User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Conducting cancer trials amid the COVID-19 pandemic
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
COVID-19 linked to multiple cardiovascular presentations
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s becoming clear that COVID-19 infection can involve the cardiovascular system in many different ways, and this has “evolving” potential implications for treatment, say a team of cardiologists on the frontlines of the COVID-19 battle in New York City.
In an article published online April 3 in Circulation, Justin Fried, MD, Division of Cardiology, Columbia University, New York City, and colleagues present four case studies of COVID-19 patients with various cardiovascular presentations.
Case 1 is a 64-year-old woman whose predominant symptoms on admission were cardiac in nature, including chest pain and ST elevation, but without fever, cough, or other symptoms suggestive of COVID-19.
“In patients presenting with what appears to be a typical cardiac syndrome, COVID-19 infection should be in the differential during the current pandemic, even in the absence of fever or cough,” the clinicians advise.
Case 2 is a 38-year-old man with cardiogenic shock and acute respiratory distress with profound hypoxia who was rescued with veno-arterial-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO).
The initial presentation of this patient was more characteristic of severe COVID-19 disease, and cardiac involvement only became apparent after the initiation of ECMO, Fried and colleagues report.
Based on this case, they advise a “low threshold” to assess for cardiogenic shock in patients with acute systolic heart failure related to COVID-19. If inotropic support fails in these patients, intra-aortic balloon pump should be considered first for mechanical circulatory support because it requires the least maintenance from medical support staff.
In addition, in their experience, when a patient on VV ECMO develops superimposed cardiogenic shock, adding an arterial conduit at a relatively low blood flow rate may provide the necessary circulatory support without inducing left ventricular distension, they note.
“Our experience confirms that rescue of patients even with profound cardiogenic or mixed shock may be possible with temporary hemodynamic support at centers with availability of such devices,” Fried and colleagues report.
Case 3 is a 64-year-old woman with underlying cardiac disease who developed profound decompensation with COVID-19 infection.
This case demonstrates that the infection can cause decompensation of underlying heart failure and may lead to mixed shock, the clinicians say.
“Invasive hemodynamic monitoring, if feasible, may be helpful to manage the cardiac component of shock in such cases. Medications that prolong the QT interval are being considered for COVID-19 patients and may require closer monitoring in patients with underlying structural heart disease,” they note.
Case 4 is a 51-year-old man who underwent a heart transplant in 2007 and a kidney transplant in 2010. He had COVID-19 symptoms akin to those seen in nonimmunosuppressed patients with COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic presents a “unique challenge” for solid organ transplant recipients, with only “limited” data on how to adjust immunosuppression during COVID-19 infection, Fried and colleagues say.
The pandemic also creates a challenge for the management of heart failure patients on the heart transplant wait list; the risks of delaying a transplant need to be balanced against the risks of donor infection and uncertainty regarding the impact of post-transplant immunosuppression protocols, they note.
As reported by Medscape Medical News, the American Heart Association has developed a COVID-19 patient registry to collect data on cardiovascular conditions and outcomes related to COVID-19 infection.
To participate in the registry, contact [email protected].
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tips for self-care during the COVID-19 crisis
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
I think it’s fair to say, none of us have seen anything like this before. Yet here we are, and we must lead. We are many weeks into the COVID-19 crisis. We moved our offices home and tried not to miss a beat. Our patients need us more than ever – and in different ways.
Lest we become like the shoemaker’s daughter who has no shoes, let’s make sure we take care of ourselves. The shock waves from this pandemic are going to be massive and long lasting. I am already witnessing massive psychological growth on the part of my patients, and I hope, myself and my family. We must be strong as individuals and as a group of professionals.
Now more than ever, we need to set boundaries. So many are suffering. We must take stock of our own lives. Many of us are extremely fortunate. We have homes, families, and plenty of food. We are doctors performing essential services, and we can do so without risking our lives.
The priority is to make sure you are safe, and keeping your family and loved ones safe. As physicians, we have learned to distance ourselves from illness, but the coronavirus has affected us in disproportionate numbers.
To be physically and mentally strong, we must get enough sleep. This is exhausting for some and energizing for others. It is definitely a marathon not a sprint, so pace yourself. Eat well. This is no time for empty calories, and that goes for alcohol as well.
Create new routines. Exercise at the same time each day or perhaps twice a day. Try to be productive during certain hours, and relax at other times. Eat at similar times each day. We must strive to quickly create a “new normal” as we spend our days at home.
Find safe alternatives to your usual workout routine. Use YouTube and Instagram to help you find ways to stay fit in your own home. Ask friends for tips and consider sharing workout time with them via Zoom or FaceTime. New options are coming on line daily.
Make sure you are getting enough information to stay safe, and follow the advice of experts. Then turn off the news. I offer the same advice for financial worries. Try not to stress too much about finances right now. Most of us are feeling the pain of lost income and lost savings. Many of us have spouses or partners who suddenly found themselves out of work. Most likely, we will have ample ability to recover financially as we move forward and find ourselves with more work than ever.
Meditate. This may be advice you have been telling your patients for years but never found the time to try yourself. You can begin very simply with an app called Headspace or Calm. Google “5-minute meditation” on YouTube or find a meditation of any length you desire. If not now, when?
Reach out to one another. We can all use a caring word, or some humor or advice about how to move our practices online.
You may find your concentration is decreased, so be realistic in your expectations of yourself. I am finding shorter sessions more often are providing more comfort to some patients. Other patients are digging deeper than ever emotionally, and the work is becoming more rewarding.
Make sure you take a break to engage in positive activities. Read a book. Listen to soft music. Dim the lights. Watch the sunset, or be in nature if you can do so safely. Watch a TedTalk. Brush up on a foreign language. Take a deep breath. Journal. Puzzles, games, cooking, magazines, and humor all provide much needed respite from the stress. If you are lucky enough to be with family, try to take advantage of this unique time.
Try to avoid or minimize conflict with others. We need one another now more than ever. If you lose your cool, forgive yourself and make amends.
Even in these most challenging times, we must focus on what we are grateful for. Express gratitude to those around you as it will lift their mood as well. I know I am extremely grateful to be able to continue meaningful work when so many are unable to do so.
The next waves of this virus will be hitting our specialty directly so be strong and be prepared. It is an honor to serve, and we must rise to the occasion.
Dr. Ritvo, a psychiatrist with more than 25 years’ experience, practices in Miami Beach, Fla. She is the author of “Bekindr – The Transformative Power of Kindness” (Hellertown, Pa.: Momosa Publishing, 2018), and is the founder of the Bekindr Global Initiative, a movement aimed at cultivating kindness in the world. Dr. Ritvo also is the cofounder of the Bold Beauty Project, a nonprofit group that pairs women with disabilities with photographers who create art exhibitions to raise awareness.
AMA president calls for greater reliance on science in COVID-19 fight
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
The president of the American Medical Association is calling on politicians and the media to rely on science and evidence to help the public through the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We live in a time when misinformation, falsehoods, and outright lies spread like viruses online, through social media and even, at times, in the media at large,” Patrice A. Harris, MD, said during an April 7 address. “We have witnessed a concerning shift over the last several decades where policy decisions seem to be driven by ideology and politics instead of facts and evidence. The result is a growing mistrust in American institutions, in science, and in the counsel of leading experts whose lives are dedicated to the pursuit of evidence and reason.”
To that end, she called on everyone – from politicians to the general public – to trust the scientific evidence.
Dr. Harris noted that the scientific data on COVID-19 have already yielded important lessons about who is more likely to be affected and how easily the virus can spread. The data also point to the effectiveness of stay-at-home and shelter-in-place orders. “This is our best chance to slow the spread of the virus,” she said, adding that the enhanced emphasis on hand washing and other hygiene practices “may seem ‘simplistic,’ but they are, in fact, based in science and evidence.”
And, as the pandemic continues, Dr. Harris said that now is the time to rely on science. She said the AMA “calls on all elected officials to affirm science, evidence, and fact in their words and actions,” and she urged that the government’s scientific institutions be led by experts who are “protected from political influence.”
It is incumbent upon everyone to actively work to contain and stop the spread of misinformation related to COVID-19, she said. “We must ensure the war is against the virus and not against science,” Dr. Harris said.
NCCN panel: Defer nonurgent skin cancer care during pandemic
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Nearly 24 tests for the novel coronavirus are available
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
according to the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
“Based on what we know about influenza, it’s unlikely that all of these tests are going to perform exactly the same way,” said Angela M. Caliendo, MD, executive vice chair of the department of medicine at Brown University in Providence, R.I., at a press briefing. Although these tests are good, no test is perfect, she added.
The development and availability of testing has improved over time, but clinical laboratories still face challenges, said Kimberly E. Hanson, MD, associate professor of internal medicine at University of Utah, Salt Lake City. These challenges include shortages of devices for specimen collection, media, test tubes, and reagents. Although the goal is to test all symptomatic patients, these shortages require laboratories to prioritize health care workers and the sickest patients.
Tests are being approved through an abbreviated process
Two types of test, rapid tests and serology tests, are in use. Rapid tests use polymerase chain reactions to detect the virus in a clinical specimen. This type of testing is used to diagnose infection. Serology tests measure antibodies to the virus and are more appropriate for indicating whether a patient has been exposed to the virus.
The declaration of a national emergency enabled the FDA to activate its EUA policy, which allows for quicker approval of tests. Normally, a test must be assessed in the laboratory (such as with a mock specimen or an inactivated virus) and in a clinical study of patients. Under the EUA, clinical assessment is not required for the approval of a test. Consequently, the clinical performance of a test approved under EUA is unknown.
Collecting a specimen of good quality is critical to the quality of the test result, said Dr. Caliendo, the secretary of IDSA’s board of directors. Clinicians and investigators have used nasopharyngeal swabs, sputum, and specimens collected from deep within the lung. “We’re still collecting data to determine which is the best specimen type.” As coronavirus testing expands, particularly to drive-through testing sites, “we may be using people who are not as experienced, and so you might not get as high a quality specimen in that situation,” Dr. Caliendo added.
The timing of the test influences the quality of the result, as well, because the amount of virus is lower at the onset of symptoms than it is later. Another factor that affects the quality of the results is the test’s sensitivity.
The time to obtain results varies
The value of having several tests available is that it enables many patients to be tested simultaneously, said Dr. Hanson, a member of IDSA’s board of directors. It also helps to reduce potential problems with the supply of test kits. A test manufacturer, however, may supply parts of the test kit but not the whole kit. This requires the hospital or laboratory to obtain the remaining parts from other suppliers. Furthermore, test manufacturers may need to prioritize areas with high rates of infection or transmission when they ship their tests, which limits testing in other areas.
One reason for the lack of a national plan for testing is that the virus has affected different regions at different times, said Dr. Caliendo. Some tests are more difficult to perform than others, and not all laboratories are equally sophisticated, which can limit testing. It is necessary to test not only symptomatic patients who have been hospitalized, but also symptomatic patients in the community, said Dr. Caliendo. “Ideally, we’re going to need to couple acute diagnostics [testing while people are sick] with serologic testing. Serologic testing is going to be important for us to see who has been infected. That will give us an idea of who is left in our community who is at risk for developing infection.”
How quickly test results are available depends on the type of test and where it is administered. Recently established drive-through clinics can provide results in about 30 minutes. Tests performed in hospitals may take between 1 and 6 hours to yield results. “The issue is, do we have reagents that day?” said Dr. Caliendo. “We have to be careful whom we choose to test, and we screen that in the hospital so that we have enough tests to run as we need them.” But many locations have backlogs. “When you have a backlog of testing, you’re going to wait days, unfortunately, to get a result,” said Dr. Caliendo.
Dr. Caliendo and Dr. Hanson did not report disclosures for this briefing.
Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19: Is tocilizumab effective?
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
A large amount of data suggest that mild or severe cytokine storms, accompanied by high expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), occur in patients with severe coronavirus disease and can be an important cause of death. Blocking the signal transduction pathway of IL-6 is expected to become a new method for the treatment of patients with severe COVID-19, with the IL-6 inhibitor, tocilizumab (Actemra), poised to become an effective drug for these patients, according to the authors of a review published online in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
The reviewers from China detailed the metabolic pathways and regulation of cytokine release syndrome, especially with respect to what is known about severe COVID-19, and discussed the results of recent trials with tocilizumab, which is currently used for treatment of CRS in a variety of cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Tocilizumab is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against human IL-6 receptor of immunoglobulin IgG1 subtype and has been approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The antibody specifically binds soluble- and membrane-bound IL-6 receptors (sIL-6R and mIL-6R) and inhibits sIL-6R– and mIL-6R–mediated signal transduction. It has been shown to be effective in the treatment of severe CRS patients. In 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tocilizumab for the treatment of CRS caused by CAR-T (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy) therapy.
A small clinical trial in China examined the effectiveness of tocilizumab in 21 patients who met the criteria for severe or critical COVID-19, including respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation, shock, or admission to the ICU with other organ failure. After a few days of tocilizumab treatment, the body temperatures returned to normal (initially, all 21 patients had fevers), and all other symptoms were significantly improved, according to the authors. A total of 75% (15/20) of the patients reduced their oxygen intake, and 1 patient did not need oxygen. CT scanning showed that 90.5% (19/21) of the patients had absorption of pulmonary lesions, and lab tests showed that the proportion of peripheral blood lymphocytes and C-reactive protein in the patients returned to normal.
The main deficiency of the study was that only the level of IL-6 in peripheral blood before treatment with tocilizumab was reported (mean value, 132.38 ± 278.54 pg/mL), but the level of IL-6 following treatment was not given, according to the reviewers. Serum levels of IL-6 in normal patients are undetectable or very low.
Based upon their analysis of COVID-19’s possible mechanism and the small samples of clinical data available, tocilizumab appeared effective, and “we suggest that it should be used in critically ill COVID-19 patients with significantly elevated IL-6,” the authors stated.
“CRS occurs in a large number of patients with severe COVID-19, which is also an important cause of death. IL-6 is the key molecule of CRS, so IL-6R antagonist tocilizumab may be an important drug to save patients’ lives,” the researchers concluded.
This study was supported by China Mega-Project for Infectious Diseases and the China Mega-Project for Innovative Drugs. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Zhang C et al. Int J Antimicrobial Agents. 2020. doi. org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105954.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS
U.S. hospitals facing severe challenges from COVID-19, HHS report says
Hospitals across the country encountered severe challenges as the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic swept over them, and they anticipated much worse to come, according to a new report from the Office of Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
From March 23 to 27, the OIG interviewed 323 hospitals of several types in 46 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. The report it pulled together from these interviews is intended to help HHS manage the crisis, rather than to review its response to the pandemic, the OIG said.
The most significant hospital challenges, the report states, were testing and caring for patients with known or suspected COVID-19 and protecting staff members. In addition, the hospitals faced challenges in maintaining or expanding their capacities to treat COVID-19 patients and ensuring the adequacy of basic supplies.
The critical shortages of ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and test kits in hospitals have been widely reported by the media. But the OIG report also focused on some areas that have received less press attention.
To begin with, the shortage of tests has not only slowed the national response to the pandemic, but has had a major impact on inpatient care, according to the report’s authors. The limited number of test kits means that only symptomatic staff members and patients can be tested; in some hospitals, there aren’t even enough tests for that, and some facilities subdivided the test kits they had, the report states.
Moreover, the test results often took 7 days or more to come back from commercial or government labs, the report states. In the meantime, symptomatic patients were presumed to have the coronavirus. While awaiting the results, they had to stay in the hospital, using beds and requiring staff who could otherwise have been assigned to other patients.
The doctors and nurse who cared for these presumptive COVID-19 patients also had to take time suiting up in PPE before seeing them; much of that scarce PPE was wasted on those who were later found not to have the illness.
As one administrator explained to OIG, “Sitting with 60 patients with presumed positives in our hospital isn’t healthy for anybody.”
Delayed test results also reduced hospitals’ ability to provide care by sidelining clinicians who reported COVID-19 symptoms. In one hospital, 20% to 25% of staff were determined to be presumptively positive for COVID-19. As a result of their tests not being analyzed promptly, these doctors and nurses were prevented from providing clinical services for longer than necessary.
Supply Shortages
The report also described some factors contributing to mask shortages. Because of the fear factor, for example, all staff members in one hospital were wearing masks, instead of just those in designated areas. An administrator said the hospital was using 2,000 masks a day, 10 times the number before the COVID-19 crisis.
Another hospital received 2,300 N95 masks from a state reserve, but they were unusable because the elastic bands had dry-rotted.
Meanwhile, some vendors were profiteering. Masks that used to cost 50 cents now sold for $6 each, one administrator said.
To combat the supply chain disruptions, some facilities were buying PPE from nontraditional sources such as online retailers, home supply stores, paint stores, autobody supply shops, and beauty salons. Other hospitals were using non–medical-grade PPE such as construction masks and handmade masks and gowns.
Other hospitals reported they were conserving and reusing PPE to stretch their supplies. In some cases, they had even changed policies to reduce the extent and frequency of patient interactions with clinicians so the latter would have to change their gear less often.
Shortages of other critical supplies and materials were also reported. Hospitals were running out of supplies that supported patient rooms, such as IV poles, medical gas, linens, toilet paper, and food.
Hospitals across the country were also expecting or experiencing a shortage of ventilators, although none said any patients had been denied access to them. Some institutions were adapting anesthesia machines and single-use emergency transport ventilators.
Also concerning to hospitals was the shortage of intensive-care specialists and nurses to operate the ventilators and care for critically ill patients. Some facilities were training anesthesiologists, hospitalists, and other nonintensivists on how to use the lifesaving equipment.
Meanwhile, patients with COVID-19 symptoms were continuing to show up in droves at emergency departments. Hospitals were concerned about potential shortages of ICU beds, negative-pressure rooms, and isolation units. Given limited bed availability, some administrators said, it was getting hard to separate COVID-19 from non–COVID-19 patients.
What Hospitals Want
As the COVID-19 crisis continues to mount, many hospitals are facing financial emergencies as well, the report noted.
“Hospitals described increasing costs and decreasing revenues as a threat to their financial viability. Hospitals reported that ceasing elective procedures and other services decreased revenues at the same time that their costs have increased as they prepare for a potential surge of patients. Many hospitals reported that their cash reserves were quickly depleting, which could disrupt ongoing hospital operations,” the authors write.
This report was conducted a few days before the passage of the CURES Act, which earmarked $100 billion for hospitals on the frontline of the crisis. As a recent analysis of financial hospital data revealed, however, even with the 20% bump in Medicare payments for COVID-19 care that this cash infusion represents, many hospitals will face a cash-flow crunch within 60 to 90 days, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
Besides higher Medicare payments, the OIG report said, hospitals wanted the government to drop the 14-day waiting period for reimbursement and to offer them loans and grants.
Hospitals also want federal and state governments to relax regulations on professional licensing of, and business relationships with, doctors and other clinicians. They’d like the government to:
- Let them reassign licensed professionals within their hospitals and across healthcare networks
- Provide flexibility with respect to licensed professionals practicing across state lines
- Provide relief from regulations that may restrict using contracted staff or physicians based on business relationships
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals across the country encountered severe challenges as the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic swept over them, and they anticipated much worse to come, according to a new report from the Office of Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
From March 23 to 27, the OIG interviewed 323 hospitals of several types in 46 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. The report it pulled together from these interviews is intended to help HHS manage the crisis, rather than to review its response to the pandemic, the OIG said.
The most significant hospital challenges, the report states, were testing and caring for patients with known or suspected COVID-19 and protecting staff members. In addition, the hospitals faced challenges in maintaining or expanding their capacities to treat COVID-19 patients and ensuring the adequacy of basic supplies.
The critical shortages of ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and test kits in hospitals have been widely reported by the media. But the OIG report also focused on some areas that have received less press attention.
To begin with, the shortage of tests has not only slowed the national response to the pandemic, but has had a major impact on inpatient care, according to the report’s authors. The limited number of test kits means that only symptomatic staff members and patients can be tested; in some hospitals, there aren’t even enough tests for that, and some facilities subdivided the test kits they had, the report states.
Moreover, the test results often took 7 days or more to come back from commercial or government labs, the report states. In the meantime, symptomatic patients were presumed to have the coronavirus. While awaiting the results, they had to stay in the hospital, using beds and requiring staff who could otherwise have been assigned to other patients.
The doctors and nurse who cared for these presumptive COVID-19 patients also had to take time suiting up in PPE before seeing them; much of that scarce PPE was wasted on those who were later found not to have the illness.
As one administrator explained to OIG, “Sitting with 60 patients with presumed positives in our hospital isn’t healthy for anybody.”
Delayed test results also reduced hospitals’ ability to provide care by sidelining clinicians who reported COVID-19 symptoms. In one hospital, 20% to 25% of staff were determined to be presumptively positive for COVID-19. As a result of their tests not being analyzed promptly, these doctors and nurses were prevented from providing clinical services for longer than necessary.
Supply Shortages
The report also described some factors contributing to mask shortages. Because of the fear factor, for example, all staff members in one hospital were wearing masks, instead of just those in designated areas. An administrator said the hospital was using 2,000 masks a day, 10 times the number before the COVID-19 crisis.
Another hospital received 2,300 N95 masks from a state reserve, but they were unusable because the elastic bands had dry-rotted.
Meanwhile, some vendors were profiteering. Masks that used to cost 50 cents now sold for $6 each, one administrator said.
To combat the supply chain disruptions, some facilities were buying PPE from nontraditional sources such as online retailers, home supply stores, paint stores, autobody supply shops, and beauty salons. Other hospitals were using non–medical-grade PPE such as construction masks and handmade masks and gowns.
Other hospitals reported they were conserving and reusing PPE to stretch their supplies. In some cases, they had even changed policies to reduce the extent and frequency of patient interactions with clinicians so the latter would have to change their gear less often.
Shortages of other critical supplies and materials were also reported. Hospitals were running out of supplies that supported patient rooms, such as IV poles, medical gas, linens, toilet paper, and food.
Hospitals across the country were also expecting or experiencing a shortage of ventilators, although none said any patients had been denied access to them. Some institutions were adapting anesthesia machines and single-use emergency transport ventilators.
Also concerning to hospitals was the shortage of intensive-care specialists and nurses to operate the ventilators and care for critically ill patients. Some facilities were training anesthesiologists, hospitalists, and other nonintensivists on how to use the lifesaving equipment.
Meanwhile, patients with COVID-19 symptoms were continuing to show up in droves at emergency departments. Hospitals were concerned about potential shortages of ICU beds, negative-pressure rooms, and isolation units. Given limited bed availability, some administrators said, it was getting hard to separate COVID-19 from non–COVID-19 patients.
What Hospitals Want
As the COVID-19 crisis continues to mount, many hospitals are facing financial emergencies as well, the report noted.
“Hospitals described increasing costs and decreasing revenues as a threat to their financial viability. Hospitals reported that ceasing elective procedures and other services decreased revenues at the same time that their costs have increased as they prepare for a potential surge of patients. Many hospitals reported that their cash reserves were quickly depleting, which could disrupt ongoing hospital operations,” the authors write.
This report was conducted a few days before the passage of the CURES Act, which earmarked $100 billion for hospitals on the frontline of the crisis. As a recent analysis of financial hospital data revealed, however, even with the 20% bump in Medicare payments for COVID-19 care that this cash infusion represents, many hospitals will face a cash-flow crunch within 60 to 90 days, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
Besides higher Medicare payments, the OIG report said, hospitals wanted the government to drop the 14-day waiting period for reimbursement and to offer them loans and grants.
Hospitals also want federal and state governments to relax regulations on professional licensing of, and business relationships with, doctors and other clinicians. They’d like the government to:
- Let them reassign licensed professionals within their hospitals and across healthcare networks
- Provide flexibility with respect to licensed professionals practicing across state lines
- Provide relief from regulations that may restrict using contracted staff or physicians based on business relationships
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals across the country encountered severe challenges as the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic swept over them, and they anticipated much worse to come, according to a new report from the Office of Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
From March 23 to 27, the OIG interviewed 323 hospitals of several types in 46 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. The report it pulled together from these interviews is intended to help HHS manage the crisis, rather than to review its response to the pandemic, the OIG said.
The most significant hospital challenges, the report states, were testing and caring for patients with known or suspected COVID-19 and protecting staff members. In addition, the hospitals faced challenges in maintaining or expanding their capacities to treat COVID-19 patients and ensuring the adequacy of basic supplies.
The critical shortages of ventilators, personal protective equipment (PPE), and test kits in hospitals have been widely reported by the media. But the OIG report also focused on some areas that have received less press attention.
To begin with, the shortage of tests has not only slowed the national response to the pandemic, but has had a major impact on inpatient care, according to the report’s authors. The limited number of test kits means that only symptomatic staff members and patients can be tested; in some hospitals, there aren’t even enough tests for that, and some facilities subdivided the test kits they had, the report states.
Moreover, the test results often took 7 days or more to come back from commercial or government labs, the report states. In the meantime, symptomatic patients were presumed to have the coronavirus. While awaiting the results, they had to stay in the hospital, using beds and requiring staff who could otherwise have been assigned to other patients.
The doctors and nurse who cared for these presumptive COVID-19 patients also had to take time suiting up in PPE before seeing them; much of that scarce PPE was wasted on those who were later found not to have the illness.
As one administrator explained to OIG, “Sitting with 60 patients with presumed positives in our hospital isn’t healthy for anybody.”
Delayed test results also reduced hospitals’ ability to provide care by sidelining clinicians who reported COVID-19 symptoms. In one hospital, 20% to 25% of staff were determined to be presumptively positive for COVID-19. As a result of their tests not being analyzed promptly, these doctors and nurses were prevented from providing clinical services for longer than necessary.
Supply Shortages
The report also described some factors contributing to mask shortages. Because of the fear factor, for example, all staff members in one hospital were wearing masks, instead of just those in designated areas. An administrator said the hospital was using 2,000 masks a day, 10 times the number before the COVID-19 crisis.
Another hospital received 2,300 N95 masks from a state reserve, but they were unusable because the elastic bands had dry-rotted.
Meanwhile, some vendors were profiteering. Masks that used to cost 50 cents now sold for $6 each, one administrator said.
To combat the supply chain disruptions, some facilities were buying PPE from nontraditional sources such as online retailers, home supply stores, paint stores, autobody supply shops, and beauty salons. Other hospitals were using non–medical-grade PPE such as construction masks and handmade masks and gowns.
Other hospitals reported they were conserving and reusing PPE to stretch their supplies. In some cases, they had even changed policies to reduce the extent and frequency of patient interactions with clinicians so the latter would have to change their gear less often.
Shortages of other critical supplies and materials were also reported. Hospitals were running out of supplies that supported patient rooms, such as IV poles, medical gas, linens, toilet paper, and food.
Hospitals across the country were also expecting or experiencing a shortage of ventilators, although none said any patients had been denied access to them. Some institutions were adapting anesthesia machines and single-use emergency transport ventilators.
Also concerning to hospitals was the shortage of intensive-care specialists and nurses to operate the ventilators and care for critically ill patients. Some facilities were training anesthesiologists, hospitalists, and other nonintensivists on how to use the lifesaving equipment.
Meanwhile, patients with COVID-19 symptoms were continuing to show up in droves at emergency departments. Hospitals were concerned about potential shortages of ICU beds, negative-pressure rooms, and isolation units. Given limited bed availability, some administrators said, it was getting hard to separate COVID-19 from non–COVID-19 patients.
What Hospitals Want
As the COVID-19 crisis continues to mount, many hospitals are facing financial emergencies as well, the report noted.
“Hospitals described increasing costs and decreasing revenues as a threat to their financial viability. Hospitals reported that ceasing elective procedures and other services decreased revenues at the same time that their costs have increased as they prepare for a potential surge of patients. Many hospitals reported that their cash reserves were quickly depleting, which could disrupt ongoing hospital operations,” the authors write.
This report was conducted a few days before the passage of the CURES Act, which earmarked $100 billion for hospitals on the frontline of the crisis. As a recent analysis of financial hospital data revealed, however, even with the 20% bump in Medicare payments for COVID-19 care that this cash infusion represents, many hospitals will face a cash-flow crunch within 60 to 90 days, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
Besides higher Medicare payments, the OIG report said, hospitals wanted the government to drop the 14-day waiting period for reimbursement and to offer them loans and grants.
Hospitals also want federal and state governments to relax regulations on professional licensing of, and business relationships with, doctors and other clinicians. They’d like the government to:
- Let them reassign licensed professionals within their hospitals and across healthcare networks
- Provide flexibility with respect to licensed professionals practicing across state lines
- Provide relief from regulations that may restrict using contracted staff or physicians based on business relationships
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many children with COVID-19 don’t have cough or fever
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.
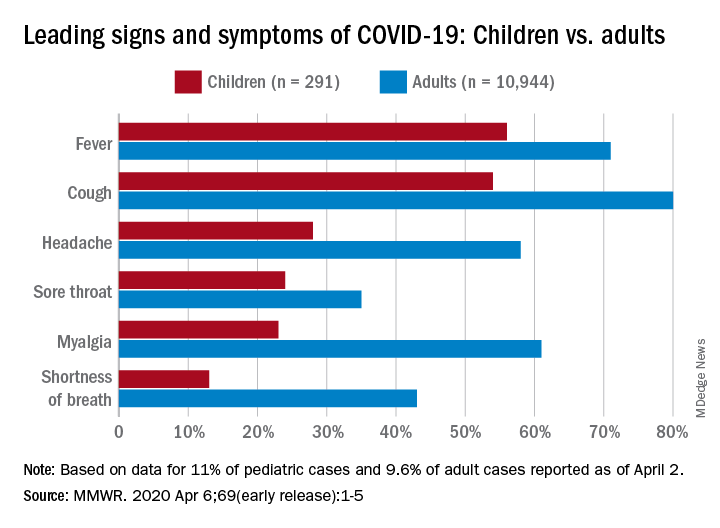
Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
according to the Centers for Disease and Prevention Control.

Among pediatric patients younger than 18 years in the United States, 73% had at least one of the trio of symptoms, compared with 93% of adults aged 18-64, noted Lucy A. McNamara, PhD, and the CDC’s COVID-19 response team, based on a preliminary analysis of the 149,082 cases reported as of April 2.
By a small margin, fever – present in 58% of pediatric patients – was the most common sign or symptom of COVID-19, compared with cough at 54% and shortness of breath in 13%. In adults, cough (81%) was seen most often, followed by fever (71%) and shortness of breath (43%), the investigators reported in the MMWR.
In both children and adults, headache and myalgia were more common than shortness of breath, as was sore throat in children, the team added.
“These findings are largely consistent with a report on pediatric COVID-19 patients aged <16 years in China, which found that only 41.5% of pediatric patients had fever [and] 48.5% had cough,” they wrote.
The CDC analysis of pediatric patients was limited by its small sample size, with data on signs and symptoms available for only 11% (291) of the 2,572 children known to have COVID-19 as of April 2. The adult population included 10,944 individuals, who represented 9.6% of the 113,985 U.S. patients aged 18-65, the response team said.
“As the number of COVID-19 cases continues to increase in many parts of the United States, it will be important to adapt COVID-19 surveillance strategies to maintain collection of critical case information without overburdening jurisdiction health departments,” they said.
SOURCE: McNamara LA et al. MMWR 2020 Apr 6;69(early release):1-5.
FROM MMWR
AAP issues guidance on managing infants born to mothers with COVID-19
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.
“Pediatric cases of COVID-19 are so far reported as less severe than disease occurring among older individuals,” Karen M. Puopolo, MD, PhD, a neonatologist and chief of the section on newborn pediatrics at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, and coauthors wrote in the 18-page document, which was released on April 2, 2020, along with an abbreviated “Frequently Asked Questions” summary. However, one study of children with COVID-19 in China found that 12% of confirmed cases occurred among 731 infants aged less than 1 year; 24% of those 86 infants “suffered severe or critical illness” (Pediatrics. 2020 March. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-0702). There were no deaths reported among these infants. Other case reports have documented COVID-19 in children aged as young as 2 days.
The document, which was assembled by members of the AAP Committee on Fetus and Newborn, Section on Neonatal Perinatal Medicine, and Committee on Infectious Diseases, pointed out that “considerable uncertainty” exists about the possibility for vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant women to their newborns. “Evidence-based guidelines for managing antenatal, intrapartum, and neonatal care around COVID-19 would require an understanding of whether the virus can be transmitted transplacentally; a determination of which maternal body fluids may be infectious; and data of adequate statistical power that describe which maternal, intrapartum, and neonatal factors influence perinatal transmission,” according to the document. “In the midst of the pandemic these data do not exist, with only limited information currently available to address these issues.”
Based on the best available evidence, the guidance authors recommend that clinicians temporarily separate newborns from affected mothers to minimize the risk of postnatal infant infection from maternal respiratory secretions. “Newborns should be bathed as soon as reasonably possible after birth to remove virus potentially present on skin surfaces,” they wrote. “Clinical staff should use airborne, droplet, and contact precautions until newborn virologic status is known to be negative by SARS-CoV-2 [polymerase chain reaction] testing.”
While SARS-CoV-2 has not been detected in breast milk to date, the authors noted that mothers with COVID-19 can express breast milk to be fed to their infants by uninfected caregivers until specific maternal criteria are met. In addition, infants born to mothers with COVID-19 should be tested for SARS-CoV-2 at 24 hours and, if still in the birth facility, at 48 hours after birth. Centers with limited resources for testing may make individual risk/benefit decisions regarding testing.
For infants infected with SARS-CoV-2 but have no symptoms of the disease, they “may be discharged home on a case-by-case basis with appropriate precautions and plans for frequent outpatient follow-up contacts (either by phone, telemedicine, or in office) through 14 days after birth,” according to the document.
If both infant and mother are discharged from the hospital and the mother still has COVID-19 symptoms, she should maintain at least 6 feet of distance from the baby; if she is in closer proximity she should use a mask and hand hygiene. The mother can stop such precautions until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, and it is at least 7 days since her symptoms first occurred.
In cases where infants require ongoing neonatal intensive care, mothers infected with COVID-19 should not visit their newborn until she is afebrile without the use of antipyretics for at least 72 hours, her respiratory symptoms are improved, and she has negative results of a molecular assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 from at least two consecutive nasopharyngeal swab specimens collected at least 24 hours apart.