User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
Unexpected rosuvastatin-canagliflozin adverse effect reported
A 76-year-old woman presented recently to a Toronto-area hospital with acute onset muscle pain, limb weakness, difficulty walking, and rhabdomyolysis associated with a sharp spike in her plasma level of rosuvastatin – a drug she had been on uneventfully for more than 5 years, within days of starting for the first time treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin (Invokana).
The patient’s Canadian clinicians stopped her treatment with both rosuvastatin and canagliflozin, administered intravenous crystalloid fluids, and within days her pain subsided and her limb weakness gradually improved, allowing her discharge 10 days later while she was ambulating with a walker.
“To our knowledge this is the first published report of a drug interaction between rosuvastatin and canagliflozin,” wrote the authors of the case report (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549). They cited the importance of the observation given the widespread use today of rosuvastatin for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol and exerting pleiotropic effects; and canagliflozin for its modest effects for reducing hyperglycemia, as well as its important role in reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, and having a mild but important diuretic effect. “We encourage clinicians to remain vigilant for features of myotoxicity when canagliflozin and rosuvastatin are coprescribed,” they wrote, avoiding discussion of whether this may represent class or drug-specific effects.
“It’s reasonable to be mindful of this risk, but this is not a reason to not use rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in a patient,” nor for the time being to avoid any other combination of a statin and SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitor, said David Juurlink, MD, head of the division of clinical pharmacology and toxicology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto and lead author of the report. “Few drug interactions have absolute contraindications. The admonition is just to be careful. It’s premature to say they shouldn’t be used together,” he said in an interview.
“We don’t know how much of an outlier this patient is. But it would be important to tell patients” on this or a similar combination to alert their clinicians if they start to have muscle aches, which should be a “red flag” to stop the statin, the SGLT2 inhibitor, or both until the situation can be fully assessed, Dr. Juurlink advised.
Sky high rosuvastatin levels
The linchpin of the observed adverse effects appeared to be a startlingly high elevation of the patient’s plasma rosuvastatin level when she was hospitalized 15 days after starting canagliflozin and 12 days after the onset of her thigh pain and weakness. Testing showed a plasma rosuvastatin concentration of 176 ng/mL, “more than 15-fold higher than the mean value expected” in patients taking 40 mg rosuvastatin daily, the maximum labeled dosage for the drug and what the affected patient had been taking without prior incident for more than 5 years. The patient’s canagliflozin dosage was 100 mg/day, the standard starting dosage according to the drug’s label.
The report’s authors noted that genetic assessment of the patient, a woman originally from the Philippines who was “high functioning,” and diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, showed she was heterozygous for a polymorphism, c.421C>A, which is linked with increased rosuvastatin plasma levels in the plasma. They also cited a report that canagliflozin can interact with proteins involved in hepatic drug uptake.
“We speculate that, in our patient, the addition of canagliflozin enhanced intestinal rosuvastatin absorption, inhibited its hepatocellular uptake, and impaired its excretion into bile canaliculi and the proximal tubule, resulting in rosuvastatin accumulation and leading to hepatotoxicity and myotoxicity,” the clinicians wrote in their report.
“There is little doubt this was a drug interaction, but it does not apply uniformly to everyone.” The severity of the interaction would depend on the dosages, the comorbidities a patient has, and their genetic profile, Dr. Juurlink said.
Concern and skepticism
Other clinicians who regularly prescribe these drugs expressed concern about the observation as well as skepticism about the prevalence of patients who could potentially experience similar effects.
“We don’t know how common are these genetic abnormalities. If this is extremely rare, then it doesn’t have many clinical implications, but if a large portion of the population has this [genetic] abnormality, it’s something we’d need to pay attention to,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview. “It will be important to know the prevalence” of the genetic polymorphism carried by the reported patient, said Dr. Nissen, who has done research on lipid-lowering medications and drug safety.
“This could be important, or a very rare one-off. I can’t say which,” based on what’s currently known, he said. “There are many unanswered questions that make it hard to know how important this will be. It requires further investigation. There is a lot of uncertainty.”
Dr. Nissen particularly endorsed studies that approach this issue by looking at the prevalence rates of the implicated genetic polymorphism rather than pharmacovigilance studies that make epidemiologic assessments of adverse-effect prevalence. Studies that look for adverse-effect associations in large patient populations are “sloppy, and unless the interaction is incredibly intense they are not very sensitive,” he said.
But Dr. Juurlink, a pharmacoepidemiologist whose specialty includes studies of this sort, said that they could be useful if carefully designed. He suggested, for example, comparing in large patient databases the observed incidence of rhabdomyolysis among patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and also on rosuvastatin with those on pravastatin, a statin with a different metabolic profile. Another approach to further examining the observation would be dosage studies with rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in healthy volunteers, he said.
Dr. Nissen noted that rosuvastatin is a key agent from the statin class because it’s the “most effective” for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol. “Rosuvastatin is a go-to drug,” he declared. On the other hand, canagliflozin is “a little less used” than other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), he said.
One in a million?
“This was a freak accident. I don’t find it at all concerning. It was definitely one in a million,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of The Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “None of us have seen it” in either the several cardiovascular outcome trials now run on multiple drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class that included many patients also taking a statin, or in routine practice, he said. Dr. Handelsman noted that in his practice he had never seen a similar case despite treating “hundreds if not thousands of patients” with type 2 diabetes, virtually all of whom were on a statin and were also treated with an SGLT2 inhibitor, including many with canagliflozin.
Dr. Handelsman cited the notably low estimated glomerular filtration rate in the reported patient, who was described as having a serum creatinine level of 150 mcmol/L (1.7 mg/dL) prior to canagliflozin treatment that then rose to 194 mcmol/L (2.19 mg/dL) at the time of hospitalization, which corresponds to estimated glomerular filtration rates of 29-31 and 21-23 mL/min per 1.73 m2, respectively, depending on the calculator used, rates that were possibly below the labeled minimum rate of 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for patients starting canagliflozin treatment. The case report cited the patient as having stage 3B chronic kidney disease, which corresponds to a eGFR of 30-44* mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“I think the patient had acute kidney injury” on starting canagliflozin “that may have affected the [rosuvastatin] metabolism,” Dr. Handelsman suggested. “She had severe kidney dysfunction to start with that fell further with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment,” a well described and usually transient effect of starting drugs in this class because of changes the SGLT2 inhibitors cause in renal blood flow. He noted that the patient had not been receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker, which may have contributed to her acute problems with fluid balance. Most similar patients with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease risk, and chronic kidney disease would be on stable treatment with a drug that inhibits the renin-angiotensin system before starting an SGLT2 inhibitor, and not already having a RAS inhibitor on board before starting canagliflozin may have somehow contributed to the observed adverse effects, Dr. Handelsman said.
Dr. Juurlink was skeptical that the kidneys played a major role. “An abrupt change in renal function can influence statin clearance, but this was a 15-fold increase. You can’t explain such a dramatic increase by a transient reduction in renal function,” he said.
Dr. Juurlink and coauthors had no disclosures. Dr. Nissen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to companies that market drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class.
SOURCE: Brailovski E et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549.
*Correction: This value was missing from the original article.
A 76-year-old woman presented recently to a Toronto-area hospital with acute onset muscle pain, limb weakness, difficulty walking, and rhabdomyolysis associated with a sharp spike in her plasma level of rosuvastatin – a drug she had been on uneventfully for more than 5 years, within days of starting for the first time treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin (Invokana).
The patient’s Canadian clinicians stopped her treatment with both rosuvastatin and canagliflozin, administered intravenous crystalloid fluids, and within days her pain subsided and her limb weakness gradually improved, allowing her discharge 10 days later while she was ambulating with a walker.
“To our knowledge this is the first published report of a drug interaction between rosuvastatin and canagliflozin,” wrote the authors of the case report (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549). They cited the importance of the observation given the widespread use today of rosuvastatin for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol and exerting pleiotropic effects; and canagliflozin for its modest effects for reducing hyperglycemia, as well as its important role in reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, and having a mild but important diuretic effect. “We encourage clinicians to remain vigilant for features of myotoxicity when canagliflozin and rosuvastatin are coprescribed,” they wrote, avoiding discussion of whether this may represent class or drug-specific effects.
“It’s reasonable to be mindful of this risk, but this is not a reason to not use rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in a patient,” nor for the time being to avoid any other combination of a statin and SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitor, said David Juurlink, MD, head of the division of clinical pharmacology and toxicology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto and lead author of the report. “Few drug interactions have absolute contraindications. The admonition is just to be careful. It’s premature to say they shouldn’t be used together,” he said in an interview.
“We don’t know how much of an outlier this patient is. But it would be important to tell patients” on this or a similar combination to alert their clinicians if they start to have muscle aches, which should be a “red flag” to stop the statin, the SGLT2 inhibitor, or both until the situation can be fully assessed, Dr. Juurlink advised.
Sky high rosuvastatin levels
The linchpin of the observed adverse effects appeared to be a startlingly high elevation of the patient’s plasma rosuvastatin level when she was hospitalized 15 days after starting canagliflozin and 12 days after the onset of her thigh pain and weakness. Testing showed a plasma rosuvastatin concentration of 176 ng/mL, “more than 15-fold higher than the mean value expected” in patients taking 40 mg rosuvastatin daily, the maximum labeled dosage for the drug and what the affected patient had been taking without prior incident for more than 5 years. The patient’s canagliflozin dosage was 100 mg/day, the standard starting dosage according to the drug’s label.
The report’s authors noted that genetic assessment of the patient, a woman originally from the Philippines who was “high functioning,” and diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, showed she was heterozygous for a polymorphism, c.421C>A, which is linked with increased rosuvastatin plasma levels in the plasma. They also cited a report that canagliflozin can interact with proteins involved in hepatic drug uptake.
“We speculate that, in our patient, the addition of canagliflozin enhanced intestinal rosuvastatin absorption, inhibited its hepatocellular uptake, and impaired its excretion into bile canaliculi and the proximal tubule, resulting in rosuvastatin accumulation and leading to hepatotoxicity and myotoxicity,” the clinicians wrote in their report.
“There is little doubt this was a drug interaction, but it does not apply uniformly to everyone.” The severity of the interaction would depend on the dosages, the comorbidities a patient has, and their genetic profile, Dr. Juurlink said.
Concern and skepticism
Other clinicians who regularly prescribe these drugs expressed concern about the observation as well as skepticism about the prevalence of patients who could potentially experience similar effects.
“We don’t know how common are these genetic abnormalities. If this is extremely rare, then it doesn’t have many clinical implications, but if a large portion of the population has this [genetic] abnormality, it’s something we’d need to pay attention to,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview. “It will be important to know the prevalence” of the genetic polymorphism carried by the reported patient, said Dr. Nissen, who has done research on lipid-lowering medications and drug safety.
“This could be important, or a very rare one-off. I can’t say which,” based on what’s currently known, he said. “There are many unanswered questions that make it hard to know how important this will be. It requires further investigation. There is a lot of uncertainty.”
Dr. Nissen particularly endorsed studies that approach this issue by looking at the prevalence rates of the implicated genetic polymorphism rather than pharmacovigilance studies that make epidemiologic assessments of adverse-effect prevalence. Studies that look for adverse-effect associations in large patient populations are “sloppy, and unless the interaction is incredibly intense they are not very sensitive,” he said.
But Dr. Juurlink, a pharmacoepidemiologist whose specialty includes studies of this sort, said that they could be useful if carefully designed. He suggested, for example, comparing in large patient databases the observed incidence of rhabdomyolysis among patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and also on rosuvastatin with those on pravastatin, a statin with a different metabolic profile. Another approach to further examining the observation would be dosage studies with rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in healthy volunteers, he said.
Dr. Nissen noted that rosuvastatin is a key agent from the statin class because it’s the “most effective” for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol. “Rosuvastatin is a go-to drug,” he declared. On the other hand, canagliflozin is “a little less used” than other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), he said.
One in a million?
“This was a freak accident. I don’t find it at all concerning. It was definitely one in a million,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of The Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “None of us have seen it” in either the several cardiovascular outcome trials now run on multiple drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class that included many patients also taking a statin, or in routine practice, he said. Dr. Handelsman noted that in his practice he had never seen a similar case despite treating “hundreds if not thousands of patients” with type 2 diabetes, virtually all of whom were on a statin and were also treated with an SGLT2 inhibitor, including many with canagliflozin.
Dr. Handelsman cited the notably low estimated glomerular filtration rate in the reported patient, who was described as having a serum creatinine level of 150 mcmol/L (1.7 mg/dL) prior to canagliflozin treatment that then rose to 194 mcmol/L (2.19 mg/dL) at the time of hospitalization, which corresponds to estimated glomerular filtration rates of 29-31 and 21-23 mL/min per 1.73 m2, respectively, depending on the calculator used, rates that were possibly below the labeled minimum rate of 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for patients starting canagliflozin treatment. The case report cited the patient as having stage 3B chronic kidney disease, which corresponds to a eGFR of 30-44* mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“I think the patient had acute kidney injury” on starting canagliflozin “that may have affected the [rosuvastatin] metabolism,” Dr. Handelsman suggested. “She had severe kidney dysfunction to start with that fell further with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment,” a well described and usually transient effect of starting drugs in this class because of changes the SGLT2 inhibitors cause in renal blood flow. He noted that the patient had not been receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker, which may have contributed to her acute problems with fluid balance. Most similar patients with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease risk, and chronic kidney disease would be on stable treatment with a drug that inhibits the renin-angiotensin system before starting an SGLT2 inhibitor, and not already having a RAS inhibitor on board before starting canagliflozin may have somehow contributed to the observed adverse effects, Dr. Handelsman said.
Dr. Juurlink was skeptical that the kidneys played a major role. “An abrupt change in renal function can influence statin clearance, but this was a 15-fold increase. You can’t explain such a dramatic increase by a transient reduction in renal function,” he said.
Dr. Juurlink and coauthors had no disclosures. Dr. Nissen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to companies that market drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class.
SOURCE: Brailovski E et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549.
*Correction: This value was missing from the original article.
A 76-year-old woman presented recently to a Toronto-area hospital with acute onset muscle pain, limb weakness, difficulty walking, and rhabdomyolysis associated with a sharp spike in her plasma level of rosuvastatin – a drug she had been on uneventfully for more than 5 years, within days of starting for the first time treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor canagliflozin (Invokana).
The patient’s Canadian clinicians stopped her treatment with both rosuvastatin and canagliflozin, administered intravenous crystalloid fluids, and within days her pain subsided and her limb weakness gradually improved, allowing her discharge 10 days later while she was ambulating with a walker.
“To our knowledge this is the first published report of a drug interaction between rosuvastatin and canagliflozin,” wrote the authors of the case report (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549). They cited the importance of the observation given the widespread use today of rosuvastatin for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol and exerting pleiotropic effects; and canagliflozin for its modest effects for reducing hyperglycemia, as well as its important role in reducing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, slowing progression of chronic kidney disease, and having a mild but important diuretic effect. “We encourage clinicians to remain vigilant for features of myotoxicity when canagliflozin and rosuvastatin are coprescribed,” they wrote, avoiding discussion of whether this may represent class or drug-specific effects.
“It’s reasonable to be mindful of this risk, but this is not a reason to not use rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in a patient,” nor for the time being to avoid any other combination of a statin and SGLT2 (sodium-glucose cotransporter 2) inhibitor, said David Juurlink, MD, head of the division of clinical pharmacology and toxicology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto and lead author of the report. “Few drug interactions have absolute contraindications. The admonition is just to be careful. It’s premature to say they shouldn’t be used together,” he said in an interview.
“We don’t know how much of an outlier this patient is. But it would be important to tell patients” on this or a similar combination to alert their clinicians if they start to have muscle aches, which should be a “red flag” to stop the statin, the SGLT2 inhibitor, or both until the situation can be fully assessed, Dr. Juurlink advised.
Sky high rosuvastatin levels
The linchpin of the observed adverse effects appeared to be a startlingly high elevation of the patient’s plasma rosuvastatin level when she was hospitalized 15 days after starting canagliflozin and 12 days after the onset of her thigh pain and weakness. Testing showed a plasma rosuvastatin concentration of 176 ng/mL, “more than 15-fold higher than the mean value expected” in patients taking 40 mg rosuvastatin daily, the maximum labeled dosage for the drug and what the affected patient had been taking without prior incident for more than 5 years. The patient’s canagliflozin dosage was 100 mg/day, the standard starting dosage according to the drug’s label.
The report’s authors noted that genetic assessment of the patient, a woman originally from the Philippines who was “high functioning,” and diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, showed she was heterozygous for a polymorphism, c.421C>A, which is linked with increased rosuvastatin plasma levels in the plasma. They also cited a report that canagliflozin can interact with proteins involved in hepatic drug uptake.
“We speculate that, in our patient, the addition of canagliflozin enhanced intestinal rosuvastatin absorption, inhibited its hepatocellular uptake, and impaired its excretion into bile canaliculi and the proximal tubule, resulting in rosuvastatin accumulation and leading to hepatotoxicity and myotoxicity,” the clinicians wrote in their report.
“There is little doubt this was a drug interaction, but it does not apply uniformly to everyone.” The severity of the interaction would depend on the dosages, the comorbidities a patient has, and their genetic profile, Dr. Juurlink said.
Concern and skepticism
Other clinicians who regularly prescribe these drugs expressed concern about the observation as well as skepticism about the prevalence of patients who could potentially experience similar effects.
“We don’t know how common are these genetic abnormalities. If this is extremely rare, then it doesn’t have many clinical implications, but if a large portion of the population has this [genetic] abnormality, it’s something we’d need to pay attention to,” Steven E. Nissen, MD, chair of cardiovascular medicine at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, said in an interview. “It will be important to know the prevalence” of the genetic polymorphism carried by the reported patient, said Dr. Nissen, who has done research on lipid-lowering medications and drug safety.
“This could be important, or a very rare one-off. I can’t say which,” based on what’s currently known, he said. “There are many unanswered questions that make it hard to know how important this will be. It requires further investigation. There is a lot of uncertainty.”
Dr. Nissen particularly endorsed studies that approach this issue by looking at the prevalence rates of the implicated genetic polymorphism rather than pharmacovigilance studies that make epidemiologic assessments of adverse-effect prevalence. Studies that look for adverse-effect associations in large patient populations are “sloppy, and unless the interaction is incredibly intense they are not very sensitive,” he said.
But Dr. Juurlink, a pharmacoepidemiologist whose specialty includes studies of this sort, said that they could be useful if carefully designed. He suggested, for example, comparing in large patient databases the observed incidence of rhabdomyolysis among patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor and also on rosuvastatin with those on pravastatin, a statin with a different metabolic profile. Another approach to further examining the observation would be dosage studies with rosuvastatin and canagliflozin in healthy volunteers, he said.
Dr. Nissen noted that rosuvastatin is a key agent from the statin class because it’s the “most effective” for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol. “Rosuvastatin is a go-to drug,” he declared. On the other hand, canagliflozin is “a little less used” than other drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class, specifically dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and empagliflozin (Jardiance), he said.
One in a million?
“This was a freak accident. I don’t find it at all concerning. It was definitely one in a million,” Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of The Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., said in an interview. “None of us have seen it” in either the several cardiovascular outcome trials now run on multiple drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class that included many patients also taking a statin, or in routine practice, he said. Dr. Handelsman noted that in his practice he had never seen a similar case despite treating “hundreds if not thousands of patients” with type 2 diabetes, virtually all of whom were on a statin and were also treated with an SGLT2 inhibitor, including many with canagliflozin.
Dr. Handelsman cited the notably low estimated glomerular filtration rate in the reported patient, who was described as having a serum creatinine level of 150 mcmol/L (1.7 mg/dL) prior to canagliflozin treatment that then rose to 194 mcmol/L (2.19 mg/dL) at the time of hospitalization, which corresponds to estimated glomerular filtration rates of 29-31 and 21-23 mL/min per 1.73 m2, respectively, depending on the calculator used, rates that were possibly below the labeled minimum rate of 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for patients starting canagliflozin treatment. The case report cited the patient as having stage 3B chronic kidney disease, which corresponds to a eGFR of 30-44* mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“I think the patient had acute kidney injury” on starting canagliflozin “that may have affected the [rosuvastatin] metabolism,” Dr. Handelsman suggested. “She had severe kidney dysfunction to start with that fell further with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment,” a well described and usually transient effect of starting drugs in this class because of changes the SGLT2 inhibitors cause in renal blood flow. He noted that the patient had not been receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin-receptor blocker, which may have contributed to her acute problems with fluid balance. Most similar patients with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease risk, and chronic kidney disease would be on stable treatment with a drug that inhibits the renin-angiotensin system before starting an SGLT2 inhibitor, and not already having a RAS inhibitor on board before starting canagliflozin may have somehow contributed to the observed adverse effects, Dr. Handelsman said.
Dr. Juurlink was skeptical that the kidneys played a major role. “An abrupt change in renal function can influence statin clearance, but this was a 15-fold increase. You can’t explain such a dramatic increase by a transient reduction in renal function,” he said.
Dr. Juurlink and coauthors had no disclosures. Dr. Nissen had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to companies that market drugs in the SGLT2 inhibitor class.
SOURCE: Brailovski E et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Aug 3. doi: 10.7326/L20-0549.
*Correction: This value was missing from the original article.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Most younger MI patients wouldn’t get statins under guidelines
Clinical guidelines for cholesterol management may have two blind spots when it comes to heart attack prevention: Most younger adults with premature coronary artery disease who’ve had a myocardial infarction don’t meet guideline criteria for preventative statin therapy, and survivors under age 55 don’t meet the criteria for continuing nonstatin lipid-lowering treatments, a large single-center retrospective study has shown.
“The classic approach we’ve taken to identifying young adults for prevention is inadequate in younger adults,” corresponding author Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “While awaiting more definitive research we should at minimum be using all the tools at our disposal, including broader use of coronary artery calcium [CAC] scoring, to identify young people who may benefit from statin therapy.”
The retrospective observational study analyzed records of 6,639 adults who had cardiac catheterization at Duke University Medical Center from 1995 to 2012 for a first myocardial infarction with obstructive coronary artery disease. The study considered those under age 55 years as “younger” patients, comprising 41% of the study group (2,733); 35% were “middle-aged” at 55-65 years (2,324) and 24% were “older,” at 66-75 years (1,582).
The report, published online Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, noted that most of the adults with premature CAD did not meet criteria for preventative statin therapy before their first MI based on ACC/American Heart Association clinical guidelines from 2013 and 2018. It also noted that younger MI survivors are also less frequently eligible for secondary prevention with intensive nonstatin lipid-lowering therapies than are older adults despite a much longer potential life span – and opportunity for another MI – for the former.
The researchers sought to evaluate the real-world implications of changes made in the 2018 guideline for adults who develop premature ischemic heart disease, and found that fewer younger patients qualify for preventative statin therapy under the 2018 guidelines.
“Younger individuals with very high-risk criteria are at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, a finding supporting the appropriate implementation of intensive lipid-lowering therapies in these patients,” wrote lead author Michel Zeitouni, MD, MSc, and colleagues.
Key findings
The investigators reported that younger adults were significantly less likely to meet a class I recommendation for statins under the 2013 guideline (42.9%), compared with their middle-aged (70%) and older (82.5%) counterparts; and under the 2018 guideline, at 39.4%, 59.5%, and 77.4%, respectively (both P < .001).
Similarly, when both class I and class IIa recommendations were accounted for, younger patients were significantly less likely than were middle-aged and older patients to be eligible for statins before their index MI under both the 2013 (56.7%, 79.5%, and 85.2%, respectively and 2018 guidelines (46.4%, 73.5%, and 88.2%, respectively (both P < .01).
After their first MI, one in four younger patients (28.3%) met the very high-risk criteria compared with 40% of middle-aged and 81.4% of older patients (P trend < .001). In 8 years of follow-up, patients with very high-risk criteria based on the 2018 guideline had twice the rate of death, nonfatal MI, or stroke (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.15; 95% confidence interval, 1.98-2.33; P < .001).
The researchers acknowledged that the 2018 guideline took the important step of implementing risk enhancers – patient characteristics such as obesity and metabolic syndrome – along with the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score to better identify high-risk young individuals who need statins. However, they also noted that the ability of the guidelines to identify young adults before their first MI “remains suboptimal.”
How to protect younger patients
“The 2018 guidelines will be most effective if we as providers do our best to identify risk enhancers and if we can use CAC scoring more broadly,” Dr. Navar said, noting that although CAC scoring has been shown to improve risk prediction, insurance coverage can be problematic.
“We also need to be careful to screen for the presence of the risk enhancers, such as inflammatory disease, family history, and women-specific risk factors, to make sure we aren’t missing an important high-risk group,” she added.
Other solutions to better identify at-risk younger adults include considering upgrades to the guidelines’ class IIb recommendation to class IIa to emphasize the importance of recognizing lower-risk younger adults, and recommending statins for patients at higher lifetime risk than age- and sex-matched peers, the researchers noted. “In our cohort, young individuals admitted for a first MI had a higher lifetime ASCVD risk score than did patients in the older age categories,” Dr. Zeitouni and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Navar said that these findings are a reminder that guidelines aren’t mandates. “Guidelines are meant to be a starting point for patients and physicians,” she said. “The absence of a recommendation doesn’t mean something isn’t recommended, but that there is not enough data to say one way or another.”
The study “provides important evidence” that the 2018 guidelines exempted about half of the younger adults who had a first MI from preventative statin therapy, Ron Blankstein, MD, and Avinainder Singh, MD, MMSc, noted in an editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:665-8).
“Data from both the Duke and Young-MI registries should force us to reexamine how we allocate statin use among young individuals,” they noted. Dr. Blankstein is with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Singh is with Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Zeitouni reported receiving lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Dr. Navar reported financial relationships with Amarin, Janssen, Amgen, Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Esperion, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, The Medicine Company, New Amsterdam, Cerner and Pfizer. Dr. Blankstein reported receiving research support from Amgen. Dr. Singh has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: M. Zeitouni et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020 Aug 3;76:653-64.
Clinical guidelines for cholesterol management may have two blind spots when it comes to heart attack prevention: Most younger adults with premature coronary artery disease who’ve had a myocardial infarction don’t meet guideline criteria for preventative statin therapy, and survivors under age 55 don’t meet the criteria for continuing nonstatin lipid-lowering treatments, a large single-center retrospective study has shown.
“The classic approach we’ve taken to identifying young adults for prevention is inadequate in younger adults,” corresponding author Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “While awaiting more definitive research we should at minimum be using all the tools at our disposal, including broader use of coronary artery calcium [CAC] scoring, to identify young people who may benefit from statin therapy.”
The retrospective observational study analyzed records of 6,639 adults who had cardiac catheterization at Duke University Medical Center from 1995 to 2012 for a first myocardial infarction with obstructive coronary artery disease. The study considered those under age 55 years as “younger” patients, comprising 41% of the study group (2,733); 35% were “middle-aged” at 55-65 years (2,324) and 24% were “older,” at 66-75 years (1,582).
The report, published online Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, noted that most of the adults with premature CAD did not meet criteria for preventative statin therapy before their first MI based on ACC/American Heart Association clinical guidelines from 2013 and 2018. It also noted that younger MI survivors are also less frequently eligible for secondary prevention with intensive nonstatin lipid-lowering therapies than are older adults despite a much longer potential life span – and opportunity for another MI – for the former.
The researchers sought to evaluate the real-world implications of changes made in the 2018 guideline for adults who develop premature ischemic heart disease, and found that fewer younger patients qualify for preventative statin therapy under the 2018 guidelines.
“Younger individuals with very high-risk criteria are at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, a finding supporting the appropriate implementation of intensive lipid-lowering therapies in these patients,” wrote lead author Michel Zeitouni, MD, MSc, and colleagues.
Key findings
The investigators reported that younger adults were significantly less likely to meet a class I recommendation for statins under the 2013 guideline (42.9%), compared with their middle-aged (70%) and older (82.5%) counterparts; and under the 2018 guideline, at 39.4%, 59.5%, and 77.4%, respectively (both P < .001).
Similarly, when both class I and class IIa recommendations were accounted for, younger patients were significantly less likely than were middle-aged and older patients to be eligible for statins before their index MI under both the 2013 (56.7%, 79.5%, and 85.2%, respectively and 2018 guidelines (46.4%, 73.5%, and 88.2%, respectively (both P < .01).
After their first MI, one in four younger patients (28.3%) met the very high-risk criteria compared with 40% of middle-aged and 81.4% of older patients (P trend < .001). In 8 years of follow-up, patients with very high-risk criteria based on the 2018 guideline had twice the rate of death, nonfatal MI, or stroke (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.15; 95% confidence interval, 1.98-2.33; P < .001).
The researchers acknowledged that the 2018 guideline took the important step of implementing risk enhancers – patient characteristics such as obesity and metabolic syndrome – along with the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score to better identify high-risk young individuals who need statins. However, they also noted that the ability of the guidelines to identify young adults before their first MI “remains suboptimal.”
How to protect younger patients
“The 2018 guidelines will be most effective if we as providers do our best to identify risk enhancers and if we can use CAC scoring more broadly,” Dr. Navar said, noting that although CAC scoring has been shown to improve risk prediction, insurance coverage can be problematic.
“We also need to be careful to screen for the presence of the risk enhancers, such as inflammatory disease, family history, and women-specific risk factors, to make sure we aren’t missing an important high-risk group,” she added.
Other solutions to better identify at-risk younger adults include considering upgrades to the guidelines’ class IIb recommendation to class IIa to emphasize the importance of recognizing lower-risk younger adults, and recommending statins for patients at higher lifetime risk than age- and sex-matched peers, the researchers noted. “In our cohort, young individuals admitted for a first MI had a higher lifetime ASCVD risk score than did patients in the older age categories,” Dr. Zeitouni and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Navar said that these findings are a reminder that guidelines aren’t mandates. “Guidelines are meant to be a starting point for patients and physicians,” she said. “The absence of a recommendation doesn’t mean something isn’t recommended, but that there is not enough data to say one way or another.”
The study “provides important evidence” that the 2018 guidelines exempted about half of the younger adults who had a first MI from preventative statin therapy, Ron Blankstein, MD, and Avinainder Singh, MD, MMSc, noted in an editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:665-8).
“Data from both the Duke and Young-MI registries should force us to reexamine how we allocate statin use among young individuals,” they noted. Dr. Blankstein is with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Singh is with Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Zeitouni reported receiving lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Dr. Navar reported financial relationships with Amarin, Janssen, Amgen, Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Esperion, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, The Medicine Company, New Amsterdam, Cerner and Pfizer. Dr. Blankstein reported receiving research support from Amgen. Dr. Singh has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: M. Zeitouni et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020 Aug 3;76:653-64.
Clinical guidelines for cholesterol management may have two blind spots when it comes to heart attack prevention: Most younger adults with premature coronary artery disease who’ve had a myocardial infarction don’t meet guideline criteria for preventative statin therapy, and survivors under age 55 don’t meet the criteria for continuing nonstatin lipid-lowering treatments, a large single-center retrospective study has shown.
“The classic approach we’ve taken to identifying young adults for prevention is inadequate in younger adults,” corresponding author Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “While awaiting more definitive research we should at minimum be using all the tools at our disposal, including broader use of coronary artery calcium [CAC] scoring, to identify young people who may benefit from statin therapy.”
The retrospective observational study analyzed records of 6,639 adults who had cardiac catheterization at Duke University Medical Center from 1995 to 2012 for a first myocardial infarction with obstructive coronary artery disease. The study considered those under age 55 years as “younger” patients, comprising 41% of the study group (2,733); 35% were “middle-aged” at 55-65 years (2,324) and 24% were “older,” at 66-75 years (1,582).
The report, published online Aug. 3 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, noted that most of the adults with premature CAD did not meet criteria for preventative statin therapy before their first MI based on ACC/American Heart Association clinical guidelines from 2013 and 2018. It also noted that younger MI survivors are also less frequently eligible for secondary prevention with intensive nonstatin lipid-lowering therapies than are older adults despite a much longer potential life span – and opportunity for another MI – for the former.
The researchers sought to evaluate the real-world implications of changes made in the 2018 guideline for adults who develop premature ischemic heart disease, and found that fewer younger patients qualify for preventative statin therapy under the 2018 guidelines.
“Younger individuals with very high-risk criteria are at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, a finding supporting the appropriate implementation of intensive lipid-lowering therapies in these patients,” wrote lead author Michel Zeitouni, MD, MSc, and colleagues.
Key findings
The investigators reported that younger adults were significantly less likely to meet a class I recommendation for statins under the 2013 guideline (42.9%), compared with their middle-aged (70%) and older (82.5%) counterparts; and under the 2018 guideline, at 39.4%, 59.5%, and 77.4%, respectively (both P < .001).
Similarly, when both class I and class IIa recommendations were accounted for, younger patients were significantly less likely than were middle-aged and older patients to be eligible for statins before their index MI under both the 2013 (56.7%, 79.5%, and 85.2%, respectively and 2018 guidelines (46.4%, 73.5%, and 88.2%, respectively (both P < .01).
After their first MI, one in four younger patients (28.3%) met the very high-risk criteria compared with 40% of middle-aged and 81.4% of older patients (P trend < .001). In 8 years of follow-up, patients with very high-risk criteria based on the 2018 guideline had twice the rate of death, nonfatal MI, or stroke (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.15; 95% confidence interval, 1.98-2.33; P < .001).
The researchers acknowledged that the 2018 guideline took the important step of implementing risk enhancers – patient characteristics such as obesity and metabolic syndrome – along with the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score to better identify high-risk young individuals who need statins. However, they also noted that the ability of the guidelines to identify young adults before their first MI “remains suboptimal.”
How to protect younger patients
“The 2018 guidelines will be most effective if we as providers do our best to identify risk enhancers and if we can use CAC scoring more broadly,” Dr. Navar said, noting that although CAC scoring has been shown to improve risk prediction, insurance coverage can be problematic.
“We also need to be careful to screen for the presence of the risk enhancers, such as inflammatory disease, family history, and women-specific risk factors, to make sure we aren’t missing an important high-risk group,” she added.
Other solutions to better identify at-risk younger adults include considering upgrades to the guidelines’ class IIb recommendation to class IIa to emphasize the importance of recognizing lower-risk younger adults, and recommending statins for patients at higher lifetime risk than age- and sex-matched peers, the researchers noted. “In our cohort, young individuals admitted for a first MI had a higher lifetime ASCVD risk score than did patients in the older age categories,” Dr. Zeitouni and colleagues wrote.
Dr. Navar said that these findings are a reminder that guidelines aren’t mandates. “Guidelines are meant to be a starting point for patients and physicians,” she said. “The absence of a recommendation doesn’t mean something isn’t recommended, but that there is not enough data to say one way or another.”
The study “provides important evidence” that the 2018 guidelines exempted about half of the younger adults who had a first MI from preventative statin therapy, Ron Blankstein, MD, and Avinainder Singh, MD, MMSc, noted in an editorial (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76:665-8).
“Data from both the Duke and Young-MI registries should force us to reexamine how we allocate statin use among young individuals,” they noted. Dr. Blankstein is with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Singh is with Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Dr. Zeitouni reported receiving lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer. Dr. Navar reported financial relationships with Amarin, Janssen, Amgen, Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Esperion, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, The Medicine Company, New Amsterdam, Cerner and Pfizer. Dr. Blankstein reported receiving research support from Amgen. Dr. Singh has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: M. Zeitouni et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020 Aug 3;76:653-64.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
COVID-19 taking financial toll on people in U.S. with diabetes
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic is taking a particularly severe financial toll on people with diabetes, new research from the United States suggests.
Results from a national online survey of 5,000 people with diabetes conducted between June 26 and July 1, 2020, were posted July 29 on the American Diabetes Association website.
The survey, conducted by the diabetes research company dQ&A in association with the ADA, revealed that Americans with diabetes are experiencing extreme financial pressures, leading to medication and supply rationing.
A high proportion of respondents had either lost income or are working in jobs that place them at risk for catching the novel coronavirus.
“These new numbers show the urgency needed to adopt measures to protect and assist the millions of people with diabetes who are suffering through this pandemic,” Tracey D. Brown, CEO of the ADA, said in a statement.
She called for states to extend health care coverage to people who have lost their jobs, for the eradication of insulin copays during the pandemic, and for increased COVID-19 testing capacity in high-risk communities.
“If these actions aren’t taken immediately, we will continue to see devastating impacts and outcomes for millions of vulnerable Americans,” Ms. Brown stressed.
COVID-19 has worsened financial pressures for people with diabetes
In the survey, 24% of respondents reported having used savings, loans, or stimulus check money to pay for diabetes care in the past 3 months. Among those who have lost income, half are using savings or stimulus money.
A quarter of respondents said they have been self-rationing supplies to cut costs.
Extrapolating to the entire U.S. population with diabetes, dQ&A estimated that roughly 650,000 are skipping insulin doses or taking less than prescribed, and 3 million are skipping blood glucose tests.
In June, the unemployment rate for people with diabetes was 18%, higher than the national rate of 12%.
Also higher is the proportion of those working prior to the pandemic who have since lost income: 33%, compared with 29% for the general population.
Among those who are self-employed, 7 in 10 of those with diabetes have lost some or all of their income.
Many with diabetes who are employed are vulnerable to exposure
Of those who remain employed, half said they can’t work from home.
Of those, 60% work in essential industries, with 22% in health care. A large majority, 90%, reported lack of social distancing at work and nearly a third work in places that don’t require masks.
“People with diabetes are helping to provide the services we all depend on during this pandemic, even as it puts their own well-being at risk,” the report said.
