User login
Habitual fish intake may prevent frailty in RA patients
Key clinical point: Frailty is positively associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and habitual fish intake may help prevent progression of frailty and RA.
Major finding: The presence of frailty was significantly associated with the disease activity score (Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate; odds ratio [OR], 1.70; P less than .0001). Patients who consumed fish more than twice per week had a lower prevalence of frailty than those who consumed fish twice per week or lesser (OR, 0.35; P = .00060).
Study details: The data come from a cross-sectional study of 306 female outpatients with RA from the KURAMA cohort database.
Disclosures: KURAMA cohort study was supported by AMED and a grant from the Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. M. Hashimoto, R Watanabe, K Nishitani, H Ito, K Ohmura, and S Matsuda reported to receive grants and/or speaker fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Bristol-Meyers, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Asahi-Kasei Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, etc. Some of the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Minamino H et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84479-0.
Key clinical point: Frailty is positively associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and habitual fish intake may help prevent progression of frailty and RA.
Major finding: The presence of frailty was significantly associated with the disease activity score (Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate; odds ratio [OR], 1.70; P less than .0001). Patients who consumed fish more than twice per week had a lower prevalence of frailty than those who consumed fish twice per week or lesser (OR, 0.35; P = .00060).
Study details: The data come from a cross-sectional study of 306 female outpatients with RA from the KURAMA cohort database.
Disclosures: KURAMA cohort study was supported by AMED and a grant from the Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. M. Hashimoto, R Watanabe, K Nishitani, H Ito, K Ohmura, and S Matsuda reported to receive grants and/or speaker fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Bristol-Meyers, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Asahi-Kasei Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, etc. Some of the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Minamino H et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84479-0.
Key clinical point: Frailty is positively associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and habitual fish intake may help prevent progression of frailty and RA.
Major finding: The presence of frailty was significantly associated with the disease activity score (Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate; odds ratio [OR], 1.70; P less than .0001). Patients who consumed fish more than twice per week had a lower prevalence of frailty than those who consumed fish twice per week or lesser (OR, 0.35; P = .00060).
Study details: The data come from a cross-sectional study of 306 female outpatients with RA from the KURAMA cohort database.
Disclosures: KURAMA cohort study was supported by AMED and a grant from the Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd. M. Hashimoto, R Watanabe, K Nishitani, H Ito, K Ohmura, and S Matsuda reported to receive grants and/or speaker fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Bristol-Meyers, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Asahi-Kasei Pharma, Daiichi-Sankyo, etc. Some of the authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Minamino H et al. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84479-0.
RA tied to worse long-term outcomes after myocardial infarction
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with poor long-term prognosis after myocardial infarction (MI).
Major finding: At 14-year follow-up after MI, the cumulative all-cause mortality risk was significantly higher among patients with vs. without RA (80.4% vs. 72.3%; hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; P less than .0001). Patients with RA had a higher risk for new MI (HR, 1.22; P = .0001) and revascularization (HR, 1.27; P = .002) after discharge from index MI.
Study details: This was a nationwide, multicenter, cohort register study of real-life MI patients with RA (n=1,614) retrospectively compared with propensity score-matched MI patients without RA (n=8,070).
Disclosures: This study was supported by grant funding from the Finnish Cultural Foundation, the Paulo Foundation, and the Finnish Governmental VTR-funding. A Palomäki, AM Kerola, M Malmberg, and V Kytö reported relevant relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The other author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Palomäki A et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Mar 1. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab204.
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with poor long-term prognosis after myocardial infarction (MI).
Major finding: At 14-year follow-up after MI, the cumulative all-cause mortality risk was significantly higher among patients with vs. without RA (80.4% vs. 72.3%; hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; P less than .0001). Patients with RA had a higher risk for new MI (HR, 1.22; P = .0001) and revascularization (HR, 1.27; P = .002) after discharge from index MI.
Study details: This was a nationwide, multicenter, cohort register study of real-life MI patients with RA (n=1,614) retrospectively compared with propensity score-matched MI patients without RA (n=8,070).
Disclosures: This study was supported by grant funding from the Finnish Cultural Foundation, the Paulo Foundation, and the Finnish Governmental VTR-funding. A Palomäki, AM Kerola, M Malmberg, and V Kytö reported relevant relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The other author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Palomäki A et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Mar 1. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab204.
Key clinical point: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with poor long-term prognosis after myocardial infarction (MI).
Major finding: At 14-year follow-up after MI, the cumulative all-cause mortality risk was significantly higher among patients with vs. without RA (80.4% vs. 72.3%; hazard ratio [HR], 1.25; P less than .0001). Patients with RA had a higher risk for new MI (HR, 1.22; P = .0001) and revascularization (HR, 1.27; P = .002) after discharge from index MI.
Study details: This was a nationwide, multicenter, cohort register study of real-life MI patients with RA (n=1,614) retrospectively compared with propensity score-matched MI patients without RA (n=8,070).
Disclosures: This study was supported by grant funding from the Finnish Cultural Foundation, the Paulo Foundation, and the Finnish Governmental VTR-funding. A Palomäki, AM Kerola, M Malmberg, and V Kytö reported relevant relationships with various pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The other author declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Palomäki A et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Mar 1. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab204.
MBDA score not sufficiently responsive to assess RA disease activity
Key clinical point: Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity (MBDA) should not be preferred to assess clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity after repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: RCI-mediated improvements in Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate and Clinical Disease Activity Index scores suggested clinically meaningful improvement with more than 84% of patients meeting the minimal clinically important difference/minimally important difference criteria, which ranged from 26.3% to 34.7% for MBDA.
Study details: The data come from a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study of 259 patients with active RA despite treatment with stable glucocorticoid dose and 1 or 2 disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Patients achieving low disease activity during open-label period were randomly assigned to either 80 U of RCI (n=77) or placebo (n=76) during the 12-week double-blind period.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. R Fleischmann, DE Furst, and OG Segurado reported receiving clinical trial grants and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. J Liu and J Zhu declared being employees of Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
Source: Fleischmann R et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Feb 28. doi: 10.1002/acr.24583.
Key clinical point: Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity (MBDA) should not be preferred to assess clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity after repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: RCI-mediated improvements in Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate and Clinical Disease Activity Index scores suggested clinically meaningful improvement with more than 84% of patients meeting the minimal clinically important difference/minimally important difference criteria, which ranged from 26.3% to 34.7% for MBDA.
Study details: The data come from a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study of 259 patients with active RA despite treatment with stable glucocorticoid dose and 1 or 2 disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Patients achieving low disease activity during open-label period were randomly assigned to either 80 U of RCI (n=77) or placebo (n=76) during the 12-week double-blind period.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. R Fleischmann, DE Furst, and OG Segurado reported receiving clinical trial grants and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. J Liu and J Zhu declared being employees of Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
Source: Fleischmann R et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Feb 28. doi: 10.1002/acr.24583.
Key clinical point: Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity (MBDA) should not be preferred to assess clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity after repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: RCI-mediated improvements in Disease Activity Score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate and Clinical Disease Activity Index scores suggested clinically meaningful improvement with more than 84% of patients meeting the minimal clinically important difference/minimally important difference criteria, which ranged from 26.3% to 34.7% for MBDA.
Study details: The data come from a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study of 259 patients with active RA despite treatment with stable glucocorticoid dose and 1 or 2 disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Patients achieving low disease activity during open-label period were randomly assigned to either 80 U of RCI (n=77) or placebo (n=76) during the 12-week double-blind period.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. R Fleischmann, DE Furst, and OG Segurado reported receiving clinical trial grants and consulting fees from various pharmaceutical companies including Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. J Liu and J Zhu declared being employees of Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
Source: Fleischmann R et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Feb 28. doi: 10.1002/acr.24583.
Durability of tocilizumab response in patients with RA
Key clinical point: Median durability of tocilizumab (TCZ) response was more than 3 years when measured as maintenance of minimum clinically important difference (MCID) in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) score in patients with RA initiating TCZ.
Major finding: Overall, durability of response among patients who initiated TCZ and achieved MCID in CDAI remained more than 50% after 3 years of follow-up. The proportion of patients maintaining MCID durability at 1, 2, and 3 years was 64.4% (95% CI, 59.2%-69.6%), 56.0% (95% CI, 50.0%-62.0%), and 51.8% (95% CI, 44.7%-58.9%), respectively.
Study details: The findings are from an observational study of 1,789 patients with RA who initiated TCZ and were enrolled in the US-based Corrona RA Registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Corrona LLC, and the analysis was funded by Genentech, Inc. DA Pappas, T Blachley, and K Emeanuru declared being employees and/or shareholders of Corrona, LLC. JH Best, WG Reiss, and S Zlotnick declared being current/former employees and/or shareholders of Genentech, Inc.
Source: Pappas DA et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Feb 25. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00285-0.
Key clinical point: Median durability of tocilizumab (TCZ) response was more than 3 years when measured as maintenance of minimum clinically important difference (MCID) in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) score in patients with RA initiating TCZ.
Major finding: Overall, durability of response among patients who initiated TCZ and achieved MCID in CDAI remained more than 50% after 3 years of follow-up. The proportion of patients maintaining MCID durability at 1, 2, and 3 years was 64.4% (95% CI, 59.2%-69.6%), 56.0% (95% CI, 50.0%-62.0%), and 51.8% (95% CI, 44.7%-58.9%), respectively.
Study details: The findings are from an observational study of 1,789 patients with RA who initiated TCZ and were enrolled in the US-based Corrona RA Registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Corrona LLC, and the analysis was funded by Genentech, Inc. DA Pappas, T Blachley, and K Emeanuru declared being employees and/or shareholders of Corrona, LLC. JH Best, WG Reiss, and S Zlotnick declared being current/former employees and/or shareholders of Genentech, Inc.
Source: Pappas DA et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Feb 25. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00285-0.
Key clinical point: Median durability of tocilizumab (TCZ) response was more than 3 years when measured as maintenance of minimum clinically important difference (MCID) in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) score in patients with RA initiating TCZ.
Major finding: Overall, durability of response among patients who initiated TCZ and achieved MCID in CDAI remained more than 50% after 3 years of follow-up. The proportion of patients maintaining MCID durability at 1, 2, and 3 years was 64.4% (95% CI, 59.2%-69.6%), 56.0% (95% CI, 50.0%-62.0%), and 51.8% (95% CI, 44.7%-58.9%), respectively.
Study details: The findings are from an observational study of 1,789 patients with RA who initiated TCZ and were enrolled in the US-based Corrona RA Registry.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Corrona LLC, and the analysis was funded by Genentech, Inc. DA Pappas, T Blachley, and K Emeanuru declared being employees and/or shareholders of Corrona, LLC. JH Best, WG Reiss, and S Zlotnick declared being current/former employees and/or shareholders of Genentech, Inc.
Source: Pappas DA et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Feb 25. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00285-0.
Additional iguratimod may allow tapering MTX dose in RA with remission
Key clinical point: The addition of iguratimod (IGU) can effectively reduce methotrexate (MTX) dose required by rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with long-term clinical remission.
Major finding: MTX dose could be reduced from 8.6±2.4 mg/week to 4.7±2.2 mg/week at 36 weeks. Despite MTX dose reduction, disease activity score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate was maintained at 1.48 at baseline and 1.69 at 36 weeks (P = .911). Other than drug discontinuation by 2 patients in the IGU addition group, no other adverse events were observed.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective analysis of 47 patients with RA who had sustained clinical remission with MTX for more than 24 weeks. Patients either continued constant MTX dose (n=25) or were treated with additional IGU and tapered MTX dose (n=22).
Disclosures: No source of funding was declared. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yoshikawa A et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 16. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1892945.
Key clinical point: The addition of iguratimod (IGU) can effectively reduce methotrexate (MTX) dose required by rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with long-term clinical remission.
Major finding: MTX dose could be reduced from 8.6±2.4 mg/week to 4.7±2.2 mg/week at 36 weeks. Despite MTX dose reduction, disease activity score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate was maintained at 1.48 at baseline and 1.69 at 36 weeks (P = .911). Other than drug discontinuation by 2 patients in the IGU addition group, no other adverse events were observed.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective analysis of 47 patients with RA who had sustained clinical remission with MTX for more than 24 weeks. Patients either continued constant MTX dose (n=25) or were treated with additional IGU and tapered MTX dose (n=22).
Disclosures: No source of funding was declared. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yoshikawa A et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 16. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1892945.
Key clinical point: The addition of iguratimod (IGU) can effectively reduce methotrexate (MTX) dose required by rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with long-term clinical remission.
Major finding: MTX dose could be reduced from 8.6±2.4 mg/week to 4.7±2.2 mg/week at 36 weeks. Despite MTX dose reduction, disease activity score 28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate was maintained at 1.48 at baseline and 1.69 at 36 weeks (P = .911). Other than drug discontinuation by 2 patients in the IGU addition group, no other adverse events were observed.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective analysis of 47 patients with RA who had sustained clinical remission with MTX for more than 24 weeks. Patients either continued constant MTX dose (n=25) or were treated with additional IGU and tapered MTX dose (n=22).
Disclosures: No source of funding was declared. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yoshikawa A et al. Mod Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 16. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2021.1892945.
JAK inhibitors vs. rituximab in patients with RA and pulmonary disease
Key clinical point: Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKis: baricitinib or tofacitinib) vs. rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients with concurrent interstitial lung disease (ILD) or bronchiectasis did not increase the rate of hospitalization or mortality because of a respiratory cause.
Major finding: Respiratory events were reported in 5 patients treated with JAKi (18%; 7 hospitalizations, 2 of whom died) and 4 patients treated with rituximab (21%; 4 hospitalizations, 1 of whom died). Respiratory event survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.38; P = .64) and the rate of drug discontinuation HR, 1.9; P = .251) did not differ significantly between groups.
Study details: A retrospective analysis of patients with RA and concurrent ILD or bronchiectasis who received JAKis (n=28: baricitinib, n=26; tofacitinib, n=2) or rituximab (n=19) for a mean of 1.1 and 2.14 years, respectively.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The lead author received sponsorship from Lilly and Pfizer to attend educational conferences. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Citation: Cronin O et al. Rheumatol Int. 2021 Mar 15. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04835-1.
Key clinical point: Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKis: baricitinib or tofacitinib) vs. rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients with concurrent interstitial lung disease (ILD) or bronchiectasis did not increase the rate of hospitalization or mortality because of a respiratory cause.
Major finding: Respiratory events were reported in 5 patients treated with JAKi (18%; 7 hospitalizations, 2 of whom died) and 4 patients treated with rituximab (21%; 4 hospitalizations, 1 of whom died). Respiratory event survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.38; P = .64) and the rate of drug discontinuation HR, 1.9; P = .251) did not differ significantly between groups.
Study details: A retrospective analysis of patients with RA and concurrent ILD or bronchiectasis who received JAKis (n=28: baricitinib, n=26; tofacitinib, n=2) or rituximab (n=19) for a mean of 1.1 and 2.14 years, respectively.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The lead author received sponsorship from Lilly and Pfizer to attend educational conferences. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Citation: Cronin O et al. Rheumatol Int. 2021 Mar 15. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04835-1.
Key clinical point: Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKis: baricitinib or tofacitinib) vs. rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients with concurrent interstitial lung disease (ILD) or bronchiectasis did not increase the rate of hospitalization or mortality because of a respiratory cause.
Major finding: Respiratory events were reported in 5 patients treated with JAKi (18%; 7 hospitalizations, 2 of whom died) and 4 patients treated with rituximab (21%; 4 hospitalizations, 1 of whom died). Respiratory event survival (hazard ratio [HR], 1.38; P = .64) and the rate of drug discontinuation HR, 1.9; P = .251) did not differ significantly between groups.
Study details: A retrospective analysis of patients with RA and concurrent ILD or bronchiectasis who received JAKis (n=28: baricitinib, n=26; tofacitinib, n=2) or rituximab (n=19) for a mean of 1.1 and 2.14 years, respectively.
Disclosures: The study did not receive any funding. The lead author received sponsorship from Lilly and Pfizer to attend educational conferences. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Citation: Cronin O et al. Rheumatol Int. 2021 Mar 15. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04835-1.
Peficitinib safe and effective for long-term management of RA
Key clinical point: Peficitinib (ASP015K) showed improvement in clinical outcomes, which was maintained throughout the treatment duration of 32 months along with a generally tolerable safety profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: The American College of Rheumatology (ACR)20, ACR50, and ACR70 response rates were maintained throughout from baseline (71.6%, 52.1%, and 34.7%, respectively) to the end of treatment (78.7%, 63.3%, and 44.1%, respectively). Treatment-emergent adverse events, mostly grade 1 or 2 in severity, were experienced by 94.4% of patients, leading to drug discontinuation in 16.6% of patients.
Study details: Findings are from the final analysis of an open-label long-term extension study involving 843 Asian patients with RA who previously completed phase 2b and phase 3 studies of peficitinib.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Astellas Pharma, Inc. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants, speaker’s fees, consultancy fees, personal fees, and/or honoraria from various sources including Astellas Pharma, Inc. Four of the authors reported being employees of Astellas Pharma, Inc.
Source: Takeuchi T et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00280-5.
Key clinical point: Peficitinib (ASP015K) showed improvement in clinical outcomes, which was maintained throughout the treatment duration of 32 months along with a generally tolerable safety profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: The American College of Rheumatology (ACR)20, ACR50, and ACR70 response rates were maintained throughout from baseline (71.6%, 52.1%, and 34.7%, respectively) to the end of treatment (78.7%, 63.3%, and 44.1%, respectively). Treatment-emergent adverse events, mostly grade 1 or 2 in severity, were experienced by 94.4% of patients, leading to drug discontinuation in 16.6% of patients.
Study details: Findings are from the final analysis of an open-label long-term extension study involving 843 Asian patients with RA who previously completed phase 2b and phase 3 studies of peficitinib.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Astellas Pharma, Inc. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants, speaker’s fees, consultancy fees, personal fees, and/or honoraria from various sources including Astellas Pharma, Inc. Four of the authors reported being employees of Astellas Pharma, Inc.
Source: Takeuchi T et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00280-5.
Key clinical point: Peficitinib (ASP015K) showed improvement in clinical outcomes, which was maintained throughout the treatment duration of 32 months along with a generally tolerable safety profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Major finding: The American College of Rheumatology (ACR)20, ACR50, and ACR70 response rates were maintained throughout from baseline (71.6%, 52.1%, and 34.7%, respectively) to the end of treatment (78.7%, 63.3%, and 44.1%, respectively). Treatment-emergent adverse events, mostly grade 1 or 2 in severity, were experienced by 94.4% of patients, leading to drug discontinuation in 16.6% of patients.
Study details: Findings are from the final analysis of an open-label long-term extension study involving 843 Asian patients with RA who previously completed phase 2b and phase 3 studies of peficitinib.
Disclosures: This work was funded by the Astellas Pharma, Inc. The authors including the lead author reported receiving grants, speaker’s fees, consultancy fees, personal fees, and/or honoraria from various sources including Astellas Pharma, Inc. Four of the authors reported being employees of Astellas Pharma, Inc.
Source: Takeuchi T et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 Mar 3. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00280-5.
Sustained remission more likely with biological vs. triple therapy after inadequate response to MTX
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who initiated biological vs. triple therapy after inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX) were more likely to achieve sustained remission (SR).
Major finding: Patients initiating biological vs. triple therapy were more likely to achieve short-term and long-term SR at 1 year (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.18-2.71 and aOR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.00-3.48, respectively) and 2 years (aOR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.21-3.06 and aOR, 1.62; 95% CI, 0.94-2.79, respectively) from treatment initiation.
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of 1,502 patients with relatively early RA who initiated biological (biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs+MTX; n=1,155) or triple (MTX+sulfasalazine+hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine; n=347) therapy as the first treatment strategy after inadequate response to MTX monotherapy.
Disclosures: This work funded by the Swedish Rheumatism Association, the Medical Faculty of Lund University, Alfred Österlund ́s Foundation, Greta and Johan Kock ́s foundation, the King Gustaf V Foundation, Lund University Hospital, Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation, and Anna-Greta Crafoord Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 7. doi: 10.1002/art.41720.
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who initiated biological vs. triple therapy after inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX) were more likely to achieve sustained remission (SR).
Major finding: Patients initiating biological vs. triple therapy were more likely to achieve short-term and long-term SR at 1 year (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.18-2.71 and aOR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.00-3.48, respectively) and 2 years (aOR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.21-3.06 and aOR, 1.62; 95% CI, 0.94-2.79, respectively) from treatment initiation.
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of 1,502 patients with relatively early RA who initiated biological (biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs+MTX; n=1,155) or triple (MTX+sulfasalazine+hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine; n=347) therapy as the first treatment strategy after inadequate response to MTX monotherapy.
Disclosures: This work funded by the Swedish Rheumatism Association, the Medical Faculty of Lund University, Alfred Österlund ́s Foundation, Greta and Johan Kock ́s foundation, the King Gustaf V Foundation, Lund University Hospital, Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation, and Anna-Greta Crafoord Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 7. doi: 10.1002/art.41720.
Key clinical point: Patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who initiated biological vs. triple therapy after inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX) were more likely to achieve sustained remission (SR).
Major finding: Patients initiating biological vs. triple therapy were more likely to achieve short-term and long-term SR at 1 year (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.18-2.71 and aOR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.00-3.48, respectively) and 2 years (aOR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.21-3.06 and aOR, 1.62; 95% CI, 0.94-2.79, respectively) from treatment initiation.
Study details: Findings are from an analysis of 1,502 patients with relatively early RA who initiated biological (biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs+MTX; n=1,155) or triple (MTX+sulfasalazine+hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine; n=347) therapy as the first treatment strategy after inadequate response to MTX monotherapy.
Disclosures: This work funded by the Swedish Rheumatism Association, the Medical Faculty of Lund University, Alfred Österlund ́s Foundation, Greta and Johan Kock ́s foundation, the King Gustaf V Foundation, Lund University Hospital, Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation, and Anna-Greta Crafoord Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Källmark H et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 7. doi: 10.1002/art.41720.
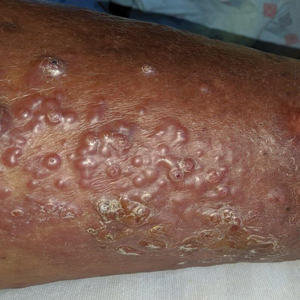
Vesicles and Bullae on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).
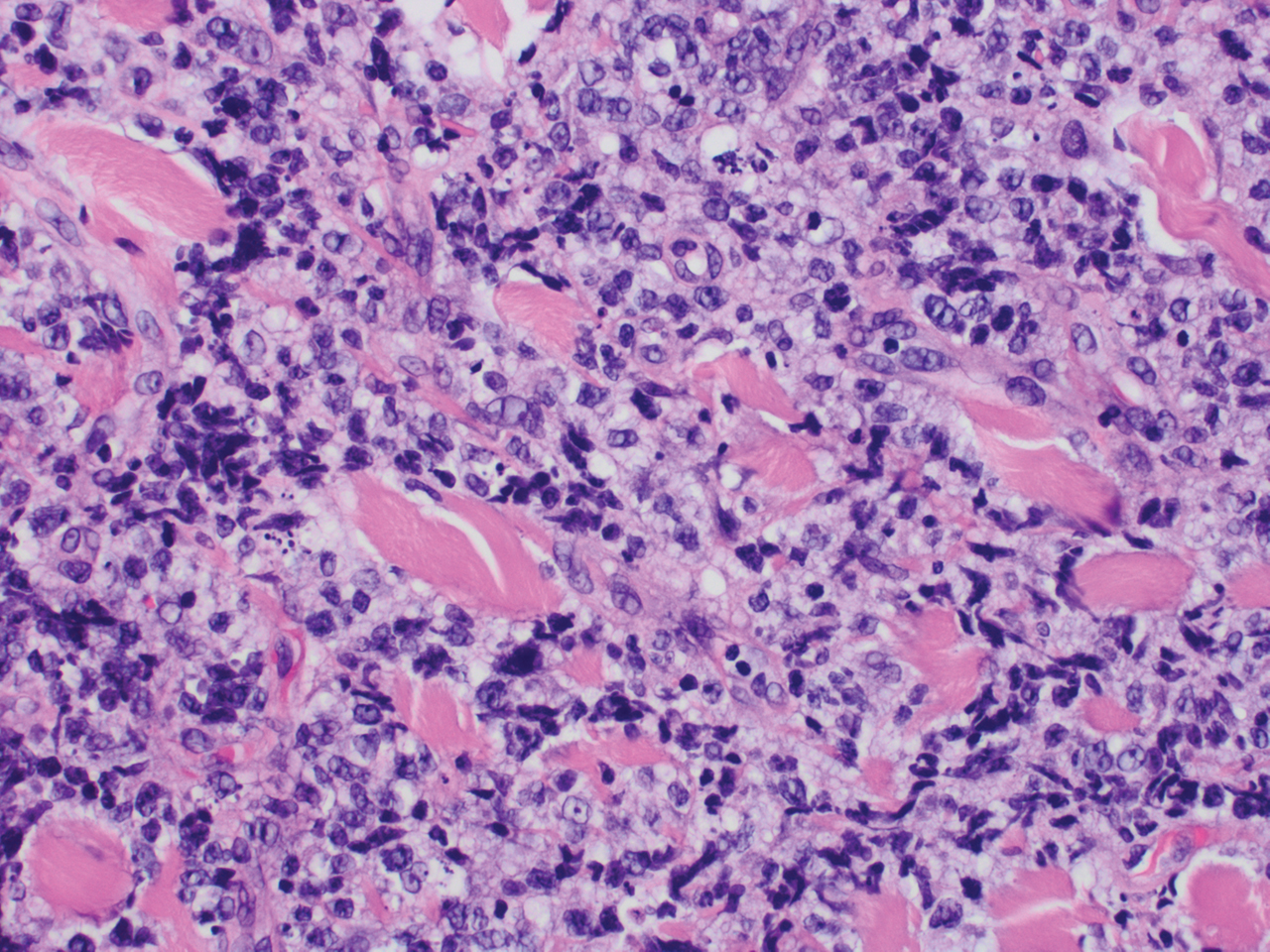
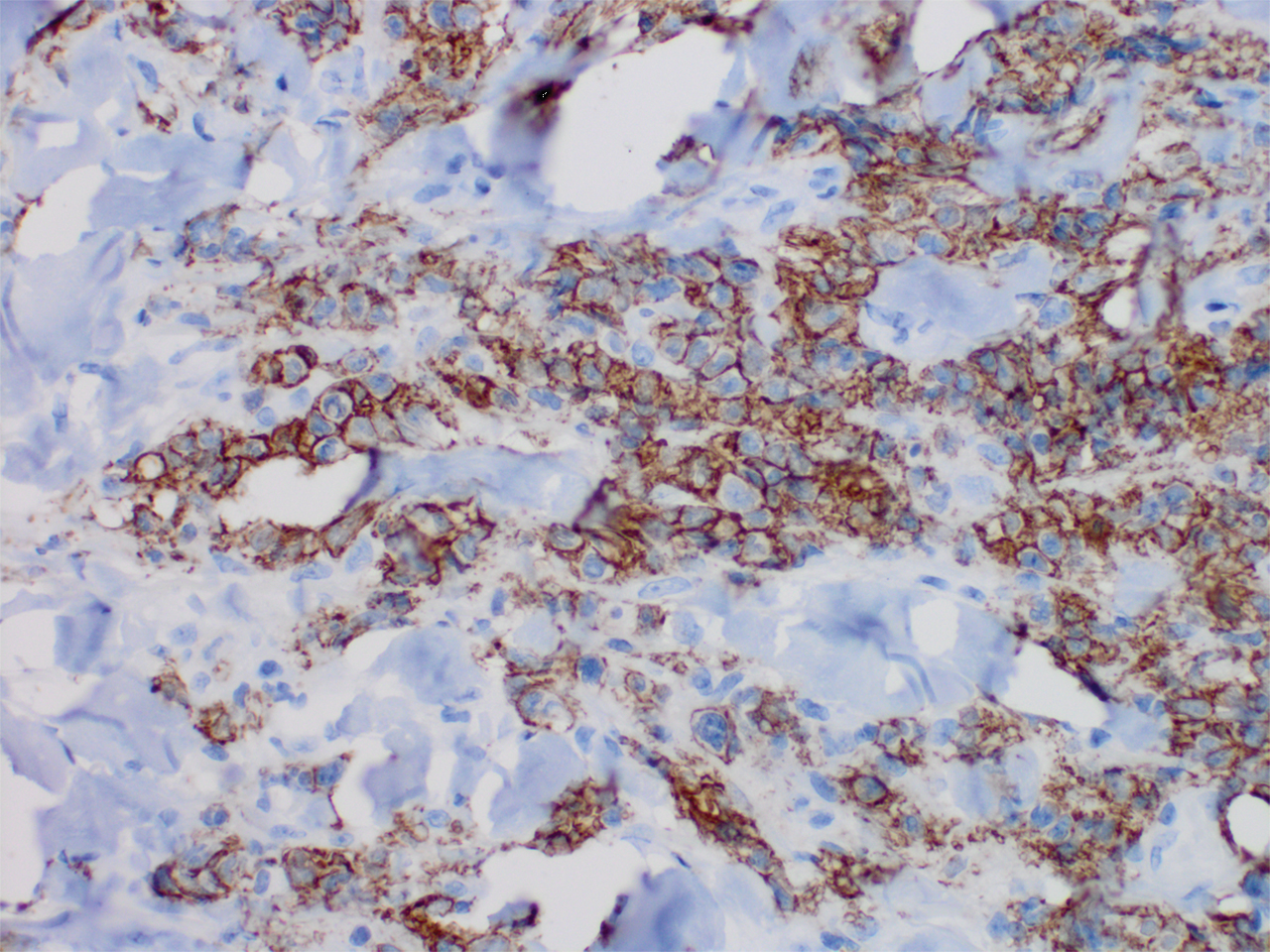
Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).


Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous B-cell Lymphoma
Histopathology revealed a dense and diffuse lymphocytic infiltrate throughout the dermis with occasional individual cell necrosis. On closer inspection, the infiltrate consisted of intermediate-sized lymphocytes, some with a vesiculated nucleus and ample amount of cytoplasm, while others contained hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1). These cells stained strongly positive for B-cell marker (CD20), while only a few mature lymphocytes demonstrated T-cell phenotype (CD3)(Figure 2).


Although the patient recounted a 3-month history of lower leg edema, he also reported that the rash began a few weeks after his diagnosis of systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma. Throughout this time, he was seen by various physicians who attributed the edema and skin changes to chronic stasis, peripheral venous insufficiency, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. His primary care physician prescribed an antifungal lotion, which he discontinued on his own due to lack of improvement. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was started on intravenous cefazolin and subcutaneous heparin. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs was ordered to rule out a deep venous thrombosis. Dermatology was consulted and proceeded with a punch biopsy to investigate for cutaneous B-cell lymphoma (BCL) with a plan to follow up as an outpatient for results upon discharge. He also was prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily for symptomatic relief.
The patient's left axillary lymph node was biopsied for pathologic evaluation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed expression of B-cell markers CD20, CD79a, and PAX5, along with the antiapoptotic markers BCL-2 and BCL-6. Fluorescence in situ hybridization displayed gene rearrangements of BCL-2, BCL-6, and t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 in the majority of cells. CD3 and CD5 immunostains were negative, indicating that T cells were not involved in this process. Flow cytometry identified a monoclonal κ B-cell population in 40% to 50% of the total cells, which co-expressed CD10, CD19, CD22, and CD38; the cells were negative for CD5, CD20, and CD23. Cell size was variably enlarged and CD71 positive, otherwise known as transferrin receptor 1, indicating the mediation of iron transport into cells of erythroid lineage that is necessary for proliferation.1 Bone marrow core biopsy did not identify features of bone marrow involvement by the lymphoma. Based on these results, the patient was diagnosed with systemic B-cell follicular lymphoma grade 3b stage IIIA. Oncology initiated a systemic chemotherapy regimen with obinutuzumab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin), vincristine sulfate, and prednisone.
Skin involvement in B-cell follicular lymphoma can be primary or secondary. Although all subtypes of BCL can have secondary cutaneous involvement, it is most common in advanced-stage disease (stages III or IV).2 Cutaneous manifestations of primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma (PCFCL) and systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma secondarily involving the skin can be difficult to distinguish clinically and histopathologically; both appear as solitary or grouped plaques and nodules most commonly on the head, neck, or trunk, and rarely on the legs.3 Although the pathologic features of these two diagnoses can seem almost identical, it is important to differentiate them due to their differing prognosis and management. Patients with follicular lymphoma involving the skin are more likely than those with PCFCL to develop lymphadenopathy and B symptoms.3 Primary cutaneous follicle-center lymphoma also generally runs an indolent course and requires local therapy, while secondary involvement of the skin due to systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma has a worse prognosis and requires systemic chemotherapy treatment.4
Immunohistochemical markers are the most helpful tool used to distinguish PCFCL from systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma involving the skin. Tumors of B-cell origin are expected to express associated B-cell markers such as CD20, CD79a, and PAX52; BCL-6, a marker of germinal center cells, also is expected to stain positive.2 CD10 is positive in a majority of cases with a follicular growth pattern, while those with a diffuse pattern of growth may have a negative stain.2 The most valuable histopathologic indicator differentiating primary and secondary skin involvement is the intensity of BCL-2 expression.5 The prognostic significance of the t(14;18)/IgH-BCL2 rearrangement is controversial, with rearrangement identified in more than 75% of systemic/nodal follicular lymphoma cases and less commonly found in PCFCL, with one report arguing an incidence ranging from 1% to 40%.5
A comprehensive history and physical examination are necessary to develop a differential diagnosis. Our patient's lower leg edema and extensive medical history made the diagnosis more complicated. Pitting edema was present on physical examination, making elephantiasis nostras verrucosa less likely, as it would instead present with nonpitting edema and a woody feel.6 Our patient did not have epidemiologic exposure to filariasis through foreign travel and did not present with any classic signs or symptoms of lymphatic filariasis, such as fever, eosinophilia, chyluria, or hydrocele.7 Although a negative history of HIV makes Kaposi sarcoma and bacillary angiomatosis less likely diagnoses, a biopsy would be useful to rule out these conditions. Positive inguinal lymphadenopathy present on physical examination may have contributed to lymphatic flow obstruction leading to the leg lymphedema in our patient.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
- Marsee DK, Pinkus GS, Yu H. CD71 (transferrin receptor): an effective marker for erythroid precursors in bone marrow biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:429-435.
- Jaffe ES. Navigating the cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: avoiding the rocky shoals. Mod Pathol. 2020;33(suppl 1):96-106.
- Skala SL, Hristov B, Hristov AC. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1313-1321.
- Suárez AL, Pulitzer M, Horwitz S, et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: part I. clinical features, diagnosis, and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:329.e1-13; quiz 341-342.
- Servitje O, Climent F, Colomo L, et al. Primary cutaneous vs secondary cutaneous follicular lymphomas: a comparative study focused on BCL2, CD10, and t(14;18) expression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;46:182-189.
- Fredman R, Tenenhaus M. Elephantiasis nostras verrucose [published online October 12, 2012]. Eplasty. 2012;12:ic14.
- Lourens GB, Ferrell DK. Lymphatic filariasis. Nurs Clin of North Am. 2019;54:181-192.
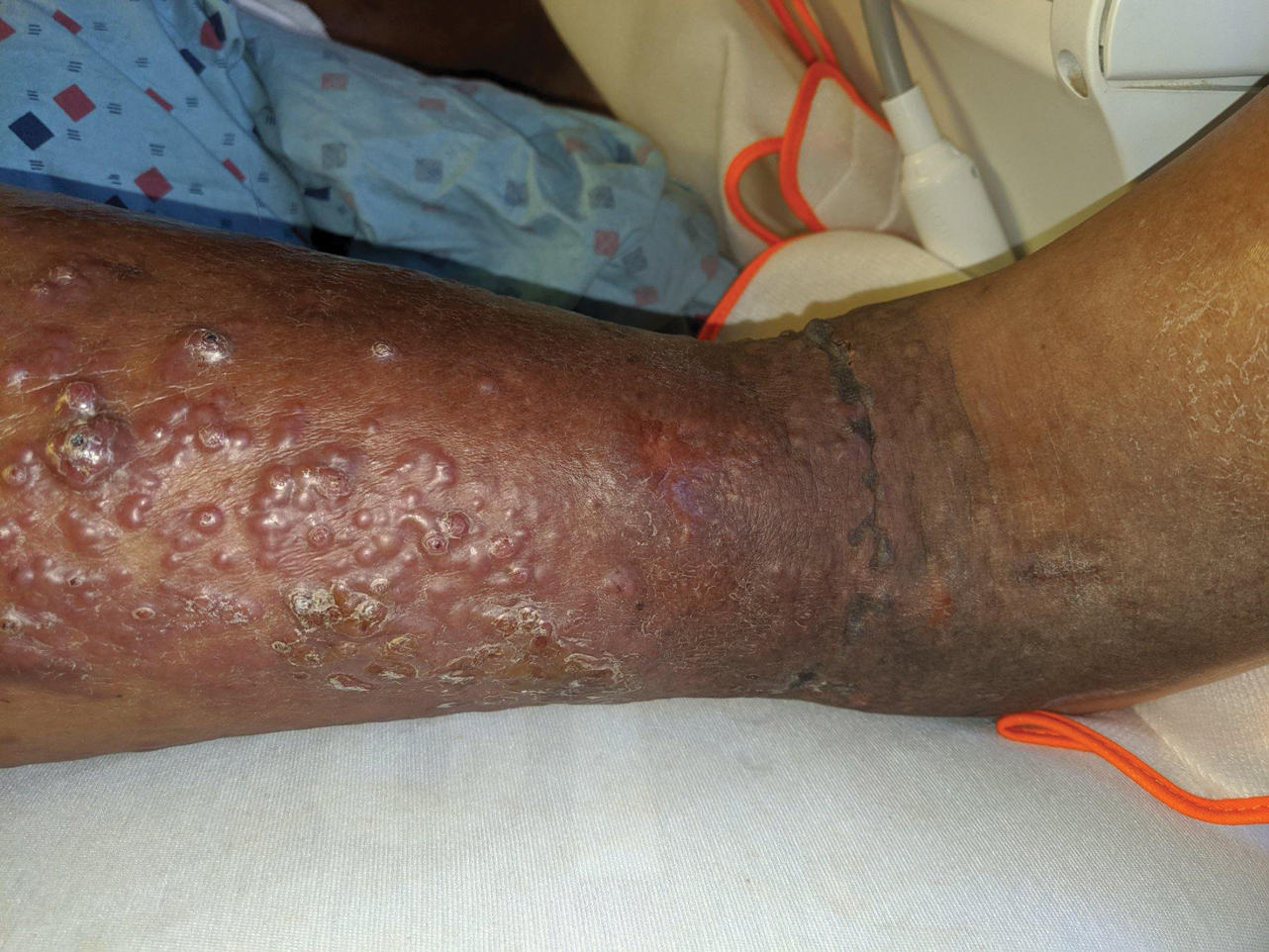
A 60-year-old man presented to the emergency department with slowly progressing edema of the lower legs of 3 months’ duration. In the week prior to presentation to the emergency department, he noticed a sudden eruption of vesicles and bullae on the right leg that drained clear fluid and healed with brown crust. The lesions were associated with mild burning, pruritus, and pain. He denied fever, chills, recent travel, or injury. His medical history was notable for poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, hyperlipidemia, and chronic anemia. Physical examination revealed multiple scattered erythematous vesicles and bullae on the right leg on a background of hyperpigmentation. Bilateral 2+ pitting edema of the legs also was present. A punch biopsy of a lesion was performed.
Bimekizumab superior to adalimumab in head-to-head psoriasis study
for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the head-to-head, phase 3 BE SURE trial, Jerry Bagel, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
“Results demonstrated that bimekizumab was superior to adalimumab over 16 weeks of treatment in terms of the speed, depth, and durability of skin clearance,” reported Dr. Bagel, a dermatologist at the Psoriasis Center of Central New Jersey, East Windsor.
The Food and Drug Administration is now reviewing UCB’s application for marketing approval of bimekizumab for treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis in adults.
BE SURE was a 478-patient, double-blind, phase 3 trial in which patients were randomized to one of three regimens: 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks; the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab (Humira) at 40 mg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, followed by a switch to bimekizumab at 320 mg every 4 weeks; or 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then ratcheting back to dosing every 8 weeks. The trial concluded at week 56, Dr. Bagel explained at the conference sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The two coprimary endpoints were the 16-week rates of a 90% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, or PASI 90 response, and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, meaning clear or almost clear. Bimekizumab every 4 weeks bested adalimumab on both endpoints, with a PASI 90 rate of 86.2%, compared with 47.2%, and a IGA 0/1 rate of 85.3% versus 57.2%. The 16-week PASI 100 response rate was 60.8% with bimekizumab and 23.9% with adalimumab.
The response to bimekizumab was notably fast: already by week 4, the PASI 75 rate was 76.4%, compared with 31.4% with adalimumab. And once patients switched from adalimumab to bimekizumab at week 24, their response rates shot up rapidly. Bimekizumab was equally effective whether dosed at 320 mg every 4 weeks or at maintenance dosing every 8 weeks, such that at week 56 patients in all three study arms had PASI 90 rates of 82%-84%.
The most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events associated with bimekizumab were oral candidiasis, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection. The oral candidiasis, which occurred in 13.2% of patients on bimekizumab every 4 weeks, was mainly mild to moderate, localized, and in no instance led to discontinuation of therapy, according to Dr. Bagel.
“Very impressive data,” commented session comoderator Linda Stein Gold, MD. “This study shows some data that’s potentially unprecedented. Bimekizumab was superior to one of the drugs that we know, we’ve used, and know is very, very effective.”
“Note the speed of this drug,” added comoderator Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn. “It achieved at week 4 the efficacy that it took adalimumab until week 16 to reach. So it is a very fast drug. Bimekizumab will be the fastest drug you’ve ever, ever worked with.”
“You’ll see in the bimekizumab studies about a fivefold increased frequency of oral candidiasis relative to our more legacy IL-17 inhibitors, such as ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab. I think that means approximately one in five or one in six patients will have some form of candidiasis when you treat them with bimekizumab,” he said. Therefore, he added, “in some patients you’ll have to manage oral candidiasis. Most affected patients don’t leave the studies, so it’s manageable, but you’ll have to become something of an authority on how to treat with, for example, oral antifungal swish-and-swallow, swish-and-spit, or oral fluconazole. And some of these patients will have recurrent infections.”
It’s a prospect that doesn’t concern Dr. Stein Gold. “This is a side effect that we can treat. We can see it, we’re comfortable with it, and it’s certainly something we can get a handle on,” said Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology clinical research at the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
BE SURE was funded by UCB. Dr. Bagel reported serving as a speaker for, consultant to, and paid investigator for AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Novartis, and Ortho Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stein Gold and Dr. Strober reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the head-to-head, phase 3 BE SURE trial, Jerry Bagel, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
“Results demonstrated that bimekizumab was superior to adalimumab over 16 weeks of treatment in terms of the speed, depth, and durability of skin clearance,” reported Dr. Bagel, a dermatologist at the Psoriasis Center of Central New Jersey, East Windsor.
The Food and Drug Administration is now reviewing UCB’s application for marketing approval of bimekizumab for treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis in adults.
BE SURE was a 478-patient, double-blind, phase 3 trial in which patients were randomized to one of three regimens: 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks; the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab (Humira) at 40 mg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, followed by a switch to bimekizumab at 320 mg every 4 weeks; or 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then ratcheting back to dosing every 8 weeks. The trial concluded at week 56, Dr. Bagel explained at the conference sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The two coprimary endpoints were the 16-week rates of a 90% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, or PASI 90 response, and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, meaning clear or almost clear. Bimekizumab every 4 weeks bested adalimumab on both endpoints, with a PASI 90 rate of 86.2%, compared with 47.2%, and a IGA 0/1 rate of 85.3% versus 57.2%. The 16-week PASI 100 response rate was 60.8% with bimekizumab and 23.9% with adalimumab.
The response to bimekizumab was notably fast: already by week 4, the PASI 75 rate was 76.4%, compared with 31.4% with adalimumab. And once patients switched from adalimumab to bimekizumab at week 24, their response rates shot up rapidly. Bimekizumab was equally effective whether dosed at 320 mg every 4 weeks or at maintenance dosing every 8 weeks, such that at week 56 patients in all three study arms had PASI 90 rates of 82%-84%.
The most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events associated with bimekizumab were oral candidiasis, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection. The oral candidiasis, which occurred in 13.2% of patients on bimekizumab every 4 weeks, was mainly mild to moderate, localized, and in no instance led to discontinuation of therapy, according to Dr. Bagel.
“Very impressive data,” commented session comoderator Linda Stein Gold, MD. “This study shows some data that’s potentially unprecedented. Bimekizumab was superior to one of the drugs that we know, we’ve used, and know is very, very effective.”
“Note the speed of this drug,” added comoderator Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn. “It achieved at week 4 the efficacy that it took adalimumab until week 16 to reach. So it is a very fast drug. Bimekizumab will be the fastest drug you’ve ever, ever worked with.”
“You’ll see in the bimekizumab studies about a fivefold increased frequency of oral candidiasis relative to our more legacy IL-17 inhibitors, such as ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab. I think that means approximately one in five or one in six patients will have some form of candidiasis when you treat them with bimekizumab,” he said. Therefore, he added, “in some patients you’ll have to manage oral candidiasis. Most affected patients don’t leave the studies, so it’s manageable, but you’ll have to become something of an authority on how to treat with, for example, oral antifungal swish-and-swallow, swish-and-spit, or oral fluconazole. And some of these patients will have recurrent infections.”
It’s a prospect that doesn’t concern Dr. Stein Gold. “This is a side effect that we can treat. We can see it, we’re comfortable with it, and it’s certainly something we can get a handle on,” said Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology clinical research at the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
BE SURE was funded by UCB. Dr. Bagel reported serving as a speaker for, consultant to, and paid investigator for AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Novartis, and Ortho Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stein Gold and Dr. Strober reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
for treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in the head-to-head, phase 3 BE SURE trial, Jerry Bagel, MD, said at Innovations in Dermatology: Virtual Spring Conference 2021.
“Results demonstrated that bimekizumab was superior to adalimumab over 16 weeks of treatment in terms of the speed, depth, and durability of skin clearance,” reported Dr. Bagel, a dermatologist at the Psoriasis Center of Central New Jersey, East Windsor.
The Food and Drug Administration is now reviewing UCB’s application for marketing approval of bimekizumab for treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis in adults.
BE SURE was a 478-patient, double-blind, phase 3 trial in which patients were randomized to one of three regimens: 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks; the tumor necrosis factor blocker adalimumab (Humira) at 40 mg every 2 weeks for 24 weeks, followed by a switch to bimekizumab at 320 mg every 4 weeks; or 320 mg of bimekizumab every 4 weeks for 16 weeks, then ratcheting back to dosing every 8 weeks. The trial concluded at week 56, Dr. Bagel explained at the conference sponsored by MedscapeLIVE! and the producers of the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar and Caribbean Dermatology Symposium.
The two coprimary endpoints were the 16-week rates of a 90% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, or PASI 90 response, and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, meaning clear or almost clear. Bimekizumab every 4 weeks bested adalimumab on both endpoints, with a PASI 90 rate of 86.2%, compared with 47.2%, and a IGA 0/1 rate of 85.3% versus 57.2%. The 16-week PASI 100 response rate was 60.8% with bimekizumab and 23.9% with adalimumab.
The response to bimekizumab was notably fast: already by week 4, the PASI 75 rate was 76.4%, compared with 31.4% with adalimumab. And once patients switched from adalimumab to bimekizumab at week 24, their response rates shot up rapidly. Bimekizumab was equally effective whether dosed at 320 mg every 4 weeks or at maintenance dosing every 8 weeks, such that at week 56 patients in all three study arms had PASI 90 rates of 82%-84%.
The most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events associated with bimekizumab were oral candidiasis, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection. The oral candidiasis, which occurred in 13.2% of patients on bimekizumab every 4 weeks, was mainly mild to moderate, localized, and in no instance led to discontinuation of therapy, according to Dr. Bagel.
“Very impressive data,” commented session comoderator Linda Stein Gold, MD. “This study shows some data that’s potentially unprecedented. Bimekizumab was superior to one of the drugs that we know, we’ve used, and know is very, very effective.”
“Note the speed of this drug,” added comoderator Bruce E. Strober, MD, PhD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and Central Connecticut Dermatology, Cromwell, Conn. “It achieved at week 4 the efficacy that it took adalimumab until week 16 to reach. So it is a very fast drug. Bimekizumab will be the fastest drug you’ve ever, ever worked with.”
“You’ll see in the bimekizumab studies about a fivefold increased frequency of oral candidiasis relative to our more legacy IL-17 inhibitors, such as ixekizumab, secukinumab, and brodalumab. I think that means approximately one in five or one in six patients will have some form of candidiasis when you treat them with bimekizumab,” he said. Therefore, he added, “in some patients you’ll have to manage oral candidiasis. Most affected patients don’t leave the studies, so it’s manageable, but you’ll have to become something of an authority on how to treat with, for example, oral antifungal swish-and-swallow, swish-and-spit, or oral fluconazole. And some of these patients will have recurrent infections.”
It’s a prospect that doesn’t concern Dr. Stein Gold. “This is a side effect that we can treat. We can see it, we’re comfortable with it, and it’s certainly something we can get a handle on,” said Dr. Stein Gold, director of dermatology clinical research at the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit.
BE SURE was funded by UCB. Dr. Bagel reported serving as a speaker for, consultant to, and paid investigator for AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Leo Pharma, Novartis, and Ortho Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stein Gold and Dr. Strober reported having financial relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
MedscapeLIVE! and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY