User login
The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management® is an independent, peer-reviewed journal offering evidence-based, practical information for improving the quality, safety, and value of health care.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Cardiology groups push back on hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin for COVID-19
The .
“Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin have been touted for potential prophylaxis or treatment for COVID-19; both drugs are listed as definite causes of torsade de pointes” and increase in the risk of other arrhythmias and sudden death, the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Rhythm Society said in a joint statement April 8 in Circulation.
The statement came amid ongoing promotion by the Trump administration of hydroxychloroquine, in particular, for COVID-19 despite lack of strong data.
In addition to underlying cardiovascular disease, “seriously ill patients often have comorbidities that can increase risk of serious arrhythmias,” including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, fever, and systemic inflammation, the groups said.
They recommended withholding the drugs in patients with baseline QT prolongation (e.g., QTc of at least 500 msec) or with known congenital long QT syndrome; monitoring cardiac rhythm and QT interval and withdrawing hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin if QTc exceeds 500 msec; correcting hypokalemia to levels greater than 4 mEq/L and hypomagnesemia to more than 2 mg/dL; and avoiding other QTc-prolonging agents when possible.
The groups noted that, “in patients critically ill with COVID-19 infection, frequent caregiver contact may need to be minimized, so optimal electrocardiographic interval and rhythm monitoring may not be possible.” There is also a possible compounding arrhythmic effect when hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin are used together, but that has not been studied.
There’s a known risk of torsade de pointes with chloroquine and a possible risk with the antiviral HIV combination drug lopinavir-ritonavir, two other candidates for COVID-19 treatment. Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine, both antimalarials, might help prevent or treat infection by interfering with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, which the COVID-19 virus uses for cell entry, the groups said.
“The urgency of COVID-19 must not diminish the scientific rigor with which we approach COVID-19 treatment. While these medications may work against COVID-19 individually or in combination, we recommend caution with these medications for patients with existing cardiovascular disease,” Robert A. Harrington, MD, AHA president and chair of the department of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, emphasized in a press release.
SOURCE: Roden DM et al. Circulation. 2020 Apr 8. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047521.
The .
“Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin have been touted for potential prophylaxis or treatment for COVID-19; both drugs are listed as definite causes of torsade de pointes” and increase in the risk of other arrhythmias and sudden death, the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Rhythm Society said in a joint statement April 8 in Circulation.
The statement came amid ongoing promotion by the Trump administration of hydroxychloroquine, in particular, for COVID-19 despite lack of strong data.
In addition to underlying cardiovascular disease, “seriously ill patients often have comorbidities that can increase risk of serious arrhythmias,” including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, fever, and systemic inflammation, the groups said.
They recommended withholding the drugs in patients with baseline QT prolongation (e.g., QTc of at least 500 msec) or with known congenital long QT syndrome; monitoring cardiac rhythm and QT interval and withdrawing hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin if QTc exceeds 500 msec; correcting hypokalemia to levels greater than 4 mEq/L and hypomagnesemia to more than 2 mg/dL; and avoiding other QTc-prolonging agents when possible.
The groups noted that, “in patients critically ill with COVID-19 infection, frequent caregiver contact may need to be minimized, so optimal electrocardiographic interval and rhythm monitoring may not be possible.” There is also a possible compounding arrhythmic effect when hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin are used together, but that has not been studied.
There’s a known risk of torsade de pointes with chloroquine and a possible risk with the antiviral HIV combination drug lopinavir-ritonavir, two other candidates for COVID-19 treatment. Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine, both antimalarials, might help prevent or treat infection by interfering with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, which the COVID-19 virus uses for cell entry, the groups said.
“The urgency of COVID-19 must not diminish the scientific rigor with which we approach COVID-19 treatment. While these medications may work against COVID-19 individually or in combination, we recommend caution with these medications for patients with existing cardiovascular disease,” Robert A. Harrington, MD, AHA president and chair of the department of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, emphasized in a press release.
SOURCE: Roden DM et al. Circulation. 2020 Apr 8. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047521.
The .
“Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin have been touted for potential prophylaxis or treatment for COVID-19; both drugs are listed as definite causes of torsade de pointes” and increase in the risk of other arrhythmias and sudden death, the American Heart Association, the American College of Cardiology, and the Heart Rhythm Society said in a joint statement April 8 in Circulation.
The statement came amid ongoing promotion by the Trump administration of hydroxychloroquine, in particular, for COVID-19 despite lack of strong data.
In addition to underlying cardiovascular disease, “seriously ill patients often have comorbidities that can increase risk of serious arrhythmias,” including hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, fever, and systemic inflammation, the groups said.
They recommended withholding the drugs in patients with baseline QT prolongation (e.g., QTc of at least 500 msec) or with known congenital long QT syndrome; monitoring cardiac rhythm and QT interval and withdrawing hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin if QTc exceeds 500 msec; correcting hypokalemia to levels greater than 4 mEq/L and hypomagnesemia to more than 2 mg/dL; and avoiding other QTc-prolonging agents when possible.
The groups noted that, “in patients critically ill with COVID-19 infection, frequent caregiver contact may need to be minimized, so optimal electrocardiographic interval and rhythm monitoring may not be possible.” There is also a possible compounding arrhythmic effect when hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin are used together, but that has not been studied.
There’s a known risk of torsade de pointes with chloroquine and a possible risk with the antiviral HIV combination drug lopinavir-ritonavir, two other candidates for COVID-19 treatment. Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine, both antimalarials, might help prevent or treat infection by interfering with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors, which the COVID-19 virus uses for cell entry, the groups said.
“The urgency of COVID-19 must not diminish the scientific rigor with which we approach COVID-19 treatment. While these medications may work against COVID-19 individually or in combination, we recommend caution with these medications for patients with existing cardiovascular disease,” Robert A. Harrington, MD, AHA president and chair of the department of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, emphasized in a press release.
SOURCE: Roden DM et al. Circulation. 2020 Apr 8. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047521.
COVID-19: Are acute stroke patients avoiding emergency care?
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(EDs).
Stroke specialists in New Orleans, Chicago, Seattle, and elsewhere told Medscape Medical News they are seeing a precipitous drop in the number of acute strokes at their institutions – and not just in the number of milder cases. Doctors on Twitter are sharing similar reports and are using social media to highlight this issue.
Gabriel Vidal, MD, a vascular and interventional neurologist at the Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, Louisiana, said there are “definitely” fewer patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) seeking care at his facility and others throughout the New Orleans area, which has been hard hit by COVID-19.
“Even in Louisiana, we have a very large 53-hospital telestroke network, and the number of consults has diminished greatly,” Vidal added.
In Chicago, emergency medical service activations for patients with suspected strokes are down about 30%, Shyam Prabhakaran, MD, professor and chair of neurology at the University of Chicago Biological Sciences, Illinois, told Medscape Medical News.
“It appears to be that mild stroke and TIA patients may be more likely to stay at home and seek alternative care rather than come to the ED,” Prabhakaran said. However, “the severe strokes may be less affected and continue to come to emergency departments.”
“Getting the Word Out”
That may not be the whole story in Seattle, Washington, where a stroke specialist at Harborview Medical Center reported a drop in patients across the stroke-severity spectrum.
Some patients with milder strokes no longer come to Harborview for a comprehensive evaluation and workup, but that is only “a partial explanation,” said David Tirschwell, MD, medical director of comprehensive stroke care at the University of Washington (UW) Medicine Stroke Center at Harborview and a professor of neurology at UW.
“The thrombectomies are down also,” he added. “It’s hard to have great numbers in real time, but it’s probably safe to say it’s at least a 50% reduction in the number of admissions.”
As a stroke referral center, his institution is seeing fewer local cases and referrals from outside hospitals. “I think both of those sources for admissions of stroke cases are down,” Tirschwell said.
Recognizing the seriousness of forgoing essential care for acute stroke, neurologists, institutions, and medical groups are taking to social media to potentially save lives.
“Across our @FLStrokeReg we are seeing less patients with #stroke symptoms coming to our hospitals. We need to get the word out that our teams are working hard to safely provide care when needed during #COVID19,” tweeted Ralph Sacco, MD, chief and professor of neurology, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine in South Florida.
Although Florida Stroke Registry data are not publicly available, anecdotal reports suggest that stroke admissions are down among many hospitals, Sacco told Medscape Medical News.
Furthermore, this is not a phenomenon only in the United States. “This has also been reported in other nations hit by COVID-19,” he said.
China is a prime example. There, many stroke centers have shown reduced functioning “because of fear of in-hospital cross infection and lack of experienced stroke care experts,” Jing Zhao, MD, PhD, and colleagues write in an editorial published online March 31 in Stroke.
