User login
Inspiring Encounters in the Treatment of Myasthenia Gravis
Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, recounts shadowing a neurologist during an early phase of academic training and how witnessing examinations of patients with conditions like myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis inspired a career path in neuromuscular medicine.
Dr Gwathmey also reflects on the evolution of myasthenia gravis treatment over the past two decades, noting the introduction of new medications like eculizumab, complement inhibitors, and FcRn inhibitors — offering more targeted options and hope for patients with fewer side effects — and anticipates further advancements in treatment leading to improved disease control.
Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, recounts shadowing a neurologist during an early phase of academic training and how witnessing examinations of patients with conditions like myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis inspired a career path in neuromuscular medicine.
Dr Gwathmey also reflects on the evolution of myasthenia gravis treatment over the past two decades, noting the introduction of new medications like eculizumab, complement inhibitors, and FcRn inhibitors — offering more targeted options and hope for patients with fewer side effects — and anticipates further advancements in treatment leading to improved disease control.
Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, recounts shadowing a neurologist during an early phase of academic training and how witnessing examinations of patients with conditions like myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis inspired a career path in neuromuscular medicine.
Dr Gwathmey also reflects on the evolution of myasthenia gravis treatment over the past two decades, noting the introduction of new medications like eculizumab, complement inhibitors, and FcRn inhibitors — offering more targeted options and hope for patients with fewer side effects — and anticipates further advancements in treatment leading to improved disease control.

Myasthenia Gravis: Lessons on a Comprehensive Approach to Patient Care
Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, expresses gratitude for the impactful relationships and mentorship in the field of myasthenia gravis. Dr Chip Howard at the University of North Carolina is distinguished as a humble and inclusive mentor, considered influential in the field.
Dr Howard's influence goes beyond the efficacy of medications, emphasizing the importance of considering patient care comprehensively, including side effects and overall safety. This perspective has significantly shaped Dr Silvestri’s treatment approach, leading to a more holistic and patient-centered care paradigm for individuals with myasthenia gravis.
Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, expresses gratitude for the impactful relationships and mentorship in the field of myasthenia gravis. Dr Chip Howard at the University of North Carolina is distinguished as a humble and inclusive mentor, considered influential in the field.
Dr Howard's influence goes beyond the efficacy of medications, emphasizing the importance of considering patient care comprehensively, including side effects and overall safety. This perspective has significantly shaped Dr Silvestri’s treatment approach, leading to a more holistic and patient-centered care paradigm for individuals with myasthenia gravis.
Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD, expresses gratitude for the impactful relationships and mentorship in the field of myasthenia gravis. Dr Chip Howard at the University of North Carolina is distinguished as a humble and inclusive mentor, considered influential in the field.
Dr Howard's influence goes beyond the efficacy of medications, emphasizing the importance of considering patient care comprehensively, including side effects and overall safety. This perspective has significantly shaped Dr Silvestri’s treatment approach, leading to a more holistic and patient-centered care paradigm for individuals with myasthenia gravis.

Myasthenia Gravis: A Mentor's Emphasis on Patient-Centered Outcomes
During her time in training at the University of Virginia, Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, gained invaluable insights into myasthenia gravis (MG) care and research from the late Dr Ted Burns and Dr Larry Phillips. Dr Burns, a renowned leader in MG research, emphasized patient-centric approaches, fostering the development of crucial outcome measures like the MG composite scale and MG-QOL-15.
Burns' dedication to listening to patients' experiences shaped the development of health-related quality-of-life instruments used in MG clinical trials. For Dr Gwathmey, learning under Dr Burns underscored the significance of patient experiences in treatment decisions and highlighted the importance of incorporating patient perspectives in clinical care and research endeavors.
During her time in training at the University of Virginia, Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, gained invaluable insights into myasthenia gravis (MG) care and research from the late Dr Ted Burns and Dr Larry Phillips. Dr Burns, a renowned leader in MG research, emphasized patient-centric approaches, fostering the development of crucial outcome measures like the MG composite scale and MG-QOL-15.
Burns' dedication to listening to patients' experiences shaped the development of health-related quality-of-life instruments used in MG clinical trials. For Dr Gwathmey, learning under Dr Burns underscored the significance of patient experiences in treatment decisions and highlighted the importance of incorporating patient perspectives in clinical care and research endeavors.
During her time in training at the University of Virginia, Kelly G. Gwathmey, MD, gained invaluable insights into myasthenia gravis (MG) care and research from the late Dr Ted Burns and Dr Larry Phillips. Dr Burns, a renowned leader in MG research, emphasized patient-centric approaches, fostering the development of crucial outcome measures like the MG composite scale and MG-QOL-15.
Burns' dedication to listening to patients' experiences shaped the development of health-related quality-of-life instruments used in MG clinical trials. For Dr Gwathmey, learning under Dr Burns underscored the significance of patient experiences in treatment decisions and highlighted the importance of incorporating patient perspectives in clinical care and research endeavors.

AML: Genetic Testing Unlocks Hope
For adult patients, “we’ve seen a series of remarkable and well-overdue advances in a space that had not changed much over the prior decades,” hematologist/oncologist Thomas William LeBlanc, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
According to the National Cancer Institute, AML will be newly diagnosed in 20,800 patients in 2024, at a median age of 69, and will cause 11,220 deaths. As many as 70% of adult patients will reach complete remission, and 45% of those will live for more than 3 years and potentially be cured. As for children, the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society says the 5-year survival rate from 2012-2018 was 69% for those under 15 years old.
As the American Cancer Society notes, the goal of AML treatment “is to put the leukemia into complete remission (the bone marrow and blood cell counts return to normal), preferably a complete molecular remission (no signs of leukemia in the bone marrow, even using sensitive lab tests), and to keep it that way.”
Chemotherapy Strategies Shift Over Time
In terms of the treatment of adults with AML, “targeted therapies, in addition to the expanding role of venetoclax, has really altered our approach to AML from diagnosis, including after relapse, and later in the disease,” hematologist/oncologist Andrew M. Brunner, MD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. “The ability to explore these options as monotherapy and in novel combinations has dramatically expanded our treatment options.”
Much depends on the underlying genetic profile of the disease, he said. “There certainly have been gains in patient survival in AML, but those improvements remain fairly heterogeneous and dependent on the underlying genetic profile of the disease. For instance, advances in FLT3- and IDH1/2-mutated AML are a direct result of the improvements in targeted therapies directed at these mutations. Similarly, some molecular and cytogenetic subtypes of AML are particularly responsive to venetoclax-based regimens, and these regimens have been expanded to previously undertreated populations, particularly those over age 60.”
Specifically, Dr. LeBlanc said, the Food and Drug Administration has approved “3 different FLT3 inhibitors, 2 IDH1 inhibitors, 1 IDH2 inhibitor, a BCL-2 inhibitor, a smoothened/hedgehog pathway inhibitor, an oral maintenance chemotherapy/hypomethylating agent (CC-486/oral azacitidine), a CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, and even a novel formulation of two older chemotherapies that improves efficacy in a poor prognosis subgroup (CPX-351/liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine).”
There’s also been a shift in treatment protocols for patients who were not fit for intensive chemotherapy. In the past, he said, it was standard “to give single-agent hypomethylating chemotherapy with azacitidine or decitabine, or in some contexts, low-dose chemotherapy with cytarabine. Today, many patients who are older and/or more frail are receiving novel therapies either alone or in combination, with greater efficacy and longer duration of response than previously seen with chemotherapy alone.”
Outcomes Improve but Remain Grim in High-Risk Cases
As a result, Dr. LeBlanc said, “we’re definitely seeing much better outcomes in AML overall. It takes some time to prove this via outcomes data assessments in a large population, but I expect that registries will show significant improvements in overall survival in the coming years, owing to the many new FDA approvals in AML”
Dr. LeBlanc highlighted national data from 2013-2019 showing that the 5-year relative survival rate from AML is 31.7%. That’s up from 26% just a few years ago, and the numbers “always lag several years behind the current year of practice,” he said. However, “the major area where we still have relatively poor outcomes and significant unmet needs remains the ‘adverse risk’ group of patients, particularly those who are older and/or not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which generally is the only potentially curative option for adverse-risk AML.”
He went on to say that “this risk grouping includes those with TP53 mutations, most of which confer a particularly poor prognosis. Exciting therapies that many of us were hoping would prove effective in this subgroup have unfortunately failed in recent clinical trials. We still have a lot of work to do in adverse-risk AML particularly, and also for those whose leukemia has relapsed.”
Mikkael Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of the Division of Hematology at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine/Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, agreed that more progress is needed, since survival rates are low even as lifespans improve. One key will be “better identifying subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia, and identifying the therapies that will benefit those people most,” he said in an interview. On the other side, it’s important to identify “when aggressive therapies aren’t going to work in somebody and maybe turn toward less-aggressive approaches so we can maximize that person’s quality of life.”
What advice do AML experts have for their colleagues? Dr. LeBlanc said “older patients are not often enough considered for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, which could potentially cure their AML when given as a consolidation treatment for those in remission. I have several patients who are healthy and in their 70s who have enormously benefited from transplants and are now being several years out from transplant with adverse risk AML and without relapse. They’ve had no significant impairments of their quality of life, including no significant graft vs. host disease.”
Dr. Sekeres highlighted the American Society of Hematology’s guidelines for treating older adults with AML, which are currently being updated. It’s crucial to order genetic testing “up front,” he said. “I’m often pleasantly surprised when genetic testing returns and reveals that I have other treatment options.”
However, it’s crucial to understand a patient’s priorities. “I’ve had patients who are 75 who say to me, ‘Do everything under the sun to get rid of my leukemia, I want to live as long as possible.’ And I’ve had patients who say, ‘I want to see as little of doctors and nurses as I can. I want you to maximize my quality of life and keep me out of the hospital.’ ”
Dr. Sekeres also noted that insurers may not cover some pill-based AML treatments such as venetoclax. “We work with our patients and assistance programs. For the most part, we’re pretty successful at getting these drugs for our patients,” he said.
In Pediatrics, Clinical Trials Are Crucial
AML in children is less well-known than in adults, since the number of cases is so small. The disease is diagnosed in about 500 children a year in the United States, according to St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, adding, however, that AML is “the most common second cancer among children treated for other cancers.”
AML in children gained attention earlier this year when the 2-year-old daughter of a Boston Herald NFL reporter died of the disease following a bone marrow transplant and chemotherapy. Despite the agonies of her treatment, reporter Doug Kyed told a reporter that his daughter Hallie “was still able to find joy every day.”
In an interview, hematologist/oncologist Sarah K. Tasian, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said researchers are discovering that pediatric AML is significantly different on from a biological perspective from adult AML. “We’ve come to understand a lot more about who these patients are, what makes these leukemias tick, and what their Achilles’ heels are. Then we can align that with the clinical trials outcome data that we have.”
About 80%-90% of pediatric patients with AML nationwide are enrolled in clinical trials, Dr. Tasian said, and an international consortium called the Children’s Oncology Group gathers data about genetics. About 60%-70% of patients will be cured, she added.
However, “we’ve kind of been stuck for about the last 20 years,” she said. “A lot of improving the survival of patients has not been because we’ve been better at chemotherapy or using new chemo, but because we’ve gotten better at supportive care, at treating infections that can be fatal.”
There haven’t been major conflicts with insurers over coverage, she said, although drug shortages are a problem, especially in relapsed AML.
As for advice to colleagues, Dr. Tasian counseled them to understand the importance of genetic testing and the expanding role of stem cell transplants. “We are now transplanting somewhere between 30% and 50% of children with AML, which is a higher rate than we used to do,” she said. The number is up thanks to genetic testing that reveals which patients are most likely to benefit.
Also, she noted, “the chemotherapy that we get to these patients is really strong, and patients have a lot of complications. Really pay attention to supportive care.”
Dr. LeBlanc reported ties with AbbVie, Agios/Servier, Astellas, BMS/Celgene, Genentech, Pfizer, Incyte, Rige, Deverra, GSK, Jazz, and Seattle Genetics. Dr. Sekeres discloses relationships with BMS and Kurome. Dr. Tasian serves as the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Pediatric Acute Leukemia consortium clinical trials leader and works with pharmaceutical companies on clinical trials under confidentiality agreements. Dr. Brunner has no disclosures.
For adult patients, “we’ve seen a series of remarkable and well-overdue advances in a space that had not changed much over the prior decades,” hematologist/oncologist Thomas William LeBlanc, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
According to the National Cancer Institute, AML will be newly diagnosed in 20,800 patients in 2024, at a median age of 69, and will cause 11,220 deaths. As many as 70% of adult patients will reach complete remission, and 45% of those will live for more than 3 years and potentially be cured. As for children, the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society says the 5-year survival rate from 2012-2018 was 69% for those under 15 years old.
As the American Cancer Society notes, the goal of AML treatment “is to put the leukemia into complete remission (the bone marrow and blood cell counts return to normal), preferably a complete molecular remission (no signs of leukemia in the bone marrow, even using sensitive lab tests), and to keep it that way.”
Chemotherapy Strategies Shift Over Time
In terms of the treatment of adults with AML, “targeted therapies, in addition to the expanding role of venetoclax, has really altered our approach to AML from diagnosis, including after relapse, and later in the disease,” hematologist/oncologist Andrew M. Brunner, MD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. “The ability to explore these options as monotherapy and in novel combinations has dramatically expanded our treatment options.”
Much depends on the underlying genetic profile of the disease, he said. “There certainly have been gains in patient survival in AML, but those improvements remain fairly heterogeneous and dependent on the underlying genetic profile of the disease. For instance, advances in FLT3- and IDH1/2-mutated AML are a direct result of the improvements in targeted therapies directed at these mutations. Similarly, some molecular and cytogenetic subtypes of AML are particularly responsive to venetoclax-based regimens, and these regimens have been expanded to previously undertreated populations, particularly those over age 60.”
Specifically, Dr. LeBlanc said, the Food and Drug Administration has approved “3 different FLT3 inhibitors, 2 IDH1 inhibitors, 1 IDH2 inhibitor, a BCL-2 inhibitor, a smoothened/hedgehog pathway inhibitor, an oral maintenance chemotherapy/hypomethylating agent (CC-486/oral azacitidine), a CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, and even a novel formulation of two older chemotherapies that improves efficacy in a poor prognosis subgroup (CPX-351/liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine).”
There’s also been a shift in treatment protocols for patients who were not fit for intensive chemotherapy. In the past, he said, it was standard “to give single-agent hypomethylating chemotherapy with azacitidine or decitabine, or in some contexts, low-dose chemotherapy with cytarabine. Today, many patients who are older and/or more frail are receiving novel therapies either alone or in combination, with greater efficacy and longer duration of response than previously seen with chemotherapy alone.”
Outcomes Improve but Remain Grim in High-Risk Cases
As a result, Dr. LeBlanc said, “we’re definitely seeing much better outcomes in AML overall. It takes some time to prove this via outcomes data assessments in a large population, but I expect that registries will show significant improvements in overall survival in the coming years, owing to the many new FDA approvals in AML”
Dr. LeBlanc highlighted national data from 2013-2019 showing that the 5-year relative survival rate from AML is 31.7%. That’s up from 26% just a few years ago, and the numbers “always lag several years behind the current year of practice,” he said. However, “the major area where we still have relatively poor outcomes and significant unmet needs remains the ‘adverse risk’ group of patients, particularly those who are older and/or not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which generally is the only potentially curative option for adverse-risk AML.”
He went on to say that “this risk grouping includes those with TP53 mutations, most of which confer a particularly poor prognosis. Exciting therapies that many of us were hoping would prove effective in this subgroup have unfortunately failed in recent clinical trials. We still have a lot of work to do in adverse-risk AML particularly, and also for those whose leukemia has relapsed.”
Mikkael Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of the Division of Hematology at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine/Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, agreed that more progress is needed, since survival rates are low even as lifespans improve. One key will be “better identifying subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia, and identifying the therapies that will benefit those people most,” he said in an interview. On the other side, it’s important to identify “when aggressive therapies aren’t going to work in somebody and maybe turn toward less-aggressive approaches so we can maximize that person’s quality of life.”
What advice do AML experts have for their colleagues? Dr. LeBlanc said “older patients are not often enough considered for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, which could potentially cure their AML when given as a consolidation treatment for those in remission. I have several patients who are healthy and in their 70s who have enormously benefited from transplants and are now being several years out from transplant with adverse risk AML and without relapse. They’ve had no significant impairments of their quality of life, including no significant graft vs. host disease.”
Dr. Sekeres highlighted the American Society of Hematology’s guidelines for treating older adults with AML, which are currently being updated. It’s crucial to order genetic testing “up front,” he said. “I’m often pleasantly surprised when genetic testing returns and reveals that I have other treatment options.”
However, it’s crucial to understand a patient’s priorities. “I’ve had patients who are 75 who say to me, ‘Do everything under the sun to get rid of my leukemia, I want to live as long as possible.’ And I’ve had patients who say, ‘I want to see as little of doctors and nurses as I can. I want you to maximize my quality of life and keep me out of the hospital.’ ”
Dr. Sekeres also noted that insurers may not cover some pill-based AML treatments such as venetoclax. “We work with our patients and assistance programs. For the most part, we’re pretty successful at getting these drugs for our patients,” he said.
In Pediatrics, Clinical Trials Are Crucial
AML in children is less well-known than in adults, since the number of cases is so small. The disease is diagnosed in about 500 children a year in the United States, according to St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, adding, however, that AML is “the most common second cancer among children treated for other cancers.”
AML in children gained attention earlier this year when the 2-year-old daughter of a Boston Herald NFL reporter died of the disease following a bone marrow transplant and chemotherapy. Despite the agonies of her treatment, reporter Doug Kyed told a reporter that his daughter Hallie “was still able to find joy every day.”
In an interview, hematologist/oncologist Sarah K. Tasian, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said researchers are discovering that pediatric AML is significantly different on from a biological perspective from adult AML. “We’ve come to understand a lot more about who these patients are, what makes these leukemias tick, and what their Achilles’ heels are. Then we can align that with the clinical trials outcome data that we have.”
About 80%-90% of pediatric patients with AML nationwide are enrolled in clinical trials, Dr. Tasian said, and an international consortium called the Children’s Oncology Group gathers data about genetics. About 60%-70% of patients will be cured, she added.
However, “we’ve kind of been stuck for about the last 20 years,” she said. “A lot of improving the survival of patients has not been because we’ve been better at chemotherapy or using new chemo, but because we’ve gotten better at supportive care, at treating infections that can be fatal.”
There haven’t been major conflicts with insurers over coverage, she said, although drug shortages are a problem, especially in relapsed AML.
As for advice to colleagues, Dr. Tasian counseled them to understand the importance of genetic testing and the expanding role of stem cell transplants. “We are now transplanting somewhere between 30% and 50% of children with AML, which is a higher rate than we used to do,” she said. The number is up thanks to genetic testing that reveals which patients are most likely to benefit.
Also, she noted, “the chemotherapy that we get to these patients is really strong, and patients have a lot of complications. Really pay attention to supportive care.”
Dr. LeBlanc reported ties with AbbVie, Agios/Servier, Astellas, BMS/Celgene, Genentech, Pfizer, Incyte, Rige, Deverra, GSK, Jazz, and Seattle Genetics. Dr. Sekeres discloses relationships with BMS and Kurome. Dr. Tasian serves as the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Pediatric Acute Leukemia consortium clinical trials leader and works with pharmaceutical companies on clinical trials under confidentiality agreements. Dr. Brunner has no disclosures.
For adult patients, “we’ve seen a series of remarkable and well-overdue advances in a space that had not changed much over the prior decades,” hematologist/oncologist Thomas William LeBlanc, MD, associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, said in an interview.
According to the National Cancer Institute, AML will be newly diagnosed in 20,800 patients in 2024, at a median age of 69, and will cause 11,220 deaths. As many as 70% of adult patients will reach complete remission, and 45% of those will live for more than 3 years and potentially be cured. As for children, the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society says the 5-year survival rate from 2012-2018 was 69% for those under 15 years old.
As the American Cancer Society notes, the goal of AML treatment “is to put the leukemia into complete remission (the bone marrow and blood cell counts return to normal), preferably a complete molecular remission (no signs of leukemia in the bone marrow, even using sensitive lab tests), and to keep it that way.”
Chemotherapy Strategies Shift Over Time
In terms of the treatment of adults with AML, “targeted therapies, in addition to the expanding role of venetoclax, has really altered our approach to AML from diagnosis, including after relapse, and later in the disease,” hematologist/oncologist Andrew M. Brunner, MD, of Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview. “The ability to explore these options as monotherapy and in novel combinations has dramatically expanded our treatment options.”
Much depends on the underlying genetic profile of the disease, he said. “There certainly have been gains in patient survival in AML, but those improvements remain fairly heterogeneous and dependent on the underlying genetic profile of the disease. For instance, advances in FLT3- and IDH1/2-mutated AML are a direct result of the improvements in targeted therapies directed at these mutations. Similarly, some molecular and cytogenetic subtypes of AML are particularly responsive to venetoclax-based regimens, and these regimens have been expanded to previously undertreated populations, particularly those over age 60.”
Specifically, Dr. LeBlanc said, the Food and Drug Administration has approved “3 different FLT3 inhibitors, 2 IDH1 inhibitors, 1 IDH2 inhibitor, a BCL-2 inhibitor, a smoothened/hedgehog pathway inhibitor, an oral maintenance chemotherapy/hypomethylating agent (CC-486/oral azacitidine), a CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate, and even a novel formulation of two older chemotherapies that improves efficacy in a poor prognosis subgroup (CPX-351/liposomal daunorubicin and cytarabine).”
There’s also been a shift in treatment protocols for patients who were not fit for intensive chemotherapy. In the past, he said, it was standard “to give single-agent hypomethylating chemotherapy with azacitidine or decitabine, or in some contexts, low-dose chemotherapy with cytarabine. Today, many patients who are older and/or more frail are receiving novel therapies either alone or in combination, with greater efficacy and longer duration of response than previously seen with chemotherapy alone.”
Outcomes Improve but Remain Grim in High-Risk Cases
As a result, Dr. LeBlanc said, “we’re definitely seeing much better outcomes in AML overall. It takes some time to prove this via outcomes data assessments in a large population, but I expect that registries will show significant improvements in overall survival in the coming years, owing to the many new FDA approvals in AML”
Dr. LeBlanc highlighted national data from 2013-2019 showing that the 5-year relative survival rate from AML is 31.7%. That’s up from 26% just a few years ago, and the numbers “always lag several years behind the current year of practice,” he said. However, “the major area where we still have relatively poor outcomes and significant unmet needs remains the ‘adverse risk’ group of patients, particularly those who are older and/or not candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which generally is the only potentially curative option for adverse-risk AML.”
He went on to say that “this risk grouping includes those with TP53 mutations, most of which confer a particularly poor prognosis. Exciting therapies that many of us were hoping would prove effective in this subgroup have unfortunately failed in recent clinical trials. We still have a lot of work to do in adverse-risk AML particularly, and also for those whose leukemia has relapsed.”
Mikkael Sekeres, MD, MS, chief of the Division of Hematology at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine/Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, agreed that more progress is needed, since survival rates are low even as lifespans improve. One key will be “better identifying subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia, and identifying the therapies that will benefit those people most,” he said in an interview. On the other side, it’s important to identify “when aggressive therapies aren’t going to work in somebody and maybe turn toward less-aggressive approaches so we can maximize that person’s quality of life.”
What advice do AML experts have for their colleagues? Dr. LeBlanc said “older patients are not often enough considered for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, which could potentially cure their AML when given as a consolidation treatment for those in remission. I have several patients who are healthy and in their 70s who have enormously benefited from transplants and are now being several years out from transplant with adverse risk AML and without relapse. They’ve had no significant impairments of their quality of life, including no significant graft vs. host disease.”
Dr. Sekeres highlighted the American Society of Hematology’s guidelines for treating older adults with AML, which are currently being updated. It’s crucial to order genetic testing “up front,” he said. “I’m often pleasantly surprised when genetic testing returns and reveals that I have other treatment options.”
However, it’s crucial to understand a patient’s priorities. “I’ve had patients who are 75 who say to me, ‘Do everything under the sun to get rid of my leukemia, I want to live as long as possible.’ And I’ve had patients who say, ‘I want to see as little of doctors and nurses as I can. I want you to maximize my quality of life and keep me out of the hospital.’ ”
Dr. Sekeres also noted that insurers may not cover some pill-based AML treatments such as venetoclax. “We work with our patients and assistance programs. For the most part, we’re pretty successful at getting these drugs for our patients,” he said.
In Pediatrics, Clinical Trials Are Crucial
AML in children is less well-known than in adults, since the number of cases is so small. The disease is diagnosed in about 500 children a year in the United States, according to St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, adding, however, that AML is “the most common second cancer among children treated for other cancers.”
AML in children gained attention earlier this year when the 2-year-old daughter of a Boston Herald NFL reporter died of the disease following a bone marrow transplant and chemotherapy. Despite the agonies of her treatment, reporter Doug Kyed told a reporter that his daughter Hallie “was still able to find joy every day.”
In an interview, hematologist/oncologist Sarah K. Tasian, MD, of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said researchers are discovering that pediatric AML is significantly different on from a biological perspective from adult AML. “We’ve come to understand a lot more about who these patients are, what makes these leukemias tick, and what their Achilles’ heels are. Then we can align that with the clinical trials outcome data that we have.”
About 80%-90% of pediatric patients with AML nationwide are enrolled in clinical trials, Dr. Tasian said, and an international consortium called the Children’s Oncology Group gathers data about genetics. About 60%-70% of patients will be cured, she added.
However, “we’ve kind of been stuck for about the last 20 years,” she said. “A lot of improving the survival of patients has not been because we’ve been better at chemotherapy or using new chemo, but because we’ve gotten better at supportive care, at treating infections that can be fatal.”
There haven’t been major conflicts with insurers over coverage, she said, although drug shortages are a problem, especially in relapsed AML.
As for advice to colleagues, Dr. Tasian counseled them to understand the importance of genetic testing and the expanding role of stem cell transplants. “We are now transplanting somewhere between 30% and 50% of children with AML, which is a higher rate than we used to do,” she said. The number is up thanks to genetic testing that reveals which patients are most likely to benefit.
Also, she noted, “the chemotherapy that we get to these patients is really strong, and patients have a lot of complications. Really pay attention to supportive care.”
Dr. LeBlanc reported ties with AbbVie, Agios/Servier, Astellas, BMS/Celgene, Genentech, Pfizer, Incyte, Rige, Deverra, GSK, Jazz, and Seattle Genetics. Dr. Sekeres discloses relationships with BMS and Kurome. Dr. Tasian serves as the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Pediatric Acute Leukemia consortium clinical trials leader and works with pharmaceutical companies on clinical trials under confidentiality agreements. Dr. Brunner has no disclosures.
Risankizumab in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical, Endoscopic Outcomes Remain Stable for up to 3 Years
STOCKHOLM — , according to results of the FORTIFY extension study.
“For me, most striking are the endoscopic endpoints,” Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD, AGAF, said in an interview. In the most conservative analysis, “you see a benefit the longer you follow the patients ... We haven’t seen this with many — if any — other compounds before.”
Dr. Ferrante, from University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, added that patients showed less antibody formation in response to risankizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)–23 p19 inhibitor, compared with anti–tumor necrosis factor agents.
“Most patients seemed to continue on treatment without the formation of antibodies to risankizumab becoming a problem,” he said. Also, for patients who achieve a good response to risankizumab, the effects were the same whether “they received this biologic first line, or only after failing other compounds.”
Generally, “I think we all have the impression that the IL-23 inhibitors have good efficacy, probably even better than other compounds available,” said Dr. Ferrante. “And, importantly, this is true without any increased adverse effects.”
“Now, with these new long-term data in risankizumab, we see the benefit-risk ratio continues to be favorable,” he added.