It concluded that “these numbers represent a conservative estimate of the pandemic’s impact. They are generated from an ongoing online study of the diabetes population amongst people who have opted in to participate.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Early palliative care fails to improve QOL in advanced heart failure
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
A new palliative care intervention for U.S. patients with advanced heart failure did not improve quality of life or mood after 16 weeks of participation in a randomized trial.
“Future analyses and studies will examine both the patient factors and intervention components to find the right palliative care dose, for the right patient, at the right time,” wrote Marie A. Bakitas, DNSc, of the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and coauthors. The study was published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“My first reaction is disappointment,” Larry Allen, MD, of the University of Colorado in Denver, said in an interview. “We had hoped to see the ENABLE program, which had been successful in cancer, translate to the heart failure setting.”
Improvement of palliative care in heart failure patients might rest on who needs it most
“One thing to note,” Dr. Allen added in an interview, “is that, in this population of patients, some of the measures they were trying to improve were already relatively mild to start with. It may not be that the intervention didn’t help but that they picked a patient population that wasn’t particularly in need. If you treat someone who doesn’t have a problem, it’s hard to make them better.”
In a separate interview, Dr. Bakitas acknowledged a similar sentiment. “We were a little surprised until we looked at our sample,” she said. “We realized that we had recruited all these very high-functioning, good quality-of-life patients. What we then did was look at a subsample of patients who had low quality of life at baseline. Low and behold, the intervention had an effect. The patients who started with a poor quality of life had a statistically and clinically significant benefit. Their KCCQ score increased by over 5 points.”
As for next steps. Dr. Bakitas noted that they’re twofold: “One is refining the patient population who can benefit, and the second is working on the intervention and figuring out which pieces are the ones that provide the most benefit.
“Because of logistics and practical issues, not everyone in the study got all the intervention that they should have. Think of it like a drug trial; if someone misses a pill, they don’t get the full dose that we thought would work. We need to make sure our interventions have the right pieces in place. We don’t want to develop a great intervention that’s not practical for patients.”
Study design and outcomes
To determine the benefits of early palliative care for patients with heart failure, the researchers developed the ENABLE CHF-PC (Educate, Nurture, Advise, Before Life Ends Comprehensive Heartcare for Patients and Caregivers) intervention. This nurse-led program includes an in-person consultant followed by six telehealth nurse coaching sessions lasting 30-40 minutes and then monthly follow-up calls through either 48 weeks or the patient’s death.
To test the effectiveness of their intervention after 16 weeks, the researchers launched a two-site, single-blind randomized clinical trial made up of 415 patients who were 50 years or older with advanced heart failure. Among the patients, 53% were men and the mean age was 64 years; 55% were African American, 26% lived in a rural area, and 46% had a high school education or less. The average length of time since heart failure diagnosis was 5.1 years.
Patients were randomized evenly to receive either the ENABLE CHF-PC intervention (208) or usual care. The primary outcomes were quality of life (QOL), which was measured by the heart failure–specific 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and the 14-item Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Palliative-14 (FACIT Pal-14), and mood, which was measured by the 14-item Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Pain was measured via 3-item pain intensity and 2-item pain interference scales.
Effect size was measured as Cohen d or d-equivalent, where a small effect is 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is about 0.854.
At baseline, the mean KCCQ score of 52.6 at baseline indicated a “fairly good” QOL across all patients. After 16 weeks, the mean KCCQ score improved 3.9 points in the intervention group, compared with 2.3 points in the usual care group (d = 0.07; [95% confidence interval, –0.09-0.24]). In addition, the mean FACIT-Pal-14 score improved 1.4 points in the intervention group compared to 0.2 points in the usual care group (d = 0.12 [95% CI, –0.03-0.28]). Only small differences were observed between groups regarding anxiety and depression, but pain intensity (difference, –2.8; SE, 0.9; d = –0.26 [95% CI, –0.43-0.09]) and pain interference (difference, –2.3; SE, 1; d = –0.21 [95% CI, –0.40 to –0.02]) demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically important decrease.
As heart failure care evolves, so must palliative care
Though the study and intervention developed by Dr. Bakitas and colleagues is commendable, it is only somewhat surprising that it did not drastically improve patients’ quality of life, Nathan E. Goldstein, MD, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
He noted several reasons for the lack of improvement, including a large proportion of patients still being in the early stages of the disease. Ultimately, however, he wonders if innovation in heart failure care ultimately impacted the study while it was occurring. Medications and technological advancements evolve rapidly in this field, he said, especially over the course of a 3-year study period.
To continue this work and produce real benefits in patients with advanced heart failure, Dr. Goldstein emphasized the need for “dynamic palliative care interventions that can adapt to the constantly changing landscape of the patient’s needs caused by the underlying nature of the disease, as well as the innovations in the field of cardiology.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including data attrition at 16 weeks that was higher than expected – a turn of events they attributed to “unique socioeconomic factors … and lack of regular health care appointments” among some participants. In addition, a minority of patients were unable to stick to the study protocol, which has led the researchers to begin investigating video alternatives to in-person consultation.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institutes of Nursing Research. Four of the authors reported received grants from the National Institutes of Nursing Research outside the submitted work or during the study. Dr. Goldstein reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Bakitas MA et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 July 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2861.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Heart damage even after COVID-19 ‘recovery’ evokes specter of later heart failure
Evidence that the heart can take a major hit in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, especially those already with cardiovascular disease (CV) or its risk factors, has been sadly apparent from the pandemic’s earliest days.
Less clear from case studies and small series to date has been whether SARS-CoV-2 directly attacks the heart and whether acute cardiac effects of the illness may lead to some kind of lingering cardiomyopathy.
The field’s grasp of those issues advanced a bit in two new reports published July 27 in JAMA Cardiology that seem to validate concerns the virus can infect the myocardium, without necessarily causing myocarditis and the possibility that some “recovered” patients may be left with persisting myocardial injury and inflammation that potentially could later manifest as heart failure.
Persisting inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance
A prospective cohort study with 100 patients recovered from a recent bout of the disease showed evidence of ventricular dysfunction, greater ventricular mass, and in 78% of the cohort, signs of myocardial inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
Two-thirds of the cohort, whose acute COVID-19 severity had “ranged from asymptomatic to minor-to-moderate symptoms,” had recovered at home, whereas the remaining “severely unwell patients” had been hospitalized, wrote the authors, led by Valentina O. Püntmann, MD, PhD, University Hospital Frankfurt (Germany).
None of the patients had a history of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, although some had hypertension, diabetes, or evidence of coronary disease.
“Our findings demonstrate that participants with a relative paucity of preexisting cardiovascular condition and with mostly home-based recovery had frequent cardiac inflammatory involvement, which was similar to the hospitalized subgroup with regards to severity and extent,” the group noted.
“There is a considerable ongoing myocardial inflammation in the heart muscle weeks after recovery from COVID-19 illness. This finding is important because it may herald a considerable burden of heart failure in a few years down the line,” Dr. Püntmann said in an interview.
Early diagnosis would offer “a good chance that early treatment could reduce the relentless course of inflammatory damage or even halt it,” she said.
“The relatively clear onset of COVID-19 illness provides an opportunity, which we often do not have with other conditions, to take a proactive action and to look for heart involvement early, within a few weeks of recovery.”
The study’s CMR evidence of inflammation edema, scarring, and pericardial effusion are among “the major diagnostic criteria for inflammatory and viral myocarditis,” observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, from Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who wasn’t part of either new study.
The findings suggest – consistent with previous evidence – that some patients with recent COVID-19 may be left with ongoing myocardial inflammation, and this study further adds that it could potentially become subacute or even chronic and in some may not be totally reversible, she said in an interview. How long the effects are likely to persist “remains to be determined. We need longer-term outcomes data.”
Viral presence without myocarditis
The accompanying report featured a postmortem analysis of hearts from 39 patients with mostly severe COVID-19 that pointed to a significant SARS-CoV-2 presence and signs that the virus vigorously replicated in the myocardium.
But there was no evidence that the infection led to fulminant myocarditis. Rather, the virus had apparently infiltrated the heart by localizing in interstitial cells or in macrophages that took up in the myocardium without actually entering myocytes, concluded the report’s authors, led by Diana Lindner, PhD, from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg (Germany).
The findings suggest “that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in cardiac tissue does not necessarily cause an inflammatory reaction consistent with clinical myocarditis,” the group wrote.
Previously in the literature, in “cases in which myocardial inflammation was present, there was also evidence of clinical myocarditis, and therefore the current cases underlie a different pathophysiology,” they concluded.
No evidence of the virus was seen in 15 cases, about 61% of the group. In 16 of the remaining 24 hearts, the viral load exceeded 1,000 copies per mcg of RNA, a substantial presence. Those 16 showed increased expression of inflammatory cytokines but no inflammatory cell infiltrates or changes in leukocyte counts, the researchers noted.
“Findings of suggested viral replication in the cases with a very high viral load are showing that we need to do more studies to find out long-term consequences, which we do not know right now,” senior author Dirk Westermann, MD, also from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg, said.
Implications for heart failure
The postmortem findings from Dr. Lindner and associates “provide intriguing evidence that COVID-19 is associated with at least some component of myocardial injury, perhaps as the result of direct viral infection of the heart,” wrote Clyde W. Yancy, MD, MSc, from Northwestern University, Chicago, and Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, in an editorial accompanying both reports.
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues – on the backdrop of earlier COVID-19 observations – suggests the potential for “residual left ventricular dysfunction and ongoing inflammation” in the months following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Both developments may be “of sufficient concern to represent a nidus for new-onset heart failure and other cardiovascular complications,” contend Dr. Yancy and Dr. Fonarow.
“When added to the postmortem pathological findings from Lindner et al, we see the plot thickening and we are inclined to raise a new and very evident concern that cardiomyopathy and heart failure related to COVID-19 may potentially evolve as the natural history of this infection becomes clearer,” they wrote.
Some patients, having recovered from the acute illness, may be left with a chronic inflammatory state that probably puts them at increased risk for future heart failure, agreed Dr. Bozkurt when interviewed. “They could show further decline in cardiac function, and their recovery might take longer than with the usual viral illnesses that we see,” she said.
“There could also be a risk of sudden death. Inflammation sometimes gives rise to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia, which I would be very worried about, especially if the myocardium is stressed,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “So competitive sports in those patients potentially could be risky.”
COVID-19 cohort vs. matched control subjects
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues prospectively entered 100 patients recently recovered from an acute bout of COVID-19, either at home or at a hospital, who were followed in a registry based at University Hospital Frankfurt. Their median age was 49 years; 47% were female. They were compared with 50 age- and sex-matched control patients and 50 apparently healthy volunteers matched for risk factors, the group noted.
On the same day as the CMR assessment, the recently recovered patients, compared with the healthy control subjects and risk-factor matched control subjects, respectively, showed (P ≤ .001 in each case):
- A reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction: 56% vs. 60% and 61%.
- A higher LV end-diastolic volume index: 86 mL/m2 vs. 80 mL/m2 and 75 mL/m2.
- A greater LV mass index: 51 g/m2 vs. 47 g/m2 and 53 g/m2.
- A higher hs-TnT level: 5.6 pg/mL vs. 3.2 pg/mL and 3.9 pg/mL.
- A greater prevalence of hs-TnT levels 3 pg/mL or more: 71% vs. 11% and 31%.
At CMR, 78% of the recovered COVID-19 patients showed abnormalities that included raised myocardial native T1 and T2 mapping, which is suggestive of fibrosis and edema from inflammation, compared with the two control groups (P < .001 for all differences), “independent of preexisting conditions, severity and overall course of the acute illness, and the time from the original diagnosis,” the group wrote. Native T1 and T2 mapping correlated significantly with hs-TnT.
“We now have the diagnostic means to detect cardiac inflammation early, and we need make every effort to apply them in every day practice,”Dr. Püntmann said in the interview.
“Using cardiac MRI will allow us to raise our game against COVID-19 and proactively develop efficient cardioprotective treatments,” she said. “Until we have effective means of protecting from the infection, that is vaccination, we must act swiftly and within the means at hand.”
The analysis evokes several other ways patients with COVID-19 might be screened for significant myocardial involvement.
“Strategies could include checking troponins, not only at admission but maybe at discharge and perhaps even those individuals who are at home and are not necessarily requiring care,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
“Biomarker profiling and screening for ongoing inflammation probably are going to be important components of COVID-19, especially for those with subclinical risk and disease.”
Dr. Westermann proposed that troponin elevations at discharge “might be a good starting point” for selecting COVID-19 patients for functional testing or imaging to screen for cardiac sequelae. Performing such tests routinely now “would be overwhelming given the massive increase in patients we still see today.”
Dr. Püntmann had no disclosures; statements of potential conflict for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Bozkurt has previously disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lantheus Medical Imaging, and Respicardia; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA ; and having unspecified relationships with Abbott Laboratories. Dr. Lindner had no disclosures; Dr. Westermann reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, and Medtronic. Dr. Yancy is a deputy editor and Dr. Fonarow a section editor for JAMA Cardiology. Dr. Yancy had no other disclosures. Dr. Fonarow reported receiving personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Evidence that the heart can take a major hit in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, especially those already with cardiovascular disease (CV) or its risk factors, has been sadly apparent from the pandemic’s earliest days.
Less clear from case studies and small series to date has been whether SARS-CoV-2 directly attacks the heart and whether acute cardiac effects of the illness may lead to some kind of lingering cardiomyopathy.
The field’s grasp of those issues advanced a bit in two new reports published July 27 in JAMA Cardiology that seem to validate concerns the virus can infect the myocardium, without necessarily causing myocarditis and the possibility that some “recovered” patients may be left with persisting myocardial injury and inflammation that potentially could later manifest as heart failure.
Persisting inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance
A prospective cohort study with 100 patients recovered from a recent bout of the disease showed evidence of ventricular dysfunction, greater ventricular mass, and in 78% of the cohort, signs of myocardial inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
Two-thirds of the cohort, whose acute COVID-19 severity had “ranged from asymptomatic to minor-to-moderate symptoms,” had recovered at home, whereas the remaining “severely unwell patients” had been hospitalized, wrote the authors, led by Valentina O. Püntmann, MD, PhD, University Hospital Frankfurt (Germany).
None of the patients had a history of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, although some had hypertension, diabetes, or evidence of coronary disease.
“Our findings demonstrate that participants with a relative paucity of preexisting cardiovascular condition and with mostly home-based recovery had frequent cardiac inflammatory involvement, which was similar to the hospitalized subgroup with regards to severity and extent,” the group noted.
“There is a considerable ongoing myocardial inflammation in the heart muscle weeks after recovery from COVID-19 illness. This finding is important because it may herald a considerable burden of heart failure in a few years down the line,” Dr. Püntmann said in an interview.
Early diagnosis would offer “a good chance that early treatment could reduce the relentless course of inflammatory damage or even halt it,” she said.
“The relatively clear onset of COVID-19 illness provides an opportunity, which we often do not have with other conditions, to take a proactive action and to look for heart involvement early, within a few weeks of recovery.”
The study’s CMR evidence of inflammation edema, scarring, and pericardial effusion are among “the major diagnostic criteria for inflammatory and viral myocarditis,” observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, from Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who wasn’t part of either new study.
The findings suggest – consistent with previous evidence – that some patients with recent COVID-19 may be left with ongoing myocardial inflammation, and this study further adds that it could potentially become subacute or even chronic and in some may not be totally reversible, she said in an interview. How long the effects are likely to persist “remains to be determined. We need longer-term outcomes data.”
Viral presence without myocarditis
The accompanying report featured a postmortem analysis of hearts from 39 patients with mostly severe COVID-19 that pointed to a significant SARS-CoV-2 presence and signs that the virus vigorously replicated in the myocardium.
But there was no evidence that the infection led to fulminant myocarditis. Rather, the virus had apparently infiltrated the heart by localizing in interstitial cells or in macrophages that took up in the myocardium without actually entering myocytes, concluded the report’s authors, led by Diana Lindner, PhD, from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg (Germany).
The findings suggest “that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in cardiac tissue does not necessarily cause an inflammatory reaction consistent with clinical myocarditis,” the group wrote.
Previously in the literature, in “cases in which myocardial inflammation was present, there was also evidence of clinical myocarditis, and therefore the current cases underlie a different pathophysiology,” they concluded.
No evidence of the virus was seen in 15 cases, about 61% of the group. In 16 of the remaining 24 hearts, the viral load exceeded 1,000 copies per mcg of RNA, a substantial presence. Those 16 showed increased expression of inflammatory cytokines but no inflammatory cell infiltrates or changes in leukocyte counts, the researchers noted.
“Findings of suggested viral replication in the cases with a very high viral load are showing that we need to do more studies to find out long-term consequences, which we do not know right now,” senior author Dirk Westermann, MD, also from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg, said.
Implications for heart failure
The postmortem findings from Dr. Lindner and associates “provide intriguing evidence that COVID-19 is associated with at least some component of myocardial injury, perhaps as the result of direct viral infection of the heart,” wrote Clyde W. Yancy, MD, MSc, from Northwestern University, Chicago, and Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, in an editorial accompanying both reports.
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues – on the backdrop of earlier COVID-19 observations – suggests the potential for “residual left ventricular dysfunction and ongoing inflammation” in the months following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Both developments may be “of sufficient concern to represent a nidus for new-onset heart failure and other cardiovascular complications,” contend Dr. Yancy and Dr. Fonarow.
“When added to the postmortem pathological findings from Lindner et al, we see the plot thickening and we are inclined to raise a new and very evident concern that cardiomyopathy and heart failure related to COVID-19 may potentially evolve as the natural history of this infection becomes clearer,” they wrote.
Some patients, having recovered from the acute illness, may be left with a chronic inflammatory state that probably puts them at increased risk for future heart failure, agreed Dr. Bozkurt when interviewed. “They could show further decline in cardiac function, and their recovery might take longer than with the usual viral illnesses that we see,” she said.
“There could also be a risk of sudden death. Inflammation sometimes gives rise to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia, which I would be very worried about, especially if the myocardium is stressed,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “So competitive sports in those patients potentially could be risky.”
COVID-19 cohort vs. matched control subjects
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues prospectively entered 100 patients recently recovered from an acute bout of COVID-19, either at home or at a hospital, who were followed in a registry based at University Hospital Frankfurt. Their median age was 49 years; 47% were female. They were compared with 50 age- and sex-matched control patients and 50 apparently healthy volunteers matched for risk factors, the group noted.
On the same day as the CMR assessment, the recently recovered patients, compared with the healthy control subjects and risk-factor matched control subjects, respectively, showed (P ≤ .001 in each case):
- A reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction: 56% vs. 60% and 61%.
- A higher LV end-diastolic volume index: 86 mL/m2 vs. 80 mL/m2 and 75 mL/m2.
- A greater LV mass index: 51 g/m2 vs. 47 g/m2 and 53 g/m2.
- A higher hs-TnT level: 5.6 pg/mL vs. 3.2 pg/mL and 3.9 pg/mL.
- A greater prevalence of hs-TnT levels 3 pg/mL or more: 71% vs. 11% and 31%.
At CMR, 78% of the recovered COVID-19 patients showed abnormalities that included raised myocardial native T1 and T2 mapping, which is suggestive of fibrosis and edema from inflammation, compared with the two control groups (P < .001 for all differences), “independent of preexisting conditions, severity and overall course of the acute illness, and the time from the original diagnosis,” the group wrote. Native T1 and T2 mapping correlated significantly with hs-TnT.
“We now have the diagnostic means to detect cardiac inflammation early, and we need make every effort to apply them in every day practice,”Dr. Püntmann said in the interview.
“Using cardiac MRI will allow us to raise our game against COVID-19 and proactively develop efficient cardioprotective treatments,” she said. “Until we have effective means of protecting from the infection, that is vaccination, we must act swiftly and within the means at hand.”
The analysis evokes several other ways patients with COVID-19 might be screened for significant myocardial involvement.
“Strategies could include checking troponins, not only at admission but maybe at discharge and perhaps even those individuals who are at home and are not necessarily requiring care,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
“Biomarker profiling and screening for ongoing inflammation probably are going to be important components of COVID-19, especially for those with subclinical risk and disease.”
Dr. Westermann proposed that troponin elevations at discharge “might be a good starting point” for selecting COVID-19 patients for functional testing or imaging to screen for cardiac sequelae. Performing such tests routinely now “would be overwhelming given the massive increase in patients we still see today.”
Dr. Püntmann had no disclosures; statements of potential conflict for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Bozkurt has previously disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lantheus Medical Imaging, and Respicardia; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA ; and having unspecified relationships with Abbott Laboratories. Dr. Lindner had no disclosures; Dr. Westermann reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, and Medtronic. Dr. Yancy is a deputy editor and Dr. Fonarow a section editor for JAMA Cardiology. Dr. Yancy had no other disclosures. Dr. Fonarow reported receiving personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Evidence that the heart can take a major hit in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, especially those already with cardiovascular disease (CV) or its risk factors, has been sadly apparent from the pandemic’s earliest days.
Less clear from case studies and small series to date has been whether SARS-CoV-2 directly attacks the heart and whether acute cardiac effects of the illness may lead to some kind of lingering cardiomyopathy.
The field’s grasp of those issues advanced a bit in two new reports published July 27 in JAMA Cardiology that seem to validate concerns the virus can infect the myocardium, without necessarily causing myocarditis and the possibility that some “recovered” patients may be left with persisting myocardial injury and inflammation that potentially could later manifest as heart failure.
Persisting inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance
A prospective cohort study with 100 patients recovered from a recent bout of the disease showed evidence of ventricular dysfunction, greater ventricular mass, and in 78% of the cohort, signs of myocardial inflammation by cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
Two-thirds of the cohort, whose acute COVID-19 severity had “ranged from asymptomatic to minor-to-moderate symptoms,” had recovered at home, whereas the remaining “severely unwell patients” had been hospitalized, wrote the authors, led by Valentina O. Püntmann, MD, PhD, University Hospital Frankfurt (Germany).
None of the patients had a history of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, although some had hypertension, diabetes, or evidence of coronary disease.
“Our findings demonstrate that participants with a relative paucity of preexisting cardiovascular condition and with mostly home-based recovery had frequent cardiac inflammatory involvement, which was similar to the hospitalized subgroup with regards to severity and extent,” the group noted.
“There is a considerable ongoing myocardial inflammation in the heart muscle weeks after recovery from COVID-19 illness. This finding is important because it may herald a considerable burden of heart failure in a few years down the line,” Dr. Püntmann said in an interview.
Early diagnosis would offer “a good chance that early treatment could reduce the relentless course of inflammatory damage or even halt it,” she said.
“The relatively clear onset of COVID-19 illness provides an opportunity, which we often do not have with other conditions, to take a proactive action and to look for heart involvement early, within a few weeks of recovery.”
The study’s CMR evidence of inflammation edema, scarring, and pericardial effusion are among “the major diagnostic criteria for inflammatory and viral myocarditis,” observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, from Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who wasn’t part of either new study.
The findings suggest – consistent with previous evidence – that some patients with recent COVID-19 may be left with ongoing myocardial inflammation, and this study further adds that it could potentially become subacute or even chronic and in some may not be totally reversible, she said in an interview. How long the effects are likely to persist “remains to be determined. We need longer-term outcomes data.”
Viral presence without myocarditis
The accompanying report featured a postmortem analysis of hearts from 39 patients with mostly severe COVID-19 that pointed to a significant SARS-CoV-2 presence and signs that the virus vigorously replicated in the myocardium.
But there was no evidence that the infection led to fulminant myocarditis. Rather, the virus had apparently infiltrated the heart by localizing in interstitial cells or in macrophages that took up in the myocardium without actually entering myocytes, concluded the report’s authors, led by Diana Lindner, PhD, from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg (Germany).
The findings suggest “that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in cardiac tissue does not necessarily cause an inflammatory reaction consistent with clinical myocarditis,” the group wrote.
Previously in the literature, in “cases in which myocardial inflammation was present, there was also evidence of clinical myocarditis, and therefore the current cases underlie a different pathophysiology,” they concluded.
No evidence of the virus was seen in 15 cases, about 61% of the group. In 16 of the remaining 24 hearts, the viral load exceeded 1,000 copies per mcg of RNA, a substantial presence. Those 16 showed increased expression of inflammatory cytokines but no inflammatory cell infiltrates or changes in leukocyte counts, the researchers noted.
“Findings of suggested viral replication in the cases with a very high viral load are showing that we need to do more studies to find out long-term consequences, which we do not know right now,” senior author Dirk Westermann, MD, also from the University Heart and Vascular Centre, Hamburg, said.
Implications for heart failure
The postmortem findings from Dr. Lindner and associates “provide intriguing evidence that COVID-19 is associated with at least some component of myocardial injury, perhaps as the result of direct viral infection of the heart,” wrote Clyde W. Yancy, MD, MSc, from Northwestern University, Chicago, and Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, from the University of California, Los Angeles, in an editorial accompanying both reports.
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues – on the backdrop of earlier COVID-19 observations – suggests the potential for “residual left ventricular dysfunction and ongoing inflammation” in the months following a COVID-19 diagnosis. Both developments may be “of sufficient concern to represent a nidus for new-onset heart failure and other cardiovascular complications,” contend Dr. Yancy and Dr. Fonarow.
“When added to the postmortem pathological findings from Lindner et al, we see the plot thickening and we are inclined to raise a new and very evident concern that cardiomyopathy and heart failure related to COVID-19 may potentially evolve as the natural history of this infection becomes clearer,” they wrote.
Some patients, having recovered from the acute illness, may be left with a chronic inflammatory state that probably puts them at increased risk for future heart failure, agreed Dr. Bozkurt when interviewed. “They could show further decline in cardiac function, and their recovery might take longer than with the usual viral illnesses that we see,” she said.
“There could also be a risk of sudden death. Inflammation sometimes gives rise to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia, which I would be very worried about, especially if the myocardium is stressed,” Dr. Bozkurt said. “So competitive sports in those patients potentially could be risky.”
COVID-19 cohort vs. matched control subjects
The CMR study from Dr. Püntmann and colleagues prospectively entered 100 patients recently recovered from an acute bout of COVID-19, either at home or at a hospital, who were followed in a registry based at University Hospital Frankfurt. Their median age was 49 years; 47% were female. They were compared with 50 age- and sex-matched control patients and 50 apparently healthy volunteers matched for risk factors, the group noted.
On the same day as the CMR assessment, the recently recovered patients, compared with the healthy control subjects and risk-factor matched control subjects, respectively, showed (P ≤ .001 in each case):
- A reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction: 56% vs. 60% and 61%.
- A higher LV end-diastolic volume index: 86 mL/m2 vs. 80 mL/m2 and 75 mL/m2.
- A greater LV mass index: 51 g/m2 vs. 47 g/m2 and 53 g/m2.
- A higher hs-TnT level: 5.6 pg/mL vs. 3.2 pg/mL and 3.9 pg/mL.
- A greater prevalence of hs-TnT levels 3 pg/mL or more: 71% vs. 11% and 31%.
At CMR, 78% of the recovered COVID-19 patients showed abnormalities that included raised myocardial native T1 and T2 mapping, which is suggestive of fibrosis and edema from inflammation, compared with the two control groups (P < .001 for all differences), “independent of preexisting conditions, severity and overall course of the acute illness, and the time from the original diagnosis,” the group wrote. Native T1 and T2 mapping correlated significantly with hs-TnT.
“We now have the diagnostic means to detect cardiac inflammation early, and we need make every effort to apply them in every day practice,”Dr. Püntmann said in the interview.
“Using cardiac MRI will allow us to raise our game against COVID-19 and proactively develop efficient cardioprotective treatments,” she said. “Until we have effective means of protecting from the infection, that is vaccination, we must act swiftly and within the means at hand.”
The analysis evokes several other ways patients with COVID-19 might be screened for significant myocardial involvement.
“Strategies could include checking troponins, not only at admission but maybe at discharge and perhaps even those individuals who are at home and are not necessarily requiring care,” Dr. Bozkurt said.
“Biomarker profiling and screening for ongoing inflammation probably are going to be important components of COVID-19, especially for those with subclinical risk and disease.”
Dr. Westermann proposed that troponin elevations at discharge “might be a good starting point” for selecting COVID-19 patients for functional testing or imaging to screen for cardiac sequelae. Performing such tests routinely now “would be overwhelming given the massive increase in patients we still see today.”
Dr. Püntmann had no disclosures; statements of potential conflict for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Bozkurt has previously disclosed receiving consultant fees or honoraria from Bayer Healthcare, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lantheus Medical Imaging, and Respicardia; serving on a data safety monitoring board for LivaNova USA ; and having unspecified relationships with Abbott Laboratories. Dr. Lindner had no disclosures; Dr. Westermann reported receiving personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novartis, and Medtronic. Dr. Yancy is a deputy editor and Dr. Fonarow a section editor for JAMA Cardiology. Dr. Yancy had no other disclosures. Dr. Fonarow reported receiving personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CHF Solutions, Edwards Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
SCD-HeFT 10-year results: Primary-prevention ICD insights in nonischemic heart failure
A 10-year follow-up analysis based on one of cardiology’s most influential trials has shed further light on one of its key issues: how to sharpen selection of patients most likely to benefit from a primary prevention implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
In a new report from SCD-HeFT, the survival advantage in patients with heart failure seen 5 years after receiving ICDs, compared with a non-ICD control group, narrowed a bit but remained significant after an additional 5 years. But not all patients with devices shared in that long-term ICD benefit. Patients with either ischemic disease or nonischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM) with devices showed a similar mortality risk reduction in the trial’s previously reported 5-year outcomes. That advantage, compared with non-ICD control patients, persisted throughout the subsequent 5 years for ischemic patients but tapered to nil for those with NICM.
The NICM patients “had what appears to be some accrual of benefit maybe out to about 6 years, and then the curves appear to come together where there’s no apparent further benefit after 6 years,” Jeanne E. Poole, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
In both the 10-year analysis and the earlier results, ICD survival gains went preferentially to patients who enrolled with New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II symptoms. Patients who entered in NYHA class III “didn’t appear to have any benefit whatsoever” in either period, Dr. Poole said.
“The simple message is that the same groups of patients that benefited strongly from the ICD in the original SCD-HeFT – the NYHA class 2 patients and those with ischemic cardiomyopathy – were really the ones who benefited the greatest over the long term,” she said.
Dr. Poole is lead author on the SCD-HeFT 10-year analysis, which was published in the July 28 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Why the ICD survival effect disappeared midway in patients with NICM “is hard to sort out,” she said. Many in the control group were offered such devices after the trial concluded. Among those, it’s possible that disproportionately more control patients with NICM, compared with patients with ischemic disease, were fitted with ICDs that were also cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, Dr. Poole and her colleagues speculated. That could have shifted their late outcomes to be more in line with patients who had received ICDs when the trial started.
Or “it is possible that the intermediate-term benefit of ICD therapy in NICM is overwhelmed by nonarrhythmic death in extended follow-up” given that ICDs prolong survival only by preventing arrhythmic death, noted an editorial accompanying the new SCD-HeFT publication.
Another possibility: Because NICM is a heterogeneous disorder with many potential causes, perhaps “the absence of long-term mortality benefit among SCD-HeFT participants with NICM was due to an unintended but preferential enrollment of subtypes at relatively lower risk for arrhythmic death in the longer term,” proposed Eric C. Stecker, MD, MPH, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and coauthors in their editorial.
“What are the take-away messages from the current analysis by Poole et al?” they asked. “These findings strongly support the clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of ICD therapy for the majority of patients with severe but mildly symptomatic ischemic cardiomyopathy who do not have an excessive comorbidity burden.”
But “the implications for patients with NICM are less clear,” they wrote. “Given evidence for intermediate-term benefit and the limitations inherent to assessing longer-term benefit, we do not believe it is appropriate to walk back guideline recommendations regarding ICD implantation for NICM patients.”
The findings in nonischemic patients invite comparison with the randomized DANISH trial, which entered only patients with NICM and, over more than 5 years, saw no primary-prevention ICD advantage for the end point of all-cause mortality.
But patients who received ICDs showed a reduction in arrhythmic death, a secondary end point. And mortality in the trial showed a significant interaction with patient age; survival went up sharply with ICDs for those younger than 60 years.
Also in DANISH, “the ICD treatment effect appears to vary over time, with an earlier phase showing possible survival benefit and a later phase showing attenuation of that benefit,” similar to what was seen long-term in SCD-HeFT, in which the interaction between mortality and time since implantation was significant at P = .0015, observe Dr. Poole and colleagues.
However, Dr. Poole cautioned when interviewed, patient management in DANISH, conducted exclusively in Denmark, may not have been representative of the rest of the world, complicating comparisons with other studies. For example, nearly 60% of all patients in DANISH had defibrillating CRT devices. Virtually everyone was on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, and almost 60% were taking aldosterone inhibitors.
“DANISH is an unusually high bar and probably does not reflect all patients with heart failure, and certainly does not reflect patients in the United States in terms of those high levels of guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Poole said. The message from DANISH, she said, seems to be that patients with NICM who are definitely on goal-directed heart failure medications with CRT devices “probably don’t have a meaningful benefit from an ICD, on total mortality, because their sudden death rates are simply so low.”
SCD-HeFT had originally assigned 2,521 patients with heart failure of NYHA class II or III and an left ventricular ejection fraction of less than 35% to receive an ICD, amiodarone without an ICD, or an amiodarone placebo and no ICD; patients in the latter cohorts made up the non-ICD control group.
Those who received an ICD, compared with the non-ICD control patients, showed a 23% drop in all-cause mortality over a median of 45.5 months ending on October 31, 2003, Dr. Poole and colleagues noted in their current report. The trial’s primary results were unveiled 2005.
The current analysis, based on data collected in 2010 and 2011, followed the 1,855 patients alive at the trial’s official conclusion and combined outcomes before and after that time for a median follow-up of 11 years, Dr. Poole and colleagues reported.
In the ICD group, the overall hazard ratio for mortality by intention-to-treat was 0.87 (95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98; P = .028), compared with the non-ICD control group.
In their report, Poole and associates clarified one of the foremost potential confounders in the current analysis: device implantations after the trial in patients who had been in the non-ICD groups. From partial clinical data collected after the trial, they wrote, the estimated rate of subsequent ICD implantation in non-ICD control patients was about 55%. Such a low number is consistent with clinical practice in the United States, where “a surprisingly low number of patients who are eligible actually end up getting devices,” Dr. Poole said.
Subsequent ICD use in the former non-ICD control patients presumably boosted their survival over the long term, narrowing the gap between their all-cause mortality and that of the original ICD patients, Dr. Poole observed. Despite that, the ICD-group’s late survival advantage remained significant.
SCD-HeFT was sponsored by Medtronic, Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The current analysis was partially supported by a grant from St. Jude Medical. Dr. Poole disclosed receiving research support from Medtronic, Biotronik, AtriCure, and Kestra; serving as a speaker for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and MediaSphere Medical and on an advisory board for Boston Scientific; serving on a committee for Medtronic and on a data and safety monitoring board for EBR Systems; and receiving royalties from Elsevier and compensation from the Heart Rhythm Society for serving as editor in chief for the Heart Rhythm O2 journal. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Stecker and coauthors disclosed that they have no relevant relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A 10-year follow-up analysis based on one of cardiology’s most influential trials has shed further light on one of its key issues: how to sharpen selection of patients most likely to benefit from a primary prevention implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
In a new report from SCD-HeFT, the survival advantage in patients with heart failure seen 5 years after receiving ICDs, compared with a non-ICD control group, narrowed a bit but remained significant after an additional 5 years. But not all patients with devices shared in that long-term ICD benefit. Patients with either ischemic disease or nonischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM) with devices showed a similar mortality risk reduction in the trial’s previously reported 5-year outcomes. That advantage, compared with non-ICD control patients, persisted throughout the subsequent 5 years for ischemic patients but tapered to nil for those with NICM.
The NICM patients “had what appears to be some accrual of benefit maybe out to about 6 years, and then the curves appear to come together where there’s no apparent further benefit after 6 years,” Jeanne E. Poole, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
In both the 10-year analysis and the earlier results, ICD survival gains went preferentially to patients who enrolled with New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II symptoms. Patients who entered in NYHA class III “didn’t appear to have any benefit whatsoever” in either period, Dr. Poole said.
“The simple message is that the same groups of patients that benefited strongly from the ICD in the original SCD-HeFT – the NYHA class 2 patients and those with ischemic cardiomyopathy – were really the ones who benefited the greatest over the long term,” she said.
Dr. Poole is lead author on the SCD-HeFT 10-year analysis, which was published in the July 28 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Why the ICD survival effect disappeared midway in patients with NICM “is hard to sort out,” she said. Many in the control group were offered such devices after the trial concluded. Among those, it’s possible that disproportionately more control patients with NICM, compared with patients with ischemic disease, were fitted with ICDs that were also cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, Dr. Poole and her colleagues speculated. That could have shifted their late outcomes to be more in line with patients who had received ICDs when the trial started.
Or “it is possible that the intermediate-term benefit of ICD therapy in NICM is overwhelmed by nonarrhythmic death in extended follow-up” given that ICDs prolong survival only by preventing arrhythmic death, noted an editorial accompanying the new SCD-HeFT publication.
Another possibility: Because NICM is a heterogeneous disorder with many potential causes, perhaps “the absence of long-term mortality benefit among SCD-HeFT participants with NICM was due to an unintended but preferential enrollment of subtypes at relatively lower risk for arrhythmic death in the longer term,” proposed Eric C. Stecker, MD, MPH, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and coauthors in their editorial.
“What are the take-away messages from the current analysis by Poole et al?” they asked. “These findings strongly support the clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of ICD therapy for the majority of patients with severe but mildly symptomatic ischemic cardiomyopathy who do not have an excessive comorbidity burden.”
But “the implications for patients with NICM are less clear,” they wrote. “Given evidence for intermediate-term benefit and the limitations inherent to assessing longer-term benefit, we do not believe it is appropriate to walk back guideline recommendations regarding ICD implantation for NICM patients.”
The findings in nonischemic patients invite comparison with the randomized DANISH trial, which entered only patients with NICM and, over more than 5 years, saw no primary-prevention ICD advantage for the end point of all-cause mortality.
But patients who received ICDs showed a reduction in arrhythmic death, a secondary end point. And mortality in the trial showed a significant interaction with patient age; survival went up sharply with ICDs for those younger than 60 years.
Also in DANISH, “the ICD treatment effect appears to vary over time, with an earlier phase showing possible survival benefit and a later phase showing attenuation of that benefit,” similar to what was seen long-term in SCD-HeFT, in which the interaction between mortality and time since implantation was significant at P = .0015, observe Dr. Poole and colleagues.
However, Dr. Poole cautioned when interviewed, patient management in DANISH, conducted exclusively in Denmark, may not have been representative of the rest of the world, complicating comparisons with other studies. For example, nearly 60% of all patients in DANISH had defibrillating CRT devices. Virtually everyone was on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, and almost 60% were taking aldosterone inhibitors.
“DANISH is an unusually high bar and probably does not reflect all patients with heart failure, and certainly does not reflect patients in the United States in terms of those high levels of guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Poole said. The message from DANISH, she said, seems to be that patients with NICM who are definitely on goal-directed heart failure medications with CRT devices “probably don’t have a meaningful benefit from an ICD, on total mortality, because their sudden death rates are simply so low.”
SCD-HeFT had originally assigned 2,521 patients with heart failure of NYHA class II or III and an left ventricular ejection fraction of less than 35% to receive an ICD, amiodarone without an ICD, or an amiodarone placebo and no ICD; patients in the latter cohorts made up the non-ICD control group.
Those who received an ICD, compared with the non-ICD control patients, showed a 23% drop in all-cause mortality over a median of 45.5 months ending on October 31, 2003, Dr. Poole and colleagues noted in their current report. The trial’s primary results were unveiled 2005.
The current analysis, based on data collected in 2010 and 2011, followed the 1,855 patients alive at the trial’s official conclusion and combined outcomes before and after that time for a median follow-up of 11 years, Dr. Poole and colleagues reported.
In the ICD group, the overall hazard ratio for mortality by intention-to-treat was 0.87 (95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98; P = .028), compared with the non-ICD control group.
In their report, Poole and associates clarified one of the foremost potential confounders in the current analysis: device implantations after the trial in patients who had been in the non-ICD groups. From partial clinical data collected after the trial, they wrote, the estimated rate of subsequent ICD implantation in non-ICD control patients was about 55%. Such a low number is consistent with clinical practice in the United States, where “a surprisingly low number of patients who are eligible actually end up getting devices,” Dr. Poole said.
Subsequent ICD use in the former non-ICD control patients presumably boosted their survival over the long term, narrowing the gap between their all-cause mortality and that of the original ICD patients, Dr. Poole observed. Despite that, the ICD-group’s late survival advantage remained significant.
SCD-HeFT was sponsored by Medtronic, Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The current analysis was partially supported by a grant from St. Jude Medical. Dr. Poole disclosed receiving research support from Medtronic, Biotronik, AtriCure, and Kestra; serving as a speaker for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and MediaSphere Medical and on an advisory board for Boston Scientific; serving on a committee for Medtronic and on a data and safety monitoring board for EBR Systems; and receiving royalties from Elsevier and compensation from the Heart Rhythm Society for serving as editor in chief for the Heart Rhythm O2 journal. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Stecker and coauthors disclosed that they have no relevant relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A 10-year follow-up analysis based on one of cardiology’s most influential trials has shed further light on one of its key issues: how to sharpen selection of patients most likely to benefit from a primary prevention implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
In a new report from SCD-HeFT, the survival advantage in patients with heart failure seen 5 years after receiving ICDs, compared with a non-ICD control group, narrowed a bit but remained significant after an additional 5 years. But not all patients with devices shared in that long-term ICD benefit. Patients with either ischemic disease or nonischemic cardiomyopathy (NICM) with devices showed a similar mortality risk reduction in the trial’s previously reported 5-year outcomes. That advantage, compared with non-ICD control patients, persisted throughout the subsequent 5 years for ischemic patients but tapered to nil for those with NICM.
The NICM patients “had what appears to be some accrual of benefit maybe out to about 6 years, and then the curves appear to come together where there’s no apparent further benefit after 6 years,” Jeanne E. Poole, MD, of the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
In both the 10-year analysis and the earlier results, ICD survival gains went preferentially to patients who enrolled with New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II symptoms. Patients who entered in NYHA class III “didn’t appear to have any benefit whatsoever” in either period, Dr. Poole said.
“The simple message is that the same groups of patients that benefited strongly from the ICD in the original SCD-HeFT – the NYHA class 2 patients and those with ischemic cardiomyopathy – were really the ones who benefited the greatest over the long term,” she said.
Dr. Poole is lead author on the SCD-HeFT 10-year analysis, which was published in the July 28 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Why the ICD survival effect disappeared midway in patients with NICM “is hard to sort out,” she said. Many in the control group were offered such devices after the trial concluded. Among those, it’s possible that disproportionately more control patients with NICM, compared with patients with ischemic disease, were fitted with ICDs that were also cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices, Dr. Poole and her colleagues speculated. That could have shifted their late outcomes to be more in line with patients who had received ICDs when the trial started.
Or “it is possible that the intermediate-term benefit of ICD therapy in NICM is overwhelmed by nonarrhythmic death in extended follow-up” given that ICDs prolong survival only by preventing arrhythmic death, noted an editorial accompanying the new SCD-HeFT publication.
Another possibility: Because NICM is a heterogeneous disorder with many potential causes, perhaps “the absence of long-term mortality benefit among SCD-HeFT participants with NICM was due to an unintended but preferential enrollment of subtypes at relatively lower risk for arrhythmic death in the longer term,” proposed Eric C. Stecker, MD, MPH, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and coauthors in their editorial.
“What are the take-away messages from the current analysis by Poole et al?” they asked. “These findings strongly support the clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness of ICD therapy for the majority of patients with severe but mildly symptomatic ischemic cardiomyopathy who do not have an excessive comorbidity burden.”
But “the implications for patients with NICM are less clear,” they wrote. “Given evidence for intermediate-term benefit and the limitations inherent to assessing longer-term benefit, we do not believe it is appropriate to walk back guideline recommendations regarding ICD implantation for NICM patients.”
The findings in nonischemic patients invite comparison with the randomized DANISH trial, which entered only patients with NICM and, over more than 5 years, saw no primary-prevention ICD advantage for the end point of all-cause mortality.
But patients who received ICDs showed a reduction in arrhythmic death, a secondary end point. And mortality in the trial showed a significant interaction with patient age; survival went up sharply with ICDs for those younger than 60 years.
Also in DANISH, “the ICD treatment effect appears to vary over time, with an earlier phase showing possible survival benefit and a later phase showing attenuation of that benefit,” similar to what was seen long-term in SCD-HeFT, in which the interaction between mortality and time since implantation was significant at P = .0015, observe Dr. Poole and colleagues.
However, Dr. Poole cautioned when interviewed, patient management in DANISH, conducted exclusively in Denmark, may not have been representative of the rest of the world, complicating comparisons with other studies. For example, nearly 60% of all patients in DANISH had defibrillating CRT devices. Virtually everyone was on ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, and almost 60% were taking aldosterone inhibitors.
“DANISH is an unusually high bar and probably does not reflect all patients with heart failure, and certainly does not reflect patients in the United States in terms of those high levels of guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Poole said. The message from DANISH, she said, seems to be that patients with NICM who are definitely on goal-directed heart failure medications with CRT devices “probably don’t have a meaningful benefit from an ICD, on total mortality, because their sudden death rates are simply so low.”
SCD-HeFT had originally assigned 2,521 patients with heart failure of NYHA class II or III and an left ventricular ejection fraction of less than 35% to receive an ICD, amiodarone without an ICD, or an amiodarone placebo and no ICD; patients in the latter cohorts made up the non-ICD control group.
Those who received an ICD, compared with the non-ICD control patients, showed a 23% drop in all-cause mortality over a median of 45.5 months ending on October 31, 2003, Dr. Poole and colleagues noted in their current report. The trial’s primary results were unveiled 2005.
The current analysis, based on data collected in 2010 and 2011, followed the 1,855 patients alive at the trial’s official conclusion and combined outcomes before and after that time for a median follow-up of 11 years, Dr. Poole and colleagues reported.
In the ICD group, the overall hazard ratio for mortality by intention-to-treat was 0.87 (95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98; P = .028), compared with the non-ICD control group.
In their report, Poole and associates clarified one of the foremost potential confounders in the current analysis: device implantations after the trial in patients who had been in the non-ICD groups. From partial clinical data collected after the trial, they wrote, the estimated rate of subsequent ICD implantation in non-ICD control patients was about 55%. Such a low number is consistent with clinical practice in the United States, where “a surprisingly low number of patients who are eligible actually end up getting devices,” Dr. Poole said.
Subsequent ICD use in the former non-ICD control patients presumably boosted their survival over the long term, narrowing the gap between their all-cause mortality and that of the original ICD patients, Dr. Poole observed. Despite that, the ICD-group’s late survival advantage remained significant.
SCD-HeFT was sponsored by Medtronic, Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The current analysis was partially supported by a grant from St. Jude Medical. Dr. Poole disclosed receiving research support from Medtronic, Biotronik, AtriCure, and Kestra; serving as a speaker for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and MediaSphere Medical and on an advisory board for Boston Scientific; serving on a committee for Medtronic and on a data and safety monitoring board for EBR Systems; and receiving royalties from Elsevier and compensation from the Heart Rhythm Society for serving as editor in chief for the Heart Rhythm O2 journal. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Stecker and coauthors disclosed that they have no relevant relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Low vitamin D linked to increased COVID-19 risk
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Low plasma vitamin D levels emerged as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization in a large, population-based study.
Participants positive for COVID-19 were 50% more likely to have low vs normal 25(OH)D levels in a multivariate analysis that controlled for other confounders, for example.
The take home message for physicians is to “test patients’ vitamin D levels and keep them optimal for the overall health – as well as for a better immunoresponse to COVID-19,” senior author Milana Frenkel-Morgenstern, PhD, head of the Cancer Genomics and BioComputing of Complex Diseases Lab at Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, Israel, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 23 in The FEBS Journal.
Previous and ongoing studies are evaluating a potential role for vitamin D to prevent or minimize the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection, building on years of research addressing vitamin D for other viral respiratory infections. The evidence to date regarding COVID-19, primarily observational studies, has yielded mixed results.
Multiple experts weighed in on the controversy in a previous report. Many point out the limitations of observational data, particularly when it comes to ruling out other factors that could affect the severity of COVID-19 infection. In addition, in a video report, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, DrPH, of Harvard Medical School in Boston, cited an observational study from three South Asian hospitals that found more severe COVID-19 patients had lower vitamin D levels, as well as other “compelling evidence” suggesting an association.
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues studied data for 7,807 people, of whom 10.1% were COVID-19 positive. They assessed electronic health records for demographics, potential confounders, and outcomes between February 1 and April 30.
Participants positive for COVID-19 tended to be younger and were more likely to be men and live in a lower socioeconomic area, compared with the participants who were negative for COVID-19, in a univariate analysis.
Key findings
A higher proportion of COVID-19–positive patients had low plasma 25(OH)D concentrations, about 90% versus 85% of participants who were negative for COVID-19. The difference was statistically significant (P < .001). Furthermore, the increased likelihood for low vitamin D levels among those positive for COVID-19 held in a multivariate analysis that controlled for demographics and psychiatric and somatic disorders (adjusted odds ratio, 1.50). The difference remained statistically significant (P < .001).
The study also was noteworthy for what it did not find among participants with COVID-19. For example, the prevalence of dementia, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disorders, and hypertension were significantly higher among the COVID-19 negative participants.
“Severe social contacts restrictions that were imposed on all the population and were even more emphasized in this highly vulnerable population” could explain these findings, the researchers noted.
“We assume that following the Israeli Ministry of Health instructions, patients with chronic medical conditions significantly reduced their social contacts” and thereby reduced their infection risk.
In contrast to previous reports, obesity was not a significant factor associated with increased likelihood for COVID-19 infection or hospitalization in the current study.
The researchers also linked low plasma 25(OH)D level to an increased likelihood of hospitalization for COVID-19 infection (crude OR, 2.09; P < .05).
After controlling for demographics and chronic disorders, the aOR decreased to 1.95 (P = .061) in a multivariate analysis. The only factor that remained statistically significant for hospitalization was age over 50 years (aOR, 2.71; P < .001).
Implications and future plans
The large number of participants and the “real world,” population-based design are strengths of the study. Considering potential confounders is another strength, the researchers noted. The retrospective database design was a limitation.
Going forward, Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern and colleagues will “try to decipher the potential role of vitamin D in prevention and/or treatment of COVID-19” through three additional studies, she said. Also, they would like to conduct a meta-analysis to combine data from different countries to further explore the potential role of vitamin D in COVID-19.
“A compelling case”
“This is a strong study – large, adjusted for confounders, consistent with the biology and other clinical studies of vitamin D, infections, and COVID-19,” Wayne Jonas, MD, a practicing family physician and executive director of Samueli Integrative Health Programs, said in an interview.
Because the research was retrospective and observational, a causative link between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 risk cannot be interpreted from the findings. “That would need a prospective, randomized study,” said Dr. Jonas, who was not involved with the current study.
However, “the study makes a compelling case for possibly screening vitamin D levels for judging risk of COVID infection and hospitalization,” Dr. Jonas said, “and the compelling need for a large, randomized vitamin D supplement study to see if it can help prevent infection.”
“Given that vitamin D is largely safe, such a study could be done quickly and on healthy people with minimal risk for harm,” he added.
More confounders likely?
“I think the study is of interest,” Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, who also was not affiliated with the research, said in an interview.
“Whilst the authors adjusted for some confounders, there is a strong potential for residual confounding,” said Dr. Sattar, a coauthor of a UK Biobank study that did not find an association between vitamin D stages and COVID-19 infection in multivariate models.
For example, Dr. Sattar said, “Robust adjustment for social class is important since both Vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity are both strongly associated with social class.” Further, it remains unknown when and what time of year the vitamin D concentrations were measured in the current study.
“In the end, only a robust randomized trial can tell us whether vitamin D supplementation helps lessen COVID-19 severity,” Dr. Sattar added. “I am not hopeful we will find this is the case – but I am glad some such trials are [ongoing].”
Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern received a COVID-19 Data Sciences Institute grant to support this work. Dr. Frenkel-Morgenstern, Dr. Jonas, and Dr. Sattar have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypertension medication adjustment less likely with polypill
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
A secondary analysis of a major study of polypill therapy for hypertension found that patients who don’t reach blood pressure targets are less likely to have their medications adjusted if they’re on fixed-dose combination therapy.
However, hypertension patients on low-dose, triple-pill combination therapy are more likely to achieve blood pressure control than are those on usual care.
The secondary analysis of Triple Pill vs. Usual Care Management for Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Hypertension (TRIUMPH) was published online in JAMA Cardiology (2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739). The trial randomized 700 patients with hypertension in Sri Lanka to triple-pill fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy or usual care during February 2016–May 2017, with follow-up ending in October 2017.
A greater proportion of FDC patients reached target BP by the end of the study compared with usual care, 70% vs. 55%. However, the study found that therapeutic inertia – the failure to intensify therapy in nonresponsive patients – was more common in the FDC group at 6- and 12-week follow-up: 87% vs. 64% and 90% vs. 65%, respectively; both differences were significant different at P < .001).
The once-daily FDC pill contained telmisartan 20 mg, amlodipine 2.5 mg; and chlorthalidone 12.5 mg.
“Using a triple low-dose combination blood-pressure pill reduced the need to uptitrate BP therapy as more patients are at target, but doctors were less likely to uptitrate with triple-pill therapy when it was needed,” lead author Nelson Wang, MD, a research fellow at the George Institute for Global Health in suburban Sydney, said in an interview.
“Overall, there were fewer treatment inertia episodes in the triple-pill group than in the usual care group, but this was driven by the fact that fewer triple-pill patients needed uptitration when coming to their follow-up visits,” Dr. Wang added.
The analysis found that clinicians who prescribed triple-pill FDC used 23 unique drug treatment regimens per 100 treated patients compared with 54 different regiments with usual care (P < .001). “There was a large simplification in care,” Dr. Wang said of the FDC approach.
Dr. Wang and colleagues called for greater efforts to address therapeutic inertia, particularly with FDC therapies, and suggested potential strategies consisting of patient education, incentives for appropriate treatment adjustments, and feedback mechanisms and reminders for physicians.
“There may also be a need for more dosage options with the FDC triple pill to allow physicians to intensify therapy without fear of overtreatment and adverse drug effects,” they wrote.
In an accompanying editorial (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 Jul 22. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2693), Ann Marie Navar, MD, PhD, associate professor of cardiology at Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., noted that initiating treatment with FDC therapy doesn’t preclude a more personalized approach for patients who don’t achieve their BP target. “The real choice now is the choice of initial treatment,” she wrote, adding that future treatment guidelines should consider extending an FDC-first approach to patients with less severe levels of hypertension.
“The study showed there’s room for a both a population-based fixed-drug combination approach and a personalized approach to how we think about hypertension management with fixed-dose therapy,” she said in an interview. “It’s not a one-and-done situation.”
Dr. Wang has no financial relationships to disclose. Study coauthors received funding from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Dr. Navar has no relevant financial relationships to report.
SOURCE: Wang N et al. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.2739.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
COVID-19 fears would keep most Hispanics with stroke, MI symptoms home
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.
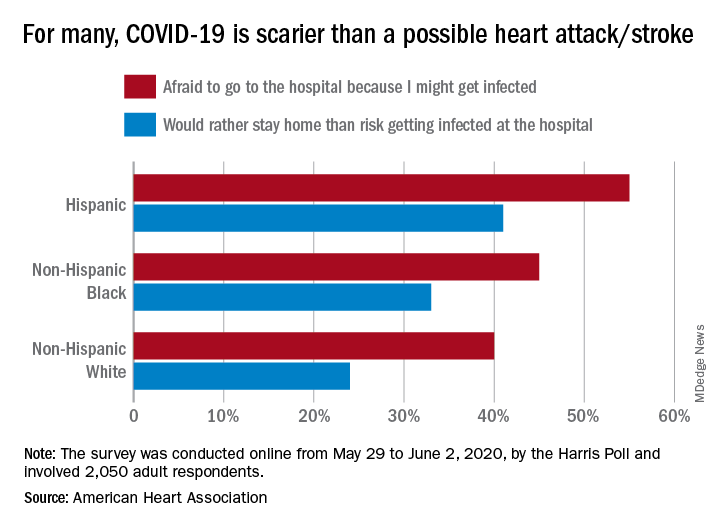
Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.

Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
More than half of Hispanic adults would be afraid to go to a hospital for a possible heart attack or stroke because they might get infected with SARS-CoV-2, according to a new survey from the American Heart Association.

Compared with Hispanic respondents, 55% of whom said they feared COVID-19, significantly fewer Blacks (45%) and Whites (40%) would be scared to go to the hospital if they thought they were having a heart attack or stroke, the AHA said based on the survey of 2,050 adults, which was conducted May 29 to June 2, 2020, by the Harris Poll.
Hispanics also were significantly more likely to stay home if they thought they were experiencing a heart attack or stroke (41%), rather than risk getting infected at the hospital, than were Blacks (33%), who were significantly more likely than Whites (24%) to stay home, the AHA reported.
White respondents, on the other hand, were the most likely to believe (89%) that a hospital would give them the same quality of care provided to everyone else. Hispanics and Blacks had significantly lower rates, at 78% and 74%, respectively, the AHA noted.
These findings are “yet another challenge for Black and Hispanic communities, who are more likely to have underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes and dying of COVID-19 at disproportionately high rates,” Rafael Ortiz, MD, American Heart Association volunteer medical expert and chief of neuro-endovascular surgery at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, said in the AHA statement.
The survey was performed in conjunction with the AHA’s “Don’t Die of Doubt” campaign, which “reminds Americans, especially in Hispanic and Black communities, that the hospital remains the safest place to be if experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke.”
Among all the survey respondents, 57% said they would feel better if hospitals treated COVID-19 patients in a separate area. A number of other possible precautions ranked lower in helping them feel better:
- Screen all visitors, patients, and staff for COVID-19 symptoms when they enter the hospital: 39%.
- Require all patients, visitors, and staff to wear masks: 30%.
- Put increased cleaning protocols in place to disinfect multiple times per day: 23%.
- “Nothing would make me feel comfortable”: 6%.
Despite all the concerns about the risk of coronavirus infection, however, most Americans (77%) still believe that hospitals are the safest place to be in the event of a medical emergency, and 84% said that hospitals are prepared to safely treat emergencies that are not related to the pandemic, the AHA reported.
“Health care professionals know what to do even when things seem chaotic, and emergency departments have made plans behind the scenes to keep patients and healthcare workers safe even during a pandemic,” Dr. Ortiz pointed out.
Cleaner data confirm severe COVID-19 link to diabetes, hypertension
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
Further refinement of data from patients hospitalized worldwide for COVID-19 disease showed a 12% prevalence rate of patients with diabetes in this population and a 17% prevalence rate for hypertension.
These are lower rates than previously reported for COVID-19 patients with either of these two comorbidities, yet the findings still document important epidemiologic links between diabetes, hypertension, and COVID-19, said the study’s authors.
A meta-analysis of data from 15,794 patients hospitalized because of COVID-19 disease that was drawn from 65 carefully curated reports published from December 1, 2019, to April 6, 2020, also showed that, among the hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes (either type 1 or type 2), the rate of patients who required ICU admission was 96% higher than among those without diabetes and mortality was 2.78-fold higher, both statistically significant differences.
The rate of ICU admissions among those hospitalized with COVID-19 who also had hypertension was 2.95-fold above those without hypertension, and mortality was 2.39-fold higher, also statistically significant differences, reported a team of researchers in the recently published report.
The new meta-analysis was notable for the extra effort investigators employed to eliminate duplicated patients from their database of COVID-19 patients included in various published reports, a potential source of bias that likely introduced errors into prior meta-analyses that used similar data. “We found an overwhelming proportion of studies at high risk of data repetition,” the report said. Virtually all of the included studies were retrospective case studies, nearly two-thirds had data from a single center, and 71% of the studies included only patients in China.
“We developed a method to identify reports that had a high risk for repetitions” of included patients, said Fady Hannah-Shmouni, MD, a senior author of the study. “We also used methods to minimize bias, we excluded certain patients populations, and we applied a uniform definition of COVID-19 disease severity,” specifically patients who died or needed ICU admission, because the definitions used originally by many of the reports were very heterogeneous, said Dr. Hannah-Shmouni, principal investigator for Endocrine, Genetics, and Hypertension at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Despite the effort to eliminate case duplications, the analysis remains subject to additional confounders, in part because of a lack of comprehensive patient information on factors such as smoking, body mass index, socioeconomic status, and the specific type of diabetes or hypertension a patient had. “Even with these limitations, we were able to show that the prevalence of hypertension and diabetes is elevated in patients with COVID-19, that patients with diabetes have increased risk for both death and ICU admissions, and that there is the potential for reverse causality in the reporting of hypertension as a risk factor for COVID-19,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said in an interview. “We believe the explosion of data that associated hypertension and COVID-19 may be partially the result of reverse causality.”
One possible example of this reverse causality is the overlap between hypertension and age as potential risk factors for COVID-19 disease or increased infection severity. People “older than 80 frequently develop severe disease if infected with the novel coronavirus, and 80% of people older than 80 have hypertension, so it’s not surprising that hypertension is highly prevalent among hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” but this “does not imply a causal relationship between hypertension and severe COVID-19; the risk of hypertension probably depends on older age,” noted Ernesto L. Schiffrin, MD, a coauthor of the study, as well as professor of medicine at McGill University and director of the Hypertension and Vascular Research Unit at the Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, both in Montreal. “My current opinion, on the basis of the totality of data, is that hypertension does not worsen [COVID-19] outcomes, but patients who are elderly, obese, diabetic, or immunocompromised are susceptible to more severe COVID-19 and worse outcomes,” said Dr. Schiffrin in an interview.
The new findings show “there is certainly an interplay between the virus, diabetes, and hypertension and other risk factors,” and while still limited by biases, the new findings “get closer” to correctly estimating the COVID-19 risks associated with these comorbidities,” Dr. Hannah-Shmouni said.
The connections identified between COVID-19, diabetes, and hypertension mean that patients with these chronic diseases should receive education about their COVID-19 risks and should have adequate access to the drugs and supplies they need to control blood pressure and hyperglycemia. Patients with diabetes also need to be current on vaccinations to reduce their risk for pneumonia. And recognition of the heightened COVID-19 risk for people with these comorbidities is important among people who work in relevant government agencies, health care workers, and patient advocacy groups, he added.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Hannah-Shmouni and Dr. Schiffrin had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Barrera FJ et al. J Endocn Soc. 2020 July 21. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa102.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE ENDOCRINE SOCIETY