Preliminary data show that “thrombectomies in Shanghai decreased by 50% in the first month after the Spring Festival compared with the same period in 2019,” write the editorialists, who are from Kings College London and the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
“Although the control of the COVID-19 is very important, at the same time, the management of stroke must not be neglected,” they add.
“Over 9000 new stroke cases occur each day in China alone. It cannot be right that treatment for one potentially curable disease is euthanized at the expense of another.”
Fear Factor?
The reasons individuals who may have experienced a stroke are avoiding emergency care is unclear at the moment. “I’m not really sure anyone really understands why, quite honestly,” Tirschwell said.
Until survey data or other data emerge, many experts are assuming that fear of COVID-19 is trumping other medical concerns, including emergency treatment of stroke.
“We believe this could represent patients being fearful to come to medical facilities with stroke-like symptoms, given the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Sacco, who is also incoming editor-in-chief of Stroke.
The BBC has been getting the word out in the United Kingdom via social media, with a tweet to “Dial 999 for stroke emergencies despite coronavirus.”
The World Stroke Campaign is also using Twitter to emphasize the need for urgent stroke care when appropriate:
“Don’t let concerns about COVID19 prevent you from seeking emergency treatment for stroke. If you spot the signs of stroke act FAST. Get emergency medical assistance,” the group urged in a tweet.
Don’t Hesitate
The American Heart Association (AHA) has addressed this troubling trend as well.
“People with serious symptoms shouldn’t ignore them,” Sarah Perlman, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, states in an article on the AHA website.
Perlman added that some individuals who have signs of stroke and heart disease may hesitate to seek care because of fear that they are adding to an overburdened healthcare staff and system. However, she dismissed those concerns outright.
“If you’re experiencing warning signs of a heart attack or stroke, call 911,” she said. “Clearly, if there’s an emergency, we are available and capable and eager to take care of you.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19: Dramatic changes to telepsychiatry rules and regs
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the wake of the coronavirus pandemic,
Under the 1135 emergency waiver, Medicare has expanded telehealth services to include patients across the country – not just in rural areas or under other limited conditions, as was previously the case. In addition, there’s now a waiver to the Ryan Haight Act that allows the prescribing of controlled substances via telemedicine.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, from University of California, Davis, reported that outpatient service at his center was converted to an almost 100% telepsychiatry service from mid- to late March.
He and John Torous, MD, director of digital psychiatry at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, led a free webinar late last month sponsored by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA).
During the hour-long event, they answered questions and offered tips on changes in licensure, patient safety, new prescribing rules, and equipment needed.
“Clinicians need to be aware of these changes so they can ensure they are reaching as many people as possible and taking advantage of the reduced barriers to offering safe and effective video visits,” Dr. Torous said in an interview.
‘This is huge’
The new 1135 waiver “basically says CMS will pay for any patient on Medicare who is seen by video by any provider who is correctly licensed in any state in this country,” Dr. Yellowlees told webinar attendees.
“You don’t need to be licensed in the state where the patient is if the patient is on Medicare. This opens up a huge number of patients we can now see on video,” he said. “And you can bill at normal Medicare rates for whatever you normally get for your in-person patients.”
Although this temporary rule only applies to Medicare and not to private insurers, or to patients on Medicaid, “these are really big changes. This is huge,” Dr. Torous said.
Previously, the “originating site” rule stated that, for the most part, clinicians had to be licensed in the state where the patient was located and not where the physician was stationed.
Asked about college students receiving mental health care who were in school in the psychiatrist’s area but are now back home in a state where the clinician doesn’t have a license, Dr. Yellowlees said that scenario could be a bit “tricky.”
“Most of those patients probably aren’t on Medicare. Legally, you [usually] can’t see them on video if they have private insurance or Medicaid. So, hopefully you can give them a 3-month supply of medication and then recommend they see a local provider,” he said.
Still, all states have their own rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. He and Dr. Torous noted that the Federation of State Medical Boards has a “very up-to-date” listing of policies at FSMB.org, all of which are organized by state. In addition, the American Psychiatric Association provides a telepsychiatry toolkit on its website.
Ryan Haight Act and prescribing
Physicians are now permitted to prescribe medication to patients assessed via telemedicine.
For those with substance use disorders, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has announced a new waiver for the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act.
The waiver states that “practitioners in all areas of the United States may issue prescriptions for all schedule II-V controlled substances” – as long as it’s for a legitimate medical purpose; real-time, two-way interactive communication with patients has been used; and the clinician “is acting in accordance with applicable Federal and State laws.”
“It’s now possible to prescribe all the normal psychiatric drugs but also benzodiazepines, stimulants, and potentially narcotics over telepsychiatry,” even at a first visit via video, Dr. Yellowlees said.
However, he noted at this point the waiver is current for only 60 days. “This isn’t a permanent condition. It could be extended or even shortened at any given time.”
In addition, SAMHSA has relaxed some of its own regulations regarding telehealth and opioid treatment programs. An FAQ section on the organization’s website provides guidance for providing methadone and buprenorphine treatment.
“Some of the previous regulations will probably be put back in place later on, but the new changes are helpful now,” Dr. Yellowlees said.
Simple equipment needed
Regarding equipment, Dr. Yellowlees noted that the most important component is just a laptop, tablet, or smartphone – for the clinician and for the patient.
“You don’t need fancy new technology with a separate camera or microphone,” he said. However, it might be worth investing in a little better system down the line, he added.
Simple platforms that can be used to meet virtually with patients include FaceTime, Google Hangouts, and Skype.
Although some of these (such as FaceTime) are not HIPAA compliant, “that’s okay for now” under the new rules, Dr. Yellowlees said. While the health system/commercial version of Skype is compliant, the normal consumer-downloaded version is not, he noted.
“I would still strongly suggest using HIPAA-compliant video-conferencing programs in the long run,” he added.
Either way, it’s important for various safety practices to be put into place. For example, clinicians should be careful because the consumer version of Skype can show names of patients who were previously spoken with.
A business associate agreement (BAA) is something that HIPAA-compliant video systems will offer and which should be signed. It’s an agreement that “you’ll be, essentially, looking through a tunnel at the persona at the other end, and the company cannot get inside the tunnel and watch you while you’re having your interview,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“There are multiple videoconferencing systems around that you can use,” he added. “The three major ones are from Zoom, Vidyo, and VSee, but there are probably 40 or 50 more.”
“There are a lot out there, and we’re certainly not endorsing any one of them,” Dr. Torous added.
When evaluating potential programs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested looking at Yelp-style reviews or telemedicine review sites, or talk with colleagues.
“Basically, you want systems that offer high-definition video quality and the ability to ‘lock’ and ‘unlock’ the rooms. And you want it to have an app so mobile devices can use it,” he said.
Phone vs. video
Some patients, especially older ones, may be resistant to the idea of video chats, preferring to talk via telephone instead.
“If you can use video, it’s better to do that if you can, especially when setting up the systems are relatively simple,” Dr. Yellowlees said, adding that it might just be an issue of patients needing help to get started.
However, “for some people, this is a barrier that we have to respect,” Dr. Torous said.
Either way, clinicians should check the American Medical Association’s website for information about coding for both video and phone visits.
Asked whether a clinician needs written consent from patients for conducting telepsychiatry visits, Dr. Yellowlees said it’s important to check state-by-state rules. For example, California allows a verbal consent.
In many cases, “simply jot down a note that consent was given and how” and write down the address where the patient is located at time of visit, such as for their home, he said.
If a patient wants to conduct a telehealth session while in their car, Dr. Yellowlees suggested getting the address of the parking lot. For safety, clinicians also are advised asking for the cell phone number of the patient as well as that of a loved one.
Vital signs
When it comes to checking vital signs, Dr. Yellowlees suggested asking patients to purchase an inexpensive blood pressure (BP) monitor, thermometer, etc, prior to an appointment.
“Ask them to do a BP test on video and show you the readings. For the AIMS [Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale] test, or to check for tardive dyskinesia, instruct patients to come close to the camera to show movement.”
In addition, most psychiatric rating scales are available online, which patients can fill out before a telehealth visit. The Serious Mental Illness (SMI) Adviser mobile app also includes several of these scales, Dr. Torous noted.
Overall, “there have been dramatic changes in the rules and regulations governing [telepsychiatry] that, for the next 60 days, make it easier to offer telehealth to patients,” Dr. Torous said.
Therefore, all psychiatrists need to “get on board,” as soon as possible, Dr. Yellowlees added.
