User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
FDA warns of serious infection risk after FMT
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a Safety Alert warning of the potential risk of serious, life-threatening infection in patients who receive fecal microbiota transplant for Clostridioides difficile infection.
The FDA has received six reports of infection associated with fecal microbiota transplant from a stool bank company based in the United States: Two patients had enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) infection, and four had shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC). The two EPEC infections came from two separate donors, but the four STEC infections came from a single donor, according to the FDA.
In addition, two patients died after receiving fecal microbiota transplant from the donor associated with the STEC infections. These patients died before any of the STEC infections were reported to the FDA; as their stool was not tested for STEC, it is unclear whether it contributed to their deaths.
The use of fecal microbiota transplant is still investigational, and as such, patients should be made aware by health care providers of the risks, which include the potential for transmission of pathogenic bacteria and the resultant adverse events, the FDA said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a Safety Alert warning of the potential risk of serious, life-threatening infection in patients who receive fecal microbiota transplant for Clostridioides difficile infection.
The FDA has received six reports of infection associated with fecal microbiota transplant from a stool bank company based in the United States: Two patients had enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) infection, and four had shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC). The two EPEC infections came from two separate donors, but the four STEC infections came from a single donor, according to the FDA.
In addition, two patients died after receiving fecal microbiota transplant from the donor associated with the STEC infections. These patients died before any of the STEC infections were reported to the FDA; as their stool was not tested for STEC, it is unclear whether it contributed to their deaths.
The use of fecal microbiota transplant is still investigational, and as such, patients should be made aware by health care providers of the risks, which include the potential for transmission of pathogenic bacteria and the resultant adverse events, the FDA said in the press release.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued a Safety Alert warning of the potential risk of serious, life-threatening infection in patients who receive fecal microbiota transplant for Clostridioides difficile infection.
The FDA has received six reports of infection associated with fecal microbiota transplant from a stool bank company based in the United States: Two patients had enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) infection, and four had shiga toxin–producing E. coli (STEC). The two EPEC infections came from two separate donors, but the four STEC infections came from a single donor, according to the FDA.
In addition, two patients died after receiving fecal microbiota transplant from the donor associated with the STEC infections. These patients died before any of the STEC infections were reported to the FDA; as their stool was not tested for STEC, it is unclear whether it contributed to their deaths.
The use of fecal microbiota transplant is still investigational, and as such, patients should be made aware by health care providers of the risks, which include the potential for transmission of pathogenic bacteria and the resultant adverse events, the FDA said in the press release.
Your medical conference is canceled. Now what?
Khadija Hafidh, MD, was already booked on a 14-hour, direct flight from Dubai to Los Angeles, when the American College of Physicians (ACP) announced it was canceling its internal medicine meeting scheduled for April.
Canceling her hotel reservation was not a problem, and she was assured a refund for the conference fee, but her airline ticket was another matter, said Dr. Hafidh, an internist and diabetologist with the Dubai Health Authority.
“The airline I booked my ticket with is willing to waive the change fees, but will deduct a cancellation fee if I choose not to take the trip,” Dr. Hafidh said in an interview. “The cancellation fees is $300. A bit steep I must admit.”
Dr. Hafidh now faces a dilemma: Lose the $300 and cancel, or change her flight dates to June for the American Diabetes Association meeting in Chicago.
“But then again, we aren’t sure if that meeting will take place,” Dr. Hafidh said. “A few weeks ago I thought this whole thing was just a storm in a tea cup. However when it was declared a pandemic yesterday, it brought about another dimension.”
More than 25 medical meetings and conferences across the globe have been canceled or postponed because of COVID-19 concerns. The sudden cancellations have caused reservation woes and travel headaches for thousands of physicians who planned to attend the meetings. Some societies are considering the idea of virtual conferences, while other associations have scrapped their meetings until next year.
For physicians facing a canceled conference, the most likely question is, what now? Read on for tips and suggestions.
Reservation refunds vary
Refunds on airfare because of conference cancellations differ, depending on the airline and where you were traveling. Some airlines, such as United Airlines, have waived all change fees for tickets issued March 3, 2020, through March 31, 2020, and passengers can change their dates for up to 12 months after the ticket was issued.
Full refunds often depend on whether your ticket was nonrefundable when purchased. Many airlines, such as Delta, are providing full refunds if the airline canceled your flight. JetBlue is waiving all change and cancellation fees for customers scheduled to travel March 10, 2020, through April 30, 2020.
Las Vegas–based dermatologist H.L. Greenberg, MD, was satisfied with the credit he received from Southwest Airlines after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) canceled its Denver meeting. He and his staff were looking forward to the gathering, but he noted that the meeting would likely have been limited, even if it had take place as scheduled.
“I am disappointed that I won’t be able to meet with colleagues and industry to explore what the latest advances and interests are in dermatology,” he said. “Because many academic institutions were forbidding their faculty from traveling, the content of the meeting was going to be severely diminished. It’s just a rough time for everyone.”
Meanwhile, Asa Radix, MD, PhD, a New York–based internist, received a full refund for his Amtrak ticket to Boston when the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) scheduled for early March was converted to a virtual meeting. Dr. Radix, senior director of research and education at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York, left another meeting in Brazil early to get to the Boston conference, he said.
“I was packed, but really that was a minor inconvenience,” he said in an interview. “I appreciate that they prioritized health concerns and changed to a virtual meeting. I received full refunds, no issues whatsoever. [It was] really great since I had no travel insurance.”
Check with your individual airline or train line for information about ticket refunds and credits. Many airlines are currently making special accommodations because of COVID-19. If your flight was covered by trip insurance, also called travel assistance, you are generally protected against unforeseen financial losses such as cancellations. The U.S. Department of Transportation provides this general online resource about airline refunds.
Hotel refunds probable
Most meeting organizations who have made the decision to cancel or postpone a conference also have canceled block hotel reservations reserved for the meeting. Medical associations are not directly refunding the hotel costs, but the majority of hotels are refunding reservations with no questions asked. Physicians interviewed for this story all reported no trouble getting refunds for their hotel reservations. However, attendees who did not book a hotel in official housing blocks should contact the hotel directly to cancel.
What about registration fees?
In response to COVID-19 cancellations, most conference leaders are refunding registration fees in full for both attendees and exhibitors. The refund may not be automatic, some associations such as ACP and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state it may take up to 45 days for the funds to be credited, depending on the payment used.
If the conference you planned to attend was postponed, the registration fee may be assigned to the new meeting dates and the money may not be refunded. Registration fees for the Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium, for example, delayed until an unconfirmed date, and for the European Association of Urology (EAU) meeting, postponed until July, will be automatically credited to the rescheduled meeting, according to the websites. If attendees cannot attend the rescheduled EAU meeting, the association will not provide a refund and the registration will not apply to the 2021 meeting, according to its website. However, the group is providing registrants with a free access code for the EAU20 Resource Centre, which contains websites of sessions and scientific content.
A number of physicians have expressed disappointment with the EAU’s postponement on social media. On Twitter, some doctors wrote that the rescheduled dates were bad timing, while others lamented the refund refusal.
The EAU said it regrets that some delegates will experience financial losses, but that the organization has already experienced a significant outlay that cannot be recovered including venue, logistics, travel, and accommodation costs.
"We are doing what we can to absorb costs, but we need to be realistic about what is affordable; should the organization have to refund all or even most registrations, it would significantly jeopardize the viability of the organization," the EAU said in a statement. "These are difficult times, not only for the EAU, but on a global scale. Where there are specific cases of hardship or very extenuating financial circumstances, we will be willing to review individual cases. So far, we believe that we have done what we can do to meet the conflicting demands presented by the postponement of the congress, but this is a situation which changes from day to day, and we need to continuously evaluate what might be the best course of action." *
Contact your medical association directly for details on postponements.
What if I’m a presenter?
In an attempt to save the hard work and time that planners and presenters have invested into now-canceled meetings, some conferences are moving to a digital format. The Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) was the first to convert its in-person conference to a virtual meeting, held from March 8 to 11, 2020. At-home attendees logged onto CROI’s digital platform to hear plenaries, oral abstracts, themed discussion sessions, and symposia.
Dr. Radix was one of many CROI speakers who changed his presentation on HIV prevalence among transgender men to a virtual format.
“We were provided with detailed instructions from CROI about how to do this,” said Dr. Radix, who tweeted about the experience. “For my presentation, I used the video option in PowerPoint; it seemed the most straightforward and didn’t require buying additional software. It was fairly easy to follow the instructions to create the video but it was disappointing to present to an empty room.”
Matthew Spinelli, MD, an HIV researcher with the University of California, San Francisco, who also presented virtually, said it was remarkable that CROI leaders were able to put together the virtual program in such a short time. He delivered his presentation on the accuracy of a real-time urine tenofovir test using PowerPoint and a podcast microphone.
“It seemed to work pretty well,” he said in an interview. “It’s not the same as being there in person, there’s a lot of networking and chance conversations that happen when you’re all in the same place, but it was the right decision to cancel. If I have to be at home or at work doing social distancing, this was the best possible way of doing it.”
Following in CROI’s footsteps, the National Kidney Foundation’s spring conference has moved to a live virtual conference. The 2020 Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) global health conference also will move to a digital format. Other societies are considering similar virtual options. Check with your meeting website for more details on digital options and attendee access.
*The article was updated on 03/16/2020.
Khadija Hafidh, MD, was already booked on a 14-hour, direct flight from Dubai to Los Angeles, when the American College of Physicians (ACP) announced it was canceling its internal medicine meeting scheduled for April.
Canceling her hotel reservation was not a problem, and she was assured a refund for the conference fee, but her airline ticket was another matter, said Dr. Hafidh, an internist and diabetologist with the Dubai Health Authority.
“The airline I booked my ticket with is willing to waive the change fees, but will deduct a cancellation fee if I choose not to take the trip,” Dr. Hafidh said in an interview. “The cancellation fees is $300. A bit steep I must admit.”
Dr. Hafidh now faces a dilemma: Lose the $300 and cancel, or change her flight dates to June for the American Diabetes Association meeting in Chicago.
“But then again, we aren’t sure if that meeting will take place,” Dr. Hafidh said. “A few weeks ago I thought this whole thing was just a storm in a tea cup. However when it was declared a pandemic yesterday, it brought about another dimension.”
More than 25 medical meetings and conferences across the globe have been canceled or postponed because of COVID-19 concerns. The sudden cancellations have caused reservation woes and travel headaches for thousands of physicians who planned to attend the meetings. Some societies are considering the idea of virtual conferences, while other associations have scrapped their meetings until next year.
