User login
Access to certified stroke centers divided by race, income
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hard habit to break
“I love practicing medicine.”
The speaker was one of my patients. A distinguished, friendly, gentleman in his mid-to-late 70s, here to see me for a minor problem. He still practices medicine part time.
Since his neurologic issue was simple, we spent a fair amount of the time chatting. We’d both seen changes in medicine over time, he more than I, obviously.
Some good, some bad. Fancier toys, better drugs, more paperwork (even if it’s not all on paper anymore).
But we both still like what we do, and have no plans to give it up anytime soon.
Some doctors end up hating their jobs and leave the field. I understand that, and I don’t blame them. It’s not an easy one.
But I still enjoy the job. I look forward to seeing patients each day, turning over their cases, trying to figure them out, and doing what I can to help people.
I see that it is similar with attorneys. Maybe it’s part of the time and commitment you put into getting to a job that makes it hard to walk away as you get older. Or maybe (probably more likely) it’s some intrinsic part of the personality that drove you to get there.
I’m roughly two-thirds of the way through my career, but still don’t have any plans to close down. Granted, that’s practical – I have kids in college, a mortgage, and office overhead. My colleague across the desk can stop practicing whenever he wants, but gets satisfaction, validation, and enjoyment from doing the same job. At this point in his life that’s more important than the money.
I hope to someday feel that same way. I don’t want to always work the 80-90 hours a week I do now, but I can’t imagine not doing this, either.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“I love practicing medicine.”
The speaker was one of my patients. A distinguished, friendly, gentleman in his mid-to-late 70s, here to see me for a minor problem. He still practices medicine part time.
Since his neurologic issue was simple, we spent a fair amount of the time chatting. We’d both seen changes in medicine over time, he more than I, obviously.
Some good, some bad. Fancier toys, better drugs, more paperwork (even if it’s not all on paper anymore).
But we both still like what we do, and have no plans to give it up anytime soon.
Some doctors end up hating their jobs and leave the field. I understand that, and I don’t blame them. It’s not an easy one.
But I still enjoy the job. I look forward to seeing patients each day, turning over their cases, trying to figure them out, and doing what I can to help people.
I see that it is similar with attorneys. Maybe it’s part of the time and commitment you put into getting to a job that makes it hard to walk away as you get older. Or maybe (probably more likely) it’s some intrinsic part of the personality that drove you to get there.
I’m roughly two-thirds of the way through my career, but still don’t have any plans to close down. Granted, that’s practical – I have kids in college, a mortgage, and office overhead. My colleague across the desk can stop practicing whenever he wants, but gets satisfaction, validation, and enjoyment from doing the same job. At this point in his life that’s more important than the money.
I hope to someday feel that same way. I don’t want to always work the 80-90 hours a week I do now, but I can’t imagine not doing this, either.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“I love practicing medicine.”
The speaker was one of my patients. A distinguished, friendly, gentleman in his mid-to-late 70s, here to see me for a minor problem. He still practices medicine part time.
Since his neurologic issue was simple, we spent a fair amount of the time chatting. We’d both seen changes in medicine over time, he more than I, obviously.
Some good, some bad. Fancier toys, better drugs, more paperwork (even if it’s not all on paper anymore).
But we both still like what we do, and have no plans to give it up anytime soon.
Some doctors end up hating their jobs and leave the field. I understand that, and I don’t blame them. It’s not an easy one.
But I still enjoy the job. I look forward to seeing patients each day, turning over their cases, trying to figure them out, and doing what I can to help people.
I see that it is similar with attorneys. Maybe it’s part of the time and commitment you put into getting to a job that makes it hard to walk away as you get older. Or maybe (probably more likely) it’s some intrinsic part of the personality that drove you to get there.
I’m roughly two-thirds of the way through my career, but still don’t have any plans to close down. Granted, that’s practical – I have kids in college, a mortgage, and office overhead. My colleague across the desk can stop practicing whenever he wants, but gets satisfaction, validation, and enjoyment from doing the same job. At this point in his life that’s more important than the money.
I hope to someday feel that same way. I don’t want to always work the 80-90 hours a week I do now, but I can’t imagine not doing this, either.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Air pollution mediates temperature’s impact on COPD
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) based on data from 117 individuals.
COPD is attributed to environmental factors including air pollution, and air pollution has been linked to increased risk of hospitalization and mortality because of acute COPD exacerbation, wrote Huan Minh Tran, PhD, of Taipei (Taiwan) Medical University and colleagues. However, the effects of air pollution on climate-associated health outcomes in COPD have not been explored, they said.
In a study published in Science of The Total Environment the researchers identified 117 adult COPD patients at a single center in Taiwan. They measured lung function, 6-minute walking distance, oxygen desaturation, white blood cell count, and percent emphysema (defined as low attenuation area [LAA]) and linked them to 0- to 1-year, 0- to 3-year, and 0- to 5-year lags in exposures to relative humidity (RH), temperature, and air pollution. The mean age of the participants was 72.9 years; 93% were men.
Pollution was defined in terms of fine particulate matter (PM2.5).
Overall, an increase in RH by 1% was associated with increases in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
A 1% increase in RH also was associated with a decrease in the total-lobe LAA.
As for temperature, an increase of 1° C was associated with decreased oxygen desaturation and with decreases in right-, left-, and upper-lobe LAA values.
When the researchers examined the impact of pollution, they found that a 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was associated with a decrease in the FEV1 as well as with an increase in oxygen desaturation. A 1 mcg/m3 increase in PM10 and PM2.5 was associated with increases in the total-, right-, left, and upper-lobe LAA; increases in lower-lobe LAA were associated with an increase in PM2.5 only.
“This is reasonable because PM2.5 can travel and deposit in distal parts of the lung, while PM10 is preferably deposited in the larger airways of the upper lung regions,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
A one part per billion increase in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) was associated with decreased FEV1 and increased upper-lobe LAA.
“We observed that NO2 fully mediated the association between RH and FEV1, while PM2.5 fully mediated associations of temperature with oxygen saturation and emphysema severity in COPD patients,” the researchers added.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small and homogeneous male, Taiwanese population, which may limit generalizability, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of control for factors such as body mass index, occupational exposure, comorbidities, medication use, and indoor air pollution, they said.
However, the results suggest that air pollution could have an effect on the established associations between climate and adverse health outcomes in COPD, and more research is needed. Climate change–related air pollution is an important public health issue, especially with regards to respiratory disease,” they concluded.
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT
Skin reactions after COVID-19 vaccination have six patterns
Skin manifestations of COVID-19 were among the topics presented in several sessions at the 49th Congress of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Specialists agreed that fewer skin changes associated with this virus have been seen with the latest variants of SARS-CoV-2. They highlighted the results of the most remarkable research on this topic that were presented in this forum.
In the study, which was carried out by Spanish dermatologists with the support of the AEDV, researchers analyzed skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine.
Study author Cristina Galván, MD, a dermatologist at the University Hospital of Móstoles, Madrid, said, of the dermatological manifestations caused as a reaction to these vaccines.”
The study was carried out during the first months of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Galván told this news organization. It was proposed as a continuation of a COVID skin study that was published in the British Journal of Dermatology. That study documented the first classification of skin lesions associated with COVID-19. Dr. Galván is the lead author of the latter study.
“The objectives of this study were to characterize and classify skin reactions after vaccination, identify their chronology, and analyze the associations with a series of antecedents: dermatological and allergic diseases, previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, and skin reactions associated with COVID-19,” said Dr. Galván. The study was a team effort, she added.
“It was conducted between Feb. 15 and May 12, 2021, and information was gathered on 405 reactions that appeared during the 21 days after any dose of the COVID-19 vaccines approved at that time in Spain: the Pfizer/BioNTech, Moderna, and University of Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines,” she added.
Dr. Galván explained that the study shows very clear patterns and investigators reached conclusions that match those of other groups that have investigated this topic. “Six reaction patterns were described according to their frequency. The first is the ‘COVID-19 arm,’ which consists of a local reaction at the injection site and occurs almost exclusively in women and in 70% of cases after inoculation with the Moderna serum. It is a manifestation that resolves well and does not always recur in subsequent doses. More than half are of delayed onset: biopsied patients show signs of a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. In line with all the publications in this regard, it was found that this reaction is not a reason to skip or delay a dose.”
Herpes zoster reactivation
The second pattern is urticarial, which, according to the specialist, occurs with equal frequency after the administration of all vaccines and is well controlled with antihistamines. “This is a very nonspecific pattern, which does not prevent it from still being frequent. It was not associated with drug intake.
“The morbilliform pattern is more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. It affects the trunk and extremities, and up to a quarter of the cases required systemic corticosteroids. The papulovesicular and pityriasis rosea–like patterns are equally frequent in all vaccines. The latter is found in a younger age group. Finally, there is the purpuric pattern, more localized in the extremities and more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. On biopsy, this pattern showed small-vessel vasculitis.”
Less frequently, reactivations or de novo onset of different dermatologic diseases were found. “Varicella-zoster virus reactivations were observed with a frequency of 13.8%, being more common after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine,” said Dr. Galván. “Other studies have corroborated this increase in herpes zoster, although it has been seen that the absolute number is low, so the benefits of the vaccine outweigh this eventual complication. At the same time and along the same lines, vaccination against herpes zoster is recommended for those over 50 years of age.”
Another fact revealed by the study is that these reactions were not significantly more severe in people with dermatologic diseases, those with previous infection, or those with skin manifestation associated with COVID-19.
Dr. Galván highlighted that, except for the COVID-19 arm, these patterns were among those associated with the disease, “which supports [the idea] that it does not demonstrate that the host’s immune reaction to the infection was playing a role.”
Women and young people
“As for pseudoperniosis, it is poorly represented in our series: 0.7% compared to 2% in the American registry. Although neither the SARS-CoV-2–pseudoperniosis association nor its pathophysiology is clear, the idea is that if this manifestation is related to the host’s immune response during infection, pseudoperniosis after vaccination could also be linked to the immune response to the vaccine,” said Dr. Galván.
