User login
Xanthogranulomatous Reaction to Trametinib for Metastatic Malignant Melanoma
A decade ago, the few agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of metastatic melanoma demonstrated low therapeutic success rates (ie, <15%–20%).1 Since then, advances in molecular biology have identified oncogenes that contribute to melanoma progression.2 Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by targeting mutant BRAF and mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) has created promising pharmacologic treatment opportunities.3 Due to the recent US Food and Drug Administration approval of these therapies for treatment of melanoma, it is important to better characterize these adverse events (AEs) so that we can manage them. We present the development of an unusual cutaneous reaction to trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in a man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma.
Case Report
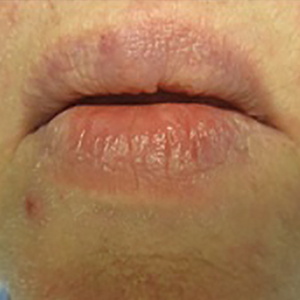
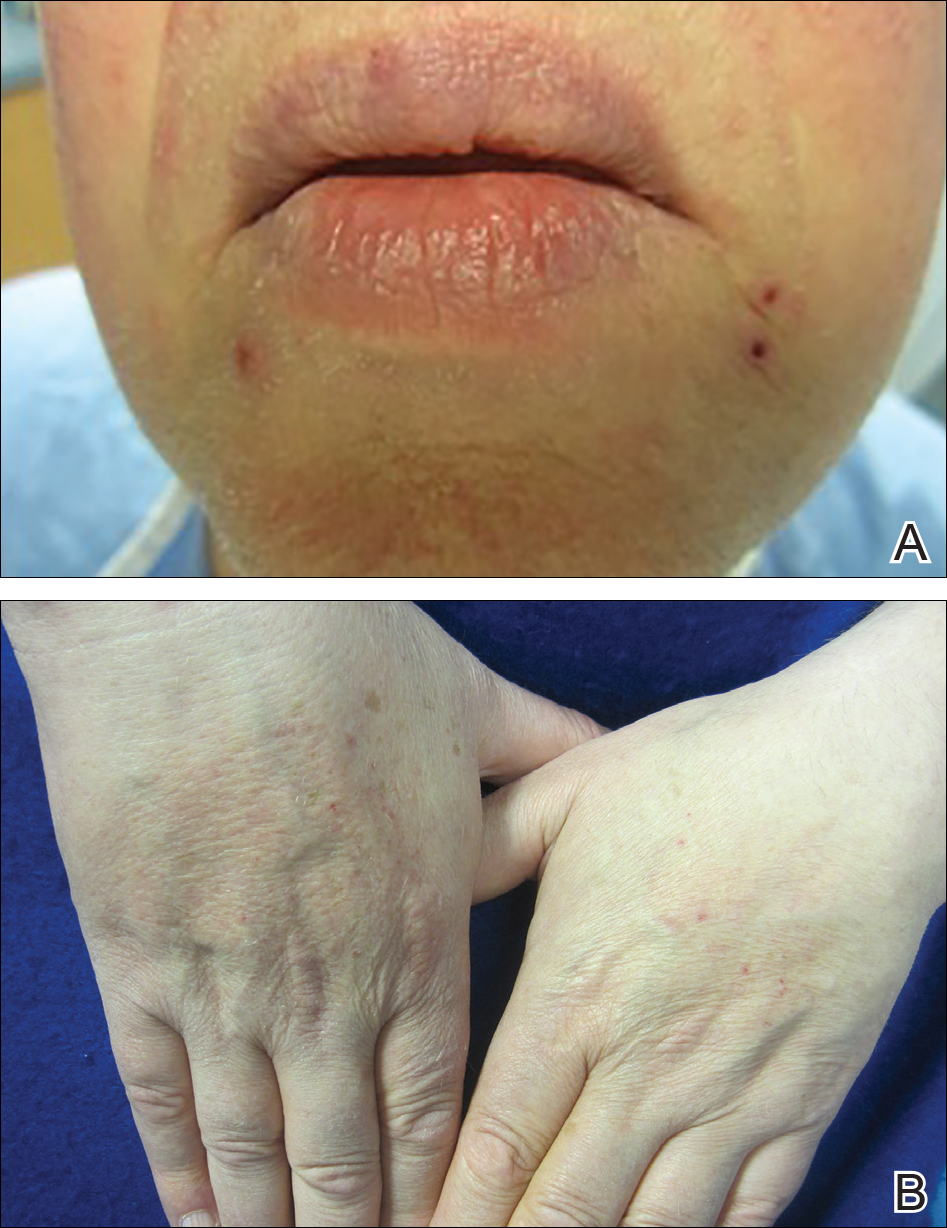
A 66-year-old man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma with metastases to the brain and lungs presented with recurring pruritic erythematous papules on the face and bilateral forearms that began shortly after initiating therapy with trametinib. The cutaneous eruption had initially presented on the face, forearms, and dorsal hands when trametinib was used in combination with vemurafenib, a BRAF inhibitor, and ipilimumab, a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4–blocking antibody; however, lesions initially were minimal and self-resolving. When trametinib was reintroduced as monotherapy due to fever attributed to the combination treatment regimen, the cutaneous eruption recurred more severely. Physical examination revealed erythematous scaly papules limited to the face and bilateral upper extremities, including the flexural surfaces.
A biopsy from the flexural surface of the right forearm revealed a dense perivascular lymphoid and xanthomatous infiltrate in the dermis (Figure 1). Poorly formed granulomas within the mid reticular dermis demonstrated focal palisading of histiocytes with prominent giant cells at the periphery. Histiocytes and giant cells showed foamy or xanthomatous cytoplasm. Within the reaction, degenerative and swollen collagen fibers were noted with no mucin deposition, which was confirmed with negative colloidal iron staining.
Brief cessation of trametinib along with application of clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% resulted in resolution of the cutaneous eruption. Later, trametinib was reintroduced in combination with vemurafenib, though therapy was intermittently discontinued due to various side effects. Skin lesions continued to recur (Figure 2) while the patient was on trametinib but remained minimal and continued to respond to topical clobetasol propionate. One year later, the patient continues to tolerate combination therapy with trametinib and vemurafenib.
Comment
BRAF Inhibitors
Normally, activated BRAF phosphorylates and stimulates MEK proteins, ultimately influencing cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.3-5 BRAF mutations that constitutively activate this pathway have been detected in several malignancies, including papillary thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, and brain tumors, but they are particularly prevalent in melanoma.4,6 The majority of BRAF-positive malignant melanomas are associated with V600E, in which valine is substituted for glutamic acid at codon 600. The next most common BRAF mutation is V600K, in which valine is substituted for lysine.2,7 Together these constitute approximately 95% of BRAF mutations in melanoma patients.5
MEK Inhibitors
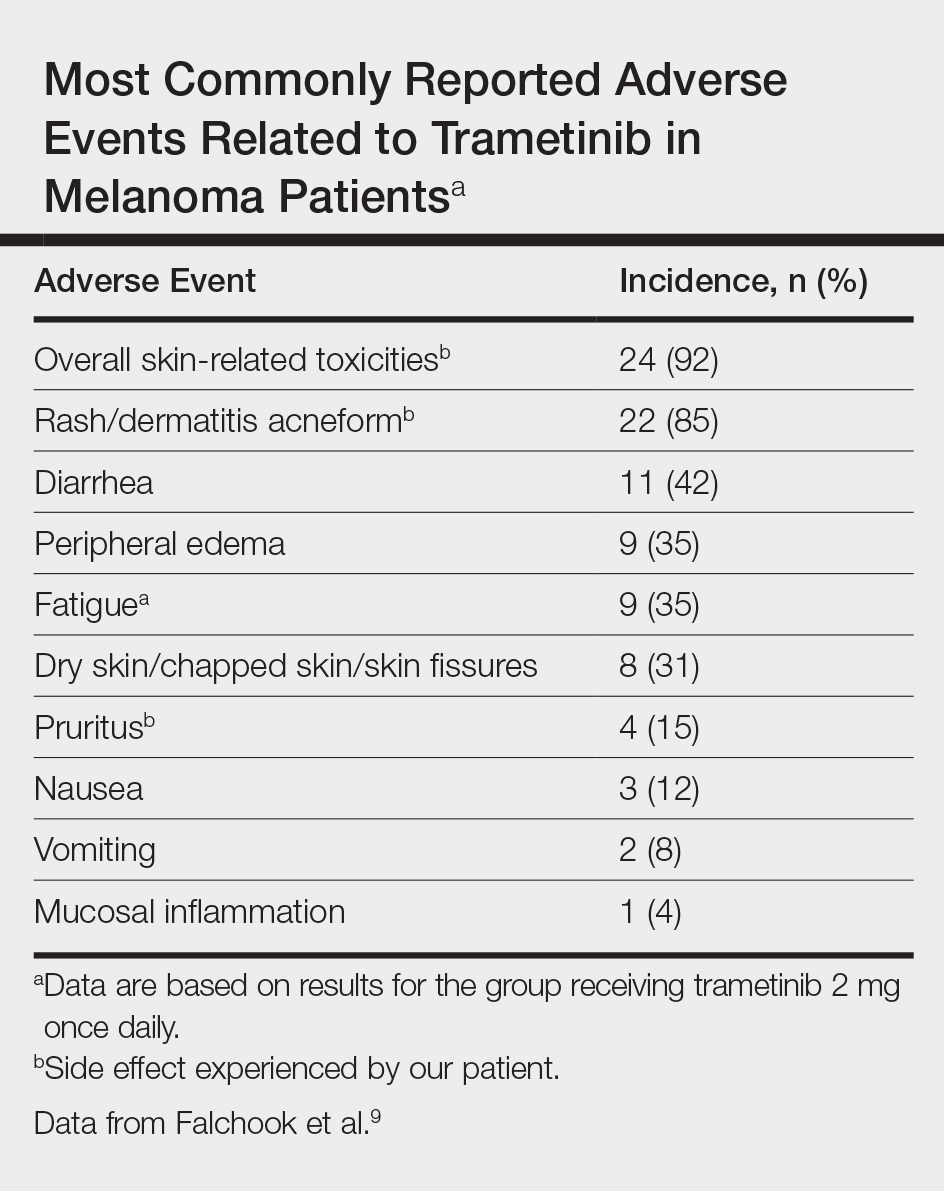
Initially, BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) were introduced to the market for treating melanoma with great success; however, resistance to BRAFi therapy quickly was identified within months of initiating therapy, leading to investigations for combination therapy with MEK inhibitors (MEKi).2,5 MEK inhibition decreases cellular proliferation and also leads to apoptosis of melanoma cells in patients with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations.2,8 Trametinib, in particular, is a reversible, highly selective allosteric inhibitor of both MEK1 and MEK2. While on trametinib, patients with metastatic melanoma have experienced 3 times as long progression-free survival as well as 81% overall survival compared to 67% overall survival at 6 months in patients on chemotherapy, dacarbazine, or paclitaxel.5 However, AEs are quite common with trametinib, with cutaneous AEs being a leading side effect. Several large trials have reported that 57% to 92% of patients on trametinib report cutaneous AEs, with the majority of cases being described as papulopustular or acneform (Table).5,9
Combination Therapy
Fortunately, combination treatment with a BRAFi may alleviate MEKi-induced cutaneous drug reactions. In one study, acneform eruptions were identified in only 10% of those on combination therapy—trametinib with the BRAFi dabrafenib—compared to 77% of patients on trametinib monotherapy.10 Strikingly, cutaneous AEs occurred in 100% of trametinib-treated mice compared to 30% of combination-treated mice in another study, while the benefits of MEKi remained similar in both groups.11 Because BRAFi and MEKi combination therapy improves progression-free survival while minimizing AEs, we support the use of combination therapy instead of BRAFi or MEKi monotherapy.5
Histologic Evidence of AEs
Histology of trametinib-associated cutaneous reactions is not well characterized, which is in contrast to our understanding of cutaneous AEs associated with BRAFi in which transient acantholytic dermatosis (seen in 45% of patients) and verrucal keratosis (seen in 18% of patients) have been well characterized on histology.12 Interestingly, cutaneous granulomatous eruptions have been attributed to BRAFi therapy in 4 patients.13,14 One patient was on monotherapy with vemurafenib and granulomatous dermatitis with focal necrosis was seen on histology.13 The other 3 patients were on combination therapy with trametinib; 2 had histology-proven sarcoidal granulomatous inflammation, and 1 demonstrated perifollicular granulomatous inflammation and granulomatous inflammation surrounding a focus of melanoma cells.13,14 Although these granulomatous reactions were attributed to BRAFi or combination therapy, the association with trametinib remains unclear. On the other hand, our patient’s granulomatous reaction was exacerbated on trametinib monotherapy, suggesting a relationship to trametinib itself rather than BRAFi.
Conclusion
With the discovery of molecular targeting in melanoma, BRAFi and MEKi therapies provide major milestones in metastatic melanoma management. As more patients are treated with these agents, it is important that we better characterize their associated side effects. Our case of an unusual xanthogranulomatous reaction to trametinib adds to the knowledge base of possible cutaneous reactions caused by this drug. We hope that prospective studies will further investigate and differentiate the cutaneous AEs described so that we can better manage these patients.
- Eggermont AM, Schadendorf D. Melanoma and immunotherapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:547-564.
- Chung C, Reilly S. Trametinib: a novel signal transduction inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic cutaneous melanoma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72:101-110.
- Montagut C, Settleman J. Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy [published online February 12, 2009]. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:125-134.
- Hertzman Johansson C, Egyhazi Brage S. BRAF inhibitors in cancer therapy [published online December 8, 2013]. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142:176-182.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al; METRIC Study Group. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma [published online June 4, 2012]. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer [published online June 9, 2002]. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Houben R, Becker JC, Kappel A, et al. Constitutive activation of the Ras-Raf signaling pathway in metastatic melanoma is associated with poor prognosis. J Carcinog. 2004;3:6.
- Roberts PF, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291-3310.
- Falchook GS, Lewis KD, Infante JR, et al. Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase 2 dose-escalation trial [published online July 16, 2012]. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:782-789.
- Anforth R, Liu M, Nguyen B, et al. Acneiform eruptions: a common cutaneous toxicity of the MEK inhibitor trametinib [published online December 9, 2013]. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:250-254.
- Gadiot J, Hooijkaas AI, Deken MA, et al. Synchronous BRAF(V600E) and MEK inhibition leads to superior control of murine melanoma by limiting MEK inhibitor induced skin toxicity. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1649-1658.
- Anforth R, Carlos G, Clements A, et al. Cutaneous adverse events in patients treated with BRAF inhibitor-based therapies for metastatic melanoma for longer than 52 weeks [published online November 21, 2014]. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:239-243.
- Park JJ, Hawryluk EB, Tahan SR, et al. Cutaneous granulomatous eruption and successful response to potent topical steroids in patients undergoing targeted BRAF inhibitor treatment for metastatic melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:307-311.
- Green JS, Norris DA, Wisell K. Novel cutaneous effects of combination chemotherapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:172-176.
A decade ago, the few agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of metastatic melanoma demonstrated low therapeutic success rates (ie, <15%–20%).1 Since then, advances in molecular biology have identified oncogenes that contribute to melanoma progression.2 Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by targeting mutant BRAF and mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) has created promising pharmacologic treatment opportunities.3 Due to the recent US Food and Drug Administration approval of these therapies for treatment of melanoma, it is important to better characterize these adverse events (AEs) so that we can manage them. We present the development of an unusual cutaneous reaction to trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in a man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma.
Case Report
A 66-year-old man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma with metastases to the brain and lungs presented with recurring pruritic erythematous papules on the face and bilateral forearms that began shortly after initiating therapy with trametinib. The cutaneous eruption had initially presented on the face, forearms, and dorsal hands when trametinib was used in combination with vemurafenib, a BRAF inhibitor, and ipilimumab, a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4–blocking antibody; however, lesions initially were minimal and self-resolving. When trametinib was reintroduced as monotherapy due to fever attributed to the combination treatment regimen, the cutaneous eruption recurred more severely. Physical examination revealed erythematous scaly papules limited to the face and bilateral upper extremities, including the flexural surfaces.
A biopsy from the flexural surface of the right forearm revealed a dense perivascular lymphoid and xanthomatous infiltrate in the dermis (Figure 1). Poorly formed granulomas within the mid reticular dermis demonstrated focal palisading of histiocytes with prominent giant cells at the periphery. Histiocytes and giant cells showed foamy or xanthomatous cytoplasm. Within the reaction, degenerative and swollen collagen fibers were noted with no mucin deposition, which was confirmed with negative colloidal iron staining.

Brief cessation of trametinib along with application of clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% resulted in resolution of the cutaneous eruption. Later, trametinib was reintroduced in combination with vemurafenib, though therapy was intermittently discontinued due to various side effects. Skin lesions continued to recur (Figure 2) while the patient was on trametinib but remained minimal and continued to respond to topical clobetasol propionate. One year later, the patient continues to tolerate combination therapy with trametinib and vemurafenib.

