User login
Boys may carry the weight, or overweight, of adults’ infertility
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
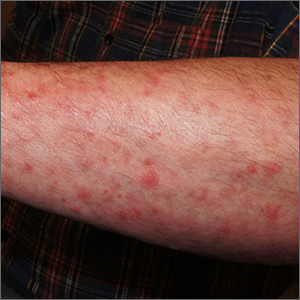
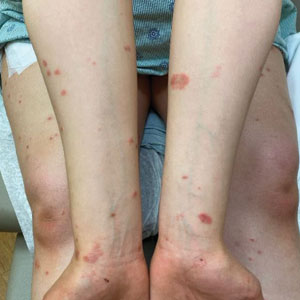
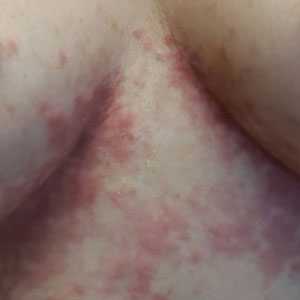
Itchy pustules over hair follicles
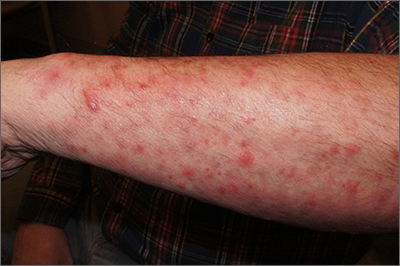
A potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of pus and dry superficial skin taken from 1 of the pustules revealed multiple hyphae and confirmed a diagnosis of nodular granulomatous perifolliculitis, also called Majocchi granuloma.
Majocchi granuloma is a reactive process of inflammation caused by infection of the follicular unit(s) by a dermatophyte—most often the same Trichophyton species responsible for more superficial tinea. On exam, there may be a solitary papule, pustule, or nodule. More often, there are multiple papules and pustules grouped within an annular plaque in hair-bearing areas on the head, trunk, or extremities. Majocchi granuloma can occur in patients who are healthy and those who are immunosuppressed.1 It can also occur when a topical steroid is applied to unsuspected tinea, as occurred here. In this case, the patient was accustomed to having multiple skin plaques of psoriasis and assumed this was a stubborn manifestation of that.
Because the infection penetrates deeper than most topical therapies can effectively reach at adequate concentrations, systemic medications are the treatments of choice. Terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are all effective options but need to be used for several weeks to be effective.
This patient received terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks and the pustules cleared completely. He continued with his other psoriasis medications throughout his treatment.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. İlkit M, Durdu M, Karakaş M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2012.669503

A potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of pus and dry superficial skin taken from 1 of the pustules revealed multiple hyphae and confirmed a diagnosis of nodular granulomatous perifolliculitis, also called Majocchi granuloma.
Majocchi granuloma is a reactive process of inflammation caused by infection of the follicular unit(s) by a dermatophyte—most often the same Trichophyton species responsible for more superficial tinea. On exam, there may be a solitary papule, pustule, or nodule. More often, there are multiple papules and pustules grouped within an annular plaque in hair-bearing areas on the head, trunk, or extremities. Majocchi granuloma can occur in patients who are healthy and those who are immunosuppressed.1 It can also occur when a topical steroid is applied to unsuspected tinea, as occurred here. In this case, the patient was accustomed to having multiple skin plaques of psoriasis and assumed this was a stubborn manifestation of that.
Because the infection penetrates deeper than most topical therapies can effectively reach at adequate concentrations, systemic medications are the treatments of choice. Terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are all effective options but need to be used for several weeks to be effective.
This patient received terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks and the pustules cleared completely. He continued with his other psoriasis medications throughout his treatment.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.

A potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of pus and dry superficial skin taken from 1 of the pustules revealed multiple hyphae and confirmed a diagnosis of nodular granulomatous perifolliculitis, also called Majocchi granuloma.
Majocchi granuloma is a reactive process of inflammation caused by infection of the follicular unit(s) by a dermatophyte—most often the same Trichophyton species responsible for more superficial tinea. On exam, there may be a solitary papule, pustule, or nodule. More often, there are multiple papules and pustules grouped within an annular plaque in hair-bearing areas on the head, trunk, or extremities. Majocchi granuloma can occur in patients who are healthy and those who are immunosuppressed.1 It can also occur when a topical steroid is applied to unsuspected tinea, as occurred here. In this case, the patient was accustomed to having multiple skin plaques of psoriasis and assumed this was a stubborn manifestation of that.
Because the infection penetrates deeper than most topical therapies can effectively reach at adequate concentrations, systemic medications are the treatments of choice. Terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are all effective options but need to be used for several weeks to be effective.
This patient received terbinafine 250 mg/d for 6 weeks and the pustules cleared completely. He continued with his other psoriasis medications throughout his treatment.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained). Dr. Karnes is the medical director of MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME.
1. İlkit M, Durdu M, Karakaş M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2012.669503
1. İlkit M, Durdu M, Karakaş M. Majocchi’s granuloma: a symptom complex caused by fungal pathogens. Med Mycol. 2012;50:449-457. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2012.669503
Mental health promotion
May is Mental Health Awareness Month, providing us a chance to go beyond discussing the screening, diagnosis, and evidence-based treatments for the mental illnesses of youth. The World Health Organization defines good mental health as “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her own community.” While the science of mental health promotion and disease prevention in childhood and adolescence is relatively young, there are several discrete domains in which you can follow and support your patient’s developing mental health. This begins with the well-being of new parents, and then moves into how parents are helping their children to develop skills to manage their basic daily needs and impulses, their thoughts and feelings, their stresses and their relationships. With a little support from you, parents can confidently help their children develop the foundations for good mental health.
First year of life: Parental mental health
Perhaps the strongest risk factor for serious mental illness in childhood and adulthood is parental neglect during the first year of life, and neglect in the first several months of life is the most commonly reported form of child abuse. Infant neglect is associated with parental depression (and other mental illnesses), parental substance use, and a parent’s own experience of childhood abuse or neglect. Neglect is more common with teenaged parents and parents living in poverty. Pediatricians are uniquely connected to families during the first year of a child’s life. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening new mothers for depression at 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month infant check-ups with the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Screen. Even without a positive screen, new parents may need the fortifications of extra community support to adapt to the changes parenthood brings.
At checkups, ask (both) parents how they are managing the stresses of a new baby. Are they getting restful sleep? Do they have social supports? Are they connected to a community (friends, extended family, faith) or isolated? Are they developing confidence as parents or feeling overwhelmed? Simple guidance, such as “sleep when the baby sleeps” and reassurance that taking good care of themselves is taking good care of the baby is always helpful. Sometimes you will need to refer for treatment or to community supports. Have your list of online and in-person resources at the ready to provide parents with these prescriptions. Supporting parental mental health and adjustment in the first year of life is possibly the most important building block for their child’s future mental health.
Toddlers and up: Emotional literacy
Emotional literacy (sometimes called “emotional intelligence”) is the capacity to recognize, identify, and manage feelings in oneself and in others. This skill begins to develop in infancy when parents respond to their baby’s cries with attunement, feeding or changing them if needed, and at other times simply reflecting their feelings and soothing them with movement, singing, or quiet talking. As children grow, so does their range of feelings, and their (cognitive) capacity to identify and manage them. Parents support this development by being available whenever their young children experience strong emotions, calmly listening, and acknowledging their discomfort. Parents can offer words for describing those feelings, and even be curious with their young children where in their bodies they are feeling them, how they can stay patient while the feeling passes or things they might be able to do to feel better. Parents may want to remove their child’s distress, but staying calm, curious, and present while helping their child to manage it will build their child’s emotional health. Parents can nurture this development in a less intense way by reading books about feelings together and noticing and identifying feelings in other children or in cartoon characters.
School-age children: Adding mindfulness
While a child’s cognitive development unfolds naturally, school-age children can cultivate awareness of their thoughts. This becomes possible after awareness of feelings and parents can help their older children consider whether something they are experiencing is a thought, a feeling, or a fact. They do so in the same way they helped their child develop emotional literacy: By responding with calm, curiosity, and confidence every time their child comes to them in distress (especially mild distress, like boredom!) or with a challenge or a question. With a difficult situation, parents start by helping their child to identify thoughts and feelings before impulsively acting on them. Parents can help children identify what’s in their control, try different approaches, and be flexible if their first efforts don’t work. Children need to learn that failing at things is how we learn and grow. Just like learning to ride a bike, it builds their frustration tolerance, their knowledge that they can do difficult things, and that distress subsides. These are critical building blocks for adolescence, when the challenges become greater and they manage them more independently.
Learning “mindfulness” (a practice that cultivates nonjudgmental awareness of one’s own thoughts, feelings, and sensations) can help children (and parents) to cultivate quiet self-awareness outside of moments of difficulty. “Stop, Breathe, and Think” and “Mindful gNATs” are two free apps that are recommended by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry for children (and their parents) to use to practice this awareness of thoughts and feelings.
Early and later adolescence: Stress management skills
Building on this awareness of thoughts and emotions, adolescents develop adaptive coping skills by facing challenges with the support of their parents nearby. Parents should still be ready to respond to charged emotional moments with calm and curiosity, validating their child’s distress while helping them to consider healthy responses. Helping their teenager to describe their experience, differentiating feelings from thoughts (and facts), and considering different choices within their control is foundational to resilience in adulthood. Parents also help their teenagers by reminding them of the need for good self-care (sleep, exercise, nutrition), nourishing social relationships, and protecting time for rest and recharging activities. Sometimes, parents will think with their teenager about why they are engaged in an activity that is stressful, whether it is authentically important to them, and why. Adolescents should be deepening their sense of identity, interests, talents, and even values, and stressful moments are rich opportunities to do so, with the support of caring adults. Without intentionally building these skills, adolescents will be more prone to managing stress with avoidance or unhealthy coping, such as excessive eating, video gaming, drugs, or alcohol.
Infancy and up: Behavioral healthy habits (sleep, physical activity, nutrition, and screen time)
Healthy habits sound simple, but establishing them is not always easy. The idea of a habit is that it makes managing something challenging or important more automatic, and thus easier and more reliable. Many of the same habits that promote physical health in adulthood also promote mental health: adequate, restful sleep; daily physical activity; a nutritious diet and a healthy relationship with food; and managing screen time in a developmentally appropriate way. Infants depend entirely on their parents for regulation of these behaviors. As their children grow, parents will adapt these routines so that their children are gradually regulating these needs and activities more independently. In each of these areas, children need clear expectations and routines, consistent consequences and positive feedback, and the modeling and patient support of their parents. Educate parents about what good sleep hygiene looks like at each age. Discuss ways to support regular physical activity, especially as a family. Ask the parents about nutrition, including how they manage picky eating; how many family meals they enjoy together; and whether food is ever used to manage boredom or distress. Finally, talk with parents about a developmentally appropriate approach to rules and expectations around screen time and the importance of using family-based rules. Establishing expectations and routines during early childhood means children learn how good it feels to have restful sleep, regular exercise, and happy, healthy family meals. In adolescence, parents can then focus on helping their children to manage temptation, challenge, disappointment, and frustration more independently.
Infancy and up: Relational health
Children develop the skills needed for healthy relationships at home, and they are connected to all of the skills described above. Children need attuned, responsive, and reliable parenting to build a capacity for trust of others, to learn how to communicate honestly and effectively, to learn to expect and offer compassion and respect, and to learn how to handle disagreement and conflict. They learn these skills by watching their parents and by developing the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral healthy habits with their parents’ help. They need a consistently safe and responsive environment at home. They need parents who are attuned and flexible, while maintaining routines and high expectations. They need parents who make time for them when they are sad or struggling, and make time for joy, play, and mindless fun. While a detailed assessment of how the family is functioning may go beyond a check-up, you can ask about those routines that build healthy habits (family mealtime, sleep routines, screen time rules), communication style, and what the family enjoys doing together. Learning about how a family is building these healthy habits and how connected they are to one another can give you a clear snapshot of how well a child may be doing on their mental health growth curve, and what areas might benefit from more active guidance and support.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
May is Mental Health Awareness Month, providing us a chance to go beyond discussing the screening, diagnosis, and evidence-based treatments for the mental illnesses of youth. The World Health Organization defines good mental health as “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her own community.” While the science of mental health promotion and disease prevention in childhood and adolescence is relatively young, there are several discrete domains in which you can follow and support your patient’s developing mental health. This begins with the well-being of new parents, and then moves into how parents are helping their children to develop skills to manage their basic daily needs and impulses, their thoughts and feelings, their stresses and their relationships. With a little support from you, parents can confidently help their children develop the foundations for good mental health.
First year of life: Parental mental health
Perhaps the strongest risk factor for serious mental illness in childhood and adulthood is parental neglect during the first year of life, and neglect in the first several months of life is the most commonly reported form of child abuse. Infant neglect is associated with parental depression (and other mental illnesses), parental substance use, and a parent’s own experience of childhood abuse or neglect. Neglect is more common with teenaged parents and parents living in poverty. Pediatricians are uniquely connected to families during the first year of a child’s life. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening new mothers for depression at 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month infant check-ups with the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Screen. Even without a positive screen, new parents may need the fortifications of extra community support to adapt to the changes parenthood brings.
At checkups, ask (both) parents how they are managing the stresses of a new baby. Are they getting restful sleep? Do they have social supports? Are they connected to a community (friends, extended family, faith) or isolated? Are they developing confidence as parents or feeling overwhelmed? Simple guidance, such as “sleep when the baby sleeps” and reassurance that taking good care of themselves is taking good care of the baby is always helpful. Sometimes you will need to refer for treatment or to community supports. Have your list of online and in-person resources at the ready to provide parents with these prescriptions. Supporting parental mental health and adjustment in the first year of life is possibly the most important building block for their child’s future mental health.
Toddlers and up: Emotional literacy
Emotional literacy (sometimes called “emotional intelligence”) is the capacity to recognize, identify, and manage feelings in oneself and in others. This skill begins to develop in infancy when parents respond to their baby’s cries with attunement, feeding or changing them if needed, and at other times simply reflecting their feelings and soothing them with movement, singing, or quiet talking. As children grow, so does their range of feelings, and their (cognitive) capacity to identify and manage them. Parents support this development by being available whenever their young children experience strong emotions, calmly listening, and acknowledging their discomfort. Parents can offer words for describing those feelings, and even be curious with their young children where in their bodies they are feeling them, how they can stay patient while the feeling passes or things they might be able to do to feel better. Parents may want to remove their child’s distress, but staying calm, curious, and present while helping their child to manage it will build their child’s emotional health. Parents can nurture this development in a less intense way by reading books about feelings together and noticing and identifying feelings in other children or in cartoon characters.
School-age children: Adding mindfulness
While a child’s cognitive development unfolds naturally, school-age children can cultivate awareness of their thoughts. This becomes possible after awareness of feelings and parents can help their older children consider whether something they are experiencing is a thought, a feeling, or a fact. They do so in the same way they helped their child develop emotional literacy: By responding with calm, curiosity, and confidence every time their child comes to them in distress (especially mild distress, like boredom!) or with a challenge or a question. With a difficult situation, parents start by helping their child to identify thoughts and feelings before impulsively acting on them. Parents can help children identify what’s in their control, try different approaches, and be flexible if their first efforts don’t work. Children need to learn that failing at things is how we learn and grow. Just like learning to ride a bike, it builds their frustration tolerance, their knowledge that they can do difficult things, and that distress subsides. These are critical building blocks for adolescence, when the challenges become greater and they manage them more independently.
Learning “mindfulness” (a practice that cultivates nonjudgmental awareness of one’s own thoughts, feelings, and sensations) can help children (and parents) to cultivate quiet self-awareness outside of moments of difficulty. “Stop, Breathe, and Think” and “Mindful gNATs” are two free apps that are recommended by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry for children (and their parents) to use to practice this awareness of thoughts and feelings.
Early and later adolescence: Stress management skills
Building on this awareness of thoughts and emotions, adolescents develop adaptive coping skills by facing challenges with the support of their parents nearby. Parents should still be ready to respond to charged emotional moments with calm and curiosity, validating their child’s distress while helping them to consider healthy responses. Helping their teenager to describe their experience, differentiating feelings from thoughts (and facts), and considering different choices within their control is foundational to resilience in adulthood. Parents also help their teenagers by reminding them of the need for good self-care (sleep, exercise, nutrition), nourishing social relationships, and protecting time for rest and recharging activities. Sometimes, parents will think with their teenager about why they are engaged in an activity that is stressful, whether it is authentically important to them, and why. Adolescents should be deepening their sense of identity, interests, talents, and even values, and stressful moments are rich opportunities to do so, with the support of caring adults. Without intentionally building these skills, adolescents will be more prone to managing stress with avoidance or unhealthy coping, such as excessive eating, video gaming, drugs, or alcohol.
Infancy and up: Behavioral healthy habits (sleep, physical activity, nutrition, and screen time)
Healthy habits sound simple, but establishing them is not always easy. The idea of a habit is that it makes managing something challenging or important more automatic, and thus easier and more reliable. Many of the same habits that promote physical health in adulthood also promote mental health: adequate, restful sleep; daily physical activity; a nutritious diet and a healthy relationship with food; and managing screen time in a developmentally appropriate way. Infants depend entirely on their parents for regulation of these behaviors. As their children grow, parents will adapt these routines so that their children are gradually regulating these needs and activities more independently. In each of these areas, children need clear expectations and routines, consistent consequences and positive feedback, and the modeling and patient support of their parents. Educate parents about what good sleep hygiene looks like at each age. Discuss ways to support regular physical activity, especially as a family. Ask the parents about nutrition, including how they manage picky eating; how many family meals they enjoy together; and whether food is ever used to manage boredom or distress. Finally, talk with parents about a developmentally appropriate approach to rules and expectations around screen time and the importance of using family-based rules. Establishing expectations and routines during early childhood means children learn how good it feels to have restful sleep, regular exercise, and happy, healthy family meals. In adolescence, parents can then focus on helping their children to manage temptation, challenge, disappointment, and frustration more independently.
Infancy and up: Relational health
Children develop the skills needed for healthy relationships at home, and they are connected to all of the skills described above. Children need attuned, responsive, and reliable parenting to build a capacity for trust of others, to learn how to communicate honestly and effectively, to learn to expect and offer compassion and respect, and to learn how to handle disagreement and conflict. They learn these skills by watching their parents and by developing the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral healthy habits with their parents’ help. They need a consistently safe and responsive environment at home. They need parents who are attuned and flexible, while maintaining routines and high expectations. They need parents who make time for them when they are sad or struggling, and make time for joy, play, and mindless fun. While a detailed assessment of how the family is functioning may go beyond a check-up, you can ask about those routines that build healthy habits (family mealtime, sleep routines, screen time rules), communication style, and what the family enjoys doing together. Learning about how a family is building these healthy habits and how connected they are to one another can give you a clear snapshot of how well a child may be doing on their mental health growth curve, and what areas might benefit from more active guidance and support.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
May is Mental Health Awareness Month, providing us a chance to go beyond discussing the screening, diagnosis, and evidence-based treatments for the mental illnesses of youth. The World Health Organization defines good mental health as “a state of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her own community.” While the science of mental health promotion and disease prevention in childhood and adolescence is relatively young, there are several discrete domains in which you can follow and support your patient’s developing mental health. This begins with the well-being of new parents, and then moves into how parents are helping their children to develop skills to manage their basic daily needs and impulses, their thoughts and feelings, their stresses and their relationships. With a little support from you, parents can confidently help their children develop the foundations for good mental health.
First year of life: Parental mental health
Perhaps the strongest risk factor for serious mental illness in childhood and adulthood is parental neglect during the first year of life, and neglect in the first several months of life is the most commonly reported form of child abuse. Infant neglect is associated with parental depression (and other mental illnesses), parental substance use, and a parent’s own experience of childhood abuse or neglect. Neglect is more common with teenaged parents and parents living in poverty. Pediatricians are uniquely connected to families during the first year of a child’s life. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends screening new mothers for depression at 1-, 2-, 4-, and 6-month infant check-ups with the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Screen. Even without a positive screen, new parents may need the fortifications of extra community support to adapt to the changes parenthood brings.
At checkups, ask (both) parents how they are managing the stresses of a new baby. Are they getting restful sleep? Do they have social supports? Are they connected to a community (friends, extended family, faith) or isolated? Are they developing confidence as parents or feeling overwhelmed? Simple guidance, such as “sleep when the baby sleeps” and reassurance that taking good care of themselves is taking good care of the baby is always helpful. Sometimes you will need to refer for treatment or to community supports. Have your list of online and in-person resources at the ready to provide parents with these prescriptions. Supporting parental mental health and adjustment in the first year of life is possibly the most important building block for their child’s future mental health.
Toddlers and up: Emotional literacy
Emotional literacy (sometimes called “emotional intelligence”) is the capacity to recognize, identify, and manage feelings in oneself and in others. This skill begins to develop in infancy when parents respond to their baby’s cries with attunement, feeding or changing them if needed, and at other times simply reflecting their feelings and soothing them with movement, singing, or quiet talking. As children grow, so does their range of feelings, and their (cognitive) capacity to identify and manage them. Parents support this development by being available whenever their young children experience strong emotions, calmly listening, and acknowledging their discomfort. Parents can offer words for describing those feelings, and even be curious with their young children where in their bodies they are feeling them, how they can stay patient while the feeling passes or things they might be able to do to feel better. Parents may want to remove their child’s distress, but staying calm, curious, and present while helping their child to manage it will build their child’s emotional health. Parents can nurture this development in a less intense way by reading books about feelings together and noticing and identifying feelings in other children or in cartoon characters.
School-age children: Adding mindfulness
While a child’s cognitive development unfolds naturally, school-age children can cultivate awareness of their thoughts. This becomes possible after awareness of feelings and parents can help their older children consider whether something they are experiencing is a thought, a feeling, or a fact. They do so in the same way they helped their child develop emotional literacy: By responding with calm, curiosity, and confidence every time their child comes to them in distress (especially mild distress, like boredom!) or with a challenge or a question. With a difficult situation, parents start by helping their child to identify thoughts and feelings before impulsively acting on them. Parents can help children identify what’s in their control, try different approaches, and be flexible if their first efforts don’t work. Children need to learn that failing at things is how we learn and grow. Just like learning to ride a bike, it builds their frustration tolerance, their knowledge that they can do difficult things, and that distress subsides. These are critical building blocks for adolescence, when the challenges become greater and they manage them more independently.
Learning “mindfulness” (a practice that cultivates nonjudgmental awareness of one’s own thoughts, feelings, and sensations) can help children (and parents) to cultivate quiet self-awareness outside of moments of difficulty. “Stop, Breathe, and Think” and “Mindful gNATs” are two free apps that are recommended by the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry for children (and their parents) to use to practice this awareness of thoughts and feelings.
Early and later adolescence: Stress management skills
Building on this awareness of thoughts and emotions, adolescents develop adaptive coping skills by facing challenges with the support of their parents nearby. Parents should still be ready to respond to charged emotional moments with calm and curiosity, validating their child’s distress while helping them to consider healthy responses. Helping their teenager to describe their experience, differentiating feelings from thoughts (and facts), and considering different choices within their control is foundational to resilience in adulthood. Parents also help their teenagers by reminding them of the need for good self-care (sleep, exercise, nutrition), nourishing social relationships, and protecting time for rest and recharging activities. Sometimes, parents will think with their teenager about why they are engaged in an activity that is stressful, whether it is authentically important to them, and why. Adolescents should be deepening their sense of identity, interests, talents, and even values, and stressful moments are rich opportunities to do so, with the support of caring adults. Without intentionally building these skills, adolescents will be more prone to managing stress with avoidance or unhealthy coping, such as excessive eating, video gaming, drugs, or alcohol.
Infancy and up: Behavioral healthy habits (sleep, physical activity, nutrition, and screen time)
Healthy habits sound simple, but establishing them is not always easy. The idea of a habit is that it makes managing something challenging or important more automatic, and thus easier and more reliable. Many of the same habits that promote physical health in adulthood also promote mental health: adequate, restful sleep; daily physical activity; a nutritious diet and a healthy relationship with food; and managing screen time in a developmentally appropriate way. Infants depend entirely on their parents for regulation of these behaviors. As their children grow, parents will adapt these routines so that their children are gradually regulating these needs and activities more independently. In each of these areas, children need clear expectations and routines, consistent consequences and positive feedback, and the modeling and patient support of their parents. Educate parents about what good sleep hygiene looks like at each age. Discuss ways to support regular physical activity, especially as a family. Ask the parents about nutrition, including how they manage picky eating; how many family meals they enjoy together; and whether food is ever used to manage boredom or distress. Finally, talk with parents about a developmentally appropriate approach to rules and expectations around screen time and the importance of using family-based rules. Establishing expectations and routines during early childhood means children learn how good it feels to have restful sleep, regular exercise, and happy, healthy family meals. In adolescence, parents can then focus on helping their children to manage temptation, challenge, disappointment, and frustration more independently.
Infancy and up: Relational health
Children develop the skills needed for healthy relationships at home, and they are connected to all of the skills described above. Children need attuned, responsive, and reliable parenting to build a capacity for trust of others, to learn how to communicate honestly and effectively, to learn to expect and offer compassion and respect, and to learn how to handle disagreement and conflict. They learn these skills by watching their parents and by developing the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral healthy habits with their parents’ help. They need a consistently safe and responsive environment at home. They need parents who are attuned and flexible, while maintaining routines and high expectations. They need parents who make time for them when they are sad or struggling, and make time for joy, play, and mindless fun. While a detailed assessment of how the family is functioning may go beyond a check-up, you can ask about those routines that build healthy habits (family mealtime, sleep routines, screen time rules), communication style, and what the family enjoys doing together. Learning about how a family is building these healthy habits and how connected they are to one another can give you a clear snapshot of how well a child may be doing on their mental health growth curve, and what areas might benefit from more active guidance and support.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Email them at [email protected].
New protocol could cut fasting period to detect insulinomas
SEATTLE – , therefore yielding significant hospital cost savings, new data suggest.
Insulinomas are small, rare types of pancreatic tumors that are benign but secrete excess insulin, leading to hypoglycemia. More than 99% of people with insulinomas develop hypoglycemia within 72 hours, hence, the use of a 72-hour fast to detect these tumors.
But most people who are evaluated for hypoglycemia do not have an insulinoma and fasting in hospital for 3 days is burdensome and costly.
As part of a quality improvement project, Cleveland Clinic endocrinology fellow Michelle D. Lundholm, MD, and colleagues modified their hospital’s protocol to include measurement of beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), a marker of insulin suppression, every 12 hours with a cutoff of ≥ 2.7mmol/L for stopping the fast if hypoglycemia (venous glucose ≤ 45mg/dL) hasn’t occurred. This intervention cut in half the number of patients who needed to fast for the full 72 hours, without missing any insulinomas.
“We are excited to share how a relatively simple adjustment to our protocol allowed us to successfully reduce the burden of fasting on patients and more effectively utilize hospital resources. We hope that this encourages other centers to consider doing the same,” Dr. Lundholm said in an interview.
“These data support a 48-hour fast. The literature supports that’s sufficient to detect 95% of insulinomas. ... But, given our small insulinoma cohort, we are looking forward to learning from other studies,” she added.
Dr. Lundholm presented the late-breaking oral abstract at the annual scientific & clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology.
Asked to comment, session moderator Jenna Sarvaideo, MD, said: “We’re often steeped in tradition. That’s why this abstract and this quality improvement project is so exciting to me because it challenges the history. … and I think it’s ultimately helping patients.”
Dr. Sarvaideo, of Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center, Milwaukee, noted that, typically, although the fast will be stopped before 72 hours if the patient develops hypoglycemia, “often they don’t, so we keep going on and on. If we just paid more attention to the beta-hydroxybutyrate, I think that would be practice changing.”
She added that more data would be optimal, given that there were under 100 patients in the study, “but I do think that devising protocols is … very much still at the hands of the endocrinologists. I think that this work could make groups reevaluate their protocol and change it, maybe even with a small dataset and then move on from there and see what they see.”
Indeed, Dr. Lundholm pointed out that some institutions, such as the Mayo Clinic, already include 6-hour BHB measurements (along with glucose and insulin) in their protocols.
“For any institution that already draws regular BHB levels like this, it would be very easy to implement a new stopping criterion without adding any additional costs,” she said in an interview.
All insulinomas became apparent in less than 48 hours
The first report to look at the value of testing BHB at regular intervals was published by the Mayo Clinic in 2005 after they noticed patients without insulinoma were complaining of ketosis symptoms such as foul breath and digestive problems toward the end of the fast.
However, although BHB testing is used today as part of the evaluation, it’s typically only drawn at the start of the protocol and again at the time of hypoglycemia or at the end of 72 hours because more frequent values hadn’t been thought to be useful for guiding clinical management, Dr. Lundholm explained.
Between January 2018 and June 2020, Dr. Lundholm and colleagues followed 34 Cleveland Clinic patients who completed the usual 72-hour fast protocol. Overall, 71% were female, and 26% had undergone prior bariatric surgery procedures. Eleven (32%) developed hypoglycemia and stopped fasting. The other 23 (68%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Dr. Lundholm and colleagues determined that the fast could have ended earlier in 35% of patients based on an elevated BHB without missing any insulinomas.
And so, in June 2020 the group revised their protocol to include the BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L stopping criterion. Of the 30 patients evaluated from June 2020 to January 2023, 87% were female and 17% had undergone a bariatric procedure.
Here, 15 (50%) reached a BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L and ended their fast at an average of 43.8 hours. Another seven (23%) ended the fast after developing hypoglycemia. Just eight patients (27%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Overall, this resulted in approximately 376 fewer cumulative hours of inpatient admission than if patients had fasted for the full time.
Of the 64 patients who have completed the fasting protocol since 2018, seven (11%) who did have an insulinoma developed hypoglycemia within 48 hours and with a BHB < 2.7 mmol/L (median, 0.15).
Advantages: cost, adherence
A day in a general medicine bed at Cleveland Clinic was quoted as costing $2,420, based on publicly available information as of Jan. 1, 2023. “If half of patients leave 1 day earlier, this equates to about $1,210 per patient in savings from bed costs alone,” Dr. Lundholm told this news organization.
The revised protocol required an additional two to four blood draws, depending on the length of the fast. “The cost of these extra blood tests varies by lab and by count, but even at its highest does not exceed the amount of savings from bed costs,” she noted.
Patient adherence is another potential benefit of the revised protocol.
“Any study that requires 72 hours of patient cooperation is a challenge, particularly in an uncomfortable position like fasting. When we looked at these adherence numbers, we found that the percentage of patients who prematurely ended their fast decreased from 35% to 17% with the updated protocol,” Dr. Lundholm continued.
“This translates to fewer inconclusive results and fewer readmissions for repeat 72-hour fasting. While this was not our primary outcome, it was another noted benefit of our change,” she said.
Dr. Lundholm and Dr. Sarvaideo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE – , therefore yielding significant hospital cost savings, new data suggest.
Insulinomas are small, rare types of pancreatic tumors that are benign but secrete excess insulin, leading to hypoglycemia. More than 99% of people with insulinomas develop hypoglycemia within 72 hours, hence, the use of a 72-hour fast to detect these tumors.
But most people who are evaluated for hypoglycemia do not have an insulinoma and fasting in hospital for 3 days is burdensome and costly.
As part of a quality improvement project, Cleveland Clinic endocrinology fellow Michelle D. Lundholm, MD, and colleagues modified their hospital’s protocol to include measurement of beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), a marker of insulin suppression, every 12 hours with a cutoff of ≥ 2.7mmol/L for stopping the fast if hypoglycemia (venous glucose ≤ 45mg/dL) hasn’t occurred. This intervention cut in half the number of patients who needed to fast for the full 72 hours, without missing any insulinomas.
“We are excited to share how a relatively simple adjustment to our protocol allowed us to successfully reduce the burden of fasting on patients and more effectively utilize hospital resources. We hope that this encourages other centers to consider doing the same,” Dr. Lundholm said in an interview.
“These data support a 48-hour fast. The literature supports that’s sufficient to detect 95% of insulinomas. ... But, given our small insulinoma cohort, we are looking forward to learning from other studies,” she added.
Dr. Lundholm presented the late-breaking oral abstract at the annual scientific & clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology.
Asked to comment, session moderator Jenna Sarvaideo, MD, said: “We’re often steeped in tradition. That’s why this abstract and this quality improvement project is so exciting to me because it challenges the history. … and I think it’s ultimately helping patients.”
Dr. Sarvaideo, of Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center, Milwaukee, noted that, typically, although the fast will be stopped before 72 hours if the patient develops hypoglycemia, “often they don’t, so we keep going on and on. If we just paid more attention to the beta-hydroxybutyrate, I think that would be practice changing.”
She added that more data would be optimal, given that there were under 100 patients in the study, “but I do think that devising protocols is … very much still at the hands of the endocrinologists. I think that this work could make groups reevaluate their protocol and change it, maybe even with a small dataset and then move on from there and see what they see.”
Indeed, Dr. Lundholm pointed out that some institutions, such as the Mayo Clinic, already include 6-hour BHB measurements (along with glucose and insulin) in their protocols.
“For any institution that already draws regular BHB levels like this, it would be very easy to implement a new stopping criterion without adding any additional costs,” she said in an interview.
All insulinomas became apparent in less than 48 hours
The first report to look at the value of testing BHB at regular intervals was published by the Mayo Clinic in 2005 after they noticed patients without insulinoma were complaining of ketosis symptoms such as foul breath and digestive problems toward the end of the fast.
However, although BHB testing is used today as part of the evaluation, it’s typically only drawn at the start of the protocol and again at the time of hypoglycemia or at the end of 72 hours because more frequent values hadn’t been thought to be useful for guiding clinical management, Dr. Lundholm explained.
Between January 2018 and June 2020, Dr. Lundholm and colleagues followed 34 Cleveland Clinic patients who completed the usual 72-hour fast protocol. Overall, 71% were female, and 26% had undergone prior bariatric surgery procedures. Eleven (32%) developed hypoglycemia and stopped fasting. The other 23 (68%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Dr. Lundholm and colleagues determined that the fast could have ended earlier in 35% of patients based on an elevated BHB without missing any insulinomas.