For physicians facing a canceled conference, the most likely question is, what now? Read on for tips and suggestions.
Reservation refunds vary
Refunds on airfare because of conference cancellations differ, depending on the airline and where you were traveling. Some airlines, such as United Airlines, have waived all change fees for tickets issued March 3, 2020, through March 31, 2020, and passengers can change their dates for up to 12 months after the ticket was issued.
Full refunds often depend on whether your ticket was nonrefundable when purchased. Many airlines, such as Delta, are providing full refunds if the airline canceled your flight. JetBlue is waiving all change and cancellation fees for customers scheduled to travel March 10, 2020, through April 30, 2020.
Las Vegas–based dermatologist H.L. Greenberg, MD, was satisfied with the credit he received from Southwest Airlines after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) canceled its Denver meeting. He and his staff were looking forward to the gathering, but he noted that the meeting would likely have been limited, even if it had take place as scheduled.
“I am disappointed that I won’t be able to meet with colleagues and industry to explore what the latest advances and interests are in dermatology,” he said. “Because many academic institutions were forbidding their faculty from traveling, the content of the meeting was going to be severely diminished. It’s just a rough time for everyone.”
Meanwhile, Asa Radix, MD, PhD, a New York–based internist, received a full refund for his Amtrak ticket to Boston when the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) scheduled for early March was converted to a virtual meeting. Dr. Radix, senior director of research and education at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York, left another meeting in Brazil early to get to the Boston conference, he said.
“I was packed, but really that was a minor inconvenience,” he said in an interview. “I appreciate that they prioritized health concerns and changed to a virtual meeting. I received full refunds, no issues whatsoever. [It was] really great since I had no travel insurance.”
Check with your individual airline or train line for information about ticket refunds and credits. Many airlines are currently making special accommodations because of COVID-19. If your flight was covered by trip insurance, also called travel assistance, you are generally protected against unforeseen financial losses such as cancellations. The U.S. Department of Transportation provides this general online resource about airline refunds.
Hotel refunds probable
Most meeting organizations who have made the decision to cancel or postpone a conference also have canceled block hotel reservations reserved for the meeting. Medical associations are not directly refunding the hotel costs, but the majority of hotels are refunding reservations with no questions asked. Physicians interviewed for this story all reported no trouble getting refunds for their hotel reservations. However, attendees who did not book a hotel in official housing blocks should contact the hotel directly to cancel.
What about registration fees?
In response to COVID-19 cancellations, most conference leaders are refunding registration fees in full for both attendees and exhibitors. The refund may not be automatic, some associations such as ACP and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state it may take up to 45 days for the funds to be credited, depending on the payment used.
If the conference you planned to attend was postponed, the registration fee may be assigned to the new meeting dates and the money may not be refunded. Registration fees for the Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium, for example, delayed until an unconfirmed date, and for the European Association of Urology (EAU) meeting, postponed until July, will be automatically credited to the rescheduled meeting, according to the websites. If attendees cannot attend the rescheduled EAU meeting, the association will not provide a refund and the registration will not apply to the 2021 meeting, according to its website. However, the group is providing registrants with a free access code for the EAU20 Resource Centre, which contains websites of sessions and scientific content.
A number of physicians have expressed disappointment with the EAU’s postponement on social media. On Twitter, some doctors wrote that the rescheduled dates were bad timing, while others lamented the refund refusal.
The EAU said it regrets that some delegates will experience financial losses, but that the organization has already experienced a significant outlay that cannot be recovered including venue, logistics, travel, and accommodation costs.
"We are doing what we can to absorb costs, but we need to be realistic about what is affordable; should the organization have to refund all or even most registrations, it would significantly jeopardize the viability of the organization," the EAU said in a statement. "These are difficult times, not only for the EAU, but on a global scale. Where there are specific cases of hardship or very extenuating financial circumstances, we will be willing to review individual cases. So far, we believe that we have done what we can do to meet the conflicting demands presented by the postponement of the congress, but this is a situation which changes from day to day, and we need to continuously evaluate what might be the best course of action." *
Contact your medical association directly for details on postponements.
What if I’m a presenter?
In an attempt to save the hard work and time that planners and presenters have invested into now-canceled meetings, some conferences are moving to a digital format. The Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) was the first to convert its in-person conference to a virtual meeting, held from March 8 to 11, 2020. At-home attendees logged onto CROI’s digital platform to hear plenaries, oral abstracts, themed discussion sessions, and symposia.
Dr. Radix was one of many CROI speakers who changed his presentation on HIV prevalence among transgender men to a virtual format.
“We were provided with detailed instructions from CROI about how to do this,” said Dr. Radix, who tweeted about the experience. “For my presentation, I used the video option in PowerPoint; it seemed the most straightforward and didn’t require buying additional software. It was fairly easy to follow the instructions to create the video but it was disappointing to present to an empty room.”
Matthew Spinelli, MD, an HIV researcher with the University of California, San Francisco, who also presented virtually, said it was remarkable that CROI leaders were able to put together the virtual program in such a short time. He delivered his presentation on the accuracy of a real-time urine tenofovir test using PowerPoint and a podcast microphone.
“It seemed to work pretty well,” he said in an interview. “It’s not the same as being there in person, there’s a lot of networking and chance conversations that happen when you’re all in the same place, but it was the right decision to cancel. If I have to be at home or at work doing social distancing, this was the best possible way of doing it.”
Following in CROI’s footsteps, the National Kidney Foundation’s spring conference has moved to a live virtual conference. The 2020 Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) global health conference also will move to a digital format. Other societies are considering similar virtual options. Check with your meeting website for more details on digital options and attendee access.
*The article was updated on 03/16/2020.
Khadija Hafidh, MD, was already booked on a 14-hour, direct flight from Dubai to Los Angeles, when the American College of Physicians (ACP) announced it was canceling its internal medicine meeting scheduled for April.
Canceling her hotel reservation was not a problem, and she was assured a refund for the conference fee, but her airline ticket was another matter, said Dr. Hafidh, an internist and diabetologist with the Dubai Health Authority.
“The airline I booked my ticket with is willing to waive the change fees, but will deduct a cancellation fee if I choose not to take the trip,” Dr. Hafidh said in an interview. “The cancellation fees is $300. A bit steep I must admit.”
Dr. Hafidh now faces a dilemma: Lose the $300 and cancel, or change her flight dates to June for the American Diabetes Association meeting in Chicago.
“But then again, we aren’t sure if that meeting will take place,” Dr. Hafidh said. “A few weeks ago I thought this whole thing was just a storm in a tea cup. However when it was declared a pandemic yesterday, it brought about another dimension.”
More than 25 medical meetings and conferences across the globe have been canceled or postponed because of COVID-19 concerns. The sudden cancellations have caused reservation woes and travel headaches for thousands of physicians who planned to attend the meetings. Some societies are considering the idea of virtual conferences, while other associations have scrapped their meetings until next year.
For physicians facing a canceled conference, the most likely question is, what now? Read on for tips and suggestions.
Reservation refunds vary
Refunds on airfare because of conference cancellations differ, depending on the airline and where you were traveling. Some airlines, such as United Airlines, have waived all change fees for tickets issued March 3, 2020, through March 31, 2020, and passengers can change their dates for up to 12 months after the ticket was issued.
Full refunds often depend on whether your ticket was nonrefundable when purchased. Many airlines, such as Delta, are providing full refunds if the airline canceled your flight. JetBlue is waiving all change and cancellation fees for customers scheduled to travel March 10, 2020, through April 30, 2020.
Las Vegas–based dermatologist H.L. Greenberg, MD, was satisfied with the credit he received from Southwest Airlines after the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) canceled its Denver meeting. He and his staff were looking forward to the gathering, but he noted that the meeting would likely have been limited, even if it had take place as scheduled.
“I am disappointed that I won’t be able to meet with colleagues and industry to explore what the latest advances and interests are in dermatology,” he said. “Because many academic institutions were forbidding their faculty from traveling, the content of the meeting was going to be severely diminished. It’s just a rough time for everyone.”
Meanwhile, Asa Radix, MD, PhD, a New York–based internist, received a full refund for his Amtrak ticket to Boston when the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) scheduled for early March was converted to a virtual meeting. Dr. Radix, senior director of research and education at the Callen-Lorde Community Health Center in New York, left another meeting in Brazil early to get to the Boston conference, he said.
“I was packed, but really that was a minor inconvenience,” he said in an interview. “I appreciate that they prioritized health concerns and changed to a virtual meeting. I received full refunds, no issues whatsoever. [It was] really great since I had no travel insurance.”
Check with your individual airline or train line for information about ticket refunds and credits. Many airlines are currently making special accommodations because of COVID-19. If your flight was covered by trip insurance, also called travel assistance, you are generally protected against unforeseen financial losses such as cancellations. The U.S. Department of Transportation provides this general online resource about airline refunds.
Hotel refunds probable
Most meeting organizations who have made the decision to cancel or postpone a conference also have canceled block hotel reservations reserved for the meeting. Medical associations are not directly refunding the hotel costs, but the majority of hotels are refunding reservations with no questions asked. Physicians interviewed for this story all reported no trouble getting refunds for their hotel reservations. However, attendees who did not book a hotel in official housing blocks should contact the hotel directly to cancel.
What about registration fees?
In response to COVID-19 cancellations, most conference leaders are refunding registration fees in full for both attendees and exhibitors. The refund may not be automatic, some associations such as ACP and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists state it may take up to 45 days for the funds to be credited, depending on the payment used.
If the conference you planned to attend was postponed, the registration fee may be assigned to the new meeting dates and the money may not be refunded. Registration fees for the Minimally Invasive Surgery Symposium, for example, delayed until an unconfirmed date, and for the European Association of Urology (EAU) meeting, postponed until July, will be automatically credited to the rescheduled meeting, according to the websites. If attendees cannot attend the rescheduled EAU meeting, the association will not provide a refund and the registration will not apply to the 2021 meeting, according to its website. However, the group is providing registrants with a free access code for the EAU20 Resource Centre, which contains websites of sessions and scientific content.
A number of physicians have expressed disappointment with the EAU’s postponement on social media. On Twitter, some doctors wrote that the rescheduled dates were bad timing, while others lamented the refund refusal.
The EAU said it regrets that some delegates will experience financial losses, but that the organization has already experienced a significant outlay that cannot be recovered including venue, logistics, travel, and accommodation costs.
"We are doing what we can to absorb costs, but we need to be realistic about what is affordable; should the organization have to refund all or even most registrations, it would significantly jeopardize the viability of the organization," the EAU said in a statement. "These are difficult times, not only for the EAU, but on a global scale. Where there are specific cases of hardship or very extenuating financial circumstances, we will be willing to review individual cases. So far, we believe that we have done what we can do to meet the conflicting demands presented by the postponement of the congress, but this is a situation which changes from day to day, and we need to continuously evaluate what might be the best course of action." *
Contact your medical association directly for details on postponements.
What if I’m a presenter?
In an attempt to save the hard work and time that planners and presenters have invested into now-canceled meetings, some conferences are moving to a digital format. The Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) was the first to convert its in-person conference to a virtual meeting, held from March 8 to 11, 2020. At-home attendees logged onto CROI’s digital platform to hear plenaries, oral abstracts, themed discussion sessions, and symposia.
Dr. Radix was one of many CROI speakers who changed his presentation on HIV prevalence among transgender men to a virtual format.
“We were provided with detailed instructions from CROI about how to do this,” said Dr. Radix, who tweeted about the experience. “For my presentation, I used the video option in PowerPoint; it seemed the most straightforward and didn’t require buying additional software. It was fairly easy to follow the instructions to create the video but it was disappointing to present to an empty room.”
Matthew Spinelli, MD, an HIV researcher with the University of California, San Francisco, who also presented virtually, said it was remarkable that CROI leaders were able to put together the virtual program in such a short time. He delivered his presentation on the accuracy of a real-time urine tenofovir test using PowerPoint and a podcast microphone.
“It seemed to work pretty well,” he said in an interview. “It’s not the same as being there in person, there’s a lot of networking and chance conversations that happen when you’re all in the same place, but it was the right decision to cancel. If I have to be at home or at work doing social distancing, this was the best possible way of doing it.”
Following in CROI’s footsteps, the National Kidney Foundation’s spring conference has moved to a live virtual conference. The 2020 Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) global health conference also will move to a digital format. Other societies are considering similar virtual options. Check with your meeting website for more details on digital options and attendee access.
*The article was updated on 03/16/2020.
COVID-19: Older patients with cancer especially vulnerable
For oncologists and other clinicians caring for patients with cancer, the COVID-19 pandemic represents a dynamic clinical challenge that is changing daily and that can feel overwhelming at times, say experts.
“Oncology clinicians are well versed in caring for immunosuppressed patients with cancer, of all ages,” Merry-Jennifer Markham, MD, interim chief of the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Florida Health, Gainesville, told Medscape Medical News.
However, she emphasized that, during this COVID-19 outbreak, “we must be especially diligent about screening for symptoms and exposure, and we must recognize that our older patients with cancer may be especially vulnerable.”
Patients with cancer who are in active treatment are immunosuppressed and are more susceptible to infection and to complications from infection, Markham pointed out. “While we don’t yet have much data on how COVID-19 impacts patients with cancer, I have to suspect that patients undergoing active cancer treatment may be especially vulnerable to the more severe illness associated with COVID-19,” she said.
Indeed, a recent report from China that was published in the Lancet Oncology supports this. The authors suggest that patients with cancer are at higher risk for COVID-19 and have a worse prognosis if they become infected than do those without cancer.
Commonsense rules
Commonsense rules apply for all patients with cancer, regardless of age, said Markham. Measures include thorough handwashing, staying home when sick, and avoiding sick contacts.
Markham, who acts as an expert spokesperson for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, provides information on what patients with cancer need to know about COVID-19 at Cancer.net, the society’s website for patients with cancer.
“Unfortunately, this outbreak of COVID-19 is happening rapidly and in real time,” Markham noted. “The entire medical community is learning as we go, rather than having the luxury of years of evidence-based literature to guide us.”
Another expert agrees. “Unfortunately, there are not a lot of data on how COVID-19 affects cancer patients,” Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, director of Quality for Cancer Services in the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, said in an interview.
“We need to minimize the risk for patients and minimize our own exposure by treating this situation like we would a really bad flu season,” Smith told Medscape Medical News. “Some patients have had a bad outcome, but the vast majority do not. The best we can do is stay calm and focused.”
At Mount Sinai, for patients with cancer, routine, nonurgent appointments are being rescheduled for May, Smith said. Those in active treatment are screened by telephone 24 to 48 hours before arrival, after which they undergo a full risk assessment in an isolation room. Those with a respiratory infection are given a mask.
“Patients are very anxious and worried about COVID-19,” said Smith, who has young children and an elderly parent at home. “We don’t have all the answers, and this can heighten anxiety.”
To help allay fears, social workers are asking patients with cancer who express anxiety to discuss their concerns and provide information. A one-page handout on both flu and COVID-10 is available in the waiting room.
The Web portal MyChart gives patients access to updated information on COVID-19 precautions and provides links to the hospital website and to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Patients who are not feeling well can speak to someone or get answers if they have additional questions.
When counseling patients, Smith advises them to use “an abundance of caution” and to be creative in efforts to minimize risk. “My suggestion is to use FaceTime and Skype to connect and communicate with your community,” she said.
Some churches are conducting services via teleconferencing to minimize risk, and seniors’ centers that offer yoga and other classes are also beginning to provide services virtually, she pointed out.
Data from China
A report published February 14 in the Lancet Oncology appears to be the first analysis in the literature to focus on COVID-19 in patients with cancer.
“Patients with cancer are more susceptible to infection than individuals without cancer because of their systemic immunosuppressive state caused by the malignancy and anticancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or surgery,” write the authors, led by Wenhua Liang, MD, of Guangzhou Medical University. However, in correspondence published in the Lancet Oncology, other experts in China question some of Liang’s and colleagues’ findings.
The report by Liang and colleagues concerns a prospective cohort of 1590 patients with COVID-19.
There were 2007 laboratory-confirmed cases of COVID-19 among patients admitted to 575 hospitals throughout China as of January 31. Of those cases, 417 were excluded from the analysis because of insufficient information regarding disease history.
The team reports that of 18 patients with cancer and COVID-19, 39% were at significantly higher risk for “severe events.” By comparison, of 1572 patients with COVID-19 who did not have cancer, 8% were at significantly higher risk (P = .0003). These events included rapid clinical deterioration that required admission to intensive care; invasive ventilation; or death.
Patients with cancer experienced a much more rapid deterioration in clinical status than did those without cancer. The median time to severe events was 13 days, vs 43 days (hazard ratio [HR] adjusted for age, 3.56; P < .0001).
The analysis also shows that patients who underwent chemotherapy or surgery in the past month had a 75% risk of experiencing clinically severe events, compared with a 43% risk for those who had not received recent treatment.
After adjusting for other risk factors, including age and smoking history, older age was the only risk factor for severe events (odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.97 – 2.12; P = .072), the study authors say.
Patients with lung cancer did not have a higher probability of severe events compared with patients with other cancer types (20% vs 62%, respectively; P = .294).
Liang and colleagues conclude that these findings provide “a timely reminder to physicians that more intensive attention should be paid to patients with cancer, in case of rapid deterioration.”
The team also proposes three strategies for managing patients with cancer who are at risk for COVID-19 or any other severe infectious disease. They recommend that intentional postponement of adjuvant chemotherapy or elective surgery be considered for patients with stable cancer who live in areas where disease is endemic. Stronger “personal protection provisions” could also be made for patients with cancer or for cancer survivors. Lastly, for patients with cancer who have COVID-19, especially those who are older or who have comorbidities, more intensive surveillance or treatment should be considered.
However, in comments in the Lancet Oncology, other authors in China say these findings should be interpreted with caution.
One group suggests that the increased susceptibility to COVID-19 in patients with cancer could be the result of higher rates of smoking compared with patients who did not have cancer. “Overall, current evidence remains insufficient to explain a conclusive association between cancer and COVID-19,” say Huahao Shen, PhD, of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, and colleagues.
Another group suggests that the significantly higher median age of patients with cancer compared with noncancer patients (63 years vs 49 years) may have contributed to poor prognosis.
These authors, led by Li Zhang, MD, PhD, and Hanping Wang, MD, of Peking Union Medical College and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, emphasize that patients with cancer need online medical counseling and that critical cases need to be identified and treated.
“In endemic areas outside Wuhan, decisions on whether or not to postpone cancer treatment need to made on a patient-by-patient basis and according to the risk to the patient and the prevailing situation because delays could lead to tumor progression and ultimately poorer outcomes,” they write.
The study was funded by the China National Science Foundation and the Key Project of Guangzhou Scientific Research Project. Liang and coauthors, Shen and coauthors, Zhang, Wang, and Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Markham has relationships with Aduro Biotech, Lilly, Tesaro, Novartis, and VBL Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For oncologists and other clinicians caring for patients with cancer, the COVID-19 pandemic represents a dynamic clinical challenge that is changing daily and that can feel overwhelming at times, say experts.
“Oncology clinicians are well versed in caring for immunosuppressed patients with cancer, of all ages,” Merry-Jennifer Markham, MD, interim chief of the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Florida Health, Gainesville, told Medscape Medical News.
However, she emphasized that, during this COVID-19 outbreak, “we must be especially diligent about screening for symptoms and exposure, and we must recognize that our older patients with cancer may be especially vulnerable.”
Patients with cancer who are in active treatment are immunosuppressed and are more susceptible to infection and to complications from infection, Markham pointed out. “While we don’t yet have much data on how COVID-19 impacts patients with cancer, I have to suspect that patients undergoing active cancer treatment may be especially vulnerable to the more severe illness associated with COVID-19,” she said.
Indeed, a recent report from China that was published in the Lancet Oncology supports this. The authors suggest that patients with cancer are at higher risk for COVID-19 and have a worse prognosis if they become infected than do those without cancer.
Commonsense rules
Commonsense rules apply for all patients with cancer, regardless of age, said Markham. Measures include thorough handwashing, staying home when sick, and avoiding sick contacts.
Markham, who acts as an expert spokesperson for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, provides information on what patients with cancer need to know about COVID-19 at Cancer.net, the society’s website for patients with cancer.
“Unfortunately, this outbreak of COVID-19 is happening rapidly and in real time,” Markham noted. “The entire medical community is learning as we go, rather than having the luxury of years of evidence-based literature to guide us.”
Another expert agrees. “Unfortunately, there are not a lot of data on how COVID-19 affects cancer patients,” Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, director of Quality for Cancer Services in the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, said in an interview.
“We need to minimize the risk for patients and minimize our own exposure by treating this situation like we would a really bad flu season,” Smith told Medscape Medical News. “Some patients have had a bad outcome, but the vast majority do not. The best we can do is stay calm and focused.”
At Mount Sinai, for patients with cancer, routine, nonurgent appointments are being rescheduled for May, Smith said. Those in active treatment are screened by telephone 24 to 48 hours before arrival, after which they undergo a full risk assessment in an isolation room. Those with a respiratory infection are given a mask.
“Patients are very anxious and worried about COVID-19,” said Smith, who has young children and an elderly parent at home. “We don’t have all the answers, and this can heighten anxiety.”
To help allay fears, social workers are asking patients with cancer who express anxiety to discuss their concerns and provide information. A one-page handout on both flu and COVID-10 is available in the waiting room.
The Web portal MyChart gives patients access to updated information on COVID-19 precautions and provides links to the hospital website and to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Patients who are not feeling well can speak to someone or get answers if they have additional questions.
When counseling patients, Smith advises them to use “an abundance of caution” and to be creative in efforts to minimize risk. “My suggestion is to use FaceTime and Skype to connect and communicate with your community,” she said.
Some churches are conducting services via teleconferencing to minimize risk, and seniors’ centers that offer yoga and other classes are also beginning to provide services virtually, she pointed out.
Data from China
A report published February 14 in the Lancet Oncology appears to be the first analysis in the literature to focus on COVID-19 in patients with cancer.
“Patients with cancer are more susceptible to infection than individuals without cancer because of their systemic immunosuppressive state caused by the malignancy and anticancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or surgery,” write the authors, led by Wenhua Liang, MD, of Guangzhou Medical University. However, in correspondence published in the Lancet Oncology, other experts in China question some of Liang’s and colleagues’ findings.
The report by Liang and colleagues concerns a prospective cohort of 1590 patients with COVID-19.
There were 2007 laboratory-confirmed cases of COVID-19 among patients admitted to 575 hospitals throughout China as of January 31. Of those cases, 417 were excluded from the analysis because of insufficient information regarding disease history.
The team reports that of 18 patients with cancer and COVID-19, 39% were at significantly higher risk for “severe events.” By comparison, of 1572 patients with COVID-19 who did not have cancer, 8% were at significantly higher risk (P = .0003). These events included rapid clinical deterioration that required admission to intensive care; invasive ventilation; or death.
Patients with cancer experienced a much more rapid deterioration in clinical status than did those without cancer. The median time to severe events was 13 days, vs 43 days (hazard ratio [HR] adjusted for age, 3.56; P < .0001).
The analysis also shows that patients who underwent chemotherapy or surgery in the past month had a 75% risk of experiencing clinically severe events, compared with a 43% risk for those who had not received recent treatment.
After adjusting for other risk factors, including age and smoking history, older age was the only risk factor for severe events (odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.97 – 2.12; P = .072), the study authors say.
Patients with lung cancer did not have a higher probability of severe events compared with patients with other cancer types (20% vs 62%, respectively; P = .294).
Liang and colleagues conclude that these findings provide “a timely reminder to physicians that more intensive attention should be paid to patients with cancer, in case of rapid deterioration.”
The team also proposes three strategies for managing patients with cancer who are at risk for COVID-19 or any other severe infectious disease. They recommend that intentional postponement of adjuvant chemotherapy or elective surgery be considered for patients with stable cancer who live in areas where disease is endemic. Stronger “personal protection provisions” could also be made for patients with cancer or for cancer survivors. Lastly, for patients with cancer who have COVID-19, especially those who are older or who have comorbidities, more intensive surveillance or treatment should be considered.
However, in comments in the Lancet Oncology, other authors in China say these findings should be interpreted with caution.
One group suggests that the increased susceptibility to COVID-19 in patients with cancer could be the result of higher rates of smoking compared with patients who did not have cancer. “Overall, current evidence remains insufficient to explain a conclusive association between cancer and COVID-19,” say Huahao Shen, PhD, of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, and colleagues.
Another group suggests that the significantly higher median age of patients with cancer compared with noncancer patients (63 years vs 49 years) may have contributed to poor prognosis.
These authors, led by Li Zhang, MD, PhD, and Hanping Wang, MD, of Peking Union Medical College and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, emphasize that patients with cancer need online medical counseling and that critical cases need to be identified and treated.
“In endemic areas outside Wuhan, decisions on whether or not to postpone cancer treatment need to made on a patient-by-patient basis and according to the risk to the patient and the prevailing situation because delays could lead to tumor progression and ultimately poorer outcomes,” they write.
The study was funded by the China National Science Foundation and the Key Project of Guangzhou Scientific Research Project. Liang and coauthors, Shen and coauthors, Zhang, Wang, and Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Markham has relationships with Aduro Biotech, Lilly, Tesaro, Novartis, and VBL Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For oncologists and other clinicians caring for patients with cancer, the COVID-19 pandemic represents a dynamic clinical challenge that is changing daily and that can feel overwhelming at times, say experts.
“Oncology clinicians are well versed in caring for immunosuppressed patients with cancer, of all ages,” Merry-Jennifer Markham, MD, interim chief of the Division of Hematology and Oncology at the University of Florida Health, Gainesville, told Medscape Medical News.
However, she emphasized that, during this COVID-19 outbreak, “we must be especially diligent about screening for symptoms and exposure, and we must recognize that our older patients with cancer may be especially vulnerable.”
Patients with cancer who are in active treatment are immunosuppressed and are more susceptible to infection and to complications from infection, Markham pointed out. “While we don’t yet have much data on how COVID-19 impacts patients with cancer, I have to suspect that patients undergoing active cancer treatment may be especially vulnerable to the more severe illness associated with COVID-19,” she said.
Indeed, a recent report from China that was published in the Lancet Oncology supports this. The authors suggest that patients with cancer are at higher risk for COVID-19 and have a worse prognosis if they become infected than do those without cancer.
Commonsense rules
Commonsense rules apply for all patients with cancer, regardless of age, said Markham. Measures include thorough handwashing, staying home when sick, and avoiding sick contacts.
Markham, who acts as an expert spokesperson for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, provides information on what patients with cancer need to know about COVID-19 at Cancer.net, the society’s website for patients with cancer.
“Unfortunately, this outbreak of COVID-19 is happening rapidly and in real time,” Markham noted. “The entire medical community is learning as we go, rather than having the luxury of years of evidence-based literature to guide us.”
Another expert agrees. “Unfortunately, there are not a lot of data on how COVID-19 affects cancer patients,” Cardinale Smith, MD, PhD, director of Quality for Cancer Services in the Mount Sinai Health System, New York City, said in an interview.
“We need to minimize the risk for patients and minimize our own exposure by treating this situation like we would a really bad flu season,” Smith told Medscape Medical News. “Some patients have had a bad outcome, but the vast majority do not. The best we can do is stay calm and focused.”
At Mount Sinai, for patients with cancer, routine, nonurgent appointments are being rescheduled for May, Smith said. Those in active treatment are screened by telephone 24 to 48 hours before arrival, after which they undergo a full risk assessment in an isolation room. Those with a respiratory infection are given a mask.
“Patients are very anxious and worried about COVID-19,” said Smith, who has young children and an elderly parent at home. “We don’t have all the answers, and this can heighten anxiety.”
To help allay fears, social workers are asking patients with cancer who express anxiety to discuss their concerns and provide information. A one-page handout on both flu and COVID-10 is available in the waiting room.
The Web portal MyChart gives patients access to updated information on COVID-19 precautions and provides links to the hospital website and to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Patients who are not feeling well can speak to someone or get answers if they have additional questions.
When counseling patients, Smith advises them to use “an abundance of caution” and to be creative in efforts to minimize risk. “My suggestion is to use FaceTime and Skype to connect and communicate with your community,” she said.
Some churches are conducting services via teleconferencing to minimize risk, and seniors’ centers that offer yoga and other classes are also beginning to provide services virtually, she pointed out.
Data from China
A report published February 14 in the Lancet Oncology appears to be the first analysis in the literature to focus on COVID-19 in patients with cancer.
“Patients with cancer are more susceptible to infection than individuals without cancer because of their systemic immunosuppressive state caused by the malignancy and anticancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or surgery,” write the authors, led by Wenhua Liang, MD, of Guangzhou Medical University. However, in correspondence published in the Lancet Oncology, other experts in China question some of Liang’s and colleagues’ findings.
The report by Liang and colleagues concerns a prospective cohort of 1590 patients with COVID-19.
There were 2007 laboratory-confirmed cases of COVID-19 among patients admitted to 575 hospitals throughout China as of January 31. Of those cases, 417 were excluded from the analysis because of insufficient information regarding disease history.
The team reports that of 18 patients with cancer and COVID-19, 39% were at significantly higher risk for “severe events.” By comparison, of 1572 patients with COVID-19 who did not have cancer, 8% were at significantly higher risk (P = .0003). These events included rapid clinical deterioration that required admission to intensive care; invasive ventilation; or death.
Patients with cancer experienced a much more rapid deterioration in clinical status than did those without cancer. The median time to severe events was 13 days, vs 43 days (hazard ratio [HR] adjusted for age, 3.56; P < .0001).
The analysis also shows that patients who underwent chemotherapy or surgery in the past month had a 75% risk of experiencing clinically severe events, compared with a 43% risk for those who had not received recent treatment.
After adjusting for other risk factors, including age and smoking history, older age was the only risk factor for severe events (odds ratio [OR], 1.43; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.97 – 2.12; P = .072), the study authors say.
Patients with lung cancer did not have a higher probability of severe events compared with patients with other cancer types (20% vs 62%, respectively; P = .294).
Liang and colleagues conclude that these findings provide “a timely reminder to physicians that more intensive attention should be paid to patients with cancer, in case of rapid deterioration.”
The team also proposes three strategies for managing patients with cancer who are at risk for COVID-19 or any other severe infectious disease. They recommend that intentional postponement of adjuvant chemotherapy or elective surgery be considered for patients with stable cancer who live in areas where disease is endemic. Stronger “personal protection provisions” could also be made for patients with cancer or for cancer survivors. Lastly, for patients with cancer who have COVID-19, especially those who are older or who have comorbidities, more intensive surveillance or treatment should be considered.
However, in comments in the Lancet Oncology, other authors in China say these findings should be interpreted with caution.
One group suggests that the increased susceptibility to COVID-19 in patients with cancer could be the result of higher rates of smoking compared with patients who did not have cancer. “Overall, current evidence remains insufficient to explain a conclusive association between cancer and COVID-19,” say Huahao Shen, PhD, of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, and colleagues.
Another group suggests that the significantly higher median age of patients with cancer compared with noncancer patients (63 years vs 49 years) may have contributed to poor prognosis.
These authors, led by Li Zhang, MD, PhD, and Hanping Wang, MD, of Peking Union Medical College and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, emphasize that patients with cancer need online medical counseling and that critical cases need to be identified and treated.
“In endemic areas outside Wuhan, decisions on whether or not to postpone cancer treatment need to made on a patient-by-patient basis and according to the risk to the patient and the prevailing situation because delays could lead to tumor progression and ultimately poorer outcomes,” they write.
The study was funded by the China National Science Foundation and the Key Project of Guangzhou Scientific Research Project. Liang and coauthors, Shen and coauthors, Zhang, Wang, and Smith have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Markham has relationships with Aduro Biotech, Lilly, Tesaro, Novartis, and VBL Therapeutics.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Health professionals fight against COVID-19 myths and misinformation
Misinformation about the COVID-19 travels faster than the virus and complicates the job of doctors who are treating those infected and responding to concerns of their other patients.
An array of myths springing up around this disease can be found on the Internet. The main themes appear to be false narratives about the origin of the virus, the size of the outbreak in the United States and in other countries, the availability of cures and treatments, and ways to prevent infection. Widespread misinformation hampers public health efforts to control the disease outbreak, confuses the public, and requires medical professionals to spend time refuting myths and re-educating patients.
A group of infectious disease experts became so alarmed by the misinformation trend they published a statement in The Lancet decrying the spread of false statements being circulated by some media outlets. “The rapid, open, and transparent sharing of data on this outbreak is now being threatened by rumours and misinformation ... Conspiracy theories do nothing but create fear, rumours, and prejudice that jeopardise our global collaboration in the fight against this virus,” wrote Charles H. Calisher, PhD, of Colorado State University, Fort Collins, and colleagues.
What can physicians do to counter misinformation?
Pulmonologist and critical care physician Cedric “Jamie” Rutland, MD, who practices in Riverside, Calif., sees misinformation about the novel coronavirus every day at home and on the job. His patients worry that everyone who gets infected will die or end up in the ICU. His neighbors ask him to pilfer surgical masks to protect them from the false notion that Chinese people in their community posed some kind of COVID-19 risk.
As he pondered how to counter myths with facts, Dr. Rutland turned to an unusual resource: His 7-year-old daughter Amelia. He explained to her how COVID-19 works and found that she could easily understand the basics. Now, Dr. Rutland draws upon the lessons from chats with his daughter as he explains COVID-19 to his patient audience on his YouTube channel “Medicine Deconstructed.” Simplicity, but not too much simplicity, is key, he said. Dr. Rutland uses a visual aid – a rough drawing of a virus – and shows how inflammation and antibodies enter the picture after infection. “I just teach them that if you’re a healthy person, this is how the body works, and this is what the immune system will do,” he said. “For the most part, you can calm people down when you make time for education.”
What are best practices? In a series of interviews, specialists emphasized the importance of fact-finding, wide-ranging communication, and – perhaps most difficult of all – humility.
Dr. Rutland emphasizes thoughtful communication based on facts and humility when communicating to patients about this potential health risk. “A lot of people finish medical school and think, ‘Everyone should trust me because I’m the pulmonologist or the GI doc.’ That’s not how it works. You still have to earn people’s trust,” he said.
Make sure all staff get reliable information
Hospitals are scrambling to keep staff safe with up-to-date directives and debunk false narratives about the virus. Keeping all hospital staff informed with verified and authoritative facts about the coronavirus is a key objective of the Massachusetts General Hospital’s Center for Disaster Medicine. The Center’s coronavirus educational materials are distributed to all staffers from physicians to janitors. “These provide information that they need to understand the risks and keep themselves safe,” said Eileen Searle, PhD, the Biothreats Clinical Operations program manager in the CDM.
According to Dr. Searle, the hospital keeps a continually updated COVID-19 Frequently Asked Questions document in its internal computer system. All employees can access it, she said, and it’s updated to include questions as they come up.
Even valets and front-desk volunteers are encouraged to read the FAQ, she said, since “they’re the first people that family and patients are interacting with.” The document “gives them reassurance about delivering messages,” she said.
Use patience with your patients
Dr. Rutland urges colleagues to take the time to listen to patients and educate them. “Reduce the gap between you and them,” said Dr. Rutland, who treats patients in Orange and Riverside counties. “Take off your white coat, sit down, and talk to the person about their concerns.”
Boston cardiologist Haider Warraich, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said it’s important to “put medical information into a greater human context.” For example, he has told patients that he’s still taking his daughter to school despite COVID-19 risks. “I take the information I provide and apply it to my own life,” he said.
The Washington State Department of Health offers this advice to physicians to counter false information and stigma: “Stay updated and informed on COVID-19 to avoid miscommunication or inaccurate information. Talk openly about the harm of stigma. View people directly impacted by stigma as people first. Be conscious of your language. Acknowledge access and language barriers.”
Speak out on social media – but don’t fight
Should medical professionals speak out about COVID-19 misinformation via social media? It’s an individual decision, Dr. Warraich said, “but my sense is that it’s never been more important for physicians to be part of the fray and help quell the epidemic of misinformation that almost always follows any type of medial calamity.”
Dr. Rutland, vice president and founding member of the Association for Healthcare Social Media, cautioned that effective communication via social media requires care. Avoid confrontation, he advised. “Don’t call people stupid or say things like, ‘I went to medical school and I’m smarter than you.’ ”
Instead, he said, “it’s important to just state the facts: These are the people who are dying, these are the people who are getting infected.”
And, he added, remember to push the most important message of all: Wash your hands!
Public health organizations fight the ‘infodemic’
In a trend that hearkens back to the days of snake oil cures for all maladies, advertisements for fake treatments are popping up on the Internet and on other media.
Facebook and Amazon have acted to remove these ads but these messages continue to flood social media such as Twitter, WhatsApp, and other sites. Discussion groups on platforms such as Reddit continue to pump out misinformation about COVID-19. Conspiracy theories that link the virus to espionage and bioweapons are making the rounds on the Internet and talk radio. Wrong information about the effectiveness of non-N95 face masks to protect wearers against infection is widespread, leading to shortages for medical personnel and price gouging. Pernicious rumors about the effectiveness of substances such a vinegar, silver, garlic, lemon juice, and even vodka to disinfect hands and surfaces abound on the Internet. An especially dangerous stream of misinformation stigmatizes ethnic groups and individuals as sources of the infection.
The World Health Organization identified early in the COVID-19 outbreak the global wave of misinformation about the virus and dubbed the problem the “infodemic.” The WHO “Q & A” page on COVID-19 is updated frequently and addresses myths and rumors currently circulating.
According to the WHO website, the agency has reached out to social media players such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Pinterest, TikTok, and Weibo, the microblogging site in China. WHO has worked with these sites to curb the “infodemic” of misinformation and has used these sites for public education outreach on COVID-19. “Myth busting” infographics posted on a WHO web page are also reposted on major social media sites.
The CDC has followed with its own “frequently asked questions” page to address questions and rumors. State health agencies have put up COVID-19 pages to address public concerns and offer advice on prevention. The Maryland Department of Health web page directly addresses dangerous misinformation: “Do not stigmatize people of any specific ethnicities or racial background. Viruses do not target people from specific populations, ethnicities or racial backgrounds. Stay informed and seek information from reliable, official sources. Be wary of myths, rumors and misinformation circulating online and elsewhere. Health information shared through social media is frequently inaccurate, unless coming from an official, reliable source such as the CDC, MDH or local health departments.”
The Washington State Department of Health has taken a more assertive stance on stigma. The COVID-19 web page recommends to the public: “Show compassion and support for individuals and communities more closely impacted. Avoid stigmatizing people who are in quarantine. They are making the right choice for their communities. Do not make assumptions about someone’s health status based on their ethnicity, race or national origin.”
Misinformation about the COVID-19 travels faster than the virus and complicates the job of doctors who are treating those infected and responding to concerns of their other patients.
An array of myths springing up around this disease can be found on the Internet. The main themes appear to be false narratives about the origin of the virus, the size of the outbreak in the United States and in other countries, the availability of cures and treatments, and ways to prevent infection. Widespread misinformation hampers public health efforts to control the disease outbreak, confuses the public, and requires medical professionals to spend time refuting myths and re-educating patients.
A group of infectious disease experts became so alarmed by the misinformation trend they published a statement in The Lancet decrying the spread of false statements being circulated by some media outlets. “The rapid, open, and transparent sharing of data on this outbreak is now being threatened by rumours and misinformation ... Conspiracy theories do nothing but create fear, rumours, and prejudice that jeopardise our global collaboration in the fight against this virus,” wrote Charles H. Calisher, PhD, of Colorado State University, Fort Collins, and colleagues.
What can physicians do to counter misinformation?
Pulmonologist and critical care physician Cedric “Jamie” Rutland, MD, who practices in Riverside, Calif., sees misinformation about the novel coronavirus every day at home and on the job. His patients worry that everyone who gets infected will die or end up in the ICU. His neighbors ask him to pilfer surgical masks to protect them from the false notion that Chinese people in their community posed some kind of COVID-19 risk.
As he pondered how to counter myths with facts, Dr. Rutland turned to an unusual resource: His 7-year-old daughter Amelia. He explained to her how COVID-19 works and found that she could easily understand the basics. Now, Dr. Rutland draws upon the lessons from chats with his daughter as he explains COVID-19 to his patient audience on his YouTube channel “Medicine Deconstructed.” Simplicity, but not too much simplicity, is key, he said. Dr. Rutland uses a visual aid – a rough drawing of a virus – and shows how inflammation and antibodies enter the picture after infection. “I just teach them that if you’re a healthy person, this is how the body works, and this is what the immune system will do,” he said. “For the most part, you can calm people down when you make time for education.”
What are best practices? In a series of interviews, specialists emphasized the importance of fact-finding, wide-ranging communication, and – perhaps most difficult of all – humility.
Dr. Rutland emphasizes thoughtful communication based on facts and humility when communicating to patients about this potential health risk. “A lot of people finish medical school and think, ‘Everyone should trust me because I’m the pulmonologist or the GI doc.’ That’s not how it works. You still have to earn people’s trust,” he said.
Make sure all staff get reliable information
Hospitals are scrambling to keep staff safe with up-to-date directives and debunk false narratives about the virus. Keeping all hospital staff informed with verified and authoritative facts about the coronavirus is a key objective of the Massachusetts General Hospital’s Center for Disaster Medicine. The Center’s coronavirus educational materials are distributed to all staffers from physicians to janitors. “These provide information that they need to understand the risks and keep themselves safe,” said Eileen Searle, PhD, the Biothreats Clinical Operations program manager in the CDM.