Comment
BRAF Inhibitors
Normally, activated BRAF phosphorylates and stimulates MEK proteins, ultimately influencing cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.3-5 BRAF mutations that constitutively activate this pathway have been detected in several malignancies, including papillary thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, and brain tumors, but they are particularly prevalent in melanoma.4,6 The majority of BRAF-positive malignant melanomas are associated with V600E, in which valine is substituted for glutamic acid at codon 600. The next most common BRAF mutation is V600K, in which valine is substituted for lysine.2,7 Together these constitute approximately 95% of BRAF mutations in melanoma patients.5
MEK Inhibitors
Initially, BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) were introduced to the market for treating melanoma with great success; however, resistance to BRAFi therapy quickly was identified within months of initiating therapy, leading to investigations for combination therapy with MEK inhibitors (MEKi).2,5 MEK inhibition decreases cellular proliferation and also leads to apoptosis of melanoma cells in patients with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations.2,8 Trametinib, in particular, is a reversible, highly selective allosteric inhibitor of both MEK1 and MEK2. While on trametinib, patients with metastatic melanoma have experienced 3 times as long progression-free survival as well as 81% overall survival compared to 67% overall survival at 6 months in patients on chemotherapy, dacarbazine, or paclitaxel.5 However, AEs are quite common with trametinib, with cutaneous AEs being a leading side effect. Several large trials have reported that 57% to 92% of patients on trametinib report cutaneous AEs, with the majority of cases being described as papulopustular or acneform (Table).5,9

Combination Therapy
Fortunately, combination treatment with a BRAFi may alleviate MEKi-induced cutaneous drug reactions. In one study, acneform eruptions were identified in only 10% of those on combination therapy—trametinib with the BRAFi dabrafenib—compared to 77% of patients on trametinib monotherapy.10 Strikingly, cutaneous AEs occurred in 100% of trametinib-treated mice compared to 30% of combination-treated mice in another study, while the benefits of MEKi remained similar in both groups.11 Because BRAFi and MEKi combination therapy improves progression-free survival while minimizing AEs, we support the use of combination therapy instead of BRAFi or MEKi monotherapy.5
Histologic Evidence of AEs
Histology of trametinib-associated cutaneous reactions is not well characterized, which is in contrast to our understanding of cutaneous AEs associated with BRAFi in which transient acantholytic dermatosis (seen in 45% of patients) and verrucal keratosis (seen in 18% of patients) have been well characterized on histology.12 Interestingly, cutaneous granulomatous eruptions have been attributed to BRAFi therapy in 4 patients.13,14 One patient was on monotherapy with vemurafenib and granulomatous dermatitis with focal necrosis was seen on histology.13 The other 3 patients were on combination therapy with trametinib; 2 had histology-proven sarcoidal granulomatous inflammation, and 1 demonstrated perifollicular granulomatous inflammation and granulomatous inflammation surrounding a focus of melanoma cells.13,14 Although these granulomatous reactions were attributed to BRAFi or combination therapy, the association with trametinib remains unclear. On the other hand, our patient’s granulomatous reaction was exacerbated on trametinib monotherapy, suggesting a relationship to trametinib itself rather than BRAFi.
Conclusion
With the discovery of molecular targeting in melanoma, BRAFi and MEKi therapies provide major milestones in metastatic melanoma management. As more patients are treated with these agents, it is important that we better characterize their associated side effects. Our case of an unusual xanthogranulomatous reaction to trametinib adds to the knowledge base of possible cutaneous reactions caused by this drug. We hope that prospective studies will further investigate and differentiate the cutaneous AEs described so that we can better manage these patients.
A decade ago, the few agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of metastatic melanoma demonstrated low therapeutic success rates (ie, <15%–20%).1 Since then, advances in molecular biology have identified oncogenes that contribute to melanoma progression.2 Inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway by targeting mutant BRAF and mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) has created promising pharmacologic treatment opportunities.3 Due to the recent US Food and Drug Administration approval of these therapies for treatment of melanoma, it is important to better characterize these adverse events (AEs) so that we can manage them. We present the development of an unusual cutaneous reaction to trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, in a man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma.
Case Report
A 66-year-old man with stage IV M1b malignant melanoma with metastases to the brain and lungs presented with recurring pruritic erythematous papules on the face and bilateral forearms that began shortly after initiating therapy with trametinib. The cutaneous eruption had initially presented on the face, forearms, and dorsal hands when trametinib was used in combination with vemurafenib, a BRAF inhibitor, and ipilimumab, a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4–blocking antibody; however, lesions initially were minimal and self-resolving. When trametinib was reintroduced as monotherapy due to fever attributed to the combination treatment regimen, the cutaneous eruption recurred more severely. Physical examination revealed erythematous scaly papules limited to the face and bilateral upper extremities, including the flexural surfaces.
A biopsy from the flexural surface of the right forearm revealed a dense perivascular lymphoid and xanthomatous infiltrate in the dermis (Figure 1). Poorly formed granulomas within the mid reticular dermis demonstrated focal palisading of histiocytes with prominent giant cells at the periphery. Histiocytes and giant cells showed foamy or xanthomatous cytoplasm. Within the reaction, degenerative and swollen collagen fibers were noted with no mucin deposition, which was confirmed with negative colloidal iron staining.

Brief cessation of trametinib along with application of clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% resulted in resolution of the cutaneous eruption. Later, trametinib was reintroduced in combination with vemurafenib, though therapy was intermittently discontinued due to various side effects. Skin lesions continued to recur (Figure 2) while the patient was on trametinib but remained minimal and continued to respond to topical clobetasol propionate. One year later, the patient continues to tolerate combination therapy with trametinib and vemurafenib.

Comment
BRAF Inhibitors
Normally, activated BRAF phosphorylates and stimulates MEK proteins, ultimately influencing cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation.3-5 BRAF mutations that constitutively activate this pathway have been detected in several malignancies, including papillary thyroid cancer, colorectal cancer, and brain tumors, but they are particularly prevalent in melanoma.4,6 The majority of BRAF-positive malignant melanomas are associated with V600E, in which valine is substituted for glutamic acid at codon 600. The next most common BRAF mutation is V600K, in which valine is substituted for lysine.2,7 Together these constitute approximately 95% of BRAF mutations in melanoma patients.5
MEK Inhibitors
Initially, BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi) were introduced to the market for treating melanoma with great success; however, resistance to BRAFi therapy quickly was identified within months of initiating therapy, leading to investigations for combination therapy with MEK inhibitors (MEKi).2,5 MEK inhibition decreases cellular proliferation and also leads to apoptosis of melanoma cells in patients with BRAF V600E or V600K mutations.2,8 Trametinib, in particular, is a reversible, highly selective allosteric inhibitor of both MEK1 and MEK2. While on trametinib, patients with metastatic melanoma have experienced 3 times as long progression-free survival as well as 81% overall survival compared to 67% overall survival at 6 months in patients on chemotherapy, dacarbazine, or paclitaxel.5 However, AEs are quite common with trametinib, with cutaneous AEs being a leading side effect. Several large trials have reported that 57% to 92% of patients on trametinib report cutaneous AEs, with the majority of cases being described as papulopustular or acneform (Table).5,9

Combination Therapy
Fortunately, combination treatment with a BRAFi may alleviate MEKi-induced cutaneous drug reactions. In one study, acneform eruptions were identified in only 10% of those on combination therapy—trametinib with the BRAFi dabrafenib—compared to 77% of patients on trametinib monotherapy.10 Strikingly, cutaneous AEs occurred in 100% of trametinib-treated mice compared to 30% of combination-treated mice in another study, while the benefits of MEKi remained similar in both groups.11 Because BRAFi and MEKi combination therapy improves progression-free survival while minimizing AEs, we support the use of combination therapy instead of BRAFi or MEKi monotherapy.5
Histologic Evidence of AEs
Histology of trametinib-associated cutaneous reactions is not well characterized, which is in contrast to our understanding of cutaneous AEs associated with BRAFi in which transient acantholytic dermatosis (seen in 45% of patients) and verrucal keratosis (seen in 18% of patients) have been well characterized on histology.12 Interestingly, cutaneous granulomatous eruptions have been attributed to BRAFi therapy in 4 patients.13,14 One patient was on monotherapy with vemurafenib and granulomatous dermatitis with focal necrosis was seen on histology.13 The other 3 patients were on combination therapy with trametinib; 2 had histology-proven sarcoidal granulomatous inflammation, and 1 demonstrated perifollicular granulomatous inflammation and granulomatous inflammation surrounding a focus of melanoma cells.13,14 Although these granulomatous reactions were attributed to BRAFi or combination therapy, the association with trametinib remains unclear. On the other hand, our patient’s granulomatous reaction was exacerbated on trametinib monotherapy, suggesting a relationship to trametinib itself rather than BRAFi.
Conclusion
With the discovery of molecular targeting in melanoma, BRAFi and MEKi therapies provide major milestones in metastatic melanoma management. As more patients are treated with these agents, it is important that we better characterize their associated side effects. Our case of an unusual xanthogranulomatous reaction to trametinib adds to the knowledge base of possible cutaneous reactions caused by this drug. We hope that prospective studies will further investigate and differentiate the cutaneous AEs described so that we can better manage these patients.
- Eggermont AM, Schadendorf D. Melanoma and immunotherapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:547-564.
- Chung C, Reilly S. Trametinib: a novel signal transduction inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic cutaneous melanoma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72:101-110.
- Montagut C, Settleman J. Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy [published online February 12, 2009]. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:125-134.
- Hertzman Johansson C, Egyhazi Brage S. BRAF inhibitors in cancer therapy [published online December 8, 2013]. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142:176-182.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al; METRIC Study Group. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma [published online June 4, 2012]. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer [published online June 9, 2002]. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Houben R, Becker JC, Kappel A, et al. Constitutive activation of the Ras-Raf signaling pathway in metastatic melanoma is associated with poor prognosis. J Carcinog. 2004;3:6.
- Roberts PF, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291-3310.
- Falchook GS, Lewis KD, Infante JR, et al. Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase 2 dose-escalation trial [published online July 16, 2012]. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:782-789.
- Anforth R, Liu M, Nguyen B, et al. Acneiform eruptions: a common cutaneous toxicity of the MEK inhibitor trametinib [published online December 9, 2013]. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:250-254.
- Gadiot J, Hooijkaas AI, Deken MA, et al. Synchronous BRAF(V600E) and MEK inhibition leads to superior control of murine melanoma by limiting MEK inhibitor induced skin toxicity. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1649-1658.
- Anforth R, Carlos G, Clements A, et al. Cutaneous adverse events in patients treated with BRAF inhibitor-based therapies for metastatic melanoma for longer than 52 weeks [published online November 21, 2014]. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:239-243.
- Park JJ, Hawryluk EB, Tahan SR, et al. Cutaneous granulomatous eruption and successful response to potent topical steroids in patients undergoing targeted BRAF inhibitor treatment for metastatic melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:307-311.
- Green JS, Norris DA, Wisell K. Novel cutaneous effects of combination chemotherapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:172-176.
- Eggermont AM, Schadendorf D. Melanoma and immunotherapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2009;23:547-564.
- Chung C, Reilly S. Trametinib: a novel signal transduction inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic cutaneous melanoma. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015;72:101-110.
- Montagut C, Settleman J. Targeting the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway in cancer therapy [published online February 12, 2009]. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:125-134.
- Hertzman Johansson C, Egyhazi Brage S. BRAF inhibitors in cancer therapy [published online December 8, 2013]. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142:176-182.
- Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al; METRIC Study Group. Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma [published online June 4, 2012]. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:107-114.
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer [published online June 9, 2002]. Nature. 2002;417:949-954.
- Houben R, Becker JC, Kappel A, et al. Constitutive activation of the Ras-Raf signaling pathway in metastatic melanoma is associated with poor prognosis. J Carcinog. 2004;3:6.
- Roberts PF, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:3291-3310.
- Falchook GS, Lewis KD, Infante JR, et al. Activity of the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase 2 dose-escalation trial [published online July 16, 2012]. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:782-789.
- Anforth R, Liu M, Nguyen B, et al. Acneiform eruptions: a common cutaneous toxicity of the MEK inhibitor trametinib [published online December 9, 2013]. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55:250-254.
- Gadiot J, Hooijkaas AI, Deken MA, et al. Synchronous BRAF(V600E) and MEK inhibition leads to superior control of murine melanoma by limiting MEK inhibitor induced skin toxicity. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:1649-1658.
- Anforth R, Carlos G, Clements A, et al. Cutaneous adverse events in patients treated with BRAF inhibitor-based therapies for metastatic melanoma for longer than 52 weeks [published online November 21, 2014]. Br J Dermatol. 2015;172:239-243.
- Park JJ, Hawryluk EB, Tahan SR, et al. Cutaneous granulomatous eruption and successful response to potent topical steroids in patients undergoing targeted BRAF inhibitor treatment for metastatic melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:307-311.
- Green JS, Norris DA, Wisell K. Novel cutaneous effects of combination chemotherapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors: a report of two cases. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:172-176.
Practice Points
- With the discovery of molecular targeting in melanoma, BRAF and MEK inhibitors have been increasingly utilized as therapies in metastatic melanoma management.
- Trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, is commonly associated with cutaneous adverse reactions, particularly acneform eruptions.
- We report a patient on trametinib who developed an eruption with an unusual xanthogranulomatous reaction pattern noted on histology.
Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in a Skin Graft
Case Report
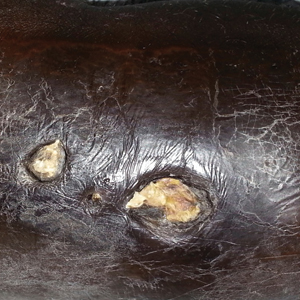
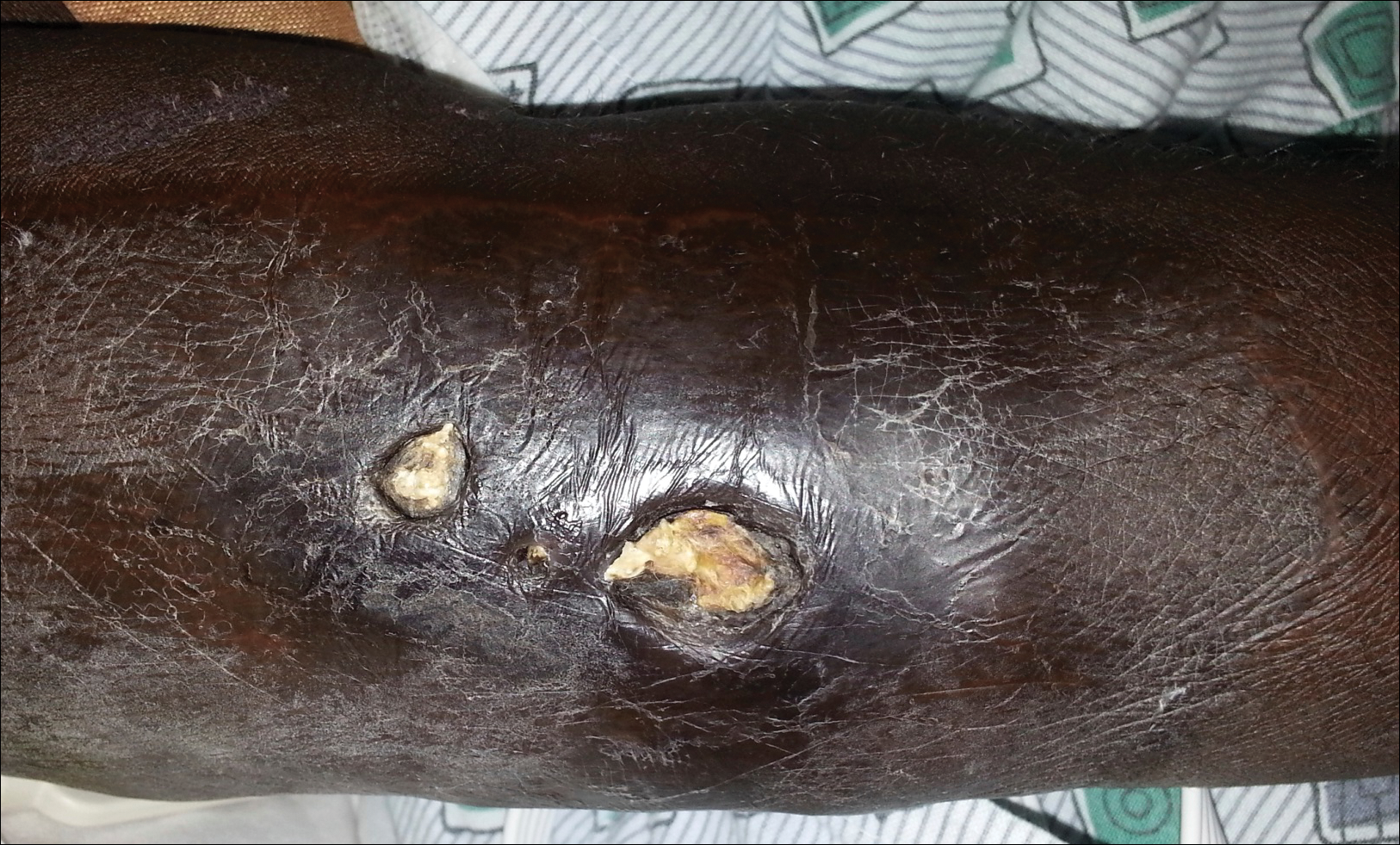
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.
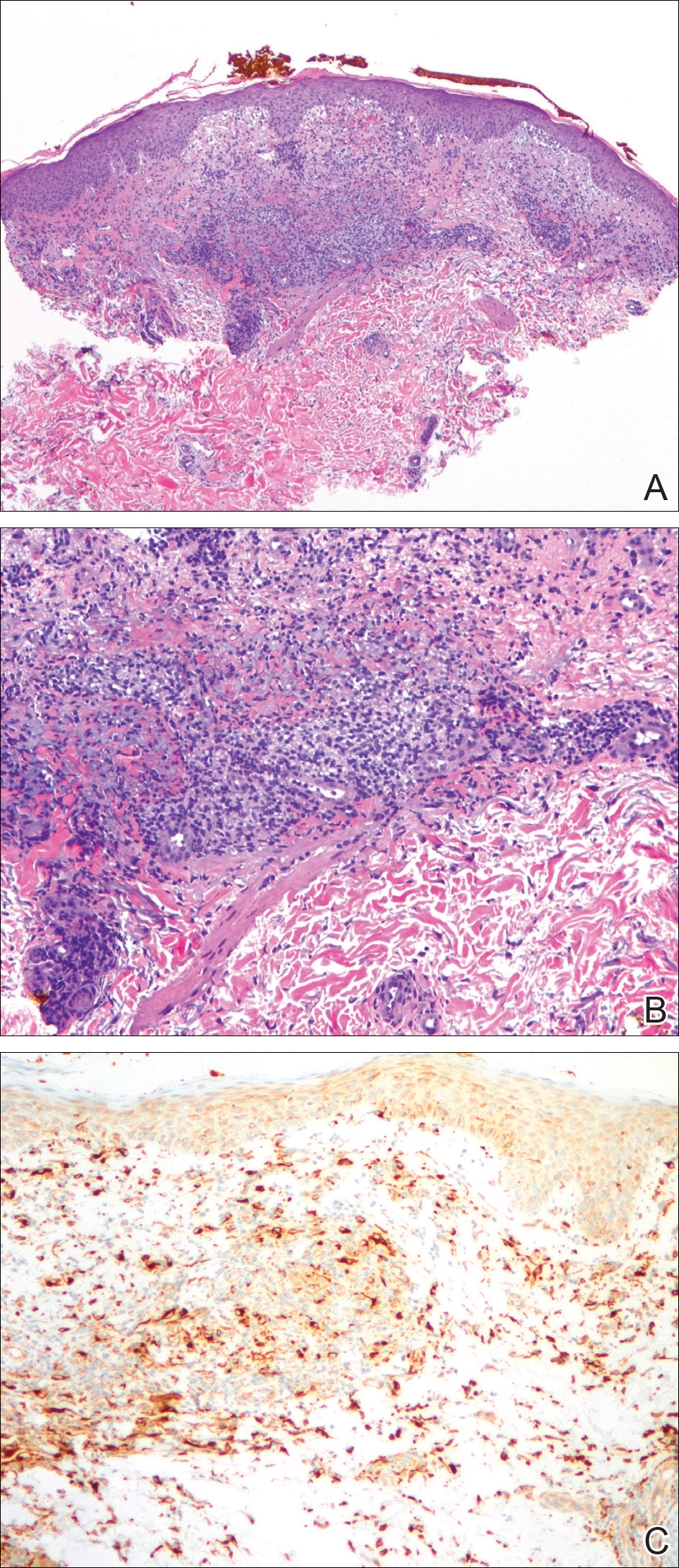
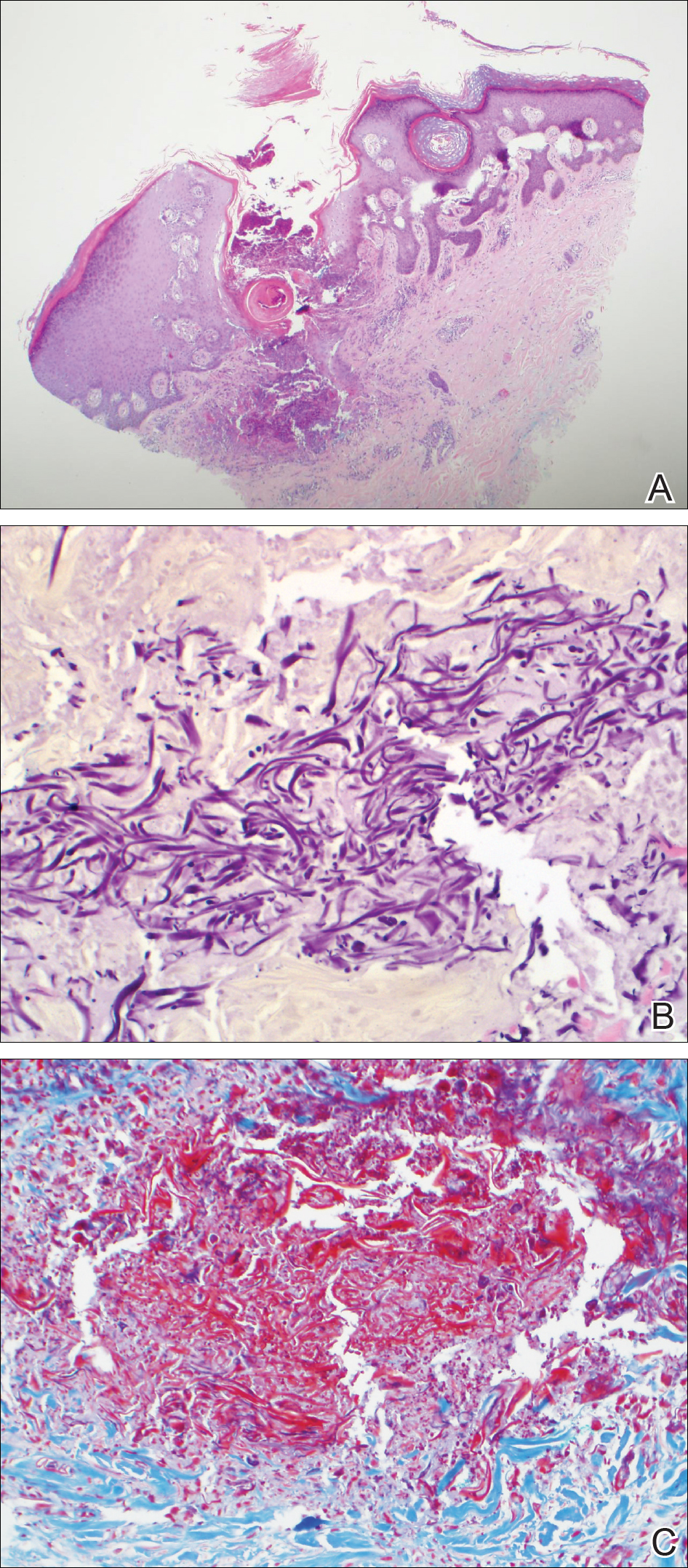
A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).
Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
Case Report
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.

A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).

Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
Case Report
A 57-year-old black woman with a history of dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease, diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension, diastolic congestive heart failure, and chronic bronchitis was admitted to Howard University Hospital (Washington, DC) for acute chest pain and shortness of breath. During her hospital stay the dermatology team was consulted for evaluation of two 1.6-cm teardrop-shaped, yellow-white-chalky plaques noted in the center of an atrophic, hyperpigmented, shiny, contracted split-thickness skin graft (STSG) on the right posterior forearm (Figure 1). Twenty years prior, the patient received STSGs on the right and left forearm secondary to caustic burns. Two months before the current admission she noticed 2 adjacent teardrop-shaped white plaques within the center of the STSG on the right forearm. At a 3-month follow-up, she had developed more lesions within both graft sites of the bilateral forearm. There was no notable pruritus associated with the lesions.

A 4-mm punch biopsy showed an orthokeratotic plug with basophilic inflammatory debris adjacent to acanthotic epidermis, necrotic basophilic debris at the superficial dermis with epidermal canals extending from the base of the lesion superiorly, and transepidermal elimination of elastic fibers (Figure 2A). A Verhoeff-van Gieson stain revealed the necrotic basophilic debris located in the superficial dermis admixed with a cluster of black wavy elastic fibers establishing the identity of the perforating substance (Figure 2B). Masson trichrome stain revealed loss of collagen structure within the aggregate of elastic fibers adjacent to the epidermis and no collagen within epidermal canals (Figure 2C). These histopathologic findings together with the clinical presentation were consistent with a diagnosis of acquired perforating dermatosis (APD).

