User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
After the Match: Next steps for new residents, unmatched
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.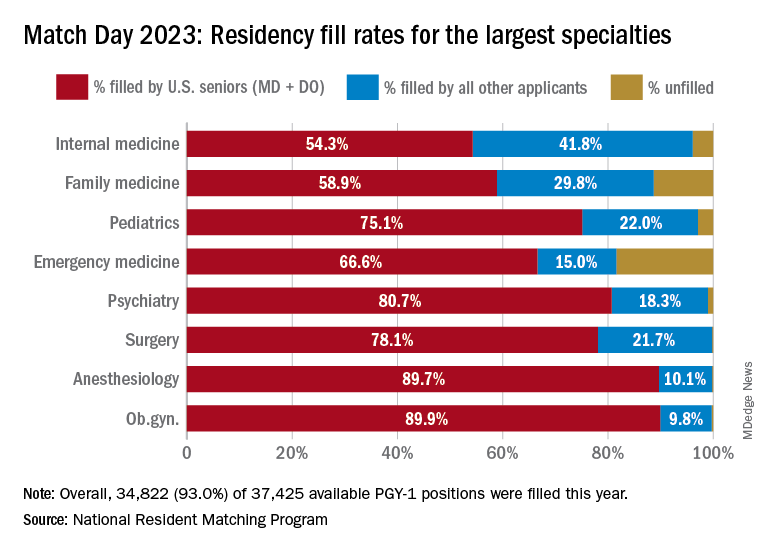
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Old-school printer helps scientists quickly spot bacteria in blood
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Like mother, like daughter? Moms pass obesity risk to girls
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Girls between 4 and 9 years old were more likely to have high fat mass and a high body mass index if their mothers had excess adiposity – but this relationship was not seen between mothers and sons, or between fathers and sons or daughters, in a new study.
The researchers measured fat mass, lean mass, and BMI in the sons and daughters when they were age 4 (before a phenomenon known as “adiposity rebound”), ages 6-7 (around the adiposity rebound), and ages 8-9 (before or at the onset of puberty).
They also obtained measurements from the mothers and fathers when the offspring were ages 8-9.
The group found “a strong association between the fat mass of mothers and their daughters but not their sons,” Rebecca J. Moon, BM, PhD, and colleagues report.
“It would be important to establish persistence through puberty,” according to the researchers, “but nonetheless, these findings are clinically important, highlighting girls who are born to mothers with high BMI and excess adiposity are at high risk of themselves of becoming overweight/obese or having unfavorable body composition early in childhood.”
The mother-daughter relationship for fat mass appears to be established by age 4 years, note Dr. Moon, of the MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton (England), and colleagues.
Therefore, “early awareness and intervention is needed in mothers with excess adiposity, and potentially beginning even in the periconception and in utero period.”
Because 97% of the mothers and fathers were White, the findings may not be generalizable to other populations, they caution.
The results, from the Southampton Women’s Survey prospective cohort study, were published online in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
One of the first studies to look at fat mass, not just BMI
Children with overweight or obesity are more likely to have excess weight in adulthood that puts them at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and osteoarthritis. Previous research has reported that children with overweight or obesity were more likely to have mothers with adiposity.
However, most prior studies have looked at BMI alone and did not measure fat mass, and it was not known how a father’s obesity might affect offspring or how risk may differ in boy versus girl children.
Researchers analyzed data from a subset of participants in the Southampton Women’s Survey of 3,158 women who were aged 20-34 in 1998-2002 and delivered a liveborn infant.
The current study included 240 mother-father-offspring trios who had data for BMI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans (whole body less head).
Mothers were a mean age of 31 years at delivery and had a median pre-pregnancy BMI of 23.7 kg/m2.
The offspring were 129 boys (54%) and 111 girls.
The offspring had DXA scans at ages 4, 6-7, and 8-9 years, and the mothers and fathers had a DXA scan at the last time point.
At ages 6-7 and ages 8-9, BMI and fat mass of the girls reflected that of their mothers (a significant association).
At age 4, BMI and fat mass of the daughters tended to be associated with that of their mothers, but the 95% confidence interval crossed zero.
There were no significant mother-son, father-son, or father-daughter associations for BMI or fat mass at each of the three studied ages.
The study received funding from the Medical Research Council, the British Heart Foundation, the National Institute for Health and Care Research Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, the Seventh Framework Program, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Moon has reported receiving travel bursaries from Kyowa Kirin unrelated to the current study. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Living kidney donors should receive money for their costs of donating
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the division of medical ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We try very hard to get organ donation from those who die. That’s a commendable thing to do. I think doctors should always be discussing the opportunity to donate organs upon death, even in primary care settings.
It’s good to find out what people’s attitudes are. Let them learn about organ donation as something they can think about. Let them talk about it with family and friends and partners so that they know their wishes.
However, despite these efforts to encourage organ donation, we still have far fewer organs than we could use to transplant people, many people die on waiting lists because there are no organs to give them, and we’re in a situation where demand for organ transplant is actually increasing.
There is more capacity to do transplants both in the United States and elsewhere, and more people are living longer, so organ failure starts to become more common before, let’s say, terminal illness is really there. Now, we have more people who might benefit from organ transplant in an aging population.
One place to turn to help reduce the shortage of organs is to living donation. At least insofar as kidneys go, kidney donation from living persons has become a prominent source of organs for those who need kidneys – most of whom are surviving on dialysis, by the way, at a very high cost and often with a quality of life that they don’t find particularly easy to accept.
Transplant is far preferred, even though they have to take immunosuppression to keep those organ transplants going, and that has its own risks and side effects. They still get more mobility. They still are able to have a broader diet. They enjoy life far more than they do having to show up for dialysis three times a week for a couple of hours, every week, for every week that they live.
There is an interest in living kidney donation. One battle has been that, well, maybe we could get more kidneys if we just paid people to sell us their kidneys. That has been resisted, and I’ve been resistant to that idea, too, because I worry that it leads to exploitation.
The people who sell their kidneys are poor. They’re often in debt. They feel coerced by their circumstances, so they make a kidney sale. This happens in countries like India, where there are markets underground, and you see that it’s the poorest of the poor who do this, and they don’t really work their way out of debt. They just wind up without a kidney, help relieve their debt a little bit, and pretty soon, because they don’t have a job or an income except that sale of a kidney, they’re not much better off than they were before they started.
Also, people who sell kidneys for money are more likely not to admit to their own health problems, raising risks about the quality of organs. Then, of course, it puts doctors in a position to take out an organ for pay, even though it doesn’t benefit you, so that you can sell it. This raises some questions about whether that’s consistent with medical ethics.
A different idea has emerged. New York State Governor Kathy Hochul just signed legislation that allows living donors to be compensated for legitimate costs. That’s a little different matter. You’re not buying the organ, but you’re saying that if you experience health care problems due to complications from a donation, if you need money for transportation, if you lost money because you did this altruistically and you had to take time off from work and had expenses for a babysitter, restaurants, or other things, the state is going to try to create funds that will compensate you.
That, I think we should agree, is not a bad idea. You’re in a situation there where you don’t want to make people who are heroic, altruistic, and trying to help others by donating a kidney end up financially worse off.
I think there’s a difference between making someone financially whole after the decision to make a kidney available and creating a market where the poorest of the poor come forward to just sell because they see no other choice in terms of how to get rid of debts. I see these situations as not ethically equivalent, so I support efforts to try to compensate people who are our heroes. I don’t think we should ask them to financially suffer.
We’ll watch to see what happens as the New York state law comes into effect. By the way, New York is one of the states that really lags in the supply of organs for transplant, so this measure is particularly important for that state. Many other states should be considering this legislation as well.
It’s one thing to reward, if you will, donors by making sure they don’t suffer financial loss. It’s a very different thing to say, let’s have a free market and we’ll pay whoever it is that’s willing to sell us a kidney to do so. The former seems to me to be humane and just, whereas the latter risks exploitation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the division of medical ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We try very hard to get organ donation from those who die. That’s a commendable thing to do. I think doctors should always be discussing the opportunity to donate organs upon death, even in primary care settings.
It’s good to find out what people’s attitudes are. Let them learn about organ donation as something they can think about. Let them talk about it with family and friends and partners so that they know their wishes.
However, despite these efforts to encourage organ donation, we still have far fewer organs than we could use to transplant people, many people die on waiting lists because there are no organs to give them, and we’re in a situation where demand for organ transplant is actually increasing.
There is more capacity to do transplants both in the United States and elsewhere, and more people are living longer, so organ failure starts to become more common before, let’s say, terminal illness is really there. Now, we have more people who might benefit from organ transplant in an aging population.
One place to turn to help reduce the shortage of organs is to living donation. At least insofar as kidneys go, kidney donation from living persons has become a prominent source of organs for those who need kidneys – most of whom are surviving on dialysis, by the way, at a very high cost and often with a quality of life that they don’t find particularly easy to accept.
Transplant is far preferred, even though they have to take immunosuppression to keep those organ transplants going, and that has its own risks and side effects. They still get more mobility. They still are able to have a broader diet. They enjoy life far more than they do having to show up for dialysis three times a week for a couple of hours, every week, for every week that they live.
There is an interest in living kidney donation. One battle has been that, well, maybe we could get more kidneys if we just paid people to sell us their kidneys. That has been resisted, and I’ve been resistant to that idea, too, because I worry that it leads to exploitation.
The people who sell their kidneys are poor. They’re often in debt. They feel coerced by their circumstances, so they make a kidney sale. This happens in countries like India, where there are markets underground, and you see that it’s the poorest of the poor who do this, and they don’t really work their way out of debt. They just wind up without a kidney, help relieve their debt a little bit, and pretty soon, because they don’t have a job or an income except that sale of a kidney, they’re not much better off than they were before they started.
Also, people who sell kidneys for money are more likely not to admit to their own health problems, raising risks about the quality of organs. Then, of course, it puts doctors in a position to take out an organ for pay, even though it doesn’t benefit you, so that you can sell it. This raises some questions about whether that’s consistent with medical ethics.
A different idea has emerged. New York State Governor Kathy Hochul just signed legislation that allows living donors to be compensated for legitimate costs. That’s a little different matter. You’re not buying the organ, but you’re saying that if you experience health care problems due to complications from a donation, if you need money for transportation, if you lost money because you did this altruistically and you had to take time off from work and had expenses for a babysitter, restaurants, or other things, the state is going to try to create funds that will compensate you.
That, I think we should agree, is not a bad idea. You’re in a situation there where you don’t want to make people who are heroic, altruistic, and trying to help others by donating a kidney end up financially worse off.
I think there’s a difference between making someone financially whole after the decision to make a kidney available and creating a market where the poorest of the poor come forward to just sell because they see no other choice in terms of how to get rid of debts. I see these situations as not ethically equivalent, so I support efforts to try to compensate people who are our heroes. I don’t think we should ask them to financially suffer.
We’ll watch to see what happens as the New York state law comes into effect. By the way, New York is one of the states that really lags in the supply of organs for transplant, so this measure is particularly important for that state. Many other states should be considering this legislation as well.
It’s one thing to reward, if you will, donors by making sure they don’t suffer financial loss. It’s a very different thing to say, let’s have a free market and we’ll pay whoever it is that’s willing to sell us a kidney to do so. The former seems to me to be humane and just, whereas the latter risks exploitation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the division of medical ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine in New York City.
We try very hard to get organ donation from those who die. That’s a commendable thing to do. I think doctors should always be discussing the opportunity to donate organs upon death, even in primary care settings.
It’s good to find out what people’s attitudes are. Let them learn about organ donation as something they can think about. Let them talk about it with family and friends and partners so that they know their wishes.
However, despite these efforts to encourage organ donation, we still have far fewer organs than we could use to transplant people, many people die on waiting lists because there are no organs to give them, and we’re in a situation where demand for organ transplant is actually increasing.
There is more capacity to do transplants both in the United States and elsewhere, and more people are living longer, so organ failure starts to become more common before, let’s say, terminal illness is really there. Now, we have more people who might benefit from organ transplant in an aging population.
One place to turn to help reduce the shortage of organs is to living donation. At least insofar as kidneys go, kidney donation from living persons has become a prominent source of organs for those who need kidneys – most of whom are surviving on dialysis, by the way, at a very high cost and often with a quality of life that they don’t find particularly easy to accept.
Transplant is far preferred, even though they have to take immunosuppression to keep those organ transplants going, and that has its own risks and side effects. They still get more mobility. They still are able to have a broader diet. They enjoy life far more than they do having to show up for dialysis three times a week for a couple of hours, every week, for every week that they live.
There is an interest in living kidney donation. One battle has been that, well, maybe we could get more kidneys if we just paid people to sell us their kidneys. That has been resisted, and I’ve been resistant to that idea, too, because I worry that it leads to exploitation.
The people who sell their kidneys are poor. They’re often in debt. They feel coerced by their circumstances, so they make a kidney sale. This happens in countries like India, where there are markets underground, and you see that it’s the poorest of the poor who do this, and they don’t really work their way out of debt. They just wind up without a kidney, help relieve their debt a little bit, and pretty soon, because they don’t have a job or an income except that sale of a kidney, they’re not much better off than they were before they started.
Also, people who sell kidneys for money are more likely not to admit to their own health problems, raising risks about the quality of organs. Then, of course, it puts doctors in a position to take out an organ for pay, even though it doesn’t benefit you, so that you can sell it. This raises some questions about whether that’s consistent with medical ethics.
A different idea has emerged. New York State Governor Kathy Hochul just signed legislation that allows living donors to be compensated for legitimate costs. That’s a little different matter. You’re not buying the organ, but you’re saying that if you experience health care problems due to complications from a donation, if you need money for transportation, if you lost money because you did this altruistically and you had to take time off from work and had expenses for a babysitter, restaurants, or other things, the state is going to try to create funds that will compensate you.
That, I think we should agree, is not a bad idea. You’re in a situation there where you don’t want to make people who are heroic, altruistic, and trying to help others by donating a kidney end up financially worse off.
I think there’s a difference between making someone financially whole after the decision to make a kidney available and creating a market where the poorest of the poor come forward to just sell because they see no other choice in terms of how to get rid of debts. I see these situations as not ethically equivalent, so I support efforts to try to compensate people who are our heroes. I don’t think we should ask them to financially suffer.
We’ll watch to see what happens as the New York state law comes into effect. By the way, New York is one of the states that really lags in the supply of organs for transplant, so this measure is particularly important for that state. Many other states should be considering this legislation as well.
It’s one thing to reward, if you will, donors by making sure they don’t suffer financial loss. It’s a very different thing to say, let’s have a free market and we’ll pay whoever it is that’s willing to sell us a kidney to do so. The former seems to me to be humane and just, whereas the latter risks exploitation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
State medical board chair steps down amid Medicaid fraud accusations
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
He has stepped down as board chair, and state officials have suspended all Medicaid payments to Dr. Hyatt and his practice, Pinnacle Premier Psychiatry in Rogers, Arkansas.
Dr. Hyatt billed 99.95% of the claims for his patients’ hospital care to Medicaid at the highest severity level, according to an affidavit filed by an investigator with the Medicaid Fraud Control Unit, Arkansas Attorney General’s Office. Other Arkansas psychiatrists billed that same level in only about 39% of claims, the affidavit states.
The possible upcoding alleged in the affidavit was a red flag that prompted the state to temporarily suspend Dr. Hyatt’s Medicaid payments.
Dr. Hyatt has until this Friday to file an appeal. He did not respond to requests from this news organization for comment.
The affidavit pointed to other concerns. For example, a whistleblower who worked at the Northwest Medical Center where Dr. Hyatt admitted patients claimed that Dr. Hyatt was only on the floor a few minutes a day and that he had no contact with patients. A review of hundreds of hours of video by state investigators revealed that Dr. Hyatt did not enter patients’ rooms, nor did he have any contact with patients, according to the affidavit. Dr. Hyatt served as the hospital’s behavioral unit director from 2018 until his contract was abruptly terminated in May 2022, according to the affidavit.
However, Dr. Hyatt claimed to have conducted daily face-to-face evaluation and management with patients, according to the affidavit. In addition, the whistleblower claimed that Dr. Hyatt did not want patients to know his name and instructed staff to cover up his name on patient armbands.
Detaining patients
Dr. Hyatt also faces accusations that he held patients against their will, according to civil lawsuits filed in Washington County, Ark., reports the Arkansas Advocate.
Karla Adrian-Caceres filed suit on Jan. 17. Ms. Adrian-Caceres also named Brooke Green, Northwest Arkansas Hospitals, and 25 unidentified hospital employees as defendants.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres, an engineering student at the University of Arkansas, arrived at the Northwest Medical Emergency Department after accidentally taking too many Tylenol on Jan. 18, 2022. She was then taken by ambulance to a Northwest psychiatric facility in Springdale, court records show.
According to the complaint, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said that she was given a sedative and asked to sign consent for admission while on the way to Northwest. She said that she “signed some documents without being able to read or understand them at the time.”
When she asked when she could go home, Ms. Adrian-Caceres said, “more than one employee told her there was a minimum stay and that if she asked to leave, they would take her to court where a judge would give her a longer stay because the judge always sides with Dr. Hyatt and Northwest,” according to court documents. Northwest employees stripped Ms. Adrian-Caceres, searched her body, took all of her possessions from her and issued underwear and a uniform, according to the lawsuit.
Ms. Adrian-Caceres’ mother, Katty Caceres, claimed in the lawsuit that she was prohibited from seeing her daughter. Ms. Caceres spoke with five different employees, four of whom had only their first names on their badges. Each of them reportedly said that they could not help, or that the plaintiff “would be in there for some time” and that it was Dr. Hyatt’s decision regarding how long that would be, according to court documents.
Katty Caceres hired a local attorney named Aaron Cash to represent her daughter. On Jan. 20, 2022, Mr. Cash faxed a letter to the hospital demanding her release. When Ms. Caceres arrived to pick up her daughter, she claimed that staff members indicated that the daughter was there voluntarily and refused to release her “at the direction of Dr Hyatt.” During a phone call later that day, the plaintiff told her mother that her status was being changed to an involuntary hold, court documents show.
“At one point she was threatened with the longer time in there if she kept asking to leave,” Mr. Cash told this news organization. In addition, staff members reportedly told Ms. Adrian-Caceres that the “judge always sided with Dr Hyatt” and she “would get way longer there, 30-45 days if [she] went before the judge,” according to Mr. Cash.
