User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Your patient bequeathed money to you: Can you accept it?
Michael Victoroff, MD, described the phone call he received from an attorney asking a thorny ethics question involving a patient’s gift to another physician. Dr. Victoroff, a past member of the ethics committee of the American Academy of Family Physicians, had definite thoughts about it.
“The attorney was representing the daughters of an elderly gentleman who had moved from the East Coast to Colorado to be closer to them,” said Dr. Victoroff, who teaches bioethics in the MBA program at the University of Denver and also practices at the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
“The father visited his new primary care physician frequently because he had multiple health issues.”
The patient was happy with the doctor’s medical care and over time that they developed a friendship. Dr. Victoroff emphasized that no sexual or romantic impropriety ever took place between the patient and his physician.
“But the social relationship went beyond the ordinary doctor-patient boundaries. The patient ultimately named the doctor as his health care proxy in the event that he became unable to make decisions regarding his care. He also mentioned he was going to leave her $100,000 in his will,” says Dr. Victoroff.
The physician did accept the role of proxy, “which raises a whole host of ethical issues,” says Dr. Victoroff. As it happened, she was never called upon to exercise that decision-making authority, since the patient died suddenly and was mentally competent at the time.
for her to accept such a substantial bequest from a patient, and they hired an attorney to contest the will.
No law against it
Dennis Hursh, attorney and managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, noted in an interview that, “the problem isn’t legal per se. Rather, the problem is an ethical one.”
Legally speaking, there’s no prohibition against receiving a bequest or other form of gift from a patient. “People are free to dispose of their estates in whatever way they see fit, and no law technically precludes a physician from accepting a bequest,” says Dr. Victoroff. “But this presupposes there is nothing improper going on, such as extortion, deception, coercion, or exercising undue influence.”
The issue of bequeathing money to their physician gained attention in a recent case that took place in Australia. Peter Alexakis, MD, received a whopping bequest of $24 million from a patient. The elderly patient had changed his will to name Dr. Alexakis as the sole beneficiary – after Dr. Alexakis had visited him at home 92 times during the preceding months. The original heirs filed a lawsuit in Australia’s Supreme Court against Dr. Alexakis, contesting the will.
The lawsuit was unsuccessful in court, but Dr. Alexakis was found guilty of malpractice by Australia’s Health Care Complaints Commission after being reported to the HCCC by the palliative care physicians who were treating the patient. They alleged that Dr. Alexakis had interfered with their care of the patient. The more serious allegation was that the doctor had engaged in a deliberate strategy to exploit the relationship for financial gain.
Dr. Alexakis was chastised by the HCCC for engaging in “obtuse” and “suspicious” behavior and for “blurring the boundaries of the doctor-patient relationship.”
There are three domains – legal, ethical, and practical – when it comes to accepting bequests or any gifts from patients, says Dr. Victoroff.
“[In] the legal domain, for example, if you receive a bequest from anyone, patient or otherwise, you have to know your local laws about estates and taxes and so forth and obey them,” he said.
Attorney Hursh pointed out that the Australian doctor wasn’t found guilty of wrongdoing in a court of law but rather of unethical conduct by the Australian medical licensing entity.
Patients giving gifts is often a part of a physician’s life
When Ian Schorr, MD, first started out in practice, he was surprised that patients began bringing him gifts of food to express gratitude for his care.
“I thought it was unethical to accept their gifts, so I turned them down and wouldn’t accept so much as a cookie,” Dr. Schorr, a now-retired ophthalmologist, told this news organization. “But that changed because my office staff told me that some patients were feeling disappointed and insulted. I realized that some people want to express appreciation in ways that go beyond a monetary payment.”
The next time he received a gift from a patient, he “accepted it gracefully.” And he wrote a thank you note, which he continued to do any time he received a gift from a patient.
Kenneth Prager, MD, professor of clinical medicine, director of clinical ethics and chairman of the Medical Ethics Committee at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, says, “I have literally received hundreds of gifts, the vast majority being tokens of patients’ appreciation,” he said. “I’ll get boxes of chocolate or cakes, or sometimes articles of clothing.”
Occasionally, Dr. Prager receives a “somewhat larger gift” – for example, two tickets to a baseball game. “To reject these gifts would be a slap in the face to the patient,” he says, but “where it gets more ethically cloudy is when a gift is very substantial.”
Dr. Prager has never been offered a “substantial” gift or bequest personally. “But a patient whose brother I cared for has indicated that she has left instructions in her will to endow an associate chair of ethics in my honor, and I didn’t decline that,” he said.
The AMA Code of Ethics confirms that accepting gifts offered “as an expression of gratitude or a reflection of the patient’s cultural tradition” can “enhance the patient-physician relationship.” But sometimes gifts “may signal psychological needs that require the physician’s attention.” Accepting such gifts is “likely to damage the patient-physician relationship.”
Potential damage to the therapeutic relationship applies to all physicians but especially for psychiatrists and mental health professionals. “There are more stringent ethical requirements when it comes to these disciplines, where gift-giving gets into the territory of transference or may have particular psychological meaning, and accepting the gift may muddy the therapeutic waters,” Dr. Victoroff said.
Impact on the patient’s family and on other patients
The AMA statement encourages physicians to be “sensitive to the gift’s value, relative to the patient’s or physician’s means.” Physicians should decline gifts that are “disproportionately or inappropriately large, or when the physician would be uncomfortable to have colleagues know the gift had been accepted.”
They should also decline a bequest from a patient if they have reason to believe that to accept it “would present an emotional or financial hardship to the patient’s family.”
“If Bill Gates were leaving $100,000 to his doctor, I imagine Melinda would be just fine,” Mr. Hursh said. “But under ordinary circumstances, if the patient’s family might feel the impact of the bequest, it would be unethical to accept it and could be grounds for revocation of the doctor’s license.”
The AMA statement also warns physicians that by offering a gift, some patients may be seeking to “secure or influence care or to secure preferential treatment,” which can “undermine physicians’ obligation to provide services fairly to all patients.”
For this reason, bequests are “sticky,” said Laurel Lyckholm, MD, professor of hematology and oncology at West Virginia University School of Medicine. In the case of institutions where patients or community members donate money, “we know whose names are on the plaques that hang on the hospital walls, so it’s a delicate balance. What if there’s only one bed or one ventilator? Will the wife of the donor get preferential treatment?”
Follow institutional policy
A “very small gift, such as a fruitcake, is fine,” says Dr. Lyckholm, author of an essay on accepting gifts from patients. She said there’s a dollar amount ($15) that her institution mandates, above which a gift – even food – is considered too expensive to accept. “I was a nurse before I became a physician, and people always tried to give us gifts because we were so close to the minute-by-minute care of the patients,” she said. “We were not allowed to accept money or anything lavish.”
But in the case of small gifts, “the risk-benefit analysis is that there’s much more risk not to take it and to hurt the patient’s feelings.”
Gifts above $15 are given to charity. “I explain to patients that I’m not allowed to take such a large gift, but I’d love to give it to the hospital’s Rosenbaum Family House that provides patients and their relatives with lodging, or to the homeless shelter in Morgantown.”
Dr. Lyckholm, who serves on the ethics committee at J.W. Ruby Memorial Hospital, once was offered expensive tickets and said to the patient, “This is so incredibly thoughtful and kind, but I can’t accept them. I would like to give the tickets to a charity that can auction them off.”
She advises physicians to find out their institution’s policies. Many institutions have policies about what gifts their staff – whether physicians, nurses, or other health care professionals – can accept.
Passing the ‘smell test’
Accepting a large gift from a patient could potentially make it look like you might have exercised undue influence.
“That concern brings us to the third domain, which is very practical and all about appearances and perceptions,” Dr. Victoroff said.
He noted that there is “an inherent power differential between a physician and a patient. The very nature of the relationship can create a risk of ‘undue influence’ on the doctor’s part, even if it’s not apparent to the doctor.” For this reason, it’s necessary to be utterly transparent about how the bequest came about.
He suggests that if a patient informs you that he or she would like to leave money to you, it might be wise to suggest a meeting with the patient’s family, thus establishing some transparency.
It may not be possible to meet with the patient’s family for logistical reasons or because the patient would prefer not to involve their family in their estate planning. But in any case, it’s advisable to document any conversation in the patient’s chart, Dr. Victoroff advised.
“You should make a contemporaneous note that the patient initiated the suggestion and that you counseled them about the implications, no differently than you would with an interaction of a clinical nature,” he suggests. That way, if money has been left to you and is disputed, there’s a clear record that you didn’t solicit it or use any undue influence to bring it about.
He also recommended getting advice from a trusted colleague or a member of your institution’s ethics committee. “Taking time to get a second opinion about an ethical question is a safeguard, like having a chaperone in the room during an examination.”
Ultimately, “there is no human relationship without potential conflicts of interest. Our job is to manage those as best as we can, and sunlight is the best antidote to bad appearances,” Dr. Victoroff said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Michael Victoroff, MD, described the phone call he received from an attorney asking a thorny ethics question involving a patient’s gift to another physician. Dr. Victoroff, a past member of the ethics committee of the American Academy of Family Physicians, had definite thoughts about it.
“The attorney was representing the daughters of an elderly gentleman who had moved from the East Coast to Colorado to be closer to them,” said Dr. Victoroff, who teaches bioethics in the MBA program at the University of Denver and also practices at the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
“The father visited his new primary care physician frequently because he had multiple health issues.”
The patient was happy with the doctor’s medical care and over time that they developed a friendship. Dr. Victoroff emphasized that no sexual or romantic impropriety ever took place between the patient and his physician.
“But the social relationship went beyond the ordinary doctor-patient boundaries. The patient ultimately named the doctor as his health care proxy in the event that he became unable to make decisions regarding his care. He also mentioned he was going to leave her $100,000 in his will,” says Dr. Victoroff.
The physician did accept the role of proxy, “which raises a whole host of ethical issues,” says Dr. Victoroff. As it happened, she was never called upon to exercise that decision-making authority, since the patient died suddenly and was mentally competent at the time.
for her to accept such a substantial bequest from a patient, and they hired an attorney to contest the will.
No law against it
Dennis Hursh, attorney and managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, noted in an interview that, “the problem isn’t legal per se. Rather, the problem is an ethical one.”
Legally speaking, there’s no prohibition against receiving a bequest or other form of gift from a patient. “People are free to dispose of their estates in whatever way they see fit, and no law technically precludes a physician from accepting a bequest,” says Dr. Victoroff. “But this presupposes there is nothing improper going on, such as extortion, deception, coercion, or exercising undue influence.”
The issue of bequeathing money to their physician gained attention in a recent case that took place in Australia. Peter Alexakis, MD, received a whopping bequest of $24 million from a patient. The elderly patient had changed his will to name Dr. Alexakis as the sole beneficiary – after Dr. Alexakis had visited him at home 92 times during the preceding months. The original heirs filed a lawsuit in Australia’s Supreme Court against Dr. Alexakis, contesting the will.
The lawsuit was unsuccessful in court, but Dr. Alexakis was found guilty of malpractice by Australia’s Health Care Complaints Commission after being reported to the HCCC by the palliative care physicians who were treating the patient. They alleged that Dr. Alexakis had interfered with their care of the patient. The more serious allegation was that the doctor had engaged in a deliberate strategy to exploit the relationship for financial gain.
Dr. Alexakis was chastised by the HCCC for engaging in “obtuse” and “suspicious” behavior and for “blurring the boundaries of the doctor-patient relationship.”
There are three domains – legal, ethical, and practical – when it comes to accepting bequests or any gifts from patients, says Dr. Victoroff.