According to Dr. Searle, the hospital keeps a continually updated COVID-19 Frequently Asked Questions document in its internal computer system. All employees can access it, she said, and it’s updated to include questions as they come up.
Even valets and front-desk volunteers are encouraged to read the FAQ, she said, since “they’re the first people that family and patients are interacting with.” The document “gives them reassurance about delivering messages,” she said.
Use patience with your patients
Dr. Rutland urges colleagues to take the time to listen to patients and educate them. “Reduce the gap between you and them,” said Dr. Rutland, who treats patients in Orange and Riverside counties. “Take off your white coat, sit down, and talk to the person about their concerns.”
Boston cardiologist Haider Warraich, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said it’s important to “put medical information into a greater human context.” For example, he has told patients that he’s still taking his daughter to school despite COVID-19 risks. “I take the information I provide and apply it to my own life,” he said.
The Washington State Department of Health offers this advice to physicians to counter false information and stigma: “Stay updated and informed on COVID-19 to avoid miscommunication or inaccurate information. Talk openly about the harm of stigma. View people directly impacted by stigma as people first. Be conscious of your language. Acknowledge access and language barriers.”
Speak out on social media – but don’t fight
Should medical professionals speak out about COVID-19 misinformation via social media? It’s an individual decision, Dr. Warraich said, “but my sense is that it’s never been more important for physicians to be part of the fray and help quell the epidemic of misinformation that almost always follows any type of medial calamity.”
Dr. Rutland, vice president and founding member of the Association for Healthcare Social Media, cautioned that effective communication via social media requires care. Avoid confrontation, he advised. “Don’t call people stupid or say things like, ‘I went to medical school and I’m smarter than you.’ ”
Instead, he said, “it’s important to just state the facts: These are the people who are dying, these are the people who are getting infected.”
And, he added, remember to push the most important message of all: Wash your hands!
Public health organizations fight the ‘infodemic’
In a trend that hearkens back to the days of snake oil cures for all maladies, advertisements for fake treatments are popping up on the Internet and on other media.
Facebook and Amazon have acted to remove these ads but these messages continue to flood social media such as Twitter, WhatsApp, and other sites. Discussion groups on platforms such as Reddit continue to pump out misinformation about COVID-19. Conspiracy theories that link the virus to espionage and bioweapons are making the rounds on the Internet and talk radio. Wrong information about the effectiveness of non-N95 face masks to protect wearers against infection is widespread, leading to shortages for medical personnel and price gouging. Pernicious rumors about the effectiveness of substances such a vinegar, silver, garlic, lemon juice, and even vodka to disinfect hands and surfaces abound on the Internet. An especially dangerous stream of misinformation stigmatizes ethnic groups and individuals as sources of the infection.
The World Health Organization identified early in the COVID-19 outbreak the global wave of misinformation about the virus and dubbed the problem the “infodemic.” The WHO “Q & A” page on COVID-19 is updated frequently and addresses myths and rumors currently circulating.
According to the WHO website, the agency has reached out to social media players such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Pinterest, TikTok, and Weibo, the microblogging site in China. WHO has worked with these sites to curb the “infodemic” of misinformation and has used these sites for public education outreach on COVID-19. “Myth busting” infographics posted on a WHO web page are also reposted on major social media sites.
The CDC has followed with its own “frequently asked questions” page to address questions and rumors. State health agencies have put up COVID-19 pages to address public concerns and offer advice on prevention. The Maryland Department of Health web page directly addresses dangerous misinformation: “Do not stigmatize people of any specific ethnicities or racial background. Viruses do not target people from specific populations, ethnicities or racial backgrounds. Stay informed and seek information from reliable, official sources. Be wary of myths, rumors and misinformation circulating online and elsewhere. Health information shared through social media is frequently inaccurate, unless coming from an official, reliable source such as the CDC, MDH or local health departments.”
The Washington State Department of Health has taken a more assertive stance on stigma. The COVID-19 web page recommends to the public: “Show compassion and support for individuals and communities more closely impacted. Avoid stigmatizing people who are in quarantine. They are making the right choice for their communities. Do not make assumptions about someone’s health status based on their ethnicity, race or national origin.”
Misinformation about the COVID-19 travels faster than the virus and complicates the job of doctors who are treating those infected and responding to concerns of their other patients.
An array of myths springing up around this disease can be found on the Internet. The main themes appear to be false narratives about the origin of the virus, the size of the outbreak in the United States and in other countries, the availability of cures and treatments, and ways to prevent infection. Widespread misinformation hampers public health efforts to control the disease outbreak, confuses the public, and requires medical professionals to spend time refuting myths and re-educating patients.
A group of infectious disease experts became so alarmed by the misinformation trend they published a statement in The Lancet decrying the spread of false statements being circulated by some media outlets. “The rapid, open, and transparent sharing of data on this outbreak is now being threatened by rumours and misinformation ... Conspiracy theories do nothing but create fear, rumours, and prejudice that jeopardise our global collaboration in the fight against this virus,” wrote Charles H. Calisher, PhD, of Colorado State University, Fort Collins, and colleagues.
What can physicians do to counter misinformation?
Pulmonologist and critical care physician Cedric “Jamie” Rutland, MD, who practices in Riverside, Calif., sees misinformation about the novel coronavirus every day at home and on the job. His patients worry that everyone who gets infected will die or end up in the ICU. His neighbors ask him to pilfer surgical masks to protect them from the false notion that Chinese people in their community posed some kind of COVID-19 risk.
As he pondered how to counter myths with facts, Dr. Rutland turned to an unusual resource: His 7-year-old daughter Amelia. He explained to her how COVID-19 works and found that she could easily understand the basics. Now, Dr. Rutland draws upon the lessons from chats with his daughter as he explains COVID-19 to his patient audience on his YouTube channel “Medicine Deconstructed.” Simplicity, but not too much simplicity, is key, he said. Dr. Rutland uses a visual aid – a rough drawing of a virus – and shows how inflammation and antibodies enter the picture after infection. “I just teach them that if you’re a healthy person, this is how the body works, and this is what the immune system will do,” he said. “For the most part, you can calm people down when you make time for education.”
What are best practices? In a series of interviews, specialists emphasized the importance of fact-finding, wide-ranging communication, and – perhaps most difficult of all – humility.
Dr. Rutland emphasizes thoughtful communication based on facts and humility when communicating to patients about this potential health risk. “A lot of people finish medical school and think, ‘Everyone should trust me because I’m the pulmonologist or the GI doc.’ That’s not how it works. You still have to earn people’s trust,” he said.
Make sure all staff get reliable information
Hospitals are scrambling to keep staff safe with up-to-date directives and debunk false narratives about the virus. Keeping all hospital staff informed with verified and authoritative facts about the coronavirus is a key objective of the Massachusetts General Hospital’s Center for Disaster Medicine. The Center’s coronavirus educational materials are distributed to all staffers from physicians to janitors. “These provide information that they need to understand the risks and keep themselves safe,” said Eileen Searle, PhD, the Biothreats Clinical Operations program manager in the CDM.
According to Dr. Searle, the hospital keeps a continually updated COVID-19 Frequently Asked Questions document in its internal computer system. All employees can access it, she said, and it’s updated to include questions as they come up.
Even valets and front-desk volunteers are encouraged to read the FAQ, she said, since “they’re the first people that family and patients are interacting with.” The document “gives them reassurance about delivering messages,” she said.
Use patience with your patients
Dr. Rutland urges colleagues to take the time to listen to patients and educate them. “Reduce the gap between you and them,” said Dr. Rutland, who treats patients in Orange and Riverside counties. “Take off your white coat, sit down, and talk to the person about their concerns.”
Boston cardiologist Haider Warraich, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said it’s important to “put medical information into a greater human context.” For example, he has told patients that he’s still taking his daughter to school despite COVID-19 risks. “I take the information I provide and apply it to my own life,” he said.
The Washington State Department of Health offers this advice to physicians to counter false information and stigma: “Stay updated and informed on COVID-19 to avoid miscommunication or inaccurate information. Talk openly about the harm of stigma. View people directly impacted by stigma as people first. Be conscious of your language. Acknowledge access and language barriers.”
Speak out on social media – but don’t fight
Should medical professionals speak out about COVID-19 misinformation via social media? It’s an individual decision, Dr. Warraich said, “but my sense is that it’s never been more important for physicians to be part of the fray and help quell the epidemic of misinformation that almost always follows any type of medial calamity.”
Dr. Rutland, vice president and founding member of the Association for Healthcare Social Media, cautioned that effective communication via social media requires care. Avoid confrontation, he advised. “Don’t call people stupid or say things like, ‘I went to medical school and I’m smarter than you.’ ”
Instead, he said, “it’s important to just state the facts: These are the people who are dying, these are the people who are getting infected.”
And, he added, remember to push the most important message of all: Wash your hands!
Public health organizations fight the ‘infodemic’
In a trend that hearkens back to the days of snake oil cures for all maladies, advertisements for fake treatments are popping up on the Internet and on other media.
Facebook and Amazon have acted to remove these ads but these messages continue to flood social media such as Twitter, WhatsApp, and other sites. Discussion groups on platforms such as Reddit continue to pump out misinformation about COVID-19. Conspiracy theories that link the virus to espionage and bioweapons are making the rounds on the Internet and talk radio. Wrong information about the effectiveness of non-N95 face masks to protect wearers against infection is widespread, leading to shortages for medical personnel and price gouging. Pernicious rumors about the effectiveness of substances such a vinegar, silver, garlic, lemon juice, and even vodka to disinfect hands and surfaces abound on the Internet. An especially dangerous stream of misinformation stigmatizes ethnic groups and individuals as sources of the infection.
The World Health Organization identified early in the COVID-19 outbreak the global wave of misinformation about the virus and dubbed the problem the “infodemic.” The WHO “Q & A” page on COVID-19 is updated frequently and addresses myths and rumors currently circulating.
According to the WHO website, the agency has reached out to social media players such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Pinterest, TikTok, and Weibo, the microblogging site in China. WHO has worked with these sites to curb the “infodemic” of misinformation and has used these sites for public education outreach on COVID-19. “Myth busting” infographics posted on a WHO web page are also reposted on major social media sites.
The CDC has followed with its own “frequently asked questions” page to address questions and rumors. State health agencies have put up COVID-19 pages to address public concerns and offer advice on prevention. The Maryland Department of Health web page directly addresses dangerous misinformation: “Do not stigmatize people of any specific ethnicities or racial background. Viruses do not target people from specific populations, ethnicities or racial backgrounds. Stay informed and seek information from reliable, official sources. Be wary of myths, rumors and misinformation circulating online and elsewhere. Health information shared through social media is frequently inaccurate, unless coming from an official, reliable source such as the CDC, MDH or local health departments.”
The Washington State Department of Health has taken a more assertive stance on stigma. The COVID-19 web page recommends to the public: “Show compassion and support for individuals and communities more closely impacted. Avoid stigmatizing people who are in quarantine. They are making the right choice for their communities. Do not make assumptions about someone’s health status based on their ethnicity, race or national origin.”
Cancer mortality continues to decline while cancer incidence rises in women
according to the Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer.
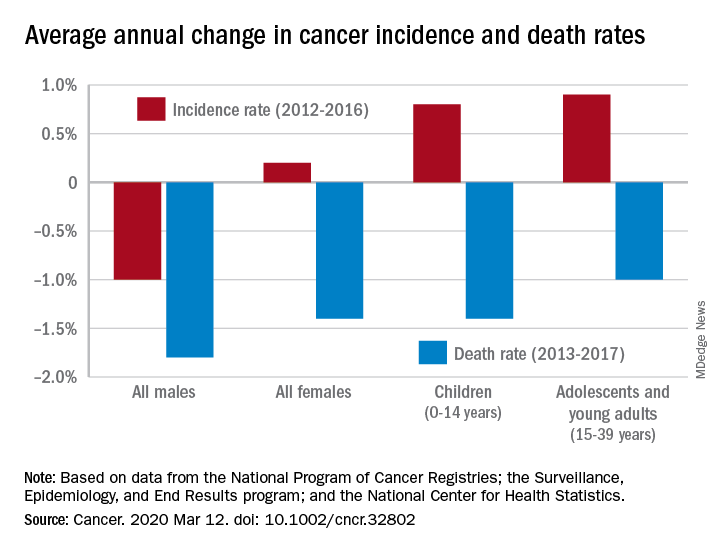
During 2013-2017, the overall age-standardized death rate for all cancers was 158.2 per 100,000 population, and the average decline over that period was 1.5% per year. The average annual change was greater for men (–1.8%) than women (–1.4%) for 2013-2017, but the death rate was higher for men (189.3 per 100,000 vs. 135.5 per 100,000) for those years, S. Jane Henley of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates reported in Cancer.
“The drops in mortality we’re seeing are real, sustained, and a strong indication of what we can do when we work to prevent and treat cancer,” William G. Cance, MD, chief medical and scientific officer of the America Cancer Society, said in a written statement accompanying the report.
Overall cancer incidence for the most recent 5-year period (2012-2016) was 447.9 per 100,000, with rates of 487.9 for men and 421.4 for women, the investigators said.
Incidence dropped by 0.6% per year overall, but that hides a major difference between men, who saw a decrease of 1.0% a year, and women, who experienced an annual increase of 0.2%.
Over those 5 years, cancer incidence also increased by 0.8% annually among children aged 0-14 years and by 0.9% in adolescents and young adults aged 15-39 years, Ms. Henley and associates said in the report, which is a collaborative effort between the CDC, the National Cancer Institute, the American Cancer Society, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries.
“[W]e must not be complacent. The cancer incidence data – especially the increase in cancer among women – is a clear reminder that there is more work ahead,” Norman E. Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, said in the accompanying statement.
SOURCE: Henley SJ et al. Cancer. 2020 Mar 12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32802.
according to the Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer.

During 2013-2017, the overall age-standardized death rate for all cancers was 158.2 per 100,000 population, and the average decline over that period was 1.5% per year. The average annual change was greater for men (–1.8%) than women (–1.4%) for 2013-2017, but the death rate was higher for men (189.3 per 100,000 vs. 135.5 per 100,000) for those years, S. Jane Henley of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates reported in Cancer.
“The drops in mortality we’re seeing are real, sustained, and a strong indication of what we can do when we work to prevent and treat cancer,” William G. Cance, MD, chief medical and scientific officer of the America Cancer Society, said in a written statement accompanying the report.
Overall cancer incidence for the most recent 5-year period (2012-2016) was 447.9 per 100,000, with rates of 487.9 for men and 421.4 for women, the investigators said.
Incidence dropped by 0.6% per year overall, but that hides a major difference between men, who saw a decrease of 1.0% a year, and women, who experienced an annual increase of 0.2%.
Over those 5 years, cancer incidence also increased by 0.8% annually among children aged 0-14 years and by 0.9% in adolescents and young adults aged 15-39 years, Ms. Henley and associates said in the report, which is a collaborative effort between the CDC, the National Cancer Institute, the American Cancer Society, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries.
“[W]e must not be complacent. The cancer incidence data – especially the increase in cancer among women – is a clear reminder that there is more work ahead,” Norman E. Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, said in the accompanying statement.
SOURCE: Henley SJ et al. Cancer. 2020 Mar 12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32802.
according to the Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer.

During 2013-2017, the overall age-standardized death rate for all cancers was 158.2 per 100,000 population, and the average decline over that period was 1.5% per year. The average annual change was greater for men (–1.8%) than women (–1.4%) for 2013-2017, but the death rate was higher for men (189.3 per 100,000 vs. 135.5 per 100,000) for those years, S. Jane Henley of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and associates reported in Cancer.
“The drops in mortality we’re seeing are real, sustained, and a strong indication of what we can do when we work to prevent and treat cancer,” William G. Cance, MD, chief medical and scientific officer of the America Cancer Society, said in a written statement accompanying the report.
Overall cancer incidence for the most recent 5-year period (2012-2016) was 447.9 per 100,000, with rates of 487.9 for men and 421.4 for women, the investigators said.
Incidence dropped by 0.6% per year overall, but that hides a major difference between men, who saw a decrease of 1.0% a year, and women, who experienced an annual increase of 0.2%.
Over those 5 years, cancer incidence also increased by 0.8% annually among children aged 0-14 years and by 0.9% in adolescents and young adults aged 15-39 years, Ms. Henley and associates said in the report, which is a collaborative effort between the CDC, the National Cancer Institute, the American Cancer Society, and the North American Association of Central Cancer Registries.
“[W]e must not be complacent. The cancer incidence data – especially the increase in cancer among women – is a clear reminder that there is more work ahead,” Norman E. Sharpless, MD, director of the National Cancer Institute, said in the accompanying statement.
SOURCE: Henley SJ et al. Cancer. 2020 Mar 12. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32802.
FROM CANCER
FDA to revise safety evaluation of type 2 diabetes drugs
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued new draft guidance for industry on evaluating the safety of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and removed the “outdated” 12-year-old requirement for standardized cardiovascular outcomes trials (CVOTs).
The new draft guidance, “Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating the Safety of New Drugs for Improving Glycemic Control,” will replace the December 2008 requirement that manufacturers conduct CVOTs to rule out unacceptable cardiovascular safety risk. That move followed concerns raised at the time about the thiazolidinedione class of glucose-lowering drugs.
Since then, “FDA has reviewed the results of several [CVOTs] conducted to meet the December 2008 guidance recommendations. None of the CVOTs to date have identified an increased risk of ischemic cardiovascular events; some of the CVOTs have instead demonstrated a reduced risk for cardiovascular events,” according to the federal register announcement.
In October 2018, the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted (10 to 9) to continue requiring CVOTs, but most panel members also recommended some changes to them, including requirements for safety data beyond cardiovascular events.
Based on the CVOT results over the years and the panel’s recommendations, “FDA is revisiting the recommendations of the December 2008 guidance and is now proposing an updated approach to evaluating the safety of new drugs and biologics to improve glycemic control.”
“The new draft guidance does not contain the recommendation that sponsors of all new therapies for type 2 diabetes uniformly rule out a specific degree of risk for ischemic cardiovascular adverse outcomes,” the FDA said.
Instead, the draft calls for at least 4000 patient-years of exposure to the new drug in phase 3 trials and inclusion of study participants with comorbid conditions and/or diabetes complications, including at least 500 with stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease, 600 with established cardiovascular disease, and at least 600 over the age of 65 years.
The FDA is soliciting stakeholder input on these and other issues, including study duration, subject demographics, specific safety concerns, and event adjudication.
In a statement, Lisa Yanoff, MD, acting director of the Division for Metabolism and Endocrinology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said: “By following previous FDA recommendations, sponsors have shown that new type 2 diabetes drugs do not have excess ischemic cardiovascular risk, which has provided reassuring cardiovascular safety information for millions of diabetes patients. Now, with this proposed approach, we will have broader, valuable safety information for these medications.”
The draft is open for comments for 90 days after March 9, 2020. It is available online, along with a link for submitting comments.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued new draft guidance for industry on evaluating the safety of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and removed the “outdated” 12-year-old requirement for standardized cardiovascular outcomes trials (CVOTs).
The new draft guidance, “Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating the Safety of New Drugs for Improving Glycemic Control,” will replace the December 2008 requirement that manufacturers conduct CVOTs to rule out unacceptable cardiovascular safety risk. That move followed concerns raised at the time about the thiazolidinedione class of glucose-lowering drugs.
Since then, “FDA has reviewed the results of several [CVOTs] conducted to meet the December 2008 guidance recommendations. None of the CVOTs to date have identified an increased risk of ischemic cardiovascular events; some of the CVOTs have instead demonstrated a reduced risk for cardiovascular events,” according to the federal register announcement.
In October 2018, the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted (10 to 9) to continue requiring CVOTs, but most panel members also recommended some changes to them, including requirements for safety data beyond cardiovascular events.
Based on the CVOT results over the years and the panel’s recommendations, “FDA is revisiting the recommendations of the December 2008 guidance and is now proposing an updated approach to evaluating the safety of new drugs and biologics to improve glycemic control.”
“The new draft guidance does not contain the recommendation that sponsors of all new therapies for type 2 diabetes uniformly rule out a specific degree of risk for ischemic cardiovascular adverse outcomes,” the FDA said.
Instead, the draft calls for at least 4000 patient-years of exposure to the new drug in phase 3 trials and inclusion of study participants with comorbid conditions and/or diabetes complications, including at least 500 with stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease, 600 with established cardiovascular disease, and at least 600 over the age of 65 years.
The FDA is soliciting stakeholder input on these and other issues, including study duration, subject demographics, specific safety concerns, and event adjudication.
In a statement, Lisa Yanoff, MD, acting director of the Division for Metabolism and Endocrinology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said: “By following previous FDA recommendations, sponsors have shown that new type 2 diabetes drugs do not have excess ischemic cardiovascular risk, which has provided reassuring cardiovascular safety information for millions of diabetes patients. Now, with this proposed approach, we will have broader, valuable safety information for these medications.”
The draft is open for comments for 90 days after March 9, 2020. It is available online, along with a link for submitting comments.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued new draft guidance for industry on evaluating the safety of new drugs for type 2 diabetes and removed the “outdated” 12-year-old requirement for standardized cardiovascular outcomes trials (CVOTs).
The new draft guidance, “Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating the Safety of New Drugs for Improving Glycemic Control,” will replace the December 2008 requirement that manufacturers conduct CVOTs to rule out unacceptable cardiovascular safety risk. That move followed concerns raised at the time about the thiazolidinedione class of glucose-lowering drugs.
Since then, “FDA has reviewed the results of several [CVOTs] conducted to meet the December 2008 guidance recommendations. None of the CVOTs to date have identified an increased risk of ischemic cardiovascular events; some of the CVOTs have instead demonstrated a reduced risk for cardiovascular events,” according to the federal register announcement.
In October 2018, the FDA’s Endocrinologic and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee narrowly voted (10 to 9) to continue requiring CVOTs, but most panel members also recommended some changes to them, including requirements for safety data beyond cardiovascular events.
Based on the CVOT results over the years and the panel’s recommendations, “FDA is revisiting the recommendations of the December 2008 guidance and is now proposing an updated approach to evaluating the safety of new drugs and biologics to improve glycemic control.”
“The new draft guidance does not contain the recommendation that sponsors of all new therapies for type 2 diabetes uniformly rule out a specific degree of risk for ischemic cardiovascular adverse outcomes,” the FDA said.
Instead, the draft calls for at least 4000 patient-years of exposure to the new drug in phase 3 trials and inclusion of study participants with comorbid conditions and/or diabetes complications, including at least 500 with stage 3-4 chronic kidney disease, 600 with established cardiovascular disease, and at least 600 over the age of 65 years.
The FDA is soliciting stakeholder input on these and other issues, including study duration, subject demographics, specific safety concerns, and event adjudication.
In a statement, Lisa Yanoff, MD, acting director of the Division for Metabolism and Endocrinology Products in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said: “By following previous FDA recommendations, sponsors have shown that new type 2 diabetes drugs do not have excess ischemic cardiovascular risk, which has provided reassuring cardiovascular safety information for millions of diabetes patients. Now, with this proposed approach, we will have broader, valuable safety information for these medications.”
The draft is open for comments for 90 days after March 9, 2020. It is available online, along with a link for submitting comments.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early GI symptoms in COVID-19 may indicate fecal transmission
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fecal-oral transmission may be part of the COVID-19 clinical picture, according to two reports published in Gastroenterology. The researchers find that RNA and proteins from SARS-CoV-2, the viral cause of COVID-19, are shed in feces early in infection and persist after respiratory symptoms abate.
But the discovery is preliminary. “There is evidence of the virus in stool, but not evidence of infectious virus,” David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at the Eastern Virginia School of Medicine in Norfolk, told Medscape Medical News.
The findings are not entirely unexpected. Both of the coronaviruses behind SARS and MERS are shed in stool, Jinyang Gu, MD, from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in Shanghai, China, and colleagues, note in one of the newly published articles.
In addition, as COVID-19 spread beyond China, clinicians began noticing initial mild gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, preceding the hallmark fever, dry cough, and dyspnea. The first patient diagnosed in the United States with COVID-19 reported having 2 days of nausea and vomiting, with viral RNA detected in fecal and respiratory specimens, according to an earlier report.
Gu and colleagues warn that initial investigations would likely have not considered cases that manifested initially only as mild gastrointestinal symptoms.
Although early reports indicated that only about 10% of people with COVID-19 have GI symptoms, it isn’t known whether some infected individuals have only GI symptoms, Johnson said.
The GI manifestations are consistent with the distribution of ACE2 receptors, which serve as entry points for SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS. The receptors are most abundant in the cell membranes of lung AT2 cells, as well as in enterocytes in the ileum and colon.
“Altogether, many efforts should be made to be alert on the initial digestive symptoms of COVID-19 for early detection, early diagnosis, early isolation and early intervention,” Gu and colleagues conclude.
But Johnson cautions, “gastroenterologists are not the ones managing diagnosis of COVID-19. It is diagnosed as a respiratory illness, but we are seeing concomitant gastrointestinal shedding in stool and saliva, and GI symptoms.”
Samples From 73 Patients Studied
In the second article published, Fei Xiao, MD, of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangdong Province, China, and colleagues report detecting viral RNA in samples from the mouths, noses, throats, urine, and feces of 73 patients hospitalized during the first 2 weeks of February.
Of the 73 hospitalized patients, 39 (53.24%; 25 males and 14 females) had viral RNA in their feces, present from 1 to 12 days. Seventeen (23.29%) of the patients continued to have viral RNA in their stool after respiratory symptoms had improved.
One patient underwent endoscopy. There was no evidence of damage to the GI epithelium, but the clinicians detected slightly elevated levels of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
The researcher used laser scanning confocal microscopy to analyze samples taken during the endoscopy. They found evidence of both ACE2 receptors and viral nucleocapsid proteins in the gastric, duodenal, and rectal glandular epithelial cells.
Finding evidence of SARS-CoV-2 throughout the GI system, if not direct infectivity, suggests a fecal-oral route of transmission, the researchers conclude. “Our immunofluorescent data showed that ACE2 protein, a cell receptor for SARS-CoV-2, is abundantly expressed in the glandular cells of gastric, duodenal and rectal epithelia, supporting the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cells.”
Detection of viral RNA at different time points in infection, they write, suggests that the virions are continually secreted and therefore likely infectious, which is under investigation. “Prevention of fecal-oral transmission should be taken into consideration to control the spread of the virus,” they write.
Current recommendations do not require that patients’ fecal samples be tested before being considered noninfectious. However, given their findings and evidence from other studies, Xiao and colleagues recommend that real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) testing of fecal samples be added to current protocols.
Johnson offers practical suggestions based on the “potty hygiene” suggestions he gives to patients dealing with fecal shedding in Clostridioides difficile infection.
“To combat the microaerosolization of C. diff spores, I have patients do a complete bacteriocidal washing out of the toilet bowl, as well as clean surface areas and especially toothbrushes.” Keeping the bowl closed when not in use is important too in preventing “fecal-oral transmission of remnants” of toilet contents, he adds.
The new papers add to other reports suggesting that virus-bearing droplets may reach people in various ways, Johnson said. “Maybe the virus isn’t only spread by a cough or a sneeze.”
The researchers and commentator have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk factors for death from COVID-19 identified in Wuhan patients
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients who did not survive hospitalization for COVID-19 in Wuhan were more likely to be older, have comorbidities, and elevated D-dimer, according to the first study to examine risk factors associated with death among adults hospitalized with COVID-19. “Older age, showing signs of sepsis on admission, underlying diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, and the prolonged use of noninvasive ventilation were important factors in the deaths of these patients,” coauthor Zhibo Liu said in a news release. Abnormal blood clotting was part of the clinical picture too.
Fei Zhou, MD, from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and colleagues conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter cohort study of 191 patients, 137 of whom were discharged and 54 of whom died in the hospital.
The study, published online today in The Lancet, included all adult inpatients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital who had been discharged or died by January 31 of this year. Severely ill patients in the province were transferred to these hospitals until February 1.
The researchers compared demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data from electronic medical records between survivors and those who succumbed to the disease. The analysis also tested serial samples for viral RNA. Overall, 91 (48%) of the 191 patients had comorbidity. Most common was hypertension (30%), followed by diabetes (19%) and coronary heart disease (8%).
The odds of dying in the hospital increased with age (odds ratio 1.10; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.17; per year increase in age), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5.65, 2.61-12.23; P < .0001), and D-dimer level exceeding 1 mcg/L on admission. The SOFA was previously called the “sepsis-related organ failure assessment score” and assesses rate of organ failure in intensive care units. Elevated D-dimer indicates increased risk of abnormal blood clotting, such as deep vein thrombosis.
Nonsurvivors compared with survivors had higher frequencies of respiratory failure (98% vs 36%), sepsis (100%, vs 42%), and secondary infections (50% vs 1%).
The average age of survivors was 52 years compared to 69 for those who died. Liu cited weakening of the immune system and increased inflammation, which damages organs and also promotes viral replication, as explanations for the age effect.
From the time of initial symptoms, median time to discharge from the hospital was 22 days. Average time to death was 18.5 days.
Fever persisted for a median of 12 days among all patients, and cough persisted for a median 19 days; 45% of the survivors were still coughing on discharge. In survivors, shortness of breath improved after 13 days, but persisted until death in the others.
Viral shedding persisted for a median duration of 20 days in survivors, ranging from 8 to 37. The virus (SARS-CoV-2) was detectable in nonsurvivors until death. Antiviral treatment did not curtail viral shedding.
But the viral shedding data come with a caveat. “The extended viral shedding noted in our study has important implications for guiding decisions around isolation precautions and antiviral treatment in patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. However, we need to be clear that viral shedding time should not be confused with other self-isolation guidance for people who may have been exposed to COVID-19 but do not have symptoms, as this guidance is based on the incubation time of the virus,” explained colead author Bin Cao.
“Older age, elevated D-dimer levels, and high SOFA score could help clinicians to identify at an early stage those patients with COVID-19 who have poor prognosis. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future,” the researchers conclude.
A limitation in interpreting the findings of the study is that hospitalized patients do not represent the entire infected population. The researchers caution that “the number of deaths does not reflect the true mortality of COVID-19.” They also note that they did not have enough genetic material to accurately assess duration of viral shedding.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves immunotherapy combo for liver cancer
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WHO declares COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.
The World Health Organization has formally declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.

“WHO has been assessing this outbreak around the clock and we are deeply concerned both by the alarming levels of spread and severity, and by the alarming levels of inaction,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said during a March 11 press briefing. “We therefore made the assessment that COVID-19 can be characterized as a pandemic.”
He noted that this is the first time a coronavirus has been seen as a pandemic.
The Director-General cautioned that just looking at the number of countries affected, 114 countries, “does not tell the full story. ... We cannot say this loudly enough, or clearly enough, or often enough: All countries can still change the course of this pandemic.”
He reiterated the need for a whole-of-government and a whole-of-society approach to dealing with this, including taking precautions such as isolating, testing, and treating every case and tracing every contact, as well as readying hospitals and health care professionals.
“Let’s look out for each other, because we need each other,” he said.