Many of these reactions are more intense in women. “Before starting to use these vaccines, we already knew that messenger RNA vaccines (a powerful activator of innate immunity) induce frequent reactions, that adjuvants and excipients (polyethylene glycol and polysorbate) also generate them, and that other factors influence reactogenicity, among those of us of the same age and sex, reactions being more frequent in younger people and in women,” said Dr. Galván. “This may be one of the reasons why the COVID-19 arm is so much more prevalent in the female population and that 80% of all reactions that were collected were in women.”
In relation to the fact that manifestations differed, depending on the type of inoculated serum, Dr. Galván said, “Some reactions are just as common after any of the vaccines. However, others are not, as is the case with the COVID-19 arm for the Moderna vaccine or reactivations of the herpes virus, more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine.
“Undoubtedly, behind these differences are particularities in the immune reaction caused by each of the vaccines and their composition, including the excipients,” she said.
Regarding the fact that these reactions were the same throughout the vaccine regimen or that they varied in intensity, depending on the dose, Dr. Galván said, “In our study, as in those carried out by other groups, there were no significant differences in terms of frequency after the first and second doses. One thing to keep in mind is that, due to the temporary design of our study and the time at which it was conducted, it was not possible to collect reactions after second doses of AstraZeneca.
“Manifestations have generally been mild and well controlled. Many of them did not recur after the second dose, and the vast majority did not prevent completion of the vaccination scheme, but we must not lose sight of the fact that 20% of these manifestations were assessed by the dermatologist as serious or very serious,” Dr. Galván added.
Regarding the next steps planned for this line of research, Dr. Galván commented, “We are awaiting the evolution of the reported cases and the reactions that may arise, although for now, our group does not have any open studies. The most important thing now is to be alert and report the data observed in the pharmacovigilance systems, in open registries, and in scientific literature to generate evidence.”
Dr. Galván has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Skin manifestations of COVID-19 were among the topics presented in several sessions at the 49th Congress of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Specialists agreed that fewer skin changes associated with this virus have been seen with the latest variants of SARS-CoV-2. They highlighted the results of the most remarkable research on this topic that were presented in this forum.
In the study, which was carried out by Spanish dermatologists with the support of the AEDV, researchers analyzed skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine.
Study author Cristina Galván, MD, a dermatologist at the University Hospital of Móstoles, Madrid, said, of the dermatological manifestations caused as a reaction to these vaccines.”
The study was carried out during the first months of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Galván told this news organization. It was proposed as a continuation of a COVID skin study that was published in the British Journal of Dermatology. That study documented the first classification of skin lesions associated with COVID-19. Dr. Galván is the lead author of the latter study.
“The objectives of this study were to characterize and classify skin reactions after vaccination, identify their chronology, and analyze the associations with a series of antecedents: dermatological and allergic diseases, previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, and skin reactions associated with COVID-19,” said Dr. Galván. The study was a team effort, she added.
“It was conducted between Feb. 15 and May 12, 2021, and information was gathered on 405 reactions that appeared during the 21 days after any dose of the COVID-19 vaccines approved at that time in Spain: the Pfizer/BioNTech, Moderna, and University of Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines,” she added.
Dr. Galván explained that the study shows very clear patterns and investigators reached conclusions that match those of other groups that have investigated this topic. “Six reaction patterns were described according to their frequency. The first is the ‘COVID-19 arm,’ which consists of a local reaction at the injection site and occurs almost exclusively in women and in 70% of cases after inoculation with the Moderna serum. It is a manifestation that resolves well and does not always recur in subsequent doses. More than half are of delayed onset: biopsied patients show signs of a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. In line with all the publications in this regard, it was found that this reaction is not a reason to skip or delay a dose.”
Herpes zoster reactivation
The second pattern is urticarial, which, according to the specialist, occurs with equal frequency after the administration of all vaccines and is well controlled with antihistamines. “This is a very nonspecific pattern, which does not prevent it from still being frequent. It was not associated with drug intake.
“The morbilliform pattern is more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. It affects the trunk and extremities, and up to a quarter of the cases required systemic corticosteroids. The papulovesicular and pityriasis rosea–like patterns are equally frequent in all vaccines. The latter is found in a younger age group. Finally, there is the purpuric pattern, more localized in the extremities and more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. On biopsy, this pattern showed small-vessel vasculitis.”
Less frequently, reactivations or de novo onset of different dermatologic diseases were found. “Varicella-zoster virus reactivations were observed with a frequency of 13.8%, being more common after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine,” said Dr. Galván. “Other studies have corroborated this increase in herpes zoster, although it has been seen that the absolute number is low, so the benefits of the vaccine outweigh this eventual complication. At the same time and along the same lines, vaccination against herpes zoster is recommended for those over 50 years of age.”
Another fact revealed by the study is that these reactions were not significantly more severe in people with dermatologic diseases, those with previous infection, or those with skin manifestation associated with COVID-19.
Dr. Galván highlighted that, except for the COVID-19 arm, these patterns were among those associated with the disease, “which supports [the idea] that it does not demonstrate that the host’s immune reaction to the infection was playing a role.”
Women and young people
“As for pseudoperniosis, it is poorly represented in our series: 0.7% compared to 2% in the American registry. Although neither the SARS-CoV-2–pseudoperniosis association nor its pathophysiology is clear, the idea is that if this manifestation is related to the host’s immune response during infection, pseudoperniosis after vaccination could also be linked to the immune response to the vaccine,” said Dr. Galván.
Many of these reactions are more intense in women. “Before starting to use these vaccines, we already knew that messenger RNA vaccines (a powerful activator of innate immunity) induce frequent reactions, that adjuvants and excipients (polyethylene glycol and polysorbate) also generate them, and that other factors influence reactogenicity, among those of us of the same age and sex, reactions being more frequent in younger people and in women,” said Dr. Galván. “This may be one of the reasons why the COVID-19 arm is so much more prevalent in the female population and that 80% of all reactions that were collected were in women.”
In relation to the fact that manifestations differed, depending on the type of inoculated serum, Dr. Galván said, “Some reactions are just as common after any of the vaccines. However, others are not, as is the case with the COVID-19 arm for the Moderna vaccine or reactivations of the herpes virus, more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine.
“Undoubtedly, behind these differences are particularities in the immune reaction caused by each of the vaccines and their composition, including the excipients,” she said.
Regarding the fact that these reactions were the same throughout the vaccine regimen or that they varied in intensity, depending on the dose, Dr. Galván said, “In our study, as in those carried out by other groups, there were no significant differences in terms of frequency after the first and second doses. One thing to keep in mind is that, due to the temporary design of our study and the time at which it was conducted, it was not possible to collect reactions after second doses of AstraZeneca.
“Manifestations have generally been mild and well controlled. Many of them did not recur after the second dose, and the vast majority did not prevent completion of the vaccination scheme, but we must not lose sight of the fact that 20% of these manifestations were assessed by the dermatologist as serious or very serious,” Dr. Galván added.
Regarding the next steps planned for this line of research, Dr. Galván commented, “We are awaiting the evolution of the reported cases and the reactions that may arise, although for now, our group does not have any open studies. The most important thing now is to be alert and report the data observed in the pharmacovigilance systems, in open registries, and in scientific literature to generate evidence.”
Dr. Galván has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Skin manifestations of COVID-19 were among the topics presented in several sessions at the 49th Congress of the Spanish Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. Specialists agreed that fewer skin changes associated with this virus have been seen with the latest variants of SARS-CoV-2. They highlighted the results of the most remarkable research on this topic that were presented in this forum.
In the study, which was carried out by Spanish dermatologists with the support of the AEDV, researchers analyzed skin reactions associated with the COVID-19 vaccine.
Study author Cristina Galván, MD, a dermatologist at the University Hospital of Móstoles, Madrid, said, of the dermatological manifestations caused as a reaction to these vaccines.”
The study was carried out during the first months of COVID-19 vaccination, Dr. Galván told this news organization. It was proposed as a continuation of a COVID skin study that was published in the British Journal of Dermatology. That study documented the first classification of skin lesions associated with COVID-19. Dr. Galván is the lead author of the latter study.
“The objectives of this study were to characterize and classify skin reactions after vaccination, identify their chronology, and analyze the associations with a series of antecedents: dermatological and allergic diseases, previous SARS-CoV-2 infection, and skin reactions associated with COVID-19,” said Dr. Galván. The study was a team effort, she added.
“It was conducted between Feb. 15 and May 12, 2021, and information was gathered on 405 reactions that appeared during the 21 days after any dose of the COVID-19 vaccines approved at that time in Spain: the Pfizer/BioNTech, Moderna, and University of Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccines,” she added.
Dr. Galván explained that the study shows very clear patterns and investigators reached conclusions that match those of other groups that have investigated this topic. “Six reaction patterns were described according to their frequency. The first is the ‘COVID-19 arm,’ which consists of a local reaction at the injection site and occurs almost exclusively in women and in 70% of cases after inoculation with the Moderna serum. It is a manifestation that resolves well and does not always recur in subsequent doses. More than half are of delayed onset: biopsied patients show signs of a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. In line with all the publications in this regard, it was found that this reaction is not a reason to skip or delay a dose.”
Herpes zoster reactivation
The second pattern is urticarial, which, according to the specialist, occurs with equal frequency after the administration of all vaccines and is well controlled with antihistamines. “This is a very nonspecific pattern, which does not prevent it from still being frequent. It was not associated with drug intake.
“The morbilliform pattern is more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. It affects the trunk and extremities, and up to a quarter of the cases required systemic corticosteroids. The papulovesicular and pityriasis rosea–like patterns are equally frequent in all vaccines. The latter is found in a younger age group. Finally, there is the purpuric pattern, more localized in the extremities and more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines. On biopsy, this pattern showed small-vessel vasculitis.”
Less frequently, reactivations or de novo onset of different dermatologic diseases were found. “Varicella-zoster virus reactivations were observed with a frequency of 13.8%, being more common after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine,” said Dr. Galván. “Other studies have corroborated this increase in herpes zoster, although it has been seen that the absolute number is low, so the benefits of the vaccine outweigh this eventual complication. At the same time and along the same lines, vaccination against herpes zoster is recommended for those over 50 years of age.”
Another fact revealed by the study is that these reactions were not significantly more severe in people with dermatologic diseases, those with previous infection, or those with skin manifestation associated with COVID-19.
Dr. Galván highlighted that, except for the COVID-19 arm, these patterns were among those associated with the disease, “which supports [the idea] that it does not demonstrate that the host’s immune reaction to the infection was playing a role.”
