User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
Most COVID-19 survivors return to work within 2 years
The burden of persistent COVID-19 symptoms appeared to improve over time, but a higher percentage of former patients reported poor health, compared with the general population. This suggests that some patients need more time to completely recover from COVID-19, wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. Previous research has shown that the health effects of COVID-19 last for up to a year, but data from longer-term studies are limited, said Lixue Huang, MD, of Capital Medical University, Beijing, one of the study authors, and colleagues.
Methods and results
In the new study, the researchers reviewed data from 1,192 adult patients who were discharged from the hospital after surviving COVID-19 between Jan. 7, 2020, and May 29, 2020. The researchers measured the participants’ health outcomes at 6 months, 12 months, and 2 years after their onset of symptoms. A community-based dataset of 3,383 adults with no history of COVID-19 served as controls to measure the recovery of the COVID-19 patients. The median age of the patients at the time of hospital discharge was 57 years, and 46% were women. The median follow-up time after the onset of symptoms was 185 days, 349 days, and 685 days for the 6-month, 12-month, and 2-year visits, respectively. The researchers measured health outcomes using a 6-min walking distance (6MWD) test, laboratory tests, and questionnaires about symptoms, mental health, health-related quality of life, returning to work, and health care use since leaving the hospital.
Overall, the proportion of COVID-19 survivors with at least one symptom decreased from 68% at 6 months to 55% at 2 years (P < .0001). The most frequent symptoms were fatigue and muscle weakness, reported by approximately one-third of the patients (31%); sleep problems also were reported by 31% of the patients.
The proportion of individuals with poor results on the 6MWD decreased continuously over time, not only in COVID-19 survivors overall, but also in three subgroups of varying initial disease severity. Of the 494 survivors who reported working before becoming ill, 438 (89%) had returned to their original jobs 2 years later. The most common reasons for not returning to work were decreased physical function, unwillingness to return, and unemployment, the researchers noted.
However, at 2 years, COVID-19 survivors reported more pain and discomfort, as well as more anxiety and depression, compared with the controls (23% vs. 5% and 12% vs. 5%, respectively).
In addition, significantly more survivors who needed high levels of respiratory support while hospitalized had lung diffusion impairment (65%), reduced residual volume (62%), and total lung capacity (39%), compared with matched controls (36%, 20%, and 6%, respectively) at 2 years.
Long-COVID concerns
Approximately half of the survivors had symptoms of long COVID at 2 years. These individuals were more likely to report pain or discomfort or anxiety or depression, as well as mobility problems, compared to survivors without long COVID. Participants with long-COVID symptoms were more than twice as likely to have an outpatient clinic visit (odds ratio, 2.82), and not quite twice as likely to be rehospitalized (OR, 1.64).
“We found that [health-related quality of life], exercise capacity, and mental health continued to improve throughout the 2 years regardless of initial disease severity, but about half still had symptomatic sequelae at 2 years,” the researchers wrote in their paper.
Findings can inform doctor-patient discussions
“We are increasingly recognizing that the health effects of COVID-19 may persist beyond acute illness, therefore this is a timely study to assess the long-term impact of COVID-19 with a long follow-up period,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
The findings are consistent with the existing literature, said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study. The data from the study “can help clinicians have discussions regarding expected recovery and long-term prognosis for patients with COVID-19,” he noted.
What patients should know is that “studies such as this can help COVID-19 survivors understand and monitor persistent symptoms they may experience, and bring them to the attention of their clinicians,” said Dr. Pal.
However, “As a single-center study with high attrition of subjects during the study period, the findings may not be generalizable,” Dr. Pal emphasized. “Larger-scale studies and patient registries distributed over different geographical areas and time periods will help obtain a better understanding of the nature and prevalence of long COVID,” he said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of formerly hospitalized controls with respiratory infections other than COVID-19 to determine which outcomes are COVID-19 specific, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of data from only patients at a single center, and from the early stages of the pandemic, as well as the use of self-reports for comorbidities and health outcomes, they said.
However, the results represent the longest-known published longitudinal follow-up of patients who recovered from acute COVID-19, the researchers emphasized. Study strengths included the large sample size, longitudinal design, and long-term follow-up with non-COVID controls to determine outcomes. The researchers noted their plans to conduct annual follow-ups in the current study population. They added that more research is needed to explore rehabilitation programs to promote recovery for COVID-19 survivors and to reduce the effects of long COVID.
The study was supported by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, China Evergrande Group, Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, Ping An Insurance (Group), and New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated on 5/16/2022.
The burden of persistent COVID-19 symptoms appeared to improve over time, but a higher percentage of former patients reported poor health, compared with the general population. This suggests that some patients need more time to completely recover from COVID-19, wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. Previous research has shown that the health effects of COVID-19 last for up to a year, but data from longer-term studies are limited, said Lixue Huang, MD, of Capital Medical University, Beijing, one of the study authors, and colleagues.
Methods and results
In the new study, the researchers reviewed data from 1,192 adult patients who were discharged from the hospital after surviving COVID-19 between Jan. 7, 2020, and May 29, 2020. The researchers measured the participants’ health outcomes at 6 months, 12 months, and 2 years after their onset of symptoms. A community-based dataset of 3,383 adults with no history of COVID-19 served as controls to measure the recovery of the COVID-19 patients. The median age of the patients at the time of hospital discharge was 57 years, and 46% were women. The median follow-up time after the onset of symptoms was 185 days, 349 days, and 685 days for the 6-month, 12-month, and 2-year visits, respectively. The researchers measured health outcomes using a 6-min walking distance (6MWD) test, laboratory tests, and questionnaires about symptoms, mental health, health-related quality of life, returning to work, and health care use since leaving the hospital.
Overall, the proportion of COVID-19 survivors with at least one symptom decreased from 68% at 6 months to 55% at 2 years (P < .0001). The most frequent symptoms were fatigue and muscle weakness, reported by approximately one-third of the patients (31%); sleep problems also were reported by 31% of the patients.
The proportion of individuals with poor results on the 6MWD decreased continuously over time, not only in COVID-19 survivors overall, but also in three subgroups of varying initial disease severity. Of the 494 survivors who reported working before becoming ill, 438 (89%) had returned to their original jobs 2 years later. The most common reasons for not returning to work were decreased physical function, unwillingness to return, and unemployment, the researchers noted.
However, at 2 years, COVID-19 survivors reported more pain and discomfort, as well as more anxiety and depression, compared with the controls (23% vs. 5% and 12% vs. 5%, respectively).
In addition, significantly more survivors who needed high levels of respiratory support while hospitalized had lung diffusion impairment (65%), reduced residual volume (62%), and total lung capacity (39%), compared with matched controls (36%, 20%, and 6%, respectively) at 2 years.
Long-COVID concerns
Approximately half of the survivors had symptoms of long COVID at 2 years. These individuals were more likely to report pain or discomfort or anxiety or depression, as well as mobility problems, compared to survivors without long COVID. Participants with long-COVID symptoms were more than twice as likely to have an outpatient clinic visit (odds ratio, 2.82), and not quite twice as likely to be rehospitalized (OR, 1.64).
“We found that [health-related quality of life], exercise capacity, and mental health continued to improve throughout the 2 years regardless of initial disease severity, but about half still had symptomatic sequelae at 2 years,” the researchers wrote in their paper.
Findings can inform doctor-patient discussions
“We are increasingly recognizing that the health effects of COVID-19 may persist beyond acute illness, therefore this is a timely study to assess the long-term impact of COVID-19 with a long follow-up period,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
The findings are consistent with the existing literature, said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study. The data from the study “can help clinicians have discussions regarding expected recovery and long-term prognosis for patients with COVID-19,” he noted.
What patients should know is that “studies such as this can help COVID-19 survivors understand and monitor persistent symptoms they may experience, and bring them to the attention of their clinicians,” said Dr. Pal.
However, “As a single-center study with high attrition of subjects during the study period, the findings may not be generalizable,” Dr. Pal emphasized. “Larger-scale studies and patient registries distributed over different geographical areas and time periods will help obtain a better understanding of the nature and prevalence of long COVID,” he said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of formerly hospitalized controls with respiratory infections other than COVID-19 to determine which outcomes are COVID-19 specific, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of data from only patients at a single center, and from the early stages of the pandemic, as well as the use of self-reports for comorbidities and health outcomes, they said.
However, the results represent the longest-known published longitudinal follow-up of patients who recovered from acute COVID-19, the researchers emphasized. Study strengths included the large sample size, longitudinal design, and long-term follow-up with non-COVID controls to determine outcomes. The researchers noted their plans to conduct annual follow-ups in the current study population. They added that more research is needed to explore rehabilitation programs to promote recovery for COVID-19 survivors and to reduce the effects of long COVID.
The study was supported by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, China Evergrande Group, Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, Ping An Insurance (Group), and New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated on 5/16/2022.
The burden of persistent COVID-19 symptoms appeared to improve over time, but a higher percentage of former patients reported poor health, compared with the general population. This suggests that some patients need more time to completely recover from COVID-19, wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. Previous research has shown that the health effects of COVID-19 last for up to a year, but data from longer-term studies are limited, said Lixue Huang, MD, of Capital Medical University, Beijing, one of the study authors, and colleagues.
Methods and results
In the new study, the researchers reviewed data from 1,192 adult patients who were discharged from the hospital after surviving COVID-19 between Jan. 7, 2020, and May 29, 2020. The researchers measured the participants’ health outcomes at 6 months, 12 months, and 2 years after their onset of symptoms. A community-based dataset of 3,383 adults with no history of COVID-19 served as controls to measure the recovery of the COVID-19 patients. The median age of the patients at the time of hospital discharge was 57 years, and 46% were women. The median follow-up time after the onset of symptoms was 185 days, 349 days, and 685 days for the 6-month, 12-month, and 2-year visits, respectively. The researchers measured health outcomes using a 6-min walking distance (6MWD) test, laboratory tests, and questionnaires about symptoms, mental health, health-related quality of life, returning to work, and health care use since leaving the hospital.
Overall, the proportion of COVID-19 survivors with at least one symptom decreased from 68% at 6 months to 55% at 2 years (P < .0001). The most frequent symptoms were fatigue and muscle weakness, reported by approximately one-third of the patients (31%); sleep problems also were reported by 31% of the patients.
The proportion of individuals with poor results on the 6MWD decreased continuously over time, not only in COVID-19 survivors overall, but also in three subgroups of varying initial disease severity. Of the 494 survivors who reported working before becoming ill, 438 (89%) had returned to their original jobs 2 years later. The most common reasons for not returning to work were decreased physical function, unwillingness to return, and unemployment, the researchers noted.
However, at 2 years, COVID-19 survivors reported more pain and discomfort, as well as more anxiety and depression, compared with the controls (23% vs. 5% and 12% vs. 5%, respectively).
In addition, significantly more survivors who needed high levels of respiratory support while hospitalized had lung diffusion impairment (65%), reduced residual volume (62%), and total lung capacity (39%), compared with matched controls (36%, 20%, and 6%, respectively) at 2 years.
Long-COVID concerns
Approximately half of the survivors had symptoms of long COVID at 2 years. These individuals were more likely to report pain or discomfort or anxiety or depression, as well as mobility problems, compared to survivors without long COVID. Participants with long-COVID symptoms were more than twice as likely to have an outpatient clinic visit (odds ratio, 2.82), and not quite twice as likely to be rehospitalized (OR, 1.64).
“We found that [health-related quality of life], exercise capacity, and mental health continued to improve throughout the 2 years regardless of initial disease severity, but about half still had symptomatic sequelae at 2 years,” the researchers wrote in their paper.
Findings can inform doctor-patient discussions
“We are increasingly recognizing that the health effects of COVID-19 may persist beyond acute illness, therefore this is a timely study to assess the long-term impact of COVID-19 with a long follow-up period,” said Suman Pal, MD, an internal medicine physician at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, in an interview.
The findings are consistent with the existing literature, said Dr. Pal, who was not involved in the study. The data from the study “can help clinicians have discussions regarding expected recovery and long-term prognosis for patients with COVID-19,” he noted.
What patients should know is that “studies such as this can help COVID-19 survivors understand and monitor persistent symptoms they may experience, and bring them to the attention of their clinicians,” said Dr. Pal.
However, “As a single-center study with high attrition of subjects during the study period, the findings may not be generalizable,” Dr. Pal emphasized. “Larger-scale studies and patient registries distributed over different geographical areas and time periods will help obtain a better understanding of the nature and prevalence of long COVID,” he said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of formerly hospitalized controls with respiratory infections other than COVID-19 to determine which outcomes are COVID-19 specific, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the use of data from only patients at a single center, and from the early stages of the pandemic, as well as the use of self-reports for comorbidities and health outcomes, they said.
However, the results represent the longest-known published longitudinal follow-up of patients who recovered from acute COVID-19, the researchers emphasized. Study strengths included the large sample size, longitudinal design, and long-term follow-up with non-COVID controls to determine outcomes. The researchers noted their plans to conduct annual follow-ups in the current study population. They added that more research is needed to explore rehabilitation programs to promote recovery for COVID-19 survivors and to reduce the effects of long COVID.
The study was supported by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development of Pulmonary Tuberculosis, China Evergrande Group, Jack Ma Foundation, Sino Biopharmaceutical, Ping An Insurance (Group), and New Sunshine Charity Foundation. The researchers and Dr. Pal had no financial conflicts to disclose.
This article was updated on 5/16/2022.
FROM THE LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
COVID-19 patients remain sedentary after hospital discharge
After hospitalization, COVID-19 patients 9 hours per day of sedentary time at 3-6 months after discharge, according to data from 37 individuals.
COVID-19 patients experience a wide range of clinical manifestations, and roughly half of those who were hospitalized for COVID-19 report persisting symptoms both physical and mental up to a year after discharge, Bram van Bakel, MD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in a presentation at the presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
However, data on physical activity patterns and the impact on recovery after postinfection hospital discharge are limited, he said. Dr. van Bakel and colleagues aimed to assess physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration in COVID-19 patients at 3-6 months after hospital discharge to explore the association with patient characteristics, disease severity and cardiac dysfunction.
“We hypothesized that COVID-19 survivors will demonstrate low volumes of physical activity and a high sedentary time, especially those with a more severe disease course,” such as longer hospital duration and admission to intensive care, cardiac dysfunction, and persistent symptoms at 3-6 months post discharge, he said.
Dr. van Bakel and colleagues enrolled 37 adult patients in a cross-sectional cohort study. They objectively assessed physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration for 24 hrs/day during 8 subsequent days in COVID-19 survivors at 3-6 months post hospitalization. The average age of the patients was 60 years, 78% were male, and the average assessment time was 125 days after hospital discharge.
The researchers compared activity patterns based on patient and disease characteristics, cardiac biomarker release during hospitalization, abnormal transthoracic echocardiogram regarding left and right ventricular function and volumes at 3-6 months of follow-up, and the persistence of symptoms after discharge.
Overall, patients spent a median of 4.2 hours per day in light-intensity physical activity, and 1 hour per day in moderate to vigorous physical activity. The overall median time spent sitting was 9.8 hours per day; this was accumulated in approximately 6 prolonged sitting periods of 30 minutes or more and 41.1 short sitting periods of less than 30 minutes.
The median sleep duration was 9.8 hours per day; sleep duration was significantly higher in women, compared with men (9.2 vs. 8.5 hours/day; P = .03), and in patients with persistent symptoms, compared with those without persistent symptoms (9.1 hrs/day vs. 8.3 hrs/day; P = .02). No other differences in activity or sitting patterns appeared among subgroups. Sedentary time of 10 hours or more per day overall puts individuals at increased risk for detrimental health effects, Dr. van Bakel said.
The study findings were limited by the small sample and cross-sectional design, he noted.
However, the results suggest that COVID-19 patients spent most of their time sedentary within the first 3-6 months after hospital discharge. The similar activity patterns across subgroups support a uniform approach to rehabilitation for these patients to target persisting symptoms and prevent long-term health consequences, said Dr. van Bakel. Further studies are warranted in a larger cohort with a prospective design and longitudinal follow-up.
The current study “highlights the need for ongoing rehabilitation in severe COVID-19 survivors after hospitalization to restore premorbid function and endurance,” Alba Miranda Azola, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“The findings regarding inactivity are not surprising,” said Dr. Azola. “Immobility during hospitalization results in muscle atrophy and marked decreased endurance. The need for prolonged use of sedation and paralytics during intensive care stays of severe COVID-19 patients is associated with critical illness myopathy. Also, many patients continue to experience hypoxia and dyspnea on exertion for several months after leaving the hospital. The functional impairments and limited activity tolerance often preclude patients from engaging on outpatient rehabilitation programs.
“I do think it surprising that the level of inactivity observed was independent of disease severity and patient factors, but it definitely speaks to the importance of establishing post hospitalization follow-up care that focuses on restoring function and mobility,” Dr. Azola noted.
The study findings may have long-term clinical implications, as COVID-19 survivors who experience functional decline that limits activity and who continue to lead a sedentary lifestyle may be at increased risk for health issues such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes, Dr. Azola said.
Rigorous research is needed to study the functional and health impact of rehabilitation interventions during and after hospitalization, she emphasized. “Additionally, studies are needed on innovative rehabilitation interventions that improve accessibility to services to patients.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose.
After hospitalization, COVID-19 patients 9 hours per day of sedentary time at 3-6 months after discharge, according to data from 37 individuals.
COVID-19 patients experience a wide range of clinical manifestations, and roughly half of those who were hospitalized for COVID-19 report persisting symptoms both physical and mental up to a year after discharge, Bram van Bakel, MD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in a presentation at the presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
However, data on physical activity patterns and the impact on recovery after postinfection hospital discharge are limited, he said. Dr. van Bakel and colleagues aimed to assess physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration in COVID-19 patients at 3-6 months after hospital discharge to explore the association with patient characteristics, disease severity and cardiac dysfunction.
“We hypothesized that COVID-19 survivors will demonstrate low volumes of physical activity and a high sedentary time, especially those with a more severe disease course,” such as longer hospital duration and admission to intensive care, cardiac dysfunction, and persistent symptoms at 3-6 months post discharge, he said.
Dr. van Bakel and colleagues enrolled 37 adult patients in a cross-sectional cohort study. They objectively assessed physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration for 24 hrs/day during 8 subsequent days in COVID-19 survivors at 3-6 months post hospitalization. The average age of the patients was 60 years, 78% were male, and the average assessment time was 125 days after hospital discharge.
The researchers compared activity patterns based on patient and disease characteristics, cardiac biomarker release during hospitalization, abnormal transthoracic echocardiogram regarding left and right ventricular function and volumes at 3-6 months of follow-up, and the persistence of symptoms after discharge.
Overall, patients spent a median of 4.2 hours per day in light-intensity physical activity, and 1 hour per day in moderate to vigorous physical activity. The overall median time spent sitting was 9.8 hours per day; this was accumulated in approximately 6 prolonged sitting periods of 30 minutes or more and 41.1 short sitting periods of less than 30 minutes.
The median sleep duration was 9.8 hours per day; sleep duration was significantly higher in women, compared with men (9.2 vs. 8.5 hours/day; P = .03), and in patients with persistent symptoms, compared with those without persistent symptoms (9.1 hrs/day vs. 8.3 hrs/day; P = .02). No other differences in activity or sitting patterns appeared among subgroups. Sedentary time of 10 hours or more per day overall puts individuals at increased risk for detrimental health effects, Dr. van Bakel said.
The study findings were limited by the small sample and cross-sectional design, he noted.
However, the results suggest that COVID-19 patients spent most of their time sedentary within the first 3-6 months after hospital discharge. The similar activity patterns across subgroups support a uniform approach to rehabilitation for these patients to target persisting symptoms and prevent long-term health consequences, said Dr. van Bakel. Further studies are warranted in a larger cohort with a prospective design and longitudinal follow-up.
The current study “highlights the need for ongoing rehabilitation in severe COVID-19 survivors after hospitalization to restore premorbid function and endurance,” Alba Miranda Azola, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“The findings regarding inactivity are not surprising,” said Dr. Azola. “Immobility during hospitalization results in muscle atrophy and marked decreased endurance. The need for prolonged use of sedation and paralytics during intensive care stays of severe COVID-19 patients is associated with critical illness myopathy. Also, many patients continue to experience hypoxia and dyspnea on exertion for several months after leaving the hospital. The functional impairments and limited activity tolerance often preclude patients from engaging on outpatient rehabilitation programs.
“I do think it surprising that the level of inactivity observed was independent of disease severity and patient factors, but it definitely speaks to the importance of establishing post hospitalization follow-up care that focuses on restoring function and mobility,” Dr. Azola noted.
The study findings may have long-term clinical implications, as COVID-19 survivors who experience functional decline that limits activity and who continue to lead a sedentary lifestyle may be at increased risk for health issues such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes, Dr. Azola said.
Rigorous research is needed to study the functional and health impact of rehabilitation interventions during and after hospitalization, she emphasized. “Additionally, studies are needed on innovative rehabilitation interventions that improve accessibility to services to patients.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose.
After hospitalization, COVID-19 patients 9 hours per day of sedentary time at 3-6 months after discharge, according to data from 37 individuals.
COVID-19 patients experience a wide range of clinical manifestations, and roughly half of those who were hospitalized for COVID-19 report persisting symptoms both physical and mental up to a year after discharge, Bram van Bakel, MD, of Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, said in a presentation at the presentation at the annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology.
However, data on physical activity patterns and the impact on recovery after postinfection hospital discharge are limited, he said. Dr. van Bakel and colleagues aimed to assess physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration in COVID-19 patients at 3-6 months after hospital discharge to explore the association with patient characteristics, disease severity and cardiac dysfunction.
“We hypothesized that COVID-19 survivors will demonstrate low volumes of physical activity and a high sedentary time, especially those with a more severe disease course,” such as longer hospital duration and admission to intensive care, cardiac dysfunction, and persistent symptoms at 3-6 months post discharge, he said.
Dr. van Bakel and colleagues enrolled 37 adult patients in a cross-sectional cohort study. They objectively assessed physical activity, sedentary behavior, and sleep duration for 24 hrs/day during 8 subsequent days in COVID-19 survivors at 3-6 months post hospitalization. The average age of the patients was 60 years, 78% were male, and the average assessment time was 125 days after hospital discharge.
The researchers compared activity patterns based on patient and disease characteristics, cardiac biomarker release during hospitalization, abnormal transthoracic echocardiogram regarding left and right ventricular function and volumes at 3-6 months of follow-up, and the persistence of symptoms after discharge.
Overall, patients spent a median of 4.2 hours per day in light-intensity physical activity, and 1 hour per day in moderate to vigorous physical activity. The overall median time spent sitting was 9.8 hours per day; this was accumulated in approximately 6 prolonged sitting periods of 30 minutes or more and 41.1 short sitting periods of less than 30 minutes.
The median sleep duration was 9.8 hours per day; sleep duration was significantly higher in women, compared with men (9.2 vs. 8.5 hours/day; P = .03), and in patients with persistent symptoms, compared with those without persistent symptoms (9.1 hrs/day vs. 8.3 hrs/day; P = .02). No other differences in activity or sitting patterns appeared among subgroups. Sedentary time of 10 hours or more per day overall puts individuals at increased risk for detrimental health effects, Dr. van Bakel said.
The study findings were limited by the small sample and cross-sectional design, he noted.
However, the results suggest that COVID-19 patients spent most of their time sedentary within the first 3-6 months after hospital discharge. The similar activity patterns across subgroups support a uniform approach to rehabilitation for these patients to target persisting symptoms and prevent long-term health consequences, said Dr. van Bakel. Further studies are warranted in a larger cohort with a prospective design and longitudinal follow-up.
The current study “highlights the need for ongoing rehabilitation in severe COVID-19 survivors after hospitalization to restore premorbid function and endurance,” Alba Miranda Azola, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview.
“The findings regarding inactivity are not surprising,” said Dr. Azola. “Immobility during hospitalization results in muscle atrophy and marked decreased endurance. The need for prolonged use of sedation and paralytics during intensive care stays of severe COVID-19 patients is associated with critical illness myopathy. Also, many patients continue to experience hypoxia and dyspnea on exertion for several months after leaving the hospital. The functional impairments and limited activity tolerance often preclude patients from engaging on outpatient rehabilitation programs.
“I do think it surprising that the level of inactivity observed was independent of disease severity and patient factors, but it definitely speaks to the importance of establishing post hospitalization follow-up care that focuses on restoring function and mobility,” Dr. Azola noted.
The study findings may have long-term clinical implications, as COVID-19 survivors who experience functional decline that limits activity and who continue to lead a sedentary lifestyle may be at increased risk for health issues such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes, Dr. Azola said.
Rigorous research is needed to study the functional and health impact of rehabilitation interventions during and after hospitalization, she emphasized. “Additionally, studies are needed on innovative rehabilitation interventions that improve accessibility to services to patients.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Azola had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ESC PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY 2022
FDA working to improve U.S. baby formula supply
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
The Food and Drug Administration announced on May 10 that it is taking several steps to improve the supply of baby formula in the United States.
The nationwide formula shortage has grown worse in recent weeks due to supply chain issues and a recall of certain Abbott Nutrition products, including major labels such as Similac, Alimentum, and EleCare.
“We recognize that many consumers have been unable to access infant formula and critical medical foods they are accustomed to using and are frustrated by their inability to do so,” FDA Commissioner Robert Califf, MD, said in a statement.
“We are doing everything in our power to ensure there is adequate product available where and when they need it,” he said.
About three-quarters of babies are fed formula for the first 6 months of their lives as a substitute for human milk, Axios reported.
In mid-February, the FDA warned consumers not to use certain powdered infant formula products from Abbott’s facility in Sturgis, Mich. Since then, the FDA has been working with Abbott and other manufacturers to increase the supply in the U.S. market.
“In fact, other infant formula manufacturers are meeting or exceeding capacity levels to meet current demand,” the FDA said in the statement. “Notably, more infant formula was purchased in the month of April than in the month prior to the recall.”
The FDA released a list of steps the agency is taking to increase supply, such as meeting with major infant formula makers to increase output and prioritize product lines in high demand, particularly specialty formulas for infants with allergies or specific diet needs.
But other manufacturers have struggled to quickly increase production because their operations tend to focus on a steady level of supply, according to The New York Times.
“Some industries are very good at ramping up and ramping down,” Rudi Leuschner, PhD, an associate professor of supply chain management at Rutgers Business School, Newark, N.J., told the newspaper.
“You flip a switch and they can produce 10 times as much,” he said. “Baby formula is not that type of a product.”
The FDA is also keeping an eye on the infant formula shortage by using the agency’s 21 Forward food supply chain continuity system. The system was developed during the pandemic to provide a full understanding of how COVID-19 is impacting food supply chains, the FDA said.
The FDA is compiling data on trends for in-stock rates at national and regional levels to understand where infant formula is available and where it should go.
Products are also being brought in from other countries, the FDA said. The agency is trying to speed up the process to get more formula into the U.S. and move it more quickly around the country.
For babies on a special diet, the FDA has decided to release some Abbott products that have been on hold at the Sturgis facility to those who need an urgent supply of metabolic formulas, on a case-by-case basis.
“In these circumstances, the benefit of allowing caregivers, in consultation with their health care providers, to access these products may outweigh the potential risk of bacterial infection,” the FDA said in the statement.
The FDA continues to advise against making homemade infant formulas and recommends talking to the child’s health care provider for recommendations on changing feeding practices or switching to other formulas, if necessary.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMd.com.
SARS-CoV-2 stays in GI tract long after it clears the lungs
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggested.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that, in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors noted that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue. But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors noted that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford University, said in an interview that, though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long COVID–type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that, among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors noted that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month study period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggested.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that, in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors noted that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue. But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors noted that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford University, said in an interview that, though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long COVID–type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that, among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors noted that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month study period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggested.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that, in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors noted that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue. But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors noted that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford University, said in an interview that, though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long COVID–type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that, among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors noted that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month study period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MED
SARS-CoV-2 stays in GI tract long after it clears the lungs
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggest.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors note that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue.
But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors note that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford, told this news organization that though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long-COVID type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors note in this study that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they write.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared to Medscape.com.
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggest.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors note that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue.
But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors note that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford, told this news organization that though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long-COVID type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors note in this study that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they write.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared to Medscape.com.
New data present further evidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection can settle in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and that it can persist long after the infection has cleared the lungs.
Infection of the GI tract may figure prominently in long COVID, the study authors suggest.
Led by Aravind Natarajan, PhD, with the departments of genetics and medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, they analyzed fecal RNA shedding up to 10 months after a COVID-19 diagnosis in 673 stool samples from 113 patients with mild to moderate disease.
They found that in the week after diagnosis, COVID RNA remnants were present in the stool of approximately half (49.2%) of the patients. Seven months later, about 4% of them shed fecal viral RNA.
The authors note that there was no ongoing SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in respiratory samples of patients at the 4-month mark.
Using self-reported symptoms regularly collected by questionnaire, they also found a correlation of long-term fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
The findings were published online in Med.
Implications of long-term viral shedding
Previous studies have found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in respiratory and fecal samples and have documented viral replication in lung and intestinal tissue.
But before the current study, little had been known about long-term shedding, especially in those who have mild COVID. Most studies of viral shedding have been with severe COVID cases.
The authors note that most studies of this kind are cross-sectional. The few other longitudinal studies have focused on early time points just after diagnosis.
Senior author Ami S. Bhatt, MD, associate professor in the departments of medicine and hematology at Stanford, told this news organization that though the viral genetic material in the feces lingers, on the basis of available evidence, it is highly unlikely to be contagious in most cases.
She said that understanding the dynamics of fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material will help interpret wastewater-based studies that are trying to determine population prevalence of the virus.
“While we don’t know the exact clinical importance of the longer-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19, some have speculated that those who have long-term shedding of SARS-CoV-2 may have ongoing infections that might benefit from treatment,” she said.
“Our data support the idea that the long-term GI-related symptoms in some people might be the consequence of an ongoing infection in the GI tract, even after the respiratory infection has cleared,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“Alternatively, the presence of ongoing viral genetic material in the gut might be a trigger for the immune system to continually be active against the virus, and our immune system reaction may be the reason for long-COVID type symptoms,” she added. “This area is ripe for additional studies.”
Dr. Bhatt and colleagues will continue studying viral shedding in fecal samples as part of the nationwide RECOVER Initiative.
When reached for comment, David A. Johnson, MD, professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, said in an interview that previous studies have indicated that the virus may be detected in the stool for a month or more and for about 2 weeks on average. Whether the virus is infectious has been in question.
But it’s not so much that the virus is infectious in the GI tract and causing symptoms, he said. Rather, there are biomic changes related to COVID, including a loss of diversity in the gut bacteria, which disrupts the balance.
“This may actually in some way predispose some patients to impaired clearance of their symptoms,” Dr. Johnson explained. “There seems to be a growing recognition that this entity called long-haul COVID may be related to specific bacterial disruptions, and the more rapidly you can resolve these disruptions, the less likely you are to continue with long-haul symptoms.”
He said that among people who have mild COVID, the virus typically clears and gut bacteria return to normal. With severe or persistent illness, gut dysbiosis persists, he said.
“People need to be aware that the GI tract is involved in a sizable percent of patients with COVID,” Dr. Johnson said. “The GI-tract testing may reflect that the virus is there, but persistence of the detectable test positivity is very unlikely to reflect active virus.”
The authors note in this study that they collected only six samples from the participants over the 10-month period.
“Follow-up studies with more frequent sampling, especially in the first 2 months after diagnosis, may help build a more nuanced model of decline of fecal viral RNA concentration over time,” they write.
The study was supported by a Stanford ChemH-IMA grant, fellowships from the AACR and the National Science Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Johnson report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Johnson is a regular contributor to Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared to Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases climb slowly but steadily
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.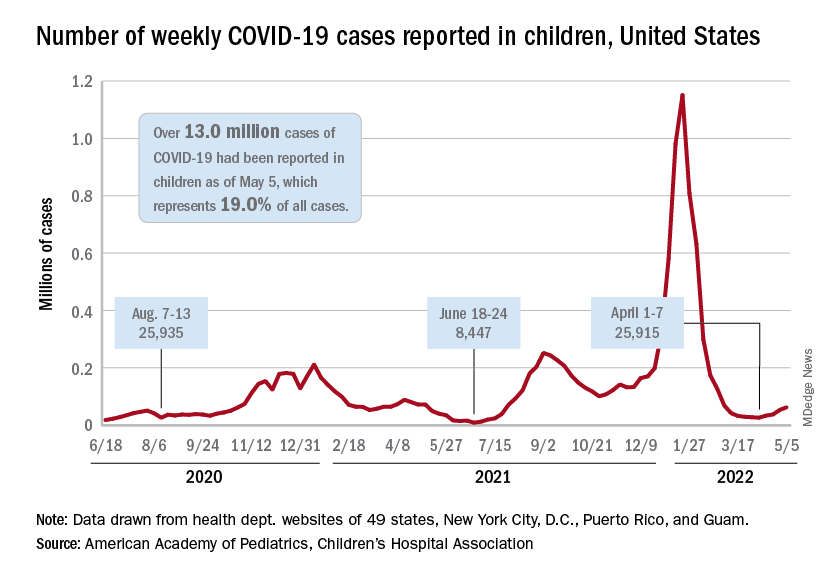
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.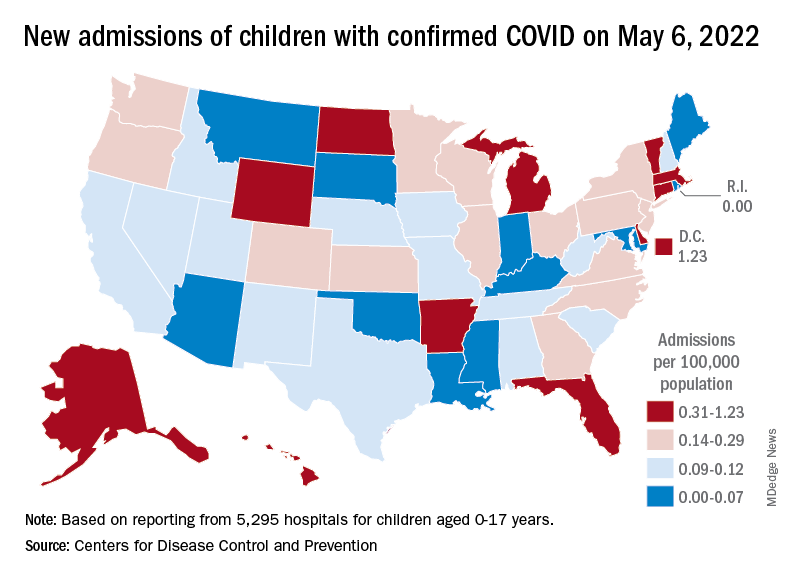
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
The current sustained increase in COVID-19 has brought the total number of cases in children to over 13 million since the start of the pandemic, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, when cases dropped to their lowest point since last summer. The cumulative number of cases in children is 13,052,988, which accounts for 19.0% of all cases reported in the United States, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
Other measures of incidence show the same steady rise. The rate of new admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID-19, which had dipped as low as 0.13 per 100,000 population on April 11, was up to 0.19 per 100,000 on May 6, and the 7-day average for total admissions was 136 per day for May 1-7, compared with 118 for the last week of April, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
At the state level, new admission rates for May 6 show wide variation, even regionally. Rhode Island came in with a 0.00 per 100,000 on that day, while Vermont recorded 0.88 admissions per 100,000, the highest of any state and lower only than the District of Columbia’s 1.23 per 100,000. Connecticut (0.45) and Massachusetts (0.33) also were in the highest group (see map), while Maine was in the lowest, CDC data show.
Nationally, emergency department visits also have been rising over the last month or so. Children aged 0-11 years, who were down to a 7-day average of 0.5% of ED visits with diagnosed COVID-19 in early April, saw that number rise to 1.4% on May 5. Children aged 12-15 years went from a rate of 0.3% in late March to the current 1.2%, as did 16- to 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
The vaccination effort, meanwhile, continues to lose steam, at least among children who are currently eligible. Initial vaccinations in those aged 5-11 slipped to their lowest-ever 1-week total, 47,000 for April 28 to May 4, while children aged 16-17 continued a long-term slide that has the weekly count down to just 29,000, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
Here’s how those latest recipients changed the populations of vaccinated children in the last week: 35.4% of all 5- to 11-year-olds had received at least one dose as of May 4, compared with 35.3% on April 27, with increases from 67.4% to 67.5% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 72.7% to 72.8% among those aged 16-17, the CDC reported.
My choice? Unvaccinated pose outsize risk to vaccinated
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
COVID fallout: ‘Alarming’ dip in routine vax for pregnant women
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
The percentage of low-income pregnant mothers who received influenza and Tdap vaccinations fell sharply during the COVID-19 pandemic, especially in Black and Hispanic patients, a new study finds.
The percentage of patients who received the influenza vaccines at two Medicaid clinics in Houston dropped from 78% before the pandemic to 61% during it (adjusted odds ratio, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.26-0.53; P < .01), researchers reported at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The percentage receiving the Tdap vaccine dipped from 85% to 76% (aOR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.40-0.79; P < .01).
New York–Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center pediatrician Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, who’s familiar with the study findings, called them “alarming” and said in an interview that they should be “a call to action for providers.”
“Continuing the status quo in our routine preventative health care and clinic operations means that we are losing ground in reduction and elimination of vaccine-preventable diseases,” Dr. Permar said in an interview.
According to corresponding author Bani Ratan, MD, an ob.gyn. with the Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, there’s been little if any previous research into routine, non-COVID vaccination in pregnant women during the pandemic.
For the study, researchers retrospectively analyzed the records of 939 pregnant women who entered prenatal care before 20 weeks (462 from May–November 2019, and 477 from May–November 2020) and delivered at full term.
Among ethnic groups, non-Hispanic Blacks saw the largest decline in influenza vaccines. Among them, the percentage who got them fell from 64% (73/114) to 35% (35/101; aOR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.17-0.52; P < .01). Only Hispanics had a statistically significant decline in Tdap vaccination (OR, 0.52, 95% CI, 0.34-0.80; P < .01, percentages not provided).
Another study presented at ACOG examined vaccination rates during the pandemic and found that Tdap vaccination rates dipped among pregnant women in a Philadelphia-area health care system.
Possible causes for the decline in routine vaccination include hesitancy linked to the COVID-19 vaccines and fewer office visits because of telemedicine, said Dr. Batan in an interview.
Dr. Permar blamed the role of vaccine misinformation during the pandemic and the mistrust caused by the exclusion of pregnant women from early vaccine trials. She added that “challenges in health care staffing and issues of health care provider burnout that worsened during the pandemic likely contributed to a fraying of the focus on preventive health maintenance simply due to bandwidth of health professionals.”
In a separate study presented at ACOG, researchers at the State University of New York, Syracuse, reported on a survey of 157 pregnant women of whom just 38.2% were vaccinated against COVID-19. Among the unvaccinated, who were more likely to have less education, 66% reported that lack of data about vaccination was their primary concern.
No funding or disclosures are reported by study authors. Dr. Permar reported consulting for Merck, Moderna, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Dynavax, and Hookipa on cytomegalovirus vaccine programs.
*This story was updated on 5/11/2022.
FROM ACOG 2022
CDC predicts a rise in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths in coming weeks
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID booster mounts ‘brisk’ response in patients with cancer
New data shed light on the durability of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the impact of booster doses for patients with cancer undergoing systemic therapy or who have received a stem cell transplant (SCT).
In a cross-sectional study of 453 such patients, anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibodies peaked 1 month after the second dose of an mRNA vaccine and remained stable over the next 6 months.
Notably, compared with the primary vaccine course, patients experienced a 20-fold increase in anti-RBD antibodies after the third vaccine dose, “indicative of a brisk anamnestic response from memory B cells,” Qamar Khan, MD, a medical oncologist at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, and colleagues report.
The study appeared online in JAMA Oncology.
Given the risk of poor outcomes among patients with cancer and recipients of SCTs who get COVID, Dr. Khan and colleagues wanted to understand the durability of the antibody response to COVID vaccines in this population.
Among the 453 patients enrolled in the study, 70% had solid tumors and 30% had hematologic malignancies. Just over 40% were receiving chemotherapy, 16% were receiving immunotherapy, 14% were receiving a targeted oral agent, 5% were receiving chemoimmunotherapy, and 25% had received an SCT.
Regarding vaccine type, 61% received the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, 36% received the Moderna mRNA vaccine, and 4% got the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The mean age of the cohort was 60.4 years; 56% were women.
Prior to vaccination, the geometric mean titer (GMT) of anti-RBD antibodies for all patients was 1.7; it increased to 18.65 2 weeks after the first dose.
At 1 month after the second mRNA dose (or 2 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine), GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies reached 470.38 and then decreased to 425.8 at 3 months after the second dose (or 4 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine). Patients who were male, older than 65 years, and who had been diagnosed with a hematologic malignant tumor were more likely to have lower anti-RBD GMT 3 months after the second vaccine dose.
GMTs subsequently increased to 447.23 6 months after the second dose (7 months for Johnson & Johnson).
One month after the third dose, GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies rose to 9,224.85 – more than 20 times the previous GMT value.
According to the investigators, roughly 80% of these patients remained above the threshold of an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher at 6 months.
“While still an arbitrary cutoff, an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher has been associated with protection and has been used to evaluate the effectiveness of a third dose of an mRNA vaccine in a randomized clinical trial of patients who received a solid organ transplant,” Dr. Khan and colleagues write.
“Although more data are needed to confirm this level as protective, if established, anti-RBD can potentially be used to prioritize additional vaccine doses, especially in regions of the world with limited vaccine resources,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported in part by the University of Kansas Cancer Center and the Investigator Initiated Steering Committee, by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and a University of Kansas Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data shed light on the durability of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the impact of booster doses for patients with cancer undergoing systemic therapy or who have received a stem cell transplant (SCT).
In a cross-sectional study of 453 such patients, anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibodies peaked 1 month after the second dose of an mRNA vaccine and remained stable over the next 6 months.
Notably, compared with the primary vaccine course, patients experienced a 20-fold increase in anti-RBD antibodies after the third vaccine dose, “indicative of a brisk anamnestic response from memory B cells,” Qamar Khan, MD, a medical oncologist at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, and colleagues report.
The study appeared online in JAMA Oncology.
Given the risk of poor outcomes among patients with cancer and recipients of SCTs who get COVID, Dr. Khan and colleagues wanted to understand the durability of the antibody response to COVID vaccines in this population.
Among the 453 patients enrolled in the study, 70% had solid tumors and 30% had hematologic malignancies. Just over 40% were receiving chemotherapy, 16% were receiving immunotherapy, 14% were receiving a targeted oral agent, 5% were receiving chemoimmunotherapy, and 25% had received an SCT.
Regarding vaccine type, 61% received the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, 36% received the Moderna mRNA vaccine, and 4% got the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The mean age of the cohort was 60.4 years; 56% were women.
Prior to vaccination, the geometric mean titer (GMT) of anti-RBD antibodies for all patients was 1.7; it increased to 18.65 2 weeks after the first dose.
At 1 month after the second mRNA dose (or 2 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine), GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies reached 470.38 and then decreased to 425.8 at 3 months after the second dose (or 4 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine). Patients who were male, older than 65 years, and who had been diagnosed with a hematologic malignant tumor were more likely to have lower anti-RBD GMT 3 months after the second vaccine dose.
GMTs subsequently increased to 447.23 6 months after the second dose (7 months for Johnson & Johnson).
One month after the third dose, GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies rose to 9,224.85 – more than 20 times the previous GMT value.
According to the investigators, roughly 80% of these patients remained above the threshold of an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher at 6 months.
“While still an arbitrary cutoff, an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher has been associated with protection and has been used to evaluate the effectiveness of a third dose of an mRNA vaccine in a randomized clinical trial of patients who received a solid organ transplant,” Dr. Khan and colleagues write.
“Although more data are needed to confirm this level as protective, if established, anti-RBD can potentially be used to prioritize additional vaccine doses, especially in regions of the world with limited vaccine resources,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported in part by the University of Kansas Cancer Center and the Investigator Initiated Steering Committee, by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and a University of Kansas Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data shed light on the durability of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the impact of booster doses for patients with cancer undergoing systemic therapy or who have received a stem cell transplant (SCT).
In a cross-sectional study of 453 such patients, anti–SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (anti-RBD) antibodies peaked 1 month after the second dose of an mRNA vaccine and remained stable over the next 6 months.
Notably, compared with the primary vaccine course, patients experienced a 20-fold increase in anti-RBD antibodies after the third vaccine dose, “indicative of a brisk anamnestic response from memory B cells,” Qamar Khan, MD, a medical oncologist at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, and colleagues report.
The study appeared online in JAMA Oncology.
Given the risk of poor outcomes among patients with cancer and recipients of SCTs who get COVID, Dr. Khan and colleagues wanted to understand the durability of the antibody response to COVID vaccines in this population.
Among the 453 patients enrolled in the study, 70% had solid tumors and 30% had hematologic malignancies. Just over 40% were receiving chemotherapy, 16% were receiving immunotherapy, 14% were receiving a targeted oral agent, 5% were receiving chemoimmunotherapy, and 25% had received an SCT.
Regarding vaccine type, 61% received the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine, 36% received the Moderna mRNA vaccine, and 4% got the Janssen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine. The mean age of the cohort was 60.4 years; 56% were women.
Prior to vaccination, the geometric mean titer (GMT) of anti-RBD antibodies for all patients was 1.7; it increased to 18.65 2 weeks after the first dose.
At 1 month after the second mRNA dose (or 2 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine), GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies reached 470.38 and then decreased to 425.8 at 3 months after the second dose (or 4 months after the Johnson & Johnson vaccine). Patients who were male, older than 65 years, and who had been diagnosed with a hematologic malignant tumor were more likely to have lower anti-RBD GMT 3 months after the second vaccine dose.
GMTs subsequently increased to 447.23 6 months after the second dose (7 months for Johnson & Johnson).
One month after the third dose, GMTs of anti-RBD antibodies rose to 9,224.85 – more than 20 times the previous GMT value.
According to the investigators, roughly 80% of these patients remained above the threshold of an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher at 6 months.
“While still an arbitrary cutoff, an anti-RBD level of 100 U/mL or higher has been associated with protection and has been used to evaluate the effectiveness of a third dose of an mRNA vaccine in a randomized clinical trial of patients who received a solid organ transplant,” Dr. Khan and colleagues write.
“Although more data are needed to confirm this level as protective, if established, anti-RBD can potentially be used to prioritize additional vaccine doses, especially in regions of the world with limited vaccine resources,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported in part by the University of Kansas Cancer Center and the Investigator Initiated Steering Committee, by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and a University of Kansas Cancer Center Support Grant from the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Khan reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY