User login
Republican or Democrat, Americans vote for face masks
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.
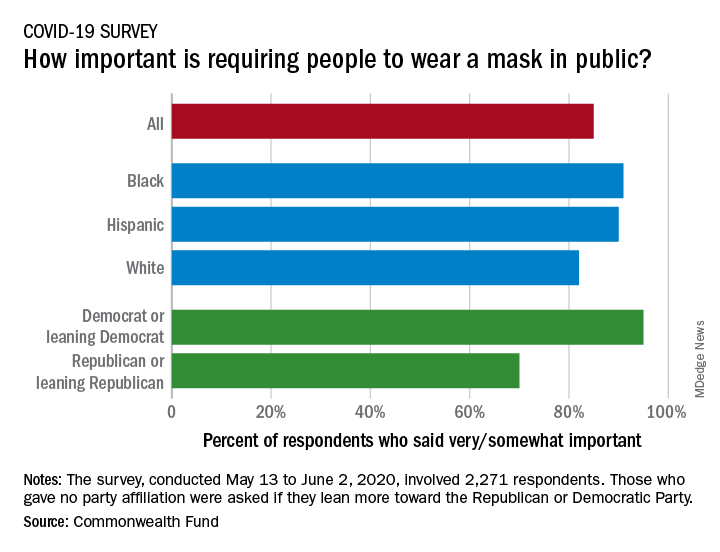
Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Most Americans support the required use of face masks in public, along with universal COVID-19 testing, to provide a safe work environment during the pandemic, according to a new report from the Commonwealth Fund.

Results of a recent survey show that 85% of adults believe that it is very or somewhat important to require everyone to wear a face mask “at work, when shopping, and on public transportation,” said Sara R. Collins, PhD, vice president for health care coverage and access at the fund, and associates.
In that survey, conducted from May 13 to June 2, 2020, and involving 2,271 respondents, regular COVID-19 testing for everyone was supported by 81% of the sample as way to ensure a safe work environment until a vaccine is available, the researchers said in the report.
Support on both issues was consistently high across both racial/ethnic and political lines. Mandatory mask use gained 91% support among black respondents, 90% in Hispanics, and 82% in whites. There was greater distance between the political parties, but 70% of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents support mask use, compared with 95% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents, they said.
Regarding regular testing, 66% of Republicans and those leaning Republican said that it was very/somewhat important to ensure a safe work environment, as did 91% on the Democratic side. Hispanics offered the most support by race/ethnicity, with 90% saying that testing was very/somewhat important, compared with 86% of black respondents and 78% of white respondents, Dr. Collins and associates said.
Two-thirds of Republicans said that it was very/somewhat important for the government to trace the contacts of any person who tested positive for COVID-19, a sentiment shared by 91% of Democrats. That type of tracing was supported by 88% of blacks, 85% of Hispanics, and 79% of whites, based on the polling results.
The survey, conducted for the Commonwealth Fund by the survey and market research firm SSRS, had a margin of error of ± 2.4 percentage points.
Letter from the Board of Editors: Call to action (again)
This editorial is the first to be published in GI & Hepatology News since the murder of George Floyd in Minneapolis. The corner of 38th and Chicago is 9 miles from my home in Bloomington, Minn. This corner became the epicenter of protests that have spread around the nation and world. Early on, protests were accompanied by widespread riots, looting, and destruction. In the ensuing weeks, this corner has become a memorial for Mr. Floyd and a place where people now go to reflect, pray, pay tribute, and pledge to work for change.
A coalition of willing businesses has formed in the area around 38th and Chicago. The largest employer in the area is Allina Health (I sit on the Governing Board of Allina Health). Our flagship hospital is 8 blocks from the site of George Floyd’s memorial. We will be a change leader by committing funds for local rebuilding, ensuring use of construction firms that promote minority workers (as was done when the Viking’s stadium was built), examining our investment portfolio with racial equity as one guiding principle, increasing our focus on barriers to access, enhancing equity education of our workforce, and working with city and state leaders to promote police reform.
As the Editor in Chief of the official newspaper of the AGA, I invited our board of editors to stand united in our condemnation of the racial injustices that led to the protests we now see. We each agree with the message from the combined Governing Boards of our GI societies (published June 2, 2020) stating “As health care providers, we have dedicated our lives to caring for our fellow human beings. Therefore, we are compelled to speak out against any treatment that results in unacceptable disparities that marginalize the vulnerable among us.”
Our responsibility as editors is to guide the content we deliver, ensuring its relevancy to our readers. In this light, we commit to delivering content that highlights racial injustices and health disparities for all people, as we seek to understand the many factors that result in barriers to health. We will emphasize content that leads to impactful change and will highlight progress we make as a specialty. We hope our collective work will help ensure that George Floyd’s memory, and the memories of all such victims, become a catalyst for permanent cultural change.
Editor in Chief, GI & Hepatology News
John I. Allen, MD, MBA, AGAF
Editor in Chief, The New Gastroenterologist
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Associate Editors
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Kim L. Isaacs, MD, PhD, AGAF
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc
Larry R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF
Sonia S. Kupfer, MD
Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD
This editorial is the first to be published in GI & Hepatology News since the murder of George Floyd in Minneapolis. The corner of 38th and Chicago is 9 miles from my home in Bloomington, Minn. This corner became the epicenter of protests that have spread around the nation and world. Early on, protests were accompanied by widespread riots, looting, and destruction. In the ensuing weeks, this corner has become a memorial for Mr. Floyd and a place where people now go to reflect, pray, pay tribute, and pledge to work for change.
A coalition of willing businesses has formed in the area around 38th and Chicago. The largest employer in the area is Allina Health (I sit on the Governing Board of Allina Health). Our flagship hospital is 8 blocks from the site of George Floyd’s memorial. We will be a change leader by committing funds for local rebuilding, ensuring use of construction firms that promote minority workers (as was done when the Viking’s stadium was built), examining our investment portfolio with racial equity as one guiding principle, increasing our focus on barriers to access, enhancing equity education of our workforce, and working with city and state leaders to promote police reform.
As the Editor in Chief of the official newspaper of the AGA, I invited our board of editors to stand united in our condemnation of the racial injustices that led to the protests we now see. We each agree with the message from the combined Governing Boards of our GI societies (published June 2, 2020) stating “As health care providers, we have dedicated our lives to caring for our fellow human beings. Therefore, we are compelled to speak out against any treatment that results in unacceptable disparities that marginalize the vulnerable among us.”
Our responsibility as editors is to guide the content we deliver, ensuring its relevancy to our readers. In this light, we commit to delivering content that highlights racial injustices and health disparities for all people, as we seek to understand the many factors that result in barriers to health. We will emphasize content that leads to impactful change and will highlight progress we make as a specialty. We hope our collective work will help ensure that George Floyd’s memory, and the memories of all such victims, become a catalyst for permanent cultural change.
Editor in Chief, GI & Hepatology News
John I. Allen, MD, MBA, AGAF
Editor in Chief, The New Gastroenterologist
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Associate Editors
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Kim L. Isaacs, MD, PhD, AGAF
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc
Larry R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF
Sonia S. Kupfer, MD
Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD
This editorial is the first to be published in GI & Hepatology News since the murder of George Floyd in Minneapolis. The corner of 38th and Chicago is 9 miles from my home in Bloomington, Minn. This corner became the epicenter of protests that have spread around the nation and world. Early on, protests were accompanied by widespread riots, looting, and destruction. In the ensuing weeks, this corner has become a memorial for Mr. Floyd and a place where people now go to reflect, pray, pay tribute, and pledge to work for change.
A coalition of willing businesses has formed in the area around 38th and Chicago. The largest employer in the area is Allina Health (I sit on the Governing Board of Allina Health). Our flagship hospital is 8 blocks from the site of George Floyd’s memorial. We will be a change leader by committing funds for local rebuilding, ensuring use of construction firms that promote minority workers (as was done when the Viking’s stadium was built), examining our investment portfolio with racial equity as one guiding principle, increasing our focus on barriers to access, enhancing equity education of our workforce, and working with city and state leaders to promote police reform.
As the Editor in Chief of the official newspaper of the AGA, I invited our board of editors to stand united in our condemnation of the racial injustices that led to the protests we now see. We each agree with the message from the combined Governing Boards of our GI societies (published June 2, 2020) stating “As health care providers, we have dedicated our lives to caring for our fellow human beings. Therefore, we are compelled to speak out against any treatment that results in unacceptable disparities that marginalize the vulnerable among us.”
Our responsibility as editors is to guide the content we deliver, ensuring its relevancy to our readers. In this light, we commit to delivering content that highlights racial injustices and health disparities for all people, as we seek to understand the many factors that result in barriers to health. We will emphasize content that leads to impactful change and will highlight progress we make as a specialty. We hope our collective work will help ensure that George Floyd’s memory, and the memories of all such victims, become a catalyst for permanent cultural change.
Editor in Chief, GI & Hepatology News
John I. Allen, MD, MBA, AGAF
Editor in Chief, The New Gastroenterologist
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Associate Editors
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Ziad Gellad, MD, MPH, AGAF
Kim L. Isaacs, MD, PhD, AGAF
Charles J. Kahi, MD, MS, AGAF
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc
Larry R. Kosinski, MD, MBA, AGAF
Sonia S. Kupfer, MD
Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD
Zoledronic acid fails to impact abdominal aortic calcification
A single yearly dose of zoledronic acid had no impact on the progression of abdominal aortic calcification in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, based on data from 502 women.
Although bisphosphonates have been shown to reduce the formation and progression of vascular calcification in animal studies, the impact on aortic calcification in humans has not been studied, wrote Guoqi Cai, PhD, of the University of Tasmania, Australia, and colleagues.