Women and young people
“As for pseudoperniosis, it is poorly represented in our series: 0.7% compared to 2% in the American registry. Although neither the SARS-CoV-2–pseudoperniosis association nor its pathophysiology is clear, the idea is that if this manifestation is related to the host’s immune response during infection, pseudoperniosis after vaccination could also be linked to the immune response to the vaccine,” said Dr. Galván.
Many of these reactions are more intense in women. “Before starting to use these vaccines, we already knew that messenger RNA vaccines (a powerful activator of innate immunity) induce frequent reactions, that adjuvants and excipients (polyethylene glycol and polysorbate) also generate them, and that other factors influence reactogenicity, among those of us of the same age and sex, reactions being more frequent in younger people and in women,” said Dr. Galván. “This may be one of the reasons why the COVID-19 arm is so much more prevalent in the female population and that 80% of all reactions that were collected were in women.”
In relation to the fact that manifestations differed, depending on the type of inoculated serum, Dr. Galván said, “Some reactions are just as common after any of the vaccines. However, others are not, as is the case with the COVID-19 arm for the Moderna vaccine or reactivations of the herpes virus, more frequent after the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine.
“Undoubtedly, behind these differences are particularities in the immune reaction caused by each of the vaccines and their composition, including the excipients,” she said.
Regarding the fact that these reactions were the same throughout the vaccine regimen or that they varied in intensity, depending on the dose, Dr. Galván said, “In our study, as in those carried out by other groups, there were no significant differences in terms of frequency after the first and second doses. One thing to keep in mind is that, due to the temporary design of our study and the time at which it was conducted, it was not possible to collect reactions after second doses of AstraZeneca.
“Manifestations have generally been mild and well controlled. Many of them did not recur after the second dose, and the vast majority did not prevent completion of the vaccination scheme, but we must not lose sight of the fact that 20% of these manifestations were assessed by the dermatologist as serious or very serious,” Dr. Galván added.
Regarding the next steps planned for this line of research, Dr. Galván commented, “We are awaiting the evolution of the reported cases and the reactions that may arise, although for now, our group does not have any open studies. The most important thing now is to be alert and report the data observed in the pharmacovigilance systems, in open registries, and in scientific literature to generate evidence.”
Dr. Galván has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Monkeypox mutating faster than expected
The monkeypox virus is evolving 6-12 times faster than would be expected, according to a new study.
The virus is thought to have a single origin, the genetic data suggests, and is a likely descendant of the strain involved in the 2017-2018 monkeypox outbreak in Nigeria. It’s not clear if these mutations have aided the transmissibility of the virus among people or have any other clinical implications, João Paulo Gomes, PhD, from Portugal’s National Institute of Health, Lisbon, said in an email.
Since the monkeypox outbreak began in May, nearly 7,000 cases of monkeypox have been reported across 52 countries and territories.
Orthopoxviruses – the genus to which monkeypox belongs – are large DNA viruses that usually only gain one or two mutations every year. (For comparison, SARS-CoV-2 gains around two mutations every month.) One would expect 5 to 10 mutations in the 2022 monkeypox virus, compared with the 2017 strain, Dr. Gomes said.
In the study, Dr. Gomes and colleagues analyzed 15 monkeypox DNA sequences made available by Portugal and the National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, Md., between May 20 and May 27, 2022. The analysis revealed that this most recent strain differed by 50 single-nucleotide polymorphisms, compared with previous strains of the virus in 2017-2018.
“This is far beyond what we would expect, specifically for orthopoxvirus,” Andrew Lover, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst School of Public Health & Health Sciences, told this news organization. He was not involved with the research. “That suggests [the virus] is trying to figure out the best way to deal with a new host species,” he added.
Rodents are thought to be the natural hosts of the monkeypox virus, he explained, and, in 2022, the infection transferred to humans. “Moving into a new species can ‘turbocharge’ mutations as the virus adapts to a new biological environment,” he explained, though it is not clear if the new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team detected help the 2022 virus spread more easily among people.
Researchers also found that the 2022 virus belonged in clade 3 of the virus, which is part of the less-lethal West-African clade. While the West-African clade has a fatality rate of less than 1%, the Central African clade has a fatality rate of over 10%.
The rapid changes in the viral genome could be driven by a family of proteins thought to play a role in antiviral immunity: apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3). These enzymes can make changes to a viral genome, Dr. Gomes explained, “but sometimes the system is not ‘well regulated,’ and the changes in the genome are not detrimental to the virus.” These APOBEC3-driven mutations have a signature pattern, he said, which was also detected in most of the 50 new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team identified.
However, it is not known if these mutations have clinical implications, Dr. Lover said.
The 2022 monkeypox virus does appear to behave differently than previous strains of the virus, he noted. In the current outbreak, sexual transmission appears to be very common, which is not the case for previous outbreaks, he said. Also, while monkeypox traditionally presents with a rash that can spread to all parts of the body, there have been several instances of patients presenting with just a few “very innocuous lesions,” he added.
Dr. Gomes hopes that specialized lab groups will now be able to tease out whether there is a connection between these identified mutations and changes in the behavior of the virus, including transmissibility.
While none of the findings in this analysis raises any serious concerns, the study “suggests there [are] definitely gaps in our knowledge about monkeypox,” Dr. Lover said. As for the global health response, he said, “We probably should err on the side of caution. ... There are clearly things that we absolutely don’t understand here, in terms of how quickly mutations are popping up.”
Dr. Gomes and Dr. Lover report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The monkeypox virus is evolving 6-12 times faster than would be expected, according to a new study.
The virus is thought to have a single origin, the genetic data suggests, and is a likely descendant of the strain involved in the 2017-2018 monkeypox outbreak in Nigeria. It’s not clear if these mutations have aided the transmissibility of the virus among people or have any other clinical implications, João Paulo Gomes, PhD, from Portugal’s National Institute of Health, Lisbon, said in an email.
Since the monkeypox outbreak began in May, nearly 7,000 cases of monkeypox have been reported across 52 countries and territories.
Orthopoxviruses – the genus to which monkeypox belongs – are large DNA viruses that usually only gain one or two mutations every year. (For comparison, SARS-CoV-2 gains around two mutations every month.) One would expect 5 to 10 mutations in the 2022 monkeypox virus, compared with the 2017 strain, Dr. Gomes said.
In the study, Dr. Gomes and colleagues analyzed 15 monkeypox DNA sequences made available by Portugal and the National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, Md., between May 20 and May 27, 2022. The analysis revealed that this most recent strain differed by 50 single-nucleotide polymorphisms, compared with previous strains of the virus in 2017-2018.
“This is far beyond what we would expect, specifically for orthopoxvirus,” Andrew Lover, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst School of Public Health & Health Sciences, told this news organization. He was not involved with the research. “That suggests [the virus] is trying to figure out the best way to deal with a new host species,” he added.
Rodents are thought to be the natural hosts of the monkeypox virus, he explained, and, in 2022, the infection transferred to humans. “Moving into a new species can ‘turbocharge’ mutations as the virus adapts to a new biological environment,” he explained, though it is not clear if the new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team detected help the 2022 virus spread more easily among people.
Researchers also found that the 2022 virus belonged in clade 3 of the virus, which is part of the less-lethal West-African clade. While the West-African clade has a fatality rate of less than 1%, the Central African clade has a fatality rate of over 10%.
The rapid changes in the viral genome could be driven by a family of proteins thought to play a role in antiviral immunity: apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3). These enzymes can make changes to a viral genome, Dr. Gomes explained, “but sometimes the system is not ‘well regulated,’ and the changes in the genome are not detrimental to the virus.” These APOBEC3-driven mutations have a signature pattern, he said, which was also detected in most of the 50 new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team identified.
However, it is not known if these mutations have clinical implications, Dr. Lover said.
The 2022 monkeypox virus does appear to behave differently than previous strains of the virus, he noted. In the current outbreak, sexual transmission appears to be very common, which is not the case for previous outbreaks, he said. Also, while monkeypox traditionally presents with a rash that can spread to all parts of the body, there have been several instances of patients presenting with just a few “very innocuous lesions,” he added.
Dr. Gomes hopes that specialized lab groups will now be able to tease out whether there is a connection between these identified mutations and changes in the behavior of the virus, including transmissibility.
While none of the findings in this analysis raises any serious concerns, the study “suggests there [are] definitely gaps in our knowledge about monkeypox,” Dr. Lover said. As for the global health response, he said, “We probably should err on the side of caution. ... There are clearly things that we absolutely don’t understand here, in terms of how quickly mutations are popping up.”
Dr. Gomes and Dr. Lover report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The monkeypox virus is evolving 6-12 times faster than would be expected, according to a new study.
The virus is thought to have a single origin, the genetic data suggests, and is a likely descendant of the strain involved in the 2017-2018 monkeypox outbreak in Nigeria. It’s not clear if these mutations have aided the transmissibility of the virus among people or have any other clinical implications, João Paulo Gomes, PhD, from Portugal’s National Institute of Health, Lisbon, said in an email.
Since the monkeypox outbreak began in May, nearly 7,000 cases of monkeypox have been reported across 52 countries and territories.
Orthopoxviruses – the genus to which monkeypox belongs – are large DNA viruses that usually only gain one or two mutations every year. (For comparison, SARS-CoV-2 gains around two mutations every month.) One would expect 5 to 10 mutations in the 2022 monkeypox virus, compared with the 2017 strain, Dr. Gomes said.
In the study, Dr. Gomes and colleagues analyzed 15 monkeypox DNA sequences made available by Portugal and the National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda, Md., between May 20 and May 27, 2022. The analysis revealed that this most recent strain differed by 50 single-nucleotide polymorphisms, compared with previous strains of the virus in 2017-2018.
“This is far beyond what we would expect, specifically for orthopoxvirus,” Andrew Lover, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Massachusetts Amherst School of Public Health & Health Sciences, told this news organization. He was not involved with the research. “That suggests [the virus] is trying to figure out the best way to deal with a new host species,” he added.
Rodents are thought to be the natural hosts of the monkeypox virus, he explained, and, in 2022, the infection transferred to humans. “Moving into a new species can ‘turbocharge’ mutations as the virus adapts to a new biological environment,” he explained, though it is not clear if the new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team detected help the 2022 virus spread more easily among people.
Researchers also found that the 2022 virus belonged in clade 3 of the virus, which is part of the less-lethal West-African clade. While the West-African clade has a fatality rate of less than 1%, the Central African clade has a fatality rate of over 10%.
The rapid changes in the viral genome could be driven by a family of proteins thought to play a role in antiviral immunity: apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3 (APOBEC3). These enzymes can make changes to a viral genome, Dr. Gomes explained, “but sometimes the system is not ‘well regulated,’ and the changes in the genome are not detrimental to the virus.” These APOBEC3-driven mutations have a signature pattern, he said, which was also detected in most of the 50 new mutations Dr. Gomes’s team identified.
However, it is not known if these mutations have clinical implications, Dr. Lover said.
The 2022 monkeypox virus does appear to behave differently than previous strains of the virus, he noted. In the current outbreak, sexual transmission appears to be very common, which is not the case for previous outbreaks, he said. Also, while monkeypox traditionally presents with a rash that can spread to all parts of the body, there have been several instances of patients presenting with just a few “very innocuous lesions,” he added.
Dr. Gomes hopes that specialized lab groups will now be able to tease out whether there is a connection between these identified mutations and changes in the behavior of the virus, including transmissibility.
While none of the findings in this analysis raises any serious concerns, the study “suggests there [are] definitely gaps in our knowledge about monkeypox,” Dr. Lover said. As for the global health response, he said, “We probably should err on the side of caution. ... There are clearly things that we absolutely don’t understand here, in terms of how quickly mutations are popping up.”
Dr. Gomes and Dr. Lover report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Induced by the Second-Generation Antipsychotic Cariprazine
To the Editor:
A 57-year-old woman presented to an outpatient clinic with severe pruritus and burning of the skin as well as subjective fevers and chills. She had been discharged from a psychiatric hospital for attempted suicide 1 day prior. There were no recent changes in the medication regimen, which consisted of linaclotide, fluoxetine, lorazepam, and gabapentin. While admitted, the patient was started on the atypical antipsychotic cariprazine. Within 24 hours of the first dose, she developed severe facial erythema that progressed to diffuse erythema over more than 60% of the body surface area. The attending psychiatrist promptly discontinued cariprazine. During the next 24 hours, there were no reports of fever, leukocytosis, or signs of systemic organ involvement. Given the patient’s mental and medical stability, she was discharged with instructions to follow up with the outpatient dermatology clinic.
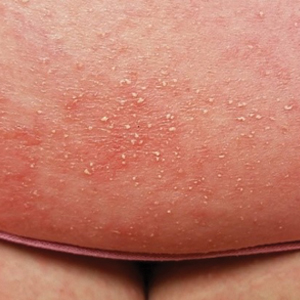
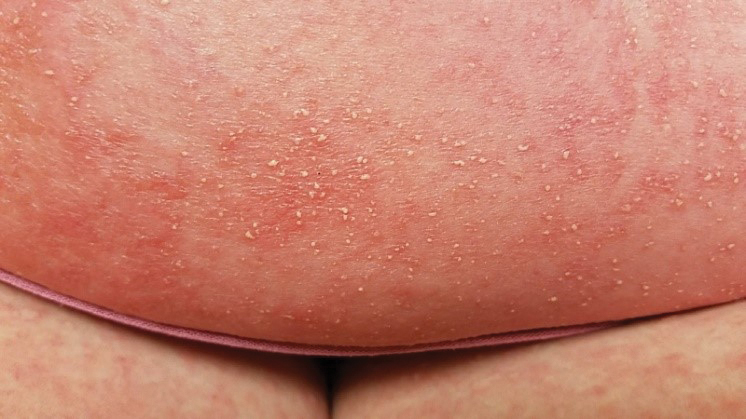
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed innumerable 1- to 4-mm pustules coalescing to lakes of pus on an erythematous base over more than 60% of the body surface area (Figure 1). The mucous membranes were clear of lesions, the Nikolsky sign was negative, and the patient’s temperature was 99.6 °F in the office. Complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel results were within reference range.
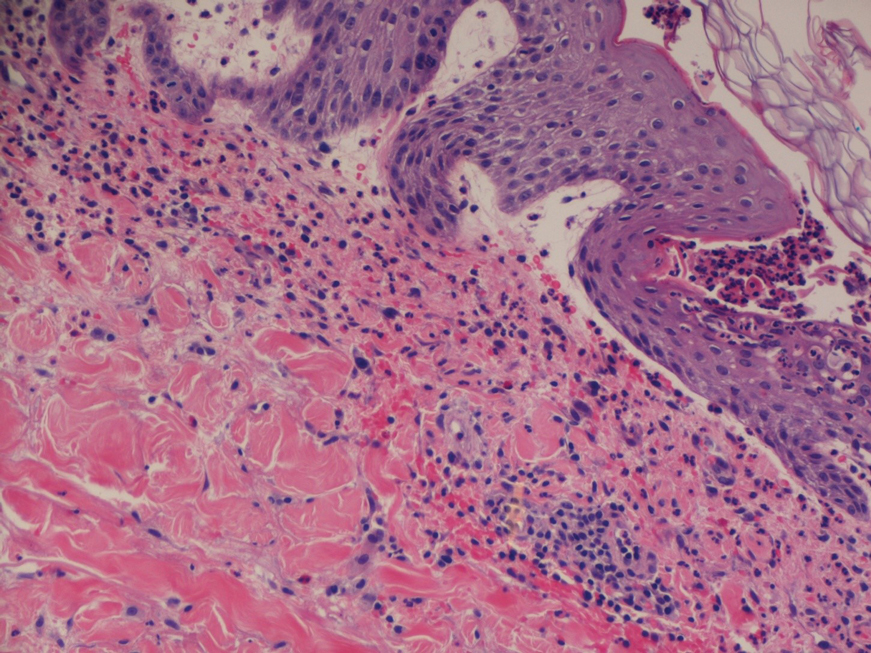
A 4-mm abdominal punch biopsy showed subcorneal neutrophilic pustules, papillary dermal edema, and superficial dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation with numerous neutrophils, eosinophils, and extravasated red blood cells, consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)(Figure 2). The patient was started on wet wraps with triamcinolone cream 0.1%.
Two days later, physical examination revealed the erythema noted on initial examination had notably decreased, and the patient no longer reported burning or pruritus. One week after initial presentation to the clinic, the patient’s rash had resolved, and only a few small areas of desquamation remained.
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a severe cutaneous adverse reaction characterized by the development of numerous nonfollicular sterile pustules on an edematous and erythematous base. In almost 90% of reported cases, the cause is related to use of antibiotics, antifungals, antimalarials, or diltiazem (a calcium channel blocker). This rare cutaneous reaction occurs in 1 to 5 patients per million per year1; it carries a 1% to 2% mortality rate with proper supportive treatment.
The clinical symptoms of AGEP typically present 24 to 48 hours after drug initiation with the rapid development of dozens to thousands of 1- to 4-mm pustules, typically localized to the flexor surfaces and face. In the setting of AGEP, acute onset of fever and leukocytosis typically occur at the time of the cutaneous eruption. These features were absent in this patient. The eruption usually starts on the face and then migrates to the trunk and extremities, sparing the palms and soles. Systemic involvement most commonly presents as hepatic, renal, or pulmonary insufficiency, which has been seen in 20% of cases.2
The immunologic response associated with the reaction has been studied in vitro. Drug-specific CD8 T cells use perforin/granzyme B and Fas ligand mechanisms to induce apoptosis of the keratinocytes within the epidermis, leading to vesicle formation.3 During the very first stages of formation, vesicles mainly comprise CD8 T cells and keratinocytes. These cells then begin producing CXC-18, a potent neutrophil chemokine, leading to extensive chemotaxis of neutrophils into vesicles, which then rapidly transform to pustules.3 This rapid transformation leads to the lakes of pustules, a description often associated with AGEP.
Treatment of AGEP is mainly supportive and consists of discontinuing use of the causative agent. Topical corticosteroids can be used during the pustular phase for symptom management. There is no evidence that systemic steroids reduce the duration of the disease.2 Other supportive measures such as application of wet wraps can be used to provide comfort.
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions commonly are associated with psychiatric pharmacotherapy, but first-and second-generation antipsychotics rarely are associated with these types of reactions. In this patient, the causative agent of the AGEP was cariprazine, an atypical antipsychotic that had no reported association with AGEP or cutaneous adverse drug reactions prior to this presentation.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Feldmeyer L, Heidemeyer K, Yawalkar N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: pathogenesis, genetic background, clinical variants and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1214.
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848.
To the Editor:
A 57-year-old woman presented to an outpatient clinic with severe pruritus and burning of the skin as well as subjective fevers and chills. She had been discharged from a psychiatric hospital for attempted suicide 1 day prior. There were no recent changes in the medication regimen, which consisted of linaclotide, fluoxetine, lorazepam, and gabapentin. While admitted, the patient was started on the atypical antipsychotic cariprazine. Within 24 hours of the first dose, she developed severe facial erythema that progressed to diffuse erythema over more than 60% of the body surface area. The attending psychiatrist promptly discontinued cariprazine. During the next 24 hours, there were no reports of fever, leukocytosis, or signs of systemic organ involvement. Given the patient’s mental and medical stability, she was discharged with instructions to follow up with the outpatient dermatology clinic.
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed innumerable 1- to 4-mm pustules coalescing to lakes of pus on an erythematous base over more than 60% of the body surface area (Figure 1). The mucous membranes were clear of lesions, the Nikolsky sign was negative, and the patient’s temperature was 99.6 °F in the office. Complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel results were within reference range.

A 4-mm abdominal punch biopsy showed subcorneal neutrophilic pustules, papillary dermal edema, and superficial dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation with numerous neutrophils, eosinophils, and extravasated red blood cells, consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)(Figure 2). The patient was started on wet wraps with triamcinolone cream 0.1%.

Two days later, physical examination revealed the erythema noted on initial examination had notably decreased, and the patient no longer reported burning or pruritus. One week after initial presentation to the clinic, the patient’s rash had resolved, and only a few small areas of desquamation remained.