The webinar was funded in part by a grant from SAMHSA.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves first generic albuterol inhaler
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the first generic of Proventil HFA (albuterol sulfate) metered-dose inhaler, 90 mcg/inhalation, according to a release from the agency. This inhaler is indicated for prevention of bronchospasm in patients aged 4 years and older. Specifically, these are patients with reversible obstructive airway disease or exercise-induced bronchospasm.
“The FDA recognizes the increased demand for albuterol products during the novel coronavirus pandemic,” said FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD.
The most common side effects include upper respiratory tract infection, rhinitis, nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, tremor, and nervousness.
This approval comes as part of FDA’s efforts to guide industry through the development process of generic products, according to the release. Complex combination products – such as this inhaler, which comprises both medication and a delivery system – can be more challenging to develop than solid oral dosage forms, such as tablets.
The FDA released a draft guidance in March 2020 specific to proposed generic albuterol sulfate metered-dose inhalers, including drug products referencing Proventil HFA. As with other similar guidances, it details the steps companies need to take in developing generics in order to submit complete applications for those products. The full news release regarding this approval is available on the FDA website.
This article was updated 4/8/20.
ACOG offers guidance on optimizing patient care in the midst of COVID-19
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) posted a useful resource on its website on March 30 for clinicians practicing ambulatory gynecology. The guidance, “COVID-19 FAQs for Obstetrician–Gynecologists, Gynecology” (https://www.acog.org/), is based on expert opinion and is intended to supplement guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as previously issued ACOG guidance.1
Which patients need to be seen, and when
The ACOG guidance provides examples of patients needing in-person appointments, video or telephone visits, or for whom deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak would be appropriate. Highlights include:
In-person appointments
- suspected ectopic pregnancy
- profuse vaginal bleeding
Video or telephone visits
- contraceptive counseling and prescribing
- management of menopausal symptoms
Deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak
- routine well-woman visits for average-risk patients.
Cervical screening
With respect to patients with abnormal cervical cancer screening results, ACOG recommends the ASCCP’s guidance that2:
- for patients with low-grade test results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be deferred up to 6 to 12 months
- for patients with high-grade results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be performed within 3 months.
Contraception
Regarding contraceptive services, the ACOG guidance suggests that placement of intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants should continue “where possible.” If initiation of long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) is not feasible, the guidance recommends that use of self-administered contraceptives (including subcutaneous injections, oral, transdermal patch, and vaginal ring contraception) be encouraged as a bridge to later initiation of LARC.
The guidance suggests that removal of IUDs and implants be postponed when possible.
Finally, the guidance suggests that patients with an existing IUD or implant who seek removal and replacement of their contraceptives be counseled regarding extended use of these devices.
Individualize your approach
ACOG emphasizes that no single solution applies to all situations and that each practice or clinic should evaluate the individual situation, including the availability of local and regional resources, staffing, and personal protective equipment; the prevalence of COVID-19 in the region; and the type of practice.
A roadmap for care
This guidance from ACOG should help clinicians caring for women during the COVID-19 outbreak to counsel and guide patients in a prudent manner.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. COVID-19 FAQs for obstetrician-gynecologists, gynecology. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/physician-faqs/covid19-faqs-for-ob-gyns-gynecology. Accessed April 3, 2020.
- ASCCP website. ASCCP interim guidance for timing of diagnostic and treatment procedures for patients with abnormal cervical screening tests. https://www.asccp.org/covid-19. Accessed April 3, 2020.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) posted a useful resource on its website on March 30 for clinicians practicing ambulatory gynecology. The guidance, “COVID-19 FAQs for Obstetrician–Gynecologists, Gynecology” (https://www.acog.org/), is based on expert opinion and is intended to supplement guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as previously issued ACOG guidance.1
Which patients need to be seen, and when
The ACOG guidance provides examples of patients needing in-person appointments, video or telephone visits, or for whom deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak would be appropriate. Highlights include:
In-person appointments
- suspected ectopic pregnancy
- profuse vaginal bleeding
Video or telephone visits
- contraceptive counseling and prescribing
- management of menopausal symptoms
Deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak
- routine well-woman visits for average-risk patients.
Cervical screening
With respect to patients with abnormal cervical cancer screening results, ACOG recommends the ASCCP’s guidance that2:
- for patients with low-grade test results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be deferred up to 6 to 12 months
- for patients with high-grade results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be performed within 3 months.
Contraception
Regarding contraceptive services, the ACOG guidance suggests that placement of intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants should continue “where possible.” If initiation of long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) is not feasible, the guidance recommends that use of self-administered contraceptives (including subcutaneous injections, oral, transdermal patch, and vaginal ring contraception) be encouraged as a bridge to later initiation of LARC.
The guidance suggests that removal of IUDs and implants be postponed when possible.
Finally, the guidance suggests that patients with an existing IUD or implant who seek removal and replacement of their contraceptives be counseled regarding extended use of these devices.
Individualize your approach
ACOG emphasizes that no single solution applies to all situations and that each practice or clinic should evaluate the individual situation, including the availability of local and regional resources, staffing, and personal protective equipment; the prevalence of COVID-19 in the region; and the type of practice.
A roadmap for care
This guidance from ACOG should help clinicians caring for women during the COVID-19 outbreak to counsel and guide patients in a prudent manner.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) posted a useful resource on its website on March 30 for clinicians practicing ambulatory gynecology. The guidance, “COVID-19 FAQs for Obstetrician–Gynecologists, Gynecology” (https://www.acog.org/), is based on expert opinion and is intended to supplement guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as well as previously issued ACOG guidance.1
Which patients need to be seen, and when
The ACOG guidance provides examples of patients needing in-person appointments, video or telephone visits, or for whom deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak would be appropriate. Highlights include:
In-person appointments
- suspected ectopic pregnancy
- profuse vaginal bleeding
Video or telephone visits
- contraceptive counseling and prescribing
- management of menopausal symptoms
Deferral of a visit until after the COVID-19 outbreak
- routine well-woman visits for average-risk patients.
Cervical screening
With respect to patients with abnormal cervical cancer screening results, ACOG recommends the ASCCP’s guidance that2:
- for patients with low-grade test results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be deferred up to 6 to 12 months
- for patients with high-grade results, colposcopy/cervical biopsies be performed within 3 months.
Contraception
Regarding contraceptive services, the ACOG guidance suggests that placement of intrauterine devices (IUDs) and contraceptive implants should continue “where possible.” If initiation of long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) is not feasible, the guidance recommends that use of self-administered contraceptives (including subcutaneous injections, oral, transdermal patch, and vaginal ring contraception) be encouraged as a bridge to later initiation of LARC.
The guidance suggests that removal of IUDs and implants be postponed when possible.
Finally, the guidance suggests that patients with an existing IUD or implant who seek removal and replacement of their contraceptives be counseled regarding extended use of these devices.
Individualize your approach
ACOG emphasizes that no single solution applies to all situations and that each practice or clinic should evaluate the individual situation, including the availability of local and regional resources, staffing, and personal protective equipment; the prevalence of COVID-19 in the region; and the type of practice.
A roadmap for care
This guidance from ACOG should help clinicians caring for women during the COVID-19 outbreak to counsel and guide patients in a prudent manner.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. COVID-19 FAQs for obstetrician-gynecologists, gynecology. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/physician-faqs/covid19-faqs-for-ob-gyns-gynecology. Accessed April 3, 2020.
- ASCCP website. ASCCP interim guidance for timing of diagnostic and treatment procedures for patients with abnormal cervical screening tests. https://www.asccp.org/covid-19. Accessed April 3, 2020.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. COVID-19 FAQs for obstetrician-gynecologists, gynecology. https://www.acog.org/clinical-information/physician-faqs/covid19-faqs-for-ob-gyns-gynecology. Accessed April 3, 2020.
- ASCCP website. ASCCP interim guidance for timing of diagnostic and treatment procedures for patients with abnormal cervical screening tests. https://www.asccp.org/covid-19. Accessed April 3, 2020.
When is preventive treatment of migraine appropriate?
STOWE, VT – , said Rebecca Burch, MD, staff attending neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Clinical observation suggests that preventive treatment provides benefits for appropriately selected migraineurs, although few data confirm a modifying effect on disease course, she said at the Stowe Headache Symposium sponsored by the Headache Cooperative of New England. In her overview, Dr. Burch discussed when preventive treatment is appropriate, which patients are candidates for preventive therapy, and what the levels of evidence are for the preventive therapies.
Identifying candidates for preventive treatment
Migraine is the second most disabling condition worldwide and imposes a large social and economic burden, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy reduces the disability associated with migraine. It reduces headache frequency and, thus, the risk that episodic migraine will transform into chronic migraine. By reducing the number of headache days, preventive treatment also may reduce the overuse of acute medication, which is a risk factor for migraine chronification.
