User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
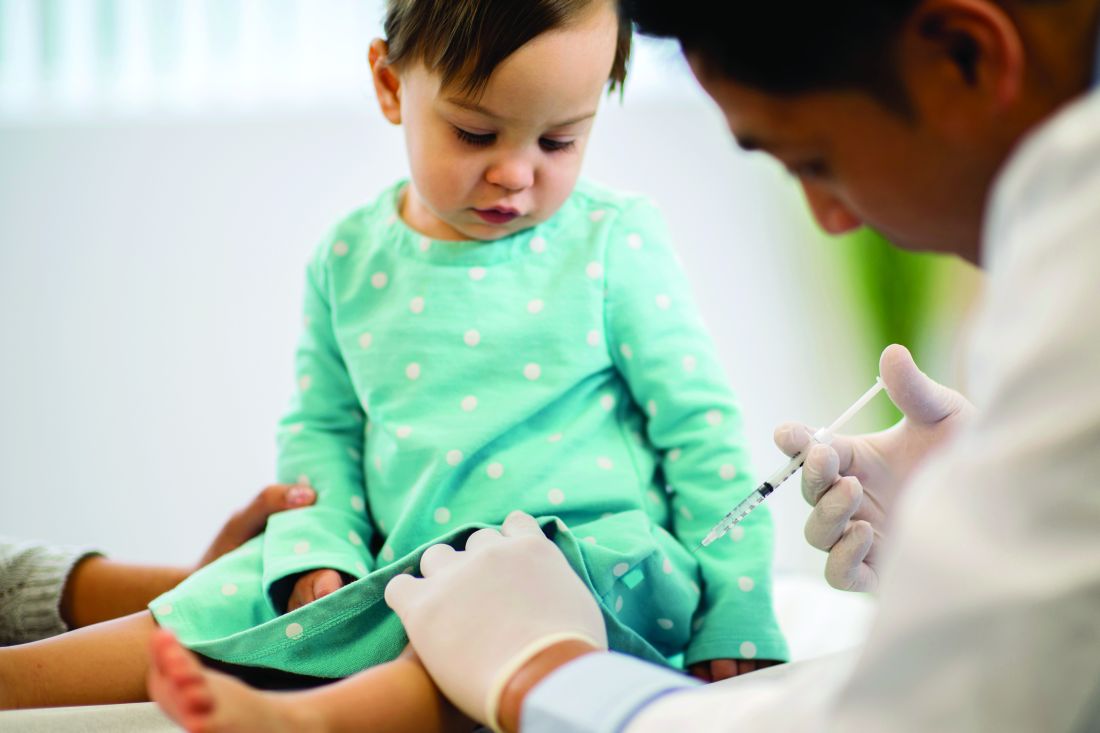
Telemedicine checklist may smooth visits with older patients
During the pandemic, physicians have raced to set up or expand telemedicine, uncovering both advantages and shortcomings.
Although many of the suggestions, published online in Annals of Internal Medicine, are useful for all patients, Carrie Nieman, MD, MPH, and Esther S. Oh, MD, PhD, developed the list with older patients in mind.
“I have a number of patients into their 90s and with hearing loss, and we have had very successful video-based telemedicine visits,” Dr. Nieman, with the Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore said in an interview. “Age should not be considered synonymous with inability or unwillingness to use technology.”
Their recommendations included the following:
- Assume some degree of hearing loss, which affects about two-thirds of adults aged 70 years and older.
- Ask patients to wear headphones or a headset or confirm that they are wearing their hearing aids and are in a quiet location.
- Use a headset.
- When possible, use video and have the camera focused on your face.
- Use captioning when available and provide a written summary of key points and instructions.
- Pay attention to cues, such as nodding along or looking to a loved one, that suggest a patient may not be following the conversation.
“If cognitive impairment is suspected, several screening tools can be used over the telephone to identify individuals who may need more comprehensive, in-person assessment,” wrote Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh, who is with the division of geriatric medicine and gerontology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. For example, data suggest that a modified version of the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Delirium Symptom Interview could be useful tools. “A formal diagnosis of dementia is not recommended solely based on a telephone-based cognitive screening,” however, Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh said.
For patients with hearing loss, video visits avoid a current limitation of in-person visits: face masks that hinder patients’ ability to read lips and other visual cues. “For many of us, we rely on these types of cues more than we think,” Dr. Nieman said in an interview.
“When you have doubts about whether you and your patient are on the same page, check in with the patient,” Dr. Nieman said. “When appropriate, having a loved one or a care partner join an encounter, or at least a portion of the encounter, can be helpful to both the patient and the provider.”
Many older patients unprepared
Millions of older patients may not have been ready for the rapid shift to telemedicine brought on by COVID-19, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine suggests. Between 32% and 38% of older adults in the United States may not have been ready for video visits, largely because of inexperience with technology. Approximately 20% could have difficulty with telephone visits because of problems hearing or communicating or because of dementia.
Kenneth Lam, MD, of the division of geriatrics at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and colleagues arrived at these estimates after analyzing data from more than 4,500 participants in the National Health and Aging Trends Study that was conducted in 2018. The study is nationally representative of Medicare beneficiaries 65 years or older.
The aim of the study “was to call attention to what clinicians were already experiencing on the front lines,” Dr. Lam said. In an interview, he imagined two scenarios based on his colleagues’ accounts of telemedicine visits.
In one case, a 72-year-old woman logs into Zoom Health on her iPad without any trouble. “She explains she just pushed on the URL and everything loaded up and you have a great visit,” Dr. Lam said. “This is likely to be the case for over 50% of the older people you see; I share this picture to combat ageism, which is, truthfully, just inaccurate stereotyping of older people and gets in the way of actionable, data-driven policies.
“However, for around one in three older adults (and closer to three out of every four of those over the age of 85), you will book an appointment and they will say they don’t have an email address or a computer or know how to go online,” Dr. Lam said. “Or suppose they decide to try it out. ... Come appointment time, you log on and they pick up, but now their sound doesn’t work. They keep saying they can see you but they can’t hear you. ... They accidentally hang up. You place another call, and they ask if you can switch to a phone conversation instead.”
By phone, the physician can address concerns about the patient’s blood pressure, which the patient has been measuring daily. “But when it comes to looking at the swelling in their legs, you’re out of luck, and you’ve been on this call for 45 minutes,” Dr. Lam said.
Have a backup plan
Making sure patients are prepared and having a backup plan can help, said Kaitlin Willham, MD, of UCSF and the San Francisco VA Medical Center.
She says older patients fall into a wide range of categories in terms of skills and access to equipment. Knowing which category a patient falls into and having relevant support available to troubleshoot are important.
During the pandemic, Dr. Willham has conducted many more telemedicine visits with patients who are at their place of residence, whether a private home or a residential care facility. “Even outside of the current crisis, there are benefits to home video visits,” Dr. Willham said. “A home video visit can provide a more holistic view of the patient than an office visit, allowing the clinician to see how the person lives, what they might be challenged by. It allows the clinician to identify areas of intervention and, if there is a care partner, involving that person in the plan. If the visit starts without major technical or communication barriers, they are generally very well received.”
For patients with problems hearing for whom headphones or amplification devices are not available, “using a landline for the audio portion of the visit can help, as can having someone with the patient reiterate what was said,” Dr. Willham suggested. “Many video platforms also enable the clinician to type messages or share a screen with a live document. These options can work well when there is very severe or complete lack of hearing.”
Sometimes an in-person visit is the right way to go, even when technical hurdles can be overcome.
“Although many older adults are willing and able to learn to use telemedicine, an equitable health system should recognize that for some, such as those with dementia and social isolation, in-person visits are already difficult and telemedicine may be impossible,” Dr. Lam and coauthors wrote. “For these patients, clinics and geriatric models of care such as home visits are essential.”
Dr. Nieman, Dr. Oh, and one of Dr. Lam’s coauthors have received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Oh also has received funding from the Roberts Family Fund. Dr. Nieman serves as a board member of the nonprofit organization Access HEARS and is on the board of trustees of the Hearing Loss Association of America.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
During the pandemic, physicians have raced to set up or expand telemedicine, uncovering both advantages and shortcomings.
Although many of the suggestions, published online in Annals of Internal Medicine, are useful for all patients, Carrie Nieman, MD, MPH, and Esther S. Oh, MD, PhD, developed the list with older patients in mind.
“I have a number of patients into their 90s and with hearing loss, and we have had very successful video-based telemedicine visits,” Dr. Nieman, with the Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore said in an interview. “Age should not be considered synonymous with inability or unwillingness to use technology.”
Their recommendations included the following:
- Assume some degree of hearing loss, which affects about two-thirds of adults aged 70 years and older.
- Ask patients to wear headphones or a headset or confirm that they are wearing their hearing aids and are in a quiet location.
- Use a headset.
- When possible, use video and have the camera focused on your face.
- Use captioning when available and provide a written summary of key points and instructions.
- Pay attention to cues, such as nodding along or looking to a loved one, that suggest a patient may not be following the conversation.
“If cognitive impairment is suspected, several screening tools can be used over the telephone to identify individuals who may need more comprehensive, in-person assessment,” wrote Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh, who is with the division of geriatric medicine and gerontology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. For example, data suggest that a modified version of the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Delirium Symptom Interview could be useful tools. “A formal diagnosis of dementia is not recommended solely based on a telephone-based cognitive screening,” however, Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh said.
For patients with hearing loss, video visits avoid a current limitation of in-person visits: face masks that hinder patients’ ability to read lips and other visual cues. “For many of us, we rely on these types of cues more than we think,” Dr. Nieman said in an interview.
“When you have doubts about whether you and your patient are on the same page, check in with the patient,” Dr. Nieman said. “When appropriate, having a loved one or a care partner join an encounter, or at least a portion of the encounter, can be helpful to both the patient and the provider.”
Many older patients unprepared
Millions of older patients may not have been ready for the rapid shift to telemedicine brought on by COVID-19, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine suggests. Between 32% and 38% of older adults in the United States may not have been ready for video visits, largely because of inexperience with technology. Approximately 20% could have difficulty with telephone visits because of problems hearing or communicating or because of dementia.
Kenneth Lam, MD, of the division of geriatrics at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and colleagues arrived at these estimates after analyzing data from more than 4,500 participants in the National Health and Aging Trends Study that was conducted in 2018. The study is nationally representative of Medicare beneficiaries 65 years or older.
The aim of the study “was to call attention to what clinicians were already experiencing on the front lines,” Dr. Lam said. In an interview, he imagined two scenarios based on his colleagues’ accounts of telemedicine visits.
In one case, a 72-year-old woman logs into Zoom Health on her iPad without any trouble. “She explains she just pushed on the URL and everything loaded up and you have a great visit,” Dr. Lam said. “This is likely to be the case for over 50% of the older people you see; I share this picture to combat ageism, which is, truthfully, just inaccurate stereotyping of older people and gets in the way of actionable, data-driven policies.
“However, for around one in three older adults (and closer to three out of every four of those over the age of 85), you will book an appointment and they will say they don’t have an email address or a computer or know how to go online,” Dr. Lam said. “Or suppose they decide to try it out. ... Come appointment time, you log on and they pick up, but now their sound doesn’t work. They keep saying they can see you but they can’t hear you. ... They accidentally hang up. You place another call, and they ask if you can switch to a phone conversation instead.”
By phone, the physician can address concerns about the patient’s blood pressure, which the patient has been measuring daily. “But when it comes to looking at the swelling in their legs, you’re out of luck, and you’ve been on this call for 45 minutes,” Dr. Lam said.
Have a backup plan
Making sure patients are prepared and having a backup plan can help, said Kaitlin Willham, MD, of UCSF and the San Francisco VA Medical Center.
She says older patients fall into a wide range of categories in terms of skills and access to equipment. Knowing which category a patient falls into and having relevant support available to troubleshoot are important.
During the pandemic, Dr. Willham has conducted many more telemedicine visits with patients who are at their place of residence, whether a private home or a residential care facility. “Even outside of the current crisis, there are benefits to home video visits,” Dr. Willham said. “A home video visit can provide a more holistic view of the patient than an office visit, allowing the clinician to see how the person lives, what they might be challenged by. It allows the clinician to identify areas of intervention and, if there is a care partner, involving that person in the plan. If the visit starts without major technical or communication barriers, they are generally very well received.”
For patients with problems hearing for whom headphones or amplification devices are not available, “using a landline for the audio portion of the visit can help, as can having someone with the patient reiterate what was said,” Dr. Willham suggested. “Many video platforms also enable the clinician to type messages or share a screen with a live document. These options can work well when there is very severe or complete lack of hearing.”
Sometimes an in-person visit is the right way to go, even when technical hurdles can be overcome.
“Although many older adults are willing and able to learn to use telemedicine, an equitable health system should recognize that for some, such as those with dementia and social isolation, in-person visits are already difficult and telemedicine may be impossible,” Dr. Lam and coauthors wrote. “For these patients, clinics and geriatric models of care such as home visits are essential.”
Dr. Nieman, Dr. Oh, and one of Dr. Lam’s coauthors have received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Oh also has received funding from the Roberts Family Fund. Dr. Nieman serves as a board member of the nonprofit organization Access HEARS and is on the board of trustees of the Hearing Loss Association of America.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
During the pandemic, physicians have raced to set up or expand telemedicine, uncovering both advantages and shortcomings.
Although many of the suggestions, published online in Annals of Internal Medicine, are useful for all patients, Carrie Nieman, MD, MPH, and Esther S. Oh, MD, PhD, developed the list with older patients in mind.
“I have a number of patients into their 90s and with hearing loss, and we have had very successful video-based telemedicine visits,” Dr. Nieman, with the Cochlear Center for Hearing and Public Health at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore said in an interview. “Age should not be considered synonymous with inability or unwillingness to use technology.”
Their recommendations included the following:
- Assume some degree of hearing loss, which affects about two-thirds of adults aged 70 years and older.
- Ask patients to wear headphones or a headset or confirm that they are wearing their hearing aids and are in a quiet location.
- Use a headset.
- When possible, use video and have the camera focused on your face.
- Use captioning when available and provide a written summary of key points and instructions.
- Pay attention to cues, such as nodding along or looking to a loved one, that suggest a patient may not be following the conversation.
“If cognitive impairment is suspected, several screening tools can be used over the telephone to identify individuals who may need more comprehensive, in-person assessment,” wrote Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh, who is with the division of geriatric medicine and gerontology at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. For example, data suggest that a modified version of the Mini–Mental State Examination and the Delirium Symptom Interview could be useful tools. “A formal diagnosis of dementia is not recommended solely based on a telephone-based cognitive screening,” however, Dr. Nieman and Dr. Oh said.
For patients with hearing loss, video visits avoid a current limitation of in-person visits: face masks that hinder patients’ ability to read lips and other visual cues. “For many of us, we rely on these types of cues more than we think,” Dr. Nieman said in an interview.
“When you have doubts about whether you and your patient are on the same page, check in with the patient,” Dr. Nieman said. “When appropriate, having a loved one or a care partner join an encounter, or at least a portion of the encounter, can be helpful to both the patient and the provider.”
Many older patients unprepared
Millions of older patients may not have been ready for the rapid shift to telemedicine brought on by COVID-19, a recent study in JAMA Internal Medicine suggests. Between 32% and 38% of older adults in the United States may not have been ready for video visits, largely because of inexperience with technology. Approximately 20% could have difficulty with telephone visits because of problems hearing or communicating or because of dementia.
Kenneth Lam, MD, of the division of geriatrics at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and colleagues arrived at these estimates after analyzing data from more than 4,500 participants in the National Health and Aging Trends Study that was conducted in 2018. The study is nationally representative of Medicare beneficiaries 65 years or older.
The aim of the study “was to call attention to what clinicians were already experiencing on the front lines,” Dr. Lam said. In an interview, he imagined two scenarios based on his colleagues’ accounts of telemedicine visits.
In one case, a 72-year-old woman logs into Zoom Health on her iPad without any trouble. “She explains she just pushed on the URL and everything loaded up and you have a great visit,” Dr. Lam said. “This is likely to be the case for over 50% of the older people you see; I share this picture to combat ageism, which is, truthfully, just inaccurate stereotyping of older people and gets in the way of actionable, data-driven policies.
“However, for around one in three older adults (and closer to three out of every four of those over the age of 85), you will book an appointment and they will say they don’t have an email address or a computer or know how to go online,” Dr. Lam said. “Or suppose they decide to try it out. ... Come appointment time, you log on and they pick up, but now their sound doesn’t work. They keep saying they can see you but they can’t hear you. ... They accidentally hang up. You place another call, and they ask if you can switch to a phone conversation instead.”
By phone, the physician can address concerns about the patient’s blood pressure, which the patient has been measuring daily. “But when it comes to looking at the swelling in their legs, you’re out of luck, and you’ve been on this call for 45 minutes,” Dr. Lam said.
Have a backup plan
Making sure patients are prepared and having a backup plan can help, said Kaitlin Willham, MD, of UCSF and the San Francisco VA Medical Center.
She says older patients fall into a wide range of categories in terms of skills and access to equipment. Knowing which category a patient falls into and having relevant support available to troubleshoot are important.
During the pandemic, Dr. Willham has conducted many more telemedicine visits with patients who are at their place of residence, whether a private home or a residential care facility. “Even outside of the current crisis, there are benefits to home video visits,” Dr. Willham said. “A home video visit can provide a more holistic view of the patient than an office visit, allowing the clinician to see how the person lives, what they might be challenged by. It allows the clinician to identify areas of intervention and, if there is a care partner, involving that person in the plan. If the visit starts without major technical or communication barriers, they are generally very well received.”
For patients with problems hearing for whom headphones or amplification devices are not available, “using a landline for the audio portion of the visit can help, as can having someone with the patient reiterate what was said,” Dr. Willham suggested. “Many video platforms also enable the clinician to type messages or share a screen with a live document. These options can work well when there is very severe or complete lack of hearing.”
Sometimes an in-person visit is the right way to go, even when technical hurdles can be overcome.
“Although many older adults are willing and able to learn to use telemedicine, an equitable health system should recognize that for some, such as those with dementia and social isolation, in-person visits are already difficult and telemedicine may be impossible,” Dr. Lam and coauthors wrote. “For these patients, clinics and geriatric models of care such as home visits are essential.”