“[In] the legal domain, for example, if you receive a bequest from anyone, patient or otherwise, you have to know your local laws about estates and taxes and so forth and obey them,” he said.
Attorney Hursh pointed out that the Australian doctor wasn’t found guilty of wrongdoing in a court of law but rather of unethical conduct by the Australian medical licensing entity.
Patients giving gifts is often a part of a physician’s life
When Ian Schorr, MD, first started out in practice, he was surprised that patients began bringing him gifts of food to express gratitude for his care.
“I thought it was unethical to accept their gifts, so I turned them down and wouldn’t accept so much as a cookie,” Dr. Schorr, a now-retired ophthalmologist, told this news organization. “But that changed because my office staff told me that some patients were feeling disappointed and insulted. I realized that some people want to express appreciation in ways that go beyond a monetary payment.”
The next time he received a gift from a patient, he “accepted it gracefully.” And he wrote a thank you note, which he continued to do any time he received a gift from a patient.
Kenneth Prager, MD, professor of clinical medicine, director of clinical ethics and chairman of the Medical Ethics Committee at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, says, “I have literally received hundreds of gifts, the vast majority being tokens of patients’ appreciation,” he said. “I’ll get boxes of chocolate or cakes, or sometimes articles of clothing.”
Occasionally, Dr. Prager receives a “somewhat larger gift” – for example, two tickets to a baseball game. “To reject these gifts would be a slap in the face to the patient,” he says, but “where it gets more ethically cloudy is when a gift is very substantial.”
Dr. Prager has never been offered a “substantial” gift or bequest personally. “But a patient whose brother I cared for has indicated that she has left instructions in her will to endow an associate chair of ethics in my honor, and I didn’t decline that,” he said.
The AMA Code of Ethics confirms that accepting gifts offered “as an expression of gratitude or a reflection of the patient’s cultural tradition” can “enhance the patient-physician relationship.” But sometimes gifts “may signal psychological needs that require the physician’s attention.” Accepting such gifts is “likely to damage the patient-physician relationship.”
Potential damage to the therapeutic relationship applies to all physicians but especially for psychiatrists and mental health professionals. “There are more stringent ethical requirements when it comes to these disciplines, where gift-giving gets into the territory of transference or may have particular psychological meaning, and accepting the gift may muddy the therapeutic waters,” Dr. Victoroff said.
Impact on the patient’s family and on other patients
The AMA statement encourages physicians to be “sensitive to the gift’s value, relative to the patient’s or physician’s means.” Physicians should decline gifts that are “disproportionately or inappropriately large, or when the physician would be uncomfortable to have colleagues know the gift had been accepted.”
They should also decline a bequest from a patient if they have reason to believe that to accept it “would present an emotional or financial hardship to the patient’s family.”
“If Bill Gates were leaving $100,000 to his doctor, I imagine Melinda would be just fine,” Mr. Hursh said. “But under ordinary circumstances, if the patient’s family might feel the impact of the bequest, it would be unethical to accept it and could be grounds for revocation of the doctor’s license.”
The AMA statement also warns physicians that by offering a gift, some patients may be seeking to “secure or influence care or to secure preferential treatment,” which can “undermine physicians’ obligation to provide services fairly to all patients.”
For this reason, bequests are “sticky,” said Laurel Lyckholm, MD, professor of hematology and oncology at West Virginia University School of Medicine. In the case of institutions where patients or community members donate money, “we know whose names are on the plaques that hang on the hospital walls, so it’s a delicate balance. What if there’s only one bed or one ventilator? Will the wife of the donor get preferential treatment?”
Follow institutional policy
A “very small gift, such as a fruitcake, is fine,” says Dr. Lyckholm, author of an essay on accepting gifts from patients. She said there’s a dollar amount ($15) that her institution mandates, above which a gift – even food – is considered too expensive to accept. “I was a nurse before I became a physician, and people always tried to give us gifts because we were so close to the minute-by-minute care of the patients,” she said. “We were not allowed to accept money or anything lavish.”
But in the case of small gifts, “the risk-benefit analysis is that there’s much more risk not to take it and to hurt the patient’s feelings.”
Gifts above $15 are given to charity. “I explain to patients that I’m not allowed to take such a large gift, but I’d love to give it to the hospital’s Rosenbaum Family House that provides patients and their relatives with lodging, or to the homeless shelter in Morgantown.”
Dr. Lyckholm, who serves on the ethics committee at J.W. Ruby Memorial Hospital, once was offered expensive tickets and said to the patient, “This is so incredibly thoughtful and kind, but I can’t accept them. I would like to give the tickets to a charity that can auction them off.”
She advises physicians to find out their institution’s policies. Many institutions have policies about what gifts their staff – whether physicians, nurses, or other health care professionals – can accept.
Passing the ‘smell test’
Accepting a large gift from a patient could potentially make it look like you might have exercised undue influence.
“That concern brings us to the third domain, which is very practical and all about appearances and perceptions,” Dr. Victoroff said.
He noted that there is “an inherent power differential between a physician and a patient. The very nature of the relationship can create a risk of ‘undue influence’ on the doctor’s part, even if it’s not apparent to the doctor.” For this reason, it’s necessary to be utterly transparent about how the bequest came about.
He suggests that if a patient informs you that he or she would like to leave money to you, it might be wise to suggest a meeting with the patient’s family, thus establishing some transparency.
It may not be possible to meet with the patient’s family for logistical reasons or because the patient would prefer not to involve their family in their estate planning. But in any case, it’s advisable to document any conversation in the patient’s chart, Dr. Victoroff advised.
“You should make a contemporaneous note that the patient initiated the suggestion and that you counseled them about the implications, no differently than you would with an interaction of a clinical nature,” he suggests. That way, if money has been left to you and is disputed, there’s a clear record that you didn’t solicit it or use any undue influence to bring it about.
He also recommended getting advice from a trusted colleague or a member of your institution’s ethics committee. “Taking time to get a second opinion about an ethical question is a safeguard, like having a chaperone in the room during an examination.”
Ultimately, “there is no human relationship without potential conflicts of interest. Our job is to manage those as best as we can, and sunlight is the best antidote to bad appearances,” Dr. Victoroff said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Michael Victoroff, MD, described the phone call he received from an attorney asking a thorny ethics question involving a patient’s gift to another physician. Dr. Victoroff, a past member of the ethics committee of the American Academy of Family Physicians, had definite thoughts about it.
“The attorney was representing the daughters of an elderly gentleman who had moved from the East Coast to Colorado to be closer to them,” said Dr. Victoroff, who teaches bioethics in the MBA program at the University of Denver and also practices at the University of Colorado School of Medicine.
“The father visited his new primary care physician frequently because he had multiple health issues.”
The patient was happy with the doctor’s medical care and over time that they developed a friendship. Dr. Victoroff emphasized that no sexual or romantic impropriety ever took place between the patient and his physician.
“But the social relationship went beyond the ordinary doctor-patient boundaries. The patient ultimately named the doctor as his health care proxy in the event that he became unable to make decisions regarding his care. He also mentioned he was going to leave her $100,000 in his will,” says Dr. Victoroff.
The physician did accept the role of proxy, “which raises a whole host of ethical issues,” says Dr. Victoroff. As it happened, she was never called upon to exercise that decision-making authority, since the patient died suddenly and was mentally competent at the time.
for her to accept such a substantial bequest from a patient, and they hired an attorney to contest the will.
No law against it
Dennis Hursh, attorney and managing partner of Physician Agreements Health Law, a Pennsylvania-based law firm that represents physicians, noted in an interview that, “the problem isn’t legal per se. Rather, the problem is an ethical one.”
Legally speaking, there’s no prohibition against receiving a bequest or other form of gift from a patient. “People are free to dispose of their estates in whatever way they see fit, and no law technically precludes a physician from accepting a bequest,” says Dr. Victoroff. “But this presupposes there is nothing improper going on, such as extortion, deception, coercion, or exercising undue influence.”
The issue of bequeathing money to their physician gained attention in a recent case that took place in Australia. Peter Alexakis, MD, received a whopping bequest of $24 million from a patient. The elderly patient had changed his will to name Dr. Alexakis as the sole beneficiary – after Dr. Alexakis had visited him at home 92 times during the preceding months. The original heirs filed a lawsuit in Australia’s Supreme Court against Dr. Alexakis, contesting the will.
The lawsuit was unsuccessful in court, but Dr. Alexakis was found guilty of malpractice by Australia’s Health Care Complaints Commission after being reported to the HCCC by the palliative care physicians who were treating the patient. They alleged that Dr. Alexakis had interfered with their care of the patient. The more serious allegation was that the doctor had engaged in a deliberate strategy to exploit the relationship for financial gain.
Dr. Alexakis was chastised by the HCCC for engaging in “obtuse” and “suspicious” behavior and for “blurring the boundaries of the doctor-patient relationship.”
There are three domains – legal, ethical, and practical – when it comes to accepting bequests or any gifts from patients, says Dr. Victoroff.
“[In] the legal domain, for example, if you receive a bequest from anyone, patient or otherwise, you have to know your local laws about estates and taxes and so forth and obey them,” he said.
Attorney Hursh pointed out that the Australian doctor wasn’t found guilty of wrongdoing in a court of law but rather of unethical conduct by the Australian medical licensing entity.
Patients giving gifts is often a part of a physician’s life
When Ian Schorr, MD, first started out in practice, he was surprised that patients began bringing him gifts of food to express gratitude for his care.
“I thought it was unethical to accept their gifts, so I turned them down and wouldn’t accept so much as a cookie,” Dr. Schorr, a now-retired ophthalmologist, told this news organization. “But that changed because my office staff told me that some patients were feeling disappointed and insulted. I realized that some people want to express appreciation in ways that go beyond a monetary payment.”
The next time he received a gift from a patient, he “accepted it gracefully.” And he wrote a thank you note, which he continued to do any time he received a gift from a patient.
Kenneth Prager, MD, professor of clinical medicine, director of clinical ethics and chairman of the Medical Ethics Committee at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, says, “I have literally received hundreds of gifts, the vast majority being tokens of patients’ appreciation,” he said. “I’ll get boxes of chocolate or cakes, or sometimes articles of clothing.”
Occasionally, Dr. Prager receives a “somewhat larger gift” – for example, two tickets to a baseball game. “To reject these gifts would be a slap in the face to the patient,” he says, but “where it gets more ethically cloudy is when a gift is very substantial.”
Dr. Prager has never been offered a “substantial” gift or bequest personally. “But a patient whose brother I cared for has indicated that she has left instructions in her will to endow an associate chair of ethics in my honor, and I didn’t decline that,” he said.
The AMA Code of Ethics confirms that accepting gifts offered “as an expression of gratitude or a reflection of the patient’s cultural tradition” can “enhance the patient-physician relationship.” But sometimes gifts “may signal psychological needs that require the physician’s attention.” Accepting such gifts is “likely to damage the patient-physician relationship.”
Potential damage to the therapeutic relationship applies to all physicians but especially for psychiatrists and mental health professionals. “There are more stringent ethical requirements when it comes to these disciplines, where gift-giving gets into the territory of transference or may have particular psychological meaning, and accepting the gift may muddy the therapeutic waters,” Dr. Victoroff said.
Impact on the patient’s family and on other patients
The AMA statement encourages physicians to be “sensitive to the gift’s value, relative to the patient’s or physician’s means.” Physicians should decline gifts that are “disproportionately or inappropriately large, or when the physician would be uncomfortable to have colleagues know the gift had been accepted.”