In a post hoc analysis published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from the HORIZON Pivotal Fracture trial of women with osteoporosis.
The study population included 234 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received an annual infusion of 5 mg zoledronic acid (ZA) and 268 who received a placebo. The mean age of the women was 72.5 years. Overall, abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) was present in 292 women (58%) at baseline, defined as an AAC score greater than 0, and AAC scores were similar between the intervention and placebo groups.
Over 3 years, AAC progressed similarly between the ZA and placebo groups (29% and 31%, respectively). Progression was defined as an increase in AAC score, which was measured by comparing spinal x-rays at baseline and after 3 years. In a subgroup analysis, progression of AAC was similar between the ZA and placebo groups with and without baseline AAC.
“The lack of effect on the progression of vascular calcification with zoledronic acid treatment in this study does not rule out a potential role of bisphosphonates in reducing cardiovascular mortality mediated through other mechanisms,” the researchers noted.
No correlation appeared between change in AAC score and change in bone mineral density at the total hip and femoral neck during the study period in any of the groups.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the post hoc analysis, potential lack of sensitivity of the AAC-8 scale in measuring small AAC changes, and homogenous study population, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first to examine the impact of zoledronic acid on aortic calcification in humans, and was strengthened by the randomized design, the researchers said. Although other studies on the impact of bisphosphonates on vascular calcification have been inconsistent, the “finding that zoledronic acid was not protective against vascular calcification agrees with previous trials of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates conducted in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” as well as chronic kidney disease patients and renal transplant patients, they said.
“Thus, our findings do not support the use of zoledronic acid for the treatment of vascular calcification,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Novartis. Dr. Cai had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Cai G. et al. Osteoporosis Int. 2020 May 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05430-z.
A single yearly dose of zoledronic acid had no impact on the progression of abdominal aortic calcification in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, based on data from 502 women.
Although bisphosphonates have been shown to reduce the formation and progression of vascular calcification in animal studies, the impact on aortic calcification in humans has not been studied, wrote Guoqi Cai, PhD, of the University of Tasmania, Australia, and colleagues.
In a post hoc analysis published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from the HORIZON Pivotal Fracture trial of women with osteoporosis.
The study population included 234 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received an annual infusion of 5 mg zoledronic acid (ZA) and 268 who received a placebo. The mean age of the women was 72.5 years. Overall, abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) was present in 292 women (58%) at baseline, defined as an AAC score greater than 0, and AAC scores were similar between the intervention and placebo groups.
Over 3 years, AAC progressed similarly between the ZA and placebo groups (29% and 31%, respectively). Progression was defined as an increase in AAC score, which was measured by comparing spinal x-rays at baseline and after 3 years. In a subgroup analysis, progression of AAC was similar between the ZA and placebo groups with and without baseline AAC.
“The lack of effect on the progression of vascular calcification with zoledronic acid treatment in this study does not rule out a potential role of bisphosphonates in reducing cardiovascular mortality mediated through other mechanisms,” the researchers noted.
No correlation appeared between change in AAC score and change in bone mineral density at the total hip and femoral neck during the study period in any of the groups.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the post hoc analysis, potential lack of sensitivity of the AAC-8 scale in measuring small AAC changes, and homogenous study population, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first to examine the impact of zoledronic acid on aortic calcification in humans, and was strengthened by the randomized design, the researchers said. Although other studies on the impact of bisphosphonates on vascular calcification have been inconsistent, the “finding that zoledronic acid was not protective against vascular calcification agrees with previous trials of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates conducted in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” as well as chronic kidney disease patients and renal transplant patients, they said.
“Thus, our findings do not support the use of zoledronic acid for the treatment of vascular calcification,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Novartis. Dr. Cai had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Cai G. et al. Osteoporosis Int. 2020 May 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05430-z.
A single yearly dose of zoledronic acid had no impact on the progression of abdominal aortic calcification in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, based on data from 502 women.
Although bisphosphonates have been shown to reduce the formation and progression of vascular calcification in animal studies, the impact on aortic calcification in humans has not been studied, wrote Guoqi Cai, PhD, of the University of Tasmania, Australia, and colleagues.
In a post hoc analysis published in Osteoporosis International, the researchers reviewed data from the HORIZON Pivotal Fracture trial of women with osteoporosis.
The study population included 234 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who received an annual infusion of 5 mg zoledronic acid (ZA) and 268 who received a placebo. The mean age of the women was 72.5 years. Overall, abdominal aortic calcification (AAC) was present in 292 women (58%) at baseline, defined as an AAC score greater than 0, and AAC scores were similar between the intervention and placebo groups.
Over 3 years, AAC progressed similarly between the ZA and placebo groups (29% and 31%, respectively). Progression was defined as an increase in AAC score, which was measured by comparing spinal x-rays at baseline and after 3 years. In a subgroup analysis, progression of AAC was similar between the ZA and placebo groups with and without baseline AAC.
“The lack of effect on the progression of vascular calcification with zoledronic acid treatment in this study does not rule out a potential role of bisphosphonates in reducing cardiovascular mortality mediated through other mechanisms,” the researchers noted.
No correlation appeared between change in AAC score and change in bone mineral density at the total hip and femoral neck during the study period in any of the groups.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the post hoc analysis, potential lack of sensitivity of the AAC-8 scale in measuring small AAC changes, and homogenous study population, the researchers noted.
However, the study is the first to examine the impact of zoledronic acid on aortic calcification in humans, and was strengthened by the randomized design, the researchers said. Although other studies on the impact of bisphosphonates on vascular calcification have been inconsistent, the “finding that zoledronic acid was not protective against vascular calcification agrees with previous trials of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates conducted in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis,” as well as chronic kidney disease patients and renal transplant patients, they said.
“Thus, our findings do not support the use of zoledronic acid for the treatment of vascular calcification,” they concluded.
The study was supported by Novartis. Dr. Cai had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Cai G. et al. Osteoporosis Int. 2020 May 2. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05430-z.
FROM OSTEOPOROSIS INTERNATIONAL
Triple inhaler combo quells COPD exacerbations
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
Phase 3 trial findings compared outcomes for COPD patients who had triple fixed-dose inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist with patients who received one of two dual-therapy combinations. The results were presented at the American Thoracic Society’s virtual clinical trial session.
A total of 8,509 patients were randomized on a 1:1:1:1 basis to receive twice daily:
- Single-inhaler combinations of the inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) budesonide at one of two doses, the long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrrolate, and the long-acting beta2 agonist (LABA) formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination glycopyrrolate and formoterol.
- Dual-therapy combination budesonide and formoterol.
The annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations was 1.08 and 1.07 for the triple combinations with 320 mcg and 180 mcg doses of budesonide, respectively, compared with 1.42 for glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and 1.24 for budesonide-formoterol.
Both triple combinations were significantly superior to the dual therapies for controlling exacerbations, reported Klaus F. Rabe, MD, PhD, from LungenClinic Grosshansdorf and Christian-Albrechts University Kiel (Germany), and colleagues in the ETHOS (Efficacy and Safety of Triple Therapy in Obstructive Lung Disease) trial (NCT02465567).
“Our findings show the benefits of triple therapy with a budesonide-glycopyrrolate-formoterol combination over dual therapy with a LAMA-LABA or an inhaled glucocorticoid-LABA combination with respect to the annual rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations, symptoms, and health-related quality of life in patients with moderate to very-severe COPD who are at risk of exacerbations,” they wrote in a study published online in the New England Journal of Medicine..
The trial showed for the first time that “triple therapy that has half the dose of steroid compared to a standard ICS/LABA combination has had greater efficacy for the exacerbation endpoint,” Dr. Rabe said during his presentation.
Triple-therapy combinations with an ICS, LAMA, and LABA are recommended for patients with COPD who remain symptomatic or experience further exacerbations on dual–ICS/LABA or –LAMA/LABA combinations. The triple combinations have been shown in several studies to lower risk of exacerbations and are associated with both better lung function and health-related quality of life, compared with dual therapies, the investigators noted.
However, concerns about adverse events associated with long-term ICS use – including pneumonia, cataracts, and increased fracture risk, possibly related to treatment duration, dose level, or type of corticosteroid used – spurred the ETHOS investigators to compare triple and dual fixed-dose combinations for efficacy and safety over 1 year.
Large study
They enrolled 8,509 adults aged 40-80 years with symptomatic COPD (defined as score of 10 or higher on the 40-point COPD Assessment Test). All patients were receiving at least two inhaled maintenance therapies at the time of screening, and had a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) to forced vital capacity of less than 0.7, with a postbronchodilator FEV1 of 25%-65% of the predicted normal value. The patients all had a smoking history of at least 10 pack-years and a documented history of at least one moderate or severe COPD exacerbation in the year before screening.
The patients were randomized in equal proportions to receive triple therapy with budesonide at 320- or 160-mcg doses plus glycopyrrolate 18 mcg, and formoterol 9.6 mcg twice daily, or to dual therapy with either glycopyrrolate plus formoterol at the same doses, or 320 mcg budesonide plus 9.6 mcg formoterol.
As noted, for the primary endpoint of the estimated annual rate of moderate or severe exacerbations, the triple combinations were associated with significantly lower rates, with a 24% lower rate (rate ratio, 0.76) with 320 mcg budesonide triple therapy, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 13% lower rate (RR, 0.87), compared with budesonide formoterol (P < .001 and P = .003, respectively).
The triple combination with the 160-mcg budesonide dose was associated with a 25% lower annual rate of exacerbations (RR, 0.75) vs. glycopyrrolate-formoterol, and a 14% lower rate (RR, 0.86) vs. budesonide-formoterol (P < .001 and P = .002, respectively).
Secondary efficacy endpoints also favored the triple combination, including a 20% lower rate ratio of severe exacerbations over 52 weeks for the 320-mcg budesonide group, compared with the budesonide-formoterol group (P = .02).
The 320-mcg dose combination was also associated with a 46% lower risk for all-cause mortality, compared with glycopyrrolate-formoterol (hazard ratio, 0.54; P = .0111).
Confirmed pneumonia was seen in 4.2% of patients on the 320-mcg budesonide dose, 3.5% of those in the 160-mcg group, and 4.5% of patients treated with budesonide-formoterol. The incidence of any adverse effect was similar across the treatment groups, ranging from 61.7% to 64.5%.
Balance exacerbation, pneumonia risk
In the question-and-answer session following his online presentation, Dr. Rabe was asked how the investigators reconciled their data showing increased incidence of pneumonia in budenoside-containing formulations with claims by the maker of the budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort, AstraZeneca) that budesonide is not associated with increased risk of pneumonia.
“We have to say that there are individuals that we have to balance the benefit of [less] exacerbation against the risk of pneumonia,” he replied, but noted that the size of the effect, observed both in ETHOS and in the KRONOS trial, was relatively small.
“This definitely adds some information for us to think about when we’re trying to do risk-benefit analysis,” commented MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS, from the University of Michigan, who moderated the session but was not involved in the study.
The ETHOS trial was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Rabe disclosed consulting/advisory board activity with that company and others. Dr. Han has previously disclosed consulting/advising and research funding relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Rabe KF et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1916046.
FROM ATS 2020
Real-world data support adjuvant immunotherapy for stage III melanoma
Among patients with stage IIIC disease, the 2-year survival rate was 70% in those who received immunotherapy and 59% in those who did not (P < .01). The median overall survival in this group was 32.8 months with immunotherapy and 28 months without it (P < .01).
Among patients with stage IIIA disease, the 2-year survival rate was 94% with immunotherapy and 91% without it (P = .03).
There was a trend toward a 2-year survival benefit with immunotherapy in patients with stage IIIB disease and in all 4,094 stage III patients, but the differences were not significant. The 2-year survival rate was 84% with immunotherapy and 81% without it among patients with stage IIIB disease (P = .35). The survival rates were 83% and 80%, respectively, in all stage III patients (P = .051).
This was an early analysis, noted investigator Justin Moyers, MD, of Loma Linda (Calif.) University. Ipilimumab was approved as adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma patients in 2015, the year patients from this analysis were diagnosed.
“There’s really only 2 full years of survival data,” Dr. Moyers said. “I think given time, we will see a benefit amongst all the substages.”
In the meantime, “I would definitely not use this data to say whether or not [immunotherapy] should be given,” Dr. Moyers said.
The researchers were just using the database – which captures 52% of U.S. melanoma cases – to see if “real-world data mimics the clinical trial data,” Dr. Moyers said.
Overall, the findings support “adjuvant immunotherapy in the real-world setting,” he said.
The researchers also looked at treatment patterns in 2015-2016 across 8,160 patients with stage III melanoma, 4,094 of whom were included in the aforementioned survival analysis. There were 2,260 patients (27.7%) who received immunotherapy after surgery during that time period.
Uptake of adjuvant immunotherapy “was low to start, but those patients did better than ones who did not get” it, said AACR president Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
Immunotherapy recipients were younger, on average (54.8 years vs. 62.4 years). Patients with Charlson comorbidity scores above zero and those on Medicare were less likely to receive immunotherapy (18.4% Medicare vs. over 30% with other payers). There also were trends of decreased use with lower income and lower high school graduation rates.
The finding “highlights the negative impact of socioeconomic [factors] on access to proven therapy,” Dr. Ribas said.
As for low use among Medicare patients, uptake of new treatments, in general, “seems to be faster with private insurance,” he noted.
The study excluded patients who received systemic therapies other than immunotherapy, as well as those who received immunotherapy before surgery. Among study limitations, the specific immunotherapies patients received was unknown.
There was no external funding for this study. Dr. Moyers reported travel compensation from Astellas Pharmaceuticals in 2018. Dr. Ribas disclosed relationships with Amgen, Chugai, Merck, Sanofi, Tango, Arcus, Bioncotech, Compugen, CytomX, FLX Bio, ImaginAb, Isoplexis, Merus, Rgenix, and PACT.
SOURCE: Moyers J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 4338.
Among patients with stage IIIC disease, the 2-year survival rate was 70% in those who received immunotherapy and 59% in those who did not (P < .01). The median overall survival in this group was 32.8 months with immunotherapy and 28 months without it (P < .01).
Among patients with stage IIIA disease, the 2-year survival rate was 94% with immunotherapy and 91% without it (P = .03).
There was a trend toward a 2-year survival benefit with immunotherapy in patients with stage IIIB disease and in all 4,094 stage III patients, but the differences were not significant. The 2-year survival rate was 84% with immunotherapy and 81% without it among patients with stage IIIB disease (P = .35). The survival rates were 83% and 80%, respectively, in all stage III patients (P = .051).
This was an early analysis, noted investigator Justin Moyers, MD, of Loma Linda (Calif.) University. Ipilimumab was approved as adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma patients in 2015, the year patients from this analysis were diagnosed.
“There’s really only 2 full years of survival data,” Dr. Moyers said. “I think given time, we will see a benefit amongst all the substages.”
In the meantime, “I would definitely not use this data to say whether or not [immunotherapy] should be given,” Dr. Moyers said.
The researchers were just using the database – which captures 52% of U.S. melanoma cases – to see if “real-world data mimics the clinical trial data,” Dr. Moyers said.
Overall, the findings support “adjuvant immunotherapy in the real-world setting,” he said.
The researchers also looked at treatment patterns in 2015-2016 across 8,160 patients with stage III melanoma, 4,094 of whom were included in the aforementioned survival analysis. There were 2,260 patients (27.7%) who received immunotherapy after surgery during that time period.
Uptake of adjuvant immunotherapy “was low to start, but those patients did better than ones who did not get” it, said AACR president Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
Immunotherapy recipients were younger, on average (54.8 years vs. 62.4 years). Patients with Charlson comorbidity scores above zero and those on Medicare were less likely to receive immunotherapy (18.4% Medicare vs. over 30% with other payers). There also were trends of decreased use with lower income and lower high school graduation rates.
The finding “highlights the negative impact of socioeconomic [factors] on access to proven therapy,” Dr. Ribas said.
As for low use among Medicare patients, uptake of new treatments, in general, “seems to be faster with private insurance,” he noted.
The study excluded patients who received systemic therapies other than immunotherapy, as well as those who received immunotherapy before surgery. Among study limitations, the specific immunotherapies patients received was unknown.
There was no external funding for this study. Dr. Moyers reported travel compensation from Astellas Pharmaceuticals in 2018. Dr. Ribas disclosed relationships with Amgen, Chugai, Merck, Sanofi, Tango, Arcus, Bioncotech, Compugen, CytomX, FLX Bio, ImaginAb, Isoplexis, Merus, Rgenix, and PACT.
SOURCE: Moyers J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 4338.
Among patients with stage IIIC disease, the 2-year survival rate was 70% in those who received immunotherapy and 59% in those who did not (P < .01). The median overall survival in this group was 32.8 months with immunotherapy and 28 months without it (P < .01).
Among patients with stage IIIA disease, the 2-year survival rate was 94% with immunotherapy and 91% without it (P = .03).
There was a trend toward a 2-year survival benefit with immunotherapy in patients with stage IIIB disease and in all 4,094 stage III patients, but the differences were not significant. The 2-year survival rate was 84% with immunotherapy and 81% without it among patients with stage IIIB disease (P = .35). The survival rates were 83% and 80%, respectively, in all stage III patients (P = .051).
This was an early analysis, noted investigator Justin Moyers, MD, of Loma Linda (Calif.) University. Ipilimumab was approved as adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma patients in 2015, the year patients from this analysis were diagnosed.
“There’s really only 2 full years of survival data,” Dr. Moyers said. “I think given time, we will see a benefit amongst all the substages.”
In the meantime, “I would definitely not use this data to say whether or not [immunotherapy] should be given,” Dr. Moyers said.
The researchers were just using the database – which captures 52% of U.S. melanoma cases – to see if “real-world data mimics the clinical trial data,” Dr. Moyers said.
Overall, the findings support “adjuvant immunotherapy in the real-world setting,” he said.
The researchers also looked at treatment patterns in 2015-2016 across 8,160 patients with stage III melanoma, 4,094 of whom were included in the aforementioned survival analysis. There were 2,260 patients (27.7%) who received immunotherapy after surgery during that time period.
Uptake of adjuvant immunotherapy “was low to start, but those patients did better than ones who did not get” it, said AACR president Antoni Ribas, MD, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved in the study.
Immunotherapy recipients were younger, on average (54.8 years vs. 62.4 years). Patients with Charlson comorbidity scores above zero and those on Medicare were less likely to receive immunotherapy (18.4% Medicare vs. over 30% with other payers). There also were trends of decreased use with lower income and lower high school graduation rates.
The finding “highlights the negative impact of socioeconomic [factors] on access to proven therapy,” Dr. Ribas said.
As for low use among Medicare patients, uptake of new treatments, in general, “seems to be faster with private insurance,” he noted.
The study excluded patients who received systemic therapies other than immunotherapy, as well as those who received immunotherapy before surgery. Among study limitations, the specific immunotherapies patients received was unknown.
There was no external funding for this study. Dr. Moyers reported travel compensation from Astellas Pharmaceuticals in 2018. Dr. Ribas disclosed relationships with Amgen, Chugai, Merck, Sanofi, Tango, Arcus, Bioncotech, Compugen, CytomX, FLX Bio, ImaginAb, Isoplexis, Merus, Rgenix, and PACT.
SOURCE: Moyers J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract 4338.
FROM AACR 2020
Three stages to COVID-19 brain damage, new review suggests
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In stage 1, viral damage is limited to epithelial cells of the nose and mouth, and in stage 2 blood clots that form in the lungs may travel to the brain, leading to stroke. In stage 3, the virus crosses the blood-brain barrier and invades the brain.
“Our major take-home points are that patients with COVID-19 symptoms, such as shortness of breath, headache, or dizziness, may have neurological symptoms that, at the time of hospitalization, might not be noticed or prioritized, or whose neurological symptoms may become apparent only after they leave the hospital,” lead author Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center in McLean, Va., said.
“Hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should have a neurological evaluation and ideally a brain MRI before leaving the hospital; and, if there are abnormalities, they should follow up with a neurologist in 3-4 months,” said Dr. Fotuhi, who is also affiliate staff at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
The review was published online June 8 in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Wreaks CNS havoc
It has become “increasingly evident” that SARS-CoV-2 can cause neurologic manifestations, including anosmia, seizures, stroke, confusion, encephalopathy, and total paralysis, the authors wrote.
They noted that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, which facilitates the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin. After ACE2 has bound to respiratory epithelial cells and then to epithelial cells in blood vessels, SARS-CoV-2 triggers the formation of a “cytokine storm.”
These cytokines, in turn, increase vascular permeability, edema, and widespread inflammation, as well as triggering “hypercoagulation cascades,” which cause small and large blood clots that affect multiple organs.
If SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier, directly entering the brain, it can contribute to demyelination or neurodegeneration.
“We very thoroughly reviewed the literature published between Jan. 1 and May 1, 2020, about neurological issues [in COVID-19] and what I found interesting is that so many neurological things can happen due to a virus which is so small,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“This virus’ DNA has such limited information, and yet it can wreak havoc on our nervous system because it kicks off such a potent defense system in our body that damages our nervous system,” he said.
Three-stage classification
- Stage 1: The extent of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptors is limited to the nasal and gustatory epithelial cells, with the cytokine storm remaining “low and controlled.” During this stage, patients may experience smell or taste impairments, but often recover without any interventions.
- Stage 2: A “robust immune response” is activated by the virus, leading to inflammation in the blood vessels, increased hypercoagulability factors, and the formation of blood clots in cerebral arteries and veins. The patient may therefore experience either large or small strokes. Additional stage 2 symptoms include fatigue, hemiplegia, sensory loss, , tetraplegia, , or ataxia.
- Stage 3: The cytokine storm in the blood vessels is so severe that it causes an “explosive inflammatory response” and penetrates the blood-brain barrier, leading to the entry of cytokines, blood components, and viral particles into the brain parenchyma and causing neuronal cell death and encephalitis. This stage can be characterized by seizures, confusion, , coma, loss of consciousness, or death.
“Patients in stage 3 are more likely to have long-term consequences, because there is evidence that the virus particles have actually penetrated the brain, and we know that SARS-CoV-2 can remain dormant in neurons for many years,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“Studies of coronaviruses have shown a link between the viruses and the risk of multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease even decades later,” he added.
“Based on several reports in recent months, between 36% to 55% of patients with COVID-19 that are hospitalized have some neurological symptoms, but if you don’t look for them, you won’t see them,” Dr. Fotuhi noted.
As a result, patients should be monitored over time after discharge, as they may develop cognitive dysfunction down the road.
Additionally, “it is imperative for patients [hospitalized with COVID-19] to get a baseline MRI before leaving the hospital so that we have a starting point for future evaluation and treatment,” said Dr. Fotuhi.
“The good news is that neurological manifestations of COVID-19 are treatable,” and “can improve with intensive training,” including lifestyle changes – such as a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress reduction, improved sleep, biofeedback, and brain rehabilitation, Dr. Fotuhi added.
Routine MRI not necessary
Kenneth Tyler, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, disagreed that all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 should routinely receive an MRI.
“Whenever you are using a piece of equipment on patients who are COVID-19 infected, you risk introducing the infection to uninfected patients,” he said. Instead, “the indication is in patients who develop unexplained neurological manifestations – altered mental status or focal seizures, for example – because in those cases, you do need to understand whether there are underlying structural abnormalities,” said Dr. Tyler, who was not involved in the review.
Also commenting on the review, Vanja Douglas, MD, associate professor of clinical neurology, University of California, San Francisco, described the review as “thorough” and suggested it may “help us understand how to design observational studies to test whether the associations are due to severe respiratory illness or are specific to SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Dr. Douglas, who was not involved in the review, added that it is “helpful in giving us a sense of which neurologic syndromes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, and therefore which patients neurologists may want to screen more carefully during the pandemic.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Fotuhi disclosed no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor reported receiving consulting fees as a member of the scientific advisory board for Brainreader and reports royalties for expert witness consultation in conjunction with Neurevolution. Dr. Tyler and Dr. Douglas disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The wave of the future
Longtime CEO bids farewell to SHM
Changing times
After more than 20 years, my leadership role as CEO at the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) has ended with the transition to Dr. Eric Howell as the new SHM CEO on July 1, 2020. Looking back, I think we can all be proud of how we have helped to shape the specialty of hospital medicine over these two decades and of how strong SHM has become to support our new specialty.
In 2000, few people knew what a hospitalist was (or more importantly what we could become) and the specialty of hospital medicine had not even been named yet. Today the reputation of SHM is firmly established and the specialty has been defined by a unique curriculum through the Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine for both adult and pediatric patients, and by several textbooks in hospital medicine. There are divisions or departments of hospital medicine at many hospitals and academic medical centers. We even managed to convince the American Board of Internal Medicine, the American Board of Family Medicine, and the American Board of Medical Specialties to create a credential of Focused Practice in Hospital Medicine as the first-ever certification not tied to specific fellowship training.
To recognize the contributions of our members, SHM has established Awards of Excellence and the Fellow and Senior Fellow in Hospital Medicine (FHM and SFHM) designations. We have gone from a small national association in Philadelphia to create 68 active chapters and more than 20 Special Interest Groups. In my time at SHM I have attended more than 75-chapter meetings and met with thousands of hospitalists in 46 states. We now have over 20,000 members at SHM, making us the fastest growing medical specialty ever.
When I started at the National Association of Inpatient Physicians (NAIP) our only meeting was an annual CME meeting for about 150-200 people. We now hold a national meeting every year for more than 4,000 attendees that is the “Center of the Universe for Hospital Medicine.” Understanding that we needed to educate the people who will lead change in our health care system, we developed from scratch a set of Leadership Academies that has already educated more than 2,500 hospitalist leaders. To train the educators in quality improvement in medical education we developed our Quality and Safety Educator Academy (QSEA) programs, and to promote career development of academic hospitalists we created our Academic Hospitalist Academy.
SHM is the leader in adult in-practice learning, specifically designed for hospitalists. SHM members have access to a state-of-the-art comprehensive hospitalist-based online education system as well as board review and maintenance of certification (MOC) review tools in our SPARK program, specifically for hospital medicine.
In the area of quality improvement, most medical societies convene a panel of experts, develop guidelines, publish them, and hope that change will occur. SHM has been much more proactive, creating the Center for Quality Improvement that has raised more than $10 million and developed Quality Improvement programs in more than 400 hospitals over the years, winning the prestigious Eisenberg Award along the way.
When I started at NAIP in 2000, our only communication tools were a 4-page newsletter and an email listserv. Along the way we have developed a broadly read newsmagazine (The Hospitalist), a well-recognized peer reviewed journal (Journal of Hospital Medicine), a robust website, and a significant social media presence.
From the very early days we knew that our specialty would not be totally successful by only facing inward. Change was coming to our health care system and hospitalists were going to be right in the middle. Despite our young age and limited resources, we have always hit above our weight class in advocacy. We actively participated in the development of the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare), making suggestions in payment reform, expanding the workforce with visa reform, and expanding the team of clinicians. Along the way SHM members rose to run the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and serve as U.S. Surgeon General.
Today in these troubled times, SHM continues to be a positive voice in promoting the use of PPE, the need for increased COVID-19 testing, and the recognition of our nation’s 60,000 hospitalists as essential frontline workers in the COVID-19 pandemic. With its longstanding role in promoting diversity and overcoming social injustice, SHM has had a positive national voice during the protests over police brutality.
We have proved to be a good partner with many other organizations and consistently were invited to partner in coalitions with the ED physicians (ACEP), the critical care docs (SCCM), the hospitals (AHA), the house of medicine (AMA), other internists (ACP), surgeons (ACS), and pediatricians (AAP), and so many other much more established societies, because we could be an active, flexible, and knowledgeable partner for more than 20 years.
Today, SHM and hospital medicine are clearly recognized as a force in the rapidly evolving health care system. With this comes not only influence but also responsibility, and I am certain the SHM Board, membership, and staff are ready for this challenge. The economic toll of our current pandemic will see colleges and other major companies and institutions go out of business and leave the landscape. SHM has a deep foundation and a well of strength to call on and will survive and thrive into the future.
SHM has been a good fit for me professionally and personally. Many of my skills and strengths have served SHM in our “early” years. I am very proud of what we have been able to accomplish TOGETHER. In the end it is the people I have been fortunate enough to meet and work with throughout these past 20 years that will stay with me, many of whom are lifelong friends. My mother, even today at 93, has always asked me to leave anything I do better off than when I came in the door. As I look back at my time helping to shape and lead SHM, I am sure I have answered my mother’s challenge and more.
I look forward to seeing many of you at a future SHM meeting and reveling in the way that hospitalists will actively play an important role in shaping our health care system in the future.
Dr. Wellikson is retiring as CEO of SHM.
Live long and prosper
Back in 2000, I was extremely fortunate to land my dream job as a hospitalist at Johns Hopkins Bayview in Baltimore. That dream exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year career as faculty in the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine I grew our tiny, 4 physician hospitalist group at Johns Hopkins Bayview into a multihospital program, complete with more than 150 physicians. That exceedingly rewarding work helped to shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my promotion to professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins in 2016.
Most professionals are lucky if they find one inspiring institution; I have found two. SHM has been my professional home since I became a hospitalist in 2000, and in that time I have dedicated as much creative energy to SHM as I have at Johns Hopkins.
Even at this time when the medical profession, and the entire world, has been rocked by the coronavirus, the fundamentals that have made SHM so successful will serve us well through the effects of this pandemic and beyond. It takes a skilled leader to nurture a professional society through the growth from only a few hundred members to thousands upon thousands, and at the same time crafting the profession into one of quality and high impact. These past 22 years Dr. Larry Wellikson, our retiring CEO, has skillfully accomplished just that by building lasting programs and people.
As you might imagine, my approach will work to add onto the legacy that Larry has left us. Yes, we will have to adapt SHM to the realities of the near future: virtual meetings, in-person events (yes, those will return one day) with appropriate social distancing until the coronavirus has faded, modified chapter meetings, and more. Someday the world will find a new normal, and SHM will evolve to meet the needs of our members and the patients we serve.
Through this pandemic and beyond, my vision – in partnership with the Board of Directors – will be to:
- Continue the work to enhance member engagement. We are primarily a membership organization, after all.
- Maintain our profession’s leadership role in the care continuum, particularly acute care.
- Be a deliberate sponsor of diversity and inclusion. I believe social justice is a moral imperative, and good business.
- Invest in teams: Chapters, special interest groups, and committees are key to success.
- Be financially prudent, so that this organization can serve its members through the best of times and those most challenging times.
Back in 2000 I joined my dream society, the Society of Hospital Medicine. That society exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year membership I started an SHM Chapter, was a leader in the Leadership Academies, joined the Board of Directors, participated in Annual Conferences, and helped lead the SHM Center for Quality Improvement. That exceedingly rewarding partnership helped shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my next role at SHM. I am excited and grateful to be the CEO of SHM.
I’ll end with something I use every day – “Eric Howell’s Core Values”:
- Make the world a better place.
- Invest in people.
- Be ethical and transparent.
- Do what you love.
- Try to use Star Trek references whenever possible. (Okay, this last one is not really a core value, but maybe a character trait?) At least the Vulcan greeting is appropriate for our times: Live long and prosper.
Dr. Howell is the new CEO for SHM as of July 1, 2020.
Longtime CEO bids farewell to SHM
Longtime CEO bids farewell to SHM
Changing times
After more than 20 years, my leadership role as CEO at the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) has ended with the transition to Dr. Eric Howell as the new SHM CEO on July 1, 2020. Looking back, I think we can all be proud of how we have helped to shape the specialty of hospital medicine over these two decades and of how strong SHM has become to support our new specialty.
In 2000, few people knew what a hospitalist was (or more importantly what we could become) and the specialty of hospital medicine had not even been named yet. Today the reputation of SHM is firmly established and the specialty has been defined by a unique curriculum through the Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine for both adult and pediatric patients, and by several textbooks in hospital medicine. There are divisions or departments of hospital medicine at many hospitals and academic medical centers. We even managed to convince the American Board of Internal Medicine, the American Board of Family Medicine, and the American Board of Medical Specialties to create a credential of Focused Practice in Hospital Medicine as the first-ever certification not tied to specific fellowship training.
To recognize the contributions of our members, SHM has established Awards of Excellence and the Fellow and Senior Fellow in Hospital Medicine (FHM and SFHM) designations. We have gone from a small national association in Philadelphia to create 68 active chapters and more than 20 Special Interest Groups. In my time at SHM I have attended more than 75-chapter meetings and met with thousands of hospitalists in 46 states. We now have over 20,000 members at SHM, making us the fastest growing medical specialty ever.
When I started at the National Association of Inpatient Physicians (NAIP) our only meeting was an annual CME meeting for about 150-200 people. We now hold a national meeting every year for more than 4,000 attendees that is the “Center of the Universe for Hospital Medicine.” Understanding that we needed to educate the people who will lead change in our health care system, we developed from scratch a set of Leadership Academies that has already educated more than 2,500 hospitalist leaders. To train the educators in quality improvement in medical education we developed our Quality and Safety Educator Academy (QSEA) programs, and to promote career development of academic hospitalists we created our Academic Hospitalist Academy.
SHM is the leader in adult in-practice learning, specifically designed for hospitalists. SHM members have access to a state-of-the-art comprehensive hospitalist-based online education system as well as board review and maintenance of certification (MOC) review tools in our SPARK program, specifically for hospital medicine.
In the area of quality improvement, most medical societies convene a panel of experts, develop guidelines, publish them, and hope that change will occur. SHM has been much more proactive, creating the Center for Quality Improvement that has raised more than $10 million and developed Quality Improvement programs in more than 400 hospitals over the years, winning the prestigious Eisenberg Award along the way.
When I started at NAIP in 2000, our only communication tools were a 4-page newsletter and an email listserv. Along the way we have developed a broadly read newsmagazine (The Hospitalist), a well-recognized peer reviewed journal (Journal of Hospital Medicine), a robust website, and a significant social media presence.
From the very early days we knew that our specialty would not be totally successful by only facing inward. Change was coming to our health care system and hospitalists were going to be right in the middle. Despite our young age and limited resources, we have always hit above our weight class in advocacy. We actively participated in the development of the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare), making suggestions in payment reform, expanding the workforce with visa reform, and expanding the team of clinicians. Along the way SHM members rose to run the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and serve as U.S. Surgeon General.
Today in these troubled times, SHM continues to be a positive voice in promoting the use of PPE, the need for increased COVID-19 testing, and the recognition of our nation’s 60,000 hospitalists as essential frontline workers in the COVID-19 pandemic. With its longstanding role in promoting diversity and overcoming social injustice, SHM has had a positive national voice during the protests over police brutality.
We have proved to be a good partner with many other organizations and consistently were invited to partner in coalitions with the ED physicians (ACEP), the critical care docs (SCCM), the hospitals (AHA), the house of medicine (AMA), other internists (ACP), surgeons (ACS), and pediatricians (AAP), and so many other much more established societies, because we could be an active, flexible, and knowledgeable partner for more than 20 years.
Today, SHM and hospital medicine are clearly recognized as a force in the rapidly evolving health care system. With this comes not only influence but also responsibility, and I am certain the SHM Board, membership, and staff are ready for this challenge. The economic toll of our current pandemic will see colleges and other major companies and institutions go out of business and leave the landscape. SHM has a deep foundation and a well of strength to call on and will survive and thrive into the future.
SHM has been a good fit for me professionally and personally. Many of my skills and strengths have served SHM in our “early” years. I am very proud of what we have been able to accomplish TOGETHER. In the end it is the people I have been fortunate enough to meet and work with throughout these past 20 years that will stay with me, many of whom are lifelong friends. My mother, even today at 93, has always asked me to leave anything I do better off than when I came in the door. As I look back at my time helping to shape and lead SHM, I am sure I have answered my mother’s challenge and more.
I look forward to seeing many of you at a future SHM meeting and reveling in the way that hospitalists will actively play an important role in shaping our health care system in the future.
Dr. Wellikson is retiring as CEO of SHM.
Live long and prosper
Back in 2000, I was extremely fortunate to land my dream job as a hospitalist at Johns Hopkins Bayview in Baltimore. That dream exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year career as faculty in the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine I grew our tiny, 4 physician hospitalist group at Johns Hopkins Bayview into a multihospital program, complete with more than 150 physicians. That exceedingly rewarding work helped to shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my promotion to professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins in 2016.
Most professionals are lucky if they find one inspiring institution; I have found two. SHM has been my professional home since I became a hospitalist in 2000, and in that time I have dedicated as much creative energy to SHM as I have at Johns Hopkins.
Even at this time when the medical profession, and the entire world, has been rocked by the coronavirus, the fundamentals that have made SHM so successful will serve us well through the effects of this pandemic and beyond. It takes a skilled leader to nurture a professional society through the growth from only a few hundred members to thousands upon thousands, and at the same time crafting the profession into one of quality and high impact. These past 22 years Dr. Larry Wellikson, our retiring CEO, has skillfully accomplished just that by building lasting programs and people.
As you might imagine, my approach will work to add onto the legacy that Larry has left us. Yes, we will have to adapt SHM to the realities of the near future: virtual meetings, in-person events (yes, those will return one day) with appropriate social distancing until the coronavirus has faded, modified chapter meetings, and more. Someday the world will find a new normal, and SHM will evolve to meet the needs of our members and the patients we serve.
Through this pandemic and beyond, my vision – in partnership with the Board of Directors – will be to:
- Continue the work to enhance member engagement. We are primarily a membership organization, after all.
- Maintain our profession’s leadership role in the care continuum, particularly acute care.
- Be a deliberate sponsor of diversity and inclusion. I believe social justice is a moral imperative, and good business.
- Invest in teams: Chapters, special interest groups, and committees are key to success.
- Be financially prudent, so that this organization can serve its members through the best of times and those most challenging times.
Back in 2000 I joined my dream society, the Society of Hospital Medicine. That society exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year membership I started an SHM Chapter, was a leader in the Leadership Academies, joined the Board of Directors, participated in Annual Conferences, and helped lead the SHM Center for Quality Improvement. That exceedingly rewarding partnership helped shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my next role at SHM. I am excited and grateful to be the CEO of SHM.
I’ll end with something I use every day – “Eric Howell’s Core Values”:
- Make the world a better place.
- Invest in people.
- Be ethical and transparent.
- Do what you love.
- Try to use Star Trek references whenever possible. (Okay, this last one is not really a core value, but maybe a character trait?) At least the Vulcan greeting is appropriate for our times: Live long and prosper.
Dr. Howell is the new CEO for SHM as of July 1, 2020.
Changing times
After more than 20 years, my leadership role as CEO at the Society of Hospital Medicine (SHM) has ended with the transition to Dr. Eric Howell as the new SHM CEO on July 1, 2020. Looking back, I think we can all be proud of how we have helped to shape the specialty of hospital medicine over these two decades and of how strong SHM has become to support our new specialty.
In 2000, few people knew what a hospitalist was (or more importantly what we could become) and the specialty of hospital medicine had not even been named yet. Today the reputation of SHM is firmly established and the specialty has been defined by a unique curriculum through the Core Competencies in Hospital Medicine for both adult and pediatric patients, and by several textbooks in hospital medicine. There are divisions or departments of hospital medicine at many hospitals and academic medical centers. We even managed to convince the American Board of Internal Medicine, the American Board of Family Medicine, and the American Board of Medical Specialties to create a credential of Focused Practice in Hospital Medicine as the first-ever certification not tied to specific fellowship training.
To recognize the contributions of our members, SHM has established Awards of Excellence and the Fellow and Senior Fellow in Hospital Medicine (FHM and SFHM) designations. We have gone from a small national association in Philadelphia to create 68 active chapters and more than 20 Special Interest Groups. In my time at SHM I have attended more than 75-chapter meetings and met with thousands of hospitalists in 46 states. We now have over 20,000 members at SHM, making us the fastest growing medical specialty ever.
When I started at the National Association of Inpatient Physicians (NAIP) our only meeting was an annual CME meeting for about 150-200 people. We now hold a national meeting every year for more than 4,000 attendees that is the “Center of the Universe for Hospital Medicine.” Understanding that we needed to educate the people who will lead change in our health care system, we developed from scratch a set of Leadership Academies that has already educated more than 2,500 hospitalist leaders. To train the educators in quality improvement in medical education we developed our Quality and Safety Educator Academy (QSEA) programs, and to promote career development of academic hospitalists we created our Academic Hospitalist Academy.
SHM is the leader in adult in-practice learning, specifically designed for hospitalists. SHM members have access to a state-of-the-art comprehensive hospitalist-based online education system as well as board review and maintenance of certification (MOC) review tools in our SPARK program, specifically for hospital medicine.
In the area of quality improvement, most medical societies convene a panel of experts, develop guidelines, publish them, and hope that change will occur. SHM has been much more proactive, creating the Center for Quality Improvement that has raised more than $10 million and developed Quality Improvement programs in more than 400 hospitals over the years, winning the prestigious Eisenberg Award along the way.
When I started at NAIP in 2000, our only communication tools were a 4-page newsletter and an email listserv. Along the way we have developed a broadly read newsmagazine (The Hospitalist), a well-recognized peer reviewed journal (Journal of Hospital Medicine), a robust website, and a significant social media presence.
From the very early days we knew that our specialty would not be totally successful by only facing inward. Change was coming to our health care system and hospitalists were going to be right in the middle. Despite our young age and limited resources, we have always hit above our weight class in advocacy. We actively participated in the development of the Affordable Care Act (Obamacare), making suggestions in payment reform, expanding the workforce with visa reform, and expanding the team of clinicians. Along the way SHM members rose to run the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and serve as U.S. Surgeon General.
Today in these troubled times, SHM continues to be a positive voice in promoting the use of PPE, the need for increased COVID-19 testing, and the recognition of our nation’s 60,000 hospitalists as essential frontline workers in the COVID-19 pandemic. With its longstanding role in promoting diversity and overcoming social injustice, SHM has had a positive national voice during the protests over police brutality.
We have proved to be a good partner with many other organizations and consistently were invited to partner in coalitions with the ED physicians (ACEP), the critical care docs (SCCM), the hospitals (AHA), the house of medicine (AMA), other internists (ACP), surgeons (ACS), and pediatricians (AAP), and so many other much more established societies, because we could be an active, flexible, and knowledgeable partner for more than 20 years.
Today, SHM and hospital medicine are clearly recognized as a force in the rapidly evolving health care system. With this comes not only influence but also responsibility, and I am certain the SHM Board, membership, and staff are ready for this challenge. The economic toll of our current pandemic will see colleges and other major companies and institutions go out of business and leave the landscape. SHM has a deep foundation and a well of strength to call on and will survive and thrive into the future.
SHM has been a good fit for me professionally and personally. Many of my skills and strengths have served SHM in our “early” years. I am very proud of what we have been able to accomplish TOGETHER. In the end it is the people I have been fortunate enough to meet and work with throughout these past 20 years that will stay with me, many of whom are lifelong friends. My mother, even today at 93, has always asked me to leave anything I do better off than when I came in the door. As I look back at my time helping to shape and lead SHM, I am sure I have answered my mother’s challenge and more.
I look forward to seeing many of you at a future SHM meeting and reveling in the way that hospitalists will actively play an important role in shaping our health care system in the future.
Dr. Wellikson is retiring as CEO of SHM.
Live long and prosper
Back in 2000, I was extremely fortunate to land my dream job as a hospitalist at Johns Hopkins Bayview in Baltimore. That dream exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year career as faculty in the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine I grew our tiny, 4 physician hospitalist group at Johns Hopkins Bayview into a multihospital program, complete with more than 150 physicians. That exceedingly rewarding work helped to shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my promotion to professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins in 2016.
Most professionals are lucky if they find one inspiring institution; I have found two. SHM has been my professional home since I became a hospitalist in 2000, and in that time I have dedicated as much creative energy to SHM as I have at Johns Hopkins.
Even at this time when the medical profession, and the entire world, has been rocked by the coronavirus, the fundamentals that have made SHM so successful will serve us well through the effects of this pandemic and beyond. It takes a skilled leader to nurture a professional society through the growth from only a few hundred members to thousands upon thousands, and at the same time crafting the profession into one of quality and high impact. These past 22 years Dr. Larry Wellikson, our retiring CEO, has skillfully accomplished just that by building lasting programs and people.
As you might imagine, my approach will work to add onto the legacy that Larry has left us. Yes, we will have to adapt SHM to the realities of the near future: virtual meetings, in-person events (yes, those will return one day) with appropriate social distancing until the coronavirus has faded, modified chapter meetings, and more. Someday the world will find a new normal, and SHM will evolve to meet the needs of our members and the patients we serve.
Through this pandemic and beyond, my vision – in partnership with the Board of Directors – will be to:
- Continue the work to enhance member engagement. We are primarily a membership organization, after all.
- Maintain our profession’s leadership role in the care continuum, particularly acute care.
- Be a deliberate sponsor of diversity and inclusion. I believe social justice is a moral imperative, and good business.
- Invest in teams: Chapters, special interest groups, and committees are key to success.
- Be financially prudent, so that this organization can serve its members through the best of times and those most challenging times.
Back in 2000 I joined my dream society, the Society of Hospital Medicine. That society exceeded my wildest aspirations. During my 20-year membership I started an SHM Chapter, was a leader in the Leadership Academies, joined the Board of Directors, participated in Annual Conferences, and helped lead the SHM Center for Quality Improvement. That exceedingly rewarding partnership helped shape the field of hospital medicine nationally and provided the foundation for my next role at SHM. I am excited and grateful to be the CEO of SHM.
I’ll end with something I use every day – “Eric Howell’s Core Values”:
- Make the world a better place.
- Invest in people.
- Be ethical and transparent.
- Do what you love.
- Try to use Star Trek references whenever possible. (Okay, this last one is not really a core value, but maybe a character trait?) At least the Vulcan greeting is appropriate for our times: Live long and prosper.
Dr. Howell is the new CEO for SHM as of July 1, 2020.
Topline results for novel intranasal med to treat opioid overdose
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Topline results show positive results for the experimental intranasal nalmefene product OX125 for opioid overdose reversal, Orexo, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on June 30.
A crossover, comparative bioavailability study was conducted in healthy volunteers to assess nalmefene absorption of three development formulations of OX125. Preliminary results showed “extensive and rapid absorption” across all three formulations versus an intramuscular injection of nalmefene, Orexo reported.
“As the U.S. heroin crisis has developed to a fentanyl crisis, the medical need for novel and more powerful opioid rescue medications is vast,” Nikolaj Sørensen, president and CEO of Orexo, said in a press release.
“The need has also escalated due to the COVID-19 pandemic as the consequences of social distancing and economic weakness are expected to lead to a significant increase in mental health issues and substance use disorders,” Mr. Sørensen added.
Robert Rönn, vice president and head of research and development at Orexo, noted in the same release that the company will now be working with the Food and Drug Administration “to identify the optimal route to market.”
There were more than 31,000 fatalities from highly potent synthetic opioids in the United States in 2018, the manufacturer reported. “Like naloxone, nalmefene is an opioid antagonist that acts by blocking the effects of opioids at the opioid receptors.”
However, nalmefene has a longer half-life than naloxone. These longer-acting properties may be “of particular value to protect against renarcotization (second overdose), as the antagonist wears off,” according to an Orexo press release.
In addition to showing rapid absorption across all formulations studied, study results showed “good tolerability, supporting the viability” of the treatment as an opioid overdose rescue medication, the company said.
“This is not only a proof of concept for our wholly owned OX125 product, but also a demonstration of the value of our novel nasal technology platform,” Mr. Rönn said.
“Alongside OX124, our naloxone rescue project, OX125 will be an important lifesaving addition in our commitment to helping patients suffering from opioid addiction in all phases,” Mr. Sørensen added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Pride profile: Keshav Khanijow, MD
Keshav Khanijow, MD, is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and assistant professor at Northwestern University, Chicago. Originally from the San Francisco Bay area, he studied anthropology as an undergrad at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, then went to medical school at the University of California, San Francisco, followed by internal medicine residency and a hospital medicine fellowship at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He came out as gay in 2006 as an undergrad. He is a founding member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s LGBTQ+ Task Force and is involved with SHM’s Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group.
What challenges have you faced because of your sexual orientation in the different stages of your career, from training to now as a practicing physician?
In my early training, there weren’t a lot of accessible LGBTQ role models to talk about balancing my personal identities with my professional aspirations. Being a double minority as both South Asian and a gay male, made it that much more difficult. “What is it like to work in health care as a gay cismale? Will being out on my personal statement affect my entry into medical school? Should I list my LGBTQ activism activities or not?” Those were important to me.
And did you make your activism known?
Thankfully, I did. I joke that my application might as well have been printed on rainbow paper, if you will. I decided to be out because I wanted to be part of an environment that would accept me for who I was. But it was a difficult decision.
In medical school at UCSF, it’s San Francisco, so they were a little ahead of the game. They had a lot of social networking opportunities with LGBTQ and ally faculty. Those connections were important in helping me explore different fields, and I even got to write my first publication. That said, networking could sometimes be challenging, especially when it came to residency interviews. While many people would talk about family activities and engagements, I’d only been out to my family for a few years. As such, there would be somewhat of a disconnect. On the flip side, there were LGBTQ celebrations and cultural concepts important to me, but I couldn’t always connect on those fronts either.
When it comes to patients, I do have a bit of a higher-pitched voice, and my mannerisms can be gender nonconforming. While it did make me the target of some cruel middle school humor, I’ve come to be proud of myself, mannerisms and all. That said, I have had patients make remarks to me about being gay, whether it be positive or negative. For LGBTQ patients, they’re like, “this is great, I have a gay doctor. They’ll know a bit more about what I’m talking about or be able to relate to the community pressures I face.”
But sometimes homophobic patients can be a bit more cold. I’ve never had anyone say that they don’t want to have me as their physician, but I definitely have patients who disagree with me and say, essentially, “oh well, you don’t know what you’re talking about because you’re gay.” Of course, there have also been comments based on my ethnicity as well.
What specific progress could you point to that you’ve seen over the course of your training and your career so far with regard to LGBTQ health care workers’ experience and LGBTQ patients?
When I was in college, there was a case in 2007 where a woman wasn’t able to see her partner or children before dying in a Florida hospital. Since then, there’s been great strides with a 2011 executive order extending hospital visitation rights to LGBTQ families. In 2013, there was the legalization of same-sex marriage. More recently, in June 2020, the Supreme Court extended protections against workplace discrimination to LGBTQ employees.
But there are certain things that continue to be problems, such as the recent Final Rule from the Department of Health & Human Services that fails to protect our LGBTQ patients and friends against discrimination in health care.
Can you remember a specific episode with a patient who was in the LGBTQ community that was particularly satisfying or moving?
There are two that I think about. In medical school, I was working in a more conservative area of California, and there was a patient who identified as lesbian. She felt more able to talk about her fears of raising a family in a conservative area. She even said, “I feel you can understand the stuff, I can talk to you a bit more about it freely, which is really nice.” Later on, I was able to see them on another rotation I was on, after she’d had a baby with her partner. I was honored that they considered me a part of their family’s journey.
A couple years ago as an attending hospitalist, I had a gay male patient that came in for hepatitis A treatment. Although we typically think of hepatitis A as a foodborne illness, oral-anal sex (rimming) is also a risk factor. After having an open discussion with him about his sexual practices, I said, “it was probably an STI in your case,” and was able to give him guidelines on how to prevent giving it to anyone else during the recovery period. He was very appreciative, and I was glad to have been there for that patient.
What is SHM’s role in regard to improving the care of LGBTQ patients, improving inclusiveness for LGBTQ health professionals?
Continuing to have educational activities, whether it be lectures at the annual conference or online learning modules, will be critical to care for our LGBTQ patients. With regard to membership, we need to make sure that hospitalists feel included and protected. To this end, our Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group was working toward having gender-neutral bathrooms and personal pronoun tags for the in-person 2020 annual conference before it was converted to an online format.
Does it ever get tiring for you to work on “social issues” in addition to strictly medical issues?
I will say I definitely experienced a moment in time during residency where I had to take a step back and recenter myself. Sometimes, realizing how much work needs to get done, coupled with the challenges of one’s personal life, can be daunting. That said, I can only stare at a problem so long before needing to work on creating a solution. At the end of the day I didn’t want to run away from these newfound problems of exclusion – I wanted to be a part of the solution.
In my hospital medicine fellowship, I was lucky to have Flora Kisuule, MD, as a mentor who encouraged me to take my prior work with LGBTQ health and leverage it into hospital medicine projects. As such, I was able to combine a topic I was passionate about with my interests in research and teaching so that they work synergistically. After all, the social issues affect our medical histories, just as our medical issues affect our social being. They go hand in hand.
Keshav Khanijow, MD, is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and assistant professor at Northwestern University, Chicago. Originally from the San Francisco Bay area, he studied anthropology as an undergrad at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, then went to medical school at the University of California, San Francisco, followed by internal medicine residency and a hospital medicine fellowship at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He came out as gay in 2006 as an undergrad. He is a founding member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s LGBTQ+ Task Force and is involved with SHM’s Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group.
What challenges have you faced because of your sexual orientation in the different stages of your career, from training to now as a practicing physician?
In my early training, there weren’t a lot of accessible LGBTQ role models to talk about balancing my personal identities with my professional aspirations. Being a double minority as both South Asian and a gay male, made it that much more difficult. “What is it like to work in health care as a gay cismale? Will being out on my personal statement affect my entry into medical school? Should I list my LGBTQ activism activities or not?” Those were important to me.
And did you make your activism known?
Thankfully, I did. I joke that my application might as well have been printed on rainbow paper, if you will. I decided to be out because I wanted to be part of an environment that would accept me for who I was. But it was a difficult decision.
In medical school at UCSF, it’s San Francisco, so they were a little ahead of the game. They had a lot of social networking opportunities with LGBTQ and ally faculty. Those connections were important in helping me explore different fields, and I even got to write my first publication. That said, networking could sometimes be challenging, especially when it came to residency interviews. While many people would talk about family activities and engagements, I’d only been out to my family for a few years. As such, there would be somewhat of a disconnect. On the flip side, there were LGBTQ celebrations and cultural concepts important to me, but I couldn’t always connect on those fronts either.
When it comes to patients, I do have a bit of a higher-pitched voice, and my mannerisms can be gender nonconforming. While it did make me the target of some cruel middle school humor, I’ve come to be proud of myself, mannerisms and all. That said, I have had patients make remarks to me about being gay, whether it be positive or negative. For LGBTQ patients, they’re like, “this is great, I have a gay doctor. They’ll know a bit more about what I’m talking about or be able to relate to the community pressures I face.”
But sometimes homophobic patients can be a bit more cold. I’ve never had anyone say that they don’t want to have me as their physician, but I definitely have patients who disagree with me and say, essentially, “oh well, you don’t know what you’re talking about because you’re gay.” Of course, there have also been comments based on my ethnicity as well.
What specific progress could you point to that you’ve seen over the course of your training and your career so far with regard to LGBTQ health care workers’ experience and LGBTQ patients?
When I was in college, there was a case in 2007 where a woman wasn’t able to see her partner or children before dying in a Florida hospital. Since then, there’s been great strides with a 2011 executive order extending hospital visitation rights to LGBTQ families. In 2013, there was the legalization of same-sex marriage. More recently, in June 2020, the Supreme Court extended protections against workplace discrimination to LGBTQ employees.
But there are certain things that continue to be problems, such as the recent Final Rule from the Department of Health & Human Services that fails to protect our LGBTQ patients and friends against discrimination in health care.
Can you remember a specific episode with a patient who was in the LGBTQ community that was particularly satisfying or moving?
There are two that I think about. In medical school, I was working in a more conservative area of California, and there was a patient who identified as lesbian. She felt more able to talk about her fears of raising a family in a conservative area. She even said, “I feel you can understand the stuff, I can talk to you a bit more about it freely, which is really nice.” Later on, I was able to see them on another rotation I was on, after she’d had a baby with her partner. I was honored that they considered me a part of their family’s journey.
A couple years ago as an attending hospitalist, I had a gay male patient that came in for hepatitis A treatment. Although we typically think of hepatitis A as a foodborne illness, oral-anal sex (rimming) is also a risk factor. After having an open discussion with him about his sexual practices, I said, “it was probably an STI in your case,” and was able to give him guidelines on how to prevent giving it to anyone else during the recovery period. He was very appreciative, and I was glad to have been there for that patient.
What is SHM’s role in regard to improving the care of LGBTQ patients, improving inclusiveness for LGBTQ health professionals?
Continuing to have educational activities, whether it be lectures at the annual conference or online learning modules, will be critical to care for our LGBTQ patients. With regard to membership, we need to make sure that hospitalists feel included and protected. To this end, our Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group was working toward having gender-neutral bathrooms and personal pronoun tags for the in-person 2020 annual conference before it was converted to an online format.
Does it ever get tiring for you to work on “social issues” in addition to strictly medical issues?
I will say I definitely experienced a moment in time during residency where I had to take a step back and recenter myself. Sometimes, realizing how much work needs to get done, coupled with the challenges of one’s personal life, can be daunting. That said, I can only stare at a problem so long before needing to work on creating a solution. At the end of the day I didn’t want to run away from these newfound problems of exclusion – I wanted to be a part of the solution.
In my hospital medicine fellowship, I was lucky to have Flora Kisuule, MD, as a mentor who encouraged me to take my prior work with LGBTQ health and leverage it into hospital medicine projects. As such, I was able to combine a topic I was passionate about with my interests in research and teaching so that they work synergistically. After all, the social issues affect our medical histories, just as our medical issues affect our social being. They go hand in hand.
Keshav Khanijow, MD, is a hospitalist at Northwestern Memorial Hospital and assistant professor at Northwestern University, Chicago. Originally from the San Francisco Bay area, he studied anthropology as an undergrad at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, then went to medical school at the University of California, San Francisco, followed by internal medicine residency and a hospital medicine fellowship at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center. He came out as gay in 2006 as an undergrad. He is a founding member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s LGBTQ+ Task Force and is involved with SHM’s Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group.
What challenges have you faced because of your sexual orientation in the different stages of your career, from training to now as a practicing physician?
In my early training, there weren’t a lot of accessible LGBTQ role models to talk about balancing my personal identities with my professional aspirations. Being a double minority as both South Asian and a gay male, made it that much more difficult. “What is it like to work in health care as a gay cismale? Will being out on my personal statement affect my entry into medical school? Should I list my LGBTQ activism activities or not?” Those were important to me.
And did you make your activism known?
Thankfully, I did. I joke that my application might as well have been printed on rainbow paper, if you will. I decided to be out because I wanted to be part of an environment that would accept me for who I was. But it was a difficult decision.
In medical school at UCSF, it’s San Francisco, so they were a little ahead of the game. They had a lot of social networking opportunities with LGBTQ and ally faculty. Those connections were important in helping me explore different fields, and I even got to write my first publication. That said, networking could sometimes be challenging, especially when it came to residency interviews. While many people would talk about family activities and engagements, I’d only been out to my family for a few years. As such, there would be somewhat of a disconnect. On the flip side, there were LGBTQ celebrations and cultural concepts important to me, but I couldn’t always connect on those fronts either.
When it comes to patients, I do have a bit of a higher-pitched voice, and my mannerisms can be gender nonconforming. While it did make me the target of some cruel middle school humor, I’ve come to be proud of myself, mannerisms and all. That said, I have had patients make remarks to me about being gay, whether it be positive or negative. For LGBTQ patients, they’re like, “this is great, I have a gay doctor. They’ll know a bit more about what I’m talking about or be able to relate to the community pressures I face.”
But sometimes homophobic patients can be a bit more cold. I’ve never had anyone say that they don’t want to have me as their physician, but I definitely have patients who disagree with me and say, essentially, “oh well, you don’t know what you’re talking about because you’re gay.” Of course, there have also been comments based on my ethnicity as well.
What specific progress could you point to that you’ve seen over the course of your training and your career so far with regard to LGBTQ health care workers’ experience and LGBTQ patients?
When I was in college, there was a case in 2007 where a woman wasn’t able to see her partner or children before dying in a Florida hospital. Since then, there’s been great strides with a 2011 executive order extending hospital visitation rights to LGBTQ families. In 2013, there was the legalization of same-sex marriage. More recently, in June 2020, the Supreme Court extended protections against workplace discrimination to LGBTQ employees.
But there are certain things that continue to be problems, such as the recent Final Rule from the Department of Health & Human Services that fails to protect our LGBTQ patients and friends against discrimination in health care.
Can you remember a specific episode with a patient who was in the LGBTQ community that was particularly satisfying or moving?
There are two that I think about. In medical school, I was working in a more conservative area of California, and there was a patient who identified as lesbian. She felt more able to talk about her fears of raising a family in a conservative area. She even said, “I feel you can understand the stuff, I can talk to you a bit more about it freely, which is really nice.” Later on, I was able to see them on another rotation I was on, after she’d had a baby with her partner. I was honored that they considered me a part of their family’s journey.
A couple years ago as an attending hospitalist, I had a gay male patient that came in for hepatitis A treatment. Although we typically think of hepatitis A as a foodborne illness, oral-anal sex (rimming) is also a risk factor. After having an open discussion with him about his sexual practices, I said, “it was probably an STI in your case,” and was able to give him guidelines on how to prevent giving it to anyone else during the recovery period. He was very appreciative, and I was glad to have been there for that patient.
What is SHM’s role in regard to improving the care of LGBTQ patients, improving inclusiveness for LGBTQ health professionals?
Continuing to have educational activities, whether it be lectures at the annual conference or online learning modules, will be critical to care for our LGBTQ patients. With regard to membership, we need to make sure that hospitalists feel included and protected. To this end, our Diversity and Inclusion Special Interest Group was working toward having gender-neutral bathrooms and personal pronoun tags for the in-person 2020 annual conference before it was converted to an online format.
Does it ever get tiring for you to work on “social issues” in addition to strictly medical issues?
I will say I definitely experienced a moment in time during residency where I had to take a step back and recenter myself. Sometimes, realizing how much work needs to get done, coupled with the challenges of one’s personal life, can be daunting. That said, I can only stare at a problem so long before needing to work on creating a solution. At the end of the day I didn’t want to run away from these newfound problems of exclusion – I wanted to be a part of the solution.
In my hospital medicine fellowship, I was lucky to have Flora Kisuule, MD, as a mentor who encouraged me to take my prior work with LGBTQ health and leverage it into hospital medicine projects. As such, I was able to combine a topic I was passionate about with my interests in research and teaching so that they work synergistically. After all, the social issues affect our medical histories, just as our medical issues affect our social being. They go hand in hand.
Cognitive deficits complex in youths with type 2 diabetes
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
Teens and young adults with diabetes have cognitive deficits that vary by diabetes type and could negatively impact their medical literacy and self-care, an investigator reported at the virtual annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
Individuals with youth-onset type 1 or 2 diabetes all performed below average on tests that measure flexible thinking and problem solving, according to the investigator, who reported an analysis including 1,380 individuals enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
That finding suggests that diabetes diagnosed before age 20 contributes to poor fluid cognitive function, which consists of skills that facilitate goal-directed behaviors, according to investigator Allison Shapiro, MPH, PhD, of the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
However, individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) performed even worse than those with type 1 diabetes (T1D) on the fluid cognitive function tests, even after adjustment for demographic factors and other confounders, Dr. Shapiro said in her presentation.
Further analysis revealed that individuals with T2D performed significantly worse on measures of crystallized cognition, a domain that includes skills such as vocabulary and language. That suggests the poor fluid cognitive abilities in youths with diabetes may in fact be a result of poor crystallized cognitive development, according to the investigator.
“Among adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes specifically, intervention should focus on developing both fluid cognitive skills and crystallized cognitive skills,” Dr. Shapiro said.
Deficits in fluid cognitive function (such as reasoning or processing speed) can negatively affect diabetes self-care, thereby potentially increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications, while deficits in crystallized cognitive function (such as vocabulary and understanding of language) could impact medical literacy further compounding the self-care issues.
The study is believed to be one of the first to compare cognitive function deficits in youths with type 1 or 2 diabetes. Although studies in adults clearly show a detrimental relationship between diabetes and cognitive function, according to Dr. Shapiro, the bulk of the research in youths has focused on T1D.
“While limited work has been done in youth-onset type 2 diabetes, cognitive deficits are consistently observed, compared to youth without diabetes,” she said.
Results of this study emphasize the importance of dietary changes and other lifestyle interventions in young patients with diabetes, according to David Della-Morte, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Miami.
“Even the youngest patients may develop cognitive dysfunction,” Dr. Della-Morte said in an interview. “That means that lifestyle is very important, especially in obese patients that are prone to develop type 2 diabetes.”
The analysis by Dr. Shapiro and coinvestigators included 1,095 youths and young adults with T1D and 285 with T2D who had undergone a cognition assessment as part of a study visit. They were aged an average of 22 years, and had an average diabetes duration of 11 years.
The overall fluid cognition score was significantly lower in those individuals with T2D, compared with those with T1D, investigators found. Compared with the national average score of 100, the T2D group scored 84.7, or a full standard deviation below that average, said Dr. Shapiro, while those with T1D scored 95.5 (P < .001).
Participants with T2D also scored significantly lower in individual measures of fluid cognition, including processing speed, inhibitory control and attention, working memory, and episodic memory, she reported. At first glance, that suggested youth-onset T2D has a specific effect on fluid cognition; however, the story remains incomplete without looking at crystallized cognition markers such as vocabulary and language.
Toward that end, a picture vocabulary test conducted as part of the cognitive assessment showed a significant difference between those with T2D, who on average scored 91.5, and those with T1D, who scored 103.6 (P < .001). Accounting for those picture vocabulary scores attenuated the differences between groups in fluid cognitive scores, suggesting that differences in crystallized cognitive function underly the observed differences in fluid cognitive function between groups, Dr. Shapiro said.
Skills such as vocabulary and language are thought to be stable and not influenced by neurologic changes brought on by disease processes such as youth-onset diabetes, but rather, influenced by factors such as childcare and education, according to Dr. Shapiro.
“Crystallized cognition therefore provides a window into an individual’s cognitive functioning, independent of their disease or premorbid to the onset of their disease,” she said.
Dr. Shapiro said she had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Shapiro A et al. ADA 2020, Abstract 279-OR.
FROM ADA 2020