Dr. Nieman, Dr. Oh, and one of Dr. Lam’s coauthors have received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Oh also has received funding from the Roberts Family Fund. Dr. Nieman serves as a board member of the nonprofit organization Access HEARS and is on the board of trustees of the Hearing Loss Association of America.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
PPE shortage could last years without strategic plan, experts warn
Officials said logistical challenges continue 7 months after the coronavirus reached the United States, as the flu season approaches and as some state emergency management agencies prepare for a fall surge in COVID-19 cases.
Although the disarray is not as widespread as it was this spring, hospitals said rolling shortages of supplies range from specialized beds to disposable isolation gowns to thermometers.
“A few weeks ago, we were having a very difficult time getting the sanitary wipes. You just couldn’t get them,” said Bernard Klein, MD, chief executive of Providence Holy Cross Medical Center in Mission Hills, Calif., near Los Angeles. “We actually had to manufacture our own.”
This same dynamic has played out across a number of critical supplies in his hospital. First masks, then isolation gowns and now a specialized bed that allows nurses to turn COVID-19 patients onto their bellies – equipment that helps workers with what can otherwise be a six-person job.
“We’ve seen whole families come to our hospital with COVID, and several members hospitalized at the same time,” said Dr. Klein. “It’s very, very sad.”
Testing supplies ran short as the predominantly Latino community served by Providence Holy Cross was hit hard by COVID, and even as nearby hospitals could process 15-minute tests.
“If we had a more coordinated response with a partnership between the medical field, the government and the private industry, it would help improve the supply chain to the areas that need it most,” Dr. Klein said.
Dr. Klein said he expected to deal with equipment and supply shortages throughout 2021, especially as flu season approaches.
“Most people focus on those N95 respirators,” said Carmela Coyle, CEO of the California Hospital Association, an industry group that represents more than 400 hospitals across one of America’s hardest-hit states.
She said she believed COVID-19-related supply challenges will persist through 2022.
“We have been challenged with shortages of isolation gowns, face shields, which you’re now starting to see in public places. Any one piece that’s in shortage or not available creates risk for patients and for health care workers,” said Ms. Coyle.
At the same time, trade associations representing manufacturers said persuading customers to shift to American suppliers had been difficult.
“I also have industry that’s working only at 10-20% capacity, who can make PPE in our own backyard, but have no orders,” said Kim Glas, CEO of the National Council of Textile Organizations, whose members make reusable cloth gowns.
Manufacturers in her organization have made “hundreds of millions of products,” but, without long-term government contracts, many are apprehensive to invest in the equipment needed to scale up the business and eventually lower prices.
“If there continues to be an upward trajectory of COVID-19 cases, not just in the U.S. but globally, you can see those supply chains breaking down again,” Ms. Glas said. “It is a health care security issue.”
For the past 2 decades, personal protective equipment was supplied to health care institutions in lean supply chains in the same way toilet paper was to grocery stores. Chains between major manufacturers and end users were so efficient, there was no need to stockpile goods.
But in March, the supply chain broke when major Asian PPE exporters embargoed materials or shut down just as demand increased exponentially. Thus, health care institutions were in much the same position as regular grocery shoppers, who were trying to buy great quantities of a product they never needed to stockpile before.
“I am very concerned about long-term PPE shortages for the foreseeable future,” said Susan Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association.
“There’s no question the situation is better than it was a couple of months ago,” said Bailey. However, many health care organizations, including her own, have struggled to obtain PPE. Bailey practices at a 10-doctor allergy clinic and was met with a 10,000-mask minimum when they tried to order N95 respirators.
“We have not seen evidence of a long-term strategic plan for the manufacture, acquisition and distribution of PPE” from the government, said Dr. Bailey. “The supply chain needs to be strengthened dramatically, and we need less dependence on foreign goods to manufacture our own PPE in the U.S.”
Some products have now come back to be made in the United States – although factories are not expected to be able to reach demand until mid-2021.
“A lot has been done in the last 6 months. We are largely out of the hole, and we have planted the seeds to render the United States self-sufficient,” said Dave Rousse, president of the Association of the Nonwoven Fabrics Industry.
In 2019, 850 tons of the material used in disposable masks was made in the United States. Around 10,000 tons is expected to be made in 2021, satisfying perhaps 80% of demand. But PPE is a suite of items – including gloves, gowns and face shields – not all of which have seen the same success.
“Thermometers are becoming a real issue,” said Cindy Juhas, chief strategy officer of CME, an American health care product distributor. “They’re expecting even a problem with needles and syringes for the amount of vaccines they have to make.”
Federal government efforts to address the supply chain have foundered. The Federal Emergency Management Agency, in charge of the COVID-19 response, told congressional interviewers in June it had “no involvement” in distributing PPE to hot spots.
Project Airbridge, an initiative headed by Jared Kushner, President Donald Trump’s son-in-law, flew PPE from international suppliers to the U.S. at taxpayer expense but was phased out. And the government has not responded to the AMA’s calls for more distribution data.
Arguably, Dr. Klein is among the best placed to weather such disruptions. He is part of a 51-hospital chain with purchasing power, and among the institutions that distributors prioritize when selling supplies. But tribulations continue even in hospitals, as shortages have pushed buyers to look directly for manufacturers, often through a swamp of companies that have sprung up overnight.
Now distributors are being called upon not just by their traditional customers – hospitals and long-term care homes – but by nearly every segment of society. First responders, schools, clinics and even food businesses are all buying medical equipment now.
“There’s going to be lots of other shortages we haven’t even thought about,” said Ms. Juhas.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Officials said logistical challenges continue 7 months after the coronavirus reached the United States, as the flu season approaches and as some state emergency management agencies prepare for a fall surge in COVID-19 cases.
Although the disarray is not as widespread as it was this spring, hospitals said rolling shortages of supplies range from specialized beds to disposable isolation gowns to thermometers.
“A few weeks ago, we were having a very difficult time getting the sanitary wipes. You just couldn’t get them,” said Bernard Klein, MD, chief executive of Providence Holy Cross Medical Center in Mission Hills, Calif., near Los Angeles. “We actually had to manufacture our own.”
This same dynamic has played out across a number of critical supplies in his hospital. First masks, then isolation gowns and now a specialized bed that allows nurses to turn COVID-19 patients onto their bellies – equipment that helps workers with what can otherwise be a six-person job.
“We’ve seen whole families come to our hospital with COVID, and several members hospitalized at the same time,” said Dr. Klein. “It’s very, very sad.”
Testing supplies ran short as the predominantly Latino community served by Providence Holy Cross was hit hard by COVID, and even as nearby hospitals could process 15-minute tests.
“If we had a more coordinated response with a partnership between the medical field, the government and the private industry, it would help improve the supply chain to the areas that need it most,” Dr. Klein said.
Dr. Klein said he expected to deal with equipment and supply shortages throughout 2021, especially as flu season approaches.
“Most people focus on those N95 respirators,” said Carmela Coyle, CEO of the California Hospital Association, an industry group that represents more than 400 hospitals across one of America’s hardest-hit states.
She said she believed COVID-19-related supply challenges will persist through 2022.
“We have been challenged with shortages of isolation gowns, face shields, which you’re now starting to see in public places. Any one piece that’s in shortage or not available creates risk for patients and for health care workers,” said Ms. Coyle.
At the same time, trade associations representing manufacturers said persuading customers to shift to American suppliers had been difficult.
“I also have industry that’s working only at 10-20% capacity, who can make PPE in our own backyard, but have no orders,” said Kim Glas, CEO of the National Council of Textile Organizations, whose members make reusable cloth gowns.
Manufacturers in her organization have made “hundreds of millions of products,” but, without long-term government contracts, many are apprehensive to invest in the equipment needed to scale up the business and eventually lower prices.
“If there continues to be an upward trajectory of COVID-19 cases, not just in the U.S. but globally, you can see those supply chains breaking down again,” Ms. Glas said. “It is a health care security issue.”
For the past 2 decades, personal protective equipment was supplied to health care institutions in lean supply chains in the same way toilet paper was to grocery stores. Chains between major manufacturers and end users were so efficient, there was no need to stockpile goods.
But in March, the supply chain broke when major Asian PPE exporters embargoed materials or shut down just as demand increased exponentially. Thus, health care institutions were in much the same position as regular grocery shoppers, who were trying to buy great quantities of a product they never needed to stockpile before.
“I am very concerned about long-term PPE shortages for the foreseeable future,” said Susan Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association.
“There’s no question the situation is better than it was a couple of months ago,” said Bailey. However, many health care organizations, including her own, have struggled to obtain PPE. Bailey practices at a 10-doctor allergy clinic and was met with a 10,000-mask minimum when they tried to order N95 respirators.
“We have not seen evidence of a long-term strategic plan for the manufacture, acquisition and distribution of PPE” from the government, said Dr. Bailey. “The supply chain needs to be strengthened dramatically, and we need less dependence on foreign goods to manufacture our own PPE in the U.S.”
Some products have now come back to be made in the United States – although factories are not expected to be able to reach demand until mid-2021.
“A lot has been done in the last 6 months. We are largely out of the hole, and we have planted the seeds to render the United States self-sufficient,” said Dave Rousse, president of the Association of the Nonwoven Fabrics Industry.
In 2019, 850 tons of the material used in disposable masks was made in the United States. Around 10,000 tons is expected to be made in 2021, satisfying perhaps 80% of demand. But PPE is a suite of items – including gloves, gowns and face shields – not all of which have seen the same success.
“Thermometers are becoming a real issue,” said Cindy Juhas, chief strategy officer of CME, an American health care product distributor. “They’re expecting even a problem with needles and syringes for the amount of vaccines they have to make.”
Federal government efforts to address the supply chain have foundered. The Federal Emergency Management Agency, in charge of the COVID-19 response, told congressional interviewers in June it had “no involvement” in distributing PPE to hot spots.
Project Airbridge, an initiative headed by Jared Kushner, President Donald Trump’s son-in-law, flew PPE from international suppliers to the U.S. at taxpayer expense but was phased out. And the government has not responded to the AMA’s calls for more distribution data.
Arguably, Dr. Klein is among the best placed to weather such disruptions. He is part of a 51-hospital chain with purchasing power, and among the institutions that distributors prioritize when selling supplies. But tribulations continue even in hospitals, as shortages have pushed buyers to look directly for manufacturers, often through a swamp of companies that have sprung up overnight.
Now distributors are being called upon not just by their traditional customers – hospitals and long-term care homes – but by nearly every segment of society. First responders, schools, clinics and even food businesses are all buying medical equipment now.
“There’s going to be lots of other shortages we haven’t even thought about,” said Ms. Juhas.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Officials said logistical challenges continue 7 months after the coronavirus reached the United States, as the flu season approaches and as some state emergency management agencies prepare for a fall surge in COVID-19 cases.
Although the disarray is not as widespread as it was this spring, hospitals said rolling shortages of supplies range from specialized beds to disposable isolation gowns to thermometers.
“A few weeks ago, we were having a very difficult time getting the sanitary wipes. You just couldn’t get them,” said Bernard Klein, MD, chief executive of Providence Holy Cross Medical Center in Mission Hills, Calif., near Los Angeles. “We actually had to manufacture our own.”
This same dynamic has played out across a number of critical supplies in his hospital. First masks, then isolation gowns and now a specialized bed that allows nurses to turn COVID-19 patients onto their bellies – equipment that helps workers with what can otherwise be a six-person job.
“We’ve seen whole families come to our hospital with COVID, and several members hospitalized at the same time,” said Dr. Klein. “It’s very, very sad.”
Testing supplies ran short as the predominantly Latino community served by Providence Holy Cross was hit hard by COVID, and even as nearby hospitals could process 15-minute tests.
“If we had a more coordinated response with a partnership between the medical field, the government and the private industry, it would help improve the supply chain to the areas that need it most,” Dr. Klein said.
Dr. Klein said he expected to deal with equipment and supply shortages throughout 2021, especially as flu season approaches.
“Most people focus on those N95 respirators,” said Carmela Coyle, CEO of the California Hospital Association, an industry group that represents more than 400 hospitals across one of America’s hardest-hit states.
She said she believed COVID-19-related supply challenges will persist through 2022.
“We have been challenged with shortages of isolation gowns, face shields, which you’re now starting to see in public places. Any one piece that’s in shortage or not available creates risk for patients and for health care workers,” said Ms. Coyle.
At the same time, trade associations representing manufacturers said persuading customers to shift to American suppliers had been difficult.
“I also have industry that’s working only at 10-20% capacity, who can make PPE in our own backyard, but have no orders,” said Kim Glas, CEO of the National Council of Textile Organizations, whose members make reusable cloth gowns.
Manufacturers in her organization have made “hundreds of millions of products,” but, without long-term government contracts, many are apprehensive to invest in the equipment needed to scale up the business and eventually lower prices.
“If there continues to be an upward trajectory of COVID-19 cases, not just in the U.S. but globally, you can see those supply chains breaking down again,” Ms. Glas said. “It is a health care security issue.”
For the past 2 decades, personal protective equipment was supplied to health care institutions in lean supply chains in the same way toilet paper was to grocery stores. Chains between major manufacturers and end users were so efficient, there was no need to stockpile goods.
But in March, the supply chain broke when major Asian PPE exporters embargoed materials or shut down just as demand increased exponentially. Thus, health care institutions were in much the same position as regular grocery shoppers, who were trying to buy great quantities of a product they never needed to stockpile before.
“I am very concerned about long-term PPE shortages for the foreseeable future,” said Susan Bailey, MD, president of the American Medical Association.
“There’s no question the situation is better than it was a couple of months ago,” said Bailey. However, many health care organizations, including her own, have struggled to obtain PPE. Bailey practices at a 10-doctor allergy clinic and was met with a 10,000-mask minimum when they tried to order N95 respirators.
“We have not seen evidence of a long-term strategic plan for the manufacture, acquisition and distribution of PPE” from the government, said Dr. Bailey. “The supply chain needs to be strengthened dramatically, and we need less dependence on foreign goods to manufacture our own PPE in the U.S.”
Some products have now come back to be made in the United States – although factories are not expected to be able to reach demand until mid-2021.
“A lot has been done in the last 6 months. We are largely out of the hole, and we have planted the seeds to render the United States self-sufficient,” said Dave Rousse, president of the Association of the Nonwoven Fabrics Industry.
In 2019, 850 tons of the material used in disposable masks was made in the United States. Around 10,000 tons is expected to be made in 2021, satisfying perhaps 80% of demand. But PPE is a suite of items – including gloves, gowns and face shields – not all of which have seen the same success.
“Thermometers are becoming a real issue,” said Cindy Juhas, chief strategy officer of CME, an American health care product distributor. “They’re expecting even a problem with needles and syringes for the amount of vaccines they have to make.”
Federal government efforts to address the supply chain have foundered. The Federal Emergency Management Agency, in charge of the COVID-19 response, told congressional interviewers in June it had “no involvement” in distributing PPE to hot spots.
Project Airbridge, an initiative headed by Jared Kushner, President Donald Trump’s son-in-law, flew PPE from international suppliers to the U.S. at taxpayer expense but was phased out. And the government has not responded to the AMA’s calls for more distribution data.
Arguably, Dr. Klein is among the best placed to weather such disruptions. He is part of a 51-hospital chain with purchasing power, and among the institutions that distributors prioritize when selling supplies. But tribulations continue even in hospitals, as shortages have pushed buyers to look directly for manufacturers, often through a swamp of companies that have sprung up overnight.
Now distributors are being called upon not just by their traditional customers – hospitals and long-term care homes – but by nearly every segment of society. First responders, schools, clinics and even food businesses are all buying medical equipment now.
“There’s going to be lots of other shortages we haven’t even thought about,” said Ms. Juhas.
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Pooled COVID-19 testing feasible, greatly reduces supply use
‘Straightforward, cost effective, and efficient’
Combining specimens from several low-risk inpatients in a single test for SARS-CoV-2 infection allowed hospital staff to stretch testing supplies and provide test results quickly for many more patients than they might have otherwise, researchers found.
“We believe this strategy conserved [personal protective equipment (PPE)], led to a marked reduction in staff and patient anxiety, and improved patient care,” wrote David Mastrianni, MD, and colleagues from Saratoga Hospital in Saratoga Springs, N.Y. “Our impression is that testing all admitted patients has also been reassuring to our community.”
The researchers published their findings July 20 in the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
“What was really important about this study was they were actually able to implement pooled testing after communication with the [Food and Drug Administration],” Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, SFHM, the journal’s editor-in-chief, said in an interview.
“Pooled testing combines samples from multiple people within a single test. The benefit is, if the test is negative [you know that] everyone whose sample was combined … is negative. So you’ve effectively tested anywhere from three to five people with the resources required for only one test,” Dr. Shah continued.
The challenge is that, if the test is positive, everyone in that testing group must be retested individually because one or more of them has the infection, said Dr. Shah, director of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Mastrianni said early in the pandemic they started getting the “New York surge” at their hospital, located approximately 3 hours from New York City. They wanted to test all of the inpatients at their hospital for COVID-19 and they had a rapid in-house test that worked well, “but we just didn’t have enough cartridges, and we couldn’t get deliveries, and we started pooling.” In fact, they ran out of testing supplies at one point during the study but were able to replenish their supply in about a day, he noted.
For the current study, all patients admitted to the hospital, including those admitted for observation, underwent testing for SARS-CoV-2. Staff in the emergency department designated patients as low risk if they had no symptoms or other clinical evidence of COVID-19; those patients underwent pooled testing.
Patients with clinical evidence of COVID-19, such as respiratory symptoms or laboratory or radiographic findings consistent with infection, were considered high risk and were tested on an individual basis and thus excluded from the current analysis.
The pooled testing strategy required some patients to be held in the emergency department until there were three available for pooled testing. On several occasions when this was not practical, specimens from two patients were pooled.
Between April 17 and May 11, clinicians tested 530 patients via pooled testing using 179 cartridges (172 with swabs from three patients and 7 with swabs from two patients). There were four positive pooled tests, which necessitated the use of an additional 11 cartridges. Overall, the testing used 190 cartridges, which is 340 fewer than would have been used if all patients had been tested individually.
Among the low-risk patients, the positive rate was 0.8% (4/530). No patients from pools that were negative tested positive later during their hospitalization or developed evidence of the infection.
Team effort, flexibility needed
Dr. Mastrianni said he expected their study to find that pooled testing saved testing resources, but he “was surprised by the complexity of the logistics in the hospital, and how it really required getting everybody to work together. …There were a lot of details, and it really took a lot of teamwork.”
The nursing supervisor in the emergency department was in charge of the batch and coordinated with the laboratory, he explained. There were many moving parts to manage, including monitoring how many patients were being admitted, what their conditions were, whether they were high or low risk, and where they would house those patients as the emergency department became increasingly busy. “It’s a lot for them, but they’ve adapted really well,” Dr. Mastrianni said.