Mr. Cash said nine other patients have contacted his firm with similar allegations against Dr. Hyatt.
“We’ve talked to many people that have experienced the same threats,” Mr. Cash said. “When they’re asking to leave, they get these threats, they get coerced … and they’re never taken to court. They’re never given opportunity to talk to a judge or to have a public defender appointed.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Liquid albuterol shortage effects reduced by alternative drugs, similar shortages may be increasingly common
The shortage of 0.5% albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, first reported by the FDA last October, gained increasing attention earlier this month when Akorn Pharmaceuticals – one of just two companies making the product – shut down after years of financial and regulatory troubles.
The other manufacturer, Nephron Pharmaceuticals, is producing 0.5% albuterol “as fast as possible” to overcome the shortage, CEO Lou Kennedy said in a written comment.
Meanwhile, the more commonly used version of liquid albuterol, with a concentration of 0.083%, remains in “good supply from several manufacturers,” according to an FDA spokesperson.
Still, headlines concerning the shortage have caused “a bit of a panic” for patients with asthma and parents with asthmatic children, according to David R. Stukus, MD, professor of clinical pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Nationwide Children’s, Columbus, Ohio.
Much of the media coverage has lacked context, causing unnecessary worry, he said, as the shortage only affects one type of albuterol generally reserved for inpatient and emergency use.
“The shortage has not impacted our albuterol inhalers thus far,” Dr. Stukus said in an interview. “So I certainly don’t want people with asthma to panic that they’re going to run out of their inhaler anytime soon.”
Even infants and toddlers can use inhalers
Although Dr. Stukus noted that certain patients do require nebulizers, such as those with conditions that physically limit their breathing, like muscular dystrophy, most patients can use inhalers just fine. He said it’s a “pretty common misconception, even among medical professionals,” that infants and toddlers need nebulizers instead.
“In our institution, for example, we rarely ever start babies on a nebulizer when we diagnose them with asthma,” Dr. Stukus said. “We often just start right away with an inhaler with a spacer and a face mask.”
The shortage of liquid albuterol may therefore have a silver lining, he suggested, as it prompts clinicians to reconsider their routine practice.
“When situations like this arise, it’s a great opportunity for all of us to just take a step back and reevaluate the way we do things,” Dr. Stukus said. “Sometimes we just get caught up with inertia and we continue to do things the same way even though new options are available, or evidence has changed to the contrary.”
Nathan Rabinovitch, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology at National Jewish Health, Denver, said that his center had trouble obtaining liquid albuterol about 2 weeks ago, so they pivoted to the more expensive levalbuterol for about a week and a half, until their albuterol supply was restored.
While Dr. Rabinovitch agreed that most children don’t need a nebulizer, he said about 5%-10% of kids with severe asthma should have one on hand in case their inhaler fails to control an exacerbation.
Personal preferences may also considered, he added.
“If [a parent] says, ‘I like to use the nebulizer. The kid likes it,’ I’m fine if they just use a nebulizer.”
One possible downside of relying on a nebulizer, however, is portability, according to Kelly O’Shea, MD, assistant professor in the division of allergy and clinical immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“If you’re out at the park or out at a soccer game with your kids, and they are having trouble breathing ... and they need their albuterol, you don’t have that ability if you are tied to a nebulizer,” Dr. O’Shea said in an interview. “As long as a parent feels comfortable – they feel like [their child] can get deep breaths in, I agree that you can use [an inhaler] in the infant and toddler population.”
She also agreed that a nebulizer may serve as a kind of second step if an inhaler isn’t controlling an exacerbation; however, she emphasized that a nebulizer should not be considered a replacement for professional care, and should not give a false sense of security.
“I caution parents to make sure that when they need it, they also take the next step and head over to the emergency room,” Dr. O’Shea said.
Generic drug shortages becoming more common
While the present scarcity of liquid albuterol appears relatively mild in terms of clinical impact, it brings up broader concerns about generic drug supply, and why shortages like this are becoming more common, according to Katie J. Suda, PharmD, MS, professor of medicine and pharmacy, and associate director, center for pharmaceutical policy and prescribing at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Drug shortages continue to increase in frequency, and the duration and severity of the shortages are also getting worse,” Dr. Suda said in an interview.
The reasons for these shortages can be elusive, according to 2022 report by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, which found that more than half of shortages came with no explanation from manufacturers.
The same report showed that only 5% of shortages were due to a “business decision,” but this factor is likely more central than publicly stated.
A recent FDA analysis on drug shortages, for instance, lists “lack of incentives to produce less profitable drugs,” as the first “root cause,” and Dr. Suda agrees.
“It’s important that we have generic medicines to decrease costs to our health systems, as well as for our patients,” Dr. Suda said. “But frequently, with those generic products, the price is driven so low that it increases the risk of a shortage.”
The drive to maintain profit margins may motivate companies to cut corners in production, Dr. Suda explained. She emphasized that this connection is speculative, because motivations are effectively unknowable, but the rationale is supported by past and present shortages.
Akorn Pharmaceuticals, for example, received a warning letter from the FDA in 2019 because of a variety of manufacturing issues, including defective bottles, questionable data, and metal shavings on aseptic filling equipment.
When a manufacturer like Akorn fails, the effects can be far-reaching, Dr. Suda said, noting their broad catalog of agents. Beyond liquid albuterol, Akorn was producing cardiac drugs, antibiotics, vitamins, local anesthetics, eye products, and others.
Drug shortages cause “a significant strain on our health care system,” Dr. Suda said, and substituting other medications increases risk of medical errors.
Fortunately, the increasing number of drug shortages is not going unnoticed, according to Dr. Suda. The FDA and multiple other organizations, including the ASHP, American Medical Association, and National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, are all taking steps to ensure that essential medicines are in steady supply, including moves to gather more data from manufacturers.
“I hope that a lot of the efforts that are moving forward ... will help us decrease the impact of shortages on our patients,” Dr. Suda said.
Lou Kennedy is the CEO of Nephron Pharmaceuticals, which commercially produces liquid albuterol. The other interviewees disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
The shortage of 0.5% albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, first reported by the FDA last October, gained increasing attention earlier this month when Akorn Pharmaceuticals – one of just two companies making the product – shut down after years of financial and regulatory troubles.
The other manufacturer, Nephron Pharmaceuticals, is producing 0.5% albuterol “as fast as possible” to overcome the shortage, CEO Lou Kennedy said in a written comment.
Meanwhile, the more commonly used version of liquid albuterol, with a concentration of 0.083%, remains in “good supply from several manufacturers,” according to an FDA spokesperson.
Still, headlines concerning the shortage have caused “a bit of a panic” for patients with asthma and parents with asthmatic children, according to David R. Stukus, MD, professor of clinical pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Nationwide Children’s, Columbus, Ohio.
Much of the media coverage has lacked context, causing unnecessary worry, he said, as the shortage only affects one type of albuterol generally reserved for inpatient and emergency use.
“The shortage has not impacted our albuterol inhalers thus far,” Dr. Stukus said in an interview. “So I certainly don’t want people with asthma to panic that they’re going to run out of their inhaler anytime soon.”
Even infants and toddlers can use inhalers
Although Dr. Stukus noted that certain patients do require nebulizers, such as those with conditions that physically limit their breathing, like muscular dystrophy, most patients can use inhalers just fine. He said it’s a “pretty common misconception, even among medical professionals,” that infants and toddlers need nebulizers instead.
“In our institution, for example, we rarely ever start babies on a nebulizer when we diagnose them with asthma,” Dr. Stukus said. “We often just start right away with an inhaler with a spacer and a face mask.”
The shortage of liquid albuterol may therefore have a silver lining, he suggested, as it prompts clinicians to reconsider their routine practice.
“When situations like this arise, it’s a great opportunity for all of us to just take a step back and reevaluate the way we do things,” Dr. Stukus said. “Sometimes we just get caught up with inertia and we continue to do things the same way even though new options are available, or evidence has changed to the contrary.”
Nathan Rabinovitch, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology at National Jewish Health, Denver, said that his center had trouble obtaining liquid albuterol about 2 weeks ago, so they pivoted to the more expensive levalbuterol for about a week and a half, until their albuterol supply was restored.
While Dr. Rabinovitch agreed that most children don’t need a nebulizer, he said about 5%-10% of kids with severe asthma should have one on hand in case their inhaler fails to control an exacerbation.
Personal preferences may also considered, he added.
“If [a parent] says, ‘I like to use the nebulizer. The kid likes it,’ I’m fine if they just use a nebulizer.”
One possible downside of relying on a nebulizer, however, is portability, according to Kelly O’Shea, MD, assistant professor in the division of allergy and clinical immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“If you’re out at the park or out at a soccer game with your kids, and they are having trouble breathing ... and they need their albuterol, you don’t have that ability if you are tied to a nebulizer,” Dr. O’Shea said in an interview. “As long as a parent feels comfortable – they feel like [their child] can get deep breaths in, I agree that you can use [an inhaler] in the infant and toddler population.”
She also agreed that a nebulizer may serve as a kind of second step if an inhaler isn’t controlling an exacerbation; however, she emphasized that a nebulizer should not be considered a replacement for professional care, and should not give a false sense of security.