They should also decline a bequest from a patient if they have reason to believe that to accept it “would present an emotional or financial hardship to the patient’s family.”
“If Bill Gates were leaving $100,000 to his doctor, I imagine Melinda would be just fine,” Mr. Hursh said. “But under ordinary circumstances, if the patient’s family might feel the impact of the bequest, it would be unethical to accept it and could be grounds for revocation of the doctor’s license.”
The AMA statement also warns physicians that by offering a gift, some patients may be seeking to “secure or influence care or to secure preferential treatment,” which can “undermine physicians’ obligation to provide services fairly to all patients.”
For this reason, bequests are “sticky,” said Laurel Lyckholm, MD, professor of hematology and oncology at West Virginia University School of Medicine. In the case of institutions where patients or community members donate money, “we know whose names are on the plaques that hang on the hospital walls, so it’s a delicate balance. What if there’s only one bed or one ventilator? Will the wife of the donor get preferential treatment?”
Follow institutional policy
A “very small gift, such as a fruitcake, is fine,” says Dr. Lyckholm, author of an essay on accepting gifts from patients. She said there’s a dollar amount ($15) that her institution mandates, above which a gift – even food – is considered too expensive to accept. “I was a nurse before I became a physician, and people always tried to give us gifts because we were so close to the minute-by-minute care of the patients,” she said. “We were not allowed to accept money or anything lavish.”
But in the case of small gifts, “the risk-benefit analysis is that there’s much more risk not to take it and to hurt the patient’s feelings.”
Gifts above $15 are given to charity. “I explain to patients that I’m not allowed to take such a large gift, but I’d love to give it to the hospital’s Rosenbaum Family House that provides patients and their relatives with lodging, or to the homeless shelter in Morgantown.”
Dr. Lyckholm, who serves on the ethics committee at J.W. Ruby Memorial Hospital, once was offered expensive tickets and said to the patient, “This is so incredibly thoughtful and kind, but I can’t accept them. I would like to give the tickets to a charity that can auction them off.”
She advises physicians to find out their institution’s policies. Many institutions have policies about what gifts their staff – whether physicians, nurses, or other health care professionals – can accept.
Passing the ‘smell test’
Accepting a large gift from a patient could potentially make it look like you might have exercised undue influence.
“That concern brings us to the third domain, which is very practical and all about appearances and perceptions,” Dr. Victoroff said.
He noted that there is “an inherent power differential between a physician and a patient. The very nature of the relationship can create a risk of ‘undue influence’ on the doctor’s part, even if it’s not apparent to the doctor.” For this reason, it’s necessary to be utterly transparent about how the bequest came about.
He suggests that if a patient informs you that he or she would like to leave money to you, it might be wise to suggest a meeting with the patient’s family, thus establishing some transparency.
It may not be possible to meet with the patient’s family for logistical reasons or because the patient would prefer not to involve their family in their estate planning. But in any case, it’s advisable to document any conversation in the patient’s chart, Dr. Victoroff advised.
“You should make a contemporaneous note that the patient initiated the suggestion and that you counseled them about the implications, no differently than you would with an interaction of a clinical nature,” he suggests. That way, if money has been left to you and is disputed, there’s a clear record that you didn’t solicit it or use any undue influence to bring it about.
He also recommended getting advice from a trusted colleague or a member of your institution’s ethics committee. “Taking time to get a second opinion about an ethical question is a safeguard, like having a chaperone in the room during an examination.”
Ultimately, “there is no human relationship without potential conflicts of interest. Our job is to manage those as best as we can, and sunlight is the best antidote to bad appearances,” Dr. Victoroff said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Missed opportunities’ for accurate diagnosing of women with vaginitis
Although the standard of care of diagnosing vaginitis is clinical evaluation, many practices do not perform accurate and comprehensive clinical examinations for a variety for reasons, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends molecular testing, wrote Casey N. Pinto, PhD, of Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues. The CDC also recommends testing women with vaginitis for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neissaria gonorrhoeae (NG) given the high rate of coinfections between vaginitis and these sexually transmitted infections, but data on cotesting in clinical practice are limited, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from a commercial administrative claims database for 1,359,289 women aged 18-50 years who were diagnosed with vaginitis between 2012 and 2017.
The women were categorized into groups based on type of vaginitis diagnosis: nucleic amplification test (NAAT), DNA probe test, traditional lab test, and those diagnosed clinically at an index visit but with no CPT code for further testing.
Overall, nearly half of the women (49.2%) had no CPT code for further vaginitis testing beyond clinical diagnosis. Of those with CPT codes for testing, 50.9% underwent traditional point-of-care testing, wet mount, or culture, 23.5% had a DNA probe, and 20.6% had NAAT testing.
Approximately one-third (34%) of women were cotested for CT/NG. Testing rates varied widely across the type of vaginitis test, from 70.8% of women who received NAAT to 22.8% of women with no CPT code. In multivariate analysis including age, region, and the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), those tested with NAAT were eight times more likely to be cotested for CT/NG than those with no CPT code (odds ratio, 8.77; P < .0001).
Women who received a traditional test or DNA probe test for vaginitis also were more likely to have CT/NG testing than women with no CPT code, but only 1.8-2.5 times as likely.
“Our data suggest that most clinicians are not engaging the standard of care for testing and diagnosing vaginitis, or not engaging in comprehensive care by cotesting for vaginitis and CT/NG when patients may be at risk, resulting in missed opportunities for accurate diagnosis and potential associated coinfections,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. The higher rates for CT/NG testing among women receiving either NAAT or DNA probe vaginitis testing could be attributed to bundled testing, they noted, and the lower rate of CT/NG testing for patients with no CPT code could stem from limited access to microscopy or clinician preference for clinical diagnosis only, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on testing and diagnoses prior to the study period and not billed to insurance, and by the inability to account for variables including race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more comprehensive care in vaginitis testing to take advantage of opportunities to identify CT or NG in women diagnosed with vaginitis, they concluded.
The study was supported by Becton, Dickinson and Company. Lead author Dr. Pinto disclosed consulting for Becton, Dickinson and Company, and receiving an honorarium from Roche.
Although the standard of care of diagnosing vaginitis is clinical evaluation, many practices do not perform accurate and comprehensive clinical examinations for a variety for reasons, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends molecular testing, wrote Casey N. Pinto, PhD, of Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues. The CDC also recommends testing women with vaginitis for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neissaria gonorrhoeae (NG) given the high rate of coinfections between vaginitis and these sexually transmitted infections, but data on cotesting in clinical practice are limited, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from a commercial administrative claims database for 1,359,289 women aged 18-50 years who were diagnosed with vaginitis between 2012 and 2017.
The women were categorized into groups based on type of vaginitis diagnosis: nucleic amplification test (NAAT), DNA probe test, traditional lab test, and those diagnosed clinically at an index visit but with no CPT code for further testing.
Overall, nearly half of the women (49.2%) had no CPT code for further vaginitis testing beyond clinical diagnosis. Of those with CPT codes for testing, 50.9% underwent traditional point-of-care testing, wet mount, or culture, 23.5% had a DNA probe, and 20.6% had NAAT testing.
Approximately one-third (34%) of women were cotested for CT/NG. Testing rates varied widely across the type of vaginitis test, from 70.8% of women who received NAAT to 22.8% of women with no CPT code. In multivariate analysis including age, region, and the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), those tested with NAAT were eight times more likely to be cotested for CT/NG than those with no CPT code (odds ratio, 8.77; P < .0001).
Women who received a traditional test or DNA probe test for vaginitis also were more likely to have CT/NG testing than women with no CPT code, but only 1.8-2.5 times as likely.
“Our data suggest that most clinicians are not engaging the standard of care for testing and diagnosing vaginitis, or not engaging in comprehensive care by cotesting for vaginitis and CT/NG when patients may be at risk, resulting in missed opportunities for accurate diagnosis and potential associated coinfections,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. The higher rates for CT/NG testing among women receiving either NAAT or DNA probe vaginitis testing could be attributed to bundled testing, they noted, and the lower rate of CT/NG testing for patients with no CPT code could stem from limited access to microscopy or clinician preference for clinical diagnosis only, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on testing and diagnoses prior to the study period and not billed to insurance, and by the inability to account for variables including race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more comprehensive care in vaginitis testing to take advantage of opportunities to identify CT or NG in women diagnosed with vaginitis, they concluded.
The study was supported by Becton, Dickinson and Company. Lead author Dr. Pinto disclosed consulting for Becton, Dickinson and Company, and receiving an honorarium from Roche.
Although the standard of care of diagnosing vaginitis is clinical evaluation, many practices do not perform accurate and comprehensive clinical examinations for a variety for reasons, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention currently recommends molecular testing, wrote Casey N. Pinto, PhD, of Penn State University, Hershey, and colleagues. The CDC also recommends testing women with vaginitis for Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neissaria gonorrhoeae (NG) given the high rate of coinfections between vaginitis and these sexually transmitted infections, but data on cotesting in clinical practice are limited, they said.
In a study published in Sexually Transmitted Diseases, the researchers reviewed data from a commercial administrative claims database for 1,359,289 women aged 18-50 years who were diagnosed with vaginitis between 2012 and 2017.
The women were categorized into groups based on type of vaginitis diagnosis: nucleic amplification test (NAAT), DNA probe test, traditional lab test, and those diagnosed clinically at an index visit but with no CPT code for further testing.
Overall, nearly half of the women (49.2%) had no CPT code for further vaginitis testing beyond clinical diagnosis. Of those with CPT codes for testing, 50.9% underwent traditional point-of-care testing, wet mount, or culture, 23.5% had a DNA probe, and 20.6% had NAAT testing.
Approximately one-third (34%) of women were cotested for CT/NG. Testing rates varied widely across the type of vaginitis test, from 70.8% of women who received NAAT to 22.8% of women with no CPT code. In multivariate analysis including age, region, and the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), those tested with NAAT were eight times more likely to be cotested for CT/NG than those with no CPT code (odds ratio, 8.77; P < .0001).
Women who received a traditional test or DNA probe test for vaginitis also were more likely to have CT/NG testing than women with no CPT code, but only 1.8-2.5 times as likely.
“Our data suggest that most clinicians are not engaging the standard of care for testing and diagnosing vaginitis, or not engaging in comprehensive care by cotesting for vaginitis and CT/NG when patients may be at risk, resulting in missed opportunities for accurate diagnosis and potential associated coinfections,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. The higher rates for CT/NG testing among women receiving either NAAT or DNA probe vaginitis testing could be attributed to bundled testing, they noted, and the lower rate of CT/NG testing for patients with no CPT code could stem from limited access to microscopy or clinician preference for clinical diagnosis only, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data on testing and diagnoses prior to the study period and not billed to insurance, and by the inability to account for variables including race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, the researchers noted.
However, the results highlight the need for more comprehensive care in vaginitis testing to take advantage of opportunities to identify CT or NG in women diagnosed with vaginitis, they concluded.
The study was supported by Becton, Dickinson and Company. Lead author Dr. Pinto disclosed consulting for Becton, Dickinson and Company, and receiving an honorarium from Roche.
FROM SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
MS drugs during pregnancy show no safety signals
AURORA, COLO. – Several drugs for multiple sclerosis (MS) that are contraindicated during pregnancy nevertheless have not shown concerning safety signals in a series of small studies presented as posters at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. The industry-sponsored research included an assessment of pregnancy and infant outcomes for cladribine, ocrelizumab, ofatumumab, and ozanimod, all of which are not recommended during pregnancy based primarily on minimal data that suggests, but does not confirm, possible teratogenicity.