Pooling tests seems to work best for three to five patients at a time; larger batches increase the chance of having a positive test, and thus identifying the sick individual(s) becomes more challenging and expensive, Dr. Shah said.
“It’s a fine line between having a pool large enough that you save on testing supplies and testing costs but not having the pool so large that you dramatically increase your likelihood of having a positive test,” Dr. Shah said.
Hospitals will likely need to be flexible and adapt as the local positivity rate changes and supply levels vary, according to the authors.
“Pooled testing is mainly dependent on the COVID-19 positive rate in the population of interest in addition to the sensitivity of the [reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)] method used for COVID-19 testing,” said Baha Abdalhamid, MD, PhD, of the department of pathology and microbiology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha.
“Each laboratory and hospital needs to do their own validation testing because it is dependent on the positive rate of COVID-19,” added Dr. Abdalhamid, who was not involved in the current study.
It’s important for clinicians to “do a good history to find who’s high risk and who’s low risk,” Dr. Mastrianni said. Clinicians also need to remember that, although a patient may test negative initially, they may still have COVID-19, he warned. That test reflects a single point in time, and a patient could be infected and not yet be ill, so clinicians need to be alert to a change in the patient’s status.
Best for settings with low-risk individuals
“Pooled COVID-19 testing is a straightforward, cost-effective, and efficient approach,” Dr. Abdalhamid said. He and his colleagues found pooled testing could increase testing capability by 69% or more when the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection is 10% or lower.
He said the approach would be helpful in other settings “as long as the positive rate is equal to or less than 10%. Asymptomatic population or surveillance groups such as students, athletes, and military service members are [an] interesting population to test using pooling testing because we expect these populations to have low positive rates, which makes pooled testing ideal.”
Benefit outweighs risk
“There is risk of missing specimens with low concentration of the virus,” Dr. Abdalhamid cautioned. “These specimens might be missed due to the dilution factor of pooling [false-negative specimens]. We did not have a single false-negative specimen in our proof-of-concept study. In addition, there are practical approaches to deal with false-negative pooled specimens.
“The benefit definitely outweighs the risk of false-negative specimens because false-negative results rarely occur, if any. In addition, there is significant saving of time, reagents, and supplies in [a] pooled specimens approach as well as expansion of the test for higher number of patients,” Dr. Abdalhamid continued.
Dr. Mastrianni’s hospital currently has enough testing cartridges, but they are continuing to conduct pooled testing to conserve resources for the benefit of their own hospital and for the nation as a whole, he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abdalhamid and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Straightforward, cost effective, and efficient’
‘Straightforward, cost effective, and efficient’
Combining specimens from several low-risk inpatients in a single test for SARS-CoV-2 infection allowed hospital staff to stretch testing supplies and provide test results quickly for many more patients than they might have otherwise, researchers found.
“We believe this strategy conserved [personal protective equipment (PPE)], led to a marked reduction in staff and patient anxiety, and improved patient care,” wrote David Mastrianni, MD, and colleagues from Saratoga Hospital in Saratoga Springs, N.Y. “Our impression is that testing all admitted patients has also been reassuring to our community.”
The researchers published their findings July 20 in the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
“What was really important about this study was they were actually able to implement pooled testing after communication with the [Food and Drug Administration],” Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, SFHM, the journal’s editor-in-chief, said in an interview.
“Pooled testing combines samples from multiple people within a single test. The benefit is, if the test is negative [you know that] everyone whose sample was combined … is negative. So you’ve effectively tested anywhere from three to five people with the resources required for only one test,” Dr. Shah continued.
The challenge is that, if the test is positive, everyone in that testing group must be retested individually because one or more of them has the infection, said Dr. Shah, director of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Mastrianni said early in the pandemic they started getting the “New York surge” at their hospital, located approximately 3 hours from New York City. They wanted to test all of the inpatients at their hospital for COVID-19 and they had a rapid in-house test that worked well, “but we just didn’t have enough cartridges, and we couldn’t get deliveries, and we started pooling.” In fact, they ran out of testing supplies at one point during the study but were able to replenish their supply in about a day, he noted.
For the current study, all patients admitted to the hospital, including those admitted for observation, underwent testing for SARS-CoV-2. Staff in the emergency department designated patients as low risk if they had no symptoms or other clinical evidence of COVID-19; those patients underwent pooled testing.
Patients with clinical evidence of COVID-19, such as respiratory symptoms or laboratory or radiographic findings consistent with infection, were considered high risk and were tested on an individual basis and thus excluded from the current analysis.
The pooled testing strategy required some patients to be held in the emergency department until there were three available for pooled testing. On several occasions when this was not practical, specimens from two patients were pooled.
Between April 17 and May 11, clinicians tested 530 patients via pooled testing using 179 cartridges (172 with swabs from three patients and 7 with swabs from two patients). There were four positive pooled tests, which necessitated the use of an additional 11 cartridges. Overall, the testing used 190 cartridges, which is 340 fewer than would have been used if all patients had been tested individually.
Among the low-risk patients, the positive rate was 0.8% (4/530). No patients from pools that were negative tested positive later during their hospitalization or developed evidence of the infection.
Team effort, flexibility needed
Dr. Mastrianni said he expected their study to find that pooled testing saved testing resources, but he “was surprised by the complexity of the logistics in the hospital, and how it really required getting everybody to work together. …There were a lot of details, and it really took a lot of teamwork.”
The nursing supervisor in the emergency department was in charge of the batch and coordinated with the laboratory, he explained. There were many moving parts to manage, including monitoring how many patients were being admitted, what their conditions were, whether they were high or low risk, and where they would house those patients as the emergency department became increasingly busy. “It’s a lot for them, but they’ve adapted really well,” Dr. Mastrianni said.
Pooling tests seems to work best for three to five patients at a time; larger batches increase the chance of having a positive test, and thus identifying the sick individual(s) becomes more challenging and expensive, Dr. Shah said.
“It’s a fine line between having a pool large enough that you save on testing supplies and testing costs but not having the pool so large that you dramatically increase your likelihood of having a positive test,” Dr. Shah said.
Hospitals will likely need to be flexible and adapt as the local positivity rate changes and supply levels vary, according to the authors.
“Pooled testing is mainly dependent on the COVID-19 positive rate in the population of interest in addition to the sensitivity of the [reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)] method used for COVID-19 testing,” said Baha Abdalhamid, MD, PhD, of the department of pathology and microbiology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha.
“Each laboratory and hospital needs to do their own validation testing because it is dependent on the positive rate of COVID-19,” added Dr. Abdalhamid, who was not involved in the current study.
It’s important for clinicians to “do a good history to find who’s high risk and who’s low risk,” Dr. Mastrianni said. Clinicians also need to remember that, although a patient may test negative initially, they may still have COVID-19, he warned. That test reflects a single point in time, and a patient could be infected and not yet be ill, so clinicians need to be alert to a change in the patient’s status.
Best for settings with low-risk individuals
“Pooled COVID-19 testing is a straightforward, cost-effective, and efficient approach,” Dr. Abdalhamid said. He and his colleagues found pooled testing could increase testing capability by 69% or more when the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection is 10% or lower.
He said the approach would be helpful in other settings “as long as the positive rate is equal to or less than 10%. Asymptomatic population or surveillance groups such as students, athletes, and military service members are [an] interesting population to test using pooling testing because we expect these populations to have low positive rates, which makes pooled testing ideal.”
Benefit outweighs risk
“There is risk of missing specimens with low concentration of the virus,” Dr. Abdalhamid cautioned. “These specimens might be missed due to the dilution factor of pooling [false-negative specimens]. We did not have a single false-negative specimen in our proof-of-concept study. In addition, there are practical approaches to deal with false-negative pooled specimens.
“The benefit definitely outweighs the risk of false-negative specimens because false-negative results rarely occur, if any. In addition, there is significant saving of time, reagents, and supplies in [a] pooled specimens approach as well as expansion of the test for higher number of patients,” Dr. Abdalhamid continued.
Dr. Mastrianni’s hospital currently has enough testing cartridges, but they are continuing to conduct pooled testing to conserve resources for the benefit of their own hospital and for the nation as a whole, he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abdalhamid and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Combining specimens from several low-risk inpatients in a single test for SARS-CoV-2 infection allowed hospital staff to stretch testing supplies and provide test results quickly for many more patients than they might have otherwise, researchers found.
“We believe this strategy conserved [personal protective equipment (PPE)], led to a marked reduction in staff and patient anxiety, and improved patient care,” wrote David Mastrianni, MD, and colleagues from Saratoga Hospital in Saratoga Springs, N.Y. “Our impression is that testing all admitted patients has also been reassuring to our community.”
The researchers published their findings July 20 in the Journal of Hospital Medicine.
“What was really important about this study was they were actually able to implement pooled testing after communication with the [Food and Drug Administration],” Samir S. Shah, MD, MSCE, SFHM, the journal’s editor-in-chief, said in an interview.
“Pooled testing combines samples from multiple people within a single test. The benefit is, if the test is negative [you know that] everyone whose sample was combined … is negative. So you’ve effectively tested anywhere from three to five people with the resources required for only one test,” Dr. Shah continued.
The challenge is that, if the test is positive, everyone in that testing group must be retested individually because one or more of them has the infection, said Dr. Shah, director of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Dr. Mastrianni said early in the pandemic they started getting the “New York surge” at their hospital, located approximately 3 hours from New York City. They wanted to test all of the inpatients at their hospital for COVID-19 and they had a rapid in-house test that worked well, “but we just didn’t have enough cartridges, and we couldn’t get deliveries, and we started pooling.” In fact, they ran out of testing supplies at one point during the study but were able to replenish their supply in about a day, he noted.
For the current study, all patients admitted to the hospital, including those admitted for observation, underwent testing for SARS-CoV-2. Staff in the emergency department designated patients as low risk if they had no symptoms or other clinical evidence of COVID-19; those patients underwent pooled testing.
Patients with clinical evidence of COVID-19, such as respiratory symptoms or laboratory or radiographic findings consistent with infection, were considered high risk and were tested on an individual basis and thus excluded from the current analysis.
The pooled testing strategy required some patients to be held in the emergency department until there were three available for pooled testing. On several occasions when this was not practical, specimens from two patients were pooled.
Between April 17 and May 11, clinicians tested 530 patients via pooled testing using 179 cartridges (172 with swabs from three patients and 7 with swabs from two patients). There were four positive pooled tests, which necessitated the use of an additional 11 cartridges. Overall, the testing used 190 cartridges, which is 340 fewer than would have been used if all patients had been tested individually.
Among the low-risk patients, the positive rate was 0.8% (4/530). No patients from pools that were negative tested positive later during their hospitalization or developed evidence of the infection.
Team effort, flexibility needed
Dr. Mastrianni said he expected their study to find that pooled testing saved testing resources, but he “was surprised by the complexity of the logistics in the hospital, and how it really required getting everybody to work together. …There were a lot of details, and it really took a lot of teamwork.”
The nursing supervisor in the emergency department was in charge of the batch and coordinated with the laboratory, he explained. There were many moving parts to manage, including monitoring how many patients were being admitted, what their conditions were, whether they were high or low risk, and where they would house those patients as the emergency department became increasingly busy. “It’s a lot for them, but they’ve adapted really well,” Dr. Mastrianni said.
Pooling tests seems to work best for three to five patients at a time; larger batches increase the chance of having a positive test, and thus identifying the sick individual(s) becomes more challenging and expensive, Dr. Shah said.
“It’s a fine line between having a pool large enough that you save on testing supplies and testing costs but not having the pool so large that you dramatically increase your likelihood of having a positive test,” Dr. Shah said.
Hospitals will likely need to be flexible and adapt as the local positivity rate changes and supply levels vary, according to the authors.
“Pooled testing is mainly dependent on the COVID-19 positive rate in the population of interest in addition to the sensitivity of the [reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)] method used for COVID-19 testing,” said Baha Abdalhamid, MD, PhD, of the department of pathology and microbiology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha.
“Each laboratory and hospital needs to do their own validation testing because it is dependent on the positive rate of COVID-19,” added Dr. Abdalhamid, who was not involved in the current study.
It’s important for clinicians to “do a good history to find who’s high risk and who’s low risk,” Dr. Mastrianni said. Clinicians also need to remember that, although a patient may test negative initially, they may still have COVID-19, he warned. That test reflects a single point in time, and a patient could be infected and not yet be ill, so clinicians need to be alert to a change in the patient’s status.
Best for settings with low-risk individuals
“Pooled COVID-19 testing is a straightforward, cost-effective, and efficient approach,” Dr. Abdalhamid said. He and his colleagues found pooled testing could increase testing capability by 69% or more when the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection is 10% or lower.
He said the approach would be helpful in other settings “as long as the positive rate is equal to or less than 10%. Asymptomatic population or surveillance groups such as students, athletes, and military service members are [an] interesting population to test using pooling testing because we expect these populations to have low positive rates, which makes pooled testing ideal.”
Benefit outweighs risk
“There is risk of missing specimens with low concentration of the virus,” Dr. Abdalhamid cautioned. “These specimens might be missed due to the dilution factor of pooling [false-negative specimens]. We did not have a single false-negative specimen in our proof-of-concept study. In addition, there are practical approaches to deal with false-negative pooled specimens.
“The benefit definitely outweighs the risk of false-negative specimens because false-negative results rarely occur, if any. In addition, there is significant saving of time, reagents, and supplies in [a] pooled specimens approach as well as expansion of the test for higher number of patients,” Dr. Abdalhamid continued.
Dr. Mastrianni’s hospital currently has enough testing cartridges, but they are continuing to conduct pooled testing to conserve resources for the benefit of their own hospital and for the nation as a whole, he said.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Abdalhamid and Dr. Shah have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Does metformin reduce risk for death in COVID-19?
Accumulating observational data suggest that metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes might reduce the risk for death from COVID-19, but the randomized trials needed to prove this are unlikely to be carried out, according to experts.
The latest results, which are not yet peer reviewed, were published online July 31. The study was conducted by Andrew B. Crouse, PhD, of the Hugh Kaul Precision Medicine Institute, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
The researchers found that among more than 600 patients with diabetes and COVID-19, use of metformin was associated with a nearly 70% reduction in mortality after adjustment for multiple confounders.
Data from four previous studies that also show a reduction in mortality among metformin users compared to nonusers were summarized in a “mini review” by André J. Scheen, MD, PhD, published Aug. 1 in Diabetes and Metabolism.
Dr. Scheen, of the division of diabetes, nutrition, and metabolic disorders and the division of clinical pharmacology at Liège (Belgium) University, discussed possible mechanisms behind this observation.
“Because metformin exerts various effects beyond its glucose-lowering action, among which are anti-inflammatory effects, it may be speculated that this biguanide might positively influence the prognosis of patients with [type 2 diabetes] hospitalized for COVID-19,” he said.
“However, given the potential confounders inherently found in observational studies, caution is required before drawing any firm conclusions in the absence of randomized controlled trials,” Dr. Scheen wrote.
Indeed, when asked to comment, endocrinologist Kasia Lipska, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview: “Metformin users tend to do better in many different settings with respect to many different outcomes. To me, it is still unclear whether metformin is truly a miracle drug or whether it is simply used more often among people who are healthier and who do not have contraindications to its use.”
She added, “I don’t think we have enough data to suggest metformin use for COVID-19 mitigation at this point.”
Alabama authors say confounding effects ‘unlikely’
In the retrospective analysis of electronic health records from their institution, Dr. Crouse and colleagues reviewed data from 604 patients who were confirmed to have tested positive for COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and June 22, 2020. Of those individuals, 40% had diabetes.
Death occurred in 11% (n = 67); the odds ratio (OR) for death among those with, vs. without, diabetes was 3.62 (P < .0001).
Individuals with diabetes accounted for >60% of all deaths. In multiple logistic regression, age 50-70 vs. <50, male sex, and diabetes emerged as independent predictors of death.
Of the 42 patients with diabetes who died, 8 (19%) had used metformin, and 34 (81%) had not*, a significant difference (OR, 0.38; P = .0221). Insulin use, on the other hand, had no effect on mortality (P = .5728).
“In fact, with 11% [being] the mortality of metformin users, [this] was comparable to that of the general COVID-19-positive population and dramatically lower than the 23% mortality observed in subjects with diabetes and not on metformin,” the authors said.
The survival benefit observed with metformin remained after exclusion of patients with classic metformin contraindications, such as chronic kidney disease and heart failure (OR, 0.17; P = .0231).
“This makes any potential confounding effects from skewing metformin users toward healthier subjects without these additional comorbidities very unlikely,” Dr. Crouse and colleagues contended.
After further analysis that controlled for other covariates (age, sex, obesity status, and hypertension), age, sex, and metformin use remained independent predictors of mortality.
For metformin, the odds ratio was 0.33 (P = .0210).
But, Dr. Lipska pointed out, “Observational studies can take into account confounders that are measured. However, unmeasured confounders may still affect the conclusions of these studies ... Propensity score matching to account for the likelihood of use of metformin could be used to better account for differences between metformin users and nonusers.”
If metformin does reduce COVID-19 deaths, multiple mechanisms likely
In his article, Dr. Scheen noted that several mechanisms have been proposed for the possible beneficial effect of metformin on COVID-19 outcomes, including direct improvements in glucose control, body weight, and insulin resistance; reduction in inflammation; inhibition of virus penetration via phosphorylation of ACE2; inhibition of an immune hyperactivation pathway; and neutrophil reduction. All remain theoretical, he emphasized.
He noted that some authors have raised concerns about possible harms from the use of metformin by patients with type 2 diabetes who are hospitalized for COVID-19, particularly because of the potential risk for lactic acidosis in cases of multiple organ failure.
In totality, four studies suggest 25% death reduction with metformin
Taken together, the four observational studies that Dr. Scheen reviewed showed that metformin had a positive effect, with an overall 25% reduction in death (P < .00001), albeit with relatively high heterogeneity (I² = 61%).
The largest of these, from the United States, included 6,256 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and involved propensity matching. A significant reduction in mortality with metformin use was seen in women but not men (odds ratio, 0.759).
The French Coronavirus-SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes Outcomes (CORONADO) study of 1,317 patients with diabetes and confirmed COVID-19 who were admitted to 53 French hospitals also showed a significant survival benefit for metformin, although the study wasn’t designed to address that issue.
In that study, the odds ratio for death on day 7 in prior metformin users compared to nonusers was 0.59. This finding lost significance but remained a trend after full adjustments (0.80).
Two smaller observational studies produced similar trends toward survival benefit with metformin.
Nonetheless, Dr. Scheen cautioned: “Firm conclusions about the impact of metformin therapy can only be drawn from double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and such trials are almost impossible in the context of COVID-19.”
He added: “Because metformin is out of patent and very inexpensive, no pharmaceutical company is likely to be interested in planning a study to demonstrate the benefits of metformin on COVID-19-related clinical outcomes.”
Dr. Lipska agreed: “RCTs are unlikely to be conducted to settle these issues. In their absence, metformin use should be based on its safety and effectiveness profile.”
Dr. Scheen concluded, however, that “there are at least no negative safety indications, so there is no reason to stop metformin therapy during COVID-19 infection except in cases of severe gastrointestinal symptoms, hypoxia and/or multiple organ failure.”
Dr. Lipska has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and works under contract for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to develop publicly reported quality measures. Dr. Scheen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
*A previous version reversed these two outcomes in error.
Accumulating observational data suggest that metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes might reduce the risk for death from COVID-19, but the randomized trials needed to prove this are unlikely to be carried out, according to experts.
The latest results, which are not yet peer reviewed, were published online July 31. The study was conducted by Andrew B. Crouse, PhD, of the Hugh Kaul Precision Medicine Institute, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
The researchers found that among more than 600 patients with diabetes and COVID-19, use of metformin was associated with a nearly 70% reduction in mortality after adjustment for multiple confounders.
Data from four previous studies that also show a reduction in mortality among metformin users compared to nonusers were summarized in a “mini review” by André J. Scheen, MD, PhD, published Aug. 1 in Diabetes and Metabolism.
Dr. Scheen, of the division of diabetes, nutrition, and metabolic disorders and the division of clinical pharmacology at Liège (Belgium) University, discussed possible mechanisms behind this observation.
“Because metformin exerts various effects beyond its glucose-lowering action, among which are anti-inflammatory effects, it may be speculated that this biguanide might positively influence the prognosis of patients with [type 2 diabetes] hospitalized for COVID-19,” he said.
“However, given the potential confounders inherently found in observational studies, caution is required before drawing any firm conclusions in the absence of randomized controlled trials,” Dr. Scheen wrote.
Indeed, when asked to comment, endocrinologist Kasia Lipska, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview: “Metformin users tend to do better in many different settings with respect to many different outcomes. To me, it is still unclear whether metformin is truly a miracle drug or whether it is simply used more often among people who are healthier and who do not have contraindications to its use.”
She added, “I don’t think we have enough data to suggest metformin use for COVID-19 mitigation at this point.”
Alabama authors say confounding effects ‘unlikely’
In the retrospective analysis of electronic health records from their institution, Dr. Crouse and colleagues reviewed data from 604 patients who were confirmed to have tested positive for COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and June 22, 2020. Of those individuals, 40% had diabetes.
Death occurred in 11% (n = 67); the odds ratio (OR) for death among those with, vs. without, diabetes was 3.62 (P < .0001).
Individuals with diabetes accounted for >60% of all deaths. In multiple logistic regression, age 50-70 vs. <50, male sex, and diabetes emerged as independent predictors of death.
Of the 42 patients with diabetes who died, 8 (19%) had used metformin, and 34 (81%) had not*, a significant difference (OR, 0.38; P = .0221). Insulin use, on the other hand, had no effect on mortality (P = .5728).
“In fact, with 11% [being] the mortality of metformin users, [this] was comparable to that of the general COVID-19-positive population and dramatically lower than the 23% mortality observed in subjects with diabetes and not on metformin,” the authors said.
The survival benefit observed with metformin remained after exclusion of patients with classic metformin contraindications, such as chronic kidney disease and heart failure (OR, 0.17; P = .0231).
“This makes any potential confounding effects from skewing metformin users toward healthier subjects without these additional comorbidities very unlikely,” Dr. Crouse and colleagues contended.
After further analysis that controlled for other covariates (age, sex, obesity status, and hypertension), age, sex, and metformin use remained independent predictors of mortality.
For metformin, the odds ratio was 0.33 (P = .0210).
But, Dr. Lipska pointed out, “Observational studies can take into account confounders that are measured. However, unmeasured confounders may still affect the conclusions of these studies ... Propensity score matching to account for the likelihood of use of metformin could be used to better account for differences between metformin users and nonusers.”
If metformin does reduce COVID-19 deaths, multiple mechanisms likely
In his article, Dr. Scheen noted that several mechanisms have been proposed for the possible beneficial effect of metformin on COVID-19 outcomes, including direct improvements in glucose control, body weight, and insulin resistance; reduction in inflammation; inhibition of virus penetration via phosphorylation of ACE2; inhibition of an immune hyperactivation pathway; and neutrophil reduction. All remain theoretical, he emphasized.
He noted that some authors have raised concerns about possible harms from the use of metformin by patients with type 2 diabetes who are hospitalized for COVID-19, particularly because of the potential risk for lactic acidosis in cases of multiple organ failure.
In totality, four studies suggest 25% death reduction with metformin
Taken together, the four observational studies that Dr. Scheen reviewed showed that metformin had a positive effect, with an overall 25% reduction in death (P < .00001), albeit with relatively high heterogeneity (I² = 61%).
The largest of these, from the United States, included 6,256 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and involved propensity matching. A significant reduction in mortality with metformin use was seen in women but not men (odds ratio, 0.759).
The French Coronavirus-SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes Outcomes (CORONADO) study of 1,317 patients with diabetes and confirmed COVID-19 who were admitted to 53 French hospitals also showed a significant survival benefit for metformin, although the study wasn’t designed to address that issue.
In that study, the odds ratio for death on day 7 in prior metformin users compared to nonusers was 0.59. This finding lost significance but remained a trend after full adjustments (0.80).
Two smaller observational studies produced similar trends toward survival benefit with metformin.
Nonetheless, Dr. Scheen cautioned: “Firm conclusions about the impact of metformin therapy can only be drawn from double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and such trials are almost impossible in the context of COVID-19.”
He added: “Because metformin is out of patent and very inexpensive, no pharmaceutical company is likely to be interested in planning a study to demonstrate the benefits of metformin on COVID-19-related clinical outcomes.”
Dr. Lipska agreed: “RCTs are unlikely to be conducted to settle these issues. In their absence, metformin use should be based on its safety and effectiveness profile.”
Dr. Scheen concluded, however, that “there are at least no negative safety indications, so there is no reason to stop metformin therapy during COVID-19 infection except in cases of severe gastrointestinal symptoms, hypoxia and/or multiple organ failure.”
Dr. Lipska has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and works under contract for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to develop publicly reported quality measures. Dr. Scheen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
*A previous version reversed these two outcomes in error.
Accumulating observational data suggest that metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes might reduce the risk for death from COVID-19, but the randomized trials needed to prove this are unlikely to be carried out, according to experts.
The latest results, which are not yet peer reviewed, were published online July 31. The study was conducted by Andrew B. Crouse, PhD, of the Hugh Kaul Precision Medicine Institute, University of Alabama at Birmingham, and colleagues.
The researchers found that among more than 600 patients with diabetes and COVID-19, use of metformin was associated with a nearly 70% reduction in mortality after adjustment for multiple confounders.
Data from four previous studies that also show a reduction in mortality among metformin users compared to nonusers were summarized in a “mini review” by André J. Scheen, MD, PhD, published Aug. 1 in Diabetes and Metabolism.
Dr. Scheen, of the division of diabetes, nutrition, and metabolic disorders and the division of clinical pharmacology at Liège (Belgium) University, discussed possible mechanisms behind this observation.
“Because metformin exerts various effects beyond its glucose-lowering action, among which are anti-inflammatory effects, it may be speculated that this biguanide might positively influence the prognosis of patients with [type 2 diabetes] hospitalized for COVID-19,” he said.
“However, given the potential confounders inherently found in observational studies, caution is required before drawing any firm conclusions in the absence of randomized controlled trials,” Dr. Scheen wrote.
Indeed, when asked to comment, endocrinologist Kasia Lipska, MD, of Yale University, New Haven, Conn., said in an interview: “Metformin users tend to do better in many different settings with respect to many different outcomes. To me, it is still unclear whether metformin is truly a miracle drug or whether it is simply used more often among people who are healthier and who do not have contraindications to its use.”
She added, “I don’t think we have enough data to suggest metformin use for COVID-19 mitigation at this point.”
Alabama authors say confounding effects ‘unlikely’
In the retrospective analysis of electronic health records from their institution, Dr. Crouse and colleagues reviewed data from 604 patients who were confirmed to have tested positive for COVID-19 between Feb. 25 and June 22, 2020. Of those individuals, 40% had diabetes.
Death occurred in 11% (n = 67); the odds ratio (OR) for death among those with, vs. without, diabetes was 3.62 (P < .0001).
Individuals with diabetes accounted for >60% of all deaths. In multiple logistic regression, age 50-70 vs. <50, male sex, and diabetes emerged as independent predictors of death.
Of the 42 patients with diabetes who died, 8 (19%) had used metformin, and 34 (81%) had not*, a significant difference (OR, 0.38; P = .0221). Insulin use, on the other hand, had no effect on mortality (P = .5728).
“In fact, with 11% [being] the mortality of metformin users, [this] was comparable to that of the general COVID-19-positive population and dramatically lower than the 23% mortality observed in subjects with diabetes and not on metformin,” the authors said.
The survival benefit observed with metformin remained after exclusion of patients with classic metformin contraindications, such as chronic kidney disease and heart failure (OR, 0.17; P = .0231).
“This makes any potential confounding effects from skewing metformin users toward healthier subjects without these additional comorbidities very unlikely,” Dr. Crouse and colleagues contended.
After further analysis that controlled for other covariates (age, sex, obesity status, and hypertension), age, sex, and metformin use remained independent predictors of mortality.
For metformin, the odds ratio was 0.33 (P = .0210).
But, Dr. Lipska pointed out, “Observational studies can take into account confounders that are measured. However, unmeasured confounders may still affect the conclusions of these studies ... Propensity score matching to account for the likelihood of use of metformin could be used to better account for differences between metformin users and nonusers.”
If metformin does reduce COVID-19 deaths, multiple mechanisms likely
In his article, Dr. Scheen noted that several mechanisms have been proposed for the possible beneficial effect of metformin on COVID-19 outcomes, including direct improvements in glucose control, body weight, and insulin resistance; reduction in inflammation; inhibition of virus penetration via phosphorylation of ACE2; inhibition of an immune hyperactivation pathway; and neutrophil reduction. All remain theoretical, he emphasized.
He noted that some authors have raised concerns about possible harms from the use of metformin by patients with type 2 diabetes who are hospitalized for COVID-19, particularly because of the potential risk for lactic acidosis in cases of multiple organ failure.
In totality, four studies suggest 25% death reduction with metformin
Taken together, the four observational studies that Dr. Scheen reviewed showed that metformin had a positive effect, with an overall 25% reduction in death (P < .00001), albeit with relatively high heterogeneity (I² = 61%).
The largest of these, from the United States, included 6,256 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and involved propensity matching. A significant reduction in mortality with metformin use was seen in women but not men (odds ratio, 0.759).
The French Coronavirus-SARS-CoV-2 and Diabetes Outcomes (CORONADO) study of 1,317 patients with diabetes and confirmed COVID-19 who were admitted to 53 French hospitals also showed a significant survival benefit for metformin, although the study wasn’t designed to address that issue.
In that study, the odds ratio for death on day 7 in prior metformin users compared to nonusers was 0.59. This finding lost significance but remained a trend after full adjustments (0.80).
Two smaller observational studies produced similar trends toward survival benefit with metformin.
Nonetheless, Dr. Scheen cautioned: “Firm conclusions about the impact of metformin therapy can only be drawn from double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and such trials are almost impossible in the context of COVID-19.”
He added: “Because metformin is out of patent and very inexpensive, no pharmaceutical company is likely to be interested in planning a study to demonstrate the benefits of metformin on COVID-19-related clinical outcomes.”
Dr. Lipska agreed: “RCTs are unlikely to be conducted to settle these issues. In their absence, metformin use should be based on its safety and effectiveness profile.”
Dr. Scheen concluded, however, that “there are at least no negative safety indications, so there is no reason to stop metformin therapy during COVID-19 infection except in cases of severe gastrointestinal symptoms, hypoxia and/or multiple organ failure.”
Dr. Lipska has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and works under contract for the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to develop publicly reported quality measures. Dr. Scheen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
*A previous version reversed these two outcomes in error.
COVID-19 and masks: Doctor, may I be excused?
In the last 2 months, at least 10 patients have asked Constantine George, MD, for a written medical exemption so they won’t have to wear a mask in public. Dr. George, the chief medical officer of Vedius, an app for a travelers’ concierge medical service in Las Vegas, turned them all down.
Elena Christofides, MD, an endocrinologist in Columbus, Ohio, has also refused patients’ requests for exemptions.
“It’s very rare for someone to need an exemption,” says Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer for the American Lung Association and a lung specialist at ChristianaCare Health System in Newark, Del.
The opposition is sometimes strong. Recently, a video of Lenka Koloma of Laguna Niguel, Calif., who founded the antimask Freedom to Breathe Agency, went viral. She was in a California supermarket, maskless, telling an employee she was breaking the law by requiring patrons to wear masks.
“People need oxygen,” she said. “That alone is a medical condition.” Her webpage has a “Face Mask Exempt Card” that cites the Americans with Disabilities Act and posts a Department of Justice ADA violation reporting number. The DOJ issued a statement calling the cards fraudulent.
Figuring out if a patient’s request to opt out of wearing a mask is legitimate is a ‘’new frontier” for doctors, says Mical Raz, MD, a professor in public policy and health at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and a hospitalist at the university medical center.
Should some people skip masks?
Experts say there are very few medical reasons for people to skip masks. “If you look at the research, patients with COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder], those with reactive airway, even those can breathe through a mask,” Dr. George said. Requests for exemptions due to medical reasons are usually without basis. “Obviously, if someone is incapacitated, for example, with mental health issues, that’s case by case.”
Dr. Christofides said one of her patients cited anxiety and the other cited headaches as reasons not to wear a mask. “I told the one who asked for anxiety [reasons] that she could wear ones that were less tight.” The patient with headaches told Dr. Christofides that she had a buildup of carbon dioxide in the mask because of industrial exposure. Baloney, Dr. Christofides told her.
Dr. Rizzo says one rare example of someone who can’t wear a mask might be a patient with an advanced lung condition so severe, they need extra oxygen. “These are the extreme patients where any change in oxygen and carbon dioxide could make a difference,” he said. But “that’s also the population that shouldn’t be going out in the first place.”
Dr. Raz cowrote a commentary about mask exemptions, saying doctors are faced with difficult decisions and must keep a delicate balance between public health and individual disability needs. “Inappropriate medical exemptions may inadvertently hasten viral spread and threaten public health,” she wrote.
In an interview, she says that some people do have a hard time tolerating a mask. “Probably the most common reasons are mental health issues, such as anxiety, panic and PTSD, and children with sensory processing disorders (making them oversensitive to their environment). I think there are very few pulmonary reasons.”
CDC, professional organization guidelines
The CDC says people should wear masks in public and when around people who don’t live in the same household. Beyond that, it simply says masks should not be worn by children under age 2, “or anyone who has trouble breathing, is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.”
In mid-July, four professional organizations released a statement in response to the CDC recommendation for facial coverings. Jointly issued by the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Lung Association, the American Thoracic Society and the COPD Foundation, it states in part that people with normal lungs and “even many individuals with underlying chronic lung disease should be able to wear a non-N95 facial covering without affecting their oxygen or carbon dioxide levels.”
It acknowledges that some people will seek an exemption and doctors must weigh the patient’s concerns against the need to stop the spread of the virus. “In some instances, physician reassurance regarding the safety of the facial coverings may be all that is needed,” it states.
Addressing the excuses
Here are some of the common medical reasons people give for not being able to tolerate a mask:
Claustrophobia or anxiety. Dr. Raz and others suggests a “desensitizing” period, wearing the mask for longer and longer periods of time to get used to it. Parents could suggest kids wear a mask when doing something they like, such as watching television, so they equate it with something pleasant. Switching to a different kind of mask or one that fits better could also help.
Masks cause Legionnaires’ disease. Not true, experts say. Legionnaires’ is a severe form of pneumonia, the result of inhaling tiny water droplets with legionella bacteria.
It’s difficult to read lips. People can buy masks with a clear window that makes their mouth and lips visible.
Trouble breathing. Brief periods of mask use won’t have a bad effect on oxygen levels for most people.
“There is not an inherent right to be out in a pandemic with an unmasked face,” Dr. Raz says. But “you are entitled to an accommodation.” That might be using curbside pickup for food and medication. That requires much less time wearing a mask than entering a store would.
There are no “boilerplate” cards or letters to excuse people provided by the four organizations that addressed the issue, Dr. Rizzo said. If he were to write a letter asking for an exemption, he would personalize it for an individual patient’s medical condition. As to whether a state would honor it, he cannot say. The states have a patchwork of recommendations, making it difficult to say.
Dr. Rizzo tells lung disease patients who are able to go out that wearing a mask for 15-20 minutes to do an errand won’t harm their oxygen levels. And he reminds them that having an exemption, in the form of a doctor’s letter, may bring more problems. “Even with an exemption, someone may confront them” for their lack of a face covering. People with COPD have a higher risk of getting a severe illness from COVID-19, according to the CDC.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In the last 2 months, at least 10 patients have asked Constantine George, MD, for a written medical exemption so they won’t have to wear a mask in public. Dr. George, the chief medical officer of Vedius, an app for a travelers’ concierge medical service in Las Vegas, turned them all down.
Elena Christofides, MD, an endocrinologist in Columbus, Ohio, has also refused patients’ requests for exemptions.
“It’s very rare for someone to need an exemption,” says Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer for the American Lung Association and a lung specialist at ChristianaCare Health System in Newark, Del.
The opposition is sometimes strong. Recently, a video of Lenka Koloma of Laguna Niguel, Calif., who founded the antimask Freedom to Breathe Agency, went viral. She was in a California supermarket, maskless, telling an employee she was breaking the law by requiring patrons to wear masks.
“People need oxygen,” she said. “That alone is a medical condition.” Her webpage has a “Face Mask Exempt Card” that cites the Americans with Disabilities Act and posts a Department of Justice ADA violation reporting number. The DOJ issued a statement calling the cards fraudulent.
Figuring out if a patient’s request to opt out of wearing a mask is legitimate is a ‘’new frontier” for doctors, says Mical Raz, MD, a professor in public policy and health at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and a hospitalist at the university medical center.
Should some people skip masks?
Experts say there are very few medical reasons for people to skip masks. “If you look at the research, patients with COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder], those with reactive airway, even those can breathe through a mask,” Dr. George said. Requests for exemptions due to medical reasons are usually without basis. “Obviously, if someone is incapacitated, for example, with mental health issues, that’s case by case.”
Dr. Christofides said one of her patients cited anxiety and the other cited headaches as reasons not to wear a mask. “I told the one who asked for anxiety [reasons] that she could wear ones that were less tight.” The patient with headaches told Dr. Christofides that she had a buildup of carbon dioxide in the mask because of industrial exposure. Baloney, Dr. Christofides told her.
Dr. Rizzo says one rare example of someone who can’t wear a mask might be a patient with an advanced lung condition so severe, they need extra oxygen. “These are the extreme patients where any change in oxygen and carbon dioxide could make a difference,” he said. But “that’s also the population that shouldn’t be going out in the first place.”
Dr. Raz cowrote a commentary about mask exemptions, saying doctors are faced with difficult decisions and must keep a delicate balance between public health and individual disability needs. “Inappropriate medical exemptions may inadvertently hasten viral spread and threaten public health,” she wrote.
In an interview, she says that some people do have a hard time tolerating a mask. “Probably the most common reasons are mental health issues, such as anxiety, panic and PTSD, and children with sensory processing disorders (making them oversensitive to their environment). I think there are very few pulmonary reasons.”
CDC, professional organization guidelines
The CDC says people should wear masks in public and when around people who don’t live in the same household. Beyond that, it simply says masks should not be worn by children under age 2, “or anyone who has trouble breathing, is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.”
In mid-July, four professional organizations released a statement in response to the CDC recommendation for facial coverings. Jointly issued by the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Lung Association, the American Thoracic Society and the COPD Foundation, it states in part that people with normal lungs and “even many individuals with underlying chronic lung disease should be able to wear a non-N95 facial covering without affecting their oxygen or carbon dioxide levels.”
It acknowledges that some people will seek an exemption and doctors must weigh the patient’s concerns against the need to stop the spread of the virus. “In some instances, physician reassurance regarding the safety of the facial coverings may be all that is needed,” it states.
Addressing the excuses
Here are some of the common medical reasons people give for not being able to tolerate a mask:
Claustrophobia or anxiety. Dr. Raz and others suggests a “desensitizing” period, wearing the mask for longer and longer periods of time to get used to it. Parents could suggest kids wear a mask when doing something they like, such as watching television, so they equate it with something pleasant. Switching to a different kind of mask or one that fits better could also help.
Masks cause Legionnaires’ disease. Not true, experts say. Legionnaires’ is a severe form of pneumonia, the result of inhaling tiny water droplets with legionella bacteria.
It’s difficult to read lips. People can buy masks with a clear window that makes their mouth and lips visible.
Trouble breathing. Brief periods of mask use won’t have a bad effect on oxygen levels for most people.
“There is not an inherent right to be out in a pandemic with an unmasked face,” Dr. Raz says. But “you are entitled to an accommodation.” That might be using curbside pickup for food and medication. That requires much less time wearing a mask than entering a store would.
There are no “boilerplate” cards or letters to excuse people provided by the four organizations that addressed the issue, Dr. Rizzo said. If he were to write a letter asking for an exemption, he would personalize it for an individual patient’s medical condition. As to whether a state would honor it, he cannot say. The states have a patchwork of recommendations, making it difficult to say.
Dr. Rizzo tells lung disease patients who are able to go out that wearing a mask for 15-20 minutes to do an errand won’t harm their oxygen levels. And he reminds them that having an exemption, in the form of a doctor’s letter, may bring more problems. “Even with an exemption, someone may confront them” for their lack of a face covering. People with COPD have a higher risk of getting a severe illness from COVID-19, according to the CDC.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
In the last 2 months, at least 10 patients have asked Constantine George, MD, for a written medical exemption so they won’t have to wear a mask in public. Dr. George, the chief medical officer of Vedius, an app for a travelers’ concierge medical service in Las Vegas, turned them all down.
Elena Christofides, MD, an endocrinologist in Columbus, Ohio, has also refused patients’ requests for exemptions.
“It’s very rare for someone to need an exemption,” says Albert Rizzo, MD, chief medical officer for the American Lung Association and a lung specialist at ChristianaCare Health System in Newark, Del.
The opposition is sometimes strong. Recently, a video of Lenka Koloma of Laguna Niguel, Calif., who founded the antimask Freedom to Breathe Agency, went viral. She was in a California supermarket, maskless, telling an employee she was breaking the law by requiring patrons to wear masks.
“People need oxygen,” she said. “That alone is a medical condition.” Her webpage has a “Face Mask Exempt Card” that cites the Americans with Disabilities Act and posts a Department of Justice ADA violation reporting number. The DOJ issued a statement calling the cards fraudulent.
Figuring out if a patient’s request to opt out of wearing a mask is legitimate is a ‘’new frontier” for doctors, says Mical Raz, MD, a professor in public policy and health at the University of Rochester (N.Y.), and a hospitalist at the university medical center.
Should some people skip masks?
Experts say there are very few medical reasons for people to skip masks. “If you look at the research, patients with COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder], those with reactive airway, even those can breathe through a mask,” Dr. George said. Requests for exemptions due to medical reasons are usually without basis. “Obviously, if someone is incapacitated, for example, with mental health issues, that’s case by case.”
Dr. Christofides said one of her patients cited anxiety and the other cited headaches as reasons not to wear a mask. “I told the one who asked for anxiety [reasons] that she could wear ones that were less tight.” The patient with headaches told Dr. Christofides that she had a buildup of carbon dioxide in the mask because of industrial exposure. Baloney, Dr. Christofides told her.
Dr. Rizzo says one rare example of someone who can’t wear a mask might be a patient with an advanced lung condition so severe, they need extra oxygen. “These are the extreme patients where any change in oxygen and carbon dioxide could make a difference,” he said. But “that’s also the population that shouldn’t be going out in the first place.”
Dr. Raz cowrote a commentary about mask exemptions, saying doctors are faced with difficult decisions and must keep a delicate balance between public health and individual disability needs. “Inappropriate medical exemptions may inadvertently hasten viral spread and threaten public health,” she wrote.
In an interview, she says that some people do have a hard time tolerating a mask. “Probably the most common reasons are mental health issues, such as anxiety, panic and PTSD, and children with sensory processing disorders (making them oversensitive to their environment). I think there are very few pulmonary reasons.”
CDC, professional organization guidelines
The CDC says people should wear masks in public and when around people who don’t live in the same household. Beyond that, it simply says masks should not be worn by children under age 2, “or anyone who has trouble breathing, is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.”
In mid-July, four professional organizations released a statement in response to the CDC recommendation for facial coverings. Jointly issued by the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Lung Association, the American Thoracic Society and the COPD Foundation, it states in part that people with normal lungs and “even many individuals with underlying chronic lung disease should be able to wear a non-N95 facial covering without affecting their oxygen or carbon dioxide levels.”
It acknowledges that some people will seek an exemption and doctors must weigh the patient’s concerns against the need to stop the spread of the virus. “In some instances, physician reassurance regarding the safety of the facial coverings may be all that is needed,” it states.
Addressing the excuses
Here are some of the common medical reasons people give for not being able to tolerate a mask:
Claustrophobia or anxiety. Dr. Raz and others suggests a “desensitizing” period, wearing the mask for longer and longer periods of time to get used to it. Parents could suggest kids wear a mask when doing something they like, such as watching television, so they equate it with something pleasant. Switching to a different kind of mask or one that fits better could also help.
Masks cause Legionnaires’ disease. Not true, experts say. Legionnaires’ is a severe form of pneumonia, the result of inhaling tiny water droplets with legionella bacteria.
It’s difficult to read lips. People can buy masks with a clear window that makes their mouth and lips visible.
Trouble breathing. Brief periods of mask use won’t have a bad effect on oxygen levels for most people.
“There is not an inherent right to be out in a pandemic with an unmasked face,” Dr. Raz says. But “you are entitled to an accommodation.” That might be using curbside pickup for food and medication. That requires much less time wearing a mask than entering a store would.
There are no “boilerplate” cards or letters to excuse people provided by the four organizations that addressed the issue, Dr. Rizzo said. If he were to write a letter asking for an exemption, he would personalize it for an individual patient’s medical condition. As to whether a state would honor it, he cannot say. The states have a patchwork of recommendations, making it difficult to say.
Dr. Rizzo tells lung disease patients who are able to go out that wearing a mask for 15-20 minutes to do an errand won’t harm their oxygen levels. And he reminds them that having an exemption, in the form of a doctor’s letter, may bring more problems. “Even with an exemption, someone may confront them” for their lack of a face covering. People with COPD have a higher risk of getting a severe illness from COVID-19, according to the CDC.
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Action and awareness are needed to increase immunization rates
August was National Immunization Awareness Month. ... just in time to address the precipitous drop in immunization delivered during the early months of the pandemic.
In May, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported substantial reductions in vaccine doses ordered through the Vaccines for Children program after the declaration of national emergency because of COVID-19 on March 13. Approximately 2.5 million fewer doses of routine, noninfluenza vaccines were administered between Jan. 6 and April 2020, compared with a similar period last year (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 May 15;69[19]:591-3). Declines in immunization rates were echoed by states and municipalities across the United States. Last month, the health system in which I work reported 40,000 children behind on at least one vaccine.
We all know that, when immunization rates drop, outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases follow. In order and that is going to take more than a single month.
Identify patients who’ve missed vaccinations
Simply being open and ready to vaccinate is not enough. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urges providers to identify patients who have missed vaccines, and call them to schedule in-person visits. Proactively let parents know about strategies implemented in your office to ensure a safe environment.
Pediatricians are accustomed to an influx of patients in the summer, as parents make sure their children have all of the vaccines required for school attendance. As noted in a Washington Post article from Aug. 4, 2020, schools have traditionally served as a backstop for immunization rates. But as many school districts opt to take education online this fall, the implications for vaccine requirements are unclear. District of Columbia public schools continue to require immunization for virtual school attendance, but it is not clear how easily this can be enforced. To read about how other school districts have chosen to address – or not address – immunization requirements for school, visit the the Immunization Action Coalition’s Repository of Resources for Maintaining Immunization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. The repository links to international, national, and state-level policies and guidance and advocacy materials, including talking points, webinars, press releases, media articles from around the United States and social media posts, as well as telehealth resources.
Get some inspiration to talk about vaccination
Need a little inspiration for talking to parents about vaccines? Check out the CDC’s #HowIRecommend video series. These are short videos, most under a minute in length, that explain the importance of vaccination, how to effectively address questions from parents about vaccine safety, and how clinicians routinely recommend same day vaccination to their patients. These videos are part of the CDC’s National Immunization Awareness Month (NIAM) toolkit for communication with health care professionals. A companion toolkit for communicating with parents and patients contains sample social media messages with graphics, along with educational resources to share with parents.
The “Comprehensive Vaccine Education Program – From Training to Practice,” a free online program offered by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, takes a deeper dive into strategies to combat vaccine misinformation and address vaccine hesitancy. Available modules cover vaccine fundamentals, vaccine safety, clinical manifestations of vaccine-preventable diseases, and communication skills that lead to more effective conversations with patients and parents. The curriculum also includes the newest edition of The Vaccine Handbook app, a comprehensive source of practical information for vaccine providers.
Educate young children about vaccines
Don’t leave young children out of the conversation. Vax-Force is a children’s book that explores how vaccination works inside the human body. Dr. Vaxson the pediatrician explains how trusted doctors and scientists made Vicky the Vaccine. Her mission is to tell Willy the White Blood Cell and his Antibuddies how to find and fight bad-guy germs like measles, tetanus, and polio. The book was written by Kelsey Rowe, MD, while she was a medical student at Saint Louis University School of Medicine. Dr. Rowe, now a pediatric resident, notes, “In a world where anti-vaccination rhetoric threatens the health of our global community, this book’s mission is to teach children and adults alike that getting vaccinations is a safe, effective, and even exciting thing to do.” The book is available for purchase at https://www.vax-force.com/, and a small part of every sale is donated to Unicef USA.
Consider vaccination advocacy in your communities
Vaccinate Your Family, a national, nonprofit organization dedicated to protecting people of all ages from vaccine-preventable diseases, suggests that health care providers need to take an active role in raising immunization rates, not just in their own practices, but in their communities. One way to do this is to submit an opinion piece or letter to the editor to a local newspaper describing why it’s important for parents to make sure their child’s immunizations are current. Those who have never written an opinion-editorial should look at the guidance developed by Voices for Vaccines.
How are we doing?
Early data suggest a rebound in immunization rates in May and June, but that is unlikely to close the gap created by disruptions in health care delivery earlier in the year. Collectively, we need to set ambitious goals. Are we just trying to reach prepandemic immunization levels? In Kentucky, where I practice, only 71% of kids aged 19-45 months had received all doses of seven routinely recommended vaccines (≥4 DTaP doses, ≥3 polio doses, ≥1 MMR dose, Hib full series, ≥3 HepB doses, ≥1 varicella dose, and ≥4 PCV doses) based on 2017 National Immunization Survey data. The Healthy People 2020 target goal is 80%. Only 55% of Kentucky girls aged 13-17 years received at least one dose of HPV vaccine, and rates in boys were even lower. Flu vaccine coverage in children 6 months to 17 years also was 55%. The status quo sets the bar too low. To see how your state is doing, check out the interactive map developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Are we attempting to avoid disaster or can we seize the opportunity to protect more children than ever from vaccine-preventable diseases? The latter would really be something to celebrate.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
August was National Immunization Awareness Month. ... just in time to address the precipitous drop in immunization delivered during the early months of the pandemic.
In May, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported substantial reductions in vaccine doses ordered through the Vaccines for Children program after the declaration of national emergency because of COVID-19 on March 13. Approximately 2.5 million fewer doses of routine, noninfluenza vaccines were administered between Jan. 6 and April 2020, compared with a similar period last year (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 May 15;69[19]:591-3). Declines in immunization rates were echoed by states and municipalities across the United States. Last month, the health system in which I work reported 40,000 children behind on at least one vaccine.
We all know that, when immunization rates drop, outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases follow. In order and that is going to take more than a single month.
Identify patients who’ve missed vaccinations
Simply being open and ready to vaccinate is not enough. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urges providers to identify patients who have missed vaccines, and call them to schedule in-person visits. Proactively let parents know about strategies implemented in your office to ensure a safe environment.
Pediatricians are accustomed to an influx of patients in the summer, as parents make sure their children have all of the vaccines required for school attendance. As noted in a Washington Post article from Aug. 4, 2020, schools have traditionally served as a backstop for immunization rates. But as many school districts opt to take education online this fall, the implications for vaccine requirements are unclear. District of Columbia public schools continue to require immunization for virtual school attendance, but it is not clear how easily this can be enforced. To read about how other school districts have chosen to address – or not address – immunization requirements for school, visit the the Immunization Action Coalition’s Repository of Resources for Maintaining Immunization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. The repository links to international, national, and state-level policies and guidance and advocacy materials, including talking points, webinars, press releases, media articles from around the United States and social media posts, as well as telehealth resources.
Get some inspiration to talk about vaccination
Need a little inspiration for talking to parents about vaccines? Check out the CDC’s #HowIRecommend video series. These are short videos, most under a minute in length, that explain the importance of vaccination, how to effectively address questions from parents about vaccine safety, and how clinicians routinely recommend same day vaccination to their patients. These videos are part of the CDC’s National Immunization Awareness Month (NIAM) toolkit for communication with health care professionals. A companion toolkit for communicating with parents and patients contains sample social media messages with graphics, along with educational resources to share with parents.
The “Comprehensive Vaccine Education Program – From Training to Practice,” a free online program offered by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, takes a deeper dive into strategies to combat vaccine misinformation and address vaccine hesitancy. Available modules cover vaccine fundamentals, vaccine safety, clinical manifestations of vaccine-preventable diseases, and communication skills that lead to more effective conversations with patients and parents. The curriculum also includes the newest edition of The Vaccine Handbook app, a comprehensive source of practical information for vaccine providers.
Educate young children about vaccines
Don’t leave young children out of the conversation. Vax-Force is a children’s book that explores how vaccination works inside the human body. Dr. Vaxson the pediatrician explains how trusted doctors and scientists made Vicky the Vaccine. Her mission is to tell Willy the White Blood Cell and his Antibuddies how to find and fight bad-guy germs like measles, tetanus, and polio. The book was written by Kelsey Rowe, MD, while she was a medical student at Saint Louis University School of Medicine. Dr. Rowe, now a pediatric resident, notes, “In a world where anti-vaccination rhetoric threatens the health of our global community, this book’s mission is to teach children and adults alike that getting vaccinations is a safe, effective, and even exciting thing to do.” The book is available for purchase at https://www.vax-force.com/, and a small part of every sale is donated to Unicef USA.
Consider vaccination advocacy in your communities
Vaccinate Your Family, a national, nonprofit organization dedicated to protecting people of all ages from vaccine-preventable diseases, suggests that health care providers need to take an active role in raising immunization rates, not just in their own practices, but in their communities. One way to do this is to submit an opinion piece or letter to the editor to a local newspaper describing why it’s important for parents to make sure their child’s immunizations are current. Those who have never written an opinion-editorial should look at the guidance developed by Voices for Vaccines.
How are we doing?
Early data suggest a rebound in immunization rates in May and June, but that is unlikely to close the gap created by disruptions in health care delivery earlier in the year. Collectively, we need to set ambitious goals. Are we just trying to reach prepandemic immunization levels? In Kentucky, where I practice, only 71% of kids aged 19-45 months had received all doses of seven routinely recommended vaccines (≥4 DTaP doses, ≥3 polio doses, ≥1 MMR dose, Hib full series, ≥3 HepB doses, ≥1 varicella dose, and ≥4 PCV doses) based on 2017 National Immunization Survey data. The Healthy People 2020 target goal is 80%. Only 55% of Kentucky girls aged 13-17 years received at least one dose of HPV vaccine, and rates in boys were even lower. Flu vaccine coverage in children 6 months to 17 years also was 55%. The status quo sets the bar too low. To see how your state is doing, check out the interactive map developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Are we attempting to avoid disaster or can we seize the opportunity to protect more children than ever from vaccine-preventable diseases? The latter would really be something to celebrate.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
August was National Immunization Awareness Month. ... just in time to address the precipitous drop in immunization delivered during the early months of the pandemic.
In May, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported substantial reductions in vaccine doses ordered through the Vaccines for Children program after the declaration of national emergency because of COVID-19 on March 13. Approximately 2.5 million fewer doses of routine, noninfluenza vaccines were administered between Jan. 6 and April 2020, compared with a similar period last year (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 May 15;69[19]:591-3). Declines in immunization rates were echoed by states and municipalities across the United States. Last month, the health system in which I work reported 40,000 children behind on at least one vaccine.
We all know that, when immunization rates drop, outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases follow. In order and that is going to take more than a single month.
Identify patients who’ve missed vaccinations
Simply being open and ready to vaccinate is not enough. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention urges providers to identify patients who have missed vaccines, and call them to schedule in-person visits. Proactively let parents know about strategies implemented in your office to ensure a safe environment.
Pediatricians are accustomed to an influx of patients in the summer, as parents make sure their children have all of the vaccines required for school attendance. As noted in a Washington Post article from Aug. 4, 2020, schools have traditionally served as a backstop for immunization rates. But as many school districts opt to take education online this fall, the implications for vaccine requirements are unclear. District of Columbia public schools continue to require immunization for virtual school attendance, but it is not clear how easily this can be enforced. To read about how other school districts have chosen to address – or not address – immunization requirements for school, visit the the Immunization Action Coalition’s Repository of Resources for Maintaining Immunization during the COVID-19 Pandemic. The repository links to international, national, and state-level policies and guidance and advocacy materials, including talking points, webinars, press releases, media articles from around the United States and social media posts, as well as telehealth resources.
Get some inspiration to talk about vaccination
Need a little inspiration for talking to parents about vaccines? Check out the CDC’s #HowIRecommend video series. These are short videos, most under a minute in length, that explain the importance of vaccination, how to effectively address questions from parents about vaccine safety, and how clinicians routinely recommend same day vaccination to their patients. These videos are part of the CDC’s National Immunization Awareness Month (NIAM) toolkit for communication with health care professionals. A companion toolkit for communicating with parents and patients contains sample social media messages with graphics, along with educational resources to share with parents.
The “Comprehensive Vaccine Education Program – From Training to Practice,” a free online program offered by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, takes a deeper dive into strategies to combat vaccine misinformation and address vaccine hesitancy. Available modules cover vaccine fundamentals, vaccine safety, clinical manifestations of vaccine-preventable diseases, and communication skills that lead to more effective conversations with patients and parents. The curriculum also includes the newest edition of The Vaccine Handbook app, a comprehensive source of practical information for vaccine providers.
Educate young children about vaccines
Don’t leave young children out of the conversation. Vax-Force is a children’s book that explores how vaccination works inside the human body. Dr. Vaxson the pediatrician explains how trusted doctors and scientists made Vicky the Vaccine. Her mission is to tell Willy the White Blood Cell and his Antibuddies how to find and fight bad-guy germs like measles, tetanus, and polio. The book was written by Kelsey Rowe, MD, while she was a medical student at Saint Louis University School of Medicine. Dr. Rowe, now a pediatric resident, notes, “In a world where anti-vaccination rhetoric threatens the health of our global community, this book’s mission is to teach children and adults alike that getting vaccinations is a safe, effective, and even exciting thing to do.” The book is available for purchase at https://www.vax-force.com/, and a small part of every sale is donated to Unicef USA.
Consider vaccination advocacy in your communities
Vaccinate Your Family, a national, nonprofit organization dedicated to protecting people of all ages from vaccine-preventable diseases, suggests that health care providers need to take an active role in raising immunization rates, not just in their own practices, but in their communities. One way to do this is to submit an opinion piece or letter to the editor to a local newspaper describing why it’s important for parents to make sure their child’s immunizations are current. Those who have never written an opinion-editorial should look at the guidance developed by Voices for Vaccines.
How are we doing?
Early data suggest a rebound in immunization rates in May and June, but that is unlikely to close the gap created by disruptions in health care delivery earlier in the year. Collectively, we need to set ambitious goals. Are we just trying to reach prepandemic immunization levels? In Kentucky, where I practice, only 71% of kids aged 19-45 months had received all doses of seven routinely recommended vaccines (≥4 DTaP doses, ≥3 polio doses, ≥1 MMR dose, Hib full series, ≥3 HepB doses, ≥1 varicella dose, and ≥4 PCV doses) based on 2017 National Immunization Survey data. The Healthy People 2020 target goal is 80%. Only 55% of Kentucky girls aged 13-17 years received at least one dose of HPV vaccine, and rates in boys were even lower. Flu vaccine coverage in children 6 months to 17 years also was 55%. The status quo sets the bar too low. To see how your state is doing, check out the interactive map developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Are we attempting to avoid disaster or can we seize the opportunity to protect more children than ever from vaccine-preventable diseases? The latter would really be something to celebrate.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
Determining cause of skin lesions in COVID-19 patients remains challenging
published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
SARS-CoV-2 infection has been associated with a range of skin conditions, wrote Antonio Martinez-Lopez, MD, of Virgen de las Nieves University Hospital, Granada, Spain, and colleagues, who provided an overview of the cutaneous side effects associated with drugs used to treat COVID-19 infection.
“Cutaneous manifestations have recently been described in patients with the new coronavirus infection, similar to cutaneous involvement occurring in common viral infections,” they said. Infected individuals have experienced maculopapular eruption, pseudo-chilblain lesions, urticaria, monomorphic disseminated vesicular lesions, acral vesicular-pustulous lesions, and livedo or necrosis, they noted.
Diagnosing skin manifestations in patients with COVID-19 remains a challenge, because it is unclear whether the skin lesions are related to the virus, the authors said. “Skin diseases not related to coronavirus, other seasonal viral infections, and drug reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis, especially in those patients suffering from nonspecific manifestations such as urticaria or maculopapular eruptions,” they wrote.
However, “urticarial lesions and maculopapular eruptions in SARS-CoV-2 infections usually appear at the same time as the systemic symptoms, while drug adverse reactions are likely to arise hours to days after the start of the treatment,” they said.
The reviewers noted several cutaneous side effects associated with several of the often-prescribed drugs for COVID-19 infection. The antimalarials hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine had been authorized for COVID-19 treatment by the Food and Drug Administration, but this emergency authorization was rescinded in June. They noted that up to 11.5% of patients on these drugs may experience cutaneous adverse effects, including some that “can be mistaken for skin manifestations of SARS-CoV-2, especially those with maculopapular rash or exanthematous reactions.” Another side effect is exacerbation of psoriasis, which has been described in patients with COVID-19, the authors said.
The oral antiretroviral combination lopinavir/ritonavir, under investigation in clinical trials for COVID-19, has been associated with skin rashes in as many as 5% of adults in HIV studies. Usually appearing after treatment is started, the maculopapular pruritic rash is “usually well tolerated,” they said, although there have been reports of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Alopecia areata is among the other side effects reported.
Remdesivir also has been authorized for emergency treatment of COVID-19, and the small amount of data available suggest that cutaneous manifestations may be infrequent, the reviewers said. In a recent study of 53 patients treated with remdesivir for 10 days, approximately 8% developed a rash, but the study did not include any information “about rash morphology, distribution, or timeline in relation to remdesivir that may help clinicians differentiate from cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19,” they said.
Other potential treatments for complications of COVID-19 include imatinib, tocilizumab, anakinra, immunoglobulins, corticosteroids, colchicine, and low molecular weight heparins; all have the potential for association with skin reactions, but data on skin manifestations associated with COVID-19 are limited, the authors wrote.
Notably, data on the use of systemic corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients are controversial, although preliminary data showed some reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients who were on respiratory support, they noted. “With regard to differential diagnosis of cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19, the vascular fragility associated with corticosteroid use, especially in elderly patients, may be similar to the thrombotic complications of COVID-19 infection.”
Knowledge about the virology of COVID-19 continues to evolve rapidly, and the number of drugs being studied as treatments continues to expand, the authors pointed out.
“By considering adverse drug reactions in the differential diagnosis, dermatologists can be useful in assisting in the care of these patients,” they wrote. Drugs, rather than the infection, may be the cause of skin reactions in some COVID-19 patients, and “management is often symptomatic, but it is sometimes necessary to modify or discontinue the treatment, and some conditions can even be life-threatening,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Martinez-Lopez A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.006.
published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
SARS-CoV-2 infection has been associated with a range of skin conditions, wrote Antonio Martinez-Lopez, MD, of Virgen de las Nieves University Hospital, Granada, Spain, and colleagues, who provided an overview of the cutaneous side effects associated with drugs used to treat COVID-19 infection.
“Cutaneous manifestations have recently been described in patients with the new coronavirus infection, similar to cutaneous involvement occurring in common viral infections,” they said. Infected individuals have experienced maculopapular eruption, pseudo-chilblain lesions, urticaria, monomorphic disseminated vesicular lesions, acral vesicular-pustulous lesions, and livedo or necrosis, they noted.
Diagnosing skin manifestations in patients with COVID-19 remains a challenge, because it is unclear whether the skin lesions are related to the virus, the authors said. “Skin diseases not related to coronavirus, other seasonal viral infections, and drug reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis, especially in those patients suffering from nonspecific manifestations such as urticaria or maculopapular eruptions,” they wrote.
However, “urticarial lesions and maculopapular eruptions in SARS-CoV-2 infections usually appear at the same time as the systemic symptoms, while drug adverse reactions are likely to arise hours to days after the start of the treatment,” they said.
The reviewers noted several cutaneous side effects associated with several of the often-prescribed drugs for COVID-19 infection. The antimalarials hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine had been authorized for COVID-19 treatment by the Food and Drug Administration, but this emergency authorization was rescinded in June. They noted that up to 11.5% of patients on these drugs may experience cutaneous adverse effects, including some that “can be mistaken for skin manifestations of SARS-CoV-2, especially those with maculopapular rash or exanthematous reactions.” Another side effect is exacerbation of psoriasis, which has been described in patients with COVID-19, the authors said.
The oral antiretroviral combination lopinavir/ritonavir, under investigation in clinical trials for COVID-19, has been associated with skin rashes in as many as 5% of adults in HIV studies. Usually appearing after treatment is started, the maculopapular pruritic rash is “usually well tolerated,” they said, although there have been reports of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Alopecia areata is among the other side effects reported.
Remdesivir also has been authorized for emergency treatment of COVID-19, and the small amount of data available suggest that cutaneous manifestations may be infrequent, the reviewers said. In a recent study of 53 patients treated with remdesivir for 10 days, approximately 8% developed a rash, but the study did not include any information “about rash morphology, distribution, or timeline in relation to remdesivir that may help clinicians differentiate from cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19,” they said.
Other potential treatments for complications of COVID-19 include imatinib, tocilizumab, anakinra, immunoglobulins, corticosteroids, colchicine, and low molecular weight heparins; all have the potential for association with skin reactions, but data on skin manifestations associated with COVID-19 are limited, the authors wrote.
Notably, data on the use of systemic corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients are controversial, although preliminary data showed some reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients who were on respiratory support, they noted. “With regard to differential diagnosis of cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19, the vascular fragility associated with corticosteroid use, especially in elderly patients, may be similar to the thrombotic complications of COVID-19 infection.”
Knowledge about the virology of COVID-19 continues to evolve rapidly, and the number of drugs being studied as treatments continues to expand, the authors pointed out.
“By considering adverse drug reactions in the differential diagnosis, dermatologists can be useful in assisting in the care of these patients,” they wrote. Drugs, rather than the infection, may be the cause of skin reactions in some COVID-19 patients, and “management is often symptomatic, but it is sometimes necessary to modify or discontinue the treatment, and some conditions can even be life-threatening,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Martinez-Lopez A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.006.
published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
SARS-CoV-2 infection has been associated with a range of skin conditions, wrote Antonio Martinez-Lopez, MD, of Virgen de las Nieves University Hospital, Granada, Spain, and colleagues, who provided an overview of the cutaneous side effects associated with drugs used to treat COVID-19 infection.
“Cutaneous manifestations have recently been described in patients with the new coronavirus infection, similar to cutaneous involvement occurring in common viral infections,” they said. Infected individuals have experienced maculopapular eruption, pseudo-chilblain lesions, urticaria, monomorphic disseminated vesicular lesions, acral vesicular-pustulous lesions, and livedo or necrosis, they noted.
Diagnosing skin manifestations in patients with COVID-19 remains a challenge, because it is unclear whether the skin lesions are related to the virus, the authors said. “Skin diseases not related to coronavirus, other seasonal viral infections, and drug reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis, especially in those patients suffering from nonspecific manifestations such as urticaria or maculopapular eruptions,” they wrote.
However, “urticarial lesions and maculopapular eruptions in SARS-CoV-2 infections usually appear at the same time as the systemic symptoms, while drug adverse reactions are likely to arise hours to days after the start of the treatment,” they said.
The reviewers noted several cutaneous side effects associated with several of the often-prescribed drugs for COVID-19 infection. The antimalarials hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine had been authorized for COVID-19 treatment by the Food and Drug Administration, but this emergency authorization was rescinded in June. They noted that up to 11.5% of patients on these drugs may experience cutaneous adverse effects, including some that “can be mistaken for skin manifestations of SARS-CoV-2, especially those with maculopapular rash or exanthematous reactions.” Another side effect is exacerbation of psoriasis, which has been described in patients with COVID-19, the authors said.
The oral antiretroviral combination lopinavir/ritonavir, under investigation in clinical trials for COVID-19, has been associated with skin rashes in as many as 5% of adults in HIV studies. Usually appearing after treatment is started, the maculopapular pruritic rash is “usually well tolerated,” they said, although there have been reports of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Alopecia areata is among the other side effects reported.
Remdesivir also has been authorized for emergency treatment of COVID-19, and the small amount of data available suggest that cutaneous manifestations may be infrequent, the reviewers said. In a recent study of 53 patients treated with remdesivir for 10 days, approximately 8% developed a rash, but the study did not include any information “about rash morphology, distribution, or timeline in relation to remdesivir that may help clinicians differentiate from cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19,” they said.
Other potential treatments for complications of COVID-19 include imatinib, tocilizumab, anakinra, immunoglobulins, corticosteroids, colchicine, and low molecular weight heparins; all have the potential for association with skin reactions, but data on skin manifestations associated with COVID-19 are limited, the authors wrote.
Notably, data on the use of systemic corticosteroids for COVID-19 patients are controversial, although preliminary data showed some reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients who were on respiratory support, they noted. “With regard to differential diagnosis of cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19, the vascular fragility associated with corticosteroid use, especially in elderly patients, may be similar to the thrombotic complications of COVID-19 infection.”
Knowledge about the virology of COVID-19 continues to evolve rapidly, and the number of drugs being studied as treatments continues to expand, the authors pointed out.
“By considering adverse drug reactions in the differential diagnosis, dermatologists can be useful in assisting in the care of these patients,” they wrote. Drugs, rather than the infection, may be the cause of skin reactions in some COVID-19 patients, and “management is often symptomatic, but it is sometimes necessary to modify or discontinue the treatment, and some conditions can even be life-threatening,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Martinez-Lopez A et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.08.006.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Pandemic effect: Telemedicine is now a ‘must-have’ service
If people try telemedicine, they’ll like telemedicine. And if they want to avoid a doctor’s office, as most people do these days, they’ll try telemedicine. That is the message coming from 1,000 people surveyed for DocASAP, a provider of online patient access and engagement systems.

Here are a couple of numbers: 92% of those who made a telemedicine visit said they were satisfied with the overall appointment experience, and 91% said that they are more likely to schedule a telemedicine visit instead of an in-person appointment. All of the survey respondents had visited a health care provider in the past year, and 40% already had made a telemedicine visit, DocASAP reported.
Puneet Maheshwari, DocASAP cofounder and CEO, said in a statement. “As providers continue to adopt innovative technology to power a more seamless, end-to-end digital consumer experience, I expect telehealth to become fully integrated into overall care management.”
For now, though, COVID-19 is an overriding concern and health care facilities are suspect. When respondents were asked to identify the types of public facilities where they felt safe, hospitals were named by 32%, doctors’ offices by 26%, and ED/urgent care by just 12%, the DocASAP report said. Even public transportation got 13%.
The safest place to be, according to 42% of the respondents? The grocery store.
Of those surveyed, 43% “indicated they will not feel safe entering any health care setting until at least the fall,” the company said. An even higher share of patients, 68%, canceled or postponed an in-person appointment during the pandemic.
“No longer are remote health services viewed as ‘nice to have’ – they are now a must-have care delivery option,” DocASAP said in their report.
Safety concerns involving COVID-19, named by 47% of the sample, were the leading factor that would influence patients’ decision to schedule a telemedicine visit. Insurance coverage was next at 43%, followed by “ease of accessing quality care” at 40%, the report said.
Among those who had made a telemedicine visit, scheduling the appointment was the most satisfying aspect of the experience, according to 54% of respondents, with day-of-appointment wait time next at 38% and quality of the video/audio technology tied with preappointment communication at almost 33%, the survey data show.
Conversely, scheduling the appointment also was declared the most frustrating aspect of the telemedicine experience, although the total in that category was a much lower 29%.
“The pandemic has thrust profound change on every aspect of life, particularly health care. … Innovations – like digital and telehealth solutions – designed to meet patient needs will likely become embedded into the health care delivery system,” DocASAP said.
The survey was commissioned by DocASAP and conducted by marketing research company OnePoll on June 29-30, 2020.
If people try telemedicine, they’ll like telemedicine. And if they want to avoid a doctor’s office, as most people do these days, they’ll try telemedicine. That is the message coming from 1,000 people surveyed for DocASAP, a provider of online patient access and engagement systems.

Here are a couple of numbers: 92% of those who made a telemedicine visit said they were satisfied with the overall appointment experience, and 91% said that they are more likely to schedule a telemedicine visit instead of an in-person appointment. All of the survey respondents had visited a health care provider in the past year, and 40% already had made a telemedicine visit, DocASAP reported.
Puneet Maheshwari, DocASAP cofounder and CEO, said in a statement. “As providers continue to adopt innovative technology to power a more seamless, end-to-end digital consumer experience, I expect telehealth to become fully integrated into overall care management.”
For now, though, COVID-19 is an overriding concern and health care facilities are suspect. When respondents were asked to identify the types of public facilities where they felt safe, hospitals were named by 32%, doctors’ offices by 26%, and ED/urgent care by just 12%, the DocASAP report said. Even public transportation got 13%.
The safest place to be, according to 42% of the respondents? The grocery store.
Of those surveyed, 43% “indicated they will not feel safe entering any health care setting until at least the fall,” the company said. An even higher share of patients, 68%, canceled or postponed an in-person appointment during the pandemic.
“No longer are remote health services viewed as ‘nice to have’ – they are now a must-have care delivery option,” DocASAP said in their report.
Safety concerns involving COVID-19, named by 47% of the sample, were the leading factor that would influence patients’ decision to schedule a telemedicine visit. Insurance coverage was next at 43%, followed by “ease of accessing quality care” at 40%, the report said.
Among those who had made a telemedicine visit, scheduling the appointment was the most satisfying aspect of the experience, according to 54% of respondents, with day-of-appointment wait time next at 38% and quality of the video/audio technology tied with preappointment communication at almost 33%, the survey data show.
Conversely, scheduling the appointment also was declared the most frustrating aspect of the telemedicine experience, although the total in that category was a much lower 29%.
“The pandemic has thrust profound change on every aspect of life, particularly health care. … Innovations – like digital and telehealth solutions – designed to meet patient needs will likely become embedded into the health care delivery system,” DocASAP said.
The survey was commissioned by DocASAP and conducted by marketing research company OnePoll on June 29-30, 2020.
If people try telemedicine, they’ll like telemedicine. And if they want to avoid a doctor’s office, as most people do these days, they’ll try telemedicine. That is the message coming from 1,000 people surveyed for DocASAP, a provider of online patient access and engagement systems.

Here are a couple of numbers: 92% of those who made a telemedicine visit said they were satisfied with the overall appointment experience, and 91% said that they are more likely to schedule a telemedicine visit instead of an in-person appointment. All of the survey respondents had visited a health care provider in the past year, and 40% already had made a telemedicine visit, DocASAP reported.
Puneet Maheshwari, DocASAP cofounder and CEO, said in a statement. “As providers continue to adopt innovative technology to power a more seamless, end-to-end digital consumer experience, I expect telehealth to become fully integrated into overall care management.”
For now, though, COVID-19 is an overriding concern and health care facilities are suspect. When respondents were asked to identify the types of public facilities where they felt safe, hospitals were named by 32%, doctors’ offices by 26%, and ED/urgent care by just 12%, the DocASAP report said. Even public transportation got 13%.
The safest place to be, according to 42% of the respondents? The grocery store.
Of those surveyed, 43% “indicated they will not feel safe entering any health care setting until at least the fall,” the company said. An even higher share of patients, 68%, canceled or postponed an in-person appointment during the pandemic.
“No longer are remote health services viewed as ‘nice to have’ – they are now a must-have care delivery option,” DocASAP said in their report.
Safety concerns involving COVID-19, named by 47% of the sample, were the leading factor that would influence patients’ decision to schedule a telemedicine visit. Insurance coverage was next at 43%, followed by “ease of accessing quality care” at 40%, the report said.
Among those who had made a telemedicine visit, scheduling the appointment was the most satisfying aspect of the experience, according to 54% of respondents, with day-of-appointment wait time next at 38% and quality of the video/audio technology tied with preappointment communication at almost 33%, the survey data show.
Conversely, scheduling the appointment also was declared the most frustrating aspect of the telemedicine experience, although the total in that category was a much lower 29%.
“The pandemic has thrust profound change on every aspect of life, particularly health care. … Innovations – like digital and telehealth solutions – designed to meet patient needs will likely become embedded into the health care delivery system,” DocASAP said.
The survey was commissioned by DocASAP and conducted by marketing research company OnePoll on June 29-30, 2020.
Pandemic hampers reopening of joint replacement gold mine
Dr. Ira Weintraub, a recently retired orthopedic surgeon who now works at a medical billing consultancy, saw a hip replacement bill for over $400,000 earlier this year.
“The patient stayed in the hospital 17 days, which is only 17 times normal. The bill got paid,” mused Weintraub, chief medical officer of Portland, Oregon-based WellRithms, which helps self-funded employers and workers’ compensation insurers make sense of large, complex medical bills and ensure they pay the fair amount.
Charges like that go a long way toward explaining why hospitals are eager to restore joint replacements to pre-COVID levels as quickly as possible – an eagerness tempered only by safety concerns amid a resurgence of the coronavirus in some regions of the country. Revenue losses at hospitals and outpatient surgery centers may have exceeded $5 billion from canceled knee and hip replacements alone during a roughly two-month hiatus on elective procedures earlier this year.
The cost of joint replacement surgery varies widely – though, on average, it is in the tens, not hundreds, of thousands of dollars. Still, given the high and rapidly growing volume, it’s easy to see why joint replacement operations have become a vital chunk of revenue at most U.S. hospitals.
The rate of knee and hip replacements more than doubled from 2000 to 2015, according to inpatient discharge data from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. And that growth is likely to continue: Knee replacements are expected to triple between now and 2040, with hip replacements not far behind, according to projections published last year in the Journal of Rheumatology.
Joint procedures are usually not emergencies, and they were among the first to be scrubbed or delayed when hospitals froze elective surgeries in March – and again in July in some areas plagued by renewed COVID outbreaks.
“Without orthopedic volumes returning to something near their pre-pandemic levels, it will make it difficult for health systems to get back to anywhere near break-even from a bottom-line perspective,” said Stephen Thome, a principal in health care consulting at Grant Thornton, an advisory, audit and tax firm.
It’s impossible to know exactly how much knee and hip replacements are worth to hospitals, because no definitive data on total volume or price exists.
But using published estimates of volume, extrapolating average commercial payments from published Medicare rates based on a study, and making an educated guess of patient coinsurance, Thome helped KHN arrive at an annual market value for American hospitals and surgery centers of between $15.5 billion and $21.5 billion for knee replacements alone.
That suggests a revenue loss of $1.3 billion to $1.8 billion per month for the period the surgeries were shut down. These figures include ambulatory surgery centers not owned by hospitals, which also suspended most operations in late March, all of April and into May.
If you add hip replacements, which account for about half the volume of knees and are paid at similar rates, the total annual value rises to a range of $23 billion to $32 billion, with monthly revenue losses from $1.9 billion to $2.7 billion.
The American Hospital Association projects total revenue lost at U.S. hospitals will reach $323 billion by year’s end, not counting additional losses from surgeries canceled during the current coronavirus spike. That amount is partially offset by $69 billion in federal relief dollars hospitals have received so far, according to the association. The California Hospital Association puts the net revenue loss for hospitals in that state at about $10.5 billion, said spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea.
Hospitals resumed joint replacement surgeries in early to mid-May, with the timing and ramp-up speed varying by region and hospital. Some hospitals restored volume quickly; others took a more cautious route and continue to lose revenue. Still others have had to shut down again.
At the NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital in New York City, “people are starting to come in and you see the operating rooms full again,” said Dr. Claudette Lajam, chief orthopedic safety officer.
At St. Jude Medical Center in Fullerton, California, where the coronavirus is raging, inpatient joint replacements resumed in the second or third week of May – cautiously at first, but volume is “very close to pre-pandemic levels at this point,” said Dr. Kevin Khajavi, chairman of the hospital’s orthopedic surgery department. However, “we are constantly monitoring the situation to determine if we have to scale back once again,” he said.
In large swaths of Texas, elective surgeries were once again suspended in July because of the COVID-19 resurgence. The same is true at many hospitals in Florida, Alabama, South Carolina and Nevada.
The Mayo Clinic in Phoenix suspended nonemergency joint replacement surgeries in early July. It resumed outpatient replacement procedures the week of July 27, but still has not resumed nonemergency inpatient procedures, said Dr. Mark Spangehl, an orthopedic surgeon there. In terms of medical urgency, joint replacements are “at the bottom of the totem pole,” Spangehl said.
In terms of cash flow, however, joint replacements are decidedly not at the bottom of the totem pole. They have become a cash cow as the number of patients undergoing them has skyrocketed in recent decades.
The volume is being driven by an aging population, an epidemic of obesity and a significant rise in the number of younger people replacing joints worn out by years of sports and exercise.
It’s also being driven by the cash. Once only done in hospitals, the operations are now increasingly performed at ambulatory surgery centers – especially on younger, healthier patients who don’t require hospitalization.
The surgery centers are often physician-owned, but private equity groups such as Bain Capital and KKR & Co. have taken an interest in them, drawn by their high growth potential, robust financial returns and ability to offer competitive prices.
“[G]enerally the savings should be very good – but I do see a lot of outlier surgery centers where they are charging exorbitant amounts of money – $100,000 wouldn’t be too much,” said WellRithm’s Weintraub, who co-owned such a surgery center in Portland.
Fear of catching the coronavirus in a hospital is reinforcing the outpatient trend. Matthew Davis, a 58-year-old resident of Washington, was scheduled for a hip replacement on March 30 but got cold feet because of COVID-19, and canceled just before all elective surgeries were halted. When it came time to reschedule in June, he overcame his reservations in large part because the surgeon planned to perform the procedure at a free-standing surgery center.
“That was key to me – avoiding an overnight hospital stay to minimize my exposure,” Davis said. “These joint replacements are almost industrial-scale. They are cranking out joint replacements 9 to 5. I went in at 6:30 a.m. and I was walking out the door at 11:30.”
Acutely aware of the financial benefits, hospitals and surgery clinics have been marketing joint replacements for years, competing for coveted rankings and running ads that show healthy aging people, all smiles, engaged in vigorous activity.
However, a 2014 study concluded that one-third of knee replacements were not warranted, mainly because the symptoms of the patients were not severe enough to justify the procedures.
“The whole marketing of health care is so manipulative to the consuming public,” said Lisa McGiffert, a longtime consumer advocate and co-founder of the Patient Safety Action Network. “People might be encouraged to get a knee replacement, when in reality something less invasive could have improved their condition.”
McGiffert recounted a conversation with an orthopedic surgeon in Washington state who told her about a patient who requested a knee replacement, even though he had not tried any lower-impact treatments to fix the problem. “I asked the surgeon, ‘You didn’t do it, did you?’ And he said, ‘Of course I did. He would just have gone to somebody else.’ ”
This Kaiser Health News story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Dr. Ira Weintraub, a recently retired orthopedic surgeon who now works at a medical billing consultancy, saw a hip replacement bill for over $400,000 earlier this year.
“The patient stayed in the hospital 17 days, which is only 17 times normal. The bill got paid,” mused Weintraub, chief medical officer of Portland, Oregon-based WellRithms, which helps self-funded employers and workers’ compensation insurers make sense of large, complex medical bills and ensure they pay the fair amount.
Charges like that go a long way toward explaining why hospitals are eager to restore joint replacements to pre-COVID levels as quickly as possible – an eagerness tempered only by safety concerns amid a resurgence of the coronavirus in some regions of the country. Revenue losses at hospitals and outpatient surgery centers may have exceeded $5 billion from canceled knee and hip replacements alone during a roughly two-month hiatus on elective procedures earlier this year.
The cost of joint replacement surgery varies widely – though, on average, it is in the tens, not hundreds, of thousands of dollars. Still, given the high and rapidly growing volume, it’s easy to see why joint replacement operations have become a vital chunk of revenue at most U.S. hospitals.
The rate of knee and hip replacements more than doubled from 2000 to 2015, according to inpatient discharge data from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. And that growth is likely to continue: Knee replacements are expected to triple between now and 2040, with hip replacements not far behind, according to projections published last year in the Journal of Rheumatology.
Joint procedures are usually not emergencies, and they were among the first to be scrubbed or delayed when hospitals froze elective surgeries in March – and again in July in some areas plagued by renewed COVID outbreaks.
“Without orthopedic volumes returning to something near their pre-pandemic levels, it will make it difficult for health systems to get back to anywhere near break-even from a bottom-line perspective,” said Stephen Thome, a principal in health care consulting at Grant Thornton, an advisory, audit and tax firm.
It’s impossible to know exactly how much knee and hip replacements are worth to hospitals, because no definitive data on total volume or price exists.
But using published estimates of volume, extrapolating average commercial payments from published Medicare rates based on a study, and making an educated guess of patient coinsurance, Thome helped KHN arrive at an annual market value for American hospitals and surgery centers of between $15.5 billion and $21.5 billion for knee replacements alone.
That suggests a revenue loss of $1.3 billion to $1.8 billion per month for the period the surgeries were shut down. These figures include ambulatory surgery centers not owned by hospitals, which also suspended most operations in late March, all of April and into May.
If you add hip replacements, which account for about half the volume of knees and are paid at similar rates, the total annual value rises to a range of $23 billion to $32 billion, with monthly revenue losses from $1.9 billion to $2.7 billion.
The American Hospital Association projects total revenue lost at U.S. hospitals will reach $323 billion by year’s end, not counting additional losses from surgeries canceled during the current coronavirus spike. That amount is partially offset by $69 billion in federal relief dollars hospitals have received so far, according to the association. The California Hospital Association puts the net revenue loss for hospitals in that state at about $10.5 billion, said spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea.
Hospitals resumed joint replacement surgeries in early to mid-May, with the timing and ramp-up speed varying by region and hospital. Some hospitals restored volume quickly; others took a more cautious route and continue to lose revenue. Still others have had to shut down again.
At the NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital in New York City, “people are starting to come in and you see the operating rooms full again,” said Dr. Claudette Lajam, chief orthopedic safety officer.
At St. Jude Medical Center in Fullerton, California, where the coronavirus is raging, inpatient joint replacements resumed in the second or third week of May – cautiously at first, but volume is “very close to pre-pandemic levels at this point,” said Dr. Kevin Khajavi, chairman of the hospital’s orthopedic surgery department. However, “we are constantly monitoring the situation to determine if we have to scale back once again,” he said.
In large swaths of Texas, elective surgeries were once again suspended in July because of the COVID-19 resurgence. The same is true at many hospitals in Florida, Alabama, South Carolina and Nevada.
The Mayo Clinic in Phoenix suspended nonemergency joint replacement surgeries in early July. It resumed outpatient replacement procedures the week of July 27, but still has not resumed nonemergency inpatient procedures, said Dr. Mark Spangehl, an orthopedic surgeon there. In terms of medical urgency, joint replacements are “at the bottom of the totem pole,” Spangehl said.
In terms of cash flow, however, joint replacements are decidedly not at the bottom of the totem pole. They have become a cash cow as the number of patients undergoing them has skyrocketed in recent decades.
The volume is being driven by an aging population, an epidemic of obesity and a significant rise in the number of younger people replacing joints worn out by years of sports and exercise.
It’s also being driven by the cash. Once only done in hospitals, the operations are now increasingly performed at ambulatory surgery centers – especially on younger, healthier patients who don’t require hospitalization.
The surgery centers are often physician-owned, but private equity groups such as Bain Capital and KKR & Co. have taken an interest in them, drawn by their high growth potential, robust financial returns and ability to offer competitive prices.
“[G]enerally the savings should be very good – but I do see a lot of outlier surgery centers where they are charging exorbitant amounts of money – $100,000 wouldn’t be too much,” said WellRithm’s Weintraub, who co-owned such a surgery center in Portland.
Fear of catching the coronavirus in a hospital is reinforcing the outpatient trend. Matthew Davis, a 58-year-old resident of Washington, was scheduled for a hip replacement on March 30 but got cold feet because of COVID-19, and canceled just before all elective surgeries were halted. When it came time to reschedule in June, he overcame his reservations in large part because the surgeon planned to perform the procedure at a free-standing surgery center.
“That was key to me – avoiding an overnight hospital stay to minimize my exposure,” Davis said. “These joint replacements are almost industrial-scale. They are cranking out joint replacements 9 to 5. I went in at 6:30 a.m. and I was walking out the door at 11:30.”
Acutely aware of the financial benefits, hospitals and surgery clinics have been marketing joint replacements for years, competing for coveted rankings and running ads that show healthy aging people, all smiles, engaged in vigorous activity.
However, a 2014 study concluded that one-third of knee replacements were not warranted, mainly because the symptoms of the patients were not severe enough to justify the procedures.
“The whole marketing of health care is so manipulative to the consuming public,” said Lisa McGiffert, a longtime consumer advocate and co-founder of the Patient Safety Action Network. “People might be encouraged to get a knee replacement, when in reality something less invasive could have improved their condition.”
McGiffert recounted a conversation with an orthopedic surgeon in Washington state who told her about a patient who requested a knee replacement, even though he had not tried any lower-impact treatments to fix the problem. “I asked the surgeon, ‘You didn’t do it, did you?’ And he said, ‘Of course I did. He would just have gone to somebody else.’ ”
This Kaiser Health News story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Dr. Ira Weintraub, a recently retired orthopedic surgeon who now works at a medical billing consultancy, saw a hip replacement bill for over $400,000 earlier this year.
“The patient stayed in the hospital 17 days, which is only 17 times normal. The bill got paid,” mused Weintraub, chief medical officer of Portland, Oregon-based WellRithms, which helps self-funded employers and workers’ compensation insurers make sense of large, complex medical bills and ensure they pay the fair amount.
Charges like that go a long way toward explaining why hospitals are eager to restore joint replacements to pre-COVID levels as quickly as possible – an eagerness tempered only by safety concerns amid a resurgence of the coronavirus in some regions of the country. Revenue losses at hospitals and outpatient surgery centers may have exceeded $5 billion from canceled knee and hip replacements alone during a roughly two-month hiatus on elective procedures earlier this year.
The cost of joint replacement surgery varies widely – though, on average, it is in the tens, not hundreds, of thousands of dollars. Still, given the high and rapidly growing volume, it’s easy to see why joint replacement operations have become a vital chunk of revenue at most U.S. hospitals.
The rate of knee and hip replacements more than doubled from 2000 to 2015, according to inpatient discharge data from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. And that growth is likely to continue: Knee replacements are expected to triple between now and 2040, with hip replacements not far behind, according to projections published last year in the Journal of Rheumatology.
Joint procedures are usually not emergencies, and they were among the first to be scrubbed or delayed when hospitals froze elective surgeries in March – and again in July in some areas plagued by renewed COVID outbreaks.
“Without orthopedic volumes returning to something near their pre-pandemic levels, it will make it difficult for health systems to get back to anywhere near break-even from a bottom-line perspective,” said Stephen Thome, a principal in health care consulting at Grant Thornton, an advisory, audit and tax firm.
It’s impossible to know exactly how much knee and hip replacements are worth to hospitals, because no definitive data on total volume or price exists.
But using published estimates of volume, extrapolating average commercial payments from published Medicare rates based on a study, and making an educated guess of patient coinsurance, Thome helped KHN arrive at an annual market value for American hospitals and surgery centers of between $15.5 billion and $21.5 billion for knee replacements alone.
That suggests a revenue loss of $1.3 billion to $1.8 billion per month for the period the surgeries were shut down. These figures include ambulatory surgery centers not owned by hospitals, which also suspended most operations in late March, all of April and into May.
If you add hip replacements, which account for about half the volume of knees and are paid at similar rates, the total annual value rises to a range of $23 billion to $32 billion, with monthly revenue losses from $1.9 billion to $2.7 billion.
The American Hospital Association projects total revenue lost at U.S. hospitals will reach $323 billion by year’s end, not counting additional losses from surgeries canceled during the current coronavirus spike. That amount is partially offset by $69 billion in federal relief dollars hospitals have received so far, according to the association. The California Hospital Association puts the net revenue loss for hospitals in that state at about $10.5 billion, said spokesperson Jan Emerson-Shea.
Hospitals resumed joint replacement surgeries in early to mid-May, with the timing and ramp-up speed varying by region and hospital. Some hospitals restored volume quickly; others took a more cautious route and continue to lose revenue. Still others have had to shut down again.
At the NYU Langone Orthopedic Hospital in New York City, “people are starting to come in and you see the operating rooms full again,” said Dr. Claudette Lajam, chief orthopedic safety officer.
At St. Jude Medical Center in Fullerton, California, where the coronavirus is raging, inpatient joint replacements resumed in the second or third week of May – cautiously at first, but volume is “very close to pre-pandemic levels at this point,” said Dr. Kevin Khajavi, chairman of the hospital’s orthopedic surgery department. However, “we are constantly monitoring the situation to determine if we have to scale back once again,” he said.
In large swaths of Texas, elective surgeries were once again suspended in July because of the COVID-19 resurgence. The same is true at many hospitals in Florida, Alabama, South Carolina and Nevada.
The Mayo Clinic in Phoenix suspended nonemergency joint replacement surgeries in early July. It resumed outpatient replacement procedures the week of July 27, but still has not resumed nonemergency inpatient procedures, said Dr. Mark Spangehl, an orthopedic surgeon there. In terms of medical urgency, joint replacements are “at the bottom of the totem pole,” Spangehl said.
In terms of cash flow, however, joint replacements are decidedly not at the bottom of the totem pole. They have become a cash cow as the number of patients undergoing them has skyrocketed in recent decades.
The volume is being driven by an aging population, an epidemic of obesity and a significant rise in the number of younger people replacing joints worn out by years of sports and exercise.
It’s also being driven by the cash. Once only done in hospitals, the operations are now increasingly performed at ambulatory surgery centers – especially on younger, healthier patients who don’t require hospitalization.
The surgery centers are often physician-owned, but private equity groups such as Bain Capital and KKR & Co. have taken an interest in them, drawn by their high growth potential, robust financial returns and ability to offer competitive prices.
“[G]enerally the savings should be very good – but I do see a lot of outlier surgery centers where they are charging exorbitant amounts of money – $100,000 wouldn’t be too much,” said WellRithm’s Weintraub, who co-owned such a surgery center in Portland.
Fear of catching the coronavirus in a hospital is reinforcing the outpatient trend. Matthew Davis, a 58-year-old resident of Washington, was scheduled for a hip replacement on March 30 but got cold feet because of COVID-19, and canceled just before all elective surgeries were halted. When it came time to reschedule in June, he overcame his reservations in large part because the surgeon planned to perform the procedure at a free-standing surgery center.
“That was key to me – avoiding an overnight hospital stay to minimize my exposure,” Davis said. “These joint replacements are almost industrial-scale. They are cranking out joint replacements 9 to 5. I went in at 6:30 a.m. and I was walking out the door at 11:30.”
Acutely aware of the financial benefits, hospitals and surgery clinics have been marketing joint replacements for years, competing for coveted rankings and running ads that show healthy aging people, all smiles, engaged in vigorous activity.
However, a 2014 study concluded that one-third of knee replacements were not warranted, mainly because the symptoms of the patients were not severe enough to justify the procedures.
“The whole marketing of health care is so manipulative to the consuming public,” said Lisa McGiffert, a longtime consumer advocate and co-founder of the Patient Safety Action Network. “People might be encouraged to get a knee replacement, when in reality something less invasive could have improved their condition.”
McGiffert recounted a conversation with an orthopedic surgeon in Washington state who told her about a patient who requested a knee replacement, even though he had not tried any lower-impact treatments to fix the problem. “I asked the surgeon, ‘You didn’t do it, did you?’ And he said, ‘Of course I did. He would just have gone to somebody else.’ ”
This Kaiser Health News story first published on California Healthline, a service of the California Health Care Foundation.
Studies gauge role of schools, kids in spread of COVID-19
When officials closed U.S. schools in March to limit the spread of COVID-19, they may have prevented more than 1 million cases over a 26-day period, a new estimate published online July 29 in JAMA suggests.
But school closures also left blind spots in understanding how children and schools affect disease transmission.
“School closures early in pandemic responses thwarted larger-scale investigations of schools as a source of community transmission,” researchers noted in a separate study, published online July 30 in JAMA Pediatrics, that examined levels of viral RNA in children and adults with COVID-19.
“Our analyses suggest children younger than 5 years with mild to moderate COVID-19 have high amounts of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in their nasopharynx, compared with older children and adults,” reported Taylor Heald-Sargent, MD, PhD, and colleagues. “Thus, young children can potentially be important drivers of SARS-CoV-2 spread in the general population, as has been demonstrated with respiratory syncytial virus, where children with high viral loads are more likely to transmit.”
Although the study “was not designed to prove that younger children spread COVID-19 as much as adults,” it is a possibility, Dr. Heald-Sargent, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in a related news release. “We need to take that into account in efforts to reduce transmission as we continue to learn more about this virus.”.
The study included 145 patients with mild or moderate illness who were within 1 week of symptom onset. The researchers used reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs collected at inpatient, outpatient, emergency department, or drive-through testing sites to measure SARS-CoV-2 levels. The investigators compared PCR amplification cycle threshold (CT) values for children younger than 5 years (n = 46), children aged 5-17 years (n = 51), and adults aged 18-65 years (n = 48); lower CT values indicate higher amounts of viral nucleic acid.
Median CT values for older children and adults were similar (about 11), whereas the median CT value for young children was significantly lower (6.5). The differences between young children and adults “approximate a 10-fold to 100-fold greater amount of SARS-CoV-2 in the upper respiratory tract of young children,” the researchers wrote.
“Behavioral habits of young children and close quarters in school and day care settings raise concern for SARS-CoV-2 amplification in this population as public health restrictions are eased,” they write.
Modeling the impact of school closures
In the JAMA study, Katherine A. Auger, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues examined at the U.S. population level whether closing schools, as all 50 states did in March, was associated with relative decreases in COVID-19 incidence and mortality.
To isolate the effect of school closures, the researchers used an interrupted time series analysis and included other state-level nonpharmaceutical interventions and variables in their regression models.
“Per week, the incidence was estimated to have been 39% of what it would have been had schools remained open,” Dr. Auger and colleagues wrote. “Extrapolating the absolute differences of 423.9 cases and 12.6 deaths per 100,000 to 322.2 million residents nationally suggests that school closure may have been associated with approximately 1.37 million fewer cases of COVID-19 over a 26-day period and 40,600 fewer deaths over a 16-day period; however, these figures do not account for uncertainty in the model assumptions and the resulting estimates.”
Relative reductions in incidence and mortality were largest in states that closed schools when the incidence of COVID-19 was low, the authors found.
Decisions with high stakes
In an accompanying editorial, Julie M. Donohue, PhD, and Elizabeth Miller, MD, PhD, both affiliated with the University of Pittsburgh, emphasized that the results are estimates. “School closures were enacted in close proximity ... to other physical distancing measures, such as nonessential business closures and stay-at-home orders, making it difficult to disentangle the potential effect of each intervention.”
Although the findings “suggest a role for school closures in virus mitigation, school and health officials must balance this with academic, health, and economic consequences,” Dr. Donohue and Dr. Miller added. “Given the strong connection between education, income, and life expectancy, school closures could have long-term deleterious consequences for child health, likely reaching into adulthood.” Schools provide “meals and nutrition, health care including behavioral health supports, physical activity, social interaction, supports for students with special education needs and disabilities, and other vital resources for healthy development.”
In a viewpoint article also published in JAMA, authors involved in the creation of a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine reported on the reopening of schools recommend that districts “make every effort to prioritize reopening with an emphasis on providing in-person instruction for students in kindergarten through grade 5 as well as those students with special needs who might be best served by in-person instruction.
“To reopen safely, school districts are encouraged to ensure ventilation and air filtration, clean surfaces frequently, provide facilities for regular handwashing, and provide space for physical distancing,” write Kenne A. Dibner, PhD, of the NASEM in Washington, D.C., and coauthors.
Furthermore, districts “need to consider transparent communication of the reality that while measures can be implemented to lower the risk of transmitting COVID-19 when schools reopen, there is no way to eliminate that risk entirely. It is critical to share both the risks and benefits of different scenarios,” they wrote.
The JAMA modeling study received funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institutes of Health. The NASEM report was funded by the Brady Education Foundation and the Spencer Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
When officials closed U.S. schools in March to limit the spread of COVID-19, they may have prevented more than 1 million cases over a 26-day period, a new estimate published online July 29 in JAMA suggests.
But school closures also left blind spots in understanding how children and schools affect disease transmission.
“School closures early in pandemic responses thwarted larger-scale investigations of schools as a source of community transmission,” researchers noted in a separate study, published online July 30 in JAMA Pediatrics, that examined levels of viral RNA in children and adults with COVID-19.
“Our analyses suggest children younger than 5 years with mild to moderate COVID-19 have high amounts of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in their nasopharynx, compared with older children and adults,” reported Taylor Heald-Sargent, MD, PhD, and colleagues. “Thus, young children can potentially be important drivers of SARS-CoV-2 spread in the general population, as has been demonstrated with respiratory syncytial virus, where children with high viral loads are more likely to transmit.”
Although the study “was not designed to prove that younger children spread COVID-19 as much as adults,” it is a possibility, Dr. Heald-Sargent, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in a related news release. “We need to take that into account in efforts to reduce transmission as we continue to learn more about this virus.”.
The study included 145 patients with mild or moderate illness who were within 1 week of symptom onset. The researchers used reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs collected at inpatient, outpatient, emergency department, or drive-through testing sites to measure SARS-CoV-2 levels. The investigators compared PCR amplification cycle threshold (CT) values for children younger than 5 years (n = 46), children aged 5-17 years (n = 51), and adults aged 18-65 years (n = 48); lower CT values indicate higher amounts of viral nucleic acid.
Median CT values for older children and adults were similar (about 11), whereas the median CT value for young children was significantly lower (6.5). The differences between young children and adults “approximate a 10-fold to 100-fold greater amount of SARS-CoV-2 in the upper respiratory tract of young children,” the researchers wrote.
“Behavioral habits of young children and close quarters in school and day care settings raise concern for SARS-CoV-2 amplification in this population as public health restrictions are eased,” they write.
Modeling the impact of school closures
In the JAMA study, Katherine A. Auger, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues examined at the U.S. population level whether closing schools, as all 50 states did in March, was associated with relative decreases in COVID-19 incidence and mortality.
To isolate the effect of school closures, the researchers used an interrupted time series analysis and included other state-level nonpharmaceutical interventions and variables in their regression models.
“Per week, the incidence was estimated to have been 39% of what it would have been had schools remained open,” Dr. Auger and colleagues wrote. “Extrapolating the absolute differences of 423.9 cases and 12.6 deaths per 100,000 to 322.2 million residents nationally suggests that school closure may have been associated with approximately 1.37 million fewer cases of COVID-19 over a 26-day period and 40,600 fewer deaths over a 16-day period; however, these figures do not account for uncertainty in the model assumptions and the resulting estimates.”
Relative reductions in incidence and mortality were largest in states that closed schools when the incidence of COVID-19 was low, the authors found.
Decisions with high stakes
In an accompanying editorial, Julie M. Donohue, PhD, and Elizabeth Miller, MD, PhD, both affiliated with the University of Pittsburgh, emphasized that the results are estimates. “School closures were enacted in close proximity ... to other physical distancing measures, such as nonessential business closures and stay-at-home orders, making it difficult to disentangle the potential effect of each intervention.”
Although the findings “suggest a role for school closures in virus mitigation, school and health officials must balance this with academic, health, and economic consequences,” Dr. Donohue and Dr. Miller added. “Given the strong connection between education, income, and life expectancy, school closures could have long-term deleterious consequences for child health, likely reaching into adulthood.” Schools provide “meals and nutrition, health care including behavioral health supports, physical activity, social interaction, supports for students with special education needs and disabilities, and other vital resources for healthy development.”
In a viewpoint article also published in JAMA, authors involved in the creation of a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine reported on the reopening of schools recommend that districts “make every effort to prioritize reopening with an emphasis on providing in-person instruction for students in kindergarten through grade 5 as well as those students with special needs who might be best served by in-person instruction.
“To reopen safely, school districts are encouraged to ensure ventilation and air filtration, clean surfaces frequently, provide facilities for regular handwashing, and provide space for physical distancing,” write Kenne A. Dibner, PhD, of the NASEM in Washington, D.C., and coauthors.
Furthermore, districts “need to consider transparent communication of the reality that while measures can be implemented to lower the risk of transmitting COVID-19 when schools reopen, there is no way to eliminate that risk entirely. It is critical to share both the risks and benefits of different scenarios,” they wrote.
The JAMA modeling study received funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institutes of Health. The NASEM report was funded by the Brady Education Foundation and the Spencer Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.
When officials closed U.S. schools in March to limit the spread of COVID-19, they may have prevented more than 1 million cases over a 26-day period, a new estimate published online July 29 in JAMA suggests.
But school closures also left blind spots in understanding how children and schools affect disease transmission.
“School closures early in pandemic responses thwarted larger-scale investigations of schools as a source of community transmission,” researchers noted in a separate study, published online July 30 in JAMA Pediatrics, that examined levels of viral RNA in children and adults with COVID-19.
“Our analyses suggest children younger than 5 years with mild to moderate COVID-19 have high amounts of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in their nasopharynx, compared with older children and adults,” reported Taylor Heald-Sargent, MD, PhD, and colleagues. “Thus, young children can potentially be important drivers of SARS-CoV-2 spread in the general population, as has been demonstrated with respiratory syncytial virus, where children with high viral loads are more likely to transmit.”
Although the study “was not designed to prove that younger children spread COVID-19 as much as adults,” it is a possibility, Dr. Heald-Sargent, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist at Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital and assistant professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in a related news release. “We need to take that into account in efforts to reduce transmission as we continue to learn more about this virus.”.
The study included 145 patients with mild or moderate illness who were within 1 week of symptom onset. The researchers used reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) on nasopharyngeal swabs collected at inpatient, outpatient, emergency department, or drive-through testing sites to measure SARS-CoV-2 levels. The investigators compared PCR amplification cycle threshold (CT) values for children younger than 5 years (n = 46), children aged 5-17 years (n = 51), and adults aged 18-65 years (n = 48); lower CT values indicate higher amounts of viral nucleic acid.
Median CT values for older children and adults were similar (about 11), whereas the median CT value for young children was significantly lower (6.5). The differences between young children and adults “approximate a 10-fold to 100-fold greater amount of SARS-CoV-2 in the upper respiratory tract of young children,” the researchers wrote.
“Behavioral habits of young children and close quarters in school and day care settings raise concern for SARS-CoV-2 amplification in this population as public health restrictions are eased,” they write.
Modeling the impact of school closures
In the JAMA study, Katherine A. Auger, MD, of Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, and colleagues examined at the U.S. population level whether closing schools, as all 50 states did in March, was associated with relative decreases in COVID-19 incidence and mortality.
To isolate the effect of school closures, the researchers used an interrupted time series analysis and included other state-level nonpharmaceutical interventions and variables in their regression models.
“Per week, the incidence was estimated to have been 39% of what it would have been had schools remained open,” Dr. Auger and colleagues wrote. “Extrapolating the absolute differences of 423.9 cases and 12.6 deaths per 100,000 to 322.2 million residents nationally suggests that school closure may have been associated with approximately 1.37 million fewer cases of COVID-19 over a 26-day period and 40,600 fewer deaths over a 16-day period; however, these figures do not account for uncertainty in the model assumptions and the resulting estimates.”
Relative reductions in incidence and mortality were largest in states that closed schools when the incidence of COVID-19 was low, the authors found.
Decisions with high stakes
In an accompanying editorial, Julie M. Donohue, PhD, and Elizabeth Miller, MD, PhD, both affiliated with the University of Pittsburgh, emphasized that the results are estimates. “School closures were enacted in close proximity ... to other physical distancing measures, such as nonessential business closures and stay-at-home orders, making it difficult to disentangle the potential effect of each intervention.”
Although the findings “suggest a role for school closures in virus mitigation, school and health officials must balance this with academic, health, and economic consequences,” Dr. Donohue and Dr. Miller added. “Given the strong connection between education, income, and life expectancy, school closures could have long-term deleterious consequences for child health, likely reaching into adulthood.” Schools provide “meals and nutrition, health care including behavioral health supports, physical activity, social interaction, supports for students with special education needs and disabilities, and other vital resources for healthy development.”
In a viewpoint article also published in JAMA, authors involved in the creation of a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine reported on the reopening of schools recommend that districts “make every effort to prioritize reopening with an emphasis on providing in-person instruction for students in kindergarten through grade 5 as well as those students with special needs who might be best served by in-person instruction.
“To reopen safely, school districts are encouraged to ensure ventilation and air filtration, clean surfaces frequently, provide facilities for regular handwashing, and provide space for physical distancing,” write Kenne A. Dibner, PhD, of the NASEM in Washington, D.C., and coauthors.
Furthermore, districts “need to consider transparent communication of the reality that while measures can be implemented to lower the risk of transmitting COVID-19 when schools reopen, there is no way to eliminate that risk entirely. It is critical to share both the risks and benefits of different scenarios,” they wrote.
The JAMA modeling study received funding from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institutes of Health. The NASEM report was funded by the Brady Education Foundation and the Spencer Foundation. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this story originally appeared on Medscape.com.