“I caution parents to make sure that when they need it, they also take the next step and head over to the emergency room,” Dr. O’Shea said.
Generic drug shortages becoming more common
While the present scarcity of liquid albuterol appears relatively mild in terms of clinical impact, it brings up broader concerns about generic drug supply, and why shortages like this are becoming more common, according to Katie J. Suda, PharmD, MS, professor of medicine and pharmacy, and associate director, center for pharmaceutical policy and prescribing at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Drug shortages continue to increase in frequency, and the duration and severity of the shortages are also getting worse,” Dr. Suda said in an interview.
The reasons for these shortages can be elusive, according to 2022 report by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, which found that more than half of shortages came with no explanation from manufacturers.
The same report showed that only 5% of shortages were due to a “business decision,” but this factor is likely more central than publicly stated.
A recent FDA analysis on drug shortages, for instance, lists “lack of incentives to produce less profitable drugs,” as the first “root cause,” and Dr. Suda agrees.
“It’s important that we have generic medicines to decrease costs to our health systems, as well as for our patients,” Dr. Suda said. “But frequently, with those generic products, the price is driven so low that it increases the risk of a shortage.”
The drive to maintain profit margins may motivate companies to cut corners in production, Dr. Suda explained. She emphasized that this connection is speculative, because motivations are effectively unknowable, but the rationale is supported by past and present shortages.
Akorn Pharmaceuticals, for example, received a warning letter from the FDA in 2019 because of a variety of manufacturing issues, including defective bottles, questionable data, and metal shavings on aseptic filling equipment.
When a manufacturer like Akorn fails, the effects can be far-reaching, Dr. Suda said, noting their broad catalog of agents. Beyond liquid albuterol, Akorn was producing cardiac drugs, antibiotics, vitamins, local anesthetics, eye products, and others.
Drug shortages cause “a significant strain on our health care system,” Dr. Suda said, and substituting other medications increases risk of medical errors.
Fortunately, the increasing number of drug shortages is not going unnoticed, according to Dr. Suda. The FDA and multiple other organizations, including the ASHP, American Medical Association, and National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, are all taking steps to ensure that essential medicines are in steady supply, including moves to gather more data from manufacturers.
“I hope that a lot of the efforts that are moving forward ... will help us decrease the impact of shortages on our patients,” Dr. Suda said.
Lou Kennedy is the CEO of Nephron Pharmaceuticals, which commercially produces liquid albuterol. The other interviewees disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
The shortage of 0.5% albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, first reported by the FDA last October, gained increasing attention earlier this month when Akorn Pharmaceuticals – one of just two companies making the product – shut down after years of financial and regulatory troubles.
The other manufacturer, Nephron Pharmaceuticals, is producing 0.5% albuterol “as fast as possible” to overcome the shortage, CEO Lou Kennedy said in a written comment.
Meanwhile, the more commonly used version of liquid albuterol, with a concentration of 0.083%, remains in “good supply from several manufacturers,” according to an FDA spokesperson.
Still, headlines concerning the shortage have caused “a bit of a panic” for patients with asthma and parents with asthmatic children, according to David R. Stukus, MD, professor of clinical pediatrics in the division of allergy and immunology at Nationwide Children’s, Columbus, Ohio.
Much of the media coverage has lacked context, causing unnecessary worry, he said, as the shortage only affects one type of albuterol generally reserved for inpatient and emergency use.
“The shortage has not impacted our albuterol inhalers thus far,” Dr. Stukus said in an interview. “So I certainly don’t want people with asthma to panic that they’re going to run out of their inhaler anytime soon.”
Even infants and toddlers can use inhalers
Although Dr. Stukus noted that certain patients do require nebulizers, such as those with conditions that physically limit their breathing, like muscular dystrophy, most patients can use inhalers just fine. He said it’s a “pretty common misconception, even among medical professionals,” that infants and toddlers need nebulizers instead.
“In our institution, for example, we rarely ever start babies on a nebulizer when we diagnose them with asthma,” Dr. Stukus said. “We often just start right away with an inhaler with a spacer and a face mask.”
The shortage of liquid albuterol may therefore have a silver lining, he suggested, as it prompts clinicians to reconsider their routine practice.
“When situations like this arise, it’s a great opportunity for all of us to just take a step back and reevaluate the way we do things,” Dr. Stukus said. “Sometimes we just get caught up with inertia and we continue to do things the same way even though new options are available, or evidence has changed to the contrary.”
Nathan Rabinovitch, MD, professor of pediatrics in the division of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology at National Jewish Health, Denver, said that his center had trouble obtaining liquid albuterol about 2 weeks ago, so they pivoted to the more expensive levalbuterol for about a week and a half, until their albuterol supply was restored.
While Dr. Rabinovitch agreed that most children don’t need a nebulizer, he said about 5%-10% of kids with severe asthma should have one on hand in case their inhaler fails to control an exacerbation.
Personal preferences may also considered, he added.
“If [a parent] says, ‘I like to use the nebulizer. The kid likes it,’ I’m fine if they just use a nebulizer.”
One possible downside of relying on a nebulizer, however, is portability, according to Kelly O’Shea, MD, assistant professor in the division of allergy and clinical immunology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“If you’re out at the park or out at a soccer game with your kids, and they are having trouble breathing ... and they need their albuterol, you don’t have that ability if you are tied to a nebulizer,” Dr. O’Shea said in an interview. “As long as a parent feels comfortable – they feel like [their child] can get deep breaths in, I agree that you can use [an inhaler] in the infant and toddler population.”
She also agreed that a nebulizer may serve as a kind of second step if an inhaler isn’t controlling an exacerbation; however, she emphasized that a nebulizer should not be considered a replacement for professional care, and should not give a false sense of security.
“I caution parents to make sure that when they need it, they also take the next step and head over to the emergency room,” Dr. O’Shea said.
Generic drug shortages becoming more common
While the present scarcity of liquid albuterol appears relatively mild in terms of clinical impact, it brings up broader concerns about generic drug supply, and why shortages like this are becoming more common, according to Katie J. Suda, PharmD, MS, professor of medicine and pharmacy, and associate director, center for pharmaceutical policy and prescribing at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Drug shortages continue to increase in frequency, and the duration and severity of the shortages are also getting worse,” Dr. Suda said in an interview.
The reasons for these shortages can be elusive, according to 2022 report by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, which found that more than half of shortages came with no explanation from manufacturers.
The same report showed that only 5% of shortages were due to a “business decision,” but this factor is likely more central than publicly stated.
A recent FDA analysis on drug shortages, for instance, lists “lack of incentives to produce less profitable drugs,” as the first “root cause,” and Dr. Suda agrees.
“It’s important that we have generic medicines to decrease costs to our health systems, as well as for our patients,” Dr. Suda said. “But frequently, with those generic products, the price is driven so low that it increases the risk of a shortage.”
The drive to maintain profit margins may motivate companies to cut corners in production, Dr. Suda explained. She emphasized that this connection is speculative, because motivations are effectively unknowable, but the rationale is supported by past and present shortages.
Akorn Pharmaceuticals, for example, received a warning letter from the FDA in 2019 because of a variety of manufacturing issues, including defective bottles, questionable data, and metal shavings on aseptic filling equipment.
When a manufacturer like Akorn fails, the effects can be far-reaching, Dr. Suda said, noting their broad catalog of agents. Beyond liquid albuterol, Akorn was producing cardiac drugs, antibiotics, vitamins, local anesthetics, eye products, and others.
Drug shortages cause “a significant strain on our health care system,” Dr. Suda said, and substituting other medications increases risk of medical errors.
Fortunately, the increasing number of drug shortages is not going unnoticed, according to Dr. Suda. The FDA and multiple other organizations, including the ASHP, American Medical Association, and National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, are all taking steps to ensure that essential medicines are in steady supply, including moves to gather more data from manufacturers.
“I hope that a lot of the efforts that are moving forward ... will help us decrease the impact of shortages on our patients,” Dr. Suda said.
Lou Kennedy is the CEO of Nephron Pharmaceuticals, which commercially produces liquid albuterol. The other interviewees disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Screen time and teenagers: Principles for parents
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released results of the most recent Youth Risk Behavior Survey, their once-a-decade survey of youth mental health and risk-taking behaviors. The headlines aren’t good: Self-reported rates of anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts, and suicide attempts in adolescents have increased substantially from 2011 to 2021. This echoes epidemiologic data showing increasing rates of anxiety and depression over the last decade in 12- to 24-year-olds, but not in older age cohorts.
This trend started well before COVID, coinciding with the explosive growth in use of smartphones, apps, and social media platforms. Facebook launched in 2004, the iPhone in 2007, Instagram in 2010, and TikTok in 2016. A 2018 Pew Research survey of 13- to 17-year-olds found that 97% of them used at least one social media platform and 45% described themselves as online “almost constantly.” Social media does have great potential benefits for adolescents.
We all experienced how it supported relationships during COVID. It can provide supportive networks for teenagers isolated by exclusion, illness, or disability. It can support exploration of esoteric interests, expression of identity, entertainment, and relaxation. But certain children, as was true before social media, seem vulnerable to the bullying, loneliness, isolation, and disengagement that social media may exacerbate.