“When these new medications hit the market, maternal-fetal medicine physicians and obstetricians are left with very scant data on how to counsel patients, and it’s often based on theory, case reports, or animal studies,” said Teodora Kolarova, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at the University of Washington, Seattle, who was not involved in any of the research. “Although these sample sizes seem small, the population they are sampling from – patients with MS who take immunomodulators who then experience a pregnancy – is much smaller than all pregnant patients.”
Taken together, the findings suggest no increased risk of miscarriage or congenital malformation, compared with baseline risk, Dr. Kolarova said.
“As a whole, these studies are overall reassuring with, of course, some caveats, including timing of medication exposure, limited sample size, and limited outcome data,” Dr. Kolarova said. She noted that embryonic organ formation is complete by 10 weeks gestation, by which time an unplanned pregnancy may not have been recognized yet. “In the subset of patients in the studies that were exposed during the first trimester, there was no increase in congenital malformations from a baseline risk of about 2%-3% in the general population, which is helpful for patient counseling.”
Counseling during the childbearing years
That kind of counseling is important yet absent for many people capable of pregnancy, suggests separate research also presented at the conference by Suma Shah, MD, an associate professor of neurology at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Dr. Shah gave 13-question surveys to female MS patients of all ages at her institution and presented an analysis of data from 38 completed surveys. Among those taking disease-modifying therapies, their medications included ocrelizumab, rituximab, teriflunomide, fingolimod, fumarates, interferons, natalizumab, and cladribine.
“MS disproportionately impacts women among 20 to 40 years, and that’s a really big part of their childbearing years when there are big decisions being made about whether they’re going to choose to grow family or not,” said Dr. Shah. The average age of those who completed the survey was 44. Dr. Shah noted that a lot of research has looked at the safety of older disease-modifying agents in pregnancy, but that information doesn’t appear to be filtering down to patients. “What I really wanted to look at is what do our parent patients understand about whether or not they can even think about pregnancy – and there’s a lot of work to be done.”
Just under a third of survey respondents said they did not have as many children as they would like, and a quarter said they were told they couldn’t have children if they had a diagnosis of MS.
“That was a little heartbreaking to hear because that’s not the truth,” Dr. Shah said. She said it’s necessary to have a more detailed conversation looking at tailored decisions for patients. “Both of those things – patients not being able to grow their family to the number that they desire, and not feeling like they can grow a family – I would think in 2023 we would have come farther than that, and there’s still a lot of room there to improve.”
She advised clinicians not to assume that MS patients know what their options are regarding family planning. “There’s still a lot of room for conversations,” she said. She also explicitly recommends discussing family planning and pregnancy planning with every patient, no matter their gender, early and often.
Cladribine shows no miscarriage, malformations
Dr. Kolarova noted that one of the studies, on cladribine, had a fairly robust sample size with its 180 pregnancy exposures. In that study, led by Kerstin Hellwig, MD, of Ruhr University in Bochum, Germany, data came from the global surveillance program MAPLE-MS, established to assess cladribine effects on pregnancy and infant outcomes. The researchers analyzed data from 76 mothers and 9 fathers who, at any time from 2017 to 2022, were taking cladribine during pregnancy or up to 6 months before pregnancy. Outcomes included live birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, elective abortion, ectopic pregnancy, and major congenital anomalies.
Just over half the mothers (53.9%) were exposed before pregnancy, and about a quarter (26.3%) were exposed during the first trimester. The timing was unknown for most of the other mothers (18.4%). Among the fathers, two-thirds (66.7%) were exposed before pregnancy, and one-third had unknown timing.
Among the 180 pregnancies in the maternal cohort, 42.2% had known outcomes. Nearly half the women (48.7%) taking cladribine had live births, 28.9% had elective abortions, and 21.1% had miscarriages. Only 9 of the 22 pregnancies in the paternal cohort had known outcomes, which included 88.9% live births and 11.1% miscarriages. None of the pregnancies resulted in stillbirth or in a live birth with major congenital anomalies.
”Robust conclusions cannot be made about the risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes with cladribine tablets, but no increase has been signaled thus far,” the researchers reported. ”It is necessary to counsel patients to prevent pregnancy and to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets intake and for at least 6 months after the last cladribine tablet intake in each treatment year.”
Emily Evans, MD, MBE, medical director at U.S. Neurology and Immunology in Rockland, Mass., speaking on behalf of the findings, said they were fairly encouraging.
“Of course, we don’t encourage patients to get pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets,” Dr. Evans said, but “within those individuals who have gotten pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine, or who have fathered a child within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets, we’re seeing overall encouraging outcomes. We’re specifically not seeing any differences in the rates of spontaneous abortions, and we’re not seeing any differences in the rates of congenital malformations.”
Ocrelizumab and ofatumumab: No infections so far
Current recommendations for ocrelizumab are to avoid pregnancy for 6 months after the last infusion and stop any breastfeeding during therapy. Yet these recommendations are only because of insufficient data rather than evidence of risk, according to Lana Zhovtis Ryerson, MD, of the NYU Multiple Sclerosis Comprehensive Care Center in New York. She and her colleagues identified all women of childbearing age who had received ocrelizumab within 1 year of pregnancy at their NYU institution. A retrospective chart review found 18 women, with an average age of 35, an average 11 years of an MS diagnosis, and an average 11 months taking ocrelizumab.
Among the 18 pregnancies, four women had a first trimester miscarriage, one had a second trimester miscarriage, and one had an abortion. The miscarriage rate could have been partly influenced by the older maternal population, the authors noted. Of the remaining 12 live births, one infant was premature at 34 weeks, and three infants stayed in NICU but were discharged within 2 weeks.
One patient experienced an MS relapse postpartum, despite receiving ocrelizumab within 45 days of delivery. Of the 16 women who agreed to participate in a Pregnancy Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) developed by the CDC, two women chose to breastfeed, and seven said their neurologist recommended against breastfeeding. None of the children’s pediatricians advised delaying vaccinations.
“This small sample observational study has not identified a potential additional risk with ocrelizumab for an adverse pregnancy outcome,” the authors concluded, but they added that ongoing studies, MINORE and SOPRANINO, can help guide future recommendations.
Though still limited, slightly more data exists on ofatumumab during pregnancy, including transient B-cell depletion and lymphopenia in infants whose mothers received anti-CD20 antibodies during pregnancy. However, research has found minimal IgG transfer in the first trimester, though it begins rising in the second trimester, and in utero ofatumumab exposure did not lead to any maternal toxicity or adverse prenatal or postnatal developmental effects in cynomolgus monkeys.
Riley Love, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neuroscience, and her colleagues both prospectively and retrospectively examined pregnancy and infant outcomes for up to 1 year post partum in women with MS who took ofatumumab during pregnancy or in the 6 months leading up to pregnancy. Their population included 104 prospective cases, most of which (84%) included first trimester exposure, and 14 retrospective cases. One in five of the prospective cases occurred during a clinical trial, while the remaining 80% occurred in postmarketing surveillance.
The prospectively followed women were an average 32 years old and were an average 7 weeks pregnant at the time of reporting. Among the 106 fetuses (including two twin pregnancies), only 30 outcomes had data at the cutoff time, including 16 live births, 9 abortions, and 5 miscarriages. None of the live births had congenital anomalies or serious infections. Another 30 pregnancies were lost to follow-up, and 46 were ongoing.
In the 14 retrospective cases, 57% of women were exposed in the first trimester, and 43% were exposed leading up to pregnancy. Half the cases occurred during clinical trials, and half in postmarketing surveillance. The women were an average 32 years old and were an average 10 weeks pregnant at reporting. Among the 14 pregnancies, nine were miscarriages, one was aborted, and four were born live with no congenital anomalies.
The authors did not draw any conclusions from the findings; they cited too little data and an ongoing study by Novartis to investigate ofatumumab in pregnancy.
“Therapies such as ofatumumab and ocrelizumab can lead to increased risk of infection due to transient B-cell depletion in neonates, but the two studies looking at this did not demonstrate increased infectious morbidity for these infants,” Dr. Kolarova said. “As with all poster presentations, I look forward to reading the full papers once they are published as they will often include a lot more detail about when during pregnancy medication exposure occurred and more detailed outcome data that was assessed.”
Ozanimod outcomes within general population’s ‘expected ranges’
The final study looked at outcomes of pregnancies in people taking ozanimod and in the partners of people taking ozanimod in a clinical trial setting. The findings show low rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies that the authors concluded were within the typical range expected for the general population.
“While pregnancy should be avoided when taking and for 3 months after stopping ozanimod to allow for drug elimination, there is no evidence to date of increased occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes with ozanimod exposure during early pregnancy,” wrote Anthony Krakovich, of Bristol Myers Squibb in Princeton, N.J., and his associates.
Ozanimod is an oral sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 and 5 modulator whose therapeutic mechanism is not fully understood “but may involve the reduction of lymphocyte migration into the central nervous system and intestine,” the authors wrote. S1P receptors are involved in vascular formation during embryogenesis, and animal studies in rats and rabbits have shown toxicity to the embryo and fetus from S1P receptor modulators, including death and malformations. S1P receptor modulator labels therefore note potential fetal risk and the need for effective contraception while taking the drug.
The study prospectively tracked clinical trial participants taking ozanimod as healthy volunteers or for relapsing MS, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease. Most of the participants who became pregnant (73%) had relapsing MS, while 18% had ulcerative colitis and 8% had Crohn’s disease.
In female patients receiving ozanimod, 78 pregnancies resulted in 12 miscarriages (including one twin), 15 abortions, and 42 live births, with 6 pregnancies ongoing at the time of reporting and no data available for the remaining 4 pregnancies. Among the 42 live births, 4 were premature but otherwise healthy, 1 had a duplex kidney, and the other 37 infants were typical with no apparent health concerns. These rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies were within the expected ranges for the general population, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also assessed pregnancy outcomes for partners of male participants taking ozanimod. The 29 partner pregnancies resulted in 21 live births and one miscarriage, with one pregnancy ongoing and no information available for the other seven. The live births included 5 premature infants (including twins), 13 typical and healthy infants, 1 with Hirschsprung’s disease, 1 with a congenital hydrocele, and 1 with a partial atrioventricular septal defect. Again, the researchers concluded that these rates were within the typical range for the general population and that “no teratogenicity was observed.”
“We often encourage patients with MS, regardless of disease activity and therapies, to seek preconception evaluations with Maternal-Fetal Medicine and their neurologists in order to make plans for pregnancy and postpartum care,” Dr. Kolarova said. “That being said, access to subspecialized health care is not available to all, and pregnancy prior to such consultation does occur. These studies provide novel information that we have not had access to in the past and can improve patient counseling regarding their risks and options.”
The study on cladribine was funded by Merck KGaA, at which two authors are employed. Dr. Hellwig reported consulting, speaker, and/or research support from Bayer, Biogen, Teva, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Schering Healthcare, Serono, and Merck, and one author is a former employee of EMD Serono. The study on ocrelizumab was funded by Genentech. Dr. Zhovtis Ryerson reported personal fees from Biogen, Genentech, and Novartis, and research grants from Biogen, Genentech, and CMSC. The other authors had no disclosures. The study on ofatumumab was funded by Novartis. Dr. Bove has received research funds from Biogen, Novartis, and Roche Genentech, and consulting fees from EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, and TG Therapeutics; she has an ownership interest in Global Consult MD. Five authors are Novartis employees. Her coauthors, including Dr. Hellwig, reported advisory, consulting, research, speaking, or traveling fees from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene BMS, EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, Lundbeck, Merck, Pfizer, Roche Genentech, Sanofi Genzyme, Schering Healthcare, Teva, TG Therapeutics, and Novartis. The study on ozanimod was funded by Bristol Myers Squibb. Dr. Krakovich and another author are employees and/or shareholders of Bristol Myers Squibb. The other authors reported consulting, speaking, advisory board, and/or research fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Arena, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelhei, Celgene, Celltrion, EXCEMED, Falk Benelux, Ferring, Forward Pharma, Genentech, Genzyme, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Pfizer, Prometheus Labs, Protagonist, Roche, Sanofi, Synthon, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kolarova had no disclosures. Dr. Shah has received research support from Biogen and VeraSci.
AURORA, COLO. – Several drugs for multiple sclerosis (MS) that are contraindicated during pregnancy nevertheless have not shown concerning safety signals in a series of small studies presented as posters at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. The industry-sponsored research included an assessment of pregnancy and infant outcomes for cladribine, ocrelizumab, ofatumumab, and ozanimod, all of which are not recommended during pregnancy based primarily on minimal data that suggests, but does not confirm, possible teratogenicity.
“When these new medications hit the market, maternal-fetal medicine physicians and obstetricians are left with very scant data on how to counsel patients, and it’s often based on theory, case reports, or animal studies,” said Teodora Kolarova, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at the University of Washington, Seattle, who was not involved in any of the research. “Although these sample sizes seem small, the population they are sampling from – patients with MS who take immunomodulators who then experience a pregnancy – is much smaller than all pregnant patients.”
Taken together, the findings suggest no increased risk of miscarriage or congenital malformation, compared with baseline risk, Dr. Kolarova said.
“As a whole, these studies are overall reassuring with, of course, some caveats, including timing of medication exposure, limited sample size, and limited outcome data,” Dr. Kolarova said. She noted that embryonic organ formation is complete by 10 weeks gestation, by which time an unplanned pregnancy may not have been recognized yet. “In the subset of patients in the studies that were exposed during the first trimester, there was no increase in congenital malformations from a baseline risk of about 2%-3% in the general population, which is helpful for patient counseling.”
Counseling during the childbearing years
That kind of counseling is important yet absent for many people capable of pregnancy, suggests separate research also presented at the conference by Suma Shah, MD, an associate professor of neurology at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Dr. Shah gave 13-question surveys to female MS patients of all ages at her institution and presented an analysis of data from 38 completed surveys. Among those taking disease-modifying therapies, their medications included ocrelizumab, rituximab, teriflunomide, fingolimod, fumarates, interferons, natalizumab, and cladribine.
“MS disproportionately impacts women among 20 to 40 years, and that’s a really big part of their childbearing years when there are big decisions being made about whether they’re going to choose to grow family or not,” said Dr. Shah. The average age of those who completed the survey was 44. Dr. Shah noted that a lot of research has looked at the safety of older disease-modifying agents in pregnancy, but that information doesn’t appear to be filtering down to patients. “What I really wanted to look at is what do our parent patients understand about whether or not they can even think about pregnancy – and there’s a lot of work to be done.”
Just under a third of survey respondents said they did not have as many children as they would like, and a quarter said they were told they couldn’t have children if they had a diagnosis of MS.
“That was a little heartbreaking to hear because that’s not the truth,” Dr. Shah said. She said it’s necessary to have a more detailed conversation looking at tailored decisions for patients. “Both of those things – patients not being able to grow their family to the number that they desire, and not feeling like they can grow a family – I would think in 2023 we would have come farther than that, and there’s still a lot of room there to improve.”
She advised clinicians not to assume that MS patients know what their options are regarding family planning. “There’s still a lot of room for conversations,” she said. She also explicitly recommends discussing family planning and pregnancy planning with every patient, no matter their gender, early and often.
Cladribine shows no miscarriage, malformations
Dr. Kolarova noted that one of the studies, on cladribine, had a fairly robust sample size with its 180 pregnancy exposures. In that study, led by Kerstin Hellwig, MD, of Ruhr University in Bochum, Germany, data came from the global surveillance program MAPLE-MS, established to assess cladribine effects on pregnancy and infant outcomes. The researchers analyzed data from 76 mothers and 9 fathers who, at any time from 2017 to 2022, were taking cladribine during pregnancy or up to 6 months before pregnancy. Outcomes included live birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, elective abortion, ectopic pregnancy, and major congenital anomalies.
Just over half the mothers (53.9%) were exposed before pregnancy, and about a quarter (26.3%) were exposed during the first trimester. The timing was unknown for most of the other mothers (18.4%). Among the fathers, two-thirds (66.7%) were exposed before pregnancy, and one-third had unknown timing.
Among the 180 pregnancies in the maternal cohort, 42.2% had known outcomes. Nearly half the women (48.7%) taking cladribine had live births, 28.9% had elective abortions, and 21.1% had miscarriages. Only 9 of the 22 pregnancies in the paternal cohort had known outcomes, which included 88.9% live births and 11.1% miscarriages. None of the pregnancies resulted in stillbirth or in a live birth with major congenital anomalies.
”Robust conclusions cannot be made about the risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes with cladribine tablets, but no increase has been signaled thus far,” the researchers reported. ”It is necessary to counsel patients to prevent pregnancy and to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets intake and for at least 6 months after the last cladribine tablet intake in each treatment year.”
Emily Evans, MD, MBE, medical director at U.S. Neurology and Immunology in Rockland, Mass., speaking on behalf of the findings, said they were fairly encouraging.
“Of course, we don’t encourage patients to get pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets,” Dr. Evans said, but “within those individuals who have gotten pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine, or who have fathered a child within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets, we’re seeing overall encouraging outcomes. We’re specifically not seeing any differences in the rates of spontaneous abortions, and we’re not seeing any differences in the rates of congenital malformations.”
Ocrelizumab and ofatumumab: No infections so far
Current recommendations for ocrelizumab are to avoid pregnancy for 6 months after the last infusion and stop any breastfeeding during therapy. Yet these recommendations are only because of insufficient data rather than evidence of risk, according to Lana Zhovtis Ryerson, MD, of the NYU Multiple Sclerosis Comprehensive Care Center in New York. She and her colleagues identified all women of childbearing age who had received ocrelizumab within 1 year of pregnancy at their NYU institution. A retrospective chart review found 18 women, with an average age of 35, an average 11 years of an MS diagnosis, and an average 11 months taking ocrelizumab.
Among the 18 pregnancies, four women had a first trimester miscarriage, one had a second trimester miscarriage, and one had an abortion. The miscarriage rate could have been partly influenced by the older maternal population, the authors noted. Of the remaining 12 live births, one infant was premature at 34 weeks, and three infants stayed in NICU but were discharged within 2 weeks.
One patient experienced an MS relapse postpartum, despite receiving ocrelizumab within 45 days of delivery. Of the 16 women who agreed to participate in a Pregnancy Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) developed by the CDC, two women chose to breastfeed, and seven said their neurologist recommended against breastfeeding. None of the children’s pediatricians advised delaying vaccinations.
“This small sample observational study has not identified a potential additional risk with ocrelizumab for an adverse pregnancy outcome,” the authors concluded, but they added that ongoing studies, MINORE and SOPRANINO, can help guide future recommendations.
Though still limited, slightly more data exists on ofatumumab during pregnancy, including transient B-cell depletion and lymphopenia in infants whose mothers received anti-CD20 antibodies during pregnancy. However, research has found minimal IgG transfer in the first trimester, though it begins rising in the second trimester, and in utero ofatumumab exposure did not lead to any maternal toxicity or adverse prenatal or postnatal developmental effects in cynomolgus monkeys.
Riley Love, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neuroscience, and her colleagues both prospectively and retrospectively examined pregnancy and infant outcomes for up to 1 year post partum in women with MS who took ofatumumab during pregnancy or in the 6 months leading up to pregnancy. Their population included 104 prospective cases, most of which (84%) included first trimester exposure, and 14 retrospective cases. One in five of the prospective cases occurred during a clinical trial, while the remaining 80% occurred in postmarketing surveillance.
The prospectively followed women were an average 32 years old and were an average 7 weeks pregnant at the time of reporting. Among the 106 fetuses (including two twin pregnancies), only 30 outcomes had data at the cutoff time, including 16 live births, 9 abortions, and 5 miscarriages. None of the live births had congenital anomalies or serious infections. Another 30 pregnancies were lost to follow-up, and 46 were ongoing.
In the 14 retrospective cases, 57% of women were exposed in the first trimester, and 43% were exposed leading up to pregnancy. Half the cases occurred during clinical trials, and half in postmarketing surveillance. The women were an average 32 years old and were an average 10 weeks pregnant at reporting. Among the 14 pregnancies, nine were miscarriages, one was aborted, and four were born live with no congenital anomalies.
The authors did not draw any conclusions from the findings; they cited too little data and an ongoing study by Novartis to investigate ofatumumab in pregnancy.
“Therapies such as ofatumumab and ocrelizumab can lead to increased risk of infection due to transient B-cell depletion in neonates, but the two studies looking at this did not demonstrate increased infectious morbidity for these infants,” Dr. Kolarova said. “As with all poster presentations, I look forward to reading the full papers once they are published as they will often include a lot more detail about when during pregnancy medication exposure occurred and more detailed outcome data that was assessed.”
Ozanimod outcomes within general population’s ‘expected ranges’
The final study looked at outcomes of pregnancies in people taking ozanimod and in the partners of people taking ozanimod in a clinical trial setting. The findings show low rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies that the authors concluded were within the typical range expected for the general population.
“While pregnancy should be avoided when taking and for 3 months after stopping ozanimod to allow for drug elimination, there is no evidence to date of increased occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes with ozanimod exposure during early pregnancy,” wrote Anthony Krakovich, of Bristol Myers Squibb in Princeton, N.J., and his associates.
Ozanimod is an oral sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 and 5 modulator whose therapeutic mechanism is not fully understood “but may involve the reduction of lymphocyte migration into the central nervous system and intestine,” the authors wrote. S1P receptors are involved in vascular formation during embryogenesis, and animal studies in rats and rabbits have shown toxicity to the embryo and fetus from S1P receptor modulators, including death and malformations. S1P receptor modulator labels therefore note potential fetal risk and the need for effective contraception while taking the drug.
The study prospectively tracked clinical trial participants taking ozanimod as healthy volunteers or for relapsing MS, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease. Most of the participants who became pregnant (73%) had relapsing MS, while 18% had ulcerative colitis and 8% had Crohn’s disease.
In female patients receiving ozanimod, 78 pregnancies resulted in 12 miscarriages (including one twin), 15 abortions, and 42 live births, with 6 pregnancies ongoing at the time of reporting and no data available for the remaining 4 pregnancies. Among the 42 live births, 4 were premature but otherwise healthy, 1 had a duplex kidney, and the other 37 infants were typical with no apparent health concerns. These rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies were within the expected ranges for the general population, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also assessed pregnancy outcomes for partners of male participants taking ozanimod. The 29 partner pregnancies resulted in 21 live births and one miscarriage, with one pregnancy ongoing and no information available for the other seven. The live births included 5 premature infants (including twins), 13 typical and healthy infants, 1 with Hirschsprung’s disease, 1 with a congenital hydrocele, and 1 with a partial atrioventricular septal defect. Again, the researchers concluded that these rates were within the typical range for the general population and that “no teratogenicity was observed.”
“We often encourage patients with MS, regardless of disease activity and therapies, to seek preconception evaluations with Maternal-Fetal Medicine and their neurologists in order to make plans for pregnancy and postpartum care,” Dr. Kolarova said. “That being said, access to subspecialized health care is not available to all, and pregnancy prior to such consultation does occur. These studies provide novel information that we have not had access to in the past and can improve patient counseling regarding their risks and options.”
The study on cladribine was funded by Merck KGaA, at which two authors are employed. Dr. Hellwig reported consulting, speaker, and/or research support from Bayer, Biogen, Teva, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Schering Healthcare, Serono, and Merck, and one author is a former employee of EMD Serono. The study on ocrelizumab was funded by Genentech. Dr. Zhovtis Ryerson reported personal fees from Biogen, Genentech, and Novartis, and research grants from Biogen, Genentech, and CMSC. The other authors had no disclosures. The study on ofatumumab was funded by Novartis. Dr. Bove has received research funds from Biogen, Novartis, and Roche Genentech, and consulting fees from EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, and TG Therapeutics; she has an ownership interest in Global Consult MD. Five authors are Novartis employees. Her coauthors, including Dr. Hellwig, reported advisory, consulting, research, speaking, or traveling fees from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene BMS, EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, Lundbeck, Merck, Pfizer, Roche Genentech, Sanofi Genzyme, Schering Healthcare, Teva, TG Therapeutics, and Novartis. The study on ozanimod was funded by Bristol Myers Squibb. Dr. Krakovich and another author are employees and/or shareholders of Bristol Myers Squibb. The other authors reported consulting, speaking, advisory board, and/or research fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Arena, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelhei, Celgene, Celltrion, EXCEMED, Falk Benelux, Ferring, Forward Pharma, Genentech, Genzyme, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Pfizer, Prometheus Labs, Protagonist, Roche, Sanofi, Synthon, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kolarova had no disclosures. Dr. Shah has received research support from Biogen and VeraSci.
AURORA, COLO. – Several drugs for multiple sclerosis (MS) that are contraindicated during pregnancy nevertheless have not shown concerning safety signals in a series of small studies presented as posters at the annual meeting of the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers. The industry-sponsored research included an assessment of pregnancy and infant outcomes for cladribine, ocrelizumab, ofatumumab, and ozanimod, all of which are not recommended during pregnancy based primarily on minimal data that suggests, but does not confirm, possible teratogenicity.
“When these new medications hit the market, maternal-fetal medicine physicians and obstetricians are left with very scant data on how to counsel patients, and it’s often based on theory, case reports, or animal studies,” said Teodora Kolarova, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine physician at the University of Washington, Seattle, who was not involved in any of the research. “Although these sample sizes seem small, the population they are sampling from – patients with MS who take immunomodulators who then experience a pregnancy – is much smaller than all pregnant patients.”
Taken together, the findings suggest no increased risk of miscarriage or congenital malformation, compared with baseline risk, Dr. Kolarova said.
“As a whole, these studies are overall reassuring with, of course, some caveats, including timing of medication exposure, limited sample size, and limited outcome data,” Dr. Kolarova said. She noted that embryonic organ formation is complete by 10 weeks gestation, by which time an unplanned pregnancy may not have been recognized yet. “In the subset of patients in the studies that were exposed during the first trimester, there was no increase in congenital malformations from a baseline risk of about 2%-3% in the general population, which is helpful for patient counseling.”
Counseling during the childbearing years
That kind of counseling is important yet absent for many people capable of pregnancy, suggests separate research also presented at the conference by Suma Shah, MD, an associate professor of neurology at Duke University, Durham, N.C. Dr. Shah gave 13-question surveys to female MS patients of all ages at her institution and presented an analysis of data from 38 completed surveys. Among those taking disease-modifying therapies, their medications included ocrelizumab, rituximab, teriflunomide, fingolimod, fumarates, interferons, natalizumab, and cladribine.
“MS disproportionately impacts women among 20 to 40 years, and that’s a really big part of their childbearing years when there are big decisions being made about whether they’re going to choose to grow family or not,” said Dr. Shah. The average age of those who completed the survey was 44. Dr. Shah noted that a lot of research has looked at the safety of older disease-modifying agents in pregnancy, but that information doesn’t appear to be filtering down to patients. “What I really wanted to look at is what do our parent patients understand about whether or not they can even think about pregnancy – and there’s a lot of work to be done.”
Just under a third of survey respondents said they did not have as many children as they would like, and a quarter said they were told they couldn’t have children if they had a diagnosis of MS.
“That was a little heartbreaking to hear because that’s not the truth,” Dr. Shah said. She said it’s necessary to have a more detailed conversation looking at tailored decisions for patients. “Both of those things – patients not being able to grow their family to the number that they desire, and not feeling like they can grow a family – I would think in 2023 we would have come farther than that, and there’s still a lot of room there to improve.”
She advised clinicians not to assume that MS patients know what their options are regarding family planning. “There’s still a lot of room for conversations,” she said. She also explicitly recommends discussing family planning and pregnancy planning with every patient, no matter their gender, early and often.
Cladribine shows no miscarriage, malformations
Dr. Kolarova noted that one of the studies, on cladribine, had a fairly robust sample size with its 180 pregnancy exposures. In that study, led by Kerstin Hellwig, MD, of Ruhr University in Bochum, Germany, data came from the global surveillance program MAPLE-MS, established to assess cladribine effects on pregnancy and infant outcomes. The researchers analyzed data from 76 mothers and 9 fathers who, at any time from 2017 to 2022, were taking cladribine during pregnancy or up to 6 months before pregnancy. Outcomes included live birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, elective abortion, ectopic pregnancy, and major congenital anomalies.
Just over half the mothers (53.9%) were exposed before pregnancy, and about a quarter (26.3%) were exposed during the first trimester. The timing was unknown for most of the other mothers (18.4%). Among the fathers, two-thirds (66.7%) were exposed before pregnancy, and one-third had unknown timing.
Among the 180 pregnancies in the maternal cohort, 42.2% had known outcomes. Nearly half the women (48.7%) taking cladribine had live births, 28.9% had elective abortions, and 21.1% had miscarriages. Only 9 of the 22 pregnancies in the paternal cohort had known outcomes, which included 88.9% live births and 11.1% miscarriages. None of the pregnancies resulted in stillbirth or in a live birth with major congenital anomalies.
”Robust conclusions cannot be made about the risks of adverse pregnancy outcomes with cladribine tablets, but no increase has been signaled thus far,” the researchers reported. ”It is necessary to counsel patients to prevent pregnancy and to use effective contraception during cladribine tablets intake and for at least 6 months after the last cladribine tablet intake in each treatment year.”
Emily Evans, MD, MBE, medical director at U.S. Neurology and Immunology in Rockland, Mass., speaking on behalf of the findings, said they were fairly encouraging.
“Of course, we don’t encourage patients to get pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets,” Dr. Evans said, but “within those individuals who have gotten pregnant within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine, or who have fathered a child within 6 months of their last dose of cladribine tablets, we’re seeing overall encouraging outcomes. We’re specifically not seeing any differences in the rates of spontaneous abortions, and we’re not seeing any differences in the rates of congenital malformations.”
Ocrelizumab and ofatumumab: No infections so far
Current recommendations for ocrelizumab are to avoid pregnancy for 6 months after the last infusion and stop any breastfeeding during therapy. Yet these recommendations are only because of insufficient data rather than evidence of risk, according to Lana Zhovtis Ryerson, MD, of the NYU Multiple Sclerosis Comprehensive Care Center in New York. She and her colleagues identified all women of childbearing age who had received ocrelizumab within 1 year of pregnancy at their NYU institution. A retrospective chart review found 18 women, with an average age of 35, an average 11 years of an MS diagnosis, and an average 11 months taking ocrelizumab.
Among the 18 pregnancies, four women had a first trimester miscarriage, one had a second trimester miscarriage, and one had an abortion. The miscarriage rate could have been partly influenced by the older maternal population, the authors noted. Of the remaining 12 live births, one infant was premature at 34 weeks, and three infants stayed in NICU but were discharged within 2 weeks.
One patient experienced an MS relapse postpartum, despite receiving ocrelizumab within 45 days of delivery. Of the 16 women who agreed to participate in a Pregnancy Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) developed by the CDC, two women chose to breastfeed, and seven said their neurologist recommended against breastfeeding. None of the children’s pediatricians advised delaying vaccinations.
“This small sample observational study has not identified a potential additional risk with ocrelizumab for an adverse pregnancy outcome,” the authors concluded, but they added that ongoing studies, MINORE and SOPRANINO, can help guide future recommendations.
Though still limited, slightly more data exists on ofatumumab during pregnancy, including transient B-cell depletion and lymphopenia in infants whose mothers received anti-CD20 antibodies during pregnancy. However, research has found minimal IgG transfer in the first trimester, though it begins rising in the second trimester, and in utero ofatumumab exposure did not lead to any maternal toxicity or adverse prenatal or postnatal developmental effects in cynomolgus monkeys.
Riley Love, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, Weill Institute for Neuroscience, and her colleagues both prospectively and retrospectively examined pregnancy and infant outcomes for up to 1 year post partum in women with MS who took ofatumumab during pregnancy or in the 6 months leading up to pregnancy. Their population included 104 prospective cases, most of which (84%) included first trimester exposure, and 14 retrospective cases. One in five of the prospective cases occurred during a clinical trial, while the remaining 80% occurred in postmarketing surveillance.
The prospectively followed women were an average 32 years old and were an average 7 weeks pregnant at the time of reporting. Among the 106 fetuses (including two twin pregnancies), only 30 outcomes had data at the cutoff time, including 16 live births, 9 abortions, and 5 miscarriages. None of the live births had congenital anomalies or serious infections. Another 30 pregnancies were lost to follow-up, and 46 were ongoing.
In the 14 retrospective cases, 57% of women were exposed in the first trimester, and 43% were exposed leading up to pregnancy. Half the cases occurred during clinical trials, and half in postmarketing surveillance. The women were an average 32 years old and were an average 10 weeks pregnant at reporting. Among the 14 pregnancies, nine were miscarriages, one was aborted, and four were born live with no congenital anomalies.
The authors did not draw any conclusions from the findings; they cited too little data and an ongoing study by Novartis to investigate ofatumumab in pregnancy.
“Therapies such as ofatumumab and ocrelizumab can lead to increased risk of infection due to transient B-cell depletion in neonates, but the two studies looking at this did not demonstrate increased infectious morbidity for these infants,” Dr. Kolarova said. “As with all poster presentations, I look forward to reading the full papers once they are published as they will often include a lot more detail about when during pregnancy medication exposure occurred and more detailed outcome data that was assessed.”
Ozanimod outcomes within general population’s ‘expected ranges’
The final study looked at outcomes of pregnancies in people taking ozanimod and in the partners of people taking ozanimod in a clinical trial setting. The findings show low rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies that the authors concluded were within the typical range expected for the general population.
“While pregnancy should be avoided when taking and for 3 months after stopping ozanimod to allow for drug elimination, there is no evidence to date of increased occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes with ozanimod exposure during early pregnancy,” wrote Anthony Krakovich, of Bristol Myers Squibb in Princeton, N.J., and his associates.
Ozanimod is an oral sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor 1 and 5 modulator whose therapeutic mechanism is not fully understood “but may involve the reduction of lymphocyte migration into the central nervous system and intestine,” the authors wrote. S1P receptors are involved in vascular formation during embryogenesis, and animal studies in rats and rabbits have shown toxicity to the embryo and fetus from S1P receptor modulators, including death and malformations. S1P receptor modulator labels therefore note potential fetal risk and the need for effective contraception while taking the drug.
The study prospectively tracked clinical trial participants taking ozanimod as healthy volunteers or for relapsing MS, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn’s disease. Most of the participants who became pregnant (73%) had relapsing MS, while 18% had ulcerative colitis and 8% had Crohn’s disease.
In female patients receiving ozanimod, 78 pregnancies resulted in 12 miscarriages (including one twin), 15 abortions, and 42 live births, with 6 pregnancies ongoing at the time of reporting and no data available for the remaining 4 pregnancies. Among the 42 live births, 4 were premature but otherwise healthy, 1 had a duplex kidney, and the other 37 infants were typical with no apparent health concerns. These rates of miscarriage, preterm birth, and congenital anomalies were within the expected ranges for the general population, the researchers wrote.
The researchers also assessed pregnancy outcomes for partners of male participants taking ozanimod. The 29 partner pregnancies resulted in 21 live births and one miscarriage, with one pregnancy ongoing and no information available for the other seven. The live births included 5 premature infants (including twins), 13 typical and healthy infants, 1 with Hirschsprung’s disease, 1 with a congenital hydrocele, and 1 with a partial atrioventricular septal defect. Again, the researchers concluded that these rates were within the typical range for the general population and that “no teratogenicity was observed.”
“We often encourage patients with MS, regardless of disease activity and therapies, to seek preconception evaluations with Maternal-Fetal Medicine and their neurologists in order to make plans for pregnancy and postpartum care,” Dr. Kolarova said. “That being said, access to subspecialized health care is not available to all, and pregnancy prior to such consultation does occur. These studies provide novel information that we have not had access to in the past and can improve patient counseling regarding their risks and options.”
The study on cladribine was funded by Merck KGaA, at which two authors are employed. Dr. Hellwig reported consulting, speaker, and/or research support from Bayer, Biogen, Teva, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Schering Healthcare, Serono, and Merck, and one author is a former employee of EMD Serono. The study on ocrelizumab was funded by Genentech. Dr. Zhovtis Ryerson reported personal fees from Biogen, Genentech, and Novartis, and research grants from Biogen, Genentech, and CMSC. The other authors had no disclosures. The study on ofatumumab was funded by Novartis. Dr. Bove has received research funds from Biogen, Novartis, and Roche Genentech, and consulting fees from EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, and TG Therapeutics; she has an ownership interest in Global Consult MD. Five authors are Novartis employees. Her coauthors, including Dr. Hellwig, reported advisory, consulting, research, speaking, or traveling fees from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene BMS, EMD Serono, Horizon, Janssen, Lundbeck, Merck, Pfizer, Roche Genentech, Sanofi Genzyme, Schering Healthcare, Teva, TG Therapeutics, and Novartis. The study on ozanimod was funded by Bristol Myers Squibb. Dr. Krakovich and another author are employees and/or shareholders of Bristol Myers Squibb. The other authors reported consulting, speaking, advisory board, and/or research fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Arena, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelhei, Celgene, Celltrion, EXCEMED, Falk Benelux, Ferring, Forward Pharma, Genentech, Genzyme, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Pfizer, Prometheus Labs, Protagonist, Roche, Sanofi, Synthon, Takeda, and Teva. Dr. Kolarova had no disclosures. Dr. Shah has received research support from Biogen and VeraSci.
FROM CMSC 2023
Underprescribed menopause relief: Women suffer needlessly
The result: Countless women grapple with the physical and emotional toll of this life transition.
These shortcomings have led to an influx of doctors moving from traditional practice to virtual startups that focus on women’s health issues, treating patients who come to them desperate and frustrated after years of unresolved issues.
The solution is often so simple it is almost maddening, specialists say: vaginal creams containing low-dose estrogen which can address the symptoms of menopause, from vaginal dryness to recurrent urinary tract infections.
“Hands down, this is one of the most meaningful interventions I’ve ever offered to a patient and yet it is underutilized,” said Ashley Winter, MD, chief medical officer and urologist at Odela Health, a digital women’s health clinic. “A lot of companies are blossoming in this menopause space because it is underserved by traditional health care – your gynecologist typically deals with reproduction, and typically when women are done with child-bearing, they’re kind of discharged from the care of their gynecologist.”
More than 1 million women in the United States go through menopause each year. According to a 2022 survey, 4 in 10 women report menopause symptoms that have been disruptive enough to interfere with their work performance on at least a weekly basis.
And yet, many women are not getting appropriate treatment.
Partially to blame is the harmful legacy of faulty data, doctors say. The early results of the federally funded Women’s Health Initiative, released in 2002, showed that hormone therapy (HT) led to increased risk for heart attacks, strokes, and breast cancer. But further analysis showed the opposite: Hormonal therapies have a helpful effect on cardiovascular and bone health and generally reduce risk of death in younger women or those in the early postmenopausal period.
Hormone therapy delivers estrogen, sometimes with progesterone, to the body through gels, creams, patches, pills, suppositories, or a device fitted inside the uterus. Systemic HT sends hormones into the bloodstream, while local HT – like vaginal estrogen cream – specifically treats vaginal symptoms of menopause.
Myths about the health risks linked to systemic and topical HT have long been debunked, and research on topical HT in particular shows it poses no risk for cancer or other chronic diseases.
Yet while 2 decades have passed since the misinformation first started to spread, people remain woefully uninformed about hormone treatments.
The FDA still requires that estrogen products carry a black-box warning on the early data, even though it has since been proven false.
“This is one of the most damaging PR misadventures of modern medicine in my opinion,” Dr. Winter said. “It has literally killed women, and it’s made them miserable.”
The public has a glaring lack of knowledge about menopause management, said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director for the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health.
Treating with low-dose estrogen isn’t a radical approach – in fact, it is the standard of care for women experiencing many menopause symptoms, Dr. Faubion said. But the topic does have nuance, and some people get lost in the specifics.
“I don’t think there’s a lot of knowledge on the risk-benefits of hormone therapy in general,” Dr. Faubion said. “New information comes out so frequently it’s difficult to keep track of. The answer is complicated and depends on dose, duration of treatment, what formulation you’re on. It’s difficult for a lot of people to understand.”
But Dr. Winter said the lack of public knowledge reflects a bigger problem: Knowledge gaps exist among doctors, too, stemming from insufficient training on menopause-related issues.
During her 6-year urology residency, she never learned the role of vaginal estrogen on urinary problems, Dr. Winter said. Only during a 1-year fellowship on sexual dysfunction did she hear about the treatment.
“Despite dealing with urinary issues, incontinence, blood in the urine – training to manage all those concerns – the role of local hormones in the vagina for managing all them was never taught, never discussed,” Dr. Winter said. “I never prescribed any of it.”
A year ago, Dr. Winter left her job at Kaiser Permanente to join Odela. After years of prescribing medications for overactive bladder with little to no results, she said, she now uses the knowledge she gained during her fellowship by helping women who have spent years battling debilitating symptoms.
Urologists are not the only clinicians who lack appropriate training. Obstetrics and gynecology residencies offer little knowledge on menopause treatments, said Ghazaleh Moayedi, DO, an ob.gyn. and complex family planning specialist for Texas-based Pegasus Health Justice Center.
The problem is partly a systems-based one, she said. Training programs often direct patients who are uninsured, or covered through public insurance, to medical residents. Patients who qualify for Medicaid or Medicare are often either pregnant or over 65, Dr. Moayedi said, so women actively going through the transition can slip through the cracks.
“What that means in a state like Texas where I’m based, where it is difficult to qualify for Medicaid, is that the people we see who do qualify are pregnant,” she said. “And you’re not on Medicare until you’re 65. So most ob.gyn. residents don’t graduate with expansive experience in menopause.”
According to Medicaid.gov, 80% of the national population covered by Medicaid is age 45 and younger.
When doctors have proper training and prescribe local hormones, patients don’t always follow the treatment plan, said Andrea Rapkin, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
That failure to follow treatment is yet another example of remaining doubts from the misinformation spread through early research, Dr. Rapkin said.
“I’ll prescribe an estrogen product, and I’ll find out they didn’t take it even though I’ll reassure them,” she said. “I do think there are some lingering concerns, but I’m glad to see there is a growing interest in vaginal hormones.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The result: Countless women grapple with the physical and emotional toll of this life transition.
These shortcomings have led to an influx of doctors moving from traditional practice to virtual startups that focus on women’s health issues, treating patients who come to them desperate and frustrated after years of unresolved issues.
The solution is often so simple it is almost maddening, specialists say: vaginal creams containing low-dose estrogen which can address the symptoms of menopause, from vaginal dryness to recurrent urinary tract infections.
“Hands down, this is one of the most meaningful interventions I’ve ever offered to a patient and yet it is underutilized,” said Ashley Winter, MD, chief medical officer and urologist at Odela Health, a digital women’s health clinic. “A lot of companies are blossoming in this menopause space because it is underserved by traditional health care – your gynecologist typically deals with reproduction, and typically when women are done with child-bearing, they’re kind of discharged from the care of their gynecologist.”
More than 1 million women in the United States go through menopause each year. According to a 2022 survey, 4 in 10 women report menopause symptoms that have been disruptive enough to interfere with their work performance on at least a weekly basis.
And yet, many women are not getting appropriate treatment.
Partially to blame is the harmful legacy of faulty data, doctors say. The early results of the federally funded Women’s Health Initiative, released in 2002, showed that hormone therapy (HT) led to increased risk for heart attacks, strokes, and breast cancer. But further analysis showed the opposite: Hormonal therapies have a helpful effect on cardiovascular and bone health and generally reduce risk of death in younger women or those in the early postmenopausal period.
Hormone therapy delivers estrogen, sometimes with progesterone, to the body through gels, creams, patches, pills, suppositories, or a device fitted inside the uterus. Systemic HT sends hormones into the bloodstream, while local HT – like vaginal estrogen cream – specifically treats vaginal symptoms of menopause.
Myths about the health risks linked to systemic and topical HT have long been debunked, and research on topical HT in particular shows it poses no risk for cancer or other chronic diseases.
Yet while 2 decades have passed since the misinformation first started to spread, people remain woefully uninformed about hormone treatments.
The FDA still requires that estrogen products carry a black-box warning on the early data, even though it has since been proven false.
“This is one of the most damaging PR misadventures of modern medicine in my opinion,” Dr. Winter said. “It has literally killed women, and it’s made them miserable.”
The public has a glaring lack of knowledge about menopause management, said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director for the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health.
Treating with low-dose estrogen isn’t a radical approach – in fact, it is the standard of care for women experiencing many menopause symptoms, Dr. Faubion said. But the topic does have nuance, and some people get lost in the specifics.
“I don’t think there’s a lot of knowledge on the risk-benefits of hormone therapy in general,” Dr. Faubion said. “New information comes out so frequently it’s difficult to keep track of. The answer is complicated and depends on dose, duration of treatment, what formulation you’re on. It’s difficult for a lot of people to understand.”
But Dr. Winter said the lack of public knowledge reflects a bigger problem: Knowledge gaps exist among doctors, too, stemming from insufficient training on menopause-related issues.
During her 6-year urology residency, she never learned the role of vaginal estrogen on urinary problems, Dr. Winter said. Only during a 1-year fellowship on sexual dysfunction did she hear about the treatment.
“Despite dealing with urinary issues, incontinence, blood in the urine – training to manage all those concerns – the role of local hormones in the vagina for managing all them was never taught, never discussed,” Dr. Winter said. “I never prescribed any of it.”
A year ago, Dr. Winter left her job at Kaiser Permanente to join Odela. After years of prescribing medications for overactive bladder with little to no results, she said, she now uses the knowledge she gained during her fellowship by helping women who have spent years battling debilitating symptoms.
Urologists are not the only clinicians who lack appropriate training. Obstetrics and gynecology residencies offer little knowledge on menopause treatments, said Ghazaleh Moayedi, DO, an ob.gyn. and complex family planning specialist for Texas-based Pegasus Health Justice Center.
The problem is partly a systems-based one, she said. Training programs often direct patients who are uninsured, or covered through public insurance, to medical residents. Patients who qualify for Medicaid or Medicare are often either pregnant or over 65, Dr. Moayedi said, so women actively going through the transition can slip through the cracks.
“What that means in a state like Texas where I’m based, where it is difficult to qualify for Medicaid, is that the people we see who do qualify are pregnant,” she said. “And you’re not on Medicare until you’re 65. So most ob.gyn. residents don’t graduate with expansive experience in menopause.”
According to Medicaid.gov, 80% of the national population covered by Medicaid is age 45 and younger.
When doctors have proper training and prescribe local hormones, patients don’t always follow the treatment plan, said Andrea Rapkin, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
That failure to follow treatment is yet another example of remaining doubts from the misinformation spread through early research, Dr. Rapkin said.
“I’ll prescribe an estrogen product, and I’ll find out they didn’t take it even though I’ll reassure them,” she said. “I do think there are some lingering concerns, but I’m glad to see there is a growing interest in vaginal hormones.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The result: Countless women grapple with the physical and emotional toll of this life transition.
These shortcomings have led to an influx of doctors moving from traditional practice to virtual startups that focus on women’s health issues, treating patients who come to them desperate and frustrated after years of unresolved issues.
The solution is often so simple it is almost maddening, specialists say: vaginal creams containing low-dose estrogen which can address the symptoms of menopause, from vaginal dryness to recurrent urinary tract infections.
“Hands down, this is one of the most meaningful interventions I’ve ever offered to a patient and yet it is underutilized,” said Ashley Winter, MD, chief medical officer and urologist at Odela Health, a digital women’s health clinic. “A lot of companies are blossoming in this menopause space because it is underserved by traditional health care – your gynecologist typically deals with reproduction, and typically when women are done with child-bearing, they’re kind of discharged from the care of their gynecologist.”
More than 1 million women in the United States go through menopause each year. According to a 2022 survey, 4 in 10 women report menopause symptoms that have been disruptive enough to interfere with their work performance on at least a weekly basis.
And yet, many women are not getting appropriate treatment.
Partially to blame is the harmful legacy of faulty data, doctors say. The early results of the federally funded Women’s Health Initiative, released in 2002, showed that hormone therapy (HT) led to increased risk for heart attacks, strokes, and breast cancer. But further analysis showed the opposite: Hormonal therapies have a helpful effect on cardiovascular and bone health and generally reduce risk of death in younger women or those in the early postmenopausal period.
Hormone therapy delivers estrogen, sometimes with progesterone, to the body through gels, creams, patches, pills, suppositories, or a device fitted inside the uterus. Systemic HT sends hormones into the bloodstream, while local HT – like vaginal estrogen cream – specifically treats vaginal symptoms of menopause.
Myths about the health risks linked to systemic and topical HT have long been debunked, and research on topical HT in particular shows it poses no risk for cancer or other chronic diseases.
Yet while 2 decades have passed since the misinformation first started to spread, people remain woefully uninformed about hormone treatments.
The FDA still requires that estrogen products carry a black-box warning on the early data, even though it has since been proven false.
“This is one of the most damaging PR misadventures of modern medicine in my opinion,” Dr. Winter said. “It has literally killed women, and it’s made them miserable.”
The public has a glaring lack of knowledge about menopause management, said Stephanie Faubion, MD, medical director for the North American Menopause Society and director of Mayo Clinic’s Center for Women’s Health.
Treating with low-dose estrogen isn’t a radical approach – in fact, it is the standard of care for women experiencing many menopause symptoms, Dr. Faubion said. But the topic does have nuance, and some people get lost in the specifics.
“I don’t think there’s a lot of knowledge on the risk-benefits of hormone therapy in general,” Dr. Faubion said. “New information comes out so frequently it’s difficult to keep track of. The answer is complicated and depends on dose, duration of treatment, what formulation you’re on. It’s difficult for a lot of people to understand.”
But Dr. Winter said the lack of public knowledge reflects a bigger problem: Knowledge gaps exist among doctors, too, stemming from insufficient training on menopause-related issues.
During her 6-year urology residency, she never learned the role of vaginal estrogen on urinary problems, Dr. Winter said. Only during a 1-year fellowship on sexual dysfunction did she hear about the treatment.
“Despite dealing with urinary issues, incontinence, blood in the urine – training to manage all those concerns – the role of local hormones in the vagina for managing all them was never taught, never discussed,” Dr. Winter said. “I never prescribed any of it.”
A year ago, Dr. Winter left her job at Kaiser Permanente to join Odela. After years of prescribing medications for overactive bladder with little to no results, she said, she now uses the knowledge she gained during her fellowship by helping women who have spent years battling debilitating symptoms.
Urologists are not the only clinicians who lack appropriate training. Obstetrics and gynecology residencies offer little knowledge on menopause treatments, said Ghazaleh Moayedi, DO, an ob.gyn. and complex family planning specialist for Texas-based Pegasus Health Justice Center.
The problem is partly a systems-based one, she said. Training programs often direct patients who are uninsured, or covered through public insurance, to medical residents. Patients who qualify for Medicaid or Medicare are often either pregnant or over 65, Dr. Moayedi said, so women actively going through the transition can slip through the cracks.
“What that means in a state like Texas where I’m based, where it is difficult to qualify for Medicaid, is that the people we see who do qualify are pregnant,” she said. “And you’re not on Medicare until you’re 65. So most ob.gyn. residents don’t graduate with expansive experience in menopause.”
According to Medicaid.gov, 80% of the national population covered by Medicaid is age 45 and younger.
When doctors have proper training and prescribe local hormones, patients don’t always follow the treatment plan, said Andrea Rapkin, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
That failure to follow treatment is yet another example of remaining doubts from the misinformation spread through early research, Dr. Rapkin said.
“I’ll prescribe an estrogen product, and I’ll find out they didn’t take it even though I’ll reassure them,” she said. “I do think there are some lingering concerns, but I’m glad to see there is a growing interest in vaginal hormones.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Five ways to avert a malpractice lawsuit with better EHR techniques
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Domestic violence in health care is real and underreported
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.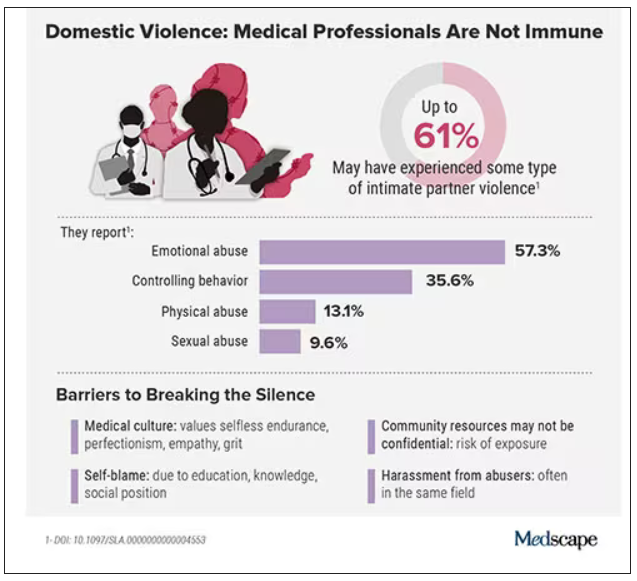
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in five doctors with long COVID can no longer work: Survey
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resident creates AI alternative to U.S. News med school ranking
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Q&A: What to know about the new BA 2.86 COVID variant
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Mammography breast density reporting: What it means for clinicians
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.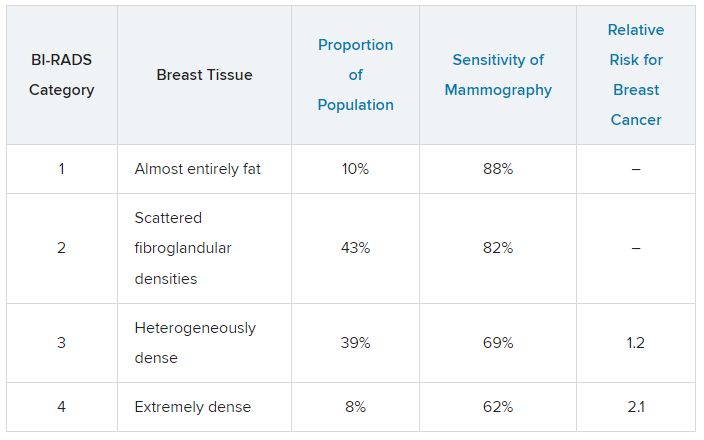
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today, I’m going to talk about the 2023 Food and Drug Administration regulation that requires breast density to be reported on all mammogram results nationwide, and for that report to go to both clinicians and patients. Previously this was the rule in some states, but not in others. This is important because 40%-50% of women have dense breasts. I’m going to discuss what that means for you, and for our patients.
First
Breast density describes the appearance of the breast on mammography. Appearance varies on the basis of breast tissue composition, with fibroglandular tissue being more dense than fatty tissue. Breast density is important because it relates to both the risk for cancer and the ability of mammography to detect cancer.
Breast density is defined and classified according to the American College of Radiology’s BI-RADS four-category scale. Categories 1 and 2 refer to breast tissue that is not dense, accounting for about 50% of the population. Categories 3 and 4 describe heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue, which occur in approximately 40% and 50% of women, respectively. When speaking about dense breast tissue readings on mammography, we are referring to categories 3 and 4.
Women with dense breast tissue have an increased risk of developing breast cancer and are less likely to have early breast cancer detected on mammography.
Let’s go over the details by category:
For women in categories 1 and 2 (considered not dense breast tissue), the sensitivity of mammography for detecting early breast cancer is 80%-90%. In categories 3 and 4, the sensitivity of mammography drops to 60%-70%.
Compared with women with average breast density, the risk of developing breast cancer is 20% higher in women with BI-RADS category 3 breasts, and more than twice as high (relative risk, 2.1) in those with BI-RADS category 4 breasts. Thus, the risk of developing breast cancer is higher, but the sensitivity of the test is lower.
The clinical question is, what should we do about this? For women who have a normal mammogram with dense breasts, should follow-up testing be done, and if so, what test? The main follow-up testing options are either ultrasound or MRI, usually ultrasound. Additional testing will detect additional cancers that were not picked up on the initial mammogram and will also lead to additional biopsies for false-positive tests from the additional testing.
An American College of Gynecology and Obstetrics practice advisory nicely summarizes the evidence and clarifies that this decision is made in the context of a lack of published evidence demonstrating improved outcomes, specifically no reduction in breast cancer mortality, with supplemental testing. The official ACOG stance is that they “do not recommend routine use of alternative or adjunctive tests to screening mammography in women with dense breasts who are asymptomatic and have no additional risk factors.”
This is an area where it is important to understand the data. We are all going to be getting test results back that indicate level of breast density, and those test results will also be sent to our patients, so we are going to be asked about this by interested patients. Should this be something that we talk to patients about, utilizing shared decision-making to decide about whether follow-up testing is necessary in women with dense breasts? That is something each clinician will need to decide, and knowing the data is a critically important step in that decision.
Neil Skolnik, MD, is a professor, department of family medicine, at Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pennsylvania) Jefferson Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.