Dr. Ferrante presented the data (Abstract DOP 53) on February 23 at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Open-Label Extension up to 152 Weeks
The ongoing FORTIFY maintenance open-label extension study is evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of risankizumab in patients with moderate to severe CD.
These data follow the initial 52-week study published in 2022 showing that subcutaneous risankizumab was a safe and efficacious treatment for maintenance of remission in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Dr. Ferrante also led that study.
Participants in this open-label extension study who had already completed 52-weeks maintenance dosing received 180-mg subcutaneous risankizumab every 8 weeks (n = 872) at week 56. Those who had received prior rescue therapy, a single 1200-mg intravenous risankizumab dose followed by 360-mg subcutaneously every 8 weeks, continued with this latter regimen (n = 275). Data for analysis were pooled from both treatment groups (risankizumab 180 mg and 360 mg), and clinical outcomes were evaluated every 6 months.
Data for the population, after patients who received rescue treatment were imputed as nonresponders, showed Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) clinical response of 84.9% at week 56 and 52.7% at week 152. CDAI clinical remission was 66.7% at week 56 and 47.2% at week 152 for this population.
For endoscopic outcomes, additional benefit was seen over time. Endoscopic response, considered to be the best available predictor of long-term outcomes, was 50.8% at week 56 and 52.5% at week 152. Endoscopic remission was 35.8% at week 56 and 41.8% at week 152, and ulcer-free endoscopy was seen in 28.6% patients at week 56 and 35.5% at week 152.
The safety profile of risankizumab is consistent and supports long-term treatment, Dr. Ferrante said.
Treatment emergent adverse events included major adverse cardiovascular events in five patients on risankizumab and 50 serious infections.
‘Effective and Durable Option’
Providing comment, Tim Raine, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist & IBD lead at Cambridge University Hospitals, United Kingdom, remarked on the value of long-term extension studies for understanding the impact of continued drug administration beyond the typical 1-year time horizon of registrational clinical trials given that CD is currently incurable.
“However, there are limitations with long-term extension studies,” he said in an interview. In particular, the patients who remain in the study tend to be “those who have had a good experience with the drug and remain motivated to take part in ongoing monitoring.”
But “patients will drop out of a long-term extension study for reasons that may or may not reflect loss of benefit from the drug, and this can be problematic with handling of missing data,” he explained.
In light of this issue, “the investigators have used the most stringent way of handling these patients, regarding all who drop out as instances of failure of the drug. This offers the most robust assessment of durability of response that may slightly underestimate the true long-term efficacy,” said Dr. Raine.
“Nevertheless, the response and remission rates for clinical endpoints suggest good durability of effect out to 3 years of follow-up. The endoscopic data are also encouraging,” he asserted.
“Taken together, these data suggest that risankizumab can offer an effective and durable option for some patients with Crohn’s disease and is associated with a favorable safety profile.”
Dr. Ferrante disclosed ties with AbbVie, Agomab Therapeutics, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, EG, Eli Lilly, Falk, Ferring, Janssen, Janssen-Cilag, Lamepro, Medtronic, MRM, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, Takeda, ThermoFisher, Truvion Healthcare, and Viatris. Dr. Raine disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arena, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, BMS, Celgene, Ferring, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Heptares, LabGenius, Janssen, Mylan, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Takeda, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — , according to results of the FORTIFY extension study.
“For me, most striking are the endoscopic endpoints,” Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD, AGAF, said in an interview. In the most conservative analysis, “you see a benefit the longer you follow the patients ... We haven’t seen this with many — if any — other compounds before.”
Dr. Ferrante, from University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, added that patients showed less antibody formation in response to risankizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)–23 p19 inhibitor, compared with anti–tumor necrosis factor agents.
“Most patients seemed to continue on treatment without the formation of antibodies to risankizumab becoming a problem,” he said. Also, for patients who achieve a good response to risankizumab, the effects were the same whether “they received this biologic first line, or only after failing other compounds.”
Generally, “I think we all have the impression that the IL-23 inhibitors have good efficacy, probably even better than other compounds available,” said Dr. Ferrante. “And, importantly, this is true without any increased adverse effects.”
“Now, with these new long-term data in risankizumab, we see the benefit-risk ratio continues to be favorable,” he added.
Dr. Ferrante presented the data (Abstract DOP 53) on February 23 at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Open-Label Extension up to 152 Weeks
The ongoing FORTIFY maintenance open-label extension study is evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of risankizumab in patients with moderate to severe CD.
These data follow the initial 52-week study published in 2022 showing that subcutaneous risankizumab was a safe and efficacious treatment for maintenance of remission in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Dr. Ferrante also led that study.
Participants in this open-label extension study who had already completed 52-weeks maintenance dosing received 180-mg subcutaneous risankizumab every 8 weeks (n = 872) at week 56. Those who had received prior rescue therapy, a single 1200-mg intravenous risankizumab dose followed by 360-mg subcutaneously every 8 weeks, continued with this latter regimen (n = 275). Data for analysis were pooled from both treatment groups (risankizumab 180 mg and 360 mg), and clinical outcomes were evaluated every 6 months.
Data for the population, after patients who received rescue treatment were imputed as nonresponders, showed Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) clinical response of 84.9% at week 56 and 52.7% at week 152. CDAI clinical remission was 66.7% at week 56 and 47.2% at week 152 for this population.
For endoscopic outcomes, additional benefit was seen over time. Endoscopic response, considered to be the best available predictor of long-term outcomes, was 50.8% at week 56 and 52.5% at week 152. Endoscopic remission was 35.8% at week 56 and 41.8% at week 152, and ulcer-free endoscopy was seen in 28.6% patients at week 56 and 35.5% at week 152.
The safety profile of risankizumab is consistent and supports long-term treatment, Dr. Ferrante said.
Treatment emergent adverse events included major adverse cardiovascular events in five patients on risankizumab and 50 serious infections.
‘Effective and Durable Option’
Providing comment, Tim Raine, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist & IBD lead at Cambridge University Hospitals, United Kingdom, remarked on the value of long-term extension studies for understanding the impact of continued drug administration beyond the typical 1-year time horizon of registrational clinical trials given that CD is currently incurable.
“However, there are limitations with long-term extension studies,” he said in an interview. In particular, the patients who remain in the study tend to be “those who have had a good experience with the drug and remain motivated to take part in ongoing monitoring.”
But “patients will drop out of a long-term extension study for reasons that may or may not reflect loss of benefit from the drug, and this can be problematic with handling of missing data,” he explained.
In light of this issue, “the investigators have used the most stringent way of handling these patients, regarding all who drop out as instances of failure of the drug. This offers the most robust assessment of durability of response that may slightly underestimate the true long-term efficacy,” said Dr. Raine.
“Nevertheless, the response and remission rates for clinical endpoints suggest good durability of effect out to 3 years of follow-up. The endoscopic data are also encouraging,” he asserted.
“Taken together, these data suggest that risankizumab can offer an effective and durable option for some patients with Crohn’s disease and is associated with a favorable safety profile.”
Dr. Ferrante disclosed ties with AbbVie, Agomab Therapeutics, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, EG, Eli Lilly, Falk, Ferring, Janssen, Janssen-Cilag, Lamepro, Medtronic, MRM, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, Takeda, ThermoFisher, Truvion Healthcare, and Viatris. Dr. Raine disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arena, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, BMS, Celgene, Ferring, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Heptares, LabGenius, Janssen, Mylan, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Takeda, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — , according to results of the FORTIFY extension study.
“For me, most striking are the endoscopic endpoints,” Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD, AGAF, said in an interview. In the most conservative analysis, “you see a benefit the longer you follow the patients ... We haven’t seen this with many — if any — other compounds before.”
Dr. Ferrante, from University Hospitals Leuven in Belgium, added that patients showed less antibody formation in response to risankizumab, an anti-interleukin (IL)–23 p19 inhibitor, compared with anti–tumor necrosis factor agents.
“Most patients seemed to continue on treatment without the formation of antibodies to risankizumab becoming a problem,” he said. Also, for patients who achieve a good response to risankizumab, the effects were the same whether “they received this biologic first line, or only after failing other compounds.”
Generally, “I think we all have the impression that the IL-23 inhibitors have good efficacy, probably even better than other compounds available,” said Dr. Ferrante. “And, importantly, this is true without any increased adverse effects.”
“Now, with these new long-term data in risankizumab, we see the benefit-risk ratio continues to be favorable,” he added.
Dr. Ferrante presented the data (Abstract DOP 53) on February 23 at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Open-Label Extension up to 152 Weeks
The ongoing FORTIFY maintenance open-label extension study is evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of risankizumab in patients with moderate to severe CD.
These data follow the initial 52-week study published in 2022 showing that subcutaneous risankizumab was a safe and efficacious treatment for maintenance of remission in patients with moderately to severely active CD. Dr. Ferrante also led that study.
Participants in this open-label extension study who had already completed 52-weeks maintenance dosing received 180-mg subcutaneous risankizumab every 8 weeks (n = 872) at week 56. Those who had received prior rescue therapy, a single 1200-mg intravenous risankizumab dose followed by 360-mg subcutaneously every 8 weeks, continued with this latter regimen (n = 275). Data for analysis were pooled from both treatment groups (risankizumab 180 mg and 360 mg), and clinical outcomes were evaluated every 6 months.
Data for the population, after patients who received rescue treatment were imputed as nonresponders, showed Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) clinical response of 84.9% at week 56 and 52.7% at week 152. CDAI clinical remission was 66.7% at week 56 and 47.2% at week 152 for this population.
For endoscopic outcomes, additional benefit was seen over time. Endoscopic response, considered to be the best available predictor of long-term outcomes, was 50.8% at week 56 and 52.5% at week 152. Endoscopic remission was 35.8% at week 56 and 41.8% at week 152, and ulcer-free endoscopy was seen in 28.6% patients at week 56 and 35.5% at week 152.
The safety profile of risankizumab is consistent and supports long-term treatment, Dr. Ferrante said.
Treatment emergent adverse events included major adverse cardiovascular events in five patients on risankizumab and 50 serious infections.
‘Effective and Durable Option’
Providing comment, Tim Raine, MD, a consultant gastroenterologist & IBD lead at Cambridge University Hospitals, United Kingdom, remarked on the value of long-term extension studies for understanding the impact of continued drug administration beyond the typical 1-year time horizon of registrational clinical trials given that CD is currently incurable.
“However, there are limitations with long-term extension studies,” he said in an interview. In particular, the patients who remain in the study tend to be “those who have had a good experience with the drug and remain motivated to take part in ongoing monitoring.”
But “patients will drop out of a long-term extension study for reasons that may or may not reflect loss of benefit from the drug, and this can be problematic with handling of missing data,” he explained.
In light of this issue, “the investigators have used the most stringent way of handling these patients, regarding all who drop out as instances of failure of the drug. This offers the most robust assessment of durability of response that may slightly underestimate the true long-term efficacy,” said Dr. Raine.
“Nevertheless, the response and remission rates for clinical endpoints suggest good durability of effect out to 3 years of follow-up. The endoscopic data are also encouraging,” he asserted.
“Taken together, these data suggest that risankizumab can offer an effective and durable option for some patients with Crohn’s disease and is associated with a favorable safety profile.”
Dr. Ferrante disclosed ties with AbbVie, Agomab Therapeutics, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, EG, Eli Lilly, Falk, Ferring, Janssen, Janssen-Cilag, Lamepro, Medtronic, MRM, MSD, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, Takeda, ThermoFisher, Truvion Healthcare, and Viatris. Dr. Raine disclosed ties with AbbVie, Arena, Aslan, AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, BMS, Celgene, Ferring, Galapagos, Gilead, GSK, Heptares, LabGenius, Janssen, Mylan, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Takeda, and UCB.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCO 2024
Capsule Endoscopy–Guided Treatment Reduces Flares in Crohn’s Disease Compared With Standard Care
STOCKHOLM — , a new study showed.
Capsule endoscopy reveals small-intestinal inflammation in over 70% of patients with CD who are in clinical remission, said Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, from Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel. The question remains however, which patients would benefit from treatment intensification.
The randomized controlled CURE-CD trial showed that patients who have high inflammatory activity — a Lewis score ≥ 350 as seen in video capsule endoscopy findings — experienced statistically significantly fewer relapses during the 2-year follow-up vs patients with the same amount of inflammation who continued their standard treatment, he said.
Dr. Ben-Horin presented the results at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation on behalf of the Israeli IBD Research Nucleus.
He and his colleagues aimed to examine the value of video capsule endoscopy to guide proactive treat-to-target strategy in patients with CD who are in clinical remission, adding onto their previous work published in 2019 that established the benefit of video capsule endoscopy over calprotectin in predicting relapse.
The prospective randomized controlled trial recruited 60 patients with CD involving the small bowel who were in clinical remission (Crohn’s Disease Activity Index [CDAI] < 150). Patients underwent clinical, biomarker, and imaging checks as well as video capsule endoscopies at baseline and every 6 months thereafter for up to 24 months.
A total of 40 patients with a Lewis score ≥ 350 and who were considered high-risk were randomized to either proactive treatment optimization (targeting video capsule endoscopy mucosal healing, n = 20) or to continued standard care (n = 20) for 24 months. Patients with a Lewis score < 350 who were considered to be low-risk continued standard care (n = 20) which may or may not have been biologic.
The primary outcome was the rate of clinical relapse (disease exacerbation comprised of a CDAI increase > 70 points or hospitalization/surgery) by 24 months in high-risk patients who received standard care vs proactive care.
Secondary outcomes included risk for flare in the low-risk group (all on standard care) vs the high-risk group also on standard care, predictive profiles for flare of calprotectin, MRI, intestinal ultrasound, and Lewis score over the 24 months.
A Nearly Threefold Difference
Treatment intensification in the high-risk proactive strategy group was split between therapeutic drug monitoring–based biologic dose-escalation (n = 11 in 20), starting a biologic (8 in 20), or swapping a biologic (1 in 20).