Several studies have shown an association between high daily screen time and adolescent anxiety and depression. These findings have not been consistently duplicated, and those that were could not establish causality. There appears to be a strong link between certain illnesses (ADHD, depression, anorexia nervosa) and excessive screen use, which can in turn worsen symptoms. But it is hard to know which came first or how they are related.
Now, a very large long-term observational study has suggested that there may be critical windows in adolescence (11-13 years in girls and 14-16 in boys and again at 19 years for both) during which time excessive screen time can put that child’s developing mental health at risk. This is nuanced and interesting progress, but you don’t have to wait another decade to offer the families in your practice some common sense guidance when they are asking how to balance their children’s needs to be independent and socially connected (and the fact that smartphones and social media are pervasive) with the risks of overuse. Equipped with these guiding principles, parents can set individualized, flexible ground rules, and adjust them as their children grow into young adults.
First: Know your child
Parents are, of course, the experts on their own child – their talents, interests, challenges, vulnerabilities, and developmental progress. Children with poor impulse control (including those with ADHD) are going to have greater difficulty turning away from highly addictive activities on their devices. Children who are anxious and shy may be prone to avoiding the stress of real-life situations, preferring virtual ones. Children with a history of depression may be vulnerable to relapse if their sleep and exercise routines are disrupted by excessive use. And children with eating disorders are especially vulnerable to the superficial social comparisons and “likes” that Instagram offers. Children with these vulnerabilities will benefit if their parents are aware of and can talk about these vulnerabilities, ideally with their child. They should be prepared to work with their teens to develop strategies that can help them learn how to manage their social media usage. These might include stopping screen use after a certain hour, leaving devices outside of bedrooms at night, and setting up apps that monitor and alert them about excessive use. They might use resources such as the AAP’s Family Media Plan (Media and Children [aap.org]), but simply taking the time to have regular, open, honest conversations about what is known and unknown about the potential risks of social media use is very protective.
Second: Use adolescent development as your guide
For those children who do not have a known vulnerability to overuse, consider the following areas that are essential to healthy development in adolescence as guideposts to help parents in setting reasonable ground rules: building independence, cultivating healthy social relationships, learning about their identity, managing their strong emotions, and developing the skills of self-care. If screen time supports these developmental areas, then it’s probably healthy. If it interferes with them, then not. And remember, parents should routinely discuss these principles with their children as well.
Independence
Key questions. Does their use of a device enable them to function more independently – that is, to arrange for rides, manage their schedules, homework, shifts, and so forth – on their own? Could it be done with a “dumb” device (text/call only)?
Social relationships
One-way viewing (Instagram, Facebook) with superficial acquaintances may promote isolation, anxiety, and depression, does not facilitate deepened relationships, and may be using up time that they could be investing in genuine social connections. But if they are using their devices to stay connected to good friends who live far away or just have different schedules, they can promote genuine, satisfying, bilateral social connections.
Key questions. Are they engaged in two-way communication with their devices? Are they staying connected to friends with whom they have a genuine, substantial relationship?
Investigating and experimenting with interests (identity)
Teenagers are supposed to be learning in deep and nuanced ways about their own interests and abilities during these years. This requires a lot of time invested in exploration and experimentation and a considerable amount of failure. Any activity that consumes a lot of their time without deepening meaningful knowledge of their interests and abilities (that is, activity that is only an escape or distraction) will interfere with their discovering their authentic identity.
Key questions. Is their use of devices facilitating this genuine exploration (setting up internships, practicing programming, or exploring interests that must be virtual)? Or is their device use just consuming precious time they could be using to genuinely explore potential interests?
Managing anxiety or distress
Exploring their identity and building social connections will involve a lot of stress, failure, disappointment, and even heartbreak. Learning to manage these uncomfortable feelings is an important part of adolescence. Distraction with a diverting entertainment can be one of several strategies for managing stress and distress. But if it becomes the only strategy, it can keep teens from getting “back in the game” and experiencing the fun, success, meaning, and joy that are also a big part of this exploration.
Key questions. Do they turn to their devices first when sad or stressed? Are they also able to use other strategies, such as talking with friends/family, exercising, or engaging in a meaningful pursuit to help them manage stress? Do they feel better after a little time spent on their device, or as if they will only feel good if they can stay on the device?
Self-care
Getting adequate, restful sleep (8-10 hours/night), finding regular time for exercise, cultivating healthy eating habits, and discovering what healthy strategies help them to unwind or relax is critical to a teenager’s healthiest development, and to healthy adult life. Some screens may help with motivating and tracking exercise, but screens in the bedroom interfere with going to bed, and with falling and staying asleep. Most teenagers are very busy and managing a lot of (normal) stress; the senseless fun or relaxation that are part of video games or surfing the Web are quick, practical, and effective ways to unwind. Don’t discourage your teenager from enjoying them. Instead, focus on also helping them to find other healthy ways to relax: hot baths, exercise, time with pets, crafts, reading, and listening to music are just a few examples. As they are building their identity, they should also be discovering how they best slow down and calm down.
Key questions. How many hours of sleep do they usually get on a school night? Is their phone (or other screen) in their bedroom during sleep? How do they relax? Do they have several strategies that do not require screens? Do they exercise regularly (3-5 times weekly)? Do they complain that they do not have enough time for exercise?
Third: Be mindful of what you model
Many of these principles can apply to our own use of smartphones, computers, and so on. Remind parents that their teenager will ultimately consider and follow their example much more than their commands. They should be prepared to talk about how they are thinking about the risks and benefits of social media use, how they are developing rules and expectations, and why they decided on them. These conversations model thoughtful and flexible decision-making.
It is critical that parents acknowledge that there are wonderful benefits to technology, including senseless fun. Then, it is easier to discuss how escaping into screen use can be hard to resist, and why it is important to practice resisting some temptations. Parents should find ways to follow the same rules they set for their teenager, or making them “family rules.” It’s important for our teenagers to learn about how to set these limits, as eventually they will be setting their own!
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released results of the most recent Youth Risk Behavior Survey, their once-a-decade survey of youth mental health and risk-taking behaviors. The headlines aren’t good: Self-reported rates of anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts, and suicide attempts in adolescents have increased substantially from 2011 to 2021. This echoes epidemiologic data showing increasing rates of anxiety and depression over the last decade in 12- to 24-year-olds, but not in older age cohorts.
This trend started well before COVID, coinciding with the explosive growth in use of smartphones, apps, and social media platforms. Facebook launched in 2004, the iPhone in 2007, Instagram in 2010, and TikTok in 2016. A 2018 Pew Research survey of 13- to 17-year-olds found that 97% of them used at least one social media platform and 45% described themselves as online “almost constantly.” Social media does have great potential benefits for adolescents.
We all experienced how it supported relationships during COVID. It can provide supportive networks for teenagers isolated by exclusion, illness, or disability. It can support exploration of esoteric interests, expression of identity, entertainment, and relaxation. But certain children, as was true before social media, seem vulnerable to the bullying, loneliness, isolation, and disengagement that social media may exacerbate.
Several studies have shown an association between high daily screen time and adolescent anxiety and depression. These findings have not been consistently duplicated, and those that were could not establish causality. There appears to be a strong link between certain illnesses (ADHD, depression, anorexia nervosa) and excessive screen use, which can in turn worsen symptoms. But it is hard to know which came first or how they are related.
Now, a very large long-term observational study has suggested that there may be critical windows in adolescence (11-13 years in girls and 14-16 in boys and again at 19 years for both) during which time excessive screen time can put that child’s developing mental health at risk. This is nuanced and interesting progress, but you don’t have to wait another decade to offer the families in your practice some common sense guidance when they are asking how to balance their children’s needs to be independent and socially connected (and the fact that smartphones and social media are pervasive) with the risks of overuse. Equipped with these guiding principles, parents can set individualized, flexible ground rules, and adjust them as their children grow into young adults.
First: Know your child
Parents are, of course, the experts on their own child – their talents, interests, challenges, vulnerabilities, and developmental progress. Children with poor impulse control (including those with ADHD) are going to have greater difficulty turning away from highly addictive activities on their devices. Children who are anxious and shy may be prone to avoiding the stress of real-life situations, preferring virtual ones. Children with a history of depression may be vulnerable to relapse if their sleep and exercise routines are disrupted by excessive use. And children with eating disorders are especially vulnerable to the superficial social comparisons and “likes” that Instagram offers. Children with these vulnerabilities will benefit if their parents are aware of and can talk about these vulnerabilities, ideally with their child. They should be prepared to work with their teens to develop strategies that can help them learn how to manage their social media usage. These might include stopping screen use after a certain hour, leaving devices outside of bedrooms at night, and setting up apps that monitor and alert them about excessive use. They might use resources such as the AAP’s Family Media Plan (Media and Children [aap.org]), but simply taking the time to have regular, open, honest conversations about what is known and unknown about the potential risks of social media use is very protective.
Second: Use adolescent development as your guide
For those children who do not have a known vulnerability to overuse, consider the following areas that are essential to healthy development in adolescence as guideposts to help parents in setting reasonable ground rules: building independence, cultivating healthy social relationships, learning about their identity, managing their strong emotions, and developing the skills of self-care. If screen time supports these developmental areas, then it’s probably healthy. If it interferes with them, then not. And remember, parents should routinely discuss these principles with their children as well.
Independence
Key questions. Does their use of a device enable them to function more independently – that is, to arrange for rides, manage their schedules, homework, shifts, and so forth – on their own? Could it be done with a “dumb” device (text/call only)?
Social relationships
One-way viewing (Instagram, Facebook) with superficial acquaintances may promote isolation, anxiety, and depression, does not facilitate deepened relationships, and may be using up time that they could be investing in genuine social connections. But if they are using their devices to stay connected to good friends who live far away or just have different schedules, they can promote genuine, satisfying, bilateral social connections.
Key questions. Are they engaged in two-way communication with their devices? Are they staying connected to friends with whom they have a genuine, substantial relationship?
Investigating and experimenting with interests (identity)
Teenagers are supposed to be learning in deep and nuanced ways about their own interests and abilities during these years. This requires a lot of time invested in exploration and experimentation and a considerable amount of failure. Any activity that consumes a lot of their time without deepening meaningful knowledge of their interests and abilities (that is, activity that is only an escape or distraction) will interfere with their discovering their authentic identity.
Key questions. Is their use of devices facilitating this genuine exploration (setting up internships, practicing programming, or exploring interests that must be virtual)? Or is their device use just consuming precious time they could be using to genuinely explore potential interests?
Managing anxiety or distress
Exploring their identity and building social connections will involve a lot of stress, failure, disappointment, and even heartbreak. Learning to manage these uncomfortable feelings is an important part of adolescence. Distraction with a diverting entertainment can be one of several strategies for managing stress and distress. But if it becomes the only strategy, it can keep teens from getting “back in the game” and experiencing the fun, success, meaning, and joy that are also a big part of this exploration.
Key questions. Do they turn to their devices first when sad or stressed? Are they also able to use other strategies, such as talking with friends/family, exercising, or engaging in a meaningful pursuit to help them manage stress? Do they feel better after a little time spent on their device, or as if they will only feel good if they can stay on the device?
Self-care
Getting adequate, restful sleep (8-10 hours/night), finding regular time for exercise, cultivating healthy eating habits, and discovering what healthy strategies help them to unwind or relax is critical to a teenager’s healthiest development, and to healthy adult life. Some screens may help with motivating and tracking exercise, but screens in the bedroom interfere with going to bed, and with falling and staying asleep. Most teenagers are very busy and managing a lot of (normal) stress; the senseless fun or relaxation that are part of video games or surfing the Web are quick, practical, and effective ways to unwind. Don’t discourage your teenager from enjoying them. Instead, focus on also helping them to find other healthy ways to relax: hot baths, exercise, time with pets, crafts, reading, and listening to music are just a few examples. As they are building their identity, they should also be discovering how they best slow down and calm down.
Key questions. How many hours of sleep do they usually get on a school night? Is their phone (or other screen) in their bedroom during sleep? How do they relax? Do they have several strategies that do not require screens? Do they exercise regularly (3-5 times weekly)? Do they complain that they do not have enough time for exercise?
Third: Be mindful of what you model
Many of these principles can apply to our own use of smartphones, computers, and so on. Remind parents that their teenager will ultimately consider and follow their example much more than their commands. They should be prepared to talk about how they are thinking about the risks and benefits of social media use, how they are developing rules and expectations, and why they decided on them. These conversations model thoughtful and flexible decision-making.
It is critical that parents acknowledge that there are wonderful benefits to technology, including senseless fun. Then, it is easier to discuss how escaping into screen use can be hard to resist, and why it is important to practice resisting some temptations. Parents should find ways to follow the same rules they set for their teenager, or making them “family rules.” It’s important for our teenagers to learn about how to set these limits, as eventually they will be setting their own!
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently released results of the most recent Youth Risk Behavior Survey, their once-a-decade survey of youth mental health and risk-taking behaviors. The headlines aren’t good: Self-reported rates of anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts, and suicide attempts in adolescents have increased substantially from 2011 to 2021. This echoes epidemiologic data showing increasing rates of anxiety and depression over the last decade in 12- to 24-year-olds, but not in older age cohorts.
This trend started well before COVID, coinciding with the explosive growth in use of smartphones, apps, and social media platforms. Facebook launched in 2004, the iPhone in 2007, Instagram in 2010, and TikTok in 2016. A 2018 Pew Research survey of 13- to 17-year-olds found that 97% of them used at least one social media platform and 45% described themselves as online “almost constantly.” Social media does have great potential benefits for adolescents.
We all experienced how it supported relationships during COVID. It can provide supportive networks for teenagers isolated by exclusion, illness, or disability. It can support exploration of esoteric interests, expression of identity, entertainment, and relaxation. But certain children, as was true before social media, seem vulnerable to the bullying, loneliness, isolation, and disengagement that social media may exacerbate.
Several studies have shown an association between high daily screen time and adolescent anxiety and depression. These findings have not been consistently duplicated, and those that were could not establish causality. There appears to be a strong link between certain illnesses (ADHD, depression, anorexia nervosa) and excessive screen use, which can in turn worsen symptoms. But it is hard to know which came first or how they are related.
Now, a very large long-term observational study has suggested that there may be critical windows in adolescence (11-13 years in girls and 14-16 in boys and again at 19 years for both) during which time excessive screen time can put that child’s developing mental health at risk. This is nuanced and interesting progress, but you don’t have to wait another decade to offer the families in your practice some common sense guidance when they are asking how to balance their children’s needs to be independent and socially connected (and the fact that smartphones and social media are pervasive) with the risks of overuse. Equipped with these guiding principles, parents can set individualized, flexible ground rules, and adjust them as their children grow into young adults.
First: Know your child
Parents are, of course, the experts on their own child – their talents, interests, challenges, vulnerabilities, and developmental progress. Children with poor impulse control (including those with ADHD) are going to have greater difficulty turning away from highly addictive activities on their devices. Children who are anxious and shy may be prone to avoiding the stress of real-life situations, preferring virtual ones. Children with a history of depression may be vulnerable to relapse if their sleep and exercise routines are disrupted by excessive use. And children with eating disorders are especially vulnerable to the superficial social comparisons and “likes” that Instagram offers. Children with these vulnerabilities will benefit if their parents are aware of and can talk about these vulnerabilities, ideally with their child. They should be prepared to work with their teens to develop strategies that can help them learn how to manage their social media usage. These might include stopping screen use after a certain hour, leaving devices outside of bedrooms at night, and setting up apps that monitor and alert them about excessive use. They might use resources such as the AAP’s Family Media Plan (Media and Children [aap.org]), but simply taking the time to have regular, open, honest conversations about what is known and unknown about the potential risks of social media use is very protective.
Second: Use adolescent development as your guide
For those children who do not have a known vulnerability to overuse, consider the following areas that are essential to healthy development in adolescence as guideposts to help parents in setting reasonable ground rules: building independence, cultivating healthy social relationships, learning about their identity, managing their strong emotions, and developing the skills of self-care. If screen time supports these developmental areas, then it’s probably healthy. If it interferes with them, then not. And remember, parents should routinely discuss these principles with their children as well.
Independence
Key questions. Does their use of a device enable them to function more independently – that is, to arrange for rides, manage their schedules, homework, shifts, and so forth – on their own? Could it be done with a “dumb” device (text/call only)?
Social relationships
One-way viewing (Instagram, Facebook) with superficial acquaintances may promote isolation, anxiety, and depression, does not facilitate deepened relationships, and may be using up time that they could be investing in genuine social connections. But if they are using their devices to stay connected to good friends who live far away or just have different schedules, they can promote genuine, satisfying, bilateral social connections.
Key questions. Are they engaged in two-way communication with their devices? Are they staying connected to friends with whom they have a genuine, substantial relationship?
Investigating and experimenting with interests (identity)
Teenagers are supposed to be learning in deep and nuanced ways about their own interests and abilities during these years. This requires a lot of time invested in exploration and experimentation and a considerable amount of failure. Any activity that consumes a lot of their time without deepening meaningful knowledge of their interests and abilities (that is, activity that is only an escape or distraction) will interfere with their discovering their authentic identity.
Key questions. Is their use of devices facilitating this genuine exploration (setting up internships, practicing programming, or exploring interests that must be virtual)? Or is their device use just consuming precious time they could be using to genuinely explore potential interests?
Managing anxiety or distress
Exploring their identity and building social connections will involve a lot of stress, failure, disappointment, and even heartbreak. Learning to manage these uncomfortable feelings is an important part of adolescence. Distraction with a diverting entertainment can be one of several strategies for managing stress and distress. But if it becomes the only strategy, it can keep teens from getting “back in the game” and experiencing the fun, success, meaning, and joy that are also a big part of this exploration.
Key questions. Do they turn to their devices first when sad or stressed? Are they also able to use other strategies, such as talking with friends/family, exercising, or engaging in a meaningful pursuit to help them manage stress? Do they feel better after a little time spent on their device, or as if they will only feel good if they can stay on the device?
Self-care
Getting adequate, restful sleep (8-10 hours/night), finding regular time for exercise, cultivating healthy eating habits, and discovering what healthy strategies help them to unwind or relax is critical to a teenager’s healthiest development, and to healthy adult life. Some screens may help with motivating and tracking exercise, but screens in the bedroom interfere with going to bed, and with falling and staying asleep. Most teenagers are very busy and managing a lot of (normal) stress; the senseless fun or relaxation that are part of video games or surfing the Web are quick, practical, and effective ways to unwind. Don’t discourage your teenager from enjoying them. Instead, focus on also helping them to find other healthy ways to relax: hot baths, exercise, time with pets, crafts, reading, and listening to music are just a few examples. As they are building their identity, they should also be discovering how they best slow down and calm down.
