User login
Depression: Think outside of the box for diagnosis, treatment
In the treatment of depression, clinicians are commonly dealing with a mix of comorbidities that are more complex than just depression, and as such, effective treatment options may likewise require thinking outside of the box – and beyond the definitions of the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision).
“The DSM-5 isn’t handed to us on tablets from Mount Sinai,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Mulva Clinic for the Neurosciences at the University of Texas at Austin. He spoke at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“Our patients don’t fall into these very convenient buckets,” Dr. Nemeroff said. “The problem with depression is patients have very high rates of morbidity and comorbidity.”
The array of potential psychiatric comorbidities that are common in depression is somewhat staggering: As many as 70% of patients also have social anxiety disorder; 67% of patients have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD); up to 65% of patients have panic disorder; 48% of patients have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD); and 42% have generalized anxiety disorder, Dr. Nemeroff said.
And while the DSM-5 may have all those bases covered, in real world clinical practice, cracking the code of each patient’s unique and often more complicated psychiatric profile – and how to best manage it – can be a challenge. But Dr. Nemeroff said important clues can guide the clinician’s path.
A key starting point is making sure to gauge the severity of the patient’s core depression with one of the validated depression scales – whether it’s the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory, the clinician-rated Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression, the clinician-rated Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale, or the Inventory of Depressive Symptoms, clinicians should pick one and track the score with each visit, Dr. Nemeroff advised.
“It doesn’t matter which tool you prefer – most tend to like the Beck Depression Scale, but the bottom line is that you have to get a measure of severity at every visit,” he said.
Among the most important comorbidities to identify as soon as possible is bipolar disorder, due to the potential worsening of the condition that can occur among those patients if treated with antidepressants, Dr. Nemeroff said.
“The question of whether the patient is bipolar should always be in the back of your mind,” he cautioned. “And if patients have been started on antidepressants, the clues may become evident very quickly.”
The most important indicator that the patient has bipolar disorder “is if they tell you that they were prescribed an antidepressant and it resulted in an increase in what we know to be hypomania – they may describe it as agitation or an inability to sleep,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Of note, the effect is much more common with SNRIs [serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors] than SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], he said.
“The effect is particularly notable with venlafaxine,” he said. “But SNRIs all have the propensity to switch people with depression into hypomania, but only patients who have bipolar disorder.”
“If you give a patient 150 mg of venlafaxine and they switch to developing hypomania, you now have the diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and you can treat them appropriately.”
Other important clues of bipolarity in depressed patients include:
- Family history: Most cases are genetically driven.
- Earlier age of onset (younger than age 25): “If the patient tells you they were depressed prepuberty, you should be thinking about the possibility of bipolar disorder, as it often presents as depression in childhood.”
- Psychotic features: As many as 80% of patients with psychotic depression end up being bipolar, Dr. Nemeroff said.
- Atypical depression: For example, depression with hypersomnia, or having an increased appetite instead of decreased, or a high amount of anxiety.
Remission should be the goal of treatment, and Dr. Nemeroff said that in efforts to accomplish that with the help of medications, psychiatrists may need to think “outside of the box” – or beyond the label.
“Many practitioners become slaves to the PDR [Physicians’ Desk Reference],” he said. “It is only a guide to what the clinical trials show, and not a mandate in terms of dosing.”
“There’s often strong data in the literature that supports going to a higher dose, if necessary, and I have [plenty] of patients, for instance, on 450 or 600 mg of venlafaxine who had not responded to 150 or even 300 mg.”
Treatment resistance
When patients continue to fail to respond, regardless of dosing or medication adjustments, Dr. Nemeroff suggested that clinicians should consider the potential important reasons. For instance, in addition to comorbid psychiatric conditions, practitioners should determine if there are medical conditions that they are not aware of.
“Does the patient have an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid dysfunction, early Parkinson’s disease, or even something like cancer?” he said.
There is also the inevitable question of whether the patient is indeed taking the medication. “We know that 30% of our patients do not follow their prescriptions, so of course that’s an important question to ask,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Finally, while some pharmacogenomic tests are emerging with the suggestion of identifying which patients may or may not respond to certain drugs, Dr. Nemeroff says he’s seen little convincing evidence of their benefits.
“We have a problem in this field in that we don’t have the kinds of markers that they do in oncology, so we’re left with having to generally play trial and error,” he said.
“But when it comes to these pharmacogenomic tests, there’s just no ‘there there’,” he asserted. “From what I’ve seen so far, it’s frankly neuro-mythology.”
Dr. Nemeroff disclosed that he receives grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and serves as a consultant for and/or on the advisory boards of multiple pharmaceutical companies.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
In the treatment of depression, clinicians are commonly dealing with a mix of comorbidities that are more complex than just depression, and as such, effective treatment options may likewise require thinking outside of the box – and beyond the definitions of the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision).
“The DSM-5 isn’t handed to us on tablets from Mount Sinai,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Mulva Clinic for the Neurosciences at the University of Texas at Austin. He spoke at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“Our patients don’t fall into these very convenient buckets,” Dr. Nemeroff said. “The problem with depression is patients have very high rates of morbidity and comorbidity.”
The array of potential psychiatric comorbidities that are common in depression is somewhat staggering: As many as 70% of patients also have social anxiety disorder; 67% of patients have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD); up to 65% of patients have panic disorder; 48% of patients have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD); and 42% have generalized anxiety disorder, Dr. Nemeroff said.
And while the DSM-5 may have all those bases covered, in real world clinical practice, cracking the code of each patient’s unique and often more complicated psychiatric profile – and how to best manage it – can be a challenge. But Dr. Nemeroff said important clues can guide the clinician’s path.
A key starting point is making sure to gauge the severity of the patient’s core depression with one of the validated depression scales – whether it’s the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory, the clinician-rated Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression, the clinician-rated Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale, or the Inventory of Depressive Symptoms, clinicians should pick one and track the score with each visit, Dr. Nemeroff advised.
“It doesn’t matter which tool you prefer – most tend to like the Beck Depression Scale, but the bottom line is that you have to get a measure of severity at every visit,” he said.
Among the most important comorbidities to identify as soon as possible is bipolar disorder, due to the potential worsening of the condition that can occur among those patients if treated with antidepressants, Dr. Nemeroff said.
“The question of whether the patient is bipolar should always be in the back of your mind,” he cautioned. “And if patients have been started on antidepressants, the clues may become evident very quickly.”
The most important indicator that the patient has bipolar disorder “is if they tell you that they were prescribed an antidepressant and it resulted in an increase in what we know to be hypomania – they may describe it as agitation or an inability to sleep,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Of note, the effect is much more common with SNRIs [serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors] than SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], he said.
“The effect is particularly notable with venlafaxine,” he said. “But SNRIs all have the propensity to switch people with depression into hypomania, but only patients who have bipolar disorder.”
“If you give a patient 150 mg of venlafaxine and they switch to developing hypomania, you now have the diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and you can treat them appropriately.”
Other important clues of bipolarity in depressed patients include:
- Family history: Most cases are genetically driven.
- Earlier age of onset (younger than age 25): “If the patient tells you they were depressed prepuberty, you should be thinking about the possibility of bipolar disorder, as it often presents as depression in childhood.”
- Psychotic features: As many as 80% of patients with psychotic depression end up being bipolar, Dr. Nemeroff said.
- Atypical depression: For example, depression with hypersomnia, or having an increased appetite instead of decreased, or a high amount of anxiety.
Remission should be the goal of treatment, and Dr. Nemeroff said that in efforts to accomplish that with the help of medications, psychiatrists may need to think “outside of the box” – or beyond the label.
“Many practitioners become slaves to the PDR [Physicians’ Desk Reference],” he said. “It is only a guide to what the clinical trials show, and not a mandate in terms of dosing.”
“There’s often strong data in the literature that supports going to a higher dose, if necessary, and I have [plenty] of patients, for instance, on 450 or 600 mg of venlafaxine who had not responded to 150 or even 300 mg.”
Treatment resistance
When patients continue to fail to respond, regardless of dosing or medication adjustments, Dr. Nemeroff suggested that clinicians should consider the potential important reasons. For instance, in addition to comorbid psychiatric conditions, practitioners should determine if there are medical conditions that they are not aware of.
“Does the patient have an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid dysfunction, early Parkinson’s disease, or even something like cancer?” he said.
There is also the inevitable question of whether the patient is indeed taking the medication. “We know that 30% of our patients do not follow their prescriptions, so of course that’s an important question to ask,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Finally, while some pharmacogenomic tests are emerging with the suggestion of identifying which patients may or may not respond to certain drugs, Dr. Nemeroff says he’s seen little convincing evidence of their benefits.
“We have a problem in this field in that we don’t have the kinds of markers that they do in oncology, so we’re left with having to generally play trial and error,” he said.
“But when it comes to these pharmacogenomic tests, there’s just no ‘there there’,” he asserted. “From what I’ve seen so far, it’s frankly neuro-mythology.”
Dr. Nemeroff disclosed that he receives grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and serves as a consultant for and/or on the advisory boards of multiple pharmaceutical companies.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
In the treatment of depression, clinicians are commonly dealing with a mix of comorbidities that are more complex than just depression, and as such, effective treatment options may likewise require thinking outside of the box – and beyond the definitions of the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision).
“The DSM-5 isn’t handed to us on tablets from Mount Sinai,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair in the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the Mulva Clinic for the Neurosciences at the University of Texas at Austin. He spoke at the 21st Annual Psychopharmacology Update presented by Current Psychiatry and the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists.
“Our patients don’t fall into these very convenient buckets,” Dr. Nemeroff said. “The problem with depression is patients have very high rates of morbidity and comorbidity.”
The array of potential psychiatric comorbidities that are common in depression is somewhat staggering: As many as 70% of patients also have social anxiety disorder; 67% of patients have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD); up to 65% of patients have panic disorder; 48% of patients have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD); and 42% have generalized anxiety disorder, Dr. Nemeroff said.
And while the DSM-5 may have all those bases covered, in real world clinical practice, cracking the code of each patient’s unique and often more complicated psychiatric profile – and how to best manage it – can be a challenge. But Dr. Nemeroff said important clues can guide the clinician’s path.
A key starting point is making sure to gauge the severity of the patient’s core depression with one of the validated depression scales – whether it’s the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory, the clinician-rated Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression, the clinician-rated Montgomery Asberg Depression Rating Scale, or the Inventory of Depressive Symptoms, clinicians should pick one and track the score with each visit, Dr. Nemeroff advised.
“It doesn’t matter which tool you prefer – most tend to like the Beck Depression Scale, but the bottom line is that you have to get a measure of severity at every visit,” he said.
Among the most important comorbidities to identify as soon as possible is bipolar disorder, due to the potential worsening of the condition that can occur among those patients if treated with antidepressants, Dr. Nemeroff said.
“The question of whether the patient is bipolar should always be in the back of your mind,” he cautioned. “And if patients have been started on antidepressants, the clues may become evident very quickly.”
The most important indicator that the patient has bipolar disorder “is if they tell you that they were prescribed an antidepressant and it resulted in an increase in what we know to be hypomania – they may describe it as agitation or an inability to sleep,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Of note, the effect is much more common with SNRIs [serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors] than SSRIs [selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors], he said.
“The effect is particularly notable with venlafaxine,” he said. “But SNRIs all have the propensity to switch people with depression into hypomania, but only patients who have bipolar disorder.”
“If you give a patient 150 mg of venlafaxine and they switch to developing hypomania, you now have the diagnosis of bipolar disorder, and you can treat them appropriately.”
Other important clues of bipolarity in depressed patients include:
- Family history: Most cases are genetically driven.
- Earlier age of onset (younger than age 25): “If the patient tells you they were depressed prepuberty, you should be thinking about the possibility of bipolar disorder, as it often presents as depression in childhood.”
- Psychotic features: As many as 80% of patients with psychotic depression end up being bipolar, Dr. Nemeroff said.
- Atypical depression: For example, depression with hypersomnia, or having an increased appetite instead of decreased, or a high amount of anxiety.
Remission should be the goal of treatment, and Dr. Nemeroff said that in efforts to accomplish that with the help of medications, psychiatrists may need to think “outside of the box” – or beyond the label.
“Many practitioners become slaves to the PDR [Physicians’ Desk Reference],” he said. “It is only a guide to what the clinical trials show, and not a mandate in terms of dosing.”
“There’s often strong data in the literature that supports going to a higher dose, if necessary, and I have [plenty] of patients, for instance, on 450 or 600 mg of venlafaxine who had not responded to 150 or even 300 mg.”
Treatment resistance
When patients continue to fail to respond, regardless of dosing or medication adjustments, Dr. Nemeroff suggested that clinicians should consider the potential important reasons. For instance, in addition to comorbid psychiatric conditions, practitioners should determine if there are medical conditions that they are not aware of.
“Does the patient have an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid dysfunction, early Parkinson’s disease, or even something like cancer?” he said.
There is also the inevitable question of whether the patient is indeed taking the medication. “We know that 30% of our patients do not follow their prescriptions, so of course that’s an important question to ask,” Dr. Nemeroff said.
Finally, while some pharmacogenomic tests are emerging with the suggestion of identifying which patients may or may not respond to certain drugs, Dr. Nemeroff says he’s seen little convincing evidence of their benefits.
“We have a problem in this field in that we don’t have the kinds of markers that they do in oncology, so we’re left with having to generally play trial and error,” he said.
“But when it comes to these pharmacogenomic tests, there’s just no ‘there there’,” he asserted. “From what I’ve seen so far, it’s frankly neuro-mythology.”
Dr. Nemeroff disclosed that he receives grant/research support from the National Institutes of Health and serves as a consultant for and/or on the advisory boards of multiple pharmaceutical companies.
The Psychopharmacology Update was sponsored by Medscape Live. Medscape Live and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY UPDATE
Serum trace metals relate to lower risk of sleep disorders
, based on data from 3,660 individuals.
Previous research has shown an association between trace metals and sleep and sleep patterns, but data on the impact of serum trace metals on sleep disorders have been limited, wrote Ming-Gang Deng, MD, of Wuhan (China) University and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers reviewed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2016 to calculate the odds ratios of sleep disorders and serum zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and selenium (Se). The study population included adults aged 18 years and older, with an average age of 47.6 years. Approximately half of the participants were men, and the majority was non-Hispanic white. Serum Zn, Cu, and Se were identified at the Environmental Health Sciences Laboratory of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health. The lower limits of detection for Zn, Cu, and Se were 2.9 mcg/dL, 2.5 mcg/dL, and 4.5 mcg/L, respectively. Sleep disorders were assessed based on self-reports of discussions with health professionals about sleep disorders, and via the Sleep Disorder Questionnaire.
After adjusting for sociodemographic, behavioral characteristics, and health characteristics, adults in the highest tertiles of serum Zn had a 30% reduced risk of sleep disorders, compared with those in the lowest tertiles of serum Zn (odds ratio, 0.70; P = .035). In measures of trace metals ratios, serum Zn/Cu and Zn/Se also were significantly associated with reduced risk of sleep disorders for individuals in the highest tertiles, compared with those in the lowest tertiles (OR, 0.62 and OR, 0.68, respectively).
However, serum Cu, Se and Cu/Se were not associated with sleep disorder risk.
Sociodemographic factors included age, sex, race, education level, family income level; behavioral characteristics included smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and caffeine intake.
The researchers also used a restricted cubic spline model to examine the dose-response relationships between serum trace metals, serum trace metals ratios, and sleep disorders. In this analysis, higher levels of serum Zn, Zn/Cu, and Zn/Se were related to reduced risk of sleep disorders, while no significant association appeared between serum Cu, Se, or Cu/Se and sleep disorders risk.
The findings showing a lack of association between Se and sleep disorders were not consistent with previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Previous research has shown that a higher Se was less likely to be associated with trouble falling asleep, and has shown a potential treatment effect of Se on obstructive sleep apnea, they said.
“Although serum Cu and Se levels were not correlated to sleep disorders in our study, the Zn/Cu and Zn/Se may provide some novel insights,” they wrote. For example, Zn/Cu has been used as a predictor of several clinical complications related to an increased risk of sleep disorders including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and major depressive disorder, they noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, use of self-reports, and the inability to examine relationships between trace metals and specific sleep disorder symptoms, such as restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and obstructive sleep apnea, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large national sample, and support data from previous studies, they said.
“The inverse associations of serum Zn, and Zn/Cu, Zn/Se with sleep disorders enlightened us that increasing Zn intake may be an excellent approach to prevent sleep disorders due to its benefits from these three aspects,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from 3,660 individuals.
Previous research has shown an association between trace metals and sleep and sleep patterns, but data on the impact of serum trace metals on sleep disorders have been limited, wrote Ming-Gang Deng, MD, of Wuhan (China) University and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers reviewed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2016 to calculate the odds ratios of sleep disorders and serum zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and selenium (Se). The study population included adults aged 18 years and older, with an average age of 47.6 years. Approximately half of the participants were men, and the majority was non-Hispanic white. Serum Zn, Cu, and Se were identified at the Environmental Health Sciences Laboratory of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health. The lower limits of detection for Zn, Cu, and Se were 2.9 mcg/dL, 2.5 mcg/dL, and 4.5 mcg/L, respectively. Sleep disorders were assessed based on self-reports of discussions with health professionals about sleep disorders, and via the Sleep Disorder Questionnaire.
After adjusting for sociodemographic, behavioral characteristics, and health characteristics, adults in the highest tertiles of serum Zn had a 30% reduced risk of sleep disorders, compared with those in the lowest tertiles of serum Zn (odds ratio, 0.70; P = .035). In measures of trace metals ratios, serum Zn/Cu and Zn/Se also were significantly associated with reduced risk of sleep disorders for individuals in the highest tertiles, compared with those in the lowest tertiles (OR, 0.62 and OR, 0.68, respectively).
However, serum Cu, Se and Cu/Se were not associated with sleep disorder risk.
Sociodemographic factors included age, sex, race, education level, family income level; behavioral characteristics included smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and caffeine intake.
The researchers also used a restricted cubic spline model to examine the dose-response relationships between serum trace metals, serum trace metals ratios, and sleep disorders. In this analysis, higher levels of serum Zn, Zn/Cu, and Zn/Se were related to reduced risk of sleep disorders, while no significant association appeared between serum Cu, Se, or Cu/Se and sleep disorders risk.
The findings showing a lack of association between Se and sleep disorders were not consistent with previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Previous research has shown that a higher Se was less likely to be associated with trouble falling asleep, and has shown a potential treatment effect of Se on obstructive sleep apnea, they said.
“Although serum Cu and Se levels were not correlated to sleep disorders in our study, the Zn/Cu and Zn/Se may provide some novel insights,” they wrote. For example, Zn/Cu has been used as a predictor of several clinical complications related to an increased risk of sleep disorders including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and major depressive disorder, they noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, use of self-reports, and the inability to examine relationships between trace metals and specific sleep disorder symptoms, such as restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and obstructive sleep apnea, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large national sample, and support data from previous studies, they said.
“The inverse associations of serum Zn, and Zn/Cu, Zn/Se with sleep disorders enlightened us that increasing Zn intake may be an excellent approach to prevent sleep disorders due to its benefits from these three aspects,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from 3,660 individuals.
Previous research has shown an association between trace metals and sleep and sleep patterns, but data on the impact of serum trace metals on sleep disorders have been limited, wrote Ming-Gang Deng, MD, of Wuhan (China) University and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, the researchers reviewed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011-2016 to calculate the odds ratios of sleep disorders and serum zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and selenium (Se). The study population included adults aged 18 years and older, with an average age of 47.6 years. Approximately half of the participants were men, and the majority was non-Hispanic white. Serum Zn, Cu, and Se were identified at the Environmental Health Sciences Laboratory of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health. The lower limits of detection for Zn, Cu, and Se were 2.9 mcg/dL, 2.5 mcg/dL, and 4.5 mcg/L, respectively. Sleep disorders were assessed based on self-reports of discussions with health professionals about sleep disorders, and via the Sleep Disorder Questionnaire.
After adjusting for sociodemographic, behavioral characteristics, and health characteristics, adults in the highest tertiles of serum Zn had a 30% reduced risk of sleep disorders, compared with those in the lowest tertiles of serum Zn (odds ratio, 0.70; P = .035). In measures of trace metals ratios, serum Zn/Cu and Zn/Se also were significantly associated with reduced risk of sleep disorders for individuals in the highest tertiles, compared with those in the lowest tertiles (OR, 0.62 and OR, 0.68, respectively).
However, serum Cu, Se and Cu/Se were not associated with sleep disorder risk.