By 24 months, clinical flare occurred in 5 in 20 (25%) of the high-risk proactive group vs 14 (70%) of the high-risk standard-care group (odds ratio [OR], 0.14; 95% CI, 0.04-0.57; P = .006), Dr. Ben-Horin reported.
The data also showed that low-risk patients had a lower incidence of clinical flare at approximately 45% compared with 70% in high-risk patients also on standard care (P = .11 by intention-to-treat analysis; P = .06 by per-protocol analysis).
In an interview, Dr. Ben-Horin said that despite the results, there remained a “big dilemma” about who should be treated if they show mucosal inflammation on video capsule endoscopy.
“Crohn’s disease is a progressive disease, and we don’t want flares down the road in a patient that currently feels okay but has underlying inflammation,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s important to consider that our therapies are sometimes associated with adverse events, they can be very costly, and become a huge burden to our healthcare systems and to some of the patients.”
It is important to ask whether we should or treat patients in remission more aggressively “because not everyone will progress and some of them may never flare,” he explained.
The findings offer three layers of added evidence to the field, Dr. Ben-Horin said. First, it offers further support to the treat-to-target approach if tailored to a high-risk group. Second, the study suggests that treat-to-target studies should be looking only at the high-risk patients and not the entire study population. “This is the first study of its kind to take this approach,” he pointed out.
“Thirdly, our results build on our preceding trial to show that using video capsule endoscopy enables us to stratify the risk of patients’ with small-bowel Crohn’s disease and tailor their treatment accordingly, probably more accurately than calprotectin or C-reactive protein.”
Asked to comment on the results, Maria Abreu, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist who specializes in inflammatory bowel disease at the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, said that though it was a small study, it highlights that patients need to be closely monitored with objective, quantifiable tests for the best outcomes.
She continued: “Capsule endoscopy is certainly the most sensitive test we have and lends itself in short order to artificial intelligence interpretation and quantification to make it even more robust.”
“We now need to nuance who needs a capsule vs intestinal ultrasound vs a colonoscopy, and that is likely to depend on disease location and manifestations of the disease,” ie, mucosa-only or transmural-predominant disease, she noted.
Dr. Ben-Horin has declared that the trial was funded by the Helmsley Charitable Trust. The VCE was partly provided by Medtronic. He disclosed advisory board fees and/or consulting and/or research support from Janssen, AbbVie, CellTrion, Takeda, Schering Plough, Pfizer, Ferring, Falk Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche, Galmed, EviNature, Galmed, PredictaMed, NeoPharm.
Dr. Abreu has served as a consultant and scientific advisory board member for AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen Biotech, and Prometheus Biosciences, University of California, Berkeley; a speaker for Alimentiv; and has had projects funded by Pfizer, Prometheus Laboratories, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — , a new study showed.
Capsule endoscopy reveals small-intestinal inflammation in over 70% of patients with CD who are in clinical remission, said Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, from Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel. The question remains however, which patients would benefit from treatment intensification.
The randomized controlled CURE-CD trial showed that patients who have high inflammatory activity — a Lewis score ≥ 350 as seen in video capsule endoscopy findings — experienced statistically significantly fewer relapses during the 2-year follow-up vs patients with the same amount of inflammation who continued their standard treatment, he said.
Dr. Ben-Horin presented the results at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation on behalf of the Israeli IBD Research Nucleus.
He and his colleagues aimed to examine the value of video capsule endoscopy to guide proactive treat-to-target strategy in patients with CD who are in clinical remission, adding onto their previous work published in 2019 that established the benefit of video capsule endoscopy over calprotectin in predicting relapse.
The prospective randomized controlled trial recruited 60 patients with CD involving the small bowel who were in clinical remission (Crohn’s Disease Activity Index [CDAI] < 150). Patients underwent clinical, biomarker, and imaging checks as well as video capsule endoscopies at baseline and every 6 months thereafter for up to 24 months.
A total of 40 patients with a Lewis score ≥ 350 and who were considered high-risk were randomized to either proactive treatment optimization (targeting video capsule endoscopy mucosal healing, n = 20) or to continued standard care (n = 20) for 24 months. Patients with a Lewis score < 350 who were considered to be low-risk continued standard care (n = 20) which may or may not have been biologic.
The primary outcome was the rate of clinical relapse (disease exacerbation comprised of a CDAI increase > 70 points or hospitalization/surgery) by 24 months in high-risk patients who received standard care vs proactive care.
Secondary outcomes included risk for flare in the low-risk group (all on standard care) vs the high-risk group also on standard care, predictive profiles for flare of calprotectin, MRI, intestinal ultrasound, and Lewis score over the 24 months.
A Nearly Threefold Difference
Treatment intensification in the high-risk proactive strategy group was split between therapeutic drug monitoring–based biologic dose-escalation (n = 11 in 20), starting a biologic (8 in 20), or swapping a biologic (1 in 20).
By 24 months, clinical flare occurred in 5 in 20 (25%) of the high-risk proactive group vs 14 (70%) of the high-risk standard-care group (odds ratio [OR], 0.14; 95% CI, 0.04-0.57; P = .006), Dr. Ben-Horin reported.
The data also showed that low-risk patients had a lower incidence of clinical flare at approximately 45% compared with 70% in high-risk patients also on standard care (P = .11 by intention-to-treat analysis; P = .06 by per-protocol analysis).
In an interview, Dr. Ben-Horin said that despite the results, there remained a “big dilemma” about who should be treated if they show mucosal inflammation on video capsule endoscopy.
“Crohn’s disease is a progressive disease, and we don’t want flares down the road in a patient that currently feels okay but has underlying inflammation,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s important to consider that our therapies are sometimes associated with adverse events, they can be very costly, and become a huge burden to our healthcare systems and to some of the patients.”
It is important to ask whether we should or treat patients in remission more aggressively “because not everyone will progress and some of them may never flare,” he explained.
The findings offer three layers of added evidence to the field, Dr. Ben-Horin said. First, it offers further support to the treat-to-target approach if tailored to a high-risk group. Second, the study suggests that treat-to-target studies should be looking only at the high-risk patients and not the entire study population. “This is the first study of its kind to take this approach,” he pointed out.
“Thirdly, our results build on our preceding trial to show that using video capsule endoscopy enables us to stratify the risk of patients’ with small-bowel Crohn’s disease and tailor their treatment accordingly, probably more accurately than calprotectin or C-reactive protein.”
Asked to comment on the results, Maria Abreu, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist who specializes in inflammatory bowel disease at the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, said that though it was a small study, it highlights that patients need to be closely monitored with objective, quantifiable tests for the best outcomes.
She continued: “Capsule endoscopy is certainly the most sensitive test we have and lends itself in short order to artificial intelligence interpretation and quantification to make it even more robust.”
“We now need to nuance who needs a capsule vs intestinal ultrasound vs a colonoscopy, and that is likely to depend on disease location and manifestations of the disease,” ie, mucosa-only or transmural-predominant disease, she noted.
Dr. Ben-Horin has declared that the trial was funded by the Helmsley Charitable Trust. The VCE was partly provided by Medtronic. He disclosed advisory board fees and/or consulting and/or research support from Janssen, AbbVie, CellTrion, Takeda, Schering Plough, Pfizer, Ferring, Falk Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche, Galmed, EviNature, Galmed, PredictaMed, NeoPharm.
Dr. Abreu has served as a consultant and scientific advisory board member for AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen Biotech, and Prometheus Biosciences, University of California, Berkeley; a speaker for Alimentiv; and has had projects funded by Pfizer, Prometheus Laboratories, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM — , a new study showed.
Capsule endoscopy reveals small-intestinal inflammation in over 70% of patients with CD who are in clinical remission, said Shomron Ben-Horin, MD, from Sheba Medical Center, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel. The question remains however, which patients would benefit from treatment intensification.
The randomized controlled CURE-CD trial showed that patients who have high inflammatory activity — a Lewis score ≥ 350 as seen in video capsule endoscopy findings — experienced statistically significantly fewer relapses during the 2-year follow-up vs patients with the same amount of inflammation who continued their standard treatment, he said.
Dr. Ben-Horin presented the results at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation on behalf of the Israeli IBD Research Nucleus.
He and his colleagues aimed to examine the value of video capsule endoscopy to guide proactive treat-to-target strategy in patients with CD who are in clinical remission, adding onto their previous work published in 2019 that established the benefit of video capsule endoscopy over calprotectin in predicting relapse.
The prospective randomized controlled trial recruited 60 patients with CD involving the small bowel who were in clinical remission (Crohn’s Disease Activity Index [CDAI] < 150). Patients underwent clinical, biomarker, and imaging checks as well as video capsule endoscopies at baseline and every 6 months thereafter for up to 24 months.
A total of 40 patients with a Lewis score ≥ 350 and who were considered high-risk were randomized to either proactive treatment optimization (targeting video capsule endoscopy mucosal healing, n = 20) or to continued standard care (n = 20) for 24 months. Patients with a Lewis score < 350 who were considered to be low-risk continued standard care (n = 20) which may or may not have been biologic.
The primary outcome was the rate of clinical relapse (disease exacerbation comprised of a CDAI increase > 70 points or hospitalization/surgery) by 24 months in high-risk patients who received standard care vs proactive care.
Secondary outcomes included risk for flare in the low-risk group (all on standard care) vs the high-risk group also on standard care, predictive profiles for flare of calprotectin, MRI, intestinal ultrasound, and Lewis score over the 24 months.
A Nearly Threefold Difference
Treatment intensification in the high-risk proactive strategy group was split between therapeutic drug monitoring–based biologic dose-escalation (n = 11 in 20), starting a biologic (8 in 20), or swapping a biologic (1 in 20).
By 24 months, clinical flare occurred in 5 in 20 (25%) of the high-risk proactive group vs 14 (70%) of the high-risk standard-care group (odds ratio [OR], 0.14; 95% CI, 0.04-0.57; P = .006), Dr. Ben-Horin reported.
The data also showed that low-risk patients had a lower incidence of clinical flare at approximately 45% compared with 70% in high-risk patients also on standard care (P = .11 by intention-to-treat analysis; P = .06 by per-protocol analysis).
In an interview, Dr. Ben-Horin said that despite the results, there remained a “big dilemma” about who should be treated if they show mucosal inflammation on video capsule endoscopy.
“Crohn’s disease is a progressive disease, and we don’t want flares down the road in a patient that currently feels okay but has underlying inflammation,” he said. “On the other hand, it’s important to consider that our therapies are sometimes associated with adverse events, they can be very costly, and become a huge burden to our healthcare systems and to some of the patients.”
It is important to ask whether we should or treat patients in remission more aggressively “because not everyone will progress and some of them may never flare,” he explained.
The findings offer three layers of added evidence to the field, Dr. Ben-Horin said. First, it offers further support to the treat-to-target approach if tailored to a high-risk group. Second, the study suggests that treat-to-target studies should be looking only at the high-risk patients and not the entire study population. “This is the first study of its kind to take this approach,” he pointed out.
“Thirdly, our results build on our preceding trial to show that using video capsule endoscopy enables us to stratify the risk of patients’ with small-bowel Crohn’s disease and tailor their treatment accordingly, probably more accurately than calprotectin or C-reactive protein.”
Asked to comment on the results, Maria Abreu, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist who specializes in inflammatory bowel disease at the University of Miami, Miami, Florida, said that though it was a small study, it highlights that patients need to be closely monitored with objective, quantifiable tests for the best outcomes.
She continued: “Capsule endoscopy is certainly the most sensitive test we have and lends itself in short order to artificial intelligence interpretation and quantification to make it even more robust.”
“We now need to nuance who needs a capsule vs intestinal ultrasound vs a colonoscopy, and that is likely to depend on disease location and manifestations of the disease,” ie, mucosa-only or transmural-predominant disease, she noted.
Dr. Ben-Horin has declared that the trial was funded by the Helmsley Charitable Trust. The VCE was partly provided by Medtronic. He disclosed advisory board fees and/or consulting and/or research support from Janssen, AbbVie, CellTrion, Takeda, Schering Plough, Pfizer, Ferring, Falk Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Roche, Galmed, EviNature, Galmed, PredictaMed, NeoPharm.
Dr. Abreu has served as a consultant and scientific advisory board member for AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen Biotech, and Prometheus Biosciences, University of California, Berkeley; a speaker for Alimentiv; and has had projects funded by Pfizer, Prometheus Laboratories, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCO 2024
Photoexposed Rash in an Older Adult
The Diagnosis: Pellagra
The patient was diagnosed with pellagra based on the clinical and laboratory findings. He was discharged with nicotinamide 250 mg and folic acid 5 mg supplementation daily. After 3 months, all symptoms resolved.
Pellagra is a condition usually associated with the 4 Ds: dermatitis; diarrhea; dementia; and, if untreated, death.1 The word pellagra is derived from the Italian terms pelle and agra, which mean skin and rough, respectively.2 Spanish physician Gasper Casal first described pellagra in 1762 after observing the disease in poorer peasants in Asturias who mainly relied on maize and rarely consumed fresh meat.1,2 Joseph Goldberger conducted research in the early 20th century, provoking the disease in jail prisoners by modifying their diets. However, it was not until 1926 that Goldberger discovered the true cause of the illness to be a poor diet and named what would become known as nicotinamide as the pellagra preventative factor.1,2 Niacin (vitamin B3), the deficient molecule in pellagra, also is known as nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, or niacinamide. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is converted into nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide (NAD) and its phosphate NADP.1,2 It has been hypothesized that pellagra symptoms arise from insufficient amounts of NAD and NADP, making the body unable to support cellular energy transfer processes.3
Pellagra manifests 50 to 60 days after starting a diet low in niacin. Niacin and nicotinamide are absorbed from the digested food to the stomach through a sodiumdependent mechanism, and then nicotinamide may be transformed into nicotinic acid with microsomal deamidation.3 Niacin may be obtained from one’s diet or produced from tryptophan. Foods with the highest amounts of niacin include liver, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, pork, mushrooms, avocados, almonds, and legumes.1,3 Coffee also contains trigonelline, which may be transformed into nicotinic acid when roasted, increasing the niacin level by 30 times.3 Approximately 60 mg of dietary tryptophan is needed to produce up to 1 mg of niacin in the presence of B2 and B6 vitamins. This mechanism provides approximately half of the needs for niacin.3 Insufficient dietary intake of niacin or the essential amino acid tryptophan can cause pellagra (primary pellagra), which is a concern in resource-limited countries. Alternatively, the body may not be able to properly utilize niacin for metabolic processes (secondary pellagra), which occurs more frequently in developed countries.1 Secondary pellagra also may be caused by alcoholism, colitis, cirrhosis, carcinoid tumors, Hartnup disease, or gastrointestinal tuberculosis, as these conditions prevent niacin from being consumed, absorbed, or processed. Certain medications can cause pellagra by interfering with the tryptophan-niacin pathway, including isoniazid, 5-fluorouracil, pyrazinamide, 6-mercaptopurine, hydantoins, ethionamide, phenobarbital, azathioprine, and chloramphenicol.2
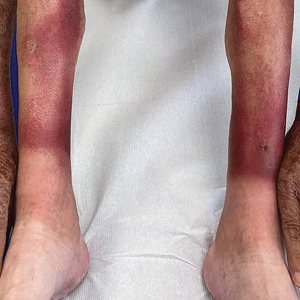
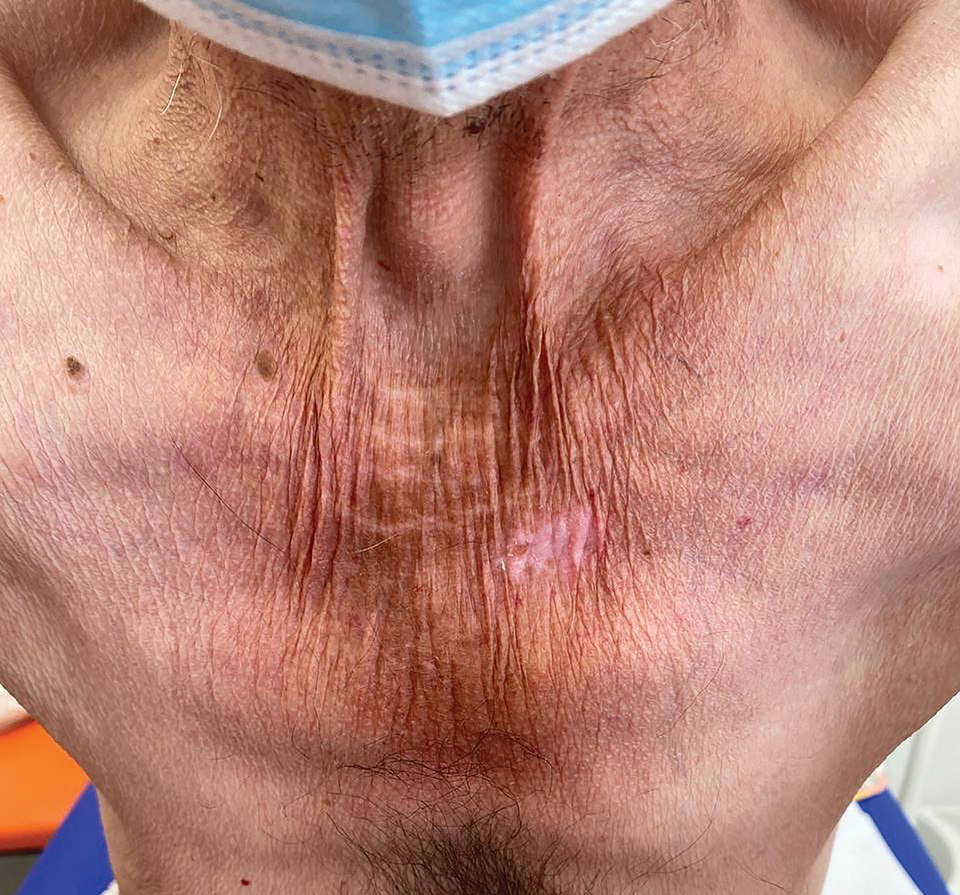
The clinical manifestations of pellagra are diverse because it affects tissues with high turnover rates. Clinical features of pellagra include symmetric photosensitive skin eruptions, gastrointestinal tract symptoms, and neurologic and mental disorders.3 The first signs of pellagra may include muscle weakness, digestive concerns, and psychological or emotional discomfort.2 Pellagra dermatitis manifests as an acute or intermittent, bilaterally symmetrical eruption on sun-exposed areas and is markedly distinct from healthy skin.3 Some individuals may experience vesiculation and bullae development (wet pellagra). The erythema is first brilliant red then turns into a cinnamon-brown color. Over time, the skin becomes thickened, scaly, cracked, and hyperpigmented.1 The dryness of the skin likely is due to a remarkable decrease in wax ester and sebaceous gland atrophy seen on histopathology.4 Pellagra most frequently affects the back of the hands (77%–97% of cases), which can extend upward to create the so-called pellagra glove or gauntlet.3 It is common to see symmetrical eruptions in the shape of a butterfly following an anatomical pattern innervated by the trigeminal nerve, which resembles lupus erythematosus on the face. Another common manifestation is Casal necklace, a well-marginated eruption frequently seen on the front of the neck (Figure).2 On the foot, lesions often do not develop close to the malleoli but rather terminate distally on the backs of the toes. Sometimes a boot pattern may form that covers the front and back of the leg.1-3
The pathophysiology of photosensitivity in pellagra was hypothesized by Karthikeyan and Thappa.3 They discovered an excessive synthesis of a phototoxic substance, kynurenic acid, and a deficiency in urocanic acid, which normally protects the skin by absorbing light in the UVB range. Niacin deprivation leads to the production of kynurenic acid through the tryptophan-kynurenine-nicotinic acid pathway and reduces the amount of urocanic acid by affecting the enzyme histidase in the stratum corneum.1-3 In one-third of patients, pellagra affects the oral mucosa, causing characteristic symptoms such as glossitis, angular stomatitis, and cheilitis.2 In nearly 50% of patients, poor appetite, nausea, epigastric discomfort, diarrhea, and excessive salivation are present. Most of the gastrointestinal tract is affected by mucosal inflammation and atrophy, which can cause malnutrition and cachexia due to anorexia and malabsorptive diarrhea.2 Headache, irritability, poor concentration, hallucinations, photophobia, tremor, and depression are some of the neuropsychiatric symptoms. Patients experience delirium and disorientation as pellagra progresses, followed by a comatose state and ultimately death.2
The patient’s history and physical examination are used to make the diagnosis, with particular attention to the patient’s dietary details. The diagnosis is made in part ex juvantibus by seeing how the patient responds to higher niacin doses. Anemia, hypoproteinemia, elevated blood calcium, reduced serum potassium and phosphorus, abnormal liver function tests, and elevated serum porphyrin levels also indicate pellagra. Niacin 300 mg in divided doses for up to 4 weeks has been recommended by the World Health Organization to treat pellagra.5 The flushing seen with niacin administration is not linked to the usage of nicotinamide. The recommended nicotinamide dosage for adults is 100 mg orally every 6 hours until most acute symptoms have disappeared, followed by oral administration of 50 mg every 8 to 12 hours until all skin lesions have healed.2
Among the differential diagnoses, necrolytic migratory erythema is characterized by an episodic eruption of crusted, erosive, annular erythematous plaques with blister development, which occurs in 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome. The perioral region, perineum, lower belly, thighs, and distal extremities are the usual locations.6,7 Laboratory test results include elevated fasting serum glucagon (>1000 ng/L) and normocytic anemia, which aided in ruling out this diagnosis in our patient. Generalized acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus may appear as a broad morbilliform eruption. The hands frequently exhibit erythema and edema, especially across the dorsal and interphalangeal regions.8 Other typical findings of systemic lupus erythematosus such as antinuclear antibody were not seen in our patient, making this diagnosis unlikely. Porphyria cutanea tarda also must be considered in the differential diagnosis. The hepatic deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase is the primary cause of this condition. Although it is characterized by blistering lesions, patients more frequently describe increased skin fragility in sun-exposed regions. Hypertrichosis, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, hirsutism, or scarring may appear in the later stage of the disease.9 Phototoxic reaction was ruled out because the patient spent most of the time at home, and no new drugs had been prescribed in the previous months.
- Prabhu D, Dawe RS, Mponda K. Pellagra a review exploring causes and mechanisms, including isoniazid-induced pellagra. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:99-104. doi:10.1111 /phpp.12659
- Hegyi J, Schwartz RA, Hegyi V. Pellagra: dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhea. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:1-5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01959.x
- Karthikeyan K, Thappa DM. Pellagra and skin. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:476-481. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01551.x
- Dogliotti M, Liebowitz M, Downing DT, et al. Nutritional influences of pellagra on sebum composition. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:25-28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb15423.x
- World Health Organization. Pellagra and Its Prevention and Control in Major Emergencies. Published February 23, 2000. Accessed February 15, 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NHD-00.10
- Liu JW, Qian YT, Ma DL. Necrolytic migratory erythema. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1180. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1658
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645. doi:10.1111/ijd.13947
- Walling HW, Sontheimer RD. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: issues in diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:365-381. doi:10.2165/11310780-000000000-00000
- Singal AK. Porphyria cutanea tarda: recent update. Mol Genet Metab. 2019;128:271-281. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.01.004
The Diagnosis: Pellagra
The patient was diagnosed with pellagra based on the clinical and laboratory findings. He was discharged with nicotinamide 250 mg and folic acid 5 mg supplementation daily. After 3 months, all symptoms resolved.
Pellagra is a condition usually associated with the 4 Ds: dermatitis; diarrhea; dementia; and, if untreated, death.1 The word pellagra is derived from the Italian terms pelle and agra, which mean skin and rough, respectively.2 Spanish physician Gasper Casal first described pellagra in 1762 after observing the disease in poorer peasants in Asturias who mainly relied on maize and rarely consumed fresh meat.1,2 Joseph Goldberger conducted research in the early 20th century, provoking the disease in jail prisoners by modifying their diets. However, it was not until 1926 that Goldberger discovered the true cause of the illness to be a poor diet and named what would become known as nicotinamide as the pellagra preventative factor.1,2 Niacin (vitamin B3), the deficient molecule in pellagra, also is known as nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, or niacinamide. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is converted into nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide (NAD) and its phosphate NADP.1,2 It has been hypothesized that pellagra symptoms arise from insufficient amounts of NAD and NADP, making the body unable to support cellular energy transfer processes.3
Pellagra manifests 50 to 60 days after starting a diet low in niacin. Niacin and nicotinamide are absorbed from the digested food to the stomach through a sodiumdependent mechanism, and then nicotinamide may be transformed into nicotinic acid with microsomal deamidation.3 Niacin may be obtained from one’s diet or produced from tryptophan. Foods with the highest amounts of niacin include liver, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, pork, mushrooms, avocados, almonds, and legumes.1,3 Coffee also contains trigonelline, which may be transformed into nicotinic acid when roasted, increasing the niacin level by 30 times.3 Approximately 60 mg of dietary tryptophan is needed to produce up to 1 mg of niacin in the presence of B2 and B6 vitamins. This mechanism provides approximately half of the needs for niacin.3 Insufficient dietary intake of niacin or the essential amino acid tryptophan can cause pellagra (primary pellagra), which is a concern in resource-limited countries. Alternatively, the body may not be able to properly utilize niacin for metabolic processes (secondary pellagra), which occurs more frequently in developed countries.1 Secondary pellagra also may be caused by alcoholism, colitis, cirrhosis, carcinoid tumors, Hartnup disease, or gastrointestinal tuberculosis, as these conditions prevent niacin from being consumed, absorbed, or processed. Certain medications can cause pellagra by interfering with the tryptophan-niacin pathway, including isoniazid, 5-fluorouracil, pyrazinamide, 6-mercaptopurine, hydantoins, ethionamide, phenobarbital, azathioprine, and chloramphenicol.2
The clinical manifestations of pellagra are diverse because it affects tissues with high turnover rates. Clinical features of pellagra include symmetric photosensitive skin eruptions, gastrointestinal tract symptoms, and neurologic and mental disorders.3 The first signs of pellagra may include muscle weakness, digestive concerns, and psychological or emotional discomfort.2 Pellagra dermatitis manifests as an acute or intermittent, bilaterally symmetrical eruption on sun-exposed areas and is markedly distinct from healthy skin.3 Some individuals may experience vesiculation and bullae development (wet pellagra). The erythema is first brilliant red then turns into a cinnamon-brown color. Over time, the skin becomes thickened, scaly, cracked, and hyperpigmented.1 The dryness of the skin likely is due to a remarkable decrease in wax ester and sebaceous gland atrophy seen on histopathology.4 Pellagra most frequently affects the back of the hands (77%–97% of cases), which can extend upward to create the so-called pellagra glove or gauntlet.3 It is common to see symmetrical eruptions in the shape of a butterfly following an anatomical pattern innervated by the trigeminal nerve, which resembles lupus erythematosus on the face. Another common manifestation is Casal necklace, a well-marginated eruption frequently seen on the front of the neck (Figure).2 On the foot, lesions often do not develop close to the malleoli but rather terminate distally on the backs of the toes. Sometimes a boot pattern may form that covers the front and back of the leg.1-3

The pathophysiology of photosensitivity in pellagra was hypothesized by Karthikeyan and Thappa.3 They discovered an excessive synthesis of a phototoxic substance, kynurenic acid, and a deficiency in urocanic acid, which normally protects the skin by absorbing light in the UVB range. Niacin deprivation leads to the production of kynurenic acid through the tryptophan-kynurenine-nicotinic acid pathway and reduces the amount of urocanic acid by affecting the enzyme histidase in the stratum corneum.1-3 In one-third of patients, pellagra affects the oral mucosa, causing characteristic symptoms such as glossitis, angular stomatitis, and cheilitis.2 In nearly 50% of patients, poor appetite, nausea, epigastric discomfort, diarrhea, and excessive salivation are present. Most of the gastrointestinal tract is affected by mucosal inflammation and atrophy, which can cause malnutrition and cachexia due to anorexia and malabsorptive diarrhea.2 Headache, irritability, poor concentration, hallucinations, photophobia, tremor, and depression are some of the neuropsychiatric symptoms. Patients experience delirium and disorientation as pellagra progresses, followed by a comatose state and ultimately death.2
The patient’s history and physical examination are used to make the diagnosis, with particular attention to the patient’s dietary details. The diagnosis is made in part ex juvantibus by seeing how the patient responds to higher niacin doses. Anemia, hypoproteinemia, elevated blood calcium, reduced serum potassium and phosphorus, abnormal liver function tests, and elevated serum porphyrin levels also indicate pellagra. Niacin 300 mg in divided doses for up to 4 weeks has been recommended by the World Health Organization to treat pellagra.5 The flushing seen with niacin administration is not linked to the usage of nicotinamide. The recommended nicotinamide dosage for adults is 100 mg orally every 6 hours until most acute symptoms have disappeared, followed by oral administration of 50 mg every 8 to 12 hours until all skin lesions have healed.2
Among the differential diagnoses, necrolytic migratory erythema is characterized by an episodic eruption of crusted, erosive, annular erythematous plaques with blister development, which occurs in 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome. The perioral region, perineum, lower belly, thighs, and distal extremities are the usual locations.6,7 Laboratory test results include elevated fasting serum glucagon (>1000 ng/L) and normocytic anemia, which aided in ruling out this diagnosis in our patient. Generalized acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus may appear as a broad morbilliform eruption. The hands frequently exhibit erythema and edema, especially across the dorsal and interphalangeal regions.8 Other typical findings of systemic lupus erythematosus such as antinuclear antibody were not seen in our patient, making this diagnosis unlikely. Porphyria cutanea tarda also must be considered in the differential diagnosis. The hepatic deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase is the primary cause of this condition. Although it is characterized by blistering lesions, patients more frequently describe increased skin fragility in sun-exposed regions. Hypertrichosis, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, hirsutism, or scarring may appear in the later stage of the disease.9 Phototoxic reaction was ruled out because the patient spent most of the time at home, and no new drugs had been prescribed in the previous months.
The Diagnosis: Pellagra
The patient was diagnosed with pellagra based on the clinical and laboratory findings. He was discharged with nicotinamide 250 mg and folic acid 5 mg supplementation daily. After 3 months, all symptoms resolved.
Pellagra is a condition usually associated with the 4 Ds: dermatitis; diarrhea; dementia; and, if untreated, death.1 The word pellagra is derived from the Italian terms pelle and agra, which mean skin and rough, respectively.2 Spanish physician Gasper Casal first described pellagra in 1762 after observing the disease in poorer peasants in Asturias who mainly relied on maize and rarely consumed fresh meat.1,2 Joseph Goldberger conducted research in the early 20th century, provoking the disease in jail prisoners by modifying their diets. However, it was not until 1926 that Goldberger discovered the true cause of the illness to be a poor diet and named what would become known as nicotinamide as the pellagra preventative factor.1,2 Niacin (vitamin B3), the deficient molecule in pellagra, also is known as nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, or niacinamide. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is converted into nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide (NAD) and its phosphate NADP.1,2 It has been hypothesized that pellagra symptoms arise from insufficient amounts of NAD and NADP, making the body unable to support cellular energy transfer processes.3
Pellagra manifests 50 to 60 days after starting a diet low in niacin. Niacin and nicotinamide are absorbed from the digested food to the stomach through a sodiumdependent mechanism, and then nicotinamide may be transformed into nicotinic acid with microsomal deamidation.3 Niacin may be obtained from one’s diet or produced from tryptophan. Foods with the highest amounts of niacin include liver, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, pork, mushrooms, avocados, almonds, and legumes.1,3 Coffee also contains trigonelline, which may be transformed into nicotinic acid when roasted, increasing the niacin level by 30 times.3 Approximately 60 mg of dietary tryptophan is needed to produce up to 1 mg of niacin in the presence of B2 and B6 vitamins. This mechanism provides approximately half of the needs for niacin.3 Insufficient dietary intake of niacin or the essential amino acid tryptophan can cause pellagra (primary pellagra), which is a concern in resource-limited countries. Alternatively, the body may not be able to properly utilize niacin for metabolic processes (secondary pellagra), which occurs more frequently in developed countries.1 Secondary pellagra also may be caused by alcoholism, colitis, cirrhosis, carcinoid tumors, Hartnup disease, or gastrointestinal tuberculosis, as these conditions prevent niacin from being consumed, absorbed, or processed. Certain medications can cause pellagra by interfering with the tryptophan-niacin pathway, including isoniazid, 5-fluorouracil, pyrazinamide, 6-mercaptopurine, hydantoins, ethionamide, phenobarbital, azathioprine, and chloramphenicol.2
The clinical manifestations of pellagra are diverse because it affects tissues with high turnover rates. Clinical features of pellagra include symmetric photosensitive skin eruptions, gastrointestinal tract symptoms, and neurologic and mental disorders.3 The first signs of pellagra may include muscle weakness, digestive concerns, and psychological or emotional discomfort.2 Pellagra dermatitis manifests as an acute or intermittent, bilaterally symmetrical eruption on sun-exposed areas and is markedly distinct from healthy skin.3 Some individuals may experience vesiculation and bullae development (wet pellagra). The erythema is first brilliant red then turns into a cinnamon-brown color. Over time, the skin becomes thickened, scaly, cracked, and hyperpigmented.1 The dryness of the skin likely is due to a remarkable decrease in wax ester and sebaceous gland atrophy seen on histopathology.4 Pellagra most frequently affects the back of the hands (77%–97% of cases), which can extend upward to create the so-called pellagra glove or gauntlet.3 It is common to see symmetrical eruptions in the shape of a butterfly following an anatomical pattern innervated by the trigeminal nerve, which resembles lupus erythematosus on the face. Another common manifestation is Casal necklace, a well-marginated eruption frequently seen on the front of the neck (Figure).2 On the foot, lesions often do not develop close to the malleoli but rather terminate distally on the backs of the toes. Sometimes a boot pattern may form that covers the front and back of the leg.1-3

The pathophysiology of photosensitivity in pellagra was hypothesized by Karthikeyan and Thappa.3 They discovered an excessive synthesis of a phototoxic substance, kynurenic acid, and a deficiency in urocanic acid, which normally protects the skin by absorbing light in the UVB range. Niacin deprivation leads to the production of kynurenic acid through the tryptophan-kynurenine-nicotinic acid pathway and reduces the amount of urocanic acid by affecting the enzyme histidase in the stratum corneum.1-3 In one-third of patients, pellagra affects the oral mucosa, causing characteristic symptoms such as glossitis, angular stomatitis, and cheilitis.2 In nearly 50% of patients, poor appetite, nausea, epigastric discomfort, diarrhea, and excessive salivation are present. Most of the gastrointestinal tract is affected by mucosal inflammation and atrophy, which can cause malnutrition and cachexia due to anorexia and malabsorptive diarrhea.2 Headache, irritability, poor concentration, hallucinations, photophobia, tremor, and depression are some of the neuropsychiatric symptoms. Patients experience delirium and disorientation as pellagra progresses, followed by a comatose state and ultimately death.2
The patient’s history and physical examination are used to make the diagnosis, with particular attention to the patient’s dietary details. The diagnosis is made in part ex juvantibus by seeing how the patient responds to higher niacin doses. Anemia, hypoproteinemia, elevated blood calcium, reduced serum potassium and phosphorus, abnormal liver function tests, and elevated serum porphyrin levels also indicate pellagra. Niacin 300 mg in divided doses for up to 4 weeks has been recommended by the World Health Organization to treat pellagra.5 The flushing seen with niacin administration is not linked to the usage of nicotinamide. The recommended nicotinamide dosage for adults is 100 mg orally every 6 hours until most acute symptoms have disappeared, followed by oral administration of 50 mg every 8 to 12 hours until all skin lesions have healed.2
Among the differential diagnoses, necrolytic migratory erythema is characterized by an episodic eruption of crusted, erosive, annular erythematous plaques with blister development, which occurs in 70% of patients with glucagonoma syndrome. The perioral region, perineum, lower belly, thighs, and distal extremities are the usual locations.6,7 Laboratory test results include elevated fasting serum glucagon (>1000 ng/L) and normocytic anemia, which aided in ruling out this diagnosis in our patient. Generalized acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus may appear as a broad morbilliform eruption. The hands frequently exhibit erythema and edema, especially across the dorsal and interphalangeal regions.8 Other typical findings of systemic lupus erythematosus such as antinuclear antibody were not seen in our patient, making this diagnosis unlikely. Porphyria cutanea tarda also must be considered in the differential diagnosis. The hepatic deficiency of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase is the primary cause of this condition. Although it is characterized by blistering lesions, patients more frequently describe increased skin fragility in sun-exposed regions. Hypertrichosis, hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, hirsutism, or scarring may appear in the later stage of the disease.9 Phototoxic reaction was ruled out because the patient spent most of the time at home, and no new drugs had been prescribed in the previous months.
- Prabhu D, Dawe RS, Mponda K. Pellagra a review exploring causes and mechanisms, including isoniazid-induced pellagra. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:99-104. doi:10.1111 /phpp.12659
- Hegyi J, Schwartz RA, Hegyi V. Pellagra: dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhea. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:1-5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01959.x
- Karthikeyan K, Thappa DM. Pellagra and skin. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:476-481. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01551.x
- Dogliotti M, Liebowitz M, Downing DT, et al. Nutritional influences of pellagra on sebum composition. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:25-28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb15423.x
- World Health Organization. Pellagra and Its Prevention and Control in Major Emergencies. Published February 23, 2000. Accessed February 15, 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NHD-00.10
- Liu JW, Qian YT, Ma DL. Necrolytic migratory erythema. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1180. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1658
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645. doi:10.1111/ijd.13947
- Walling HW, Sontheimer RD. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: issues in diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:365-381. doi:10.2165/11310780-000000000-00000
- Singal AK. Porphyria cutanea tarda: recent update. Mol Genet Metab. 2019;128:271-281. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.01.004
- Prabhu D, Dawe RS, Mponda K. Pellagra a review exploring causes and mechanisms, including isoniazid-induced pellagra. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2021;37:99-104. doi:10.1111 /phpp.12659
- Hegyi J, Schwartz RA, Hegyi V. Pellagra: dermatitis, dementia, and diarrhea. Int J Dermatol. 2004;43:1-5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01959.x
- Karthikeyan K, Thappa DM. Pellagra and skin. Int J Dermatol. 2002;41:476-481. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01551.x
- Dogliotti M, Liebowitz M, Downing DT, et al. Nutritional influences of pellagra on sebum composition. Br J Dermatol. 1977;97:25-28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb15423.x
- World Health Organization. Pellagra and Its Prevention and Control in Major Emergencies. Published February 23, 2000. Accessed February 15, 2024. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NHD-00.10
- Liu JW, Qian YT, Ma DL. Necrolytic migratory erythema. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1180. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1658
- Tolliver S, Graham J, Kaffenberger BH. A review of cutaneous manifestations within glucagonoma syndrome: necrolytic migratory erythema. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:642-645. doi:10.1111/ijd.13947
- Walling HW, Sontheimer RD. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: issues in diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:365-381. doi:10.2165/11310780-000000000-00000
- Singal AK. Porphyria cutanea tarda: recent update. Mol Genet Metab. 2019;128:271-281. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.01.004
A 66-year-old man presented with an intermittent pruriginous symmetric rash on the dorsal aspects of the arms, legs, and upper chest of 4 months' duration. The patient’s hands, forearms, and neck were diffusely hyperpigmented, dry, cracked, and scaling with a ring of peripheral erythema. He also experienced recurrent photosensitivity reactions on the legs. His poor clinical condition including confusion and diarrhea hindered intake of a balanced diet. He also reported a history of excessive alcohol use. The patient’s vital signs were normal, and Doppler ultrasonography ruled out deep venous thrombosis of the lower legs. A complete blood cell count showed anemia with decreased hemoglobin levels (117 g/L [reference range, 140–180 g/L]) and increased mean corpuscular volume (107.1 fL [reference range, 80–100 fL]). Additionally, low serum levels of albumin, folate, and vitamin B12 were noted. The patient had been taking hydrochlorothiazide and salicylic acid for hypertension with no recent changes in his medication regimen.
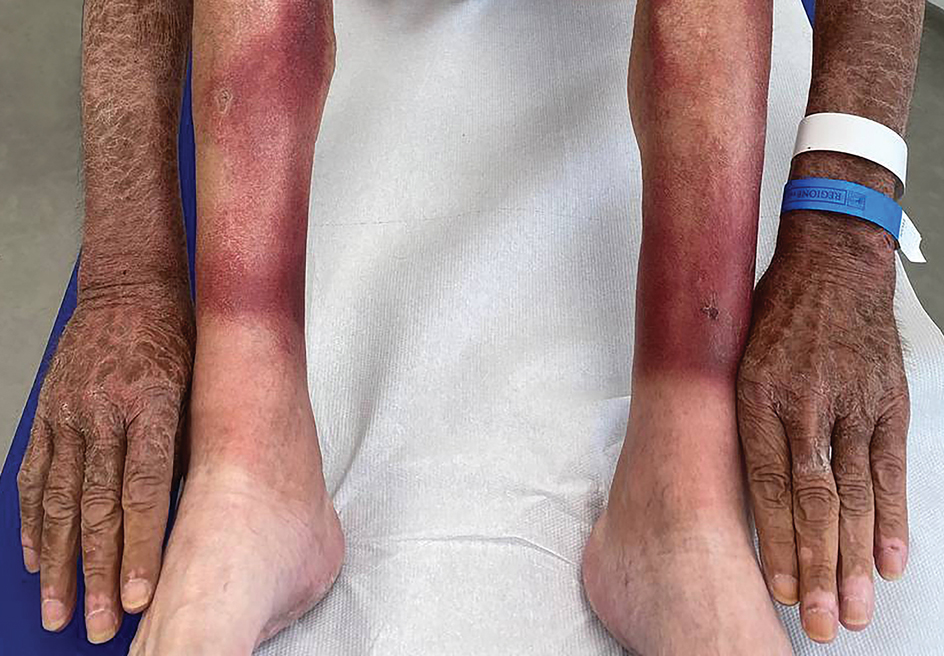
Moderate to Severe TBI Linked to Brain Cancer Risk
Moderate, severe, and penetrating traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with an elevated risk of developing brain cancer, new research suggested. However, mild TBI appears to confer no increased risk.
In a large cohort of post-9/11 US veterans, those who suffered moderate/severe TBI had a nearly twofold increased risk for a subsequent brain cancer diagnosis, while those with penetrating TBI had a greater than threefold increased risk.
“While the absolute number of brain cancer diagnoses was small, these diagnoses are associated with profoundly poor outcomes. Further research of this rare but devastating condition is needed to better identify those at risk and develop screening protocols,” wrote investigators led by Ian Stewart, MD, with the Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland.
The study was published online on February 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Common War Wound
TBI is one of the most common battlefield wounds among veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. But evidence to date on the potential association of TBI with the subsequent risk for brain cancer is conflicting, the authors noted.
To investigate further, they reviewed the records of nearly 2 million mostly male US veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. A total of 449,880 people experienced TBI, which was mild in 385,848 cases, moderate/severe in 46,859 cases, and penetrating in 17,173 cases.
During a median follow-up of 7.2 years, brain cancer occurred in 318 veterans without TBI (0.02%), 80 with mild TBI (0.02%), 17 with moderate/severe TBI (0.04%), and 10 or fewer with penetrating TBI (0.06% or less).
There was a stepwise increase in brain cancer incidence with worse TBI severity. Crude incidence rates per 100,000 person-years were 3.06 for no TBI, 2.85 for mild TBI, 4.88 for moderate/severe TBI, and 10.34 for penetrating TBI.
In the fully adjusted model, moderate/severe TBI showed a near-doubling of brain cancer risk vs no TBI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.90; 95% CI, 1.16-3.12), while penetrating TBI was associated with a greater than tripling of risk (aHR, 3.33; 95% CI, 1.71-6.49). There was no significantly increased risk after mild TBI.
There are plausible biological mechanisms linking TBI to brain cancer, the authors noted, including alterations in metabolism, inflammation, astrocyte proliferation, and stem cell migration and differentiation.
They caution that with few female veterans and a predominantly young cohort, the findings may not extend to the general population.
Meaningful New Data
In an accompanying editorial, Elie Massaad, MD, MSc, and Ali Kiapour, PhD, MMSc, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted that federal data show glioblastoma, the most aggressive malignant brain tumor, is the third leading cause of cancer-related death among active duty personnel.
“Post-9/11 veterans deployed to Iraq, Afghanistan, and elsewhere face a 26% higher glioblastoma rate vs the general public, with an average age of onset decades earlier than in broader populations,” they wrote.
Overall, they noted this new research provides “meaningful data clarifying associations between combat-related TBI severity and subsequent brain cancer risk among post-9/11 veterans.
“Elucidating potential connections between battlefield trauma and longer-term health outcomes is imperative to inform prevention and care approaches for those who have served,” they added.
This study was supported by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs endorsed by the Department of Defense through the Psychological Health/Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program Long-Term Impact of Military Relevant Brain Injury Consortium. The authors and editorialists had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderate, severe, and penetrating traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with an elevated risk of developing brain cancer, new research suggested. However, mild TBI appears to confer no increased risk.
In a large cohort of post-9/11 US veterans, those who suffered moderate/severe TBI had a nearly twofold increased risk for a subsequent brain cancer diagnosis, while those with penetrating TBI had a greater than threefold increased risk.
“While the absolute number of brain cancer diagnoses was small, these diagnoses are associated with profoundly poor outcomes. Further research of this rare but devastating condition is needed to better identify those at risk and develop screening protocols,” wrote investigators led by Ian Stewart, MD, with the Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland.
The study was published online on February 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Common War Wound
TBI is one of the most common battlefield wounds among veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. But evidence to date on the potential association of TBI with the subsequent risk for brain cancer is conflicting, the authors noted.
To investigate further, they reviewed the records of nearly 2 million mostly male US veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. A total of 449,880 people experienced TBI, which was mild in 385,848 cases, moderate/severe in 46,859 cases, and penetrating in 17,173 cases.
During a median follow-up of 7.2 years, brain cancer occurred in 318 veterans without TBI (0.02%), 80 with mild TBI (0.02%), 17 with moderate/severe TBI (0.04%), and 10 or fewer with penetrating TBI (0.06% or less).
There was a stepwise increase in brain cancer incidence with worse TBI severity. Crude incidence rates per 100,000 person-years were 3.06 for no TBI, 2.85 for mild TBI, 4.88 for moderate/severe TBI, and 10.34 for penetrating TBI.
In the fully adjusted model, moderate/severe TBI showed a near-doubling of brain cancer risk vs no TBI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.90; 95% CI, 1.16-3.12), while penetrating TBI was associated with a greater than tripling of risk (aHR, 3.33; 95% CI, 1.71-6.49). There was no significantly increased risk after mild TBI.
There are plausible biological mechanisms linking TBI to brain cancer, the authors noted, including alterations in metabolism, inflammation, astrocyte proliferation, and stem cell migration and differentiation.
They caution that with few female veterans and a predominantly young cohort, the findings may not extend to the general population.
Meaningful New Data
In an accompanying editorial, Elie Massaad, MD, MSc, and Ali Kiapour, PhD, MMSc, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted that federal data show glioblastoma, the most aggressive malignant brain tumor, is the third leading cause of cancer-related death among active duty personnel.
“Post-9/11 veterans deployed to Iraq, Afghanistan, and elsewhere face a 26% higher glioblastoma rate vs the general public, with an average age of onset decades earlier than in broader populations,” they wrote.
Overall, they noted this new research provides “meaningful data clarifying associations between combat-related TBI severity and subsequent brain cancer risk among post-9/11 veterans.
“Elucidating potential connections between battlefield trauma and longer-term health outcomes is imperative to inform prevention and care approaches for those who have served,” they added.
This study was supported by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs endorsed by the Department of Defense through the Psychological Health/Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program Long-Term Impact of Military Relevant Brain Injury Consortium. The authors and editorialists had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderate, severe, and penetrating traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with an elevated risk of developing brain cancer, new research suggested. However, mild TBI appears to confer no increased risk.
In a large cohort of post-9/11 US veterans, those who suffered moderate/severe TBI had a nearly twofold increased risk for a subsequent brain cancer diagnosis, while those with penetrating TBI had a greater than threefold increased risk.
“While the absolute number of brain cancer diagnoses was small, these diagnoses are associated with profoundly poor outcomes. Further research of this rare but devastating condition is needed to better identify those at risk and develop screening protocols,” wrote investigators led by Ian Stewart, MD, with the Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland.
The study was published online on February 15 in JAMA Network Open.
Common War Wound
TBI is one of the most common battlefield wounds among veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. But evidence to date on the potential association of TBI with the subsequent risk for brain cancer is conflicting, the authors noted.
To investigate further, they reviewed the records of nearly 2 million mostly male US veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. A total of 449,880 people experienced TBI, which was mild in 385,848 cases, moderate/severe in 46,859 cases, and penetrating in 17,173 cases.
During a median follow-up of 7.2 years, brain cancer occurred in 318 veterans without TBI (0.02%), 80 with mild TBI (0.02%), 17 with moderate/severe TBI (0.04%), and 10 or fewer with penetrating TBI (0.06% or less).
There was a stepwise increase in brain cancer incidence with worse TBI severity. Crude incidence rates per 100,000 person-years were 3.06 for no TBI, 2.85 for mild TBI, 4.88 for moderate/severe TBI, and 10.34 for penetrating TBI.
In the fully adjusted model, moderate/severe TBI showed a near-doubling of brain cancer risk vs no TBI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.90; 95% CI, 1.16-3.12), while penetrating TBI was associated with a greater than tripling of risk (aHR, 3.33; 95% CI, 1.71-6.49). There was no significantly increased risk after mild TBI.
There are plausible biological mechanisms linking TBI to brain cancer, the authors noted, including alterations in metabolism, inflammation, astrocyte proliferation, and stem cell migration and differentiation.
They caution that with few female veterans and a predominantly young cohort, the findings may not extend to the general population.
Meaningful New Data
In an accompanying editorial, Elie Massaad, MD, MSc, and Ali Kiapour, PhD, MMSc, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, noted that federal data show glioblastoma, the most aggressive malignant brain tumor, is the third leading cause of cancer-related death among active duty personnel.
“Post-9/11 veterans deployed to Iraq, Afghanistan, and elsewhere face a 26% higher glioblastoma rate vs the general public, with an average age of onset decades earlier than in broader populations,” they wrote.
Overall, they noted this new research provides “meaningful data clarifying associations between combat-related TBI severity and subsequent brain cancer risk among post-9/11 veterans.
“Elucidating potential connections between battlefield trauma and longer-term health outcomes is imperative to inform prevention and care approaches for those who have served,” they added.
This study was supported by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Health Affairs endorsed by the Department of Defense through the Psychological Health/Traumatic Brain Injury Research Program Long-Term Impact of Military Relevant Brain Injury Consortium. The authors and editorialists had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Commentary: Comorbidities in Migraine, March 2024
Additionally, several recently published reviews have examined the risks of comorbidities that are not neurologic or cardiovascular, such as allergies, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Although these types of associations are not inherently obvious in terms of migraine pathophysiology, determining whether there is a link may help shed a light on some contributing factors that could play a role in migraine or in the comorbid disorders.
Authors of a study published in the January 2024 issue of the European Journal of Medical Research sought to examine the relationship between allergic rhinitis and migraine. They noted that several studies, as well as a statement from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study, published in 2013, reported an increased frequency of migraines in patients with allergic rhinitis. The researchers used data extracted from the UK Biobank, comprising 25,486 patients diagnosed with allergic rhinitis and 87,097 controls and 8547 migraine cases and 176,107 controls. They performed statistical analysis using bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization with publicly available summary-level statistics of large genome-wide association studies to estimate the possible causal effects. The researchers did not find any clear causal or genetic association between allergic rhinitis and migraine risk. However, the lack of causation between migraine and allergic rhinitis does not contradict previous studies that point to the prevalence of comorbidity of the two conditions. It's also important to note that congestion is a known migraine trigger, and the results of the study do not contradict that relationship. Given the variability of results from different research studies, the authors suggested that more research is warranted to help untangle the complex association between allergic rhinitis and migraine.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is another condition with a higher prevalence in patients who have migraine. A January 2024 article in Scientific Reports described the results of a nationwide population-based study that was conducted using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. This study included 10,131,193 individuals. The researchers found that the risk for development of IBD in patients with migraine was significantly higher, by 1.3 times, compared with the general population. These results are similar to previous studies, such as a meta-analysis published in May 2023 in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine, which reported a pooled prevalence of migraine in IBD cases of 19%, with 1.5-fold higher odds of developing migraine in IBD cases when compared with controls.[3] These studies were both aimed at examining epidemiologic data rather than uncovering a physiologic or genetic cause of the link, and neither study described an explanation for this connection.
A Mendelian randomization study published in May 2023 in Headache investigated potential genetic links between migraine and IBD. As with the January 2024 European Journal of Medical Research study that was done to search for a genetic association between migraine and allergic rhinitis, the authors stated that there was no evidence of a shared genetic basis or of a causal association between migraine and either IBD or celiac disease.[4] Although the evidence doesn't point to a causal relationship, it's important to note that diet plays a role in migraine management, and diet is especially important in managing IBD. Consideration of dietary factors could be beneficial for preventing symptoms — and is even more important for avoiding exacerbation of symptoms.
A high body mass index (BMI) is correlated with migraine. A study published in January 2024 in BMC Geriatrics analyzed data from people who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 1999 and 2004 by the Centers for Disease Control and the National Center for Health Statistics, comprising a total of 31,126 participants. The researchers found a linear association between BMI and migraine. They also noted that increased BMI was related to a significantly higher risk for migraine in the group with diabetes, but this positive relationship between BMI and migraine seemed to be smaller in the group without diabetes. The authors considered inflammation associated with obesity as a possible contributing factor for this link but acknowledged that the pathophysiologic mechanism is unknown and suggested that there is a high likelihood of confounding factors. Given that diabetes and obesity are both correlated with an increased risk for vascular disease and migraine is associated with a slight increase in cardiovascular risk, it could be especially important to identify these comorbidities in individual patients.
Migraine is common, and many comorbidities have been verified with population studies. Although there are some explanations for the links between migraine and vascular or neurologic conditions, the cause of associations between migraine and other conditions is not known. Some theories that have begun to be investigated include inflammation and genetics. Eventually, further research and understanding of contributing factors could potentially provide explanations that may help in diagnosing migraine or associated disorders at an early stage — and might even be used to help guide treatment.
Additional References
1. Ashina M, Katsarava Z, Do TP, et al. Migraine: Epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet. 2021;397:1485-1495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32160-7 Source
2. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: Epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37:631-649. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001 Source
3. Olfati H, Mirmosayyeb O, Hosseinabadi AM, Ghajarzadeh M. The prevalence of migraine in inflammatory bowel disease, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Prev Med. 2023;14:66. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_413_21 Source
4. Welander NZ, Rukh G, Rask-Andersen M, Harder AV, et al and International Headache Genetics Consortium. Migraine, inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Headache. 2023;63:642-651. doi: 10.1111/head.14470 Source
Additionally, several recently published reviews have examined the risks of comorbidities that are not neurologic or cardiovascular, such as allergies, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Although these types of associations are not inherently obvious in terms of migraine pathophysiology, determining whether there is a link may help shed a light on some contributing factors that could play a role in migraine or in the comorbid disorders.
Authors of a study published in the January 2024 issue of the European Journal of Medical Research sought to examine the relationship between allergic rhinitis and migraine. They noted that several studies, as well as a statement from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study, published in 2013, reported an increased frequency of migraines in patients with allergic rhinitis. The researchers used data extracted from the UK Biobank, comprising 25,486 patients diagnosed with allergic rhinitis and 87,097 controls and 8547 migraine cases and 176,107 controls. They performed statistical analysis using bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization with publicly available summary-level statistics of large genome-wide association studies to estimate the possible causal effects. The researchers did not find any clear causal or genetic association between allergic rhinitis and migraine risk. However, the lack of causation between migraine and allergic rhinitis does not contradict previous studies that point to the prevalence of comorbidity of the two conditions. It's also important to note that congestion is a known migraine trigger, and the results of the study do not contradict that relationship. Given the variability of results from different research studies, the authors suggested that more research is warranted to help untangle the complex association between allergic rhinitis and migraine.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is another condition with a higher prevalence in patients who have migraine. A January 2024 article in Scientific Reports described the results of a nationwide population-based study that was conducted using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. This study included 10,131,193 individuals. The researchers found that the risk for development of IBD in patients with migraine was significantly higher, by 1.3 times, compared with the general population. These results are similar to previous studies, such as a meta-analysis published in May 2023 in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine, which reported a pooled prevalence of migraine in IBD cases of 19%, with 1.5-fold higher odds of developing migraine in IBD cases when compared with controls.[3] These studies were both aimed at examining epidemiologic data rather than uncovering a physiologic or genetic cause of the link, and neither study described an explanation for this connection.
A Mendelian randomization study published in May 2023 in Headache investigated potential genetic links between migraine and IBD. As with the January 2024 European Journal of Medical Research study that was done to search for a genetic association between migraine and allergic rhinitis, the authors stated that there was no evidence of a shared genetic basis or of a causal association between migraine and either IBD or celiac disease.[4] Although the evidence doesn't point to a causal relationship, it's important to note that diet plays a role in migraine management, and diet is especially important in managing IBD. Consideration of dietary factors could be beneficial for preventing symptoms — and is even more important for avoiding exacerbation of symptoms.
A high body mass index (BMI) is correlated with migraine. A study published in January 2024 in BMC Geriatrics analyzed data from people who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 1999 and 2004 by the Centers for Disease Control and the National Center for Health Statistics, comprising a total of 31,126 participants. The researchers found a linear association between BMI and migraine. They also noted that increased BMI was related to a significantly higher risk for migraine in the group with diabetes, but this positive relationship between BMI and migraine seemed to be smaller in the group without diabetes. The authors considered inflammation associated with obesity as a possible contributing factor for this link but acknowledged that the pathophysiologic mechanism is unknown and suggested that there is a high likelihood of confounding factors. Given that diabetes and obesity are both correlated with an increased risk for vascular disease and migraine is associated with a slight increase in cardiovascular risk, it could be especially important to identify these comorbidities in individual patients.
Migraine is common, and many comorbidities have been verified with population studies. Although there are some explanations for the links between migraine and vascular or neurologic conditions, the cause of associations between migraine and other conditions is not known. Some theories that have begun to be investigated include inflammation and genetics. Eventually, further research and understanding of contributing factors could potentially provide explanations that may help in diagnosing migraine or associated disorders at an early stage — and might even be used to help guide treatment.
Additional References
1. Ashina M, Katsarava Z, Do TP, et al. Migraine: Epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet. 2021;397:1485-1495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32160-7 Source
2. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: Epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37:631-649. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001 Source
3. Olfati H, Mirmosayyeb O, Hosseinabadi AM, Ghajarzadeh M. The prevalence of migraine in inflammatory bowel disease, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Prev Med. 2023;14:66. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_413_21 Source
4. Welander NZ, Rukh G, Rask-Andersen M, Harder AV, et al and International Headache Genetics Consortium. Migraine, inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Headache. 2023;63:642-651. doi: 10.1111/head.14470 Source
Additionally, several recently published reviews have examined the risks of comorbidities that are not neurologic or cardiovascular, such as allergies, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Although these types of associations are not inherently obvious in terms of migraine pathophysiology, determining whether there is a link may help shed a light on some contributing factors that could play a role in migraine or in the comorbid disorders.
Authors of a study published in the January 2024 issue of the European Journal of Medical Research sought to examine the relationship between allergic rhinitis and migraine. They noted that several studies, as well as a statement from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study, published in 2013, reported an increased frequency of migraines in patients with allergic rhinitis. The researchers used data extracted from the UK Biobank, comprising 25,486 patients diagnosed with allergic rhinitis and 87,097 controls and 8547 migraine cases and 176,107 controls. They performed statistical analysis using bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization with publicly available summary-level statistics of large genome-wide association studies to estimate the possible causal effects. The researchers did not find any clear causal or genetic association between allergic rhinitis and migraine risk. However, the lack of causation between migraine and allergic rhinitis does not contradict previous studies that point to the prevalence of comorbidity of the two conditions. It's also important to note that congestion is a known migraine trigger, and the results of the study do not contradict that relationship. Given the variability of results from different research studies, the authors suggested that more research is warranted to help untangle the complex association between allergic rhinitis and migraine.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is another condition with a higher prevalence in patients who have migraine. A January 2024 article in Scientific Reports described the results of a nationwide population-based study that was conducted using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. This study included 10,131,193 individuals. The researchers found that the risk for development of IBD in patients with migraine was significantly higher, by 1.3 times, compared with the general population. These results are similar to previous studies, such as a meta-analysis published in May 2023 in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine, which reported a pooled prevalence of migraine in IBD cases of 19%, with 1.5-fold higher odds of developing migraine in IBD cases when compared with controls.[3] These studies were both aimed at examining epidemiologic data rather than uncovering a physiologic or genetic cause of the link, and neither study described an explanation for this connection.
A Mendelian randomization study published in May 2023 in Headache investigated potential genetic links between migraine and IBD. As with the January 2024 European Journal of Medical Research study that was done to search for a genetic association between migraine and allergic rhinitis, the authors stated that there was no evidence of a shared genetic basis or of a causal association between migraine and either IBD or celiac disease.[4] Although the evidence doesn't point to a causal relationship, it's important to note that diet plays a role in migraine management, and diet is especially important in managing IBD. Consideration of dietary factors could be beneficial for preventing symptoms — and is even more important for avoiding exacerbation of symptoms.
A high body mass index (BMI) is correlated with migraine. A study published in January 2024 in BMC Geriatrics analyzed data from people who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 1999 and 2004 by the Centers for Disease Control and the National Center for Health Statistics, comprising a total of 31,126 participants. The researchers found a linear association between BMI and migraine. They also noted that increased BMI was related to a significantly higher risk for migraine in the group with diabetes, but this positive relationship between BMI and migraine seemed to be smaller in the group without diabetes. The authors considered inflammation associated with obesity as a possible contributing factor for this link but acknowledged that the pathophysiologic mechanism is unknown and suggested that there is a high likelihood of confounding factors. Given that diabetes and obesity are both correlated with an increased risk for vascular disease and migraine is associated with a slight increase in cardiovascular risk, it could be especially important to identify these comorbidities in individual patients.
Migraine is common, and many comorbidities have been verified with population studies. Although there are some explanations for the links between migraine and vascular or neurologic conditions, the cause of associations between migraine and other conditions is not known. Some theories that have begun to be investigated include inflammation and genetics. Eventually, further research and understanding of contributing factors could potentially provide explanations that may help in diagnosing migraine or associated disorders at an early stage — and might even be used to help guide treatment.
Additional References
1. Ashina M, Katsarava Z, Do TP, et al. Migraine: Epidemiology and systems of care. Lancet. 2021;397:1485-1495. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32160-7 Source
2. Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: Epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37:631-649. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2019.06.001 Source
3. Olfati H, Mirmosayyeb O, Hosseinabadi AM, Ghajarzadeh M. The prevalence of migraine in inflammatory bowel disease, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Prev Med. 2023;14:66. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_413_21 Source
4. Welander NZ, Rukh G, Rask-Andersen M, Harder AV, et al and International Headache Genetics Consortium. Migraine, inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Headache. 2023;63:642-651. doi: 10.1111/head.14470 Source
Prenatal Prescription Opioids Tied to Increased Risk for Preterm Birth
TOPLINE:
Taking a prescription opioid for pain management during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth, data from a new case-control study of over 25,000 Medicaid patients showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed data on pregnant patients enrolled in Tennessee Medicaid who experienced birth of a single baby at ≥ 24 weeks gestation (25,391 with opioid use disorder and 225,696 without).
- Median age of participants was 23 years; 58.1% were non-Hispanic White, 38.7% Black, 2.6% Hispanic, and 0.5% Asian.
- Controls were matched based on pregnancy start date, race, ethnicity, age at delivery (within 2 years), and history of prior preterm birth.
- Sensitivity analysis included the exclusion of opioid prescriptions dispensed within 3 days of the index date to account for potential opioid prescribing associated with labor pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 18,702 patients (7.4%) filled an opioid prescription during the 60 days prior to the index date.
- Each doubling of opioid morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) prescribed during the 60 days was associated with a 4% increase in the odds of spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure in the matched controls (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.04; 95% CI, 1.01-1.08).
- Overall, 1573 pregnancies filled prescriptions for 900 MMEs or greater, which was associated with at least a 21% increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure (aOR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.10-1.33).
- Researchers found no significant difference in odds of spontaneous preterm birth among included opioid types after adjusting for confounders and opioid MMD.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association may appear modest, especially considering that common, one-time prescriptions often fall in the 150-225 MME range, but these findings may provide more caution when prescribing multiple, higher strength opioids,” the authors wrote. “We also caution against the conclusion that lower doses, especially those below 100 MME, are safe; the confidence bands over the low dose range still include odds ratios that are consistent with meaningful harm.”
SOURCE:
Sarah S. Osmundson, MD, MS, of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, was the senior and corresponding author on the study. The study was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data are based on opioids prescribed and lack detail on actual use of opioids and nonprescription analgesics. Findings may not be generalizable to other populations or settings outside Medicaid.
DISCLOSURES:
No source of study funding listed. Dr. Osmundson reported receiving grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Taking a prescription opioid for pain management during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth, data from a new case-control study of over 25,000 Medicaid patients showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed data on pregnant patients enrolled in Tennessee Medicaid who experienced birth of a single baby at ≥ 24 weeks gestation (25,391 with opioid use disorder and 225,696 without).
- Median age of participants was 23 years; 58.1% were non-Hispanic White, 38.7% Black, 2.6% Hispanic, and 0.5% Asian.
- Controls were matched based on pregnancy start date, race, ethnicity, age at delivery (within 2 years), and history of prior preterm birth.
- Sensitivity analysis included the exclusion of opioid prescriptions dispensed within 3 days of the index date to account for potential opioid prescribing associated with labor pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 18,702 patients (7.4%) filled an opioid prescription during the 60 days prior to the index date.
- Each doubling of opioid morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) prescribed during the 60 days was associated with a 4% increase in the odds of spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure in the matched controls (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.04; 95% CI, 1.01-1.08).
- Overall, 1573 pregnancies filled prescriptions for 900 MMEs or greater, which was associated with at least a 21% increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure (aOR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.10-1.33).
- Researchers found no significant difference in odds of spontaneous preterm birth among included opioid types after adjusting for confounders and opioid MMD.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association may appear modest, especially considering that common, one-time prescriptions often fall in the 150-225 MME range, but these findings may provide more caution when prescribing multiple, higher strength opioids,” the authors wrote. “We also caution against the conclusion that lower doses, especially those below 100 MME, are safe; the confidence bands over the low dose range still include odds ratios that are consistent with meaningful harm.”
SOURCE:
Sarah S. Osmundson, MD, MS, of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, was the senior and corresponding author on the study. The study was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data are based on opioids prescribed and lack detail on actual use of opioids and nonprescription analgesics. Findings may not be generalizable to other populations or settings outside Medicaid.
DISCLOSURES:
No source of study funding listed. Dr. Osmundson reported receiving grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Taking a prescription opioid for pain management during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth, data from a new case-control study of over 25,000 Medicaid patients showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers retrospectively reviewed data on pregnant patients enrolled in Tennessee Medicaid who experienced birth of a single baby at ≥ 24 weeks gestation (25,391 with opioid use disorder and 225,696 without).
- Median age of participants was 23 years; 58.1% were non-Hispanic White, 38.7% Black, 2.6% Hispanic, and 0.5% Asian.
- Controls were matched based on pregnancy start date, race, ethnicity, age at delivery (within 2 years), and history of prior preterm birth.
- Sensitivity analysis included the exclusion of opioid prescriptions dispensed within 3 days of the index date to account for potential opioid prescribing associated with labor pain.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 18,702 patients (7.4%) filled an opioid prescription during the 60 days prior to the index date.
- Each doubling of opioid morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) prescribed during the 60 days was associated with a 4% increase in the odds of spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure in the matched controls (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.04; 95% CI, 1.01-1.08).
- Overall, 1573 pregnancies filled prescriptions for 900 MMEs or greater, which was associated with at least a 21% increased risk for spontaneous preterm birth compared with no opioid exposure (aOR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.10-1.33).
- Researchers found no significant difference in odds of spontaneous preterm birth among included opioid types after adjusting for confounders and opioid MMD.
IN PRACTICE:
“This association may appear modest, especially considering that common, one-time prescriptions often fall in the 150-225 MME range, but these findings may provide more caution when prescribing multiple, higher strength opioids,” the authors wrote. “We also caution against the conclusion that lower doses, especially those below 100 MME, are safe; the confidence bands over the low dose range still include odds ratios that are consistent with meaningful harm.”
SOURCE:
Sarah S. Osmundson, MD, MS, of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, was the senior and corresponding author on the study. The study was published online on February 14 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Data are based on opioids prescribed and lack detail on actual use of opioids and nonprescription analgesics. Findings may not be generalizable to other populations or settings outside Medicaid.
DISCLOSURES:
No source of study funding listed. Dr. Osmundson reported receiving grant support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse during the conduct of the study. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.