User login
-
CDC issues new return-to-work guidelines
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is releasing new guidance on return-to-work rules for critical workers exposed to a COVID-19 case, or a suspected case, replacing previous guidance to stay home for 14 days.
“One of the most important things we can do is keep our critical workforce working,” CDC Director Robert Redfield said at a White House briefing on April 8. “In certain circumstances they can go back to work,” he said.
Neither Redfield nor the other governmental officials specified what counts as an essential worker, although it has generally referred to food-service and health care workers.
They must take their temperature before work, wear a facial mask at all times and practice social distancing when at work, the new guidance says. They cannot share headsets or other objects used near the face.
Employers must take the worker’s temperature and assess each one for symptoms before work starts, sending a worker home if he or she is sick. Employers must increase the cleaning of frequently used surfaces, increase air exchange in the building and test the use of face masks to be sure they do not interfere with workflow.
Pressed on whether he would reopen the country at the end of the 30-day Stop the Spread effort on April 30 — since one model has revised the U.S. death toll down from 100,000-240,000 to 61,000 — President Donald Trump said meetings will take place soon to discuss the decision and that he will ‘’rely very heavily” on health experts.
“We know now for sure that the mitigation we have been doing is having a positive effect,” said Anthony Fauci, MD, a coronavirus task force member and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
This article first appeared on WebMD.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is releasing new guidance on return-to-work rules for critical workers exposed to a COVID-19 case, or a suspected case, replacing previous guidance to stay home for 14 days.
“One of the most important things we can do is keep our critical workforce working,” CDC Director Robert Redfield said at a White House briefing on April 8. “In certain circumstances they can go back to work,” he said.
Neither Redfield nor the other governmental officials specified what counts as an essential worker, although it has generally referred to food-service and health care workers.
They must take their temperature before work, wear a facial mask at all times and practice social distancing when at work, the new guidance says. They cannot share headsets or other objects used near the face.
Employers must take the worker’s temperature and assess each one for symptoms before work starts, sending a worker home if he or she is sick. Employers must increase the cleaning of frequently used surfaces, increase air exchange in the building and test the use of face masks to be sure they do not interfere with workflow.
Pressed on whether he would reopen the country at the end of the 30-day Stop the Spread effort on April 30 — since one model has revised the U.S. death toll down from 100,000-240,000 to 61,000 — President Donald Trump said meetings will take place soon to discuss the decision and that he will ‘’rely very heavily” on health experts.
“We know now for sure that the mitigation we have been doing is having a positive effect,” said Anthony Fauci, MD, a coronavirus task force member and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
This article first appeared on WebMD.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is releasing new guidance on return-to-work rules for critical workers exposed to a COVID-19 case, or a suspected case, replacing previous guidance to stay home for 14 days.
“One of the most important things we can do is keep our critical workforce working,” CDC Director Robert Redfield said at a White House briefing on April 8. “In certain circumstances they can go back to work,” he said.
Neither Redfield nor the other governmental officials specified what counts as an essential worker, although it has generally referred to food-service and health care workers.
They must take their temperature before work, wear a facial mask at all times and practice social distancing when at work, the new guidance says. They cannot share headsets or other objects used near the face.
Employers must take the worker’s temperature and assess each one for symptoms before work starts, sending a worker home if he or she is sick. Employers must increase the cleaning of frequently used surfaces, increase air exchange in the building and test the use of face masks to be sure they do not interfere with workflow.
Pressed on whether he would reopen the country at the end of the 30-day Stop the Spread effort on April 30 — since one model has revised the U.S. death toll down from 100,000-240,000 to 61,000 — President Donald Trump said meetings will take place soon to discuss the decision and that he will ‘’rely very heavily” on health experts.
“We know now for sure that the mitigation we have been doing is having a positive effect,” said Anthony Fauci, MD, a coronavirus task force member and director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
This article first appeared on WebMD.
Home-based chemo skyrockets at one U.S. center
Major organization opposes concept
In the fall of 2019, the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia started a pilot program of home-based chemotherapy for two treatment regimens (one via infusion and one via injection). Six months later, the Cancer Care at Home program had treated 40 patients.
The uptake within the university’s large regional health system was acceptable but not rapid, admitted Amy Laughlin, MD, a hematology-oncology fellow involved with the program.
Then COVID-19 arrived, along with related travel restrictions.
Suddenly, in a 5-week period (March to April 7), 175 patients had been treated – a 300% increase from the first half year. Program staff jumped from 12 to 80 employees. The list of chemotherapies delivered went from two to seven, with more coming.
“We’re not the pilot anymore – we’re the standard of care,” Laughlin told Medscape Medical News.
“The impact [on patients] is amazing,” she said. “As long as you are selecting the right patients and right therapy, it is feasible and even preferable for a lot of patients.”
For example, patients with hormone-positive breast cancer who receive leuprolide (to shut down the ovaries and suppress estrogen production) ordinarily would have to visit a Penn facility for an injection every month, potentially for years. Now, a nurse can meet patients at home (or before the COVID-19 pandemic, even at their place of work) and administer the injection, saving the patient travel time and associated costs.
This home-based chemotherapy service does not appear to be offered elsewhere in the United States, and a major oncology organization – the Community Oncology Alliance – is opposed to the practice because of patient safety concerns.
The service is not offered at a sample of cancer centers queried by Medscape Medical News, including the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, the Huntsman Cancer Institute in Salt Lake City, Utah, and Moores Cancer Center, the University of California, San Diego.
Opposition because of safety concerns
On April 9, the Community Oncology Alliance (COA) issued a statement saying it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The COA warned that “many of the side effects caused by cancer treatment can have a rapid, unpredictable onset that places patients in incredible jeopardy and can even be life-threatening.”
In contrast, in a recent communication related to COVID-19, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network tacitly endorsed the concept, stating that a number of chemotherapies may potentially be administered at home, but it did not include guidelines for doing so.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that chemotherapy at home is “an issue [we] are monitoring closely,” according to a spokesperson.
What’s involved
Criteria for home-based chemotherapy at Penn include use of anticancer therapies that a patient has previously tolerated and low toxicity (that can be readily managed in the home setting). In addition, patients must be capable of following a med chart.
The chemotherapy is reconstituted at a Penn facility in a Philadelphia suburb. A courier then delivers the drug to the patient’s home, where it is administered by an oncology-trained nurse. Drugs must be stable for at least a few hours to qualify for the program.
The Penn program started with two regimens: EPOCH (etoposide, vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and prednisone) for lymphoma, and leuprolide acetate injections for either breast or prostate cancer.
The two treatments are polar opposites in terms of complexity, common usage, and time required, which was intended, said Laughlin.
Time to deliver the chemo varies from a matter of minutes with leuprolide to more than 2 hours for rituximab, a lymphoma drug that may be added to EPOCH.
The current list of at-home chemo agents in the Penn program also includes bortezomib, lanreotide, zoledronic acid, and denosumab. Soon to come are rituximab and pembrolizumab for lung cancer and head and neck cancer.
Already practiced in some European countries
Home-based chemotherapy dates from at least the 1980s in the medical literature and is practiced in some European countries.
A 2018 randomized study of adjuvant treatment with capecitabine and oxaliplatin for stage II/III colon cancer in Denmark, where home-based care has been practiced for the past 2 years and is growing in use, concluded that “it might be a valuable alternative to treatment at an outpatient clinic.”
However, in the study, there was no difference in quality of life between the home and outpatient settings, which is somewhat surprising, inasmuch as a major appeal to receiving chemotherapy at home is that it is less disruptive compared to receiving it in a hospital or clinic, which requires travel.
Also, chemo at home “may be resource intensive” and have a “lower throughput of patients due to transportation time,” cautioned the Danish investigators, who were from Herlev and Gentofte Hospital.
A 2015 review called home chemo “a safe and patient‐centered alternative to hospital‐ and outpatient‐based service.” Jenna Evans, PhD, McMaster University, Toronto, Canada, and lead author of that review, says there are two major barriers to infusion chemotherapy in homes.
One is inadequate resources in the community, such as oncology-trained nurses to deliver treatment, and the other is perceptions of safety and quality, including among healthcare providers.
COVID-19 might prompt more chemo at home, said Evans, a health policy expert, in an email to Medscape Medical News. “It is not unusual for change of this type and scale to require a seismic event to become more mainstream,” she argued.
Reimbursement for home-based chemo is usually the same as for chemo in a free-standing infusion suite, says Cassandra Redmond, PharmD, MBA, director of pharmacy, Penn Home Infusion Therapy.
Private insurers and Medicare cover a subset of infused medications at home, but coverage is limited. “The opportunity now is to expand these initiatives ... to include other cancer therapies,” she said about coverage.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Major organization opposes concept
Major organization opposes concept
In the fall of 2019, the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia started a pilot program of home-based chemotherapy for two treatment regimens (one via infusion and one via injection). Six months later, the Cancer Care at Home program had treated 40 patients.
The uptake within the university’s large regional health system was acceptable but not rapid, admitted Amy Laughlin, MD, a hematology-oncology fellow involved with the program.
Then COVID-19 arrived, along with related travel restrictions.
Suddenly, in a 5-week period (March to April 7), 175 patients had been treated – a 300% increase from the first half year. Program staff jumped from 12 to 80 employees. The list of chemotherapies delivered went from two to seven, with more coming.
“We’re not the pilot anymore – we’re the standard of care,” Laughlin told Medscape Medical News.
“The impact [on patients] is amazing,” she said. “As long as you are selecting the right patients and right therapy, it is feasible and even preferable for a lot of patients.”
For example, patients with hormone-positive breast cancer who receive leuprolide (to shut down the ovaries and suppress estrogen production) ordinarily would have to visit a Penn facility for an injection every month, potentially for years. Now, a nurse can meet patients at home (or before the COVID-19 pandemic, even at their place of work) and administer the injection, saving the patient travel time and associated costs.
This home-based chemotherapy service does not appear to be offered elsewhere in the United States, and a major oncology organization – the Community Oncology Alliance – is opposed to the practice because of patient safety concerns.
The service is not offered at a sample of cancer centers queried by Medscape Medical News, including the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, the Huntsman Cancer Institute in Salt Lake City, Utah, and Moores Cancer Center, the University of California, San Diego.
Opposition because of safety concerns
On April 9, the Community Oncology Alliance (COA) issued a statement saying it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The COA warned that “many of the side effects caused by cancer treatment can have a rapid, unpredictable onset that places patients in incredible jeopardy and can even be life-threatening.”
In contrast, in a recent communication related to COVID-19, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network tacitly endorsed the concept, stating that a number of chemotherapies may potentially be administered at home, but it did not include guidelines for doing so.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that chemotherapy at home is “an issue [we] are monitoring closely,” according to a spokesperson.
What’s involved
Criteria for home-based chemotherapy at Penn include use of anticancer therapies that a patient has previously tolerated and low toxicity (that can be readily managed in the home setting). In addition, patients must be capable of following a med chart.
The chemotherapy is reconstituted at a Penn facility in a Philadelphia suburb. A courier then delivers the drug to the patient’s home, where it is administered by an oncology-trained nurse. Drugs must be stable for at least a few hours to qualify for the program.
The Penn program started with two regimens: EPOCH (etoposide, vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and prednisone) for lymphoma, and leuprolide acetate injections for either breast or prostate cancer.
The two treatments are polar opposites in terms of complexity, common usage, and time required, which was intended, said Laughlin.
Time to deliver the chemo varies from a matter of minutes with leuprolide to more than 2 hours for rituximab, a lymphoma drug that may be added to EPOCH.
The current list of at-home chemo agents in the Penn program also includes bortezomib, lanreotide, zoledronic acid, and denosumab. Soon to come are rituximab and pembrolizumab for lung cancer and head and neck cancer.
Already practiced in some European countries
Home-based chemotherapy dates from at least the 1980s in the medical literature and is practiced in some European countries.
A 2018 randomized study of adjuvant treatment with capecitabine and oxaliplatin for stage II/III colon cancer in Denmark, where home-based care has been practiced for the past 2 years and is growing in use, concluded that “it might be a valuable alternative to treatment at an outpatient clinic.”
However, in the study, there was no difference in quality of life between the home and outpatient settings, which is somewhat surprising, inasmuch as a major appeal to receiving chemotherapy at home is that it is less disruptive compared to receiving it in a hospital or clinic, which requires travel.
Also, chemo at home “may be resource intensive” and have a “lower throughput of patients due to transportation time,” cautioned the Danish investigators, who were from Herlev and Gentofte Hospital.
A 2015 review called home chemo “a safe and patient‐centered alternative to hospital‐ and outpatient‐based service.” Jenna Evans, PhD, McMaster University, Toronto, Canada, and lead author of that review, says there are two major barriers to infusion chemotherapy in homes.
One is inadequate resources in the community, such as oncology-trained nurses to deliver treatment, and the other is perceptions of safety and quality, including among healthcare providers.
COVID-19 might prompt more chemo at home, said Evans, a health policy expert, in an email to Medscape Medical News. “It is not unusual for change of this type and scale to require a seismic event to become more mainstream,” she argued.
Reimbursement for home-based chemo is usually the same as for chemo in a free-standing infusion suite, says Cassandra Redmond, PharmD, MBA, director of pharmacy, Penn Home Infusion Therapy.
Private insurers and Medicare cover a subset of infused medications at home, but coverage is limited. “The opportunity now is to expand these initiatives ... to include other cancer therapies,” she said about coverage.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the fall of 2019, the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia started a pilot program of home-based chemotherapy for two treatment regimens (one via infusion and one via injection). Six months later, the Cancer Care at Home program had treated 40 patients.
The uptake within the university’s large regional health system was acceptable but not rapid, admitted Amy Laughlin, MD, a hematology-oncology fellow involved with the program.
Then COVID-19 arrived, along with related travel restrictions.
Suddenly, in a 5-week period (March to April 7), 175 patients had been treated – a 300% increase from the first half year. Program staff jumped from 12 to 80 employees. The list of chemotherapies delivered went from two to seven, with more coming.
“We’re not the pilot anymore – we’re the standard of care,” Laughlin told Medscape Medical News.
“The impact [on patients] is amazing,” she said. “As long as you are selecting the right patients and right therapy, it is feasible and even preferable for a lot of patients.”
For example, patients with hormone-positive breast cancer who receive leuprolide (to shut down the ovaries and suppress estrogen production) ordinarily would have to visit a Penn facility for an injection every month, potentially for years. Now, a nurse can meet patients at home (or before the COVID-19 pandemic, even at their place of work) and administer the injection, saving the patient travel time and associated costs.
This home-based chemotherapy service does not appear to be offered elsewhere in the United States, and a major oncology organization – the Community Oncology Alliance – is opposed to the practice because of patient safety concerns.
The service is not offered at a sample of cancer centers queried by Medscape Medical News, including the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, the Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, the Huntsman Cancer Institute in Salt Lake City, Utah, and Moores Cancer Center, the University of California, San Diego.
Opposition because of safety concerns
On April 9, the Community Oncology Alliance (COA) issued a statement saying it “fundamentally opposes home infusion of chemotherapy, cancer immunotherapy, and cancer treatment supportive drugs because of serious patient safety concerns.”
The COA warned that “many of the side effects caused by cancer treatment can have a rapid, unpredictable onset that places patients in incredible jeopardy and can even be life-threatening.”
In contrast, in a recent communication related to COVID-19, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network tacitly endorsed the concept, stating that a number of chemotherapies may potentially be administered at home, but it did not include guidelines for doing so.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology said that chemotherapy at home is “an issue [we] are monitoring closely,” according to a spokesperson.
What’s involved
Criteria for home-based chemotherapy at Penn include use of anticancer therapies that a patient has previously tolerated and low toxicity (that can be readily managed in the home setting). In addition, patients must be capable of following a med chart.
The chemotherapy is reconstituted at a Penn facility in a Philadelphia suburb. A courier then delivers the drug to the patient’s home, where it is administered by an oncology-trained nurse. Drugs must be stable for at least a few hours to qualify for the program.
The Penn program started with two regimens: EPOCH (etoposide, vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and prednisone) for lymphoma, and leuprolide acetate injections for either breast or prostate cancer.
The two treatments are polar opposites in terms of complexity, common usage, and time required, which was intended, said Laughlin.
Time to deliver the chemo varies from a matter of minutes with leuprolide to more than 2 hours for rituximab, a lymphoma drug that may be added to EPOCH.
The current list of at-home chemo agents in the Penn program also includes bortezomib, lanreotide, zoledronic acid, and denosumab. Soon to come are rituximab and pembrolizumab for lung cancer and head and neck cancer.
Already practiced in some European countries
Home-based chemotherapy dates from at least the 1980s in the medical literature and is practiced in some European countries.
A 2018 randomized study of adjuvant treatment with capecitabine and oxaliplatin for stage II/III colon cancer in Denmark, where home-based care has been practiced for the past 2 years and is growing in use, concluded that “it might be a valuable alternative to treatment at an outpatient clinic.”
However, in the study, there was no difference in quality of life between the home and outpatient settings, which is somewhat surprising, inasmuch as a major appeal to receiving chemotherapy at home is that it is less disruptive compared to receiving it in a hospital or clinic, which requires travel.
Also, chemo at home “may be resource intensive” and have a “lower throughput of patients due to transportation time,” cautioned the Danish investigators, who were from Herlev and Gentofte Hospital.
A 2015 review called home chemo “a safe and patient‐centered alternative to hospital‐ and outpatient‐based service.” Jenna Evans, PhD, McMaster University, Toronto, Canada, and lead author of that review, says there are two major barriers to infusion chemotherapy in homes.
One is inadequate resources in the community, such as oncology-trained nurses to deliver treatment, and the other is perceptions of safety and quality, including among healthcare providers.
COVID-19 might prompt more chemo at home, said Evans, a health policy expert, in an email to Medscape Medical News. “It is not unusual for change of this type and scale to require a seismic event to become more mainstream,” she argued.
Reimbursement for home-based chemo is usually the same as for chemo in a free-standing infusion suite, says Cassandra Redmond, PharmD, MBA, director of pharmacy, Penn Home Infusion Therapy.
Private insurers and Medicare cover a subset of infused medications at home, but coverage is limited. “The opportunity now is to expand these initiatives ... to include other cancer therapies,” she said about coverage.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The 7 strategies of highly effective people facing the COVID-19 pandemic
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
A few weeks ago, I saw more than 60 responses to a post on Nextdoor.com entitled, “Toilet paper strategies?”
Asking for help is a great coping mechanism when one is struggling to find a strategy, even if it’s for toilet paper. What other kinds of coping strategies can help us through this historic and unprecedented time?
The late Stephen R. Covey, PhD, wrote about the coping strategies of highly effective people in his book, “The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People.”1 For, no matter how smart, perfect, or careful you may be, life will never be trouble free. When trouble comes, it’s important to have coping strategies that help you navigate through choppy waters. Whether you are a practitioner trying to help your patients or someone who wants to maximize their personal resilience during a worldwide pandemic, here are my conceptualizations of the seven top strategies highly effective people use when facing challenges.
Strategy #1: Begin with the end in mind
In 2007, this strategy helped me not only survive but thrive when I battled for my right to practice as a holistic psychiatrist against the Maryland Board of Physicians.2 From the first moment when I read the letter from the board, to the last when I read the administrative law judge’s dismissal, I turned to this strategy to help me cope with unrelenting stress.
I imagined myself remembering being the kind of person I wanted to be, wrote that script for myself, and created those memories for my future self. I wanted to remember myself as being brave, calm, strong, and grounded, so I behaved each day as if I were all of those things.
As Dr. Covey wrote, “ ‘Begin with the end in mind’ is based on the principle that all things are created twice. There’s a mental or first creation, and a physical or second creation to all things.” Imagine who you would like to remember yourself being a year or two down the road. Do you want to remember yourself showing good judgment and being positive and compassionate during this pandemic? Then, follow the script you’ve created in your mind and be that person now, knowing that you are forming memories for your future self. Your future self will look back at who you are right now with appreciation and satisfaction. Of course, this is a habit that you can apply to your entire life.
Strategy #2: Be proactive
Between the event and the outcome is you. You are the interpreter and transformer of the event, with the freedom to apply your will and intention on the event. Whether it is living through a pandemic or dealing with misplaced keys, every day you are revealing your nature through how you deal with life. To be proactive is different from being reactive. Within each of us there is a will, the drive, to rise above our difficult environments.
Dr. Covey wrote, “the ability to subordinate an impulse to a value is the essence of the proactive person.” A woman shared with me that she created an Excel spreadsheet with some of the things she plans to do with her free time while she stays in her NYC apartment. She doesn’t want to slip into a passive state and waste her time. That’s being proactive.
Strategy #3: Set proper priorities
Or, as Dr. Covey would say, “Put first things first.” During a pandemic, when the world seems to be precariously tilting at an angle, it’s easy to cling to outdated standards, expectations, and behavioral patterns. Doing so heightens our sense of regret, fear, and scarcity. Valuing gratitude will empower you to deal with financial loss differently because you can still remain grateful despite uncontrollable losses. We can choose “to have or to be” as psychoanalyst, Erich Fromm, PhD, would say.3 If your happiness is measured by how much money you have, then it would make sense that, when the amount shrinks, so does your happiness. However, if your happiness is a side effect of who you are, you will remain a mountain before the winds and tides of circumstance.
Strategy #4: Create a win/win mentality
This state of mind is built on character. Dr. Covey separates character into three categories: integrity, maturity, and abundance mentality. A lack of character resulted in the hoarding of toilet paper in many communities and the cry for help from Nextdoor.com. I noticed that, in the 60+ responses that included advice about using bidets, old towels, and even leaves, no one offered to share a bag of toilet paper. That’s because people experienced the fear of scarcity, in turn, causing the scarcity they feared.
During a pandemic, a highly effective person or company thinks beyond themselves to create a win/win scenario. At a grocery store in my neighborhood, a man stands at its entrance with a bottle of disinfectant spray in one hand for the shoppers and a sign on the sidewalk with guidelines for purchasing products to avoid hoarding. He tells you where the wipes are for the carts as you enter the store. People line up 6 feet apart, waiting to enter, to limit the number of shoppers inside the store, facilitating proper physical distancing. Instead of maximizing profits at the expense of everyone’s health and safety, the process is a win/win for everyone, from shoppers to employees.
Strategy #5: Develop empathy and understanding
Seeking to first understand and then be understood is one of the most powerful tools of effective people. In my holistic practice, every patient comes in with their own unique needs that evolve and transform over time. I must remain open, or I fail to deliver appropriately.
Learning to listen and then to clearly communicate ideas is essential to effective health care. During this time, it is critical that health care providers and political leaders first listen/understand and then communicate clearly to serve everyone in the best way possible.
In our brains, the frontal lobes (the adult in the room) manages our amygdala (the child in the room) when we get enough sleep, meditate, spend time in nature, exercise, and eat healthy food.4 Stress can interfere with the frontal lobe’s ability to maintain empathy, inhibit unhealthy impulses, and delay gratification. During the pandemic, we can help to shift from the stress response, or “fight-or-flight” response, driven by the sympathetic nervous system to a “rest-and-digest” response driven by the parasympathetic system through coherent breathing, taking slow, deep, relaxed breaths (6 seconds on inhalation and 6 seconds on exhalation). The vagus nerve connected to our diaphragm will help the heart return to a healthy rhythm.5
Strategy #6: Synergize and integrate
All of life is interdependent, each part no more or less important than any other. Is oxygen more important than hydrogen? Is H2O different from the oxygen and hydrogen atoms that make it?
During a pandemic, it’s important for us to appreciate each other’s contributions and work synergistically for the good of the whole. Our survival depends on valuing each other and our planet. This perspective informs the practice of physical distancing and staying home to minimize the spread of the virus and its impact on the health care system, regardless of whether an individual belongs in the high-risk group or not.
Many high-achieving people train in extremely competitive settings in which survival depends on individual performance rather than mutual cooperation. This training process encourages a disregard for others. Good leaders, however, understand that cooperation and mutual respect are essential to personal well-being.
Strategy #7: Practice self-care
There are five aspects of our lives that depend on our self-care: spiritual, mental, emotional, physical, and social. Unfortunately, many kind-hearted people are kinder to others than to themselves. There is really only one person who can truly take care of you properly, and that is yourself. In Seattle, where many suffered early in the pandemic, holistic psychiatrist David Kopacz, MD, is reminding people to nurture themselves in his post, “Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes!”6 Indeed, that is what many must do since eating out is not an option now. If you find yourself stuck at home with more time on your hands, take the opportunity to care for yourself. Ask yourself what you really need during this time, and make the effort to provide it to yourself.
After the pandemic is over, will you have grown from the experiences and become a better person from it? Despite our current circumstances, we can continue to grow as individuals and as a community, armed with strategies that can benefit all of us.
References
1. Covey SR. The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People. New York: Simon & Schuster; 1989.
2. Lee AW. Townsend Letter. 2009 Jun;311:22-3.
3. Fromm E. To Have or To Be? New York: Continuum International Publishing; 2005.
4. Rushlau K. Integrative Healthcare Symposium. 2020 Feb 21.
5. Gerbarg PL. Mind Body Practices for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Presentation at Integrative Medicine for Mental Health Conference. 2016 Sep.
6. Kopacz D. Nurture Yourself During the Pandemic: Try New Recipes! Being Fully Human. 2020 Mar 22.
Dr. Lee specializes in integrative and holistic psychiatry and has a private practice in Gaithersburg, Md. She has no disclosures.
American Lung Association announces $25 million initiative to end COVID-19
The goals of the COVID-19 Action Initiative will be to expand the ALA’s respiratory research program, improve public health measures, and create an advanced network to prevent future respiratory virus pandemics. In cooperation with the public and private sectors, the initiative will promote research collaboration and develop new vaccines, diagnostic tests, and therapies. The initiative will take advantage of the ALA’s current research network and will also fund respiratory virus research. It also will fund education and advocacy to support public health measures against current and future respiratory viruses.
The COVID-19 Action Initiative will fund respiratory virus research through three main activities. It will expand COVID-19 research within the current clinical trials of the Airways Clinical Research Center (ACRC) Network. Second, it will fund coronavirus awards and grants for preventive research, vaccines, antivirals, and efforts to promote preparedness for future outbreaks. Third, it will provide ACRC pilot grants to evaluate the effect of COVID-19 on patients with chronic lung disease.
“More than 36 million people in the U.S. suffer from lung disease, which places them at higher risk for experiencing complications of COVID-19, making it even more critical that we urgently work on reducing its impact,” said Harold Wimmer, president and CEO of the ALA, in a press release.
The ALA has $8 million available and earmarked for the initiative. The association plans to raise additional funds during the next 3 years by reaching out to corporate partners, public health entities, and individuals. “With the help of our staff and volunteers, and with the support and donations of generous Americans, we can stand together and face the challenges to lung health of today and tomorrow,” said Mr. Wimmer in a press briefing.
The goals of the COVID-19 Action Initiative will be to expand the ALA’s respiratory research program, improve public health measures, and create an advanced network to prevent future respiratory virus pandemics. In cooperation with the public and private sectors, the initiative will promote research collaboration and develop new vaccines, diagnostic tests, and therapies. The initiative will take advantage of the ALA’s current research network and will also fund respiratory virus research. It also will fund education and advocacy to support public health measures against current and future respiratory viruses.
The COVID-19 Action Initiative will fund respiratory virus research through three main activities. It will expand COVID-19 research within the current clinical trials of the Airways Clinical Research Center (ACRC) Network. Second, it will fund coronavirus awards and grants for preventive research, vaccines, antivirals, and efforts to promote preparedness for future outbreaks. Third, it will provide ACRC pilot grants to evaluate the effect of COVID-19 on patients with chronic lung disease.
“More than 36 million people in the U.S. suffer from lung disease, which places them at higher risk for experiencing complications of COVID-19, making it even more critical that we urgently work on reducing its impact,” said Harold Wimmer, president and CEO of the ALA, in a press release.
The ALA has $8 million available and earmarked for the initiative. The association plans to raise additional funds during the next 3 years by reaching out to corporate partners, public health entities, and individuals. “With the help of our staff and volunteers, and with the support and donations of generous Americans, we can stand together and face the challenges to lung health of today and tomorrow,” said Mr. Wimmer in a press briefing.
The goals of the COVID-19 Action Initiative will be to expand the ALA’s respiratory research program, improve public health measures, and create an advanced network to prevent future respiratory virus pandemics. In cooperation with the public and private sectors, the initiative will promote research collaboration and develop new vaccines, diagnostic tests, and therapies. The initiative will take advantage of the ALA’s current research network and will also fund respiratory virus research. It also will fund education and advocacy to support public health measures against current and future respiratory viruses.
The COVID-19 Action Initiative will fund respiratory virus research through three main activities. It will expand COVID-19 research within the current clinical trials of the Airways Clinical Research Center (ACRC) Network. Second, it will fund coronavirus awards and grants for preventive research, vaccines, antivirals, and efforts to promote preparedness for future outbreaks. Third, it will provide ACRC pilot grants to evaluate the effect of COVID-19 on patients with chronic lung disease.
“More than 36 million people in the U.S. suffer from lung disease, which places them at higher risk for experiencing complications of COVID-19, making it even more critical that we urgently work on reducing its impact,” said Harold Wimmer, president and CEO of the ALA, in a press release.
The ALA has $8 million available and earmarked for the initiative. The association plans to raise additional funds during the next 3 years by reaching out to corporate partners, public health entities, and individuals. “With the help of our staff and volunteers, and with the support and donations of generous Americans, we can stand together and face the challenges to lung health of today and tomorrow,” said Mr. Wimmer in a press briefing.
Almost 90% of COVID-19 admissions involve comorbidities
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
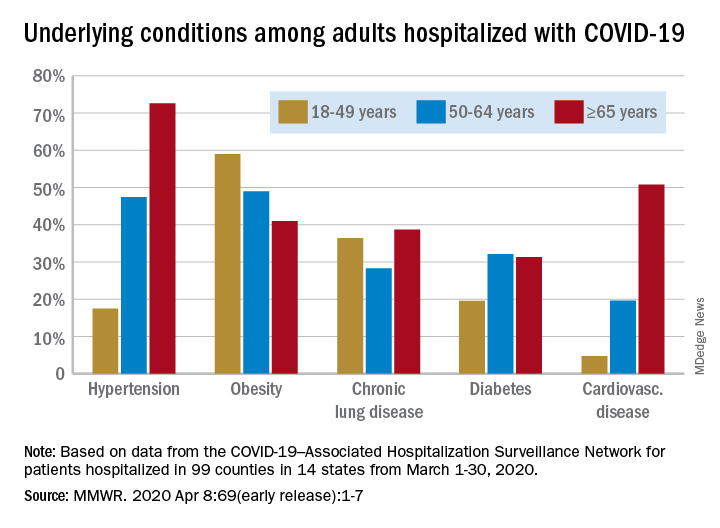
Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
The hospitalization rate for COVID-19 is 4.6 per 100,000 population, and almost 90% of hospitalized patients have some type of underlying condition, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Data collected by the newly created COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET) put the exact prevalence of underlying conditions at 89.3% for patients hospitalized during March 1-30, 2020, Shikha Garg, MD, of the CDC’s COVID-NET team and associates wrote in the MMWR.
The hospitalization rate, based on COVID-NET data for March 1-28, increased with patient age. Those aged 65 years and older were admitted at a rate of 13.8 per 100,000, with 50- to 64-year-olds next at 7.4 per 100,000 and 18- to 49-year-olds at 2.5, they wrote.
The patients aged 65 years and older also were the most likely to have one or more underlying conditions, at 94.4%, compared with 86.4% of those aged 50-64 years and 85.4% of individuals who were aged 18-44 years, the investigators reported.
Hypertension was the most common comorbidity among the oldest patients, with a prevalence of 72.6%, followed by cardiovascular disease at 50.8% and obesity at 41%. In the two younger groups, obesity was the condition most often seen in COVID-19 patients, with prevalences of 49% in 50- to 64-year-olds and 59% in those aged 18-49, Dr. Garg and associates wrote.
“These findings underscore the importance of preventive measures (e.g., social distancing, respiratory hygiene, and wearing face coverings in public settings where social distancing measures are difficult to maintain) to protect older adults and persons with underlying medical conditions,” the investigators wrote.
COVID-NET surveillance includes laboratory-confirmed hospitalizations in 99 counties in 14 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Iowa, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oregon, Tennessee, and Utah. Those counties represent about 10% of the U.S. population.
SOURCE: Garg S et al. MMWR. 2020 Apr 8;69(early release):1-7.
FROM THE MMWR
COVID 19: Psychiatric patients may be among the hardest hit
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic represents a looming crisis for patients with severe mental illness (SMI) and the healthcare systems that serve them, one expert warns.
However, Benjamin Druss, MD, MPH, from Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Georgia, says there are strategies that can help minimize the risk of exposure and transmission of the virus in SMI patients.
In a viewpoint published online April 3 in JAMA Psychiatry, Druss, professor and chair in mental health, notes that “disasters disproportionately affect poor and vulnerable populations, and patients with serious mental illness may be among the hardest hit.”
In an interview with Medscape Medical News, Druss said patients with SMI have “a whole range of vulnerabilities” that put them at higher risk for COVID-19.
These include high rates of smoking, cardiovascular and lung disease, poverty, and homelessness. In fact, estimates show 25% of the US homeless population has a serious mental illness, said Druss.
“You have to keep an eye on these overlapping circles of vulnerable populations: those with disabilities in general and people with serious mental illness in particular; people who are poor; and people who have limited social networks,” he said.
Tailored Communication Vital
It’s important for patients with SMI to have up-to-date, accurate information about mitigating risk and knowing when to seek medical treatment for COVID-19, Druss noted.
Communication materials developed for the general population need to be tailored to address limited health literacy and challenges in implementing physical distancing recommendations, he said.
Patients with SMI also need support in maintaining healthy habits, including diet and physical activity, as well as self-management of chronic mental and physical health conditions, he added.
He noted that even in the face of current constraints on mental health care delivery, ensuring access to services is essential. The increased emphasis on caring for, and keeping in touch with, SMI patients through telepsychiatry is one effective way of addressing this issue, said Druss.
Since mental health clinicians are often the first responders for people with SMI, these professionals need training to recognize the signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and learn basic strategies to mitigate the spread of disease, not only for their patients but also for themselves, he added.
“Any given provider is going to be responsible for many, many patients, so keeping physically and mentally healthy will be vital.”
In order to ease the strain of COVID-19 on community mental health centers and psychiatric hospitals, which are at high risk for outbreaks and have limited capacity to treat medical illness, these institutions need contingency plans to detect and contain outbreaks if they occur.
“Careful planning and execution at multiple levels will be essential for minimizing the adverse outcomes of this pandemic for this vulnerable population,” Druss writes.
Voice of Experience
Commenting on the article for Medscape Medical News, Lloyd I. Sederer, MD, distinguished advisor for the New York State Office of Mental Health and adjunct professor at the Columbia School of Public Health in New York City, commended Druss for highlighting the need for more mental health services during the pandemic.
However, although Druss “has made some very good general statements,” these don’t really apply “in the wake of a real catastrophic event, which is what we’re having here,” Sederer said.
Sederer led Project Liberty, a massive mental health disaster response effort established in the wake of the Sept. 11 attacks in New York. Druss seems to infer that the mental health workforce is capable of expanding, but “what we learned is that the mental health system in this country is vastly undersupplied,” said Sederer.
During a disaster, the system “actually contracts” because clinics close and workforces are reduced. In this environment, some patients with a serious mental illness let their treatment “erode,” Sederer said.
While Druss called for clinics to have protocols for identifying and referring patients at risk for COVID-19, Sederer pointed out that “all the clinics are closed.”
However, he did note that many mental health clinics and hospitals are continuing to reach out to their vulnerable patients during this crisis.
On the 10th anniversary of the 9/11 attacks, Sederer and colleagues published an article in Psychiatric Services that highlighted the “lessons learned” from the Project Liberty experience. One of the biggest lessons was the need for crisis counseling, which is “a recognized, proven intervention,” said Sederer.
Such an initiative involves trained outreach workers, identifying the untreated seriously mentally ill in the community, and “literally shepherding them to services,” he added.
In this current pandemic, it would be up to the federal government to mobilize such a crisis counseling initiative, Sederer explained.
Sederer noted that rapid relief groups like the Federal Emergency Management Agency do not cover mental health services. In order to be effective, disaster-related mental health services need to include funding for treatment, including focused therapies and medication.
Druss and Sederer have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First protocol on how to use lung ultrasound to triage COVID-19
The first protocol for the use of lung ultrasound to quantitatively and reproducibly assess the degree of lung involvement in patients suspected of having COVID-19 infection has been published by a team of Italian experts with experience using the technology on the front line.
Particularly in Spain and Italy — where the pandemic has struck hardest in Europe — hard-pressed clinicians seeking to quickly understand whether patients with seemingly mild disease could be harboring more serious lung involvement have increasingly relied upon lung ultrasound in the emergency room.
Now Libertario Demi, PhD, head of the ultrasound laboratory, University of Trento, Italy, and colleagues have developed a protocol, published online March 30 in the Journal of Ultrasound Medicine, to standardize practice.
Their research, which builds on previous work by the team, offers broad agreement with industry-led algorithms and emphasizes the use of wireless, handheld ultrasound devices, ideally consisting of a separate probe and tablet, to make sterilization easy.
Firms such as the Butterfly Network, Phillips, Clarius, GE Healthcare, and Siemens are among numerous companies that produce one or more such devices, including some that are completely integrated.
Not Universally Accepted
However, lung ultrasound is not yet universally accepted as a tool for diagnosing pneumonia in the context of COVID-19 and triaging patients.
The National Health Service in England does not even mention lung ultrasound in its radiology decision tool for suspected COVID-19, specifying instead chest X-ray as the first-line diagnostic imaging tool, with CT scanning in equivocal cases.
But Giovanni Volpicelli, MD, University Hospital San Luigi Gonzaga, Turin, Italy, who has previously described his experience to Medscape Medical News, says many patients with COVID-19 in his hospital presented with a negative chest X-ray but were found to have interstitial pneumonia on lung ultrasound.
Moreover, while CT scan remains the gold standard, the risk of nosocomial infection is more easily controlled if patients do not have to be transported to the radiology department but remain in the emergency room and instead undergo lung ultrasound there, he stressed.
Experts Share Experience of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19
In developing and publishing their protocol, Demi, senior author of the article, and other colleagues from the heavily affected cities of Northern Italy, say their aim is “to share our experience and to propose a standardization with respect to the use of lung ultrasound in the management of COVID-19 patients.”
They reviewed an anonymized database of around 60,000 ultrasound images of confirmed COVID-19 cases and reviewers were blinded to patients’ clinical backgrounds.
For image acquisition, the authors recommend scanning 14 areas in each patient for 10 seconds, making the scans intercostal to cover the widest possible surface area.
They advise the use of a single focal point on the pleural line, which they write, optimizes the beam shape for observing the lung surface.
The authors also urge that the mechanical index (MI) be kept low because high MIs sustained for long periods “may result in damaging the lung.”
They also stress that cosmetic filters and modalities such as harmonic imaging, contrast, doppler, and compounding should be avoided, alongside saturation phenomena.
What Constitutes Intermediate Disease?
Once the images have been taken, they are scored on a 0-3 scale for each of the 14 areas, with no weighting on any individual area.
A score of 0 is given when the pleural line is continuous and regular, with the presence of A-lines, denoting that the lungs are unaffected.
An area is given a score of 3 when the scan shows dense and largely extended white lung tissue, with or without consolidations, indicating severe disease.
At both ends of this spectrum, there is agreement between the Italian protocol and an algorithm developed by the Butterfly Network.
However, the two differ when it comes to scoring intermediate cases. On the Butterfly algorithm, the suggestion is to look for B-lines, caused by fluid and cellular infiltration into the interstitium, and to weigh that against the need for supplementary oxygen.
The Italian team, in contrast, says a score of 1 is given when the pleural line is indented, with vertical areas of white visible below.
A score of 2 is given when the pleural line is broken, with small to large areas of consolidation and associated areas of white below.
Demi told Medscape Medical News that they did not refer to B-lines in their protocol as their visibility depends entirely on the imaging frequency and the probe used.
“This means that scoring on B-lines, people with different machines would give completely different scores for the same patient.”
He continued: “We prefer to refer to horizontal and vertical artifacts, and provide an analysis of the patterns, which is related to the physics of the interactions between the ultrasound waves and lung surface.”
In response, Mike Stone, MD, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center, Portland, Oregon, and director of education at Butterfly, said there appears to be wide variation in lung findings that “may or may not correlate with the severity of symptoms.”
He told Medscape Medical News it is “hard to know exactly if someone with pure B-lines will progress to serious illness or if someone with some subpleural consolidations will do well.”
A Negative Ultrasound Is the Most Useful
Volpicelli believes that, in any case, any patient with an intermediate pattern will require further diagnosis, such as other imaging modalities and blood exams, and the real role of lung ultrasound is in assessing patients at either end of the spectrum.
“In other words, there are situations where lung ultrasound can be considered definitive,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For instance, if I see a patient with mild signs of the disease, just fever, and I perform lung ultrasound and see nothing, lung ultrasound rules out pneumonia.”
“This patient may have COVID-19 of course, but they do not have pneumonia, and they can be treated at home, awaiting the result of the swab test. And this is useful because you can reduce the burden in the emergency department.”
Volpicelli continued: “On the other hand, there are patients with acute respiratory failure in respiratory distress. If the lung ultrasound is normal, you can rule out COVID-19 and you need to use other diagnostic procedures to understand the problem.”
“This is also very important for us because it’s crucial to be able to remove the patient from the isolation area and perform CT scan, chest radiography, and all the other diagnostic tools that we need.”
Are Wireless Machines Needed? Not Necessarily
With regard to the use of wireless technology, the Italian team says that “in the setting of COVID-19, wireless probes and tablets represent the most appropriate ultrasound equipment” because they can “easily be wrapped in single-use plastic covers, reducing the risk of contamination,” and making sterilization easy.
Stone suggests that integrated portable devices, however, are no more likely to cause cross-contamination than separate probes and tablets, as they can fit within a sterile sheath as a single unit.
Volpicelli, for his part, doesn’t like what he sees as undue focus on wireless devices for lung ultrasound in the COVID-19 protocols.
He is concerned that recommending them as the best approach may be sending out the wrong message, which could be very “dangerous” as people may then think they cannot perform this screening with standard ultrasound machines.
For him, the issue of cross contamination with standard lung ultrasound machines is “nonexistent. Cleaning the machine is quite easy and I do it hundreds of times per week.”
He does acknowledge, however, that if the lung ultrasound is performed under certain circumstances, for example when a patient is using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, “the risk of having the machine contaminated is a little bit higher.”
“In these situations...we have a more intensive cleaning procedure to avoid cross-contamination.”
He stressed: “Not all centers have wireless machines, whereas a normal machine is usually in all hospitals.”
“The advantages of using lung ultrasound [in COVID-19] are too great to be limited by something that is not important in my opinion,” he concluded.
Stone is director of education at the Butterfly Network. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first protocol for the use of lung ultrasound to quantitatively and reproducibly assess the degree of lung involvement in patients suspected of having COVID-19 infection has been published by a team of Italian experts with experience using the technology on the front line.
Particularly in Spain and Italy — where the pandemic has struck hardest in Europe — hard-pressed clinicians seeking to quickly understand whether patients with seemingly mild disease could be harboring more serious lung involvement have increasingly relied upon lung ultrasound in the emergency room.
Now Libertario Demi, PhD, head of the ultrasound laboratory, University of Trento, Italy, and colleagues have developed a protocol, published online March 30 in the Journal of Ultrasound Medicine, to standardize practice.
Their research, which builds on previous work by the team, offers broad agreement with industry-led algorithms and emphasizes the use of wireless, handheld ultrasound devices, ideally consisting of a separate probe and tablet, to make sterilization easy.
Firms such as the Butterfly Network, Phillips, Clarius, GE Healthcare, and Siemens are among numerous companies that produce one or more such devices, including some that are completely integrated.
Not Universally Accepted
However, lung ultrasound is not yet universally accepted as a tool for diagnosing pneumonia in the context of COVID-19 and triaging patients.
The National Health Service in England does not even mention lung ultrasound in its radiology decision tool for suspected COVID-19, specifying instead chest X-ray as the first-line diagnostic imaging tool, with CT scanning in equivocal cases.
But Giovanni Volpicelli, MD, University Hospital San Luigi Gonzaga, Turin, Italy, who has previously described his experience to Medscape Medical News, says many patients with COVID-19 in his hospital presented with a negative chest X-ray but were found to have interstitial pneumonia on lung ultrasound.
Moreover, while CT scan remains the gold standard, the risk of nosocomial infection is more easily controlled if patients do not have to be transported to the radiology department but remain in the emergency room and instead undergo lung ultrasound there, he stressed.
Experts Share Experience of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19
In developing and publishing their protocol, Demi, senior author of the article, and other colleagues from the heavily affected cities of Northern Italy, say their aim is “to share our experience and to propose a standardization with respect to the use of lung ultrasound in the management of COVID-19 patients.”
They reviewed an anonymized database of around 60,000 ultrasound images of confirmed COVID-19 cases and reviewers were blinded to patients’ clinical backgrounds.
For image acquisition, the authors recommend scanning 14 areas in each patient for 10 seconds, making the scans intercostal to cover the widest possible surface area.
They advise the use of a single focal point on the pleural line, which they write, optimizes the beam shape for observing the lung surface.
The authors also urge that the mechanical index (MI) be kept low because high MIs sustained for long periods “may result in damaging the lung.”
They also stress that cosmetic filters and modalities such as harmonic imaging, contrast, doppler, and compounding should be avoided, alongside saturation phenomena.
What Constitutes Intermediate Disease?
Once the images have been taken, they are scored on a 0-3 scale for each of the 14 areas, with no weighting on any individual area.
A score of 0 is given when the pleural line is continuous and regular, with the presence of A-lines, denoting that the lungs are unaffected.
An area is given a score of 3 when the scan shows dense and largely extended white lung tissue, with or without consolidations, indicating severe disease.
At both ends of this spectrum, there is agreement between the Italian protocol and an algorithm developed by the Butterfly Network.
However, the two differ when it comes to scoring intermediate cases. On the Butterfly algorithm, the suggestion is to look for B-lines, caused by fluid and cellular infiltration into the interstitium, and to weigh that against the need for supplementary oxygen.
The Italian team, in contrast, says a score of 1 is given when the pleural line is indented, with vertical areas of white visible below.
A score of 2 is given when the pleural line is broken, with small to large areas of consolidation and associated areas of white below.
Demi told Medscape Medical News that they did not refer to B-lines in their protocol as their visibility depends entirely on the imaging frequency and the probe used.
“This means that scoring on B-lines, people with different machines would give completely different scores for the same patient.”
He continued: “We prefer to refer to horizontal and vertical artifacts, and provide an analysis of the patterns, which is related to the physics of the interactions between the ultrasound waves and lung surface.”
In response, Mike Stone, MD, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center, Portland, Oregon, and director of education at Butterfly, said there appears to be wide variation in lung findings that “may or may not correlate with the severity of symptoms.”
He told Medscape Medical News it is “hard to know exactly if someone with pure B-lines will progress to serious illness or if someone with some subpleural consolidations will do well.”
A Negative Ultrasound Is the Most Useful
Volpicelli believes that, in any case, any patient with an intermediate pattern will require further diagnosis, such as other imaging modalities and blood exams, and the real role of lung ultrasound is in assessing patients at either end of the spectrum.
“In other words, there are situations where lung ultrasound can be considered definitive,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For instance, if I see a patient with mild signs of the disease, just fever, and I perform lung ultrasound and see nothing, lung ultrasound rules out pneumonia.”
“This patient may have COVID-19 of course, but they do not have pneumonia, and they can be treated at home, awaiting the result of the swab test. And this is useful because you can reduce the burden in the emergency department.”
Volpicelli continued: “On the other hand, there are patients with acute respiratory failure in respiratory distress. If the lung ultrasound is normal, you can rule out COVID-19 and you need to use other diagnostic procedures to understand the problem.”
“This is also very important for us because it’s crucial to be able to remove the patient from the isolation area and perform CT scan, chest radiography, and all the other diagnostic tools that we need.”
Are Wireless Machines Needed? Not Necessarily
With regard to the use of wireless technology, the Italian team says that “in the setting of COVID-19, wireless probes and tablets represent the most appropriate ultrasound equipment” because they can “easily be wrapped in single-use plastic covers, reducing the risk of contamination,” and making sterilization easy.
Stone suggests that integrated portable devices, however, are no more likely to cause cross-contamination than separate probes and tablets, as they can fit within a sterile sheath as a single unit.
Volpicelli, for his part, doesn’t like what he sees as undue focus on wireless devices for lung ultrasound in the COVID-19 protocols.
He is concerned that recommending them as the best approach may be sending out the wrong message, which could be very “dangerous” as people may then think they cannot perform this screening with standard ultrasound machines.
For him, the issue of cross contamination with standard lung ultrasound machines is “nonexistent. Cleaning the machine is quite easy and I do it hundreds of times per week.”
He does acknowledge, however, that if the lung ultrasound is performed under certain circumstances, for example when a patient is using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, “the risk of having the machine contaminated is a little bit higher.”
“In these situations...we have a more intensive cleaning procedure to avoid cross-contamination.”
He stressed: “Not all centers have wireless machines, whereas a normal machine is usually in all hospitals.”
“The advantages of using lung ultrasound [in COVID-19] are too great to be limited by something that is not important in my opinion,” he concluded.
Stone is director of education at the Butterfly Network. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The first protocol for the use of lung ultrasound to quantitatively and reproducibly assess the degree of lung involvement in patients suspected of having COVID-19 infection has been published by a team of Italian experts with experience using the technology on the front line.
Particularly in Spain and Italy — where the pandemic has struck hardest in Europe — hard-pressed clinicians seeking to quickly understand whether patients with seemingly mild disease could be harboring more serious lung involvement have increasingly relied upon lung ultrasound in the emergency room.
Now Libertario Demi, PhD, head of the ultrasound laboratory, University of Trento, Italy, and colleagues have developed a protocol, published online March 30 in the Journal of Ultrasound Medicine, to standardize practice.
Their research, which builds on previous work by the team, offers broad agreement with industry-led algorithms and emphasizes the use of wireless, handheld ultrasound devices, ideally consisting of a separate probe and tablet, to make sterilization easy.
Firms such as the Butterfly Network, Phillips, Clarius, GE Healthcare, and Siemens are among numerous companies that produce one or more such devices, including some that are completely integrated.
Not Universally Accepted
However, lung ultrasound is not yet universally accepted as a tool for diagnosing pneumonia in the context of COVID-19 and triaging patients.
The National Health Service in England does not even mention lung ultrasound in its radiology decision tool for suspected COVID-19, specifying instead chest X-ray as the first-line diagnostic imaging tool, with CT scanning in equivocal cases.
But Giovanni Volpicelli, MD, University Hospital San Luigi Gonzaga, Turin, Italy, who has previously described his experience to Medscape Medical News, says many patients with COVID-19 in his hospital presented with a negative chest X-ray but were found to have interstitial pneumonia on lung ultrasound.
Moreover, while CT scan remains the gold standard, the risk of nosocomial infection is more easily controlled if patients do not have to be transported to the radiology department but remain in the emergency room and instead undergo lung ultrasound there, he stressed.
Experts Share Experience of Lung Ultrasound in COVID-19
In developing and publishing their protocol, Demi, senior author of the article, and other colleagues from the heavily affected cities of Northern Italy, say their aim is “to share our experience and to propose a standardization with respect to the use of lung ultrasound in the management of COVID-19 patients.”
They reviewed an anonymized database of around 60,000 ultrasound images of confirmed COVID-19 cases and reviewers were blinded to patients’ clinical backgrounds.
For image acquisition, the authors recommend scanning 14 areas in each patient for 10 seconds, making the scans intercostal to cover the widest possible surface area.
They advise the use of a single focal point on the pleural line, which they write, optimizes the beam shape for observing the lung surface.
The authors also urge that the mechanical index (MI) be kept low because high MIs sustained for long periods “may result in damaging the lung.”
They also stress that cosmetic filters and modalities such as harmonic imaging, contrast, doppler, and compounding should be avoided, alongside saturation phenomena.
What Constitutes Intermediate Disease?
Once the images have been taken, they are scored on a 0-3 scale for each of the 14 areas, with no weighting on any individual area.
A score of 0 is given when the pleural line is continuous and regular, with the presence of A-lines, denoting that the lungs are unaffected.
An area is given a score of 3 when the scan shows dense and largely extended white lung tissue, with or without consolidations, indicating severe disease.
At both ends of this spectrum, there is agreement between the Italian protocol and an algorithm developed by the Butterfly Network.
However, the two differ when it comes to scoring intermediate cases. On the Butterfly algorithm, the suggestion is to look for B-lines, caused by fluid and cellular infiltration into the interstitium, and to weigh that against the need for supplementary oxygen.
The Italian team, in contrast, says a score of 1 is given when the pleural line is indented, with vertical areas of white visible below.
A score of 2 is given when the pleural line is broken, with small to large areas of consolidation and associated areas of white below.
Demi told Medscape Medical News that they did not refer to B-lines in their protocol as their visibility depends entirely on the imaging frequency and the probe used.
“This means that scoring on B-lines, people with different machines would give completely different scores for the same patient.”
He continued: “We prefer to refer to horizontal and vertical artifacts, and provide an analysis of the patterns, which is related to the physics of the interactions between the ultrasound waves and lung surface.”
In response, Mike Stone, MD, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center, Portland, Oregon, and director of education at Butterfly, said there appears to be wide variation in lung findings that “may or may not correlate with the severity of symptoms.”
He told Medscape Medical News it is “hard to know exactly if someone with pure B-lines will progress to serious illness or if someone with some subpleural consolidations will do well.”
A Negative Ultrasound Is the Most Useful
Volpicelli believes that, in any case, any patient with an intermediate pattern will require further diagnosis, such as other imaging modalities and blood exams, and the real role of lung ultrasound is in assessing patients at either end of the spectrum.
“In other words, there are situations where lung ultrasound can be considered definitive,” he told Medscape Medical News. “For instance, if I see a patient with mild signs of the disease, just fever, and I perform lung ultrasound and see nothing, lung ultrasound rules out pneumonia.”
“This patient may have COVID-19 of course, but they do not have pneumonia, and they can be treated at home, awaiting the result of the swab test. And this is useful because you can reduce the burden in the emergency department.”
Volpicelli continued: “On the other hand, there are patients with acute respiratory failure in respiratory distress. If the lung ultrasound is normal, you can rule out COVID-19 and you need to use other diagnostic procedures to understand the problem.”
“This is also very important for us because it’s crucial to be able to remove the patient from the isolation area and perform CT scan, chest radiography, and all the other diagnostic tools that we need.”
Are Wireless Machines Needed? Not Necessarily
With regard to the use of wireless technology, the Italian team says that “in the setting of COVID-19, wireless probes and tablets represent the most appropriate ultrasound equipment” because they can “easily be wrapped in single-use plastic covers, reducing the risk of contamination,” and making sterilization easy.
Stone suggests that integrated portable devices, however, are no more likely to cause cross-contamination than separate probes and tablets, as they can fit within a sterile sheath as a single unit.
Volpicelli, for his part, doesn’t like what he sees as undue focus on wireless devices for lung ultrasound in the COVID-19 protocols.
He is concerned that recommending them as the best approach may be sending out the wrong message, which could be very “dangerous” as people may then think they cannot perform this screening with standard ultrasound machines.
For him, the issue of cross contamination with standard lung ultrasound machines is “nonexistent. Cleaning the machine is quite easy and I do it hundreds of times per week.”
He does acknowledge, however, that if the lung ultrasound is performed under certain circumstances, for example when a patient is using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, “the risk of having the machine contaminated is a little bit higher.”
“In these situations...we have a more intensive cleaning procedure to avoid cross-contamination.”
He stressed: “Not all centers have wireless machines, whereas a normal machine is usually in all hospitals.”
“The advantages of using lung ultrasound [in COVID-19] are too great to be limited by something that is not important in my opinion,” he concluded.
Stone is director of education at the Butterfly Network. No other conflicts of interest were declared.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular problems already apparent in children with hemophilia A
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
Negative cardiovascular health indicators were found to be higher in children with hemophilia A, compared with healthy children, according to a small research study.
Biochemical, imaging, and metabolic analyses were performed to compare 17 boys with severe hemophilia A to 23 healthy boys designated as controls.
The myocardial performance index (MPI) was evaluated using tissue Doppler echocardiography. In addition, peripheral and central blood pressure and arterial stiffness were assessed, as were carotid intima–media thicknesses (CIMTs), serum glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipoprotein levels.
Increased MPI is considered an indicator of global deterioration in myocardial functions.
There were no differences between the two groups in terms of age and biochemical parameters, according to the researchers. There were also no significant differences found between the groups in terms of CIMT, peripheral blood pressure, and central systolic blood pressure.
However, the HDL cholesterol levels in the hemophilia group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < .05). Five of the hemophilia patients had insulin resistance (29.4%), whereas four had low HDL cholesterol levels (23.5%).
The researchers found that the MPI values in the hemophilia group were higher than those in the control group (0.41 vs. 0.34; P = .004). In addition, left ventricle ejection time (ET), which is a predictor of mortality in heart failure and ischemic heart disease, was shorter in the hemophilia group than it was in the control group (266.6 vs. 284.4; P = .014).
As arterial stiffness increases, ejection time decreases owing to the deteriorating myocardial systolic functions, and it has also been reported in the literature that arterial stiffness affects left ventricular systolic functions, according to the authors.
“Arterial stiffness and high [central diastolic blood pressure] developing in patients with severe hemophilia A since their childhood are important risk factors for coronary artery diseases. Predisposition to dyslipidemia and [insulin resistance] noted in the hemophilia group also negatively contributes to this process. Adolescent patients with hemophilia should be monitored for hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and [insulin resistance],” the authors concluded.
The study received no external funding. The authors did not report disclosures.
SOURCE: Özdemir ZC et al. Thrombosis Res. 2020;189:102-7.
FROM THROMBOSIS RESEARCH
Concerns for clinicians over 65 grow in the face of COVID-19
When Judith Salerno, MD, heard that New York was calling for volunteer clinicians to assist with the COVID-19 response, she didn’t hesitate to sign up.
Although Dr. Salerno, 68, has held administrative, research, and policy roles for 25 years, she has kept her medical license active and always found ways to squeeze some clinical work into her busy schedule.
“I have what I could consider ‘rusty’ clinical skills, but pretty good clinical judgment,” said Dr. Salerno, president of the New York Academy of Medicine. “I thought in this situation that I could resurrect and hone those skills, even if it was just taking care of routine patients and working on a team, there was a lot of good I can do.”
Dr. Salerno is among 80,000 health care professionals who have volunteered to work temporarily in New York during the COVID-19 pandemic as of March 31, 2020, according to New York state officials. In mid-March, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo (D) issued a plea for retired physicians and nurses to help the state by signing up for on-call work. Other states have made similar appeals for retired health care professionals to return to medicine in an effort to relieve overwhelmed hospital staffs and aid capacity if health care workers become ill. Such redeployments, however, are raising concerns about exposing senior physicians to a virus that causes more severe illness in individuals aged over 65 years and kills them at a higher rate.
At the same time, a significant portion of the current health care workforce is aged 55 years and older, placing them at higher risk for serious illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19, said Douglas O. Staiger, PhD, a researcher and economics professor at Dartmouth College, Hanover, N.H. Dr. Staiger recently coauthored a viewpoint in JAMA called “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus disease 2019,” which outlines the risks and mortality rates from the novel coronavirus among patients aged 55 years and older.
Among the 1.2 million practicing physicians in the United States, about 20% are aged 55-64 years and an estimated 9% are 65 years or older, according to the paper. Of the nation’s nearly 2 million registered nurses employed in hospitals, about 19% are aged 55-64 years, and an estimated 3% are aged 65 years or older.
“In some metro areas, this proportion is even higher,” Dr. Staiger said in an interview. “Hospitals and other health care providers should consider ways of utilizing older clinicians’ skills and experience in a way that minimizes their risk of exposure to COVID-19, such as transferring them from jobs interacting with patients to more supervisory, administrative, or telehealth roles. This is increasingly important as retired physicians and nurses are being asked to return to the workforce.”
Protecting staff, screening volunteers
Hematologist-oncologist David H. Henry, MD, said his eight-physician group practice at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has already taken steps to protect him from COVID exposure.
At the request of his younger colleagues, Dr. Henry, 69, said he is no longer seeing patients in the hospital where there is increased exposure risk to the virus. He and the staff also limit their time in the office to 2-3 days a week and practice telemedicine the rest of the week, Dr. Henry said in an interview.
“Whether you’re a person trying to stay at home because you’re quote ‘nonessential,’ or you’re a health care worker and you have to keep seeing patients to some extent, the less we’re face to face with others the better,” said Dr. Henry, who hosts the Blood & Cancer podcast for MDedge News. “There’s an extreme and a middle ground. If they told me just to stay home that wouldn’t help anybody. If they said, ‘business as usual,’ that would be wrong. This is a middle strategy, which is reasonable, rational, and will help dial this dangerous time down as fast as possible.”
On a recent weekend when Dr. Henry would normally have been on call in the hospital, he took phone calls for his colleagues at home while they saw patients in the hospital. This included calls with patients who had questions and consultation calls with other physicians.
“They are helping me and I am helping them,” Dr. Henry said. “Taking those calls makes it easier for my partners to see all those patients. We all want to help and be there, within reason. You want to step up an do your job, but you want to be safe.”
Peter D. Quinn, DMD, MD, chief executive physician of the Penn Medicine Medical Group, said safeguarding the health of its workforce is a top priority as Penn Medicine works to fight the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This includes ensuring that all employees adhere to Centers for Disease Control and Penn Medicine infection prevention guidance as they continue their normal clinical work,” Dr. Quinn said in an interview. “Though age alone is not a criterion to remove frontline staff from direct clinical care during the COVID-19 outbreak, certain conditions such as cardiac or lung disease may be, and clinicians who have concerns are urged to speak with their leadership about options to fill clinical or support roles remotely.”
Meanwhile, for states calling on retired health professionals to assist during the pandemic, thorough screenings that identify high-risk volunteers are essential to protect vulnerable clinicians, said Nathaniel Hibbs, DO, president of the Colorado chapter of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
After Colorado issued a statewide request for retired clinicians to help, Dr. Hibbs became concerned that the state’s website initially included only a basic set of questions for interested volunteers.
“It didn’t have screening questions for prior health problems, comorbidities, or things like high blood pressure, heart disease, lung disease – the high-risk factors that we associate with bad outcomes if people get infected with COVID,” Dr. Hibbs said in an interview.
To address this, Dr. Hibbs and associates recently provided recommendations to the state about its screening process that advised collecting more health information from volunteers and considering lower-risk assignments for high-risk individuals. State officials indicated they would strongly consider the recommendations, Dr. Hibbs said.
The Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment did not respond to messages seeking comment. Officials at the New York State Department of Health declined to be interviewed for this article but confirmed that they are reviewing the age and background of all volunteers, and individual hospitals will also review each volunteer to find suitable jobs.
The American Medical Association on March 30 issued guidance for retired physicians about rejoining the workforce to help with the COVID response. The guidance outlines license considerations, contribution options, professional liability considerations, and questions to ask volunteer coordinators.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, many physicians over the age of 65 will provide care to patients,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “Whether ‘senior’ physicians should be on the front line of patient care at this time is a complex issue that must balance several factors against the benefit these physicians can provide. As with all people in high-risk age groups, careful consideration must be given to the health and safety of retired physicians and their immediate family members, especially those with chronic medical conditions.”
Tapping talent, sharing knowledge
When Barbara L. Schuster, MD, 69, filled out paperwork to join the Georgia Medical Reserve Corps, she answered a range of questions, including inquiries about her age, specialty, licensing, and whether she had any major medical conditions.
“They sent out instructions that said, if you are over the age of 60, we really don’t want you to be doing inpatient or ambulatory with active patients,” said Dr. Schuster, a retired medical school dean in the Athens, Ga., area. “Unless they get to a point where it’s going to be you or nobody, I think that they try to protect us for both our sake and also theirs.”
Dr. Schuster opted for telehealth or administrative duties, but has not yet been called upon to help. The Athens area has not seen high numbers of COVID-19 patients, compared with other parts of the country, and there have not been many volunteer opportunities for physicians thus far, she said. In the meantime, Dr. Schuster has found other ways to give her time, such as answering questions from community members on both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 topics, and offering guidance to medical students.
“I’ve spent an increasing number of hours on Zoom, Skype, or FaceTime meeting with them to talk about various issues,” Dr. Schuster said.
As hospitals and organizations ramp up pandemic preparation, now is the time to consider roles for older clinicians and how they can best contribute, said Peter I. Buerhaus, PhD, RN, a nurse and director of the Center for Interdisciplinary Health Workforce Studies at Montana State University, Bozeman, Mont. Dr. Buerhaus was the first author of the recent JAMA viewpoint “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus 2019.”
“It’s important for hospitals that are anticipating a surge of critically ill patients to assess their workforce’s capability, including the proportion of older clinicians,” he said. “Is there something organizations can do differently to lessen older physicians’ and nurses’ direct patient contact and reduce their risk of infection?”
Dr. Buerhaus’ JAMA piece offers a range of ideas and assignments for older clinicians during the pandemic, including consulting with younger staff, advising on resources, assisting with clinical and organizational problem solving, aiding clinicians and managers with challenging decisions, consulting with patient families, advising managers and executives, being public spokespersons, and working with public and community health organizations.
“Older clinicians are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill if infected, but yet they’re also the ones who perhaps some of the best minds and experiences to help organizations combat the pandemic,” Dr. Buerhaus said. “These clinicians have great backgrounds and skills and 20, 30, 40 years of experience to draw on, including dealing with prior medical emergencies. I would hope that organizations, if they can, use the time before becoming a hotspot as an opportunity where the younger workforce could be teamed up with some of the older clinicians and learn as much as possible. It’s a great opportunity to share this wealth of knowledge with the workforce that will carry on after the pandemic.”
Since responding to New York’s call for volunteers, Dr. Salerno has been assigned to a palliative care inpatient team at a Manhattan hospital where she is working with large numbers of ICU patients and their families.
“My experience as a geriatrician helps me in talking with anxious and concerned families, especially when they are unable to see or communicate with their critically ill loved ones,” she said.
Before she was assigned the post, Dr. Salerno said she heard concerns from her adult children, who would prefer their mom take on a volunteer telehealth role. At the time, Dr. Salerno said she was not opposed to a telehealth assignment, but stressed to her family that she would go where she was needed.
“I’m healthy enough to run an organization, work long hours, long weeks; I have the stamina. The only thing working against me is age,” she said. “To say I’m not concerned is not honest. Of course I’m concerned. Am I afraid? No. I’m hoping that we can all be kept safe.”
When Judith Salerno, MD, heard that New York was calling for volunteer clinicians to assist with the COVID-19 response, she didn’t hesitate to sign up.
Although Dr. Salerno, 68, has held administrative, research, and policy roles for 25 years, she has kept her medical license active and always found ways to squeeze some clinical work into her busy schedule.
“I have what I could consider ‘rusty’ clinical skills, but pretty good clinical judgment,” said Dr. Salerno, president of the New York Academy of Medicine. “I thought in this situation that I could resurrect and hone those skills, even if it was just taking care of routine patients and working on a team, there was a lot of good I can do.”
Dr. Salerno is among 80,000 health care professionals who have volunteered to work temporarily in New York during the COVID-19 pandemic as of March 31, 2020, according to New York state officials. In mid-March, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo (D) issued a plea for retired physicians and nurses to help the state by signing up for on-call work. Other states have made similar appeals for retired health care professionals to return to medicine in an effort to relieve overwhelmed hospital staffs and aid capacity if health care workers become ill. Such redeployments, however, are raising concerns about exposing senior physicians to a virus that causes more severe illness in individuals aged over 65 years and kills them at a higher rate.
At the same time, a significant portion of the current health care workforce is aged 55 years and older, placing them at higher risk for serious illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19, said Douglas O. Staiger, PhD, a researcher and economics professor at Dartmouth College, Hanover, N.H. Dr. Staiger recently coauthored a viewpoint in JAMA called “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus disease 2019,” which outlines the risks and mortality rates from the novel coronavirus among patients aged 55 years and older.
Among the 1.2 million practicing physicians in the United States, about 20% are aged 55-64 years and an estimated 9% are 65 years or older, according to the paper. Of the nation’s nearly 2 million registered nurses employed in hospitals, about 19% are aged 55-64 years, and an estimated 3% are aged 65 years or older.
“In some metro areas, this proportion is even higher,” Dr. Staiger said in an interview. “Hospitals and other health care providers should consider ways of utilizing older clinicians’ skills and experience in a way that minimizes their risk of exposure to COVID-19, such as transferring them from jobs interacting with patients to more supervisory, administrative, or telehealth roles. This is increasingly important as retired physicians and nurses are being asked to return to the workforce.”
Protecting staff, screening volunteers
Hematologist-oncologist David H. Henry, MD, said his eight-physician group practice at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has already taken steps to protect him from COVID exposure.
At the request of his younger colleagues, Dr. Henry, 69, said he is no longer seeing patients in the hospital where there is increased exposure risk to the virus. He and the staff also limit their time in the office to 2-3 days a week and practice telemedicine the rest of the week, Dr. Henry said in an interview.
“Whether you’re a person trying to stay at home because you’re quote ‘nonessential,’ or you’re a health care worker and you have to keep seeing patients to some extent, the less we’re face to face with others the better,” said Dr. Henry, who hosts the Blood & Cancer podcast for MDedge News. “There’s an extreme and a middle ground. If they told me just to stay home that wouldn’t help anybody. If they said, ‘business as usual,’ that would be wrong. This is a middle strategy, which is reasonable, rational, and will help dial this dangerous time down as fast as possible.”
On a recent weekend when Dr. Henry would normally have been on call in the hospital, he took phone calls for his colleagues at home while they saw patients in the hospital. This included calls with patients who had questions and consultation calls with other physicians.
“They are helping me and I am helping them,” Dr. Henry said. “Taking those calls makes it easier for my partners to see all those patients. We all want to help and be there, within reason. You want to step up an do your job, but you want to be safe.”
Peter D. Quinn, DMD, MD, chief executive physician of the Penn Medicine Medical Group, said safeguarding the health of its workforce is a top priority as Penn Medicine works to fight the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This includes ensuring that all employees adhere to Centers for Disease Control and Penn Medicine infection prevention guidance as they continue their normal clinical work,” Dr. Quinn said in an interview. “Though age alone is not a criterion to remove frontline staff from direct clinical care during the COVID-19 outbreak, certain conditions such as cardiac or lung disease may be, and clinicians who have concerns are urged to speak with their leadership about options to fill clinical or support roles remotely.”
Meanwhile, for states calling on retired health professionals to assist during the pandemic, thorough screenings that identify high-risk volunteers are essential to protect vulnerable clinicians, said Nathaniel Hibbs, DO, president of the Colorado chapter of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
After Colorado issued a statewide request for retired clinicians to help, Dr. Hibbs became concerned that the state’s website initially included only a basic set of questions for interested volunteers.
“It didn’t have screening questions for prior health problems, comorbidities, or things like high blood pressure, heart disease, lung disease – the high-risk factors that we associate with bad outcomes if people get infected with COVID,” Dr. Hibbs said in an interview.
To address this, Dr. Hibbs and associates recently provided recommendations to the state about its screening process that advised collecting more health information from volunteers and considering lower-risk assignments for high-risk individuals. State officials indicated they would strongly consider the recommendations, Dr. Hibbs said.
The Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment did not respond to messages seeking comment. Officials at the New York State Department of Health declined to be interviewed for this article but confirmed that they are reviewing the age and background of all volunteers, and individual hospitals will also review each volunteer to find suitable jobs.
The American Medical Association on March 30 issued guidance for retired physicians about rejoining the workforce to help with the COVID response. The guidance outlines license considerations, contribution options, professional liability considerations, and questions to ask volunteer coordinators.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, many physicians over the age of 65 will provide care to patients,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “Whether ‘senior’ physicians should be on the front line of patient care at this time is a complex issue that must balance several factors against the benefit these physicians can provide. As with all people in high-risk age groups, careful consideration must be given to the health and safety of retired physicians and their immediate family members, especially those with chronic medical conditions.”
Tapping talent, sharing knowledge
When Barbara L. Schuster, MD, 69, filled out paperwork to join the Georgia Medical Reserve Corps, she answered a range of questions, including inquiries about her age, specialty, licensing, and whether she had any major medical conditions.
“They sent out instructions that said, if you are over the age of 60, we really don’t want you to be doing inpatient or ambulatory with active patients,” said Dr. Schuster, a retired medical school dean in the Athens, Ga., area. “Unless they get to a point where it’s going to be you or nobody, I think that they try to protect us for both our sake and also theirs.”
Dr. Schuster opted for telehealth or administrative duties, but has not yet been called upon to help. The Athens area has not seen high numbers of COVID-19 patients, compared with other parts of the country, and there have not been many volunteer opportunities for physicians thus far, she said. In the meantime, Dr. Schuster has found other ways to give her time, such as answering questions from community members on both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 topics, and offering guidance to medical students.
“I’ve spent an increasing number of hours on Zoom, Skype, or FaceTime meeting with them to talk about various issues,” Dr. Schuster said.
As hospitals and organizations ramp up pandemic preparation, now is the time to consider roles for older clinicians and how they can best contribute, said Peter I. Buerhaus, PhD, RN, a nurse and director of the Center for Interdisciplinary Health Workforce Studies at Montana State University, Bozeman, Mont. Dr. Buerhaus was the first author of the recent JAMA viewpoint “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus 2019.”
“It’s important for hospitals that are anticipating a surge of critically ill patients to assess their workforce’s capability, including the proportion of older clinicians,” he said. “Is there something organizations can do differently to lessen older physicians’ and nurses’ direct patient contact and reduce their risk of infection?”
Dr. Buerhaus’ JAMA piece offers a range of ideas and assignments for older clinicians during the pandemic, including consulting with younger staff, advising on resources, assisting with clinical and organizational problem solving, aiding clinicians and managers with challenging decisions, consulting with patient families, advising managers and executives, being public spokespersons, and working with public and community health organizations.
“Older clinicians are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill if infected, but yet they’re also the ones who perhaps some of the best minds and experiences to help organizations combat the pandemic,” Dr. Buerhaus said. “These clinicians have great backgrounds and skills and 20, 30, 40 years of experience to draw on, including dealing with prior medical emergencies. I would hope that organizations, if they can, use the time before becoming a hotspot as an opportunity where the younger workforce could be teamed up with some of the older clinicians and learn as much as possible. It’s a great opportunity to share this wealth of knowledge with the workforce that will carry on after the pandemic.”
Since responding to New York’s call for volunteers, Dr. Salerno has been assigned to a palliative care inpatient team at a Manhattan hospital where she is working with large numbers of ICU patients and their families.
“My experience as a geriatrician helps me in talking with anxious and concerned families, especially when they are unable to see or communicate with their critically ill loved ones,” she said.
Before she was assigned the post, Dr. Salerno said she heard concerns from her adult children, who would prefer their mom take on a volunteer telehealth role. At the time, Dr. Salerno said she was not opposed to a telehealth assignment, but stressed to her family that she would go where she was needed.
“I’m healthy enough to run an organization, work long hours, long weeks; I have the stamina. The only thing working against me is age,” she said. “To say I’m not concerned is not honest. Of course I’m concerned. Am I afraid? No. I’m hoping that we can all be kept safe.”
When Judith Salerno, MD, heard that New York was calling for volunteer clinicians to assist with the COVID-19 response, she didn’t hesitate to sign up.
Although Dr. Salerno, 68, has held administrative, research, and policy roles for 25 years, she has kept her medical license active and always found ways to squeeze some clinical work into her busy schedule.
“I have what I could consider ‘rusty’ clinical skills, but pretty good clinical judgment,” said Dr. Salerno, president of the New York Academy of Medicine. “I thought in this situation that I could resurrect and hone those skills, even if it was just taking care of routine patients and working on a team, there was a lot of good I can do.”
Dr. Salerno is among 80,000 health care professionals who have volunteered to work temporarily in New York during the COVID-19 pandemic as of March 31, 2020, according to New York state officials. In mid-March, New York Governor Andrew Cuomo (D) issued a plea for retired physicians and nurses to help the state by signing up for on-call work. Other states have made similar appeals for retired health care professionals to return to medicine in an effort to relieve overwhelmed hospital staffs and aid capacity if health care workers become ill. Such redeployments, however, are raising concerns about exposing senior physicians to a virus that causes more severe illness in individuals aged over 65 years and kills them at a higher rate.
At the same time, a significant portion of the current health care workforce is aged 55 years and older, placing them at higher risk for serious illness, hospitalization, and death from COVID-19, said Douglas O. Staiger, PhD, a researcher and economics professor at Dartmouth College, Hanover, N.H. Dr. Staiger recently coauthored a viewpoint in JAMA called “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus disease 2019,” which outlines the risks and mortality rates from the novel coronavirus among patients aged 55 years and older.
Among the 1.2 million practicing physicians in the United States, about 20% are aged 55-64 years and an estimated 9% are 65 years or older, according to the paper. Of the nation’s nearly 2 million registered nurses employed in hospitals, about 19% are aged 55-64 years, and an estimated 3% are aged 65 years or older.
“In some metro areas, this proportion is even higher,” Dr. Staiger said in an interview. “Hospitals and other health care providers should consider ways of utilizing older clinicians’ skills and experience in a way that minimizes their risk of exposure to COVID-19, such as transferring them from jobs interacting with patients to more supervisory, administrative, or telehealth roles. This is increasingly important as retired physicians and nurses are being asked to return to the workforce.”
Protecting staff, screening volunteers
Hematologist-oncologist David H. Henry, MD, said his eight-physician group practice at Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has already taken steps to protect him from COVID exposure.
At the request of his younger colleagues, Dr. Henry, 69, said he is no longer seeing patients in the hospital where there is increased exposure risk to the virus. He and the staff also limit their time in the office to 2-3 days a week and practice telemedicine the rest of the week, Dr. Henry said in an interview.
“Whether you’re a person trying to stay at home because you’re quote ‘nonessential,’ or you’re a health care worker and you have to keep seeing patients to some extent, the less we’re face to face with others the better,” said Dr. Henry, who hosts the Blood & Cancer podcast for MDedge News. “There’s an extreme and a middle ground. If they told me just to stay home that wouldn’t help anybody. If they said, ‘business as usual,’ that would be wrong. This is a middle strategy, which is reasonable, rational, and will help dial this dangerous time down as fast as possible.”
On a recent weekend when Dr. Henry would normally have been on call in the hospital, he took phone calls for his colleagues at home while they saw patients in the hospital. This included calls with patients who had questions and consultation calls with other physicians.
“They are helping me and I am helping them,” Dr. Henry said. “Taking those calls makes it easier for my partners to see all those patients. We all want to help and be there, within reason. You want to step up an do your job, but you want to be safe.”
Peter D. Quinn, DMD, MD, chief executive physician of the Penn Medicine Medical Group, said safeguarding the health of its workforce is a top priority as Penn Medicine works to fight the COVID-19 pandemic.
“This includes ensuring that all employees adhere to Centers for Disease Control and Penn Medicine infection prevention guidance as they continue their normal clinical work,” Dr. Quinn said in an interview. “Though age alone is not a criterion to remove frontline staff from direct clinical care during the COVID-19 outbreak, certain conditions such as cardiac or lung disease may be, and clinicians who have concerns are urged to speak with their leadership about options to fill clinical or support roles remotely.”
Meanwhile, for states calling on retired health professionals to assist during the pandemic, thorough screenings that identify high-risk volunteers are essential to protect vulnerable clinicians, said Nathaniel Hibbs, DO, president of the Colorado chapter of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
After Colorado issued a statewide request for retired clinicians to help, Dr. Hibbs became concerned that the state’s website initially included only a basic set of questions for interested volunteers.
“It didn’t have screening questions for prior health problems, comorbidities, or things like high blood pressure, heart disease, lung disease – the high-risk factors that we associate with bad outcomes if people get infected with COVID,” Dr. Hibbs said in an interview.
To address this, Dr. Hibbs and associates recently provided recommendations to the state about its screening process that advised collecting more health information from volunteers and considering lower-risk assignments for high-risk individuals. State officials indicated they would strongly consider the recommendations, Dr. Hibbs said.
The Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment did not respond to messages seeking comment. Officials at the New York State Department of Health declined to be interviewed for this article but confirmed that they are reviewing the age and background of all volunteers, and individual hospitals will also review each volunteer to find suitable jobs.
The American Medical Association on March 30 issued guidance for retired physicians about rejoining the workforce to help with the COVID response. The guidance outlines license considerations, contribution options, professional liability considerations, and questions to ask volunteer coordinators.
“Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, many physicians over the age of 65 will provide care to patients,” AMA President Patrice A. Harris, MD, said in a statement. “Whether ‘senior’ physicians should be on the front line of patient care at this time is a complex issue that must balance several factors against the benefit these physicians can provide. As with all people in high-risk age groups, careful consideration must be given to the health and safety of retired physicians and their immediate family members, especially those with chronic medical conditions.”
Tapping talent, sharing knowledge
When Barbara L. Schuster, MD, 69, filled out paperwork to join the Georgia Medical Reserve Corps, she answered a range of questions, including inquiries about her age, specialty, licensing, and whether she had any major medical conditions.
“They sent out instructions that said, if you are over the age of 60, we really don’t want you to be doing inpatient or ambulatory with active patients,” said Dr. Schuster, a retired medical school dean in the Athens, Ga., area. “Unless they get to a point where it’s going to be you or nobody, I think that they try to protect us for both our sake and also theirs.”
Dr. Schuster opted for telehealth or administrative duties, but has not yet been called upon to help. The Athens area has not seen high numbers of COVID-19 patients, compared with other parts of the country, and there have not been many volunteer opportunities for physicians thus far, she said. In the meantime, Dr. Schuster has found other ways to give her time, such as answering questions from community members on both COVID-19 and non–COVID-19 topics, and offering guidance to medical students.
“I’ve spent an increasing number of hours on Zoom, Skype, or FaceTime meeting with them to talk about various issues,” Dr. Schuster said.
As hospitals and organizations ramp up pandemic preparation, now is the time to consider roles for older clinicians and how they can best contribute, said Peter I. Buerhaus, PhD, RN, a nurse and director of the Center for Interdisciplinary Health Workforce Studies at Montana State University, Bozeman, Mont. Dr. Buerhaus was the first author of the recent JAMA viewpoint “Older clinicians and the surge in novel coronavirus 2019.”
“It’s important for hospitals that are anticipating a surge of critically ill patients to assess their workforce’s capability, including the proportion of older clinicians,” he said. “Is there something organizations can do differently to lessen older physicians’ and nurses’ direct patient contact and reduce their risk of infection?”
Dr. Buerhaus’ JAMA piece offers a range of ideas and assignments for older clinicians during the pandemic, including consulting with younger staff, advising on resources, assisting with clinical and organizational problem solving, aiding clinicians and managers with challenging decisions, consulting with patient families, advising managers and executives, being public spokespersons, and working with public and community health organizations.
“Older clinicians are at increased risk of becoming seriously ill if infected, but yet they’re also the ones who perhaps some of the best minds and experiences to help organizations combat the pandemic,” Dr. Buerhaus said. “These clinicians have great backgrounds and skills and 20, 30, 40 years of experience to draw on, including dealing with prior medical emergencies. I would hope that organizations, if they can, use the time before becoming a hotspot as an opportunity where the younger workforce could be teamed up with some of the older clinicians and learn as much as possible. It’s a great opportunity to share this wealth of knowledge with the workforce that will carry on after the pandemic.”
Since responding to New York’s call for volunteers, Dr. Salerno has been assigned to a palliative care inpatient team at a Manhattan hospital where she is working with large numbers of ICU patients and their families.
“My experience as a geriatrician helps me in talking with anxious and concerned families, especially when they are unable to see or communicate with their critically ill loved ones,” she said.
Before she was assigned the post, Dr. Salerno said she heard concerns from her adult children, who would prefer their mom take on a volunteer telehealth role. At the time, Dr. Salerno said she was not opposed to a telehealth assignment, but stressed to her family that she would go where she was needed.
“I’m healthy enough to run an organization, work long hours, long weeks; I have the stamina. The only thing working against me is age,” she said. “To say I’m not concerned is not honest. Of course I’m concerned. Am I afraid? No. I’m hoping that we can all be kept safe.”
Managing pediatric heme/onc departments during the pandemic
Given the possibility that children with hematologic malignancies may have increased susceptibility to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), clinicians from China and the United States have proposed a plan for preventing and managing outbreaks in hospitals’ pediatric hematology and oncology departments.
The plan is focused primarily on infection prevention and control strategies, Yulei He, MD, of Chengdu (China) Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital and colleagues explained in an article published in The Lancet Haematology.
The authors noted that close contact with COVID-19 patients is thought to be the main route of transmission, and a retrospective study indicated that 41.3% of initial COVID-19 cases were caused by hospital-related transmission.
“Children with hematological malignancies might have increased susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2 because of immunodeficiency; therefore, procedures are needed to avoid hospital-related transmission and infection for these patients,” the authors wrote.
Preventing the spread of infection
Dr. He and colleagues advised that medical staff be kept up-to-date with the latest information about COVID-19 and perform assessments regularly to identify cases in their departments.
The authors also recommended establishing a COVID-19 expert committee – consisting of infectious disease physicians, hematologists, oncologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and hospital infection control staff – to make medical decisions in multidisciplinary consultation meetings. In addition, the authors recommended regional management strategies be adopted to minimize cross infection within the hospital. Specifically, the authors proposed creating the following four zones:
1. A surveillance and screening zone for patients potentially infected with SARS-CoV-2
2. A suspected-case quarantine zone where patients thought to have COVID-19 are isolated in single rooms
3. A confirmed-case quarantine zone where patients are treated for COVID-19
4. A hematology/oncology ward for treating non–COVID-19 patients with malignancies.
Dr. He and colleagues also stressed the importance of providing personal protective equipment for all zones, along with instructions for proper use and disposal. The authors recommended developing and following specific protocols for outpatient visits in the hematology/oncology ward, and providing COVID-19 prevention and control information to families and health care workers.
Managing cancer treatment
For patients with acute leukemias who have induction chemotherapy planned, Dr. He and colleagues argued that scheduled chemotherapy should not be interrupted unless COVID-19 is suspected or diagnosed. The authors said treatment should not be delayed more than 7 days during induction, consolidation, or the intermediate phase of chemotherapy because the virus has an incubation period of 2-7 days. This will allow a short period of observation to screen for potential infection.
The authors recommended that patients with lymphoma and solid tumors first undergo COVID-19 screening and then receive treatment in hematology/oncology wards “according to their chemotherapy schedule, and without delay, until they are in complete remission.”
“If the patient is in complete remission, we recommend a treatment delay of no more than 7 days to allow a short period of observation to screen for COVID-19,” the authors added.
Maintenance chemotherapy should not be delayed for more than 14 days, Dr. He and colleagues wrote. “This increase in the maximum delay before chemotherapy strikes a balance between the potential risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and tumor recurrence, since pediatric patients in this phase of treatment have a reduced risk of tumor recurrence,” the authors added.
Caring for patients with COVID-19
For inpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, Dr. He and colleagues recommended the following:
- Prioritize COVID-19 treatment for children with primary disease remission.
- For children not in remission, prioritize treatment for critical patients.
- Isolated patients should be treated for COVID-19, and their chemotherapy should be temporarily suspended or reduced in intensity..
Dr. He and colleagues noted that, by following these recommendations for infection prevention, they had no cases of COVID-19 among children in their hematology/oncology departments. However, the authors said the recommendations “could fail to some extent” based on “differences in medical resources, health care settings, and the policy of the specific government.”
The authors said their recommendations should be updated continuously as new information and clinical evidence emerges.
Dr. He and colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: He Y et al. Lancet Haematol. doi: 10/1016/s2352-3026(20)30104-6.
Given the possibility that children with hematologic malignancies may have increased susceptibility to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), clinicians from China and the United States have proposed a plan for preventing and managing outbreaks in hospitals’ pediatric hematology and oncology departments.
The plan is focused primarily on infection prevention and control strategies, Yulei He, MD, of Chengdu (China) Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital and colleagues explained in an article published in The Lancet Haematology.
The authors noted that close contact with COVID-19 patients is thought to be the main route of transmission, and a retrospective study indicated that 41.3% of initial COVID-19 cases were caused by hospital-related transmission.
“Children with hematological malignancies might have increased susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2 because of immunodeficiency; therefore, procedures are needed to avoid hospital-related transmission and infection for these patients,” the authors wrote.
Preventing the spread of infection
Dr. He and colleagues advised that medical staff be kept up-to-date with the latest information about COVID-19 and perform assessments regularly to identify cases in their departments.
The authors also recommended establishing a COVID-19 expert committee – consisting of infectious disease physicians, hematologists, oncologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and hospital infection control staff – to make medical decisions in multidisciplinary consultation meetings. In addition, the authors recommended regional management strategies be adopted to minimize cross infection within the hospital. Specifically, the authors proposed creating the following four zones:
1. A surveillance and screening zone for patients potentially infected with SARS-CoV-2
2. A suspected-case quarantine zone where patients thought to have COVID-19 are isolated in single rooms
3. A confirmed-case quarantine zone where patients are treated for COVID-19
4. A hematology/oncology ward for treating non–COVID-19 patients with malignancies.
Dr. He and colleagues also stressed the importance of providing personal protective equipment for all zones, along with instructions for proper use and disposal. The authors recommended developing and following specific protocols for outpatient visits in the hematology/oncology ward, and providing COVID-19 prevention and control information to families and health care workers.
Managing cancer treatment
For patients with acute leukemias who have induction chemotherapy planned, Dr. He and colleagues argued that scheduled chemotherapy should not be interrupted unless COVID-19 is suspected or diagnosed. The authors said treatment should not be delayed more than 7 days during induction, consolidation, or the intermediate phase of chemotherapy because the virus has an incubation period of 2-7 days. This will allow a short period of observation to screen for potential infection.
The authors recommended that patients with lymphoma and solid tumors first undergo COVID-19 screening and then receive treatment in hematology/oncology wards “according to their chemotherapy schedule, and without delay, until they are in complete remission.”
“If the patient is in complete remission, we recommend a treatment delay of no more than 7 days to allow a short period of observation to screen for COVID-19,” the authors added.
Maintenance chemotherapy should not be delayed for more than 14 days, Dr. He and colleagues wrote. “This increase in the maximum delay before chemotherapy strikes a balance between the potential risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and tumor recurrence, since pediatric patients in this phase of treatment have a reduced risk of tumor recurrence,” the authors added.
Caring for patients with COVID-19
For inpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, Dr. He and colleagues recommended the following:
- Prioritize COVID-19 treatment for children with primary disease remission.
- For children not in remission, prioritize treatment for critical patients.
- Isolated patients should be treated for COVID-19, and their chemotherapy should be temporarily suspended or reduced in intensity..
Dr. He and colleagues noted that, by following these recommendations for infection prevention, they had no cases of COVID-19 among children in their hematology/oncology departments. However, the authors said the recommendations “could fail to some extent” based on “differences in medical resources, health care settings, and the policy of the specific government.”
The authors said their recommendations should be updated continuously as new information and clinical evidence emerges.
Dr. He and colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: He Y et al. Lancet Haematol. doi: 10/1016/s2352-3026(20)30104-6.
Given the possibility that children with hematologic malignancies may have increased susceptibility to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), clinicians from China and the United States have proposed a plan for preventing and managing outbreaks in hospitals’ pediatric hematology and oncology departments.
The plan is focused primarily on infection prevention and control strategies, Yulei He, MD, of Chengdu (China) Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital and colleagues explained in an article published in The Lancet Haematology.
The authors noted that close contact with COVID-19 patients is thought to be the main route of transmission, and a retrospective study indicated that 41.3% of initial COVID-19 cases were caused by hospital-related transmission.
“Children with hematological malignancies might have increased susceptibility to infection with SARS-CoV-2 because of immunodeficiency; therefore, procedures are needed to avoid hospital-related transmission and infection for these patients,” the authors wrote.
Preventing the spread of infection
Dr. He and colleagues advised that medical staff be kept up-to-date with the latest information about COVID-19 and perform assessments regularly to identify cases in their departments.
The authors also recommended establishing a COVID-19 expert committee – consisting of infectious disease physicians, hematologists, oncologists, radiologists, pharmacists, and hospital infection control staff – to make medical decisions in multidisciplinary consultation meetings. In addition, the authors recommended regional management strategies be adopted to minimize cross infection within the hospital. Specifically, the authors proposed creating the following four zones:
1. A surveillance and screening zone for patients potentially infected with SARS-CoV-2
2. A suspected-case quarantine zone where patients thought to have COVID-19 are isolated in single rooms
3. A confirmed-case quarantine zone where patients are treated for COVID-19
4. A hematology/oncology ward for treating non–COVID-19 patients with malignancies.
Dr. He and colleagues also stressed the importance of providing personal protective equipment for all zones, along with instructions for proper use and disposal. The authors recommended developing and following specific protocols for outpatient visits in the hematology/oncology ward, and providing COVID-19 prevention and control information to families and health care workers.
Managing cancer treatment
For patients with acute leukemias who have induction chemotherapy planned, Dr. He and colleagues argued that scheduled chemotherapy should not be interrupted unless COVID-19 is suspected or diagnosed. The authors said treatment should not be delayed more than 7 days during induction, consolidation, or the intermediate phase of chemotherapy because the virus has an incubation period of 2-7 days. This will allow a short period of observation to screen for potential infection.
The authors recommended that patients with lymphoma and solid tumors first undergo COVID-19 screening and then receive treatment in hematology/oncology wards “according to their chemotherapy schedule, and without delay, until they are in complete remission.”
“If the patient is in complete remission, we recommend a treatment delay of no more than 7 days to allow a short period of observation to screen for COVID-19,” the authors added.
Maintenance chemotherapy should not be delayed for more than 14 days, Dr. He and colleagues wrote. “This increase in the maximum delay before chemotherapy strikes a balance between the potential risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and tumor recurrence, since pediatric patients in this phase of treatment have a reduced risk of tumor recurrence,” the authors added.
Caring for patients with COVID-19
For inpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, Dr. He and colleagues recommended the following:
- Prioritize COVID-19 treatment for children with primary disease remission.
- For children not in remission, prioritize treatment for critical patients.
- Isolated patients should be treated for COVID-19, and their chemotherapy should be temporarily suspended or reduced in intensity..
Dr. He and colleagues noted that, by following these recommendations for infection prevention, they had no cases of COVID-19 among children in their hematology/oncology departments. However, the authors said the recommendations “could fail to some extent” based on “differences in medical resources, health care settings, and the policy of the specific government.”
The authors said their recommendations should be updated continuously as new information and clinical evidence emerges.
Dr. He and colleagues reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: He Y et al. Lancet Haematol. doi: 10/1016/s2352-3026(20)30104-6.
FROM THE LANCET HAEMATOLOGY