Key questions. How many hours of sleep do they usually get on a school night? Is their phone (or other screen) in their bedroom during sleep? How do they relax? Do they have several strategies that do not require screens? Do they exercise regularly (3-5 times weekly)? Do they complain that they do not have enough time for exercise?
Third: Be mindful of what you model
Many of these principles can apply to our own use of smartphones, computers, and so on. Remind parents that their teenager will ultimately consider and follow their example much more than their commands. They should be prepared to talk about how they are thinking about the risks and benefits of social media use, how they are developing rules and expectations, and why they decided on them. These conversations model thoughtful and flexible decision-making.
It is critical that parents acknowledge that there are wonderful benefits to technology, including senseless fun. Then, it is easier to discuss how escaping into screen use can be hard to resist, and why it is important to practice resisting some temptations. Parents should find ways to follow the same rules they set for their teenager, or making them “family rules.” It’s important for our teenagers to learn about how to set these limits, as eventually they will be setting their own!
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
Children with ASD less likely to get vision screening
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are significantly less likely to have vision screening at well visits for 3- to 5-year-olds than are typically developing children, researchers have found.
The report, by Kimberly Hoover, MD, of Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, and colleagues, was published online in Pediatrics.
While 59.9% of children without ASD got vision screening in these visits, only 36.5% of children with ASD got the screening. Both screening rates miss the mark set by American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines.
The AAP recommends “annual instrument-based vision screening, if available, at well visits for children starting at age 12 months to 3 years, and direct visual acuity testing beginning at 4 years of age. However, in children with developmental delays, the AAP recommends instrument-based screening, such as photoscreening, as a useful alternative at any age.”
Racial, age disparities as well
Racial disparities were evident in the data as well. Of the children who had ASD, Black children had the lowest rates of screening (27.6%), while the rate for White children was 39.7%. The rate for other/multiracial children with ASD was 39.8%.
The lowest rates of screening occurred in the youngest children, at the 3-year visit.
The researchers analyzed data from 63,829 well-child visits between January 2016 and December 2019, collected from the large primary care database PEDSnet.
Photoscreening vs. acuity screening
The authors pointed out that children with ASD are less likely to complete a vision test, which can be problematic in a busy primary care office.
“Children with ASD were significantly less likely to have at least one completed vision screening (43.2%) compared with children without ASD (72.1%; P <. 01),” the authors wrote, “with only 6.9% of children with ASD having had two or more vision screenings compared with 22.3% of children without ASD.”
The researchers saw higher vision test completion rates with photoscreening, using a sophisticated camera, compared with acuity screening, which uses a wall chart and requires responses.
Less patient participation is required for photoscreening and it can be done in less than 2 minutes.
If ability to complete the vision tests is a concern, the authors wrote, photoscreening may be a better solution.
Photoscreening takes 90 seconds
“Photoscreening has high sensitivity in detecting ocular conditions in children with ASD and has an average screening time of 90 seconds, and [it has] been validated in both children with ASD and developmental delays,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Adesman, MD, chief of developmental and behavioral pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said the authors of this study quantify the gap between need and reality for vision tests for those with ASD.
“Other studies have shown that children on the autism spectrum have more than three times greater risk of having eye disease or vision problems,” he said in an interview. “You’ve got a high-risk population in need of assessment and the likelihood of them getting an assessment is much reduced.”
He said in addition to attention problems in taking the test, vision screening may get lost in the plethora of concerns parents want to talk about in well-child visits.
“If you’re the parent of a child with developmental delays, language delays, poor social engagement, there are a multitude of things the visit could be focused on and it may be that vision screening possibly gets compromised or not done,” Dr. Adesman said.
That, he said, may be a focus area for improving the screening numbers.
Neither parents nor providers should forget that vision screening is important, despite the myriad other issues to address, he said. “They don’t have to take a long time.”
When it comes to vision problems and children, “the earlier they’re identified the better,” Dr. Adesman says, particularly to identify the need for eye muscle surgery or corrective lenses, the two major interventions for strabismus or refractive error.
“If those problems are significant and go untreated, there’s a risk of loss of vision in the affected eye,” he said.
Reimbursement concerns for photoscreening
This study strongly supports the use of routine photoscreening to help eliminate the vision screening gap in children with ASD, the authors wrote.
They noted, however, that would require insurance reimbursement for primary care practices to effectively use that screening.
The researchers advised, “Providers treating patients with race, ethnicity, region, or age categories that reduce the adjusted odds of photoscreening can take steps in their practices to address these disparities, particularly in children with ASD.”
The study authors and Dr. Adesman reported no relevant financial relationships.
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are significantly less likely to have vision screening at well visits for 3- to 5-year-olds than are typically developing children, researchers have found.
The report, by Kimberly Hoover, MD, of Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, and colleagues, was published online in Pediatrics.
While 59.9% of children without ASD got vision screening in these visits, only 36.5% of children with ASD got the screening. Both screening rates miss the mark set by American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines.
The AAP recommends “annual instrument-based vision screening, if available, at well visits for children starting at age 12 months to 3 years, and direct visual acuity testing beginning at 4 years of age. However, in children with developmental delays, the AAP recommends instrument-based screening, such as photoscreening, as a useful alternative at any age.”
Racial, age disparities as well
Racial disparities were evident in the data as well. Of the children who had ASD, Black children had the lowest rates of screening (27.6%), while the rate for White children was 39.7%. The rate for other/multiracial children with ASD was 39.8%.
The lowest rates of screening occurred in the youngest children, at the 3-year visit.
The researchers analyzed data from 63,829 well-child visits between January 2016 and December 2019, collected from the large primary care database PEDSnet.
Photoscreening vs. acuity screening
The authors pointed out that children with ASD are less likely to complete a vision test, which can be problematic in a busy primary care office.
“Children with ASD were significantly less likely to have at least one completed vision screening (43.2%) compared with children without ASD (72.1%; P <. 01),” the authors wrote, “with only 6.9% of children with ASD having had two or more vision screenings compared with 22.3% of children without ASD.”
The researchers saw higher vision test completion rates with photoscreening, using a sophisticated camera, compared with acuity screening, which uses a wall chart and requires responses.
Less patient participation is required for photoscreening and it can be done in less than 2 minutes.
If ability to complete the vision tests is a concern, the authors wrote, photoscreening may be a better solution.
Photoscreening takes 90 seconds
“Photoscreening has high sensitivity in detecting ocular conditions in children with ASD and has an average screening time of 90 seconds, and [it has] been validated in both children with ASD and developmental delays,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Adesman, MD, chief of developmental and behavioral pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said the authors of this study quantify the gap between need and reality for vision tests for those with ASD.
“Other studies have shown that children on the autism spectrum have more than three times greater risk of having eye disease or vision problems,” he said in an interview. “You’ve got a high-risk population in need of assessment and the likelihood of them getting an assessment is much reduced.”
He said in addition to attention problems in taking the test, vision screening may get lost in the plethora of concerns parents want to talk about in well-child visits.
“If you’re the parent of a child with developmental delays, language delays, poor social engagement, there are a multitude of things the visit could be focused on and it may be that vision screening possibly gets compromised or not done,” Dr. Adesman said.
That, he said, may be a focus area for improving the screening numbers.
Neither parents nor providers should forget that vision screening is important, despite the myriad other issues to address, he said. “They don’t have to take a long time.”
When it comes to vision problems and children, “the earlier they’re identified the better,” Dr. Adesman says, particularly to identify the need for eye muscle surgery or corrective lenses, the two major interventions for strabismus or refractive error.
“If those problems are significant and go untreated, there’s a risk of loss of vision in the affected eye,” he said.
Reimbursement concerns for photoscreening
This study strongly supports the use of routine photoscreening to help eliminate the vision screening gap in children with ASD, the authors wrote.
They noted, however, that would require insurance reimbursement for primary care practices to effectively use that screening.
The researchers advised, “Providers treating patients with race, ethnicity, region, or age categories that reduce the adjusted odds of photoscreening can take steps in their practices to address these disparities, particularly in children with ASD.”
The study authors and Dr. Adesman reported no relevant financial relationships.
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are significantly less likely to have vision screening at well visits for 3- to 5-year-olds than are typically developing children, researchers have found.
The report, by Kimberly Hoover, MD, of Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, and colleagues, was published online in Pediatrics.
While 59.9% of children without ASD got vision screening in these visits, only 36.5% of children with ASD got the screening. Both screening rates miss the mark set by American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines.
The AAP recommends “annual instrument-based vision screening, if available, at well visits for children starting at age 12 months to 3 years, and direct visual acuity testing beginning at 4 years of age. However, in children with developmental delays, the AAP recommends instrument-based screening, such as photoscreening, as a useful alternative at any age.”
Racial, age disparities as well
Racial disparities were evident in the data as well. Of the children who had ASD, Black children had the lowest rates of screening (27.6%), while the rate for White children was 39.7%. The rate for other/multiracial children with ASD was 39.8%.
The lowest rates of screening occurred in the youngest children, at the 3-year visit.
The researchers analyzed data from 63,829 well-child visits between January 2016 and December 2019, collected from the large primary care database PEDSnet.
Photoscreening vs. acuity screening
The authors pointed out that children with ASD are less likely to complete a vision test, which can be problematic in a busy primary care office.
“Children with ASD were significantly less likely to have at least one completed vision screening (43.2%) compared with children without ASD (72.1%; P <. 01),” the authors wrote, “with only 6.9% of children with ASD having had two or more vision screenings compared with 22.3% of children without ASD.”
The researchers saw higher vision test completion rates with photoscreening, using a sophisticated camera, compared with acuity screening, which uses a wall chart and requires responses.
Less patient participation is required for photoscreening and it can be done in less than 2 minutes.
If ability to complete the vision tests is a concern, the authors wrote, photoscreening may be a better solution.
Photoscreening takes 90 seconds
“Photoscreening has high sensitivity in detecting ocular conditions in children with ASD and has an average screening time of 90 seconds, and [it has] been validated in both children with ASD and developmental delays,” the authors wrote.
Andrew Adesman, MD, chief of developmental and behavioral pediatrics at Cohen Children’s Medical Center in New Hyde Park, N.Y., said the authors of this study quantify the gap between need and reality for vision tests for those with ASD.
“Other studies have shown that children on the autism spectrum have more than three times greater risk of having eye disease or vision problems,” he said in an interview. “You’ve got a high-risk population in need of assessment and the likelihood of them getting an assessment is much reduced.”
He said in addition to attention problems in taking the test, vision screening may get lost in the plethora of concerns parents want to talk about in well-child visits.
“If you’re the parent of a child with developmental delays, language delays, poor social engagement, there are a multitude of things the visit could be focused on and it may be that vision screening possibly gets compromised or not done,” Dr. Adesman said.
That, he said, may be a focus area for improving the screening numbers.
Neither parents nor providers should forget that vision screening is important, despite the myriad other issues to address, he said. “They don’t have to take a long time.”
When it comes to vision problems and children, “the earlier they’re identified the better,” Dr. Adesman says, particularly to identify the need for eye muscle surgery or corrective lenses, the two major interventions for strabismus or refractive error.
“If those problems are significant and go untreated, there’s a risk of loss of vision in the affected eye,” he said.
Reimbursement concerns for photoscreening
This study strongly supports the use of routine photoscreening to help eliminate the vision screening gap in children with ASD, the authors wrote.
They noted, however, that would require insurance reimbursement for primary care practices to effectively use that screening.
The researchers advised, “Providers treating patients with race, ethnicity, region, or age categories that reduce the adjusted odds of photoscreening can take steps in their practices to address these disparities, particularly in children with ASD.”
The study authors and Dr. Adesman reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Match Day: Record number of residencies offered
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.
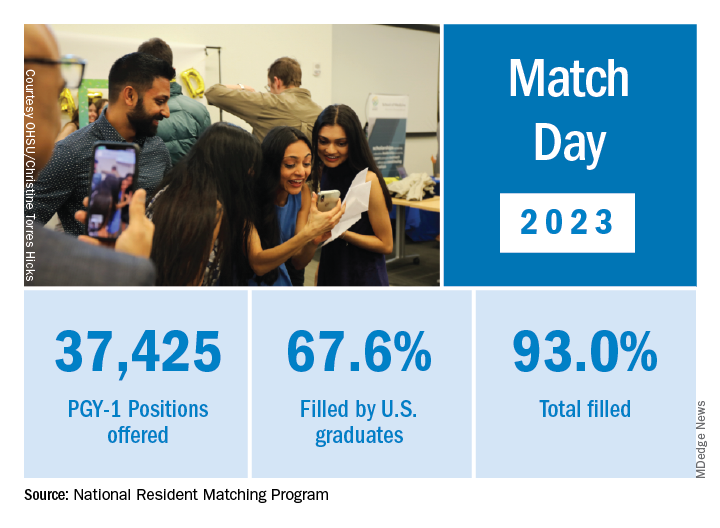
NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccinations lag in youngest children
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.
Case: A 3-year-old girl presented to the emergency department after a brief seizure at home. She looked well on physical exam except for a fever of 103° F and thick rhinorrhea.
The intern on duty methodically worked through the standard list of questions. “Immunizations up to date?” she asked.
“Absolutely,” the child’s mom responded. “She’s had everything that’s recommended.”
“Including COVID-19 vaccine?” the intern prompted.
“No.” The mom responded with a shake of her head. “We don’t do that vaccine.”
That mom is not alone.
COVID-19 vaccines for children as young as 6 months were given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in June 2022 and in February 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices included COVID-19 vaccine on the routine childhood immunization schedule.
COVID-19 vaccines are safe in young children, and they prevent the most severe outcomes associated with infection, including hospitalization. Newly released data confirm that the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Moderna and Pfizer also provide protection against symptomatic infection for at least 4 months after completion of the monovalent primary series.
In a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report released on Feb. 17, 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported the results of a test-negative design case-control study that enrolled symptomatic children tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection through Feb. 5, 2023, as part of the Increasing Community Access to Testing (ICATT) program.1 ICATT provides SARS-CoV-2 testing to persons aged at least 3 years at pharmacy and community-based testing sites nationwide.
Two doses of monovalent Moderna vaccine (complete primary series) was 60% effective against symptomatic infection (95% confidence interval, 49%-68%) 2 weeks to 2 months after receipt of the second dose. Vaccine effectiveness dropped to 36% (95% CI, 15%-52%) 3-4 months after the second dose. Three doses of monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (complete primary series) was 31% effective (95% CI, 7%-49%) at preventing symptomatic infection 2 weeks to 4 months after receipt of the third dose. A bivalent vaccine dose for eligible children is expected to provide more protection against currently circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Despite evidence of vaccine efficacy, very few parents are opting to protect their young children with the COVID-19 vaccine. The CDC reports that, as of March 1, 2023, only 8% of children under 2 years and 10.5% of children aged 2-4 years have initiated a COVID vaccine series. The American Academy of Pediatrics has emphasized that 15.0 million children between the ages of 6 months and 4 years have not yet received their first COVID-19 vaccine dose.
While the reasons underlying low COVID-19 vaccination rates in young children are complex, themes emerge. Socioeconomic disparities contributing to low vaccination rates in young children were highlighted in another recent MMWR article.2 Through Dec. 1, 2022, vaccination coverage was lower in rural counties (3.4%) than in urban counties (10.5%). Rates were lower in Black and Hispanic children than in White and Asian children.
According to the CDC, high rates of poverty in Black and Hispanic communities may affect vaccination coverage by affecting caregivers’ access to vaccination sites or ability to leave work to take their child to be vaccinated. Pediatric care providers have repeatedly been identified by parents as a source of trusted vaccine information and a strong provider recommendation is associated with vaccination, but not all families are receiving vaccine advice. In a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation survey, parents of young children with annual household incomes above $90,000 were more likely to talk to their pediatrician about a COVID-19 vaccine than families with lower incomes.3Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by general confusion and skepticism, is another factor contributing to low vaccination rates. Admittedly, the recommendations are complex and on March 14, 2023, the FDA again revised the emergency-use authorization for young children. Some caregivers continue to express concerns about vaccine side effects as well as the belief that the vaccine won’t prevent their child from getting sick.
Kendall Purcell, MD, a pediatrician with Norton Children’s Medical Group in Louisville, Ky., recommends COVID-19 vaccination for her patients because it reduces the risk of severe disease. That factored into her own decision to vaccinate her 4-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter, but she hasn’t been able to convince the parents of all her patients. “Some feel that COVID-19 is not as severe for children, so the risks don’t outweigh the benefits when it comes to vaccinating their children.” Back to our case: In the ED the intern reviewed the laboratory testing she had ordered. She then sat down with the mother of the 3-year-old girl to discuss the diagnosis: febrile seizure associated with COVID-19 infection. Febrile seizures are a well-recognized but uncommon complication of COVID-19 in children. In a retrospective cohort study using electronic health record data, febrile seizures occurred in 0.5% of 8,854 children aged 0-5 years with COVID-19 infection.4 About 9% of these children required critical care services. In another cohort of hospitalized children, neurologic complications occurred in 7% of children hospitalized with COVID-19.5 Febrile and nonfebrile seizures were most commonly observed.
“I really thought COVID-19 was no big deal in young kids,” the mom said. “Parents need the facts.”
The facts are these: Through Dec. 2, 2022, more than 3 million cases of COVID-19 have been reported in children aged younger than 5 years. While COVID is generally less severe in young children than older adults, it is difficult to predict which children will become seriously ill. When children are hospitalized, one in four requires intensive care. COVID-19 is now a vaccine-preventable disease, but too many children remain unprotected.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022-2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead. Email her at [email protected]. Ms. Ezell is a recent graduate from Indiana University Southeast with a Bachelor of Arts in English. They have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:177-182.
2. Murthy BP et al. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:183-9.
3. Lopes L et al. KFF COVID-19 vaccine monitor: July 2022. San Francisco: Kaiser Family Foundation, 2022.
4. Cadet K et al. J Child Neurol. 2022 Apr;37(5):410-5.
5. Antoon JW et al. Pediatrics. 2022 Nov 1;150(5):e2022058167.