Comment
Presentation
Acquired perforating dermatosis is a dermatologic condition characterized by multiple pruritic, dome-shaped papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs giving a craterlike appearance.1-4 A green-brown or black crust with an erythematous border typically surrounds the primary lesions.4 Acquired perforating dermatosis favors a distribution over the trunk, gluteal region, and the extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Palmoplantar, intertriginous, and mucous membrane regions typically are spared.4 Occasionally, APD may present as generalized nodules and papules. Our case consisting of lesions that were localized to STSGs on the forearms supports the typical distribution; however, the presentation of APD occurring within a skin graft is unique.
From an epidemiologic standpoint, APD is more likely to affect men than women (1.5:1 ratio). Additionally, APD’s affected age range is 29 to 96 years (mean, 56.8 years),5 which is consistent with our patient’s age. Acquired perforating dermatosis has no racial predilection, though there is a predominance among black patients with concomitant chronic renal failure, as seen in our patient.3
Pathogenesis
The etiology of APD remains unknown.6 Some believe that the uremic or calcium deposits on the skin of patients with chronic kidney disease may trigger chronic pruritus, leading to epithelial hyperplasia and the development of perforating lesions.1,3 A prominent theory in the literature is that superficial trauma, such as scratching, induces necrosis of tissue, facilitating transepidermal elimination of connective tissue components.7 The Köbner phenomenon, which can easily be induced by scratching the skin, supports this idea.8 Fujimoto et al9 suggested that scratching exposes keratinocytes to advanced glycation end product–modified extracellular matrix proteins, particularly types I and III collagen. This exposure leads to the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes with the advanced glycation end receptor (CD36) followed by the upward movement of keratinocytes with glycated collagen. Others postulate fibronectin, involved in epidermal cell signaling, locomotion, and differentiation, is an antigenic trigger because patients with DM and uremia have increased levels of fibronectin in the serum and at sites of perforating skin lesions.10
Diseases Associated With APD
Acquired perforating dermatosis is an umbrella term for perforating disease found in adults. It is associated with systemic diseases, such as DM and pruritus of renal failure.11 Our patient had both dialysis-dependent end-stage renal disease and DM. Acquired perforating dermatosis is observed in 4.5% to 11% of patients on hemodialysis12,13; however, APD may occur prior to or in the absence of dialysis.3 Other examples of systemic conditions associated with APD include obstructive uropathy, chronic nephritis, anuria, and hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Koebnerization also may trigger lesions to manifest in a linear pattern after localized trauma to the skin.7 Acquired perforating dermatosis is associated with other types of trauma, such as healing herpes zoster, or following exposure to drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors, bevacizumab, telaprevir, sorafenib, sirolimus, and indinavir.14-16 Rarely, there have been associations with a history of insect bites, scabies, lymphoma, and hepatobiliary disease.1-3
Histopathology
Acquired perforating dermatosis is classified as a perforating disease, along with reactive perforating collagenosis, elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS), perforating folliculitis, and perforating calcific elastosis. Perforating diseases are histologically characterized by the transepidermal penetration and elimination of altered connective tissue and inflammatory cells.5 Each disease differs based on their clinical and histological characteristics.
Histologic sections of APD show a plug of crusting or hyperkeratosis with variable parakeratosis, acanthosis, and occasional dyskeratotic keratinocytes. In the dermis, aggregates of neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, or multinucleated giant cells may be found.17 The histologic findings vary depending on the stage of evolution of the individual lesion. Early lesions show a concave depression with acanthosis, vacuolation of basal keratinocytes, and dermal inflammation.4 Additionally, transepidermal channels filled with keratin, pyknotic nuclear debris, inflammatory cells, elastin, or collagen can be noted.3 Over time, the elastic fibers, as detected by the Verhoeff-van Gieson stain, dissipate and the collagen acquires a basophilic staining. Adjacent to the channels, the basement membrane remains intact in early lesions but later shows discontinuities and electron-dense fibrinlike material.3 Occasionally, amorphous degenerated material within the perforations is the major histologic finding.11 Usually, the material cannot be clearly identified as collagen or elastin, but sometimes both are present.
In our case, we identified elastin as the perforating substance, which is less common than collagen, the typical perforating substance in APD. Elastin has occasionally been seen to serve as the only perforating substance from APD lesions among patients. Abe et al18 reported that the biopsy of a Japanese patient with keratotic follicular papules and serpiginous-arranged papules demonstrated elimination of atypical elastin fibers from the transepidermal channels. This patient was diagnosed with APD as well as EPS and perforating folliculitis based on the clinical presentation.18 Kim et al19 studied 30 Korean patients with APD. One had serpiginous hyperkeratotic plaques along the upper extremity and trunk that revealed transepidermal channels containing coarse elastic fibers and basophilic debris; however, due to the serpiginous morphology of lesions, both Abe et al18 and Kim et al19 favored a diagnosis of acquired EPS. Saray et al20 conducted a retrospective study of 22 Turkish patients with APD; 1 patient had a painful hyperkeratotic papule on the auricle that on histopathology showed degenerated elastin perforating through the keratotic plug, features similar to our case.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses include perforating diseases14,19 as well as other disorders that exhibit the Köbner phenomenon, such as psoriasis, lichen planus, and verruca vulgaris.21,22 Also, it is not uncommon for patients with APD to have coexisting folliculitis or prurigo nodularis.22
Treatment
Management is focused on treating the symptoms. For pruritus, sedating antihistamines and other antipruritic agents are efficacious.23 Topical, intra-lesional, or systemic corticosteroids and topical retinoids have shown variable resolution in APD lesions.24 Some case reports describe topical menthol, salicylic acid, sulfur, benzoyl peroxide, systemic antibiotics (eg, clindamycin, doxycycline), and allopurinol for elevated uric acid levels as effective treatment methods.6 Narrowband UVB phototherapy is beneficial for APD and renal disease.25,26 Renal transplantation has been curative for some patients with APD.27 Given that our patient’s lesions were asymptomatic, no treatment was offered at the time.
Conclusion
Our patient presented with APD localized exclusively to the site of a skin graft, and histologic examination identified elastin as the primary perforating substance. A medical history of DM and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
- Rodney IJ, Taylor CS, Cohen G. Derm Dx: what are these pruritic nodules? The Dermatologist. October 15, 2009. http://www.the-dermatologist.com/content/derm-dx-what-are-these-pruritic-nodules. Accessed September 18, 2018.
- Gagnon, AL, Desai T. Dermatological diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Nephropathol. 2013;2:104-109.
- Kurban MS, Boueiz A, Kibbi AG. Cutaneous manifestations of chronic kidney disease. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:255-264.
- Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis [published online May 29, 2013]. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729; 723-730.
- Karpouzis A, Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-592.
- Healy R, Cerio R, Hollingsworth A, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:621-623.
- Cordova KB, Oberg TJ, Malik M, et al. Dermatologic conditions seen in end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2009;22:45-55.
- Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: a condition that may be underdiagnosed. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-287.
- Fujimoto E, Kobayashi T, Fujimoto N, et al. AGE-modified collagens I and III induce keratinocyte terminal differentiation through AGE receptor CD36: epidermal-dermal interaction in acquired perforating dermatosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:405-414.
- Bilezikci B, Sechkin D, Demirhan B. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure: a possible role for fibronectin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003;17:230-232.
- Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:1074-1078.
- Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Lübbe J, Sorg O, Malé PJ, et al. Sirolimus-induced inflammatory papules with acquired reactive perforating collagenosis [published online January 9, 2008]. Dermatology. 2008;216:239-242.
- Pernet C, Pageaux GP, Guillot B, et al. Telaprevir-induced acquired perforating dermatosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:1371-1372.
- Severino-Freire M, Sibaud V, Tournier E, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis associated with sorafenib therapy [published online September 11, 2014]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:328-330.
- Zelger B, Hintner H, Auböck J, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis. transepidermal elimination of DNA material and possible role of leukocytes in pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:695-700.
- Abe R, Murase S, Nomura Y, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis appearing as elastosis perforans serpiginosa and perforating folliculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:653-654.
- Kim SW, Kim MS, Lee JH, et al. A clinicopathologic study of thirty cases of acquired perforating dermatosis in Korea. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:162-171.
- Saray Y, Seçkin D, Bilezikçi B. Acquired perforating dermatosis: clinicopathological features in twenty-two cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:679-688.
- Carter VH, Constantine VS. Kyrle’s disease. I. clinical findings in five cases and review of literature. Arch Dermatol. 1968;97:624-632.
- Robinson-Bostom L, Digiovanna JJ. Cutaneous manifestations of end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:975-986.
- Hong SB, Park JH, Ihm CG, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19:283-288.
- Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, et al. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:671-677.
- Ohe S, Danno K, Sasaki H, et al. Treatment of acquired perforating dermatosis with narrowband ultraviolet B. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:892-894.
- Sezer E, Erkek E. Acquired perforating dermatosis successfully treated with photodynamic therapy. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2012;28:50-52.
- Saldanha LF, Gonick HC, Rodriguez HJ, et al. Silicon-related syndrome in dialysis patients. Nephron. 1997;77:48-56.
Practice Points
- Acquired perforating dermatosis (APD) presents as pruritic crateriform papules and plaques with central keratotic plugs.
- A medical history of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease predisposes patients to APD. This case suggests that skin graft sites may be predisposed to the development of APD.
TKI discontinuation appears safe in CML
NEW YORK – Despite initial concerns that stopping tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment would be ill-advised in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), clinical trial data suggest it is a safe and reasonable strategy, according to a leading expert.
“About 95% of people in all of these trials will regain their original response when they start off on therapy again,” said Jerald P. Radich, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance.
“There’s been a few that don’t, but blast crisis has been very, very rare, thank goodness, so it looks to be fairly safe for now,” Dr. Radich said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
That being said, careful follow up is still required, Dr. Radich cautioned, noting that there was still an excess of CML in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors evident decades after radiation exposure.
“CML is a very strange disease,” he said. “You can’t eliminate the possibility of some slow-growing clone that, once you take [a patient] off tyrosine kinase therapy, is going into an accelerated phase and might take years to manifest itself.”
In one of the latest reports to shed light on what happens after discontinuation, investigators for the ENESTop study reported that treatment-free remission “seems achievable” in patients who have sustained, deep remissions after discontinuing nilotinib second-line therapy (Ann Intern Med. 2018 Apr 3;168[7]:461-70).
In ENESTop, chronic phase CML patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitors for at least 3 years were eligible to discontinue therapy if they achieved MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1IS of 0.0032% or less) and maintained that response level during a 1-year consolidation phase.
Out of 163 patients in the study, 126 met the criteria to enter the treatment-free remission phase; of that subset, 58% maintained treatment-free remission at 48 weeks, while 53% maintained it at 96 weeks, investigators said.
For 56 patients who restarted nilotinib, 55 regained at least major molecular response (MMR), and 52 regained MR4.5, while none had progression to accelerated phase or blast crisis, according to the report.
Similarly, earlier reported results from the ENESTfreedom trial showed that, of 190 patients entering the treatment-free remission phase after a median duration of 43.5 months on nilotinib, more than half remained in MMR or better at 48 weeks (Leukemia. 2017 Jul;31[7]:1525-31).
Of 86 patients who started nilotinib again after losing MMR, 98.8% regained MMR and 88.4% regained MR4.5 by the data cutoff date for the trial.
Duration and depth of response may make a “little bit of difference” in likelihood of relapse, Dr. Radich added.
In an interim analysis of a prospective multicenter, nonrandomized European discontinuation trial (EURO-SKI), investigators found that patients achieving deep molecular responses had good molecular relapse-free survival (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jun;19[6]:747-57).
Based on that, investigators suggested that patients with deep molecular responses should be considered for discontinuation to spare them from side effects and to reduce health expenditures.
Results of these and other trials are “pretty much unbelievable,” Dr. Radich said. That’s in part because mathematical modeling – extrapolated from early trials – had suggested it could take nearly 50 years to completely eradicate minimal residual disease with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and that the cumulative cure rate after 30 years of treatment could be as low as 31%.
Dr. Radich reported financial disclosures related to Amgen, Novartis, and Seattle Genetics.
NEW YORK – Despite initial concerns that stopping tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment would be ill-advised in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), clinical trial data suggest it is a safe and reasonable strategy, according to a leading expert.
“About 95% of people in all of these trials will regain their original response when they start off on therapy again,” said Jerald P. Radich, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance.
“There’s been a few that don’t, but blast crisis has been very, very rare, thank goodness, so it looks to be fairly safe for now,” Dr. Radich said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
That being said, careful follow up is still required, Dr. Radich cautioned, noting that there was still an excess of CML in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors evident decades after radiation exposure.
“CML is a very strange disease,” he said. “You can’t eliminate the possibility of some slow-growing clone that, once you take [a patient] off tyrosine kinase therapy, is going into an accelerated phase and might take years to manifest itself.”
In one of the latest reports to shed light on what happens after discontinuation, investigators for the ENESTop study reported that treatment-free remission “seems achievable” in patients who have sustained, deep remissions after discontinuing nilotinib second-line therapy (Ann Intern Med. 2018 Apr 3;168[7]:461-70).
In ENESTop, chronic phase CML patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitors for at least 3 years were eligible to discontinue therapy if they achieved MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1IS of 0.0032% or less) and maintained that response level during a 1-year consolidation phase.
Out of 163 patients in the study, 126 met the criteria to enter the treatment-free remission phase; of that subset, 58% maintained treatment-free remission at 48 weeks, while 53% maintained it at 96 weeks, investigators said.
For 56 patients who restarted nilotinib, 55 regained at least major molecular response (MMR), and 52 regained MR4.5, while none had progression to accelerated phase or blast crisis, according to the report.
Similarly, earlier reported results from the ENESTfreedom trial showed that, of 190 patients entering the treatment-free remission phase after a median duration of 43.5 months on nilotinib, more than half remained in MMR or better at 48 weeks (Leukemia. 2017 Jul;31[7]:1525-31).
Of 86 patients who started nilotinib again after losing MMR, 98.8% regained MMR and 88.4% regained MR4.5 by the data cutoff date for the trial.
Duration and depth of response may make a “little bit of difference” in likelihood of relapse, Dr. Radich added.
In an interim analysis of a prospective multicenter, nonrandomized European discontinuation trial (EURO-SKI), investigators found that patients achieving deep molecular responses had good molecular relapse-free survival (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jun;19[6]:747-57).
Based on that, investigators suggested that patients with deep molecular responses should be considered for discontinuation to spare them from side effects and to reduce health expenditures.
Results of these and other trials are “pretty much unbelievable,” Dr. Radich said. That’s in part because mathematical modeling – extrapolated from early trials – had suggested it could take nearly 50 years to completely eradicate minimal residual disease with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and that the cumulative cure rate after 30 years of treatment could be as low as 31%.
Dr. Radich reported financial disclosures related to Amgen, Novartis, and Seattle Genetics.
NEW YORK – Despite initial concerns that stopping tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment would be ill-advised in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), clinical trial data suggest it is a safe and reasonable strategy, according to a leading expert.
“About 95% of people in all of these trials will regain their original response when they start off on therapy again,” said Jerald P. Radich, MD, of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance.
“There’s been a few that don’t, but blast crisis has been very, very rare, thank goodness, so it looks to be fairly safe for now,” Dr. Radich said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
That being said, careful follow up is still required, Dr. Radich cautioned, noting that there was still an excess of CML in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors evident decades after radiation exposure.
“CML is a very strange disease,” he said. “You can’t eliminate the possibility of some slow-growing clone that, once you take [a patient] off tyrosine kinase therapy, is going into an accelerated phase and might take years to manifest itself.”
In one of the latest reports to shed light on what happens after discontinuation, investigators for the ENESTop study reported that treatment-free remission “seems achievable” in patients who have sustained, deep remissions after discontinuing nilotinib second-line therapy (Ann Intern Med. 2018 Apr 3;168[7]:461-70).
In ENESTop, chronic phase CML patients on tyrosine kinase inhibitors for at least 3 years were eligible to discontinue therapy if they achieved MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1IS of 0.0032% or less) and maintained that response level during a 1-year consolidation phase.
Out of 163 patients in the study, 126 met the criteria to enter the treatment-free remission phase; of that subset, 58% maintained treatment-free remission at 48 weeks, while 53% maintained it at 96 weeks, investigators said.
For 56 patients who restarted nilotinib, 55 regained at least major molecular response (MMR), and 52 regained MR4.5, while none had progression to accelerated phase or blast crisis, according to the report.
Similarly, earlier reported results from the ENESTfreedom trial showed that, of 190 patients entering the treatment-free remission phase after a median duration of 43.5 months on nilotinib, more than half remained in MMR or better at 48 weeks (Leukemia. 2017 Jul;31[7]:1525-31).
Of 86 patients who started nilotinib again after losing MMR, 98.8% regained MMR and 88.4% regained MR4.5 by the data cutoff date for the trial.
Duration and depth of response may make a “little bit of difference” in likelihood of relapse, Dr. Radich added.
In an interim analysis of a prospective multicenter, nonrandomized European discontinuation trial (EURO-SKI), investigators found that patients achieving deep molecular responses had good molecular relapse-free survival (Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jun;19[6]:747-57).
Based on that, investigators suggested that patients with deep molecular responses should be considered for discontinuation to spare them from side effects and to reduce health expenditures.
Results of these and other trials are “pretty much unbelievable,” Dr. Radich said. That’s in part because mathematical modeling – extrapolated from early trials – had suggested it could take nearly 50 years to completely eradicate minimal residual disease with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and that the cumulative cure rate after 30 years of treatment could be as low as 31%.
Dr. Radich reported financial disclosures related to Amgen, Novartis, and Seattle Genetics.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Brentuximab vendotin plus CHP meets PFS endpoint in ECHELON-2
Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Seattle Genetics announced top-line results in the ECHELON-2 phase 3 trial of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone) in the frontline treatment of CD-30 expressing peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
The combination achieved statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS), compared with the control arm of standard chemotherapy alone using cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP). The PFS was assessed by an Independent Review Facility (hazard ratio, 0.71; P = .0110).
The combination of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP also outperformed CHOP in overall survival, a secondary endpoint of the trial (hazard ratio, 0.66, P = .0244), according to the drug sponsors.
Full results of ECHELON-2 will be presented in December 2018 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, according to the announcement from Seattle Genetics and Takeda.
Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Seattle Genetics announced top-line results in the ECHELON-2 phase 3 trial of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone) in the frontline treatment of CD-30 expressing peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
The combination achieved statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS), compared with the control arm of standard chemotherapy alone using cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP). The PFS was assessed by an Independent Review Facility (hazard ratio, 0.71; P = .0110).
The combination of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP also outperformed CHOP in overall survival, a secondary endpoint of the trial (hazard ratio, 0.66, P = .0244), according to the drug sponsors.
Full results of ECHELON-2 will be presented in December 2018 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, according to the announcement from Seattle Genetics and Takeda.
Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Seattle Genetics announced top-line results in the ECHELON-2 phase 3 trial of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone) in the frontline treatment of CD-30 expressing peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
The combination achieved statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS), compared with the control arm of standard chemotherapy alone using cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP). The PFS was assessed by an Independent Review Facility (hazard ratio, 0.71; P = .0110).
The combination of brentuximab vedotin plus CHP also outperformed CHOP in overall survival, a secondary endpoint of the trial (hazard ratio, 0.66, P = .0244), according to the drug sponsors.
Full results of ECHELON-2 will be presented in December 2018 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, according to the announcement from Seattle Genetics and Takeda.
Chasing the millennial market
I’m not sure why I read the “Letter from the President” in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ AAP News every month. I guess it is out of curiosity about how far the guild to which I belong is drifting from where I think it should be going.
In her August 2018 letter, Colleen A. Kraft, MD, lays out the challenges pediatricians will be facing in the next several decades as the “era of health care consumerism” engulfs us, a change that she suggests will mean “redefining the patient/provider relationship.” As an example, she observes that millennial parents who want “personalized care when and where they want it” have become our “new target market.” Dr. Kraft goes on to suggest that telemedicine may provide a way to reconcile the millennials’ two seemingly incompatible demands. However, she notes that only “15% of pediatricians report using telehealth technologies to provide patient care.” Dr. Kraft recommends that to survive the rising waters of health consumerism more of us should consider climbing onto the telemedicine ship.
There is no question that millennials are aging into the childbearing and child-rearing phases of their lives. They have become the major consumers of pediatric services. Is Dr. Kraft correct that we must change how we practice pediatrics to accommodate the I-want-it-now-delivered-to-my-inbox mentality of the millennials? If we fail to adjust, will we be committing financial suicide?
She makes a valid point. If your practice isn’t providing evening and weekend hours, if your patients’ calls aren’t being answered in a timely manner, and if your receptionists are more about deflecting calls than helping patients get their questions answered, you are running the risk of choking off your income stream to an unsustainable trickle.
But how far should we chase that “target market” made up of people who believe that they can receive personalized care without putting a wrinkle in their device-driven lives? It may be that they have never experienced the benefits of real personalized service from the same person encounter after encounter. I’m convinced that if you provide quality care that is reasonably available, enough patients will stick with you to make your practice sustainable. You will lose some impatient patients to walk-in-quick-care operations, but if you are giving good personalized care, many will return to the quality you are offering. But if you aren’t willing to consider improving your availability, even being the most personable provider in town isn’t going to keep you afloat.
Now to the claim that telemedicine may hold the answer to surviving consumerism. I think we must move cautiously. The fact that only 15% of us aren’t climbing on board doesn’t mean we are all Luddites. It is very likely that many of us are still feeling the sting of investing large amounts of money and time to computerize our health records and seeing little benefit. Telemedicine means lots of things to lots of people. It won’t hurt to keep an open mind and listen as technology evolves. But if you had it to do all over again, wouldn’t you have taken more time and given more thought into signing on for your electronic medical records system?
Finally, let’s remember millennials will be followed by another generation. Although some “experts” suggest that the post-millennials will be just more of the same, I’m not so sure. Millennials and their expectations have become fodder for comedians, even from within their own cohort. The post-millennials may surprise us and provide a refreshing breath of retro and a market that is much easier to reconcile with the realities of good patient care.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I’m not sure why I read the “Letter from the President” in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ AAP News every month. I guess it is out of curiosity about how far the guild to which I belong is drifting from where I think it should be going.
In her August 2018 letter, Colleen A. Kraft, MD, lays out the challenges pediatricians will be facing in the next several decades as the “era of health care consumerism” engulfs us, a change that she suggests will mean “redefining the patient/provider relationship.” As an example, she observes that millennial parents who want “personalized care when and where they want it” have become our “new target market.” Dr. Kraft goes on to suggest that telemedicine may provide a way to reconcile the millennials’ two seemingly incompatible demands. However, she notes that only “15% of pediatricians report using telehealth technologies to provide patient care.” Dr. Kraft recommends that to survive the rising waters of health consumerism more of us should consider climbing onto the telemedicine ship.
There is no question that millennials are aging into the childbearing and child-rearing phases of their lives. They have become the major consumers of pediatric services. Is Dr. Kraft correct that we must change how we practice pediatrics to accommodate the I-want-it-now-delivered-to-my-inbox mentality of the millennials? If we fail to adjust, will we be committing financial suicide?
She makes a valid point. If your practice isn’t providing evening and weekend hours, if your patients’ calls aren’t being answered in a timely manner, and if your receptionists are more about deflecting calls than helping patients get their questions answered, you are running the risk of choking off your income stream to an unsustainable trickle.
But how far should we chase that “target market” made up of people who believe that they can receive personalized care without putting a wrinkle in their device-driven lives? It may be that they have never experienced the benefits of real personalized service from the same person encounter after encounter. I’m convinced that if you provide quality care that is reasonably available, enough patients will stick with you to make your practice sustainable. You will lose some impatient patients to walk-in-quick-care operations, but if you are giving good personalized care, many will return to the quality you are offering. But if you aren’t willing to consider improving your availability, even being the most personable provider in town isn’t going to keep you afloat.
Now to the claim that telemedicine may hold the answer to surviving consumerism. I think we must move cautiously. The fact that only 15% of us aren’t climbing on board doesn’t mean we are all Luddites. It is very likely that many of us are still feeling the sting of investing large amounts of money and time to computerize our health records and seeing little benefit. Telemedicine means lots of things to lots of people. It won’t hurt to keep an open mind and listen as technology evolves. But if you had it to do all over again, wouldn’t you have taken more time and given more thought into signing on for your electronic medical records system?
Finally, let’s remember millennials will be followed by another generation. Although some “experts” suggest that the post-millennials will be just more of the same, I’m not so sure. Millennials and their expectations have become fodder for comedians, even from within their own cohort. The post-millennials may surprise us and provide a refreshing breath of retro and a market that is much easier to reconcile with the realities of good patient care.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
I’m not sure why I read the “Letter from the President” in the American Academy of Pediatrics’ AAP News every month. I guess it is out of curiosity about how far the guild to which I belong is drifting from where I think it should be going.
In her August 2018 letter, Colleen A. Kraft, MD, lays out the challenges pediatricians will be facing in the next several decades as the “era of health care consumerism” engulfs us, a change that she suggests will mean “redefining the patient/provider relationship.” As an example, she observes that millennial parents who want “personalized care when and where they want it” have become our “new target market.” Dr. Kraft goes on to suggest that telemedicine may provide a way to reconcile the millennials’ two seemingly incompatible demands. However, she notes that only “15% of pediatricians report using telehealth technologies to provide patient care.” Dr. Kraft recommends that to survive the rising waters of health consumerism more of us should consider climbing onto the telemedicine ship.
There is no question that millennials are aging into the childbearing and child-rearing phases of their lives. They have become the major consumers of pediatric services. Is Dr. Kraft correct that we must change how we practice pediatrics to accommodate the I-want-it-now-delivered-to-my-inbox mentality of the millennials? If we fail to adjust, will we be committing financial suicide?
She makes a valid point. If your practice isn’t providing evening and weekend hours, if your patients’ calls aren’t being answered in a timely manner, and if your receptionists are more about deflecting calls than helping patients get their questions answered, you are running the risk of choking off your income stream to an unsustainable trickle.
But how far should we chase that “target market” made up of people who believe that they can receive personalized care without putting a wrinkle in their device-driven lives? It may be that they have never experienced the benefits of real personalized service from the same person encounter after encounter. I’m convinced that if you provide quality care that is reasonably available, enough patients will stick with you to make your practice sustainable. You will lose some impatient patients to walk-in-quick-care operations, but if you are giving good personalized care, many will return to the quality you are offering. But if you aren’t willing to consider improving your availability, even being the most personable provider in town isn’t going to keep you afloat.
Now to the claim that telemedicine may hold the answer to surviving consumerism. I think we must move cautiously. The fact that only 15% of us aren’t climbing on board doesn’t mean we are all Luddites. It is very likely that many of us are still feeling the sting of investing large amounts of money and time to computerize our health records and seeing little benefit. Telemedicine means lots of things to lots of people. It won’t hurt to keep an open mind and listen as technology evolves. But if you had it to do all over again, wouldn’t you have taken more time and given more thought into signing on for your electronic medical records system?
Finally, let’s remember millennials will be followed by another generation. Although some “experts” suggest that the post-millennials will be just more of the same, I’m not so sure. Millennials and their expectations have become fodder for comedians, even from within their own cohort. The post-millennials may surprise us and provide a refreshing breath of retro and a market that is much easier to reconcile with the realities of good patient care.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Leukemia Cutis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Signifies a Poor Prognosis
Case Report
A 66-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with considerable muscle weakness and infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the face, trunk, and arms of 3 months’ duration. The patient required the use of a wheelchair due to muscle weakness. On physical examination he had diffuse, infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the entire face (Figure 1A), trunk, and arms. The eyelids and lips were swollen, and the nose was distorted due to the infiltrative plaques (Figure 1B). Additionally, there were hypopigmented macules and patches scattered among the infiltrative plaques on the face, trunk, and arms (Figure 1C).
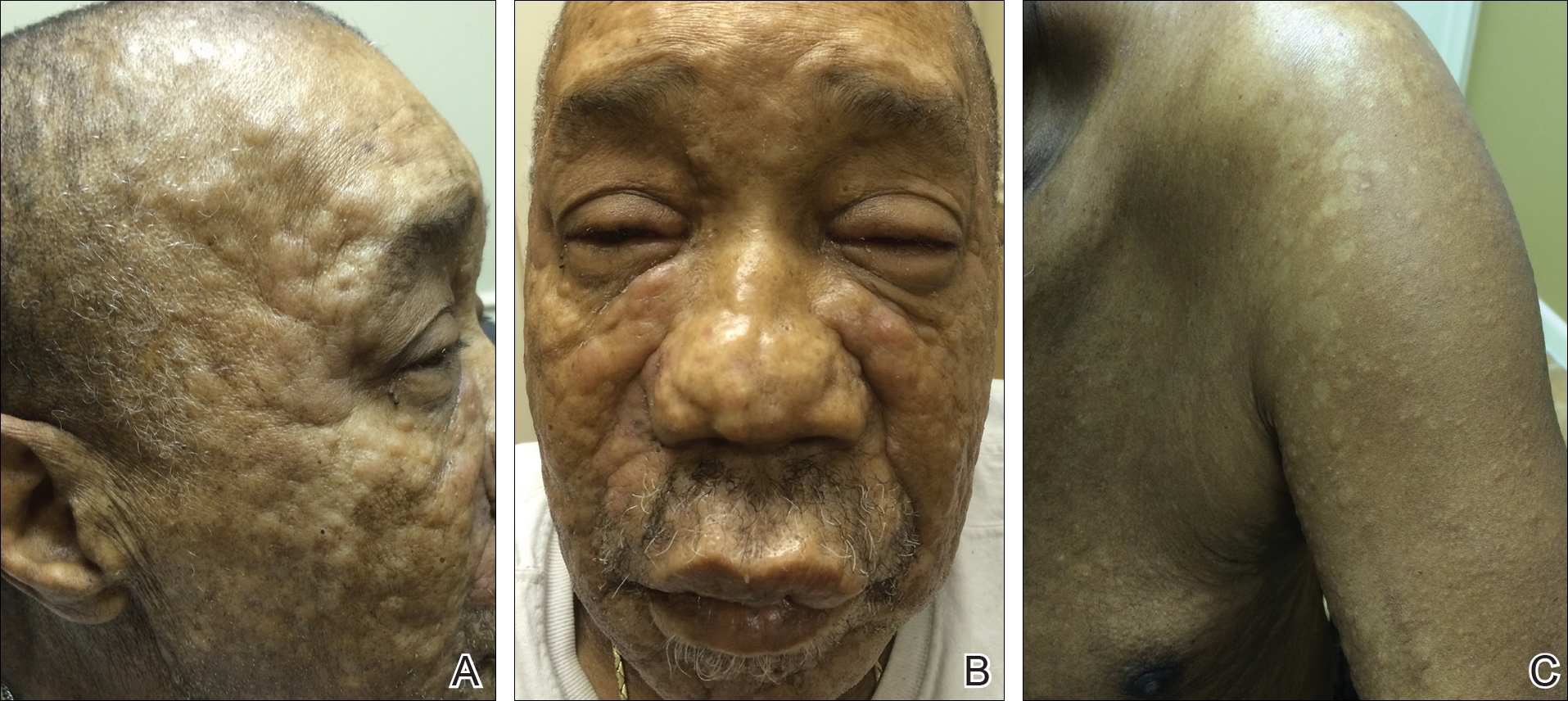
Punch biopsy specimens were obtained from the left cheek and left upper arm and were submitted for histologic examination with routine hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 2). Histopathology showed infiltrating and diffuse monomorphic cells in the dermis with large and hyperchromatic nuclei. Some nuclei were cleaved or folded in configuration. The cells displayed ample surrounding cytoplasm, which was finely granular or vacuolated. The infiltrate was accentuated in the perifollicular adventitial dermis. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD33 and negative for CD3, CD20, and myeloperoxidase. Additionally, periodic acid–Schiff and Fite stains were negative for microorganisms. These morphologic and immunohistochemical findings were consistent with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Further testing with complete blood cell count, peripheral blood smear, and bone marrow biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of AML. The patient subsequently died 5 weeks later.
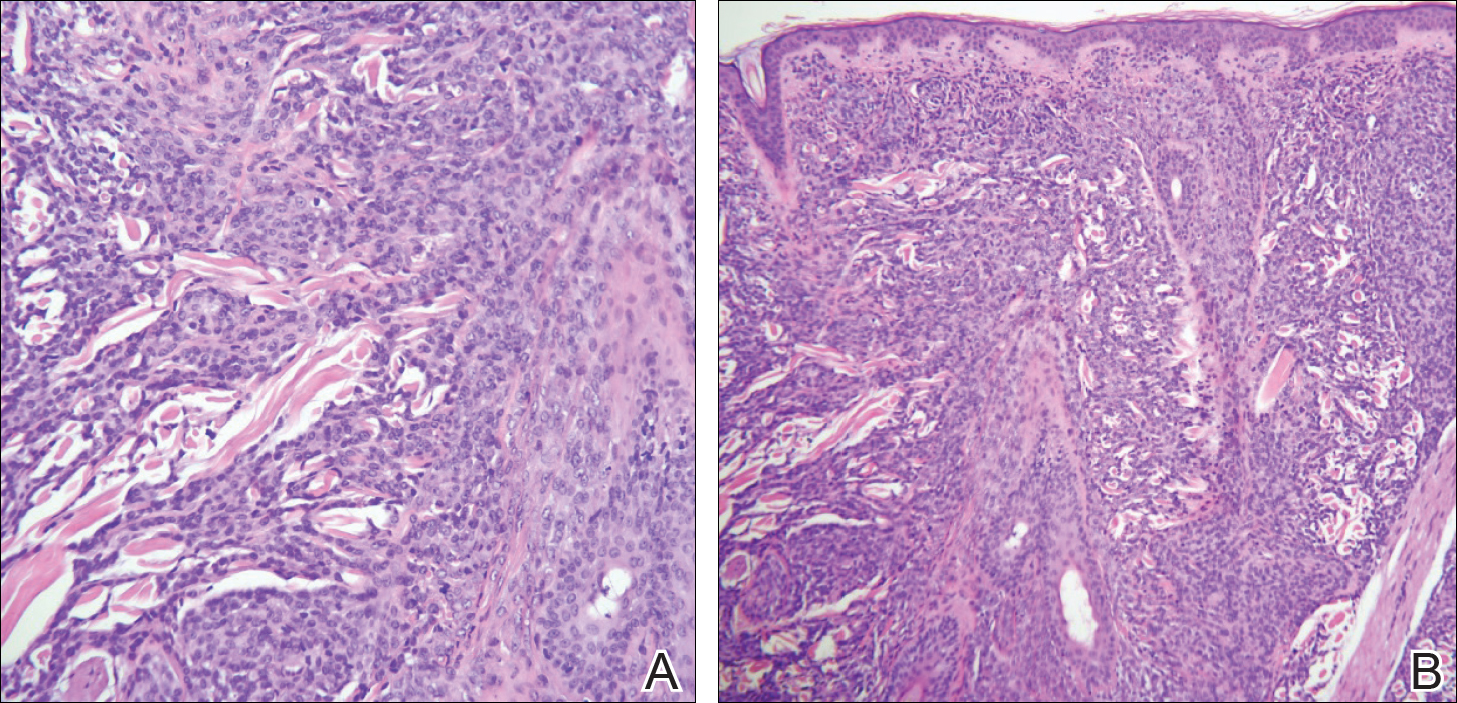
Comment
Presentation of LC
Thirty percent to 40% of leukemia patients present with a variety of nonspecific cutaneous signs, including those related to hemorrhage, infection, and drug eruptions, as well as paraneoplastic lesions.1 Cutaneous signs of leukemia are less commonly due to leukemia cutis (LC), defined as the neoplastic infiltration of the skin or subcutaneous tissue by leukemic cells. The clinical presentation of LC varies, making it difficult to diagnose without immunohistochemistry. It can pre-sent as single or multiple erythematous papules and/or nodules, infiltrated plaques, macules, palpable purpura, ulcers, ecchymoses, and/or vesicles.2 Leukemia cutis most often presents on the head, neck, trunk, and sites of current or prior trauma. Gingival hyperplasia is another associated finding in the acute monocytic and myelomonocytic types of AML.3 Additionally, chloromas or granulocytic sarcomas are dermal nodules that can pre-sent in myelogenous leukemia.4
LC and AML
Leukemia cutis most commonly is observed in AML compared to the other types of leukemia. The myelomonocytic and monocytic subtypes of AML are most often implicated.5,6 The majority of patients with LC present with a pre-established (55%–77%) or simultaneous diagnosis of systemic leukemia (23%–38%).
Histopathology
In LC, histology typically reveals a normal epidermis and nodular or diffuse infiltrating cells in the dermis. The cells can appear monomorphic, atypical, or immature, and there is occasional single-filing between collagen bundles. Causative types of neoplasms can be distinguished based on their morphologic, immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic properties.8-10
Incidence
Of the acute leukemias, AML accounts for the highest prevalence in adults,11 with an annual incidence of 14,590 cases in the United States.12 The incidence of AML increases with age; the mean age of patients diagnosed with AML is 67 years.12 Risk is increased with a history of exposure to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or cigarette smoke; preexisting myeloproliferative or myelodysplastic syndromes and mutations in DNA repair (eg, Fanconi anemia); neutropenia (eg, from elastase mutations); and Down syndrome.13
Diagnosis
More than 20% blasts in the bone marrow is required for a diagnosis of AML.14 Specific to AML is the presence of large immature precursor cells with a granular cytoplasm and, when present, highly diagnostic Auer rods.12Acute myeloid leukemia can be distinguished by staining for myeloperoxidase; Sudan Black B; or the antigens CD13, CD33, or c-kit.15
In our case, CD33 was positive, which is a characteristic finding in AML. Myeloperoxidase also can be positive in AML; however, in our case it was negative, and it can be an insensitive marker in the context of LC. Although most cases of LC present concurrently with bone marrow infiltration, some cases present before systemic involvement; for example, granulocytic sarcomas can occur months earlier than the development of systemic leukemia. Thus, early detection by a dermatologist is essential. Depending on the lesion’s appearance, the differential diagnoses can include lymphoma, drug eruptions, infectious etiologies, sarcoidosis, metastases from other malignancies, and blistering dermatoses.
Management
Systemic therapy should be the cornerstone of therapy. Induction therapy includes the combined use of cytarabine (except in acute promyelocytic leukemia [M3], for which all-trans retinoic acid is indicated) and anthracycline derivatives in a “7+3” regimen to achieve complete remission. Specifically, cytarabine (100–200 mg/m2) typically is continuously administered intravenously for 7 days combined with intravenous administration of either daunorubicin (60–90 mg/m2) or idarubicin (12 mg/m2) on days 1, 2, and 3. Postremission therapy is highly individualized depending on patients’ prognostic factors and is indicated to reduce the likelihood of relapse and to improve patient mortality. High doses of cytarabine and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation commonly are utilized.12 Resolution of hematologic atypia may result in complete or partial resolution of LC.10
Conclusion
We diagnosed AML with systemic involvement in our patient based on the cutaneous manifestation of LC. Diagnosis of LC relies on immunohistochemistry and strong clinical suspicion, as cutaneous findings are diverse and nonspecific. Early recognition is essential, as LC in the context of systemic involvement portends a poor prognosis. Our patient died 5 weeks following initial presentation.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Su WPD, Buechner SA, Chin-Yang L. Clinicopathologic correlations in leukemia cutis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11:121-128.
- Kumar M, Nair V, Mishra L, et al. Gingival hyperplasia—a clue to the diagnosis of acute leukemia? Arch Oral Sci Res. 2012;2:165-168.
- Winfield H, Smoller B. Other lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier; 2012:2037-2048.
- Babina T, Miller L, Thomas B. Leukemia cutis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:416-417.
- Tziotzios C, Makrygeorgou A. Leukemia cutis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2011;78:226-227.
- Ratnam KV, Khor CJL, Su WPD. Leukemia cutis. Dermatol Clin 1994;12:419-431.
- Cho-Vega JH, Medeiros LJ, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142.
- Buechner SA, Li CY, Su WP. Leukemia cutis. a histopathologic study of 42 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1985;7:109-119.
- Wagner G, Fenchel K, Back W, et al. Leukemia cutis—epidemiology, clinical presentation, and differential diagnoses. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10:27-36.
- O’Donnell MR, Abboud CN, Altman J, et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines acute myeloid leukemia. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2012;10:984-1021.
- Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD. Acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015:678-686.
- Aster JC, DeAngelo DJ. Acute leukemias. In: Bunn HF, Aster JC, eds. Pathophysiology of Blood Disorders. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2010:244-259.
- Damon LE, Andreadis C. Blood disorders. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2016. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2016:495-541.
- Parikh SA, Jabbour E, Koller CA. Adult acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kantarjian HM, Wolff RA, eds. The MD Anderson Manual of Medical Oncology. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011:15-32.
Case Report
A 66-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with considerable muscle weakness and infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the face, trunk, and arms of 3 months’ duration. The patient required the use of a wheelchair due to muscle weakness. On physical examination he had diffuse, infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the entire face (Figure 1A), trunk, and arms. The eyelids and lips were swollen, and the nose was distorted due to the infiltrative plaques (Figure 1B). Additionally, there were hypopigmented macules and patches scattered among the infiltrative plaques on the face, trunk, and arms (Figure 1C).

Punch biopsy specimens were obtained from the left cheek and left upper arm and were submitted for histologic examination with routine hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 2). Histopathology showed infiltrating and diffuse monomorphic cells in the dermis with large and hyperchromatic nuclei. Some nuclei were cleaved or folded in configuration. The cells displayed ample surrounding cytoplasm, which was finely granular or vacuolated. The infiltrate was accentuated in the perifollicular adventitial dermis. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD33 and negative for CD3, CD20, and myeloperoxidase. Additionally, periodic acid–Schiff and Fite stains were negative for microorganisms. These morphologic and immunohistochemical findings were consistent with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Further testing with complete blood cell count, peripheral blood smear, and bone marrow biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of AML. The patient subsequently died 5 weeks later.

Comment
Presentation of LC
Thirty percent to 40% of leukemia patients present with a variety of nonspecific cutaneous signs, including those related to hemorrhage, infection, and drug eruptions, as well as paraneoplastic lesions.1 Cutaneous signs of leukemia are less commonly due to leukemia cutis (LC), defined as the neoplastic infiltration of the skin or subcutaneous tissue by leukemic cells. The clinical presentation of LC varies, making it difficult to diagnose without immunohistochemistry. It can pre-sent as single or multiple erythematous papules and/or nodules, infiltrated plaques, macules, palpable purpura, ulcers, ecchymoses, and/or vesicles.2 Leukemia cutis most often presents on the head, neck, trunk, and sites of current or prior trauma. Gingival hyperplasia is another associated finding in the acute monocytic and myelomonocytic types of AML.3 Additionally, chloromas or granulocytic sarcomas are dermal nodules that can pre-sent in myelogenous leukemia.4
LC and AML
Leukemia cutis most commonly is observed in AML compared to the other types of leukemia. The myelomonocytic and monocytic subtypes of AML are most often implicated.5,6 The majority of patients with LC present with a pre-established (55%–77%) or simultaneous diagnosis of systemic leukemia (23%–38%).
Histopathology
In LC, histology typically reveals a normal epidermis and nodular or diffuse infiltrating cells in the dermis. The cells can appear monomorphic, atypical, or immature, and there is occasional single-filing between collagen bundles. Causative types of neoplasms can be distinguished based on their morphologic, immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic properties.8-10
Incidence
Of the acute leukemias, AML accounts for the highest prevalence in adults,11 with an annual incidence of 14,590 cases in the United States.12 The incidence of AML increases with age; the mean age of patients diagnosed with AML is 67 years.12 Risk is increased with a history of exposure to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or cigarette smoke; preexisting myeloproliferative or myelodysplastic syndromes and mutations in DNA repair (eg, Fanconi anemia); neutropenia (eg, from elastase mutations); and Down syndrome.13
Diagnosis
More than 20% blasts in the bone marrow is required for a diagnosis of AML.14 Specific to AML is the presence of large immature precursor cells with a granular cytoplasm and, when present, highly diagnostic Auer rods.12Acute myeloid leukemia can be distinguished by staining for myeloperoxidase; Sudan Black B; or the antigens CD13, CD33, or c-kit.15
In our case, CD33 was positive, which is a characteristic finding in AML. Myeloperoxidase also can be positive in AML; however, in our case it was negative, and it can be an insensitive marker in the context of LC. Although most cases of LC present concurrently with bone marrow infiltration, some cases present before systemic involvement; for example, granulocytic sarcomas can occur months earlier than the development of systemic leukemia. Thus, early detection by a dermatologist is essential. Depending on the lesion’s appearance, the differential diagnoses can include lymphoma, drug eruptions, infectious etiologies, sarcoidosis, metastases from other malignancies, and blistering dermatoses.
Management
Systemic therapy should be the cornerstone of therapy. Induction therapy includes the combined use of cytarabine (except in acute promyelocytic leukemia [M3], for which all-trans retinoic acid is indicated) and anthracycline derivatives in a “7+3” regimen to achieve complete remission. Specifically, cytarabine (100–200 mg/m2) typically is continuously administered intravenously for 7 days combined with intravenous administration of either daunorubicin (60–90 mg/m2) or idarubicin (12 mg/m2) on days 1, 2, and 3. Postremission therapy is highly individualized depending on patients’ prognostic factors and is indicated to reduce the likelihood of relapse and to improve patient mortality. High doses of cytarabine and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation commonly are utilized.12 Resolution of hematologic atypia may result in complete or partial resolution of LC.10
Conclusion
We diagnosed AML with systemic involvement in our patient based on the cutaneous manifestation of LC. Diagnosis of LC relies on immunohistochemistry and strong clinical suspicion, as cutaneous findings are diverse and nonspecific. Early recognition is essential, as LC in the context of systemic involvement portends a poor prognosis. Our patient died 5 weeks following initial presentation.
Case Report
A 66-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with considerable muscle weakness and infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the face, trunk, and arms of 3 months’ duration. The patient required the use of a wheelchair due to muscle weakness. On physical examination he had diffuse, infiltrative, flesh-colored plaques on the entire face (Figure 1A), trunk, and arms. The eyelids and lips were swollen, and the nose was distorted due to the infiltrative plaques (Figure 1B). Additionally, there were hypopigmented macules and patches scattered among the infiltrative plaques on the face, trunk, and arms (Figure 1C).

Punch biopsy specimens were obtained from the left cheek and left upper arm and were submitted for histologic examination with routine hematoxylin and eosin staining (Figure 2). Histopathology showed infiltrating and diffuse monomorphic cells in the dermis with large and hyperchromatic nuclei. Some nuclei were cleaved or folded in configuration. The cells displayed ample surrounding cytoplasm, which was finely granular or vacuolated. The infiltrate was accentuated in the perifollicular adventitial dermis. Immunohistochemistry was positive for CD33 and negative for CD3, CD20, and myeloperoxidase. Additionally, periodic acid–Schiff and Fite stains were negative for microorganisms. These morphologic and immunohistochemical findings were consistent with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Further testing with complete blood cell count, peripheral blood smear, and bone marrow biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of AML. The patient subsequently died 5 weeks later.

Comment
Presentation of LC
Thirty percent to 40% of leukemia patients present with a variety of nonspecific cutaneous signs, including those related to hemorrhage, infection, and drug eruptions, as well as paraneoplastic lesions.1 Cutaneous signs of leukemia are less commonly due to leukemia cutis (LC), defined as the neoplastic infiltration of the skin or subcutaneous tissue by leukemic cells. The clinical presentation of LC varies, making it difficult to diagnose without immunohistochemistry. It can pre-sent as single or multiple erythematous papules and/or nodules, infiltrated plaques, macules, palpable purpura, ulcers, ecchymoses, and/or vesicles.2 Leukemia cutis most often presents on the head, neck, trunk, and sites of current or prior trauma. Gingival hyperplasia is another associated finding in the acute monocytic and myelomonocytic types of AML.3 Additionally, chloromas or granulocytic sarcomas are dermal nodules that can pre-sent in myelogenous leukemia.4
LC and AML
Leukemia cutis most commonly is observed in AML compared to the other types of leukemia. The myelomonocytic and monocytic subtypes of AML are most often implicated.5,6 The majority of patients with LC present with a pre-established (55%–77%) or simultaneous diagnosis of systemic leukemia (23%–38%).
Histopathology
In LC, histology typically reveals a normal epidermis and nodular or diffuse infiltrating cells in the dermis. The cells can appear monomorphic, atypical, or immature, and there is occasional single-filing between collagen bundles. Causative types of neoplasms can be distinguished based on their morphologic, immunophenotypic, and cytogenetic properties.8-10
Incidence
Of the acute leukemias, AML accounts for the highest prevalence in adults,11 with an annual incidence of 14,590 cases in the United States.12 The incidence of AML increases with age; the mean age of patients diagnosed with AML is 67 years.12 Risk is increased with a history of exposure to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or cigarette smoke; preexisting myeloproliferative or myelodysplastic syndromes and mutations in DNA repair (eg, Fanconi anemia); neutropenia (eg, from elastase mutations); and Down syndrome.13
Diagnosis
More than 20% blasts in the bone marrow is required for a diagnosis of AML.14 Specific to AML is the presence of large immature precursor cells with a granular cytoplasm and, when present, highly diagnostic Auer rods.12Acute myeloid leukemia can be distinguished by staining for myeloperoxidase; Sudan Black B; or the antigens CD13, CD33, or c-kit.15
In our case, CD33 was positive, which is a characteristic finding in AML. Myeloperoxidase also can be positive in AML; however, in our case it was negative, and it can be an insensitive marker in the context of LC. Although most cases of LC present concurrently with bone marrow infiltration, some cases present before systemic involvement; for example, granulocytic sarcomas can occur months earlier than the development of systemic leukemia. Thus, early detection by a dermatologist is essential. Depending on the lesion’s appearance, the differential diagnoses can include lymphoma, drug eruptions, infectious etiologies, sarcoidosis, metastases from other malignancies, and blistering dermatoses.
Management
Systemic therapy should be the cornerstone of therapy. Induction therapy includes the combined use of cytarabine (except in acute promyelocytic leukemia [M3], for which all-trans retinoic acid is indicated) and anthracycline derivatives in a “7+3” regimen to achieve complete remission. Specifically, cytarabine (100–200 mg/m2) typically is continuously administered intravenously for 7 days combined with intravenous administration of either daunorubicin (60–90 mg/m2) or idarubicin (12 mg/m2) on days 1, 2, and 3. Postremission therapy is highly individualized depending on patients’ prognostic factors and is indicated to reduce the likelihood of relapse and to improve patient mortality. High doses of cytarabine and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation commonly are utilized.12 Resolution of hematologic atypia may result in complete or partial resolution of LC.10
Conclusion
We diagnosed AML with systemic involvement in our patient based on the cutaneous manifestation of LC. Diagnosis of LC relies on immunohistochemistry and strong clinical suspicion, as cutaneous findings are diverse and nonspecific. Early recognition is essential, as LC in the context of systemic involvement portends a poor prognosis. Our patient died 5 weeks following initial presentation.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Su WPD, Buechner SA, Chin-Yang L. Clinicopathologic correlations in leukemia cutis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11:121-128.
- Kumar M, Nair V, Mishra L, et al. Gingival hyperplasia—a clue to the diagnosis of acute leukemia? Arch Oral Sci Res. 2012;2:165-168.
- Winfield H, Smoller B. Other lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier; 2012:2037-2048.
- Babina T, Miller L, Thomas B. Leukemia cutis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:416-417.
- Tziotzios C, Makrygeorgou A. Leukemia cutis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2011;78:226-227.
- Ratnam KV, Khor CJL, Su WPD. Leukemia cutis. Dermatol Clin 1994;12:419-431.
- Cho-Vega JH, Medeiros LJ, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142.
- Buechner SA, Li CY, Su WP. Leukemia cutis. a histopathologic study of 42 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1985;7:109-119.
- Wagner G, Fenchel K, Back W, et al. Leukemia cutis—epidemiology, clinical presentation, and differential diagnoses. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10:27-36.
- O’Donnell MR, Abboud CN, Altman J, et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines acute myeloid leukemia. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2012;10:984-1021.
- Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD. Acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015:678-686.
- Aster JC, DeAngelo DJ. Acute leukemias. In: Bunn HF, Aster JC, eds. Pathophysiology of Blood Disorders. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2010:244-259.
- Damon LE, Andreadis C. Blood disorders. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2016. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2016:495-541.
- Parikh SA, Jabbour E, Koller CA. Adult acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kantarjian HM, Wolff RA, eds. The MD Anderson Manual of Medical Oncology. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011:15-32.
- Rao AG, Danturty I. Leukemia cutis. Indian J Dermatol. 2012;57:504.
- Su WPD, Buechner SA, Chin-Yang L. Clinicopathologic correlations in leukemia cutis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11:121-128.
- Kumar M, Nair V, Mishra L, et al. Gingival hyperplasia—a clue to the diagnosis of acute leukemia? Arch Oral Sci Res. 2012;2:165-168.
- Winfield H, Smoller B. Other lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier; 2012:2037-2048.
- Babina T, Miller L, Thomas B. Leukemia cutis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:416-417.
- Tziotzios C, Makrygeorgou A. Leukemia cutis. Cleve Clin J Med. 2011;78:226-227.
- Ratnam KV, Khor CJL, Su WPD. Leukemia cutis. Dermatol Clin 1994;12:419-431.
- Cho-Vega JH, Medeiros LJ, Prieto VG, et al. Leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008;129:130-142.
- Buechner SA, Li CY, Su WP. Leukemia cutis. a histopathologic study of 42 cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1985;7:109-119.
- Wagner G, Fenchel K, Back W, et al. Leukemia cutis—epidemiology, clinical presentation, and differential diagnoses. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10:27-36.
- O’Donnell MR, Abboud CN, Altman J, et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines acute myeloid leukemia. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2012;10:984-1021.
- Marcucci G, Bloomfield CD. Acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, et al, eds. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015:678-686.
- Aster JC, DeAngelo DJ. Acute leukemias. In: Bunn HF, Aster JC, eds. Pathophysiology of Blood Disorders. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2010:244-259.
- Damon LE, Andreadis C. Blood disorders. In: Papadakis MA, McPhee SJ, Rabow MW, eds. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment 2016. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2016:495-541.
- Parikh SA, Jabbour E, Koller CA. Adult acute myeloid leukemia. In: Kantarjian HM, Wolff RA, eds. The MD Anderson Manual of Medical Oncology. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2011:15-32.
Practice Points
- Leukemia cutis (LC) describes cutaneous and/or subcutaneous infiltration by leukemic cells and most commonly occurs in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
- The vast majority of patients presenting with LC already have systemic involvement.
- Cutaneous presentation of LC is diverse, thus diagnosis often is dependent on immunohisto-chemical findings.
Will quad therapy become the new standard in myeloma?
NEW YORK – , though data from additional randomized trials are needed to define their role in clinical practice, according to Natalie S. Callander, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center, Madison.
“The outlook for myeloma patients is quite good,” Dr. Callander said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
“Triplet therapy is the standard, and quad therapy may be in the future.”
The study that set the standard for triplets in myeloma, according to Dr. Callander, is SWOG 0777, an open-label, phase 3 trial that compared bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (VRd) to lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma.
Adding bortezomib to lenalidomide and dexamethasone significantly improved both progression-free and overall survival in the 525-patient trial, with a risk-benefit profile that was acceptable (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:519-27).
The median progression-free survival was 43 months for the triplet, versus 30 months for the two-drug regimen (P = .0018); likewise, median overall survival was significantly improved, at 75 months versus 64 months for triplet versus doublet therapy (P = .025).
“Very convincingly, just receiving that short exposure to bortezomib ended up causing a substantial increase of progression-free and overall survival,” Dr. Callander said.
The efficacy of multiple triplet regimens has been documented, including the combination of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd); cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (CyBorD); and more recently, ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd). These regimens have “excellent” response rates and survival data, Dr. Callander said.
Data is now emerging on the potential role of four-drug combinations, she added. The combination of elotuzumab plus VRd produced high response rates that were even higher after transplant, with reasonable toxicity, Dr. Callander said of phase 2 trial data presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Similarly, the combination of daratumumab plus KRd had a 100% rate of partial response or better in phase 2 data presented at ASCO in 2017, with rates of very good partial response and complete response that improved with successive cycles of therapy, she said.
Even so, “it remains to be seen whether four drugs will be the new standard,” Dr. Callander told the NCCN attendees.
Four- versus three-drug strategies are being evaluated in ongoing randomized clinical trials, including patients with previously untreated myeloma, she said. Those studies include Cassiopeia, which is evaluating bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (with or without daratumumab), and GRIFFIN, which is looking at VRd (with or without daratumumab).
Daratumumab recently received an additional indication in the treatment of myeloma, this time as part of a four-drug regimen, Dr. Callander added in a discussion on treatment options for elderly myeloma patients.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the monoclonal antibody in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) for treatment of newly diagnosed myeloma patients who are transplant ineligible.
That approval was based on results of the multicenter phase 3 ALCYONE study, showing an 18-month progression-free survival rate of 71.6% for the four-drug combination versus 50.2% for VMP alone (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:518-28).
Dr. Callander reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – , though data from additional randomized trials are needed to define their role in clinical practice, according to Natalie S. Callander, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center, Madison.
“The outlook for myeloma patients is quite good,” Dr. Callander said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
“Triplet therapy is the standard, and quad therapy may be in the future.”
The study that set the standard for triplets in myeloma, according to Dr. Callander, is SWOG 0777, an open-label, phase 3 trial that compared bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (VRd) to lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma.
Adding bortezomib to lenalidomide and dexamethasone significantly improved both progression-free and overall survival in the 525-patient trial, with a risk-benefit profile that was acceptable (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:519-27).
The median progression-free survival was 43 months for the triplet, versus 30 months for the two-drug regimen (P = .0018); likewise, median overall survival was significantly improved, at 75 months versus 64 months for triplet versus doublet therapy (P = .025).
“Very convincingly, just receiving that short exposure to bortezomib ended up causing a substantial increase of progression-free and overall survival,” Dr. Callander said.
The efficacy of multiple triplet regimens has been documented, including the combination of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd); cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (CyBorD); and more recently, ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd). These regimens have “excellent” response rates and survival data, Dr. Callander said.
Data is now emerging on the potential role of four-drug combinations, she added. The combination of elotuzumab plus VRd produced high response rates that were even higher after transplant, with reasonable toxicity, Dr. Callander said of phase 2 trial data presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Similarly, the combination of daratumumab plus KRd had a 100% rate of partial response or better in phase 2 data presented at ASCO in 2017, with rates of very good partial response and complete response that improved with successive cycles of therapy, she said.
Even so, “it remains to be seen whether four drugs will be the new standard,” Dr. Callander told the NCCN attendees.
Four- versus three-drug strategies are being evaluated in ongoing randomized clinical trials, including patients with previously untreated myeloma, she said. Those studies include Cassiopeia, which is evaluating bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (with or without daratumumab), and GRIFFIN, which is looking at VRd (with or without daratumumab).
Daratumumab recently received an additional indication in the treatment of myeloma, this time as part of a four-drug regimen, Dr. Callander added in a discussion on treatment options for elderly myeloma patients.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the monoclonal antibody in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) for treatment of newly diagnosed myeloma patients who are transplant ineligible.
That approval was based on results of the multicenter phase 3 ALCYONE study, showing an 18-month progression-free survival rate of 71.6% for the four-drug combination versus 50.2% for VMP alone (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:518-28).
Dr. Callander reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NEW YORK – , though data from additional randomized trials are needed to define their role in clinical practice, according to Natalie S. Callander, MD, of the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center, Madison.
“The outlook for myeloma patients is quite good,” Dr. Callander said at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
“Triplet therapy is the standard, and quad therapy may be in the future.”
The study that set the standard for triplets in myeloma, according to Dr. Callander, is SWOG 0777, an open-label, phase 3 trial that compared bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (VRd) to lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma.
Adding bortezomib to lenalidomide and dexamethasone significantly improved both progression-free and overall survival in the 525-patient trial, with a risk-benefit profile that was acceptable (Lancet. 2017 Feb 4;389[10068]:519-27).
The median progression-free survival was 43 months for the triplet, versus 30 months for the two-drug regimen (P = .0018); likewise, median overall survival was significantly improved, at 75 months versus 64 months for triplet versus doublet therapy (P = .025).
“Very convincingly, just receiving that short exposure to bortezomib ended up causing a substantial increase of progression-free and overall survival,” Dr. Callander said.
The efficacy of multiple triplet regimens has been documented, including the combination of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd); cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (CyBorD); and more recently, ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (IRd). These regimens have “excellent” response rates and survival data, Dr. Callander said.
Data is now emerging on the potential role of four-drug combinations, she added. The combination of elotuzumab plus VRd produced high response rates that were even higher after transplant, with reasonable toxicity, Dr. Callander said of phase 2 trial data presented at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Similarly, the combination of daratumumab plus KRd had a 100% rate of partial response or better in phase 2 data presented at ASCO in 2017, with rates of very good partial response and complete response that improved with successive cycles of therapy, she said.
Even so, “it remains to be seen whether four drugs will be the new standard,” Dr. Callander told the NCCN attendees.
Four- versus three-drug strategies are being evaluated in ongoing randomized clinical trials, including patients with previously untreated myeloma, she said. Those studies include Cassiopeia, which is evaluating bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (with or without daratumumab), and GRIFFIN, which is looking at VRd (with or without daratumumab).
Daratumumab recently received an additional indication in the treatment of myeloma, this time as part of a four-drug regimen, Dr. Callander added in a discussion on treatment options for elderly myeloma patients.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the monoclonal antibody in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone (VMP) for treatment of newly diagnosed myeloma patients who are transplant ineligible.
That approval was based on results of the multicenter phase 3 ALCYONE study, showing an 18-month progression-free survival rate of 71.6% for the four-drug combination versus 50.2% for VMP alone (N Engl J Med. 2018;378:518-28).
Dr. Callander reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Trichodysplasia Spinulosa in the Setting of Colon Cancer
Case Report
An 82-year-old woman presented to the clinic with a rash on the face that had been present for a few months. She denied any treatment or prior occurrence. Her medical history was remarkable for non-Hodgkin lymphoma that had been successfully treated with chemotherapy 4 years prior. Additionally, she recently had been diagnosed with stage IV colon cancer. She reported that surgery had been scheduled and she would start adjuvant chemotherapy soon after.
On physical examination she exhibited perioral and perinasal erythematous papules with sparing of the vermilion border. A diagnosis of perioral dermatitis was made, and she was started on topical metronidazole. At 1-month follow-up, her condition had slightly worsened and she was subsequently started on doxycycline. When she returned to the clinic again the following month, physical examination revealed agminated folliculocentric papules with central spicules on the face, nose, ears, upper extremities (Figure 1), and trunk. The differential diagnosis included multiple minute digitate hyperkeratosis, spiculosis of multiple myeloma, and trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS).
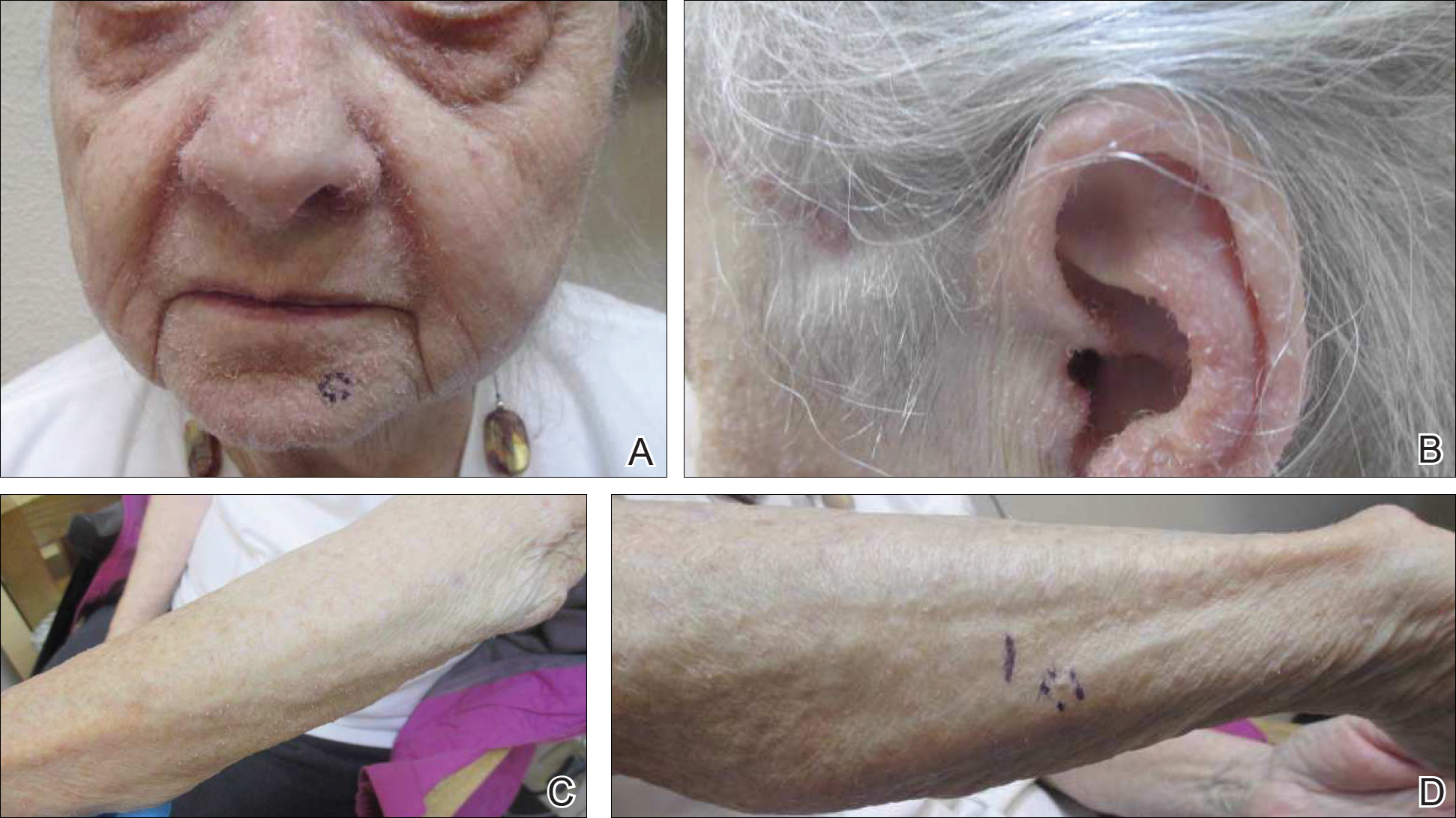
A punch biopsy of 2 separate papules on the face and upper extremity revealed dilated follicles with enlarged trichohyalin granules and dyskeratosis (Figure 2), consistent with TS. Additional testing such as electron microscopy or polymerase chain reaction was not performed to keep the patient’s medical costs down; also, the strong clinical and histopathologic evidence did not warrant further testing.
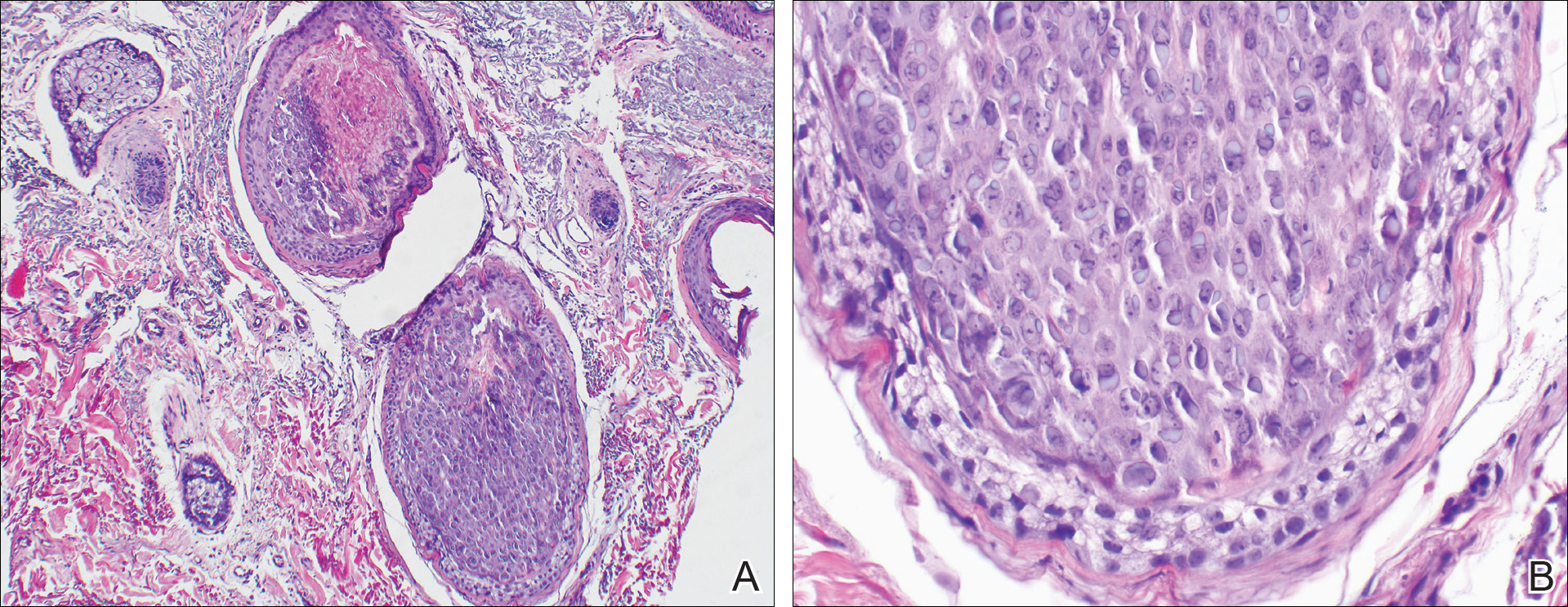
The plan was to start split-face treatment with topical acyclovir and a topical retinoid to see which agent was more effective, but the patient declined until her chemotherapy regimen had concluded. Unfortunately, the patient died 3 months later due to colon cancer.
Comment
History and Presentation
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first recognized as hairlike hyperkeratosis.1 The name by which it is currently known was later championed by Haycox et al.2 They reported a case of a 44-year-old man who underwent a combined renal-pancreas transplant and while taking immunosuppressive medication developed erythematous papules with follicular spinous processes and progressive alopecia.2 Other synonymous terms used for this condition include pilomatrix dysplasia, cyclosporine-induced folliculodystrophy, virus-associated trichodysplasia,3 and follicular dystrophy of immunosuppression.4 Trichodysplasia spinulosa can affect both adult and pediatric immunocompromised patients, including organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants and cancer patients on chemotherapy.3 The condition also has been reported to precede the recurrence of lymphoma.5
Etiology
The connection of TS with a viral etiology was first demonstrated in 1999, and subsequently it was confirmed to be a polyomavirus.2 The family name of Polyomaviridae possesses a Greek derivation with poly- meaning many and -oma meaning cancer.3 This name was given after the polyomavirus induced multiple tumors in mice.3,6 This viral family consists of multiple naked viruses with a surrounding icosahedral capsid containing 3 structural proteins known as VP1, VP2, and VP3. Their life cycle is characterized by early and late phases with respective early and late protein formation.3
Polyomavirus infections maintain an asymptomatic and latent course in immunocompetent patients.7 The prevalence and manifestation of these viruses change when the host’s immune system is altered. The first identified JC virus and BK virus of the same family have been found at increased frequencies in blood and lymphoid tissue during host immunosuppression.6 Moreover, the Merkel cell polyomavirus detected in Merkel cell carcinoma is well documented in the dermatologic literature.6,8
A specific polyomavirus has been implicated in the majority of TS cases and has subsequently received the name of TS polyomavirus.9 As a polyomavirus, it similarly produces capsid antigens and large/small T antigens. Among the viral protein antigens produced, the large tumor or LT antigen represents one of the most potent viral proteins. It has been postulated to inhibit the retinoblastoma family of proteins, leading to increased inner root sheath cells that allow for further viral replication.9,10
The disease presents with folliculocentric papules localized mainly on the central face and ears, which grow central keratin spines or spicules that can become 1 to 3 mm in length. Coinciding alopecia and madarosis also may be present.9
Diagnosis
Histologic examination reveals abnormal follicular maturation and distension. Additionally, increased proliferation and amount of trichohyalin is seen within the inner root sheath cells. Further testing via viral culture, polymerase chain reaction, electron microscopy, or immunohistochemical stains can confirm the diagnosis. Such testing may not be warranted in all cases given that classic clinical findings coupled with routine histopathology staining can provide enough evidence.10,11
Management
Currently, a universal successful treatment for TS does not exist. There have been anecdotal successes reported with topical medications such as cidofovir ointment 1%, acyclovir combined with 2-deoxy-D-glucose and epigallocatechin, corticosteroids, topical tacrolimus, topical retinoids, and imiquimod. Additionally, success has been seen with oral minocycline, oral retinoids, valacyclovir, and valganciclovir, with the latter showing the best results. Patients also have shown improvement after modifying their immunosuppressive treatment regimen.10,12
Conclusion
Given the previously published case of TS preceding the recurrence of lymphoma,5 we notified our patient’s oncologist of this potential risk. Her history of lymphoma and immunosuppressive treatment 4 years prior may represent the etiology of the cutaneous presentation; however, the TS with concurrent colon cancer presented prior to starting immunosuppressive therapy, suggesting that it also may have been a paraneoplastic process and not just a sign of immunosuppression. Therefore, we recommend that patients who present with TS should be evaluated for underlying malignancy if not already diagnosed.
- Linke M, Geraud C, Sauer C, et al. Follicular erythematous papules with keratotic spicules. Acta Derm Venereol . 2014;94:493-494.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa—a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- Moens U, Ludvigsen M, Van Ghelue M. Human polyomaviruses in skin diseases [published online September 12, 2011]. Patholog Res Int. 2011;2011:123491.
- Matthews MR, Wang RC, Reddick RL, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia spinulosa: a case with electron microscopic and molecular detection of the trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated human polyomavirus. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:420-431.
- Osswald SS, Kulick KB, Tomaszewski MM, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia in a patient with lymphoma: a case report and review. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:721-725.
- Dalianis T, Hirsch HH. Human polyomavirus in disease and cancer. Virology. 2013;437:63-72.
- Tsuzuki S, Fukumoto H, Mine S, et al. Detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus in a fatal case of myocarditis in a seven-month-old girl. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:5308-5312.
- Sadeghi M, Aronen M, Chen T, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus and trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus DNAs and antibodies in blood among the elderly. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:383.
- Van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- Krichhof MG, Shojania K, Hull MW, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: rare presentation of polyomavirus infection in immunocompromised patients. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:430-435.
- Rianthavorn P, Posuwan N, Payungporn S, et al. Polyomavirus reactivation in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012;228:197-204.
- Wanat KA, Holler PD, Dentchev T, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia: characterization of a novel polyomavirus infection with therapeutic insights. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:219-223.
Case Report
An 82-year-old woman presented to the clinic with a rash on the face that had been present for a few months. She denied any treatment or prior occurrence. Her medical history was remarkable for non-Hodgkin lymphoma that had been successfully treated with chemotherapy 4 years prior. Additionally, she recently had been diagnosed with stage IV colon cancer. She reported that surgery had been scheduled and she would start adjuvant chemotherapy soon after.
On physical examination she exhibited perioral and perinasal erythematous papules with sparing of the vermilion border. A diagnosis of perioral dermatitis was made, and she was started on topical metronidazole. At 1-month follow-up, her condition had slightly worsened and she was subsequently started on doxycycline. When she returned to the clinic again the following month, physical examination revealed agminated folliculocentric papules with central spicules on the face, nose, ears, upper extremities (Figure 1), and trunk. The differential diagnosis included multiple minute digitate hyperkeratosis, spiculosis of multiple myeloma, and trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS).

A punch biopsy of 2 separate papules on the face and upper extremity revealed dilated follicles with enlarged trichohyalin granules and dyskeratosis (Figure 2), consistent with TS. Additional testing such as electron microscopy or polymerase chain reaction was not performed to keep the patient’s medical costs down; also, the strong clinical and histopathologic evidence did not warrant further testing.

The plan was to start split-face treatment with topical acyclovir and a topical retinoid to see which agent was more effective, but the patient declined until her chemotherapy regimen had concluded. Unfortunately, the patient died 3 months later due to colon cancer.
Comment
History and Presentation
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first recognized as hairlike hyperkeratosis.1 The name by which it is currently known was later championed by Haycox et al.2 They reported a case of a 44-year-old man who underwent a combined renal-pancreas transplant and while taking immunosuppressive medication developed erythematous papules with follicular spinous processes and progressive alopecia.2 Other synonymous terms used for this condition include pilomatrix dysplasia, cyclosporine-induced folliculodystrophy, virus-associated trichodysplasia,3 and follicular dystrophy of immunosuppression.4 Trichodysplasia spinulosa can affect both adult and pediatric immunocompromised patients, including organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants and cancer patients on chemotherapy.3 The condition also has been reported to precede the recurrence of lymphoma.5
Etiology
The connection of TS with a viral etiology was first demonstrated in 1999, and subsequently it was confirmed to be a polyomavirus.2 The family name of Polyomaviridae possesses a Greek derivation with poly- meaning many and -oma meaning cancer.3 This name was given after the polyomavirus induced multiple tumors in mice.3,6 This viral family consists of multiple naked viruses with a surrounding icosahedral capsid containing 3 structural proteins known as VP1, VP2, and VP3. Their life cycle is characterized by early and late phases with respective early and late protein formation.3
Polyomavirus infections maintain an asymptomatic and latent course in immunocompetent patients.7 The prevalence and manifestation of these viruses change when the host’s immune system is altered. The first identified JC virus and BK virus of the same family have been found at increased frequencies in blood and lymphoid tissue during host immunosuppression.6 Moreover, the Merkel cell polyomavirus detected in Merkel cell carcinoma is well documented in the dermatologic literature.6,8
A specific polyomavirus has been implicated in the majority of TS cases and has subsequently received the name of TS polyomavirus.9 As a polyomavirus, it similarly produces capsid antigens and large/small T antigens. Among the viral protein antigens produced, the large tumor or LT antigen represents one of the most potent viral proteins. It has been postulated to inhibit the retinoblastoma family of proteins, leading to increased inner root sheath cells that allow for further viral replication.9,10
The disease presents with folliculocentric papules localized mainly on the central face and ears, which grow central keratin spines or spicules that can become 1 to 3 mm in length. Coinciding alopecia and madarosis also may be present.9
Diagnosis
Histologic examination reveals abnormal follicular maturation and distension. Additionally, increased proliferation and amount of trichohyalin is seen within the inner root sheath cells. Further testing via viral culture, polymerase chain reaction, electron microscopy, or immunohistochemical stains can confirm the diagnosis. Such testing may not be warranted in all cases given that classic clinical findings coupled with routine histopathology staining can provide enough evidence.10,11
Management
Currently, a universal successful treatment for TS does not exist. There have been anecdotal successes reported with topical medications such as cidofovir ointment 1%, acyclovir combined with 2-deoxy-D-glucose and epigallocatechin, corticosteroids, topical tacrolimus, topical retinoids, and imiquimod. Additionally, success has been seen with oral minocycline, oral retinoids, valacyclovir, and valganciclovir, with the latter showing the best results. Patients also have shown improvement after modifying their immunosuppressive treatment regimen.10,12
Conclusion
Given the previously published case of TS preceding the recurrence of lymphoma,5 we notified our patient’s oncologist of this potential risk. Her history of lymphoma and immunosuppressive treatment 4 years prior may represent the etiology of the cutaneous presentation; however, the TS with concurrent colon cancer presented prior to starting immunosuppressive therapy, suggesting that it also may have been a paraneoplastic process and not just a sign of immunosuppression. Therefore, we recommend that patients who present with TS should be evaluated for underlying malignancy if not already diagnosed.
Case Report
An 82-year-old woman presented to the clinic with a rash on the face that had been present for a few months. She denied any treatment or prior occurrence. Her medical history was remarkable for non-Hodgkin lymphoma that had been successfully treated with chemotherapy 4 years prior. Additionally, she recently had been diagnosed with stage IV colon cancer. She reported that surgery had been scheduled and she would start adjuvant chemotherapy soon after.
On physical examination she exhibited perioral and perinasal erythematous papules with sparing of the vermilion border. A diagnosis of perioral dermatitis was made, and she was started on topical metronidazole. At 1-month follow-up, her condition had slightly worsened and she was subsequently started on doxycycline. When she returned to the clinic again the following month, physical examination revealed agminated folliculocentric papules with central spicules on the face, nose, ears, upper extremities (Figure 1), and trunk. The differential diagnosis included multiple minute digitate hyperkeratosis, spiculosis of multiple myeloma, and trichodysplasia spinulosa (TS).

A punch biopsy of 2 separate papules on the face and upper extremity revealed dilated follicles with enlarged trichohyalin granules and dyskeratosis (Figure 2), consistent with TS. Additional testing such as electron microscopy or polymerase chain reaction was not performed to keep the patient’s medical costs down; also, the strong clinical and histopathologic evidence did not warrant further testing.

The plan was to start split-face treatment with topical acyclovir and a topical retinoid to see which agent was more effective, but the patient declined until her chemotherapy regimen had concluded. Unfortunately, the patient died 3 months later due to colon cancer.
Comment
History and Presentation
Trichodysplasia spinulosa was first recognized as hairlike hyperkeratosis.1 The name by which it is currently known was later championed by Haycox et al.2 They reported a case of a 44-year-old man who underwent a combined renal-pancreas transplant and while taking immunosuppressive medication developed erythematous papules with follicular spinous processes and progressive alopecia.2 Other synonymous terms used for this condition include pilomatrix dysplasia, cyclosporine-induced folliculodystrophy, virus-associated trichodysplasia,3 and follicular dystrophy of immunosuppression.4 Trichodysplasia spinulosa can affect both adult and pediatric immunocompromised patients, including organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressants and cancer patients on chemotherapy.3 The condition also has been reported to precede the recurrence of lymphoma.5
Etiology
The connection of TS with a viral etiology was first demonstrated in 1999, and subsequently it was confirmed to be a polyomavirus.2 The family name of Polyomaviridae possesses a Greek derivation with poly- meaning many and -oma meaning cancer.3 This name was given after the polyomavirus induced multiple tumors in mice.3,6 This viral family consists of multiple naked viruses with a surrounding icosahedral capsid containing 3 structural proteins known as VP1, VP2, and VP3. Their life cycle is characterized by early and late phases with respective early and late protein formation.3
Polyomavirus infections maintain an asymptomatic and latent course in immunocompetent patients.7 The prevalence and manifestation of these viruses change when the host’s immune system is altered. The first identified JC virus and BK virus of the same family have been found at increased frequencies in blood and lymphoid tissue during host immunosuppression.6 Moreover, the Merkel cell polyomavirus detected in Merkel cell carcinoma is well documented in the dermatologic literature.6,8
A specific polyomavirus has been implicated in the majority of TS cases and has subsequently received the name of TS polyomavirus.9 As a polyomavirus, it similarly produces capsid antigens and large/small T antigens. Among the viral protein antigens produced, the large tumor or LT antigen represents one of the most potent viral proteins. It has been postulated to inhibit the retinoblastoma family of proteins, leading to increased inner root sheath cells that allow for further viral replication.9,10
The disease presents with folliculocentric papules localized mainly on the central face and ears, which grow central keratin spines or spicules that can become 1 to 3 mm in length. Coinciding alopecia and madarosis also may be present.9
Diagnosis
Histologic examination reveals abnormal follicular maturation and distension. Additionally, increased proliferation and amount of trichohyalin is seen within the inner root sheath cells. Further testing via viral culture, polymerase chain reaction, electron microscopy, or immunohistochemical stains can confirm the diagnosis. Such testing may not be warranted in all cases given that classic clinical findings coupled with routine histopathology staining can provide enough evidence.10,11
Management
Currently, a universal successful treatment for TS does not exist. There have been anecdotal successes reported with topical medications such as cidofovir ointment 1%, acyclovir combined with 2-deoxy-D-glucose and epigallocatechin, corticosteroids, topical tacrolimus, topical retinoids, and imiquimod. Additionally, success has been seen with oral minocycline, oral retinoids, valacyclovir, and valganciclovir, with the latter showing the best results. Patients also have shown improvement after modifying their immunosuppressive treatment regimen.10,12
Conclusion
Given the previously published case of TS preceding the recurrence of lymphoma,5 we notified our patient’s oncologist of this potential risk. Her history of lymphoma and immunosuppressive treatment 4 years prior may represent the etiology of the cutaneous presentation; however, the TS with concurrent colon cancer presented prior to starting immunosuppressive therapy, suggesting that it also may have been a paraneoplastic process and not just a sign of immunosuppression. Therefore, we recommend that patients who present with TS should be evaluated for underlying malignancy if not already diagnosed.
- Linke M, Geraud C, Sauer C, et al. Follicular erythematous papules with keratotic spicules. Acta Derm Venereol . 2014;94:493-494.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa—a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- Moens U, Ludvigsen M, Van Ghelue M. Human polyomaviruses in skin diseases [published online September 12, 2011]. Patholog Res Int. 2011;2011:123491.
- Matthews MR, Wang RC, Reddick RL, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia spinulosa: a case with electron microscopic and molecular detection of the trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated human polyomavirus. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:420-431.
- Osswald SS, Kulick KB, Tomaszewski MM, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia in a patient with lymphoma: a case report and review. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:721-725.
- Dalianis T, Hirsch HH. Human polyomavirus in disease and cancer. Virology. 2013;437:63-72.
- Tsuzuki S, Fukumoto H, Mine S, et al. Detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus in a fatal case of myocarditis in a seven-month-old girl. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:5308-5312.
- Sadeghi M, Aronen M, Chen T, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus and trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus DNAs and antibodies in blood among the elderly. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:383.
- Van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- Krichhof MG, Shojania K, Hull MW, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: rare presentation of polyomavirus infection in immunocompromised patients. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:430-435.
- Rianthavorn P, Posuwan N, Payungporn S, et al. Polyomavirus reactivation in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012;228:197-204.
- Wanat KA, Holler PD, Dentchev T, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia: characterization of a novel polyomavirus infection with therapeutic insights. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:219-223.
- Linke M, Geraud C, Sauer C, et al. Follicular erythematous papules with keratotic spicules. Acta Derm Venereol . 2014;94:493-494.
- Haycox CL, Kim S, Fleckman P, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa—a newly described folliculocentric viral infection in an immunocompromised host. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1999;4:268-271.
- Moens U, Ludvigsen M, Van Ghelue M. Human polyomaviruses in skin diseases [published online September 12, 2011]. Patholog Res Int. 2011;2011:123491.
- Matthews MR, Wang RC, Reddick RL, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia spinulosa: a case with electron microscopic and molecular detection of the trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated human polyomavirus. J Cutan Pathol. 2011;38:420-431.
- Osswald SS, Kulick KB, Tomaszewski MM, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia in a patient with lymphoma: a case report and review. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:721-725.
- Dalianis T, Hirsch HH. Human polyomavirus in disease and cancer. Virology. 2013;437:63-72.
- Tsuzuki S, Fukumoto H, Mine S, et al. Detection of trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus in a fatal case of myocarditis in a seven-month-old girl. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:5308-5312.
- Sadeghi M, Aronen M, Chen T, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus and trichodysplasia spinulosa–associated polyomavirus DNAs and antibodies in blood among the elderly. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:383.
- Van der Meijden E, Kazem S, Burgers MM, et al. Seroprevalence of trichodysplasia spinulosa-associated polyomavirus. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:1355-1363.
- Krichhof MG, Shojania K, Hull MW, et al. Trichodysplasia spinulosa: rare presentation of polyomavirus infection in immunocompromised patients. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014;18:430-435.
- Rianthavorn P, Posuwan N, Payungporn S, et al. Polyomavirus reactivation in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012;228:197-204.
- Wanat KA, Holler PD, Dentchev T, et al. Viral-associated trichodysplasia: characterization of a novel polyomavirus infection with therapeutic insights. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148:219-223.
Practice Points
- Rashes have a life span and can evolve with time.
- If apparent straightforward conditions do not appear to respond to standard therapy, start to think outside the box for underlying potential causes.
Novel options for treating hairy cell leukemia
NEW YORK – Ibrutinib, and now moxetumomab pasudotox, are two novel therapies that can be tried in patients with previously treated hairy cell leukemia, although data and experience with them are so far limited in this rare disease, experts said during a panel discussion at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Since there are so few patients, data on the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib in hairy cell leukemia is largely “anecdotal,” said Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
The anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody moxetumomab pasudotox – approved for hairy cell leukemia in September – isn’t yet on the formulary at Memorial Sloan Kettering, Dr. Zelenetz added in a panel discussion of treatment options for a patient previously treated with purine analogueues and vemurafenib.
Between the two agents, moxetumomab pasudotox has more robust data in this disease, said John N. Allan, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“I think if you can get access to the drug, that’s probably the best answer,” Dr. Allan said in the case discussion.
Hairy cell leukemia is an indolent B-cell lymphoma that makes up just 2% of all lymphoid leukemias, according to NCCN guidelines.
It is a chronic disease that requires long-term management, according to Dr. Allan.
First-line treatment is usually a purine analogue, either cladribine or pentostatin, and multiple treatments are possible as long as responses of greater than 2 years are achieved, he told attendees at the NCCN conference.
For relapses more than 2 years after first-line treatment, patients can be retreated with the same purine analogue, with or without rituximab, or can be switched to the alternative purine analogue, he said.
Vemurafenib, the BRAF inhibitor, is “surprisingly” effective in 90% of classic hairy cell leukemia patients with the BRAF V600E mutation, Dr. Allan added, though only about 40% of patients achieve complete response.
In discussing therapy options for a hairy cell leukemia patient previously treated with purine analogues and vemurafenib, Dr. Allan noted that the data behind ibrutinib includes case reports and early clinical investigations.
Several phase 1 studies with small numbers of patients show response rates “in the 50% range,” he said.
“This is an option,” he said. “It’s in the guidelines, and it’s something to consider.”
Moxetumomab pasudotox was recently approved for intravenous use in adults with relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia who have had at least two previous systemic treatments, including a purine nucleoside analogue. The CD22-directed cytotoxin is the first of its kind for treating patients with hairy cell leukemia, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
In a single-arm, open-label clinical trial including 80 patients with hairy cell leukemia who had previous treatment in line with that indication, 75% had a partial or complete response, of whom 30% had a durable complete response (CR), defined as maintaining hematologic remission for at least 180 days following CR.
Following the FDA’s approval of moxetumomab pasudotox, the NCCN updated its hairy cell leukemia clinical practice guidelines to include the drug as a category 2A recommendation for relapsed/refractory treatment. Other category 2A options in that setting include ibrutinib, vemurafenib with or without rituximab, or a clinical trial.
Along with that, NCCN guideline authors added a full page on special considerations for use of moxetumomab pasudotox. That includes advice on monitoring for capillary leak syndrome and hemolytic uremic syndrome, along with guidance on capillary leak syndrome grading and management by grade.
Dr. Zelenetz reported financial disclosures related to Adaptive Biotechnology, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Hoffman La Roche, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Verastem Oncology. Dr. Allan reported disclosures related to AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Genentech, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis, and Verastem Oncology.
NEW YORK – Ibrutinib, and now moxetumomab pasudotox, are two novel therapies that can be tried in patients with previously treated hairy cell leukemia, although data and experience with them are so far limited in this rare disease, experts said during a panel discussion at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Since there are so few patients, data on the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib in hairy cell leukemia is largely “anecdotal,” said Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
The anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody moxetumomab pasudotox – approved for hairy cell leukemia in September – isn’t yet on the formulary at Memorial Sloan Kettering, Dr. Zelenetz added in a panel discussion of treatment options for a patient previously treated with purine analogueues and vemurafenib.
Between the two agents, moxetumomab pasudotox has more robust data in this disease, said John N. Allan, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“I think if you can get access to the drug, that’s probably the best answer,” Dr. Allan said in the case discussion.
Hairy cell leukemia is an indolent B-cell lymphoma that makes up just 2% of all lymphoid leukemias, according to NCCN guidelines.
It is a chronic disease that requires long-term management, according to Dr. Allan.
First-line treatment is usually a purine analogue, either cladribine or pentostatin, and multiple treatments are possible as long as responses of greater than 2 years are achieved, he told attendees at the NCCN conference.
For relapses more than 2 years after first-line treatment, patients can be retreated with the same purine analogue, with or without rituximab, or can be switched to the alternative purine analogue, he said.
Vemurafenib, the BRAF inhibitor, is “surprisingly” effective in 90% of classic hairy cell leukemia patients with the BRAF V600E mutation, Dr. Allan added, though only about 40% of patients achieve complete response.
In discussing therapy options for a hairy cell leukemia patient previously treated with purine analogues and vemurafenib, Dr. Allan noted that the data behind ibrutinib includes case reports and early clinical investigations.
Several phase 1 studies with small numbers of patients show response rates “in the 50% range,” he said.
“This is an option,” he said. “It’s in the guidelines, and it’s something to consider.”
Moxetumomab pasudotox was recently approved for intravenous use in adults with relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia who have had at least two previous systemic treatments, including a purine nucleoside analogue. The CD22-directed cytotoxin is the first of its kind for treating patients with hairy cell leukemia, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
In a single-arm, open-label clinical trial including 80 patients with hairy cell leukemia who had previous treatment in line with that indication, 75% had a partial or complete response, of whom 30% had a durable complete response (CR), defined as maintaining hematologic remission for at least 180 days following CR.
Following the FDA’s approval of moxetumomab pasudotox, the NCCN updated its hairy cell leukemia clinical practice guidelines to include the drug as a category 2A recommendation for relapsed/refractory treatment. Other category 2A options in that setting include ibrutinib, vemurafenib with or without rituximab, or a clinical trial.
Along with that, NCCN guideline authors added a full page on special considerations for use of moxetumomab pasudotox. That includes advice on monitoring for capillary leak syndrome and hemolytic uremic syndrome, along with guidance on capillary leak syndrome grading and management by grade.
Dr. Zelenetz reported financial disclosures related to Adaptive Biotechnology, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Hoffman La Roche, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Verastem Oncology. Dr. Allan reported disclosures related to AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Genentech, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis, and Verastem Oncology.
NEW YORK – Ibrutinib, and now moxetumomab pasudotox, are two novel therapies that can be tried in patients with previously treated hairy cell leukemia, although data and experience with them are so far limited in this rare disease, experts said during a panel discussion at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Since there are so few patients, data on the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib in hairy cell leukemia is largely “anecdotal,” said Andrew D. Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
The anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody moxetumomab pasudotox – approved for hairy cell leukemia in September – isn’t yet on the formulary at Memorial Sloan Kettering, Dr. Zelenetz added in a panel discussion of treatment options for a patient previously treated with purine analogueues and vemurafenib.
Between the two agents, moxetumomab pasudotox has more robust data in this disease, said John N. Allan, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
“I think if you can get access to the drug, that’s probably the best answer,” Dr. Allan said in the case discussion.
Hairy cell leukemia is an indolent B-cell lymphoma that makes up just 2% of all lymphoid leukemias, according to NCCN guidelines.
It is a chronic disease that requires long-term management, according to Dr. Allan.
First-line treatment is usually a purine analogue, either cladribine or pentostatin, and multiple treatments are possible as long as responses of greater than 2 years are achieved, he told attendees at the NCCN conference.
For relapses more than 2 years after first-line treatment, patients can be retreated with the same purine analogue, with or without rituximab, or can be switched to the alternative purine analogue, he said.
Vemurafenib, the BRAF inhibitor, is “surprisingly” effective in 90% of classic hairy cell leukemia patients with the BRAF V600E mutation, Dr. Allan added, though only about 40% of patients achieve complete response.
In discussing therapy options for a hairy cell leukemia patient previously treated with purine analogues and vemurafenib, Dr. Allan noted that the data behind ibrutinib includes case reports and early clinical investigations.
Several phase 1 studies with small numbers of patients show response rates “in the 50% range,” he said.
“This is an option,” he said. “It’s in the guidelines, and it’s something to consider.”
Moxetumomab pasudotox was recently approved for intravenous use in adults with relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia who have had at least two previous systemic treatments, including a purine nucleoside analogue. The CD22-directed cytotoxin is the first of its kind for treating patients with hairy cell leukemia, according to the Food and Drug Administration.
In a single-arm, open-label clinical trial including 80 patients with hairy cell leukemia who had previous treatment in line with that indication, 75% had a partial or complete response, of whom 30% had a durable complete response (CR), defined as maintaining hematologic remission for at least 180 days following CR.
Following the FDA’s approval of moxetumomab pasudotox, the NCCN updated its hairy cell leukemia clinical practice guidelines to include the drug as a category 2A recommendation for relapsed/refractory treatment. Other category 2A options in that setting include ibrutinib, vemurafenib with or without rituximab, or a clinical trial.
Along with that, NCCN guideline authors added a full page on special considerations for use of moxetumomab pasudotox. That includes advice on monitoring for capillary leak syndrome and hemolytic uremic syndrome, along with guidance on capillary leak syndrome grading and management by grade.
Dr. Zelenetz reported financial disclosures related to Adaptive Biotechnology, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Genentech, Gilead, Hoffman La Roche, MEI Pharma, MorphoSys AG, Novartis, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Verastem Oncology. Dr. Allan reported disclosures related to AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Genentech, Pharmacyclics, Sunesis, and Verastem Oncology.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
Dual-frequency ultrasound promising for refractory rosacea
, according to a new study in Dermatologic Surgery.
In the study, a retrospective medical record analysis of 42 rosacea patients, DFU improved symptoms, including erythema index (EI) and transepithelial water loss (TEWL), and also improved outcomes on the patient self-assessment (PSA), reported Jun Yeong Park, MD, and coauthors, from the department of dermatology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital in Anyang, South Korea.
Of the 42 patients, 26 had erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, 14 had papulopustular rosacea, and 2 had mixed disease; their mean age was 48 years, and they had had rosacea for a mean of 2 years. Patients had started DFU treatment between September 2016 and December 2016, and were not taking oral medication (besides antihistamines), topical ointments, or other laser treatments at the time. Most had been treated with various systemic therapies, topical therapies, or lasers, but had not had adequate improvement of flushing and erythema.
Patients received DFU treatment of the entire face twice per week for the first week, followed by one-week intervals, for a total of 12 weeks. Each treatment session lasted 10 minutes, and included DFU frequencies of 3/4.5 MHz at an ultrasound intensity of 2.0W/cm2 for 5 minutes, followed by 4.5 MHz at an intensity of 2.0W/cm2. Responses to treatment were based on EI, TEWL values (measured on three different sites on each cheek according to guidelines established by the European Group for Efficacy Measurements on Cosmetics and Other Topical Products), and PSA. PSA was completed on a scale of 0 (absent) to 4 (severe) for erythema, itching sensation, and burning sensation.
At 12 weeks follow-up, the mean EI dropped from 16.3 at baseline to 12.7 at 12 weeks (P less than .01). Mean TEWL values dropped from a baseline of 35.8 g m–1 h–1 to 22.8 g m–1 h–1 at 12 weeks (P less than .01).
When evaluated by rosacea subtype, a slightly higher reduction in the group with papulopustular rosacea was seen for EI and TEWL, compared with those with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype, but the differences were not statistically significant for either, the authors reported.
Between baseline and 12 weeks, the PSA values for erythema decreased from 2.6 to 1.1. Itching and burning grades also decreased, from 2.4 to 0.4 and from 2.4 to 0.3, respectively.
The findings verify that there were “improvements in the barrier function of patients with refractory rosacea, based on the TEWL level before and after treatment,” the authors noted. “Therefore, DFU may be an additional treatment option for rosacea that is resistant to other treatments.”
This study is the first to evaluate DFU in patients with refractory rosacea “who did not show signs of recovery after undergoing previous therapies,” they noted.
No disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Park J et al. Dermatol Surg 2018 Sep;44(9):1209-15. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001552.
, according to a new study in Dermatologic Surgery.
In the study, a retrospective medical record analysis of 42 rosacea patients, DFU improved symptoms, including erythema index (EI) and transepithelial water loss (TEWL), and also improved outcomes on the patient self-assessment (PSA), reported Jun Yeong Park, MD, and coauthors, from the department of dermatology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital in Anyang, South Korea.
Of the 42 patients, 26 had erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, 14 had papulopustular rosacea, and 2 had mixed disease; their mean age was 48 years, and they had had rosacea for a mean of 2 years. Patients had started DFU treatment between September 2016 and December 2016, and were not taking oral medication (besides antihistamines), topical ointments, or other laser treatments at the time. Most had been treated with various systemic therapies, topical therapies, or lasers, but had not had adequate improvement of flushing and erythema.
Patients received DFU treatment of the entire face twice per week for the first week, followed by one-week intervals, for a total of 12 weeks. Each treatment session lasted 10 minutes, and included DFU frequencies of 3/4.5 MHz at an ultrasound intensity of 2.0W/cm2 for 5 minutes, followed by 4.5 MHz at an intensity of 2.0W/cm2. Responses to treatment were based on EI, TEWL values (measured on three different sites on each cheek according to guidelines established by the European Group for Efficacy Measurements on Cosmetics and Other Topical Products), and PSA. PSA was completed on a scale of 0 (absent) to 4 (severe) for erythema, itching sensation, and burning sensation.
At 12 weeks follow-up, the mean EI dropped from 16.3 at baseline to 12.7 at 12 weeks (P less than .01). Mean TEWL values dropped from a baseline of 35.8 g m–1 h–1 to 22.8 g m–1 h–1 at 12 weeks (P less than .01).
When evaluated by rosacea subtype, a slightly higher reduction in the group with papulopustular rosacea was seen for EI and TEWL, compared with those with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype, but the differences were not statistically significant for either, the authors reported.
Between baseline and 12 weeks, the PSA values for erythema decreased from 2.6 to 1.1. Itching and burning grades also decreased, from 2.4 to 0.4 and from 2.4 to 0.3, respectively.
The findings verify that there were “improvements in the barrier function of patients with refractory rosacea, based on the TEWL level before and after treatment,” the authors noted. “Therefore, DFU may be an additional treatment option for rosacea that is resistant to other treatments.”
This study is the first to evaluate DFU in patients with refractory rosacea “who did not show signs of recovery after undergoing previous therapies,” they noted.
No disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Park J et al. Dermatol Surg 2018 Sep;44(9):1209-15. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001552.
, according to a new study in Dermatologic Surgery.
In the study, a retrospective medical record analysis of 42 rosacea patients, DFU improved symptoms, including erythema index (EI) and transepithelial water loss (TEWL), and also improved outcomes on the patient self-assessment (PSA), reported Jun Yeong Park, MD, and coauthors, from the department of dermatology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital in Anyang, South Korea.
Of the 42 patients, 26 had erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, 14 had papulopustular rosacea, and 2 had mixed disease; their mean age was 48 years, and they had had rosacea for a mean of 2 years. Patients had started DFU treatment between September 2016 and December 2016, and were not taking oral medication (besides antihistamines), topical ointments, or other laser treatments at the time. Most had been treated with various systemic therapies, topical therapies, or lasers, but had not had adequate improvement of flushing and erythema.
Patients received DFU treatment of the entire face twice per week for the first week, followed by one-week intervals, for a total of 12 weeks. Each treatment session lasted 10 minutes, and included DFU frequencies of 3/4.5 MHz at an ultrasound intensity of 2.0W/cm2 for 5 minutes, followed by 4.5 MHz at an intensity of 2.0W/cm2. Responses to treatment were based on EI, TEWL values (measured on three different sites on each cheek according to guidelines established by the European Group for Efficacy Measurements on Cosmetics and Other Topical Products), and PSA. PSA was completed on a scale of 0 (absent) to 4 (severe) for erythema, itching sensation, and burning sensation.
At 12 weeks follow-up, the mean EI dropped from 16.3 at baseline to 12.7 at 12 weeks (P less than .01). Mean TEWL values dropped from a baseline of 35.8 g m–1 h–1 to 22.8 g m–1 h–1 at 12 weeks (P less than .01).
When evaluated by rosacea subtype, a slightly higher reduction in the group with papulopustular rosacea was seen for EI and TEWL, compared with those with the erythematotelangiectatic subtype, but the differences were not statistically significant for either, the authors reported.
Between baseline and 12 weeks, the PSA values for erythema decreased from 2.6 to 1.1. Itching and burning grades also decreased, from 2.4 to 0.4 and from 2.4 to 0.3, respectively.
The findings verify that there were “improvements in the barrier function of patients with refractory rosacea, based on the TEWL level before and after treatment,” the authors noted. “Therefore, DFU may be an additional treatment option for rosacea that is resistant to other treatments.”
This study is the first to evaluate DFU in patients with refractory rosacea “who did not show signs of recovery after undergoing previous therapies,” they noted.
No disclosures were reported.
SOURCE: Park J et al. Dermatol Surg 2018 Sep;44(9):1209-15. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001552.
Key clinical point: Dual-frequency ultrasound may be an effective option for treatment-resistant rosacea.
Major finding: In 12 weeks, the erythema index dropped from 16.3 to 12.7 (P less than .01), along with drops in patient self assessment measures for erythema, itching, and burning.
Study details: A retrospective electronic medical records analysis of 42 rosacea patients.
Disclosures: No disclosures were reported.
Source: Park J et al. Dermatol Surg 2018 Sep;44(9):1209-15. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001552.