Sociodemographic factors included age, sex, race, education level, family income level; behavioral characteristics included smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and caffeine intake.
The researchers also used a restricted cubic spline model to examine the dose-response relationships between serum trace metals, serum trace metals ratios, and sleep disorders. In this analysis, higher levels of serum Zn, Zn/Cu, and Zn/Se were related to reduced risk of sleep disorders, while no significant association appeared between serum Cu, Se, or Cu/Se and sleep disorders risk.
The findings showing a lack of association between Se and sleep disorders were not consistent with previous studies, the researchers wrote in their discussion. Previous research has shown that a higher Se was less likely to be associated with trouble falling asleep, and has shown a potential treatment effect of Se on obstructive sleep apnea, they said.
“Although serum Cu and Se levels were not correlated to sleep disorders in our study, the Zn/Cu and Zn/Se may provide some novel insights,” they wrote. For example, Zn/Cu has been used as a predictor of several clinical complications related to an increased risk of sleep disorders including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and major depressive disorder, they noted.
The findings were limited by several factors including the cross-sectional design, use of self-reports, and the inability to examine relationships between trace metals and specific sleep disorder symptoms, such as restless legs syndrome, insomnia, and obstructive sleep apnea, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the large national sample, and support data from previous studies, they said.
“The inverse associations of serum Zn, and Zn/Cu, Zn/Se with sleep disorders enlightened us that increasing Zn intake may be an excellent approach to prevent sleep disorders due to its benefits from these three aspects,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS
COVID isolated people. Long COVID makes it worse
A year ago in December, mapping specialist Whitney Tyshynski, 35, was working out 5 days a week with a personal trainer near her home in Alberta, Canada, doing 5k trail runs, lifting heavy weights, and feeling good. Then, in January she got COVID-19. The symptoms never went away.
Nowadays, Ms. Tyshynski needs a walker to retrieve her mail, a half-block trip she can’t make without fear of fainting. Because she gets dizzy when she drives, she rarely goes anywhere in her car. Going for a dog walk with a friend means sitting in a car and watching the friend and the dogs in an open field. And since fainting at Costco during the summer, she’s afraid to shop by herself.
Because she lives alone and her closest relatives are an hour and a half away, Ms. Tyshynski is dependent on friends. But she’s reluctant to lean on them because they already have trouble understanding how debilitating her lingering symptoms can be.
“I’ve had people pretty much insinuate that I’m lazy,” she says.
There’s no question that COVID-19 cut people off from one another. But for those like Ms. Tyshynski who have long COVID, that disconnect has never ended. that the condition is real.
At worst, as Ms. Tyshynski has discovered, people don’t take it seriously and accuse those who have it of exaggerating their health woes. In that way, long COVID can be as isolating as the original illness.
“Isolation in long COVID comes in various forms and it’s not primarily just that physical isolation,” says Yochai Re’em, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in New York who has experienced long COVID and blogs about the condition for Psychology Today. “A different yet equally challenging type of isolation is the emotional isolation, where you need more emotional support, connection with other people who can appreciate what it is you are going through without putting their own needs and desires onto you – and that can be hard to find.”
It’s hard to find in part because of what Dr. Re’em sees as a collective belief that anyone who feels bad should be able to get better by exercising, researching, or going to a doctor.
“Society thinks you need to take some kind of action and usually that’s a physical action,” he says. “And that attitude is tremendously problematic in this illness because of the postexertional malaise that people experience: When people exert themselves, their symptoms get worse. And so the action that people take can’t be that traditional action that we’re used to taking in our society.”
Long COVID patients often have their feelings invalidated not just by friends, loved ones, and extended family, but by health care providers. That can heighten feelings of isolation, particularly for people who live alone, says Jordan Anderson, DO, a neuropsychiatrist and assistant professor of psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
The first patients Dr. Anderson saw as part of OHSU’s long COVID program contracted the virus in February 2020. Because the program addresses both the physical and mental health components of the condition, Dr. Anderson has seen a lot of people whose emotional challenges are similar to those Ms. Tyshynski faces.
“I think there’s a lack of understanding that leads to people just not necessarily taking it seriously,” he says. “Plus, the symptoms of long COVID do wax and wane. They’re not static. So people can be feeling pretty good one day and be feeling terrible the next. There’s some predictability to it, but it’s not absolutely predictable. It can be difficult for people to understand.”
Both Dr. Anderson and Dr. Re’em stress that long COVID patients need to prioritize their own energy regardless of what they’re being told by those who don’t understand the illness. Dr. Anderson offers to speak to his patients’ spouses to educate them about the realities of the condition because, he says, “any kind of lack of awareness or understanding in a family member or close support could potentially isolate the person struggling with long COVID.”
Depending on how open-minded and motivated a friend or relative is, they might develop more empathy with time and education, Dr. Re’em says. But for others, dealing with a confusing, unfamiliar chronic illness can be overwhelming and provoke anxiety.
“The hopelessness is too much for them to sit with, so instead they say things like ‘just push through it,’ or ‘just do X, Y, and Z,’ because psychologically it’s too much for them to take on that burden,” he says.
The good news is that there are plenty of web-based support groups for people with long COVID, including Body Politic (which Dr. Re’em is affiliated with), Survivor Corps, and on Facebook. “The patient community with this illness is tremendous, absolutely tremendous,” Dr. Re’em says. “Those people can be found and they can support each other.”
Some long COVID clinics run groups, as do individual practitioners such as Dr. Re’em, although those can be challenging to join. For instance, Dr. Re’em’s are only for New York state residents.
The key to finding a group is to be patient, because finding the right one takes time and energy.
“There are support groups that exist, but they are not as prevalent as I would like them to be,” Dr. Anderson says.
OHSU had an educational support group run by a social worker affiliated with the long COVID hub, but when the social worker left the program, the program was put on hold.
There’s a psychotherapy group operating out of the psychiatry department, but the patients are recruited exclusively from Dr. Anderson’s clinic and access is limited.
“The services exist, but I think that generally they’re sparse and pretty geographically dependent,” Dr. Anderson says. “I think you’d probably more likely be able to find something like this in a city or an area that has an academic institution or a place with a lot of resources rather than out in a rural community.”
Ms. Tyshynski opted not to join a group for fear it would increase the depression and anxiety that she had even before developing long COVID. When she and her family joined a cancer support group when her father was ill, she found it more depressing than helpful. Where she has found support is from the cofounder of the animal rescue society where she volunteers, a woman who has had long COVID for more than 2 years and has been a source of comfort and advice.
It’s one of the rare reminders Ms. Tyshynski has that even though she may live alone, she’s not completely alone. “Other people are going through this, too,” she says. “It helps to remember that.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A year ago in December, mapping specialist Whitney Tyshynski, 35, was working out 5 days a week with a personal trainer near her home in Alberta, Canada, doing 5k trail runs, lifting heavy weights, and feeling good. Then, in January she got COVID-19. The symptoms never went away.
Nowadays, Ms. Tyshynski needs a walker to retrieve her mail, a half-block trip she can’t make without fear of fainting. Because she gets dizzy when she drives, she rarely goes anywhere in her car. Going for a dog walk with a friend means sitting in a car and watching the friend and the dogs in an open field. And since fainting at Costco during the summer, she’s afraid to shop by herself.
Because she lives alone and her closest relatives are an hour and a half away, Ms. Tyshynski is dependent on friends. But she’s reluctant to lean on them because they already have trouble understanding how debilitating her lingering symptoms can be.
“I’ve had people pretty much insinuate that I’m lazy,” she says.
There’s no question that COVID-19 cut people off from one another. But for those like Ms. Tyshynski who have long COVID, that disconnect has never ended. that the condition is real.
At worst, as Ms. Tyshynski has discovered, people don’t take it seriously and accuse those who have it of exaggerating their health woes. In that way, long COVID can be as isolating as the original illness.
“Isolation in long COVID comes in various forms and it’s not primarily just that physical isolation,” says Yochai Re’em, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in New York who has experienced long COVID and blogs about the condition for Psychology Today. “A different yet equally challenging type of isolation is the emotional isolation, where you need more emotional support, connection with other people who can appreciate what it is you are going through without putting their own needs and desires onto you – and that can be hard to find.”
It’s hard to find in part because of what Dr. Re’em sees as a collective belief that anyone who feels bad should be able to get better by exercising, researching, or going to a doctor.
“Society thinks you need to take some kind of action and usually that’s a physical action,” he says. “And that attitude is tremendously problematic in this illness because of the postexertional malaise that people experience: When people exert themselves, their symptoms get worse. And so the action that people take can’t be that traditional action that we’re used to taking in our society.”
Long COVID patients often have their feelings invalidated not just by friends, loved ones, and extended family, but by health care providers. That can heighten feelings of isolation, particularly for people who live alone, says Jordan Anderson, DO, a neuropsychiatrist and assistant professor of psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
The first patients Dr. Anderson saw as part of OHSU’s long COVID program contracted the virus in February 2020. Because the program addresses both the physical and mental health components of the condition, Dr. Anderson has seen a lot of people whose emotional challenges are similar to those Ms. Tyshynski faces.
“I think there’s a lack of understanding that leads to people just not necessarily taking it seriously,” he says. “Plus, the symptoms of long COVID do wax and wane. They’re not static. So people can be feeling pretty good one day and be feeling terrible the next. There’s some predictability to it, but it’s not absolutely predictable. It can be difficult for people to understand.”
Both Dr. Anderson and Dr. Re’em stress that long COVID patients need to prioritize their own energy regardless of what they’re being told by those who don’t understand the illness. Dr. Anderson offers to speak to his patients’ spouses to educate them about the realities of the condition because, he says, “any kind of lack of awareness or understanding in a family member or close support could potentially isolate the person struggling with long COVID.”
Depending on how open-minded and motivated a friend or relative is, they might develop more empathy with time and education, Dr. Re’em says. But for others, dealing with a confusing, unfamiliar chronic illness can be overwhelming and provoke anxiety.
“The hopelessness is too much for them to sit with, so instead they say things like ‘just push through it,’ or ‘just do X, Y, and Z,’ because psychologically it’s too much for them to take on that burden,” he says.
The good news is that there are plenty of web-based support groups for people with long COVID, including Body Politic (which Dr. Re’em is affiliated with), Survivor Corps, and on Facebook. “The patient community with this illness is tremendous, absolutely tremendous,” Dr. Re’em says. “Those people can be found and they can support each other.”
Some long COVID clinics run groups, as do individual practitioners such as Dr. Re’em, although those can be challenging to join. For instance, Dr. Re’em’s are only for New York state residents.
The key to finding a group is to be patient, because finding the right one takes time and energy.
“There are support groups that exist, but they are not as prevalent as I would like them to be,” Dr. Anderson says.
OHSU had an educational support group run by a social worker affiliated with the long COVID hub, but when the social worker left the program, the program was put on hold.
There’s a psychotherapy group operating out of the psychiatry department, but the patients are recruited exclusively from Dr. Anderson’s clinic and access is limited.
“The services exist, but I think that generally they’re sparse and pretty geographically dependent,” Dr. Anderson says. “I think you’d probably more likely be able to find something like this in a city or an area that has an academic institution or a place with a lot of resources rather than out in a rural community.”
Ms. Tyshynski opted not to join a group for fear it would increase the depression and anxiety that she had even before developing long COVID. When she and her family joined a cancer support group when her father was ill, she found it more depressing than helpful. Where she has found support is from the cofounder of the animal rescue society where she volunteers, a woman who has had long COVID for more than 2 years and has been a source of comfort and advice.
It’s one of the rare reminders Ms. Tyshynski has that even though she may live alone, she’s not completely alone. “Other people are going through this, too,” she says. “It helps to remember that.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A year ago in December, mapping specialist Whitney Tyshynski, 35, was working out 5 days a week with a personal trainer near her home in Alberta, Canada, doing 5k trail runs, lifting heavy weights, and feeling good. Then, in January she got COVID-19. The symptoms never went away.
Nowadays, Ms. Tyshynski needs a walker to retrieve her mail, a half-block trip she can’t make without fear of fainting. Because she gets dizzy when she drives, she rarely goes anywhere in her car. Going for a dog walk with a friend means sitting in a car and watching the friend and the dogs in an open field. And since fainting at Costco during the summer, she’s afraid to shop by herself.
Because she lives alone and her closest relatives are an hour and a half away, Ms. Tyshynski is dependent on friends. But she’s reluctant to lean on them because they already have trouble understanding how debilitating her lingering symptoms can be.
“I’ve had people pretty much insinuate that I’m lazy,” she says.
There’s no question that COVID-19 cut people off from one another. But for those like Ms. Tyshynski who have long COVID, that disconnect has never ended. that the condition is real.
At worst, as Ms. Tyshynski has discovered, people don’t take it seriously and accuse those who have it of exaggerating their health woes. In that way, long COVID can be as isolating as the original illness.
“Isolation in long COVID comes in various forms and it’s not primarily just that physical isolation,” says Yochai Re’em, MD, a psychiatrist in private practice in New York who has experienced long COVID and blogs about the condition for Psychology Today. “A different yet equally challenging type of isolation is the emotional isolation, where you need more emotional support, connection with other people who can appreciate what it is you are going through without putting their own needs and desires onto you – and that can be hard to find.”
It’s hard to find in part because of what Dr. Re’em sees as a collective belief that anyone who feels bad should be able to get better by exercising, researching, or going to a doctor.
“Society thinks you need to take some kind of action and usually that’s a physical action,” he says. “And that attitude is tremendously problematic in this illness because of the postexertional malaise that people experience: When people exert themselves, their symptoms get worse. And so the action that people take can’t be that traditional action that we’re used to taking in our society.”
Long COVID patients often have their feelings invalidated not just by friends, loved ones, and extended family, but by health care providers. That can heighten feelings of isolation, particularly for people who live alone, says Jordan Anderson, DO, a neuropsychiatrist and assistant professor of psychiatry at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
The first patients Dr. Anderson saw as part of OHSU’s long COVID program contracted the virus in February 2020. Because the program addresses both the physical and mental health components of the condition, Dr. Anderson has seen a lot of people whose emotional challenges are similar to those Ms. Tyshynski faces.
“I think there’s a lack of understanding that leads to people just not necessarily taking it seriously,” he says. “Plus, the symptoms of long COVID do wax and wane. They’re not static. So people can be feeling pretty good one day and be feeling terrible the next. There’s some predictability to it, but it’s not absolutely predictable. It can be difficult for people to understand.”
Both Dr. Anderson and Dr. Re’em stress that long COVID patients need to prioritize their own energy regardless of what they’re being told by those who don’t understand the illness. Dr. Anderson offers to speak to his patients’ spouses to educate them about the realities of the condition because, he says, “any kind of lack of awareness or understanding in a family member or close support could potentially isolate the person struggling with long COVID.”
Depending on how open-minded and motivated a friend or relative is, they might develop more empathy with time and education, Dr. Re’em says. But for others, dealing with a confusing, unfamiliar chronic illness can be overwhelming and provoke anxiety.
“The hopelessness is too much for them to sit with, so instead they say things like ‘just push through it,’ or ‘just do X, Y, and Z,’ because psychologically it’s too much for them to take on that burden,” he says.
The good news is that there are plenty of web-based support groups for people with long COVID, including Body Politic (which Dr. Re’em is affiliated with), Survivor Corps, and on Facebook. “The patient community with this illness is tremendous, absolutely tremendous,” Dr. Re’em says. “Those people can be found and they can support each other.”
Some long COVID clinics run groups, as do individual practitioners such as Dr. Re’em, although those can be challenging to join. For instance, Dr. Re’em’s are only for New York state residents.
The key to finding a group is to be patient, because finding the right one takes time and energy.
“There are support groups that exist, but they are not as prevalent as I would like them to be,” Dr. Anderson says.
OHSU had an educational support group run by a social worker affiliated with the long COVID hub, but when the social worker left the program, the program was put on hold.
There’s a psychotherapy group operating out of the psychiatry department, but the patients are recruited exclusively from Dr. Anderson’s clinic and access is limited.
“The services exist, but I think that generally they’re sparse and pretty geographically dependent,” Dr. Anderson says. “I think you’d probably more likely be able to find something like this in a city or an area that has an academic institution or a place with a lot of resources rather than out in a rural community.”
Ms. Tyshynski opted not to join a group for fear it would increase the depression and anxiety that she had even before developing long COVID. When she and her family joined a cancer support group when her father was ill, she found it more depressing than helpful. Where she has found support is from the cofounder of the animal rescue society where she volunteers, a woman who has had long COVID for more than 2 years and has been a source of comfort and advice.
It’s one of the rare reminders Ms. Tyshynski has that even though she may live alone, she’s not completely alone. “Other people are going through this, too,” she says. “It helps to remember that.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA approves first-in-class drug for HIV
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the medication lenacapavir (Sunlenca) for adults living with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. .
“Following today’s decision from the FDA, lenacapavir helps to fill a critical unmet need for people with complex prior treatment histories and offers physicians a long-awaited twice-yearly option for these patients who otherwise have limited therapy choices,” said site principal investigator Sorana Segal-Maurer, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, in a statement.
HIV drug regimens generally consist of two or three HIV medicines combined in a daily pill. In 2021, the FDA approved the first injectable complete drug regimen for HIV-1, Cabenuva, which can be administered monthly or every other month. Lenacapavir is administered only twice annually, but it is also combined with other antiretrovirals. The injections and oral tablets of lenacapavir are estimated to cost $42,250 in the first year of treatment and then $39,000 annually in the subsequent years, Reuters reported.
Lenacapavir is the first of a new class of drug called capsid inhibitors to be FDA-approved for treating HIV-1. The drug blocks the HIV-1 virus’s protein shell and interferes with essential steps of the virus’s evolution. The approval, announced today, was based on a multicenter clinical trial of 72 patients with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. After a year of the medication, 30 (83%) of the 36 patients randomly assigned to take lenacapavir, in combination with other HIV medications, had undetectable viral loads.
“Today’s approval ushers in a new class of antiretroviral drugs that may help patients with HIV who have run out of treatment options,” said Debra Birnkrant, MD, director of the division of antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “The availability of new classes of antiretroviral medications may possibly help these patients live longer, healthier lives.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the medication lenacapavir (Sunlenca) for adults living with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. .
“Following today’s decision from the FDA, lenacapavir helps to fill a critical unmet need for people with complex prior treatment histories and offers physicians a long-awaited twice-yearly option for these patients who otherwise have limited therapy choices,” said site principal investigator Sorana Segal-Maurer, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, in a statement.
HIV drug regimens generally consist of two or three HIV medicines combined in a daily pill. In 2021, the FDA approved the first injectable complete drug regimen for HIV-1, Cabenuva, which can be administered monthly or every other month. Lenacapavir is administered only twice annually, but it is also combined with other antiretrovirals. The injections and oral tablets of lenacapavir are estimated to cost $42,250 in the first year of treatment and then $39,000 annually in the subsequent years, Reuters reported.
Lenacapavir is the first of a new class of drug called capsid inhibitors to be FDA-approved for treating HIV-1. The drug blocks the HIV-1 virus’s protein shell and interferes with essential steps of the virus’s evolution. The approval, announced today, was based on a multicenter clinical trial of 72 patients with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. After a year of the medication, 30 (83%) of the 36 patients randomly assigned to take lenacapavir, in combination with other HIV medications, had undetectable viral loads.
“Today’s approval ushers in a new class of antiretroviral drugs that may help patients with HIV who have run out of treatment options,” said Debra Birnkrant, MD, director of the division of antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “The availability of new classes of antiretroviral medications may possibly help these patients live longer, healthier lives.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the medication lenacapavir (Sunlenca) for adults living with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. .
“Following today’s decision from the FDA, lenacapavir helps to fill a critical unmet need for people with complex prior treatment histories and offers physicians a long-awaited twice-yearly option for these patients who otherwise have limited therapy choices,” said site principal investigator Sorana Segal-Maurer, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, in a statement.
HIV drug regimens generally consist of two or three HIV medicines combined in a daily pill. In 2021, the FDA approved the first injectable complete drug regimen for HIV-1, Cabenuva, which can be administered monthly or every other month. Lenacapavir is administered only twice annually, but it is also combined with other antiretrovirals. The injections and oral tablets of lenacapavir are estimated to cost $42,250 in the first year of treatment and then $39,000 annually in the subsequent years, Reuters reported.
Lenacapavir is the first of a new class of drug called capsid inhibitors to be FDA-approved for treating HIV-1. The drug blocks the HIV-1 virus’s protein shell and interferes with essential steps of the virus’s evolution. The approval, announced today, was based on a multicenter clinical trial of 72 patients with multidrug resistant HIV-1 infection. After a year of the medication, 30 (83%) of the 36 patients randomly assigned to take lenacapavir, in combination with other HIV medications, had undetectable viral loads.