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a severe cutaneous adverse reaction characterized by the development of numerous nonfollicular sterile pustules on an edematous and erythematous base. In almost 90% of reported cases, the cause is related to use of antibiotics, antifungals, antimalarials, or diltiazem (a calcium channel blocker). This rare cutaneous reaction occurs in 1 to 5 patients per million per year1; it carries a 1% to 2% mortality rate with proper supportive treatment.
The clinical symptoms of AGEP typically present 24 to 48 hours after drug initiation with the rapid development of dozens to thousands of 1- to 4-mm pustules, typically localized to the flexor surfaces and face. In the setting of AGEP, acute onset of fever and leukocytosis typically occur at the time of the cutaneous eruption. These features were absent in this patient. The eruption usually starts on the face and then migrates to the trunk and extremities, sparing the palms and soles. Systemic involvement most commonly presents as hepatic, renal, or pulmonary insufficiency, which has been seen in 20% of cases.2
The immunologic response associated with the reaction has been studied in vitro. Drug-specific CD8 T cells use perforin/granzyme B and Fas ligand mechanisms to induce apoptosis of the keratinocytes within the epidermis, leading to vesicle formation.3 During the very first stages of formation, vesicles mainly comprise CD8 T cells and keratinocytes. These cells then begin producing CXC-18, a potent neutrophil chemokine, leading to extensive chemotaxis of neutrophils into vesicles, which then rapidly transform to pustules.3 This rapid transformation leads to the lakes of pustules, a description often associated with AGEP.
Treatment of AGEP is mainly supportive and consists of discontinuing use of the causative agent. Topical corticosteroids can be used during the pustular phase for symptom management. There is no evidence that systemic steroids reduce the duration of the disease.2 Other supportive measures such as application of wet wraps can be used to provide comfort.
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions commonly are associated with psychiatric pharmacotherapy, but first-and second-generation antipsychotics rarely are associated with these types of reactions. In this patient, the causative agent of the AGEP was cariprazine, an atypical antipsychotic that had no reported association with AGEP or cutaneous adverse drug reactions prior to this presentation.
To the Editor:
A 57-year-old woman presented to an outpatient clinic with severe pruritus and burning of the skin as well as subjective fevers and chills. She had been discharged from a psychiatric hospital for attempted suicide 1 day prior. There were no recent changes in the medication regimen, which consisted of linaclotide, fluoxetine, lorazepam, and gabapentin. While admitted, the patient was started on the atypical antipsychotic cariprazine. Within 24 hours of the first dose, she developed severe facial erythema that progressed to diffuse erythema over more than 60% of the body surface area. The attending psychiatrist promptly discontinued cariprazine. During the next 24 hours, there were no reports of fever, leukocytosis, or signs of systemic organ involvement. Given the patient’s mental and medical stability, she was discharged with instructions to follow up with the outpatient dermatology clinic.
At the current presentation, physical examination revealed innumerable 1- to 4-mm pustules coalescing to lakes of pus on an erythematous base over more than 60% of the body surface area (Figure 1). The mucous membranes were clear of lesions, the Nikolsky sign was negative, and the patient’s temperature was 99.6 °F in the office. Complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel results were within reference range.

A 4-mm abdominal punch biopsy showed subcorneal neutrophilic pustules, papillary dermal edema, and superficial dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation with numerous neutrophils, eosinophils, and extravasated red blood cells, consistent with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)(Figure 2). The patient was started on wet wraps with triamcinolone cream 0.1%.

Two days later, physical examination revealed the erythema noted on initial examination had notably decreased, and the patient no longer reported burning or pruritus. One week after initial presentation to the clinic, the patient’s rash had resolved, and only a few small areas of desquamation remained.
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis is a severe cutaneous adverse reaction characterized by the development of numerous nonfollicular sterile pustules on an edematous and erythematous base. In almost 90% of reported cases, the cause is related to use of antibiotics, antifungals, antimalarials, or diltiazem (a calcium channel blocker). This rare cutaneous reaction occurs in 1 to 5 patients per million per year1; it carries a 1% to 2% mortality rate with proper supportive treatment.
The clinical symptoms of AGEP typically present 24 to 48 hours after drug initiation with the rapid development of dozens to thousands of 1- to 4-mm pustules, typically localized to the flexor surfaces and face. In the setting of AGEP, acute onset of fever and leukocytosis typically occur at the time of the cutaneous eruption. These features were absent in this patient. The eruption usually starts on the face and then migrates to the trunk and extremities, sparing the palms and soles. Systemic involvement most commonly presents as hepatic, renal, or pulmonary insufficiency, which has been seen in 20% of cases.2
The immunologic response associated with the reaction has been studied in vitro. Drug-specific CD8 T cells use perforin/granzyme B and Fas ligand mechanisms to induce apoptosis of the keratinocytes within the epidermis, leading to vesicle formation.3 During the very first stages of formation, vesicles mainly comprise CD8 T cells and keratinocytes. These cells then begin producing CXC-18, a potent neutrophil chemokine, leading to extensive chemotaxis of neutrophils into vesicles, which then rapidly transform to pustules.3 This rapid transformation leads to the lakes of pustules, a description often associated with AGEP.
Treatment of AGEP is mainly supportive and consists of discontinuing use of the causative agent. Topical corticosteroids can be used during the pustular phase for symptom management. There is no evidence that systemic steroids reduce the duration of the disease.2 Other supportive measures such as application of wet wraps can be used to provide comfort.
Cutaneous adverse drug reactions commonly are associated with psychiatric pharmacotherapy, but first-and second-generation antipsychotics rarely are associated with these types of reactions. In this patient, the causative agent of the AGEP was cariprazine, an atypical antipsychotic that had no reported association with AGEP or cutaneous adverse drug reactions prior to this presentation.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Feldmeyer L, Heidemeyer K, Yawalkar N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: pathogenesis, genetic background, clinical variants and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1214.
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848.
- Fernando SL. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2012;53:87-92.
- Feldmeyer L, Heidemeyer K, Yawalkar N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: pathogenesis, genetic background, clinical variants and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:1214.
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): a review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73:843-848.
Practice Points
- The second-generation antipsychotic cariprazine has been shown to be a potential causative agent in acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP).
- Treatment of AGEP is mainly supportive and consists of discontinuation of the causative agent as well as symptom control using cold compresses and topical corticosteroids.
Nevus Lipomatosis Deemed Suspicious by Airport Security
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented at the dermatology clinic with a growing lesion on the left medial thigh.
Physical examination revealed a 5-cm, pedunculated, fatty nodule on the left medial thigh that was clinically consistent with nevus lipomatosis (NL)(Figure). Although benign, trouble traveling through airport security prompted the patient to request shave removal, which subsequently was performed. Histology showed a large pedunculated nodule with prominent adipose tissue, consistent with NL. At 3-month follow-up, the patient reported getting through airport security multiple times without incident.
Nevus lipomatosis is a benign fatty lesion most commonly found on the medial thighs or trunk of adults. The lesion usually is asymptomatic but can become irritated by rubbing or catching on clothing. Our patient had symptomatic NL that caused delays getting through airport security; he experienced full resolution after simple shave removal. In rare instances, both benign and malignant skin conditions have been seen on airport scanning devices since the introduction of increased security measures following September 11, 2001. In 2016, Heymann1 reported a man with a 1.5-cm epidermal inclusion cyst detected by airport security scanners, prompting the traveler to request and carry a medically explanatory letter used to get through security. In 2015 Mayer and Adams2 described a case of nodular melanoma that was detected 20 times over a period of 2 months by airport scanners, and in 2016, Caine et al3 reported a case of desmoplastic melanoma that was detected by airport security, but after its removal was not identified by security for the next 40 flights. Noncutaneous pathology also can be detected by airport scanners. In 2013, Naraynsingh et al4 reported a man with a large left reducible inguinal hernia who was stopped by airport security and subjected to an invasive physical examination of the area. These instances demonstrate the breadth of conditions that can be cumbersome when individuals are traveling by airplane in our current security climate.
Our patient had to go through the trouble of having the benign NL lesion removed to avoid the hassle of repeatedly being stopped by airport security. The patient had the lesion removed and is doing well, but the procedure could have been avoided if systems existed to help patients with dermatologic and medical conditions at airport security. Our patient likely will never be stopped again for the suspicious lump on the left inner thigh, but many others will be stopped for similar reasons.
- Heymann WR. A cyst misinterpreted on airport scan as security threat. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1388. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3329
- Mayer JE, Adams BB. Nodular melanoma serendipitously detected by airport full body scanners. Dermatology. 2015;230:16-17. doi:10.1159/000368045
- Caine P, Javed MU, Karoo ROS. A desmoplastic melanoma detected by an airport security scanner. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2016.02.022
- Naraynsingh V, Cawich SO, Maharaj R, et al. Inguinal hernia and airport scanners: an emerging indication for repair? 2013;2013:952835. Case Rep Med. doi:10.1155/2013/952835
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented at the dermatology clinic with a growing lesion on the left medial thigh.
Physical examination revealed a 5-cm, pedunculated, fatty nodule on the left medial thigh that was clinically consistent with nevus lipomatosis (NL)(Figure). Although benign, trouble traveling through airport security prompted the patient to request shave removal, which subsequently was performed. Histology showed a large pedunculated nodule with prominent adipose tissue, consistent with NL. At 3-month follow-up, the patient reported getting through airport security multiple times without incident.

Nevus lipomatosis is a benign fatty lesion most commonly found on the medial thighs or trunk of adults. The lesion usually is asymptomatic but can become irritated by rubbing or catching on clothing. Our patient had symptomatic NL that caused delays getting through airport security; he experienced full resolution after simple shave removal. In rare instances, both benign and malignant skin conditions have been seen on airport scanning devices since the introduction of increased security measures following September 11, 2001. In 2016, Heymann1 reported a man with a 1.5-cm epidermal inclusion cyst detected by airport security scanners, prompting the traveler to request and carry a medically explanatory letter used to get through security. In 2015 Mayer and Adams2 described a case of nodular melanoma that was detected 20 times over a period of 2 months by airport scanners, and in 2016, Caine et al3 reported a case of desmoplastic melanoma that was detected by airport security, but after its removal was not identified by security for the next 40 flights. Noncutaneous pathology also can be detected by airport scanners. In 2013, Naraynsingh et al4 reported a man with a large left reducible inguinal hernia who was stopped by airport security and subjected to an invasive physical examination of the area. These instances demonstrate the breadth of conditions that can be cumbersome when individuals are traveling by airplane in our current security climate.
Our patient had to go through the trouble of having the benign NL lesion removed to avoid the hassle of repeatedly being stopped by airport security. The patient had the lesion removed and is doing well, but the procedure could have been avoided if systems existed to help patients with dermatologic and medical conditions at airport security. Our patient likely will never be stopped again for the suspicious lump on the left inner thigh, but many others will be stopped for similar reasons.
To the Editor:
A 47-year-old man presented at the dermatology clinic with a growing lesion on the left medial thigh.
Physical examination revealed a 5-cm, pedunculated, fatty nodule on the left medial thigh that was clinically consistent with nevus lipomatosis (NL)(Figure). Although benign, trouble traveling through airport security prompted the patient to request shave removal, which subsequently was performed. Histology showed a large pedunculated nodule with prominent adipose tissue, consistent with NL. At 3-month follow-up, the patient reported getting through airport security multiple times without incident.

Nevus lipomatosis is a benign fatty lesion most commonly found on the medial thighs or trunk of adults. The lesion usually is asymptomatic but can become irritated by rubbing or catching on clothing. Our patient had symptomatic NL that caused delays getting through airport security; he experienced full resolution after simple shave removal. In rare instances, both benign and malignant skin conditions have been seen on airport scanning devices since the introduction of increased security measures following September 11, 2001. In 2016, Heymann1 reported a man with a 1.5-cm epidermal inclusion cyst detected by airport security scanners, prompting the traveler to request and carry a medically explanatory letter used to get through security. In 2015 Mayer and Adams2 described a case of nodular melanoma that was detected 20 times over a period of 2 months by airport scanners, and in 2016, Caine et al3 reported a case of desmoplastic melanoma that was detected by airport security, but after its removal was not identified by security for the next 40 flights. Noncutaneous pathology also can be detected by airport scanners. In 2013, Naraynsingh et al4 reported a man with a large left reducible inguinal hernia who was stopped by airport security and subjected to an invasive physical examination of the area. These instances demonstrate the breadth of conditions that can be cumbersome when individuals are traveling by airplane in our current security climate.
Our patient had to go through the trouble of having the benign NL lesion removed to avoid the hassle of repeatedly being stopped by airport security. The patient had the lesion removed and is doing well, but the procedure could have been avoided if systems existed to help patients with dermatologic and medical conditions at airport security. Our patient likely will never be stopped again for the suspicious lump on the left inner thigh, but many others will be stopped for similar reasons.
- Heymann WR. A cyst misinterpreted on airport scan as security threat. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1388. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3329
- Mayer JE, Adams BB. Nodular melanoma serendipitously detected by airport full body scanners. Dermatology. 2015;230:16-17. doi:10.1159/000368045
- Caine P, Javed MU, Karoo ROS. A desmoplastic melanoma detected by an airport security scanner. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2016.02.022
- Naraynsingh V, Cawich SO, Maharaj R, et al. Inguinal hernia and airport scanners: an emerging indication for repair? 2013;2013:952835. Case Rep Med. doi:10.1155/2013/952835
- Heymann WR. A cyst misinterpreted on airport scan as security threat. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152:1388. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.3329
- Mayer JE, Adams BB. Nodular melanoma serendipitously detected by airport full body scanners. Dermatology. 2015;230:16-17. doi:10.1159/000368045
- Caine P, Javed MU, Karoo ROS. A desmoplastic melanoma detected by an airport security scanner. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2016.02.022
- Naraynsingh V, Cawich SO, Maharaj R, et al. Inguinal hernia and airport scanners: an emerging indication for repair? 2013;2013:952835. Case Rep Med. doi:10.1155/2013/952835
Practice Points
- Nevus lipomatosis is a benign fatty lesion that most commonly is found on the medial thighs or trunk of adults.
- Both benign and malignant skin conditions have been detected on airport scanning devices.
- At times, patients must go through the hassle of having the benign lesions removed to avoid repeated problems at airport security.
Is a single dose of HPV vaccine enough?
In an April press release, the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) of the World Health Organization (WHO) reported the findings of their review concerning the efficacy of various dose schedules for human papillomavirus (HPV). “A single-dose HPV vaccine delivers solid protection against HPV, the virus that causes cervical cancer, that is comparable to 2-dose schedules,” according to SAGE.
This statement comes on the heels of an article published in the November 2021 issue of Lancet Oncology about a study in India. It found that a single dose of the vaccine provides protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and 18 similar to that provided by two or three doses.
Will this new information lead French authorities to change their recommendations? What do French specialists think? At the 45th Congress of the French Society for Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases (SFCPCV), Geoffroy Canlorbe, MD, PhD, of the department of gynecologic and breast surgery and oncology, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, shared his thoughts.
With respect to the Indian study, Dr. Canlorbe pointed out that while its findings would need “to be confirmed by other studies,” they were, nonetheless,
India and France
During the congress press conference, he went on to say that, at this stage, the findings “cannot be extrapolated” to France. This is because the country’s situation is different. HPV vaccination coverage is low; estimates put it at 23.7%, placing the country 28th out of 31 in Europe.
“This poor coverage has nothing to do with health care–related logistical or organizational issues; instead, it has to do with people’s mistrust when it comes to vaccination. Here, people who get the first dose get the subsequent ones,” said Dr. Canlorbe. “The very fact of getting two to three doses allows the person’s body to increase the production of antibodies and get a longer-lasting response to the vaccine.”
In addition, he drew attention to several limitations of the Indian study. Initially, the team had planned to enroll 20,000 participants. In the end, there were around 17,000, and these were allocated to three cohorts: single-dose, two-dose, and three-dose. Furthermore, the primary objective, which had initially been focused on precancerous and cancerous lesions, was revised. The new aim was to compare vaccine efficacy of single dose to that of three and two doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination. In about 90% of cases, the HPV infection went away spontaneously in 2 years without inducing lesions. Finally, the participants were women in India; therefore, the results cannot necessarily be generalized to the French population.
“This information has to be confirmed. However, as far as I know, there are no new studies going on at the moment. The Indian study, on the other hand, is still in progress,” said Dr. Canlorbe.
“In France, I think that for the time being we should stick to the studies that are currently available, which have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of two or three doses,” he concluded. In support of this approach, he cited a study on the effects of the national HPV vaccination program in England; there, the vaccination coverage is 80%.
This program was associated with a 95% risk reduction for precancerous lesions and an 87% reduction in the number of cancers, confirming the good results already achieved by Sweden and Australia.
In his comments on the WHO’s stance (which differs from that of the French experts), Jean-Luc Mergui, MD, gynecologist in the department of colposcopy and hysteroscopy at Pitié-Salpêtrière, and former president of the SFCPCV, offered an eloquent comparison: “The WHO also recommends 6 months of breastfeeding as a method of contraception, but this isn’t what’s recommended in France, for the risk of getting pregnant nevertheless remains.”
Indian study highlights
Partha Basu, MD, PhD, of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in Lyon, France, and colleagues compared vaccine efficacy of a single dose of Gardasil (HPV 9-valent vaccine, recombinant) to that of two and three doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and HPV 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination.
According to the protocol, the plan was to recruit 20,000 unmarried girls, aged 10-18 years, from across India. Recruitment was initiated in September 2009. However, in response to seven unexplained deaths reported in another ongoing HPV vaccination demonstration program in the country, the Indian government issued a notification in April 2010 to stop further recruitment and HPV vaccination in all clinical trials. At this point, Dr. Basu and his team had recruited 17,729 eligible girls.
After suspension of recruitment and vaccination, their randomized trial was converted to a longitudinal, prospective, cohort study by default.
Vaccinated participants were followed up over a median duration of 9 years. In all, 4,348 participants had three doses, 4,980 had two doses (at 0 and 6 months), and 4,949 had a single dose. Cervical specimens were collected from participants 18 months after marriage or 6 months after first childbirth, whichever was earlier, to assess incident and persistent HPV infections. Participants were invited to an annual cervical cancer screening once they reached age 25 years and were married.
A single dose of HPV vaccine provides similar protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and HPV 18, the genotypes responsible for nearly 70% of cervical cancers, compared with that provided by two or three doses. Vaccine efficacy against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection among participants evaluable for the endpoint was 95.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 85.0-99.9) in the single-dose default cohort (2,135 women assessed), 93.1% (95% CI, 77.3-99.8) in the two-dose cohort (1,452 women assessed), and 93.3% (95% CI, 77.5-99.7) in three-dose recipients (1,460 women assessed).
Dr. Canlorbe reported no relevant financial relationships regarding the content of this article.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. An English version appeared on Medscape.com.
In an April press release, the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) of the World Health Organization (WHO) reported the findings of their review concerning the efficacy of various dose schedules for human papillomavirus (HPV). “A single-dose HPV vaccine delivers solid protection against HPV, the virus that causes cervical cancer, that is comparable to 2-dose schedules,” according to SAGE.
This statement comes on the heels of an article published in the November 2021 issue of Lancet Oncology about a study in India. It found that a single dose of the vaccine provides protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and 18 similar to that provided by two or three doses.
Will this new information lead French authorities to change their recommendations? What do French specialists think? At the 45th Congress of the French Society for Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases (SFCPCV), Geoffroy Canlorbe, MD, PhD, of the department of gynecologic and breast surgery and oncology, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, shared his thoughts.
With respect to the Indian study, Dr. Canlorbe pointed out that while its findings would need “to be confirmed by other studies,” they were, nonetheless,
India and France
During the congress press conference, he went on to say that, at this stage, the findings “cannot be extrapolated” to France. This is because the country’s situation is different. HPV vaccination coverage is low; estimates put it at 23.7%, placing the country 28th out of 31 in Europe.
“This poor coverage has nothing to do with health care–related logistical or organizational issues; instead, it has to do with people’s mistrust when it comes to vaccination. Here, people who get the first dose get the subsequent ones,” said Dr. Canlorbe. “The very fact of getting two to three doses allows the person’s body to increase the production of antibodies and get a longer-lasting response to the vaccine.”
In addition, he drew attention to several limitations of the Indian study. Initially, the team had planned to enroll 20,000 participants. In the end, there were around 17,000, and these were allocated to three cohorts: single-dose, two-dose, and three-dose. Furthermore, the primary objective, which had initially been focused on precancerous and cancerous lesions, was revised. The new aim was to compare vaccine efficacy of single dose to that of three and two doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination. In about 90% of cases, the HPV infection went away spontaneously in 2 years without inducing lesions. Finally, the participants were women in India; therefore, the results cannot necessarily be generalized to the French population.
“This information has to be confirmed. However, as far as I know, there are no new studies going on at the moment. The Indian study, on the other hand, is still in progress,” said Dr. Canlorbe.
“In France, I think that for the time being we should stick to the studies that are currently available, which have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of two or three doses,” he concluded. In support of this approach, he cited a study on the effects of the national HPV vaccination program in England; there, the vaccination coverage is 80%.
This program was associated with a 95% risk reduction for precancerous lesions and an 87% reduction in the number of cancers, confirming the good results already achieved by Sweden and Australia.
In his comments on the WHO’s stance (which differs from that of the French experts), Jean-Luc Mergui, MD, gynecologist in the department of colposcopy and hysteroscopy at Pitié-Salpêtrière, and former president of the SFCPCV, offered an eloquent comparison: “The WHO also recommends 6 months of breastfeeding as a method of contraception, but this isn’t what’s recommended in France, for the risk of getting pregnant nevertheless remains.”
Indian study highlights
Partha Basu, MD, PhD, of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in Lyon, France, and colleagues compared vaccine efficacy of a single dose of Gardasil (HPV 9-valent vaccine, recombinant) to that of two and three doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and HPV 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination.
According to the protocol, the plan was to recruit 20,000 unmarried girls, aged 10-18 years, from across India. Recruitment was initiated in September 2009. However, in response to seven unexplained deaths reported in another ongoing HPV vaccination demonstration program in the country, the Indian government issued a notification in April 2010 to stop further recruitment and HPV vaccination in all clinical trials. At this point, Dr. Basu and his team had recruited 17,729 eligible girls.
After suspension of recruitment and vaccination, their randomized trial was converted to a longitudinal, prospective, cohort study by default.
Vaccinated participants were followed up over a median duration of 9 years. In all, 4,348 participants had three doses, 4,980 had two doses (at 0 and 6 months), and 4,949 had a single dose. Cervical specimens were collected from participants 18 months after marriage or 6 months after first childbirth, whichever was earlier, to assess incident and persistent HPV infections. Participants were invited to an annual cervical cancer screening once they reached age 25 years and were married.
A single dose of HPV vaccine provides similar protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and HPV 18, the genotypes responsible for nearly 70% of cervical cancers, compared with that provided by two or three doses. Vaccine efficacy against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection among participants evaluable for the endpoint was 95.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 85.0-99.9) in the single-dose default cohort (2,135 women assessed), 93.1% (95% CI, 77.3-99.8) in the two-dose cohort (1,452 women assessed), and 93.3% (95% CI, 77.5-99.7) in three-dose recipients (1,460 women assessed).
Dr. Canlorbe reported no relevant financial relationships regarding the content of this article.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. An English version appeared on Medscape.com.
In an April press release, the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) of the World Health Organization (WHO) reported the findings of their review concerning the efficacy of various dose schedules for human papillomavirus (HPV). “A single-dose HPV vaccine delivers solid protection against HPV, the virus that causes cervical cancer, that is comparable to 2-dose schedules,” according to SAGE.
This statement comes on the heels of an article published in the November 2021 issue of Lancet Oncology about a study in India. It found that a single dose of the vaccine provides protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and 18 similar to that provided by two or three doses.
Will this new information lead French authorities to change their recommendations? What do French specialists think? At the 45th Congress of the French Society for Colposcopy and Cervical and Vaginal Diseases (SFCPCV), Geoffroy Canlorbe, MD, PhD, of the department of gynecologic and breast surgery and oncology, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, shared his thoughts.
With respect to the Indian study, Dr. Canlorbe pointed out that while its findings would need “to be confirmed by other studies,” they were, nonetheless,
India and France
During the congress press conference, he went on to say that, at this stage, the findings “cannot be extrapolated” to France. This is because the country’s situation is different. HPV vaccination coverage is low; estimates put it at 23.7%, placing the country 28th out of 31 in Europe.
“This poor coverage has nothing to do with health care–related logistical or organizational issues; instead, it has to do with people’s mistrust when it comes to vaccination. Here, people who get the first dose get the subsequent ones,” said Dr. Canlorbe. “The very fact of getting two to three doses allows the person’s body to increase the production of antibodies and get a longer-lasting response to the vaccine.”
In addition, he drew attention to several limitations of the Indian study. Initially, the team had planned to enroll 20,000 participants. In the end, there were around 17,000, and these were allocated to three cohorts: single-dose, two-dose, and three-dose. Furthermore, the primary objective, which had initially been focused on precancerous and cancerous lesions, was revised. The new aim was to compare vaccine efficacy of single dose to that of three and two doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination. In about 90% of cases, the HPV infection went away spontaneously in 2 years without inducing lesions. Finally, the participants were women in India; therefore, the results cannot necessarily be generalized to the French population.
“This information has to be confirmed. However, as far as I know, there are no new studies going on at the moment. The Indian study, on the other hand, is still in progress,” said Dr. Canlorbe.
“In France, I think that for the time being we should stick to the studies that are currently available, which have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of two or three doses,” he concluded. In support of this approach, he cited a study on the effects of the national HPV vaccination program in England; there, the vaccination coverage is 80%.
This program was associated with a 95% risk reduction for precancerous lesions and an 87% reduction in the number of cancers, confirming the good results already achieved by Sweden and Australia.
In his comments on the WHO’s stance (which differs from that of the French experts), Jean-Luc Mergui, MD, gynecologist in the department of colposcopy and hysteroscopy at Pitié-Salpêtrière, and former president of the SFCPCV, offered an eloquent comparison: “The WHO also recommends 6 months of breastfeeding as a method of contraception, but this isn’t what’s recommended in France, for the risk of getting pregnant nevertheless remains.”
Indian study highlights
Partha Basu, MD, PhD, of the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in Lyon, France, and colleagues compared vaccine efficacy of a single dose of Gardasil (HPV 9-valent vaccine, recombinant) to that of two and three doses in protecting against persistent HPV 16 and HPV 18 infection at 10 years postvaccination.
According to the protocol, the plan was to recruit 20,000 unmarried girls, aged 10-18 years, from across India. Recruitment was initiated in September 2009. However, in response to seven unexplained deaths reported in another ongoing HPV vaccination demonstration program in the country, the Indian government issued a notification in April 2010 to stop further recruitment and HPV vaccination in all clinical trials. At this point, Dr. Basu and his team had recruited 17,729 eligible girls.
After suspension of recruitment and vaccination, their randomized trial was converted to a longitudinal, prospective, cohort study by default.
Vaccinated participants were followed up over a median duration of 9 years. In all, 4,348 participants had three doses, 4,980 had two doses (at 0 and 6 months), and 4,949 had a single dose. Cervical specimens were collected from participants 18 months after marriage or 6 months after first childbirth, whichever was earlier, to assess incident and persistent HPV infections. Participants were invited to an annual cervical cancer screening once they reached age 25 years and were married.
A single dose of HPV vaccine provides similar protection against persistent infection from HPV 16 and HPV 18, the genotypes responsible for nearly 70% of cervical cancers, compared with that provided by two or three doses. Vaccine efficacy against persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection among participants evaluable for the endpoint was 95.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 85.0-99.9) in the single-dose default cohort (2,135 women assessed), 93.1% (95% CI, 77.3-99.8) in the two-dose cohort (1,452 women assessed), and 93.3% (95% CI, 77.5-99.7) in three-dose recipients (1,460 women assessed).
Dr. Canlorbe reported no relevant financial relationships regarding the content of this article.
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. An English version appeared on Medscape.com.
Bored? Change the world or read a book
A weekend, for most of us in solo practice, doesn’t really signify time off from work. It just means we’re not seeing patients at the office.
There’s always business stuff to do (like payroll and paying bills), legal cases to review, the never-ending forms for a million things, and all the other stuff there never seems to be enough time to do on weekdays.
So this weekend I started attacking the pile after dinner on Friday and found myself done by Saturday afternoon. Which is rare, usually I spend the better part of a weekend at my desk.
And then, unexpectedly faced with an empty desk, I found myself wondering what to do.
Boredom is one of the odder human conditions. Certainly, there are more ways to waste time now than there ever have been. TV, Netflix, phone games, TikTok, books, just to name a few.
But do we always have to be entertained? Many great scientists have said that world-changing ideas have come to them when they weren’t working, such as while showering or riding to work. Leo Szilard was crossing a London street in 1933 when he suddenly saw how a nuclear chain reaction would be self-sustaining once initiated. (Fortunately, he wasn’t hit by a car in the process.)
But I’m not Szilard. So I rationalized a reason not to exercise and sat on the couch with a book.
The remarkable human brain doesn’t shut down easily. With nothing else to do, most other mammals tend to doze off. But not us. It’s always on, trying to think of the next goal, the next move, the next whatever.
Having nothing to do sounds like a great idea, until you have nothing to do. It may be fine for a few days, but after a while you realize there’s only so long you can stare at the waves or mountains before your mind turns back to “what’s next.”
This isn’t a bad thing. Being bored is probably constructive. Without realizing it we use it to form new ideas and start new plans.
Maybe this is why we’re here. The mind that keeps working is a powerful tool, driving us forward in all walks of life. Perhaps it’s this feature that pushed the development of intelligence further and led us to form civilizations.
Perhaps it’s the real reason we keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A weekend, for most of us in solo practice, doesn’t really signify time off from work. It just means we’re not seeing patients at the office.
There’s always business stuff to do (like payroll and paying bills), legal cases to review, the never-ending forms for a million things, and all the other stuff there never seems to be enough time to do on weekdays.
So this weekend I started attacking the pile after dinner on Friday and found myself done by Saturday afternoon. Which is rare, usually I spend the better part of a weekend at my desk.
And then, unexpectedly faced with an empty desk, I found myself wondering what to do.
Boredom is one of the odder human conditions. Certainly, there are more ways to waste time now than there ever have been. TV, Netflix, phone games, TikTok, books, just to name a few.
But do we always have to be entertained? Many great scientists have said that world-changing ideas have come to them when they weren’t working, such as while showering or riding to work. Leo Szilard was crossing a London street in 1933 when he suddenly saw how a nuclear chain reaction would be self-sustaining once initiated. (Fortunately, he wasn’t hit by a car in the process.)
But I’m not Szilard. So I rationalized a reason not to exercise and sat on the couch with a book.
The remarkable human brain doesn’t shut down easily. With nothing else to do, most other mammals tend to doze off. But not us. It’s always on, trying to think of the next goal, the next move, the next whatever.
Having nothing to do sounds like a great idea, until you have nothing to do. It may be fine for a few days, but after a while you realize there’s only so long you can stare at the waves or mountains before your mind turns back to “what’s next.”
This isn’t a bad thing. Being bored is probably constructive. Without realizing it we use it to form new ideas and start new plans.
Maybe this is why we’re here. The mind that keeps working is a powerful tool, driving us forward in all walks of life. Perhaps it’s this feature that pushed the development of intelligence further and led us to form civilizations.
Perhaps it’s the real reason we keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A weekend, for most of us in solo practice, doesn’t really signify time off from work. It just means we’re not seeing patients at the office.
There’s always business stuff to do (like payroll and paying bills), legal cases to review, the never-ending forms for a million things, and all the other stuff there never seems to be enough time to do on weekdays.
So this weekend I started attacking the pile after dinner on Friday and found myself done by Saturday afternoon. Which is rare, usually I spend the better part of a weekend at my desk.
And then, unexpectedly faced with an empty desk, I found myself wondering what to do.
Boredom is one of the odder human conditions. Certainly, there are more ways to waste time now than there ever have been. TV, Netflix, phone games, TikTok, books, just to name a few.
But do we always have to be entertained? Many great scientists have said that world-changing ideas have come to them when they weren’t working, such as while showering or riding to work. Leo Szilard was crossing a London street in 1933 when he suddenly saw how a nuclear chain reaction would be self-sustaining once initiated. (Fortunately, he wasn’t hit by a car in the process.)
But I’m not Szilard. So I rationalized a reason not to exercise and sat on the couch with a book.
The remarkable human brain doesn’t shut down easily. With nothing else to do, most other mammals tend to doze off. But not us. It’s always on, trying to think of the next goal, the next move, the next whatever.
Having nothing to do sounds like a great idea, until you have nothing to do. It may be fine for a few days, but after a while you realize there’s only so long you can stare at the waves or mountains before your mind turns back to “what’s next.”
This isn’t a bad thing. Being bored is probably constructive. Without realizing it we use it to form new ideas and start new plans.
Maybe this is why we’re here. The mind that keeps working is a powerful tool, driving us forward in all walks of life. Perhaps it’s this feature that pushed the development of intelligence further and led us to form civilizations.
Perhaps it’s the real reason we keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Book Review: Quality improvement in mental health care
Sunil Khushalani and Antonio DePaolo,
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare”
(London: Routledge, Taylor & Francis, 2022)
Since the publication of our book, “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2014) almost a decade ago, “Transforming Mental Healthcare” is the first major book published about the use of a system for quality improvement across the health care continuum. That it has taken this long is probably surprising to those of us who have spent careers on trying to improve what is universally described as a system that is “broken” and in need of a major overhaul.
Every news cycle that reports mass violence typically spends a good bit of time talking about the failures of the mental health care system. One important lesson I learned when taking over the beleaguered Kings County (N.Y.) psychiatry service in 2009 (a department that has made extraordinary improvements over the years and is now exclaimed by the U.S. Department of Justice as “a model program”), is that the employees on the front line are often erroneously blamed for such failures.
The failure is systemic and usually starts at the top of the table of organization, not at the bottom. Dr. Khushalani and Dr. DePaolo have produced an excellent volume that should be purchased by every mental health care CEO and given “with thanks” to the local leaders overseeing the direct care of some of our nation’s most vulnerable patient populations.
The first part of “Transforming Mental Healthcare” provides an excellent overview of the current state of our mental health care system and its too numerous to name problems. This section could be a primer for all our legislators so their eyes can be opened to the failures on the ground that require their help in correcting. Many of the “failures” of our mental health care are societal failures – lack of affordable housing, access to care, reimbursement for care, gun access, etc. – and cannot be “fixed” by providers of care. Such problems are societal problems that call for societal and governmental solutions, and not only at the local level but from coast to coast.
The remainder of this easy to read and follow text provides many rich resources for the deliverers of mental health care. (e.g., plan-do-act, standard work, and A3 thinking).
The closing section focuses on leadership and culture – often overlooked to the detriment of any organization that doesn’t pay close attention to supporting both. Culture is cultivated and nourished by the organization’s leaders. Culture empowers staff to become problem solvers and agents of improvement. Empowered staff support and enrich their culture. Together a workplace that brings out the best of all its people is created, and burnout is held at bay.
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare” is a welcome and essential addition to the current morass, which is our mental health care delivery system, an oasis in the desert from which perhaps the lotus flower can emerge.
Dr. Merlino is emeritus professor of psychiatry, SUNY Downstate College of Medicine, Rhinebeck, N.Y., and formerly director of psychiatry at Kings County Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY. He is the coauthor of “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story.” .
Sunil Khushalani and Antonio DePaolo,
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare”
(London: Routledge, Taylor & Francis, 2022)
Since the publication of our book, “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2014) almost a decade ago, “Transforming Mental Healthcare” is the first major book published about the use of a system for quality improvement across the health care continuum. That it has taken this long is probably surprising to those of us who have spent careers on trying to improve what is universally described as a system that is “broken” and in need of a major overhaul.
Every news cycle that reports mass violence typically spends a good bit of time talking about the failures of the mental health care system. One important lesson I learned when taking over the beleaguered Kings County (N.Y.) psychiatry service in 2009 (a department that has made extraordinary improvements over the years and is now exclaimed by the U.S. Department of Justice as “a model program”), is that the employees on the front line are often erroneously blamed for such failures.
The failure is systemic and usually starts at the top of the table of organization, not at the bottom. Dr. Khushalani and Dr. DePaolo have produced an excellent volume that should be purchased by every mental health care CEO and given “with thanks” to the local leaders overseeing the direct care of some of our nation’s most vulnerable patient populations.
The first part of “Transforming Mental Healthcare” provides an excellent overview of the current state of our mental health care system and its too numerous to name problems. This section could be a primer for all our legislators so their eyes can be opened to the failures on the ground that require their help in correcting. Many of the “failures” of our mental health care are societal failures – lack of affordable housing, access to care, reimbursement for care, gun access, etc. – and cannot be “fixed” by providers of care. Such problems are societal problems that call for societal and governmental solutions, and not only at the local level but from coast to coast.
The remainder of this easy to read and follow text provides many rich resources for the deliverers of mental health care. (e.g., plan-do-act, standard work, and A3 thinking).
The closing section focuses on leadership and culture – often overlooked to the detriment of any organization that doesn’t pay close attention to supporting both. Culture is cultivated and nourished by the organization’s leaders. Culture empowers staff to become problem solvers and agents of improvement. Empowered staff support and enrich their culture. Together a workplace that brings out the best of all its people is created, and burnout is held at bay.
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare” is a welcome and essential addition to the current morass, which is our mental health care delivery system, an oasis in the desert from which perhaps the lotus flower can emerge.
Dr. Merlino is emeritus professor of psychiatry, SUNY Downstate College of Medicine, Rhinebeck, N.Y., and formerly director of psychiatry at Kings County Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY. He is the coauthor of “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story.” .
Sunil Khushalani and Antonio DePaolo,
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare”
(London: Routledge, Taylor & Francis, 2022)
Since the publication of our book, “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story” (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2014) almost a decade ago, “Transforming Mental Healthcare” is the first major book published about the use of a system for quality improvement across the health care continuum. That it has taken this long is probably surprising to those of us who have spent careers on trying to improve what is universally described as a system that is “broken” and in need of a major overhaul.
Every news cycle that reports mass violence typically spends a good bit of time talking about the failures of the mental health care system. One important lesson I learned when taking over the beleaguered Kings County (N.Y.) psychiatry service in 2009 (a department that has made extraordinary improvements over the years and is now exclaimed by the U.S. Department of Justice as “a model program”), is that the employees on the front line are often erroneously blamed for such failures.
The failure is systemic and usually starts at the top of the table of organization, not at the bottom. Dr. Khushalani and Dr. DePaolo have produced an excellent volume that should be purchased by every mental health care CEO and given “with thanks” to the local leaders overseeing the direct care of some of our nation’s most vulnerable patient populations.
The first part of “Transforming Mental Healthcare” provides an excellent overview of the current state of our mental health care system and its too numerous to name problems. This section could be a primer for all our legislators so their eyes can be opened to the failures on the ground that require their help in correcting. Many of the “failures” of our mental health care are societal failures – lack of affordable housing, access to care, reimbursement for care, gun access, etc. – and cannot be “fixed” by providers of care. Such problems are societal problems that call for societal and governmental solutions, and not only at the local level but from coast to coast.
The remainder of this easy to read and follow text provides many rich resources for the deliverers of mental health care. (e.g., plan-do-act, standard work, and A3 thinking).
The closing section focuses on leadership and culture – often overlooked to the detriment of any organization that doesn’t pay close attention to supporting both. Culture is cultivated and nourished by the organization’s leaders. Culture empowers staff to become problem solvers and agents of improvement. Empowered staff support and enrich their culture. Together a workplace that brings out the best of all its people is created, and burnout is held at bay.
“Transforming Mental Healthcare: Applying Performance Improvement Methods to Mental Healthcare” is a welcome and essential addition to the current morass, which is our mental health care delivery system, an oasis in the desert from which perhaps the lotus flower can emerge.
Dr. Merlino is emeritus professor of psychiatry, SUNY Downstate College of Medicine, Rhinebeck, N.Y., and formerly director of psychiatry at Kings County Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY. He is the coauthor of “Lean Behavioral Health: The Kings County Hospital Story.” .