options when it comes to treating pain or cough in children, and that these changes may raise some questions for health care providers and parents. However, please know that our decision today was made based on the latest evidence and with this goal in mind: keeping our kids safe,” Douglas Throckmorton, MD, the deputy center director for regulatory programs at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
In 2013, the FDA updated prescription codeine labeling to contain a boxed warning and contraindication for children up to age 18 years regarding the risk of slowed breathing from codeine prescribed after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. And in 2015, the agency issued warnings about the risk of serious breathing problems in children who had ultrarapid metabolism of codeine and tramadol.
In the current safety statement, the FDA said it will require additional labeling changes, including contraindications for use of codeine or tramadol in all children younger than 12 years of age and a new contraindication for tramadol in children younger than 18 years being treated for pain after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, warnings about their use in children 12-18 years of age with certain medical conditions, and a stronger warning recommending against their use in nursing mothers.
Single-ingredient codeine and all tramadol-containing products are FDA-approved only for use in adults, the agency noted.
The agency cited particular concerns over those who are “ultra-rapid metabolizers” of substrates of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype. These people more quickly convert codeine into potentially dangerously high levels of morphine, which can lead to fatal respiratory depression.
Supporting the restrictions and warning were data on 64 cases of respiratory depression that occurred worldwide between 1969 and 2015, when a codeine-based medicine was used in children younger than 18 years. Twenty-four of these children died.
The most frequently cited medicines in the cases were acetaminophen with codeine and promethazine with codeine with or without phenylephrine, either given to soothe postoperative pain, general pain, sore or strep throat pain, or cough and cold.
Ten of the 64 cases implicated the CYP2D6 genotype. Seven of the patients were “ultrarapid metabolizers,” five of whom died.
Data cited on tramadol included nine worldwide cases of tramadol-related respiratory depression occurring between 1969 and 2016, resulting in the deaths of three children, all under the age of 6 years, and all of whom were taking the drug for postoperative pain or fever.
All but one case of respiratory depression occurred within the first 24 hours of taking the drug. One of the patients was genotyped for CYP2D6, and found to have three functional alleles consistent with ultrarapid metabolism.
Mothers who are ultrarapid metabolizers of codeine can have high levels of morphine in their breast milk that are dangerous to their breastfed infants, whereas there is less of a threat posed by women with normal codeine metabolism because the amount of codeine secreted into the breast milk is low and dose dependent.
The FDA stated that data reveal numerous reports of respiratory depression and at least one death in infants of breastfeeding mothers taking these medicines, particularly mothers with the CYP2D6 genotype. Although there are FDA-cleared tests for ultrarapid metabolism, they are not commonly used.
The agency stated that breastfeeding women taking any opioid pain medicine, including codeine or tramadol should contact their health care provider if they notice the infant is sleeping more than 4 hours at a time, or if the infant is having difficulty breastfeeding or seems limp.
Clinicians are urged to report side effects that occur while using codeine or tramadol to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
The Food and Drug Administration is restricting the use of two opiates – codeine and tramadol – in children, and also warns they are potentially dangerous to infants of breastfeeding women.
Codeine is approved to treat pain and cough; tramadol is approved to treat pain.
“We understand that there are limited options when it comes to treating pain or cough in children, and that these changes may raise some questions for health care providers and parents. However, please know that our decision today was made based on the latest evidence and with this goal in mind: keeping our kids safe,” Douglas Throckmorton, MD, the deputy center director for regulatory programs at the FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a statement.
In 2013, the FDA updated prescription codeine labeling to contain a boxed warning and contraindication for children up to age 18 years regarding the risk of slowed breathing from codeine prescribed after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. And in 2015, the agency issued warnings about the risk of serious breathing problems in children who had ultrarapid metabolism of codeine and tramadol.
In the current safety statement, the FDA said it will require additional labeling changes, including contraindications for use of codeine or tramadol in all children younger than 12 years of age and a new contraindication for tramadol in children younger than 18 years being treated for pain after tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, warnings about their use in children 12-18 years of age with certain medical conditions, and a stronger warning recommending against their use in nursing mothers.
Single-ingredient codeine and all tramadol-containing products are FDA-approved only for use in adults, the agency noted.
The agency cited particular concerns over those who are “ultra-rapid metabolizers” of substrates of the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype. These people more quickly convert codeine into potentially dangerously high levels of morphine, which can lead to fatal respiratory depression.
Supporting the restrictions and warning were data on 64 cases of respiratory depression that occurred worldwide between 1969 and 2015, when a codeine-based medicine was used in children younger than 18 years. Twenty-four of these children died.
The most frequently cited medicines in the cases were acetaminophen with codeine and promethazine with codeine with or without phenylephrine, either given to soothe postoperative pain, general pain, sore or strep throat pain, or cough and cold.
Ten of the 64 cases implicated the CYP2D6 genotype. Seven of the patients were “ultrarapid metabolizers,” five of whom died.
Data cited on tramadol included nine worldwide cases of tramadol-related respiratory depression occurring between 1969 and 2016, resulting in the deaths of three children, all under the age of 6 years, and all of whom were taking the drug for postoperative pain or fever.
All but one case of respiratory depression occurred within the first 24 hours of taking the drug. One of the patients was genotyped for CYP2D6, and found to have three functional alleles consistent with ultrarapid metabolism.
Mothers who are ultrarapid metabolizers of codeine can have high levels of morphine in their breast milk that are dangerous to their breastfed infants, whereas there is less of a threat posed by women with normal codeine metabolism because the amount of codeine secreted into the breast milk is low and dose dependent.
The FDA stated that data reveal numerous reports of respiratory depression and at least one death in infants of breastfeeding mothers taking these medicines, particularly mothers with the CYP2D6 genotype. Although there are FDA-cleared tests for ultrarapid metabolism, they are not commonly used.
The agency stated that breastfeeding women taking any opioid pain medicine, including codeine or tramadol should contact their health care provider if they notice the infant is sleeping more than 4 hours at a time, or if the infant is having difficulty breastfeeding or seems limp.
Clinicians are urged to report side effects that occur while using codeine or tramadol to the FDA’s MedWatch Adverse Event Reporting program.
[email protected]
On Twitter @whitneymcknight
It’s been a good year for heart failure research ... mostly
WASHINGTON – It’s been a “relatively positive” year for heart failure research and advances in patient care, Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
“Having been in this field for 30 years looking at clinical trials, generally for every 10 important trials done in a year, 1 has been positive and 9 have been negative; if we look at the past year, it’s more like 5 and 6. So, not a bad year for cardiomyopathy,” declared Dr. O’Connor, CEO and executive director of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va., and president-elect of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The good news
• Empagliflozin (Jardiance) earns FDA approval for reduction in risk of cardiovascular death in type 2 diabetes patients. “This is one of the most amazing stories in heart failure,” said Dr. O’Connor, who is also professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The pivotal EMPA-REG OUTCOME study showed a highly significant 35% reduction in the secondary endpoint of risk of hospitalization for heart failure, as well the decrease in cardiovascular mortality which was the primary endpoint and proved persuasive to the FDA (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28).
“It was a remarkable development. Because of this trial, there are now a number of ongoing phase III clinical trials looking at this class of drugs in heart failure patients with and without diabetes, which makes this a very important research movement. We are now looking deeper at phenotypes and trying to get more specific with these drug therapies,” he said.
• A new and improved LVAD. This fully magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump type of left ventricular assist device for advanced heart failure showed superior event-free survival, compared with a commercially available axial continuous-flow pump LVAD in the randomized MOMENTUM-3 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:440-50).
The novel pump was designed to overcome a significant problem with axial continuous-flow LVADs: a proclivity for pump thrombosis. The magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump proved a smashing success in this regard, with zero cases of pump thrombosis occurring during the 6-month study.
“This may be the first time in the history of heart failure research that the engineers have beaten the biologists in important clinical outcomes,” the cardiologist quipped.
• Omecamtiv mecarbil successfully addresses impaired contractility in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). This drug, a selective cardiac myosin activator, resulted in increased duration of systole and improved stroke volume accompanied by reductions in heart rate, left ventricular end-diastolic and -systolic dimensions, and NT-proBNP in the 87-site, 13-country, phase II COSMIC-HF study (Lancet. 2016 Dec 10;388[10062]:2895-903).
“This is probably the most novel new drug mechanism out there in clinical trials,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
On the basis of the highly encouraging results for the surrogate endpoints assessed in COSMIC-HF, a large phase III clinical trial known as GALACTIC is underway.
• Palliative care gets a welcome boost. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in PAL-HF, a single-center study presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
“This is a very important trial of palliative care in advanced heart failure. We probably don’t have as much evidence in this space as we should,” he observed. “This was a multidisciplinary intervention in which we gave the patients a medical tool kit to alleviate pain, dyspnea, and discomfort. The tool kit included benzodiazepines, sleep medications, sublingual nitroglycerin, and morphinelike products, all very carefully monitored by staff coordinators.”
The primary outcome was change in two validated heart failure quality of life measures. Both instruments documented significant improvement compared with usual care.
“There was no decrease in mortality, which wasn’t a goal in this advanced heart failure population, and no reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but there were significant reductions in depression and anxiety,” Dr. O’Connor said.
• Vericiguat. This oral soluble cyclic guanylate cyclase stimulator missed its primary endpoint in the phase II dose-escalation SOCRATES-REDUCED trial in patients with HFrEF (JAMA. 2015 Dec 1;314[21]:2251-62), but showed an impressive improvement in quality of life. It is now the subject of the ongoing, randomized, phase III VICTORIA trial involving a planned 4,000 patients with HFrEF with the composite primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization.
The phase II SOCRATES-PRESERVED trial also missed its primary endpoint but showed a clinically meaningful improvement in quality of life in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (Eur Heart J. 2017 Mar 22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw593). Discussions are ongoing as to whether the next step should be a confirmatory phase II study or a move straight to phase III.
The bad news
• NSAIDs linked to increased risk of heart failure. European investigators analyzed five population-based databases totaling more than 8.3 million individuals and determined that current use of any of more than two dozen NSAIDs was associated with significantly increased risk of hospital admission for heart failure. The risk appeared to be dose dependent and varied between individual agents, ranging from a 16% increased risk with naproxen to an 83% increase with ketorolac (Toradol) (BMJ. 2016 Sep 28. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4857).
• Therapeutic natriuretic peptides hit bottom. The negative results for the investigational agent ularitide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in the large phase III TRUE-AHF trial presented at the 2016 meeting of the American Heart Association, following upon an earlier negative study of the related drug nesiritide (Natrecor) in more than 7,100 acute heart failure patients (N Engl J Med. 2011 Jul 7; 365:32-43), probably spells the end of the line for this strategy of boosting outcomes in acute heart failure, according to Dr. O’Connor.
Moreover, Novartis has announced that the phase III RELAX-AHF-2 trial of serelaxin in 6,600 patients with acute heart failure failed to meet its primary endpoints of reduced cardiovascular deaths or reduced worsening of heart failure. The trial will be formally presented later this year.
“Ularitide seemed to show an early improvement in heart failure events that was not sustained in-hospital, and there was absolutely no difference in mortality. The drug probably acts like a pharmacologic tourniquet, in my view. So I think this field of therapeutic natriuretic peptides is probably closed,” he said.
• ICDs don’t reduce mortality in patients with nonischemic heart failure. This was the conclusion reached in the DANISH trial, in which more than 1,100 patients with symptomatic systolic heart failure were randomized to an ICD or usual care (N Engl J Med. 2016 Sep 29;375[13]:1221-30).
“This study really shook up the field, raising the question, ‘Are we using defibrillators too frequently in this population?’ It has stimulated a lot of discussion, including within the guidelines committee,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
• Tolvaptan nixed for acute decompensated heart failure. The TACTICS-HF trial studied the use of tolvaptan (Samsca), an oral vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, to reduce dyspnea in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in the study, which showed that tolvaptan was no better than placebo at 8 and 24 hours (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Mar 21;69[11]:1399-406).
“For now, the routine use of vasopressin antagonists in acute heart failure is not to be encouraged, although there may still be subsets where it’s worth trying – certainly in severe hyponatremia,” the cardiologist said.
• GUIDE-IT gets lost. This was a roughly 1,000-patient randomized trial of a treatment strategy aimed at improving clinical outcomes by aggressively titrating evidence-based heart failure therapies in order to suppress natriuretic peptide biomarkers. GUIDE-IT was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board due to a lack of discernible difference in outcomes, compared with usual care. Dr. O’Connor, a coinvestigator, termed the soon-to-be-published study “a disappointment.”
Sleep apnea studies show silver lining
Sleep apnea is common in patients with heart failure and is associated with worse clinical heart failure outcomes. But in the large, randomized SERVE-HF trial, investigators showed that treatment of central sleep apnea with adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFrEF unexpectedly increased mortality, compared with optimal medical therapy (N Engl J Med. 2015 Sep 17;373:1095-105). In a more recent secondary analysis, however, the SERVE-HF investigators found that the increased risk for cardiovascular death associated with adaptive servo-ventilation was actually restricted to patients with a very poor left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% or less, and there was a signal of possible benefit in patients in the top tier of LVEF, at 36%-45% (Lancet Respir Med. 2016 Nov; 4[11]:873-81).
This observation dovetails nicely with the findings of the CAT-HF trial presented by Dr. O’Connor at the 2016 World Congress on Heart Failure. In this phase II study, 215 patients with acute decompensated heart failure and either obstructive or central sleep apnea were randomized to optimal medical therapy alone or in combination with adaptive servo-ventilation. There was no overall difference in outcome between the two groups; however, in the subgroup of patients with HFpEF, the risk of the primary composite endpoint was reduced by 62% with adaptive servo-ventilation.
As a result of these intriguing findings from SERVE-HF and CAT-HF, a registry and/or randomized clinical trial of adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFpEF is now being considered under NIH sponsorship, according to Dr. O’Connor.
He reported having no financial conflicts.
WASHINGTON – It’s been a “relatively positive” year for heart failure research and advances in patient care, Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
“Having been in this field for 30 years looking at clinical trials, generally for every 10 important trials done in a year, 1 has been positive and 9 have been negative; if we look at the past year, it’s more like 5 and 6. So, not a bad year for cardiomyopathy,” declared Dr. O’Connor, CEO and executive director of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va., and president-elect of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The good news
• Empagliflozin (Jardiance) earns FDA approval for reduction in risk of cardiovascular death in type 2 diabetes patients. “This is one of the most amazing stories in heart failure,” said Dr. O’Connor, who is also professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The pivotal EMPA-REG OUTCOME study showed a highly significant 35% reduction in the secondary endpoint of risk of hospitalization for heart failure, as well the decrease in cardiovascular mortality which was the primary endpoint and proved persuasive to the FDA (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28).
“It was a remarkable development. Because of this trial, there are now a number of ongoing phase III clinical trials looking at this class of drugs in heart failure patients with and without diabetes, which makes this a very important research movement. We are now looking deeper at phenotypes and trying to get more specific with these drug therapies,” he said.
• A new and improved LVAD. This fully magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump type of left ventricular assist device for advanced heart failure showed superior event-free survival, compared with a commercially available axial continuous-flow pump LVAD in the randomized MOMENTUM-3 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:440-50).
The novel pump was designed to overcome a significant problem with axial continuous-flow LVADs: a proclivity for pump thrombosis. The magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump proved a smashing success in this regard, with zero cases of pump thrombosis occurring during the 6-month study.
“This may be the first time in the history of heart failure research that the engineers have beaten the biologists in important clinical outcomes,” the cardiologist quipped.
• Omecamtiv mecarbil successfully addresses impaired contractility in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). This drug, a selective cardiac myosin activator, resulted in increased duration of systole and improved stroke volume accompanied by reductions in heart rate, left ventricular end-diastolic and -systolic dimensions, and NT-proBNP in the 87-site, 13-country, phase II COSMIC-HF study (Lancet. 2016 Dec 10;388[10062]:2895-903).
“This is probably the most novel new drug mechanism out there in clinical trials,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
On the basis of the highly encouraging results for the surrogate endpoints assessed in COSMIC-HF, a large phase III clinical trial known as GALACTIC is underway.
• Palliative care gets a welcome boost. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in PAL-HF, a single-center study presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
“This is a very important trial of palliative care in advanced heart failure. We probably don’t have as much evidence in this space as we should,” he observed. “This was a multidisciplinary intervention in which we gave the patients a medical tool kit to alleviate pain, dyspnea, and discomfort. The tool kit included benzodiazepines, sleep medications, sublingual nitroglycerin, and morphinelike products, all very carefully monitored by staff coordinators.”
The primary outcome was change in two validated heart failure quality of life measures. Both instruments documented significant improvement compared with usual care.
“There was no decrease in mortality, which wasn’t a goal in this advanced heart failure population, and no reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but there were significant reductions in depression and anxiety,” Dr. O’Connor said.
• Vericiguat. This oral soluble cyclic guanylate cyclase stimulator missed its primary endpoint in the phase II dose-escalation SOCRATES-REDUCED trial in patients with HFrEF (JAMA. 2015 Dec 1;314[21]:2251-62), but showed an impressive improvement in quality of life. It is now the subject of the ongoing, randomized, phase III VICTORIA trial involving a planned 4,000 patients with HFrEF with the composite primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization.
The phase II SOCRATES-PRESERVED trial also missed its primary endpoint but showed a clinically meaningful improvement in quality of life in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (Eur Heart J. 2017 Mar 22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw593). Discussions are ongoing as to whether the next step should be a confirmatory phase II study or a move straight to phase III.
The bad news
• NSAIDs linked to increased risk of heart failure. European investigators analyzed five population-based databases totaling more than 8.3 million individuals and determined that current use of any of more than two dozen NSAIDs was associated with significantly increased risk of hospital admission for heart failure. The risk appeared to be dose dependent and varied between individual agents, ranging from a 16% increased risk with naproxen to an 83% increase with ketorolac (Toradol) (BMJ. 2016 Sep 28. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4857).
• Therapeutic natriuretic peptides hit bottom. The negative results for the investigational agent ularitide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in the large phase III TRUE-AHF trial presented at the 2016 meeting of the American Heart Association, following upon an earlier negative study of the related drug nesiritide (Natrecor) in more than 7,100 acute heart failure patients (N Engl J Med. 2011 Jul 7; 365:32-43), probably spells the end of the line for this strategy of boosting outcomes in acute heart failure, according to Dr. O’Connor.
Moreover, Novartis has announced that the phase III RELAX-AHF-2 trial of serelaxin in 6,600 patients with acute heart failure failed to meet its primary endpoints of reduced cardiovascular deaths or reduced worsening of heart failure. The trial will be formally presented later this year.
“Ularitide seemed to show an early improvement in heart failure events that was not sustained in-hospital, and there was absolutely no difference in mortality. The drug probably acts like a pharmacologic tourniquet, in my view. So I think this field of therapeutic natriuretic peptides is probably closed,” he said.
• ICDs don’t reduce mortality in patients with nonischemic heart failure. This was the conclusion reached in the DANISH trial, in which more than 1,100 patients with symptomatic systolic heart failure were randomized to an ICD or usual care (N Engl J Med. 2016 Sep 29;375[13]:1221-30).
“This study really shook up the field, raising the question, ‘Are we using defibrillators too frequently in this population?’ It has stimulated a lot of discussion, including within the guidelines committee,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
• Tolvaptan nixed for acute decompensated heart failure. The TACTICS-HF trial studied the use of tolvaptan (Samsca), an oral vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, to reduce dyspnea in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in the study, which showed that tolvaptan was no better than placebo at 8 and 24 hours (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Mar 21;69[11]:1399-406).
“For now, the routine use of vasopressin antagonists in acute heart failure is not to be encouraged, although there may still be subsets where it’s worth trying – certainly in severe hyponatremia,” the cardiologist said.
• GUIDE-IT gets lost. This was a roughly 1,000-patient randomized trial of a treatment strategy aimed at improving clinical outcomes by aggressively titrating evidence-based heart failure therapies in order to suppress natriuretic peptide biomarkers. GUIDE-IT was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board due to a lack of discernible difference in outcomes, compared with usual care. Dr. O’Connor, a coinvestigator, termed the soon-to-be-published study “a disappointment.”
