User login
Radiologically Isolated Syndrome: A condition that often precedes an MS diagnosis in children
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
Naila Makhani, MD completed medical school training at the University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada). This was followed by a residency in child neurology and fellowship in MS and other demyelinating diseases at the University of Toronto and The Hospital for Sick Children (Toronto, Canada). Concurrent with fellowship training, Dr. Makhani obtained a Masters’ degree in public health from Harvard University. Dr. Makhani is the Director of the Pediatric MS Program at Yale and the lead investigator of a multi-center international study examining outcomes following the radiologically isolated syndrome in children.
Q1. Could you please provide an overview of Radiologically Isolated Syndrome ?
A1. Radiologically Isolated Syndrome (RIS) was first described in adults in 2009. Since then it has also been increasingly recognized and diagnosed in children. RIS is diagnosed after an MRI of the brain that the patient has sought for reasons other than suspected multiple sclerosis-- for instance, for evaluation of head trauma or headache. However, unexpectedly or incidentally, the patient’s MRI shows the typical findings that we see in multiple sclerosis, even in the absence of any typical clinical symptoms. RIS is generally considered a rare syndrome.
Q2. You created Yale Medicine’s Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis program which advocates for the eradication of MS. What criteria defines a rare disease? Does RIS meet these criteria? And if so, how?
A2. The criteria for a rare disease vary, depending on the reference. In the US, a rare disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people, in total, across the country. By contrast, in Europe, a disease is considered rare if it affects fewer than one in every 2,000 people within the country’s population.
In the case of RIS, especially in children, we suspect that this is a rare condition, but we don't know for sure, as there have been very few population-based studies. There is one large study that was conducted in Europe that found one case of RIS among approximately 5,000 otherwise healthy children, who were between 7 and 14 years of age. I think that's our best estimate of the overall prevalence of RIS in children. Using that finding, it likely would qualify as a rare condition, although, as I said, we really don't know for sure, as the prevalence may vary among different populations or age groups.
Q3. How do you investigate and manage RIS in children? What are some of the challenges?
A3. For children with radiologically isolated syndrome, we usually undertake a comprehensive workup. This includes a detailed clinical neurological exam to ensure that there are no abnormalities that would, for instance, suggest a misdiagnosis of multiple sclerosis or an alternative diagnosis. In addition to the brain MRI, we usually obtain an MRI of the spinal cord to determine whether there is any spinal cord involvement. We also obtain blood tests. We often analyze spinal fluid as well, primarily to exclude other alternative processes that may explain the MRI findings. A key challenge in this field is that there are currently no formal guidelines for the investigation and management of children with RIS. Collaborations within the pediatric MS community are needed to develop such consensus approaches to standardize care.
Q4. What are the most significant risk factors that indicate children with RIS could one day develop multiple sclerosis?
A4.This is an area of active research within our group. So far, we've found that approximately 42% of children with RIS develop multiple sclerosis in the future; on average, two years following their first abnormal MRI. Therefore, this is a high-risk group for developing multiple sclerosis in the future. Thus far, we've determined that in children with RIS, it is the presence of abnormal spinal cord imaging and an abnormality in spinal fluid – namely, the presence of oligoclonal bands – that are likely the predictors of whether these children could develop MS in the future. a child’s possible development
Q5. Based on your recent studies, are there data in children highlighting the potential for higher prevalence in one population over another?
A5. Thus far, population-based studies assessing RIS, especially in children, have been rare and thus far have not identified particular subgroups with increased prevalence. We do know that the prevalence of multiple sclerosis varies across different age groups and across gender. Whether such associations are also present for RIS is an area of active research.
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227
de Mol CL, Bruijstens AL, Jansen PR, Dremmen M, Wong Y, van der Lugt A, White T, Neuteboom RF.Mult Scler. 2021 Oct;27(11):1790-1793. doi: 10.1177/1352458521989220. Epub 2021 Jan 22.PMID: 33480814
2. Radiologically isolated syndrome in children: Clinical and radiologic outcomes.
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Brassat D, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Du W, Durand Dubief F, Kantarci O, Langille M, Narula S, Pelletier J, Rojas JI, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vermersch P, Wassmer E, Okuda DT, Pelletier D.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2017 Sep 25;4(6):e395. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000395. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 28959703
Makhani N, Lebrun C, Siva A, Narula S, Wassmer E, Brassat D, Brenton JN, Cabre P, Carra Dallière C, de Seze J, Durand Dubief F, Inglese M, Langille M, Mathey G, Neuteboom RF, Pelletier J, Pohl D, Reich DS, Ignacio Rojas J, Shabanova V, Shapiro ED, Stone RT, Tenembaum S, Tintoré M, Uygunoglu U, Vargas W, Venkateswaren S, Vermersch P, Kantarci O, Okuda DT, Pelletier D; Observatoire Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (OFSEP), Société Francophone de la Sclérose en Plaques (SFSEP), the Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (RISC) and the Pediatric Radiologically Isolated Syndrome Consortium (PARIS).Mult Scler J Exp Transl Clin. 2019 Mar 20;5(1):2055217319836664. doi: 10.1177/2055217319836664. eCollection 2019 Jan-Mar.PMID: 30915227
Vitamin D and omega-3 supplements reduce autoimmune disease risk
For those of us who cannot sit in the sun and fish all day, the next best thing for preventing autoimmune diseases may be supplementation with vitamin D and fish oil-derived omega-3 fatty acids, results of a large prospective randomized trial suggest.
Among nearly 26,000 adults enrolled in a randomized trial designed primarily to study the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 supplementation on incident cancer and cardiovascular disease, 5, and 5 years of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with an 18% reduction in confirmed and probable incident autoimmune diseases, reported Karen H. Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The clinical importance of these results is very high, given that these are nontoxic, well-tolerated supplements, and that there are no other known effective therapies to reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases,” she said during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“People do have to take the supplements a long time to start to see the reduction in risk, especially for vitamin D, but they make biological sense, and autoimmune diseases develop slowly over time, so taking it today isn’t going to reduce risk of developing something tomorrow,” Dr. Costenbader said in an interview.
“These supplements have other health benefits. Obviously, fish oil is anti-inflammatory, and vitamin D is good for osteoporosis prevention, especially in our patients who take glucocorticoids. People who are otherwise healthy and have a family history of autoimmune disease might also consider starting to take these supplements,” she said.
After watching her presentation, session co-moderator Gregg Silverman, MD, from the NYU Langone School of Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the study, commented “I’m going to [nutrition store] GNC to get some vitamins.”
When asked for comment, the other session moderator, Tracy Frech, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, said, “I think Dr. Costenbader’s work is very important and her presentation excellent. My current practice is replacement of vitamin D in all autoimmune disease patients with low levels and per bone health guidelines. Additionally, I discuss omega-3 supplementation with Sjögren’s [syndrome] patients as a consideration.”
Evidence base
Dr. Costenbader noted that in a 2013 observational study from France, vitamin D derived through ultraviolet (UV) light exposure was associated with a lower risk for incident Crohn’s disease but not ulcerative colitis, and in two analyses of data in 2014 from the Nurses’ Health Study, both high plasma levels of 25-OH vitamin D and geographic residence in areas of high UV exposure were associated with a decreased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Other observational studies have supported omega-3 fatty acids for their anti-inflammatory properties, including a 2005 Danish prospective cohort study showing a lower risk for RA in participants who reported higher levels of fatty fish intake. In a separate study conducted in 2017, healthy volunteers with higher omega-3 fatty acid/total lipid proportions in red blood cell membranes had a lower prevalence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies and rheumatoid factor and a lower incidence of progression to inflammatory arthritis, she said.
Ancillary study
Despite the evidence, however, there have been no prospective randomized trials to test the effects of either vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of autoimmune disease over time.
To rectify this, Dr. Costenbader and colleagues piggybacked an ancillary study onto the Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL), which had primary outcomes of cancer and cardiovascular disease incidence.
A total of 25,871 participants were enrolled, including 12,786 men aged 50 and older, and 13,085 women aged 55 and older.
The study had a 2 x 2 factorial design, with patients randomly assigned to vitamin D 2,000 IU/day or placebo, and then further randomized to either 1 g/day omega-3 fatty acids or placebo in both the vitamin D and placebo primary randomization arms.
At baseline 16,956 participants were assayed for 25-OH vitamin D and plasma omega 3 index, the ratio of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to total fatty acids. Participants self-reported baseline and all incident autoimmune diseases annually, with the reports confirmed by medical record review and disease criteria whenever possible.
Results
At 5 years of follow-up, confirmed incident autoimmune diseases had occurred in 123 patients in the active vitamin D group, compared with 155 in the placebo vitamin D group, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for vitamin D of 0.78 (P = .045).
In the active omega-3 arm, 130 participants developed an autoimmune disease, compared with 148 in the placebo omega-3 arm, which translated into a nonsignificant HR of 0.85.
There was no statistical interaction between the two supplements. The investigators did observe an interaction between vitamin D and body mass index, with the effect stronger among participants with low BMI (P = .02). There also was an interaction between omega-3 fatty acids with a family history of autoimmune disease (P = .03).
In multivariate analysis adjusted for age, sex, race, and other supplement arm, vitamin D alone was associated with an HR for incident autoimmune disease of 0.68 (P = .02), omega-3 alone was associated with a nonsignificant HR of 0.74, and the combination was associated with an HR of 0.69 (P = .03).
Dr. Costenbader and colleagues acknowledged that the study was limited by the lack of a high-risk or nutritionally-deficient population, where the effects of supplementation might be larger; the restriction of the sample to older adults; and to the difficulty of confirming incident autoimmune thyroid disease from patient reports.
Cheryl Koehn, an arthritis patient advocate from Vancouver, Canada, who was not involved in the study, commented in the “chat” section of the presentation that her rheumatologist “has recommended vitamin D for years now. Says basically everyone north of Boston is vitamin D deficient. I take 1,000 IU per day. Been taking it for years.” Ms. Koehn is the founder and president of Arthritis Consumer Experts, a website that provides education to those with arthritis.
“Agreed. I tell every patient to take vitamin D supplement,” commented Fatma Dedeoglu, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For those of us who cannot sit in the sun and fish all day, the next best thing for preventing autoimmune diseases may be supplementation with vitamin D and fish oil-derived omega-3 fatty acids, results of a large prospective randomized trial suggest.
Among nearly 26,000 adults enrolled in a randomized trial designed primarily to study the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 supplementation on incident cancer and cardiovascular disease, 5, and 5 years of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with an 18% reduction in confirmed and probable incident autoimmune diseases, reported Karen H. Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The clinical importance of these results is very high, given that these are nontoxic, well-tolerated supplements, and that there are no other known effective therapies to reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases,” she said during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“People do have to take the supplements a long time to start to see the reduction in risk, especially for vitamin D, but they make biological sense, and autoimmune diseases develop slowly over time, so taking it today isn’t going to reduce risk of developing something tomorrow,” Dr. Costenbader said in an interview.
“These supplements have other health benefits. Obviously, fish oil is anti-inflammatory, and vitamin D is good for osteoporosis prevention, especially in our patients who take glucocorticoids. People who are otherwise healthy and have a family history of autoimmune disease might also consider starting to take these supplements,” she said.
After watching her presentation, session co-moderator Gregg Silverman, MD, from the NYU Langone School of Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the study, commented “I’m going to [nutrition store] GNC to get some vitamins.”
When asked for comment, the other session moderator, Tracy Frech, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, said, “I think Dr. Costenbader’s work is very important and her presentation excellent. My current practice is replacement of vitamin D in all autoimmune disease patients with low levels and per bone health guidelines. Additionally, I discuss omega-3 supplementation with Sjögren’s [syndrome] patients as a consideration.”
Evidence base
Dr. Costenbader noted that in a 2013 observational study from France, vitamin D derived through ultraviolet (UV) light exposure was associated with a lower risk for incident Crohn’s disease but not ulcerative colitis, and in two analyses of data in 2014 from the Nurses’ Health Study, both high plasma levels of 25-OH vitamin D and geographic residence in areas of high UV exposure were associated with a decreased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Other observational studies have supported omega-3 fatty acids for their anti-inflammatory properties, including a 2005 Danish prospective cohort study showing a lower risk for RA in participants who reported higher levels of fatty fish intake. In a separate study conducted in 2017, healthy volunteers with higher omega-3 fatty acid/total lipid proportions in red blood cell membranes had a lower prevalence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies and rheumatoid factor and a lower incidence of progression to inflammatory arthritis, she said.
Ancillary study
Despite the evidence, however, there have been no prospective randomized trials to test the effects of either vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of autoimmune disease over time.
To rectify this, Dr. Costenbader and colleagues piggybacked an ancillary study onto the Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL), which had primary outcomes of cancer and cardiovascular disease incidence.
A total of 25,871 participants were enrolled, including 12,786 men aged 50 and older, and 13,085 women aged 55 and older.
The study had a 2 x 2 factorial design, with patients randomly assigned to vitamin D 2,000 IU/day or placebo, and then further randomized to either 1 g/day omega-3 fatty acids or placebo in both the vitamin D and placebo primary randomization arms.
At baseline 16,956 participants were assayed for 25-OH vitamin D and plasma omega 3 index, the ratio of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to total fatty acids. Participants self-reported baseline and all incident autoimmune diseases annually, with the reports confirmed by medical record review and disease criteria whenever possible.
Results
At 5 years of follow-up, confirmed incident autoimmune diseases had occurred in 123 patients in the active vitamin D group, compared with 155 in the placebo vitamin D group, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for vitamin D of 0.78 (P = .045).
In the active omega-3 arm, 130 participants developed an autoimmune disease, compared with 148 in the placebo omega-3 arm, which translated into a nonsignificant HR of 0.85.
There was no statistical interaction between the two supplements. The investigators did observe an interaction between vitamin D and body mass index, with the effect stronger among participants with low BMI (P = .02). There also was an interaction between omega-3 fatty acids with a family history of autoimmune disease (P = .03).
In multivariate analysis adjusted for age, sex, race, and other supplement arm, vitamin D alone was associated with an HR for incident autoimmune disease of 0.68 (P = .02), omega-3 alone was associated with a nonsignificant HR of 0.74, and the combination was associated with an HR of 0.69 (P = .03).
Dr. Costenbader and colleagues acknowledged that the study was limited by the lack of a high-risk or nutritionally-deficient population, where the effects of supplementation might be larger; the restriction of the sample to older adults; and to the difficulty of confirming incident autoimmune thyroid disease from patient reports.
Cheryl Koehn, an arthritis patient advocate from Vancouver, Canada, who was not involved in the study, commented in the “chat” section of the presentation that her rheumatologist “has recommended vitamin D for years now. Says basically everyone north of Boston is vitamin D deficient. I take 1,000 IU per day. Been taking it for years.” Ms. Koehn is the founder and president of Arthritis Consumer Experts, a website that provides education to those with arthritis.
“Agreed. I tell every patient to take vitamin D supplement,” commented Fatma Dedeoglu, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For those of us who cannot sit in the sun and fish all day, the next best thing for preventing autoimmune diseases may be supplementation with vitamin D and fish oil-derived omega-3 fatty acids, results of a large prospective randomized trial suggest.
Among nearly 26,000 adults enrolled in a randomized trial designed primarily to study the effects of vitamin D and omega-3 supplementation on incident cancer and cardiovascular disease, 5, and 5 years of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation was associated with an 18% reduction in confirmed and probable incident autoimmune diseases, reported Karen H. Costenbader, MD, MPH, of Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston.
“The clinical importance of these results is very high, given that these are nontoxic, well-tolerated supplements, and that there are no other known effective therapies to reduce the incidence of autoimmune diseases,” she said during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“People do have to take the supplements a long time to start to see the reduction in risk, especially for vitamin D, but they make biological sense, and autoimmune diseases develop slowly over time, so taking it today isn’t going to reduce risk of developing something tomorrow,” Dr. Costenbader said in an interview.
“These supplements have other health benefits. Obviously, fish oil is anti-inflammatory, and vitamin D is good for osteoporosis prevention, especially in our patients who take glucocorticoids. People who are otherwise healthy and have a family history of autoimmune disease might also consider starting to take these supplements,” she said.
After watching her presentation, session co-moderator Gregg Silverman, MD, from the NYU Langone School of Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the study, commented “I’m going to [nutrition store] GNC to get some vitamins.”
When asked for comment, the other session moderator, Tracy Frech, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, said, “I think Dr. Costenbader’s work is very important and her presentation excellent. My current practice is replacement of vitamin D in all autoimmune disease patients with low levels and per bone health guidelines. Additionally, I discuss omega-3 supplementation with Sjögren’s [syndrome] patients as a consideration.”
Evidence base
Dr. Costenbader noted that in a 2013 observational study from France, vitamin D derived through ultraviolet (UV) light exposure was associated with a lower risk for incident Crohn’s disease but not ulcerative colitis, and in two analyses of data in 2014 from the Nurses’ Health Study, both high plasma levels of 25-OH vitamin D and geographic residence in areas of high UV exposure were associated with a decreased incidence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Other observational studies have supported omega-3 fatty acids for their anti-inflammatory properties, including a 2005 Danish prospective cohort study showing a lower risk for RA in participants who reported higher levels of fatty fish intake. In a separate study conducted in 2017, healthy volunteers with higher omega-3 fatty acid/total lipid proportions in red blood cell membranes had a lower prevalence of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies and rheumatoid factor and a lower incidence of progression to inflammatory arthritis, she said.
Ancillary study
Despite the evidence, however, there have been no prospective randomized trials to test the effects of either vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on the incidence of autoimmune disease over time.
To rectify this, Dr. Costenbader and colleagues piggybacked an ancillary study onto the Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL), which had primary outcomes of cancer and cardiovascular disease incidence.
A total of 25,871 participants were enrolled, including 12,786 men aged 50 and older, and 13,085 women aged 55 and older.
The study had a 2 x 2 factorial design, with patients randomly assigned to vitamin D 2,000 IU/day or placebo, and then further randomized to either 1 g/day omega-3 fatty acids or placebo in both the vitamin D and placebo primary randomization arms.
At baseline 16,956 participants were assayed for 25-OH vitamin D and plasma omega 3 index, the ratio of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to total fatty acids. Participants self-reported baseline and all incident autoimmune diseases annually, with the reports confirmed by medical record review and disease criteria whenever possible.
Results
At 5 years of follow-up, confirmed incident autoimmune diseases had occurred in 123 patients in the active vitamin D group, compared with 155 in the placebo vitamin D group, translating into a hazard ratio (HR) for vitamin D of 0.78 (P = .045).
In the active omega-3 arm, 130 participants developed an autoimmune disease, compared with 148 in the placebo omega-3 arm, which translated into a nonsignificant HR of 0.85.
There was no statistical interaction between the two supplements. The investigators did observe an interaction between vitamin D and body mass index, with the effect stronger among participants with low BMI (P = .02). There also was an interaction between omega-3 fatty acids with a family history of autoimmune disease (P = .03).
In multivariate analysis adjusted for age, sex, race, and other supplement arm, vitamin D alone was associated with an HR for incident autoimmune disease of 0.68 (P = .02), omega-3 alone was associated with a nonsignificant HR of 0.74, and the combination was associated with an HR of 0.69 (P = .03).
Dr. Costenbader and colleagues acknowledged that the study was limited by the lack of a high-risk or nutritionally-deficient population, where the effects of supplementation might be larger; the restriction of the sample to older adults; and to the difficulty of confirming incident autoimmune thyroid disease from patient reports.
Cheryl Koehn, an arthritis patient advocate from Vancouver, Canada, who was not involved in the study, commented in the “chat” section of the presentation that her rheumatologist “has recommended vitamin D for years now. Says basically everyone north of Boston is vitamin D deficient. I take 1,000 IU per day. Been taking it for years.” Ms. Koehn is the founder and president of Arthritis Consumer Experts, a website that provides education to those with arthritis.
“Agreed. I tell every patient to take vitamin D supplement,” commented Fatma Dedeoglu, MD, a rheumatologist at Boston Children’s Hospital.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2021
Liquid biopsy in metastatic breast cancer management: Where does it stand in clinical practice?
Tissue biopsy remains the gold standard for characterizing tumor biology and guiding therapeutic decisions, but liquid biopsies — blood analyses that allow oncologists to detect circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the blood — are increasingly demonstrating their value. Last year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two liquid biopsy tests, Guardant360 CDx and FoundationOne Liquid CDx, that can identify more than 300 cancer-related genes in the blood. In 2019, the FDA also approved the first companion diagnostic test, therascreen, to pinpoint PIK3CA gene mutations in patients’ ctDNA and determine whether patients should receive the PI3K inhibitor alpelisib along with fulvestrant.
Here’s an overview of how liquid biopsy is being used in monitoring MBC progression and treatment — and what some oncologists think of it.
What we do and don’t know
“Identifying a patient’s targetable mutations, most notably PIK3CA mutations, is currently the main use of liquid biopsy,” said Pedram Razavi, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist who leads the liquid biopsy program for breast cancer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center in New York City. “Patients who come to MSK are offered a tumor and liquid biopsy at the time of metastatic diagnosis as part of the standard of care.”
Liquid and tissue biopsy analyses can provide a more complete picture of a patient’s condition. Whereas tissue biopsy allows oncologists to target a more saturated sample of the cancer ecosystem and a wider array of biomarkers, liquid biopsy offers important advantages as well, including a less invasive way to sequence a sample, monitor patients’ treatment response, or track tumor evolution. Liquid biopsy also provides a bigger picture view of tumor heterogeneity by pooling information from many tumor locations as opposed to one.
But, cautioned Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, liquid biopsy technology is not always sensitive enough to detect CTCs, ctDNA, or all relevant mutations. “When you collect a small tube of blood, you’re essentially trying to catch a small fish in a big sea and wading through a lot of background noise,” said Dr. Yuan, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County. “The results may be hard to interpret or come back inconclusive.”
And although emerging data suggest that liquid biopsy provides important insights about tumor dynamics — including mapping disease progression, predicting survival, and even detecting signs of cancer recurrence before metastasis develops — the tool has limited utility in clinical practice outside of identifying sensitivity to various therapies or drugs.
“Right now, a lot of research is being done to understand how to use CTC and ctDNA in particular as a means of surveillance in breast cancer, but we’re still in the beginning stages of applying that outside of clinical trials,” said Joseph A. Sparano, MD, deputy director of the Tisch Cancer Institute and chief of the division of hematology and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Personalizing treatment
The companion diagnostic test therascreen marked the beginning stages of using liquid biopsy to match treatments to genetic abnormalities in MBC. The SOLAR-1 phase 3 trial, which led to the approval of alpelisib and therascreen, found that the PI3K inhibitor plus fulvestrant almost doubled progression-free survival (PFS) (11 months vs 5.7 months in placebo-fulvestrant group) in patients with PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer.
More recent studies have shown that liquid biopsy tests can also identify ESR1 mutations and predict responses to inhibitors that target AKT1 and HER2. Investigators presenting at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting reported that next-generation sequencing of ctDNA in patients with HR-positive MBC, HER-positive MBC, or triple-negative breast cancer detected ESR1 mutations in 14% of patients (71 of 501). Moreover, ESR1 mutations were found only in HR-positive patients who had already received endocrine therapy. (The study also examined PIK3CA mutations, which occurred in about one third of patients). A more in-depth look revealed that ESR1 mutations were strongly associated with liver and bone metastases and that mutations along specific codons negatively affected overall survival (OS) and PFS: codons 537 and 538 for OS and codons 380 and 536 for PFS.
According to Debasish Tripathy, MD, professor and chairman of the department of breast medical oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, in addition to tumor sequencing, “liquid biopsy has become a great research tool to track patients in real time and predict, for instance, who will respond to a treatment and identify emerging resistance.”
In terms of predicting responses to treatment, the plasmaMATCH trial assessed ctDNA in 1,034 patients with advanced breast cancer for mutations in ESR1, HER2, and AKT1 using digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Guardant360. Results showed that 357 (34.5%) of these patients had potentially targetable aberrations, including 222 patients with ESR1 mutations, 36 patients with HER2 mutations, and 30 patients with AKT1 mutations.
Agreement between digital droplet PCR and Guardant360 testing was 96%-99%, and liquid biopsy showed 93% sensitivity compared with tumor samples. The investigators also used liquid biopsy findings to match patients’ mutations to targeted treatments: fulvestrant for those with ESR1 mutations, neratinib for HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, and the selective AKT inhibitor capivasertib for estrogen receptor–positive tumors with AKT1 mutations.
Overall, the investigators concluded that ctDNA testing offers “accurate tumor genotyping” in line with tissue-based testing and is ready for routine clinical practice to identify common as well as rare genetic alterations, such as HER2 and AKT1 mutations, that affect only about 5% of patients with advanced disease.
Predicting survival and recurrence
A particularly promising area for liquid biopsy is its usefulness in helping to predict survival outcomes and monitor patients for early signs of recurrence before metastasis occurs. But the data to support this are still in their infancy.
A highly cited study, published over 15 years ago in the New England Journal of Medicine, found that patients with MBC who had five or more CTCs per 7.5 mL of whole blood before receiving first-line therapy exhibited significantly shorter median PFS (2.7 vs 7.0 months) and OS (10 vs > 18 months) compared with patients with fewer than five CTCs. Subsequent analyses performed more than a decade later, including a meta-analysis published last year, helped validate these early findings that levels of CTCs detected in the blood independently and strongly predicted PFS and OS in patients with MBC.
In addition, ctDNA can provide important information about patients’ survival odds. In a retrospective study published last year, investigators tracked changes in ctDNA in 291 plasma samples from 84 patients with locally advanced breast cancer who participated in the I-SPY trial. Patients who remained ctDNA-positive after 3 weeks of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were significantly more likely to have residual disease after completing their treatment compared with patients who cleared ctDNA at that early stage (83% for those with nonpathologic complete response vs 52%). Notably, the presence of ctDNA between therapy initiation and completion was associated with a significantly greater risk for metastatic recurrence, whereas clearance of ctDNA after neoadjuvant therapy was linked to improved survival.
“The study is important because it highlights how tracking circulating ctDNA status in neoadjuvant-treated breast cancer can expose a patient’s risk for distant metastasis,” said Dr. Yuan. But, she added, “I think the biggest attraction of liquid biopsy will be the ability to detect molecular disease even before imaging can, and identify who has a high risk for recurrence.”
Dr. Razavi agreed that the potential to prevent metastasis by finding minimal residual disease (MRD) is the most exciting area of liquid biopsy research. “If we can find tumor DNA early before tumors have a chance to establish themselves, we could potentially change the trajectory of the disease for patients,” he said.
Several studies suggest that monitoring patients’ ctDNA levels after neoadjuvant treatment and surgery may help predict their risk for relapse and progression to metastatic disease. A 2015 analysis, which followed 20 patients with breast cancer after surgery, found that ctDNA monitoring accurately differentiated those who ultimately developed metastatic disease from those who didn’t (sensitivity, 93%; specificity, 100%) and detected metastatic disease 11 months earlier, on average, than imaging did. Another 2015 study found that the presence of ctDNA in plasma after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery predicted metastatic relapse a median of almost 8 months before clinical detection. Other recent data show the power of ultrasensitive blood tests to detect MRD and potentially find metastatic disease early.
Although an increasing number of studies show that ctDNA and CTCs are prognostic for breast cancer recurrence, a major question remains: For patients with ctDNA or CTCs but no overt disease after imaging, will initiating therapy prevent or delay the development of metastatic disease?
“We still have to do those clinical trials to determine whether detecting MRD and treating patients early actually positively affects their survival and quality of life,” Dr. Razavi said.
Tissue biopsy remains the gold standard for characterizing tumor biology and guiding therapeutic decisions, but liquid biopsies — blood analyses that allow oncologists to detect circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the blood — are increasingly demonstrating their value. Last year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two liquid biopsy tests, Guardant360 CDx and FoundationOne Liquid CDx, that can identify more than 300 cancer-related genes in the blood. In 2019, the FDA also approved the first companion diagnostic test, therascreen, to pinpoint PIK3CA gene mutations in patients’ ctDNA and determine whether patients should receive the PI3K inhibitor alpelisib along with fulvestrant.
Here’s an overview of how liquid biopsy is being used in monitoring MBC progression and treatment — and what some oncologists think of it.
What we do and don’t know
“Identifying a patient’s targetable mutations, most notably PIK3CA mutations, is currently the main use of liquid biopsy,” said Pedram Razavi, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist who leads the liquid biopsy program for breast cancer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center in New York City. “Patients who come to MSK are offered a tumor and liquid biopsy at the time of metastatic diagnosis as part of the standard of care.”
Liquid and tissue biopsy analyses can provide a more complete picture of a patient’s condition. Whereas tissue biopsy allows oncologists to target a more saturated sample of the cancer ecosystem and a wider array of biomarkers, liquid biopsy offers important advantages as well, including a less invasive way to sequence a sample, monitor patients’ treatment response, or track tumor evolution. Liquid biopsy also provides a bigger picture view of tumor heterogeneity by pooling information from many tumor locations as opposed to one.
But, cautioned Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, liquid biopsy technology is not always sensitive enough to detect CTCs, ctDNA, or all relevant mutations. “When you collect a small tube of blood, you’re essentially trying to catch a small fish in a big sea and wading through a lot of background noise,” said Dr. Yuan, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County. “The results may be hard to interpret or come back inconclusive.”
And although emerging data suggest that liquid biopsy provides important insights about tumor dynamics — including mapping disease progression, predicting survival, and even detecting signs of cancer recurrence before metastasis develops — the tool has limited utility in clinical practice outside of identifying sensitivity to various therapies or drugs.
“Right now, a lot of research is being done to understand how to use CTC and ctDNA in particular as a means of surveillance in breast cancer, but we’re still in the beginning stages of applying that outside of clinical trials,” said Joseph A. Sparano, MD, deputy director of the Tisch Cancer Institute and chief of the division of hematology and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Personalizing treatment
The companion diagnostic test therascreen marked the beginning stages of using liquid biopsy to match treatments to genetic abnormalities in MBC. The SOLAR-1 phase 3 trial, which led to the approval of alpelisib and therascreen, found that the PI3K inhibitor plus fulvestrant almost doubled progression-free survival (PFS) (11 months vs 5.7 months in placebo-fulvestrant group) in patients with PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer.
More recent studies have shown that liquid biopsy tests can also identify ESR1 mutations and predict responses to inhibitors that target AKT1 and HER2. Investigators presenting at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting reported that next-generation sequencing of ctDNA in patients with HR-positive MBC, HER-positive MBC, or triple-negative breast cancer detected ESR1 mutations in 14% of patients (71 of 501). Moreover, ESR1 mutations were found only in HR-positive patients who had already received endocrine therapy. (The study also examined PIK3CA mutations, which occurred in about one third of patients). A more in-depth look revealed that ESR1 mutations were strongly associated with liver and bone metastases and that mutations along specific codons negatively affected overall survival (OS) and PFS: codons 537 and 538 for OS and codons 380 and 536 for PFS.
According to Debasish Tripathy, MD, professor and chairman of the department of breast medical oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, in addition to tumor sequencing, “liquid biopsy has become a great research tool to track patients in real time and predict, for instance, who will respond to a treatment and identify emerging resistance.”
In terms of predicting responses to treatment, the plasmaMATCH trial assessed ctDNA in 1,034 patients with advanced breast cancer for mutations in ESR1, HER2, and AKT1 using digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Guardant360. Results showed that 357 (34.5%) of these patients had potentially targetable aberrations, including 222 patients with ESR1 mutations, 36 patients with HER2 mutations, and 30 patients with AKT1 mutations.
Agreement between digital droplet PCR and Guardant360 testing was 96%-99%, and liquid biopsy showed 93% sensitivity compared with tumor samples. The investigators also used liquid biopsy findings to match patients’ mutations to targeted treatments: fulvestrant for those with ESR1 mutations, neratinib for HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, and the selective AKT inhibitor capivasertib for estrogen receptor–positive tumors with AKT1 mutations.
Overall, the investigators concluded that ctDNA testing offers “accurate tumor genotyping” in line with tissue-based testing and is ready for routine clinical practice to identify common as well as rare genetic alterations, such as HER2 and AKT1 mutations, that affect only about 5% of patients with advanced disease.
Predicting survival and recurrence
A particularly promising area for liquid biopsy is its usefulness in helping to predict survival outcomes and monitor patients for early signs of recurrence before metastasis occurs. But the data to support this are still in their infancy.
A highly cited study, published over 15 years ago in the New England Journal of Medicine, found that patients with MBC who had five or more CTCs per 7.5 mL of whole blood before receiving first-line therapy exhibited significantly shorter median PFS (2.7 vs 7.0 months) and OS (10 vs > 18 months) compared with patients with fewer than five CTCs. Subsequent analyses performed more than a decade later, including a meta-analysis published last year, helped validate these early findings that levels of CTCs detected in the blood independently and strongly predicted PFS and OS in patients with MBC.
In addition, ctDNA can provide important information about patients’ survival odds. In a retrospective study published last year, investigators tracked changes in ctDNA in 291 plasma samples from 84 patients with locally advanced breast cancer who participated in the I-SPY trial. Patients who remained ctDNA-positive after 3 weeks of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were significantly more likely to have residual disease after completing their treatment compared with patients who cleared ctDNA at that early stage (83% for those with nonpathologic complete response vs 52%). Notably, the presence of ctDNA between therapy initiation and completion was associated with a significantly greater risk for metastatic recurrence, whereas clearance of ctDNA after neoadjuvant therapy was linked to improved survival.
“The study is important because it highlights how tracking circulating ctDNA status in neoadjuvant-treated breast cancer can expose a patient’s risk for distant metastasis,” said Dr. Yuan. But, she added, “I think the biggest attraction of liquid biopsy will be the ability to detect molecular disease even before imaging can, and identify who has a high risk for recurrence.”
Dr. Razavi agreed that the potential to prevent metastasis by finding minimal residual disease (MRD) is the most exciting area of liquid biopsy research. “If we can find tumor DNA early before tumors have a chance to establish themselves, we could potentially change the trajectory of the disease for patients,” he said.
Several studies suggest that monitoring patients’ ctDNA levels after neoadjuvant treatment and surgery may help predict their risk for relapse and progression to metastatic disease. A 2015 analysis, which followed 20 patients with breast cancer after surgery, found that ctDNA monitoring accurately differentiated those who ultimately developed metastatic disease from those who didn’t (sensitivity, 93%; specificity, 100%) and detected metastatic disease 11 months earlier, on average, than imaging did. Another 2015 study found that the presence of ctDNA in plasma after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery predicted metastatic relapse a median of almost 8 months before clinical detection. Other recent data show the power of ultrasensitive blood tests to detect MRD and potentially find metastatic disease early.
Although an increasing number of studies show that ctDNA and CTCs are prognostic for breast cancer recurrence, a major question remains: For patients with ctDNA or CTCs but no overt disease after imaging, will initiating therapy prevent or delay the development of metastatic disease?
“We still have to do those clinical trials to determine whether detecting MRD and treating patients early actually positively affects their survival and quality of life,” Dr. Razavi said.
Tissue biopsy remains the gold standard for characterizing tumor biology and guiding therapeutic decisions, but liquid biopsies — blood analyses that allow oncologists to detect circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the blood — are increasingly demonstrating their value. Last year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved two liquid biopsy tests, Guardant360 CDx and FoundationOne Liquid CDx, that can identify more than 300 cancer-related genes in the blood. In 2019, the FDA also approved the first companion diagnostic test, therascreen, to pinpoint PIK3CA gene mutations in patients’ ctDNA and determine whether patients should receive the PI3K inhibitor alpelisib along with fulvestrant.
Here’s an overview of how liquid biopsy is being used in monitoring MBC progression and treatment — and what some oncologists think of it.
What we do and don’t know
“Identifying a patient’s targetable mutations, most notably PIK3CA mutations, is currently the main use of liquid biopsy,” said Pedram Razavi, MD, PhD, a medical oncologist who leads the liquid biopsy program for breast cancer at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) Cancer Center in New York City. “Patients who come to MSK are offered a tumor and liquid biopsy at the time of metastatic diagnosis as part of the standard of care.”
Liquid and tissue biopsy analyses can provide a more complete picture of a patient’s condition. Whereas tissue biopsy allows oncologists to target a more saturated sample of the cancer ecosystem and a wider array of biomarkers, liquid biopsy offers important advantages as well, including a less invasive way to sequence a sample, monitor patients’ treatment response, or track tumor evolution. Liquid biopsy also provides a bigger picture view of tumor heterogeneity by pooling information from many tumor locations as opposed to one.
But, cautioned Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, liquid biopsy technology is not always sensitive enough to detect CTCs, ctDNA, or all relevant mutations. “When you collect a small tube of blood, you’re essentially trying to catch a small fish in a big sea and wading through a lot of background noise,” said Dr. Yuan, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County. “The results may be hard to interpret or come back inconclusive.”
And although emerging data suggest that liquid biopsy provides important insights about tumor dynamics — including mapping disease progression, predicting survival, and even detecting signs of cancer recurrence before metastasis develops — the tool has limited utility in clinical practice outside of identifying sensitivity to various therapies or drugs.
“Right now, a lot of research is being done to understand how to use CTC and ctDNA in particular as a means of surveillance in breast cancer, but we’re still in the beginning stages of applying that outside of clinical trials,” said Joseph A. Sparano, MD, deputy director of the Tisch Cancer Institute and chief of the division of hematology and medical oncology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
Personalizing treatment
The companion diagnostic test therascreen marked the beginning stages of using liquid biopsy to match treatments to genetic abnormalities in MBC. The SOLAR-1 phase 3 trial, which led to the approval of alpelisib and therascreen, found that the PI3K inhibitor plus fulvestrant almost doubled progression-free survival (PFS) (11 months vs 5.7 months in placebo-fulvestrant group) in patients with PIK3CA-mutated, HR-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer.
More recent studies have shown that liquid biopsy tests can also identify ESR1 mutations and predict responses to inhibitors that target AKT1 and HER2. Investigators presenting at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology meeting reported that next-generation sequencing of ctDNA in patients with HR-positive MBC, HER-positive MBC, or triple-negative breast cancer detected ESR1 mutations in 14% of patients (71 of 501). Moreover, ESR1 mutations were found only in HR-positive patients who had already received endocrine therapy. (The study also examined PIK3CA mutations, which occurred in about one third of patients). A more in-depth look revealed that ESR1 mutations were strongly associated with liver and bone metastases and that mutations along specific codons negatively affected overall survival (OS) and PFS: codons 537 and 538 for OS and codons 380 and 536 for PFS.
According to Debasish Tripathy, MD, professor and chairman of the department of breast medical oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, in addition to tumor sequencing, “liquid biopsy has become a great research tool to track patients in real time and predict, for instance, who will respond to a treatment and identify emerging resistance.”
In terms of predicting responses to treatment, the plasmaMATCH trial assessed ctDNA in 1,034 patients with advanced breast cancer for mutations in ESR1, HER2, and AKT1 using digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Guardant360. Results showed that 357 (34.5%) of these patients had potentially targetable aberrations, including 222 patients with ESR1 mutations, 36 patients with HER2 mutations, and 30 patients with AKT1 mutations.
Agreement between digital droplet PCR and Guardant360 testing was 96%-99%, and liquid biopsy showed 93% sensitivity compared with tumor samples. The investigators also used liquid biopsy findings to match patients’ mutations to targeted treatments: fulvestrant for those with ESR1 mutations, neratinib for HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, and the selective AKT inhibitor capivasertib for estrogen receptor–positive tumors with AKT1 mutations.
Overall, the investigators concluded that ctDNA testing offers “accurate tumor genotyping” in line with tissue-based testing and is ready for routine clinical practice to identify common as well as rare genetic alterations, such as HER2 and AKT1 mutations, that affect only about 5% of patients with advanced disease.
Predicting survival and recurrence
A particularly promising area for liquid biopsy is its usefulness in helping to predict survival outcomes and monitor patients for early signs of recurrence before metastasis occurs. But the data to support this are still in their infancy.
A highly cited study, published over 15 years ago in the New England Journal of Medicine, found that patients with MBC who had five or more CTCs per 7.5 mL of whole blood before receiving first-line therapy exhibited significantly shorter median PFS (2.7 vs 7.0 months) and OS (10 vs > 18 months) compared with patients with fewer than five CTCs. Subsequent analyses performed more than a decade later, including a meta-analysis published last year, helped validate these early findings that levels of CTCs detected in the blood independently and strongly predicted PFS and OS in patients with MBC.
In addition, ctDNA can provide important information about patients’ survival odds. In a retrospective study published last year, investigators tracked changes in ctDNA in 291 plasma samples from 84 patients with locally advanced breast cancer who participated in the I-SPY trial. Patients who remained ctDNA-positive after 3 weeks of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were significantly more likely to have residual disease after completing their treatment compared with patients who cleared ctDNA at that early stage (83% for those with nonpathologic complete response vs 52%). Notably, the presence of ctDNA between therapy initiation and completion was associated with a significantly greater risk for metastatic recurrence, whereas clearance of ctDNA after neoadjuvant therapy was linked to improved survival.
“The study is important because it highlights how tracking circulating ctDNA status in neoadjuvant-treated breast cancer can expose a patient’s risk for distant metastasis,” said Dr. Yuan. But, she added, “I think the biggest attraction of liquid biopsy will be the ability to detect molecular disease even before imaging can, and identify who has a high risk for recurrence.”
Dr. Razavi agreed that the potential to prevent metastasis by finding minimal residual disease (MRD) is the most exciting area of liquid biopsy research. “If we can find tumor DNA early before tumors have a chance to establish themselves, we could potentially change the trajectory of the disease for patients,” he said.
Several studies suggest that monitoring patients’ ctDNA levels after neoadjuvant treatment and surgery may help predict their risk for relapse and progression to metastatic disease. A 2015 analysis, which followed 20 patients with breast cancer after surgery, found that ctDNA monitoring accurately differentiated those who ultimately developed metastatic disease from those who didn’t (sensitivity, 93%; specificity, 100%) and detected metastatic disease 11 months earlier, on average, than imaging did. Another 2015 study found that the presence of ctDNA in plasma after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery predicted metastatic relapse a median of almost 8 months before clinical detection. Other recent data show the power of ultrasensitive blood tests to detect MRD and potentially find metastatic disease early.
Although an increasing number of studies show that ctDNA and CTCs are prognostic for breast cancer recurrence, a major question remains: For patients with ctDNA or CTCs but no overt disease after imaging, will initiating therapy prevent or delay the development of metastatic disease?
“We still have to do those clinical trials to determine whether detecting MRD and treating patients early actually positively affects their survival and quality of life,” Dr. Razavi said.
Artificial Intelligence: Review of Current and Future Applications in Medicine
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was first described in 1956 and refers to machines having the ability to learn as they receive and process information, resulting in the ability to “think” like humans.1 AI’s impact in medicine is increasing; currently, at least 29 AI medical devices and algorithms are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in a variety of areas, including radiograph interpretation, managing glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus, analyzing electrocardiograms (ECGs), and diagnosing sleep disorders among others.2 Significantly, in 2020, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the first reimbursement to hospitals for an AI platform, a model for early detection of strokes.3 AI is rapidly becoming an integral part of health care, and its role will only increase in the future (Table).
As knowledge in medicine is expanding exponentially, AI has great potential to assist with handling complex patient care data. The concept of exponential growth is not a natural one. As Bini described, with exponential growth the volume of knowledge amassed over the past 10 years will now occur in perhaps only 1 year.1 Likewise, equivalent advances over the past year may take just a few months. This phenomenon is partly due to the law of accelerating returns, which states that advances feed on themselves, continually increasing the rate of further advances.4 The volume of medical data doubles every 2 to 5 years.5 Fortunately, the field of AI is growing exponentially as well and can help health care practitioners (HCPs) keep pace, allowing the continued delivery of effective health care.
In this report, we review common terminology, principles, and general applications of AI, followed by current and potential applications of AI for selected medical specialties. Finally, we discuss AI’s future in health care, along with potential risks and pitfalls.
AI Overview
AI refers to machine programs that can “learn” or think based on past experiences. This functionality contrasts with simple rules-based programming available to health care for years. An example of rules-based programming is the warfarindosing.org website developed by Barnes-Jewish Hospital at Washington University Medical Center, which guides initial warfarin dosing.6,7 The prescriber inputs detailed patient information, including age, sex, height, weight, tobacco history, medications, laboratory results, and genotype if available. The application then calculates recommended warfarin dosing regimens to avoid over- or underanticoagulation. While the dosing algorithm may be complex, it depends entirely on preprogrammed rules. The program does not learn to reach its conclusions and recommendations from patient data.
In contrast, one of the most common subsets of AI is machine learning (ML). ML describes a program that “learns from experience and improves its performance as it learns.”1 With ML, the computer is initially provided with a training data set—data with known outcomes or labels. Because the initial data are input from known samples, this type of AI is known as supervised learning.8-10 As an example, we recently reported using ML to diagnose various types of cancer from pathology slides.11 In one experiment, we captured images of colon adenocarcinoma and normal colon (these 2 groups represent the training data set). Unlike traditional programming, we did not define characteristics that would differentiate colon cancer from normal; rather, the machine learned these characteristics independently by assessing the labeled images provided. A second data set (the validation data set) was used to evaluate the program and fine-tune the ML training model’s parameters. Finally, the program was presented with new images of cancer and normal cases for final assessment of accuracy (test data set). Our program learned to recognize differences from the images provided and was able to differentiate normal and cancer images with > 95% accuracy.
Advances in computer processing have allowed for the development of artificial neural networks (ANNs). While there are several types of ANNs, the most common types used for image classification and segmentation are known as convolutional neural networks (CNNs).9,12-14 The programs are designed to work similar to the human brain, specifically the visual cortex.15,16 As data are acquired, they are processed by various layers in the program. Much like neurons in the brain, one layer decides whether to advance information to the next.13,14 CNNs can be many layers deep, leading to the term deep learning: “computational models that are composed of multiple processing layers to learn representations of data with multiple levels of abstraction.”1,13,17
ANNs can process larger volumes of data. This advance has led to the development of unstructured or unsupervised learning. With this type of learning, imputing defined features (ie, predetermined answers) of the training data set described above is no longer required.1,8,10,14 The advantage of unsupervised learning is that the program can be presented raw data and extract meaningful interpretation without human input, often with less bias than may exist with supervised learning.1,18 If shown enough data, the program can extract relevant features to make conclusions independently without predefined definitions, potentially uncovering markers not previously known. For example, several studies have used unsupervised learning to search patient data to assess readmission risks of patients with congestive heart failure.10,19,20 AI compiled features independently and not previously defined, predicting patients at greater risk for readmission superior to traditional methods.
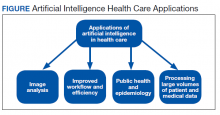
A more detailed description of the various terminologies and techniques of AI is beyond the scope of this review.9,10,17,21 However, in this basic overview, we describe 4 general areas that AI impacts health care (Figure).
Health Care Applications
Image analysis has seen the most AI health care applications.8,15 AI has shown potential in interpreting many types of medical images, including pathology slides, radiographs of various types, retina and other eye scans, and photographs of skin lesions. Many studies have demonstrated that AI can interpret these images as accurately as or even better than experienced clinicians.9,13,22-29 Studies have suggested AI interpretation of radiographs may better distinguish patients infected with COVID-19 from other causes of pneumonia, and AI interpretation of pathology slides may detect specific genetic mutations not previously identified without additional molecular tests.11,14,23,24,30-32
The second area in which AI can impact health care is improving workflow and efficiency. AI has improved surgery scheduling, saving significant revenue, and decreased patient wait times for appointments.1 AI can screen and triage radiographs, allowing attention to be directed to critical patients. This use would be valuable in many busy clinical settings, such as the recent COVID-19 pandemic.8,23 Similarly, AI can screen retina images to prioritize urgent conditions.25 AI has improved pathologists’ efficiency when used to detect breast metastases.33 Finally, AI may reduce medical errors, thereby ensuring patient safety.8,9,34
A third health care benefit of AI is in public health and epidemiology. AI can assist with clinical decision-making and diagnoses in low-income countries and areas with limited health care resources and personnel.25,29 AI can improve identification of infectious outbreaks, such as tuberculosis, malaria, dengue fever, and influenza.29,35-40 AI has been used to predict transmission patterns of the Zika virus and the current COVID-19 pandemic.41,42 Applications can stratify the risk of outbreaks based on multiple factors, including age, income, race, atypical geographic clusters, and seasonal factors like rainfall and temperature.35,36,38,43 AI has been used to assess morbidity and mortality, such as predicting disease severity with malaria and identifying treatment failures in tuberculosis.29
Finally, AI can dramatically impact health care due to processing large data sets or disconnected volumes of patient information—so-called big data.44-46 An example is the widespread use of electronic health records (EHRs) such as the Computerized Patient Record System used in Veteran Affairs medical centers (VAMCs). Much of patient information exists in written text: HCP notes, laboratory and radiology reports, medication records, etc. Natural language processing (NLP) allows platforms to sort through extensive volumes of data on complex patients at rates much faster than human capability, which has great potential to assist with diagnosis and treatment decisions.9
Medical literature is being produced at rates that exceed our ability to digest. More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019 alone.14 NLP capabilities of AI have the potential to rapidly sort through this extensive medical literature and relate specific verbiage in patient records guiding therapy.46 IBM Watson, a supercomputer based on ML and NLP, demonstrates this concept with many potential applications, only some of which relate to health care.1,9 Watson has an oncology component to assimilate multiple aspects of patient care, including clinical notes, pathology results, radiograph findings, staging, and a tumor’s genetic profile. It coordinates these inputs from the EHR and mines medical literature and research databases to recommend treatment options.1,46 AI can assess and compile far greater patient data and therapeutic options than would be feasible by individual clinicians, thus providing customized patient care.47 Watson has partnered with numerous medical centers, including MD Anderson Cancer Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with variable success.44,47-49 While the full potential of Watson appears not yet realized, these AI-driven approaches will likely play an important role in leveraging the hidden value in the expanding volume of health care information.
Medical Specialty Applications
Radiology
Currently > 70% of FDA-approved AI medical devices are in the field of radiology.2 Most radiology departments have used AI-friendly digital imaging for years, such as the picture archiving and communication systems used by numerous health care systems, including VAMCs.2,15 Gray-scale images common in radiology lend themselves to standardization, although AI is not limited to black-and- white image interpretation.15
An abundance of literature describes plain radiograph interpretation using AI. One FDA-approved platform improved X-ray diagnosis of wrist fractures when used by emergency medicine clinicians.2,50 AI has been applied to chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation of many conditions, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, malignant lung lesions, and COVID-19.23,25,28,44,51-53 For example, Nam and colleagues suggested AI is better at diagnosing malignant pulmonary nodules from CXRs than are trained radiologists.28
In addition to plain radiographs, AI has been applied to many other imaging technologies, including ultrasounds, positron emission tomography, mammograms, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).15,26,44,48,54-56 A large study demonstrated that ML platforms significantly reduced the time to diagnose intracranial hemorrhages on CT and identified subtle hemorrhages missed by radiologists.55 Other studies have claimed that AI programs may be better than radiologists in detecting cancer in screening mammograms, and 3 FDA-approved devices focus on mammogram interpretation.2,15,54,57 There is also great interest in MRI applications to detect and predict prognosis for breast cancer based on imaging findings.21,56
Aside from providing accurate diagnoses, other studies focus on AI radiograph interpretation to assist with patient screening, triage, improving time to final diagnosis, providing a rapid “second opinion,” and even monitoring disease progression and offering insights into prognosis.8,21,23,52,55,56,58 These features help in busy urban centers but may play an even greater role in areas with limited access to health care or trained specialists such as radiologists.52
Cardiology
Cardiology has the second highest number of FDA-approved AI applications.2 Many cardiology AI platforms involve image analysis, as described in several recent reviews.45,59,60 AI has been applied to echocardiography to measure ejection fractions, detect valvular disease, and assess heart failure from hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy and amyloidosis.45,48,59 Applications for cardiac CT scans and CT angiography have successfully quantified both calcified and noncalcified coronary artery plaques and lumen assessments, assessed myocardial perfusion, and performed coronary artery calcium scoring.45,59,60 Likewise, AI applications for cardiac MRI have been used to quantitate ejection fraction, large vessel flow assessment, and cardiac scar burden.45,59
For years ECG devices have provided interpretation with limited accuracy using preprogrammed parameters.48 However, the application of AI allows ECG interpretation on par with trained cardiologists. Numerous such AI applications exist, and 2 FDA-approved devices perform ECG interpretation.2,61-64 One of these devices incorporates an AI-powered stethoscope to detect atrial fibrillation and heart murmurs.65
Pathology
The advancement of whole slide imaging, wherein entire slides can be scanned and digitized at high speed and resolution, creates great potential for AI applications in pathology.12,24,32,33,66 A landmark study demonstrating the potential of AI for assessing whole slide imaging examined sentinel lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer.22 Multiple algorithms in the study demonstrated that AI was equivalent or better than pathologists in detecting metastases, especially when the pathologists were time-constrained consistent with a normal working environment. Significantly, the most accurate and efficient diagnoses were achieved when the pathologist and AI interpretations were used together.22,33
AI has shown promise in diagnosing many other entities, including cancers of the prostate (including Gleason scoring), lung, colon, breast, and skin.11,12,24,27,32,67 In addition, AI has shown great potential in scoring biomarkers important for prognosis and treatment, such as immunohistochemistry (IHC) labeling of Ki-67 and PD-L1.32 Pathologists can have difficulty classifying certain tumors or determining the site of origin for metastases, often having to rely on IHC with limited success. The unique features of image analysis with AI have the potential to assist in classifying difficult tumors and identifying sites of origin for metastatic disease based on morphology alone.11
Oncology depends heavily on molecular pathology testing to dictate treatment options and determine prognosis. Preliminary studies suggest that AI interpretation alone has the potential to delineate whether certain molecular mutations are present in tumors from various sites.11,14,24,32 One study combined histology and genomic results for AI interpretation that improved prognostic predictions.68 In addition, AI analysis may have potential in predicting tumor recurrence or prognosis based on cellular features, as demonstrated for lung cancer and melanoma.67,69,70
Ophthalmology
AI applications for ophthalmology have focused on diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinopathy of prematurity, age-related and congenital cataracts, and retinal vein occlusion.71-73 Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness and has been studied by numerous platforms with good success, most having used color fundus photography.71,72 One study showed AI could diagnose diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema with specificities similar to ophthalmologists.74 In 2018, the FDA approved the AI platform IDx-DR. This diagnostic system classifies retinal images and recommends referral for patients determined to have “more than mild diabetic retinopathy” and reexamination within a year for other patients.8,75 Significantly, the platform recommendations do not require confirmation by a clinician.8
AI has been applied to other modalities in ophthalmology such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) to diagnose retinal disease and to predict appropriate management of congenital cataracts.25,73,76 For example, an AI application using OCT has been demonstrated to match or exceed the accuracy of retinal experts in diagnosing and triaging patients with a variety of retinal pathologies, including patients needing urgent referrals.77
Dermatology
Multiple studies demonstrate AI performs at least equal to experienced dermatologists in differentiating selected skin lesions.78-81 For example, Esteva and colleagues demonstrated AI could differentiate keratinocyte carcinomas from benign seborrheic keratoses and malignant melanomas from benign nevi with accuracy equal to 21 board-certified dermatologists.78
AI is applicable to various imaging procedures common to dermatology, such as dermoscopy, very high-frequency ultrasound, and reflectance confocal microscopy.82 Several studies have demonstrated that AI interpretation compared favorably to dermatologists evaluating dermoscopy to assess melanocytic lesions.78-81,83
A limitation in these studies is that they differentiate only a few diagnoses.82 Furthermore, dermatologists have sensory input such as touch and visual examination under various conditions, something AI has yet to replicate.15,34,84 Also, most AI devices use no or limited clinical information.81 Dermatologists can recognize rarer conditions for which AI models may have had limited or no training.34 Nevertheless, a recent study assessed AI for the diagnosis of 134 separate skin disorders with promising results, including providing diagnoses with accuracy comparable to that of dermatologists and providing accurate treatment strategies.84 As Topol points out, most skin lesions are diagnosed in the primary care setting where AI can have a greater impact when used in conjunction with the clinical impression, especially where specialists are in limited supply.48,78
Finally, dermatology lends itself to using portable or smartphone applications (apps) wherein the user can photograph a lesion for analysis by AI algorithms to assess the need for further evaluation or make treatment recommendations.34,84,85 Although results from currently available apps are not encouraging, they may play a greater role as the technology advances.34,85
Oncology
Applications of AI in oncology include predicting prognosis for patients with cancer based on histologic and/or genetic information.14,68,86 Programs can predict the risk of complications before and recurrence risks after surgery for malignancies.44,87-89 AI can also assist in treatment planning and predict treatment failure with radiation therapy.90,91
AI has great potential in processing the large volumes of patient data in cancer genomics. Next-generation sequencing has allowed for the identification of millions of DNA sequences in a single tumor to detect genetic anomalies.92 Thousands of mutations can be found in individual tumor samples, and processing this information and determining its significance can be beyond human capability.14 We know little about the effects of various mutation combinations, and most tumors have a heterogeneous molecular profile among different cell populations.14,93 The presence or absence of various mutations can have diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications.93 AI has great potential to sort through these complex data and identify actionable findings.
More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019, and publications in the field of cancer genomics are increasing exponentially.14,92,93 Patel and colleagues assessed the utility of IBM Watson for Genomics against results from a molecular tumor board.93 Watson for Genomics identified potentially significant mutations not identified by the tumor board in 32% of patients. Most mutations were related to new clinical trials not yet added to the tumor board watch list, demonstrating the role AI will have in processing the large volume of genetic data required to deliver personalized medicine moving forward.
Gastroenterology
AI has shown promise in predicting risk or outcomes based on clinical parameters in various common gastroenterology problems, including gastric reflux, acute pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.94,95 AI endoscopic analysis has demonstrated potential in assessing Barrett’s esophagus, gastric Helicobacter pylori infections, gastric atrophy, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.95 Applications have been used to assess esophageal, gastric, and colonic malignancies, including depth of invasion based on endoscopic images.95 Finally, studies have evaluated AI to assess small colon polyps during colonoscopy, including differentiating benign and premalignant polyps with success comparable to gastroenterologists.94,95 AI has been shown to increase the speed and accuracy of gastroenterologists in detecting small polyps during colonoscopy.48 In a prospective randomized study, colonoscopies performed using an AI device identified significantly more small adenomatous polyps than colonoscopies without AI.96
Neurology
It has been suggested that AI technologies are well suited for application in neurology due to the subtle presentation of many neurologic diseases.16 Viz LVO, the first CMS-approved AI reimbursement for the diagnosis of strokes, analyzes CTs to detect early ischemic strokes and alerts the medical team, thus shortening time to treatment.3,97 Many other AI platforms are in use or development that use CT and MRI for the early detection of strokes as well as for treatment and prognosis.9,97
AI technologies have been applied to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases.16,98 For example, several studies have evaluated patient movements in Parkinson disease for both early diagnosis and to assess response to treatment.98 These evaluations included assessment with both external cameras as well as wearable devices and smartphone apps.
AI has also been applied to seizure disorders, attempting to determine seizure type, localize the area of seizure onset, and address the challenges of identifying seizures in neonates.99,100 Other potential applications range from early detection and prognosis predictions for cases of multiple sclerosis to restoring movement in paralysis from a variety of conditions such as spinal cord injury.9,101,102
Mental Health
Due to the interactive nature of mental health care, the field has been slower to develop AI applications.18 With heavy reliance on textual information (eg, clinic notes, mood rating scales, and documentation of conversations), successful AI applications in this field will likely rely heavily on NLP.18 However, studies investigating the application of AI to mental health have also incorporated data such as brain imaging, smartphone monitoring, and social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter.18,103,104
The risk of suicide is higher in veteran patients, and ML algorithms have had limited success in predicting suicide risk in both veteran and nonveteran populations.104-106 While early models have low positive predictive values and low sensitivities, they still promise to be a useful tool in conjunction with traditional risk assessments.106 Kessler and colleagues suggest that combining multiple rather than single ML algorithms might lead to greater success.105,106
AI may assist in diagnosing other mental health disorders, including major depressive disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), schizophrenia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and Alzheimer disease.103,104,107 These investigations are in the early stages with limited clinical applicability. However, 2 AI applications awaiting FDA approval relate to ADHD and opioid use.2 Furthermore, potential exists for AI to not only assist with prevention and diagnosis of ADHD, but also to identify optimal treatment options.2,103
General and Personalized Medicine
Additional AI applications include diagnosing patients with suspected sepsis, measuring liver iron concentrations, predicting hospital mortality at the time of admission, and more.2,108,109 AI can guide end-of-life decisions such as resuscitation status or whether to initiate mechanical ventilation.48
AI-driven smartphone apps can be beneficial to both patients and clinicians. Examples include predicting nonadherence to anticoagulation therapy, monitoring heart rhythms for atrial fibrillation or signs of hyperkalemia in patients with renal failure, and improving outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus by decreasing glycemic variability and reducing hypoglycemia.8,48,110,111 The potential for AI applications to health care and personalized medicine are almost limitless.
Discussion
With ever-increasing expectations for all health care sectors to deliver timely, fiscally-responsible, high-quality health care, AI has the potential to have numerous impacts. AI can improve diagnostic accuracy while limiting errors and impact patient safety such as assisting with prescription delivery.8,9,34 It can screen and triage patients, alerting clinicians to those needing more urgent evaluation.8,23,77,97 AI also may increase a clinician’s efficiency and speed to render a diagnosis.12,13,55,97 AI can provide a rapid second opinion, an ability especially beneficial in underserved areas with shortages of specialists.23,25,26,29,34 Similarly, AI may decrease the inter- and intraobserver variability common in many medical specialties.12,27,45 AI applications can also monitor disease progression, identifying patients at greatest risk, and provide information for prognosis.21,23,56,58 Finally, as described with applications using IBM Watson, AI can allow for an integrated approach to health care that is currently lacking.
We have described many reports suggesting AI can render diagnoses as well as or better than experienced clinicians, and speculation exists that AI will replace many roles currently performed by health care practitioners.9,26 However, most studies demonstrate that AI’s diagnostic benefits are best realized when used to supplement a clinician’s impression.8,22,30,33,52,54,56,69,84 AI is not likely to replace humans in health care in the foreseeable future. The technology can be likened to the impact of CT scans developed in the 1970s in neurology. Prior to such detailed imaging, neurologists spent extensive time performing detailed physicals to render diagnoses and locate lesions before surgery. There was mistrust of this new technology and concern that CT scans would eliminate the need for neurologists.112 On the contrary, neurology is alive and well, frequently being augmented by the technologies once speculated to replace it.
Commercial AI health care platforms represented a $2 billion industry in 2018 and are growing rapidly each year.13,32 Many AI products are offered ready for implementation for various tasks, including diagnostics, patient management, and improved efficiency. Others will likely be provided as templates suitable for modification to meet the specific needs of the facility, practice, or specialty for its patient population.
AI Risks and Limitations
AI has several risks and limitations. Although there is progress in explainable AI, at times we still struggle to understand how the output provided by machine learning algorithms was created.44,48 The many layers associated with deep learning self-determine the criteria to reach its conclusion, and these criteria can continually evolve. The parameters of deep learning are not preprogrammed, and there are too many individual data points to be extrapolated or deconvoluted for evaluation at our current level of knowledge.26,51 These apparent lack of constraints cause concern for patient safety and suggest that greater validation and continued scrutiny of validity is required.8,48 Efforts are underway to create explainable AI programs to make their processes more transparent, but such clarification is limited presently.14,26,48,77
Another challenge of AI is determining the amount of training data required to function optimally. Also, if the output describes multiple variables or diagnoses, are each equally valid?113 Furthermore, many AI applications look for a specific process, such as cancer diagnoses on CXRs. However, how coexisting conditions like cardiomegaly, emphysema, pneumonia, etc, seen on CXRs will affect the diagnosis needs to be considered.51,52 Zech and colleagues provide the example that diagnoses for pneumothorax are frequently rendered on CXRs with chest tubes in place.51 They suggest that CNNs may develop a bias toward diagnosing pneumothorax when chest tubes are present. Many current studies approach an issue in isolation, a situation not realistic in real-world clinical practice.26
Most studies on AI have been retrospective, and frequently data used to train the program are preselected.13,26 The data are typically validated on available databases rather than actual patients in the clinical setting, limiting confidence in the validity of the AI output when applied to real-world situations. Currently, fewer than 12 prospective trials had been published comparing AI with traditional clinical care.13,114 Randomized prospective clinical trials are even fewer, with none currently reported from the United States.13,114 The results from several studies have been shown to diminish when repeated prospectively.114
The FDA has created a new category known as Software as a Medical Device and has a Digital Health Innovation Action Plan to regulate AI platforms. Still, the process of AI regulation is of necessity different from traditional approval processes and is continually evolving.8 The FDA approval process cannot account for the fact that the program’s parameters may continually evolve or adapt.2
Guidelines for investigating and reporting AI research with its unique attributes are being developed. Examples include the TRIPOD-ML statement and others.49,115 In September 2020, 2 publications addressed the paucity of gold-standard randomized clinical trials in clinical AI applications.116,117 The SPIRIT-AI statement expands on the original SPIRIT statement published in 2013 to guide minimal reporting standards for AI clinical trial protocols to promote transparency of design and methodology.116 Similarly, the CONSORT-AI extension, stemming from the original CONSORT statement in 1996, aims to ensure quality reporting of randomized controlled trials in AI.117
Another risk with AI is that while an individual physician making a mistake may adversely affect 1 patient, a single mistake in an AI algorithm could potentially affect thousands of patients.48 Also, AI programs developed for patient populations at a facility may not translate to another. Referred to as overfitting, this phenomenon relates to selection bias in training data sets.15,34,49,51,52 Studies have shown that programs that underrepresent certain group characteristics such as age, sex, or race may be less effective when applied to a population in which these characteristics have differing representations.8,48,49 This problem of underrepresentation has been demonstrated in programs interpreting pathology slides, radiographs, and skin lesions.15,32,51
Admittedly, most of these challenges are not specific to AI and existed in health care previously. Physicians make mistakes, treatments are sometimes used without adequate prospective studies, and medications are given without understanding their mechanism of action, much like AI-facilitated processes reach a conclusion that cannot be fully explained.48
Conclusions
The view that AI will dramatically impact health care in the coming years will likely prove true. However, much work is needed, especially because of the paucity of prospective clinical trials as has been historically required in medical research. Any concern that AI will replace HCPs seems unwarranted. Early studies suggest that even AI programs that appear to exceed human interpretation perform best when working in cooperation with and oversight from clinicians. AI’s greatest potential appears to be its ability to augment care from health professionals, improving efficiency and accuracy, and should be anticipated with enthusiasm as the field moves forward at an exponential rate.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Makenna G. Thomas for proofreading and review of the manuscript. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital. This research has been approved by the James A. Haley Veteran’s Hospital Office of Communications and Media.
1. Bini SA. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and cognitive computing: what do these terms mean and how will they impact health care? J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2358-2361. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.067
2. Benjamens S, Dhunnoo P, Meskó B. The state of artificial intelligence-based FDA-approved medical devices and algorithms: an online database. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:118. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00324-0
3. Viz. AI powered synchronized stroke care. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.viz.ai/ischemic-stroke
4. Buchanan M. The law of accelerating returns. Nat Phys. 2008;4(7):507. doi:10.1038/nphys1010
5. IBM Watson Health computes a pair of new solutions to improve healthcare data and security. Published September 10, 2015. Accessed October 21, 2020. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/ibm-watson-health-computes-a-pair-of-new-solutions-to-improve-healthcare-data-and-security
6. Borkowski AA, Kardani A, Mastorides SM, Thomas LB. Warfarin pharmacogenomics: recommendations with available patented clinical technologies. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2014;8(2):110-115. doi:10.2174/1872208309666140904112003
7. Washington University in St. Louis. Warfarin dosing. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://www.warfarindosing.org/Source/Home.aspx
8. He J, Baxter SL, Xu J, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhang K. The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):30-36. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0307-0
9. Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, et al. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017;2(4):230-243. Published 2017 Jun 21. doi:10.1136/svn-2017-000101
10. Johnson KW, Torres Soto J, Glicksberg BS, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(23):2668-2679. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.521
11. Borkowski AA, Wilson CP, Borkowski SA, et al. Comparing artificial intelligence platforms for histopathologic cancer diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2019;36(10):456-463.
12. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. High-throughput adaptive sampling for whole-slide histopathology image analysis (HASHI) via convolutional neural networks: application to invasive breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196828. Published 2018 May 24. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0196828
13. Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, et al. Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning studies. BMJ. 2020;368:m689. Published 2020 Mar 25. doi:10.1136/bmj.m689
14. Shimizu H, Nakayama KI. Artificial intelligence in oncology. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(5):1452-1460. doi:10.1111/cas.14377
15. Talebi-Liasi F, Markowitz O. Is artificial intelligence going to replace dermatologists?. Cutis. 2020;105(1):28-31.
16. Valliani AA, Ranti D, Oermann EK. Deep learning and neurology: a systematic review. Neurol Ther. 2019;8(2):351-365. doi:10.1007/s40120-019-00153-8
17. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436-444. doi:10.1038/nature14539
18. Graham S, Depp C, Lee EE, et al. Artificial intelligence for mental health and mental illnesses: an overview. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(11):116. Published 2019 Nov 7. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1094-0
19. Golas SB, Shibahara T, Agboola S, et al. A machine learning model to predict the risk of 30-day readmissions in patients with heart failure: a retrospective analysis of electronic medical records data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018;18(1):44. Published 2018 Jun 22. doi:10.1186/s12911-018-0620-z
20. Mortazavi BJ, Downing NS, Bucholz EM, et al. Analysis of machine learning techniques for heart failure readmissions. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2016;9(6):629-640. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.116.003039
21. Meyer-Bäse A, Morra L, Meyer-Bäse U, Pinker K. Current status and future perspectives of artificial intelligence in magnetic resonance breast imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2020;2020:6805710. Published 2020 Aug 28. doi:10.1155/2020/6805710
22. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van Diest P, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. 2017;318(22):2199-2210. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.14585
23. Borkowski AA, Viswanadhan NA, Thomas LB, Guzman RD, Deland LA, Mastorides SM. Using artificial intelligence for COVID-19 chest X-ray diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2020;37(9):398-404. doi:10.12788/fp.0045
24. Coudray N, Ocampo PS, Sakellaropoulos T, et al. Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Med. 2018;24(10):1559-1567. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0177-5
25. Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell. 2018;172(5):1122-1131.e9. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
26. Liu X, Faes L, Kale AU, et al. A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(6):e271-e297. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30123-2
27. Nagpal K, Foote D, Liu Y, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer [published correction appears in NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Nov 19;2:113]. NPJ Digit Med. 2019;2:48. Published 2019 Jun 7. doi:10.1038/s41746-019-0112-2
28. Nam JG, Park S, Hwang EJ, et al. Development and validation of deep learning-based automatic detection algorithm for malignant pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs. Radiology. 2019;290(1):218-228. doi:10.1148/radiol.2018180237
29. Schwalbe N, Wahl B. Artificial intelligence and the future of global health. Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1579-1586. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30226-9
30. Bai HX, Wang R, Xiong Z, et al. Artificial intelligence augmentation of radiologist performance in distinguishing COVID-19 from pneumonia of other origin at chest CT [published correction appears in Radiology. 2021 Apr;299(1):E225]. Radiology. 2020;296(3):E156-E165. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201491
31. Li L, Qin L, Xu Z, et al. Using artificial intelligence to detect COVID-19 and community-acquired pneumonia based on pulmonary CT: evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy. Radiology. 2020;296(2):E65-E71. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200905
32. Serag A, Ion-Margineanu A, Qureshi H, et al. Translational AI and deep learning in diagnostic pathology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019;6:185. Published 2019 Oct 1. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00185

33. Wang D, Khosla A, Gargeya R, Irshad H, Beck AH. Deep learning for identifying metastatic breast cancer. ArXiv. 2016 June 18:arXiv:1606.05718v1. Published online June 18, 2016. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05718
34. Alabdulkareem A. Artificial intelligence and dermatologists: friends or foes? J Dermatology Dermatol Surg. 2019;23(2):57-60. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_19_19
35. Mollalo A, Mao L, Rashidi P, Glass GE. A GIS-based artificial neural network model for spatial distribution of tuberculosis across the continental United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(1):157. Published 2019 Jan 8. doi:10.3390/ijerph16010157
36. Haddawy P, Hasan AHMI, Kasantikul R, et al. Spatiotemporal Bayesian networks for malaria prediction. Artif Intell Med. 2018;84:127-138. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2017.12.002
37. Laureano-Rosario AE, Duncan AP, Mendez-Lazaro PA, et al. Application of artificial neural networks for dengue fever outbreak predictions in the northwest coast of Yucatan, Mexico and San Juan, Puerto Rico. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018;3(1):5. Published 2018 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3010005
38. Buczak AL, Koshute PT, Babin SM, Feighner BH, Lewis SH. A data-driven epidemiological prediction method for dengue outbreaks using local and remote sensing data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012;12:124. Published 2012 Nov 5. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-12-124
39. Scavuzzo JM, Trucco F, Espinosa M, et al. Modeling dengue vector population using remotely sensed data and machine learning. Acta Trop. 2018;185:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.05.003
40. Xue H, Bai Y, Hu H, Liang H. Influenza activity surveillance based on multiple regression model and artificial neural network. IEEE Access. 2018;6:563-575. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2771798
41. Jiang D, Hao M, Ding F, Fu J, Li M. Mapping the transmission risk of Zika virus using machine learning models. Acta Trop. 2018;185:391-399. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.06.021
42. Bragazzi NL, Dai H, Damiani G, Behzadifar M, Martini M, Wu J. How big data and artificial intelligence can help better manage the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):3176. Published 2020 May 2. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093176
43. Lake IR, Colón-González FJ, Barker GC, Morbey RA, Smith GE, Elliot AJ. Machine learning to refine decision making within a syndromic surveillance service. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):559. Published 2019 May 14. doi:10.1186/s12889-019-6916-9
44. Khan OF, Bebb G, Alimohamed NA. Artificial intelligence in medicine: what oncologists need to know about its potential-and its limitations. Oncol Exch. 2017;16(4):8-13. Accessed September 1, 2021. http://www.oncologyex.com/pdf/vol16_no4/feature_khan-ai.pdf
45. Badano LP, Keller DM, Muraru D, Torlasco C, Parati G. Artificial intelligence and cardiovascular imaging: A win-win combination. Anatol J Cardiol. 2020;24(4):214-223. doi:10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.94491
46. Murdoch TB, Detsky AS. The inevitable application of big data to health care. JAMA. 2013;309(13):1351-1352. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.393
47. Greatbatch O, Garrett A, Snape K. The impact of artificial intelligence on the current and future practice of clinical cancer genomics. Genet Res (Camb). 2019;101:e9. Published 2019 Oct 31. doi:10.1017/S0016672319000089
48. Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):44-56. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0300-7
49. Vollmer S, Mateen BA, Bohner G, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence research for patient benefit: 20 critical questions on transparency, replicability, ethics, and effectiveness [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Apr 1;369:m1312]. BMJ. 2020;368:l6927. Published 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1136/bmj.l6927
50. Lindsey R, Daluiski A, Chopra S, et al. Deep neural network improves fracture detection by clinicians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(45):11591-11596. doi:10.1073/pnas.1806905115
51. Zech JR, Badgeley MA, Liu M, Costa AB, Titano JJ, Oermann EK. Variable generalization performance of a deep learning model to detect pneumonia in chest radiographs: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2018;15(11):e1002683. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002683
52. Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. 2017;284(2):574-582. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017162326
53. Rajpurkar P, Joshi A, Pareek A, et al. CheXpedition: investigating generalization challenges for translation of chest x-ray algorithms to the clinical setting. ArXiv. 2020 Feb 26:arXiv:2002.11379v2. Revised March 11, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/2002.11379
54. Salim M, Wåhlin E, Dembrower K, et al. External evaluation of 3 commercial artificial intelligence algorithms for independent assessment of screening mammograms. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(10):1581-1588. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3321
55. Arbabshirani MR, Fornwalt BK, Mongelluzzo GJ, et al. Advanced machine learning in action: identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. NPJ Digit Med. 2018;1:9. doi:10.1038/s41746-017-0015-z
56. Sheth D, Giger ML. Artificial intelligence in the interpretation of breast cancer on MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;51(5):1310-1324. doi:10.1002/jmri.26878
57. McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020;577(7788):89-94. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
58. Booth AL, Abels E, McCaffrey P. Development of a prognostic model for mortality in COVID-19 infection using machine learning. Mod Pathol. 2021;34(3):522-531. doi:10.1038/s41379-020-00700-x
59. Xu B, Kocyigit D, Grimm R, Griffin BP, Cheng F. Applications of artificial intelligence in multimodality cardiovascular imaging: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):367-376. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.003
60. Dey D, Slomka PJ, Leeson P, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(11):1317-1335. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.12.054
61. Carewell Health. AI powered ECG diagnosis solutions. Accessed November 2, 2020. https://www.carewellhealth.com/products_aiecg.html
62. Strodthoff N, Strodthoff C. Detecting and interpreting myocardial infarction using fully convolutional neural networks. Physiol Meas. 2019;40(1):015001. doi:10.1088/1361-6579/aaf34d
63. Hannun AY, Rajpurkar P, Haghpanahi M, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):65-69. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
64. Kwon JM, Jeon KH, Kim HM, et al. Comparing the performance of artificial intelligence and conventional diagnosis criteria for detecting left ventricular hypertrophy using electrocardiography. Europace. 2020;22(3):412-419. doi:10.1093/europace/euz324

65. Eko. FDA clears Eko’s AFib and heart murmur detection algorithms, making it the first AI-powered stethoscope to screen for serious heart conditions [press release]. Published January 28, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200128005232/en/FDA-Clears-Eko’s-AFib-and-Heart-Murmur-Detection-Algorithms-Making-It-the-First-AI-Powered-Stethoscope-to-Screen-for-Serious-Heart-Conditions
66. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. Accurate and reproducible invasive breast cancer detection in whole-slide images: a deep learning approach for quantifying tumor extent. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46450. doi:10.1038/srep46450
67. Acs B, Rantalainen M, Hartman J. Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology. J Intern Med. 2020;288(1):62-81. doi:10.1111/joim.13030
68. Mobadersany P, Yousefi S, Amgad M, et al. Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(13):E2970-E2979. doi:10.1073/pnas.1717139115
69. Wang X, Janowczyk A, Zhou Y, et al. Prediction of recurrence in early stage non-small cell lung cancer using computer extracted nuclear features from digital H&E images. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13543. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13773-7
70. Kulkarni PM, Robinson EJ, Pradhan JS, et al. Deep learning based on standard H&E images of primary melanoma tumors identifies patients at risk for visceral recurrence and death. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(5):1126-1134. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1495
71. Du XL, Li WB, Hu BJ. Application of artificial intelligence in ophthalmology. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018;11(9):1555-1561. doi:10.18240/ijo.2018.09.21
72. Gunasekeran DV, Wong TY. Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology in 2020: a technology on the cusp for translation and implementation. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2020;9(2):61-66. doi:10.1097/01.APO.0000656984.56467.2c
73. Ting DSW, Pasquale LR, Peng L, et al. Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103(2):167-175. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313173
74. Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016;316(22):2402-2410. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17216
75. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA permits marketing of artificial intelligence-based device to detect certain diabetes-related eye problems [press release]. Published April 11, 2018. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-permits-marketing-artificial-intelligence-based-device-detect-certain-diabetes-related-eye
76. Long E, Chen J, Wu X, et al. Artificial intelligence manages congenital cataract with individualized prediction and telehealth computing. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:112. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00319-x
77. De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(9):1342-1350. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0107-6
78. Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017;542(7639):115-118. doi:10.1038/nature21056
79. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. Deep neural networks are superior to dermatologists in melanoma image classification. Eur J Cancer. 2019;119:11-17. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.05.023
80. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images performed on par with 145 dermatologists in a clinical melanoma image classification task. Eur J Cancer. 2019;111:148-154. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.02.005
81. Haenssle HA, Fink C, Schneiderbauer R, et al. Man against machine: diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(8):1836-1842. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy166
82. Li CX, Shen CB, Xue K, et al. Artificial intelligence in dermatology: past, present, and future. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(17):2017-2020. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000372
83. Tschandl P, Codella N, Akay BN, et al. Comparison of the accuracy of human readers versus machine-learning algorithms for pigmented skin lesion classification: an open, web-based, international, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(7):938-947. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30333-X
84. Han SS, Park I, Eun Chang SE, et al. Augmented intelligence dermatology: deep neural networks empower medical professionals in diagnosing skin cancer and predicting treatment options for 134 skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(9):1753-1761. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.01.019
85. Freeman K, Dinnes J, Chuchu N, et al. Algorithm based smartphone apps to assess risk of skin cancer in adults: systematic review of diagnostic accuracy studies [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Feb 25;368:m645]. BMJ. 2020;368:m127. Published 2020 Feb 10. doi:10.1136/bmj.m127
86. Chen YC, Ke WC, Chiu HW. Risk classification of cancer survival using ANN with gene expression data from multiple laboratories. Comput Biol Med. 2014;48:1-7. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.02.006
87. Kim W, Kim KS, Lee JE, et al. Development of novel breast cancer recurrence prediction model using support vector machine. J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(2):230-238. doi:10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.230
88. Merath K, Hyer JM, Mehta R, et al. Use of machine learning for prediction of patient risk of postoperative complications after liver, pancreatic, and colorectal surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020;24(8):1843-1851. doi:10.1007/s11605-019-04338-2
89. Santos-García G, Varela G, Novoa N, Jiménez MF. Prediction of postoperative morbidity after lung resection using an artificial neural network ensemble. Artif Intell Med. 2004;30(1):61-69. doi:10.1016/S0933-3657(03)00059-9
90. Ibragimov B, Xing L. Segmentation of organs-at-risks in head and neck CT images using convolutional neural networks. Med Phys. 2017;44(2):547-557. doi:10.1002/mp.12045
91. Lou B, Doken S, Zhuang T, et al. An image-based deep learning framework for individualizing radiotherapy dose. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(3):e136-e147. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30058-5
92. Xu J, Yang P, Xue S, et al. Translating cancer genomics into precision medicine with artificial intelligence: applications, challenges and future perspectives. Hum Genet. 2019;138(2):109-124. doi:10.1007/s00439-019-01970-5
93. Patel NM, Michelini VV, Snell JM, et al. Enhancing next‐generation sequencing‐guided cancer care through cognitive computing. Oncologist. 2018;23(2):179-185. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0170
94. Le Berre C, Sandborn WJ, Aridhi S, et al. Application of artificial intelligence to gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1):76-94.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.058
95. Yang YJ, Bang CS. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(14):1666-1683. doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1666
96. Wang P, Berzin TM, Glissen Brown JR, et al. Real-time automatic detection system increases colonoscopic polyp and adenoma detection rates: a prospective randomised controlled study. Gut. 2019;68(10):1813-1819. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317500

97. Gupta R, Krishnam SP, Schaefer PW, Lev MH, Gonzalez RG. An East Coast perspective on artificial intelligence and machine learning: part 2: ischemic stroke imaging and triage. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2020;30(4):467-478. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2020.08.002
98. Beli M, Bobi V, Badža M, Šolaja N, Duri-Jovii M, Kosti VS. Artificial intelligence for assisting diagnostics and assessment of Parkinson’s disease—a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;184:105442. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105442
99. An S, Kang C, Lee HW. Artificial intelligence and computational approaches for epilepsy. J Epilepsy Res. 2020;10(1):8-17. doi:10.14581/jer.20003
100. Pavel AM, Rennie JM, de Vries LS, et al. A machine-learning algorithm for neonatal seizure recognition: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4(10):740-749. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30239-X
101. Afzal HMR, Luo S, Ramadan S, Lechner-Scott J. The emerging role of artificial intelligence in multiple sclerosis imaging [published online ahead of print, 2020 Oct 28]. Mult Scler. 2020;1352458520966298. doi:10.1177/1352458520966298
102. Bouton CE. Restoring movement in paralysis with a bioelectronic neural bypass approach: current state and future directions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019;9(11):a034306. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a034306
103. Durstewitz D, Koppe G, Meyer-Lindenberg A. Deep neural networks in psychiatry. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(11):1583-1598. doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0365-9
104. Fonseka TM, Bhat V, Kennedy SH. The utility of artificial intelligence in suicide risk prediction and the management of suicidal behaviors. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53(10):954-964. doi:10.1177/0004867419864428
105. Kessler RC, Hwang I, Hoffmire CA, et al. Developing a practical suicide risk prediction model for targeting high-risk patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2017;26(3):e1575. doi:10.1002/mpr.1575
106. Kessler RC, Bauer MS, Bishop TM, et al. Using administrative data to predict suicide after psychiatric hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration System. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:390. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00390
107. Kessler RC, van Loo HM, Wardenaar KJ, et al. Testing a machine-learning algorithm to predict the persistence and severity of major depressive disorder from baseline self-reports. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(10):1366-1371. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.198
108. Horng S, Sontag DA, Halpern Y, Jernite Y, Shapiro NI, Nathanson LA. Creating an automated trigger for sepsis clinical decision support at emergency department triage using machine learning. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174708. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174708
109. Soffer S, Klang E, Barash Y, Grossman E, Zimlichman E. Predicting in-hospital mortality at admission to the medical ward: a big-data machine learning model. Am J Med. 2021;134(2):227-234.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.07.014
110. Labovitz DL, Shafner L, Reyes Gil M, Virmani D, Hanina A. Using artificial intelligence to reduce the risk of nonadherence in patients on anticoagulation therapy. Stroke. 2017;48(5):1416-1419. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.016281
111. Forlenza GP. Use of artificial intelligence to improve diabetes outcomes in patients using multiple daily injections therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(S2):S24-S28. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0077
112. Poser CM. CT scan and the practice of neurology. Arch Neurol. 1977;34(2):132. doi:10.1001/archneur.1977.00500140086023
113. Angus DC. Randomized clinical trials of artificial intelligence. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1043-1045. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1039
114. Topol EJ. Welcoming new guidelines for AI clinical research. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1318-1320. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1042-x
115. Collins GS, Moons KGM. Reporting of artificial intelligence prediction models. Lancet. 2019;393(10181):1577-1579. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30037-6
116. Cruz Rivera S, Liu X, Chan AW, et al. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1351-1363. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1037-7
117. Liu X, Cruz Rivera S, Moher D, Calvert MJ, Denniston AK; SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI Working Group. Reporting guidelines for clinical trial reports for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the CONSORT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1364-1374. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1034-x
118. McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys. 1943;5(4):115-133. doi:10.1007/BF02478259
119. Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of Checkers. IBM J Res Dev. 1959;3(3):535-554. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.368.2254
120. Sonoda M, Takano M, Miyahara J, Kato H. Computed radiography utilizing scanning laser stimulated luminescence. Radiology. 1983;148(3):833-838. doi:10.1148/radiology.148.3.6878707
121. Dechter R. Learning while searching in constraint-satisfaction-problems. AAAI’86: proceedings of the fifth AAAI national conference on artificial intelligence. Published 1986. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.aaai.org/Papers/AAAI/1986/AAAI86-029.pdf
122. Le Cun Y, Jackel LD, Boser B, et al. Handwritten digit recognition: applications of neural network chips and automatic learning. IEEE Commun Mag. 1989;27(11):41-46. doi:10.1109/35.41400
123. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first whole slide imaging system for digital pathology [press release]. Published April 12, 2017. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-allows-marketing-first-whole-slide-imaging-system-digital-pathology
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was first described in 1956 and refers to machines having the ability to learn as they receive and process information, resulting in the ability to “think” like humans.1 AI’s impact in medicine is increasing; currently, at least 29 AI medical devices and algorithms are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in a variety of areas, including radiograph interpretation, managing glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus, analyzing electrocardiograms (ECGs), and diagnosing sleep disorders among others.2 Significantly, in 2020, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the first reimbursement to hospitals for an AI platform, a model for early detection of strokes.3 AI is rapidly becoming an integral part of health care, and its role will only increase in the future (Table).
As knowledge in medicine is expanding exponentially, AI has great potential to assist with handling complex patient care data. The concept of exponential growth is not a natural one. As Bini described, with exponential growth the volume of knowledge amassed over the past 10 years will now occur in perhaps only 1 year.1 Likewise, equivalent advances over the past year may take just a few months. This phenomenon is partly due to the law of accelerating returns, which states that advances feed on themselves, continually increasing the rate of further advances.4 The volume of medical data doubles every 2 to 5 years.5 Fortunately, the field of AI is growing exponentially as well and can help health care practitioners (HCPs) keep pace, allowing the continued delivery of effective health care.
In this report, we review common terminology, principles, and general applications of AI, followed by current and potential applications of AI for selected medical specialties. Finally, we discuss AI’s future in health care, along with potential risks and pitfalls.
AI Overview
AI refers to machine programs that can “learn” or think based on past experiences. This functionality contrasts with simple rules-based programming available to health care for years. An example of rules-based programming is the warfarindosing.org website developed by Barnes-Jewish Hospital at Washington University Medical Center, which guides initial warfarin dosing.6,7 The prescriber inputs detailed patient information, including age, sex, height, weight, tobacco history, medications, laboratory results, and genotype if available. The application then calculates recommended warfarin dosing regimens to avoid over- or underanticoagulation. While the dosing algorithm may be complex, it depends entirely on preprogrammed rules. The program does not learn to reach its conclusions and recommendations from patient data.
In contrast, one of the most common subsets of AI is machine learning (ML). ML describes a program that “learns from experience and improves its performance as it learns.”1 With ML, the computer is initially provided with a training data set—data with known outcomes or labels. Because the initial data are input from known samples, this type of AI is known as supervised learning.8-10 As an example, we recently reported using ML to diagnose various types of cancer from pathology slides.11 In one experiment, we captured images of colon adenocarcinoma and normal colon (these 2 groups represent the training data set). Unlike traditional programming, we did not define characteristics that would differentiate colon cancer from normal; rather, the machine learned these characteristics independently by assessing the labeled images provided. A second data set (the validation data set) was used to evaluate the program and fine-tune the ML training model’s parameters. Finally, the program was presented with new images of cancer and normal cases for final assessment of accuracy (test data set). Our program learned to recognize differences from the images provided and was able to differentiate normal and cancer images with > 95% accuracy.
Advances in computer processing have allowed for the development of artificial neural networks (ANNs). While there are several types of ANNs, the most common types used for image classification and segmentation are known as convolutional neural networks (CNNs).9,12-14 The programs are designed to work similar to the human brain, specifically the visual cortex.15,16 As data are acquired, they are processed by various layers in the program. Much like neurons in the brain, one layer decides whether to advance information to the next.13,14 CNNs can be many layers deep, leading to the term deep learning: “computational models that are composed of multiple processing layers to learn representations of data with multiple levels of abstraction.”1,13,17
ANNs can process larger volumes of data. This advance has led to the development of unstructured or unsupervised learning. With this type of learning, imputing defined features (ie, predetermined answers) of the training data set described above is no longer required.1,8,10,14 The advantage of unsupervised learning is that the program can be presented raw data and extract meaningful interpretation without human input, often with less bias than may exist with supervised learning.1,18 If shown enough data, the program can extract relevant features to make conclusions independently without predefined definitions, potentially uncovering markers not previously known. For example, several studies have used unsupervised learning to search patient data to assess readmission risks of patients with congestive heart failure.10,19,20 AI compiled features independently and not previously defined, predicting patients at greater risk for readmission superior to traditional methods.
A more detailed description of the various terminologies and techniques of AI is beyond the scope of this review.9,10,17,21 However, in this basic overview, we describe 4 general areas that AI impacts health care (Figure).
Health Care Applications
Image analysis has seen the most AI health care applications.8,15 AI has shown potential in interpreting many types of medical images, including pathology slides, radiographs of various types, retina and other eye scans, and photographs of skin lesions. Many studies have demonstrated that AI can interpret these images as accurately as or even better than experienced clinicians.9,13,22-29 Studies have suggested AI interpretation of radiographs may better distinguish patients infected with COVID-19 from other causes of pneumonia, and AI interpretation of pathology slides may detect specific genetic mutations not previously identified without additional molecular tests.11,14,23,24,30-32
The second area in which AI can impact health care is improving workflow and efficiency. AI has improved surgery scheduling, saving significant revenue, and decreased patient wait times for appointments.1 AI can screen and triage radiographs, allowing attention to be directed to critical patients. This use would be valuable in many busy clinical settings, such as the recent COVID-19 pandemic.8,23 Similarly, AI can screen retina images to prioritize urgent conditions.25 AI has improved pathologists’ efficiency when used to detect breast metastases.33 Finally, AI may reduce medical errors, thereby ensuring patient safety.8,9,34
A third health care benefit of AI is in public health and epidemiology. AI can assist with clinical decision-making and diagnoses in low-income countries and areas with limited health care resources and personnel.25,29 AI can improve identification of infectious outbreaks, such as tuberculosis, malaria, dengue fever, and influenza.29,35-40 AI has been used to predict transmission patterns of the Zika virus and the current COVID-19 pandemic.41,42 Applications can stratify the risk of outbreaks based on multiple factors, including age, income, race, atypical geographic clusters, and seasonal factors like rainfall and temperature.35,36,38,43 AI has been used to assess morbidity and mortality, such as predicting disease severity with malaria and identifying treatment failures in tuberculosis.29
Finally, AI can dramatically impact health care due to processing large data sets or disconnected volumes of patient information—so-called big data.44-46 An example is the widespread use of electronic health records (EHRs) such as the Computerized Patient Record System used in Veteran Affairs medical centers (VAMCs). Much of patient information exists in written text: HCP notes, laboratory and radiology reports, medication records, etc. Natural language processing (NLP) allows platforms to sort through extensive volumes of data on complex patients at rates much faster than human capability, which has great potential to assist with diagnosis and treatment decisions.9
Medical literature is being produced at rates that exceed our ability to digest. More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019 alone.14 NLP capabilities of AI have the potential to rapidly sort through this extensive medical literature and relate specific verbiage in patient records guiding therapy.46 IBM Watson, a supercomputer based on ML and NLP, demonstrates this concept with many potential applications, only some of which relate to health care.1,9 Watson has an oncology component to assimilate multiple aspects of patient care, including clinical notes, pathology results, radiograph findings, staging, and a tumor’s genetic profile. It coordinates these inputs from the EHR and mines medical literature and research databases to recommend treatment options.1,46 AI can assess and compile far greater patient data and therapeutic options than would be feasible by individual clinicians, thus providing customized patient care.47 Watson has partnered with numerous medical centers, including MD Anderson Cancer Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with variable success.44,47-49 While the full potential of Watson appears not yet realized, these AI-driven approaches will likely play an important role in leveraging the hidden value in the expanding volume of health care information.
Medical Specialty Applications
Radiology
Currently > 70% of FDA-approved AI medical devices are in the field of radiology.2 Most radiology departments have used AI-friendly digital imaging for years, such as the picture archiving and communication systems used by numerous health care systems, including VAMCs.2,15 Gray-scale images common in radiology lend themselves to standardization, although AI is not limited to black-and- white image interpretation.15
An abundance of literature describes plain radiograph interpretation using AI. One FDA-approved platform improved X-ray diagnosis of wrist fractures when used by emergency medicine clinicians.2,50 AI has been applied to chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation of many conditions, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, malignant lung lesions, and COVID-19.23,25,28,44,51-53 For example, Nam and colleagues suggested AI is better at diagnosing malignant pulmonary nodules from CXRs than are trained radiologists.28
In addition to plain radiographs, AI has been applied to many other imaging technologies, including ultrasounds, positron emission tomography, mammograms, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).15,26,44,48,54-56 A large study demonstrated that ML platforms significantly reduced the time to diagnose intracranial hemorrhages on CT and identified subtle hemorrhages missed by radiologists.55 Other studies have claimed that AI programs may be better than radiologists in detecting cancer in screening mammograms, and 3 FDA-approved devices focus on mammogram interpretation.2,15,54,57 There is also great interest in MRI applications to detect and predict prognosis for breast cancer based on imaging findings.21,56
Aside from providing accurate diagnoses, other studies focus on AI radiograph interpretation to assist with patient screening, triage, improving time to final diagnosis, providing a rapid “second opinion,” and even monitoring disease progression and offering insights into prognosis.8,21,23,52,55,56,58 These features help in busy urban centers but may play an even greater role in areas with limited access to health care or trained specialists such as radiologists.52
Cardiology
Cardiology has the second highest number of FDA-approved AI applications.2 Many cardiology AI platforms involve image analysis, as described in several recent reviews.45,59,60 AI has been applied to echocardiography to measure ejection fractions, detect valvular disease, and assess heart failure from hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy and amyloidosis.45,48,59 Applications for cardiac CT scans and CT angiography have successfully quantified both calcified and noncalcified coronary artery plaques and lumen assessments, assessed myocardial perfusion, and performed coronary artery calcium scoring.45,59,60 Likewise, AI applications for cardiac MRI have been used to quantitate ejection fraction, large vessel flow assessment, and cardiac scar burden.45,59
For years ECG devices have provided interpretation with limited accuracy using preprogrammed parameters.48 However, the application of AI allows ECG interpretation on par with trained cardiologists. Numerous such AI applications exist, and 2 FDA-approved devices perform ECG interpretation.2,61-64 One of these devices incorporates an AI-powered stethoscope to detect atrial fibrillation and heart murmurs.65
Pathology
The advancement of whole slide imaging, wherein entire slides can be scanned and digitized at high speed and resolution, creates great potential for AI applications in pathology.12,24,32,33,66 A landmark study demonstrating the potential of AI for assessing whole slide imaging examined sentinel lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer.22 Multiple algorithms in the study demonstrated that AI was equivalent or better than pathologists in detecting metastases, especially when the pathologists were time-constrained consistent with a normal working environment. Significantly, the most accurate and efficient diagnoses were achieved when the pathologist and AI interpretations were used together.22,33
AI has shown promise in diagnosing many other entities, including cancers of the prostate (including Gleason scoring), lung, colon, breast, and skin.11,12,24,27,32,67 In addition, AI has shown great potential in scoring biomarkers important for prognosis and treatment, such as immunohistochemistry (IHC) labeling of Ki-67 and PD-L1.32 Pathologists can have difficulty classifying certain tumors or determining the site of origin for metastases, often having to rely on IHC with limited success. The unique features of image analysis with AI have the potential to assist in classifying difficult tumors and identifying sites of origin for metastatic disease based on morphology alone.11
Oncology depends heavily on molecular pathology testing to dictate treatment options and determine prognosis. Preliminary studies suggest that AI interpretation alone has the potential to delineate whether certain molecular mutations are present in tumors from various sites.11,14,24,32 One study combined histology and genomic results for AI interpretation that improved prognostic predictions.68 In addition, AI analysis may have potential in predicting tumor recurrence or prognosis based on cellular features, as demonstrated for lung cancer and melanoma.67,69,70
Ophthalmology
AI applications for ophthalmology have focused on diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinopathy of prematurity, age-related and congenital cataracts, and retinal vein occlusion.71-73 Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness and has been studied by numerous platforms with good success, most having used color fundus photography.71,72 One study showed AI could diagnose diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema with specificities similar to ophthalmologists.74 In 2018, the FDA approved the AI platform IDx-DR. This diagnostic system classifies retinal images and recommends referral for patients determined to have “more than mild diabetic retinopathy” and reexamination within a year for other patients.8,75 Significantly, the platform recommendations do not require confirmation by a clinician.8
AI has been applied to other modalities in ophthalmology such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) to diagnose retinal disease and to predict appropriate management of congenital cataracts.25,73,76 For example, an AI application using OCT has been demonstrated to match or exceed the accuracy of retinal experts in diagnosing and triaging patients with a variety of retinal pathologies, including patients needing urgent referrals.77
Dermatology
Multiple studies demonstrate AI performs at least equal to experienced dermatologists in differentiating selected skin lesions.78-81 For example, Esteva and colleagues demonstrated AI could differentiate keratinocyte carcinomas from benign seborrheic keratoses and malignant melanomas from benign nevi with accuracy equal to 21 board-certified dermatologists.78
AI is applicable to various imaging procedures common to dermatology, such as dermoscopy, very high-frequency ultrasound, and reflectance confocal microscopy.82 Several studies have demonstrated that AI interpretation compared favorably to dermatologists evaluating dermoscopy to assess melanocytic lesions.78-81,83
A limitation in these studies is that they differentiate only a few diagnoses.82 Furthermore, dermatologists have sensory input such as touch and visual examination under various conditions, something AI has yet to replicate.15,34,84 Also, most AI devices use no or limited clinical information.81 Dermatologists can recognize rarer conditions for which AI models may have had limited or no training.34 Nevertheless, a recent study assessed AI for the diagnosis of 134 separate skin disorders with promising results, including providing diagnoses with accuracy comparable to that of dermatologists and providing accurate treatment strategies.84 As Topol points out, most skin lesions are diagnosed in the primary care setting where AI can have a greater impact when used in conjunction with the clinical impression, especially where specialists are in limited supply.48,78
Finally, dermatology lends itself to using portable or smartphone applications (apps) wherein the user can photograph a lesion for analysis by AI algorithms to assess the need for further evaluation or make treatment recommendations.34,84,85 Although results from currently available apps are not encouraging, they may play a greater role as the technology advances.34,85
Oncology
Applications of AI in oncology include predicting prognosis for patients with cancer based on histologic and/or genetic information.14,68,86 Programs can predict the risk of complications before and recurrence risks after surgery for malignancies.44,87-89 AI can also assist in treatment planning and predict treatment failure with radiation therapy.90,91
AI has great potential in processing the large volumes of patient data in cancer genomics. Next-generation sequencing has allowed for the identification of millions of DNA sequences in a single tumor to detect genetic anomalies.92 Thousands of mutations can be found in individual tumor samples, and processing this information and determining its significance can be beyond human capability.14 We know little about the effects of various mutation combinations, and most tumors have a heterogeneous molecular profile among different cell populations.14,93 The presence or absence of various mutations can have diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications.93 AI has great potential to sort through these complex data and identify actionable findings.
More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019, and publications in the field of cancer genomics are increasing exponentially.14,92,93 Patel and colleagues assessed the utility of IBM Watson for Genomics against results from a molecular tumor board.93 Watson for Genomics identified potentially significant mutations not identified by the tumor board in 32% of patients. Most mutations were related to new clinical trials not yet added to the tumor board watch list, demonstrating the role AI will have in processing the large volume of genetic data required to deliver personalized medicine moving forward.
Gastroenterology
AI has shown promise in predicting risk or outcomes based on clinical parameters in various common gastroenterology problems, including gastric reflux, acute pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.94,95 AI endoscopic analysis has demonstrated potential in assessing Barrett’s esophagus, gastric Helicobacter pylori infections, gastric atrophy, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.95 Applications have been used to assess esophageal, gastric, and colonic malignancies, including depth of invasion based on endoscopic images.95 Finally, studies have evaluated AI to assess small colon polyps during colonoscopy, including differentiating benign and premalignant polyps with success comparable to gastroenterologists.94,95 AI has been shown to increase the speed and accuracy of gastroenterologists in detecting small polyps during colonoscopy.48 In a prospective randomized study, colonoscopies performed using an AI device identified significantly more small adenomatous polyps than colonoscopies without AI.96
Neurology
It has been suggested that AI technologies are well suited for application in neurology due to the subtle presentation of many neurologic diseases.16 Viz LVO, the first CMS-approved AI reimbursement for the diagnosis of strokes, analyzes CTs to detect early ischemic strokes and alerts the medical team, thus shortening time to treatment.3,97 Many other AI platforms are in use or development that use CT and MRI for the early detection of strokes as well as for treatment and prognosis.9,97
AI technologies have been applied to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases.16,98 For example, several studies have evaluated patient movements in Parkinson disease for both early diagnosis and to assess response to treatment.98 These evaluations included assessment with both external cameras as well as wearable devices and smartphone apps.
AI has also been applied to seizure disorders, attempting to determine seizure type, localize the area of seizure onset, and address the challenges of identifying seizures in neonates.99,100 Other potential applications range from early detection and prognosis predictions for cases of multiple sclerosis to restoring movement in paralysis from a variety of conditions such as spinal cord injury.9,101,102
Mental Health
Due to the interactive nature of mental health care, the field has been slower to develop AI applications.18 With heavy reliance on textual information (eg, clinic notes, mood rating scales, and documentation of conversations), successful AI applications in this field will likely rely heavily on NLP.18 However, studies investigating the application of AI to mental health have also incorporated data such as brain imaging, smartphone monitoring, and social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter.18,103,104
The risk of suicide is higher in veteran patients, and ML algorithms have had limited success in predicting suicide risk in both veteran and nonveteran populations.104-106 While early models have low positive predictive values and low sensitivities, they still promise to be a useful tool in conjunction with traditional risk assessments.106 Kessler and colleagues suggest that combining multiple rather than single ML algorithms might lead to greater success.105,106
AI may assist in diagnosing other mental health disorders, including major depressive disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), schizophrenia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and Alzheimer disease.103,104,107 These investigations are in the early stages with limited clinical applicability. However, 2 AI applications awaiting FDA approval relate to ADHD and opioid use.2 Furthermore, potential exists for AI to not only assist with prevention and diagnosis of ADHD, but also to identify optimal treatment options.2,103
General and Personalized Medicine
Additional AI applications include diagnosing patients with suspected sepsis, measuring liver iron concentrations, predicting hospital mortality at the time of admission, and more.2,108,109 AI can guide end-of-life decisions such as resuscitation status or whether to initiate mechanical ventilation.48
AI-driven smartphone apps can be beneficial to both patients and clinicians. Examples include predicting nonadherence to anticoagulation therapy, monitoring heart rhythms for atrial fibrillation or signs of hyperkalemia in patients with renal failure, and improving outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus by decreasing glycemic variability and reducing hypoglycemia.8,48,110,111 The potential for AI applications to health care and personalized medicine are almost limitless.
Discussion
With ever-increasing expectations for all health care sectors to deliver timely, fiscally-responsible, high-quality health care, AI has the potential to have numerous impacts. AI can improve diagnostic accuracy while limiting errors and impact patient safety such as assisting with prescription delivery.8,9,34 It can screen and triage patients, alerting clinicians to those needing more urgent evaluation.8,23,77,97 AI also may increase a clinician’s efficiency and speed to render a diagnosis.12,13,55,97 AI can provide a rapid second opinion, an ability especially beneficial in underserved areas with shortages of specialists.23,25,26,29,34 Similarly, AI may decrease the inter- and intraobserver variability common in many medical specialties.12,27,45 AI applications can also monitor disease progression, identifying patients at greatest risk, and provide information for prognosis.21,23,56,58 Finally, as described with applications using IBM Watson, AI can allow for an integrated approach to health care that is currently lacking.
We have described many reports suggesting AI can render diagnoses as well as or better than experienced clinicians, and speculation exists that AI will replace many roles currently performed by health care practitioners.9,26 However, most studies demonstrate that AI’s diagnostic benefits are best realized when used to supplement a clinician’s impression.8,22,30,33,52,54,56,69,84 AI is not likely to replace humans in health care in the foreseeable future. The technology can be likened to the impact of CT scans developed in the 1970s in neurology. Prior to such detailed imaging, neurologists spent extensive time performing detailed physicals to render diagnoses and locate lesions before surgery. There was mistrust of this new technology and concern that CT scans would eliminate the need for neurologists.112 On the contrary, neurology is alive and well, frequently being augmented by the technologies once speculated to replace it.
Commercial AI health care platforms represented a $2 billion industry in 2018 and are growing rapidly each year.13,32 Many AI products are offered ready for implementation for various tasks, including diagnostics, patient management, and improved efficiency. Others will likely be provided as templates suitable for modification to meet the specific needs of the facility, practice, or specialty for its patient population.
AI Risks and Limitations
AI has several risks and limitations. Although there is progress in explainable AI, at times we still struggle to understand how the output provided by machine learning algorithms was created.44,48 The many layers associated with deep learning self-determine the criteria to reach its conclusion, and these criteria can continually evolve. The parameters of deep learning are not preprogrammed, and there are too many individual data points to be extrapolated or deconvoluted for evaluation at our current level of knowledge.26,51 These apparent lack of constraints cause concern for patient safety and suggest that greater validation and continued scrutiny of validity is required.8,48 Efforts are underway to create explainable AI programs to make their processes more transparent, but such clarification is limited presently.14,26,48,77
Another challenge of AI is determining the amount of training data required to function optimally. Also, if the output describes multiple variables or diagnoses, are each equally valid?113 Furthermore, many AI applications look for a specific process, such as cancer diagnoses on CXRs. However, how coexisting conditions like cardiomegaly, emphysema, pneumonia, etc, seen on CXRs will affect the diagnosis needs to be considered.51,52 Zech and colleagues provide the example that diagnoses for pneumothorax are frequently rendered on CXRs with chest tubes in place.51 They suggest that CNNs may develop a bias toward diagnosing pneumothorax when chest tubes are present. Many current studies approach an issue in isolation, a situation not realistic in real-world clinical practice.26
Most studies on AI have been retrospective, and frequently data used to train the program are preselected.13,26 The data are typically validated on available databases rather than actual patients in the clinical setting, limiting confidence in the validity of the AI output when applied to real-world situations. Currently, fewer than 12 prospective trials had been published comparing AI with traditional clinical care.13,114 Randomized prospective clinical trials are even fewer, with none currently reported from the United States.13,114 The results from several studies have been shown to diminish when repeated prospectively.114
The FDA has created a new category known as Software as a Medical Device and has a Digital Health Innovation Action Plan to regulate AI platforms. Still, the process of AI regulation is of necessity different from traditional approval processes and is continually evolving.8 The FDA approval process cannot account for the fact that the program’s parameters may continually evolve or adapt.2
Guidelines for investigating and reporting AI research with its unique attributes are being developed. Examples include the TRIPOD-ML statement and others.49,115 In September 2020, 2 publications addressed the paucity of gold-standard randomized clinical trials in clinical AI applications.116,117 The SPIRIT-AI statement expands on the original SPIRIT statement published in 2013 to guide minimal reporting standards for AI clinical trial protocols to promote transparency of design and methodology.116 Similarly, the CONSORT-AI extension, stemming from the original CONSORT statement in 1996, aims to ensure quality reporting of randomized controlled trials in AI.117
Another risk with AI is that while an individual physician making a mistake may adversely affect 1 patient, a single mistake in an AI algorithm could potentially affect thousands of patients.48 Also, AI programs developed for patient populations at a facility may not translate to another. Referred to as overfitting, this phenomenon relates to selection bias in training data sets.15,34,49,51,52 Studies have shown that programs that underrepresent certain group characteristics such as age, sex, or race may be less effective when applied to a population in which these characteristics have differing representations.8,48,49 This problem of underrepresentation has been demonstrated in programs interpreting pathology slides, radiographs, and skin lesions.15,32,51
Admittedly, most of these challenges are not specific to AI and existed in health care previously. Physicians make mistakes, treatments are sometimes used without adequate prospective studies, and medications are given without understanding their mechanism of action, much like AI-facilitated processes reach a conclusion that cannot be fully explained.48
Conclusions
The view that AI will dramatically impact health care in the coming years will likely prove true. However, much work is needed, especially because of the paucity of prospective clinical trials as has been historically required in medical research. Any concern that AI will replace HCPs seems unwarranted. Early studies suggest that even AI programs that appear to exceed human interpretation perform best when working in cooperation with and oversight from clinicians. AI’s greatest potential appears to be its ability to augment care from health professionals, improving efficiency and accuracy, and should be anticipated with enthusiasm as the field moves forward at an exponential rate.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Makenna G. Thomas for proofreading and review of the manuscript. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital. This research has been approved by the James A. Haley Veteran’s Hospital Office of Communications and Media.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was first described in 1956 and refers to machines having the ability to learn as they receive and process information, resulting in the ability to “think” like humans.1 AI’s impact in medicine is increasing; currently, at least 29 AI medical devices and algorithms are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in a variety of areas, including radiograph interpretation, managing glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus, analyzing electrocardiograms (ECGs), and diagnosing sleep disorders among others.2 Significantly, in 2020, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced the first reimbursement to hospitals for an AI platform, a model for early detection of strokes.3 AI is rapidly becoming an integral part of health care, and its role will only increase in the future (Table).
As knowledge in medicine is expanding exponentially, AI has great potential to assist with handling complex patient care data. The concept of exponential growth is not a natural one. As Bini described, with exponential growth the volume of knowledge amassed over the past 10 years will now occur in perhaps only 1 year.1 Likewise, equivalent advances over the past year may take just a few months. This phenomenon is partly due to the law of accelerating returns, which states that advances feed on themselves, continually increasing the rate of further advances.4 The volume of medical data doubles every 2 to 5 years.5 Fortunately, the field of AI is growing exponentially as well and can help health care practitioners (HCPs) keep pace, allowing the continued delivery of effective health care.
In this report, we review common terminology, principles, and general applications of AI, followed by current and potential applications of AI for selected medical specialties. Finally, we discuss AI’s future in health care, along with potential risks and pitfalls.
AI Overview
AI refers to machine programs that can “learn” or think based on past experiences. This functionality contrasts with simple rules-based programming available to health care for years. An example of rules-based programming is the warfarindosing.org website developed by Barnes-Jewish Hospital at Washington University Medical Center, which guides initial warfarin dosing.6,7 The prescriber inputs detailed patient information, including age, sex, height, weight, tobacco history, medications, laboratory results, and genotype if available. The application then calculates recommended warfarin dosing regimens to avoid over- or underanticoagulation. While the dosing algorithm may be complex, it depends entirely on preprogrammed rules. The program does not learn to reach its conclusions and recommendations from patient data.
In contrast, one of the most common subsets of AI is machine learning (ML). ML describes a program that “learns from experience and improves its performance as it learns.”1 With ML, the computer is initially provided with a training data set—data with known outcomes or labels. Because the initial data are input from known samples, this type of AI is known as supervised learning.8-10 As an example, we recently reported using ML to diagnose various types of cancer from pathology slides.11 In one experiment, we captured images of colon adenocarcinoma and normal colon (these 2 groups represent the training data set). Unlike traditional programming, we did not define characteristics that would differentiate colon cancer from normal; rather, the machine learned these characteristics independently by assessing the labeled images provided. A second data set (the validation data set) was used to evaluate the program and fine-tune the ML training model’s parameters. Finally, the program was presented with new images of cancer and normal cases for final assessment of accuracy (test data set). Our program learned to recognize differences from the images provided and was able to differentiate normal and cancer images with > 95% accuracy.
Advances in computer processing have allowed for the development of artificial neural networks (ANNs). While there are several types of ANNs, the most common types used for image classification and segmentation are known as convolutional neural networks (CNNs).9,12-14 The programs are designed to work similar to the human brain, specifically the visual cortex.15,16 As data are acquired, they are processed by various layers in the program. Much like neurons in the brain, one layer decides whether to advance information to the next.13,14 CNNs can be many layers deep, leading to the term deep learning: “computational models that are composed of multiple processing layers to learn representations of data with multiple levels of abstraction.”1,13,17
ANNs can process larger volumes of data. This advance has led to the development of unstructured or unsupervised learning. With this type of learning, imputing defined features (ie, predetermined answers) of the training data set described above is no longer required.1,8,10,14 The advantage of unsupervised learning is that the program can be presented raw data and extract meaningful interpretation without human input, often with less bias than may exist with supervised learning.1,18 If shown enough data, the program can extract relevant features to make conclusions independently without predefined definitions, potentially uncovering markers not previously known. For example, several studies have used unsupervised learning to search patient data to assess readmission risks of patients with congestive heart failure.10,19,20 AI compiled features independently and not previously defined, predicting patients at greater risk for readmission superior to traditional methods.
A more detailed description of the various terminologies and techniques of AI is beyond the scope of this review.9,10,17,21 However, in this basic overview, we describe 4 general areas that AI impacts health care (Figure).
Health Care Applications
Image analysis has seen the most AI health care applications.8,15 AI has shown potential in interpreting many types of medical images, including pathology slides, radiographs of various types, retina and other eye scans, and photographs of skin lesions. Many studies have demonstrated that AI can interpret these images as accurately as or even better than experienced clinicians.9,13,22-29 Studies have suggested AI interpretation of radiographs may better distinguish patients infected with COVID-19 from other causes of pneumonia, and AI interpretation of pathology slides may detect specific genetic mutations not previously identified without additional molecular tests.11,14,23,24,30-32
The second area in which AI can impact health care is improving workflow and efficiency. AI has improved surgery scheduling, saving significant revenue, and decreased patient wait times for appointments.1 AI can screen and triage radiographs, allowing attention to be directed to critical patients. This use would be valuable in many busy clinical settings, such as the recent COVID-19 pandemic.8,23 Similarly, AI can screen retina images to prioritize urgent conditions.25 AI has improved pathologists’ efficiency when used to detect breast metastases.33 Finally, AI may reduce medical errors, thereby ensuring patient safety.8,9,34
A third health care benefit of AI is in public health and epidemiology. AI can assist with clinical decision-making and diagnoses in low-income countries and areas with limited health care resources and personnel.25,29 AI can improve identification of infectious outbreaks, such as tuberculosis, malaria, dengue fever, and influenza.29,35-40 AI has been used to predict transmission patterns of the Zika virus and the current COVID-19 pandemic.41,42 Applications can stratify the risk of outbreaks based on multiple factors, including age, income, race, atypical geographic clusters, and seasonal factors like rainfall and temperature.35,36,38,43 AI has been used to assess morbidity and mortality, such as predicting disease severity with malaria and identifying treatment failures in tuberculosis.29
Finally, AI can dramatically impact health care due to processing large data sets or disconnected volumes of patient information—so-called big data.44-46 An example is the widespread use of electronic health records (EHRs) such as the Computerized Patient Record System used in Veteran Affairs medical centers (VAMCs). Much of patient information exists in written text: HCP notes, laboratory and radiology reports, medication records, etc. Natural language processing (NLP) allows platforms to sort through extensive volumes of data on complex patients at rates much faster than human capability, which has great potential to assist with diagnosis and treatment decisions.9
Medical literature is being produced at rates that exceed our ability to digest. More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019 alone.14 NLP capabilities of AI have the potential to rapidly sort through this extensive medical literature and relate specific verbiage in patient records guiding therapy.46 IBM Watson, a supercomputer based on ML and NLP, demonstrates this concept with many potential applications, only some of which relate to health care.1,9 Watson has an oncology component to assimilate multiple aspects of patient care, including clinical notes, pathology results, radiograph findings, staging, and a tumor’s genetic profile. It coordinates these inputs from the EHR and mines medical literature and research databases to recommend treatment options.1,46 AI can assess and compile far greater patient data and therapeutic options than would be feasible by individual clinicians, thus providing customized patient care.47 Watson has partnered with numerous medical centers, including MD Anderson Cancer Center and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with variable success.44,47-49 While the full potential of Watson appears not yet realized, these AI-driven approaches will likely play an important role in leveraging the hidden value in the expanding volume of health care information.
Medical Specialty Applications
Radiology
Currently > 70% of FDA-approved AI medical devices are in the field of radiology.2 Most radiology departments have used AI-friendly digital imaging for years, such as the picture archiving and communication systems used by numerous health care systems, including VAMCs.2,15 Gray-scale images common in radiology lend themselves to standardization, although AI is not limited to black-and- white image interpretation.15
An abundance of literature describes plain radiograph interpretation using AI. One FDA-approved platform improved X-ray diagnosis of wrist fractures when used by emergency medicine clinicians.2,50 AI has been applied to chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation of many conditions, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, malignant lung lesions, and COVID-19.23,25,28,44,51-53 For example, Nam and colleagues suggested AI is better at diagnosing malignant pulmonary nodules from CXRs than are trained radiologists.28
In addition to plain radiographs, AI has been applied to many other imaging technologies, including ultrasounds, positron emission tomography, mammograms, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).15,26,44,48,54-56 A large study demonstrated that ML platforms significantly reduced the time to diagnose intracranial hemorrhages on CT and identified subtle hemorrhages missed by radiologists.55 Other studies have claimed that AI programs may be better than radiologists in detecting cancer in screening mammograms, and 3 FDA-approved devices focus on mammogram interpretation.2,15,54,57 There is also great interest in MRI applications to detect and predict prognosis for breast cancer based on imaging findings.21,56
Aside from providing accurate diagnoses, other studies focus on AI radiograph interpretation to assist with patient screening, triage, improving time to final diagnosis, providing a rapid “second opinion,” and even monitoring disease progression and offering insights into prognosis.8,21,23,52,55,56,58 These features help in busy urban centers but may play an even greater role in areas with limited access to health care or trained specialists such as radiologists.52
Cardiology
Cardiology has the second highest number of FDA-approved AI applications.2 Many cardiology AI platforms involve image analysis, as described in several recent reviews.45,59,60 AI has been applied to echocardiography to measure ejection fractions, detect valvular disease, and assess heart failure from hypertrophic and restrictive cardiomyopathy and amyloidosis.45,48,59 Applications for cardiac CT scans and CT angiography have successfully quantified both calcified and noncalcified coronary artery plaques and lumen assessments, assessed myocardial perfusion, and performed coronary artery calcium scoring.45,59,60 Likewise, AI applications for cardiac MRI have been used to quantitate ejection fraction, large vessel flow assessment, and cardiac scar burden.45,59
For years ECG devices have provided interpretation with limited accuracy using preprogrammed parameters.48 However, the application of AI allows ECG interpretation on par with trained cardiologists. Numerous such AI applications exist, and 2 FDA-approved devices perform ECG interpretation.2,61-64 One of these devices incorporates an AI-powered stethoscope to detect atrial fibrillation and heart murmurs.65
Pathology
The advancement of whole slide imaging, wherein entire slides can be scanned and digitized at high speed and resolution, creates great potential for AI applications in pathology.12,24,32,33,66 A landmark study demonstrating the potential of AI for assessing whole slide imaging examined sentinel lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer.22 Multiple algorithms in the study demonstrated that AI was equivalent or better than pathologists in detecting metastases, especially when the pathologists were time-constrained consistent with a normal working environment. Significantly, the most accurate and efficient diagnoses were achieved when the pathologist and AI interpretations were used together.22,33
AI has shown promise in diagnosing many other entities, including cancers of the prostate (including Gleason scoring), lung, colon, breast, and skin.11,12,24,27,32,67 In addition, AI has shown great potential in scoring biomarkers important for prognosis and treatment, such as immunohistochemistry (IHC) labeling of Ki-67 and PD-L1.32 Pathologists can have difficulty classifying certain tumors or determining the site of origin for metastases, often having to rely on IHC with limited success. The unique features of image analysis with AI have the potential to assist in classifying difficult tumors and identifying sites of origin for metastatic disease based on morphology alone.11
Oncology depends heavily on molecular pathology testing to dictate treatment options and determine prognosis. Preliminary studies suggest that AI interpretation alone has the potential to delineate whether certain molecular mutations are present in tumors from various sites.11,14,24,32 One study combined histology and genomic results for AI interpretation that improved prognostic predictions.68 In addition, AI analysis may have potential in predicting tumor recurrence or prognosis based on cellular features, as demonstrated for lung cancer and melanoma.67,69,70
Ophthalmology
AI applications for ophthalmology have focused on diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinopathy of prematurity, age-related and congenital cataracts, and retinal vein occlusion.71-73 Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness and has been studied by numerous platforms with good success, most having used color fundus photography.71,72 One study showed AI could diagnose diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema with specificities similar to ophthalmologists.74 In 2018, the FDA approved the AI platform IDx-DR. This diagnostic system classifies retinal images and recommends referral for patients determined to have “more than mild diabetic retinopathy” and reexamination within a year for other patients.8,75 Significantly, the platform recommendations do not require confirmation by a clinician.8
AI has been applied to other modalities in ophthalmology such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) to diagnose retinal disease and to predict appropriate management of congenital cataracts.25,73,76 For example, an AI application using OCT has been demonstrated to match or exceed the accuracy of retinal experts in diagnosing and triaging patients with a variety of retinal pathologies, including patients needing urgent referrals.77
Dermatology
Multiple studies demonstrate AI performs at least equal to experienced dermatologists in differentiating selected skin lesions.78-81 For example, Esteva and colleagues demonstrated AI could differentiate keratinocyte carcinomas from benign seborrheic keratoses and malignant melanomas from benign nevi with accuracy equal to 21 board-certified dermatologists.78
AI is applicable to various imaging procedures common to dermatology, such as dermoscopy, very high-frequency ultrasound, and reflectance confocal microscopy.82 Several studies have demonstrated that AI interpretation compared favorably to dermatologists evaluating dermoscopy to assess melanocytic lesions.78-81,83
A limitation in these studies is that they differentiate only a few diagnoses.82 Furthermore, dermatologists have sensory input such as touch and visual examination under various conditions, something AI has yet to replicate.15,34,84 Also, most AI devices use no or limited clinical information.81 Dermatologists can recognize rarer conditions for which AI models may have had limited or no training.34 Nevertheless, a recent study assessed AI for the diagnosis of 134 separate skin disorders with promising results, including providing diagnoses with accuracy comparable to that of dermatologists and providing accurate treatment strategies.84 As Topol points out, most skin lesions are diagnosed in the primary care setting where AI can have a greater impact when used in conjunction with the clinical impression, especially where specialists are in limited supply.48,78
Finally, dermatology lends itself to using portable or smartphone applications (apps) wherein the user can photograph a lesion for analysis by AI algorithms to assess the need for further evaluation or make treatment recommendations.34,84,85 Although results from currently available apps are not encouraging, they may play a greater role as the technology advances.34,85
Oncology
Applications of AI in oncology include predicting prognosis for patients with cancer based on histologic and/or genetic information.14,68,86 Programs can predict the risk of complications before and recurrence risks after surgery for malignancies.44,87-89 AI can also assist in treatment planning and predict treatment failure with radiation therapy.90,91
AI has great potential in processing the large volumes of patient data in cancer genomics. Next-generation sequencing has allowed for the identification of millions of DNA sequences in a single tumor to detect genetic anomalies.92 Thousands of mutations can be found in individual tumor samples, and processing this information and determining its significance can be beyond human capability.14 We know little about the effects of various mutation combinations, and most tumors have a heterogeneous molecular profile among different cell populations.14,93 The presence or absence of various mutations can have diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications.93 AI has great potential to sort through these complex data and identify actionable findings.
More than 200,000 cancer-related articles were published in 2019, and publications in the field of cancer genomics are increasing exponentially.14,92,93 Patel and colleagues assessed the utility of IBM Watson for Genomics against results from a molecular tumor board.93 Watson for Genomics identified potentially significant mutations not identified by the tumor board in 32% of patients. Most mutations were related to new clinical trials not yet added to the tumor board watch list, demonstrating the role AI will have in processing the large volume of genetic data required to deliver personalized medicine moving forward.
Gastroenterology
AI has shown promise in predicting risk or outcomes based on clinical parameters in various common gastroenterology problems, including gastric reflux, acute pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.94,95 AI endoscopic analysis has demonstrated potential in assessing Barrett’s esophagus, gastric Helicobacter pylori infections, gastric atrophy, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.95 Applications have been used to assess esophageal, gastric, and colonic malignancies, including depth of invasion based on endoscopic images.95 Finally, studies have evaluated AI to assess small colon polyps during colonoscopy, including differentiating benign and premalignant polyps with success comparable to gastroenterologists.94,95 AI has been shown to increase the speed and accuracy of gastroenterologists in detecting small polyps during colonoscopy.48 In a prospective randomized study, colonoscopies performed using an AI device identified significantly more small adenomatous polyps than colonoscopies without AI.96
Neurology
It has been suggested that AI technologies are well suited for application in neurology due to the subtle presentation of many neurologic diseases.16 Viz LVO, the first CMS-approved AI reimbursement for the diagnosis of strokes, analyzes CTs to detect early ischemic strokes and alerts the medical team, thus shortening time to treatment.3,97 Many other AI platforms are in use or development that use CT and MRI for the early detection of strokes as well as for treatment and prognosis.9,97
AI technologies have been applied to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases.16,98 For example, several studies have evaluated patient movements in Parkinson disease for both early diagnosis and to assess response to treatment.98 These evaluations included assessment with both external cameras as well as wearable devices and smartphone apps.
AI has also been applied to seizure disorders, attempting to determine seizure type, localize the area of seizure onset, and address the challenges of identifying seizures in neonates.99,100 Other potential applications range from early detection and prognosis predictions for cases of multiple sclerosis to restoring movement in paralysis from a variety of conditions such as spinal cord injury.9,101,102
Mental Health
Due to the interactive nature of mental health care, the field has been slower to develop AI applications.18 With heavy reliance on textual information (eg, clinic notes, mood rating scales, and documentation of conversations), successful AI applications in this field will likely rely heavily on NLP.18 However, studies investigating the application of AI to mental health have also incorporated data such as brain imaging, smartphone monitoring, and social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter.18,103,104
The risk of suicide is higher in veteran patients, and ML algorithms have had limited success in predicting suicide risk in both veteran and nonveteran populations.104-106 While early models have low positive predictive values and low sensitivities, they still promise to be a useful tool in conjunction with traditional risk assessments.106 Kessler and colleagues suggest that combining multiple rather than single ML algorithms might lead to greater success.105,106
AI may assist in diagnosing other mental health disorders, including major depressive disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), schizophrenia, posttraumatic stress disorder, and Alzheimer disease.103,104,107 These investigations are in the early stages with limited clinical applicability. However, 2 AI applications awaiting FDA approval relate to ADHD and opioid use.2 Furthermore, potential exists for AI to not only assist with prevention and diagnosis of ADHD, but also to identify optimal treatment options.2,103
General and Personalized Medicine
Additional AI applications include diagnosing patients with suspected sepsis, measuring liver iron concentrations, predicting hospital mortality at the time of admission, and more.2,108,109 AI can guide end-of-life decisions such as resuscitation status or whether to initiate mechanical ventilation.48
AI-driven smartphone apps can be beneficial to both patients and clinicians. Examples include predicting nonadherence to anticoagulation therapy, monitoring heart rhythms for atrial fibrillation or signs of hyperkalemia in patients with renal failure, and improving outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus by decreasing glycemic variability and reducing hypoglycemia.8,48,110,111 The potential for AI applications to health care and personalized medicine are almost limitless.
Discussion
With ever-increasing expectations for all health care sectors to deliver timely, fiscally-responsible, high-quality health care, AI has the potential to have numerous impacts. AI can improve diagnostic accuracy while limiting errors and impact patient safety such as assisting with prescription delivery.8,9,34 It can screen and triage patients, alerting clinicians to those needing more urgent evaluation.8,23,77,97 AI also may increase a clinician’s efficiency and speed to render a diagnosis.12,13,55,97 AI can provide a rapid second opinion, an ability especially beneficial in underserved areas with shortages of specialists.23,25,26,29,34 Similarly, AI may decrease the inter- and intraobserver variability common in many medical specialties.12,27,45 AI applications can also monitor disease progression, identifying patients at greatest risk, and provide information for prognosis.21,23,56,58 Finally, as described with applications using IBM Watson, AI can allow for an integrated approach to health care that is currently lacking.
We have described many reports suggesting AI can render diagnoses as well as or better than experienced clinicians, and speculation exists that AI will replace many roles currently performed by health care practitioners.9,26 However, most studies demonstrate that AI’s diagnostic benefits are best realized when used to supplement a clinician’s impression.8,22,30,33,52,54,56,69,84 AI is not likely to replace humans in health care in the foreseeable future. The technology can be likened to the impact of CT scans developed in the 1970s in neurology. Prior to such detailed imaging, neurologists spent extensive time performing detailed physicals to render diagnoses and locate lesions before surgery. There was mistrust of this new technology and concern that CT scans would eliminate the need for neurologists.112 On the contrary, neurology is alive and well, frequently being augmented by the technologies once speculated to replace it.
Commercial AI health care platforms represented a $2 billion industry in 2018 and are growing rapidly each year.13,32 Many AI products are offered ready for implementation for various tasks, including diagnostics, patient management, and improved efficiency. Others will likely be provided as templates suitable for modification to meet the specific needs of the facility, practice, or specialty for its patient population.
AI Risks and Limitations
AI has several risks and limitations. Although there is progress in explainable AI, at times we still struggle to understand how the output provided by machine learning algorithms was created.44,48 The many layers associated with deep learning self-determine the criteria to reach its conclusion, and these criteria can continually evolve. The parameters of deep learning are not preprogrammed, and there are too many individual data points to be extrapolated or deconvoluted for evaluation at our current level of knowledge.26,51 These apparent lack of constraints cause concern for patient safety and suggest that greater validation and continued scrutiny of validity is required.8,48 Efforts are underway to create explainable AI programs to make their processes more transparent, but such clarification is limited presently.14,26,48,77
Another challenge of AI is determining the amount of training data required to function optimally. Also, if the output describes multiple variables or diagnoses, are each equally valid?113 Furthermore, many AI applications look for a specific process, such as cancer diagnoses on CXRs. However, how coexisting conditions like cardiomegaly, emphysema, pneumonia, etc, seen on CXRs will affect the diagnosis needs to be considered.51,52 Zech and colleagues provide the example that diagnoses for pneumothorax are frequently rendered on CXRs with chest tubes in place.51 They suggest that CNNs may develop a bias toward diagnosing pneumothorax when chest tubes are present. Many current studies approach an issue in isolation, a situation not realistic in real-world clinical practice.26
Most studies on AI have been retrospective, and frequently data used to train the program are preselected.13,26 The data are typically validated on available databases rather than actual patients in the clinical setting, limiting confidence in the validity of the AI output when applied to real-world situations. Currently, fewer than 12 prospective trials had been published comparing AI with traditional clinical care.13,114 Randomized prospective clinical trials are even fewer, with none currently reported from the United States.13,114 The results from several studies have been shown to diminish when repeated prospectively.114
The FDA has created a new category known as Software as a Medical Device and has a Digital Health Innovation Action Plan to regulate AI platforms. Still, the process of AI regulation is of necessity different from traditional approval processes and is continually evolving.8 The FDA approval process cannot account for the fact that the program’s parameters may continually evolve or adapt.2
Guidelines for investigating and reporting AI research with its unique attributes are being developed. Examples include the TRIPOD-ML statement and others.49,115 In September 2020, 2 publications addressed the paucity of gold-standard randomized clinical trials in clinical AI applications.116,117 The SPIRIT-AI statement expands on the original SPIRIT statement published in 2013 to guide minimal reporting standards for AI clinical trial protocols to promote transparency of design and methodology.116 Similarly, the CONSORT-AI extension, stemming from the original CONSORT statement in 1996, aims to ensure quality reporting of randomized controlled trials in AI.117
Another risk with AI is that while an individual physician making a mistake may adversely affect 1 patient, a single mistake in an AI algorithm could potentially affect thousands of patients.48 Also, AI programs developed for patient populations at a facility may not translate to another. Referred to as overfitting, this phenomenon relates to selection bias in training data sets.15,34,49,51,52 Studies have shown that programs that underrepresent certain group characteristics such as age, sex, or race may be less effective when applied to a population in which these characteristics have differing representations.8,48,49 This problem of underrepresentation has been demonstrated in programs interpreting pathology slides, radiographs, and skin lesions.15,32,51
Admittedly, most of these challenges are not specific to AI and existed in health care previously. Physicians make mistakes, treatments are sometimes used without adequate prospective studies, and medications are given without understanding their mechanism of action, much like AI-facilitated processes reach a conclusion that cannot be fully explained.48
Conclusions
The view that AI will dramatically impact health care in the coming years will likely prove true. However, much work is needed, especially because of the paucity of prospective clinical trials as has been historically required in medical research. Any concern that AI will replace HCPs seems unwarranted. Early studies suggest that even AI programs that appear to exceed human interpretation perform best when working in cooperation with and oversight from clinicians. AI’s greatest potential appears to be its ability to augment care from health professionals, improving efficiency and accuracy, and should be anticipated with enthusiasm as the field moves forward at an exponential rate.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Makenna G. Thomas for proofreading and review of the manuscript. This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital. This research has been approved by the James A. Haley Veteran’s Hospital Office of Communications and Media.
1. Bini SA. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and cognitive computing: what do these terms mean and how will they impact health care? J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2358-2361. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.067
2. Benjamens S, Dhunnoo P, Meskó B. The state of artificial intelligence-based FDA-approved medical devices and algorithms: an online database. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:118. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00324-0
3. Viz. AI powered synchronized stroke care. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.viz.ai/ischemic-stroke
4. Buchanan M. The law of accelerating returns. Nat Phys. 2008;4(7):507. doi:10.1038/nphys1010
5. IBM Watson Health computes a pair of new solutions to improve healthcare data and security. Published September 10, 2015. Accessed October 21, 2020. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/ibm-watson-health-computes-a-pair-of-new-solutions-to-improve-healthcare-data-and-security
6. Borkowski AA, Kardani A, Mastorides SM, Thomas LB. Warfarin pharmacogenomics: recommendations with available patented clinical technologies. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2014;8(2):110-115. doi:10.2174/1872208309666140904112003
7. Washington University in St. Louis. Warfarin dosing. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://www.warfarindosing.org/Source/Home.aspx
8. He J, Baxter SL, Xu J, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhang K. The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):30-36. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0307-0
9. Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, et al. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017;2(4):230-243. Published 2017 Jun 21. doi:10.1136/svn-2017-000101
10. Johnson KW, Torres Soto J, Glicksberg BS, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(23):2668-2679. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.521
11. Borkowski AA, Wilson CP, Borkowski SA, et al. Comparing artificial intelligence platforms for histopathologic cancer diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2019;36(10):456-463.
12. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. High-throughput adaptive sampling for whole-slide histopathology image analysis (HASHI) via convolutional neural networks: application to invasive breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196828. Published 2018 May 24. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0196828
13. Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, et al. Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning studies. BMJ. 2020;368:m689. Published 2020 Mar 25. doi:10.1136/bmj.m689
14. Shimizu H, Nakayama KI. Artificial intelligence in oncology. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(5):1452-1460. doi:10.1111/cas.14377
15. Talebi-Liasi F, Markowitz O. Is artificial intelligence going to replace dermatologists?. Cutis. 2020;105(1):28-31.
16. Valliani AA, Ranti D, Oermann EK. Deep learning and neurology: a systematic review. Neurol Ther. 2019;8(2):351-365. doi:10.1007/s40120-019-00153-8
17. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436-444. doi:10.1038/nature14539
18. Graham S, Depp C, Lee EE, et al. Artificial intelligence for mental health and mental illnesses: an overview. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(11):116. Published 2019 Nov 7. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1094-0
19. Golas SB, Shibahara T, Agboola S, et al. A machine learning model to predict the risk of 30-day readmissions in patients with heart failure: a retrospective analysis of electronic medical records data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018;18(1):44. Published 2018 Jun 22. doi:10.1186/s12911-018-0620-z
20. Mortazavi BJ, Downing NS, Bucholz EM, et al. Analysis of machine learning techniques for heart failure readmissions. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2016;9(6):629-640. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.116.003039
21. Meyer-Bäse A, Morra L, Meyer-Bäse U, Pinker K. Current status and future perspectives of artificial intelligence in magnetic resonance breast imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2020;2020:6805710. Published 2020 Aug 28. doi:10.1155/2020/6805710
22. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van Diest P, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. 2017;318(22):2199-2210. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.14585
23. Borkowski AA, Viswanadhan NA, Thomas LB, Guzman RD, Deland LA, Mastorides SM. Using artificial intelligence for COVID-19 chest X-ray diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2020;37(9):398-404. doi:10.12788/fp.0045
24. Coudray N, Ocampo PS, Sakellaropoulos T, et al. Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Med. 2018;24(10):1559-1567. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0177-5
25. Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell. 2018;172(5):1122-1131.e9. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
26. Liu X, Faes L, Kale AU, et al. A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(6):e271-e297. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30123-2
27. Nagpal K, Foote D, Liu Y, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer [published correction appears in NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Nov 19;2:113]. NPJ Digit Med. 2019;2:48. Published 2019 Jun 7. doi:10.1038/s41746-019-0112-2
28. Nam JG, Park S, Hwang EJ, et al. Development and validation of deep learning-based automatic detection algorithm for malignant pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs. Radiology. 2019;290(1):218-228. doi:10.1148/radiol.2018180237
29. Schwalbe N, Wahl B. Artificial intelligence and the future of global health. Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1579-1586. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30226-9
30. Bai HX, Wang R, Xiong Z, et al. Artificial intelligence augmentation of radiologist performance in distinguishing COVID-19 from pneumonia of other origin at chest CT [published correction appears in Radiology. 2021 Apr;299(1):E225]. Radiology. 2020;296(3):E156-E165. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201491
31. Li L, Qin L, Xu Z, et al. Using artificial intelligence to detect COVID-19 and community-acquired pneumonia based on pulmonary CT: evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy. Radiology. 2020;296(2):E65-E71. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200905
32. Serag A, Ion-Margineanu A, Qureshi H, et al. Translational AI and deep learning in diagnostic pathology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019;6:185. Published 2019 Oct 1. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00185

33. Wang D, Khosla A, Gargeya R, Irshad H, Beck AH. Deep learning for identifying metastatic breast cancer. ArXiv. 2016 June 18:arXiv:1606.05718v1. Published online June 18, 2016. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05718
34. Alabdulkareem A. Artificial intelligence and dermatologists: friends or foes? J Dermatology Dermatol Surg. 2019;23(2):57-60. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_19_19
35. Mollalo A, Mao L, Rashidi P, Glass GE. A GIS-based artificial neural network model for spatial distribution of tuberculosis across the continental United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(1):157. Published 2019 Jan 8. doi:10.3390/ijerph16010157
36. Haddawy P, Hasan AHMI, Kasantikul R, et al. Spatiotemporal Bayesian networks for malaria prediction. Artif Intell Med. 2018;84:127-138. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2017.12.002
37. Laureano-Rosario AE, Duncan AP, Mendez-Lazaro PA, et al. Application of artificial neural networks for dengue fever outbreak predictions in the northwest coast of Yucatan, Mexico and San Juan, Puerto Rico. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018;3(1):5. Published 2018 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3010005
38. Buczak AL, Koshute PT, Babin SM, Feighner BH, Lewis SH. A data-driven epidemiological prediction method for dengue outbreaks using local and remote sensing data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012;12:124. Published 2012 Nov 5. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-12-124
39. Scavuzzo JM, Trucco F, Espinosa M, et al. Modeling dengue vector population using remotely sensed data and machine learning. Acta Trop. 2018;185:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.05.003
40. Xue H, Bai Y, Hu H, Liang H. Influenza activity surveillance based on multiple regression model and artificial neural network. IEEE Access. 2018;6:563-575. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2771798
41. Jiang D, Hao M, Ding F, Fu J, Li M. Mapping the transmission risk of Zika virus using machine learning models. Acta Trop. 2018;185:391-399. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.06.021
42. Bragazzi NL, Dai H, Damiani G, Behzadifar M, Martini M, Wu J. How big data and artificial intelligence can help better manage the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):3176. Published 2020 May 2. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093176
43. Lake IR, Colón-González FJ, Barker GC, Morbey RA, Smith GE, Elliot AJ. Machine learning to refine decision making within a syndromic surveillance service. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):559. Published 2019 May 14. doi:10.1186/s12889-019-6916-9
44. Khan OF, Bebb G, Alimohamed NA. Artificial intelligence in medicine: what oncologists need to know about its potential-and its limitations. Oncol Exch. 2017;16(4):8-13. Accessed September 1, 2021. http://www.oncologyex.com/pdf/vol16_no4/feature_khan-ai.pdf
45. Badano LP, Keller DM, Muraru D, Torlasco C, Parati G. Artificial intelligence and cardiovascular imaging: A win-win combination. Anatol J Cardiol. 2020;24(4):214-223. doi:10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.94491
46. Murdoch TB, Detsky AS. The inevitable application of big data to health care. JAMA. 2013;309(13):1351-1352. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.393
47. Greatbatch O, Garrett A, Snape K. The impact of artificial intelligence on the current and future practice of clinical cancer genomics. Genet Res (Camb). 2019;101:e9. Published 2019 Oct 31. doi:10.1017/S0016672319000089
48. Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):44-56. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0300-7
49. Vollmer S, Mateen BA, Bohner G, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence research for patient benefit: 20 critical questions on transparency, replicability, ethics, and effectiveness [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Apr 1;369:m1312]. BMJ. 2020;368:l6927. Published 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1136/bmj.l6927
50. Lindsey R, Daluiski A, Chopra S, et al. Deep neural network improves fracture detection by clinicians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(45):11591-11596. doi:10.1073/pnas.1806905115
51. Zech JR, Badgeley MA, Liu M, Costa AB, Titano JJ, Oermann EK. Variable generalization performance of a deep learning model to detect pneumonia in chest radiographs: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2018;15(11):e1002683. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002683
52. Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. 2017;284(2):574-582. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017162326
53. Rajpurkar P, Joshi A, Pareek A, et al. CheXpedition: investigating generalization challenges for translation of chest x-ray algorithms to the clinical setting. ArXiv. 2020 Feb 26:arXiv:2002.11379v2. Revised March 11, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/2002.11379
54. Salim M, Wåhlin E, Dembrower K, et al. External evaluation of 3 commercial artificial intelligence algorithms for independent assessment of screening mammograms. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(10):1581-1588. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3321
55. Arbabshirani MR, Fornwalt BK, Mongelluzzo GJ, et al. Advanced machine learning in action: identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. NPJ Digit Med. 2018;1:9. doi:10.1038/s41746-017-0015-z
56. Sheth D, Giger ML. Artificial intelligence in the interpretation of breast cancer on MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;51(5):1310-1324. doi:10.1002/jmri.26878
57. McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020;577(7788):89-94. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
58. Booth AL, Abels E, McCaffrey P. Development of a prognostic model for mortality in COVID-19 infection using machine learning. Mod Pathol. 2021;34(3):522-531. doi:10.1038/s41379-020-00700-x
59. Xu B, Kocyigit D, Grimm R, Griffin BP, Cheng F. Applications of artificial intelligence in multimodality cardiovascular imaging: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):367-376. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.003
60. Dey D, Slomka PJ, Leeson P, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(11):1317-1335. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.12.054
61. Carewell Health. AI powered ECG diagnosis solutions. Accessed November 2, 2020. https://www.carewellhealth.com/products_aiecg.html
62. Strodthoff N, Strodthoff C. Detecting and interpreting myocardial infarction using fully convolutional neural networks. Physiol Meas. 2019;40(1):015001. doi:10.1088/1361-6579/aaf34d
63. Hannun AY, Rajpurkar P, Haghpanahi M, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):65-69. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
64. Kwon JM, Jeon KH, Kim HM, et al. Comparing the performance of artificial intelligence and conventional diagnosis criteria for detecting left ventricular hypertrophy using electrocardiography. Europace. 2020;22(3):412-419. doi:10.1093/europace/euz324

65. Eko. FDA clears Eko’s AFib and heart murmur detection algorithms, making it the first AI-powered stethoscope to screen for serious heart conditions [press release]. Published January 28, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200128005232/en/FDA-Clears-Eko’s-AFib-and-Heart-Murmur-Detection-Algorithms-Making-It-the-First-AI-Powered-Stethoscope-to-Screen-for-Serious-Heart-Conditions
66. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. Accurate and reproducible invasive breast cancer detection in whole-slide images: a deep learning approach for quantifying tumor extent. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46450. doi:10.1038/srep46450
67. Acs B, Rantalainen M, Hartman J. Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology. J Intern Med. 2020;288(1):62-81. doi:10.1111/joim.13030
68. Mobadersany P, Yousefi S, Amgad M, et al. Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(13):E2970-E2979. doi:10.1073/pnas.1717139115
69. Wang X, Janowczyk A, Zhou Y, et al. Prediction of recurrence in early stage non-small cell lung cancer using computer extracted nuclear features from digital H&E images. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13543. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13773-7
70. Kulkarni PM, Robinson EJ, Pradhan JS, et al. Deep learning based on standard H&E images of primary melanoma tumors identifies patients at risk for visceral recurrence and death. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(5):1126-1134. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1495
71. Du XL, Li WB, Hu BJ. Application of artificial intelligence in ophthalmology. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018;11(9):1555-1561. doi:10.18240/ijo.2018.09.21
72. Gunasekeran DV, Wong TY. Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology in 2020: a technology on the cusp for translation and implementation. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2020;9(2):61-66. doi:10.1097/01.APO.0000656984.56467.2c
73. Ting DSW, Pasquale LR, Peng L, et al. Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103(2):167-175. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313173
74. Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016;316(22):2402-2410. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17216
75. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA permits marketing of artificial intelligence-based device to detect certain diabetes-related eye problems [press release]. Published April 11, 2018. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-permits-marketing-artificial-intelligence-based-device-detect-certain-diabetes-related-eye
76. Long E, Chen J, Wu X, et al. Artificial intelligence manages congenital cataract with individualized prediction and telehealth computing. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:112. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00319-x
77. De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(9):1342-1350. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0107-6
78. Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017;542(7639):115-118. doi:10.1038/nature21056
79. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. Deep neural networks are superior to dermatologists in melanoma image classification. Eur J Cancer. 2019;119:11-17. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.05.023
80. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images performed on par with 145 dermatologists in a clinical melanoma image classification task. Eur J Cancer. 2019;111:148-154. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.02.005
81. Haenssle HA, Fink C, Schneiderbauer R, et al. Man against machine: diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(8):1836-1842. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy166
82. Li CX, Shen CB, Xue K, et al. Artificial intelligence in dermatology: past, present, and future. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(17):2017-2020. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000372
83. Tschandl P, Codella N, Akay BN, et al. Comparison of the accuracy of human readers versus machine-learning algorithms for pigmented skin lesion classification: an open, web-based, international, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(7):938-947. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30333-X
84. Han SS, Park I, Eun Chang SE, et al. Augmented intelligence dermatology: deep neural networks empower medical professionals in diagnosing skin cancer and predicting treatment options for 134 skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(9):1753-1761. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.01.019
85. Freeman K, Dinnes J, Chuchu N, et al. Algorithm based smartphone apps to assess risk of skin cancer in adults: systematic review of diagnostic accuracy studies [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Feb 25;368:m645]. BMJ. 2020;368:m127. Published 2020 Feb 10. doi:10.1136/bmj.m127
86. Chen YC, Ke WC, Chiu HW. Risk classification of cancer survival using ANN with gene expression data from multiple laboratories. Comput Biol Med. 2014;48:1-7. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.02.006
87. Kim W, Kim KS, Lee JE, et al. Development of novel breast cancer recurrence prediction model using support vector machine. J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(2):230-238. doi:10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.230
88. Merath K, Hyer JM, Mehta R, et al. Use of machine learning for prediction of patient risk of postoperative complications after liver, pancreatic, and colorectal surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020;24(8):1843-1851. doi:10.1007/s11605-019-04338-2
89. Santos-García G, Varela G, Novoa N, Jiménez MF. Prediction of postoperative morbidity after lung resection using an artificial neural network ensemble. Artif Intell Med. 2004;30(1):61-69. doi:10.1016/S0933-3657(03)00059-9
90. Ibragimov B, Xing L. Segmentation of organs-at-risks in head and neck CT images using convolutional neural networks. Med Phys. 2017;44(2):547-557. doi:10.1002/mp.12045
91. Lou B, Doken S, Zhuang T, et al. An image-based deep learning framework for individualizing radiotherapy dose. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(3):e136-e147. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30058-5
92. Xu J, Yang P, Xue S, et al. Translating cancer genomics into precision medicine with artificial intelligence: applications, challenges and future perspectives. Hum Genet. 2019;138(2):109-124. doi:10.1007/s00439-019-01970-5
93. Patel NM, Michelini VV, Snell JM, et al. Enhancing next‐generation sequencing‐guided cancer care through cognitive computing. Oncologist. 2018;23(2):179-185. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0170
94. Le Berre C, Sandborn WJ, Aridhi S, et al. Application of artificial intelligence to gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1):76-94.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.058
95. Yang YJ, Bang CS. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(14):1666-1683. doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1666
96. Wang P, Berzin TM, Glissen Brown JR, et al. Real-time automatic detection system increases colonoscopic polyp and adenoma detection rates: a prospective randomised controlled study. Gut. 2019;68(10):1813-1819. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317500

97. Gupta R, Krishnam SP, Schaefer PW, Lev MH, Gonzalez RG. An East Coast perspective on artificial intelligence and machine learning: part 2: ischemic stroke imaging and triage. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2020;30(4):467-478. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2020.08.002
98. Beli M, Bobi V, Badža M, Šolaja N, Duri-Jovii M, Kosti VS. Artificial intelligence for assisting diagnostics and assessment of Parkinson’s disease—a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;184:105442. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105442
99. An S, Kang C, Lee HW. Artificial intelligence and computational approaches for epilepsy. J Epilepsy Res. 2020;10(1):8-17. doi:10.14581/jer.20003
100. Pavel AM, Rennie JM, de Vries LS, et al. A machine-learning algorithm for neonatal seizure recognition: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4(10):740-749. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30239-X
101. Afzal HMR, Luo S, Ramadan S, Lechner-Scott J. The emerging role of artificial intelligence in multiple sclerosis imaging [published online ahead of print, 2020 Oct 28]. Mult Scler. 2020;1352458520966298. doi:10.1177/1352458520966298
102. Bouton CE. Restoring movement in paralysis with a bioelectronic neural bypass approach: current state and future directions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019;9(11):a034306. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a034306
103. Durstewitz D, Koppe G, Meyer-Lindenberg A. Deep neural networks in psychiatry. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(11):1583-1598. doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0365-9
104. Fonseka TM, Bhat V, Kennedy SH. The utility of artificial intelligence in suicide risk prediction and the management of suicidal behaviors. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53(10):954-964. doi:10.1177/0004867419864428
105. Kessler RC, Hwang I, Hoffmire CA, et al. Developing a practical suicide risk prediction model for targeting high-risk patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2017;26(3):e1575. doi:10.1002/mpr.1575
106. Kessler RC, Bauer MS, Bishop TM, et al. Using administrative data to predict suicide after psychiatric hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration System. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:390. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00390
107. Kessler RC, van Loo HM, Wardenaar KJ, et al. Testing a machine-learning algorithm to predict the persistence and severity of major depressive disorder from baseline self-reports. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(10):1366-1371. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.198
108. Horng S, Sontag DA, Halpern Y, Jernite Y, Shapiro NI, Nathanson LA. Creating an automated trigger for sepsis clinical decision support at emergency department triage using machine learning. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174708. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174708
109. Soffer S, Klang E, Barash Y, Grossman E, Zimlichman E. Predicting in-hospital mortality at admission to the medical ward: a big-data machine learning model. Am J Med. 2021;134(2):227-234.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.07.014
110. Labovitz DL, Shafner L, Reyes Gil M, Virmani D, Hanina A. Using artificial intelligence to reduce the risk of nonadherence in patients on anticoagulation therapy. Stroke. 2017;48(5):1416-1419. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.016281
111. Forlenza GP. Use of artificial intelligence to improve diabetes outcomes in patients using multiple daily injections therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(S2):S24-S28. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0077
112. Poser CM. CT scan and the practice of neurology. Arch Neurol. 1977;34(2):132. doi:10.1001/archneur.1977.00500140086023
113. Angus DC. Randomized clinical trials of artificial intelligence. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1043-1045. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1039
114. Topol EJ. Welcoming new guidelines for AI clinical research. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1318-1320. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1042-x
115. Collins GS, Moons KGM. Reporting of artificial intelligence prediction models. Lancet. 2019;393(10181):1577-1579. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30037-6
116. Cruz Rivera S, Liu X, Chan AW, et al. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1351-1363. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1037-7
117. Liu X, Cruz Rivera S, Moher D, Calvert MJ, Denniston AK; SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI Working Group. Reporting guidelines for clinical trial reports for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the CONSORT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1364-1374. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1034-x
118. McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys. 1943;5(4):115-133. doi:10.1007/BF02478259
119. Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of Checkers. IBM J Res Dev. 1959;3(3):535-554. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.368.2254
120. Sonoda M, Takano M, Miyahara J, Kato H. Computed radiography utilizing scanning laser stimulated luminescence. Radiology. 1983;148(3):833-838. doi:10.1148/radiology.148.3.6878707
121. Dechter R. Learning while searching in constraint-satisfaction-problems. AAAI’86: proceedings of the fifth AAAI national conference on artificial intelligence. Published 1986. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.aaai.org/Papers/AAAI/1986/AAAI86-029.pdf
122. Le Cun Y, Jackel LD, Boser B, et al. Handwritten digit recognition: applications of neural network chips and automatic learning. IEEE Commun Mag. 1989;27(11):41-46. doi:10.1109/35.41400
123. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first whole slide imaging system for digital pathology [press release]. Published April 12, 2017. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-allows-marketing-first-whole-slide-imaging-system-digital-pathology
1. Bini SA. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, and cognitive computing: what do these terms mean and how will they impact health care? J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8):2358-2361. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.067
2. Benjamens S, Dhunnoo P, Meskó B. The state of artificial intelligence-based FDA-approved medical devices and algorithms: an online database. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:118. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00324-0
3. Viz. AI powered synchronized stroke care. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.viz.ai/ischemic-stroke
4. Buchanan M. The law of accelerating returns. Nat Phys. 2008;4(7):507. doi:10.1038/nphys1010
5. IBM Watson Health computes a pair of new solutions to improve healthcare data and security. Published September 10, 2015. Accessed October 21, 2020. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/ibm-watson-health-computes-a-pair-of-new-solutions-to-improve-healthcare-data-and-security
6. Borkowski AA, Kardani A, Mastorides SM, Thomas LB. Warfarin pharmacogenomics: recommendations with available patented clinical technologies. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2014;8(2):110-115. doi:10.2174/1872208309666140904112003
7. Washington University in St. Louis. Warfarin dosing. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://www.warfarindosing.org/Source/Home.aspx
8. He J, Baxter SL, Xu J, Xu J, Zhou X, Zhang K. The practical implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in medicine. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):30-36. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0307-0
9. Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, et al. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2017;2(4):230-243. Published 2017 Jun 21. doi:10.1136/svn-2017-000101
10. Johnson KW, Torres Soto J, Glicksberg BS, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(23):2668-2679. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.521
11. Borkowski AA, Wilson CP, Borkowski SA, et al. Comparing artificial intelligence platforms for histopathologic cancer diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2019;36(10):456-463.
12. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. High-throughput adaptive sampling for whole-slide histopathology image analysis (HASHI) via convolutional neural networks: application to invasive breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0196828. Published 2018 May 24. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0196828
13. Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, et al. Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning studies. BMJ. 2020;368:m689. Published 2020 Mar 25. doi:10.1136/bmj.m689
14. Shimizu H, Nakayama KI. Artificial intelligence in oncology. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(5):1452-1460. doi:10.1111/cas.14377
15. Talebi-Liasi F, Markowitz O. Is artificial intelligence going to replace dermatologists?. Cutis. 2020;105(1):28-31.
16. Valliani AA, Ranti D, Oermann EK. Deep learning and neurology: a systematic review. Neurol Ther. 2019;8(2):351-365. doi:10.1007/s40120-019-00153-8
17. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436-444. doi:10.1038/nature14539
18. Graham S, Depp C, Lee EE, et al. Artificial intelligence for mental health and mental illnesses: an overview. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(11):116. Published 2019 Nov 7. doi:10.1007/s11920-019-1094-0
19. Golas SB, Shibahara T, Agboola S, et al. A machine learning model to predict the risk of 30-day readmissions in patients with heart failure: a retrospective analysis of electronic medical records data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2018;18(1):44. Published 2018 Jun 22. doi:10.1186/s12911-018-0620-z
20. Mortazavi BJ, Downing NS, Bucholz EM, et al. Analysis of machine learning techniques for heart failure readmissions. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2016;9(6):629-640. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.116.003039
21. Meyer-Bäse A, Morra L, Meyer-Bäse U, Pinker K. Current status and future perspectives of artificial intelligence in magnetic resonance breast imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2020;2020:6805710. Published 2020 Aug 28. doi:10.1155/2020/6805710
22. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van Diest P, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. 2017;318(22):2199-2210. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.14585
23. Borkowski AA, Viswanadhan NA, Thomas LB, Guzman RD, Deland LA, Mastorides SM. Using artificial intelligence for COVID-19 chest X-ray diagnosis. Fed Pract. 2020;37(9):398-404. doi:10.12788/fp.0045
24. Coudray N, Ocampo PS, Sakellaropoulos T, et al. Classification and mutation prediction from non-small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Med. 2018;24(10):1559-1567. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0177-5
25. Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, et al. Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell. 2018;172(5):1122-1131.e9. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010
26. Liu X, Faes L, Kale AU, et al. A comparison of deep learning performance against health-care professionals in detecting diseases from medical imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(6):e271-e297. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30123-2
27. Nagpal K, Foote D, Liu Y, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer [published correction appears in NPJ Digit Med. 2019 Nov 19;2:113]. NPJ Digit Med. 2019;2:48. Published 2019 Jun 7. doi:10.1038/s41746-019-0112-2
28. Nam JG, Park S, Hwang EJ, et al. Development and validation of deep learning-based automatic detection algorithm for malignant pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs. Radiology. 2019;290(1):218-228. doi:10.1148/radiol.2018180237
29. Schwalbe N, Wahl B. Artificial intelligence and the future of global health. Lancet. 2020;395(10236):1579-1586. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30226-9
30. Bai HX, Wang R, Xiong Z, et al. Artificial intelligence augmentation of radiologist performance in distinguishing COVID-19 from pneumonia of other origin at chest CT [published correction appears in Radiology. 2021 Apr;299(1):E225]. Radiology. 2020;296(3):E156-E165. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020201491
31. Li L, Qin L, Xu Z, et al. Using artificial intelligence to detect COVID-19 and community-acquired pneumonia based on pulmonary CT: evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy. Radiology. 2020;296(2):E65-E71. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200905
32. Serag A, Ion-Margineanu A, Qureshi H, et al. Translational AI and deep learning in diagnostic pathology. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019;6:185. Published 2019 Oct 1. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00185

33. Wang D, Khosla A, Gargeya R, Irshad H, Beck AH. Deep learning for identifying metastatic breast cancer. ArXiv. 2016 June 18:arXiv:1606.05718v1. Published online June 18, 2016. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.05718
34. Alabdulkareem A. Artificial intelligence and dermatologists: friends or foes? J Dermatology Dermatol Surg. 2019;23(2):57-60. doi:10.4103/jdds.jdds_19_19
35. Mollalo A, Mao L, Rashidi P, Glass GE. A GIS-based artificial neural network model for spatial distribution of tuberculosis across the continental United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(1):157. Published 2019 Jan 8. doi:10.3390/ijerph16010157
36. Haddawy P, Hasan AHMI, Kasantikul R, et al. Spatiotemporal Bayesian networks for malaria prediction. Artif Intell Med. 2018;84:127-138. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2017.12.002
37. Laureano-Rosario AE, Duncan AP, Mendez-Lazaro PA, et al. Application of artificial neural networks for dengue fever outbreak predictions in the northwest coast of Yucatan, Mexico and San Juan, Puerto Rico. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2018;3(1):5. Published 2018 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3010005
38. Buczak AL, Koshute PT, Babin SM, Feighner BH, Lewis SH. A data-driven epidemiological prediction method for dengue outbreaks using local and remote sensing data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012;12:124. Published 2012 Nov 5. doi:10.1186/1472-6947-12-124
39. Scavuzzo JM, Trucco F, Espinosa M, et al. Modeling dengue vector population using remotely sensed data and machine learning. Acta Trop. 2018;185:167-175. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.05.003
40. Xue H, Bai Y, Hu H, Liang H. Influenza activity surveillance based on multiple regression model and artificial neural network. IEEE Access. 2018;6:563-575. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2771798
41. Jiang D, Hao M, Ding F, Fu J, Li M. Mapping the transmission risk of Zika virus using machine learning models. Acta Trop. 2018;185:391-399. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.06.021
42. Bragazzi NL, Dai H, Damiani G, Behzadifar M, Martini M, Wu J. How big data and artificial intelligence can help better manage the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):3176. Published 2020 May 2. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093176
43. Lake IR, Colón-González FJ, Barker GC, Morbey RA, Smith GE, Elliot AJ. Machine learning to refine decision making within a syndromic surveillance service. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):559. Published 2019 May 14. doi:10.1186/s12889-019-6916-9
44. Khan OF, Bebb G, Alimohamed NA. Artificial intelligence in medicine: what oncologists need to know about its potential-and its limitations. Oncol Exch. 2017;16(4):8-13. Accessed September 1, 2021. http://www.oncologyex.com/pdf/vol16_no4/feature_khan-ai.pdf
45. Badano LP, Keller DM, Muraru D, Torlasco C, Parati G. Artificial intelligence and cardiovascular imaging: A win-win combination. Anatol J Cardiol. 2020;24(4):214-223. doi:10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2020.94491
46. Murdoch TB, Detsky AS. The inevitable application of big data to health care. JAMA. 2013;309(13):1351-1352. doi:10.1001/jama.2013.393
47. Greatbatch O, Garrett A, Snape K. The impact of artificial intelligence on the current and future practice of clinical cancer genomics. Genet Res (Camb). 2019;101:e9. Published 2019 Oct 31. doi:10.1017/S0016672319000089
48. Topol EJ. High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):44-56. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0300-7
49. Vollmer S, Mateen BA, Bohner G, et al. Machine learning and artificial intelligence research for patient benefit: 20 critical questions on transparency, replicability, ethics, and effectiveness [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Apr 1;369:m1312]. BMJ. 2020;368:l6927. Published 2020 Mar 20. doi:10.1136/bmj.l6927
50. Lindsey R, Daluiski A, Chopra S, et al. Deep neural network improves fracture detection by clinicians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(45):11591-11596. doi:10.1073/pnas.1806905115
51. Zech JR, Badgeley MA, Liu M, Costa AB, Titano JJ, Oermann EK. Variable generalization performance of a deep learning model to detect pneumonia in chest radiographs: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2018;15(11):e1002683. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002683
52. Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. 2017;284(2):574-582. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017162326
53. Rajpurkar P, Joshi A, Pareek A, et al. CheXpedition: investigating generalization challenges for translation of chest x-ray algorithms to the clinical setting. ArXiv. 2020 Feb 26:arXiv:2002.11379v2. Revised March 11, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. http://arxiv.org/abs/2002.11379
54. Salim M, Wåhlin E, Dembrower K, et al. External evaluation of 3 commercial artificial intelligence algorithms for independent assessment of screening mammograms. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(10):1581-1588. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.3321
55. Arbabshirani MR, Fornwalt BK, Mongelluzzo GJ, et al. Advanced machine learning in action: identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. NPJ Digit Med. 2018;1:9. doi:10.1038/s41746-017-0015-z
56. Sheth D, Giger ML. Artificial intelligence in the interpretation of breast cancer on MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;51(5):1310-1324. doi:10.1002/jmri.26878
57. McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020;577(7788):89-94. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
58. Booth AL, Abels E, McCaffrey P. Development of a prognostic model for mortality in COVID-19 infection using machine learning. Mod Pathol. 2021;34(3):522-531. doi:10.1038/s41379-020-00700-x
59. Xu B, Kocyigit D, Grimm R, Griffin BP, Cheng F. Applications of artificial intelligence in multimodality cardiovascular imaging: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63(3):367-376. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2020.03.003
60. Dey D, Slomka PJ, Leeson P, et al. Artificial intelligence in cardiovascular imaging: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(11):1317-1335. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.12.054
61. Carewell Health. AI powered ECG diagnosis solutions. Accessed November 2, 2020. https://www.carewellhealth.com/products_aiecg.html
62. Strodthoff N, Strodthoff C. Detecting and interpreting myocardial infarction using fully convolutional neural networks. Physiol Meas. 2019;40(1):015001. doi:10.1088/1361-6579/aaf34d
63. Hannun AY, Rajpurkar P, Haghpanahi M, et al. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat Med. 2019;25(1):65-69. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0268-3
64. Kwon JM, Jeon KH, Kim HM, et al. Comparing the performance of artificial intelligence and conventional diagnosis criteria for detecting left ventricular hypertrophy using electrocardiography. Europace. 2020;22(3):412-419. doi:10.1093/europace/euz324

65. Eko. FDA clears Eko’s AFib and heart murmur detection algorithms, making it the first AI-powered stethoscope to screen for serious heart conditions [press release]. Published January 28, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200128005232/en/FDA-Clears-Eko’s-AFib-and-Heart-Murmur-Detection-Algorithms-Making-It-the-First-AI-Powered-Stethoscope-to-Screen-for-Serious-Heart-Conditions
66. Cruz-Roa A, Gilmore H, Basavanhally A, et al. Accurate and reproducible invasive breast cancer detection in whole-slide images: a deep learning approach for quantifying tumor extent. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46450. doi:10.1038/srep46450
67. Acs B, Rantalainen M, Hartman J. Artificial intelligence as the next step towards precision pathology. J Intern Med. 2020;288(1):62-81. doi:10.1111/joim.13030
68. Mobadersany P, Yousefi S, Amgad M, et al. Predicting cancer outcomes from histology and genomics using convolutional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(13):E2970-E2979. doi:10.1073/pnas.1717139115
69. Wang X, Janowczyk A, Zhou Y, et al. Prediction of recurrence in early stage non-small cell lung cancer using computer extracted nuclear features from digital H&E images. Sci Rep. 2017;7:13543. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13773-7
70. Kulkarni PM, Robinson EJ, Pradhan JS, et al. Deep learning based on standard H&E images of primary melanoma tumors identifies patients at risk for visceral recurrence and death. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(5):1126-1134. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1495
71. Du XL, Li WB, Hu BJ. Application of artificial intelligence in ophthalmology. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018;11(9):1555-1561. doi:10.18240/ijo.2018.09.21
72. Gunasekeran DV, Wong TY. Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology in 2020: a technology on the cusp for translation and implementation. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2020;9(2):61-66. doi:10.1097/01.APO.0000656984.56467.2c
73. Ting DSW, Pasquale LR, Peng L, et al. Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103(2):167-175. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313173
74. Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016;316(22):2402-2410. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.17216
75. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA permits marketing of artificial intelligence-based device to detect certain diabetes-related eye problems [press release]. Published April 11, 2018. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-permits-marketing-artificial-intelligence-based-device-detect-certain-diabetes-related-eye
76. Long E, Chen J, Wu X, et al. Artificial intelligence manages congenital cataract with individualized prediction and telehealth computing. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:112. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00319-x
77. De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(9):1342-1350. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0107-6
78. Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017;542(7639):115-118. doi:10.1038/nature21056
79. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. Deep neural networks are superior to dermatologists in melanoma image classification. Eur J Cancer. 2019;119:11-17. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.05.023
80. Brinker TJ, Hekler A, Enk AH, et al. A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images performed on par with 145 dermatologists in a clinical melanoma image classification task. Eur J Cancer. 2019;111:148-154. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.02.005
81. Haenssle HA, Fink C, Schneiderbauer R, et al. Man against machine: diagnostic performance of a deep learning convolutional neural network for dermoscopic melanoma recognition in comparison to 58 dermatologists. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(8):1836-1842. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy166
82. Li CX, Shen CB, Xue K, et al. Artificial intelligence in dermatology: past, present, and future. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(17):2017-2020. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000372
83. Tschandl P, Codella N, Akay BN, et al. Comparison of the accuracy of human readers versus machine-learning algorithms for pigmented skin lesion classification: an open, web-based, international, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(7):938-947. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30333-X
84. Han SS, Park I, Eun Chang SE, et al. Augmented intelligence dermatology: deep neural networks empower medical professionals in diagnosing skin cancer and predicting treatment options for 134 skin disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(9):1753-1761. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.01.019
85. Freeman K, Dinnes J, Chuchu N, et al. Algorithm based smartphone apps to assess risk of skin cancer in adults: systematic review of diagnostic accuracy studies [published correction appears in BMJ. 2020 Feb 25;368:m645]. BMJ. 2020;368:m127. Published 2020 Feb 10. doi:10.1136/bmj.m127
86. Chen YC, Ke WC, Chiu HW. Risk classification of cancer survival using ANN with gene expression data from multiple laboratories. Comput Biol Med. 2014;48:1-7. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2014.02.006
87. Kim W, Kim KS, Lee JE, et al. Development of novel breast cancer recurrence prediction model using support vector machine. J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(2):230-238. doi:10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.230
88. Merath K, Hyer JM, Mehta R, et al. Use of machine learning for prediction of patient risk of postoperative complications after liver, pancreatic, and colorectal surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020;24(8):1843-1851. doi:10.1007/s11605-019-04338-2
89. Santos-García G, Varela G, Novoa N, Jiménez MF. Prediction of postoperative morbidity after lung resection using an artificial neural network ensemble. Artif Intell Med. 2004;30(1):61-69. doi:10.1016/S0933-3657(03)00059-9
90. Ibragimov B, Xing L. Segmentation of organs-at-risks in head and neck CT images using convolutional neural networks. Med Phys. 2017;44(2):547-557. doi:10.1002/mp.12045
91. Lou B, Doken S, Zhuang T, et al. An image-based deep learning framework for individualizing radiotherapy dose. Lancet Digit Health. 2019;1(3):e136-e147. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30058-5
92. Xu J, Yang P, Xue S, et al. Translating cancer genomics into precision medicine with artificial intelligence: applications, challenges and future perspectives. Hum Genet. 2019;138(2):109-124. doi:10.1007/s00439-019-01970-5
93. Patel NM, Michelini VV, Snell JM, et al. Enhancing next‐generation sequencing‐guided cancer care through cognitive computing. Oncologist. 2018;23(2):179-185. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0170
94. Le Berre C, Sandborn WJ, Aridhi S, et al. Application of artificial intelligence to gastroenterology and hepatology. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(1):76-94.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.08.058
95. Yang YJ, Bang CS. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(14):1666-1683. doi:10.3748/wjg.v25.i14.1666
96. Wang P, Berzin TM, Glissen Brown JR, et al. Real-time automatic detection system increases colonoscopic polyp and adenoma detection rates: a prospective randomised controlled study. Gut. 2019;68(10):1813-1819. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317500

97. Gupta R, Krishnam SP, Schaefer PW, Lev MH, Gonzalez RG. An East Coast perspective on artificial intelligence and machine learning: part 2: ischemic stroke imaging and triage. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2020;30(4):467-478. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2020.08.002
98. Beli M, Bobi V, Badža M, Šolaja N, Duri-Jovii M, Kosti VS. Artificial intelligence for assisting diagnostics and assessment of Parkinson’s disease—a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;184:105442. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105442
99. An S, Kang C, Lee HW. Artificial intelligence and computational approaches for epilepsy. J Epilepsy Res. 2020;10(1):8-17. doi:10.14581/jer.20003
100. Pavel AM, Rennie JM, de Vries LS, et al. A machine-learning algorithm for neonatal seizure recognition: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4(10):740-749. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30239-X
101. Afzal HMR, Luo S, Ramadan S, Lechner-Scott J. The emerging role of artificial intelligence in multiple sclerosis imaging [published online ahead of print, 2020 Oct 28]. Mult Scler. 2020;1352458520966298. doi:10.1177/1352458520966298
102. Bouton CE. Restoring movement in paralysis with a bioelectronic neural bypass approach: current state and future directions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019;9(11):a034306. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a034306
103. Durstewitz D, Koppe G, Meyer-Lindenberg A. Deep neural networks in psychiatry. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24(11):1583-1598. doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0365-9
104. Fonseka TM, Bhat V, Kennedy SH. The utility of artificial intelligence in suicide risk prediction and the management of suicidal behaviors. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2019;53(10):954-964. doi:10.1177/0004867419864428
105. Kessler RC, Hwang I, Hoffmire CA, et al. Developing a practical suicide risk prediction model for targeting high-risk patients in the Veterans Health Administration. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2017;26(3):e1575. doi:10.1002/mpr.1575
106. Kessler RC, Bauer MS, Bishop TM, et al. Using administrative data to predict suicide after psychiatric hospitalization in the Veterans Health Administration System. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:390. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00390
107. Kessler RC, van Loo HM, Wardenaar KJ, et al. Testing a machine-learning algorithm to predict the persistence and severity of major depressive disorder from baseline self-reports. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(10):1366-1371. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.198
108. Horng S, Sontag DA, Halpern Y, Jernite Y, Shapiro NI, Nathanson LA. Creating an automated trigger for sepsis clinical decision support at emergency department triage using machine learning. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0174708. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174708
109. Soffer S, Klang E, Barash Y, Grossman E, Zimlichman E. Predicting in-hospital mortality at admission to the medical ward: a big-data machine learning model. Am J Med. 2021;134(2):227-234.e4. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.07.014
110. Labovitz DL, Shafner L, Reyes Gil M, Virmani D, Hanina A. Using artificial intelligence to reduce the risk of nonadherence in patients on anticoagulation therapy. Stroke. 2017;48(5):1416-1419. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.016281
111. Forlenza GP. Use of artificial intelligence to improve diabetes outcomes in patients using multiple daily injections therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(S2):S24-S28. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0077
112. Poser CM. CT scan and the practice of neurology. Arch Neurol. 1977;34(2):132. doi:10.1001/archneur.1977.00500140086023
113. Angus DC. Randomized clinical trials of artificial intelligence. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1043-1045. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1039
114. Topol EJ. Welcoming new guidelines for AI clinical research. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1318-1320. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1042-x
115. Collins GS, Moons KGM. Reporting of artificial intelligence prediction models. Lancet. 2019;393(10181):1577-1579. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30037-6
116. Cruz Rivera S, Liu X, Chan AW, et al. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1351-1363. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1037-7
117. Liu X, Cruz Rivera S, Moher D, Calvert MJ, Denniston AK; SPIRIT-AI and CONSORT-AI Working Group. Reporting guidelines for clinical trial reports for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the CONSORT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1364-1374. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1034-x
118. McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys. 1943;5(4):115-133. doi:10.1007/BF02478259
119. Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of Checkers. IBM J Res Dev. 1959;3(3):535-554. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.368.2254
120. Sonoda M, Takano M, Miyahara J, Kato H. Computed radiography utilizing scanning laser stimulated luminescence. Radiology. 1983;148(3):833-838. doi:10.1148/radiology.148.3.6878707
121. Dechter R. Learning while searching in constraint-satisfaction-problems. AAAI’86: proceedings of the fifth AAAI national conference on artificial intelligence. Published 1986. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.aaai.org/Papers/AAAI/1986/AAAI86-029.pdf
122. Le Cun Y, Jackel LD, Boser B, et al. Handwritten digit recognition: applications of neural network chips and automatic learning. IEEE Commun Mag. 1989;27(11):41-46. doi:10.1109/35.41400
123. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA allows marketing of first whole slide imaging system for digital pathology [press release]. Published April 12, 2017. Accessed September 15, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-allows-marketing-first-whole-slide-imaging-system-digital-pathology
The Meaning of Words and Why They Matter During End-of-Life Conversations
Effective communication during end-of-life is crucial for health care delivery, but misinterpretation can influence how the quality of the care is rendered and perceived.
When I was a new palliative care nurse practitioner (NP), I remember my mentor telling me that communication in our field is equivalent to surgical procedures in general surgery. Conversations need to be handled with accuracy and precision, conducted in a timely fashion, and require skills that take practice to sharpen. Over the years, I learned that unlike surgery, we do not have control over how the procedure will flow. We approach patients with a blank canvas, open to receive messages that will be shared and reacted to accordingly. The ability to communicate effectively also requires compassion, which is a trait that tends to be inherent in humans and typically is not learned from textbooks but can be cultivated with training and application.
Among the barriers identified to effective communication are avoiding emotional issues and focusing on technical topics due in part to the fear of lengthy encounters, not allowing patients or families enough time to speak, and reframing instead of validating emotions.1 Many years later, I had the chance to help care for a patient whose story reminds me of how our choice of words and how our interpretation of what we are told can influence the way we care for patients and their families.
Case Presentation
Mr. P, aged 86 years, was admitted to a teaching hospital for pneumonia and heart failure exacerbation. He was treated with diuretics and antibiotics and discharged home on room air after 3 days. He returned to the hospital after 8 days, reporting labored breathing. He was found to be hypoxic, and a further workup revealed acute hypoxic respiratory failure that was likely from severe pulmonary hypertension and exacerbation of his heart failure. Left heart disease is a common cause of pulmonary hypertension, which can lead to right ventricular failure and increased mortality.2
After meeting with his pulmonologist and cardiologist, Mr. P elected for a do-not-resuscitate code status and declined to be intubated. He also refused further diagnostics and life-prolonging treatments for his conditions, including a stress test, cardiac catheterization, and a right heart catheterization. He required bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) support at bedtime, which he also declined. He agreed to the use of supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula and always needed 5 liters of oxygen.
Palliative care was consulted to assist with goals of care discussion. This visit took place during the COVID-19 pandemic, but Mr. P had tested negative for the COVID virus, so the palliative care NP was able to meet with Mr. P in person. He shared his understanding of the serious nature of his condition and the likelihood of a limited life expectancy without further diagnostics and possible life-prolonging treatments. He said his goal was to go home and spend the remainder of his life with his wife. He had not been out of bed since his hospitalization except to transfer to a nearby chair with the help of his nurse due to exertional dyspnea and generalized weakness. Prior to his recent hospitalizations, he was independently ambulating and had no dyspnea when performing strenuous activities. Mr. P shared that his wife was aged in her 70s and was legally blind. He added that she did not require physical assistance, but he was unsure whether she could help him because they had not been in such a situation previously. They had a daughter who visited frequently and helped with driving them to doctors’ appointments and shopping. Mr. P shared that he wanted to go home. After explaining the option of home hospice, Mr. P decided he wanted to receive hospice services at home and asked palliative care NP to contact his daughter to let her know his wishes and to tell her more about how hospice can help with his care.
The palliative care NP met with Mr. P’s nurse and shared the outcome of her visit. His nurse asked the palliative care NP whether she was familiar with his daughter. The nurse added that she wanted the palliative care NP to know that Mr. P’s daughter was quite angry and upset with his doctors after being told about his prognosis. His doctors’ notes also indicated that Mr. P wanted them to contact his daughter regarding his condition and plans for discharge, concluding that he deferred to his daughter for medical decision making.
As Mr. P’s hospitalization took place during the COVID pandemic, a face-to-face meeting with his family was not possible. The NP spoke with Mr. P’s daughter over the phone to relay his wishes and goals for his care. Mr. P’s daughter cried at times during the conversation and asked whether his condition was really that serious. The NP allowed Mr. P’s daughter to express her sadness and allowed for periods of silence during the conversation while his daughter gathered her composure. The NP reinforced the clinical information she had been provided by the medical team. Mr. P’s daughter added that he was completely independent, not requiring supplemental oxygen and was otherwise healthy just a month prior. She also asked whether there was truly nothing else that could be done to prolong his life. The NP acknowledged her observations and explained how Mr. P’s body and organs had not been able to bounce back from the recent insults to his overall physical condition.
After being told that Mr. P’s options for treatment were limited not only by his advanced age and comorbidities, but also the limitations and goals for his care he had identified, his daughter supported her father’s decision. The palliative care NP provided her information on how home hospice assists in her father’s care at home, including symptom management, nursing visits, home equipment, family support, among others. Mr. P’s daughter also said she would relay the information to her mother and call the palliative care NP if they had additional questions or concerns.
The outcome of her visit with Mr. P and his daughter were relayed by the palliative care NP to his acute health care team through an official response to the consultation request via his electronic health record. The palliative care NP also alerted the palliative care social worker to follow-up with Mr. P, his daughter, and his acute health care team to coordinate hospice services at the time of his discharge from the hospital.
Mr. P was discharged from the hospital with home hospice services after a few days. Three weeks later, Mr. P passed away peacefully on the in-patient unit of his home hospice agency as his physical care needs became too much for his family to provide at home a few days before his death. The palliative care social worker later shared with the NP that Mr. P’s daughter shared her gratitude and satisfaction with the care he had received not only from palliative care, but also from everyone during his hospitalization.
Discussion
Key themes found in end-of-life (EOL) communication with families and caregivers include highlighting clinical deterioration, involvement in decision making, continuation of high-quality care after cessation of aggressive measures, tailoring to individuals, clarity, honesty, and use of techniques in delivery.2 Some of the techniques identified were pacing, staging, and repetition.3 Other techniques that can be beneficial include allowing for time to express one’s feelings, being comfortable with brief periods of silence, validating observations shared, among others. These themes were evident in the interactions that his health care team had with Mr. P and his daughter. With honesty and clarity, various members of the health care team repeatedly shared information regarding his clinical deterioration.
Family Influence
EOL decision-making roles within a family tend to originate from family interactional histories, familial roles as well as decision-making situations the family faces.4 The US medical and legal systems also recognize formal role assignments for surrogate decision makers.4 In the case of Mr. P, his advance directive (AD) identified his daughter as his surrogate decision maker. ADs are written statements made in advance by patients expressing their wishes and limitations for treatment as well as appointing surrogate decision makers when they become unable to decide for themselves in the future.5
During discussions about the goals for his care, Mr. P made his own medical decisions and elected to pursue a comfort-focused approach to care. His request for his health care team to reach out to his daughter was largely due to his need for assistance in explaining the complexity of his clinical condition to her and how hospice services would be helpful with his EOL care. Mr. P depended on his daughter to bring him to the hospital or to his doctors’ appointments, and she had been a major source of support for him and his wife. Contrary to the belief of some of his health care practitioners, Mr. P was not deferring his medical decisions to his daughter but rather allowing for her participation as his health care partner.
Communication between nurses and patients has been found to be challenging to both parties. Nurses express difficulties in areas that include supporting patients and families after they have had a difficult conversation with their physicians and responding to patients and family members’ emotions like anger.6 EOL care issues, such as family barriers to prognostic understanding, can interfere with psychosocial care.6 Families of patients approaching the EOL describe feeling mentally worn down and being unable to think straight, leading to feelings of being overwhelmed.7 They feel the need to be in a place where they can accept the content of difficult EOL conversations to be able to effectively engage.7
Studies have shown that family members of patients at the EOL experience stress, anxiety, fatigue and depression.8 Reactions that can be perceived as anger may not be so nor directed to the health care team. Questions raised regarding the accuracy of prognostication and treatment recommendations may not necessarily reflect concerns about the quality of care received but an exercise of advocacy in exploring other options on behalf of the patient. Allowing time for families to process the information received and react freely are necessary steps to facilitate reaching a place where they can acknowledge the information being relayed.
Communication Skills Training
Every member of the health care team should be equipped with the basic skills to have these conversations. The academic curricula for members of the health care team focuses on developing communication skills, but there has been a lack of content on palliative and EOL care.9
Due to time constraints and limited opportunities in the clinical setting, there has been an increasing use of simulation-based learning activities (SBLA) to enhance communication skills among nursing students.9 At this time, the impact of SBLA in enhancing communication competency is not fully known, but given the lack of clinical opportunities for students, this option is worth considering.9 When asked, nurses recognized the need for improved EOL communication education, training, and guidelines.10 They also felt that a multidisciplinary approach in EOL communication is beneficial. The inclusion of the End-of-Life Nursing Education Consortium (ELNEC) Core training in Bachelor of Science in Nursing programs have led to improved insight on palliative care and nurses’ role in palliative care and hospice among nursing students.11
The Palliative Care and Hospice Education and Training Act of 2017 amended the Public Health Service Act to include improving EOL training for health care providers, including talking about death and dying.12 Even though the Liaison Committee of Medical Education asked medical schools to incorporate EOL care education in the medical school curricula, there is still a lack of developmentally appropriate and supervised EOL education in medical schools.12 Training on grief also has been lacking and less likely to be mandatory among medical students and residents: Workshops are mostly conducted before they can be applied in the clinical setting.13 Meanwhile, resources are available to assist physicians in EOL conversations with patient and families, such as the Serious Illness Conversation Guide, The Conversation Project, and Stanford’s Letter Project.12
Conclusions
Palliative consultation is associated with an overall improvement in EOL care, communication, and support, according to families of deceased patients.14 It has also been shown to enhance patients’ quality of life and mood, improve documentation of resuscitation preferences, and lead to less aggressive care at the EOL, including less chemotherapy.15 Integration of palliative care in the care of patients hospitalized with acute heart failure has been associated with improved quality of life, decreased symptom burden and depressive symptoms, and increased participation in advance care planning.16
The involvement of palliative care in the care of patients and their families at EOL enhances goals of care discussions that improve understanding for everyone involved. It helps provide consistency with the message being delivered by the rest of the health care team to patients and families regarding prognosis and recommendations. Palliative care can provide an alternative when all other aggressive measures are no longer helpful and allow for the continuation of care with a shift in focus from prolonging life to promoting its quality. Furthermore, palliative care involvement for care of patients with life-limiting illness also has been found to improve symptom control, decrease hospitalizations and health care costs, and even improve mortality.17A multidisciplinary approach to palliative care EOL conversations is beneficial, but every member of the health care team should have the training, education, and skills to be ready to have these difficult conversations. These health care team members include physicians, advance practice clinicians, nurses, social workers, and chaplains, among others. Patients and families are likely to be in contact with different members of the health care team who should be able to carry out therapeutic conversations. Using validated tools and resources on communication techniques through evidence-based practice is helpful and should be encouraged. This provides a framework on how EOL conversations should be conducted in the clinical setting to augment the identified lack of training on EOL communication in schools. Repeated opportunities for its use over time will help improve the ability of clinicians to engage in effective EOL communication.
1. MacKenzie AR, Lasota M. Bringing life to death: the need for honest, compassionate, and effective end-of-life conversations. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2020;40:476-484. doi:10.1200/EDBK_279767
2. Krishnan U, Horn E. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (group 2 pulmonary hypertension) in adults. Accessed September 17, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pulmonary-hypertension-due-to-left-heart-disease-group-2-pulmonary-hypertension-in-adults
3. Anderson RJ, Bloch S, Armstrong M, Stone PC, Low JT. Communication between healthcare professionals and relatives of patients approaching the end-of-life: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Palliat Med. 2019;33(8):926-941. doi:10.1177/0269216319852007
4. Trees AR, Ohs JE, Murray MC. Family communication about end-of-life decisions and the enactment of the decision-maker role. Behav Sci (Basel). 2017;7(2):36. doi:10.3390/bs7020036 5. Arruda LM, Abreu KPB, Santana LBC, Sales MVC. Variables that influence the medical decision regarding advance directives and their impact on end-of-life care. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019;18:eRW4852. doi:10.31744/einstein_journal/2020RW4852
6. Banerjee SC, Manna R, Coyle N, et al. The implementation and evaluation of a communication skills training program for oncology nurses. Transl Behav Med. 2017;7(3):615-623. doi:10.1007/s13142-017-0473-5
7. Mitchell S, Spry JL, Hill E, Coad J, Dale J, Plunkett A. Parental experiences of end of life care decision-making for children with life-limiting conditions in the paediatric intensive care unit: a qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(5):e028548. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028548
8. Laryionava K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M, Reiter-Theil S, Hiddemann W, Winkler EC. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
9. Smith MB, Macieira TGR, Bumbach MD, et al. The use of simulation to teach nursing students and clinicians palliative care and end-of-life communication: a systematic review. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2018;35(8):1140-1154. doi:10.1177/1049909118761386
10. Griffiths I. What are the challenges for nurses when providing end-of-life care in intensive care units? Br J Nurs. 2019;28(16):1047-1052. doi:10.12968/bjon.2019.28.16.1047
11. Li J, Smothers A, Fang W, Borland M. Undergraduate nursing students’ perception of end-of-life care education placement in the nursing curriculum. J Hosp Palliat Nurs. 2019;21(5):E12-E18. doi:10.1097/NJH.0000000000000533
12. Sutherland R. Dying well-informed: the need for better clinical educationsurrounding facilitating end-of-life conversations. Yale J Biol Med. 2019;92(4):757-764.
13. Sikstrom L, Saikaly R, Ferguson G, Mosher PJ, Bonato S, Soklaridis S. Being there: a scoping review of grief support training in medical education. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224325. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224325
14. Yefimova M, Aslakson RA, Yang L, et al. Palliative care and end-of-life outcomes following high-risk surgery. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(2):138-146. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5083
15. Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):733-42. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000678.
16. Sidebottom AC, Jorgenson A, Richards H, Kirven J, Sillah A. Inpatient palliative care for patients with acute heart failure: outcomes from a randomized trial. J Palliat Med. 2015;18(2):134-142. doi:org/10.1089/jpm.2014.0192
17. Diop MS, Rudolph JL, Zimmerman KM, Richter MA, Skarf LM. Palliative careinterventions for patients with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Palliat Med. 2017;20(1):84-92. doi:10.1089/jpm.2016.0330
Effective communication during end-of-life is crucial for health care delivery, but misinterpretation can influence how the quality of the care is rendered and perceived.
Effective communication during end-of-life is crucial for health care delivery, but misinterpretation can influence how the quality of the care is rendered and perceived.
When I was a new palliative care nurse practitioner (NP), I remember my mentor telling me that communication in our field is equivalent to surgical procedures in general surgery. Conversations need to be handled with accuracy and precision, conducted in a timely fashion, and require skills that take practice to sharpen. Over the years, I learned that unlike surgery, we do not have control over how the procedure will flow. We approach patients with a blank canvas, open to receive messages that will be shared and reacted to accordingly. The ability to communicate effectively also requires compassion, which is a trait that tends to be inherent in humans and typically is not learned from textbooks but can be cultivated with training and application.
Among the barriers identified to effective communication are avoiding emotional issues and focusing on technical topics due in part to the fear of lengthy encounters, not allowing patients or families enough time to speak, and reframing instead of validating emotions.1 Many years later, I had the chance to help care for a patient whose story reminds me of how our choice of words and how our interpretation of what we are told can influence the way we care for patients and their families.
Case Presentation
Mr. P, aged 86 years, was admitted to a teaching hospital for pneumonia and heart failure exacerbation. He was treated with diuretics and antibiotics and discharged home on room air after 3 days. He returned to the hospital after 8 days, reporting labored breathing. He was found to be hypoxic, and a further workup revealed acute hypoxic respiratory failure that was likely from severe pulmonary hypertension and exacerbation of his heart failure. Left heart disease is a common cause of pulmonary hypertension, which can lead to right ventricular failure and increased mortality.2
After meeting with his pulmonologist and cardiologist, Mr. P elected for a do-not-resuscitate code status and declined to be intubated. He also refused further diagnostics and life-prolonging treatments for his conditions, including a stress test, cardiac catheterization, and a right heart catheterization. He required bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) support at bedtime, which he also declined. He agreed to the use of supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula and always needed 5 liters of oxygen.
Palliative care was consulted to assist with goals of care discussion. This visit took place during the COVID-19 pandemic, but Mr. P had tested negative for the COVID virus, so the palliative care NP was able to meet with Mr. P in person. He shared his understanding of the serious nature of his condition and the likelihood of a limited life expectancy without further diagnostics and possible life-prolonging treatments. He said his goal was to go home and spend the remainder of his life with his wife. He had not been out of bed since his hospitalization except to transfer to a nearby chair with the help of his nurse due to exertional dyspnea and generalized weakness. Prior to his recent hospitalizations, he was independently ambulating and had no dyspnea when performing strenuous activities. Mr. P shared that his wife was aged in her 70s and was legally blind. He added that she did not require physical assistance, but he was unsure whether she could help him because they had not been in such a situation previously. They had a daughter who visited frequently and helped with driving them to doctors’ appointments and shopping. Mr. P shared that he wanted to go home. After explaining the option of home hospice, Mr. P decided he wanted to receive hospice services at home and asked palliative care NP to contact his daughter to let her know his wishes and to tell her more about how hospice can help with his care.
The palliative care NP met with Mr. P’s nurse and shared the outcome of her visit. His nurse asked the palliative care NP whether she was familiar with his daughter. The nurse added that she wanted the palliative care NP to know that Mr. P’s daughter was quite angry and upset with his doctors after being told about his prognosis. His doctors’ notes also indicated that Mr. P wanted them to contact his daughter regarding his condition and plans for discharge, concluding that he deferred to his daughter for medical decision making.
As Mr. P’s hospitalization took place during the COVID pandemic, a face-to-face meeting with his family was not possible. The NP spoke with Mr. P’s daughter over the phone to relay his wishes and goals for his care. Mr. P’s daughter cried at times during the conversation and asked whether his condition was really that serious. The NP allowed Mr. P’s daughter to express her sadness and allowed for periods of silence during the conversation while his daughter gathered her composure. The NP reinforced the clinical information she had been provided by the medical team. Mr. P’s daughter added that he was completely independent, not requiring supplemental oxygen and was otherwise healthy just a month prior. She also asked whether there was truly nothing else that could be done to prolong his life. The NP acknowledged her observations and explained how Mr. P’s body and organs had not been able to bounce back from the recent insults to his overall physical condition.
After being told that Mr. P’s options for treatment were limited not only by his advanced age and comorbidities, but also the limitations and goals for his care he had identified, his daughter supported her father’s decision. The palliative care NP provided her information on how home hospice assists in her father’s care at home, including symptom management, nursing visits, home equipment, family support, among others. Mr. P’s daughter also said she would relay the information to her mother and call the palliative care NP if they had additional questions or concerns.
The outcome of her visit with Mr. P and his daughter were relayed by the palliative care NP to his acute health care team through an official response to the consultation request via his electronic health record. The palliative care NP also alerted the palliative care social worker to follow-up with Mr. P, his daughter, and his acute health care team to coordinate hospice services at the time of his discharge from the hospital.
Mr. P was discharged from the hospital with home hospice services after a few days. Three weeks later, Mr. P passed away peacefully on the in-patient unit of his home hospice agency as his physical care needs became too much for his family to provide at home a few days before his death. The palliative care social worker later shared with the NP that Mr. P’s daughter shared her gratitude and satisfaction with the care he had received not only from palliative care, but also from everyone during his hospitalization.
Discussion
Key themes found in end-of-life (EOL) communication with families and caregivers include highlighting clinical deterioration, involvement in decision making, continuation of high-quality care after cessation of aggressive measures, tailoring to individuals, clarity, honesty, and use of techniques in delivery.2 Some of the techniques identified were pacing, staging, and repetition.3 Other techniques that can be beneficial include allowing for time to express one’s feelings, being comfortable with brief periods of silence, validating observations shared, among others. These themes were evident in the interactions that his health care team had with Mr. P and his daughter. With honesty and clarity, various members of the health care team repeatedly shared information regarding his clinical deterioration.
Family Influence
EOL decision-making roles within a family tend to originate from family interactional histories, familial roles as well as decision-making situations the family faces.4 The US medical and legal systems also recognize formal role assignments for surrogate decision makers.4 In the case of Mr. P, his advance directive (AD) identified his daughter as his surrogate decision maker. ADs are written statements made in advance by patients expressing their wishes and limitations for treatment as well as appointing surrogate decision makers when they become unable to decide for themselves in the future.5
During discussions about the goals for his care, Mr. P made his own medical decisions and elected to pursue a comfort-focused approach to care. His request for his health care team to reach out to his daughter was largely due to his need for assistance in explaining the complexity of his clinical condition to her and how hospice services would be helpful with his EOL care. Mr. P depended on his daughter to bring him to the hospital or to his doctors’ appointments, and she had been a major source of support for him and his wife. Contrary to the belief of some of his health care practitioners, Mr. P was not deferring his medical decisions to his daughter but rather allowing for her participation as his health care partner.
Communication between nurses and patients has been found to be challenging to both parties. Nurses express difficulties in areas that include supporting patients and families after they have had a difficult conversation with their physicians and responding to patients and family members’ emotions like anger.6 EOL care issues, such as family barriers to prognostic understanding, can interfere with psychosocial care.6 Families of patients approaching the EOL describe feeling mentally worn down and being unable to think straight, leading to feelings of being overwhelmed.7 They feel the need to be in a place where they can accept the content of difficult EOL conversations to be able to effectively engage.7
Studies have shown that family members of patients at the EOL experience stress, anxiety, fatigue and depression.8 Reactions that can be perceived as anger may not be so nor directed to the health care team. Questions raised regarding the accuracy of prognostication and treatment recommendations may not necessarily reflect concerns about the quality of care received but an exercise of advocacy in exploring other options on behalf of the patient. Allowing time for families to process the information received and react freely are necessary steps to facilitate reaching a place where they can acknowledge the information being relayed.
Communication Skills Training
Every member of the health care team should be equipped with the basic skills to have these conversations. The academic curricula for members of the health care team focuses on developing communication skills, but there has been a lack of content on palliative and EOL care.9
Due to time constraints and limited opportunities in the clinical setting, there has been an increasing use of simulation-based learning activities (SBLA) to enhance communication skills among nursing students.9 At this time, the impact of SBLA in enhancing communication competency is not fully known, but given the lack of clinical opportunities for students, this option is worth considering.9 When asked, nurses recognized the need for improved EOL communication education, training, and guidelines.10 They also felt that a multidisciplinary approach in EOL communication is beneficial. The inclusion of the End-of-Life Nursing Education Consortium (ELNEC) Core training in Bachelor of Science in Nursing programs have led to improved insight on palliative care and nurses’ role in palliative care and hospice among nursing students.11
The Palliative Care and Hospice Education and Training Act of 2017 amended the Public Health Service Act to include improving EOL training for health care providers, including talking about death and dying.12 Even though the Liaison Committee of Medical Education asked medical schools to incorporate EOL care education in the medical school curricula, there is still a lack of developmentally appropriate and supervised EOL education in medical schools.12 Training on grief also has been lacking and less likely to be mandatory among medical students and residents: Workshops are mostly conducted before they can be applied in the clinical setting.13 Meanwhile, resources are available to assist physicians in EOL conversations with patient and families, such as the Serious Illness Conversation Guide, The Conversation Project, and Stanford’s Letter Project.12
Conclusions
Palliative consultation is associated with an overall improvement in EOL care, communication, and support, according to families of deceased patients.14 It has also been shown to enhance patients’ quality of life and mood, improve documentation of resuscitation preferences, and lead to less aggressive care at the EOL, including less chemotherapy.15 Integration of palliative care in the care of patients hospitalized with acute heart failure has been associated with improved quality of life, decreased symptom burden and depressive symptoms, and increased participation in advance care planning.16
The involvement of palliative care in the care of patients and their families at EOL enhances goals of care discussions that improve understanding for everyone involved. It helps provide consistency with the message being delivered by the rest of the health care team to patients and families regarding prognosis and recommendations. Palliative care can provide an alternative when all other aggressive measures are no longer helpful and allow for the continuation of care with a shift in focus from prolonging life to promoting its quality. Furthermore, palliative care involvement for care of patients with life-limiting illness also has been found to improve symptom control, decrease hospitalizations and health care costs, and even improve mortality.17A multidisciplinary approach to palliative care EOL conversations is beneficial, but every member of the health care team should have the training, education, and skills to be ready to have these difficult conversations. These health care team members include physicians, advance practice clinicians, nurses, social workers, and chaplains, among others. Patients and families are likely to be in contact with different members of the health care team who should be able to carry out therapeutic conversations. Using validated tools and resources on communication techniques through evidence-based practice is helpful and should be encouraged. This provides a framework on how EOL conversations should be conducted in the clinical setting to augment the identified lack of training on EOL communication in schools. Repeated opportunities for its use over time will help improve the ability of clinicians to engage in effective EOL communication.
When I was a new palliative care nurse practitioner (NP), I remember my mentor telling me that communication in our field is equivalent to surgical procedures in general surgery. Conversations need to be handled with accuracy and precision, conducted in a timely fashion, and require skills that take practice to sharpen. Over the years, I learned that unlike surgery, we do not have control over how the procedure will flow. We approach patients with a blank canvas, open to receive messages that will be shared and reacted to accordingly. The ability to communicate effectively also requires compassion, which is a trait that tends to be inherent in humans and typically is not learned from textbooks but can be cultivated with training and application.
Among the barriers identified to effective communication are avoiding emotional issues and focusing on technical topics due in part to the fear of lengthy encounters, not allowing patients or families enough time to speak, and reframing instead of validating emotions.1 Many years later, I had the chance to help care for a patient whose story reminds me of how our choice of words and how our interpretation of what we are told can influence the way we care for patients and their families.
Case Presentation
Mr. P, aged 86 years, was admitted to a teaching hospital for pneumonia and heart failure exacerbation. He was treated with diuretics and antibiotics and discharged home on room air after 3 days. He returned to the hospital after 8 days, reporting labored breathing. He was found to be hypoxic, and a further workup revealed acute hypoxic respiratory failure that was likely from severe pulmonary hypertension and exacerbation of his heart failure. Left heart disease is a common cause of pulmonary hypertension, which can lead to right ventricular failure and increased mortality.2
After meeting with his pulmonologist and cardiologist, Mr. P elected for a do-not-resuscitate code status and declined to be intubated. He also refused further diagnostics and life-prolonging treatments for his conditions, including a stress test, cardiac catheterization, and a right heart catheterization. He required bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP) support at bedtime, which he also declined. He agreed to the use of supplemental oxygen through a nasal cannula and always needed 5 liters of oxygen.
Palliative care was consulted to assist with goals of care discussion. This visit took place during the COVID-19 pandemic, but Mr. P had tested negative for the COVID virus, so the palliative care NP was able to meet with Mr. P in person. He shared his understanding of the serious nature of his condition and the likelihood of a limited life expectancy without further diagnostics and possible life-prolonging treatments. He said his goal was to go home and spend the remainder of his life with his wife. He had not been out of bed since his hospitalization except to transfer to a nearby chair with the help of his nurse due to exertional dyspnea and generalized weakness. Prior to his recent hospitalizations, he was independently ambulating and had no dyspnea when performing strenuous activities. Mr. P shared that his wife was aged in her 70s and was legally blind. He added that she did not require physical assistance, but he was unsure whether she could help him because they had not been in such a situation previously. They had a daughter who visited frequently and helped with driving them to doctors’ appointments and shopping. Mr. P shared that he wanted to go home. After explaining the option of home hospice, Mr. P decided he wanted to receive hospice services at home and asked palliative care NP to contact his daughter to let her know his wishes and to tell her more about how hospice can help with his care.
The palliative care NP met with Mr. P’s nurse and shared the outcome of her visit. His nurse asked the palliative care NP whether she was familiar with his daughter. The nurse added that she wanted the palliative care NP to know that Mr. P’s daughter was quite angry and upset with his doctors after being told about his prognosis. His doctors’ notes also indicated that Mr. P wanted them to contact his daughter regarding his condition and plans for discharge, concluding that he deferred to his daughter for medical decision making.
As Mr. P’s hospitalization took place during the COVID pandemic, a face-to-face meeting with his family was not possible. The NP spoke with Mr. P’s daughter over the phone to relay his wishes and goals for his care. Mr. P’s daughter cried at times during the conversation and asked whether his condition was really that serious. The NP allowed Mr. P’s daughter to express her sadness and allowed for periods of silence during the conversation while his daughter gathered her composure. The NP reinforced the clinical information she had been provided by the medical team. Mr. P’s daughter added that he was completely independent, not requiring supplemental oxygen and was otherwise healthy just a month prior. She also asked whether there was truly nothing else that could be done to prolong his life. The NP acknowledged her observations and explained how Mr. P’s body and organs had not been able to bounce back from the recent insults to his overall physical condition.
After being told that Mr. P’s options for treatment were limited not only by his advanced age and comorbidities, but also the limitations and goals for his care he had identified, his daughter supported her father’s decision. The palliative care NP provided her information on how home hospice assists in her father’s care at home, including symptom management, nursing visits, home equipment, family support, among others. Mr. P’s daughter also said she would relay the information to her mother and call the palliative care NP if they had additional questions or concerns.
The outcome of her visit with Mr. P and his daughter were relayed by the palliative care NP to his acute health care team through an official response to the consultation request via his electronic health record. The palliative care NP also alerted the palliative care social worker to follow-up with Mr. P, his daughter, and his acute health care team to coordinate hospice services at the time of his discharge from the hospital.
Mr. P was discharged from the hospital with home hospice services after a few days. Three weeks later, Mr. P passed away peacefully on the in-patient unit of his home hospice agency as his physical care needs became too much for his family to provide at home a few days before his death. The palliative care social worker later shared with the NP that Mr. P’s daughter shared her gratitude and satisfaction with the care he had received not only from palliative care, but also from everyone during his hospitalization.
Discussion
Key themes found in end-of-life (EOL) communication with families and caregivers include highlighting clinical deterioration, involvement in decision making, continuation of high-quality care after cessation of aggressive measures, tailoring to individuals, clarity, honesty, and use of techniques in delivery.2 Some of the techniques identified were pacing, staging, and repetition.3 Other techniques that can be beneficial include allowing for time to express one’s feelings, being comfortable with brief periods of silence, validating observations shared, among others. These themes were evident in the interactions that his health care team had with Mr. P and his daughter. With honesty and clarity, various members of the health care team repeatedly shared information regarding his clinical deterioration.
Family Influence
EOL decision-making roles within a family tend to originate from family interactional histories, familial roles as well as decision-making situations the family faces.4 The US medical and legal systems also recognize formal role assignments for surrogate decision makers.4 In the case of Mr. P, his advance directive (AD) identified his daughter as his surrogate decision maker. ADs are written statements made in advance by patients expressing their wishes and limitations for treatment as well as appointing surrogate decision makers when they become unable to decide for themselves in the future.5
During discussions about the goals for his care, Mr. P made his own medical decisions and elected to pursue a comfort-focused approach to care. His request for his health care team to reach out to his daughter was largely due to his need for assistance in explaining the complexity of his clinical condition to her and how hospice services would be helpful with his EOL care. Mr. P depended on his daughter to bring him to the hospital or to his doctors’ appointments, and she had been a major source of support for him and his wife. Contrary to the belief of some of his health care practitioners, Mr. P was not deferring his medical decisions to his daughter but rather allowing for her participation as his health care partner.
Communication between nurses and patients has been found to be challenging to both parties. Nurses express difficulties in areas that include supporting patients and families after they have had a difficult conversation with their physicians and responding to patients and family members’ emotions like anger.6 EOL care issues, such as family barriers to prognostic understanding, can interfere with psychosocial care.6 Families of patients approaching the EOL describe feeling mentally worn down and being unable to think straight, leading to feelings of being overwhelmed.7 They feel the need to be in a place where they can accept the content of difficult EOL conversations to be able to effectively engage.7
Studies have shown that family members of patients at the EOL experience stress, anxiety, fatigue and depression.8 Reactions that can be perceived as anger may not be so nor directed to the health care team. Questions raised regarding the accuracy of prognostication and treatment recommendations may not necessarily reflect concerns about the quality of care received but an exercise of advocacy in exploring other options on behalf of the patient. Allowing time for families to process the information received and react freely are necessary steps to facilitate reaching a place where they can acknowledge the information being relayed.
Communication Skills Training
Every member of the health care team should be equipped with the basic skills to have these conversations. The academic curricula for members of the health care team focuses on developing communication skills, but there has been a lack of content on palliative and EOL care.9
Due to time constraints and limited opportunities in the clinical setting, there has been an increasing use of simulation-based learning activities (SBLA) to enhance communication skills among nursing students.9 At this time, the impact of SBLA in enhancing communication competency is not fully known, but given the lack of clinical opportunities for students, this option is worth considering.9 When asked, nurses recognized the need for improved EOL communication education, training, and guidelines.10 They also felt that a multidisciplinary approach in EOL communication is beneficial. The inclusion of the End-of-Life Nursing Education Consortium (ELNEC) Core training in Bachelor of Science in Nursing programs have led to improved insight on palliative care and nurses’ role in palliative care and hospice among nursing students.11
The Palliative Care and Hospice Education and Training Act of 2017 amended the Public Health Service Act to include improving EOL training for health care providers, including talking about death and dying.12 Even though the Liaison Committee of Medical Education asked medical schools to incorporate EOL care education in the medical school curricula, there is still a lack of developmentally appropriate and supervised EOL education in medical schools.12 Training on grief also has been lacking and less likely to be mandatory among medical students and residents: Workshops are mostly conducted before they can be applied in the clinical setting.13 Meanwhile, resources are available to assist physicians in EOL conversations with patient and families, such as the Serious Illness Conversation Guide, The Conversation Project, and Stanford’s Letter Project.12
Conclusions
Palliative consultation is associated with an overall improvement in EOL care, communication, and support, according to families of deceased patients.14 It has also been shown to enhance patients’ quality of life and mood, improve documentation of resuscitation preferences, and lead to less aggressive care at the EOL, including less chemotherapy.15 Integration of palliative care in the care of patients hospitalized with acute heart failure has been associated with improved quality of life, decreased symptom burden and depressive symptoms, and increased participation in advance care planning.16
The involvement of palliative care in the care of patients and their families at EOL enhances goals of care discussions that improve understanding for everyone involved. It helps provide consistency with the message being delivered by the rest of the health care team to patients and families regarding prognosis and recommendations. Palliative care can provide an alternative when all other aggressive measures are no longer helpful and allow for the continuation of care with a shift in focus from prolonging life to promoting its quality. Furthermore, palliative care involvement for care of patients with life-limiting illness also has been found to improve symptom control, decrease hospitalizations and health care costs, and even improve mortality.17A multidisciplinary approach to palliative care EOL conversations is beneficial, but every member of the health care team should have the training, education, and skills to be ready to have these difficult conversations. These health care team members include physicians, advance practice clinicians, nurses, social workers, and chaplains, among others. Patients and families are likely to be in contact with different members of the health care team who should be able to carry out therapeutic conversations. Using validated tools and resources on communication techniques through evidence-based practice is helpful and should be encouraged. This provides a framework on how EOL conversations should be conducted in the clinical setting to augment the identified lack of training on EOL communication in schools. Repeated opportunities for its use over time will help improve the ability of clinicians to engage in effective EOL communication.
1. MacKenzie AR, Lasota M. Bringing life to death: the need for honest, compassionate, and effective end-of-life conversations. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2020;40:476-484. doi:10.1200/EDBK_279767
2. Krishnan U, Horn E. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (group 2 pulmonary hypertension) in adults. Accessed September 17, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pulmonary-hypertension-due-to-left-heart-disease-group-2-pulmonary-hypertension-in-adults
3. Anderson RJ, Bloch S, Armstrong M, Stone PC, Low JT. Communication between healthcare professionals and relatives of patients approaching the end-of-life: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Palliat Med. 2019;33(8):926-941. doi:10.1177/0269216319852007
4. Trees AR, Ohs JE, Murray MC. Family communication about end-of-life decisions and the enactment of the decision-maker role. Behav Sci (Basel). 2017;7(2):36. doi:10.3390/bs7020036 5. Arruda LM, Abreu KPB, Santana LBC, Sales MVC. Variables that influence the medical decision regarding advance directives and their impact on end-of-life care. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019;18:eRW4852. doi:10.31744/einstein_journal/2020RW4852
6. Banerjee SC, Manna R, Coyle N, et al. The implementation and evaluation of a communication skills training program for oncology nurses. Transl Behav Med. 2017;7(3):615-623. doi:10.1007/s13142-017-0473-5
7. Mitchell S, Spry JL, Hill E, Coad J, Dale J, Plunkett A. Parental experiences of end of life care decision-making for children with life-limiting conditions in the paediatric intensive care unit: a qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(5):e028548. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028548
8. Laryionava K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M, Reiter-Theil S, Hiddemann W, Winkler EC. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
9. Smith MB, Macieira TGR, Bumbach MD, et al. The use of simulation to teach nursing students and clinicians palliative care and end-of-life communication: a systematic review. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2018;35(8):1140-1154. doi:10.1177/1049909118761386
10. Griffiths I. What are the challenges for nurses when providing end-of-life care in intensive care units? Br J Nurs. 2019;28(16):1047-1052. doi:10.12968/bjon.2019.28.16.1047
11. Li J, Smothers A, Fang W, Borland M. Undergraduate nursing students’ perception of end-of-life care education placement in the nursing curriculum. J Hosp Palliat Nurs. 2019;21(5):E12-E18. doi:10.1097/NJH.0000000000000533
12. Sutherland R. Dying well-informed: the need for better clinical educationsurrounding facilitating end-of-life conversations. Yale J Biol Med. 2019;92(4):757-764.
13. Sikstrom L, Saikaly R, Ferguson G, Mosher PJ, Bonato S, Soklaridis S. Being there: a scoping review of grief support training in medical education. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224325. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224325
14. Yefimova M, Aslakson RA, Yang L, et al. Palliative care and end-of-life outcomes following high-risk surgery. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(2):138-146. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5083
15. Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):733-42. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000678.
16. Sidebottom AC, Jorgenson A, Richards H, Kirven J, Sillah A. Inpatient palliative care for patients with acute heart failure: outcomes from a randomized trial. J Palliat Med. 2015;18(2):134-142. doi:org/10.1089/jpm.2014.0192
17. Diop MS, Rudolph JL, Zimmerman KM, Richter MA, Skarf LM. Palliative careinterventions for patients with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Palliat Med. 2017;20(1):84-92. doi:10.1089/jpm.2016.0330
1. MacKenzie AR, Lasota M. Bringing life to death: the need for honest, compassionate, and effective end-of-life conversations. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2020;40:476-484. doi:10.1200/EDBK_279767
2. Krishnan U, Horn E. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (group 2 pulmonary hypertension) in adults. Accessed September 17, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pulmonary-hypertension-due-to-left-heart-disease-group-2-pulmonary-hypertension-in-adults
3. Anderson RJ, Bloch S, Armstrong M, Stone PC, Low JT. Communication between healthcare professionals and relatives of patients approaching the end-of-life: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Palliat Med. 2019;33(8):926-941. doi:10.1177/0269216319852007
4. Trees AR, Ohs JE, Murray MC. Family communication about end-of-life decisions and the enactment of the decision-maker role. Behav Sci (Basel). 2017;7(2):36. doi:10.3390/bs7020036 5. Arruda LM, Abreu KPB, Santana LBC, Sales MVC. Variables that influence the medical decision regarding advance directives and their impact on end-of-life care. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019;18:eRW4852. doi:10.31744/einstein_journal/2020RW4852
6. Banerjee SC, Manna R, Coyle N, et al. The implementation and evaluation of a communication skills training program for oncology nurses. Transl Behav Med. 2017;7(3):615-623. doi:10.1007/s13142-017-0473-5
7. Mitchell S, Spry JL, Hill E, Coad J, Dale J, Plunkett A. Parental experiences of end of life care decision-making for children with life-limiting conditions in the paediatric intensive care unit: a qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(5):e028548. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028548
8. Laryionava K, Pfeil TA, Dietrich M, Reiter-Theil S, Hiddemann W, Winkler EC. The second patient? Family members of cancer patients and their role in end-of-life decision making. BMC Palliat Care. 2018;17(1):29. doi:10.1186/s12904-018-0288-2
9. Smith MB, Macieira TGR, Bumbach MD, et al. The use of simulation to teach nursing students and clinicians palliative care and end-of-life communication: a systematic review. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2018;35(8):1140-1154. doi:10.1177/1049909118761386
10. Griffiths I. What are the challenges for nurses when providing end-of-life care in intensive care units? Br J Nurs. 2019;28(16):1047-1052. doi:10.12968/bjon.2019.28.16.1047
11. Li J, Smothers A, Fang W, Borland M. Undergraduate nursing students’ perception of end-of-life care education placement in the nursing curriculum. J Hosp Palliat Nurs. 2019;21(5):E12-E18. doi:10.1097/NJH.0000000000000533
12. Sutherland R. Dying well-informed: the need for better clinical educationsurrounding facilitating end-of-life conversations. Yale J Biol Med. 2019;92(4):757-764.
13. Sikstrom L, Saikaly R, Ferguson G, Mosher PJ, Bonato S, Soklaridis S. Being there: a scoping review of grief support training in medical education. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224325. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224325
14. Yefimova M, Aslakson RA, Yang L, et al. Palliative care and end-of-life outcomes following high-risk surgery. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(2):138-146. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5083
15. Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, et al. Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):733-42. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1000678.
16. Sidebottom AC, Jorgenson A, Richards H, Kirven J, Sillah A. Inpatient palliative care for patients with acute heart failure: outcomes from a randomized trial. J Palliat Med. 2015;18(2):134-142. doi:org/10.1089/jpm.2014.0192
17. Diop MS, Rudolph JL, Zimmerman KM, Richter MA, Skarf LM. Palliative careinterventions for patients with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Palliat Med. 2017;20(1):84-92. doi:10.1089/jpm.2016.0330
Pembrolizumab-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in a 95-Year-Old Veteran With Metastatic Melanoma
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and improved the prognosis for a variety of advanced solid tumors and Hodgkin lymphoma, but evidence is growing regarding severe endocrine disturbances.1,2 CPIs block inhibitory molecules on activated T cells to increase tumor cell destruction but also can breach normal tolerance, resulting in a spectrum of immune-related adverse events (irAE).1,2 Programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) inhibitors are one type of CPIs. Pembrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the PD-1 checkpoint pathway and is approved for the treatment of malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer.3,4 When the PD-1 checkpoint pathway is inhibited, T cells targeting cancer are activated, as are autoreactive T cells, such as those regulating pancreatic islet cell survival, which can lead to type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).5
Case Presentation
A 95-year-old male veteran with long-standing, stable prediabetes was treated with pembrolizumab for stage 4 melanoma. Four months after treatment initiation and 3 weeks after completion of his sixth treatment cycle of pembrolizumab (2 mg/kg every 3 weeks), he presented for surveillance positron emission tomography (PET) and was incidentally found to have a serum glucose of 423 mg/dL. Hypothesis-driven history taking revealed polyuria, polydipsia, and a 12-lb weight loss during the previous 3 months. The patient reported no abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. He showed no evidence of pancreatic metastases on recent imaging. His family history was notable for a daughter with T1DM diagnosed at a young age.
On examination, the patient’s vital signs were normal aside from a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His body mass index was 30. He was alert and oriented with comfortable respirations and no Kussmaul breathing. He exhibited dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor. Laboratory studies revealed 135 mmol/L sodium (reference, 135-145), 4.6 mmol/L potassium (reference, 3.6-5.2), 100 mmol/L chloride (reference, 99-106), bicarbonate of 26.5 mmol/L (reference, 23-29), serum blood urea nitrogen 27 mg/dL (reference, 6-24), 1.06 mg/dL creatinine (reference, 0.74-1.35), and 423 mg/dL glucose (reference, 70-100), with negative urine ketones. Further studies demonstrated 462 µmol/L fructosamine (reference, 190-270), correlating with hemoglobin A1c (
Dicussion
Immunotherapy is now an integral part of cancer treatment and can result in endocrine disturbances.1,2 Life-threatening irAEs are rare and may mimic more common conditions; thus, there is growing recognition of the need to educate health care professionals in appropriate screening and management of these conditions. CPI-induced T1DM is an uncommon but clinically significant event with an incidence of 0.4 to 1.27% and a median onset of 20 weeks after initiation of therapy (range, 1-228 weeks).8-12In case seriesfrom 3 academic centers, 59 to81% of patients with CPI-induced T1DM presented with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and only 40 to 71% of patients were autoantibody positive.13-16 These patients are older than those presenting with classic T1DM, often require intensive care unit admission, and nearly invariably require exogenous insulin injections for metabolic control.13-16
Based on the later age of onset of cancers that may be treated with CPI, patients with CPI-induced T1DM may be misdiagnosed with T2DM or hyperglycemia from other causes, such as medications or acute illness in the outpatient setting, risking suboptimal treatment.
Given the infrequent incidence and lack of controlled trials, screening and treatment recommendations for CPI-induced T1DM are based on principles derived from case series and expert opinion. Development of polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, nausea, and/or vomiting should prompt investigation for possible development or worsening of hyperglycemia, suggestive of development of T1DM.17 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines recommend that serum glucose be assessed at baseline and with each treatment cycle during induction for 12 weeks, then every 3 to 6 weeks thereafter.17 There is no reported association between the number of CPI treatments and the development of DM.8,9 Following our patient’s fifth pembrolizumab cycle, a random glucose reading was noted to be 186 mg/dL (Figure 1). Under the ASCO guidelines, ideally the patient would have received close clinical follow-up given the striking increase in plasma glucose compared with prior baseline lower values and perhaps been further evaluated with an anti-GAD antibody titer to screen for T1DM.17
This patient's case adds to the published reports of CPI-induced T1DM without DKA and represents the oldest patient experiencing this irAE in the literature.13-16 The degree of elevation of his initial fructosamine, which is comparable to an average plasma glucose of approximately 270 mg/dL, belied the rapid rate of rise of his recent plasma glucose. Given the trajectory of glycemic markers and symptoms, one could certainly be concerned about imminent decompensation to DKA. However, fortuitous point-of-care glucose reading prior to surveillance PET resulted in a new critical diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
Assessing the need for inpatient evaluation includes obtaining urine ketones and acid-base status as screening for DKA.17 Antibodies and C-peptide can be sent to support diagnosis of new onset T1DM, although the initiation of therapy should not be delayed for these results.17 As noted before, many of these patients also are antibody negative.13-16 Low C-peptide levels should prompt a high suspicion for CPI-induced T1DM, and initiation of insulin therapy should be strongly considered.17 In a case series of 27 patients, 85% exhibited a rapid loss of β-cell function, evidenced by the acute progression to hyperglycemia and low or undetectable levels of C-peptide at diagnosis.9 Likewise, our patient had a low C-peptide level and negative anti-GAD antibody titer but was treated before these results were available. Inpatient admission for close glycemic monitoring may be reasonable; several cases reported prompt diagnosis and avoidance of DKA in this setting.17
In contrast to other irAEs, there is no available evidence that high-dose corticosteroids alter the course of pembrolizumab-induced T2DM.18 Depending on the degree of hyperglycemia, endocrinology consultation and insulin treatment are appropriate where the diagnosis of T1DM is suspected even without evidence of DKA.17 For patients with T2DM, there may be a positive synergistic effect of metformin in combination with CPIs in tumor control.19 Our patient’s C-peptide improved with insulin treatment, consistent with correction of glucose toxicity and a honeymoon period in his course. However, in patients reported with pembrolizumab-induced T1DM, insulin requirement for treatment generally persists despite cessation of pembrolizumab therapy.13-16
Conclusions
Pembrolizumab-induced T1DM is a rare, but potentially life-threatening irAE. The acute risk of DKA requires early recognition and prompt treatment of patients taking CPIs. More than 90% of primary care physicians (PCPs) fulfill general medical care roles for patients with cancer; therefore, they play an essential role in evaluating symptoms during therapy.20 Further studies evaluating the role of PCPs and outcomes when PCPs are involved in oncologic care should be conducted.
With increased index of suspicion, this clinical scenario presents an opportunity for PCPs that may help reduce irAE-associated morbidity and mortality of patients on CPIs, like pembrolizumab. Figure 2 illustrates an example addendum that can be used to alert and tag a PCP of a mutual patient after initiation of CPI therapy. Determining the optimal interface between PCPs, oncologists, and endocrinologists in delivering and coordinating high-quality cancer care in the setting of immunotherapy is an important area for ongoing quality improvement.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the staff and health care professionals at VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System who were involved in the care of this patient.
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
1. Puzanov I, Diab A, Abdallah K, et al; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer Toxicity Management Working Group. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Toxicity Management Working Group. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):95. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0300-z
2. Villa NM, Farahmand A, Du L, et al. Endocrinopathies with use of cancer immunotherapies. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2018;88(2):327-332. doi:10.1111/cen.13483
3. Schachter J, Ribas A, Long GV, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet. 2017;390(10105):1853-1862. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31601-X
4. Garon EB, Hellmann MD, Rizvi NA, et al. Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(28):2518-2527. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.00934
5. Ribas A. Tumor immunotherapy directed at PD-1. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(26):2517-2519. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1205943
6. Malmstrom H, Walldius G, Grill V, Jungner I, Gudbjomsdottir S, Hammar N. Frustosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies- cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111463. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
7. Skinner S, Diaw M, Mbaye MN, et al. Evaluation of agreement between hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, and fructosamine in Senagalese individuals with and without sickle-cell trait. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0212552
8. Byun DJ, Wolchok JD, Rosenberg LM, Girotra M. Cancer immunotherapy-immune checkpoint blockade and associated endocrinopathies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):195-207. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.205
9. Stamatouli AM, Quandt Z, Perdigoto AL, et al. Collateral damage: insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes. 2018;67(8):1471-1480. doi:10.2337/dbi18-0002
10. Liu J, Zhou H, Zhang Y, et al. Reporting of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-associated diabetes, 2015-2019. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(7):e79-e80. [Published online ahead of print, 2020 May 11]. doi:10.2337/dc20-0459
11. Barroso-Sousa R, Barry WT, Garrido-Castro AC, et al. Incidence of endocrine dysfunction following the use of different immune checkpoint inhibitor regimens: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(2):173-182. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
12. de Filette J, Andreescu CE, Cools F, Bravenboer B, Velkeniers B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Horm Metab Res. 2019;51(3):145-156. doi:10.1055/a-0843-3366
13. Hughes J, Vudattu N, Sznol M, et al. Precipitation of autoimmune diabetes with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):e55-e57. doi:10.2337/dc14-2349
14. Clotman K, Janssens K, Specenier P, Weets I, De block CEM. Programmed cell death-1 inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;103(9):3144-3154. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-00728
15. Kotwal A, Haddox C, Block M, Kudva YC. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: an emerging cause of insulin-dependent diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2019;7(1):e000591. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000591
16. Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM, Hodi FS, Kaiser UB, Min L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 2019;40(1):17-65. doi:10.1210/er.2018-00006
17. Brahmer JR, Lacchetti C, Schneider BJ, et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Management of immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(17):1714-1768. doi:10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6385
18. Aleksova J, Lau PK, Soldatos G, Mcarthur G. Glucocorticoids did not reverse type 1 diabetes mellitus secondary to pembrolizumab in a patient with metastatic melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;2016:bcr2016217454. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217454
19. Afzal MZ, Mercado RR, Shirai K. Efficacy of metformin in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic malignant melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):64. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0375-1
20. Klabunde CN, Ambs A, Keating NL, et al. The role of primary care physicians in cancer care. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(9):1029-1036. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1058-x
Unmasking Our Grief
Since the start of the pandemic, health care systems have requested many in-services for staff on self-care and stress management to help health care workers (HCWs) cope with the heavy toll of COVID-19. The pandemic has set off a global mental health crisis, with unprecedented numbers of individuals meeting criteria for anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders in response to the intense stressors of living through a pandemic. These calls to assist staff with self-care and burnout prevention have been especially salient for psychologists working in palliative care and geriatrics, where fears of COVID-19 infection and numbers of patient deaths have been high.
Throughout these painful times, we have been grateful for an online community of palliative care psychologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) from across the continuum of care and across the country. This community brought together many of us who were both struggling ourselves and striving to support the teams and HCWs around us. We are psychologists who provide home-care services in North Carolina, inpatient hospice and long-term care services in California, and long-term care and outpatient palliative care services in Massachusetts. Through our shared struggles and challenges navigating the pandemic, we realized that our respective teams requested similar services, all focused on staff support.
The psychological impact of COVID-19 on HCWs was clear from the beginning. Early in the pandemic our respective teams requested us to provide staff support and education about coping to our local HCWs. Soon national groups for long-term care staff requested education programs. Through this work, we realized that the emotional needs of HCWs ran much deeper than simple self-care. At the onset of the pandemic, before realizing its chronicity, the trainings we offered focused on stress and coping strategies. We cited several frameworks for staff support and eagerly shared anything that might help us, and our colleagues, survive the immediate anxiety and tumult surrounding us.1-3 In this paper, we briefly discuss the distress affecting the geriatric care workforce, reflect on our efforts to cope as HCWs, and offer recommendations at individual and organization levels to help address our collective grief.
Impact of COVID-19
As the death toll mounted and hospitals were pushed to the brink, we saw the suffering of our fellow HCWs. The lack of personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies led to evolving and increasing anxiety for HCWs about contracting COVID-19, potentially spreading it to one’s social circle or family, fears of becoming sick and dying, and fears of inadvertently spreading the virus to medically-vulnerable patients. Increasing demands on staff required many to work outside their areas of expertise. Clinical practice guidelines changed frequently as information emerged about the virus. Staff members struggled to keep pace with the increasing number of patients, many of whom died despite heroic efforts to save them.
As the medical crisis grew, so too did social uprisings as the general public gained a strengthened awareness of the legacy and ongoing effects of systemic oppression, racism, and social inequities in the United States. Individuals grappled with their own privileges, which often hid such disparities from view. Many HCWs and clinicians of color had to navigate unsolicited questions and discussions about racial injustices while also trying to survive. As psychologists, we strove to support the HCWs around us while also struggling with our own stressors. As the magnitude of the pandemic and ongoing social injustices came into view, we realized that presentations on self-care and burnout prevention did not suffice. We needed discussions on unmasking our grief, acknowledging our traumas, and working toward collective healing.
Geriatric Care Workers
Experiences of grief and trauma hit the geriatric care workforce and especially long-term care facilities particularly hard given the high morbidity and mortality rates of COVID-19.4 The geriatric care workforce itself suffers from institutional vulnerabilities. Individuals are often underpaid, undertrained, and work within a system that continually experiences staffing shortages, high burnout, and consequently high levels of turnover.5,6 Recent immigrants and racial/ethnic minorities disproportionately make up this workforce, who often live in multigenerational households and work in multiple facilities to get by.7,8 Amid the pandemic these HCWs continued to work despite demoralizing negative media coverage of nursing homes.9 Notably, facilities with unionized staff were less likely to need second or third jobs to survive, thus reducing spread across facilities. This along with better access to PPE may have contributed to their lower COVID-19 infection and mortality rates relative to non-unionized staff.10
Similar to long-term care workers, home-care staff had related fears and anxieties, magnified by the need to enter multiple homes. This often overlooked but growing sector of the geriatric care workforce faced the added anxiety of the unknown as they entered multiple homes to provide care to their patients. These staff have little control over who may be in the home when they arrive, the sanitation/PPE practices of the patient/family, and therefore little control over their potential exposure to COVID-19. This also applies to home health aides who, although not providing medical services, are a critical part of home-care services and allow older adults to remain living independently in their home.
Reflection on Grief
As we witnessed the interactive effects of the pandemic and social inequities in geriatrics and palliative care, we frequently sought solace in online communities of psychologists working in similar settings. Over time, our regular community meetings developed a different tone: discussions about caring for others shifted to caring for ourselves. It seemed that in holding others’ pain, many of us neglected to address our own. We needed emotional support. We needed to acknowledge that we were not all okay; that the masks we wear for protection also reveal our vulnerabilities; and that protective equipment in hospitals do not protect us from the hate and bias targeting many of us face everywhere we go.
As we let ourselves be vulnerable with each other, we saw the true face of our pain: it was not stress, it was grief. We were sad, broken, mourning innumerable losses, and grieving, mostly alone. It felt overwhelming. Our minds and hearts often grew numb to find respite from pain. At times we found ourselves seeking haven in our offices, convincing ourselves that paperwork needed to be done when in reality we had no space to hold anyone else’s pain; we could barely contain our own. We could only take so much.
Without space to process, grief festers and eats away at our remaining compassion. How do we hold grace for ourselves, dare to be vulnerable, and allow ourselves to feel, when doing so opens the door to our own grief? How do we allow room for emotional processing when we learned to numb-out in order to function? And as women with diverse intersectional identities, how do we honor our humanity when we live in a society that reflects its indifference? We needed to process our pain in order to heal in the slow and uneven way that grief heals.
Caring During Tough Times
The pain we feel is real and it tears at us over time. Pushing it away disenfranchises ourselves of the opportunity to heal and grow. Our collective grief and trauma demand collective healing and acknowledgment of our individual suffering. We must honor our shared humanity and find commonality amid our differences. Typical self-care (healthy eating, sleep, basic hygiene) may not be enough to mitigate the enormity of these stressors. A glass of wine or a virtual dinner with friends may distract but does not heal our wounds.
Self-care, by definition, centers the self and ignores the larger systemic factors that maintain our struggles. It keeps the focus on the individual and in so doing, risks inducing self-blame should we continue feeling burnout. We must do more. We can advocate that systems acknowledge our grief and suffering as well as our strengths and resiliencies. We can demand that organizations recognize human limits and provide support, rather than promote environments that encourage silent perseverance. And we can deconstruct the cultural narrative that vulnerability is weakness or that we are the “heroes.” Heroism suggests superhuman qualities or extreme courage and often negates the fear and trepidation in its midst.11,12 We can also recognize how intersectional aspects of our identities make navigating the pandemic and systemic racism harder and more dangerous for some than for others.
As noted by President Biden in a speech honoring those lost to COVID-19, “We have to resist becoming numb to the sorrow.”13 The nature of our work (and that of most clinicians) is that it is expected and sometimes necessary to compartmentalize and turn off the emotions so that we can function in a professional manner. But this way of being also serves to hold us back. It does not make space for the very real emotions of trauma and grief that have pervaded HCWs during this pandemic. We must learn a different way of functioning—one where grief is acknowledged and even actively processed while still going about our work. Grief therapist Megan Devine proposes to “tend to pain and grief by bearing witness” and notes that “when we allow the reality of grief to exist, we can focus on helping ourselves—and one another—survive inside pain.”14 She advocates for self-compassion and directs us to “find ways to show our grief to others, in ways that honor the truth of our experience” saying, “we have to be willing to stop diminishing our own pain so that others can be comfortable around us.” But what does this look like among health care teams who are traumatized and grieving?
In our experience, caring for ourselves and our teams in times of prolonged stress, trauma, and grief is essential to maintain functioning over time. We strongly believe that it must occur at both the organizational and individual levels. In the throes of a crisis, teams need support immediately. To offer a timely response, we gathered knowledge of team-based care and collaboration to develop practical strategies that can be implemented swiftly to provide support across the team.15-19
The strategies we developed offer steps for creating and maintaining a supportive, compassionate, and psychologically safe work environment. First, the CARES Strategies for Practical Team Intervention highlights the importance of clear communication, assessing team needs regularly, recognizing the stress that is occurring, engaging staff in discussions, and ensuring psychological safety and comfort (Figure 1). Next, the SHARE approach is laid out to allow for interpersonal support among team members (Figure 2). Showing each other empathy, hoping for better days, acknowledging each other’s pain, reaching out for assistance, and expressing our needs allow HCWs to open up about their grief, stress, and trauma. Of note, we found these sets of strategies interdependent: a team that does not believe the leader/organization CARES is not likely to SHARE. Therefore, we also feel that it is especially important that team leaders work to create or enhance the sense of psychological safety for the team. If team members do not feel safe, they will not disclose their grief and remain stuck in the old mode of suffering in silence.
Conclusions
This pandemic and the collective efforts toward social justice advocacy have revealed our vulnerabilities as well as our strengths. These experiences have forced us to reckon with our past and consider possible futures. It has revealed the inequities in our health care system, including our failure to protect those on the ground who keep our systems running, and prompted us to consider new ways of operating in low-resourced and high-demand environments. These experiences also present us with opportunities to be better and do better as both professionals and people; to reflect on our past and consider what we want different in our lives. As we yearn for better days and brace ourselves for what is to come, we hope that teams and organizations will take advantage of these opportunities for self-reflection and continue unmasking our grief, healing our wounds, and honoring our shared humanity.
1. Blake H, Bermingham F. Psychological wellbeing for health care workers: mitigating the impact of covid-19. Version 2.0. Updated June 18, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/toolkits/play_22794
2. Harris R. FACE COVID: how to respond effectively to the corona crisis. Published 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. http://louisville.edu/counseling/coping-with-covid-19/face-covid-by-dr-russ-harris/view
3. Norcross JC, Phillips CM. Psychologist self-care during the pandemic: now more than ever [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 2]. J Health Serv Psychol. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1007/s42843-020-00010-5
4. Kaiser Family Foundation. State reports of long-term care facility cases and deaths related to COVID-19. 2020. Published April 23, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/state-reporting-of-cases-and-deaths-due-to-covid-19-in-long-term-care-facilities
5. Sterling MR, Tseng E, Poon A, et al. Experiences of home health care workers in New York City during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: a qualitative analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(11):1453-1459. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3930
6. Stone R, Wilhelm J, Bishop CE, Bryant NS, Hermer L, Squillace MR. Predictors of intent to leave the job among home health workers: analysis of the National Home Health Aide Survey. Gerontologist. 2017;57(5):890-899. doi:10.1093/geront/gnw075
7. Scales K. It’s time to care: a detailed profile of America’s direct care workforce. PHI. 2020. Published January 21, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://phinational.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Its-Time-to-Care-2020-PHI.pdf
8. Wolfe R, Harknett K, Schneider D. Inequities at work and the toll of COVID-19. Health Aff Health Policy Brief. Published June 4, 2021. doi: 10.1377/hpb20210428.863621
9. White EM, Wetle TF, Reddy A, Baier RR. Front-line nursing home staff experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic [published correction appears in J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021 May;22(5):1123]. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22(1):199-203. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.11.022
10. Dean A, Venkataramani A, Kimmel S. Mortality rates from COVID-19 are lower In unionized nursing homes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):1993-2001.doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.01011
11. Cox CL. ‘Healthcare Heroes’: problems with media focus on heroism from healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2020;46(8):510-513. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106398
12. Stokes-Parish J, Elliott R, Rolls K, Massey D. Angels and heroes: the unintended consequence of the hero narrative. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020;52(5):462-466. doi:10.1111/jnu.12591
13. Biden J. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 American lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19
14. Devine M. It’s Okay That You’re Not Okay: Meeting Grief and Loss in a Culture That Doesn’t Understand. Sounds True; 2017.
15. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Grief leadership during COVID-19. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Grief_Leadership_During_COVID19.pdf
16. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Sustaining the well-being of healthcare personnel during coronavirus and other infectious disease outbreaks. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Sustaining_Well_Being_Health care_Personnel_during.pdf
17. Fessell D, Cherniss C. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and beyond: micropractices for burnout prevention and emotional wellness. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17(6):746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.03.013
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for PTSD. Managing healthcare workers’ stress associated with the COVID-19 virus outbreak. Updated March 25, 2020, Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/covid/COVID_healthcare_workers.asp
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Organization Development (NCOD). Team Development Guide. 2017. https://vaww.va.gov/NCOD/docs/Team_Development_Guide.docx [Nonpublic source, not verified.]
Since the start of the pandemic, health care systems have requested many in-services for staff on self-care and stress management to help health care workers (HCWs) cope with the heavy toll of COVID-19. The pandemic has set off a global mental health crisis, with unprecedented numbers of individuals meeting criteria for anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders in response to the intense stressors of living through a pandemic. These calls to assist staff with self-care and burnout prevention have been especially salient for psychologists working in palliative care and geriatrics, where fears of COVID-19 infection and numbers of patient deaths have been high.
Throughout these painful times, we have been grateful for an online community of palliative care psychologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) from across the continuum of care and across the country. This community brought together many of us who were both struggling ourselves and striving to support the teams and HCWs around us. We are psychologists who provide home-care services in North Carolina, inpatient hospice and long-term care services in California, and long-term care and outpatient palliative care services in Massachusetts. Through our shared struggles and challenges navigating the pandemic, we realized that our respective teams requested similar services, all focused on staff support.
The psychological impact of COVID-19 on HCWs was clear from the beginning. Early in the pandemic our respective teams requested us to provide staff support and education about coping to our local HCWs. Soon national groups for long-term care staff requested education programs. Through this work, we realized that the emotional needs of HCWs ran much deeper than simple self-care. At the onset of the pandemic, before realizing its chronicity, the trainings we offered focused on stress and coping strategies. We cited several frameworks for staff support and eagerly shared anything that might help us, and our colleagues, survive the immediate anxiety and tumult surrounding us.1-3 In this paper, we briefly discuss the distress affecting the geriatric care workforce, reflect on our efforts to cope as HCWs, and offer recommendations at individual and organization levels to help address our collective grief.
Impact of COVID-19
As the death toll mounted and hospitals were pushed to the brink, we saw the suffering of our fellow HCWs. The lack of personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies led to evolving and increasing anxiety for HCWs about contracting COVID-19, potentially spreading it to one’s social circle or family, fears of becoming sick and dying, and fears of inadvertently spreading the virus to medically-vulnerable patients. Increasing demands on staff required many to work outside their areas of expertise. Clinical practice guidelines changed frequently as information emerged about the virus. Staff members struggled to keep pace with the increasing number of patients, many of whom died despite heroic efforts to save them.
As the medical crisis grew, so too did social uprisings as the general public gained a strengthened awareness of the legacy and ongoing effects of systemic oppression, racism, and social inequities in the United States. Individuals grappled with their own privileges, which often hid such disparities from view. Many HCWs and clinicians of color had to navigate unsolicited questions and discussions about racial injustices while also trying to survive. As psychologists, we strove to support the HCWs around us while also struggling with our own stressors. As the magnitude of the pandemic and ongoing social injustices came into view, we realized that presentations on self-care and burnout prevention did not suffice. We needed discussions on unmasking our grief, acknowledging our traumas, and working toward collective healing.
Geriatric Care Workers
Experiences of grief and trauma hit the geriatric care workforce and especially long-term care facilities particularly hard given the high morbidity and mortality rates of COVID-19.4 The geriatric care workforce itself suffers from institutional vulnerabilities. Individuals are often underpaid, undertrained, and work within a system that continually experiences staffing shortages, high burnout, and consequently high levels of turnover.5,6 Recent immigrants and racial/ethnic minorities disproportionately make up this workforce, who often live in multigenerational households and work in multiple facilities to get by.7,8 Amid the pandemic these HCWs continued to work despite demoralizing negative media coverage of nursing homes.9 Notably, facilities with unionized staff were less likely to need second or third jobs to survive, thus reducing spread across facilities. This along with better access to PPE may have contributed to their lower COVID-19 infection and mortality rates relative to non-unionized staff.10
Similar to long-term care workers, home-care staff had related fears and anxieties, magnified by the need to enter multiple homes. This often overlooked but growing sector of the geriatric care workforce faced the added anxiety of the unknown as they entered multiple homes to provide care to their patients. These staff have little control over who may be in the home when they arrive, the sanitation/PPE practices of the patient/family, and therefore little control over their potential exposure to COVID-19. This also applies to home health aides who, although not providing medical services, are a critical part of home-care services and allow older adults to remain living independently in their home.
Reflection on Grief
As we witnessed the interactive effects of the pandemic and social inequities in geriatrics and palliative care, we frequently sought solace in online communities of psychologists working in similar settings. Over time, our regular community meetings developed a different tone: discussions about caring for others shifted to caring for ourselves. It seemed that in holding others’ pain, many of us neglected to address our own. We needed emotional support. We needed to acknowledge that we were not all okay; that the masks we wear for protection also reveal our vulnerabilities; and that protective equipment in hospitals do not protect us from the hate and bias targeting many of us face everywhere we go.
As we let ourselves be vulnerable with each other, we saw the true face of our pain: it was not stress, it was grief. We were sad, broken, mourning innumerable losses, and grieving, mostly alone. It felt overwhelming. Our minds and hearts often grew numb to find respite from pain. At times we found ourselves seeking haven in our offices, convincing ourselves that paperwork needed to be done when in reality we had no space to hold anyone else’s pain; we could barely contain our own. We could only take so much.
Without space to process, grief festers and eats away at our remaining compassion. How do we hold grace for ourselves, dare to be vulnerable, and allow ourselves to feel, when doing so opens the door to our own grief? How do we allow room for emotional processing when we learned to numb-out in order to function? And as women with diverse intersectional identities, how do we honor our humanity when we live in a society that reflects its indifference? We needed to process our pain in order to heal in the slow and uneven way that grief heals.
Caring During Tough Times
The pain we feel is real and it tears at us over time. Pushing it away disenfranchises ourselves of the opportunity to heal and grow. Our collective grief and trauma demand collective healing and acknowledgment of our individual suffering. We must honor our shared humanity and find commonality amid our differences. Typical self-care (healthy eating, sleep, basic hygiene) may not be enough to mitigate the enormity of these stressors. A glass of wine or a virtual dinner with friends may distract but does not heal our wounds.
Self-care, by definition, centers the self and ignores the larger systemic factors that maintain our struggles. It keeps the focus on the individual and in so doing, risks inducing self-blame should we continue feeling burnout. We must do more. We can advocate that systems acknowledge our grief and suffering as well as our strengths and resiliencies. We can demand that organizations recognize human limits and provide support, rather than promote environments that encourage silent perseverance. And we can deconstruct the cultural narrative that vulnerability is weakness or that we are the “heroes.” Heroism suggests superhuman qualities or extreme courage and often negates the fear and trepidation in its midst.11,12 We can also recognize how intersectional aspects of our identities make navigating the pandemic and systemic racism harder and more dangerous for some than for others.
As noted by President Biden in a speech honoring those lost to COVID-19, “We have to resist becoming numb to the sorrow.”13 The nature of our work (and that of most clinicians) is that it is expected and sometimes necessary to compartmentalize and turn off the emotions so that we can function in a professional manner. But this way of being also serves to hold us back. It does not make space for the very real emotions of trauma and grief that have pervaded HCWs during this pandemic. We must learn a different way of functioning—one where grief is acknowledged and even actively processed while still going about our work. Grief therapist Megan Devine proposes to “tend to pain and grief by bearing witness” and notes that “when we allow the reality of grief to exist, we can focus on helping ourselves—and one another—survive inside pain.”14 She advocates for self-compassion and directs us to “find ways to show our grief to others, in ways that honor the truth of our experience” saying, “we have to be willing to stop diminishing our own pain so that others can be comfortable around us.” But what does this look like among health care teams who are traumatized and grieving?
In our experience, caring for ourselves and our teams in times of prolonged stress, trauma, and grief is essential to maintain functioning over time. We strongly believe that it must occur at both the organizational and individual levels. In the throes of a crisis, teams need support immediately. To offer a timely response, we gathered knowledge of team-based care and collaboration to develop practical strategies that can be implemented swiftly to provide support across the team.15-19
The strategies we developed offer steps for creating and maintaining a supportive, compassionate, and psychologically safe work environment. First, the CARES Strategies for Practical Team Intervention highlights the importance of clear communication, assessing team needs regularly, recognizing the stress that is occurring, engaging staff in discussions, and ensuring psychological safety and comfort (Figure 1). Next, the SHARE approach is laid out to allow for interpersonal support among team members (Figure 2). Showing each other empathy, hoping for better days, acknowledging each other’s pain, reaching out for assistance, and expressing our needs allow HCWs to open up about their grief, stress, and trauma. Of note, we found these sets of strategies interdependent: a team that does not believe the leader/organization CARES is not likely to SHARE. Therefore, we also feel that it is especially important that team leaders work to create or enhance the sense of psychological safety for the team. If team members do not feel safe, they will not disclose their grief and remain stuck in the old mode of suffering in silence.
Conclusions
This pandemic and the collective efforts toward social justice advocacy have revealed our vulnerabilities as well as our strengths. These experiences have forced us to reckon with our past and consider possible futures. It has revealed the inequities in our health care system, including our failure to protect those on the ground who keep our systems running, and prompted us to consider new ways of operating in low-resourced and high-demand environments. These experiences also present us with opportunities to be better and do better as both professionals and people; to reflect on our past and consider what we want different in our lives. As we yearn for better days and brace ourselves for what is to come, we hope that teams and organizations will take advantage of these opportunities for self-reflection and continue unmasking our grief, healing our wounds, and honoring our shared humanity.
Since the start of the pandemic, health care systems have requested many in-services for staff on self-care and stress management to help health care workers (HCWs) cope with the heavy toll of COVID-19. The pandemic has set off a global mental health crisis, with unprecedented numbers of individuals meeting criteria for anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders in response to the intense stressors of living through a pandemic. These calls to assist staff with self-care and burnout prevention have been especially salient for psychologists working in palliative care and geriatrics, where fears of COVID-19 infection and numbers of patient deaths have been high.
Throughout these painful times, we have been grateful for an online community of palliative care psychologists within the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) from across the continuum of care and across the country. This community brought together many of us who were both struggling ourselves and striving to support the teams and HCWs around us. We are psychologists who provide home-care services in North Carolina, inpatient hospice and long-term care services in California, and long-term care and outpatient palliative care services in Massachusetts. Through our shared struggles and challenges navigating the pandemic, we realized that our respective teams requested similar services, all focused on staff support.
The psychological impact of COVID-19 on HCWs was clear from the beginning. Early in the pandemic our respective teams requested us to provide staff support and education about coping to our local HCWs. Soon national groups for long-term care staff requested education programs. Through this work, we realized that the emotional needs of HCWs ran much deeper than simple self-care. At the onset of the pandemic, before realizing its chronicity, the trainings we offered focused on stress and coping strategies. We cited several frameworks for staff support and eagerly shared anything that might help us, and our colleagues, survive the immediate anxiety and tumult surrounding us.1-3 In this paper, we briefly discuss the distress affecting the geriatric care workforce, reflect on our efforts to cope as HCWs, and offer recommendations at individual and organization levels to help address our collective grief.
Impact of COVID-19
As the death toll mounted and hospitals were pushed to the brink, we saw the suffering of our fellow HCWs. The lack of personal protective equipment (PPE) and testing supplies led to evolving and increasing anxiety for HCWs about contracting COVID-19, potentially spreading it to one’s social circle or family, fears of becoming sick and dying, and fears of inadvertently spreading the virus to medically-vulnerable patients. Increasing demands on staff required many to work outside their areas of expertise. Clinical practice guidelines changed frequently as information emerged about the virus. Staff members struggled to keep pace with the increasing number of patients, many of whom died despite heroic efforts to save them.
As the medical crisis grew, so too did social uprisings as the general public gained a strengthened awareness of the legacy and ongoing effects of systemic oppression, racism, and social inequities in the United States. Individuals grappled with their own privileges, which often hid such disparities from view. Many HCWs and clinicians of color had to navigate unsolicited questions and discussions about racial injustices while also trying to survive. As psychologists, we strove to support the HCWs around us while also struggling with our own stressors. As the magnitude of the pandemic and ongoing social injustices came into view, we realized that presentations on self-care and burnout prevention did not suffice. We needed discussions on unmasking our grief, acknowledging our traumas, and working toward collective healing.
Geriatric Care Workers
Experiences of grief and trauma hit the geriatric care workforce and especially long-term care facilities particularly hard given the high morbidity and mortality rates of COVID-19.4 The geriatric care workforce itself suffers from institutional vulnerabilities. Individuals are often underpaid, undertrained, and work within a system that continually experiences staffing shortages, high burnout, and consequently high levels of turnover.5,6 Recent immigrants and racial/ethnic minorities disproportionately make up this workforce, who often live in multigenerational households and work in multiple facilities to get by.7,8 Amid the pandemic these HCWs continued to work despite demoralizing negative media coverage of nursing homes.9 Notably, facilities with unionized staff were less likely to need second or third jobs to survive, thus reducing spread across facilities. This along with better access to PPE may have contributed to their lower COVID-19 infection and mortality rates relative to non-unionized staff.10
Similar to long-term care workers, home-care staff had related fears and anxieties, magnified by the need to enter multiple homes. This often overlooked but growing sector of the geriatric care workforce faced the added anxiety of the unknown as they entered multiple homes to provide care to their patients. These staff have little control over who may be in the home when they arrive, the sanitation/PPE practices of the patient/family, and therefore little control over their potential exposure to COVID-19. This also applies to home health aides who, although not providing medical services, are a critical part of home-care services and allow older adults to remain living independently in their home.
Reflection on Grief
As we witnessed the interactive effects of the pandemic and social inequities in geriatrics and palliative care, we frequently sought solace in online communities of psychologists working in similar settings. Over time, our regular community meetings developed a different tone: discussions about caring for others shifted to caring for ourselves. It seemed that in holding others’ pain, many of us neglected to address our own. We needed emotional support. We needed to acknowledge that we were not all okay; that the masks we wear for protection also reveal our vulnerabilities; and that protective equipment in hospitals do not protect us from the hate and bias targeting many of us face everywhere we go.
As we let ourselves be vulnerable with each other, we saw the true face of our pain: it was not stress, it was grief. We were sad, broken, mourning innumerable losses, and grieving, mostly alone. It felt overwhelming. Our minds and hearts often grew numb to find respite from pain. At times we found ourselves seeking haven in our offices, convincing ourselves that paperwork needed to be done when in reality we had no space to hold anyone else’s pain; we could barely contain our own. We could only take so much.
Without space to process, grief festers and eats away at our remaining compassion. How do we hold grace for ourselves, dare to be vulnerable, and allow ourselves to feel, when doing so opens the door to our own grief? How do we allow room for emotional processing when we learned to numb-out in order to function? And as women with diverse intersectional identities, how do we honor our humanity when we live in a society that reflects its indifference? We needed to process our pain in order to heal in the slow and uneven way that grief heals.
Caring During Tough Times
The pain we feel is real and it tears at us over time. Pushing it away disenfranchises ourselves of the opportunity to heal and grow. Our collective grief and trauma demand collective healing and acknowledgment of our individual suffering. We must honor our shared humanity and find commonality amid our differences. Typical self-care (healthy eating, sleep, basic hygiene) may not be enough to mitigate the enormity of these stressors. A glass of wine or a virtual dinner with friends may distract but does not heal our wounds.
Self-care, by definition, centers the self and ignores the larger systemic factors that maintain our struggles. It keeps the focus on the individual and in so doing, risks inducing self-blame should we continue feeling burnout. We must do more. We can advocate that systems acknowledge our grief and suffering as well as our strengths and resiliencies. We can demand that organizations recognize human limits and provide support, rather than promote environments that encourage silent perseverance. And we can deconstruct the cultural narrative that vulnerability is weakness or that we are the “heroes.” Heroism suggests superhuman qualities or extreme courage and often negates the fear and trepidation in its midst.11,12 We can also recognize how intersectional aspects of our identities make navigating the pandemic and systemic racism harder and more dangerous for some than for others.
As noted by President Biden in a speech honoring those lost to COVID-19, “We have to resist becoming numb to the sorrow.”13 The nature of our work (and that of most clinicians) is that it is expected and sometimes necessary to compartmentalize and turn off the emotions so that we can function in a professional manner. But this way of being also serves to hold us back. It does not make space for the very real emotions of trauma and grief that have pervaded HCWs during this pandemic. We must learn a different way of functioning—one where grief is acknowledged and even actively processed while still going about our work. Grief therapist Megan Devine proposes to “tend to pain and grief by bearing witness” and notes that “when we allow the reality of grief to exist, we can focus on helping ourselves—and one another—survive inside pain.”14 She advocates for self-compassion and directs us to “find ways to show our grief to others, in ways that honor the truth of our experience” saying, “we have to be willing to stop diminishing our own pain so that others can be comfortable around us.” But what does this look like among health care teams who are traumatized and grieving?
In our experience, caring for ourselves and our teams in times of prolonged stress, trauma, and grief is essential to maintain functioning over time. We strongly believe that it must occur at both the organizational and individual levels. In the throes of a crisis, teams need support immediately. To offer a timely response, we gathered knowledge of team-based care and collaboration to develop practical strategies that can be implemented swiftly to provide support across the team.15-19
The strategies we developed offer steps for creating and maintaining a supportive, compassionate, and psychologically safe work environment. First, the CARES Strategies for Practical Team Intervention highlights the importance of clear communication, assessing team needs regularly, recognizing the stress that is occurring, engaging staff in discussions, and ensuring psychological safety and comfort (Figure 1). Next, the SHARE approach is laid out to allow for interpersonal support among team members (Figure 2). Showing each other empathy, hoping for better days, acknowledging each other’s pain, reaching out for assistance, and expressing our needs allow HCWs to open up about their grief, stress, and trauma. Of note, we found these sets of strategies interdependent: a team that does not believe the leader/organization CARES is not likely to SHARE. Therefore, we also feel that it is especially important that team leaders work to create or enhance the sense of psychological safety for the team. If team members do not feel safe, they will not disclose their grief and remain stuck in the old mode of suffering in silence.
Conclusions
This pandemic and the collective efforts toward social justice advocacy have revealed our vulnerabilities as well as our strengths. These experiences have forced us to reckon with our past and consider possible futures. It has revealed the inequities in our health care system, including our failure to protect those on the ground who keep our systems running, and prompted us to consider new ways of operating in low-resourced and high-demand environments. These experiences also present us with opportunities to be better and do better as both professionals and people; to reflect on our past and consider what we want different in our lives. As we yearn for better days and brace ourselves for what is to come, we hope that teams and organizations will take advantage of these opportunities for self-reflection and continue unmasking our grief, healing our wounds, and honoring our shared humanity.
1. Blake H, Bermingham F. Psychological wellbeing for health care workers: mitigating the impact of covid-19. Version 2.0. Updated June 18, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/toolkits/play_22794
2. Harris R. FACE COVID: how to respond effectively to the corona crisis. Published 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. http://louisville.edu/counseling/coping-with-covid-19/face-covid-by-dr-russ-harris/view
3. Norcross JC, Phillips CM. Psychologist self-care during the pandemic: now more than ever [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 2]. J Health Serv Psychol. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1007/s42843-020-00010-5
4. Kaiser Family Foundation. State reports of long-term care facility cases and deaths related to COVID-19. 2020. Published April 23, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/state-reporting-of-cases-and-deaths-due-to-covid-19-in-long-term-care-facilities
5. Sterling MR, Tseng E, Poon A, et al. Experiences of home health care workers in New York City during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: a qualitative analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(11):1453-1459. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3930
6. Stone R, Wilhelm J, Bishop CE, Bryant NS, Hermer L, Squillace MR. Predictors of intent to leave the job among home health workers: analysis of the National Home Health Aide Survey. Gerontologist. 2017;57(5):890-899. doi:10.1093/geront/gnw075
7. Scales K. It’s time to care: a detailed profile of America’s direct care workforce. PHI. 2020. Published January 21, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://phinational.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Its-Time-to-Care-2020-PHI.pdf
8. Wolfe R, Harknett K, Schneider D. Inequities at work and the toll of COVID-19. Health Aff Health Policy Brief. Published June 4, 2021. doi: 10.1377/hpb20210428.863621
9. White EM, Wetle TF, Reddy A, Baier RR. Front-line nursing home staff experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic [published correction appears in J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021 May;22(5):1123]. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22(1):199-203. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.11.022
10. Dean A, Venkataramani A, Kimmel S. Mortality rates from COVID-19 are lower In unionized nursing homes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):1993-2001.doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.01011
11. Cox CL. ‘Healthcare Heroes’: problems with media focus on heroism from healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2020;46(8):510-513. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106398
12. Stokes-Parish J, Elliott R, Rolls K, Massey D. Angels and heroes: the unintended consequence of the hero narrative. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020;52(5):462-466. doi:10.1111/jnu.12591
13. Biden J. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 American lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19
14. Devine M. It’s Okay That You’re Not Okay: Meeting Grief and Loss in a Culture That Doesn’t Understand. Sounds True; 2017.
15. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Grief leadership during COVID-19. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Grief_Leadership_During_COVID19.pdf
16. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Sustaining the well-being of healthcare personnel during coronavirus and other infectious disease outbreaks. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Sustaining_Well_Being_Health care_Personnel_during.pdf
17. Fessell D, Cherniss C. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and beyond: micropractices for burnout prevention and emotional wellness. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17(6):746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.03.013
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for PTSD. Managing healthcare workers’ stress associated with the COVID-19 virus outbreak. Updated March 25, 2020, Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/covid/COVID_healthcare_workers.asp
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Organization Development (NCOD). Team Development Guide. 2017. https://vaww.va.gov/NCOD/docs/Team_Development_Guide.docx [Nonpublic source, not verified.]
1. Blake H, Bermingham F. Psychological wellbeing for health care workers: mitigating the impact of covid-19. Version 2.0. Updated June 18, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/toolkits/play_22794
2. Harris R. FACE COVID: how to respond effectively to the corona crisis. Published 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. http://louisville.edu/counseling/coping-with-covid-19/face-covid-by-dr-russ-harris/view
3. Norcross JC, Phillips CM. Psychologist self-care during the pandemic: now more than ever [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 2]. J Health Serv Psychol. 2020;1-5. doi:10.1007/s42843-020-00010-5
4. Kaiser Family Foundation. State reports of long-term care facility cases and deaths related to COVID-19. 2020. Published April 23, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/state-reporting-of-cases-and-deaths-due-to-covid-19-in-long-term-care-facilities
5. Sterling MR, Tseng E, Poon A, et al. Experiences of home health care workers in New York City during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: a qualitative analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2020;180(11):1453-1459. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3930
6. Stone R, Wilhelm J, Bishop CE, Bryant NS, Hermer L, Squillace MR. Predictors of intent to leave the job among home health workers: analysis of the National Home Health Aide Survey. Gerontologist. 2017;57(5):890-899. doi:10.1093/geront/gnw075
7. Scales K. It’s time to care: a detailed profile of America’s direct care workforce. PHI. 2020. Published January 21, 2020. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://phinational.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Its-Time-to-Care-2020-PHI.pdf
8. Wolfe R, Harknett K, Schneider D. Inequities at work and the toll of COVID-19. Health Aff Health Policy Brief. Published June 4, 2021. doi: 10.1377/hpb20210428.863621
9. White EM, Wetle TF, Reddy A, Baier RR. Front-line nursing home staff experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic [published correction appears in J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021 May;22(5):1123]. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021;22(1):199-203. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.11.022
10. Dean A, Venkataramani A, Kimmel S. Mortality rates from COVID-19 are lower In unionized nursing homes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(11):1993-2001.doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.01011
11. Cox CL. ‘Healthcare Heroes’: problems with media focus on heroism from healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Med Ethics. 2020;46(8):510-513. doi:10.1136/medethics-2020-106398
12. Stokes-Parish J, Elliott R, Rolls K, Massey D. Angels and heroes: the unintended consequence of the hero narrative. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2020;52(5):462-466. doi:10.1111/jnu.12591
13. Biden J. Remarks by President Biden on the more than 500,000 American lives lost to COVID-19. Published February 22, 2021. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/speeches-remarks/2021/02/22/remarks-by-president-biden-on-the-more-than-500000-american-lives-lost-to-covid-19
14. Devine M. It’s Okay That You’re Not Okay: Meeting Grief and Loss in a Culture That Doesn’t Understand. Sounds True; 2017.
15. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Grief leadership during COVID-19. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Grief_Leadership_During_COVID19.pdf
16. Center for the Study of Traumatic Stress. Sustaining the well-being of healthcare personnel during coronavirus and other infectious disease outbreaks. Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.cstsonline.org/assets/media/documents/CSTS_FS_Sustaining_Well_Being_Health care_Personnel_during.pdf
17. Fessell D, Cherniss C. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and beyond: micropractices for burnout prevention and emotional wellness. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17(6):746-748. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.03.013
18. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for PTSD. Managing healthcare workers’ stress associated with the COVID-19 virus outbreak. Updated March 25, 2020, Accessed October 12, 2021. https://www.ptsd.va.gov/covid/COVID_healthcare_workers.asp
19. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, National Center for Organization Development (NCOD). Team Development Guide. 2017. https://vaww.va.gov/NCOD/docs/Team_Development_Guide.docx [Nonpublic source, not verified.]
Updated MELD score adds serum albumin, female sex
A newly updated version of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was effective for predicting short-term mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease and addressed important determinants of wait list outcomes that haven’t been addressed in previous versions, according to findings from a recent study. The new model, termed MELD 3.0, includes new variables such as female sex, serum albumin, and updated creatinine cutoffs.
“We believe that the new model represents an opportunity to lower wait list mortality in the United States and propose it to be considered to replace the current version of MELD in determining allocation priorities in liver transplantation,” wrote study authors W. Ray Kim, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and colleagues in Gastroenterology.
In patients with end-stage liver disease, the MELD score was shown to be a reliable predictor of short-term survival, according to the researchers. The original version of MELD consists of international normalized ratio of prothrombin time and serum concentrations of bilirubin and creatinine; MELDNa consists of the same with the addition of serum concentrations of total sodium. Since 2016, MELDNa has been utilized in the United States to allocate livers for transplant.
Despite the utility of the current MELD score, questions have been raised concerning the accuracy of the tool’s ability to predict mortality, including a study by Sumeet K. Asrani, MD, MSc, and colleagues. Changes in liver disease epidemiology, the introduction of newer therapies that alter prognosis, as well as increasing age and prevalence of comorbidities in transplant-eligible patients are several drivers for these concerns, according to Dr. Kim and colleagues. Also, there is an increasing concern regarding women and their potential disadvantages in the current system: At least one study has suggested that serum creatinine may overestimate renal function and consequently underestimate mortality risk in female patients, compared with men with the same creatinine level.
Dr. Kim and colleagues sought to further optimize the fit of the current MELD score by considering alternative interactions and including other variables relevant to predicting short-term mortality in patients awaiting liver transplant. The study included patients who are registered on the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network Standard Transplant Analysis and Research files newly wait-listed from 2016 through 2018. The full cohort was divided 70:30 into a development set (n = 20,587) and a validation set (n = 8,823); there were no significant differences between the sets in respect to age, sex, race, or liver disease severity.
The investigators used univariable and multivariable regression models to predict 90-day survival following wait list registration. The 90-day Kaplan-Meier survival rate in the development set was 91.3%. Additionally, model fit was tested, and the investigators used the Liver Simulated Allocation Model to estimate the impact of replacing the current version of the MELD with MELD 3.0.
In the final MELD 3.0 model, the researchers included several additional variables such as female sex and serum albumin. Additionally, the final model was characterized by interactions between bilirubin and sodium as well as between albumin and creatinine. Also, an adjustment to the current version of MELD lowering the upper bound for creatinine from 4.0 mg/dL to 3.0 mg/dL.
The MELD 3.0 featured significantly better discrimination, compared with the MELDNa (C-statistic = 0.8693 vs. 0.8622, respectively; P < .01). In addition, the researchers wrote that the new MELD 3.0 score “correctly reclassified a net of 8.8% of decedents to a higher MELD tier, affording them a meaningfully higher chance of transplantation, particularly in women.” The MELD 3.0 score with albumin also led to fewer wait-list deaths, compared with the MELDNa, according to the Liver Simulated Allocation Model analysis (P = .02); the number for MELD 3.0 without albumin was not statistically significant.
According to the investigators, a cause of concern for the MELD 3.0 was the addition of albumin, as this variable may be vulnerable to manipulation. In addition, the researchers note that, while differences in wait list mortality and survival based on race/ethnicity were observed in the study, they were unable to describe the exact root causes of worse outcomes among patients belonging to minority groups. “Thus, inclusion in a risk prediction score without fully understanding the underlying reasons for the racial disparity may have unintended consequences,” the researchers wrote.
“Based on recent data consisting of liver transplant candidates in the United States, we identify additional variables that are meaningfully associated with short-term mortality, including female sex and serum albumin. We also found evidence to support lowering the serum creatinine ceiling to 3 mg/dL,” they wrote. “Based on these data, we created an updated version of the MELD score, which improves mortality prediction compared to the current MELDNa model, including the recognition of female sex as a risk factor for death.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry. No funding was reported for the study.
Introduction of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in 2002, consisting of objective measurements of creatinine, bilirubin, and international normalized ratio, revolutionized liver allocation in the United States. To minimize patient wait-list mortality and reduce geographic variability, further improvements to allocation system including the National Share for status 1 and Regional Share for MELD score greater than 35 in 2013, adoption of MELDNa score in 2016, and most recently the introduction of the Acuity Circles distribution system were implemented. Unfortunately, MELD tends to disadvantage women whose lower muscle mass translates to lower normal creatinine levels thereby underestimating the degree of renal dysfunction and wait-list mortality. MELD performance characteristics were also shown to be less accurate in patients with alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease when compared with patients with hepatitis C, likely contributing to MELD’s decreasing accuracy in predicting mortality over the years with changing patient population.
Alexandra Shingina, MD, MSc, is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has no conflicts.
Introduction of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in 2002, consisting of objective measurements of creatinine, bilirubin, and international normalized ratio, revolutionized liver allocation in the United States. To minimize patient wait-list mortality and reduce geographic variability, further improvements to allocation system including the National Share for status 1 and Regional Share for MELD score greater than 35 in 2013, adoption of MELDNa score in 2016, and most recently the introduction of the Acuity Circles distribution system were implemented. Unfortunately, MELD tends to disadvantage women whose lower muscle mass translates to lower normal creatinine levels thereby underestimating the degree of renal dysfunction and wait-list mortality. MELD performance characteristics were also shown to be less accurate in patients with alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease when compared with patients with hepatitis C, likely contributing to MELD’s decreasing accuracy in predicting mortality over the years with changing patient population.
Alexandra Shingina, MD, MSc, is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has no conflicts.
Introduction of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in 2002, consisting of objective measurements of creatinine, bilirubin, and international normalized ratio, revolutionized liver allocation in the United States. To minimize patient wait-list mortality and reduce geographic variability, further improvements to allocation system including the National Share for status 1 and Regional Share for MELD score greater than 35 in 2013, adoption of MELDNa score in 2016, and most recently the introduction of the Acuity Circles distribution system were implemented. Unfortunately, MELD tends to disadvantage women whose lower muscle mass translates to lower normal creatinine levels thereby underestimating the degree of renal dysfunction and wait-list mortality. MELD performance characteristics were also shown to be less accurate in patients with alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease when compared with patients with hepatitis C, likely contributing to MELD’s decreasing accuracy in predicting mortality over the years with changing patient population.
Alexandra Shingina, MD, MSc, is an assistant professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn. She has no conflicts.
A newly updated version of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was effective for predicting short-term mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease and addressed important determinants of wait list outcomes that haven’t been addressed in previous versions, according to findings from a recent study. The new model, termed MELD 3.0, includes new variables such as female sex, serum albumin, and updated creatinine cutoffs.
“We believe that the new model represents an opportunity to lower wait list mortality in the United States and propose it to be considered to replace the current version of MELD in determining allocation priorities in liver transplantation,” wrote study authors W. Ray Kim, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and colleagues in Gastroenterology.
In patients with end-stage liver disease, the MELD score was shown to be a reliable predictor of short-term survival, according to the researchers. The original version of MELD consists of international normalized ratio of prothrombin time and serum concentrations of bilirubin and creatinine; MELDNa consists of the same with the addition of serum concentrations of total sodium. Since 2016, MELDNa has been utilized in the United States to allocate livers for transplant.
Despite the utility of the current MELD score, questions have been raised concerning the accuracy of the tool’s ability to predict mortality, including a study by Sumeet K. Asrani, MD, MSc, and colleagues. Changes in liver disease epidemiology, the introduction of newer therapies that alter prognosis, as well as increasing age and prevalence of comorbidities in transplant-eligible patients are several drivers for these concerns, according to Dr. Kim and colleagues. Also, there is an increasing concern regarding women and their potential disadvantages in the current system: At least one study has suggested that serum creatinine may overestimate renal function and consequently underestimate mortality risk in female patients, compared with men with the same creatinine level.
Dr. Kim and colleagues sought to further optimize the fit of the current MELD score by considering alternative interactions and including other variables relevant to predicting short-term mortality in patients awaiting liver transplant. The study included patients who are registered on the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network Standard Transplant Analysis and Research files newly wait-listed from 2016 through 2018. The full cohort was divided 70:30 into a development set (n = 20,587) and a validation set (n = 8,823); there were no significant differences between the sets in respect to age, sex, race, or liver disease severity.
The investigators used univariable and multivariable regression models to predict 90-day survival following wait list registration. The 90-day Kaplan-Meier survival rate in the development set was 91.3%. Additionally, model fit was tested, and the investigators used the Liver Simulated Allocation Model to estimate the impact of replacing the current version of the MELD with MELD 3.0.
In the final MELD 3.0 model, the researchers included several additional variables such as female sex and serum albumin. Additionally, the final model was characterized by interactions between bilirubin and sodium as well as between albumin and creatinine. Also, an adjustment to the current version of MELD lowering the upper bound for creatinine from 4.0 mg/dL to 3.0 mg/dL.
The MELD 3.0 featured significantly better discrimination, compared with the MELDNa (C-statistic = 0.8693 vs. 0.8622, respectively; P < .01). In addition, the researchers wrote that the new MELD 3.0 score “correctly reclassified a net of 8.8% of decedents to a higher MELD tier, affording them a meaningfully higher chance of transplantation, particularly in women.” The MELD 3.0 score with albumin also led to fewer wait-list deaths, compared with the MELDNa, according to the Liver Simulated Allocation Model analysis (P = .02); the number for MELD 3.0 without albumin was not statistically significant.
According to the investigators, a cause of concern for the MELD 3.0 was the addition of albumin, as this variable may be vulnerable to manipulation. In addition, the researchers note that, while differences in wait list mortality and survival based on race/ethnicity were observed in the study, they were unable to describe the exact root causes of worse outcomes among patients belonging to minority groups. “Thus, inclusion in a risk prediction score without fully understanding the underlying reasons for the racial disparity may have unintended consequences,” the researchers wrote.
“Based on recent data consisting of liver transplant candidates in the United States, we identify additional variables that are meaningfully associated with short-term mortality, including female sex and serum albumin. We also found evidence to support lowering the serum creatinine ceiling to 3 mg/dL,” they wrote. “Based on these data, we created an updated version of the MELD score, which improves mortality prediction compared to the current MELDNa model, including the recognition of female sex as a risk factor for death.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry. No funding was reported for the study.
A newly updated version of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was effective for predicting short-term mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease and addressed important determinants of wait list outcomes that haven’t been addressed in previous versions, according to findings from a recent study. The new model, termed MELD 3.0, includes new variables such as female sex, serum albumin, and updated creatinine cutoffs.
“We believe that the new model represents an opportunity to lower wait list mortality in the United States and propose it to be considered to replace the current version of MELD in determining allocation priorities in liver transplantation,” wrote study authors W. Ray Kim, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University and colleagues in Gastroenterology.
In patients with end-stage liver disease, the MELD score was shown to be a reliable predictor of short-term survival, according to the researchers. The original version of MELD consists of international normalized ratio of prothrombin time and serum concentrations of bilirubin and creatinine; MELDNa consists of the same with the addition of serum concentrations of total sodium. Since 2016, MELDNa has been utilized in the United States to allocate livers for transplant.
Despite the utility of the current MELD score, questions have been raised concerning the accuracy of the tool’s ability to predict mortality, including a study by Sumeet K. Asrani, MD, MSc, and colleagues. Changes in liver disease epidemiology, the introduction of newer therapies that alter prognosis, as well as increasing age and prevalence of comorbidities in transplant-eligible patients are several drivers for these concerns, according to Dr. Kim and colleagues. Also, there is an increasing concern regarding women and their potential disadvantages in the current system: At least one study has suggested that serum creatinine may overestimate renal function and consequently underestimate mortality risk in female patients, compared with men with the same creatinine level.
Dr. Kim and colleagues sought to further optimize the fit of the current MELD score by considering alternative interactions and including other variables relevant to predicting short-term mortality in patients awaiting liver transplant. The study included patients who are registered on the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network Standard Transplant Analysis and Research files newly wait-listed from 2016 through 2018. The full cohort was divided 70:30 into a development set (n = 20,587) and a validation set (n = 8,823); there were no significant differences between the sets in respect to age, sex, race, or liver disease severity.
The investigators used univariable and multivariable regression models to predict 90-day survival following wait list registration. The 90-day Kaplan-Meier survival rate in the development set was 91.3%. Additionally, model fit was tested, and the investigators used the Liver Simulated Allocation Model to estimate the impact of replacing the current version of the MELD with MELD 3.0.
In the final MELD 3.0 model, the researchers included several additional variables such as female sex and serum albumin. Additionally, the final model was characterized by interactions between bilirubin and sodium as well as between albumin and creatinine. Also, an adjustment to the current version of MELD lowering the upper bound for creatinine from 4.0 mg/dL to 3.0 mg/dL.
The MELD 3.0 featured significantly better discrimination, compared with the MELDNa (C-statistic = 0.8693 vs. 0.8622, respectively; P < .01). In addition, the researchers wrote that the new MELD 3.0 score “correctly reclassified a net of 8.8% of decedents to a higher MELD tier, affording them a meaningfully higher chance of transplantation, particularly in women.” The MELD 3.0 score with albumin also led to fewer wait-list deaths, compared with the MELDNa, according to the Liver Simulated Allocation Model analysis (P = .02); the number for MELD 3.0 without albumin was not statistically significant.
According to the investigators, a cause of concern for the MELD 3.0 was the addition of albumin, as this variable may be vulnerable to manipulation. In addition, the researchers note that, while differences in wait list mortality and survival based on race/ethnicity were observed in the study, they were unable to describe the exact root causes of worse outcomes among patients belonging to minority groups. “Thus, inclusion in a risk prediction score without fully understanding the underlying reasons for the racial disparity may have unintended consequences,” the researchers wrote.
“Based on recent data consisting of liver transplant candidates in the United States, we identify additional variables that are meaningfully associated with short-term mortality, including female sex and serum albumin. We also found evidence to support lowering the serum creatinine ceiling to 3 mg/dL,” they wrote. “Based on these data, we created an updated version of the MELD score, which improves mortality prediction compared to the current MELDNa model, including the recognition of female sex as a risk factor for death.”
The researchers reported no conflicts of interest with the pharmaceutical industry. No funding was reported for the study.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
Hospitalist movers and shakers - November 2021
Vineet Chopra, MD, MSc, FHM, recently became chair of the Department of Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora. He had previously been the chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Michigan Health system. He assumed his new role in October 2021.
Dr. Chopra, who specializes in research and mentorship in patient safety, helped create innovations in care delivery at the University of Michigan, including direct care hospitalist services at VA Ann Arbor Health Care and two other community hospitals.
In his safety-conscious research, Dr. Chopra focuses on preventing complications created within the hospital environment. He also is the first hospitalist to be named deputy editor of the Annals of Internal Medicine. He has written more than 250 peer-reviewed articles. Among the myriad awards he has received, Dr. Chopra recently earned the Kaiser Permanente Award for Clinical Teaching at the UM School of Medicine.
Steve Phillipson, MD, FHM, has been named regional director of hospital medicine at Aspirus Health (Wausau, Wisc.). Dr. Phillipson will oversee the hospitalist programs at 17 Aspirus hospitals in Wisconsin and Michigan.
Dr. Phillipson has worked with Aspirus since 2009, with stints in the emergency department and as a hospitalist. As Aspirus Wausau Hospital director of medicine, he chaired the facility’s COVID-19 treatment team.
Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian University Medical Center has hired Patricia (Patti) L. Fisher, MD, MHA, to be the institution’s chief medical officer. Dr. Fisher joined the medical center from Central Vermont Medical Center where she served as chief medical officer and chief safety officer, with direct oversight of hospital risk management, operations of all hospital-based services, IS services and quality including patient safety and regulatory compliance.
As a board-certified hospitalist, Dr. Fisher also served as clinical assistant professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fisher earned her medical degree from The University of Texas in Houston and completed residency through Forbes Family Practice Residency in Pittsburgh.
Martin Chaney, MD, has been chosen by the Maury Regional Health Board of Trustees to serve as interim chief executive officer. He was formerly the chief medical officer at MRH, which is based in Columbia, Tenn. Dr. Chaney began his new role in October, replacing Alan Watson, the CEO since 2012.
Dr. Chaney has spent 18 of his 25 years in medicine with MRH, where most recently he has focused on clinical quality, physician recruitment, and establishing and expanding the hospital medicine program.
Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM, has been placed on Modern Healthcare’s Top 25 Innovators list for 2021, getting recognized for innovation and leadership in creating value and safety initiatives in New York City’s public health system. Dr. Cho became NYC Health + Hospitals’ first chief value officer in 2019, and his programs have created an estimated $11 million in savings per year by preventing unnecessary testing and treatment that can lead to patient harm.
A member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s editorial advisory board, Dr. Cho is also SHM’s hospitalist liaison with the COVID-19 Real-Time Learning Network, which collaborates with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Raymond Kiser, MD, a hospitalist and nephrologist at Columbus (Ind.) Regional Health, has been named the Douglas J. Leonard Caregiver of the Year. The award is given by the Indiana Hospital Association to health care workers whose care is considered exemplary by both peers and patients.
Dr. Kiser has been with CRH for 7 years, including stints as associate chief medical officer and chief of staff.
Justin Buchholz, DO, has been elevated to medical director of the hospitalist teams at Regional Medical Center (Alamosa, Colo.) and Conejos County Hospital (La Jara, Colo.). Dr. Buchholz has been a full-time hospitalist and assistant medical director at Parkview Medical Center (Pueblo, Colo.) for the past 3 years. He also worked on a part-time basis seeing patients at the Regional Medical Center.
Dr. Buchholz completed his residency at Parkview Medical Center and was named Resident of the Year in his final year with the internal medicine program.
Kenneth Mishark, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist with the Mayo Clinic Hospital (Tucson, Ariz.), will serve on the board of directors for Anigent, a drug diversion-prevention company based in Chesterfield, Mo. He will be charged with helping Anigent better serve health systems with its drug-diversion software.
Dr. Mishark is vice-chair of diversion prevention across the whole Mayo Clinic. A one-time physician in the United States Air Force, Dr. Mishark previously has been the Mayo Clinic’s Healthcare Information Coordination Committee chair.
Core Clinical Partners (Tulsa, Okla.) has announced it will join with Hillcrest HealthCare System (Tulsa, Okla.) to provide hospitalist services to Hillcrest’s eight sites across Oklahoma. The partnership will begin at four locations in December 2021, and four others in March 2022.
In expanding its services, Core Clinical Partners will create 70 new physician positions, as well as a systemwide medical director. Core will manage hospitalist operations at Hillcrest Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital South, Hillcrest Hospital Pryor, Hillcrest Hospital Claremore, Bailey Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital Cushing, Hillcrest Hospital Henryetta, and Tulsa Spine and Specialty Hospital.
Vineet Chopra, MD, MSc, FHM, recently became chair of the Department of Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora. He had previously been the chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Michigan Health system. He assumed his new role in October 2021.
Dr. Chopra, who specializes in research and mentorship in patient safety, helped create innovations in care delivery at the University of Michigan, including direct care hospitalist services at VA Ann Arbor Health Care and two other community hospitals.
In his safety-conscious research, Dr. Chopra focuses on preventing complications created within the hospital environment. He also is the first hospitalist to be named deputy editor of the Annals of Internal Medicine. He has written more than 250 peer-reviewed articles. Among the myriad awards he has received, Dr. Chopra recently earned the Kaiser Permanente Award for Clinical Teaching at the UM School of Medicine.
Steve Phillipson, MD, FHM, has been named regional director of hospital medicine at Aspirus Health (Wausau, Wisc.). Dr. Phillipson will oversee the hospitalist programs at 17 Aspirus hospitals in Wisconsin and Michigan.
Dr. Phillipson has worked with Aspirus since 2009, with stints in the emergency department and as a hospitalist. As Aspirus Wausau Hospital director of medicine, he chaired the facility’s COVID-19 treatment team.
Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian University Medical Center has hired Patricia (Patti) L. Fisher, MD, MHA, to be the institution’s chief medical officer. Dr. Fisher joined the medical center from Central Vermont Medical Center where she served as chief medical officer and chief safety officer, with direct oversight of hospital risk management, operations of all hospital-based services, IS services and quality including patient safety and regulatory compliance.
As a board-certified hospitalist, Dr. Fisher also served as clinical assistant professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fisher earned her medical degree from The University of Texas in Houston and completed residency through Forbes Family Practice Residency in Pittsburgh.
Martin Chaney, MD, has been chosen by the Maury Regional Health Board of Trustees to serve as interim chief executive officer. He was formerly the chief medical officer at MRH, which is based in Columbia, Tenn. Dr. Chaney began his new role in October, replacing Alan Watson, the CEO since 2012.
Dr. Chaney has spent 18 of his 25 years in medicine with MRH, where most recently he has focused on clinical quality, physician recruitment, and establishing and expanding the hospital medicine program.
Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM, has been placed on Modern Healthcare’s Top 25 Innovators list for 2021, getting recognized for innovation and leadership in creating value and safety initiatives in New York City’s public health system. Dr. Cho became NYC Health + Hospitals’ first chief value officer in 2019, and his programs have created an estimated $11 million in savings per year by preventing unnecessary testing and treatment that can lead to patient harm.
A member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s editorial advisory board, Dr. Cho is also SHM’s hospitalist liaison with the COVID-19 Real-Time Learning Network, which collaborates with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Raymond Kiser, MD, a hospitalist and nephrologist at Columbus (Ind.) Regional Health, has been named the Douglas J. Leonard Caregiver of the Year. The award is given by the Indiana Hospital Association to health care workers whose care is considered exemplary by both peers and patients.
Dr. Kiser has been with CRH for 7 years, including stints as associate chief medical officer and chief of staff.
Justin Buchholz, DO, has been elevated to medical director of the hospitalist teams at Regional Medical Center (Alamosa, Colo.) and Conejos County Hospital (La Jara, Colo.). Dr. Buchholz has been a full-time hospitalist and assistant medical director at Parkview Medical Center (Pueblo, Colo.) for the past 3 years. He also worked on a part-time basis seeing patients at the Regional Medical Center.
Dr. Buchholz completed his residency at Parkview Medical Center and was named Resident of the Year in his final year with the internal medicine program.
Kenneth Mishark, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist with the Mayo Clinic Hospital (Tucson, Ariz.), will serve on the board of directors for Anigent, a drug diversion-prevention company based in Chesterfield, Mo. He will be charged with helping Anigent better serve health systems with its drug-diversion software.
Dr. Mishark is vice-chair of diversion prevention across the whole Mayo Clinic. A one-time physician in the United States Air Force, Dr. Mishark previously has been the Mayo Clinic’s Healthcare Information Coordination Committee chair.
Core Clinical Partners (Tulsa, Okla.) has announced it will join with Hillcrest HealthCare System (Tulsa, Okla.) to provide hospitalist services to Hillcrest’s eight sites across Oklahoma. The partnership will begin at four locations in December 2021, and four others in March 2022.
In expanding its services, Core Clinical Partners will create 70 new physician positions, as well as a systemwide medical director. Core will manage hospitalist operations at Hillcrest Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital South, Hillcrest Hospital Pryor, Hillcrest Hospital Claremore, Bailey Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital Cushing, Hillcrest Hospital Henryetta, and Tulsa Spine and Specialty Hospital.
Vineet Chopra, MD, MSc, FHM, recently became chair of the Department of Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora. He had previously been the chief of the Division of Hospital Medicine at the University of Michigan Health system. He assumed his new role in October 2021.
Dr. Chopra, who specializes in research and mentorship in patient safety, helped create innovations in care delivery at the University of Michigan, including direct care hospitalist services at VA Ann Arbor Health Care and two other community hospitals.
In his safety-conscious research, Dr. Chopra focuses on preventing complications created within the hospital environment. He also is the first hospitalist to be named deputy editor of the Annals of Internal Medicine. He has written more than 250 peer-reviewed articles. Among the myriad awards he has received, Dr. Chopra recently earned the Kaiser Permanente Award for Clinical Teaching at the UM School of Medicine.
Steve Phillipson, MD, FHM, has been named regional director of hospital medicine at Aspirus Health (Wausau, Wisc.). Dr. Phillipson will oversee the hospitalist programs at 17 Aspirus hospitals in Wisconsin and Michigan.
Dr. Phillipson has worked with Aspirus since 2009, with stints in the emergency department and as a hospitalist. As Aspirus Wausau Hospital director of medicine, he chaired the facility’s COVID-19 treatment team.
Hackensack (N.J.) Meridian University Medical Center has hired Patricia (Patti) L. Fisher, MD, MHA, to be the institution’s chief medical officer. Dr. Fisher joined the medical center from Central Vermont Medical Center where she served as chief medical officer and chief safety officer, with direct oversight of hospital risk management, operations of all hospital-based services, IS services and quality including patient safety and regulatory compliance.
As a board-certified hospitalist, Dr. Fisher also served as clinical assistant professor in the Department of Family Medicine at the University of Vermont, Burlington. Dr. Fisher earned her medical degree from The University of Texas in Houston and completed residency through Forbes Family Practice Residency in Pittsburgh.
Martin Chaney, MD, has been chosen by the Maury Regional Health Board of Trustees to serve as interim chief executive officer. He was formerly the chief medical officer at MRH, which is based in Columbia, Tenn. Dr. Chaney began his new role in October, replacing Alan Watson, the CEO since 2012.
Dr. Chaney has spent 18 of his 25 years in medicine with MRH, where most recently he has focused on clinical quality, physician recruitment, and establishing and expanding the hospital medicine program.
Hyung (Harry) Cho, MD, SFHM, has been placed on Modern Healthcare’s Top 25 Innovators list for 2021, getting recognized for innovation and leadership in creating value and safety initiatives in New York City’s public health system. Dr. Cho became NYC Health + Hospitals’ first chief value officer in 2019, and his programs have created an estimated $11 million in savings per year by preventing unnecessary testing and treatment that can lead to patient harm.
A member of the Society of Hospital Medicine’s editorial advisory board, Dr. Cho is also SHM’s hospitalist liaison with the COVID-19 Real-Time Learning Network, which collaborates with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Raymond Kiser, MD, a hospitalist and nephrologist at Columbus (Ind.) Regional Health, has been named the Douglas J. Leonard Caregiver of the Year. The award is given by the Indiana Hospital Association to health care workers whose care is considered exemplary by both peers and patients.
Dr. Kiser has been with CRH for 7 years, including stints as associate chief medical officer and chief of staff.
Justin Buchholz, DO, has been elevated to medical director of the hospitalist teams at Regional Medical Center (Alamosa, Colo.) and Conejos County Hospital (La Jara, Colo.). Dr. Buchholz has been a full-time hospitalist and assistant medical director at Parkview Medical Center (Pueblo, Colo.) for the past 3 years. He also worked on a part-time basis seeing patients at the Regional Medical Center.
Dr. Buchholz completed his residency at Parkview Medical Center and was named Resident of the Year in his final year with the internal medicine program.
Kenneth Mishark, MD, SFHM, a hospitalist with the Mayo Clinic Hospital (Tucson, Ariz.), will serve on the board of directors for Anigent, a drug diversion-prevention company based in Chesterfield, Mo. He will be charged with helping Anigent better serve health systems with its drug-diversion software.
Dr. Mishark is vice-chair of diversion prevention across the whole Mayo Clinic. A one-time physician in the United States Air Force, Dr. Mishark previously has been the Mayo Clinic’s Healthcare Information Coordination Committee chair.
Core Clinical Partners (Tulsa, Okla.) has announced it will join with Hillcrest HealthCare System (Tulsa, Okla.) to provide hospitalist services to Hillcrest’s eight sites across Oklahoma. The partnership will begin at four locations in December 2021, and four others in March 2022.
In expanding its services, Core Clinical Partners will create 70 new physician positions, as well as a systemwide medical director. Core will manage hospitalist operations at Hillcrest Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital South, Hillcrest Hospital Pryor, Hillcrest Hospital Claremore, Bailey Medical Center, Hillcrest Hospital Cushing, Hillcrest Hospital Henryetta, and Tulsa Spine and Specialty Hospital.
Detransitioners received poor evaluation when transitioning
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over half of people who believed they were transgender, transitioned to the opposite sex, but then regretted it and transitioned back – known as detransitioners – felt they did not receive adequate evaluation from a doctor or mental health professional before starting transition, new research indicates.
In what is thought to be the first study to ask whether detransitioners informed their original clinicians of their regret at transitioning, only 24 of the 100 surveyed said they had done so.
This strongly suggests that records on detransition may understate the real numbers, said Lisa Littman, MD, MPH, president of The Institute for Comprehensive Gender Dysphoria Research (ICGDR), who is the sole author of the study, published in Archives of Sexual Behavior.
She stressed that the findings illustrate the complexity surrounding gender dysphoria. “We need to recognize that there are many different types of experiences around gender dysphoria, transition, and detransition,” she told this news organization.
She said there is some resistance among certain health care professionals, and in society in general, to the idea that transitioning is not always successful.
‘We need to understand why this is happening’
“Detransition exists and we need to understand why this is happening,” Dr. Littman emphasized.
She observed that some supporters of “rapid transition” do not want to accept that transitioning helps some individuals but harms others.
“In the end, our goals should be providing the right treatment for the right patient, and without a thorough evaluation, clinicians are at serious risk of giving patients the wrong treatment,” she urged.
She noted that, despite some individuals feeling better after transition, these people still felt inclined to detransition because of discrimination and pressure.
“Individuals should not be pressured to detransition, nor should they be pressured to transition. Both types of pressure were reported by respondents.”
The recently recognized shift from mostly natal males to natal females seeking to transition was borne out by her study data, with the proportion of natal girls who detransitioned at 69%.
‘Shedding light’ on often ignored population
Asked to comment on the study, Laura Edwards-Leeper, PhD, a clinical psychologist from Beaverton, Ore., who specializes in gender-diverse and transgender children, welcomed Dr. Littman’s study.
It is, said Dr. Edwards-Leeper, a “critical preliminary step toward shedding light on this often-ignored and dismissed population of individuals who deserve support, compassion, and sometimes medical intervention from health care providers.”
She added that multiple online reports attest to detransitioners feeling they had not received adequate evaluation prior to medically transitioning, as well as many who expressed feeling too ashamed or angry to return to their same clinicians to detransition.
“Littman’s study provides quantitative support for both of these reported experiences, further emphasizing the importance of the field taking a closer look at the processes currently in place for those experiencing gender dysphoria,” said Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
And Miroslav L. Djordjevic, MD, PhD, professor of surgery/urology, University of Belgrade (Serbia), who is a specialist in urogenital reconstructive surgery and has performed over 2,000 gender-reassignment surgeries in transgender individuals, has recently seen many cases of regret after such surgeries, with requests for reversal operations.
“Despite the fact that medical detransition is relatively safe and without severe consequences, surgical detransition presents one of the most difficult issues in transgender medicine,” Dr. Djordjevic told this news organization.
Commending Dr. Littman on her study, he drew attention to some of the bioethical questions that arise relating to those who detransition.
“I ask what happened in the period before medical transitioning? Was there proper psychological care during medical transitioning? Who confirmed their desire for detransition – the same professionals who did the transition?” or someone else, he continued. “And who accepted these individuals for gender-affirming surgery and what were the criteria for this decision?”
Substantial study of reasons for both transitioning and detransitioning
In her article, Dr. Littman describes a 100-strong population of individuals (66 Americans, 9 British, 9 Canadian, 4 Australians, and 12 from “other” nations), ranging in age from 18 years to over 60 years with a mean age of 29.2 years, who had experienced gender dysphoria, chosen to undergo medical and/or surgical transition, and then detransitioned by discontinuing medications, having reversal surgery, or both.
Participants completed a 115-question survey providing data including age at first experience of gender dysphoria, when participants first sought transitioning care and from whom, and whether they felt pressured to do so. Friendship group dynamics were also explored.
Various narratives of participants’ transitioning-detransitioning experiences were gathered and grouped, for example, those related to discrimination pressures, experiences of trauma or mental health conditions prior to transition, and reports of internalized homophobia.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper observed that the study offers a more extensive assessment of reasons for detransitioning than any other prior research in the field, which has been sparse.
A survey published in April found that detransitioners report significant unmet medical and psychological needs, and a lack of compassion and help from medical and mental health practitioners.
But another 2021 study concluded most detransitioners only reverted to their birth sex because of societal or family pressure, discrimination, or shift to a nonbinary identity.
“However, [Dr.] Littman’s study found that only a small percentage actually detransitioned for that reason [23%], whereas the majority detransitioned because of a change in how the individual understood being a male or female, resulting in becoming comfortable in their assigned gender [60%],” noted Dr. Edwards-Leeper.
Reasons for detransitioning
Asked to expand upon the motives for detransition identified in her study, Dr. Littman told this news organization: “We found remarkable breadth in the reasons given for detransitioning.”
“I believe that we were able to capture the diversity of experiences around detransition because we reached out to communities that were strongly ‘protransition’ – like the World Professional Association for Transgender Health – and communities where individuals might be more skeptical about transition being universally beneficial, like detransition forums,” she said.
Speaking to the complexity of the experiences, 87% selected more than one reason for detransitioning.
The most common reason (60%) was becoming more comfortable identifying with their birth sex, followed by having concerns about potential medical complications from transitioning (49.0%).
Regarding those who became more comfortable with their natal sex, Dr. Littman noted that the finding adds “further support that gender dysphoria is not always permanent.”
She added that, “because most gender-dysphoric youth who are allowed to go through puberty grow up to be lesbian, gay, or bisexual (LGB) nontransgender adults, intervening too soon with medical treatments risks derailing their development as LGB individuals.”
Internalized homophobia or difficulty accepting themselves as lesbian, gay, or bisexual was reported by 23% of participants as a reason for transition and subsequent detransition.
“For these people, transitioning could be interpreted as an attempt to escape the reality of being same-sex attracted and detransitioning was part of accepting themselves as homosexual or bisexual,” explained Dr. Littman.
“Exploring their distress and discomfort around sexual orientation issues may have been more helpful to them than medical and surgical transition or at least an important part of exploration,” she added in the article.
Societal pressure, friends, and social media also play a role
The latest first-hand reports also support prior work by Dr. Littman when she first identified the concept she termed rapid-onset gender dysphoria (ROGD) to describe a sudden transgender identification, usually in the early teenage years, and with no prior indication of any gender questioning.
ROGD, Dr. Littman believes, is strongly related to psychosocial factors, such as trauma, mental health problems, or social influence contributing to the development of gender dysphoria.
The current study found that 58% of respondents expressed the belief that the cause of their gender dysphoria was something specific, such as trauma, abuse, or a mental health condition, with respondents suggesting that transitioning prevented, or delayed, them from addressing their underlying mental health conditions.
One participant is quoted as saying: “I was deeply uncomfortable with my secondary sex characteristics, which I now understand was a result of childhood trauma and associating my secondary sex characteristics with those events.”
Reflecting on their previous identification as transgender, more than a third of respondents reported that someone else told them their feelings meant they were transgender, and they believed them.
“This speaks to the effect social influence can have on people’s interpretation of their own feelings and their development of a transgender identity,” Dr. Littman remarked.
“Participants also listed several social media sources that encouraged them to believe that transitioning would help them,” she added.
Several friendship group dynamics suggestive of social influence were reported by a subset of respondents, including the fact that their friendship groups mocked people who were not transgender and their popularity increased when they announced they were going to transition.
Pendulum has swung too far the other way
Natal females, who in recent years have made up most referrals, were younger than natal males when they sought transition and decided to detransition; and they stayed “transitioned” for a shorter period than natal males. They were also more likely to have experienced a trauma less than 1 year before the onset of gender dysphoria and were more likely to have felt pressured to transition.
“Because the females in the study transitioned more recently than the males, they may have experienced a culture where there is more of a ‘push’ to transition,” Dr. Littman pointed out.
She added that, “20 years ago, gender-dysphoric patients were most likely to be underdiagnosed and undertreated. Now, the pendulum has swung the other way and patients are, in my opinion, more likely to be overdiagnosed and overtreated. I think we need to aim for somewhere between these two extremes and prioritize people getting the right treatment for the right reason for their distress.”
Dr. Djordjevic added that, with colleagues from Belgrade and the Netherlands, he has published accounts of the experiences of seven individuals who showed regret after gender-affirming surgery.
All of them were born male, “and we confirmed the very poor evaluation and transition process they underwent. We conclude that clinicians should be aware that not everyone with gender identity disorders need or want all elements of hormonal or surgical therapy,” he told this news organization.
Dr. Edwards-Leeper said that more long-term longitudinal studies are needed that follow individuals who undergo transition under different models of care.
“My prediction is that those who first engage in supportive, gender exploratory therapy, followed by comprehensive assessment, will have the best outcomes, perhaps even if they ultimately detransition, as these individuals will know that they did not jump into irreversible interventions too quickly and had time to make the best decision for themselves at the time,” she concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.