And so, in June 2020 the group revised their protocol to include the BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L stopping criterion. Of the 30 patients evaluated from June 2020 to January 2023, 87% were female and 17% had undergone a bariatric procedure.
Here, 15 (50%) reached a BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L and ended their fast at an average of 43.8 hours. Another seven (23%) ended the fast after developing hypoglycemia. Just eight patients (27%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Overall, this resulted in approximately 376 fewer cumulative hours of inpatient admission than if patients had fasted for the full time.
Of the 64 patients who have completed the fasting protocol since 2018, seven (11%) who did have an insulinoma developed hypoglycemia within 48 hours and with a BHB < 2.7 mmol/L (median, 0.15).
Advantages: cost, adherence
A day in a general medicine bed at Cleveland Clinic was quoted as costing $2,420, based on publicly available information as of Jan. 1, 2023. “If half of patients leave 1 day earlier, this equates to about $1,210 per patient in savings from bed costs alone,” Dr. Lundholm told this news organization.
The revised protocol required an additional two to four blood draws, depending on the length of the fast. “The cost of these extra blood tests varies by lab and by count, but even at its highest does not exceed the amount of savings from bed costs,” she noted.
Patient adherence is another potential benefit of the revised protocol.
“Any study that requires 72 hours of patient cooperation is a challenge, particularly in an uncomfortable position like fasting. When we looked at these adherence numbers, we found that the percentage of patients who prematurely ended their fast decreased from 35% to 17% with the updated protocol,” Dr. Lundholm continued.
“This translates to fewer inconclusive results and fewer readmissions for repeat 72-hour fasting. While this was not our primary outcome, it was another noted benefit of our change,” she said.
Dr. Lundholm and Dr. Sarvaideo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE – , therefore yielding significant hospital cost savings, new data suggest.
Insulinomas are small, rare types of pancreatic tumors that are benign but secrete excess insulin, leading to hypoglycemia. More than 99% of people with insulinomas develop hypoglycemia within 72 hours, hence, the use of a 72-hour fast to detect these tumors.
But most people who are evaluated for hypoglycemia do not have an insulinoma and fasting in hospital for 3 days is burdensome and costly.
As part of a quality improvement project, Cleveland Clinic endocrinology fellow Michelle D. Lundholm, MD, and colleagues modified their hospital’s protocol to include measurement of beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), a marker of insulin suppression, every 12 hours with a cutoff of ≥ 2.7mmol/L for stopping the fast if hypoglycemia (venous glucose ≤ 45mg/dL) hasn’t occurred. This intervention cut in half the number of patients who needed to fast for the full 72 hours, without missing any insulinomas.
“We are excited to share how a relatively simple adjustment to our protocol allowed us to successfully reduce the burden of fasting on patients and more effectively utilize hospital resources. We hope that this encourages other centers to consider doing the same,” Dr. Lundholm said in an interview.
“These data support a 48-hour fast. The literature supports that’s sufficient to detect 95% of insulinomas. ... But, given our small insulinoma cohort, we are looking forward to learning from other studies,” she added.
Dr. Lundholm presented the late-breaking oral abstract at the annual scientific & clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology.
Asked to comment, session moderator Jenna Sarvaideo, MD, said: “We’re often steeped in tradition. That’s why this abstract and this quality improvement project is so exciting to me because it challenges the history. … and I think it’s ultimately helping patients.”
Dr. Sarvaideo, of Clement J. Zablocki VA Medical Center, Milwaukee, noted that, typically, although the fast will be stopped before 72 hours if the patient develops hypoglycemia, “often they don’t, so we keep going on and on. If we just paid more attention to the beta-hydroxybutyrate, I think that would be practice changing.”
She added that more data would be optimal, given that there were under 100 patients in the study, “but I do think that devising protocols is … very much still at the hands of the endocrinologists. I think that this work could make groups reevaluate their protocol and change it, maybe even with a small dataset and then move on from there and see what they see.”
Indeed, Dr. Lundholm pointed out that some institutions, such as the Mayo Clinic, already include 6-hour BHB measurements (along with glucose and insulin) in their protocols.
“For any institution that already draws regular BHB levels like this, it would be very easy to implement a new stopping criterion without adding any additional costs,” she said in an interview.
All insulinomas became apparent in less than 48 hours
The first report to look at the value of testing BHB at regular intervals was published by the Mayo Clinic in 2005 after they noticed patients without insulinoma were complaining of ketosis symptoms such as foul breath and digestive problems toward the end of the fast.
However, although BHB testing is used today as part of the evaluation, it’s typically only drawn at the start of the protocol and again at the time of hypoglycemia or at the end of 72 hours because more frequent values hadn’t been thought to be useful for guiding clinical management, Dr. Lundholm explained.
Between January 2018 and June 2020, Dr. Lundholm and colleagues followed 34 Cleveland Clinic patients who completed the usual 72-hour fast protocol. Overall, 71% were female, and 26% had undergone prior bariatric surgery procedures. Eleven (32%) developed hypoglycemia and stopped fasting. The other 23 (68%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Dr. Lundholm and colleagues determined that the fast could have ended earlier in 35% of patients based on an elevated BHB without missing any insulinomas.
And so, in June 2020 the group revised their protocol to include the BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L stopping criterion. Of the 30 patients evaluated from June 2020 to January 2023, 87% were female and 17% had undergone a bariatric procedure.
Here, 15 (50%) reached a BHB ≥ 2.7mmol/L and ended their fast at an average of 43.8 hours. Another seven (23%) ended the fast after developing hypoglycemia. Just eight patients (27%) fasted for the full 72 hours.
Overall, this resulted in approximately 376 fewer cumulative hours of inpatient admission than if patients had fasted for the full time.
Of the 64 patients who have completed the fasting protocol since 2018, seven (11%) who did have an insulinoma developed hypoglycemia within 48 hours and with a BHB < 2.7 mmol/L (median, 0.15).
Advantages: cost, adherence
A day in a general medicine bed at Cleveland Clinic was quoted as costing $2,420, based on publicly available information as of Jan. 1, 2023. “If half of patients leave 1 day earlier, this equates to about $1,210 per patient in savings from bed costs alone,” Dr. Lundholm told this news organization.
The revised protocol required an additional two to four blood draws, depending on the length of the fast. “The cost of these extra blood tests varies by lab and by count, but even at its highest does not exceed the amount of savings from bed costs,” she noted.
Patient adherence is another potential benefit of the revised protocol.
“Any study that requires 72 hours of patient cooperation is a challenge, particularly in an uncomfortable position like fasting. When we looked at these adherence numbers, we found that the percentage of patients who prematurely ended their fast decreased from 35% to 17% with the updated protocol,” Dr. Lundholm continued.
“This translates to fewer inconclusive results and fewer readmissions for repeat 72-hour fasting. While this was not our primary outcome, it was another noted benefit of our change,” she said.
Dr. Lundholm and Dr. Sarvaideo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AACE 2023
New-Onset Pemphigoid Gestationis Following COVID-19 Vaccination
To the Editor:
Pemphigoid gestationis (PG), or gestational pemphigoid, is a rare autoimmune bullous disease (AIBD) occurring in 1 in 50,000 pregnancies. It is characterized by abrupt development of intensely pruritic papules and urticarial plaques, followed by an eruption of blisters.1 We present a case of new-onset PG that erupted 10 days following SARs-CoV-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech).
A 36-year-old pregnant woman (gravida 1, para 0, aborta 0) at 37 weeks’ gestation presented to our AIBD clinic with a pruritic dermatitis of 6 weeks’ duration that developed 10 days after receiving the second dose of BNT162b2. Multiple intensely pruritic, red bumps presented first on the forearms and within days spread to the thighs, hands, and abdomen, followed by progression to the ankles, feet, and back 2 weeks later. An initial biopsy was consistent with subacute spongiotic dermatitis with rare eosinophils. She found minimal relief from diphenhydramine or topical steroids. She denied oral, nasal, ocular, or genital involvement or history of any other skin disease. The pregnancy had been otherwise uneventful.
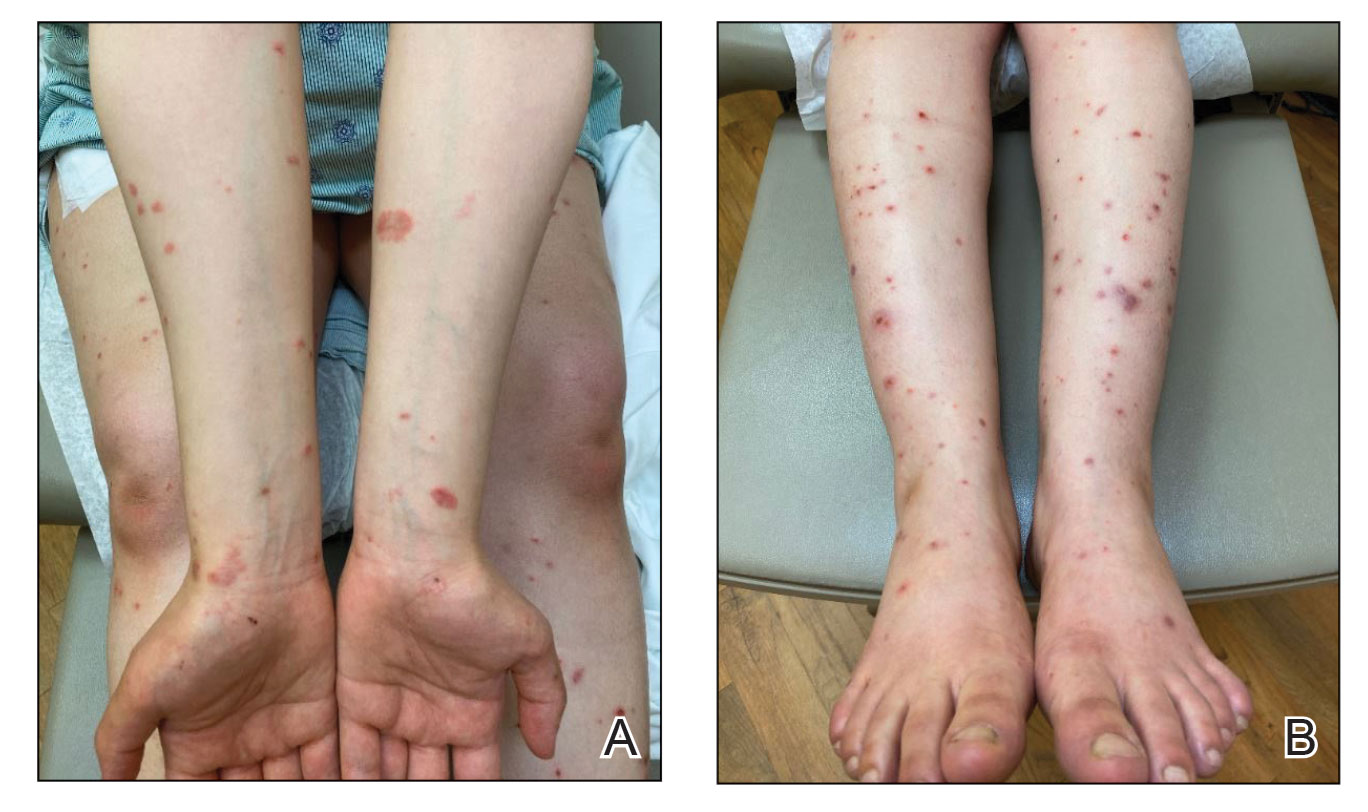
Physical examination revealed annular edematous plaques on the trunk and buttocks; excoriated and erythematous papules on the neck, trunk, arms, and legs; and scattered vesicles along the fingers, arms, hands, abdomen, back, legs, and feet (Figure 1). The Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index (BPDAI) total skin activity score was 25.3, corresponding to moderate disease activity (validated at 20–56).2 The BPDAI total pruritus component score was 20. A repeat biopsy for direct immunofluorescence showed faint linear deposits of IgG and bright linear deposits of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Indirect immunofluorescence showed linear deposits of IgG localized to the blister roof of salt-split skin at a dilution of 1:40. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-BP180 was 62 U/mL (negative, <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL), and anti-BP230 autoantibodies were less than 9 U/mL (negative <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL). Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, PG was diagnosed.
The patient was started on prednisone 20 mg and antihistamines while continuing topical steroids. Pruritus and blistering improved close to delivery. Fetal monitoring with regular biophysical profiles remained normal. The patient delivered a healthy neonate without skin lesions at 40 weeks’ gestation. The disease flared 2 days after delivery, and prednisone was increased to 40 mg and slowly tapered. Two months after delivery, the patient remained on prednisone 10 mg daily with ongoing but reduced blistering and pruritus (Figure 2). The BPDAI total skin activity and pruritus component scores remained elevated at 20.3 and 14, respectively, and anti-BP180 was 44 U/mL. After a discussion with the patient on safe systemic therapy while breastfeeding, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) was initiated. The patient received 3 monthly infusions at 2 g/kg and was able to taper the prednisone to 5 mg every other day without new lesions. Four months after completion of IVIG therapy, she achieved complete remission off all therapy.
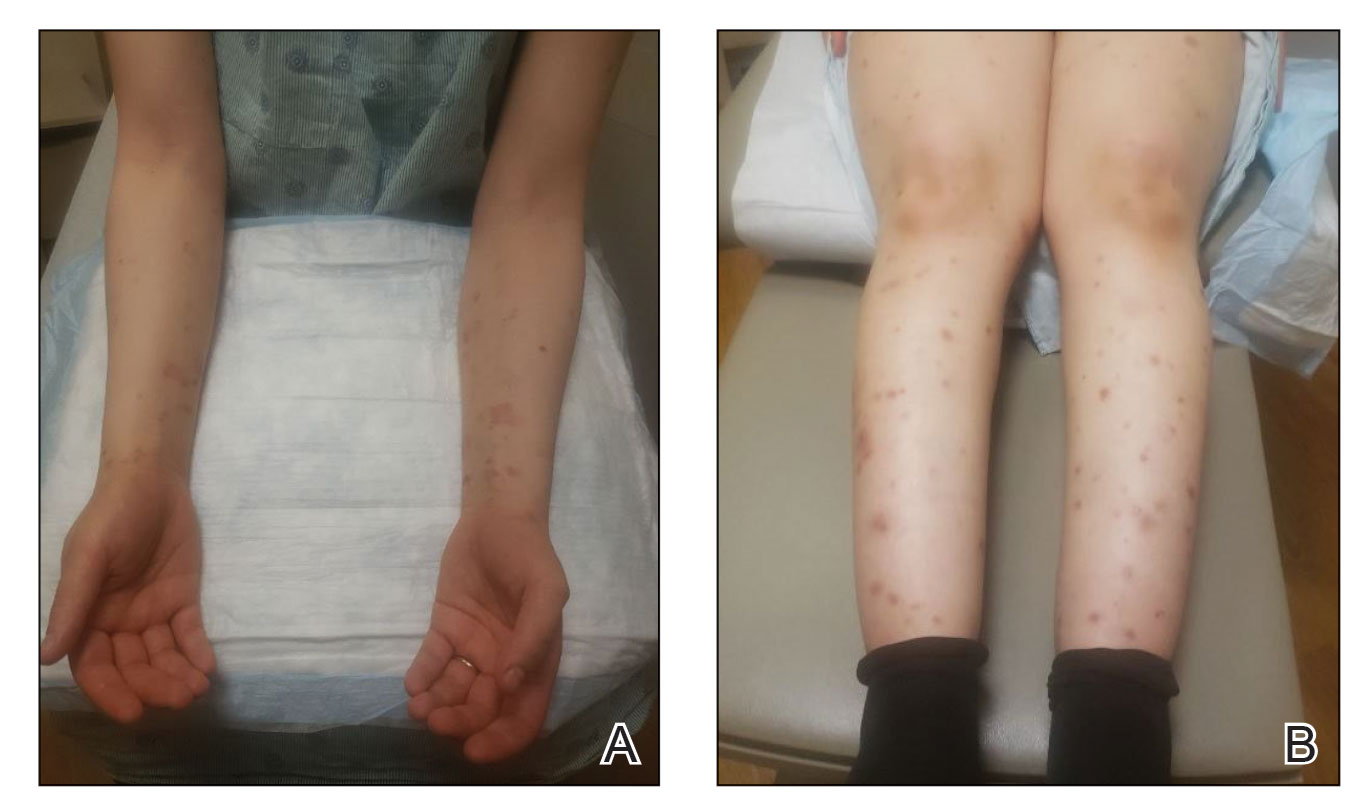
Management of PG begins with topical corticosteroids, but most patients require systemic steroid therapy.1 Remission commonly occurs close to delivery, and 75% of patients flare post partum, though the disease typically resolves 6 months following delivery.1,3,4 For persistent intrapartum cases requiring more than prednisone 20 mg daily, therapy can include dapsone, IVIG, azathioprine, rituximab, or plasmapheresis.4,5 Dapsone and IVIG are compatible with breastfeeding postpartum, but if dapsone is selected, the infant must be monitored for hemolytic anemia.5 Pemphigoid gestationis increases the risk for a premature or small-for-gestational-age neonate, necessitating regular fetal monitoring until delivery.1 Cutaneous lesions may affect the newborn, though this occurrence is rare and self-limiting.6 Pemphigoid gestationis may recur in subsequent pregnancies at a rate of 33% to 55%, with earlier and more severe presentations.4
Clinically and histologically, PG closely resembles bullous pemphigoid (BP), but the exact pathogenesis is not fully understood. Recently, another case of what was termed pseudo-PG has been described 3 days following administration of the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.7 Since the introduction of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, cases of postvaccination BP, BP-like eruptions, and pemphigus vulgaris have been described.8-11 Tomayko et al10 reported 12 cases of subepidermal eruptions, including BP, in which 7 patients developed blisters after the second dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna mRNA vaccine. Three patients who developed BP after the first dose of the vaccine and chose to receive the second dose tolerated it well, with a mild flare observed in 1 patient.10 Similarly, subsequent vaccine doses in reports of vaccine-associated AIBD resulted in increased disease activity in 21% of cases.12 COVID-19 vaccine–associated BP, similar to drug-induced BP, seemingly displays a milder course of disease compared to the classic form of BP.10,13 More follow-up is needed to better understand these reactions and inform appropriate discussions on the administration of booster doses. Currently, completion of the vaccination series against COVID-19 is advisable given the paucity of reports of postvaccination AIBD and the risk for COVID-19 infection, but careful discussions on a case-by-case basis are warranted related to the risk for disease exacerbation following subsequent vaccinations.
The clinical presentation and diagnostic evaluation of our patient’s rash were consistent with PG. The temporal relationship between vaccine administration and PG lesion onset suggests the mRNA vaccine triggered AIBD in our patient. Interestingly, AIBD associated with COVID-19 is not unique to only the vaccines and has been observed following infection with the virus itself.14 The high rate of vaccination against COVID-19 in contrast with the low number of reported cases of AIBD after vaccination supports the overall safety of COVID-19 vaccines but identifies a need for further understanding of the processes that lead to the development of autoimmune conditions in at-risk populations.
- Wiznia LE, Pomeranz MK. Skin changes and diseases in pregnancy. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
- Masmoudi W, Vaillant M, Vassileva S, et al. International validation of the Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index severity score and calculation of cut-off values for defining mild, moderate and severe types of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:1106-1112. doi:10.1111/bjd.19611
- Semkova K, Black M. Pemphigoid gestationis: current insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:138-144.
- Savervall C, Sand FL, Thomsen SF. Pemphigoid gestationis: current perspectives. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:441-449.
- Braunstein I, Werth V. Treatment of dermatologic connective tissue disease and autoimmune blistering disorders in pregnancy. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:354-363.
- Lipozencic J, Ljubojevic S, Bukvic-Mokos Z. Pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:51-55.
- de Lorenzi C, Kaya G, Toutous Trellu L. Pseudo-pemphigoid gestationis eruption following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with mRNA vaccine. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2022;9:203-206. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology9030025
- McMahon DE, Kovarik CL, Damsky W, et al. Clinical and pathologic correlation of cutaneous COVID-19 vaccine reactions including V-REPP: a registry-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:113-121.
- Solimani F, Mansour Y, Didona D, et al. Development of severe pemphigus vulgaris following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with BNT162b2. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E649-E651.
- Tomayko MM, Damsky W, Fathy R, et al. Subepidermal blistering eruptions, including bullous pemphigoid, following COVID-19 vaccination. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:750-751.
- Coto-Segura P, Fernandez-Prada M, Mir-Bonafe M, et al. Vesiculobullous skin reactions induced by COVID-19 mRNA vaccine: report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:141-143.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Woodley DT. Association between vaccination and autoimmune bullous diseases: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1160-1164.
- Stavropoulos PG, Soura E, Antoniou C. Drug-induced pemphigoid: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1133-1140.
- Olson N, Eckhardt D, Delano A. New-onset bullous pemphigoid in a COVID-19 patient. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2021;2021:5575111.
To the Editor:
Pemphigoid gestationis (PG), or gestational pemphigoid, is a rare autoimmune bullous disease (AIBD) occurring in 1 in 50,000 pregnancies. It is characterized by abrupt development of intensely pruritic papules and urticarial plaques, followed by an eruption of blisters.1 We present a case of new-onset PG that erupted 10 days following SARs-CoV-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech).
A 36-year-old pregnant woman (gravida 1, para 0, aborta 0) at 37 weeks’ gestation presented to our AIBD clinic with a pruritic dermatitis of 6 weeks’ duration that developed 10 days after receiving the second dose of BNT162b2. Multiple intensely pruritic, red bumps presented first on the forearms and within days spread to the thighs, hands, and abdomen, followed by progression to the ankles, feet, and back 2 weeks later. An initial biopsy was consistent with subacute spongiotic dermatitis with rare eosinophils. She found minimal relief from diphenhydramine or topical steroids. She denied oral, nasal, ocular, or genital involvement or history of any other skin disease. The pregnancy had been otherwise uneventful.
Physical examination revealed annular edematous plaques on the trunk and buttocks; excoriated and erythematous papules on the neck, trunk, arms, and legs; and scattered vesicles along the fingers, arms, hands, abdomen, back, legs, and feet (Figure 1). The Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index (BPDAI) total skin activity score was 25.3, corresponding to moderate disease activity (validated at 20–56).2 The BPDAI total pruritus component score was 20. A repeat biopsy for direct immunofluorescence showed faint linear deposits of IgG and bright linear deposits of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Indirect immunofluorescence showed linear deposits of IgG localized to the blister roof of salt-split skin at a dilution of 1:40. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-BP180 was 62 U/mL (negative, <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL), and anti-BP230 autoantibodies were less than 9 U/mL (negative <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL). Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, PG was diagnosed.

The patient was started on prednisone 20 mg and antihistamines while continuing topical steroids. Pruritus and blistering improved close to delivery. Fetal monitoring with regular biophysical profiles remained normal. The patient delivered a healthy neonate without skin lesions at 40 weeks’ gestation. The disease flared 2 days after delivery, and prednisone was increased to 40 mg and slowly tapered. Two months after delivery, the patient remained on prednisone 10 mg daily with ongoing but reduced blistering and pruritus (Figure 2). The BPDAI total skin activity and pruritus component scores remained elevated at 20.3 and 14, respectively, and anti-BP180 was 44 U/mL. After a discussion with the patient on safe systemic therapy while breastfeeding, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) was initiated. The patient received 3 monthly infusions at 2 g/kg and was able to taper the prednisone to 5 mg every other day without new lesions. Four months after completion of IVIG therapy, she achieved complete remission off all therapy.

Management of PG begins with topical corticosteroids, but most patients require systemic steroid therapy.1 Remission commonly occurs close to delivery, and 75% of patients flare post partum, though the disease typically resolves 6 months following delivery.1,3,4 For persistent intrapartum cases requiring more than prednisone 20 mg daily, therapy can include dapsone, IVIG, azathioprine, rituximab, or plasmapheresis.4,5 Dapsone and IVIG are compatible with breastfeeding postpartum, but if dapsone is selected, the infant must be monitored for hemolytic anemia.5 Pemphigoid gestationis increases the risk for a premature or small-for-gestational-age neonate, necessitating regular fetal monitoring until delivery.1 Cutaneous lesions may affect the newborn, though this occurrence is rare and self-limiting.6 Pemphigoid gestationis may recur in subsequent pregnancies at a rate of 33% to 55%, with earlier and more severe presentations.4
Clinically and histologically, PG closely resembles bullous pemphigoid (BP), but the exact pathogenesis is not fully understood. Recently, another case of what was termed pseudo-PG has been described 3 days following administration of the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.7 Since the introduction of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, cases of postvaccination BP, BP-like eruptions, and pemphigus vulgaris have been described.8-11 Tomayko et al10 reported 12 cases of subepidermal eruptions, including BP, in which 7 patients developed blisters after the second dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna mRNA vaccine. Three patients who developed BP after the first dose of the vaccine and chose to receive the second dose tolerated it well, with a mild flare observed in 1 patient.10 Similarly, subsequent vaccine doses in reports of vaccine-associated AIBD resulted in increased disease activity in 21% of cases.12 COVID-19 vaccine–associated BP, similar to drug-induced BP, seemingly displays a milder course of disease compared to the classic form of BP.10,13 More follow-up is needed to better understand these reactions and inform appropriate discussions on the administration of booster doses. Currently, completion of the vaccination series against COVID-19 is advisable given the paucity of reports of postvaccination AIBD and the risk for COVID-19 infection, but careful discussions on a case-by-case basis are warranted related to the risk for disease exacerbation following subsequent vaccinations.
The clinical presentation and diagnostic evaluation of our patient’s rash were consistent with PG. The temporal relationship between vaccine administration and PG lesion onset suggests the mRNA vaccine triggered AIBD in our patient. Interestingly, AIBD associated with COVID-19 is not unique to only the vaccines and has been observed following infection with the virus itself.14 The high rate of vaccination against COVID-19 in contrast with the low number of reported cases of AIBD after vaccination supports the overall safety of COVID-19 vaccines but identifies a need for further understanding of the processes that lead to the development of autoimmune conditions in at-risk populations.
To the Editor:
Pemphigoid gestationis (PG), or gestational pemphigoid, is a rare autoimmune bullous disease (AIBD) occurring in 1 in 50,000 pregnancies. It is characterized by abrupt development of intensely pruritic papules and urticarial plaques, followed by an eruption of blisters.1 We present a case of new-onset PG that erupted 10 days following SARs-CoV-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech).
A 36-year-old pregnant woman (gravida 1, para 0, aborta 0) at 37 weeks’ gestation presented to our AIBD clinic with a pruritic dermatitis of 6 weeks’ duration that developed 10 days after receiving the second dose of BNT162b2. Multiple intensely pruritic, red bumps presented first on the forearms and within days spread to the thighs, hands, and abdomen, followed by progression to the ankles, feet, and back 2 weeks later. An initial biopsy was consistent with subacute spongiotic dermatitis with rare eosinophils. She found minimal relief from diphenhydramine or topical steroids. She denied oral, nasal, ocular, or genital involvement or history of any other skin disease. The pregnancy had been otherwise uneventful.
Physical examination revealed annular edematous plaques on the trunk and buttocks; excoriated and erythematous papules on the neck, trunk, arms, and legs; and scattered vesicles along the fingers, arms, hands, abdomen, back, legs, and feet (Figure 1). The Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index (BPDAI) total skin activity score was 25.3, corresponding to moderate disease activity (validated at 20–56).2 The BPDAI total pruritus component score was 20. A repeat biopsy for direct immunofluorescence showed faint linear deposits of IgG and bright linear deposits of C3 along the basement membrane zone. Indirect immunofluorescence showed linear deposits of IgG localized to the blister roof of salt-split skin at a dilution of 1:40. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-BP180 was 62 U/mL (negative, <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL), and anti-BP230 autoantibodies were less than 9 U/mL (negative <9 U/mL; positive, ≥9 U/mL). Given these clinical and histopathologic findings, PG was diagnosed.

The patient was started on prednisone 20 mg and antihistamines while continuing topical steroids. Pruritus and blistering improved close to delivery. Fetal monitoring with regular biophysical profiles remained normal. The patient delivered a healthy neonate without skin lesions at 40 weeks’ gestation. The disease flared 2 days after delivery, and prednisone was increased to 40 mg and slowly tapered. Two months after delivery, the patient remained on prednisone 10 mg daily with ongoing but reduced blistering and pruritus (Figure 2). The BPDAI total skin activity and pruritus component scores remained elevated at 20.3 and 14, respectively, and anti-BP180 was 44 U/mL. After a discussion with the patient on safe systemic therapy while breastfeeding, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) was initiated. The patient received 3 monthly infusions at 2 g/kg and was able to taper the prednisone to 5 mg every other day without new lesions. Four months after completion of IVIG therapy, she achieved complete remission off all therapy.

Management of PG begins with topical corticosteroids, but most patients require systemic steroid therapy.1 Remission commonly occurs close to delivery, and 75% of patients flare post partum, though the disease typically resolves 6 months following delivery.1,3,4 For persistent intrapartum cases requiring more than prednisone 20 mg daily, therapy can include dapsone, IVIG, azathioprine, rituximab, or plasmapheresis.4,5 Dapsone and IVIG are compatible with breastfeeding postpartum, but if dapsone is selected, the infant must be monitored for hemolytic anemia.5 Pemphigoid gestationis increases the risk for a premature or small-for-gestational-age neonate, necessitating regular fetal monitoring until delivery.1 Cutaneous lesions may affect the newborn, though this occurrence is rare and self-limiting.6 Pemphigoid gestationis may recur in subsequent pregnancies at a rate of 33% to 55%, with earlier and more severe presentations.4
Clinically and histologically, PG closely resembles bullous pemphigoid (BP), but the exact pathogenesis is not fully understood. Recently, another case of what was termed pseudo-PG has been described 3 days following administration of the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.7 Since the introduction of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, cases of postvaccination BP, BP-like eruptions, and pemphigus vulgaris have been described.8-11 Tomayko et al10 reported 12 cases of subepidermal eruptions, including BP, in which 7 patients developed blisters after the second dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna mRNA vaccine. Three patients who developed BP after the first dose of the vaccine and chose to receive the second dose tolerated it well, with a mild flare observed in 1 patient.10 Similarly, subsequent vaccine doses in reports of vaccine-associated AIBD resulted in increased disease activity in 21% of cases.12 COVID-19 vaccine–associated BP, similar to drug-induced BP, seemingly displays a milder course of disease compared to the classic form of BP.10,13 More follow-up is needed to better understand these reactions and inform appropriate discussions on the administration of booster doses. Currently, completion of the vaccination series against COVID-19 is advisable given the paucity of reports of postvaccination AIBD and the risk for COVID-19 infection, but careful discussions on a case-by-case basis are warranted related to the risk for disease exacerbation following subsequent vaccinations.
The clinical presentation and diagnostic evaluation of our patient’s rash were consistent with PG. The temporal relationship between vaccine administration and PG lesion onset suggests the mRNA vaccine triggered AIBD in our patient. Interestingly, AIBD associated with COVID-19 is not unique to only the vaccines and has been observed following infection with the virus itself.14 The high rate of vaccination against COVID-19 in contrast with the low number of reported cases of AIBD after vaccination supports the overall safety of COVID-19 vaccines but identifies a need for further understanding of the processes that lead to the development of autoimmune conditions in at-risk populations.
- Wiznia LE, Pomeranz MK. Skin changes and diseases in pregnancy. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
- Masmoudi W, Vaillant M, Vassileva S, et al. International validation of the Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index severity score and calculation of cut-off values for defining mild, moderate and severe types of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:1106-1112. doi:10.1111/bjd.19611
- Semkova K, Black M. Pemphigoid gestationis: current insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:138-144.
- Savervall C, Sand FL, Thomsen SF. Pemphigoid gestationis: current perspectives. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:441-449.
- Braunstein I, Werth V. Treatment of dermatologic connective tissue disease and autoimmune blistering disorders in pregnancy. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:354-363.
- Lipozencic J, Ljubojevic S, Bukvic-Mokos Z. Pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:51-55.
- de Lorenzi C, Kaya G, Toutous Trellu L. Pseudo-pemphigoid gestationis eruption following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with mRNA vaccine. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2022;9:203-206. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology9030025
- McMahon DE, Kovarik CL, Damsky W, et al. Clinical and pathologic correlation of cutaneous COVID-19 vaccine reactions including V-REPP: a registry-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:113-121.
- Solimani F, Mansour Y, Didona D, et al. Development of severe pemphigus vulgaris following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with BNT162b2. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E649-E651.
- Tomayko MM, Damsky W, Fathy R, et al. Subepidermal blistering eruptions, including bullous pemphigoid, following COVID-19 vaccination. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:750-751.
- Coto-Segura P, Fernandez-Prada M, Mir-Bonafe M, et al. Vesiculobullous skin reactions induced by COVID-19 mRNA vaccine: report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:141-143.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Woodley DT. Association between vaccination and autoimmune bullous diseases: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1160-1164.
- Stavropoulos PG, Soura E, Antoniou C. Drug-induced pemphigoid: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1133-1140.
- Olson N, Eckhardt D, Delano A. New-onset bullous pemphigoid in a COVID-19 patient. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2021;2021:5575111.
- Wiznia LE, Pomeranz MK. Skin changes and diseases in pregnancy. In: Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
- Masmoudi W, Vaillant M, Vassileva S, et al. International validation of the Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index severity score and calculation of cut-off values for defining mild, moderate and severe types of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184:1106-1112. doi:10.1111/bjd.19611
- Semkova K, Black M. Pemphigoid gestationis: current insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009;145:138-144.
- Savervall C, Sand FL, Thomsen SF. Pemphigoid gestationis: current perspectives. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:441-449.
- Braunstein I, Werth V. Treatment of dermatologic connective tissue disease and autoimmune blistering disorders in pregnancy. Dermatol Ther. 2013;26:354-363.
- Lipozencic J, Ljubojevic S, Bukvic-Mokos Z. Pemphigoid gestationis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:51-55.
- de Lorenzi C, Kaya G, Toutous Trellu L. Pseudo-pemphigoid gestationis eruption following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with mRNA vaccine. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2022;9:203-206. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology9030025
- McMahon DE, Kovarik CL, Damsky W, et al. Clinical and pathologic correlation of cutaneous COVID-19 vaccine reactions including V-REPP: a registry-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:113-121.
- Solimani F, Mansour Y, Didona D, et al. Development of severe pemphigus vulgaris following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with BNT162b2. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:E649-E651.
- Tomayko MM, Damsky W, Fathy R, et al. Subepidermal blistering eruptions, including bullous pemphigoid, following COVID-19 vaccination. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148:750-751.
- Coto-Segura P, Fernandez-Prada M, Mir-Bonafe M, et al. Vesiculobullous skin reactions induced by COVID-19 mRNA vaccine: report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:141-143.
- Kasperkiewicz M, Woodley DT. Association between vaccination and autoimmune bullous diseases: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1160-1164.
- Stavropoulos PG, Soura E, Antoniou C. Drug-induced pemphigoid: a review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:1133-1140.
- Olson N, Eckhardt D, Delano A. New-onset bullous pemphigoid in a COVID-19 patient. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2021;2021:5575111.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware that COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccinations may present with various cutaneous complications.
- Pemphigoid gestationis should be considered in a pregnant or postpartum woman with an unexplained eruption of persistent, pruritic, urticarial lesions and blisters occurring postvaccination. Treatments include high-potency topical steroids and frequently systemic corticosteroids, along with steroid-sparing agents in severe cases.
Papular Reticulated Rash
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).
Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).

Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
Histopathology of the punch biopsy revealed subcorneal collections of neutrophils flanked by a spongiotic epidermis with neutrophil and eosinophil exocytosis. Rare dyskeratotic keratinocytes were identified at the dermoepidermal junction, and grampositive bacterial organisms were seen in a follicular infundibulum with purulent inflammation. The dermis demonstrated a mildly dense superficial perivascular and interstitial infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, histiocytes, scattered neutrophils, and eosinophils (Figure).

Given the combination of clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa (PP) was rendered and a urinalysis was ordered, which confirmed ketonuria. The patient was started on minocycline 100 mg twice daily and was advised to reintroduce carbohydrates into her diet. Resolution of the inflammatory component of the rash was achieved at 3-week follow-up, with residual reticulated postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare, albeit globally underrecognized, inflammatory dermatosis characterized by pruritic, symmetric, erythematous papules and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and rarely the arms and forehead that subsequently involute, leaving reticular postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.1 Prurigo pigmentosa is predominant in females (2.6:1 ratio). The mean age at presentation is 24.4 years, and it most commonly has been documented among populations in Asian countries, though it is unclear if a genetic predilection exists, as reports of PP are increasing globally with improved clinical awareness.1,2
The etiology of PP remains unknown; however, associations are well documented between PP and a ketogenic state secondary to uncontrolled diabetes, a low-carbohydrate diet, anorexia nervosa, or bariatric surgery.3 It is theorized that high serum ketones lead to perivascular ketone deposition, which induces neutrophil migration and chemotaxis,4 as substantiated by evidence of rash resolution with correction of the ketogenic state and improvement after administration of tetracyclines, a drug class known for neutrophil chemotaxis inhibition.5 Improvement of PP via these treatment mechanisms suggests that ketone bodies may play a role in the pathogenesis of PP.
Interestingly, Kafle et al6 reported that patients with PP commonly have bacterial colonies and associated inflammatory sequelae at the level of the hair follicles, which suggests that follicular involvement plays a role in the pathogenesis of PP. These findings are consistent with our patient’s histopathology consisting of gram-positive organisms and purulent inflammation at the infundibulum. The histopathologic features of PP are stage specific.1 Early stages are characterized by a superficial perivascular infiltrate of neutrophils that then spread to dermal papillae. Neutrophils then quickly sweep through the epidermis, causing spongiosis, ballooning, necrotic keratocytes, and consequent surface epithelium abscess formation. Over time, the dermal infiltrate assumes a lichenoid pattern as eosinophils and lymphocytes invade and predominate over neutrophils. Eventually, melanophages appear in the dermis as the epidermis undergoes hyperplasia, parakeratosis, and hyperpigmentation.1 The histologic differential diagnosis for PP is broad and varies based on the stage-specific progression of clinical and histopathologic findings.
Similar to PP, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus has a female predominance and resolves with subsequent dyspigmentation; however, it initially is characterized by annular plaques with central clearing or papulosquamous lesions restricted to sun-exposed skin. Photosensitivity is a prominent feature, and roughly 50% of patients meet diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus.7 Histopathology shows interface changes with increased dermal mucin and a perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate.
Papular pityriasis rosea can present as a pruritic papular rash on the back and chest; however, it most commonly is associated with a herald patch and typically follows a flulike prodrome.8 Biopsy reveals mounds of parakeratosis with mild spongiosis, perivascular inflammation, and extravasated erythrocytes.
Galli-Galli disease can present as a pruritic rash with follicular papules under the breasts and other flexural areas but histopathologically shows elongated rete ridges with dermal melanosis and acantholysis.9
Hailey-Hailey disease commonly presents in the third decade of life and can manifest as painful, pruritic, vesicular lesions on erythematous skin distributed on the back, neck, and inframammary region, as seen in our case; however, it is histopathologically associated with widespread epidermal acantholysis unlike the findings seen in our patient.10
First-line treatment of PP includes antibiotics such as minocycline, doxycycline, and dapsone due to their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis. In patients with nutritional deficiencies or ketosis, reintroduction of carbohydrates alone has been effective.5,11
Prurigo pigmentosa is an underrecognized inflammatory dermatosis with a complex stage-dependent clinicopathologic presentation. Clinicians should be aware of the etiologic and histopathologic patterns of this unique dermatosis. Rash presentation in the context of a low-carbohydrate diet should prompt biopsy as well as treatment with antibiotics and dietary reintroduction of carbohydrates.
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- de Sousa Vargas TJ, Abreu Raposo CM, Lima RB, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: report of 3 cases from Brazil and literature review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:267-274. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000643
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79. doi:10.1016/J .JDIN.2021.03.003
- Beutler BD, Cohen PR, Lee RA. Prurigo pigmentosa: literature review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16:533-543. doi:10.1007/S40257-015-0154-4
- Chiam LYT, Goh BK, Lim KS, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a report of two cases that responded to minocycline. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2230.2009.03253.X
- Kafle SU, Swe SM, Hsiao PF, et al. Folliculitis in prurigo pigmentosa: a proposed pathogenesis based on clinical and pathological observation. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:20-27. doi:10.1111/CUP.12829
- Sontheimer RD. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 25-year evolution of a prototypic subset (subphenotype) of lupus erythematosus defined by characteristic cutaneous, pathological, immunological, and genetic findings. Autoimmun Rev. 2005;4:253-263. doi:10.1016/J .AUTREV.2004.10.00
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Pityriasis rosea: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2021;17:201-211. doi:10.2174/15733963166662 00923161330
- Sprecher E, Indelman M, Khamaysi Z, et al. Galli-Galli disease is an acantholytic variant of Dowling-Degos disease. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:572-574. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.2006.07703.X
- Burge SM. Hailey-Hailey disease: the clinical features, response to treatment and prognosis. Br J Dermatol. 1992;126:275-282. doi:10.1111/J.1365-2133.1992.TB00658
- Lu L-Y, Chen C-B. Keto rash: ketoacidosis-induced prurigo pigmentosa. Mayo Clin Proc. 2022;97:20-21. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.11.019
An otherwise healthy 22-year-old woman presented with a painful eruption with burning and pruritus that had been slowly worsening as it spread over the last 4 weeks. The rash first appeared on the lower chest and inframammary folds (top) and spread to the upper chest, neck, back (bottom), arms, and lower face. Physical examination revealed multiple illdefined, erythematous papules, patches, and plaques on the chest, back, neck, and upper abdomen. Individual lesions coalesced into plaques that displayed a reticular configuration. There were no lesions in the axillae. The patient had been following a low-carbohydrate diet for 4 months. A punch biopsy was performed.
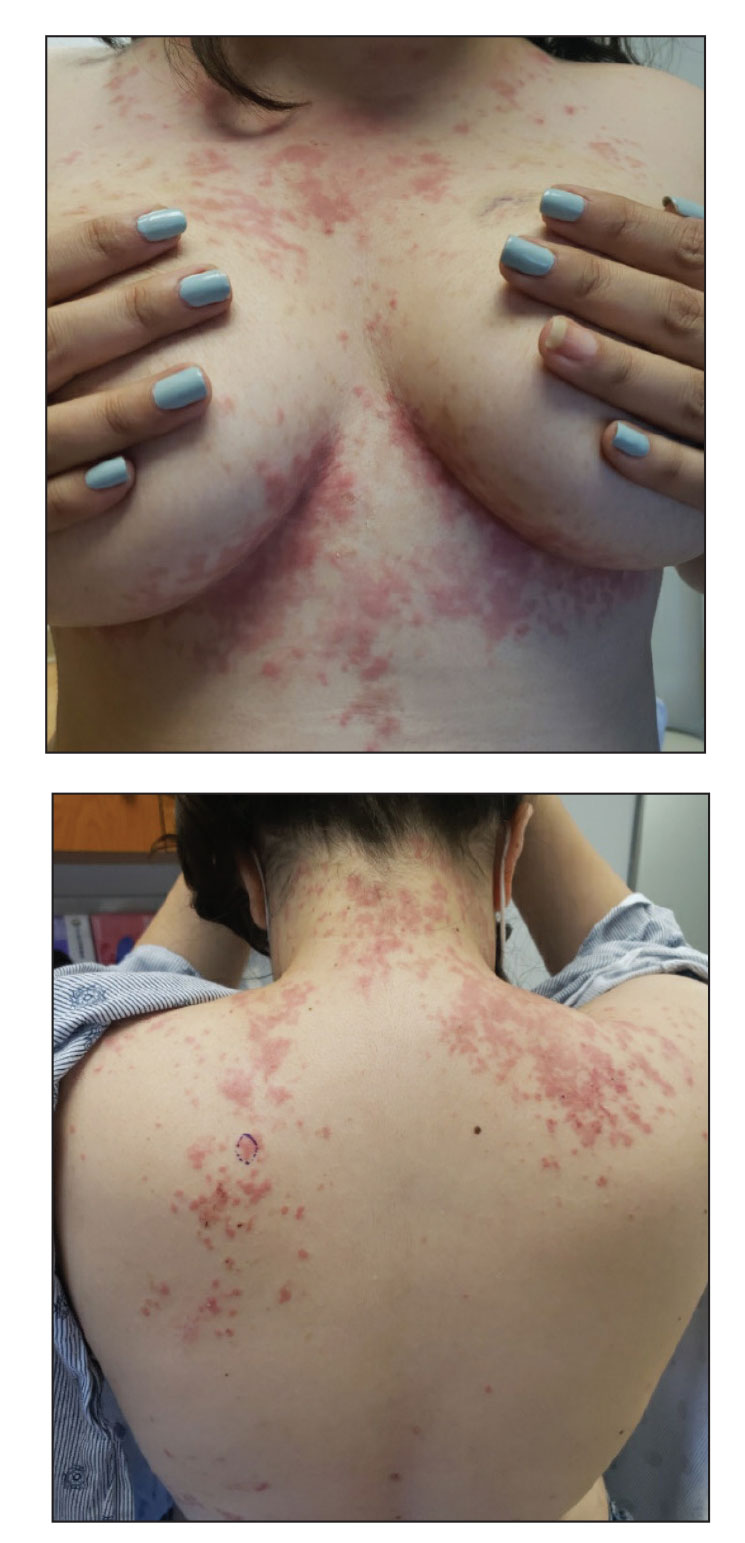
Low disease state for childhood lupus approaches validation
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANCHESTER, ENGLAND – An age-appropriate version of the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) has been developed by an international task force that will hopefully enable childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) to be treated to target in the near future.
The new childhood LLDAS (cLLDAS) has been purposefully developed to align with that already used for adults, Eve Smith, MBChB, PhD, explained at the annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology.
“There’s a lot of compelling data that’s accumulating from adult lupus and increasingly from childhood lupus that [treat to target] might be a good idea,” said Dr. Smith, who is a senior clinical fellow and honorary consultant at the University of Liverpool (England) and Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust Hospital, also in Liverpool.
Urgent need to improve childhood lupus outcomes
“We urgently need to do something to try and improve outcomes for children,” Dr. Smith said.
“We know that childhood lupus patients have got higher disease activity as compared to adults; they have a greater medication burden, particularly steroids; and they tend to have more severe organ manifestations,” she added.
Moreover, data show that one-fifth of pediatric patients with lupus have already accrued early damage, and there is much higher mortality associated with childhood lupus than there is with adult lupus.
“So, really we want to use treat to target as a way to try and improve on these aspects,” Dr. Smith said.
The treat-to-target (T2T) approach is not a new idea in lupus, with a lot of work already done in adult patients. One large study of more than 3,300 patients conducted in 13 countries has shown that patients who never achieve LLDAS are more likely to have high levels of damage, greater glucocorticoid use, worse quality of life, and higher mortality than are those who do.
Conversely, data have also shown that achieving a LLDAS is associated with a reduction in the risk for new damage, flares, and hospitalization, as well as reducing health care costs and improving patients’ overall health-related quality of life.
T2T is a recognized approach in European adult SLE guidelines, Dr. Smith said, although the approach has not really been fully realized as of yet, even in adult practice.
The cSLE T2T international task force and cLLDAS definition
With evidence accumulating on the benefits of getting children with SLE to a low disease activity state, Dr. Smith and colleague Michael Beresford, MBChB, PhD, Brough Chair, Professor of Child Health at the University of Liverpool, put out a call to develop a task force to look into the feasibility of a T2T approach.
“We had a really enthusiastic response internationally, which we were really encouraged by,” Dr. Smith said, “and we now lead a task force of 20 experts from across all five continents, and we have really strong patient involvement.”
Through a consensus process, an international cSLE T2T Task Force agreed on overarching principles and points to consider that will “lay the foundation for future T2T approaches in cSLE,” according to the recommendations statement, which was endorsed by the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Next, they looked to develop an age-appropriate definition for low disease activity.
“We’re deliberately wanting to maintain sufficient unity with the adult definition, so that we could facilitate life-course studies,” said Dr. Smith, who presented the results of a literature review and series of Delphi surveys at the meeting.
The conceptual definition of cLLDAS is similar to adults in describing it as a sustained state that is associated with a low likelihood of adverse outcome, Dr. Smith said, but with the added wording of “considering disease activity, damage, and medication toxicity.”
The definition is achieved when the SLE Disease Activity Index-2K is ≤ 4 and there is no activity in major organ systems; there are no new features of lupus disease activity since the last assessment; there is a score of ≤ 1 on Physician Global Assessment; steroid doses are ≤ 0.15 mg/kg/day or a maximum of 7.5 mg/day (whichever is lower); and immunosuppressive treatment is stable, with any changes to medication only because of side effects, adherence, changes in weight, or when in the process of reaching a target dose.
“It’s all very well having a definition, but you need to think about how that will work in practice,” Dr. Smith said. This is something that the task force is thinking about very carefully.
The task force next aims to validate the cLLDAS definition, form an extensive research agenda to inform the T2T methods, and develop innovative methods to apply the approach in practice.
The work is supported by the Wellcome Trust, National Institutes for Health Research, Versus Arthritis, and the University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and the Alder Hey Charity. Dr. Smith reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT BSR 2023
Part-time physician: Is it a viable career choice?
On average, physicians reported in the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 that they worked 50 hours per week. Five specialties, including critical care, cardiology, and general surgery reported working 55 or more hours weekly.
In 2011, The New England Journal of Medicine reported that part-time physician careers were rising. At the time, part-time doctors made up 21% of the physician workforce, up from 13% in 2005.
In a more recent survey from the California Health Care Foundation, only 12% of California physicians said they devoted 20-29 hours a week to patient care.
Amy Knoup, a senior recruitment adviser with Provider Solutions & Development), has been helping doctors find jobs for over a decade, and she’s noticed a trend.
“Not only are more physicians seeking part-time roles than they were 10 years ago, but more large health care systems are also offering part time or per diem as well,” said Ms. Knoup.
Who’s working part time, and why?
Ten years ago, the fastest growing segment of part-timers were men nearing retirement and early- to mid-career women.
Pediatricians led the part-time pack in 2002, according to an American Academy of Pediatrics study. At the time, 15% of pediatricians reported their hours as part time. However, the numbers may have increased over the years. For example, a 2021 study by the department of pediatrics, Boston Medical Center, and Boston University found that almost 30% of graduating pediatricians sought part-time work at the end of their training.
At PS&D, Ms. Knoup said she has noticed a trend toward part-timers among primary care, behavioral health, and outpatient specialties such as endocrinology. “We’re also seeing it with the inpatient side in roles that are more shift based like hospitalists, radiologists, and critical care and ER doctors.”
Another trend Ms. Knoup has noticed is with early-career doctors. “They have a different mindset,” she said. “Younger generations are acutely aware of burnout. They may have experienced it in residency or during the pandemic. They’ve had a taste of that and don’t want to go down that road again, so they’re seeking part-time roles. It’s an intentional choice.”
Tracey O’Connell, MD, a radiologist, always knew that she wanted to work part time. “I had a baby as a resident, and I was pregnant with my second child as a fellow,” she said. “I was already feeling overwhelmed with medical training and having a family.”
Dr. O’Connell worked in private practice for 16 years on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, with no nights or weekends.
“I still found it completely overwhelming,” she said. “Even though I had more days not working than working, I felt like the demands of medical life had advanced faster than human beings could adapt, and I still feel that way.”
Today she runs a part-time teleradiology practice from home but spends more time on her second career as a life coach. “Most of my clients are physicians looking for more fulfillment and sustainable ways of practicing medicine while maintaining their own identity as human beings, not just the all-consuming identity of ‘doctor,’ ” she said.
On the other end of the career spectrum is Lois Goodman, MD, an ob.gyn. in her late 70s. After 42 years in a group practice, she started her solo practice at 72, seeing patients 3 days per week. “I’m just happy to be working. That’s a tremendous payoff for me. I need to keep working for my mental health.”
How does part-time work affect physician shortages and care delivery?
Reducing clinical effort is one of the strategies physicians use to scale down overload. Still, it’s not viable as a long-term solution, said Christine Sinsky, MD, AMA’s vice president of professional satisfaction and a nationally regarded researcher on physician burnout.
“If all the physicians in a community went from working 100% FTE clinical to 50% FTE clinical, then the people in that community would have half the access to care that they had,” said Dr. Sinsky. “There’s less capacity in the system to care for patients.”
Some could argue, then, that part-time physician work may contribute to physician shortage predictions. An Association of American Medical Colleges report estimates there will be a shortage of 37,800 to 124,000 physicians by 2034.
But physicians working part-time express a contrasting point of view. “I don’t believe that part-time workers are responsible for the health care shortage but rather, a great solution,” said Dr. O’Connell. “Because in order to continue working for a long time rather than quitting when the demands exceed human capacity, working part time is a great compromise to offer a life of more sustainable well-being and longevity as a physician, and still live a wholehearted life.”
Pros and cons of being a part-time physician
Pros
Less burnout: The American Medical Association has tracked burnout rates for 22 years. By the end of 2021, nearly 63% of physicians reported burnout symptoms, compared with 38% the year before. Going part time appears to reduce burnout, suggests a study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Better work-life balance: Rachel Miller, MD, an ob.gyn., worked 60-70 hours weekly for 9 years. In 2022, she went to work as an OB hospitalist for a health care system that welcomes part-time clinicians. Since then, she has achieved a better work-life balance, putting in 26-28 hours a week. Dr. Miller now spends more time with her kids and in her additional role as an executive coach to leaders in the medical field.
More focus: “When I’m at work, I’m 100% mentally in and focused,” said Dr. Miller. “My interactions with patients are different because I’m not burned out. My demeanor and my willingness to connect are stronger.”
Better health: Mehmet Cilingiroglu, MD, with CardioSolution, traded full-time work for part time when health issues and a kidney transplant sidelined his 30-year career in 2018. “Despite my significant health issues, I’ve been able to continue working at a pace that suits me rather than having to retire,” he said. “Part-time physicians can still enjoy patient care, research, innovation, education, and training while balancing that with other areas of life.”
Errin Weisman, a DO who gave up full-time work in 2016, said cutting back makes her feel healthier, happier, and more energized. “Part-time work helps me to bring my A game each day I work and deliver the best care.” She’s also a life coach encouraging other physicians to find balance in their professional and personal lives.
Cons
Cut in pay: Obviously, the No. 1 con is you’ll make less working part time, so adjusting to a salary decrease can be a huge issue, especially if you don’t have other sources of income. Physicians paying off student loans, those caring for children or elderly parents, or those in their prime earning years needing to save for retirement may not be able to go part time.
Diminished career: The chance for promotions or being well known in your field can be diminished, as well as a loss of proficiency if you’re only performing surgery or procedures part time. In some specialties, working part time and not keeping up with (or being able to practice) newer technology developments can harm your career or reputation in the long run.
Missing out: While working part time has many benefits, physicians also experience a wide range of drawbacks. Dr. Goodman, for example, said she misses delivering babies and doing surgeries. Dr. Miller said she gave up some aspects of her specialty, like performing hysterectomies, participating in complex cases, and no longer having an office like she did as a full-time ob.gyn.
Loss of fellowship: Dr. O’Connell said she missed the camaraderie and sense of belonging when she scaled back her hours. “I felt like a fish out of water, that my values didn’t align with the group’s values,” she said. This led to self-doubt, frustrated colleagues, and a reduction in benefits.
Lost esteem: Dr. O’Connell also felt she was expected to work overtime without additional pay and was no longer eligible for bonuses. “I was treated as a team player when I was needed, but not when it came to perks and benefits and insider privilege,” she said. There may be a loss of esteem among colleagues and supervisors.
Overcoming stigma: Because part-time physician work is still not prevalent among colleagues, some may resist the idea, have less respect for it, perceive it as not being serious about your career as a physician, or associate it with being lazy or entitled.
Summing it up
Every physician must weigh the value and drawbacks of part-time work, but the more physicians who go this route, the more part-time medicine gains traction and the more physicians can learn about its values versus its drawbacks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On average, physicians reported in the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 that they worked 50 hours per week. Five specialties, including critical care, cardiology, and general surgery reported working 55 or more hours weekly.
In 2011, The New England Journal of Medicine reported that part-time physician careers were rising. At the time, part-time doctors made up 21% of the physician workforce, up from 13% in 2005.
In a more recent survey from the California Health Care Foundation, only 12% of California physicians said they devoted 20-29 hours a week to patient care.
Amy Knoup, a senior recruitment adviser with Provider Solutions & Development), has been helping doctors find jobs for over a decade, and she’s noticed a trend.
“Not only are more physicians seeking part-time roles than they were 10 years ago, but more large health care systems are also offering part time or per diem as well,” said Ms. Knoup.
Who’s working part time, and why?
Ten years ago, the fastest growing segment of part-timers were men nearing retirement and early- to mid-career women.
Pediatricians led the part-time pack in 2002, according to an American Academy of Pediatrics study. At the time, 15% of pediatricians reported their hours as part time. However, the numbers may have increased over the years. For example, a 2021 study by the department of pediatrics, Boston Medical Center, and Boston University found that almost 30% of graduating pediatricians sought part-time work at the end of their training.
At PS&D, Ms. Knoup said she has noticed a trend toward part-timers among primary care, behavioral health, and outpatient specialties such as endocrinology. “We’re also seeing it with the inpatient side in roles that are more shift based like hospitalists, radiologists, and critical care and ER doctors.”
Another trend Ms. Knoup has noticed is with early-career doctors. “They have a different mindset,” she said. “Younger generations are acutely aware of burnout. They may have experienced it in residency or during the pandemic. They’ve had a taste of that and don’t want to go down that road again, so they’re seeking part-time roles. It’s an intentional choice.”
Tracey O’Connell, MD, a radiologist, always knew that she wanted to work part time. “I had a baby as a resident, and I was pregnant with my second child as a fellow,” she said. “I was already feeling overwhelmed with medical training and having a family.”
Dr. O’Connell worked in private practice for 16 years on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, with no nights or weekends.
“I still found it completely overwhelming,” she said. “Even though I had more days not working than working, I felt like the demands of medical life had advanced faster than human beings could adapt, and I still feel that way.”
Today she runs a part-time teleradiology practice from home but spends more time on her second career as a life coach. “Most of my clients are physicians looking for more fulfillment and sustainable ways of practicing medicine while maintaining their own identity as human beings, not just the all-consuming identity of ‘doctor,’ ” she said.
On the other end of the career spectrum is Lois Goodman, MD, an ob.gyn. in her late 70s. After 42 years in a group practice, she started her solo practice at 72, seeing patients 3 days per week. “I’m just happy to be working. That’s a tremendous payoff for me. I need to keep working for my mental health.”
How does part-time work affect physician shortages and care delivery?
Reducing clinical effort is one of the strategies physicians use to scale down overload. Still, it’s not viable as a long-term solution, said Christine Sinsky, MD, AMA’s vice president of professional satisfaction and a nationally regarded researcher on physician burnout.
“If all the physicians in a community went from working 100% FTE clinical to 50% FTE clinical, then the people in that community would have half the access to care that they had,” said Dr. Sinsky. “There’s less capacity in the system to care for patients.”
Some could argue, then, that part-time physician work may contribute to physician shortage predictions. An Association of American Medical Colleges report estimates there will be a shortage of 37,800 to 124,000 physicians by 2034.
But physicians working part-time express a contrasting point of view. “I don’t believe that part-time workers are responsible for the health care shortage but rather, a great solution,” said Dr. O’Connell. “Because in order to continue working for a long time rather than quitting when the demands exceed human capacity, working part time is a great compromise to offer a life of more sustainable well-being and longevity as a physician, and still live a wholehearted life.”
Pros and cons of being a part-time physician
Pros
Less burnout: The American Medical Association has tracked burnout rates for 22 years. By the end of 2021, nearly 63% of physicians reported burnout symptoms, compared with 38% the year before. Going part time appears to reduce burnout, suggests a study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Better work-life balance: Rachel Miller, MD, an ob.gyn., worked 60-70 hours weekly for 9 years. In 2022, she went to work as an OB hospitalist for a health care system that welcomes part-time clinicians. Since then, she has achieved a better work-life balance, putting in 26-28 hours a week. Dr. Miller now spends more time with her kids and in her additional role as an executive coach to leaders in the medical field.
More focus: “When I’m at work, I’m 100% mentally in and focused,” said Dr. Miller. “My interactions with patients are different because I’m not burned out. My demeanor and my willingness to connect are stronger.”
Better health: Mehmet Cilingiroglu, MD, with CardioSolution, traded full-time work for part time when health issues and a kidney transplant sidelined his 30-year career in 2018. “Despite my significant health issues, I’ve been able to continue working at a pace that suits me rather than having to retire,” he said. “Part-time physicians can still enjoy patient care, research, innovation, education, and training while balancing that with other areas of life.”
Errin Weisman, a DO who gave up full-time work in 2016, said cutting back makes her feel healthier, happier, and more energized. “Part-time work helps me to bring my A game each day I work and deliver the best care.” She’s also a life coach encouraging other physicians to find balance in their professional and personal lives.
Cons
Cut in pay: Obviously, the No. 1 con is you’ll make less working part time, so adjusting to a salary decrease can be a huge issue, especially if you don’t have other sources of income. Physicians paying off student loans, those caring for children or elderly parents, or those in their prime earning years needing to save for retirement may not be able to go part time.
Diminished career: The chance for promotions or being well known in your field can be diminished, as well as a loss of proficiency if you’re only performing surgery or procedures part time. In some specialties, working part time and not keeping up with (or being able to practice) newer technology developments can harm your career or reputation in the long run.
Missing out: While working part time has many benefits, physicians also experience a wide range of drawbacks. Dr. Goodman, for example, said she misses delivering babies and doing surgeries. Dr. Miller said she gave up some aspects of her specialty, like performing hysterectomies, participating in complex cases, and no longer having an office like she did as a full-time ob.gyn.
Loss of fellowship: Dr. O’Connell said she missed the camaraderie and sense of belonging when she scaled back her hours. “I felt like a fish out of water, that my values didn’t align with the group’s values,” she said. This led to self-doubt, frustrated colleagues, and a reduction in benefits.
Lost esteem: Dr. O’Connell also felt she was expected to work overtime without additional pay and was no longer eligible for bonuses. “I was treated as a team player when I was needed, but not when it came to perks and benefits and insider privilege,” she said. There may be a loss of esteem among colleagues and supervisors.
Overcoming stigma: Because part-time physician work is still not prevalent among colleagues, some may resist the idea, have less respect for it, perceive it as not being serious about your career as a physician, or associate it with being lazy or entitled.
Summing it up
Every physician must weigh the value and drawbacks of part-time work, but the more physicians who go this route, the more part-time medicine gains traction and the more physicians can learn about its values versus its drawbacks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On average, physicians reported in the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2023 that they worked 50 hours per week. Five specialties, including critical care, cardiology, and general surgery reported working 55 or more hours weekly.
In 2011, The New England Journal of Medicine reported that part-time physician careers were rising. At the time, part-time doctors made up 21% of the physician workforce, up from 13% in 2005.
In a more recent survey from the California Health Care Foundation, only 12% of California physicians said they devoted 20-29 hours a week to patient care.
Amy Knoup, a senior recruitment adviser with Provider Solutions & Development), has been helping doctors find jobs for over a decade, and she’s noticed a trend.
“Not only are more physicians seeking part-time roles than they were 10 years ago, but more large health care systems are also offering part time or per diem as well,” said Ms. Knoup.
Who’s working part time, and why?
Ten years ago, the fastest growing segment of part-timers were men nearing retirement and early- to mid-career women.
Pediatricians led the part-time pack in 2002, according to an American Academy of Pediatrics study. At the time, 15% of pediatricians reported their hours as part time. However, the numbers may have increased over the years. For example, a 2021 study by the department of pediatrics, Boston Medical Center, and Boston University found that almost 30% of graduating pediatricians sought part-time work at the end of their training.
At PS&D, Ms. Knoup said she has noticed a trend toward part-timers among primary care, behavioral health, and outpatient specialties such as endocrinology. “We’re also seeing it with the inpatient side in roles that are more shift based like hospitalists, radiologists, and critical care and ER doctors.”
Another trend Ms. Knoup has noticed is with early-career doctors. “They have a different mindset,” she said. “Younger generations are acutely aware of burnout. They may have experienced it in residency or during the pandemic. They’ve had a taste of that and don’t want to go down that road again, so they’re seeking part-time roles. It’s an intentional choice.”
Tracey O’Connell, MD, a radiologist, always knew that she wanted to work part time. “I had a baby as a resident, and I was pregnant with my second child as a fellow,” she said. “I was already feeling overwhelmed with medical training and having a family.”
Dr. O’Connell worked in private practice for 16 years on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, with no nights or weekends.
“I still found it completely overwhelming,” she said. “Even though I had more days not working than working, I felt like the demands of medical life had advanced faster than human beings could adapt, and I still feel that way.”
Today she runs a part-time teleradiology practice from home but spends more time on her second career as a life coach. “Most of my clients are physicians looking for more fulfillment and sustainable ways of practicing medicine while maintaining their own identity as human beings, not just the all-consuming identity of ‘doctor,’ ” she said.
On the other end of the career spectrum is Lois Goodman, MD, an ob.gyn. in her late 70s. After 42 years in a group practice, she started her solo practice at 72, seeing patients 3 days per week. “I’m just happy to be working. That’s a tremendous payoff for me. I need to keep working for my mental health.”
How does part-time work affect physician shortages and care delivery?
Reducing clinical effort is one of the strategies physicians use to scale down overload. Still, it’s not viable as a long-term solution, said Christine Sinsky, MD, AMA’s vice president of professional satisfaction and a nationally regarded researcher on physician burnout.
“If all the physicians in a community went from working 100% FTE clinical to 50% FTE clinical, then the people in that community would have half the access to care that they had,” said Dr. Sinsky. “There’s less capacity in the system to care for patients.”
Some could argue, then, that part-time physician work may contribute to physician shortage predictions. An Association of American Medical Colleges report estimates there will be a shortage of 37,800 to 124,000 physicians by 2034.
But physicians working part-time express a contrasting point of view. “I don’t believe that part-time workers are responsible for the health care shortage but rather, a great solution,” said Dr. O’Connell. “Because in order to continue working for a long time rather than quitting when the demands exceed human capacity, working part time is a great compromise to offer a life of more sustainable well-being and longevity as a physician, and still live a wholehearted life.”
Pros and cons of being a part-time physician
Pros
Less burnout: The American Medical Association has tracked burnout rates for 22 years. By the end of 2021, nearly 63% of physicians reported burnout symptoms, compared with 38% the year before. Going part time appears to reduce burnout, suggests a study published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Better work-life balance: Rachel Miller, MD, an ob.gyn., worked 60-70 hours weekly for 9 years. In 2022, she went to work as an OB hospitalist for a health care system that welcomes part-time clinicians. Since then, she has achieved a better work-life balance, putting in 26-28 hours a week. Dr. Miller now spends more time with her kids and in her additional role as an executive coach to leaders in the medical field.
More focus: “When I’m at work, I’m 100% mentally in and focused,” said Dr. Miller. “My interactions with patients are different because I’m not burned out. My demeanor and my willingness to connect are stronger.”
Better health: Mehmet Cilingiroglu, MD, with CardioSolution, traded full-time work for part time when health issues and a kidney transplant sidelined his 30-year career in 2018. “Despite my significant health issues, I’ve been able to continue working at a pace that suits me rather than having to retire,” he said. “Part-time physicians can still enjoy patient care, research, innovation, education, and training while balancing that with other areas of life.”
Errin Weisman, a DO who gave up full-time work in 2016, said cutting back makes her feel healthier, happier, and more energized. “Part-time work helps me to bring my A game each day I work and deliver the best care.” She’s also a life coach encouraging other physicians to find balance in their professional and personal lives.
Cons
Cut in pay: Obviously, the No. 1 con is you’ll make less working part time, so adjusting to a salary decrease can be a huge issue, especially if you don’t have other sources of income. Physicians paying off student loans, those caring for children or elderly parents, or those in their prime earning years needing to save for retirement may not be able to go part time.
Diminished career: The chance for promotions or being well known in your field can be diminished, as well as a loss of proficiency if you’re only performing surgery or procedures part time. In some specialties, working part time and not keeping up with (or being able to practice) newer technology developments can harm your career or reputation in the long run.
Missing out: While working part time has many benefits, physicians also experience a wide range of drawbacks. Dr. Goodman, for example, said she misses delivering babies and doing surgeries. Dr. Miller said she gave up some aspects of her specialty, like performing hysterectomies, participating in complex cases, and no longer having an office like she did as a full-time ob.gyn.
Loss of fellowship: Dr. O’Connell said she missed the camaraderie and sense of belonging when she scaled back her hours. “I felt like a fish out of water, that my values didn’t align with the group’s values,” she said. This led to self-doubt, frustrated colleagues, and a reduction in benefits.
Lost esteem: Dr. O’Connell also felt she was expected to work overtime without additional pay and was no longer eligible for bonuses. “I was treated as a team player when I was needed, but not when it came to perks and benefits and insider privilege,” she said. There may be a loss of esteem among colleagues and supervisors.
Overcoming stigma: Because part-time physician work is still not prevalent among colleagues, some may resist the idea, have less respect for it, perceive it as not being serious about your career as a physician, or associate it with being lazy or entitled.
Summing it up
Every physician must weigh the value and drawbacks of part-time work, but the more physicians who go this route, the more part-time medicine gains traction and the more physicians can learn about its values versus its drawbacks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mohs surgery improves survival in early-stage Merkel cell carcinoma
SEATTLE – The use of
Compared with conventional wide local excision, survival was significantly improved among patients treated with Mohs, and a subgroup analysis showed that the survival benefit remained for patients with risk factors.
“At 10 years, overall survival was about 21% higher for those treated with Mohs surgery versus those treated with conventional surgery,” said lead author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, a dermatology resident at the New York University School of Medicine. “On multivariable analysis, which controlled for tumor and patient factors, Mohs was associated with an over 40% reduction in the hazard for death.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a rare, aggressive, neuroendocrine cutaneous malignancy that carries a high mortality rate. The estimated 5-year survival for patients with localized disease is about 50%, Dr. Cheraghlou noted. “That extrapolates to about 55% for T1 tumors and down to about 30% for T4 tumors.”
Although it’s considered to be a rare cancer, the incidence of MCC has been rapidly rising, and in fact it doubled during the period from the 1990s to the 2010s.
Most commonly treated with wide local excision with or without adjuvant radiation therapy, Mohs as monotherapy may offer an alternative treatment option for patients with MCC. It is generally accepted that the optimal treatment for tumors without regional lymph node involvement is surgical, but the data regarding the optimal surgical approach are mixed. Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that either Mohs surgery or wide local excision can be used.
“However, these guidelines do not indicate a preference for one modality over the other,” said Dr. Cheraghlou, “and present them as interchangeable treatment options.”
A growing body of literature supports Mohs surgery for many types of rare tumors, including MCC. For example, as previously reported at the 2021 ACMS meeting, one study found that Mohs surgery compared favorably with the standard treatment approach when it came to recurrence rates for patients with MCC. The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for patients with stage I disease and 68.6% for patients with stage IIa. These rates were comparable with rates for historical control patients who were treated with wide local excision, with or without radiation (81%-87% for stage I disease, and 63%-67% for stage II).
Study details
In the current study, Dr. Cheraghlou and colleagues sought to evaluate the association of the type of surgical approach with patient survival after excision of early-stage MCC. They conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Cancer Database to identify cases of MCC with T1/T2 tumors. A total of 2,313 patients who were diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 with pathologically confirmed negative lymph node involvement and who were treated with Mohs surgery or wide lesion excision were included in the analysis.
“About 90% were T1 tumors, about 40% were located on the head and neck, and the vast majority – about 60% – were treated with wide local excision,” he explained. “Only about 5% received Mohs surgery for treatment of the primary tumor.”
But when the researchers assessed survival outcomes, they found that treatment with Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved overall survival.
The unadjusted 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates for patients treated with Mohs was 87.4% (SE: 3.4%), 84.5% (SE: 3.9%), and 81.8% (SE: 4.6%), respectively, while for wide lesion excision, the rates were 86.1% (SE: 0.9%), 76.9% (SE: 1.2%), and 60.9% (SE: 2.0%), respectively.
For patients who underwent treatment with narrow margin excision, survival rates were similar as for those treated with wide lesion excision, with 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates of 84.8% (SE: 1.4%), 78.3% (SE: 1.7%), and 60.8% (SE: 3.6%), respectively.
On multivariable survival analysis, Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with wide lesion excision (hazard ratio, 0.594; P = .038). This was also true after multivariable analysis for patients who had one or more NCCN risk factors, for whom improved survival was also seen with Mohs (HR, 0.530; P = .026).
The results did not differ after a sensitivity analysis that included T3 and T4 tumors.
Given that the use of Mohs was so infrequent, compared with standard surgery, the researchers investigated the factors that were associated with the use of Mohs. High-volume MCC centers were significantly more likely to utilize Mohs than wide lesion excision (odds ratio, 1.993; P < .001), compared with other facilities.
“This study has important implications going forward,” Dr. Cheraghlou concluded. “We think it’s important how few patients were treated with Mohs for Merkel cell, and it was slightly more likely to happen in a high-volume center.”
The reasoning for that may be that high-volume centers are more likely to have a surgeon trained to perform Mohs surgery for MCC. “Or perhaps they are more attuned to the benefits of this procedure,” he said. “We can’t tell that from our data, but its notable that it’s such a small proportion of patients – especially when we consider that it is associated with improved survival for the patients who receive it.”
He added that efforts to increase the utilization of Mohs may yield improved local control and overall survival for these patients. “And perhaps with more data, future versions of guidelines may indicate a preference for Mohs over conventional incisions.”
No changes to current practice
Asked to comment on the study, Anthony J. Olszanski, RPh, MD, associate professor, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that while the results are intriguing, they must be interpreted with caution.
“This study was retrospective in nature, and unrecognized biases can influence results,” he said. “Additionally, given the relative rarity of Merkel cell carcinoma, the sample size is expectantly small.”
But importantly, Dr. Olszanski emphasized, Mohs may more often have been recommended for patients with lesions that appear less aggressive. “Many patients undergoing wide lesion excision may have been referred by Mohs surgeons secondary to features or characteristics of lesions which were worrisome,” he explained. “The results of this study do not opine on why Mohs would impact overall survival over wide lesion excision, a point worthy of consideration. Presently, both modalities can be considered for patients with T1/T2 MCC. The results of this study should not change current practice and would lend themselves to a more robust study.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Cheraghlou has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Olszanski has received financial support from Merck and BMS for participated on advisory boards.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE – The use of
Compared with conventional wide local excision, survival was significantly improved among patients treated with Mohs, and a subgroup analysis showed that the survival benefit remained for patients with risk factors.
“At 10 years, overall survival was about 21% higher for those treated with Mohs surgery versus those treated with conventional surgery,” said lead author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, a dermatology resident at the New York University School of Medicine. “On multivariable analysis, which controlled for tumor and patient factors, Mohs was associated with an over 40% reduction in the hazard for death.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a rare, aggressive, neuroendocrine cutaneous malignancy that carries a high mortality rate. The estimated 5-year survival for patients with localized disease is about 50%, Dr. Cheraghlou noted. “That extrapolates to about 55% for T1 tumors and down to about 30% for T4 tumors.”
Although it’s considered to be a rare cancer, the incidence of MCC has been rapidly rising, and in fact it doubled during the period from the 1990s to the 2010s.
Most commonly treated with wide local excision with or without adjuvant radiation therapy, Mohs as monotherapy may offer an alternative treatment option for patients with MCC. It is generally accepted that the optimal treatment for tumors without regional lymph node involvement is surgical, but the data regarding the optimal surgical approach are mixed. Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that either Mohs surgery or wide local excision can be used.
“However, these guidelines do not indicate a preference for one modality over the other,” said Dr. Cheraghlou, “and present them as interchangeable treatment options.”
A growing body of literature supports Mohs surgery for many types of rare tumors, including MCC. For example, as previously reported at the 2021 ACMS meeting, one study found that Mohs surgery compared favorably with the standard treatment approach when it came to recurrence rates for patients with MCC. The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for patients with stage I disease and 68.6% for patients with stage IIa. These rates were comparable with rates for historical control patients who were treated with wide local excision, with or without radiation (81%-87% for stage I disease, and 63%-67% for stage II).
Study details
In the current study, Dr. Cheraghlou and colleagues sought to evaluate the association of the type of surgical approach with patient survival after excision of early-stage MCC. They conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Cancer Database to identify cases of MCC with T1/T2 tumors. A total of 2,313 patients who were diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 with pathologically confirmed negative lymph node involvement and who were treated with Mohs surgery or wide lesion excision were included in the analysis.
“About 90% were T1 tumors, about 40% were located on the head and neck, and the vast majority – about 60% – were treated with wide local excision,” he explained. “Only about 5% received Mohs surgery for treatment of the primary tumor.”
But when the researchers assessed survival outcomes, they found that treatment with Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved overall survival.
The unadjusted 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates for patients treated with Mohs was 87.4% (SE: 3.4%), 84.5% (SE: 3.9%), and 81.8% (SE: 4.6%), respectively, while for wide lesion excision, the rates were 86.1% (SE: 0.9%), 76.9% (SE: 1.2%), and 60.9% (SE: 2.0%), respectively.
For patients who underwent treatment with narrow margin excision, survival rates were similar as for those treated with wide lesion excision, with 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates of 84.8% (SE: 1.4%), 78.3% (SE: 1.7%), and 60.8% (SE: 3.6%), respectively.
On multivariable survival analysis, Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with wide lesion excision (hazard ratio, 0.594; P = .038). This was also true after multivariable analysis for patients who had one or more NCCN risk factors, for whom improved survival was also seen with Mohs (HR, 0.530; P = .026).
The results did not differ after a sensitivity analysis that included T3 and T4 tumors.
Given that the use of Mohs was so infrequent, compared with standard surgery, the researchers investigated the factors that were associated with the use of Mohs. High-volume MCC centers were significantly more likely to utilize Mohs than wide lesion excision (odds ratio, 1.993; P < .001), compared with other facilities.
“This study has important implications going forward,” Dr. Cheraghlou concluded. “We think it’s important how few patients were treated with Mohs for Merkel cell, and it was slightly more likely to happen in a high-volume center.”
The reasoning for that may be that high-volume centers are more likely to have a surgeon trained to perform Mohs surgery for MCC. “Or perhaps they are more attuned to the benefits of this procedure,” he said. “We can’t tell that from our data, but its notable that it’s such a small proportion of patients – especially when we consider that it is associated with improved survival for the patients who receive it.”
He added that efforts to increase the utilization of Mohs may yield improved local control and overall survival for these patients. “And perhaps with more data, future versions of guidelines may indicate a preference for Mohs over conventional incisions.”
No changes to current practice
Asked to comment on the study, Anthony J. Olszanski, RPh, MD, associate professor, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that while the results are intriguing, they must be interpreted with caution.
“This study was retrospective in nature, and unrecognized biases can influence results,” he said. “Additionally, given the relative rarity of Merkel cell carcinoma, the sample size is expectantly small.”
But importantly, Dr. Olszanski emphasized, Mohs may more often have been recommended for patients with lesions that appear less aggressive. “Many patients undergoing wide lesion excision may have been referred by Mohs surgeons secondary to features or characteristics of lesions which were worrisome,” he explained. “The results of this study do not opine on why Mohs would impact overall survival over wide lesion excision, a point worthy of consideration. Presently, both modalities can be considered for patients with T1/T2 MCC. The results of this study should not change current practice and would lend themselves to a more robust study.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Cheraghlou has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Olszanski has received financial support from Merck and BMS for participated on advisory boards.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SEATTLE – The use of
Compared with conventional wide local excision, survival was significantly improved among patients treated with Mohs, and a subgroup analysis showed that the survival benefit remained for patients with risk factors.
“At 10 years, overall survival was about 21% higher for those treated with Mohs surgery versus those treated with conventional surgery,” said lead author Shayan Cheraghlou, MD, a dermatology resident at the New York University School of Medicine. “On multivariable analysis, which controlled for tumor and patient factors, Mohs was associated with an over 40% reduction in the hazard for death.”
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
MCC is a rare, aggressive, neuroendocrine cutaneous malignancy that carries a high mortality rate. The estimated 5-year survival for patients with localized disease is about 50%, Dr. Cheraghlou noted. “That extrapolates to about 55% for T1 tumors and down to about 30% for T4 tumors.”
Although it’s considered to be a rare cancer, the incidence of MCC has been rapidly rising, and in fact it doubled during the period from the 1990s to the 2010s.
Most commonly treated with wide local excision with or without adjuvant radiation therapy, Mohs as monotherapy may offer an alternative treatment option for patients with MCC. It is generally accepted that the optimal treatment for tumors without regional lymph node involvement is surgical, but the data regarding the optimal surgical approach are mixed. Current National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines state that either Mohs surgery or wide local excision can be used.
“However, these guidelines do not indicate a preference for one modality over the other,” said Dr. Cheraghlou, “and present them as interchangeable treatment options.”
A growing body of literature supports Mohs surgery for many types of rare tumors, including MCC. For example, as previously reported at the 2021 ACMS meeting, one study found that Mohs surgery compared favorably with the standard treatment approach when it came to recurrence rates for patients with MCC. The 5-year disease-specific survival rate was 91.2% for patients with stage I disease and 68.6% for patients with stage IIa. These rates were comparable with rates for historical control patients who were treated with wide local excision, with or without radiation (81%-87% for stage I disease, and 63%-67% for stage II).
Study details
In the current study, Dr. Cheraghlou and colleagues sought to evaluate the association of the type of surgical approach with patient survival after excision of early-stage MCC. They conducted a retrospective cohort study using the National Cancer Database to identify cases of MCC with T1/T2 tumors. A total of 2,313 patients who were diagnosed from 2004 to 2018 with pathologically confirmed negative lymph node involvement and who were treated with Mohs surgery or wide lesion excision were included in the analysis.
“About 90% were T1 tumors, about 40% were located on the head and neck, and the vast majority – about 60% – were treated with wide local excision,” he explained. “Only about 5% received Mohs surgery for treatment of the primary tumor.”
But when the researchers assessed survival outcomes, they found that treatment with Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved overall survival.
The unadjusted 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates for patients treated with Mohs was 87.4% (SE: 3.4%), 84.5% (SE: 3.9%), and 81.8% (SE: 4.6%), respectively, while for wide lesion excision, the rates were 86.1% (SE: 0.9%), 76.9% (SE: 1.2%), and 60.9% (SE: 2.0%), respectively.
For patients who underwent treatment with narrow margin excision, survival rates were similar as for those treated with wide lesion excision, with 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival rates of 84.8% (SE: 1.4%), 78.3% (SE: 1.7%), and 60.8% (SE: 3.6%), respectively.
On multivariable survival analysis, Mohs surgery was associated with significantly improved survival, compared with wide lesion excision (hazard ratio, 0.594; P = .038). This was also true after multivariable analysis for patients who had one or more NCCN risk factors, for whom improved survival was also seen with Mohs (HR, 0.530; P = .026).
The results did not differ after a sensitivity analysis that included T3 and T4 tumors.
Given that the use of Mohs was so infrequent, compared with standard surgery, the researchers investigated the factors that were associated with the use of Mohs. High-volume MCC centers were significantly more likely to utilize Mohs than wide lesion excision (odds ratio, 1.993; P < .001), compared with other facilities.
“This study has important implications going forward,” Dr. Cheraghlou concluded. “We think it’s important how few patients were treated with Mohs for Merkel cell, and it was slightly more likely to happen in a high-volume center.”
The reasoning for that may be that high-volume centers are more likely to have a surgeon trained to perform Mohs surgery for MCC. “Or perhaps they are more attuned to the benefits of this procedure,” he said. “We can’t tell that from our data, but its notable that it’s such a small proportion of patients – especially when we consider that it is associated with improved survival for the patients who receive it.”
He added that efforts to increase the utilization of Mohs may yield improved local control and overall survival for these patients. “And perhaps with more data, future versions of guidelines may indicate a preference for Mohs over conventional incisions.”
No changes to current practice
Asked to comment on the study, Anthony J. Olszanski, RPh, MD, associate professor, department of hematology/oncology, Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, noted that while the results are intriguing, they must be interpreted with caution.
“This study was retrospective in nature, and unrecognized biases can influence results,” he said. “Additionally, given the relative rarity of Merkel cell carcinoma, the sample size is expectantly small.”
But importantly, Dr. Olszanski emphasized, Mohs may more often have been recommended for patients with lesions that appear less aggressive. “Many patients undergoing wide lesion excision may have been referred by Mohs surgeons secondary to features or characteristics of lesions which were worrisome,” he explained. “The results of this study do not opine on why Mohs would impact overall survival over wide lesion excision, a point worthy of consideration. Presently, both modalities can be considered for patients with T1/T2 MCC. The results of this study should not change current practice and would lend themselves to a more robust study.”
No external funding of the study was reported. Dr. Cheraghlou has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Olszanski has received financial support from Merck and BMS for participated on advisory boards.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACMS 2023
Surprisingly more nonsustained VT shown in HCM using extended ECG monitoring
BARCELONA – , suggests a study that questions current risk stratification practices in HCM.
In the registry study, such arrythmias were observed in about six times as many HCM patients during 30 days of ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring as would have been identified based on the first 24 hours of the monitoring period: 65% vs. 11% of the cohort.
Also, about 62% of the patients showed NSVT at “extended” 30-day monitoring, compared with an 8% prevalence of the arrhythmia based on the more conventional ECG monitoring period of 24 hours.
Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia, an important arrhythmia used every day in clinical practice to make decisions, is “much, much more prevalent than we thought” in patients with HCM, Juan Caro Codón, MD, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “We should invest in further research regarding extended ECG monitoring in these patients.”
Dr. Caro Codón, of La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, presented the findings from the TEMPO-HCM study at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held in Barcelona and virtually.
Its results, he said, have implications for stratifying HCM patients according to their risk for sudden cardiac death in deciding who should be offered an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
The life-incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients like those in the current analysis has previously been found to be about 20%, and the life-prevalence of NSVT about 20%-30%, using traditional 24- or 48-hour Holter monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“These arrhythmias are clinically relevant events because they are linked to very meaningful clinical endpoints,” including stroke and thromboembolism, he said, “but also for sudden cardiac death.”
Extended ECG monitoring has been shown useful in the setting of cryptogenic stroke and after AF ablation, but similar findings have been scarce in HCM. Patients using personal wearable monitors such as smart watches, Dr. Caro Codón said, have come to his clinic with concerns that the devices may have signaled a problem. But the lack of relevant data leaves them without a sufficient answer.
In other findings, invited discussant Isabelle van Gelder, MD, PhD, observed after Dr. Caro Codón’s presentation that the number of patients with AF almost doubled based on extended monitoring, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring.
Based on European Society of Cardiology guidelines from 2020, “Once clinical AF has been documented, there is a class IIA recommendation to start anticoagulation,” said Dr. van Gelder, University of Groningen, the Netherlands. “Therefore, your data really are a call for more data on screening for AF in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients.”
Prospective multicenter registry
The TEMPO-HCM registry includes patients with HCM and a clinical indication for standard Holter monitoring at five hospitals in Spain. It excludes patients with an HCM-like phenotype but who lack the telltale genotype, as well as those already implanted with an ICD.
Those in the current analysis underwent 30-day ECG monitoring with a small, wearable device that Dr. Caro Codón described as about 7 cm long, worn in what is essentially a T-shirt with a pocket. Patients could remove the shirt and device to bathe or go swimming, for example, and still be monitored for most of the day.
The analysis included the registry’s first 100 patients (mean age, 57 years; 78% male). Hypertension was present in 47%, 58% were on beta-blockers, 16% had prior AF or atrial flutter, and 19% were taking anticoagulants. Only 8% were on antiarrhythmic drugs, Dr. Caro Codón reported.
The patients had good functional status (68% and 29% were in NYHA class 1 and 2, respectively) and their left ventricular ejection fraction averaged 66%. Of the 71 patients who underwent MRI, 28.2% showed late gadolinium enhancement suggesting myocardial scarring.
More arrhythmias on 30-day monitoring
The primary endpoint of clinically relevant arrhythmia (AF, atrial flutter, or NSVT) was identified during the first 24 hours of monitoring in 11% of patients. The prevalence rose to 65% (P < .001) based on 30-day monitoring.
Similarly, prevalences of the composite primary endpoint components grew on extended monitoring, but the increases reached statistical significance only for NSVT; its prevalence went from 8% to 62% (P < .001). Prevalences rose nonsignificantly from 6% to 10% for AF and 0% to 1% for sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The incidence of NSVT during monitoring climbed fastest from day 0 through about day 19 and then rose more slowly through day 30, Dr. Caro Codón said. “It actually didn’t reach a plateau during this time period, so there is the possibility that if we had continued monitoring patients, the difference between both periods may have been even higher.”
Three variables predicted the incidence of nonsustained VT during monitoring, he said: age, atrial wall thickness, and whether there was late gadolinium enhancement at MRI.
An exploratory analysis looked at the 5-year risk of sudden cardiac death using the European Society of Cardiology HCM-SCD risk calculator recommended in guidelines. Risk assessment based on the 30-day extended monitoring period, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring alone, predicted a significantly higher 5-year risk of sudden death, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“Even more importantly,” he added, “over 20%” of patients would have been reclassified into a higher-risk group and possibly considered for an ICD based on extended monitoring, compared to 24-hour monitoring.
However, given that more than 50% of patients were found to have NSVT during extended monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón proposed that decisions on whether to implant an ICD should not be so “binary” based on the presence or absence of symptoms, and proposed further investigations be conducted into the complete phenotype of these arrhythmias.
The study has limitations, he observed, including a relatively small size; but it was able to detect important differences between 24-hour and 30-day monitoring outcomes even with only 100 patients. It was also limited by a lack of clinical follow-up for information on endpoints like stroke, thromboembolism, and sudden cardiac death.
Extended monitoring detected more cases of NSVT in the study’s relatively low-risk HCM patients who would not generally have an indication for ICD implantation, observed Dr. van Gelder. Also, at present the prognostic value of NSVT for SCD “seems to be more important at younger age” – that is, younger than 30 years – in patients with HCM.
Dr. van Gelder echoed Dr. Caro Codón’s call for more data from prolonged monitoring to help stratify patients according to risk; she proposed NSVT frequency, duration, and rate as possible targets.
The study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Nuubo, which provided the ECG monitoring systems. Dr. Caro Codón and Dr. van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA – , suggests a study that questions current risk stratification practices in HCM.
In the registry study, such arrythmias were observed in about six times as many HCM patients during 30 days of ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring as would have been identified based on the first 24 hours of the monitoring period: 65% vs. 11% of the cohort.
Also, about 62% of the patients showed NSVT at “extended” 30-day monitoring, compared with an 8% prevalence of the arrhythmia based on the more conventional ECG monitoring period of 24 hours.
Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia, an important arrhythmia used every day in clinical practice to make decisions, is “much, much more prevalent than we thought” in patients with HCM, Juan Caro Codón, MD, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “We should invest in further research regarding extended ECG monitoring in these patients.”
Dr. Caro Codón, of La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, presented the findings from the TEMPO-HCM study at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held in Barcelona and virtually.
Its results, he said, have implications for stratifying HCM patients according to their risk for sudden cardiac death in deciding who should be offered an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
The life-incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients like those in the current analysis has previously been found to be about 20%, and the life-prevalence of NSVT about 20%-30%, using traditional 24- or 48-hour Holter monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“These arrhythmias are clinically relevant events because they are linked to very meaningful clinical endpoints,” including stroke and thromboembolism, he said, “but also for sudden cardiac death.”
Extended ECG monitoring has been shown useful in the setting of cryptogenic stroke and after AF ablation, but similar findings have been scarce in HCM. Patients using personal wearable monitors such as smart watches, Dr. Caro Codón said, have come to his clinic with concerns that the devices may have signaled a problem. But the lack of relevant data leaves them without a sufficient answer.
In other findings, invited discussant Isabelle van Gelder, MD, PhD, observed after Dr. Caro Codón’s presentation that the number of patients with AF almost doubled based on extended monitoring, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring.
Based on European Society of Cardiology guidelines from 2020, “Once clinical AF has been documented, there is a class IIA recommendation to start anticoagulation,” said Dr. van Gelder, University of Groningen, the Netherlands. “Therefore, your data really are a call for more data on screening for AF in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients.”
Prospective multicenter registry
The TEMPO-HCM registry includes patients with HCM and a clinical indication for standard Holter monitoring at five hospitals in Spain. It excludes patients with an HCM-like phenotype but who lack the telltale genotype, as well as those already implanted with an ICD.
Those in the current analysis underwent 30-day ECG monitoring with a small, wearable device that Dr. Caro Codón described as about 7 cm long, worn in what is essentially a T-shirt with a pocket. Patients could remove the shirt and device to bathe or go swimming, for example, and still be monitored for most of the day.
The analysis included the registry’s first 100 patients (mean age, 57 years; 78% male). Hypertension was present in 47%, 58% were on beta-blockers, 16% had prior AF or atrial flutter, and 19% were taking anticoagulants. Only 8% were on antiarrhythmic drugs, Dr. Caro Codón reported.
The patients had good functional status (68% and 29% were in NYHA class 1 and 2, respectively) and their left ventricular ejection fraction averaged 66%. Of the 71 patients who underwent MRI, 28.2% showed late gadolinium enhancement suggesting myocardial scarring.
More arrhythmias on 30-day monitoring
The primary endpoint of clinically relevant arrhythmia (AF, atrial flutter, or NSVT) was identified during the first 24 hours of monitoring in 11% of patients. The prevalence rose to 65% (P < .001) based on 30-day monitoring.
Similarly, prevalences of the composite primary endpoint components grew on extended monitoring, but the increases reached statistical significance only for NSVT; its prevalence went from 8% to 62% (P < .001). Prevalences rose nonsignificantly from 6% to 10% for AF and 0% to 1% for sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The incidence of NSVT during monitoring climbed fastest from day 0 through about day 19 and then rose more slowly through day 30, Dr. Caro Codón said. “It actually didn’t reach a plateau during this time period, so there is the possibility that if we had continued monitoring patients, the difference between both periods may have been even higher.”
Three variables predicted the incidence of nonsustained VT during monitoring, he said: age, atrial wall thickness, and whether there was late gadolinium enhancement at MRI.
An exploratory analysis looked at the 5-year risk of sudden cardiac death using the European Society of Cardiology HCM-SCD risk calculator recommended in guidelines. Risk assessment based on the 30-day extended monitoring period, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring alone, predicted a significantly higher 5-year risk of sudden death, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“Even more importantly,” he added, “over 20%” of patients would have been reclassified into a higher-risk group and possibly considered for an ICD based on extended monitoring, compared to 24-hour monitoring.
However, given that more than 50% of patients were found to have NSVT during extended monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón proposed that decisions on whether to implant an ICD should not be so “binary” based on the presence or absence of symptoms, and proposed further investigations be conducted into the complete phenotype of these arrhythmias.
The study has limitations, he observed, including a relatively small size; but it was able to detect important differences between 24-hour and 30-day monitoring outcomes even with only 100 patients. It was also limited by a lack of clinical follow-up for information on endpoints like stroke, thromboembolism, and sudden cardiac death.
Extended monitoring detected more cases of NSVT in the study’s relatively low-risk HCM patients who would not generally have an indication for ICD implantation, observed Dr. van Gelder. Also, at present the prognostic value of NSVT for SCD “seems to be more important at younger age” – that is, younger than 30 years – in patients with HCM.
Dr. van Gelder echoed Dr. Caro Codón’s call for more data from prolonged monitoring to help stratify patients according to risk; she proposed NSVT frequency, duration, and rate as possible targets.
The study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Nuubo, which provided the ECG monitoring systems. Dr. Caro Codón and Dr. van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BARCELONA – , suggests a study that questions current risk stratification practices in HCM.
In the registry study, such arrythmias were observed in about six times as many HCM patients during 30 days of ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring as would have been identified based on the first 24 hours of the monitoring period: 65% vs. 11% of the cohort.
Also, about 62% of the patients showed NSVT at “extended” 30-day monitoring, compared with an 8% prevalence of the arrhythmia based on the more conventional ECG monitoring period of 24 hours.
Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia, an important arrhythmia used every day in clinical practice to make decisions, is “much, much more prevalent than we thought” in patients with HCM, Juan Caro Codón, MD, the study’s principal investigator, said in an interview. “We should invest in further research regarding extended ECG monitoring in these patients.”
Dr. Caro Codón, of La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, presented the findings from the TEMPO-HCM study at the European Heart Rhythm Association 2023 Congress, held in Barcelona and virtually.
Its results, he said, have implications for stratifying HCM patients according to their risk for sudden cardiac death in deciding who should be offered an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
The life-incidence of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients like those in the current analysis has previously been found to be about 20%, and the life-prevalence of NSVT about 20%-30%, using traditional 24- or 48-hour Holter monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“These arrhythmias are clinically relevant events because they are linked to very meaningful clinical endpoints,” including stroke and thromboembolism, he said, “but also for sudden cardiac death.”
Extended ECG monitoring has been shown useful in the setting of cryptogenic stroke and after AF ablation, but similar findings have been scarce in HCM. Patients using personal wearable monitors such as smart watches, Dr. Caro Codón said, have come to his clinic with concerns that the devices may have signaled a problem. But the lack of relevant data leaves them without a sufficient answer.
In other findings, invited discussant Isabelle van Gelder, MD, PhD, observed after Dr. Caro Codón’s presentation that the number of patients with AF almost doubled based on extended monitoring, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring.
Based on European Society of Cardiology guidelines from 2020, “Once clinical AF has been documented, there is a class IIA recommendation to start anticoagulation,” said Dr. van Gelder, University of Groningen, the Netherlands. “Therefore, your data really are a call for more data on screening for AF in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients.”
Prospective multicenter registry
The TEMPO-HCM registry includes patients with HCM and a clinical indication for standard Holter monitoring at five hospitals in Spain. It excludes patients with an HCM-like phenotype but who lack the telltale genotype, as well as those already implanted with an ICD.
Those in the current analysis underwent 30-day ECG monitoring with a small, wearable device that Dr. Caro Codón described as about 7 cm long, worn in what is essentially a T-shirt with a pocket. Patients could remove the shirt and device to bathe or go swimming, for example, and still be monitored for most of the day.
The analysis included the registry’s first 100 patients (mean age, 57 years; 78% male). Hypertension was present in 47%, 58% were on beta-blockers, 16% had prior AF or atrial flutter, and 19% were taking anticoagulants. Only 8% were on antiarrhythmic drugs, Dr. Caro Codón reported.
The patients had good functional status (68% and 29% were in NYHA class 1 and 2, respectively) and their left ventricular ejection fraction averaged 66%. Of the 71 patients who underwent MRI, 28.2% showed late gadolinium enhancement suggesting myocardial scarring.
More arrhythmias on 30-day monitoring
The primary endpoint of clinically relevant arrhythmia (AF, atrial flutter, or NSVT) was identified during the first 24 hours of monitoring in 11% of patients. The prevalence rose to 65% (P < .001) based on 30-day monitoring.
Similarly, prevalences of the composite primary endpoint components grew on extended monitoring, but the increases reached statistical significance only for NSVT; its prevalence went from 8% to 62% (P < .001). Prevalences rose nonsignificantly from 6% to 10% for AF and 0% to 1% for sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The incidence of NSVT during monitoring climbed fastest from day 0 through about day 19 and then rose more slowly through day 30, Dr. Caro Codón said. “It actually didn’t reach a plateau during this time period, so there is the possibility that if we had continued monitoring patients, the difference between both periods may have been even higher.”
Three variables predicted the incidence of nonsustained VT during monitoring, he said: age, atrial wall thickness, and whether there was late gadolinium enhancement at MRI.
An exploratory analysis looked at the 5-year risk of sudden cardiac death using the European Society of Cardiology HCM-SCD risk calculator recommended in guidelines. Risk assessment based on the 30-day extended monitoring period, compared with the first 24 hours of monitoring alone, predicted a significantly higher 5-year risk of sudden death, Dr. Caro Codón said.
“Even more importantly,” he added, “over 20%” of patients would have been reclassified into a higher-risk group and possibly considered for an ICD based on extended monitoring, compared to 24-hour monitoring.
However, given that more than 50% of patients were found to have NSVT during extended monitoring, Dr. Caro Codón proposed that decisions on whether to implant an ICD should not be so “binary” based on the presence or absence of symptoms, and proposed further investigations be conducted into the complete phenotype of these arrhythmias.
The study has limitations, he observed, including a relatively small size; but it was able to detect important differences between 24-hour and 30-day monitoring outcomes even with only 100 patients. It was also limited by a lack of clinical follow-up for information on endpoints like stroke, thromboembolism, and sudden cardiac death.
Extended monitoring detected more cases of NSVT in the study’s relatively low-risk HCM patients who would not generally have an indication for ICD implantation, observed Dr. van Gelder. Also, at present the prognostic value of NSVT for SCD “seems to be more important at younger age” – that is, younger than 30 years – in patients with HCM.
Dr. van Gelder echoed Dr. Caro Codón’s call for more data from prolonged monitoring to help stratify patients according to risk; she proposed NSVT frequency, duration, and rate as possible targets.
The study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Nuubo, which provided the ECG monitoring systems. Dr. Caro Codón and Dr. van Gelder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EHRA