Sleep apnea studies show silver lining
Sleep apnea is common in patients with heart failure and is associated with worse clinical heart failure outcomes. But in the large, randomized SERVE-HF trial, investigators showed that treatment of central sleep apnea with adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFrEF unexpectedly increased mortality, compared with optimal medical therapy (N Engl J Med. 2015 Sep 17;373:1095-105). In a more recent secondary analysis, however, the SERVE-HF investigators found that the increased risk for cardiovascular death associated with adaptive servo-ventilation was actually restricted to patients with a very poor left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% or less, and there was a signal of possible benefit in patients in the top tier of LVEF, at 36%-45% (Lancet Respir Med. 2016 Nov; 4[11]:873-81).
This observation dovetails nicely with the findings of the CAT-HF trial presented by Dr. O’Connor at the 2016 World Congress on Heart Failure. In this phase II study, 215 patients with acute decompensated heart failure and either obstructive or central sleep apnea were randomized to optimal medical therapy alone or in combination with adaptive servo-ventilation. There was no overall difference in outcome between the two groups; however, in the subgroup of patients with HFpEF, the risk of the primary composite endpoint was reduced by 62% with adaptive servo-ventilation.
As a result of these intriguing findings from SERVE-HF and CAT-HF, a registry and/or randomized clinical trial of adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFpEF is now being considered under NIH sponsorship, according to Dr. O’Connor.
He reported having no financial conflicts.
WASHINGTON – It’s been a “relatively positive” year for heart failure research and advances in patient care, Christopher M. O’Connor, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
“Having been in this field for 30 years looking at clinical trials, generally for every 10 important trials done in a year, 1 has been positive and 9 have been negative; if we look at the past year, it’s more like 5 and 6. So, not a bad year for cardiomyopathy,” declared Dr. O’Connor, CEO and executive director of the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va., and president-elect of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The good news
• Empagliflozin (Jardiance) earns FDA approval for reduction in risk of cardiovascular death in type 2 diabetes patients. “This is one of the most amazing stories in heart failure,” said Dr. O’Connor, who is also professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The pivotal EMPA-REG OUTCOME study showed a highly significant 35% reduction in the secondary endpoint of risk of hospitalization for heart failure, as well the decrease in cardiovascular mortality which was the primary endpoint and proved persuasive to the FDA (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2117-28).
“It was a remarkable development. Because of this trial, there are now a number of ongoing phase III clinical trials looking at this class of drugs in heart failure patients with and without diabetes, which makes this a very important research movement. We are now looking deeper at phenotypes and trying to get more specific with these drug therapies,” he said.
• A new and improved LVAD. This fully magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump type of left ventricular assist device for advanced heart failure showed superior event-free survival, compared with a commercially available axial continuous-flow pump LVAD in the randomized MOMENTUM-3 trial (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:440-50).
The novel pump was designed to overcome a significant problem with axial continuous-flow LVADs: a proclivity for pump thrombosis. The magnetically levitated centrifugal-flow pump proved a smashing success in this regard, with zero cases of pump thrombosis occurring during the 6-month study.
“This may be the first time in the history of heart failure research that the engineers have beaten the biologists in important clinical outcomes,” the cardiologist quipped.
• Omecamtiv mecarbil successfully addresses impaired contractility in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). This drug, a selective cardiac myosin activator, resulted in increased duration of systole and improved stroke volume accompanied by reductions in heart rate, left ventricular end-diastolic and -systolic dimensions, and NT-proBNP in the 87-site, 13-country, phase II COSMIC-HF study (Lancet. 2016 Dec 10;388[10062]:2895-903).
“This is probably the most novel new drug mechanism out there in clinical trials,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
On the basis of the highly encouraging results for the surrogate endpoints assessed in COSMIC-HF, a large phase III clinical trial known as GALACTIC is underway.
• Palliative care gets a welcome boost. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in PAL-HF, a single-center study presented at the 2016 annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
“This is a very important trial of palliative care in advanced heart failure. We probably don’t have as much evidence in this space as we should,” he observed. “This was a multidisciplinary intervention in which we gave the patients a medical tool kit to alleviate pain, dyspnea, and discomfort. The tool kit included benzodiazepines, sleep medications, sublingual nitroglycerin, and morphinelike products, all very carefully monitored by staff coordinators.”
The primary outcome was change in two validated heart failure quality of life measures. Both instruments documented significant improvement compared with usual care.
“There was no decrease in mortality, which wasn’t a goal in this advanced heart failure population, and no reduction in heart failure hospitalizations, but there were significant reductions in depression and anxiety,” Dr. O’Connor said.
• Vericiguat. This oral soluble cyclic guanylate cyclase stimulator missed its primary endpoint in the phase II dose-escalation SOCRATES-REDUCED trial in patients with HFrEF (JAMA. 2015 Dec 1;314[21]:2251-62), but showed an impressive improvement in quality of life. It is now the subject of the ongoing, randomized, phase III VICTORIA trial involving a planned 4,000 patients with HFrEF with the composite primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization.
The phase II SOCRATES-PRESERVED trial also missed its primary endpoint but showed a clinically meaningful improvement in quality of life in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) (Eur Heart J. 2017 Mar 22. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw593). Discussions are ongoing as to whether the next step should be a confirmatory phase II study or a move straight to phase III.
The bad news
• NSAIDs linked to increased risk of heart failure. European investigators analyzed five population-based databases totaling more than 8.3 million individuals and determined that current use of any of more than two dozen NSAIDs was associated with significantly increased risk of hospital admission for heart failure. The risk appeared to be dose dependent and varied between individual agents, ranging from a 16% increased risk with naproxen to an 83% increase with ketorolac (Toradol) (BMJ. 2016 Sep 28. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4857).
• Therapeutic natriuretic peptides hit bottom. The negative results for the investigational agent ularitide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in the large phase III TRUE-AHF trial presented at the 2016 meeting of the American Heart Association, following upon an earlier negative study of the related drug nesiritide (Natrecor) in more than 7,100 acute heart failure patients (N Engl J Med. 2011 Jul 7; 365:32-43), probably spells the end of the line for this strategy of boosting outcomes in acute heart failure, according to Dr. O’Connor.
Moreover, Novartis has announced that the phase III RELAX-AHF-2 trial of serelaxin in 6,600 patients with acute heart failure failed to meet its primary endpoints of reduced cardiovascular deaths or reduced worsening of heart failure. The trial will be formally presented later this year.
“Ularitide seemed to show an early improvement in heart failure events that was not sustained in-hospital, and there was absolutely no difference in mortality. The drug probably acts like a pharmacologic tourniquet, in my view. So I think this field of therapeutic natriuretic peptides is probably closed,” he said.
• ICDs don’t reduce mortality in patients with nonischemic heart failure. This was the conclusion reached in the DANISH trial, in which more than 1,100 patients with symptomatic systolic heart failure were randomized to an ICD or usual care (N Engl J Med. 2016 Sep 29;375[13]:1221-30).
“This study really shook up the field, raising the question, ‘Are we using defibrillators too frequently in this population?’ It has stimulated a lot of discussion, including within the guidelines committee,” according to Dr. O’Connor.
• Tolvaptan nixed for acute decompensated heart failure. The TACTICS-HF trial studied the use of tolvaptan (Samsca), an oral vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist, to reduce dyspnea in patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure. Dr. O’Connor was a coinvestigator in the study, which showed that tolvaptan was no better than placebo at 8 and 24 hours (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Mar 21;69[11]:1399-406).
“For now, the routine use of vasopressin antagonists in acute heart failure is not to be encouraged, although there may still be subsets where it’s worth trying – certainly in severe hyponatremia,” the cardiologist said.
• GUIDE-IT gets lost. This was a roughly 1,000-patient randomized trial of a treatment strategy aimed at improving clinical outcomes by aggressively titrating evidence-based heart failure therapies in order to suppress natriuretic peptide biomarkers. GUIDE-IT was stopped early by the data safety monitoring board due to a lack of discernible difference in outcomes, compared with usual care. Dr. O’Connor, a coinvestigator, termed the soon-to-be-published study “a disappointment.”
Sleep apnea studies show silver lining
Sleep apnea is common in patients with heart failure and is associated with worse clinical heart failure outcomes. But in the large, randomized SERVE-HF trial, investigators showed that treatment of central sleep apnea with adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFrEF unexpectedly increased mortality, compared with optimal medical therapy (N Engl J Med. 2015 Sep 17;373:1095-105). In a more recent secondary analysis, however, the SERVE-HF investigators found that the increased risk for cardiovascular death associated with adaptive servo-ventilation was actually restricted to patients with a very poor left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% or less, and there was a signal of possible benefit in patients in the top tier of LVEF, at 36%-45% (Lancet Respir Med. 2016 Nov; 4[11]:873-81).
This observation dovetails nicely with the findings of the CAT-HF trial presented by Dr. O’Connor at the 2016 World Congress on Heart Failure. In this phase II study, 215 patients with acute decompensated heart failure and either obstructive or central sleep apnea were randomized to optimal medical therapy alone or in combination with adaptive servo-ventilation. There was no overall difference in outcome between the two groups; however, in the subgroup of patients with HFpEF, the risk of the primary composite endpoint was reduced by 62% with adaptive servo-ventilation.
As a result of these intriguing findings from SERVE-HF and CAT-HF, a registry and/or randomized clinical trial of adaptive servo-ventilation in patients with HFpEF is now being considered under NIH sponsorship, according to Dr. O’Connor.
He reported having no financial conflicts.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC 17
OSA tool uncovers risks of postoperative complications
High scores on the symptomless multivariable apnea prediction index (sMVAP) showed a strong correlation with increased risk for postsurgery complications, according to a study approved by the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
This validation helps assert the benefits of using the sMVAP as a tool to screen for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before elective inpatient surgeries, a test that is highly underutilized but very important, wrote M. Melanie Lyons, PhD, of the Center for Sleep and Circadian Neurobiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her colleagues.
“Most patients having elective surgery are not screened for obstructive sleep apnea, even though OSA is a risk factor for postoperative complications,” wrote Dr. Lyons and her colleagues. “We observe that sMVAP correlates with higher risk for OSA, hypertension, and select postoperative complications, particularly in non-bariatric groups without routine preoperative screening for OSA.”
In a retrospective study of 40,432 patients undergoing elective surgery, high sMVAP scores were strongly correlated with postoperative complications including longer hospital stays (OR = 1.83), stays in the ICU (OR = 1.44), and respiratory complications (OR = 1.85) according to the researchers (Sleep. 2017 Jan 6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw081).
Researchers separated participants into 10 categories according to the type of procedure: bariatric, orthopedic, cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, neurological, otorhinolaryngology/oral-maxillofacial/ear-nose-throat, pulmonary/thoracic, spine, and vascular.
The sMVAP calculates risk factors for OSA based on gender, age and body mass index, the researchers noted.
Those in the highest sMVAP score quintile were predominantly male (58%), with average age of 61 years, and average BMI of 40.9 kg/m2 (indicating morbid obesity). These patients reported the highest prevalence of having been previously diagnosed with OSA (26%). Comparatively, those patients in the lowest sMVAP quintile reported the lowest prevalence of an OSA diagnosis prior to undergoing their surgeries (9.3%).
Among non–bariatric surgery patients, those undergoing orthopedic procedures showed the highest correlation between complications and sMVAP scores.
The orthopedic surgery category reported a higher percentage of ICU-stay compared with bariatric surgery (14.3% vs 5.4%, P less than .0001), despite 23% of the patients who underwent an orthopedic surgery reporting previous OSA, compared with 50% of those who underwent surgery in the bariatric category.
This difference in previously reported OSA, according to Dr. Lyons and her colleagues, shows another example of the need for sMVAP in non–bariatric surgery preoperative procedure as a way to catch potentially undiagnosed OSA.
“[W]ork by Penn Bariatrics suggests that it is logical that the benefits of rigorous preoperative screening and diagnosis for OSA followed by a tailored team approach toward ensuring compliance toward treatment postoperation ... may be effective in limiting the likelihood of select postoperative complications,” the researchers wrote.
With 9.3% of all patients diagnosed with OSA, and a projected 14%-47% increase in specialty surgeries, there is an urgency in implementation of sMVAP and in conducting further studies, they noted.
This test was limited by the sample population, primarily male commercial truck drivers, the researchers noted. In addition, misclassification of OSA based on weight may have occurred in up to 20% of normal weight patients. Finally, data were collected from one hospital network, so generalizability may be limited.
Dr. M. Melanie Lyons and Dr. Junxin Li, another of the study’s authors, receive grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
High scores on the symptomless multivariable apnea prediction index (sMVAP) showed a strong correlation with increased risk for postsurgery complications, according to a study approved by the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
This validation helps assert the benefits of using the sMVAP as a tool to screen for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before elective inpatient surgeries, a test that is highly underutilized but very important, wrote M. Melanie Lyons, PhD, of the Center for Sleep and Circadian Neurobiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her colleagues.
“Most patients having elective surgery are not screened for obstructive sleep apnea, even though OSA is a risk factor for postoperative complications,” wrote Dr. Lyons and her colleagues. “We observe that sMVAP correlates with higher risk for OSA, hypertension, and select postoperative complications, particularly in non-bariatric groups without routine preoperative screening for OSA.”
In a retrospective study of 40,432 patients undergoing elective surgery, high sMVAP scores were strongly correlated with postoperative complications including longer hospital stays (OR = 1.83), stays in the ICU (OR = 1.44), and respiratory complications (OR = 1.85) according to the researchers (Sleep. 2017 Jan 6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw081).
Researchers separated participants into 10 categories according to the type of procedure: bariatric, orthopedic, cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, neurological, otorhinolaryngology/oral-maxillofacial/ear-nose-throat, pulmonary/thoracic, spine, and vascular.
The sMVAP calculates risk factors for OSA based on gender, age and body mass index, the researchers noted.
Those in the highest sMVAP score quintile were predominantly male (58%), with average age of 61 years, and average BMI of 40.9 kg/m2 (indicating morbid obesity). These patients reported the highest prevalence of having been previously diagnosed with OSA (26%). Comparatively, those patients in the lowest sMVAP quintile reported the lowest prevalence of an OSA diagnosis prior to undergoing their surgeries (9.3%).
Among non–bariatric surgery patients, those undergoing orthopedic procedures showed the highest correlation between complications and sMVAP scores.
The orthopedic surgery category reported a higher percentage of ICU-stay compared with bariatric surgery (14.3% vs 5.4%, P less than .0001), despite 23% of the patients who underwent an orthopedic surgery reporting previous OSA, compared with 50% of those who underwent surgery in the bariatric category.
This difference in previously reported OSA, according to Dr. Lyons and her colleagues, shows another example of the need for sMVAP in non–bariatric surgery preoperative procedure as a way to catch potentially undiagnosed OSA.
“[W]ork by Penn Bariatrics suggests that it is logical that the benefits of rigorous preoperative screening and diagnosis for OSA followed by a tailored team approach toward ensuring compliance toward treatment postoperation ... may be effective in limiting the likelihood of select postoperative complications,” the researchers wrote.
With 9.3% of all patients diagnosed with OSA, and a projected 14%-47% increase in specialty surgeries, there is an urgency in implementation of sMVAP and in conducting further studies, they noted.
This test was limited by the sample population, primarily male commercial truck drivers, the researchers noted. In addition, misclassification of OSA based on weight may have occurred in up to 20% of normal weight patients. Finally, data were collected from one hospital network, so generalizability may be limited.
Dr. M. Melanie Lyons and Dr. Junxin Li, another of the study’s authors, receive grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
High scores on the symptomless multivariable apnea prediction index (sMVAP) showed a strong correlation with increased risk for postsurgery complications, according to a study approved by the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
This validation helps assert the benefits of using the sMVAP as a tool to screen for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) before elective inpatient surgeries, a test that is highly underutilized but very important, wrote M. Melanie Lyons, PhD, of the Center for Sleep and Circadian Neurobiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and her colleagues.
“Most patients having elective surgery are not screened for obstructive sleep apnea, even though OSA is a risk factor for postoperative complications,” wrote Dr. Lyons and her colleagues. “We observe that sMVAP correlates with higher risk for OSA, hypertension, and select postoperative complications, particularly in non-bariatric groups without routine preoperative screening for OSA.”
In a retrospective study of 40,432 patients undergoing elective surgery, high sMVAP scores were strongly correlated with postoperative complications including longer hospital stays (OR = 1.83), stays in the ICU (OR = 1.44), and respiratory complications (OR = 1.85) according to the researchers (Sleep. 2017 Jan 6. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw081).
Researchers separated participants into 10 categories according to the type of procedure: bariatric, orthopedic, cardiac, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, neurological, otorhinolaryngology/oral-maxillofacial/ear-nose-throat, pulmonary/thoracic, spine, and vascular.
The sMVAP calculates risk factors for OSA based on gender, age and body mass index, the researchers noted.
Those in the highest sMVAP score quintile were predominantly male (58%), with average age of 61 years, and average BMI of 40.9 kg/m2 (indicating morbid obesity). These patients reported the highest prevalence of having been previously diagnosed with OSA (26%). Comparatively, those patients in the lowest sMVAP quintile reported the lowest prevalence of an OSA diagnosis prior to undergoing their surgeries (9.3%).
Among non–bariatric surgery patients, those undergoing orthopedic procedures showed the highest correlation between complications and sMVAP scores.
The orthopedic surgery category reported a higher percentage of ICU-stay compared with bariatric surgery (14.3% vs 5.4%, P less than .0001), despite 23% of the patients who underwent an orthopedic surgery reporting previous OSA, compared with 50% of those who underwent surgery in the bariatric category.
This difference in previously reported OSA, according to Dr. Lyons and her colleagues, shows another example of the need for sMVAP in non–bariatric surgery preoperative procedure as a way to catch potentially undiagnosed OSA.
“[W]ork by Penn Bariatrics suggests that it is logical that the benefits of rigorous preoperative screening and diagnosis for OSA followed by a tailored team approach toward ensuring compliance toward treatment postoperation ... may be effective in limiting the likelihood of select postoperative complications,” the researchers wrote.
With 9.3% of all patients diagnosed with OSA, and a projected 14%-47% increase in specialty surgeries, there is an urgency in implementation of sMVAP and in conducting further studies, they noted.
This test was limited by the sample population, primarily male commercial truck drivers, the researchers noted. In addition, misclassification of OSA based on weight may have occurred in up to 20% of normal weight patients. Finally, data were collected from one hospital network, so generalizability may be limited.
Dr. M. Melanie Lyons and Dr. Junxin Li, another of the study’s authors, receive grants from the National Institutes of Health. The other authors reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM SLEEP
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients with high sMVAP scores had increased odds of complications, including extended length of stay (OR = 1.83), ICU stay (OR = 1.44), and respiratory complications (OR = 1.85).
Data source: Retrospective study of 40,432 elective surgery patient records collected from the Hospital of University of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania Hospital, and Penn Presbyterian Medical Center between July 1, 2011, and June 30, 2014.
Disclosures: Dr. M. Melanie Lyons and Dr. Junxin Li receive grants from the National Institutes of Health. Other authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Dulera inhaler linked to adrenocorticotropic suppression in small case series
ORLANDO – A combination corticosteroid asthma inhaler has, for the first time, been associated with growth delay and adrenocorticotropic suppression in children.
The single-center case series is small, but the results highlight the need to regularly monitor growth and adrenal function in children using inhaled mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate (Dulera; Merck), investigators said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“We are hoping to raise awareness of this risk in our pediatric endocrinology colleagues, as well as among allergists, pulmonologists, and pediatricians who treat these children,” said Fadi Al Muhaisen, MD. “These kids should be regularly screened for growth delay and adrenal insufficiency and have their growth plotted at every visit as well.”
Dulera was approved in the United States in 2010 as a maintenance therapy for chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and older. Mometasone furoate is a potent corticosteroid, and formoterol fumarate is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist. The prescribing information says that mometasone furoate exerts less effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis than other inhaled corticosteroids, and that adrenal suppression is unlikely to occur when used at recommended dosages. These range from a low of 100 mcg/5 mcg, two puffs daily to a maximum dose of 800 mcg/20 mcg daily.
The review involved 18 children, all of whom were seen in the endocrinology clinic for growth failure or short stature and were receiving Dulera for management of their asthma. Of these, eight (44%) had a full adrenal evaluation. Six had biochemical evidence of adrenal suppression and two had normal adrenal function. The remaining 10 patients had not undergone an adrenal evaluation. None of them were on any other inhaled corticosteroid. The six children diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency had a mean age of 9.7 years, but ranged in age from 7 to 12 years. They had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids in the preceding 6 months before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at the time of diagnosis but had been using the higher dose for the preceding 18 months. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
The six children evaluated had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids during the 2 years before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at time of diagnosis, but had been using the higher dose for 18 months before that. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
All presented with growth failure, with bone age 1-3 years behind chronological age. One child was referred to the clinic after an emergency department visit for headache, nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue – symptoms of adrenal failure. That child had an adrenocroticotropin (ACTH) level of 10 pg/mL. Both his random peak cortisol measures after ACTH stimulation were less than 1 mcg/mL.
ACTH levels in four of the children were less than 5-6 pg/ml, with random and peak stimulated cortisols of around 1 mcg/mL. One patient had an ACTH level of 68 pg/mL, a random cortisol of less than 1 mcg/mL, and a peak stimulated cortisol of 8.7 mcg/mL.
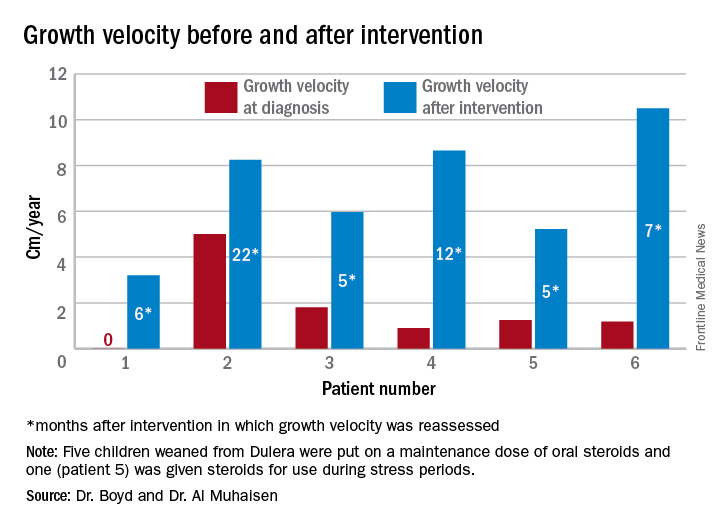
The results were all normal in the four subjects who had repeat adrenal function evaluation after intervention. Adrenal recovery took a mean of 20 months (5-30 months).
Growth accelerated rapidly after intervention, which was either initiation of maintenance oral steroids and discontinuation of Dulera or, in one patient, after Dulera was weaned. At time of adrenal insufficiency diagnosis, four patients had grown 1-2 cm in the prior year; one had not grown at all, and one had grown about 4.5 cm. After discontinuing or weaning the medication, all experienced growth spurts: 3 cm/year in 6 months; 8 cm/year in 22 months; 6 cm/year in 5 months; 8 cm/year in 12 months; 5 cm/year in 5 months; and 10 cm/year in 7 months.
There were no exacerbations in asthma, despite discontinuing the inhaled medication, Dr. Al Muhaisen said. Changing the asthma treatment required some open discussion between the investigators and the treating pulmonologists, he noted.
“We had some back-and-forth discussions, being very frank that we thought the adrenal insufficiency was directly related to this medication and that we needed to wean it and stop it as soon as possible.”
Neither Dr. Al Muhaisen nor Dr. Boyd had any financial disclosures.
ORLANDO – A combination corticosteroid asthma inhaler has, for the first time, been associated with growth delay and adrenocorticotropic suppression in children.
The single-center case series is small, but the results highlight the need to regularly monitor growth and adrenal function in children using inhaled mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate (Dulera; Merck), investigators said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“We are hoping to raise awareness of this risk in our pediatric endocrinology colleagues, as well as among allergists, pulmonologists, and pediatricians who treat these children,” said Fadi Al Muhaisen, MD. “These kids should be regularly screened for growth delay and adrenal insufficiency and have their growth plotted at every visit as well.”
Dulera was approved in the United States in 2010 as a maintenance therapy for chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and older. Mometasone furoate is a potent corticosteroid, and formoterol fumarate is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist. The prescribing information says that mometasone furoate exerts less effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis than other inhaled corticosteroids, and that adrenal suppression is unlikely to occur when used at recommended dosages. These range from a low of 100 mcg/5 mcg, two puffs daily to a maximum dose of 800 mcg/20 mcg daily.
The review involved 18 children, all of whom were seen in the endocrinology clinic for growth failure or short stature and were receiving Dulera for management of their asthma. Of these, eight (44%) had a full adrenal evaluation. Six had biochemical evidence of adrenal suppression and two had normal adrenal function. The remaining 10 patients had not undergone an adrenal evaluation. None of them were on any other inhaled corticosteroid. The six children diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency had a mean age of 9.7 years, but ranged in age from 7 to 12 years. They had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids in the preceding 6 months before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at the time of diagnosis but had been using the higher dose for the preceding 18 months. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
The six children evaluated had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids during the 2 years before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at time of diagnosis, but had been using the higher dose for 18 months before that. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
All presented with growth failure, with bone age 1-3 years behind chronological age. One child was referred to the clinic after an emergency department visit for headache, nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue – symptoms of adrenal failure. That child had an adrenocroticotropin (ACTH) level of 10 pg/mL. Both his random peak cortisol measures after ACTH stimulation were less than 1 mcg/mL.
ACTH levels in four of the children were less than 5-6 pg/ml, with random and peak stimulated cortisols of around 1 mcg/mL. One patient had an ACTH level of 68 pg/mL, a random cortisol of less than 1 mcg/mL, and a peak stimulated cortisol of 8.7 mcg/mL.

The results were all normal in the four subjects who had repeat adrenal function evaluation after intervention. Adrenal recovery took a mean of 20 months (5-30 months).
Growth accelerated rapidly after intervention, which was either initiation of maintenance oral steroids and discontinuation of Dulera or, in one patient, after Dulera was weaned. At time of adrenal insufficiency diagnosis, four patients had grown 1-2 cm in the prior year; one had not grown at all, and one had grown about 4.5 cm. After discontinuing or weaning the medication, all experienced growth spurts: 3 cm/year in 6 months; 8 cm/year in 22 months; 6 cm/year in 5 months; 8 cm/year in 12 months; 5 cm/year in 5 months; and 10 cm/year in 7 months.
There were no exacerbations in asthma, despite discontinuing the inhaled medication, Dr. Al Muhaisen said. Changing the asthma treatment required some open discussion between the investigators and the treating pulmonologists, he noted.
“We had some back-and-forth discussions, being very frank that we thought the adrenal insufficiency was directly related to this medication and that we needed to wean it and stop it as soon as possible.”
Neither Dr. Al Muhaisen nor Dr. Boyd had any financial disclosures.
ORLANDO – A combination corticosteroid asthma inhaler has, for the first time, been associated with growth delay and adrenocorticotropic suppression in children.
The single-center case series is small, but the results highlight the need to regularly monitor growth and adrenal function in children using inhaled mometasone furoate/formoterol fumarate (Dulera; Merck), investigators said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
“We are hoping to raise awareness of this risk in our pediatric endocrinology colleagues, as well as among allergists, pulmonologists, and pediatricians who treat these children,” said Fadi Al Muhaisen, MD. “These kids should be regularly screened for growth delay and adrenal insufficiency and have their growth plotted at every visit as well.”
Dulera was approved in the United States in 2010 as a maintenance therapy for chronic asthma in adults and children aged 12 years and older. Mometasone furoate is a potent corticosteroid, and formoterol fumarate is a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist. The prescribing information says that mometasone furoate exerts less effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis than other inhaled corticosteroids, and that adrenal suppression is unlikely to occur when used at recommended dosages. These range from a low of 100 mcg/5 mcg, two puffs daily to a maximum dose of 800 mcg/20 mcg daily.
The review involved 18 children, all of whom were seen in the endocrinology clinic for growth failure or short stature and were receiving Dulera for management of their asthma. Of these, eight (44%) had a full adrenal evaluation. Six had biochemical evidence of adrenal suppression and two had normal adrenal function. The remaining 10 patients had not undergone an adrenal evaluation. None of them were on any other inhaled corticosteroid. The six children diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency had a mean age of 9.7 years, but ranged in age from 7 to 12 years. They had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids in the preceding 6 months before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at the time of diagnosis but had been using the higher dose for the preceding 18 months. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
The six children evaluated had been using the medication for a mean of 1.3 years, although that varied widely, from just a few months to about 2 years. Only one had been on oral steroids during the 2 years before coming to the endocrinology clinic. Five were using the 200 mcg/5 mcg dose, two puffs daily; one child was taking one puff daily of 100 mcg/5 mcg at time of diagnosis, but had been using the higher dose for 18 months before that. Three were using concomitant nasal steroids.
All presented with growth failure, with bone age 1-3 years behind chronological age. One child was referred to the clinic after an emergency department visit for headache, nausea, diarrhea, and fatigue – symptoms of adrenal failure. That child had an adrenocroticotropin (ACTH) level of 10 pg/mL. Both his random peak cortisol measures after ACTH stimulation were less than 1 mcg/mL.
ACTH levels in four of the children were less than 5-6 pg/ml, with random and peak stimulated cortisols of around 1 mcg/mL. One patient had an ACTH level of 68 pg/mL, a random cortisol of less than 1 mcg/mL, and a peak stimulated cortisol of 8.7 mcg/mL.

The results were all normal in the four subjects who had repeat adrenal function evaluation after intervention. Adrenal recovery took a mean of 20 months (5-30 months).
Growth accelerated rapidly after intervention, which was either initiation of maintenance oral steroids and discontinuation of Dulera or, in one patient, after Dulera was weaned. At time of adrenal insufficiency diagnosis, four patients had grown 1-2 cm in the prior year; one had not grown at all, and one had grown about 4.5 cm. After discontinuing or weaning the medication, all experienced growth spurts: 3 cm/year in 6 months; 8 cm/year in 22 months; 6 cm/year in 5 months; 8 cm/year in 12 months; 5 cm/year in 5 months; and 10 cm/year in 7 months.
There were no exacerbations in asthma, despite discontinuing the inhaled medication, Dr. Al Muhaisen said. Changing the asthma treatment required some open discussion between the investigators and the treating pulmonologists, he noted.
“We had some back-and-forth discussions, being very frank that we thought the adrenal insufficiency was directly related to this medication and that we needed to wean it and stop it as soon as possible.”
Neither Dr. Al Muhaisen nor Dr. Boyd had any financial disclosures.
AT ENDO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of eight children who had an adrenal workup at an endocrinology clinic, six had adrenal suppression.
Data source: The case series comprised 18 children taking Dulera who presented with growth failure.
Disclosures: Neither Dr. Al Muhaisen nor Dr. Boyd had any financial disclosures.
Decline in U.S. flu activity puts end of season within sight
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.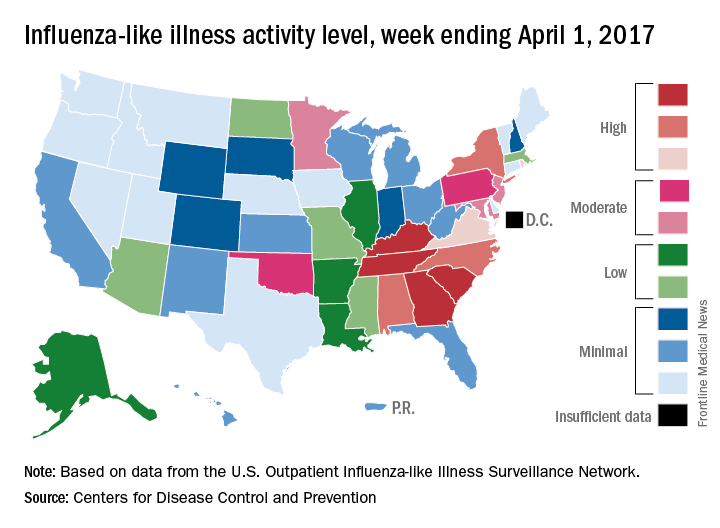
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
The Signs That Can’t Be Ignored
ANSWER
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.

ANSWER
The radiograph shows a large, round hyperdensity within the right lower lobe. This lesion is highly concerning for malignancy and warrants further work-up.
With his gastrointestinal bleed and hypercoagulability from warfarin toxicity, the patient required admission anyway. Subsequent biopsy confirmed the presence of a primary lung carcinoma.
For several days, a 60-year-old man has been feeling weak. He has also noticed that he bruises easily, and he’s experienced black, tarry stools and episodic hemoptysis. He presents to the emergency department, where the triage team sends him for further evaluation.
The patient’s history is significant for a remote diagnosis of a deep venous thrombosis in one of his lower extremities, for which he takes warfarin. He does not recall his most recent INR level. He reports smoking up to one pack of cigarettes per day and consuming alcohol regularly.
Examination reveals an older appearing male in no obvious distress. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 110 beats/min. You note bruises on both arms. The rest of his physical exam is normal. Lung sounds are clear.
Labwork ordered by the triage team indicates a hemoglobin level of 8 g/dL and an INR of 9. In addition, his stool guaiac test came back positive.
You obtain a portable chest radiograph (shown). What is your impression?