Neurologists can consider preventive therapy for migraineurs with frequent headaches, but the term “frequent” is not clearly defined. Common definitions include one headache per week and two headaches per month with significant disability. These definitions are based on expert consensus and do not have strong evidential support, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy also may be appropriate for migraineurs who overuse acute medication or who have failed acute medications. Special cases, such as patients with exceptional anxiety or disability, may also call for preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch.
Data suggest that preventive treatment for migraine is underused. The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study of 2007 found that half of patients who should be offered preventive treatment are currently receiving it. In 2016, the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes study found that 4.5% of chronic migraineurs take both acute and preventive treatment.
Other data published in Cephalalgia in 2015 indicate that adherence to migraine preventive treatment is approximately 20%. About 45% of patients discontinue medication because of side effects, and 45% cite lack of efficacy as their reason for discontinuation. Patients also mentioned cost, interactions with other medications, and the inconvenience of daily medication as other reasons for discontinuation.
Neurologists can take several steps to increase adherence to preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch. First, neurologists should confirm that patients want preventive medication. A clear discussion of the goals of preventive treatment is helpful as well. Furthermore, neurologists should explain that they are offering patients a trial, said Dr. Burch. The medication can be titrated slowly from a low dose to minimize side effects. Patients can be reassured that ineffective medications will be stopped. Neurologists can emphasize that their relationship with the patient is a partnership and that the treatment strategy will be improved over time.
Examining the evidence on treatments’ efficacy
Many drug classes, such as antiepileptics, antidepressants, beta blockers, neurotoxins, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies, include therapies that are used as preventive treatments for migraine. When selecting a medication, a neurologist should start with one that is supported by Level A or Level B evidence, said Dr. Burch. Medications with Level A evidence include divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab, eptinezumab, and onabotulinumtoxinA. Medications with Level B evidence include amitriptyline, venlafaxine, memantine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Neurologists sometimes prescribe gabapentin and verapamil, although the evidence for them is Level U. Duloxetine, nortriptyline, and pregabalin also are used, but the evidence for them has not been evaluated. “We need more evidence in these areas,” said Dr. Burch.
Neurologists should consider access (e.g., cost and insurance coverage), efficacy, side effects, and comorbidities and contraindications when choosing a preventive therapy, she added. Verapamil and memantine are well tolerated and appropriate choices if the goal is to avoid side effects in general. If weight gain or fatigue is a concern, then topiramate and venlafaxine should be considered. Neurologists should avoid prescribing antiepileptic drugs if cognitive symptoms are a concern, said Dr. Burch. Beta blockers and venlafaxine would be better options in this case.
In clinical trials of CGRP therapies, the rates of adverse events were similar between the active and control arms. “But it’s become fairly clear that the clinical trials did not fully capture the side-effect profile that we are seeing in clinical practice,” said Dr. Burch. In a paper currently in review, she and her colleagues retrospectively studied 241 patients that they had treated with CGRP monoclonal antibodies at their headache center. The most common adverse events were constipation (43%), injection-site reaction (24%), muscle or joint pain (17%), and fatigue (15%). Furthermore, CGRP antagonists were associated with maternal hypertension, fetal growth restriction, and fetal mortality in animal studies. The current recommendation is to avoid CGRP monoclonal antibodies during pregnancy or in any patient who is at risk of becoming pregnant, said Dr. Burch.
How should neurologists assess preventive efficacy?
The assessment of a medication’s preventive efficacy “is a moving target in the headache world,” said Dr. Burch. “Historically, we have used headache days per month, and that is still, according to the International Headache Society clinical trials guidelines, how we should be judging whether a medication is working or not. But that doesn’t necessarily tell us what’s going to happen to an individual patient in front of us.”
In 2017, the Institute for Clinical Effectiveness Research compared data for old and new migraine treatments in a network meta-analysis. They all tended to reduce the number of monthly migraine days by one to two, compared with placebo. When one analyzes clinical trials of the drugs using this criterion, “most of these treatments come out about the same,” said Dr. Burch.
More recently, investigators have examined responder rates. They commonly report the proportions of patients who had a reduction in headache days of 50%, 75%, or 100%, for example. To extrapolate responder rates from the trial participants to the general population, a neurologist must know which groups of patients got worse on treatment, said Dr. Burch. Furthermore, the responder rates for older medications are unknown, because they were not examined. This situation makes comparisons of newer and older therapies more complicated.
Phase 3 trials of the CGRP drugs included analyses of the therapies’ 50% responder rates. This rate was about 42% for the 70-mg dose of erenumab and 50% for the 140-mg dose. The 50% responder rates for fremanezumab were 47.7% for the 225-mg dose and 44.4% for the 675-mg dose. In two trials of galcanezumab, the 50% responder rate for the 120-mg dose was approximately 60%, and the rate for the 240-mg dose was about 59%. The 50% responder rates for eptinezumab were 50% for the 100-mg dose and 56% for the 300-mg dose. The 50% responder rate across all trials was around 50%-60% in the active group, which is roughly 25% over the placebo group, said Dr. Burch.
Another measurement of efficacy is the efficacy-to-harm ratio, which is derived from the number needed to treat and the number needed to harm. To calculate this ratio, however, harm needs to be assessed adequately during a clinical trial. Although the ratio can provide a clinically relevant overview of a drug’s effects, patients may differ from each other in the way they evaluate efficacy and harm.
In addition, many questions about preventive treatment of migraine have no clear answers yet. It is uncertain, for example, how long a patient should receive preventive treatment and when treatment should be withdrawn, said Dr. Burch. “Can we expect that a lot of people are going to need to be on it for life, or is there a subpopulation who will get better and [for whom] we can withdraw [treatment]?” she asked. “How do we identify them?” Also, more data are needed before neurologists can understand why a given patient responds to one treatment, but not to another. It is difficult to predict which patients will respond to which treatments. Finally, it remains unclear how much of patients’ improvement can be attributed to regression to the mean, rather than preventive treatment.
STOWE, VT – , said Rebecca Burch, MD, staff attending neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Clinical observation suggests that preventive treatment provides benefits for appropriately selected migraineurs, although few data confirm a modifying effect on disease course, she said at the Stowe Headache Symposium sponsored by the Headache Cooperative of New England. In her overview, Dr. Burch discussed when preventive treatment is appropriate, which patients are candidates for preventive therapy, and what the levels of evidence are for the preventive therapies.
Identifying candidates for preventive treatment
Migraine is the second most disabling condition worldwide and imposes a large social and economic burden, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy reduces the disability associated with migraine. It reduces headache frequency and, thus, the risk that episodic migraine will transform into chronic migraine. By reducing the number of headache days, preventive treatment also may reduce the overuse of acute medication, which is a risk factor for migraine chronification.
Neurologists can consider preventive therapy for migraineurs with frequent headaches, but the term “frequent” is not clearly defined. Common definitions include one headache per week and two headaches per month with significant disability. These definitions are based on expert consensus and do not have strong evidential support, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy also may be appropriate for migraineurs who overuse acute medication or who have failed acute medications. Special cases, such as patients with exceptional anxiety or disability, may also call for preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch.
Data suggest that preventive treatment for migraine is underused. The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study of 2007 found that half of patients who should be offered preventive treatment are currently receiving it. In 2016, the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes study found that 4.5% of chronic migraineurs take both acute and preventive treatment.
Other data published in Cephalalgia in 2015 indicate that adherence to migraine preventive treatment is approximately 20%. About 45% of patients discontinue medication because of side effects, and 45% cite lack of efficacy as their reason for discontinuation. Patients also mentioned cost, interactions with other medications, and the inconvenience of daily medication as other reasons for discontinuation.
Neurologists can take several steps to increase adherence to preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch. First, neurologists should confirm that patients want preventive medication. A clear discussion of the goals of preventive treatment is helpful as well. Furthermore, neurologists should explain that they are offering patients a trial, said Dr. Burch. The medication can be titrated slowly from a low dose to minimize side effects. Patients can be reassured that ineffective medications will be stopped. Neurologists can emphasize that their relationship with the patient is a partnership and that the treatment strategy will be improved over time.
Examining the evidence on treatments’ efficacy
Many drug classes, such as antiepileptics, antidepressants, beta blockers, neurotoxins, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies, include therapies that are used as preventive treatments for migraine. When selecting a medication, a neurologist should start with one that is supported by Level A or Level B evidence, said Dr. Burch. Medications with Level A evidence include divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab, eptinezumab, and onabotulinumtoxinA. Medications with Level B evidence include amitriptyline, venlafaxine, memantine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Neurologists sometimes prescribe gabapentin and verapamil, although the evidence for them is Level U. Duloxetine, nortriptyline, and pregabalin also are used, but the evidence for them has not been evaluated. “We need more evidence in these areas,” said Dr. Burch.
Neurologists should consider access (e.g., cost and insurance coverage), efficacy, side effects, and comorbidities and contraindications when choosing a preventive therapy, she added. Verapamil and memantine are well tolerated and appropriate choices if the goal is to avoid side effects in general. If weight gain or fatigue is a concern, then topiramate and venlafaxine should be considered. Neurologists should avoid prescribing antiepileptic drugs if cognitive symptoms are a concern, said Dr. Burch. Beta blockers and venlafaxine would be better options in this case.
In clinical trials of CGRP therapies, the rates of adverse events were similar between the active and control arms. “But it’s become fairly clear that the clinical trials did not fully capture the side-effect profile that we are seeing in clinical practice,” said Dr. Burch. In a paper currently in review, she and her colleagues retrospectively studied 241 patients that they had treated with CGRP monoclonal antibodies at their headache center. The most common adverse events were constipation (43%), injection-site reaction (24%), muscle or joint pain (17%), and fatigue (15%). Furthermore, CGRP antagonists were associated with maternal hypertension, fetal growth restriction, and fetal mortality in animal studies. The current recommendation is to avoid CGRP monoclonal antibodies during pregnancy or in any patient who is at risk of becoming pregnant, said Dr. Burch.
How should neurologists assess preventive efficacy?
The assessment of a medication’s preventive efficacy “is a moving target in the headache world,” said Dr. Burch. “Historically, we have used headache days per month, and that is still, according to the International Headache Society clinical trials guidelines, how we should be judging whether a medication is working or not. But that doesn’t necessarily tell us what’s going to happen to an individual patient in front of us.”
In 2017, the Institute for Clinical Effectiveness Research compared data for old and new migraine treatments in a network meta-analysis. They all tended to reduce the number of monthly migraine days by one to two, compared with placebo. When one analyzes clinical trials of the drugs using this criterion, “most of these treatments come out about the same,” said Dr. Burch.
More recently, investigators have examined responder rates. They commonly report the proportions of patients who had a reduction in headache days of 50%, 75%, or 100%, for example. To extrapolate responder rates from the trial participants to the general population, a neurologist must know which groups of patients got worse on treatment, said Dr. Burch. Furthermore, the responder rates for older medications are unknown, because they were not examined. This situation makes comparisons of newer and older therapies more complicated.
Phase 3 trials of the CGRP drugs included analyses of the therapies’ 50% responder rates. This rate was about 42% for the 70-mg dose of erenumab and 50% for the 140-mg dose. The 50% responder rates for fremanezumab were 47.7% for the 225-mg dose and 44.4% for the 675-mg dose. In two trials of galcanezumab, the 50% responder rate for the 120-mg dose was approximately 60%, and the rate for the 240-mg dose was about 59%. The 50% responder rates for eptinezumab were 50% for the 100-mg dose and 56% for the 300-mg dose. The 50% responder rate across all trials was around 50%-60% in the active group, which is roughly 25% over the placebo group, said Dr. Burch.
Another measurement of efficacy is the efficacy-to-harm ratio, which is derived from the number needed to treat and the number needed to harm. To calculate this ratio, however, harm needs to be assessed adequately during a clinical trial. Although the ratio can provide a clinically relevant overview of a drug’s effects, patients may differ from each other in the way they evaluate efficacy and harm.
In addition, many questions about preventive treatment of migraine have no clear answers yet. It is uncertain, for example, how long a patient should receive preventive treatment and when treatment should be withdrawn, said Dr. Burch. “Can we expect that a lot of people are going to need to be on it for life, or is there a subpopulation who will get better and [for whom] we can withdraw [treatment]?” she asked. “How do we identify them?” Also, more data are needed before neurologists can understand why a given patient responds to one treatment, but not to another. It is difficult to predict which patients will respond to which treatments. Finally, it remains unclear how much of patients’ improvement can be attributed to regression to the mean, rather than preventive treatment.
STOWE, VT – , said Rebecca Burch, MD, staff attending neurologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. Clinical observation suggests that preventive treatment provides benefits for appropriately selected migraineurs, although few data confirm a modifying effect on disease course, she said at the Stowe Headache Symposium sponsored by the Headache Cooperative of New England. In her overview, Dr. Burch discussed when preventive treatment is appropriate, which patients are candidates for preventive therapy, and what the levels of evidence are for the preventive therapies.
Identifying candidates for preventive treatment
Migraine is the second most disabling condition worldwide and imposes a large social and economic burden, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy reduces the disability associated with migraine. It reduces headache frequency and, thus, the risk that episodic migraine will transform into chronic migraine. By reducing the number of headache days, preventive treatment also may reduce the overuse of acute medication, which is a risk factor for migraine chronification.
Neurologists can consider preventive therapy for migraineurs with frequent headaches, but the term “frequent” is not clearly defined. Common definitions include one headache per week and two headaches per month with significant disability. These definitions are based on expert consensus and do not have strong evidential support, said Dr. Burch. Preventive therapy also may be appropriate for migraineurs who overuse acute medication or who have failed acute medications. Special cases, such as patients with exceptional anxiety or disability, may also call for preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch.
Data suggest that preventive treatment for migraine is underused. The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study of 2007 found that half of patients who should be offered preventive treatment are currently receiving it. In 2016, the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes study found that 4.5% of chronic migraineurs take both acute and preventive treatment.
Other data published in Cephalalgia in 2015 indicate that adherence to migraine preventive treatment is approximately 20%. About 45% of patients discontinue medication because of side effects, and 45% cite lack of efficacy as their reason for discontinuation. Patients also mentioned cost, interactions with other medications, and the inconvenience of daily medication as other reasons for discontinuation.
Neurologists can take several steps to increase adherence to preventive treatment, said Dr. Burch. First, neurologists should confirm that patients want preventive medication. A clear discussion of the goals of preventive treatment is helpful as well. Furthermore, neurologists should explain that they are offering patients a trial, said Dr. Burch. The medication can be titrated slowly from a low dose to minimize side effects. Patients can be reassured that ineffective medications will be stopped. Neurologists can emphasize that their relationship with the patient is a partnership and that the treatment strategy will be improved over time.
Examining the evidence on treatments’ efficacy
Many drug classes, such as antiepileptics, antidepressants, beta blockers, neurotoxins, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antibodies, include therapies that are used as preventive treatments for migraine. When selecting a medication, a neurologist should start with one that is supported by Level A or Level B evidence, said Dr. Burch. Medications with Level A evidence include divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, erenumab, galcanezumab, fremanezumab, eptinezumab, and onabotulinumtoxinA. Medications with Level B evidence include amitriptyline, venlafaxine, memantine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Neurologists sometimes prescribe gabapentin and verapamil, although the evidence for them is Level U. Duloxetine, nortriptyline, and pregabalin also are used, but the evidence for them has not been evaluated. “We need more evidence in these areas,” said Dr. Burch.
Neurologists should consider access (e.g., cost and insurance coverage), efficacy, side effects, and comorbidities and contraindications when choosing a preventive therapy, she added. Verapamil and memantine are well tolerated and appropriate choices if the goal is to avoid side effects in general. If weight gain or fatigue is a concern, then topiramate and venlafaxine should be considered. Neurologists should avoid prescribing antiepileptic drugs if cognitive symptoms are a concern, said Dr. Burch. Beta blockers and venlafaxine would be better options in this case.
In clinical trials of CGRP therapies, the rates of adverse events were similar between the active and control arms. “But it’s become fairly clear that the clinical trials did not fully capture the side-effect profile that we are seeing in clinical practice,” said Dr. Burch. In a paper currently in review, she and her colleagues retrospectively studied 241 patients that they had treated with CGRP monoclonal antibodies at their headache center. The most common adverse events were constipation (43%), injection-site reaction (24%), muscle or joint pain (17%), and fatigue (15%). Furthermore, CGRP antagonists were associated with maternal hypertension, fetal growth restriction, and fetal mortality in animal studies. The current recommendation is to avoid CGRP monoclonal antibodies during pregnancy or in any patient who is at risk of becoming pregnant, said Dr. Burch.
How should neurologists assess preventive efficacy?
The assessment of a medication’s preventive efficacy “is a moving target in the headache world,” said Dr. Burch. “Historically, we have used headache days per month, and that is still, according to the International Headache Society clinical trials guidelines, how we should be judging whether a medication is working or not. But that doesn’t necessarily tell us what’s going to happen to an individual patient in front of us.”
In 2017, the Institute for Clinical Effectiveness Research compared data for old and new migraine treatments in a network meta-analysis. They all tended to reduce the number of monthly migraine days by one to two, compared with placebo. When one analyzes clinical trials of the drugs using this criterion, “most of these treatments come out about the same,” said Dr. Burch.
More recently, investigators have examined responder rates. They commonly report the proportions of patients who had a reduction in headache days of 50%, 75%, or 100%, for example. To extrapolate responder rates from the trial participants to the general population, a neurologist must know which groups of patients got worse on treatment, said Dr. Burch. Furthermore, the responder rates for older medications are unknown, because they were not examined. This situation makes comparisons of newer and older therapies more complicated.
Phase 3 trials of the CGRP drugs included analyses of the therapies’ 50% responder rates. This rate was about 42% for the 70-mg dose of erenumab and 50% for the 140-mg dose. The 50% responder rates for fremanezumab were 47.7% for the 225-mg dose and 44.4% for the 675-mg dose. In two trials of galcanezumab, the 50% responder rate for the 120-mg dose was approximately 60%, and the rate for the 240-mg dose was about 59%. The 50% responder rates for eptinezumab were 50% for the 100-mg dose and 56% for the 300-mg dose. The 50% responder rate across all trials was around 50%-60% in the active group, which is roughly 25% over the placebo group, said Dr. Burch.
Another measurement of efficacy is the efficacy-to-harm ratio, which is derived from the number needed to treat and the number needed to harm. To calculate this ratio, however, harm needs to be assessed adequately during a clinical trial. Although the ratio can provide a clinically relevant overview of a drug’s effects, patients may differ from each other in the way they evaluate efficacy and harm.
In addition, many questions about preventive treatment of migraine have no clear answers yet. It is uncertain, for example, how long a patient should receive preventive treatment and when treatment should be withdrawn, said Dr. Burch. “Can we expect that a lot of people are going to need to be on it for life, or is there a subpopulation who will get better and [for whom] we can withdraw [treatment]?” she asked. “How do we identify them?” Also, more data are needed before neurologists can understand why a given patient responds to one treatment, but not to another. It is difficult to predict which patients will respond to which treatments. Finally, it remains unclear how much of patients’ improvement can be attributed to regression to the mean, rather than preventive treatment.
REPORTING FROM HCNE STOWE 2020
Comorbidities the rule in New York’s COVID-19 deaths
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.
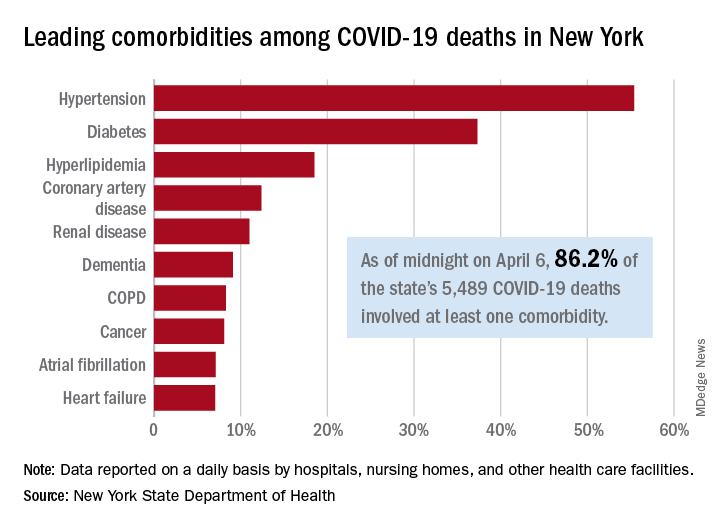
As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
In New York state, just over 86% of reported COVID-19 deaths involved at least one comorbidity, according to the state’s department of health.

As of midnight on April 6, there had been 5,489 fatalities caused by COVID-19 in the state, of which 86.2% (4,732) had at least one underlying condition, the New York State Department of Health reported April 7 on its COVID-19 tracker.
The leading comorbidity, seen in 55.4% of all deaths, was hypertension. In comparison, a recent estimate from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services put the prevalence of high blood pressure at about 45% in the overall adult population.
In New York, the rest of the 10 most common comorbidities in COVID-19 fatalities were diabetes (37.3%), hyperlipidemia (18.5%), coronary artery disease (12.4%), renal disease (11.0%), dementia (9.1%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (8.3%), cancer (8.1%), atrial fibrillation (7.1%), and heart failure (7.1%), the NYSDOH said.
Other data on the tracker site show that 63% of all deaths involved a patient who was aged 70 years or older and that 61% of COVID-19 patients who have died in New York were male and 38.8% were female (sex unknown for 0.2%). Among all individuals who have tested positive, 54.8% were male and 44.6% were female (sex unknown for 0.6%).
As of the end of day on April 6, a total of 340,058 persons had been tested in the state and 40.8% (138,863) were positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus. By county, the highest positive rates are in New York City: Queens at 57.4%, Brooklyn at 52.4%, and the Bronx at 52.3%, according to the NYSDOH.
National Watchman registry reports impressive procedural safety
Early results from the massive National Cardiovascular Data Registry Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Registry indicate that the rollout of the Watchman device into routine clinical practice is going smoothly, with a higher implant success rate and a substantially lower in-hospital complication rate than that seen in the pivotal randomized clinical trials, James V. Freeman, MD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
These real-world results are particularly impressive because the 38,158 registry participants were on average significantly older and sicker than were patients in the clinical trials. They were at higher risk of both stroke and bleeding, yet they fared better in terms of procedural safety, observed Dr. Freeman, an electrophysiologist and director of the Yale University Atrial Fibrillation Center in New Haven, Conn.
“You always worry that once you get outside of the clinical trials setting and you roll out to a large number of centers, including some that are relatively low volume, that you’re going to start to see higher rates of complications. And overall, broadly speaking, the rates of adverse events were quite reassuring,” he said.
The registry, maintained by the ACC, serves as the postmarketing surveillance tool mandated by the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The 38,158 participants make this registry the world’s largest patient experience with the Watchman device by many orders of magnitude. Dr. Freeman’s report included patients enrolled during 2016-2018 who were treated at 495 hospitals by 1,318 physician interventionalists. CMS reimbursement requires participation in the registry, which captures more than 95% of all Watchman procedures done in the United States. Although Dr. Freeman presented only the acute in-hospital outcomes, active follow-up for adverse events and medical therapy will be conducted at 45 days, 6 months, and 1 and 2 years.
Participants in the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO) Registry averaged 76.1 years of age, which is 2-4 years older than patients in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials or the 1,025-patient EWOLUTION registry. The LAAO Registry participants had a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6, compared with 3.4 in PROTECT-AF and 3.8 in PREVAIL. Their mean HAS BLED score was 3.0. Thirty percent had a prior ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, 12% had a prior intracranial hemorrhage, and 69% had a history of clinically relevant bleeding. Thirty percent had heart failure, 92% were hypertensive, and 30% had diabetes.
“The take home here is that these patients were at moderate to high risk of stroke and they also carried a high risk of bleeding and therefore had some relative contraindication to anticoagulation,” according to the cardiologist. “The patient population overall is really in accordance with the CMS guidance. We’re not seeing a lot of patients who are getting this device for a lifestyle indication. Most of these patients are really stuck between a rock and a hard place.”
Most hospitals offering the Watchman did 10-40 cases per year. The median annual physician volume was 12 cases. However, there was substantial variation in both hospital and physician volumes.
The device was deployed in 93% of procedures attempted; roughly half of cancellations were cause by LAAO thrombus detected on the day of the procedure. The acute procedural success rate when the device was deployed was 98.3%, compared with 90.9% in PROTECT-AF and 95.1% in PREVAIL. The rate of device margin residual leak of 5 mm or more among registry participants with an acutely successful procedure was 0.2%.
The rate of any major in-hospital complication in the LAAO Registry was 2.16%, the most common of which was pericardial effusion requiring intervention, which occurred in 1.39% of cases. The major bleeding rate was 1.25%. The stroke/transient ischemic attack rate was 0.17%. Systemic arterial embolism was a rare event, occurring in less than 0.01% of patients, as was acute MI, with an incidence of 0.04%. Device embolization occurred in 0.07% of patients.
By comparison, the 7-day rate of pericardial effusion requiring intervention was 4.0% in PROTECT-AF and 1.9% in PREVAIL, with procedure-related stroke rates of 1.1% and 0.7%, respectively, and device embolization rates of 0.4% and 0.7%. The major bleeding rate in PROTECT-AF was 3.5%, nearly triple that in the real-world registry.
Discussant Mark A. Estes, MD, characterized the acute outcomes in the LAAO Registry as “an improvement – a considerable improvement – over some of the early data in PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF.” He credited this to the “very robust validation procedure” the Watchman closure device has undergone, which included the clinical trials, regulatory requirements for training and patient selection, and mandatory reporting of outcomes in the registry.
He noted that a lot is happening now with the Watchman device. There are a couple of dozen prospective clinical trials, including one on the Watchman versus direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy and another on left atrial ablation plus left atrial appendage closure versus a DOAC. A new-generation Watchman device, the Watchman FLX, is approved in Europe and undergoing an ongoing FDA-mandated approval trial in the United States.
“It has a lot of technical advantages,” according to Dr. Estes, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh.
Current guidelines give LAAO a class IIb rating, meaning it “could be considered” in patients with atrial fibrillation at increased risk of stroke who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. Dr. Estes asked: Does the LAAO Registry data warrant a rating upgrade to a stronger recommendation?
Dr. Freeman replied that the new data should allay the guideline writers’ and government regulators’ concerns regarding acute procedural safety. But that’s only part of the picture. He and his coinvestigators are busy gathering data on intermediate-term outcomes, analyzing the impact of various strategies for periprocedural and long-term management of antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications with an eye toward identifying best practices, and investigating the relationship between procedural volume and outcomes, information, which could have an impact on the next iteration of the guidelines.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ACC 2020, the study was published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]1503-18).
In an accompanying editorial, Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, commented that an important contribution of the LAAO Registry is its inclusion of an enormous number of patients with contraindications to oral anticoagulation, a population excluded from the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL randomized trials.
The short-term results of the registry suggest a relaxation of the current strict requirement for surgical backup during Watchman procedures is in order, added Dr. Lakkireddy, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Columbia, and medical director of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]:1519-22).
Dr. Freeman reported serving as a consultant to Boston Scientific, which markets the Watchman, as well as to Medtronic, Janssen, and Biosense Webster.
SOURCE: Freeman JF. ACC 2020, Abstract 409-10.
Early results from the massive National Cardiovascular Data Registry Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Registry indicate that the rollout of the Watchman device into routine clinical practice is going smoothly, with a higher implant success rate and a substantially lower in-hospital complication rate than that seen in the pivotal randomized clinical trials, James V. Freeman, MD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
These real-world results are particularly impressive because the 38,158 registry participants were on average significantly older and sicker than were patients in the clinical trials. They were at higher risk of both stroke and bleeding, yet they fared better in terms of procedural safety, observed Dr. Freeman, an electrophysiologist and director of the Yale University Atrial Fibrillation Center in New Haven, Conn.
“You always worry that once you get outside of the clinical trials setting and you roll out to a large number of centers, including some that are relatively low volume, that you’re going to start to see higher rates of complications. And overall, broadly speaking, the rates of adverse events were quite reassuring,” he said.
The registry, maintained by the ACC, serves as the postmarketing surveillance tool mandated by the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The 38,158 participants make this registry the world’s largest patient experience with the Watchman device by many orders of magnitude. Dr. Freeman’s report included patients enrolled during 2016-2018 who were treated at 495 hospitals by 1,318 physician interventionalists. CMS reimbursement requires participation in the registry, which captures more than 95% of all Watchman procedures done in the United States. Although Dr. Freeman presented only the acute in-hospital outcomes, active follow-up for adverse events and medical therapy will be conducted at 45 days, 6 months, and 1 and 2 years.
Participants in the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO) Registry averaged 76.1 years of age, which is 2-4 years older than patients in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials or the 1,025-patient EWOLUTION registry. The LAAO Registry participants had a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6, compared with 3.4 in PROTECT-AF and 3.8 in PREVAIL. Their mean HAS BLED score was 3.0. Thirty percent had a prior ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, 12% had a prior intracranial hemorrhage, and 69% had a history of clinically relevant bleeding. Thirty percent had heart failure, 92% were hypertensive, and 30% had diabetes.
“The take home here is that these patients were at moderate to high risk of stroke and they also carried a high risk of bleeding and therefore had some relative contraindication to anticoagulation,” according to the cardiologist. “The patient population overall is really in accordance with the CMS guidance. We’re not seeing a lot of patients who are getting this device for a lifestyle indication. Most of these patients are really stuck between a rock and a hard place.”
Most hospitals offering the Watchman did 10-40 cases per year. The median annual physician volume was 12 cases. However, there was substantial variation in both hospital and physician volumes.
The device was deployed in 93% of procedures attempted; roughly half of cancellations were cause by LAAO thrombus detected on the day of the procedure. The acute procedural success rate when the device was deployed was 98.3%, compared with 90.9% in PROTECT-AF and 95.1% in PREVAIL. The rate of device margin residual leak of 5 mm or more among registry participants with an acutely successful procedure was 0.2%.
The rate of any major in-hospital complication in the LAAO Registry was 2.16%, the most common of which was pericardial effusion requiring intervention, which occurred in 1.39% of cases. The major bleeding rate was 1.25%. The stroke/transient ischemic attack rate was 0.17%. Systemic arterial embolism was a rare event, occurring in less than 0.01% of patients, as was acute MI, with an incidence of 0.04%. Device embolization occurred in 0.07% of patients.
By comparison, the 7-day rate of pericardial effusion requiring intervention was 4.0% in PROTECT-AF and 1.9% in PREVAIL, with procedure-related stroke rates of 1.1% and 0.7%, respectively, and device embolization rates of 0.4% and 0.7%. The major bleeding rate in PROTECT-AF was 3.5%, nearly triple that in the real-world registry.
Discussant Mark A. Estes, MD, characterized the acute outcomes in the LAAO Registry as “an improvement – a considerable improvement – over some of the early data in PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF.” He credited this to the “very robust validation procedure” the Watchman closure device has undergone, which included the clinical trials, regulatory requirements for training and patient selection, and mandatory reporting of outcomes in the registry.
He noted that a lot is happening now with the Watchman device. There are a couple of dozen prospective clinical trials, including one on the Watchman versus direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy and another on left atrial ablation plus left atrial appendage closure versus a DOAC. A new-generation Watchman device, the Watchman FLX, is approved in Europe and undergoing an ongoing FDA-mandated approval trial in the United States.
“It has a lot of technical advantages,” according to Dr. Estes, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh.
Current guidelines give LAAO a class IIb rating, meaning it “could be considered” in patients with atrial fibrillation at increased risk of stroke who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. Dr. Estes asked: Does the LAAO Registry data warrant a rating upgrade to a stronger recommendation?
Dr. Freeman replied that the new data should allay the guideline writers’ and government regulators’ concerns regarding acute procedural safety. But that’s only part of the picture. He and his coinvestigators are busy gathering data on intermediate-term outcomes, analyzing the impact of various strategies for periprocedural and long-term management of antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications with an eye toward identifying best practices, and investigating the relationship between procedural volume and outcomes, information, which could have an impact on the next iteration of the guidelines.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ACC 2020, the study was published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]1503-18).
In an accompanying editorial, Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, commented that an important contribution of the LAAO Registry is its inclusion of an enormous number of patients with contraindications to oral anticoagulation, a population excluded from the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL randomized trials.
The short-term results of the registry suggest a relaxation of the current strict requirement for surgical backup during Watchman procedures is in order, added Dr. Lakkireddy, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Columbia, and medical director of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]:1519-22).
Dr. Freeman reported serving as a consultant to Boston Scientific, which markets the Watchman, as well as to Medtronic, Janssen, and Biosense Webster.
SOURCE: Freeman JF. ACC 2020, Abstract 409-10.
Early results from the massive National Cardiovascular Data Registry Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Registry indicate that the rollout of the Watchman device into routine clinical practice is going smoothly, with a higher implant success rate and a substantially lower in-hospital complication rate than that seen in the pivotal randomized clinical trials, James V. Freeman, MD, reported at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
These real-world results are particularly impressive because the 38,158 registry participants were on average significantly older and sicker than were patients in the clinical trials. They were at higher risk of both stroke and bleeding, yet they fared better in terms of procedural safety, observed Dr. Freeman, an electrophysiologist and director of the Yale University Atrial Fibrillation Center in New Haven, Conn.
“You always worry that once you get outside of the clinical trials setting and you roll out to a large number of centers, including some that are relatively low volume, that you’re going to start to see higher rates of complications. And overall, broadly speaking, the rates of adverse events were quite reassuring,” he said.