“Today’s approval ushers in a new class of antiretroviral drugs that may help patients with HIV who have run out of treatment options,” said Debra Birnkrant, MD, director of the division of antivirals in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in a press release. “The availability of new classes of antiretroviral medications may possibly help these patients live longer, healthier lives.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID update: ASH experts discuss thrombosis, immunity
NEW ORLEANS –
In a presidential symposium at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, La Jolla Institute of Immunology scientist Shane Crotty, PhD, explained that COVID-19 has a “superpower” that allows it to be “extraordinarily stealthy.”
The virus, he said, can sneak past the body’s innate immune system, which normally responds to viral invaders within minutes to hours. “This is why you have people with high viral loads who are presymptomatic. Their innate immune system hasn’t even recognized that these people are infected.”
The adaptive immune system kicks in later. As Dr. Crotty noted, adaptive immunity is composed of three branches: B cells (the source of antibodies), CD4 “helper” T cells, and CD8 “killer” T cells. In the first year of COVID-19, his team tracked 188 subjects post infection in what he said was the largest study of its kind ever for any viral infection.
“In 8 months, 95% of people who had been infected still had measurable immune memory. In fact, most of them had multiple different compartments of immune memory still detectable, and it was likely that these individuals would still have that memory years into the future. Based on that, we made the prediction that most people who have had COVID-19 would likely be protected from reinfection – at least by severe infections – for 3 years into the future. That prediction has widely held up even in the presence of variants which weren’t around at the time.”
How do vaccines fit into the immunity picture? Dr. Crotty’s lab has tracked subjects who received 4 vaccines – Moderna, Pfizer/BioNTech, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, and Novavax. Researchers found that the mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, “are fantastic at eliciting neutralizing antibodies quickly, but then they drop off rapidly at two doses and actually continue to drop for 10 months.”
Still, he said, “when we take a look at 6 months, actually the vaccines are doing pretty incredibly well. If we compare them to an average infected individual, the mRNA vaccines all have higher neutralizing antibody titers.”
What’s happening? According to Dr. Crotty, B cells are “making guesses about what other variants might look like.” But he said research suggests that an important component of this process – germinal centers – aren’t made in some vaccinated people who are immunocompromised. (Germinal centers have been described as “microbial boot camps” for B cells.)
The good news, Dr. Crotty noted, is that a greater understanding of how COVID-19 penetrates various layers of adaptive immune defenses will lead to better ways to protect the immunocompromised. “If you think about immunity in this layered defense way, there are various ways that it could be enhanced for individuals in different categories,” he said.
Hematologist Beverley J. Hunt, MD, OBE, of St. Thomas’ Hospital/King’s Healthcare Partners in London, spoke at the ASH presidential symposium about blood clots and COVID-19. As she noted, concern arose about vaccine-related blood clots. A British team “managed quickly to come up with a diagnostic criteria,” she said. “We looked at nearly 300 patients and essentially came up with a scoring system.”
The diagnostic criteria was based on an analysis of definite or probable cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT) – all related to the AstraZeneca vaccine. The criteria appeared in a 2021 study in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The report’s data didn’t allow it to compare the efficacy of anticoagulants. However, Dr. Hunt noted that clinicians turned to plasma exchange in patients with low platelet counts and extensive thrombosis. The report stated “survival after plasma exchange was 90%, considerably better than would be predicted given the baseline characteristics.”
“Now we’re following up,” Dr. Hunt said. One question to answer: Is long-term anticoagulation helpful? “We have many patients,” she said, “who are taking an anti-platelet factor out of habit.”
Dr. Crotty and Dr. Hunt report no disclosures. This reporter is a paid participant in a COVID vaccine study run by Dr. Crotty’s lab.
NEW ORLEANS –
In a presidential symposium at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, La Jolla Institute of Immunology scientist Shane Crotty, PhD, explained that COVID-19 has a “superpower” that allows it to be “extraordinarily stealthy.”
The virus, he said, can sneak past the body’s innate immune system, which normally responds to viral invaders within minutes to hours. “This is why you have people with high viral loads who are presymptomatic. Their innate immune system hasn’t even recognized that these people are infected.”
The adaptive immune system kicks in later. As Dr. Crotty noted, adaptive immunity is composed of three branches: B cells (the source of antibodies), CD4 “helper” T cells, and CD8 “killer” T cells. In the first year of COVID-19, his team tracked 188 subjects post infection in what he said was the largest study of its kind ever for any viral infection.
“In 8 months, 95% of people who had been infected still had measurable immune memory. In fact, most of them had multiple different compartments of immune memory still detectable, and it was likely that these individuals would still have that memory years into the future. Based on that, we made the prediction that most people who have had COVID-19 would likely be protected from reinfection – at least by severe infections – for 3 years into the future. That prediction has widely held up even in the presence of variants which weren’t around at the time.”
How do vaccines fit into the immunity picture? Dr. Crotty’s lab has tracked subjects who received 4 vaccines – Moderna, Pfizer/BioNTech, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, and Novavax. Researchers found that the mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, “are fantastic at eliciting neutralizing antibodies quickly, but then they drop off rapidly at two doses and actually continue to drop for 10 months.”
Still, he said, “when we take a look at 6 months, actually the vaccines are doing pretty incredibly well. If we compare them to an average infected individual, the mRNA vaccines all have higher neutralizing antibody titers.”
What’s happening? According to Dr. Crotty, B cells are “making guesses about what other variants might look like.” But he said research suggests that an important component of this process – germinal centers – aren’t made in some vaccinated people who are immunocompromised. (Germinal centers have been described as “microbial boot camps” for B cells.)
The good news, Dr. Crotty noted, is that a greater understanding of how COVID-19 penetrates various layers of adaptive immune defenses will lead to better ways to protect the immunocompromised. “If you think about immunity in this layered defense way, there are various ways that it could be enhanced for individuals in different categories,” he said.
Hematologist Beverley J. Hunt, MD, OBE, of St. Thomas’ Hospital/King’s Healthcare Partners in London, spoke at the ASH presidential symposium about blood clots and COVID-19. As she noted, concern arose about vaccine-related blood clots. A British team “managed quickly to come up with a diagnostic criteria,” she said. “We looked at nearly 300 patients and essentially came up with a scoring system.”
The diagnostic criteria was based on an analysis of definite or probable cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT) – all related to the AstraZeneca vaccine. The criteria appeared in a 2021 study in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The report’s data didn’t allow it to compare the efficacy of anticoagulants. However, Dr. Hunt noted that clinicians turned to plasma exchange in patients with low platelet counts and extensive thrombosis. The report stated “survival after plasma exchange was 90%, considerably better than would be predicted given the baseline characteristics.”
“Now we’re following up,” Dr. Hunt said. One question to answer: Is long-term anticoagulation helpful? “We have many patients,” she said, “who are taking an anti-platelet factor out of habit.”
Dr. Crotty and Dr. Hunt report no disclosures. This reporter is a paid participant in a COVID vaccine study run by Dr. Crotty’s lab.
NEW ORLEANS –
In a presidential symposium at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, La Jolla Institute of Immunology scientist Shane Crotty, PhD, explained that COVID-19 has a “superpower” that allows it to be “extraordinarily stealthy.”
The virus, he said, can sneak past the body’s innate immune system, which normally responds to viral invaders within minutes to hours. “This is why you have people with high viral loads who are presymptomatic. Their innate immune system hasn’t even recognized that these people are infected.”
The adaptive immune system kicks in later. As Dr. Crotty noted, adaptive immunity is composed of three branches: B cells (the source of antibodies), CD4 “helper” T cells, and CD8 “killer” T cells. In the first year of COVID-19, his team tracked 188 subjects post infection in what he said was the largest study of its kind ever for any viral infection.
“In 8 months, 95% of people who had been infected still had measurable immune memory. In fact, most of them had multiple different compartments of immune memory still detectable, and it was likely that these individuals would still have that memory years into the future. Based on that, we made the prediction that most people who have had COVID-19 would likely be protected from reinfection – at least by severe infections – for 3 years into the future. That prediction has widely held up even in the presence of variants which weren’t around at the time.”
How do vaccines fit into the immunity picture? Dr. Crotty’s lab has tracked subjects who received 4 vaccines – Moderna, Pfizer/BioNTech, Janssen/Johnson & Johnson, and Novavax. Researchers found that the mRNA vaccines, Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech, “are fantastic at eliciting neutralizing antibodies quickly, but then they drop off rapidly at two doses and actually continue to drop for 10 months.”
Still, he said, “when we take a look at 6 months, actually the vaccines are doing pretty incredibly well. If we compare them to an average infected individual, the mRNA vaccines all have higher neutralizing antibody titers.”
What’s happening? According to Dr. Crotty, B cells are “making guesses about what other variants might look like.” But he said research suggests that an important component of this process – germinal centers – aren’t made in some vaccinated people who are immunocompromised. (Germinal centers have been described as “microbial boot camps” for B cells.)
The good news, Dr. Crotty noted, is that a greater understanding of how COVID-19 penetrates various layers of adaptive immune defenses will lead to better ways to protect the immunocompromised. “If you think about immunity in this layered defense way, there are various ways that it could be enhanced for individuals in different categories,” he said.
Hematologist Beverley J. Hunt, MD, OBE, of St. Thomas’ Hospital/King’s Healthcare Partners in London, spoke at the ASH presidential symposium about blood clots and COVID-19. As she noted, concern arose about vaccine-related blood clots. A British team “managed quickly to come up with a diagnostic criteria,” she said. “We looked at nearly 300 patients and essentially came up with a scoring system.”
The diagnostic criteria was based on an analysis of definite or probable cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (VITT) – all related to the AstraZeneca vaccine. The criteria appeared in a 2021 study in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The report’s data didn’t allow it to compare the efficacy of anticoagulants. However, Dr. Hunt noted that clinicians turned to plasma exchange in patients with low platelet counts and extensive thrombosis. The report stated “survival after plasma exchange was 90%, considerably better than would be predicted given the baseline characteristics.”
“Now we’re following up,” Dr. Hunt said. One question to answer: Is long-term anticoagulation helpful? “We have many patients,” she said, “who are taking an anti-platelet factor out of habit.”
Dr. Crotty and Dr. Hunt report no disclosures. This reporter is a paid participant in a COVID vaccine study run by Dr. Crotty’s lab.
AT ASH 2022
Abdominal pain and constipation
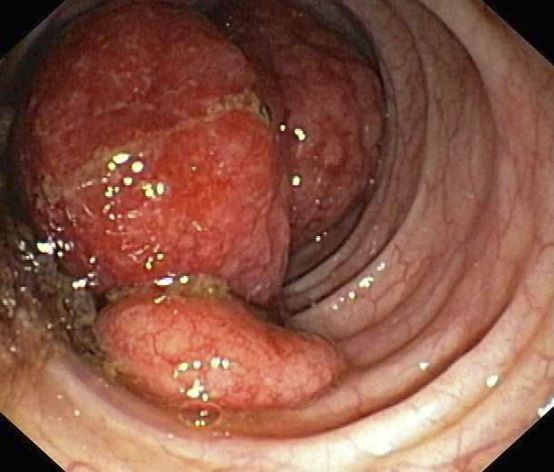
This patient's clinical presentation and endoscopy findings are consistent with a diagnosis of recurrent MCL presenting as a colonic mass.
MCL is an aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. Nearly 80% of patients have extranodal involvement at initial presentation, occurring in sites such as the bone marrow, spleen, Waldeyer ring, and the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Secondary GI involvement in MCL (involving nodal and/or other extranodal tissue) is common and may be detected at diagnosis and/or relapse. In several retrospective studies, the prevalence of secondary GI involvement in MCL ranged from 15% to 30%. However, in later studies, routine endoscopies in patients with untreated MCL showed GI involvement in up to 90% of patients, despite most patients not reporting GI symptoms.
The colon is the most commonly involved GI site; however, both the upper and lower GI tract from the stomach to the colon can be involved. Lymphomatous polyposis is the most common endoscopic presentation of MCL, but polyp, mass, or even normal-appearing mucosa may also be seen.
New and emerging treatment options are helping to improve survival in patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. According to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, the preferred second-line and subsequent regimens are:
• Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors:
o Acalabrutinib
o Ibrutinib ± rituximab
o Zanubrutinib
• Lenalidomide + rituximab (if BTK inhibitor is contraindicated)
Other regimens that may be useful in certain circumstances are:
• Bendamustine + rituximab (if not previously given)
• Bendamustine + rituximab + cytarabine (RBAC500) (if not previously given)
• Bortezomib ± rituximab
• RDHA (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine) + platinum (carboplatin, cisplatin, or oxaliplatin) (if not previously given)
• GemOx (gemcitabine, oxaliplatin) + rituximab
• Ibrutinib, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Ibrutinib + venetoclax
• Venetoclax, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Venetoclax ± rituximab
Brexucabtagene autoleucel is suggested as third-line therapy, after chemoimmunotherapy and treatment with a BTK inhibitor.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation and endoscopy findings are consistent with a diagnosis of recurrent MCL presenting as a colonic mass.
MCL is an aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. Nearly 80% of patients have extranodal involvement at initial presentation, occurring in sites such as the bone marrow, spleen, Waldeyer ring, and the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Secondary GI involvement in MCL (involving nodal and/or other extranodal tissue) is common and may be detected at diagnosis and/or relapse. In several retrospective studies, the prevalence of secondary GI involvement in MCL ranged from 15% to 30%. However, in later studies, routine endoscopies in patients with untreated MCL showed GI involvement in up to 90% of patients, despite most patients not reporting GI symptoms.
The colon is the most commonly involved GI site; however, both the upper and lower GI tract from the stomach to the colon can be involved. Lymphomatous polyposis is the most common endoscopic presentation of MCL, but polyp, mass, or even normal-appearing mucosa may also be seen.
New and emerging treatment options are helping to improve survival in patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. According to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, the preferred second-line and subsequent regimens are:
• Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors:
o Acalabrutinib
o Ibrutinib ± rituximab
o Zanubrutinib
• Lenalidomide + rituximab (if BTK inhibitor is contraindicated)
Other regimens that may be useful in certain circumstances are:
• Bendamustine + rituximab (if not previously given)
• Bendamustine + rituximab + cytarabine (RBAC500) (if not previously given)
• Bortezomib ± rituximab
• RDHA (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine) + platinum (carboplatin, cisplatin, or oxaliplatin) (if not previously given)
• GemOx (gemcitabine, oxaliplatin) + rituximab
• Ibrutinib, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Ibrutinib + venetoclax
• Venetoclax, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Venetoclax ± rituximab
Brexucabtagene autoleucel is suggested as third-line therapy, after chemoimmunotherapy and treatment with a BTK inhibitor.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
This patient's clinical presentation and endoscopy findings are consistent with a diagnosis of recurrent MCL presenting as a colonic mass.
MCL is an aggressive type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that accounts for approximately 5%-7% of all lymphomas. Nearly 80% of patients have extranodal involvement at initial presentation, occurring in sites such as the bone marrow, spleen, Waldeyer ring, and the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Secondary GI involvement in MCL (involving nodal and/or other extranodal tissue) is common and may be detected at diagnosis and/or relapse. In several retrospective studies, the prevalence of secondary GI involvement in MCL ranged from 15% to 30%. However, in later studies, routine endoscopies in patients with untreated MCL showed GI involvement in up to 90% of patients, despite most patients not reporting GI symptoms.
The colon is the most commonly involved GI site; however, both the upper and lower GI tract from the stomach to the colon can be involved. Lymphomatous polyposis is the most common endoscopic presentation of MCL, but polyp, mass, or even normal-appearing mucosa may also be seen.
New and emerging treatment options are helping to improve survival in patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. According to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, the preferred second-line and subsequent regimens are:
• Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors:
o Acalabrutinib
o Ibrutinib ± rituximab
o Zanubrutinib
• Lenalidomide + rituximab (if BTK inhibitor is contraindicated)
Other regimens that may be useful in certain circumstances are:
• Bendamustine + rituximab (if not previously given)
• Bendamustine + rituximab + cytarabine (RBAC500) (if not previously given)
• Bortezomib ± rituximab
• RDHA (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine) + platinum (carboplatin, cisplatin, or oxaliplatin) (if not previously given)
• GemOx (gemcitabine, oxaliplatin) + rituximab
• Ibrutinib, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Ibrutinib + venetoclax
• Venetoclax, lenalidomide, rituximab (category 2B)
• Venetoclax ± rituximab
Brexucabtagene autoleucel is suggested as third-line therapy, after chemoimmunotherapy and treatment with a BTK inhibitor.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 55-year-old White woman presents with complaints of left-sided abdominal pain and constipation of 10-day duration. The patient's prior medical history is notable for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) treated 2 years earlier with RDHA (rituximab, dexamethasone, cytarabine) + platinum (carboplatin, cisplatin, or oxaliplatin) followed by autologous stem cell transplantation. No lymphadenopathy is noted on physical examination. Abdominal examination reveals abdominal distension, normal bowel sounds, and left lower quadrant tenderness to palpation without guarding, rigidity, or hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory test results including CBC are within normal range. Endoscopy reveals a growth in the colon, as shown in the image.
Cochrane Review bolsters case that emollients don’t prevent AD
associated with early use of emollients.
The document, published in November 2022, updates a February 2021 version, said Robert Boyle, MD, PhD, senior author of the Cochrane Review and a pediatric allergist at Imperial College London. “The differences were slight,” he told this news organization. “Mainly, we had a little more data about food allergy outcomes, which slightly strengthened the concern about a possible increase in food allergy with emollients; and we had some new genetic information, which allowed us to add some further interaction analyses and confirm that chromosome 11 intergenic variant rs2212434 doesn’t seem to impact the effect – or lack of effect – of emollient on eczema development.”
The updated Cochrane Review concludes that, “based on low‐ to moderate-certainty evidence, skin care interventions such as emollients during the first year of life in healthy infants are probably not effective for preventing eczema; may increase risk of food allergy; and probably increase risk of skin infection.”
The latest publication should strengthen clinicians’ confidence in not recommending emollient use for preventing AD in at-risk infants – however, that message is being diluted by a stream of contradictory conclusions from poor-quality systematic reviews, say Dr. Boyle and two coauthors. “It’s a systematic problem of people churning out endless systematic reviews without much rigor,” explained the lead author Maeve Kelleher, MD, from Children’s Health Ireland, Crumlin. There have been “misleading systematic reviews published, often in high-ranking journals,” agreed Dr. Boyle.
“I have been an advocate of systematic reviews for the last 20 years, but they have gone completely out of control,” added Hywel Williams, MD, PhD, another of the Cochrane Review coauthors, who is professor of dermato-epidemiology and codirector of the Centre of Evidence Based Dermatology, at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust. In an editorial, published last year, Dr. Williams even posed the question: “Are Dermatology Systematic Reviews Spinning Out of Control?” in which he blamed “the misrepresentation of study results” – which he calls “the sin of spin” – for degrading the quality of science in dermatology.
“The field has become a ‘sausage machine’ industry that undermines the value of systematic reviews in providing a summary of the best evidence to inform patient care,” he wrote. “Fewer systematic reviews are needed in dermatology,” but “better ones” are needed, he continued, calling for all systematic reviews to be registered prospectively, and reported according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines.
Earlier this year, in a letter to the editor, Dr. Kelleher, Dr. Boyle, Dr. Williams, and several others outlined their concerns after a systemic review and meta-analysis was published, “which came to very different conclusions” than their Cochrane Review.
“It is quite common to see non-Cochrane reviews published in leading specialty journals, which interpret data in a more positive light than Cochrane reviews, which have assessed a similar dataset/topic,” Dr. Boyle said in the interview.
Such concerns also apply to the publication of another systematic review that was recently published. “Overall, early application of emollients is an effective strategy for preventing AD development in high-risk infants,” reported senior author Xiaojing Kang, MD, PhD, from People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumchi, China, and coauthors, who could not be reached for comment. In their discussion, the authors cite several criticisms of the Cochrane Review: that it included two meeting abstracts and two “ineligible” studies; did not do subgroup analysis of high-risk infants; did not look at different types of emollients; and did not examine the risk of food sensitization.
“A Cochrane Review can be quite a large and complex document to negotiate for those who are not very familiar with Cochrane’s methodology,” said Dr. Boyle. He dismissed the criticism, saying “we did do subgroup analysis of high risk infants, we did look at different types of emollient, and we did look at food sensitization and food allergy risk. We only included eligible studies. … Certainly we would include abstracts of trials, which are not reported in any other form, in order to capture as complete a picture.”
Ultimately, Dr. Boyle said, the discrepancy in conclusions between such systematic reviews and the Cochrane Review relates to quality of methodology. “Our Cochrane review was an individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis, meaning that authors of the main trials in this area shared their original datasets with us,” he said in the interview. “This is the ‘gold standard’ in systematic reviews, and allowed us to check data/ query inconsistencies and to apply a single-analysis methodology across all studies. It also allowed us to undertake some analyses, which are just not possible in aggregate data analysis based on published work without IPD.”
The most recently published systematic review had no registered protocol, “so, there is no transparency about the methods used,” he noted. “It is free and simple to register a protocol – multiple websites such as PROSPERO, open science framework, and zenodo allow this,” he said “In the journal I edit, we use availability of a registered protocol as a marker of quality. We find that systematic reviews with no registered protocol are almost universally poor quality.”
Dr. Williams is a founding member and coordinating editor of the Cochrane Skin Group 1998 to 2017. Dr. Boyle was paid by Cochrane for senior editor work, until recently, and had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Kelleher had no relevant disclosures.
associated with early use of emollients.
The document, published in November 2022, updates a February 2021 version, said Robert Boyle, MD, PhD, senior author of the Cochrane Review and a pediatric allergist at Imperial College London. “The differences were slight,” he told this news organization. “Mainly, we had a little more data about food allergy outcomes, which slightly strengthened the concern about a possible increase in food allergy with emollients; and we had some new genetic information, which allowed us to add some further interaction analyses and confirm that chromosome 11 intergenic variant rs2212434 doesn’t seem to impact the effect – or lack of effect – of emollient on eczema development.”
The updated Cochrane Review concludes that, “based on low‐ to moderate-certainty evidence, skin care interventions such as emollients during the first year of life in healthy infants are probably not effective for preventing eczema; may increase risk of food allergy; and probably increase risk of skin infection.”
The latest publication should strengthen clinicians’ confidence in not recommending emollient use for preventing AD in at-risk infants – however, that message is being diluted by a stream of contradictory conclusions from poor-quality systematic reviews, say Dr. Boyle and two coauthors. “It’s a systematic problem of people churning out endless systematic reviews without much rigor,” explained the lead author Maeve Kelleher, MD, from Children’s Health Ireland, Crumlin. There have been “misleading systematic reviews published, often in high-ranking journals,” agreed Dr. Boyle.
“I have been an advocate of systematic reviews for the last 20 years, but they have gone completely out of control,” added Hywel Williams, MD, PhD, another of the Cochrane Review coauthors, who is professor of dermato-epidemiology and codirector of the Centre of Evidence Based Dermatology, at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust. In an editorial, published last year, Dr. Williams even posed the question: “Are Dermatology Systematic Reviews Spinning Out of Control?” in which he blamed “the misrepresentation of study results” – which he calls “the sin of spin” – for degrading the quality of science in dermatology.
“The field has become a ‘sausage machine’ industry that undermines the value of systematic reviews in providing a summary of the best evidence to inform patient care,” he wrote. “Fewer systematic reviews are needed in dermatology,” but “better ones” are needed, he continued, calling for all systematic reviews to be registered prospectively, and reported according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines.
Earlier this year, in a letter to the editor, Dr. Kelleher, Dr. Boyle, Dr. Williams, and several others outlined their concerns after a systemic review and meta-analysis was published, “which came to very different conclusions” than their Cochrane Review.
“It is quite common to see non-Cochrane reviews published in leading specialty journals, which interpret data in a more positive light than Cochrane reviews, which have assessed a similar dataset/topic,” Dr. Boyle said in the interview.
Such concerns also apply to the publication of another systematic review that was recently published. “Overall, early application of emollients is an effective strategy for preventing AD development in high-risk infants,” reported senior author Xiaojing Kang, MD, PhD, from People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumchi, China, and coauthors, who could not be reached for comment. In their discussion, the authors cite several criticisms of the Cochrane Review: that it included two meeting abstracts and two “ineligible” studies; did not do subgroup analysis of high-risk infants; did not look at different types of emollients; and did not examine the risk of food sensitization.
“A Cochrane Review can be quite a large and complex document to negotiate for those who are not very familiar with Cochrane’s methodology,” said Dr. Boyle. He dismissed the criticism, saying “we did do subgroup analysis of high risk infants, we did look at different types of emollient, and we did look at food sensitization and food allergy risk. We only included eligible studies. … Certainly we would include abstracts of trials, which are not reported in any other form, in order to capture as complete a picture.”
Ultimately, Dr. Boyle said, the discrepancy in conclusions between such systematic reviews and the Cochrane Review relates to quality of methodology. “Our Cochrane review was an individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis, meaning that authors of the main trials in this area shared their original datasets with us,” he said in the interview. “This is the ‘gold standard’ in systematic reviews, and allowed us to check data/ query inconsistencies and to apply a single-analysis methodology across all studies. It also allowed us to undertake some analyses, which are just not possible in aggregate data analysis based on published work without IPD.”
The most recently published systematic review had no registered protocol, “so, there is no transparency about the methods used,” he noted. “It is free and simple to register a protocol – multiple websites such as PROSPERO, open science framework, and zenodo allow this,” he said “In the journal I edit, we use availability of a registered protocol as a marker of quality. We find that systematic reviews with no registered protocol are almost universally poor quality.”
Dr. Williams is a founding member and coordinating editor of the Cochrane Skin Group 1998 to 2017. Dr. Boyle was paid by Cochrane for senior editor work, until recently, and had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Kelleher had no relevant disclosures.
associated with early use of emollients.
The document, published in November 2022, updates a February 2021 version, said Robert Boyle, MD, PhD, senior author of the Cochrane Review and a pediatric allergist at Imperial College London. “The differences were slight,” he told this news organization. “Mainly, we had a little more data about food allergy outcomes, which slightly strengthened the concern about a possible increase in food allergy with emollients; and we had some new genetic information, which allowed us to add some further interaction analyses and confirm that chromosome 11 intergenic variant rs2212434 doesn’t seem to impact the effect – or lack of effect – of emollient on eczema development.”
The updated Cochrane Review concludes that, “based on low‐ to moderate-certainty evidence, skin care interventions such as emollients during the first year of life in healthy infants are probably not effective for preventing eczema; may increase risk of food allergy; and probably increase risk of skin infection.”
The latest publication should strengthen clinicians’ confidence in not recommending emollient use for preventing AD in at-risk infants – however, that message is being diluted by a stream of contradictory conclusions from poor-quality systematic reviews, say Dr. Boyle and two coauthors. “It’s a systematic problem of people churning out endless systematic reviews without much rigor,” explained the lead author Maeve Kelleher, MD, from Children’s Health Ireland, Crumlin. There have been “misleading systematic reviews published, often in high-ranking journals,” agreed Dr. Boyle.
“I have been an advocate of systematic reviews for the last 20 years, but they have gone completely out of control,” added Hywel Williams, MD, PhD, another of the Cochrane Review coauthors, who is professor of dermato-epidemiology and codirector of the Centre of Evidence Based Dermatology, at Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust. In an editorial, published last year, Dr. Williams even posed the question: “Are Dermatology Systematic Reviews Spinning Out of Control?” in which he blamed “the misrepresentation of study results” – which he calls “the sin of spin” – for degrading the quality of science in dermatology.
“The field has become a ‘sausage machine’ industry that undermines the value of systematic reviews in providing a summary of the best evidence to inform patient care,” he wrote. “Fewer systematic reviews are needed in dermatology,” but “better ones” are needed, he continued, calling for all systematic reviews to be registered prospectively, and reported according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines.
Earlier this year, in a letter to the editor, Dr. Kelleher, Dr. Boyle, Dr. Williams, and several others outlined their concerns after a systemic review and meta-analysis was published, “which came to very different conclusions” than their Cochrane Review.
“It is quite common to see non-Cochrane reviews published in leading specialty journals, which interpret data in a more positive light than Cochrane reviews, which have assessed a similar dataset/topic,” Dr. Boyle said in the interview.
Such concerns also apply to the publication of another systematic review that was recently published. “Overall, early application of emollients is an effective strategy for preventing AD development in high-risk infants,” reported senior author Xiaojing Kang, MD, PhD, from People’s Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumchi, China, and coauthors, who could not be reached for comment. In their discussion, the authors cite several criticisms of the Cochrane Review: that it included two meeting abstracts and two “ineligible” studies; did not do subgroup analysis of high-risk infants; did not look at different types of emollients; and did not examine the risk of food sensitization.
“A Cochrane Review can be quite a large and complex document to negotiate for those who are not very familiar with Cochrane’s methodology,” said Dr. Boyle. He dismissed the criticism, saying “we did do subgroup analysis of high risk infants, we did look at different types of emollient, and we did look at food sensitization and food allergy risk. We only included eligible studies. … Certainly we would include abstracts of trials, which are not reported in any other form, in order to capture as complete a picture.”
Ultimately, Dr. Boyle said, the discrepancy in conclusions between such systematic reviews and the Cochrane Review relates to quality of methodology. “Our Cochrane review was an individual participant data (IPD) meta-analysis, meaning that authors of the main trials in this area shared their original datasets with us,” he said in the interview. “This is the ‘gold standard’ in systematic reviews, and allowed us to check data/ query inconsistencies and to apply a single-analysis methodology across all studies. It also allowed us to undertake some analyses, which are just not possible in aggregate data analysis based on published work without IPD.”
The most recently published systematic review had no registered protocol, “so, there is no transparency about the methods used,” he noted. “It is free and simple to register a protocol – multiple websites such as PROSPERO, open science framework, and zenodo allow this,” he said “In the journal I edit, we use availability of a registered protocol as a marker of quality. We find that systematic reviews with no registered protocol are almost universally poor quality.”
Dr. Williams is a founding member and coordinating editor of the Cochrane Skin Group 1998 to 2017. Dr. Boyle was paid by Cochrane for senior editor work, until recently, and had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Kelleher had no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE COCHRANE REVIEW
Lithium toxicity: Lessons learned
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Lithium carbonate is a mood stabilizer that is effective in the treatment of bipolar disorder, particularly in controlling mania.1 Lithium can reduce the risk of suicide,2 treat aggression and self-mutilating behavior,3 and prevent steroid-induced psychosis.4 It also can raise the white cell count in patients with clozapine-induced leukopenia.5
To prevent or lower the risk of relapse, the therapeutic plasma level of lithium should be regularly monitored to ensure an optimal concentration in the CNS. The highest tolerable level of lithium in the plasma is 0.6 to 0.8 mmol/L, with the optimal level ranging up to 1.2 mmol/L.6 Regular monitoring of renal function is also required to prevent renal toxicity, particularly if the plasma level exceeds 0.8 mmol/L.7 Because of lithium’s relatively narrow therapeutic index, its interaction with other medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and carbamazepine, can also precipitate lithium toxicity.8 We describe a lesson learned from a case of lithium toxicity in an otherwise healthy patient with bipolar disorder.
Case report
An otherwise healthy 39-year-old woman diagnosed with bipolar type I disorder was receiving valproate sodium 600 mg/d and olanzapine 10 mg/d. Despite improvement in her mood, she gained 11.6 kg following 6 months of treatment. As a result, olanzapine was switched to aripiprazole 10 mg/d that was later increased to 15 mg/d, and sodium valproate was gradually optimized up to 1,000 mg/d. She later complained of hair thinning and hair loss so she self-adjusted her medication dosages, which resulted in frequent relapses. Her mood stabilizer was changed from sodium valproate to lithium 600 mg/d.
Unfortunately, after taking lithium for 15 days, she returned to us with fever associated with reduced oral intake, poor sleep, bilateral upper limb rigidity, and bilateral hand tremor. She also complained of extreme thirst and fatigue but no vomiting or diarrhea. She had difficulty falling asleep and slept for only 1 to 2 hours a day. Her symptoms worsened when a general practitioner prescribed NSAIDs for her fever and body ache. Her tremors were later generalized, which made it difficult for her to take her oral medications and disturbed her speech and movement.
On evaluation, our patient appeared comfortable and not agitated. She was orientated to time, place, and person. Her blood pressure was 139/89 mmHg, heart rate was 104 bpm, and she was afebrile. She was dehydrated with minimal urine output. She had coarse tremor in her upper and lower limbs, which were hypertonic but did not display hyperreflexia or clonus. There was no nystagmus or ataxia. A mental state examination showed no signs of manic, hypomanic, or depressive symptoms. She had slurred speech, and her affect was restricted.
Blood investigation revealed a suprathreshold lithium level of 1.70 mmol/L (normal: 0.8 to 1.2 mmol/L). Biochemical parameters showed evidence of acute kidney injury (urea: 6.1 mmol/L; creatinine: 0.140 mmol/L), with no electrolyte imbalance. There was no evidence of hypothyroidism (thyroid-stimulating hormone: 14.9 mIU/L; free thyroxine: 9.9 pmol/L), hyperparathyroidism, or hypercalcemia. Autoimmune markers were positive for antinuclear antibody (titre 1:320) and anti-double stranded DNA (76.8 IU/mL). Apart from hair loss, she denied other symptoms associated with autoimmune disease, such as joint pain, butterfly rash, or persistent fatigue. Other routine blood investigations were within normal limits. Her urine protein throughout admission had shown persistent proteinuria ranging from 3+ to 4+. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed normal sinus rhythm with no T wave inversion or QT prolongation.
Continue to: A detailed family history...
A detailed family history later confirmed a strong family history of renal disease: her mother had lupus nephritis with nephrotic syndrome, and her brother had died from complications of a rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Her renal function prior to lithium initiation was within normal limits (urea: 4.0 mmol/L; serum creatinine: 78 µmol/L).
In the ward, lithium and aripiprazole were discontinued, and she was hydrated. Combined care with the psychiatric and medical teams was established early to safeguard against potential CNS deterioration. She showed marked clinical improvement by Day 3, with the resolution of coarse tremor and rigidity as well as normalization of blood parameters. Her lithium level returned to a therapeutic level by Day 4 after lithium discontinuation, and her renal profile gradually normalized. She was restarted on aripiprazole 10 mg/d for her bipolar illness and responded well. She was discharged on Day 5 with a referral to the nephrology team for further intervention.
Lessons learned
This case highlights the issue of lithium safety in susceptible individuals and the importance of risk stratification in this group of patients. Lithium is an effective treatment for bipolar I disorder and has also been used as adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder, schizoaffective disorder, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, and the control of chronic aggression.9 Lithium is completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract following ingestion, is not metabolized, and is eliminated almost entirely by the kidneys (though trace amounts may be found in feces and perspiration).
In our case, a detailed family history of renal disease was not adequately explored until our patient presented with signs suggestive of lithium toxicity. Our patient had been prescribed lithium 600 mg/d as a maintenance therapy. Upon starting lithium, her baseline biochemical parameters were within normal limits, and renal issues were not suspected. The hair thinning and hair loss she experienced could have been an adverse effect of valproate sodium or a manifestation of an underlying autoimmune disease. Coupled with the use of NSAIDs that could have precipitated acute kidney injury, her poor oral intake and dehydration during the acute illness further impaired lithium excretion, leading to a suprathreshold plasma level despite a low dose of lithium. Therefore, before prescribing lithium, a thorough medical and family history is needed, supplemented by an evaluation of renal function, serum electrolytes, and thyroid function to determine the starting dosage of lithium. Routine vital sign assessment and ECG should also be conducted, and concurrent medications and pregnancy status should be confirmed before prescribing lithium. Regular lithium level monitoring is essential.
Measuring a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is recommended to validate renal status10 and classify and stage kidney disease.11 Combining eGFR with blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and urine microscopic analysis further improves the prediction of renal disease in early stages. We recommend considering a blood test for autoimmune markers in patients with clinical suspicion of autoimmune disease, in the presence of suggestive signs and symptoms, and/or in patients with a positive family history (Table).
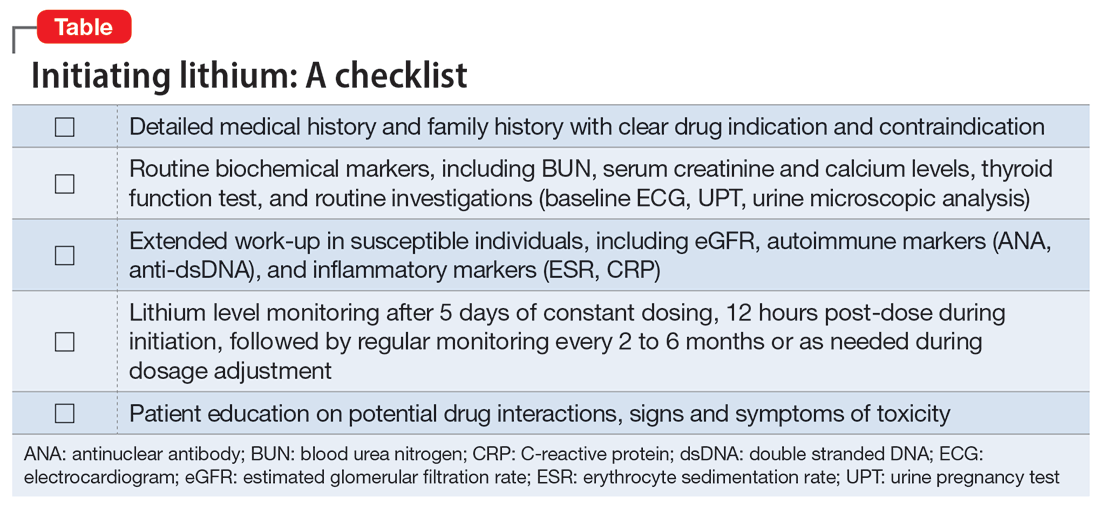
Before starting lithium, in addition to conducting a detailed clinical evaluation, information about symptoms and the risk of lithium toxicity should be discussed with patients.12 Our case serves as a timely reminder that the lack of suggestive biochemical parameters of renal disease should not rule out an underlying renal disease, and a strong family history of renal disease should warrant suspicion of a possible autoimmune origin.
We suggest that future studies evaluate the risks of lithium toxicity in susceptible groups of patients, such as those with family history of renal disease.
1. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
2. Cipriani A, Hawton K, Stockton S, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicide in mood disorders: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013; 346:f3646.
3. Correll CU, Yu X, Xiang Y, et al. Biological treatment of acute agitation or aggression with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder in the inpatient setting. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2017;29(2):92-107.
4. Abou-Saleh MT, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Coppen AJ. Lithium in the episode and suicide prophylaxis and in augmenting strategies in patients with unipolar depression. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2017;5(1):11.
5. Aydin M, Ilhan BC, Calisir S, et al. Continuing clozapine treatment with lithium in schizophrenic patients with neutropenia or leukopenia: brief review of literature with case reports. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016;6(1):33-38.
6. Nolen WA, Weisler RH. The association of the effect of lithium in the maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder with lithium plasma levels: a post hoc analysis of a double-blind study comparing switching to lithium or placebo in patients who responded to quetiapine (Trial 144). Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(1):100-109.
7. Aiff H, Attman P, Aurell M, et al. Effects of 10 to 30 years of lithium treatment on kidney function. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(5):608-614.
8. Taylor DM, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
9. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Kaplan & Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry. 9th ed. Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2002.
10. Lopez-Giacoman S, Madero M. Biomarkers in chronic kidney disease, from kidney function to kidney damage. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(1):57-73.
11. McCance RA, Robinson JR. Evaluation of renal clearances. Proc R Soc Med. 1949;42(7):475-480.
12. Gerret D, Lamont T, Paton C, et al. Prescribing and monitoring lithium therapy: summary of a safety report from the National Patient Safety Agency. BMJ. 2010;341:c6258.
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Lithium carbonate is a mood stabilizer that is effective in the treatment of bipolar disorder, particularly in controlling mania.1 Lithium can reduce the risk of suicide,2 treat aggression and self-mutilating behavior,3 and prevent steroid-induced psychosis.4 It also can raise the white cell count in patients with clozapine-induced leukopenia.5
To prevent or lower the risk of relapse, the therapeutic plasma level of lithium should be regularly monitored to ensure an optimal concentration in the CNS. The highest tolerable level of lithium in the plasma is 0.6 to 0.8 mmol/L, with the optimal level ranging up to 1.2 mmol/L.6 Regular monitoring of renal function is also required to prevent renal toxicity, particularly if the plasma level exceeds 0.8 mmol/L.7 Because of lithium’s relatively narrow therapeutic index, its interaction with other medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and carbamazepine, can also precipitate lithium toxicity.8 We describe a lesson learned from a case of lithium toxicity in an otherwise healthy patient with bipolar disorder.
Case report
An otherwise healthy 39-year-old woman diagnosed with bipolar type I disorder was receiving valproate sodium 600 mg/d and olanzapine 10 mg/d. Despite improvement in her mood, she gained 11.6 kg following 6 months of treatment. As a result, olanzapine was switched to aripiprazole 10 mg/d that was later increased to 15 mg/d, and sodium valproate was gradually optimized up to 1,000 mg/d. She later complained of hair thinning and hair loss so she self-adjusted her medication dosages, which resulted in frequent relapses. Her mood stabilizer was changed from sodium valproate to lithium 600 mg/d.
Unfortunately, after taking lithium for 15 days, she returned to us with fever associated with reduced oral intake, poor sleep, bilateral upper limb rigidity, and bilateral hand tremor. She also complained of extreme thirst and fatigue but no vomiting or diarrhea. She had difficulty falling asleep and slept for only 1 to 2 hours a day. Her symptoms worsened when a general practitioner prescribed NSAIDs for her fever and body ache. Her tremors were later generalized, which made it difficult for her to take her oral medications and disturbed her speech and movement.
On evaluation, our patient appeared comfortable and not agitated. She was orientated to time, place, and person. Her blood pressure was 139/89 mmHg, heart rate was 104 bpm, and she was afebrile. She was dehydrated with minimal urine output. She had coarse tremor in her upper and lower limbs, which were hypertonic but did not display hyperreflexia or clonus. There was no nystagmus or ataxia. A mental state examination showed no signs of manic, hypomanic, or depressive symptoms. She had slurred speech, and her affect was restricted.
Blood investigation revealed a suprathreshold lithium level of 1.70 mmol/L (normal: 0.8 to 1.2 mmol/L). Biochemical parameters showed evidence of acute kidney injury (urea: 6.1 mmol/L; creatinine: 0.140 mmol/L), with no electrolyte imbalance. There was no evidence of hypothyroidism (thyroid-stimulating hormone: 14.9 mIU/L; free thyroxine: 9.9 pmol/L), hyperparathyroidism, or hypercalcemia. Autoimmune markers were positive for antinuclear antibody (titre 1:320) and anti-double stranded DNA (76.8 IU/mL). Apart from hair loss, she denied other symptoms associated with autoimmune disease, such as joint pain, butterfly rash, or persistent fatigue. Other routine blood investigations were within normal limits. Her urine protein throughout admission had shown persistent proteinuria ranging from 3+ to 4+. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed normal sinus rhythm with no T wave inversion or QT prolongation.
Continue to: A detailed family history...
A detailed family history later confirmed a strong family history of renal disease: her mother had lupus nephritis with nephrotic syndrome, and her brother had died from complications of a rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Her renal function prior to lithium initiation was within normal limits (urea: 4.0 mmol/L; serum creatinine: 78 µmol/L).
In the ward, lithium and aripiprazole were discontinued, and she was hydrated. Combined care with the psychiatric and medical teams was established early to safeguard against potential CNS deterioration. She showed marked clinical improvement by Day 3, with the resolution of coarse tremor and rigidity as well as normalization of blood parameters. Her lithium level returned to a therapeutic level by Day 4 after lithium discontinuation, and her renal profile gradually normalized. She was restarted on aripiprazole 10 mg/d for her bipolar illness and responded well. She was discharged on Day 5 with a referral to the nephrology team for further intervention.
Lessons learned
This case highlights the issue of lithium safety in susceptible individuals and the importance of risk stratification in this group of patients. Lithium is an effective treatment for bipolar I disorder and has also been used as adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder, schizoaffective disorder, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, and the control of chronic aggression.9 Lithium is completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract following ingestion, is not metabolized, and is eliminated almost entirely by the kidneys (though trace amounts may be found in feces and perspiration).
In our case, a detailed family history of renal disease was not adequately explored until our patient presented with signs suggestive of lithium toxicity. Our patient had been prescribed lithium 600 mg/d as a maintenance therapy. Upon starting lithium, her baseline biochemical parameters were within normal limits, and renal issues were not suspected. The hair thinning and hair loss she experienced could have been an adverse effect of valproate sodium or a manifestation of an underlying autoimmune disease. Coupled with the use of NSAIDs that could have precipitated acute kidney injury, her poor oral intake and dehydration during the acute illness further impaired lithium excretion, leading to a suprathreshold plasma level despite a low dose of lithium. Therefore, before prescribing lithium, a thorough medical and family history is needed, supplemented by an evaluation of renal function, serum electrolytes, and thyroid function to determine the starting dosage of lithium. Routine vital sign assessment and ECG should also be conducted, and concurrent medications and pregnancy status should be confirmed before prescribing lithium. Regular lithium level monitoring is essential.
Measuring a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is recommended to validate renal status10 and classify and stage kidney disease.11 Combining eGFR with blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and urine microscopic analysis further improves the prediction of renal disease in early stages. We recommend considering a blood test for autoimmune markers in patients with clinical suspicion of autoimmune disease, in the presence of suggestive signs and symptoms, and/or in patients with a positive family history (Table).

Before starting lithium, in addition to conducting a detailed clinical evaluation, information about symptoms and the risk of lithium toxicity should be discussed with patients.12 Our case serves as a timely reminder that the lack of suggestive biochemical parameters of renal disease should not rule out an underlying renal disease, and a strong family history of renal disease should warrant suspicion of a possible autoimmune origin.
We suggest that future studies evaluate the risks of lithium toxicity in susceptible groups of patients, such as those with family history of renal disease.
Editor’s note: Readers’ Forum is a department for correspondence from readers that is not in response to articles published in
Lithium carbonate is a mood stabilizer that is effective in the treatment of bipolar disorder, particularly in controlling mania.1 Lithium can reduce the risk of suicide,2 treat aggression and self-mutilating behavior,3 and prevent steroid-induced psychosis.4 It also can raise the white cell count in patients with clozapine-induced leukopenia.5
To prevent or lower the risk of relapse, the therapeutic plasma level of lithium should be regularly monitored to ensure an optimal concentration in the CNS. The highest tolerable level of lithium in the plasma is 0.6 to 0.8 mmol/L, with the optimal level ranging up to 1.2 mmol/L.6 Regular monitoring of renal function is also required to prevent renal toxicity, particularly if the plasma level exceeds 0.8 mmol/L.7 Because of lithium’s relatively narrow therapeutic index, its interaction with other medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and carbamazepine, can also precipitate lithium toxicity.8 We describe a lesson learned from a case of lithium toxicity in an otherwise healthy patient with bipolar disorder.
Case report
An otherwise healthy 39-year-old woman diagnosed with bipolar type I disorder was receiving valproate sodium 600 mg/d and olanzapine 10 mg/d. Despite improvement in her mood, she gained 11.6 kg following 6 months of treatment. As a result, olanzapine was switched to aripiprazole 10 mg/d that was later increased to 15 mg/d, and sodium valproate was gradually optimized up to 1,000 mg/d. She later complained of hair thinning and hair loss so she self-adjusted her medication dosages, which resulted in frequent relapses. Her mood stabilizer was changed from sodium valproate to lithium 600 mg/d.
Unfortunately, after taking lithium for 15 days, she returned to us with fever associated with reduced oral intake, poor sleep, bilateral upper limb rigidity, and bilateral hand tremor. She also complained of extreme thirst and fatigue but no vomiting or diarrhea. She had difficulty falling asleep and slept for only 1 to 2 hours a day. Her symptoms worsened when a general practitioner prescribed NSAIDs for her fever and body ache. Her tremors were later generalized, which made it difficult for her to take her oral medications and disturbed her speech and movement.
On evaluation, our patient appeared comfortable and not agitated. She was orientated to time, place, and person. Her blood pressure was 139/89 mmHg, heart rate was 104 bpm, and she was afebrile. She was dehydrated with minimal urine output. She had coarse tremor in her upper and lower limbs, which were hypertonic but did not display hyperreflexia or clonus. There was no nystagmus or ataxia. A mental state examination showed no signs of manic, hypomanic, or depressive symptoms. She had slurred speech, and her affect was restricted.
Blood investigation revealed a suprathreshold lithium level of 1.70 mmol/L (normal: 0.8 to 1.2 mmol/L). Biochemical parameters showed evidence of acute kidney injury (urea: 6.1 mmol/L; creatinine: 0.140 mmol/L), with no electrolyte imbalance. There was no evidence of hypothyroidism (thyroid-stimulating hormone: 14.9 mIU/L; free thyroxine: 9.9 pmol/L), hyperparathyroidism, or hypercalcemia. Autoimmune markers were positive for antinuclear antibody (titre 1:320) and anti-double stranded DNA (76.8 IU/mL). Apart from hair loss, she denied other symptoms associated with autoimmune disease, such as joint pain, butterfly rash, or persistent fatigue. Other routine blood investigations were within normal limits. Her urine protein throughout admission had shown persistent proteinuria ranging from 3+ to 4+. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed normal sinus rhythm with no T wave inversion or QT prolongation.
Continue to: A detailed family history...
A detailed family history later confirmed a strong family history of renal disease: her mother had lupus nephritis with nephrotic syndrome, and her brother had died from complications of a rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Her renal function prior to lithium initiation was within normal limits (urea: 4.0 mmol/L; serum creatinine: 78 µmol/L).
In the ward, lithium and aripiprazole were discontinued, and she was hydrated. Combined care with the psychiatric and medical teams was established early to safeguard against potential CNS deterioration. She showed marked clinical improvement by Day 3, with the resolution of coarse tremor and rigidity as well as normalization of blood parameters. Her lithium level returned to a therapeutic level by Day 4 after lithium discontinuation, and her renal profile gradually normalized. She was restarted on aripiprazole 10 mg/d for her bipolar illness and responded well. She was discharged on Day 5 with a referral to the nephrology team for further intervention.
Lessons learned
This case highlights the issue of lithium safety in susceptible individuals and the importance of risk stratification in this group of patients. Lithium is an effective treatment for bipolar I disorder and has also been used as adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder, schizoaffective disorder, treatment-resistant schizophrenia, anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa, and the control of chronic aggression.9 Lithium is completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract following ingestion, is not metabolized, and is eliminated almost entirely by the kidneys (though trace amounts may be found in feces and perspiration).
In our case, a detailed family history of renal disease was not adequately explored until our patient presented with signs suggestive of lithium toxicity. Our patient had been prescribed lithium 600 mg/d as a maintenance therapy. Upon starting lithium, her baseline biochemical parameters were within normal limits, and renal issues were not suspected. The hair thinning and hair loss she experienced could have been an adverse effect of valproate sodium or a manifestation of an underlying autoimmune disease. Coupled with the use of NSAIDs that could have precipitated acute kidney injury, her poor oral intake and dehydration during the acute illness further impaired lithium excretion, leading to a suprathreshold plasma level despite a low dose of lithium. Therefore, before prescribing lithium, a thorough medical and family history is needed, supplemented by an evaluation of renal function, serum electrolytes, and thyroid function to determine the starting dosage of lithium. Routine vital sign assessment and ECG should also be conducted, and concurrent medications and pregnancy status should be confirmed before prescribing lithium. Regular lithium level monitoring is essential.
Measuring a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is recommended to validate renal status10 and classify and stage kidney disease.11 Combining eGFR with blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and urine microscopic analysis further improves the prediction of renal disease in early stages. We recommend considering a blood test for autoimmune markers in patients with clinical suspicion of autoimmune disease, in the presence of suggestive signs and symptoms, and/or in patients with a positive family history (Table).

Before starting lithium, in addition to conducting a detailed clinical evaluation, information about symptoms and the risk of lithium toxicity should be discussed with patients.12 Our case serves as a timely reminder that the lack of suggestive biochemical parameters of renal disease should not rule out an underlying renal disease, and a strong family history of renal disease should warrant suspicion of a possible autoimmune origin.
We suggest that future studies evaluate the risks of lithium toxicity in susceptible groups of patients, such as those with family history of renal disease.
1. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
2. Cipriani A, Hawton K, Stockton S, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicide in mood disorders: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013; 346:f3646.
3. Correll CU, Yu X, Xiang Y, et al. Biological treatment of acute agitation or aggression with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder in the inpatient setting. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2017;29(2):92-107.
4. Abou-Saleh MT, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Coppen AJ. Lithium in the episode and suicide prophylaxis and in augmenting strategies in patients with unipolar depression. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2017;5(1):11.
5. Aydin M, Ilhan BC, Calisir S, et al. Continuing clozapine treatment with lithium in schizophrenic patients with neutropenia or leukopenia: brief review of literature with case reports. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016;6(1):33-38.
6. Nolen WA, Weisler RH. The association of the effect of lithium in the maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder with lithium plasma levels: a post hoc analysis of a double-blind study comparing switching to lithium or placebo in patients who responded to quetiapine (Trial 144). Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(1):100-109.
7. Aiff H, Attman P, Aurell M, et al. Effects of 10 to 30 years of lithium treatment on kidney function. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(5):608-614.
8. Taylor DM, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
9. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Kaplan & Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry. 9th ed. Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2002.
10. Lopez-Giacoman S, Madero M. Biomarkers in chronic kidney disease, from kidney function to kidney damage. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(1):57-73.
11. McCance RA, Robinson JR. Evaluation of renal clearances. Proc R Soc Med. 1949;42(7):475-480.
12. Gerret D, Lamont T, Paton C, et al. Prescribing and monitoring lithium therapy: summary of a safety report from the National Patient Safety Agency. BMJ. 2010;341:c6258.
1. Goodwin GM, Haddad PM, Ferrier IN, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised third edition recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2016;30(6):495-553.
2. Cipriani A, Hawton K, Stockton S, et al. Lithium in the prevention of suicide in mood disorders: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013; 346:f3646.
3. Correll CU, Yu X, Xiang Y, et al. Biological treatment of acute agitation or aggression with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder in the inpatient setting. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2017;29(2):92-107.
4. Abou-Saleh MT, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Coppen AJ. Lithium in the episode and suicide prophylaxis and in augmenting strategies in patients with unipolar depression. Int J Bipolar Disord. 2017;5(1):11.
5. Aydin M, Ilhan BC, Calisir S, et al. Continuing clozapine treatment with lithium in schizophrenic patients with neutropenia or leukopenia: brief review of literature with case reports. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016;6(1):33-38.
6. Nolen WA, Weisler RH. The association of the effect of lithium in the maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder with lithium plasma levels: a post hoc analysis of a double-blind study comparing switching to lithium or placebo in patients who responded to quetiapine (Trial 144). Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(1):100-109.
7. Aiff H, Attman P, Aurell M, et al. Effects of 10 to 30 years of lithium treatment on kidney function. J Psychopharmacol. 2015;29(5):608-614.
8. Taylor DM, Barnes TRE, Young AH. The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; 2018.
9. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA. Kaplan & Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry. 9th ed. Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2002.
10. Lopez-Giacoman S, Madero M. Biomarkers in chronic kidney disease, from kidney function to kidney damage. World J Nephrol. 2015;4(1):57-73.
11. McCance RA, Robinson JR. Evaluation of renal clearances. Proc R Soc Med. 1949;42(7):475-480.
12. Gerret D, Lamont T, Paton C, et al. Prescribing and monitoring lithium therapy: summary of a safety report from the National Patient Safety Agency. BMJ. 2010;341:c6258.
Suicidality in an older patient with chronic kidney disease
CASE Depressed, anxious, and suicidal
Mr. J, age 72, is brought to the emergency department by law enforcement at his wife’s request due to worsening suicidal thoughts and anxiety. He has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Mr. J has been compliant with his medications, but they seem to no longer be effective. He is admitted to the geriatric psychiatry unit.
HISTORY Increased debilitation
Over the past several years, Mr. J has experienced increasing debilitation at home, including difficulty walking and an inability to perform activities of daily life. Recently, he has begun to ask for multiple pills in an attempt to take his own life.
Mr. J has been previously treated in a psychiatric clinic with duloxetine 60 mg/d, mirtazapine 30 mg/d at bedtime, buspirone 15 mg 3 times a day, and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. He is also taking amlodipine 5 mg twice daily for hypertension, lisinopril 2.5 mg/d for hypertension, furosemide 20 mg/d orally for CKD, and potassium chloride 10 mEq/d for hypokalemia secondary to CKD and furosemide use. Over the past year, his psychiatric medications have been steadily increased to target his MDD and anxiety.
EVALUATION Disorientation and Stage 3A CKD
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. J describes panic, feelings of impending doom, and profound anxiety. He states he has increasing anxiety related to “being a burden” on his family and wife. Additionally, he describes decreased appetite, difficulty sleeping, low energy, difficulty concentrating, no interest in outside activities, and feelings of hopelessness.
Mr. J’s temperature is 39.2o C; heart rate is 109 beats per minute; respiratory rate is 18 breaths per minute; blood pressure is 157/83 mm Hg; and pulse oximetry is 97%. Laboratory screening indicates a red blood cell count of 3.57, hemoglobin 11.2, hematocrit 33.8, red blood cell distribution width 17.5, blood urea nitrogen 45, creatinine 1.5 with no known baseline, and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 46 mL/min, indicating Stage 3A CKD (Table 11). Additional testing rules out other potential causes of delirium and psychosis.
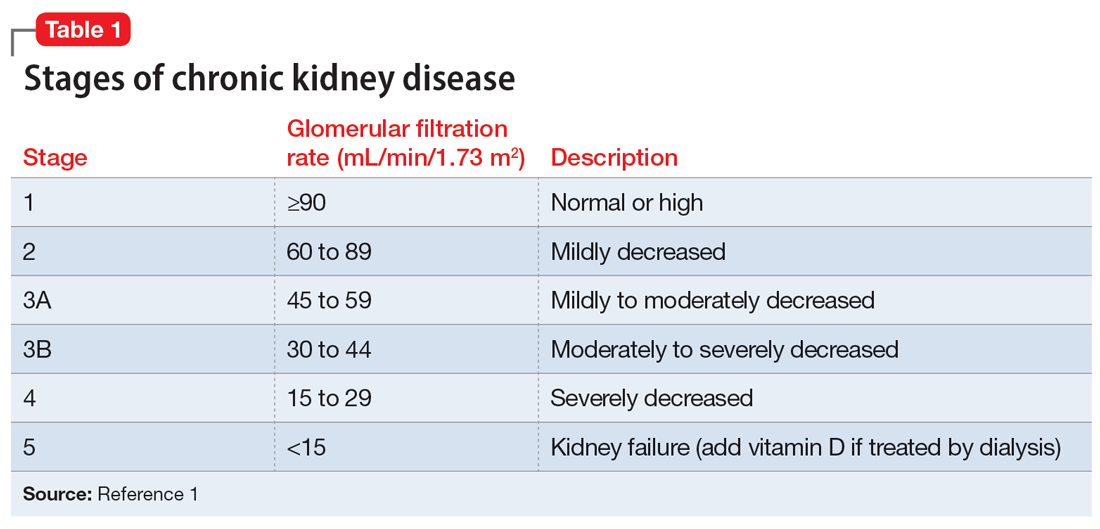
A physical exam reveals Mr. J has a fine tremor, myoclonus, muscle rigidity, and hyperreflexia. He is oriented to name, but not to date, place, or situation, and is easily confused. Mr. J uses a walker but has significant tremors while walking and immediately asks for assistance due to profound anxiety related to a fear of falling. Mr. J’s mood and affect are labile with tearful and anxious episodes. His anxiety focuses on overvalued thoughts of minor or irrelevant concerns. Additionally, he has poor insight and judgment. When asked about the cause of his anxiety, Mr. J says, “I don’t know why I’m anxious; I’m just a worrywart.” His memory is impaired, and he does not know why he is in the hospital. Mr. J scores 24 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, which indicates mild impairment.
Mr. J continues to endorse suicidal ideation but denies homicidal thoughts. Based on these symptoms, the differential diagnosis includes serotonin syndrome, MDD with suicidal ideation, generalized anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273789]
The authors’ observations
GFR is used to determine the level of renal impairment. Mr. J’s GFR of 46 mL/min indicates Stage 3A CKD (Table 11 ). Additionally, he displayed anemia and increased creatinine due to CKD. Twenty percent of patients with CKD also experience MDD.2 In a prospective observational cohort study, Hedayati et al3 found that Stage 2 to Stage 5 CKD with MDD leads to an increased risk of death, hospitalization, or progression to dialysis. It is important to properly manage Mr. J’s MDD and CKD to prevent future comorbidities. Renal impairment is common in people age >65.4 Even when GFR is normal, it is recommended to decrease dosing of medications in older adults due to age-related decreased renal excretion. As kidneys decrease in function, their ability to excrete normal amounts of medications also decreases, leading to increased serum levels and potential toxicity.
A combination of 4 serotonergic psychotropic medications may not be unusual to address treatment-resistant depression in a healthy, nongeriatric adult. However, Mr. J displayed signs of serotonin toxicity, such as hyperthermia, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, increased tremors, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, and muscle rigidity. These are classic signs of serotonin toxicity. For Mr. J, serotonin toxicity can be treated with the removal of serotonergic medications and lorazepam for symptom relief. If symptoms persist, cyproheptadine, a serotonin antagonist, can be used. Mr. J’s psychotropic medications were increased in an outpatient setting and he was unable to renally excrete higher doses of these serotonergic agents, which lead to chronic serotonin toxicity.
It is important to rule out other causes of psychosis or delirium in geriatric patients. A study by Marcantonio et al5 found that >40% of patients referred to a consulting psychiatrist for depression ultimately had delirium, and this was more likely in geriatric patients.
TREATMENT Adjustments to the medication regimen
The treatment team decides to taper and discontinue duloxetine, buspirone, and trazodone and reduce mirtazapine to 15 mg/d at bedtime. Additionally, oral lorazepam 1 mg as needed is prescribed to alleviate agitation and correct vital signs. Mr. J’s vital signs improve, with decreased temperature and normal cardiac and respiratory rhythms.
Mr. J’s Stage 3A CKD is treated with oral fluids, and his hypertension is managed with an increase of lisinopril from 2.5 mg/d to 10 mg/d. After 10 days on the psychiatric unit, he shows improvement, decreased anxiety, and remission of suicidal ideation.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273790]
The authors’ observations
In 2019, the American Geriatric Society (AGS) updated the Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults.4 The Beers Criteria were created to educate clinicians about the use of potentially inappropriate medications that have an unfavorable balance of benefits and risks compared to alternative treatments. The AGS lists medications that should be avoided or have their dosage reduced with varying levels of kidney function in older adults. Duloxetine is one of the medications listed with the recommendation to avoid for patients with a creatinine clearance <30 mL/min. Creatinine clearance is an estimation of GFR.
Although duloxetine is mentioned in the Beers Criteria, many other antidepressants have metabolites excreted by the kidneys.6 Potential adverse effects include increased bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and serotonin toxicity symptoms.7 Mr. J has Stage 3A CKD and takes 4 psychotropics, which will additively increase the serum concentration of serotonergic medications. In terms of treatment for serotonin toxicity, it is important to remove the causative medications. After discontinuing serotonergic medications, lorazepam can be administered as needed. If a patient continues to have symptoms, cyproheptadine is an option.
For patients with impaired renal function, adding nonpharmacologic options should be considered, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, electroconvulsive therapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Table 24,8-18 lists the minimum effective doses for well-known medications for treating MDD.
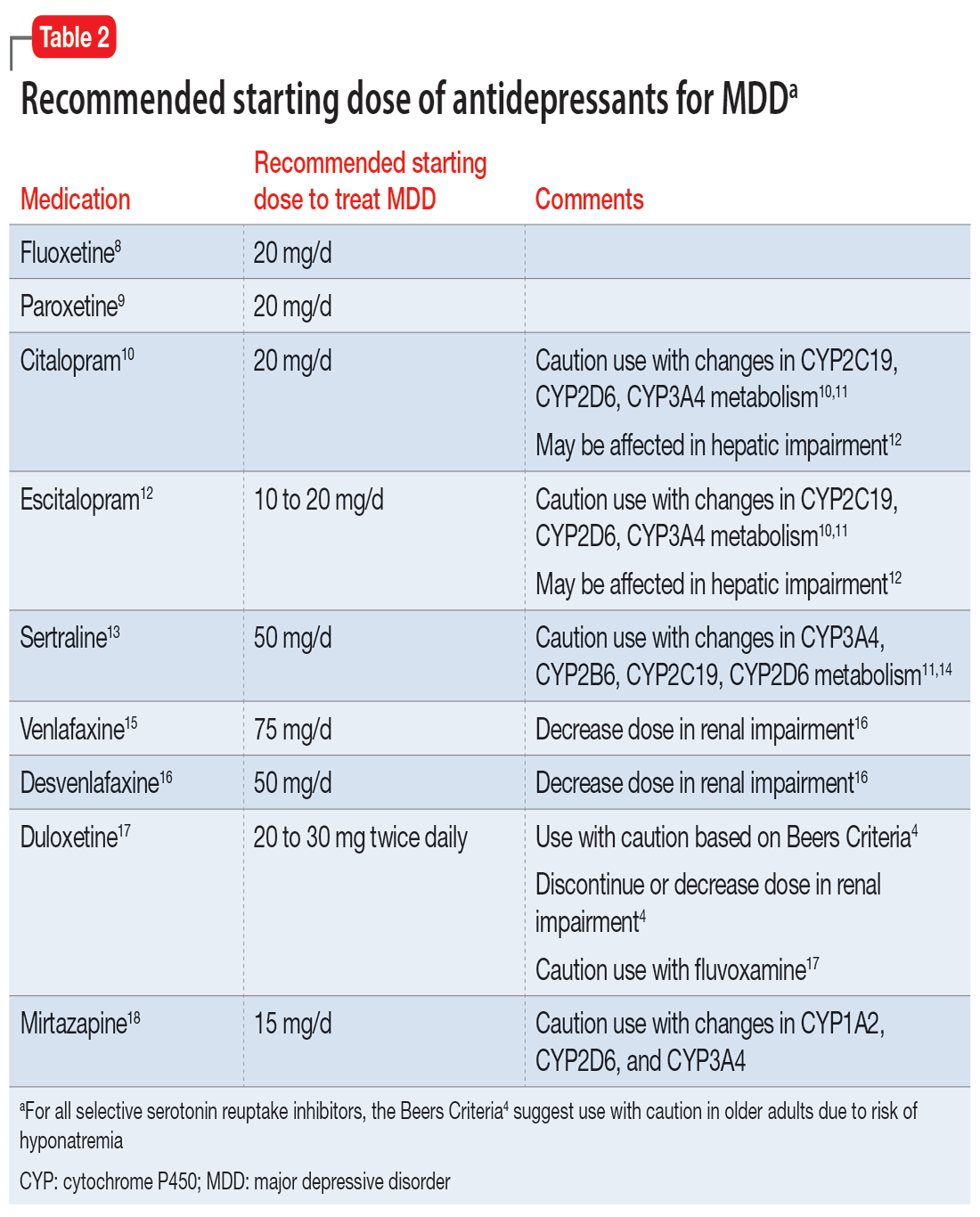
OUTCOME Improvement and discharge
Mr. J’s confusion improves, his heart rate decreases, and his feelings of panic and doom improve. He continues to have depressive symptoms, but his suicidal ideation stops. At discharge, Mr. J is receiving mirtazapine 15 mg/d, potassium chloride 10 mEq/d orally, lisinopril 20 mg/d orally at bedtime, furosemide 20 mg/d orally, and amlodipine 5 mg orally twice a day. Additionally, the treatment team recommends psychotherapy to Mr. J to address his anxiety and depression.
Bottom Line
Older patients are more sensitive to psychotropic medications, regardless of any comorbidities. It is important to review each patient’s glomerular filtration rate to better understand their renal function and adjust medications accordingly.
Related Resources
- Whittaker P, Vordenberg SE, Coe AB. Deprescribing in older adults: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):40-43. doi:10.12788/cp.0246
- Gibson G, Kennedy LH, Barlow G. Polypharmacy in older adults. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):40-46.
- Barr R, Miskle B, Thomas C. Management of major depressive disorder with psychotic features. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):30-33. doi:10.12788/cp.0092
Drug Brand Names
Amlodipine • Norvasc
Buspirone • BuSpar
Citalopram • Celexa
Cyproheptadine • Periactin
Desvenlafaxine • Pristiq
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Furosemide • Lasix
Lisinopril • Zestril
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1-S266.
2. Shirazian S, Grant CD, Aina O, et al. Depression in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: similarities and differences in diagnosis, epidemiology, and management. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(1):94-107.
3. Hedayati SS, Minhajuddin AT, Afshar M, et al. Association between major depressive episodes in patients with chronic kidney disease and initiation of dialysis, hospitalization, or death. JAMA. 2010;303(19):1946-1953.
4. 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
5. Marcantonio E, Ta T, Duthie E, et al. Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850-857.
6. Cukor D, Cohen, SD, Peterson RA, et al. Psychosocial aspects of chronic disease: ESRD as a paradigmatic illness. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(12):3042-3055.
7. Cohen SD, Norris L, Acquaviva K, et al. Screening, diagnosis, and treatment of depression in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2(6):1332-1342.
8. Sommi RW, Crismon ML, Bowden CL. Fluoxetine: a serotonin-specific, second-generation antidepressant. Pharmacotherapy. 1987;7(1):1-15.
9. Jenner PN. Paroxetine: an overview of dosage, tolerability, and safety. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1992;6(Suppl 4):69-80.
10. Montgomery SA. Selecting the optimum therapeutic dose of serotonin reuptake inhibitors: studies with citalopram. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(Suppl 1):23-27.
11. Milosavljevic F, Bukvic N, Pavlovic Z, et al. Association of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 poor and intermediate metabolizer status with antidepressant and antipsychotic exposure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(3):270-280.
12. Rao N. The clinical pharmacokinetics of escitalopram. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(4):281-290.
13. Preskorn SH, Lane RM. Sertraline 50 mg daily: the optimal dose in the treatment of depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(3):129-141.
14. Huddart R, Hicks JK, Ramsey LB, et al. PharmGKB summary: sertraline pathway, pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2020;30(2):26-33.
15. Furukawa TA, Cipriani A, Cowen PJ, et al. Optimal dose of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, venlafaxine, and mirtazapine in major depression: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(7):601-609.
16. Norman TR, Olver JS. Desvenlafaxine in the treatment of major depression: an updated overview. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(9):1087-1097.
17. Knadler MP, Lobo E, Chappell J, et al. Duloxetine: clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(5):281-294.
18. Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264.
CASE Depressed, anxious, and suicidal
Mr. J, age 72, is brought to the emergency department by law enforcement at his wife’s request due to worsening suicidal thoughts and anxiety. He has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Mr. J has been compliant with his medications, but they seem to no longer be effective. He is admitted to the geriatric psychiatry unit.
HISTORY Increased debilitation
Over the past several years, Mr. J has experienced increasing debilitation at home, including difficulty walking and an inability to perform activities of daily life. Recently, he has begun to ask for multiple pills in an attempt to take his own life.
Mr. J has been previously treated in a psychiatric clinic with duloxetine 60 mg/d, mirtazapine 30 mg/d at bedtime, buspirone 15 mg 3 times a day, and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. He is also taking amlodipine 5 mg twice daily for hypertension, lisinopril 2.5 mg/d for hypertension, furosemide 20 mg/d orally for CKD, and potassium chloride 10 mEq/d for hypokalemia secondary to CKD and furosemide use. Over the past year, his psychiatric medications have been steadily increased to target his MDD and anxiety.
EVALUATION Disorientation and Stage 3A CKD
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. J describes panic, feelings of impending doom, and profound anxiety. He states he has increasing anxiety related to “being a burden” on his family and wife. Additionally, he describes decreased appetite, difficulty sleeping, low energy, difficulty concentrating, no interest in outside activities, and feelings of hopelessness.
Mr. J’s temperature is 39.2o C; heart rate is 109 beats per minute; respiratory rate is 18 breaths per minute; blood pressure is 157/83 mm Hg; and pulse oximetry is 97%. Laboratory screening indicates a red blood cell count of 3.57, hemoglobin 11.2, hematocrit 33.8, red blood cell distribution width 17.5, blood urea nitrogen 45, creatinine 1.5 with no known baseline, and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 46 mL/min, indicating Stage 3A CKD (Table 11). Additional testing rules out other potential causes of delirium and psychosis.

A physical exam reveals Mr. J has a fine tremor, myoclonus, muscle rigidity, and hyperreflexia. He is oriented to name, but not to date, place, or situation, and is easily confused. Mr. J uses a walker but has significant tremors while walking and immediately asks for assistance due to profound anxiety related to a fear of falling. Mr. J’s mood and affect are labile with tearful and anxious episodes. His anxiety focuses on overvalued thoughts of minor or irrelevant concerns. Additionally, he has poor insight and judgment. When asked about the cause of his anxiety, Mr. J says, “I don’t know why I’m anxious; I’m just a worrywart.” His memory is impaired, and he does not know why he is in the hospital. Mr. J scores 24 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, which indicates mild impairment.
Mr. J continues to endorse suicidal ideation but denies homicidal thoughts. Based on these symptoms, the differential diagnosis includes serotonin syndrome, MDD with suicidal ideation, generalized anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273789]
The authors’ observations
GFR is used to determine the level of renal impairment. Mr. J’s GFR of 46 mL/min indicates Stage 3A CKD (Table 11 ). Additionally, he displayed anemia and increased creatinine due to CKD. Twenty percent of patients with CKD also experience MDD.2 In a prospective observational cohort study, Hedayati et al3 found that Stage 2 to Stage 5 CKD with MDD leads to an increased risk of death, hospitalization, or progression to dialysis. It is important to properly manage Mr. J’s MDD and CKD to prevent future comorbidities. Renal impairment is common in people age >65.4 Even when GFR is normal, it is recommended to decrease dosing of medications in older adults due to age-related decreased renal excretion. As kidneys decrease in function, their ability to excrete normal amounts of medications also decreases, leading to increased serum levels and potential toxicity.
A combination of 4 serotonergic psychotropic medications may not be unusual to address treatment-resistant depression in a healthy, nongeriatric adult. However, Mr. J displayed signs of serotonin toxicity, such as hyperthermia, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, increased tremors, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, and muscle rigidity. These are classic signs of serotonin toxicity. For Mr. J, serotonin toxicity can be treated with the removal of serotonergic medications and lorazepam for symptom relief. If symptoms persist, cyproheptadine, a serotonin antagonist, can be used. Mr. J’s psychotropic medications were increased in an outpatient setting and he was unable to renally excrete higher doses of these serotonergic agents, which lead to chronic serotonin toxicity.
It is important to rule out other causes of psychosis or delirium in geriatric patients. A study by Marcantonio et al5 found that >40% of patients referred to a consulting psychiatrist for depression ultimately had delirium, and this was more likely in geriatric patients.
TREATMENT Adjustments to the medication regimen
The treatment team decides to taper and discontinue duloxetine, buspirone, and trazodone and reduce mirtazapine to 15 mg/d at bedtime. Additionally, oral lorazepam 1 mg as needed is prescribed to alleviate agitation and correct vital signs. Mr. J’s vital signs improve, with decreased temperature and normal cardiac and respiratory rhythms.
Mr. J’s Stage 3A CKD is treated with oral fluids, and his hypertension is managed with an increase of lisinopril from 2.5 mg/d to 10 mg/d. After 10 days on the psychiatric unit, he shows improvement, decreased anxiety, and remission of suicidal ideation.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273790]
The authors’ observations
In 2019, the American Geriatric Society (AGS) updated the Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults.4 The Beers Criteria were created to educate clinicians about the use of potentially inappropriate medications that have an unfavorable balance of benefits and risks compared to alternative treatments. The AGS lists medications that should be avoided or have their dosage reduced with varying levels of kidney function in older adults. Duloxetine is one of the medications listed with the recommendation to avoid for patients with a creatinine clearance <30 mL/min. Creatinine clearance is an estimation of GFR.
Although duloxetine is mentioned in the Beers Criteria, many other antidepressants have metabolites excreted by the kidneys.6 Potential adverse effects include increased bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and serotonin toxicity symptoms.7 Mr. J has Stage 3A CKD and takes 4 psychotropics, which will additively increase the serum concentration of serotonergic medications. In terms of treatment for serotonin toxicity, it is important to remove the causative medications. After discontinuing serotonergic medications, lorazepam can be administered as needed. If a patient continues to have symptoms, cyproheptadine is an option.
For patients with impaired renal function, adding nonpharmacologic options should be considered, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, electroconvulsive therapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Table 24,8-18 lists the minimum effective doses for well-known medications for treating MDD.

OUTCOME Improvement and discharge
Mr. J’s confusion improves, his heart rate decreases, and his feelings of panic and doom improve. He continues to have depressive symptoms, but his suicidal ideation stops. At discharge, Mr. J is receiving mirtazapine 15 mg/d, potassium chloride 10 mEq/d orally, lisinopril 20 mg/d orally at bedtime, furosemide 20 mg/d orally, and amlodipine 5 mg orally twice a day. Additionally, the treatment team recommends psychotherapy to Mr. J to address his anxiety and depression.
Bottom Line
Older patients are more sensitive to psychotropic medications, regardless of any comorbidities. It is important to review each patient’s glomerular filtration rate to better understand their renal function and adjust medications accordingly.
Related Resources
- Whittaker P, Vordenberg SE, Coe AB. Deprescribing in older adults: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):40-43. doi:10.12788/cp.0246
- Gibson G, Kennedy LH, Barlow G. Polypharmacy in older adults. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):40-46.
- Barr R, Miskle B, Thomas C. Management of major depressive disorder with psychotic features. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):30-33. doi:10.12788/cp.0092
Drug Brand Names
Amlodipine • Norvasc
Buspirone • BuSpar
Citalopram • Celexa
Cyproheptadine • Periactin
Desvenlafaxine • Pristiq
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Furosemide • Lasix
Lisinopril • Zestril
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
CASE Depressed, anxious, and suicidal
Mr. J, age 72, is brought to the emergency department by law enforcement at his wife’s request due to worsening suicidal thoughts and anxiety. He has a history of major depressive disorder (MDD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Mr. J has been compliant with his medications, but they seem to no longer be effective. He is admitted to the geriatric psychiatry unit.
HISTORY Increased debilitation
Over the past several years, Mr. J has experienced increasing debilitation at home, including difficulty walking and an inability to perform activities of daily life. Recently, he has begun to ask for multiple pills in an attempt to take his own life.
Mr. J has been previously treated in a psychiatric clinic with duloxetine 60 mg/d, mirtazapine 30 mg/d at bedtime, buspirone 15 mg 3 times a day, and trazodone 50 mg/d at bedtime. He is also taking amlodipine 5 mg twice daily for hypertension, lisinopril 2.5 mg/d for hypertension, furosemide 20 mg/d orally for CKD, and potassium chloride 10 mEq/d for hypokalemia secondary to CKD and furosemide use. Over the past year, his psychiatric medications have been steadily increased to target his MDD and anxiety.
EVALUATION Disorientation and Stage 3A CKD
In the psychiatric unit, Mr. J describes panic, feelings of impending doom, and profound anxiety. He states he has increasing anxiety related to “being a burden” on his family and wife. Additionally, he describes decreased appetite, difficulty sleeping, low energy, difficulty concentrating, no interest in outside activities, and feelings of hopelessness.
Mr. J’s temperature is 39.2o C; heart rate is 109 beats per minute; respiratory rate is 18 breaths per minute; blood pressure is 157/83 mm Hg; and pulse oximetry is 97%. Laboratory screening indicates a red blood cell count of 3.57, hemoglobin 11.2, hematocrit 33.8, red blood cell distribution width 17.5, blood urea nitrogen 45, creatinine 1.5 with no known baseline, and an estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 46 mL/min, indicating Stage 3A CKD (Table 11). Additional testing rules out other potential causes of delirium and psychosis.

A physical exam reveals Mr. J has a fine tremor, myoclonus, muscle rigidity, and hyperreflexia. He is oriented to name, but not to date, place, or situation, and is easily confused. Mr. J uses a walker but has significant tremors while walking and immediately asks for assistance due to profound anxiety related to a fear of falling. Mr. J’s mood and affect are labile with tearful and anxious episodes. His anxiety focuses on overvalued thoughts of minor or irrelevant concerns. Additionally, he has poor insight and judgment. When asked about the cause of his anxiety, Mr. J says, “I don’t know why I’m anxious; I’m just a worrywart.” His memory is impaired, and he does not know why he is in the hospital. Mr. J scores 24 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, which indicates mild impairment.
Mr. J continues to endorse suicidal ideation but denies homicidal thoughts. Based on these symptoms, the differential diagnosis includes serotonin syndrome, MDD with suicidal ideation, generalized anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273789]
The authors’ observations
GFR is used to determine the level of renal impairment. Mr. J’s GFR of 46 mL/min indicates Stage 3A CKD (Table 11 ). Additionally, he displayed anemia and increased creatinine due to CKD. Twenty percent of patients with CKD also experience MDD.2 In a prospective observational cohort study, Hedayati et al3 found that Stage 2 to Stage 5 CKD with MDD leads to an increased risk of death, hospitalization, or progression to dialysis. It is important to properly manage Mr. J’s MDD and CKD to prevent future comorbidities. Renal impairment is common in people age >65.4 Even when GFR is normal, it is recommended to decrease dosing of medications in older adults due to age-related decreased renal excretion. As kidneys decrease in function, their ability to excrete normal amounts of medications also decreases, leading to increased serum levels and potential toxicity.
A combination of 4 serotonergic psychotropic medications may not be unusual to address treatment-resistant depression in a healthy, nongeriatric adult. However, Mr. J displayed signs of serotonin toxicity, such as hyperthermia, tachycardia, increased blood pressure, increased tremors, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, and muscle rigidity. These are classic signs of serotonin toxicity. For Mr. J, serotonin toxicity can be treated with the removal of serotonergic medications and lorazepam for symptom relief. If symptoms persist, cyproheptadine, a serotonin antagonist, can be used. Mr. J’s psychotropic medications were increased in an outpatient setting and he was unable to renally excrete higher doses of these serotonergic agents, which lead to chronic serotonin toxicity.
It is important to rule out other causes of psychosis or delirium in geriatric patients. A study by Marcantonio et al5 found that >40% of patients referred to a consulting psychiatrist for depression ultimately had delirium, and this was more likely in geriatric patients.
TREATMENT Adjustments to the medication regimen
The treatment team decides to taper and discontinue duloxetine, buspirone, and trazodone and reduce mirtazapine to 15 mg/d at bedtime. Additionally, oral lorazepam 1 mg as needed is prescribed to alleviate agitation and correct vital signs. Mr. J’s vital signs improve, with decreased temperature and normal cardiac and respiratory rhythms.
Mr. J’s Stage 3A CKD is treated with oral fluids, and his hypertension is managed with an increase of lisinopril from 2.5 mg/d to 10 mg/d. After 10 days on the psychiatric unit, he shows improvement, decreased anxiety, and remission of suicidal ideation.
Continue to: The authors' observations
[polldaddy:11273790]
The authors’ observations
In 2019, the American Geriatric Society (AGS) updated the Beers Criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults.4 The Beers Criteria were created to educate clinicians about the use of potentially inappropriate medications that have an unfavorable balance of benefits and risks compared to alternative treatments. The AGS lists medications that should be avoided or have their dosage reduced with varying levels of kidney function in older adults. Duloxetine is one of the medications listed with the recommendation to avoid for patients with a creatinine clearance <30 mL/min. Creatinine clearance is an estimation of GFR.
Although duloxetine is mentioned in the Beers Criteria, many other antidepressants have metabolites excreted by the kidneys.6 Potential adverse effects include increased bleeding, nausea, vomiting, and serotonin toxicity symptoms.7 Mr. J has Stage 3A CKD and takes 4 psychotropics, which will additively increase the serum concentration of serotonergic medications. In terms of treatment for serotonin toxicity, it is important to remove the causative medications. After discontinuing serotonergic medications, lorazepam can be administered as needed. If a patient continues to have symptoms, cyproheptadine is an option.
For patients with impaired renal function, adding nonpharmacologic options should be considered, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, electroconvulsive therapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Table 24,8-18 lists the minimum effective doses for well-known medications for treating MDD.

OUTCOME Improvement and discharge
Mr. J’s confusion improves, his heart rate decreases, and his feelings of panic and doom improve. He continues to have depressive symptoms, but his suicidal ideation stops. At discharge, Mr. J is receiving mirtazapine 15 mg/d, potassium chloride 10 mEq/d orally, lisinopril 20 mg/d orally at bedtime, furosemide 20 mg/d orally, and amlodipine 5 mg orally twice a day. Additionally, the treatment team recommends psychotherapy to Mr. J to address his anxiety and depression.
Bottom Line
Older patients are more sensitive to psychotropic medications, regardless of any comorbidities. It is important to review each patient’s glomerular filtration rate to better understand their renal function and adjust medications accordingly.
Related Resources
- Whittaker P, Vordenberg SE, Coe AB. Deprescribing in older adults: an overview. Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):40-43. doi:10.12788/cp.0246
- Gibson G, Kennedy LH, Barlow G. Polypharmacy in older adults. Current Psychiatry. 2020;19(4):40-46.
- Barr R, Miskle B, Thomas C. Management of major depressive disorder with psychotic features. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(2):30-33. doi:10.12788/cp.0092
Drug Brand Names
Amlodipine • Norvasc
Buspirone • BuSpar
Citalopram • Celexa
Cyproheptadine • Periactin
Desvenlafaxine • Pristiq
Duloxetine • Cymbalta
Escitalopram • Lexapro
Fluoxetine • Prozac
Furosemide • Lasix
Lisinopril • Zestril
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
Paroxetine • Paxil
Sertraline • Zoloft
Trazodone • Desyrel
Venlafaxine • Effexor
1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1-S266.
2. Shirazian S, Grant CD, Aina O, et al. Depression in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: similarities and differences in diagnosis, epidemiology, and management. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(1):94-107.
3. Hedayati SS, Minhajuddin AT, Afshar M, et al. Association between major depressive episodes in patients with chronic kidney disease and initiation of dialysis, hospitalization, or death. JAMA. 2010;303(19):1946-1953.
4. 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
5. Marcantonio E, Ta T, Duthie E, et al. Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850-857.
6. Cukor D, Cohen, SD, Peterson RA, et al. Psychosocial aspects of chronic disease: ESRD as a paradigmatic illness. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(12):3042-3055.
7. Cohen SD, Norris L, Acquaviva K, et al. Screening, diagnosis, and treatment of depression in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2(6):1332-1342.
8. Sommi RW, Crismon ML, Bowden CL. Fluoxetine: a serotonin-specific, second-generation antidepressant. Pharmacotherapy. 1987;7(1):1-15.
9. Jenner PN. Paroxetine: an overview of dosage, tolerability, and safety. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1992;6(Suppl 4):69-80.
10. Montgomery SA. Selecting the optimum therapeutic dose of serotonin reuptake inhibitors: studies with citalopram. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(Suppl 1):23-27.
11. Milosavljevic F, Bukvic N, Pavlovic Z, et al. Association of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 poor and intermediate metabolizer status with antidepressant and antipsychotic exposure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(3):270-280.
12. Rao N. The clinical pharmacokinetics of escitalopram. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(4):281-290.
13. Preskorn SH, Lane RM. Sertraline 50 mg daily: the optimal dose in the treatment of depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(3):129-141.
14. Huddart R, Hicks JK, Ramsey LB, et al. PharmGKB summary: sertraline pathway, pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2020;30(2):26-33.
15. Furukawa TA, Cipriani A, Cowen PJ, et al. Optimal dose of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, venlafaxine, and mirtazapine in major depression: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(7):601-609.
16. Norman TR, Olver JS. Desvenlafaxine in the treatment of major depression: an updated overview. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(9):1087-1097.
17. Knadler MP, Lobo E, Chappell J, et al. Duloxetine: clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(5):281-294.
18. Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264.
1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S1-S266.
2. Shirazian S, Grant CD, Aina O, et al. Depression in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: similarities and differences in diagnosis, epidemiology, and management. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(1):94-107.
3. Hedayati SS, Minhajuddin AT, Afshar M, et al. Association between major depressive episodes in patients with chronic kidney disease and initiation of dialysis, hospitalization, or death. JAMA. 2010;303(19):1946-1953.
4. 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694.
5. Marcantonio E, Ta T, Duthie E, et al. Delirium severity and psychomotor types: their relationship with outcomes after hip fracture repair. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50(5):850-857.
6. Cukor D, Cohen, SD, Peterson RA, et al. Psychosocial aspects of chronic disease: ESRD as a paradigmatic illness. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(12):3042-3055.
7. Cohen SD, Norris L, Acquaviva K, et al. Screening, diagnosis, and treatment of depression in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2(6):1332-1342.
8. Sommi RW, Crismon ML, Bowden CL. Fluoxetine: a serotonin-specific, second-generation antidepressant. Pharmacotherapy. 1987;7(1):1-15.
9. Jenner PN. Paroxetine: an overview of dosage, tolerability, and safety. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1992;6(Suppl 4):69-80.
10. Montgomery SA. Selecting the optimum therapeutic dose of serotonin reuptake inhibitors: studies with citalopram. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(Suppl 1):23-27.
11. Milosavljevic F, Bukvic N, Pavlovic Z, et al. Association of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 poor and intermediate metabolizer status with antidepressant and antipsychotic exposure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78(3):270-280.
12. Rao N. The clinical pharmacokinetics of escitalopram. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(4):281-290.
13. Preskorn SH, Lane RM. Sertraline 50 mg daily: the optimal dose in the treatment of depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1995;10(3):129-141.
14. Huddart R, Hicks JK, Ramsey LB, et al. PharmGKB summary: sertraline pathway, pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2020;30(2):26-33.
15. Furukawa TA, Cipriani A, Cowen PJ, et al. Optimal dose of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, venlafaxine, and mirtazapine in major depression: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(7):601-609.
16. Norman TR, Olver JS. Desvenlafaxine in the treatment of major depression: an updated overview. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021;22(9):1087-1097.
17. Knadler MP, Lobo E, Chappell J, et al. Duloxetine: clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50(5):281-294.
18. Anttila SA, Leinonen EV. A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev. 2001;7(3):249-264.
Treating PTSD: A review of 8 studies
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).
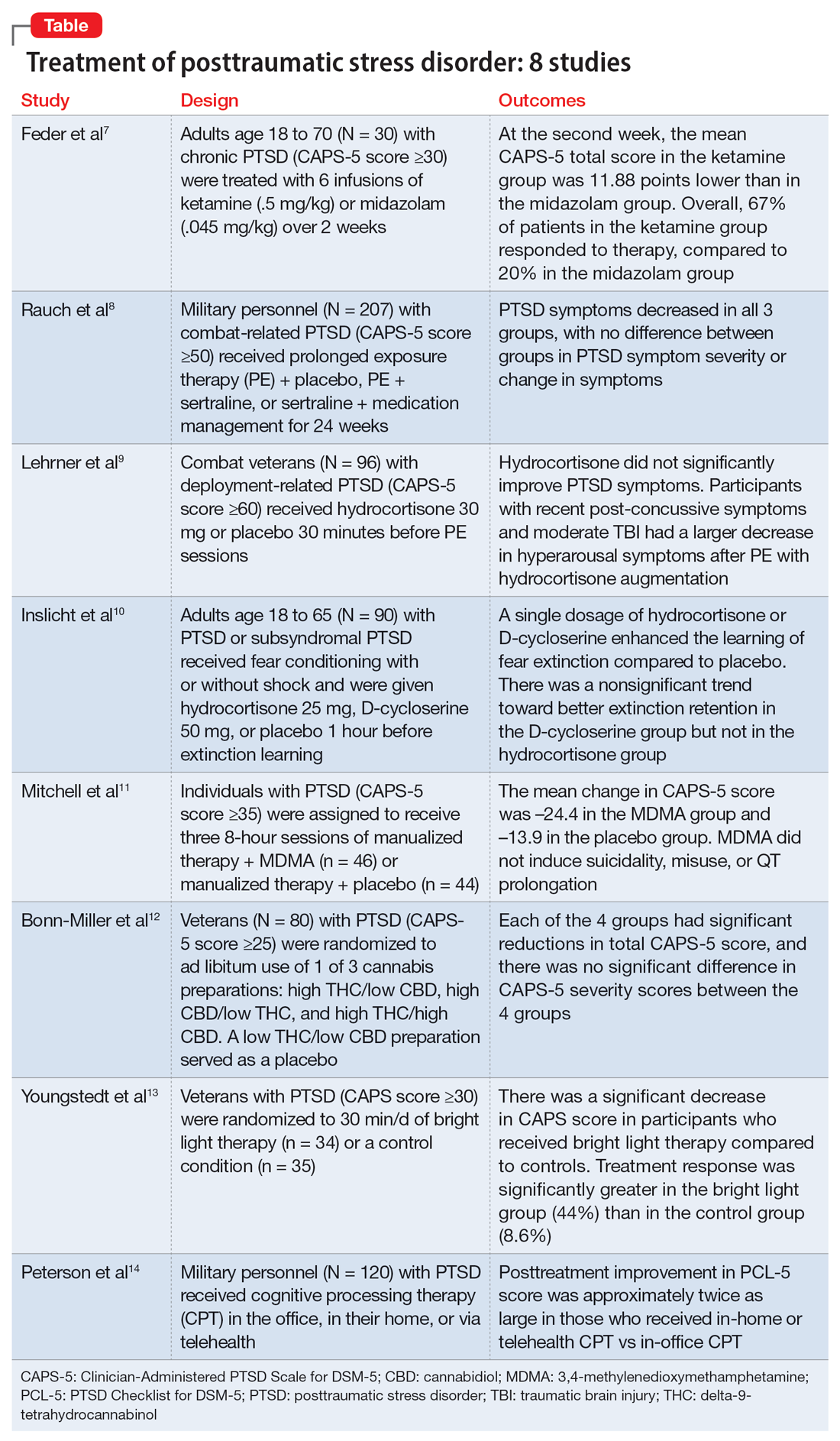
1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).

1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a chronic and disabling psychiatric disorder. The lifetime prevalence among American adults is 6.8%.1 Management of PTSD includes treating distressing symptoms, reducing avoidant behaviors, treating comorbid conditions (eg, depression, substance use disorders, or mood dysregulation), and improving adaptive functioning, which includes restoring a psychological sense of safety and trust. PTSD can be treated using evidence-based psychotherapies, pharmacotherapy, or a combination of both modalities. For adults, evidence-based treatment guidelines recommend the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy, cognitive processing therapy, cognitive therapy, and prolonged exposure therapy.2 These guidelines also recommend (with some reservations) the use of brief eclectic psychotherapy, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, and narrative exposure therapy.2 Although the evidence base for the use of medications is not as strong as that for the psychotherapies listed above, the guidelines recommend the use of fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, and venlafaxine.2
Currently available treatments for PTSD have significant limitations. For example, trauma-focused psychotherapies can have significant rates of nonresponse, partial response, or treatment dropout.3,4 Additionally, such therapies are not widely accessible. As for pharmacotherapy, very few available options are supported by evidence, and the efficacy of these options is limited, as shown by the reports that only 60% of patients with PTSD show a response to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and only 20% to 30% achieve complete remission.5 Additionally, it may take months for patients to achieve an acceptable level of improvement with medications. As a result, a substantial proportion of patients who seek treatment continue to remain symptomatic, with impaired levels of functioning. This lack of progress in PTSD treatment has been labeled as a national crisis, calling for an urgent need to find effective pharmacologic treatments for PTSD.6
In this article, we review 8 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of treatments for PTSD published within the last 5 years (Table7-14).

1. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202
Feder et al had previously found a significant and quick decrease in PTSD symptoms after a single dose of IV ketamine had. This is the first RCT to examine the effectiveness and safety of repeated IV ketamine infusions for the treatment of persistent PTSD.7
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, parallel-arm controlled trial treated 30 individuals with chronic PTSD with 6 infusions of either ketamine (0.5 mg/kg) or midazolam (0.045 mg/kg) over 2 consecutive weeks.
- Participants were individuals age 18 to 70 with a primary diagnosis of chronic PTSD according to the DSM-5 criteria and determined by The Structure Clinical Interview for DSM-5, with a score ≥30 on the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-5 (CAPS-5).
- Any severe or unstable medical condition, active suicidal or homicidal ideation, lifetime history of psychotic or bipolar disorder, current anorexia nervosa or bulimia, alcohol or substance use disorder within 3 months of screening, history of recreational ketamine or phencyclidine use on more than 1 occasion or any use in the previous 2 years, and ongoing treatment with a long-acting benzodiazepine or opioid medication were all considered exclusion criteria. Individuals who took short-acting benzodiazepines had their morning doses held on infusion days. Marijuana or cannabis derivatives were allowed.
- The primary outcome measure was a change in PTSD symptom severity as measured with CAPS-5. This was administered before the first infusion and weekly thereafter. The Impact of Event Scale-Revised, the Montgomery–Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and adverse effect measurements were used as secondary outcome measures.
- Treatment response was defined as ≥30% symptom improvement 2 weeks after the first infusion as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Individuals who responded to treatment were followed naturalistically weekly for up to 4 weeks and then monthly until loss of responder status, or up to 6 months if there was no loss of response.
Outcomes
- At the second week, the mean CAPS-5 total score in the ketamine group was 11.88 points (SE = 3.96) lower than in the midazolam group (d = 1.13; 95% CI, 0.36 to 1.91).
- In the ketamine group, 67% of patients responded to therapy, compared to 20% in the midazolam group.
- Following the 2-week course of infusions, the median period until loss of response among ketamine responders was 27.5 days.
- Ketamine infusions showed good tolerability and safety. There were no clinically significant adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Repeated ketamine infusions are effective in reducing symptom severity in individuals with chronic PTSD.
- Limitations to this study include the exclusion of individuals with comorbid bipolar disorder, current alcohol or substance use disorder, or suicidal ideations, the small sample size, and a higher rate of transient dissociative symptoms in the ketamine group.
- Future studies could evaluate the efficacy of repeated ketamine infusions in individuals with treatment-resistant PTSD. Also, further studies are required to assess the efficacy of novel interventions to prevent relapse and evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of periodic IV ketamine use as maintenance.
- Additional research might determine whether pairing psychotherapy with ketamine administration can lessen the risk of recurrence for PTSD patients after stopping ketamine infusions.
2. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126
Clinical practice recommendations for PTSD have identified trauma-focused psychotherapies and SSRIs as very effective treatments. The few studies that have compared trauma-focused psychotherapy to SSRIs or to a combination of treatments are not generalizable, have significant limitations, or are primarily concerned with refractory disorders or augmentation techniques. This study evaluated the efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy (PE) plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management in the treatment of PTSD.8
Study design
- This randomized, 4-site, 24-week clinical trial divided participants into 3 subgroups: PE plus placebo, PE plus sertraline, and sertraline plus enhanced medication management.
- Participants were veterans or service members of the Iraq and/or Afghanistan wars with combat-related PTSD and significant impairment as indicated by a CAPS score ≥50 for at least 3 months. The DSM-IV-TR version of CAPS was used because the DSM-5 version was not available at the time of the study.
- Individuals who had a current, imminent risk of suicide; active psychosis; alcohol or substance dependence in the past 8 weeks; inability to attend weekly appointments for the treatment period; prior intolerance to or failure of an adequate trial of PE or sertraline; medical illness likely to result in hospitalization or contraindication to study treatment; serious cognitive impairment; mild traumatic brain injury; or concurrent use of antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, prazosin, or sleep agents were excluded.
- Participants completed up to thirteen 90-minute sessions of PE.
- The sertraline dosage was titrated during a 10-week period and continued until Week 24. Dosages were adjusted between 50 and 200 mg/d, with the last dose increase at Week 10.
- The primary outcome measure was symptom severity of PTSD in the past month as determined by CAPS score at Week 24.
- The secondary outcome was self-reported symptoms of PTSD (PTSD checklist [PCL] Specific Stressor Version), clinically meaningful change (reduction of ≥20 points or score ≤35 on CAPS), response (reduction of ≥50% in CAPS score), and remission (CAPS score ≤35).
Outcomes
- At Week 24, 149 participants completed the study; 207 were included in the intent-to-treat analysis.
- PTSD symptoms significantly decreased over 24 weeks, according to a modified intent-to-treat analysis utilizing a mixed model of repeated measurements; nevertheless, slopes were similar across therapy groups.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Although the severity of PTSD symptoms decreased in all 3 subgroups, there was no difference in PTSD symptom severity or change in symptoms at Week 24 among all 3 subgroups.
- The main limitation of this study was the inclusion of only combat veterans.
- Further research should focus on enhancing treatment retention and should include administering sustained exposure therapy at brief intervals.
3. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924
First-line therapy for PTSD includes cognitive-behavioral therapies such as PE. However, because many people still have major adverse effects after receiving medication, improving treatment efficacy is a concern. Glucocorticoids promote extinction learning, and alterations in glucocorticoid signaling pathways have been associated with PTSD. Lehrner et al previously showed that adding hydrocortisone (HCORT) to PE therapy increased patients’ glucocorticoid sensitivity at baseline, improved treatment retention, and resulted in greater treatment improvements. This study evaluated HCORT in conjunction with PE for combat veterans with PTSD following deployment to Iraq and Afghanistan.9
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial administered HCORT 30 mg oral or placebo to 96 combat veterans 30 minutes before PE sessions.
- Participants were veterans previously deployed to Afghanistan or Iraq with deployment-related PTSD >6 months with a minimum CAPS score of 60. They were unmedicated or on a stable psychotropic regimen for ≥4 weeks.
- Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of a primary psychotic disorder (bipolar I disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder), medical or mental health condition other than PTSD that required immediate clinical attention, moderate to severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), substance abuse or dependence within the past 3 months, medical illness that contraindicated ingestion of hydrocortisone, acute suicide risk, and pregnancy or intent to become pregnant.
- The primary outcome measures included PTSD severity as assessed with CAPS.
- Secondary outcome measures included self-reported PTSD symptoms as assessed with the Posttraumatic Diagnostic Scale (PDS) and depression as assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI). These scales were administered pretreatment, posttreatment, and at 3-months follow-up.
Outcomes
- Out of 96 veterans enrolled, 60 were randomized and 52 completed the treatment.
- Five participants were considered recovered early and completed <12 sessions.
- Of those who completed treatment, 50 completed the 1-week posttreatment evaluations and 49 completed the 3-month follow-up evaluation.
- There was no difference in the proportion of dropouts (13.33%) across the conditions.
- HCORT failed to significantly improve either secondary outcomes or PTSD symptoms, according to an intent-to-treat analysis.
- However, exploratory analyses revealed that veterans with recent post-concussive symptoms and moderate TBI exposure saw a larger decrease in hyperarousal symptoms after PE therapy with HCORT augmentation.
- The reduction in avoidance symptoms with HCORT augmentation was also larger in veterans with higher baseline glucocorticoid sensitivity.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- HCORT does not improve PTSD symptoms as assessed with the CAPS and PDS, or depression as assessed with the BDI.
- The main limitation of this study is generalizability.
- Further studies are needed to determine whether PE with HCORT could benefit veterans with indicators of enhanced glucocorticoid sensitivity, mild TBI, or postconcussive syndrome.
4. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952
PE, one of the most well-researched therapies for PTSD, is based on fear extinction. Exploring pharmacotherapies that improve fear extinction learning and their potential as supplements to PE is gaining increased attention. Such pharmacotherapies aim to improve the clinical impact of PE on the extent and persistence of symptom reduction. This study evaluated the effects of HCORT and D-cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, on the learning and consolidation of fear extinction in patients with PTSD.10
Study design
- This double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-group experimental design evaluated 90 individuals with PTSD who underwent fear conditioning with stimuli that was paired (CS+) or unpaired (CS−) with shock.
- Participants were veterans and civilians age 18 to 65 recruited from VA outpatient and community clinics and internet advertisements who met the criteria for PTSD or subsyndromal PTSD (according to DSM-IV criteria) for at least 3 months.
- Exclusion criteria included schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, substance abuse or dependence, alcohol dependence, previous moderate or severe head injury, seizure or neurological disorder, current infectious illness, systemic illness affecting CNS function, or other conditions known to affect psychophysiological responses. Excluded medications were antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, alpha- and beta-adrenergics, benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, antihypertensives, sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, and steroids.
- Extinction learning took place 72 hours after extinction, and extinction retention was evaluated 1 week later. Placebo, HCORT 25 mg, or DCS 50 mg was given 1 hour before extinction learning.
- Clinical measures included PTSD diagnosis and symptom levels as determined by interview using CAPS and skin conduction response.
Outcomes
- The mean shock level, mean pre-stimulus skin conductance level (SCL) during habituation, and mean SC orienting response during the habituation phase did not differ between groups and were not associated with differential fear conditioning. Therefore, variations in shock level preference, resting SCL, or SC orienting response magnitude are unlikely to account for differences between groups during extinction learning and retention.
- During extinction learning, the DCS and HCORT groups showed a reduced differential CS+/CS− skin conductance response (SCR) compared to placebo.
- One week later, during the retention testing, there was a nonsignificant trend toward a smaller differential CS+/CS− SCR in the DCS group compared to placebo. HCORT and DCS administered as a single dosage facilitated fear extinction learning in individuals with PTSD symptoms.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- In traumatized people with PTSD symptoms, a single dosage of HCORT or DCS enhanced the learning of fear extinction compared to placebo. A nonsignificant trend toward better extinction retention in the DCS group but not the HCORT group was also visible.
- These results imply that glucocorticoids and NMDA agonists have the potential to promote extinction learning in PTSD.
- Limitations include a lack of measures of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
- Further studies could evaluate these findings with the addition of blood biomarker measures such as glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity or FKBP5.
5. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
Poor PTSD treatment results are associated with numerous comorbid conditions, such as dissociation, depression, alcohol and substance use disorders, childhood trauma, and suicidal ideation, which frequently leads to treatment resistance. Therefore, it is crucial to find a treatment that works for individuals with PTSD who also have comorbid conditions. In animal models, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), an empathogen/entactogen with stimulant properties, has been shown to enhance fear memory extinction and modulate fear memory reconsolidation. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of MDMA-assisted therapy for treating patients with severe PTSD, including those with common comorbidities.11
Study design
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-site, phase 3 clinical trial evaluated individuals randomized to receive manualized therapy with MDMA or with placebo, combined with 3 preparatory and 9 integrative therapy sessions.
- Participants were 90 individuals (46 randomized to MDMA and 44 to placebo) with PTSD with a symptom duration ≥6 months and CAPS-5 total severity score ≥35 at baseline.
- Exclusion criteria included primary psychotic disorder, bipolar I disorder, eating disorders with active purging, major depressive disorder with psychotic features, dissociative identity disorder, personality disorders, current alcohol and substance use disorders, lactation or pregnancy, and any condition that could make receiving a sympathomimetic medication dangerous due to hypertension or tachycardia, including uncontrolled hypertension, history of arrhythmia, or marked baseline prolongation of QT and/or QTc interval.
- Three 8-hour experimental sessions of either therapy with MDMA assistance or therapy with a placebo control were given during the treatment period, and they were spaced approximately 4 weeks apart.
- In each session, participants received placebo or a single divided dose of MDMA 80 to 180 mg.
- At baseline and 2 months after the last experimental sessions, PTSD symptoms were measured with CAPS-5, and functional impairment was measured with Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS).
- The primary outcome measure was CAPS-5 total severity score at 18 weeks compared to baseline for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
- The secondary outcome measure was clinician-rated functional impairment using the mean difference in SDS total scores from baseline to 18 weeks for MDMA-assisted therapy vs placebo-assisted therapy.
Outcomes
- MDMA was found to induce significant and robust attenuation in CAPS-5 score compared to placebo.
- The mean change in CAPS-5 score in completers was –24.4 in the MDMA group and –13.9 in the placebo group.
- MDMA significantly decreased the SDS total score.
- MDMA did not induce suicidality, misuse, or QT prolongation.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- MDMA-assisted therapy is significantly more effective than manualized therapy with placebo in treating patients with severe PTSD, and it is also safe and well-tolerated, even in individuals with comorbidities.
- No major safety issues were associated with MDMA-assisted treatment.
- MDMA-assisted therapy should be promptly assessed for clinical usage because it has the potential to significantly transform the way PTSD is treated.
- Limitations of this study include a smaller sample size (due to the COVID-19 pandemic); lack of ethnic and racial diversity; short duration; safety data were collected by site therapist, which limited the blinding; and the blinding of participants was difficult due to the subjective effects of MDMA, which could have resulted in expectation effects.
6. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990
Sertraline and paroxetine are the only FDA-approved medications for treating PTSD. Some evidence suggests cannabis may provide a therapeutic benefit for PTSD.15 This study examined the effects of 3 different preparations of cannabis for treating PTSD symptoms.12
Study design
- This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial used 3 active treatment groups of cannabis: high delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)/low cannabidiol (CBD), high CBD/low THC, and high THC/high CBD (THC+CBD). A low THC/low CBD preparation was used as a placebo. “High” content contained 9% to 15% concentration by weight of the respective cannabinoid, and “low” content contained <2% concentration by weight.
- Inclusion criteria included being a US military veteran, meeting DSM-5 PTSD criteria for ≥6 months, having moderate symptom severity (CAPS-5 score ≥25), abstaining from cannabis 2 weeks prior to study and agreeing not to use any non-study cannabis during the trial, and being stable on medications/therapy prior to the study.
- Exclusion criteria included women who were pregnant/nursing/child-bearing age and not taking an effective means of birth control; current/past serious mental illness, including psychotic and personality disorders; having a first-degree relative with a psychotic or bipolar disorder; having a high suicide risk based on Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale; meeting DSM-5 criteria for moderate-severe cannabis use disorder; screening positive for illicit substances; or having significant medical disease.
- Participants in Stage 1 (n = 80) were randomized to 1 of the 3 active treatments or placebo for 3 weeks. After a 2-week washout, participants in Stage 2 (n = 74) were randomized to receive for 3 weeks 1 of the 3 active treatments they had not previously received.
- During each stage, participants had ad libitum use for a maximum of 1.8 g/d.
- The primary outcome was change in PTSD symptom severity by the end of Stage 1 as assessed with CAPS-5.
- Secondary outcomes included the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the general depression subscale and anxiety subscale from the self-report Inventory of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms (IDAS), the Inventory of Psychosocial Functioning, and the Insomnia Severity Index.
Outcomes
- Six participants did not continue to Stage 2. Three participants did not finish Stage 2 due to adverse effects, and 7 did not complete outcome measurements. The overall attrition rate was 16.3%.
- There was no significant difference in total grams of smoked cannabis or placebo between the 4 treatment groups in Stage 1 at the end of 3 weeks. In Stage 2, there was a significant difference, with the THC+CBD group using more cannabis compared to the other 2 groups.
- Each of the 4 groups had significant reductions in total CAPS-5 scores at the end of Stage 1, and there was no significant difference in CAPS-5 severity scores between the 4 groups.
- In Stage 1, PCL-5 scores were not significantly different between treatment groups from baseline to the end of stage. There was a significant difference in Stage 2 between the high CBD and THC+CBD groups, with the combined group reporting greater improvement of symptoms.
- In Stage 2, the THC+CBD group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores and IDAS general depression scores, and the high THC group reported greater reductions in pre/post IDAS social anxiety scores.
- In Stage 1, 37 of 60 participants in the active groups reported at least 1 adverse event, and 45 of the 74 Stage 2 participants reported at least 1 adverse event. The most common adverse events were cough, throat irritation, and anxiety. Participants in the Stage 1 high THC group had a significant increase in reported withdrawal symptoms after 1 week of stopping use.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- This first randomized, placebo-control trial of cannabis in US veterans did not show a significant difference among treatment groups, including placebo, on the primary outcome of CAPS-5 score. All 4 groups had significant reductions in symptom severity on CAPS-5 and showed good tolerability.
- Prior beliefs about the effects of cannabis may have played a role in the reduction of PTSD symptoms in the placebo group.
- Many participants (n =34) were positive for THC during the screening process, so previous cannabis use/chronicity of cannabis use may have contributed.
- One limitation was that participants assigned to the Stage 1 high THC group had Cannabis Use Disorders Identification Test scores (which assesses cannabis use disorder risk) about 2 times greater than participants in other conditions.
- Another limitation was that total cannabis use was lower than expected, as participants in Stage 1 used 8.2 g to 14.6 g over 3 weeks, though they had access to up to 37.8 g.
- There was no placebo in Stage 2.
- Future studies should look at longer treatment periods with more participants.
7. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444
Bright light therapy is an inexpensive treatment approach that may affect serotonergic pathways.16 This study examined bright light therapy for reducing PTSD symptoms and examined if improvement of PTSD is related to a shift in circadian rhythm.13
Study design
- Veterans with combat-related PTSD had to have been stable on treatment for at least 8 weeks or to have not received any other PTSD treatments prior to the study.
- Participants were randomized to active treatment of 30 minutes daily 10,000 lux ultraviolet-filtered white light while sitting within 18 inches (n = 34) or a control condition of 30 minutes daily inactivated negative ion generator (n = 35) for 4 weeks.
- Inclusion criteria included a CAPS score ≥30.
- Exclusion criteria included high suicidality, high probability of alcohol/substance abuse in the past 3 months, bipolar disorder/mania/schizophrenia/psychosis, ophthalmologic deformities, shift work in past 2 months or travel across time zones in past 2 weeks, head trauma, high outdoor light exposure, history of winter depression, history of seizures, or myocardial infarction/stroke/cancer within 3 years.
- Primary outcomes were improvement on CAPS and Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement scale (CGI-IM) score at Week 4.
- Wrist actigraphy recordings measured sleep.
- Other measurements included the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton atypical symptoms (HAM-AS), PCL-Military (PCL-M), Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), BDI, Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI Form Y-2), Beck Suicide Scale, and Systematic Assessment for Treatment Emergent Effects questionnaire.
Outcomes
- There was a significant decrease in CAPS score in participants who received bright light therapy compared to controls. Treatment response (defined as ≥33% reduction in score) was significantly greater in the bright light (44%) vs control (8.6%) group. No participants achieved remission.
- There was a significant improvement in CGI-IM scores in the bright light group, but no significant difference in participants who were judged to improve “much” or “very much.”
- PCL-M scores did not change significantly between groups, although a significantly greater proportion of participants had treatment response in the bright light group (33%) vs control (6%).
- There were no significant changes in HAM-D, HAM-AS, STAI, BDI, actigraphic estimates of sleep, or PSQI scores.
- Bright light therapy resulted in phase advancement while control treatment had phase delay.
- There were no significant differences in adverse effects.
Continue to: Conclusions/limitations
Conclusions/limitations
- Bright light therapy may be a treatment option or adjunct for combat-related PTSD as seen by improvement on CAPS and CGI scores, as well as a greater treatment response seen on CAPS and PCL-5 scores in the bright light group.
- There was no significant difference for other measures, including depression, anxiety, and sleep.
- Limitations include excluding patients with a wide variety of medical or psychiatric comorbidities, as well as limited long-term follow up data.
- Other limitations include not knowing the precise amount of time participants stayed in front of the light device and loss of some actigraphic data (data from only 49 of 69 participants).
8. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41 doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT), a type of trauma-focused psychotherapy, is an effective treatment for PTSD in the military population.17,18 However, patients may not be able to or want to participate in such therapy due to barriers such as difficulty arranging transportation, being homebound due to injury, concerns about COVID-19, stigma, familial obligations, and job constraints. This study looked at if CPT delivered face-to-face at the patient’s home or via telehealth in home would be effective and increase accessibility.14
Study design
- Participants (n = 120) were active-duty military and veterans who met DSM-5 criteria for PTSD. They were randomized to receive CPT in the office, in their home, or via telehealth. Participants could choose not to partake in 1 modality but were then randomized to 1 of the other 2.
- Exclusion criteria included suicide/homicide risk needing intervention, items/situations pertaining to danger (ie, aggressive pet or unsafe neighborhood), significant alcohol/substance use, active psychosis, and impaired cognitive functioning.
- The primary outcome measurement was change in PCL-5 and CAPS-5 score over 6 months. The BDI-II was used to assess depressive symptoms.
- Secondary outcomes included the Reliable Change Index (defined as “an improvement of 10 or more points that was sustained at all subsequent assessments”) on the PCL-5 and remission on the CAPS-5.
- CPT was delivered in 60-minute sessions twice a week for 6 weeks. Participants who did not have electronic resources were loaned a telehealth apparatus.
Outcomes
- Overall, 57% of participants opted out of 1 modality, which resulted in fewer participants being placed into the in-home arm (n = 32). Most participants chose not to do in-home treatments (54%), followed by in-office (29%), and telehealth (17%).
- There was a significant posttreatment improvement in PCL-5 scores in all treatment arms, with improvement greater with in-home (d = 2.1) and telehealth (d = 2.0) vs in-office (d=1.3). The in-home and telehealth scores were significantly improved compared to in-office, and the difference between in-home and telehealth PCL-5 scores was minimal.
- At 6 months posttreatment, the differences between the 3 treatment groups on PCL-5 score were negligible.
- CAPS-5 scores were significantly improved in all treatment arms, with improvement largest with in-home treatment; however, the differences between the groups were not significant.
- BDI-II scores improved in all modalities but were larger in the in-home (d = 1.2) and telehealth (d = 1.1) arms than the in-office arm (d = 0.52).
- Therapist time commitment was greater for the in-home and in-office arms (2 hours/session) than the telehealth arm (1 hour/session). This difference was due to commuting time for the patient or therapist.
- The dropout rate was not statistically significant between the groups.
- Adverse events did not significantly differ per group. The most commonly reported ones included nightmares, sleep difficulty, depression, anxiety, and irritability.
Conclusions/limitations
- Patients undergoing CPT had significant improvement in PTSD symptoms, with posttreatment PCL-5 improvement approximately twice as large in those who received the in-home and telehealth modalities vs in-office treatment.
- The group differences were not seen on CAPS-5 scores at posttreatment, or PCL-5 or CAPS-5 scores at 6 months posttreatment.
- In-home CPT was declined the most, which suggests that in-home distractions or the stigma of a mental health clinician being in their home played a role in patients’ decision-making. However, in-home CPT produced the greatest amount of improvement in PTSD symptoms. The authors concluded that in-home therapy should be reserved for those who are homebound or have travel limitations.
- This study shows evidence that telehealth may be a good modality for CPT, as seen by improvement in PTSD symptoms and good acceptability and retention.
- Limitations include more patients opting out of in-home CPT, and reimbursement for travel may not be available in the real-world setting.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Delmer O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Guideline Development Panel for the Treatment of PTSD in Adults, American Psychological Association. Summary of the clinical practice guideline for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in adults. Am Psychol. 2019;74(5):596-607. doi: 10.1037/amp0000473
3. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Hoge CW, et al. Psychotherapy for military-related PTSD: a review of randomized clinical trials. JAMA. 2015;314(5):489-500.
4. Steenkamp MM, Litz BT, Marmar CR. First-line psychotherapies for military-related PTSD. JAMA. 2020;323(7):656-657.
5. Berger W, Mendlowicz MV, Marques-Portella C, et al. Pharmacologic alternatives to antidepressants in posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2009;33(3):169-180.
6. Krystal JH, Davis LL, Neylan TC, et al. It is time to address the crisis in the pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a consensus statement of the PTSD Psychopharmacology Working Group. Biol Psychiatry. 2017;82(7):e51-e59.
7. Feder A, Costi S, Rutter SB, et al. A randomized controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2021;178(2):193-202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20050596
8. Rauch SAM, Kim HM, Powell C, et al. Efficacy of prolonged exposure therapy, sertraline hydrochloride, and their combination among combat veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76(2):117-126. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3412
9. Lehrner A, Hildebrandt T, Bierer LM, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of hydrocortisone augmentation of prolonged exposure for PTSD in US combat veterans. Behav Res Ther. 2021;144:103924. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2021.103924
10. Inslicht SS, Niles AN, Metzler TJ, et al. Randomized controlled experimental study of hydrocortisone and D-cycloserine effects on fear extinction in PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(11):1945-1952. doi:10.1038/s41386-021-01222-z
11. Mitchell JM, Bogenschutz M, Lilienstein A, et al. MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):1025-1033. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01336-3
12. Bonn-Miller MO, Sisley S, Riggs P, et al. The short-term impact of 3 smoked cannabis preparations versus placebo on PTSD symptoms: a randomized cross-over clinical trial. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0246990. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0246990
13. Youngstedt SD, Kline CE, Reynolds AM, et al. Bright light treatment of combat-related PTSD: a randomized controlled trial. Milit Med. 2022;187(3-4):e435-e444. doi:10.1093/milmed/usab014
14. Peterson AL, Mintz J, Moring JC, et al. In-office, in-home, and telehealth cognitive processing therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in veterans: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2022;22(1):41. doi:10.1186/s12888-022-03699-4
15. Loflin MJ, Babson KA, Bonn-Miller MO. Cannabinoids as therapeutic for PTSD. Curr Opin Psychol. 2017;14:78-83. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2016.12.001
16. Neumeister A, Praschak-Rieder N, Besselmann B, et al. Effects of tryptophan depletion on drug-free patients with seasonal affective disorder during a stable response to bright light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1997;54(2):133-138. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140043008
17. Kaysen D, Schumm J, Pedersen ER, et al. Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorders. Addict Behav. 2014;39(2):420-427. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.08.016
18. Resick PA, Wachen JS, Mintz J, et al. A randomized clinical trial of group cognitive processing therapy compared with group present-centered therapy for PTSD among active duty military personnel. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015;83(6):1058-1068. doi:10.1037/ccp0000016