The registry, maintained by the ACC, serves as the postmarketing surveillance tool mandated by the Food and Drug Administration and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The 38,158 participants make this registry the world’s largest patient experience with the Watchman device by many orders of magnitude. Dr. Freeman’s report included patients enrolled during 2016-2018 who were treated at 495 hospitals by 1,318 physician interventionalists. CMS reimbursement requires participation in the registry, which captures more than 95% of all Watchman procedures done in the United States. Although Dr. Freeman presented only the acute in-hospital outcomes, active follow-up for adverse events and medical therapy will be conducted at 45 days, 6 months, and 1 and 2 years.
Participants in the Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO) Registry averaged 76.1 years of age, which is 2-4 years older than patients in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials or the 1,025-patient EWOLUTION registry. The LAAO Registry participants had a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4.6, compared with 3.4 in PROTECT-AF and 3.8 in PREVAIL. Their mean HAS BLED score was 3.0. Thirty percent had a prior ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, 12% had a prior intracranial hemorrhage, and 69% had a history of clinically relevant bleeding. Thirty percent had heart failure, 92% were hypertensive, and 30% had diabetes.
“The take home here is that these patients were at moderate to high risk of stroke and they also carried a high risk of bleeding and therefore had some relative contraindication to anticoagulation,” according to the cardiologist. “The patient population overall is really in accordance with the CMS guidance. We’re not seeing a lot of patients who are getting this device for a lifestyle indication. Most of these patients are really stuck between a rock and a hard place.”
Most hospitals offering the Watchman did 10-40 cases per year. The median annual physician volume was 12 cases. However, there was substantial variation in both hospital and physician volumes.
The device was deployed in 93% of procedures attempted; roughly half of cancellations were cause by LAAO thrombus detected on the day of the procedure. The acute procedural success rate when the device was deployed was 98.3%, compared with 90.9% in PROTECT-AF and 95.1% in PREVAIL. The rate of device margin residual leak of 5 mm or more among registry participants with an acutely successful procedure was 0.2%.
The rate of any major in-hospital complication in the LAAO Registry was 2.16%, the most common of which was pericardial effusion requiring intervention, which occurred in 1.39% of cases. The major bleeding rate was 1.25%. The stroke/transient ischemic attack rate was 0.17%. Systemic arterial embolism was a rare event, occurring in less than 0.01% of patients, as was acute MI, with an incidence of 0.04%. Device embolization occurred in 0.07% of patients.
By comparison, the 7-day rate of pericardial effusion requiring intervention was 4.0% in PROTECT-AF and 1.9% in PREVAIL, with procedure-related stroke rates of 1.1% and 0.7%, respectively, and device embolization rates of 0.4% and 0.7%. The major bleeding rate in PROTECT-AF was 3.5%, nearly triple that in the real-world registry.
Discussant Mark A. Estes, MD, characterized the acute outcomes in the LAAO Registry as “an improvement – a considerable improvement – over some of the early data in PREVAIL and PROTECT-AF.” He credited this to the “very robust validation procedure” the Watchman closure device has undergone, which included the clinical trials, regulatory requirements for training and patient selection, and mandatory reporting of outcomes in the registry.
He noted that a lot is happening now with the Watchman device. There are a couple of dozen prospective clinical trials, including one on the Watchman versus direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy and another on left atrial ablation plus left atrial appendage closure versus a DOAC. A new-generation Watchman device, the Watchman FLX, is approved in Europe and undergoing an ongoing FDA-mandated approval trial in the United States.
“It has a lot of technical advantages,” according to Dr. Estes, an electrophysiologist and professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh.
Current guidelines give LAAO a class IIb rating, meaning it “could be considered” in patients with atrial fibrillation at increased risk of stroke who have a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation. Dr. Estes asked: Does the LAAO Registry data warrant a rating upgrade to a stronger recommendation?
Dr. Freeman replied that the new data should allay the guideline writers’ and government regulators’ concerns regarding acute procedural safety. But that’s only part of the picture. He and his coinvestigators are busy gathering data on intermediate-term outcomes, analyzing the impact of various strategies for periprocedural and long-term management of antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications with an eye toward identifying best practices, and investigating the relationship between procedural volume and outcomes, information, which could have an impact on the next iteration of the guidelines.
Simultaneous with his presentation at ACC 2020, the study was published online (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]1503-18).
In an accompanying editorial, Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, commented that an important contribution of the LAAO Registry is its inclusion of an enormous number of patients with contraindications to oral anticoagulation, a population excluded from the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL randomized trials.
The short-term results of the registry suggest a relaxation of the current strict requirement for surgical backup during Watchman procedures is in order, added Dr. Lakkireddy, professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Columbia, and medical director of the Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Mar 13;75[13]:1519-22).
Dr. Freeman reported serving as a consultant to Boston Scientific, which markets the Watchman, as well as to Medtronic, Janssen, and Biosense Webster.
SOURCE: Freeman JF. ACC 2020, Abstract 409-10.
FROM ACC 2020
SARS-CoV-2 escapes cotton, surgical masks of infected
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
June 9, 2020 — Editor’s note: The study on which this news story is based has been retracted by the journal. The retraction notice can be found here.
according to Seongman Bae, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine in Seoul, South Korea, and associates.
The report was published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Because the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a shortage of N95 and surgical masks, cotton masks have gained interest as a substitute, as surgical masks have been shown to effectively filter influenza virus, the researchers wrote. However, the size of and concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosols generated during coughing are unknown.
To compare the effectiveness of cotton and surgical masks, a group of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 coughed into petri dishes while wearing no mask, a surgical mask, and a cotton mask. The mask surfaces were swabbed afterward to assess viral positivity on the mask itself.
The median nasopharyngeal and saliva viral load was 5.66 log copies/mL and 4.00 log copies/mL, respectively. The median viral loads after coughing was 2.56 log copies/mL without a mask, 2.42 log copies/mL with a surgical mask, and 1.85 log copies/mL with a cotton mask. All outer surfaces of the mask were positive for SARS-CoV-2, while most inner surfaces were negative.
The investigators acknowledged that the test did not include N95 masks and does not reflect the actual infection transmission, and that they didn’t know whether cotton or surgical masks shorten the travel distance of droplets while coughing.
“Further study is needed to recommend whether face masks decrease transmission of virus from asymptomatic individuals or those with suspected COVID-19 who are not coughing,” they added.
The study was funded by a grant from the government-wide R&D Fund Project for Infectious Disease Research. The investigators reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bae S et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
Correction, 4/9/20: The headline of an earlier version of this article misstated a finding of this study. Whether cotton and surgical masks can block transmission was not investigated.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Treatment for RA, SpA may not affect COVID-19 severity
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
Patients being treated for RA or spondyloarthritis who develop symptoms of COVID-19 do not appear to be at higher risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications, results from a new study in Italy suggest.
Such patients, the study authors wrote, do not need to be taken off their immunosuppressive medications if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.
In a letter published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Sara Monti, MD, and colleagues in the rheumatology department of the Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico in San Matteo, Italy, described results from an observational cohort of 320 patients (68% women; mean age, 55 years) with RA or spondyloarthritis from a single outpatient clinic. The vast majority of subjects (92%) were taking biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD), including tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, while the rest were taking targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARD).
Four patients in the cohort developed laboratory-confirmed COVID-19; another four developed symptoms highly suggestive of the disease but did not receive confirmatory testing, and five had contact with a confirmed COVID-19 case but did not develop symptoms of COVID-19.
Among the eight confirmed and suspected COVID-19 patients, only one was hospitalized. All temporarily withdrew bDMARD or tsDMARD treatment at symptom onset.
“To date, there have been no significant relapses of the rheumatic disease,” Dr. Monti and colleagues reported. “None of the patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or with a highly suggestive clinical picture developed severe respiratory complications or died. Only one patient, aged 65, required admission to hospital and low-flow oxygen supplementation for a few days.”
The findings “do not allow any conclusions on the incidence rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with rheumatic diseases, nor on the overall outcome of immunocompromised patients affected by COVID-19,” the investigators cautioned, adding that such patients should receive careful attention and follow-up. “However, our preliminary experience shows that patients with chronic arthritis treated with bDMARDs or tsDMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2, compared with the general population.”
Dr. Monti and colleagues noted that, during previous outbreaks of other coronaviruses, no increased mortality was reported for people taking immunosuppressive drugs for a range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases.
“These data can support rheumatologists [in] avoiding the unjustifiable preventive withdrawal of DMARDs, which could lead to an increased risk of relapses and morbidity from the chronic rheumatological condition,” the researchers concluded.
Dr. Monti and colleagues reported no outside funding or financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Monti S et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 April 2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES