User login
EMERGENCY MEDICINE is a practical, peer-reviewed monthly publication and Web site that meets the educational needs of emergency clinicians and urgent care clinicians for their practice.
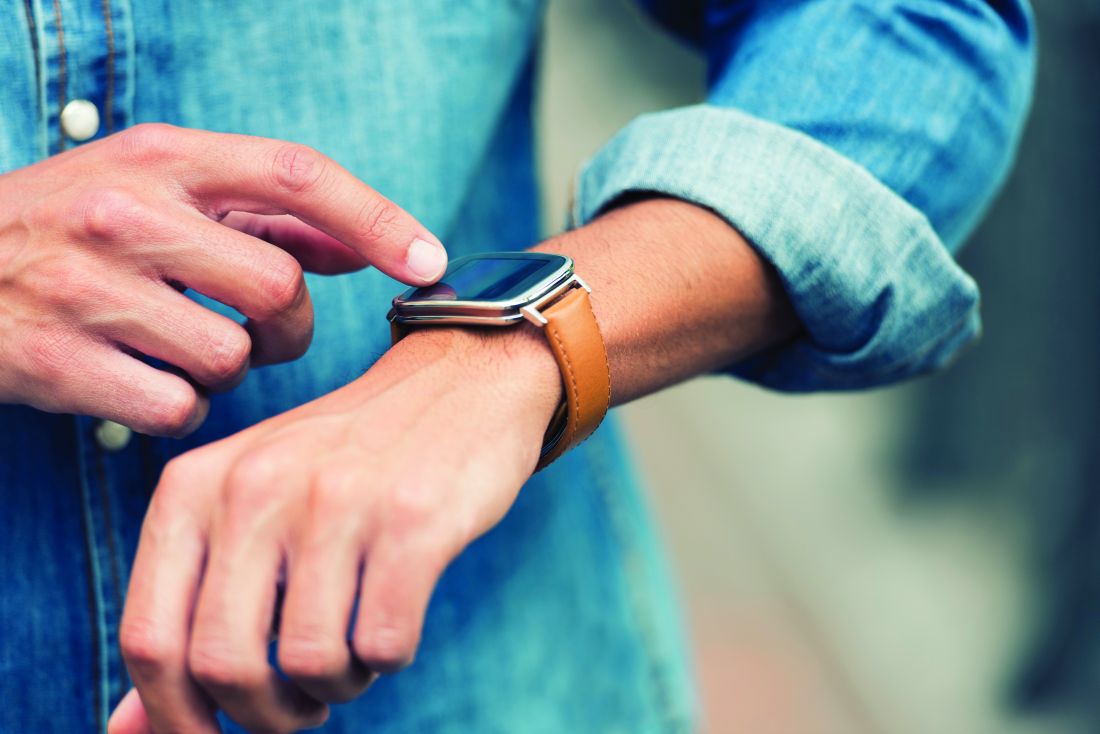
Biometric changes on fitness trackers, smartwatches detect COVID-19
A smartphone app that combines passively collected physiologic data from wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, and self-reported symptoms can discriminate between COVID-19–positive and –negative individuals among those who report symptoms, new data suggest.
After analyzing data from more than 30,000 participants, researchers from the Digital Engagement and Tracking for Early Control and Treatment (DETECT) study concluded that adding individual changes in sensor data improves models based on symptoms alone for differentiating symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 positive and symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 negative.
The combination can potentially identify infection clusters before wider community spread occurs, Giorgio Quer, PhD, and colleagues report in an article published online Oct. 29 in Nature Medicine. DETECT investigators note that marrying participant-reported symptoms with personal sensor data, such as deviation from normal sleep duration and resting heart rate, resulted in an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (interquartile range [IQR], 0.73-0.86) for differentiating between symptomatic individuals who were positive and those who were negative for COVID-19.
“By better characterizing each individual’s unique baseline, you can then identify changes that may indicate that someone has a viral illness,” said Dr. Quer, director of artificial intelligence at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. “In previous research, we found that the proportion of individuals with elevated resting heart rate and sleep duration compared with their normal could significantly improve real-time detection of influenza-like illness rates at the state level,” he said in an interview.
Thus, continuous passively captured data may be a useful adjunct to bricks-and-mortar site testing, which is generally a one-off or infrequent sampling assay and is not always easily accessible, he added. Furthermore, traditional screening with temperature and symptom reporting is inadequate. An elevation in temperature is not as common as frequently believed for people who test positive for COVID-19, Dr. Quer continued. “Early identification via sensor variables of those who are presymptomatic or even asymptomatic would be especially valuable, as people may potentially be infectious during this period, and early detection is the ultimate goal,” Dr. Quer said.
According to his group, adding these physiologic changes from baseline values significantly outperformed detection (P < .01) using a British model described in an earlier study by by Cristina Menni, PhD, and associates. That method, in which symptoms were considered alone, yielded an AUC of 0.71 (IQR, 0.63-0.79).
According to Dr. Quer, one in five Americans currently wear an electronic device. “If we could enroll even a small percentage of these individuals, we’d be able to potentially identify clusters before they have the opportunity to spread,” he said.
DETECT study details
During the period March 15 to June 7, 2020, the study enrolled 30,529 participants from all 50 states. They ranged in age from younger than 35 years (23.1%) to older than 65 years (12.8%); the majority (63.5%) were aged 35-65 years, and 62% were women. Sensor devices in use by the cohort included Fitbit activity trackers (78.4%) and Apple HealthKit (31.2%).
Participants downloaded an app called MyDataHelps, which collects smartwatch and activity tracker information, including self-reported symptoms and diagnostic testing results. The app also monitors changes from baseline in resting heart rate, sleep duration, and physical activity, as measured by steps.
Overall, 3,811 participants reported having at least one symptom of some kind (e.g., fatigue, cough, dyspnea, loss of taste or smell). Of these, 54 reported testing positive for COVID-19, and 279 reported testing negative.
Sleep and activity were significantly different for the positive and negative groups, with an AUC of 0.68 (IQR, 0.57-0.79) for the sleep metric and 0.69 (IQR, 0.61-0.77) for the activity metric, suggesting that these parameters were more affected in COVID-19–positive participants.
When the investigators combined resting heart rate, sleep, and activity into a single metric, predictive performance improved to an AUC of 0.72 (IQR, 0.64-0.80).
The next step, Dr. Quer said, is to include an alert to notify users of possible infection.
Alerting users to possible COVID-19 infection
In a similar study, an alert feature was already incorporated. The study, led by Michael P. Snyder, PhD, director of the Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, will soon be published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering. In that study, presymptomatic detection of COVID-19 was achieved in more than 80% of participants using resting heart rate.
“The median is 4 days prior to symptom formation,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “We have an alarm system to notify people when their heart rate is elevated. So a positive signal from a smartwatch can be used to follow up by polymerase chain reaction [testing].”
Dr. Snyder said these approaches offer a roadmap to containing widespread infections. “Public health authorities need to be open to these technologies and begin incorporating them into their tracking,” he said. “Right now, people do temperature checks, which are of limited value. Resting heart rate is much better information.”
Although the DETECT researchers have not yet received feedback on their results, they believe public health authorities could recommend the use of such apps. “These are devices that people routinely wear for tracking their fitness and sleep, so it would be relatively easy to use the data for viral illness tracking,” said co–lead author Jennifer Radin, PhD, an epidemiologist at Scripps. “Testing resources are still limited and don’t allow for routine serial testing of individuals who may be asymptomatic or presymptomatic. Wearables can offer a different way to routinely monitor and screen people for changes in their data that may indicate COVID-19.”
The marshaling of data through consumer digital platforms to fight the coronavirus is gaining ground. New York State and New Jersey are already embracing smartphone apps to alert individuals to possible exposure to the virus.
More than 710,000 New Yorkers have downloaded the COVID NY Alert app, launched in October to help protect individuals and communities from COVID-19 by sending alerts without compromising privacy or personal information. “Upon receiving a notification about a potential exposure, users are then able to self-quarantine, get tested, and reduce the potential exposure risk to family, friends, coworkers, and others,” Jonah Bruno, a spokesperson for the New York State Department of Health, said in an interview.
And recently the Mayo Clinic and Safe Health Systems launched a platform to store COVID-19 testing and vaccination data.
Both the Scripps and Stanford platforms are part of a global technologic response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospective studies, led by device manufacturers and academic institutions, allow individuals to voluntarily share sensor and clinical data to address the crisis. Similar approaches have been used to track COVID-19 in large populations in Germany via the Corona Data Donation app.
The study by Dr. Quer and colleagues was funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor reported grants from Janssen and personal fees from Otsuka and Livongo outside of the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Snyder has ties to Personalis, Qbio, January, SensOmics, Protos, Mirvie, and Oralome.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A smartphone app that combines passively collected physiologic data from wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, and self-reported symptoms can discriminate between COVID-19–positive and –negative individuals among those who report symptoms, new data suggest.
After analyzing data from more than 30,000 participants, researchers from the Digital Engagement and Tracking for Early Control and Treatment (DETECT) study concluded that adding individual changes in sensor data improves models based on symptoms alone for differentiating symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 positive and symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 negative.
The combination can potentially identify infection clusters before wider community spread occurs, Giorgio Quer, PhD, and colleagues report in an article published online Oct. 29 in Nature Medicine. DETECT investigators note that marrying participant-reported symptoms with personal sensor data, such as deviation from normal sleep duration and resting heart rate, resulted in an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (interquartile range [IQR], 0.73-0.86) for differentiating between symptomatic individuals who were positive and those who were negative for COVID-19.
“By better characterizing each individual’s unique baseline, you can then identify changes that may indicate that someone has a viral illness,” said Dr. Quer, director of artificial intelligence at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. “In previous research, we found that the proportion of individuals with elevated resting heart rate and sleep duration compared with their normal could significantly improve real-time detection of influenza-like illness rates at the state level,” he said in an interview.
Thus, continuous passively captured data may be a useful adjunct to bricks-and-mortar site testing, which is generally a one-off or infrequent sampling assay and is not always easily accessible, he added. Furthermore, traditional screening with temperature and symptom reporting is inadequate. An elevation in temperature is not as common as frequently believed for people who test positive for COVID-19, Dr. Quer continued. “Early identification via sensor variables of those who are presymptomatic or even asymptomatic would be especially valuable, as people may potentially be infectious during this period, and early detection is the ultimate goal,” Dr. Quer said.
According to his group, adding these physiologic changes from baseline values significantly outperformed detection (P < .01) using a British model described in an earlier study by by Cristina Menni, PhD, and associates. That method, in which symptoms were considered alone, yielded an AUC of 0.71 (IQR, 0.63-0.79).
According to Dr. Quer, one in five Americans currently wear an electronic device. “If we could enroll even a small percentage of these individuals, we’d be able to potentially identify clusters before they have the opportunity to spread,” he said.
DETECT study details
During the period March 15 to June 7, 2020, the study enrolled 30,529 participants from all 50 states. They ranged in age from younger than 35 years (23.1%) to older than 65 years (12.8%); the majority (63.5%) were aged 35-65 years, and 62% were women. Sensor devices in use by the cohort included Fitbit activity trackers (78.4%) and Apple HealthKit (31.2%).
Participants downloaded an app called MyDataHelps, which collects smartwatch and activity tracker information, including self-reported symptoms and diagnostic testing results. The app also monitors changes from baseline in resting heart rate, sleep duration, and physical activity, as measured by steps.
Overall, 3,811 participants reported having at least one symptom of some kind (e.g., fatigue, cough, dyspnea, loss of taste or smell). Of these, 54 reported testing positive for COVID-19, and 279 reported testing negative.
Sleep and activity were significantly different for the positive and negative groups, with an AUC of 0.68 (IQR, 0.57-0.79) for the sleep metric and 0.69 (IQR, 0.61-0.77) for the activity metric, suggesting that these parameters were more affected in COVID-19–positive participants.
When the investigators combined resting heart rate, sleep, and activity into a single metric, predictive performance improved to an AUC of 0.72 (IQR, 0.64-0.80).
The next step, Dr. Quer said, is to include an alert to notify users of possible infection.
Alerting users to possible COVID-19 infection
In a similar study, an alert feature was already incorporated. The study, led by Michael P. Snyder, PhD, director of the Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, will soon be published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering. In that study, presymptomatic detection of COVID-19 was achieved in more than 80% of participants using resting heart rate.
“The median is 4 days prior to symptom formation,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “We have an alarm system to notify people when their heart rate is elevated. So a positive signal from a smartwatch can be used to follow up by polymerase chain reaction [testing].”
Dr. Snyder said these approaches offer a roadmap to containing widespread infections. “Public health authorities need to be open to these technologies and begin incorporating them into their tracking,” he said. “Right now, people do temperature checks, which are of limited value. Resting heart rate is much better information.”
Although the DETECT researchers have not yet received feedback on their results, they believe public health authorities could recommend the use of such apps. “These are devices that people routinely wear for tracking their fitness and sleep, so it would be relatively easy to use the data for viral illness tracking,” said co–lead author Jennifer Radin, PhD, an epidemiologist at Scripps. “Testing resources are still limited and don’t allow for routine serial testing of individuals who may be asymptomatic or presymptomatic. Wearables can offer a different way to routinely monitor and screen people for changes in their data that may indicate COVID-19.”
The marshaling of data through consumer digital platforms to fight the coronavirus is gaining ground. New York State and New Jersey are already embracing smartphone apps to alert individuals to possible exposure to the virus.
More than 710,000 New Yorkers have downloaded the COVID NY Alert app, launched in October to help protect individuals and communities from COVID-19 by sending alerts without compromising privacy or personal information. “Upon receiving a notification about a potential exposure, users are then able to self-quarantine, get tested, and reduce the potential exposure risk to family, friends, coworkers, and others,” Jonah Bruno, a spokesperson for the New York State Department of Health, said in an interview.
And recently the Mayo Clinic and Safe Health Systems launched a platform to store COVID-19 testing and vaccination data.
Both the Scripps and Stanford platforms are part of a global technologic response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospective studies, led by device manufacturers and academic institutions, allow individuals to voluntarily share sensor and clinical data to address the crisis. Similar approaches have been used to track COVID-19 in large populations in Germany via the Corona Data Donation app.
The study by Dr. Quer and colleagues was funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor reported grants from Janssen and personal fees from Otsuka and Livongo outside of the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Snyder has ties to Personalis, Qbio, January, SensOmics, Protos, Mirvie, and Oralome.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A smartphone app that combines passively collected physiologic data from wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, and self-reported symptoms can discriminate between COVID-19–positive and –negative individuals among those who report symptoms, new data suggest.
After analyzing data from more than 30,000 participants, researchers from the Digital Engagement and Tracking for Early Control and Treatment (DETECT) study concluded that adding individual changes in sensor data improves models based on symptoms alone for differentiating symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 positive and symptomatic persons who are COVID-19 negative.
The combination can potentially identify infection clusters before wider community spread occurs, Giorgio Quer, PhD, and colleagues report in an article published online Oct. 29 in Nature Medicine. DETECT investigators note that marrying participant-reported symptoms with personal sensor data, such as deviation from normal sleep duration and resting heart rate, resulted in an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.80 (interquartile range [IQR], 0.73-0.86) for differentiating between symptomatic individuals who were positive and those who were negative for COVID-19.
“By better characterizing each individual’s unique baseline, you can then identify changes that may indicate that someone has a viral illness,” said Dr. Quer, director of artificial intelligence at Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. “In previous research, we found that the proportion of individuals with elevated resting heart rate and sleep duration compared with their normal could significantly improve real-time detection of influenza-like illness rates at the state level,” he said in an interview.
Thus, continuous passively captured data may be a useful adjunct to bricks-and-mortar site testing, which is generally a one-off or infrequent sampling assay and is not always easily accessible, he added. Furthermore, traditional screening with temperature and symptom reporting is inadequate. An elevation in temperature is not as common as frequently believed for people who test positive for COVID-19, Dr. Quer continued. “Early identification via sensor variables of those who are presymptomatic or even asymptomatic would be especially valuable, as people may potentially be infectious during this period, and early detection is the ultimate goal,” Dr. Quer said.
According to his group, adding these physiologic changes from baseline values significantly outperformed detection (P < .01) using a British model described in an earlier study by by Cristina Menni, PhD, and associates. That method, in which symptoms were considered alone, yielded an AUC of 0.71 (IQR, 0.63-0.79).
According to Dr. Quer, one in five Americans currently wear an electronic device. “If we could enroll even a small percentage of these individuals, we’d be able to potentially identify clusters before they have the opportunity to spread,” he said.
DETECT study details
During the period March 15 to June 7, 2020, the study enrolled 30,529 participants from all 50 states. They ranged in age from younger than 35 years (23.1%) to older than 65 years (12.8%); the majority (63.5%) were aged 35-65 years, and 62% were women. Sensor devices in use by the cohort included Fitbit activity trackers (78.4%) and Apple HealthKit (31.2%).
Participants downloaded an app called MyDataHelps, which collects smartwatch and activity tracker information, including self-reported symptoms and diagnostic testing results. The app also monitors changes from baseline in resting heart rate, sleep duration, and physical activity, as measured by steps.
Overall, 3,811 participants reported having at least one symptom of some kind (e.g., fatigue, cough, dyspnea, loss of taste or smell). Of these, 54 reported testing positive for COVID-19, and 279 reported testing negative.
Sleep and activity were significantly different for the positive and negative groups, with an AUC of 0.68 (IQR, 0.57-0.79) for the sleep metric and 0.69 (IQR, 0.61-0.77) for the activity metric, suggesting that these parameters were more affected in COVID-19–positive participants.
When the investigators combined resting heart rate, sleep, and activity into a single metric, predictive performance improved to an AUC of 0.72 (IQR, 0.64-0.80).
The next step, Dr. Quer said, is to include an alert to notify users of possible infection.
Alerting users to possible COVID-19 infection
In a similar study, an alert feature was already incorporated. The study, led by Michael P. Snyder, PhD, director of the Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, will soon be published online in Nature Biomedical Engineering. In that study, presymptomatic detection of COVID-19 was achieved in more than 80% of participants using resting heart rate.
“The median is 4 days prior to symptom formation,” Dr. Snyder said in an interview. “We have an alarm system to notify people when their heart rate is elevated. So a positive signal from a smartwatch can be used to follow up by polymerase chain reaction [testing].”
Dr. Snyder said these approaches offer a roadmap to containing widespread infections. “Public health authorities need to be open to these technologies and begin incorporating them into their tracking,” he said. “Right now, people do temperature checks, which are of limited value. Resting heart rate is much better information.”
Although the DETECT researchers have not yet received feedback on their results, they believe public health authorities could recommend the use of such apps. “These are devices that people routinely wear for tracking their fitness and sleep, so it would be relatively easy to use the data for viral illness tracking,” said co–lead author Jennifer Radin, PhD, an epidemiologist at Scripps. “Testing resources are still limited and don’t allow for routine serial testing of individuals who may be asymptomatic or presymptomatic. Wearables can offer a different way to routinely monitor and screen people for changes in their data that may indicate COVID-19.”
The marshaling of data through consumer digital platforms to fight the coronavirus is gaining ground. New York State and New Jersey are already embracing smartphone apps to alert individuals to possible exposure to the virus.
More than 710,000 New Yorkers have downloaded the COVID NY Alert app, launched in October to help protect individuals and communities from COVID-19 by sending alerts without compromising privacy or personal information. “Upon receiving a notification about a potential exposure, users are then able to self-quarantine, get tested, and reduce the potential exposure risk to family, friends, coworkers, and others,” Jonah Bruno, a spokesperson for the New York State Department of Health, said in an interview.
And recently the Mayo Clinic and Safe Health Systems launched a platform to store COVID-19 testing and vaccination data.
Both the Scripps and Stanford platforms are part of a global technologic response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prospective studies, led by device manufacturers and academic institutions, allow individuals to voluntarily share sensor and clinical data to address the crisis. Similar approaches have been used to track COVID-19 in large populations in Germany via the Corona Data Donation app.
The study by Dr. Quer and colleagues was funded by a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor reported grants from Janssen and personal fees from Otsuka and Livongo outside of the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Snyder has ties to Personalis, Qbio, January, SensOmics, Protos, Mirvie, and Oralome.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New return-to-play recommendations for athletes with COVID-19
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The latest recommendations from sports cardiologists on getting athletes with COVID-19 back on the playing field safely emphasize a more judicious approach to screening for cardiac injury.
The new recommendations, made by the American College of Cardiology’s Sports and Exercise Cardiology Section, are for adult athletes in competitive sports and also for two important groups: younger athletes taking part in competitive high school sports and older athletes aged 35 and older, the Masters athletes, who continue to be active throughout their lives. The document was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Because of the evolving nature of knowledge about COVID-19, updates on recommendations for safe return to play for athletes of all ages will continue to be made, senior author Aaron L. Baggish, MD, director of the cardiovascular performance program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said.
“The recommendations we released in May were entirely based on our experience taking care of hospitalized patients with COVID-19; we had no athletes in this population. We used a lot of conservative guesswork around how this would apply to otherwise healthy athletes,” Dr. Baggish said in an interview.
“But as sports started to open up, and we started to see large numbers of first professional and then college athletes come back into training, we realized that we needed to stop and ask whether the recommendations we put forward back in May were still appropriate,” Dr. Baggish said.
“Once we started to actually get into the trenches with these athletes, literally hundreds of them, and applying the testing strategies that we had initially recommended in everybody, we realized that we probably had some room for improvement, and that’s why we reconvened, to make these revisions,” he said.
Essentially, the recommendations now urge less cardiac testing. “Cardiac injury is not as common as we may have originally thought,” said Dr. Baggish.
“In the early days of COVID, people who were hospitalized had evidence of heart injury, and so we wondered if that prevalence would also be applicable to otherwise young, healthy people who got COVID. If that had been the case, we would have been in big trouble with respect to getting people back into sports. So this is why we started with a conservative screening approach and a lot of testing in order to not miss a huge burden of disease,” he said.
“But what we’ve learned over the past few months is that young people who get either asymptomatic or mild infection appear to have very, very low risk of having associated heart injury, so the need for testing in that population, when people who have infections recover fully, is almost certainly not going to be high yield,” Dr. Baggish said.
First iteration of the recommendations
Published in May in the early weeks of the pandemic, the first recommendations for safe return to play said that all athletes should stop training for at least 2 weeks after their symptoms resolve, then undergo “careful, clinical cardiovascular evaluation in combination with cardiac biomarkers and imaging.”
Additional testing with cardiac MRI, exercise testing, or ambulatory rhythm monitoring was to be done “based on the clinical course and initial testing.”
But experts caution that monitoring on such a scale in everyone is unnecessary and could even be counterproductive.
“Sending young athletes for extensive testing is not warranted and could send them to unnecessary testing, cardiac imaging, and so on,” Dr. Baggish said.
Only those athletes who continue to have symptoms or whose symptoms return when they get back to their athletic activities should go on for more screening.
“There, in essence, is the single main change from May, and that is a move away from screening with testing everyone, [and instead] confining that to the people who had moderate or greater severity disease,” he said.
Both iterations of the recommendations end with the same message.
“We are at the beginning of our knowledge about the cardiotoxic effects of COVID-19 but we are gathering evidence every day,” said Dr. Baggish. “Just as they did earlier, we acknowledge that our approaches are subject to change when we learn more about how COVID affects the heart, and specifically the hearts of athletes. This will be an ongoing process.”
Something to lean on
The recommendations are welcome, said James E. Udelson, MD, chief of the division of cardiology at Tufts Medical Center, Boston, coauthor of an accompanying editorial.
“It was a bit of the wild west out there, because each university, each college, all with good intentions, had been all struggling to figure out what to do, and how much to do. Probably the most important message from this new paper is the fact that now there is something out there that all coaches, athletes, families, schools, trainers can get some guidance from,” Dr. Udelson said in an interview.
Refining the cardiac screening criteria was a necessary step, Dr. Udelson said.
“How much cardiac imaging do you do? That is a matter of controversy,” said Dr. Udelson, who coauthored the commentary with Tufts cardiologist Ethan Rowin, MD, and Michael A. Curtis, MEd, a certified strength and conditioning specialist at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville. “The problem is that if you use a very sensitive imaging test on a lot of people, sometimes you find things that you really didn’t need to know about. They’re really not important. And now, the athlete is told he or she cannot play for 3 months because they might have myocarditis.
“Should we be too sensitive, meaning do we want to pick up anything no matter whether it’s important or not?” he added. “There will be a lot of false positives, and we are going to disqualify a lot of people. Or do you tune it a different way?”
Dr. Udelson said he would like to see commercial sports donate money to support research into the potential cardiotoxicity of COVID-19.
“If the organizations that benefit from these athletes, like the National Collegiate Athletic Association and professional sports leagues, can fund some of this research, that would be a huge help,” Dr. Udelson said.
“These are the top sports cardiologists in the country, and they have to start somewhere, and these are all based on what we know right now, as well as their own extensive experience. We all know that we are just at the beginning of our knowledge of this. But we have to have something to guide this huge community out there that is really thirsty for help.”
Dr. Baggish reports receiving research funding for the study of athletes in competitive sports from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Football League Players Association; and the American Heart Association and receiving compensation for his role as team cardiologist from the US Olympic Committee/US Olympic Training Centers, US Soccer, US Rowing, the New England Patriots, the Boston Bruins, the New England Revolution, and Harvard University. Dr. Udelson has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
MADIT-CRT: Resynchronization linked to fewer heart failure hospitalizations
Patients with mild heart failure who received a cardiac resynchronization device had significantly reduced rates of hospitalizations for heart failure during follow-up of 1,820 patients for an average of 5.6 years, identifying in this post hoc analysis another benefit from this device that patients potentially receive in addition to an established survival advantage.
Extended follow-up of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial showed that patients with either New York Heart Association (NYHA) class I or II cardiomyopathy who received a cardiac resynchronization device with a defibrillator (CRT-D) had a significant reduction in all-cause hospitalization during follow-up, compared with control patients randomized to receive an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) device. This reduction in all hospitalizations was specifically driven by a significant reduction in cardiovascular hospitalizations, and the drop in cardiovascular hospitalizations was specifically driven by a cut in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), Sabu Thomas, MD, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The data showed that during follow-up all-cause hospitalizations occurred in 73% of the CRT-D patients and 83% of those who received an ICD; cardiovascular hospitalizations happened in 29% of the CRT-D patients and in 43% of those with an ICD; and HHF occurred in 12% of the CRT-D patients and in 22% of those with an ICD, reported Dr. Thomas, a heart failure cardiologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. All three between-group differences were statistically significant for these post hoc endpoints.
These reduced hospitalizations also linked with better survival. Patients in the trial database with cardiovascular hospitalizations had a nearly fourfold higher rate of death, compared with nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Thomas said.
The findings “suggest that this device [CRT-D] has sustained benefit in these patients for up to 7 years,” said Dr. Thomas and his collaborator, Valentina Kutyifa, MD, in an interview. “However, this was only seen in patients with left bundle branch block [LBBB].” In patients with non-LBBB, CRT-D was not associated with a reduction in [cardiovascular] hospitalizations.
The LBBB connection
In a multivariate analysis, the 1,281 patients with LBBB (70% of the study cohort) who were more than 6 months out from device placement had a significant 43% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with that of control patients who received an ICD, while the 537 patients with non-LBBB showed no benefit from CRT-D treatment, compared with those who received an ICD, for reducing cardiovascular hospitalizations. (Data from two enrolled patients weren’t available for the analyses.) This finding that the HHF benefit focused in patients with LBBB was consistent with many prior observations that CRT-D was most effective in this patient subgroup.
The researchers also highlighted that their findings apply only to patients with NYHA functional class I or II heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the only types of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial (15% had class I disease).
The results also showed that, during the first 6 months on CRT-D treatment, patients with a LBBB showed a significant 43% increase in their cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with control patients, which may have been driven by device-related events. “We did not investigate this in detail, and it needs more study,” said Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa, a cardiac electrophysiologist at the University of Rochester.Their new findings extend the initial, prespecified results of the MADIT-CRT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy) trial, which was designed to examine a primary endpoint of death from any cause or a nonfatal heart failure event. During the initial average follow-up of 2.4 years, patients who received a CRT-D device had a significant relative reduction in this endpoint of 34%, compared with patients on ICD treatment, exclusively in patients with LBBB. Extended follow-up for as long as 7 years of the same cohort showed a continued significant reduction of all-cause death compared with controls, a 41% relative risk reduction, that again was only apparent in patients with LBBB.
The MADIT-CRT findings are generally consistent with prevailing CRT-D recommendations from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association from 2013 that give a class I indication (“is indicated”) for using the device in heart failure patients with LBBB, a QRS interval of at least 150 msec, NYHA class II-IV function, and a left ventricular ejection fraction no greater than 35%. A lesser, class IIa recommendation (“can be useful”) exists for patients with a narrower QRS of 120-149 msec with the other class I criteria, and for patients with non-LBBB the recommendation drops to class IIb (“may be considered”).
CRT-D ‘is mysterious,’ especially for non-LBBB patients
“Every time researchers have tried to move beyond the [existing] paradigm of who benefits from CRT-D, it’s never panned out,” commented Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, an electrophysiologist, professor, and chief of the cardiovascular division at the University of Miami. “The guidelines are pretty correct on who should get CRT-D. I wouldn’t say that no patients with non-LBBB should get it, but they are less likely to benefit,” although he conceded that responses to CRT-D are highly individualized and hard to predict.
“CRT is mysterious. I’ve had patients who did incredibly well on it,” but “once you start getting outside of where the benefits are proven, you start to run into issues,” Dr. Goldberger said in an interview. “The only solid predictor of a CRT-D response is in patients with LBBB.”
The hospitalizations for heart failure that the University of Rochester investigators assessed as an additional study outcome represent an “important endpoint, but one that is much more subjective than survival,” making its reliability “a bit of a gray area,” he said. The analyses are also limited by being post hoc and, hence, just hypothesis generating.
A recently published analysis of the same dataset by many of the same investigators hinted that CRT-D might reduce HHF in non-LBBB patients when the focus is on recurrent hospitalizations.
Despite the evidence of a survival benefit from CRT-D placement in selected patients, especially those with LBBB, “registry data have shown that use of CRT-D varies widely and has been as low as 27% of eligible patients,” noted Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa. “There is an opportunity here to understand the barriers to more widespread adoption of CRT-D in appropriate patients,” they said. It is also “possible that CRT-D is overused in non-LBBB patients” given that this subgroup receives about a third of CRT-D devices now. “Future studies should carefully investigate the role of CRT-D in non-LBBB patients.”
MADIT-CRT was funded by Boston Scientific, which markets several CRT-D devices. Dr. Thomas had no disclosures. Dr. Kutyifa has been a consultant to Biotronik and Zoll and has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Spire, and Zoll. Dr Goldberger is director of a not-for-profit think tank on risk stratification for sudden cardiac death that has received unrestricted educational grants from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
SOURCE: Thomas S et al. HFSA 2020, Abstract 019.
Patients with mild heart failure who received a cardiac resynchronization device had significantly reduced rates of hospitalizations for heart failure during follow-up of 1,820 patients for an average of 5.6 years, identifying in this post hoc analysis another benefit from this device that patients potentially receive in addition to an established survival advantage.
Extended follow-up of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial showed that patients with either New York Heart Association (NYHA) class I or II cardiomyopathy who received a cardiac resynchronization device with a defibrillator (CRT-D) had a significant reduction in all-cause hospitalization during follow-up, compared with control patients randomized to receive an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) device. This reduction in all hospitalizations was specifically driven by a significant reduction in cardiovascular hospitalizations, and the drop in cardiovascular hospitalizations was specifically driven by a cut in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), Sabu Thomas, MD, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The data showed that during follow-up all-cause hospitalizations occurred in 73% of the CRT-D patients and 83% of those who received an ICD; cardiovascular hospitalizations happened in 29% of the CRT-D patients and in 43% of those with an ICD; and HHF occurred in 12% of the CRT-D patients and in 22% of those with an ICD, reported Dr. Thomas, a heart failure cardiologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. All three between-group differences were statistically significant for these post hoc endpoints.
These reduced hospitalizations also linked with better survival. Patients in the trial database with cardiovascular hospitalizations had a nearly fourfold higher rate of death, compared with nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Thomas said.
The findings “suggest that this device [CRT-D] has sustained benefit in these patients for up to 7 years,” said Dr. Thomas and his collaborator, Valentina Kutyifa, MD, in an interview. “However, this was only seen in patients with left bundle branch block [LBBB].” In patients with non-LBBB, CRT-D was not associated with a reduction in [cardiovascular] hospitalizations.
The LBBB connection
In a multivariate analysis, the 1,281 patients with LBBB (70% of the study cohort) who were more than 6 months out from device placement had a significant 43% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with that of control patients who received an ICD, while the 537 patients with non-LBBB showed no benefit from CRT-D treatment, compared with those who received an ICD, for reducing cardiovascular hospitalizations. (Data from two enrolled patients weren’t available for the analyses.) This finding that the HHF benefit focused in patients with LBBB was consistent with many prior observations that CRT-D was most effective in this patient subgroup.
The researchers also highlighted that their findings apply only to patients with NYHA functional class I or II heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the only types of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial (15% had class I disease).
The results also showed that, during the first 6 months on CRT-D treatment, patients with a LBBB showed a significant 43% increase in their cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with control patients, which may have been driven by device-related events. “We did not investigate this in detail, and it needs more study,” said Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa, a cardiac electrophysiologist at the University of Rochester.Their new findings extend the initial, prespecified results of the MADIT-CRT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy) trial, which was designed to examine a primary endpoint of death from any cause or a nonfatal heart failure event. During the initial average follow-up of 2.4 years, patients who received a CRT-D device had a significant relative reduction in this endpoint of 34%, compared with patients on ICD treatment, exclusively in patients with LBBB. Extended follow-up for as long as 7 years of the same cohort showed a continued significant reduction of all-cause death compared with controls, a 41% relative risk reduction, that again was only apparent in patients with LBBB.
The MADIT-CRT findings are generally consistent with prevailing CRT-D recommendations from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association from 2013 that give a class I indication (“is indicated”) for using the device in heart failure patients with LBBB, a QRS interval of at least 150 msec, NYHA class II-IV function, and a left ventricular ejection fraction no greater than 35%. A lesser, class IIa recommendation (“can be useful”) exists for patients with a narrower QRS of 120-149 msec with the other class I criteria, and for patients with non-LBBB the recommendation drops to class IIb (“may be considered”).
CRT-D ‘is mysterious,’ especially for non-LBBB patients
“Every time researchers have tried to move beyond the [existing] paradigm of who benefits from CRT-D, it’s never panned out,” commented Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, an electrophysiologist, professor, and chief of the cardiovascular division at the University of Miami. “The guidelines are pretty correct on who should get CRT-D. I wouldn’t say that no patients with non-LBBB should get it, but they are less likely to benefit,” although he conceded that responses to CRT-D are highly individualized and hard to predict.
“CRT is mysterious. I’ve had patients who did incredibly well on it,” but “once you start getting outside of where the benefits are proven, you start to run into issues,” Dr. Goldberger said in an interview. “The only solid predictor of a CRT-D response is in patients with LBBB.”
The hospitalizations for heart failure that the University of Rochester investigators assessed as an additional study outcome represent an “important endpoint, but one that is much more subjective than survival,” making its reliability “a bit of a gray area,” he said. The analyses are also limited by being post hoc and, hence, just hypothesis generating.
A recently published analysis of the same dataset by many of the same investigators hinted that CRT-D might reduce HHF in non-LBBB patients when the focus is on recurrent hospitalizations.
Despite the evidence of a survival benefit from CRT-D placement in selected patients, especially those with LBBB, “registry data have shown that use of CRT-D varies widely and has been as low as 27% of eligible patients,” noted Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa. “There is an opportunity here to understand the barriers to more widespread adoption of CRT-D in appropriate patients,” they said. It is also “possible that CRT-D is overused in non-LBBB patients” given that this subgroup receives about a third of CRT-D devices now. “Future studies should carefully investigate the role of CRT-D in non-LBBB patients.”
MADIT-CRT was funded by Boston Scientific, which markets several CRT-D devices. Dr. Thomas had no disclosures. Dr. Kutyifa has been a consultant to Biotronik and Zoll and has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Spire, and Zoll. Dr Goldberger is director of a not-for-profit think tank on risk stratification for sudden cardiac death that has received unrestricted educational grants from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
SOURCE: Thomas S et al. HFSA 2020, Abstract 019.
Patients with mild heart failure who received a cardiac resynchronization device had significantly reduced rates of hospitalizations for heart failure during follow-up of 1,820 patients for an average of 5.6 years, identifying in this post hoc analysis another benefit from this device that patients potentially receive in addition to an established survival advantage.
Extended follow-up of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial showed that patients with either New York Heart Association (NYHA) class I or II cardiomyopathy who received a cardiac resynchronization device with a defibrillator (CRT-D) had a significant reduction in all-cause hospitalization during follow-up, compared with control patients randomized to receive an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) device. This reduction in all hospitalizations was specifically driven by a significant reduction in cardiovascular hospitalizations, and the drop in cardiovascular hospitalizations was specifically driven by a cut in hospitalizations for heart failure (HHF), Sabu Thomas, MD, said at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The data showed that during follow-up all-cause hospitalizations occurred in 73% of the CRT-D patients and 83% of those who received an ICD; cardiovascular hospitalizations happened in 29% of the CRT-D patients and in 43% of those with an ICD; and HHF occurred in 12% of the CRT-D patients and in 22% of those with an ICD, reported Dr. Thomas, a heart failure cardiologist at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center. All three between-group differences were statistically significant for these post hoc endpoints.
These reduced hospitalizations also linked with better survival. Patients in the trial database with cardiovascular hospitalizations had a nearly fourfold higher rate of death, compared with nonhospitalized patients, Dr. Thomas said.
The findings “suggest that this device [CRT-D] has sustained benefit in these patients for up to 7 years,” said Dr. Thomas and his collaborator, Valentina Kutyifa, MD, in an interview. “However, this was only seen in patients with left bundle branch block [LBBB].” In patients with non-LBBB, CRT-D was not associated with a reduction in [cardiovascular] hospitalizations.
The LBBB connection
In a multivariate analysis, the 1,281 patients with LBBB (70% of the study cohort) who were more than 6 months out from device placement had a significant 43% relative cut in their incidence of cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with that of control patients who received an ICD, while the 537 patients with non-LBBB showed no benefit from CRT-D treatment, compared with those who received an ICD, for reducing cardiovascular hospitalizations. (Data from two enrolled patients weren’t available for the analyses.) This finding that the HHF benefit focused in patients with LBBB was consistent with many prior observations that CRT-D was most effective in this patient subgroup.
The researchers also highlighted that their findings apply only to patients with NYHA functional class I or II heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), the only types of patients enrolled in the MADIT-CRT trial (15% had class I disease).
The results also showed that, during the first 6 months on CRT-D treatment, patients with a LBBB showed a significant 43% increase in their cardiovascular hospitalizations, compared with control patients, which may have been driven by device-related events. “We did not investigate this in detail, and it needs more study,” said Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa, a cardiac electrophysiologist at the University of Rochester.Their new findings extend the initial, prespecified results of the MADIT-CRT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation With Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy) trial, which was designed to examine a primary endpoint of death from any cause or a nonfatal heart failure event. During the initial average follow-up of 2.4 years, patients who received a CRT-D device had a significant relative reduction in this endpoint of 34%, compared with patients on ICD treatment, exclusively in patients with LBBB. Extended follow-up for as long as 7 years of the same cohort showed a continued significant reduction of all-cause death compared with controls, a 41% relative risk reduction, that again was only apparent in patients with LBBB.
The MADIT-CRT findings are generally consistent with prevailing CRT-D recommendations from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association from 2013 that give a class I indication (“is indicated”) for using the device in heart failure patients with LBBB, a QRS interval of at least 150 msec, NYHA class II-IV function, and a left ventricular ejection fraction no greater than 35%. A lesser, class IIa recommendation (“can be useful”) exists for patients with a narrower QRS of 120-149 msec with the other class I criteria, and for patients with non-LBBB the recommendation drops to class IIb (“may be considered”).
CRT-D ‘is mysterious,’ especially for non-LBBB patients
“Every time researchers have tried to move beyond the [existing] paradigm of who benefits from CRT-D, it’s never panned out,” commented Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, an electrophysiologist, professor, and chief of the cardiovascular division at the University of Miami. “The guidelines are pretty correct on who should get CRT-D. I wouldn’t say that no patients with non-LBBB should get it, but they are less likely to benefit,” although he conceded that responses to CRT-D are highly individualized and hard to predict.
“CRT is mysterious. I’ve had patients who did incredibly well on it,” but “once you start getting outside of where the benefits are proven, you start to run into issues,” Dr. Goldberger said in an interview. “The only solid predictor of a CRT-D response is in patients with LBBB.”
The hospitalizations for heart failure that the University of Rochester investigators assessed as an additional study outcome represent an “important endpoint, but one that is much more subjective than survival,” making its reliability “a bit of a gray area,” he said. The analyses are also limited by being post hoc and, hence, just hypothesis generating.
A recently published analysis of the same dataset by many of the same investigators hinted that CRT-D might reduce HHF in non-LBBB patients when the focus is on recurrent hospitalizations.
Despite the evidence of a survival benefit from CRT-D placement in selected patients, especially those with LBBB, “registry data have shown that use of CRT-D varies widely and has been as low as 27% of eligible patients,” noted Dr. Thomas and Dr. Kutyifa. “There is an opportunity here to understand the barriers to more widespread adoption of CRT-D in appropriate patients,” they said. It is also “possible that CRT-D is overused in non-LBBB patients” given that this subgroup receives about a third of CRT-D devices now. “Future studies should carefully investigate the role of CRT-D in non-LBBB patients.”
MADIT-CRT was funded by Boston Scientific, which markets several CRT-D devices. Dr. Thomas had no disclosures. Dr. Kutyifa has been a consultant to Biotronik and Zoll and has received research funding from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Spire, and Zoll. Dr Goldberger is director of a not-for-profit think tank on risk stratification for sudden cardiac death that has received unrestricted educational grants from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
SOURCE: Thomas S et al. HFSA 2020, Abstract 019.
FROM HFSA 2020
Updated heart failure measures add newer meds
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
Safety measures for lab monitoring of mineralocorticoid receptor agonist therapy, performance measures for sacubitril/valsartan, cardiac resynchronization therapy and titration of medications, and quality measures based on patient-reported outcomes are among the updates the joint task force of the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association have made to performance and quality measures for managing adults with heart failure.
The revisions, published online Nov. 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, update the 2011 ACC/AHA heart failure measure set, writing committee vice chair Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, said in an interview. The 2011 measure set predates the 2015 approval of the angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) sacubitril/valsartan for heart failure in adults.
Measures stress dosages, strength of evidence
“For the first time the heart failure performance measure sets also focus on not just the use of guideline-recommended medication at any dose, but on utilizing the doses that are evidence-based and guideline recommended so long as they are well tolerated,” said Dr. Fonarow, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. “The measure set now includes assessment of patients being treated with doses of medications at 50% or greater of target dose in the absence of contraindications or documented intolerance.”
The update includes seven new performance measures, two quality measures, and one structural measure. The performance measures come from the strongest recommendations – that is, a class of recommendation of 1 (strong) or 3 (no benefit or harmful, process to be avoided) – in the 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of American heart failure guideline update published in Circulation.
In addition to the 2017 update, the writing committee also reviewed existing performance measures. “Those management strategies, diagnostic testing, medications, and devices with the strongest evidence and highest level of guideline recommendations were further considered for inclusion in the performance measure set,” Dr. Fonarow said. “The measures went through extensive review by peer reviewers and approval from the organizations represented.”
Specifically, the update includes measures for monitoring serum potassium after starting mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists therapy, and cardiac resynchronization therapy for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction already on guideline-directed therapy. “This therapy can significantly improve functional capacity and outcomes in appropriately selected patients,” Dr. Fonarow said.
New and retired measures
The update adds two performance measures for titration of medications based on dose, either reaching 50% of the recommended dose for a variety of medications, including ARNI, or documenting that the dose wasn’t tolerated for other reason for not using the dose.
The new structural measure calls for facility participation in a heart failure registry. The revised measure set now consists of 18 measures in all.
The update retired one measure from the 2011 set: left ventricular ejection fraction assessment for inpatients. The committee cited its use above 97% as the reason, but LVEF in outpatients remains a measure.
The following tree measures have been revised:
- Patient self-care education has moved from performance measure to quality measure because of concerns about the accuracy of self-care education documentation and limited evidence of improved outcomes with better documentation.
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy for left ventricular systolic dysfunction adds ARNI therapy to align with the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA update.
- Postdischarge appointments shifts from performance to quality measure and include a 7-day limit.
Measures future research should focus on, noted Dr. Fonarow, include the use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for heart failure, including in patients without diabetes. “Since the ACC/AHA heart failure guidelines had not yet been updated to recommend these therapies they could not be included in this performance measure set,” he said.
He also said “an urgent need” exists for further research into treatments for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction along with optimal implementation strategies.
“If these ACC/AHA heart failure performance measures were applied in all settings in which patients with heart failure in the United States are being cared for, and optimal and equitable conformity with each of these measures were achieved, over 100,000 lives a year of patients with heart failure could be saved,” he said. “There’s in an urgent need to measure and improve heart failure care quality.”
Dr. Fonarow reported financial relationships with Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis.
SOURCE: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Nov 2;76:2527-64.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
COMPARE CRUSH: Crushed prehospital prasugrel misses mark in STEMI
Giving crushed prasugrel (Effient) to patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) en route to a planned primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) does not improve reperfusion rates, results of the COMPARE CRUSH trial show.
Patients assigned to prasugrel as crushed or integral tablets had similar rates of the study’s co-primary endpoints of thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 3 flow in the infarct-related artery at first angiography (31% vs. 32.7%; P = .64) and complete ST-segment resolution 1 hour post PCI (59.9% vs. 57.3%; P = .55).
“These findings hold in spite of the fact that crushed tablets of prasugrel led to more potent platelet inhibition compared with integral tablets,” said study author Georgios Vlachojannis, MD, PhD, University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
“Whether faster and more potent antiplatelet therapy can improve coronary reperfusion in contemporary STEMI treatment regimen warrants further investigation.”
The results were reported in a late-breaking clinical science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting and published simultaneously in the journal Circulation. The meeting was sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Fibrinolytics and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors have demonstrated improved coronary reperfusion and outcomes when given pre hospital. Prior studies have also shown that early administration of a crushed P2Y12 inhibitor increases bioavailability and speeds platelet inhibition in STEMI patients, Dr. Vlachojannis noted.
However, the large randomized ATLANTIC trial, which compared prehospital to cath lab administration of crushed or integral ticagrelor (Brilinta), also found no difference in either TIMI flow in the infarct-related artery or ST-segment resolution.
Between November 2017 and March 2020, the investigator-initiated COMPARE CRUSH trial randomly allocated 727 STEMI patients (mean age, 62 years; 23% female) undergoing primary PCI to receive in the ambulance a 60-mg loading dose of prasugrel as either crushed or integral tablets.
The median time from onset of symptoms to first medical contact was 59 minutes, from first medical contact to study treatment 22 minutes, and from study treatment to primary PCI 57 minutes. These times did not differ between groups.
Platelet reactivity at the beginning of coronary angiography was significantly lower in the crushed group than in the integral group (P2Y12 reactivity units 192 vs. 227; P < .01). This resulted in significantly fewer patients in the crushed group with high platelet reactivity, defined as P2Y12 reactivity units >208, prior to the start of PCI (43.3% vs. 62.6%; P < .01).
There was no difference between the crushed and integral groups in the primary safety endpoint of TIMI major and BARC type 3 or higher bleeding within 48 hours after study treatment (0.4% vs 0.7%).
Death, MI, stroke, and urgent revascularization rates were also similar between groups during index hospitalization and at 30 days. Definite stent thrombosis occurred in one patient in the crushed group and two patients in the integral group.
In an exploratory analysis, the co-primary endpoint results were consistent across multiple subgroups, although there was a trend toward greater benefit on TIMI 3 flow in the crushed tablet group in patients older than age 75 years (P for interaction = .04), presenting with anterior infarction (P for interaction = .03), or with a history of prior PCI (P for interaction < .01).
“However, these results should be regarded as hypothesis-generating,” the authors wrote. “Opioids use in the ambulance was remarkably low in our study compared with the ATLANTIC trial, which might explain that we did not observe any significant interaction.”
Notably, morphine was used in half the ATLANTIC patients and was thought to have possibly delayed the absorption of ticagrelor.
During discussion following the presentation, Sunil V. Rao, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., asked: “Based on what you found, which is really no clinical advantage but no safety issue either, are you having your patients with ST-segment MI administering crushed prasugrel now?”
Dr. Vlachojannis said they didn’t see any clinical impact but reiterated that high platelet reactivity was reduced by one-third. “If this now translates into a safer primary PCI procedure, we can’t say. The study wasn’t powered for this kind of endpoint. Is this enough to give you a recommendation, Sunil, I’m not sure.”
“What we know with COMPARE CRUSH, and this is important, is that we tried to give the medication as soon as possible and tried to give this medication in a formulation which has the most favorable pharmacodynamics profile, and we still see it’s not doing the job,” he added.
Fellow panelist Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, questioned whether treatment time may play a role in teasing out the relatively modest differences that platelet reactivity may have on clinical outcomes.
Dr. Vlachojannis said the time from symptom onset to first medical contact was very fast and similar to that in the ATLANTIC trial. “The short time intervals have certainly influenced the outcomes.”
Panelist Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, University Hospital Bern, Switzerland, followed up on the morphine issue, asking whether the investigators tested for an interaction between morphine or opioid use and platelet reactivity at the time of PCI.
“We haven’t looked into this but you probably have the ON-TIME 3 data in your mind when you’re asking this, where crushed ticagrelor given in the ambulance didn’t influence platelet reactivity at the time point of PCI,” Dr. Vlachojannis said. “We are going to look further into the data and certainly the platelet reactivity analysis is going to be very interesting in this data set.”
The study was an investigator-initiated trial sponsored by Maasstad Cardiovascular Research B.V. with unrestricted grants from Shanghai MicroPort Medical and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Vlachojannis declared receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, and research grants from Daiichi Sankyo and Shanghai MicroPort.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Giving crushed prasugrel (Effient) to patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) en route to a planned primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) does not improve reperfusion rates, results of the COMPARE CRUSH trial show.
Patients assigned to prasugrel as crushed or integral tablets had similar rates of the study’s co-primary endpoints of thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 3 flow in the infarct-related artery at first angiography (31% vs. 32.7%; P = .64) and complete ST-segment resolution 1 hour post PCI (59.9% vs. 57.3%; P = .55).
“These findings hold in spite of the fact that crushed tablets of prasugrel led to more potent platelet inhibition compared with integral tablets,” said study author Georgios Vlachojannis, MD, PhD, University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
“Whether faster and more potent antiplatelet therapy can improve coronary reperfusion in contemporary STEMI treatment regimen warrants further investigation.”
The results were reported in a late-breaking clinical science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting and published simultaneously in the journal Circulation. The meeting was sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Fibrinolytics and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors have demonstrated improved coronary reperfusion and outcomes when given pre hospital. Prior studies have also shown that early administration of a crushed P2Y12 inhibitor increases bioavailability and speeds platelet inhibition in STEMI patients, Dr. Vlachojannis noted.
However, the large randomized ATLANTIC trial, which compared prehospital to cath lab administration of crushed or integral ticagrelor (Brilinta), also found no difference in either TIMI flow in the infarct-related artery or ST-segment resolution.
Between November 2017 and March 2020, the investigator-initiated COMPARE CRUSH trial randomly allocated 727 STEMI patients (mean age, 62 years; 23% female) undergoing primary PCI to receive in the ambulance a 60-mg loading dose of prasugrel as either crushed or integral tablets.
The median time from onset of symptoms to first medical contact was 59 minutes, from first medical contact to study treatment 22 minutes, and from study treatment to primary PCI 57 minutes. These times did not differ between groups.
Platelet reactivity at the beginning of coronary angiography was significantly lower in the crushed group than in the integral group (P2Y12 reactivity units 192 vs. 227; P < .01). This resulted in significantly fewer patients in the crushed group with high platelet reactivity, defined as P2Y12 reactivity units >208, prior to the start of PCI (43.3% vs. 62.6%; P < .01).
There was no difference between the crushed and integral groups in the primary safety endpoint of TIMI major and BARC type 3 or higher bleeding within 48 hours after study treatment (0.4% vs 0.7%).
Death, MI, stroke, and urgent revascularization rates were also similar between groups during index hospitalization and at 30 days. Definite stent thrombosis occurred in one patient in the crushed group and two patients in the integral group.
In an exploratory analysis, the co-primary endpoint results were consistent across multiple subgroups, although there was a trend toward greater benefit on TIMI 3 flow in the crushed tablet group in patients older than age 75 years (P for interaction = .04), presenting with anterior infarction (P for interaction = .03), or with a history of prior PCI (P for interaction < .01).
“However, these results should be regarded as hypothesis-generating,” the authors wrote. “Opioids use in the ambulance was remarkably low in our study compared with the ATLANTIC trial, which might explain that we did not observe any significant interaction.”
Notably, morphine was used in half the ATLANTIC patients and was thought to have possibly delayed the absorption of ticagrelor.
During discussion following the presentation, Sunil V. Rao, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., asked: “Based on what you found, which is really no clinical advantage but no safety issue either, are you having your patients with ST-segment MI administering crushed prasugrel now?”
Dr. Vlachojannis said they didn’t see any clinical impact but reiterated that high platelet reactivity was reduced by one-third. “If this now translates into a safer primary PCI procedure, we can’t say. The study wasn’t powered for this kind of endpoint. Is this enough to give you a recommendation, Sunil, I’m not sure.”
“What we know with COMPARE CRUSH, and this is important, is that we tried to give the medication as soon as possible and tried to give this medication in a formulation which has the most favorable pharmacodynamics profile, and we still see it’s not doing the job,” he added.
Fellow panelist Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, questioned whether treatment time may play a role in teasing out the relatively modest differences that platelet reactivity may have on clinical outcomes.
Dr. Vlachojannis said the time from symptom onset to first medical contact was very fast and similar to that in the ATLANTIC trial. “The short time intervals have certainly influenced the outcomes.”
Panelist Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, University Hospital Bern, Switzerland, followed up on the morphine issue, asking whether the investigators tested for an interaction between morphine or opioid use and platelet reactivity at the time of PCI.
“We haven’t looked into this but you probably have the ON-TIME 3 data in your mind when you’re asking this, where crushed ticagrelor given in the ambulance didn’t influence platelet reactivity at the time point of PCI,” Dr. Vlachojannis said. “We are going to look further into the data and certainly the platelet reactivity analysis is going to be very interesting in this data set.”
The study was an investigator-initiated trial sponsored by Maasstad Cardiovascular Research B.V. with unrestricted grants from Shanghai MicroPort Medical and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Vlachojannis declared receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, and research grants from Daiichi Sankyo and Shanghai MicroPort.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Giving crushed prasugrel (Effient) to patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) en route to a planned primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) does not improve reperfusion rates, results of the COMPARE CRUSH trial show.
Patients assigned to prasugrel as crushed or integral tablets had similar rates of the study’s co-primary endpoints of thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 3 flow in the infarct-related artery at first angiography (31% vs. 32.7%; P = .64) and complete ST-segment resolution 1 hour post PCI (59.9% vs. 57.3%; P = .55).
“These findings hold in spite of the fact that crushed tablets of prasugrel led to more potent platelet inhibition compared with integral tablets,” said study author Georgios Vlachojannis, MD, PhD, University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands.
“Whether faster and more potent antiplatelet therapy can improve coronary reperfusion in contemporary STEMI treatment regimen warrants further investigation.”
The results were reported in a late-breaking clinical science session at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics virtual annual meeting and published simultaneously in the journal Circulation. The meeting was sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
Fibrinolytics and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors have demonstrated improved coronary reperfusion and outcomes when given pre hospital. Prior studies have also shown that early administration of a crushed P2Y12 inhibitor increases bioavailability and speeds platelet inhibition in STEMI patients, Dr. Vlachojannis noted.
However, the large randomized ATLANTIC trial, which compared prehospital to cath lab administration of crushed or integral ticagrelor (Brilinta), also found no difference in either TIMI flow in the infarct-related artery or ST-segment resolution.
Between November 2017 and March 2020, the investigator-initiated COMPARE CRUSH trial randomly allocated 727 STEMI patients (mean age, 62 years; 23% female) undergoing primary PCI to receive in the ambulance a 60-mg loading dose of prasugrel as either crushed or integral tablets.
The median time from onset of symptoms to first medical contact was 59 minutes, from first medical contact to study treatment 22 minutes, and from study treatment to primary PCI 57 minutes. These times did not differ between groups.
Platelet reactivity at the beginning of coronary angiography was significantly lower in the crushed group than in the integral group (P2Y12 reactivity units 192 vs. 227; P < .01). This resulted in significantly fewer patients in the crushed group with high platelet reactivity, defined as P2Y12 reactivity units >208, prior to the start of PCI (43.3% vs. 62.6%; P < .01).
There was no difference between the crushed and integral groups in the primary safety endpoint of TIMI major and BARC type 3 or higher bleeding within 48 hours after study treatment (0.4% vs 0.7%).
Death, MI, stroke, and urgent revascularization rates were also similar between groups during index hospitalization and at 30 days. Definite stent thrombosis occurred in one patient in the crushed group and two patients in the integral group.
In an exploratory analysis, the co-primary endpoint results were consistent across multiple subgroups, although there was a trend toward greater benefit on TIMI 3 flow in the crushed tablet group in patients older than age 75 years (P for interaction = .04), presenting with anterior infarction (P for interaction = .03), or with a history of prior PCI (P for interaction < .01).
“However, these results should be regarded as hypothesis-generating,” the authors wrote. “Opioids use in the ambulance was remarkably low in our study compared with the ATLANTIC trial, which might explain that we did not observe any significant interaction.”
Notably, morphine was used in half the ATLANTIC patients and was thought to have possibly delayed the absorption of ticagrelor.
During discussion following the presentation, Sunil V. Rao, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., asked: “Based on what you found, which is really no clinical advantage but no safety issue either, are you having your patients with ST-segment MI administering crushed prasugrel now?”
Dr. Vlachojannis said they didn’t see any clinical impact but reiterated that high platelet reactivity was reduced by one-third. “If this now translates into a safer primary PCI procedure, we can’t say. The study wasn’t powered for this kind of endpoint. Is this enough to give you a recommendation, Sunil, I’m not sure.”
“What we know with COMPARE CRUSH, and this is important, is that we tried to give the medication as soon as possible and tried to give this medication in a formulation which has the most favorable pharmacodynamics profile, and we still see it’s not doing the job,” he added.
Fellow panelist Philippe Gabriel Steg, MD, Imperial College London, questioned whether treatment time may play a role in teasing out the relatively modest differences that platelet reactivity may have on clinical outcomes.
Dr. Vlachojannis said the time from symptom onset to first medical contact was very fast and similar to that in the ATLANTIC trial. “The short time intervals have certainly influenced the outcomes.”
Panelist Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD, University Hospital Bern, Switzerland, followed up on the morphine issue, asking whether the investigators tested for an interaction between morphine or opioid use and platelet reactivity at the time of PCI.
“We haven’t looked into this but you probably have the ON-TIME 3 data in your mind when you’re asking this, where crushed ticagrelor given in the ambulance didn’t influence platelet reactivity at the time point of PCI,” Dr. Vlachojannis said. “We are going to look further into the data and certainly the platelet reactivity analysis is going to be very interesting in this data set.”
The study was an investigator-initiated trial sponsored by Maasstad Cardiovascular Research B.V. with unrestricted grants from Shanghai MicroPort Medical and Daiichi Sankyo. Dr. Vlachojannis declared receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, and research grants from Daiichi Sankyo and Shanghai MicroPort.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Video capsule endoscopy shows superiority, may reduce coronavirus exposure
Video capsule endoscopy (VCE) offers an alternative triage tool for acute GI bleeding that may reduce personnel exposure to SARS-CoV-2, based on a cohort study with historical controls.
VCE should be considered even when rapid coronavirus testing is available, as active bleeding is more likely to be detected when evaluated sooner, potentially sparing patients from invasive procedures, reported lead author Shahrad Hakimian, MD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worchester, and colleagues.
“Endoscopists and staff are at high risk of exposure to coronavirus through aerosols, as well as unintended, unrecognized splashes that are well known to occur frequently during routine endoscopy,” Dr. Hakimian said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Although pretesting and delaying procedures as needed may mitigate risks of viral exposure, “many urgent procedures, such as endoscopic evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding, can’t really wait,” Dr. Hakimian said.
Current guidelines recommend early upper endoscopy and/or colonoscopy for evaluation of GI bleeding, but Dr. Hakimian noted that two out of three initial tests are nondiagnostic, so multiple procedures are often needed to find an answer.
In 2018, a randomized, controlled trial coauthored by Dr. Hakimian’s colleagues demonstrated how VCE may be a better approach, as it more frequently detected active bleeding than standard of care (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-5.64).
The present study built on these findings in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hakimian and colleagues analyzed data from 50 consecutive, hemodynamically stable patients with severe anemia or suspected GI bleeding who underwent VCE as a first-line diagnostic modality from mid-March to mid-May 2020 (COVID arm). These patients were compared with 57 consecutive patients who were evaluated for acute GI bleeding or severe anemia with standard of care prior to the COVID-19 pandemic (pre-COVID arm).
Characteristics of the two cohorts were generally similar, although the COVID arm included a slightly older population, with a median age of 68 years, compared with a median age of 61.8 years for the pre-COVID arm (P = .03). Among presenting symptoms, hematochezia was less common in the COVID group (4% vs. 18%; P = .03). Comorbidities were not significantly different between cohorts.
Per the study design, 100% of patients in the COVID arm underwent VCE as their first diagnostic modality. In the pre-COVID arm, 82% of patients first underwent upper endoscopy, followed by colonoscopy (12%) and VCE (5%).
The main outcome, bleeding localization, did not differ between groups, whether this was confined to the first test, or in terms of final localization. But VCE was significantly better at detecting active bleeding or stigmata of bleeding, at a rate of 66%, compared with 28% in the pre-COVID group (P < .001). Patients in the COVID arm were also significantly less likely to need any invasive procedures (44% vs. 96%; P < .001).
No intergroup differences were observed in rates of blood transfusion, in-hospital or GI-bleed mortality, rebleeding, or readmission for bleeding.
“VCE appears to be a safe alternative to traditional diagnostic evaluation of GI bleeding in the era of COVID,” Dr. Hakimian concluded, noting that “the VCE-first strategy reduces the risk of staff exposure to endoscopic aerosols, conserves personal protective equipment, and reduces staff utilization.”
According to Neil Sengupta, MD, of the University of Chicago, “a VCE-first strategy in GI bleeding may be a useful triage tool in the COVID-19 era to determine which patients truly benefit from invasive endoscopy,” although he also noted that “further data are needed to determine the efficacy and safety of this approach.”
Lawrence Hookey, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., had a similar opinion.
“VCE appears to be a reasonable alternative in this patient group, at least as a first step,” Dr. Hookey said. “However, whether it truly makes a difference in the decision making process would have to be assessed prospectively via a randomized controlled trial or a decision analysis done in real time at various steps of the patient’s care path.”
Erik A. Holzwanger, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, suggested that these findings may “serve as a foundation” for similar studies, “as it appears COVID-19 will be an ongoing obstacle in endoscopy for the foreseeable future.”
“It would be interesting to have further discussion of timing of VCE, any COVID-19 transmission to staff during the VCE placement, and discussion of what constituted proceeding with endoscopic intervention [high-risk lesion, active bleeding] in both groups,” he added.
David Cave, MD, PhD, coauthor of the present study and the 2015 ACG clinical guideline for small bowel bleeding, said that VCE is gaining ground as the diagnostic of choice for GI bleeding, and patients prefer it, since it does not require anesthesia.
“This abstract is another clear pointer to the way in which, we should in the future, investigate gastrointestinal bleeding, both acute and chronic,” Dr. Cave said. “We are at an inflection point of transition to a new technology.”
Dr. Cave disclosed relationships with Medtronic and Olympus. The other investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
Video capsule endoscopy (VCE) offers an alternative triage tool for acute GI bleeding that may reduce personnel exposure to SARS-CoV-2, based on a cohort study with historical controls.
VCE should be considered even when rapid coronavirus testing is available, as active bleeding is more likely to be detected when evaluated sooner, potentially sparing patients from invasive procedures, reported lead author Shahrad Hakimian, MD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worchester, and colleagues.
“Endoscopists and staff are at high risk of exposure to coronavirus through aerosols, as well as unintended, unrecognized splashes that are well known to occur frequently during routine endoscopy,” Dr. Hakimian said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Although pretesting and delaying procedures as needed may mitigate risks of viral exposure, “many urgent procedures, such as endoscopic evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding, can’t really wait,” Dr. Hakimian said.
Current guidelines recommend early upper endoscopy and/or colonoscopy for evaluation of GI bleeding, but Dr. Hakimian noted that two out of three initial tests are nondiagnostic, so multiple procedures are often needed to find an answer.
In 2018, a randomized, controlled trial coauthored by Dr. Hakimian’s colleagues demonstrated how VCE may be a better approach, as it more frequently detected active bleeding than standard of care (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-5.64).
The present study built on these findings in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hakimian and colleagues analyzed data from 50 consecutive, hemodynamically stable patients with severe anemia or suspected GI bleeding who underwent VCE as a first-line diagnostic modality from mid-March to mid-May 2020 (COVID arm). These patients were compared with 57 consecutive patients who were evaluated for acute GI bleeding or severe anemia with standard of care prior to the COVID-19 pandemic (pre-COVID arm).
Characteristics of the two cohorts were generally similar, although the COVID arm included a slightly older population, with a median age of 68 years, compared with a median age of 61.8 years for the pre-COVID arm (P = .03). Among presenting symptoms, hematochezia was less common in the COVID group (4% vs. 18%; P = .03). Comorbidities were not significantly different between cohorts.
Per the study design, 100% of patients in the COVID arm underwent VCE as their first diagnostic modality. In the pre-COVID arm, 82% of patients first underwent upper endoscopy, followed by colonoscopy (12%) and VCE (5%).
The main outcome, bleeding localization, did not differ between groups, whether this was confined to the first test, or in terms of final localization. But VCE was significantly better at detecting active bleeding or stigmata of bleeding, at a rate of 66%, compared with 28% in the pre-COVID group (P < .001). Patients in the COVID arm were also significantly less likely to need any invasive procedures (44% vs. 96%; P < .001).
No intergroup differences were observed in rates of blood transfusion, in-hospital or GI-bleed mortality, rebleeding, or readmission for bleeding.
“VCE appears to be a safe alternative to traditional diagnostic evaluation of GI bleeding in the era of COVID,” Dr. Hakimian concluded, noting that “the VCE-first strategy reduces the risk of staff exposure to endoscopic aerosols, conserves personal protective equipment, and reduces staff utilization.”
According to Neil Sengupta, MD, of the University of Chicago, “a VCE-first strategy in GI bleeding may be a useful triage tool in the COVID-19 era to determine which patients truly benefit from invasive endoscopy,” although he also noted that “further data are needed to determine the efficacy and safety of this approach.”
Lawrence Hookey, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., had a similar opinion.
“VCE appears to be a reasonable alternative in this patient group, at least as a first step,” Dr. Hookey said. “However, whether it truly makes a difference in the decision making process would have to be assessed prospectively via a randomized controlled trial or a decision analysis done in real time at various steps of the patient’s care path.”
Erik A. Holzwanger, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, suggested that these findings may “serve as a foundation” for similar studies, “as it appears COVID-19 will be an ongoing obstacle in endoscopy for the foreseeable future.”
“It would be interesting to have further discussion of timing of VCE, any COVID-19 transmission to staff during the VCE placement, and discussion of what constituted proceeding with endoscopic intervention [high-risk lesion, active bleeding] in both groups,” he added.
David Cave, MD, PhD, coauthor of the present study and the 2015 ACG clinical guideline for small bowel bleeding, said that VCE is gaining ground as the diagnostic of choice for GI bleeding, and patients prefer it, since it does not require anesthesia.
“This abstract is another clear pointer to the way in which, we should in the future, investigate gastrointestinal bleeding, both acute and chronic,” Dr. Cave said. “We are at an inflection point of transition to a new technology.”
Dr. Cave disclosed relationships with Medtronic and Olympus. The other investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
Video capsule endoscopy (VCE) offers an alternative triage tool for acute GI bleeding that may reduce personnel exposure to SARS-CoV-2, based on a cohort study with historical controls.
VCE should be considered even when rapid coronavirus testing is available, as active bleeding is more likely to be detected when evaluated sooner, potentially sparing patients from invasive procedures, reported lead author Shahrad Hakimian, MD, of the University of Massachusetts Medical Center, Worchester, and colleagues.
“Endoscopists and staff are at high risk of exposure to coronavirus through aerosols, as well as unintended, unrecognized splashes that are well known to occur frequently during routine endoscopy,” Dr. Hakimian said during a virtual presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Although pretesting and delaying procedures as needed may mitigate risks of viral exposure, “many urgent procedures, such as endoscopic evaluation of gastrointestinal bleeding, can’t really wait,” Dr. Hakimian said.
Current guidelines recommend early upper endoscopy and/or colonoscopy for evaluation of GI bleeding, but Dr. Hakimian noted that two out of three initial tests are nondiagnostic, so multiple procedures are often needed to find an answer.
In 2018, a randomized, controlled trial coauthored by Dr. Hakimian’s colleagues demonstrated how VCE may be a better approach, as it more frequently detected active bleeding than standard of care (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.36-5.64).
The present study built on these findings in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dr. Hakimian and colleagues analyzed data from 50 consecutive, hemodynamically stable patients with severe anemia or suspected GI bleeding who underwent VCE as a first-line diagnostic modality from mid-March to mid-May 2020 (COVID arm). These patients were compared with 57 consecutive patients who were evaluated for acute GI bleeding or severe anemia with standard of care prior to the COVID-19 pandemic (pre-COVID arm).
Characteristics of the two cohorts were generally similar, although the COVID arm included a slightly older population, with a median age of 68 years, compared with a median age of 61.8 years for the pre-COVID arm (P = .03). Among presenting symptoms, hematochezia was less common in the COVID group (4% vs. 18%; P = .03). Comorbidities were not significantly different between cohorts.
Per the study design, 100% of patients in the COVID arm underwent VCE as their first diagnostic modality. In the pre-COVID arm, 82% of patients first underwent upper endoscopy, followed by colonoscopy (12%) and VCE (5%).
The main outcome, bleeding localization, did not differ between groups, whether this was confined to the first test, or in terms of final localization. But VCE was significantly better at detecting active bleeding or stigmata of bleeding, at a rate of 66%, compared with 28% in the pre-COVID group (P < .001). Patients in the COVID arm were also significantly less likely to need any invasive procedures (44% vs. 96%; P < .001).
No intergroup differences were observed in rates of blood transfusion, in-hospital or GI-bleed mortality, rebleeding, or readmission for bleeding.
“VCE appears to be a safe alternative to traditional diagnostic evaluation of GI bleeding in the era of COVID,” Dr. Hakimian concluded, noting that “the VCE-first strategy reduces the risk of staff exposure to endoscopic aerosols, conserves personal protective equipment, and reduces staff utilization.”
According to Neil Sengupta, MD, of the University of Chicago, “a VCE-first strategy in GI bleeding may be a useful triage tool in the COVID-19 era to determine which patients truly benefit from invasive endoscopy,” although he also noted that “further data are needed to determine the efficacy and safety of this approach.”
Lawrence Hookey, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., had a similar opinion.
“VCE appears to be a reasonable alternative in this patient group, at least as a first step,” Dr. Hookey said. “However, whether it truly makes a difference in the decision making process would have to be assessed prospectively via a randomized controlled trial or a decision analysis done in real time at various steps of the patient’s care path.”
Erik A. Holzwanger, MD, a gastroenterology fellow at Tufts Medical Center in Boston, suggested that these findings may “serve as a foundation” for similar studies, “as it appears COVID-19 will be an ongoing obstacle in endoscopy for the foreseeable future.”
“It would be interesting to have further discussion of timing of VCE, any COVID-19 transmission to staff during the VCE placement, and discussion of what constituted proceeding with endoscopic intervention [high-risk lesion, active bleeding] in both groups,” he added.
David Cave, MD, PhD, coauthor of the present study and the 2015 ACG clinical guideline for small bowel bleeding, said that VCE is gaining ground as the diagnostic of choice for GI bleeding, and patients prefer it, since it does not require anesthesia.
“This abstract is another clear pointer to the way in which, we should in the future, investigate gastrointestinal bleeding, both acute and chronic,” Dr. Cave said. “We are at an inflection point of transition to a new technology.”
Dr. Cave disclosed relationships with Medtronic and Olympus. The other investigators and interviewees reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM ACG 2020
COVID frontline physicians afraid to seek mental health care
A new poll of emergency physicians on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic shows many are fearful of seeking mental health care for fear of stigma and the potential career impact.
The results of the nationally representative poll, conducted Oct. 7-13 by the American College of Emergency Physicians, showed almost half (45%) of 862 emergency physician respondents reported being uncomfortable seeking available psychiatric care. The poll had a margin of error of plus or minus 3 percentage points.
The findings provide new insight into both the challenges of serving in emergency medicine during the pandemic and the persistent barriers to mental health care in terms of stigma and concerns about potential career setbacks.
In the poll, with another 45% report they were feeling somewhat more stressed.
When asked about causes of stress related directly to COVID-19, 83% cited concerns about family and friends contracting COVID-19. Also factoring into emergency physicians’ stress and burnout were concerns about their own safety (80%) and lack of personal protective equipment or other needed resources (60%).
In the poll, 29% of respondents reported having excellent access to mental health treatment and 42% reported having good access. Despite this, 30% of respondents still reported feeling there was a lot of stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment, with another 43% reporting they felt there was some stigma.
Poll results also showed that 24% of respondents were very concerned about what might happen with their employment if they were to seek mental health treatment, with another 33% saying they were somewhat concerned.
In recent years there have been efforts to break down cultural roadblocks in medicine that deter many physicians from seeking mental health treatment, but more needs to be done, said Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, who was elected president of ACEP at last weekend’s annual meeting, ACEP20.
“The pandemic emphatically underscores our need to change the status quo when it comes to physicians’ mental health,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, current efforts to remove such barriers include initiatives to limit inquiries into clinicians’ past or present mental health treatment.
In May, the influential Joint Commission issued a statement urging organizations to refrain from asking about any history of mental health conditions or treatment. The Joint Commission said it supports recommendations already made by the Federation of State Medical Boards and the American Medical Association to limit inquiries on licensing applications to conditions that currently impair a clinician’s ability to perform their job.
Also supporting these efforts is the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation, created in honor of an emergency physician who died by suicide in April amid the pandemic.
Lorna Breen, MD, had been working intensely in the response to the pandemic. During one shift, she covered two EDs in Manhattan at locations 5 miles apart, according to a backgrounder on the foundation’s web site.
At an ACEP press conference this week, Dr. Breen’s brother-in-law, J. Corey Feist, JD, MBA, cofounder of the foundation, noted that some states’ licensing applications for physicians include questions that fall outside of the boundaries of the Americans With Disabilities Act. He cited an analysis of state medical boards’ initial licensing questions published in 2018 in the Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
In many cases, states have posed questions that extend beyond an assessment of a physician’s current ability to care for patients, creating a needless hurdle to seeking care, wrote the paper’s lead author, Carol North, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Over the years, many medical licensure boards have asked applicants intrusive questions about whether they have any psychiatric history. This has created a major problem for applicants, and unfortunately this has discouraged many of those who need psychiatric treatment from seeking it because of fear of the questions,” Dr. North and colleagues noted. They cited Ohio as an example of a state that had overhauled its approach to questioning to bring it in compliance with the ADA.
Ohio previously required applicants to answer lengthy questions about their mental health, including:
- Within the last 10 years, have you been diagnosed with or have you been treated for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Have you, since attaining the age of eighteen or within the last 10 years, whichever period is shorter, been admitted to a hospital or other facility for the treatment of bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Do you have, or have you been diagnosed as having, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?
In the new version, the single question reads: “In the past 5 years, have you been diagnosed as having, or been hospitalized for, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?”
Other states such as New York pose no mental health questions on applications for licensure.
Still, even when states have nondiscriminatory laws, physicians may not be aware of them, said Mr. Feist at an ACEP press conference. In addition to his work with the foundation, Mr. Feist is the CEO of the University of Virginia Physicians Group.
He said his sister-in-law Dr. Breen may have worried without cause about potential consequences of seeking psychiatric treatment during the pandemic. In addition, physicians in need of psychiatric care may worry about encountering hitches with medical organizations and insurers.
“This stigma and this fear of professional action on your license or your credentialing or privileging is pervasive throughout the industry,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new poll of emergency physicians on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic shows many are fearful of seeking mental health care for fear of stigma and the potential career impact.
The results of the nationally representative poll, conducted Oct. 7-13 by the American College of Emergency Physicians, showed almost half (45%) of 862 emergency physician respondents reported being uncomfortable seeking available psychiatric care. The poll had a margin of error of plus or minus 3 percentage points.
The findings provide new insight into both the challenges of serving in emergency medicine during the pandemic and the persistent barriers to mental health care in terms of stigma and concerns about potential career setbacks.
In the poll, with another 45% report they were feeling somewhat more stressed.
When asked about causes of stress related directly to COVID-19, 83% cited concerns about family and friends contracting COVID-19. Also factoring into emergency physicians’ stress and burnout were concerns about their own safety (80%) and lack of personal protective equipment or other needed resources (60%).
In the poll, 29% of respondents reported having excellent access to mental health treatment and 42% reported having good access. Despite this, 30% of respondents still reported feeling there was a lot of stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment, with another 43% reporting they felt there was some stigma.
Poll results also showed that 24% of respondents were very concerned about what might happen with their employment if they were to seek mental health treatment, with another 33% saying they were somewhat concerned.
In recent years there have been efforts to break down cultural roadblocks in medicine that deter many physicians from seeking mental health treatment, but more needs to be done, said Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, who was elected president of ACEP at last weekend’s annual meeting, ACEP20.
“The pandemic emphatically underscores our need to change the status quo when it comes to physicians’ mental health,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, current efforts to remove such barriers include initiatives to limit inquiries into clinicians’ past or present mental health treatment.
In May, the influential Joint Commission issued a statement urging organizations to refrain from asking about any history of mental health conditions or treatment. The Joint Commission said it supports recommendations already made by the Federation of State Medical Boards and the American Medical Association to limit inquiries on licensing applications to conditions that currently impair a clinician’s ability to perform their job.
Also supporting these efforts is the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation, created in honor of an emergency physician who died by suicide in April amid the pandemic.
Lorna Breen, MD, had been working intensely in the response to the pandemic. During one shift, she covered two EDs in Manhattan at locations 5 miles apart, according to a backgrounder on the foundation’s web site.
At an ACEP press conference this week, Dr. Breen’s brother-in-law, J. Corey Feist, JD, MBA, cofounder of the foundation, noted that some states’ licensing applications for physicians include questions that fall outside of the boundaries of the Americans With Disabilities Act. He cited an analysis of state medical boards’ initial licensing questions published in 2018 in the Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
In many cases, states have posed questions that extend beyond an assessment of a physician’s current ability to care for patients, creating a needless hurdle to seeking care, wrote the paper’s lead author, Carol North, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Over the years, many medical licensure boards have asked applicants intrusive questions about whether they have any psychiatric history. This has created a major problem for applicants, and unfortunately this has discouraged many of those who need psychiatric treatment from seeking it because of fear of the questions,” Dr. North and colleagues noted. They cited Ohio as an example of a state that had overhauled its approach to questioning to bring it in compliance with the ADA.
Ohio previously required applicants to answer lengthy questions about their mental health, including:
- Within the last 10 years, have you been diagnosed with or have you been treated for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Have you, since attaining the age of eighteen or within the last 10 years, whichever period is shorter, been admitted to a hospital or other facility for the treatment of bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Do you have, or have you been diagnosed as having, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?
In the new version, the single question reads: “In the past 5 years, have you been diagnosed as having, or been hospitalized for, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?”
Other states such as New York pose no mental health questions on applications for licensure.
Still, even when states have nondiscriminatory laws, physicians may not be aware of them, said Mr. Feist at an ACEP press conference. In addition to his work with the foundation, Mr. Feist is the CEO of the University of Virginia Physicians Group.
He said his sister-in-law Dr. Breen may have worried without cause about potential consequences of seeking psychiatric treatment during the pandemic. In addition, physicians in need of psychiatric care may worry about encountering hitches with medical organizations and insurers.
“This stigma and this fear of professional action on your license or your credentialing or privileging is pervasive throughout the industry,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A new poll of emergency physicians on the front lines of the COVID-19 pandemic shows many are fearful of seeking mental health care for fear of stigma and the potential career impact.
The results of the nationally representative poll, conducted Oct. 7-13 by the American College of Emergency Physicians, showed almost half (45%) of 862 emergency physician respondents reported being uncomfortable seeking available psychiatric care. The poll had a margin of error of plus or minus 3 percentage points.
The findings provide new insight into both the challenges of serving in emergency medicine during the pandemic and the persistent barriers to mental health care in terms of stigma and concerns about potential career setbacks.
In the poll, with another 45% report they were feeling somewhat more stressed.
When asked about causes of stress related directly to COVID-19, 83% cited concerns about family and friends contracting COVID-19. Also factoring into emergency physicians’ stress and burnout were concerns about their own safety (80%) and lack of personal protective equipment or other needed resources (60%).
In the poll, 29% of respondents reported having excellent access to mental health treatment and 42% reported having good access. Despite this, 30% of respondents still reported feeling there was a lot of stigma in their workplace about seeking mental health treatment, with another 43% reporting they felt there was some stigma.
Poll results also showed that 24% of respondents were very concerned about what might happen with their employment if they were to seek mental health treatment, with another 33% saying they were somewhat concerned.
In recent years there have been efforts to break down cultural roadblocks in medicine that deter many physicians from seeking mental health treatment, but more needs to be done, said Mark Rosenberg, DO, MBA, who was elected president of ACEP at last weekend’s annual meeting, ACEP20.
“The pandemic emphatically underscores our need to change the status quo when it comes to physicians’ mental health,” Dr. Rosenberg said.
As previously reported by Medscape Medical News, current efforts to remove such barriers include initiatives to limit inquiries into clinicians’ past or present mental health treatment.
In May, the influential Joint Commission issued a statement urging organizations to refrain from asking about any history of mental health conditions or treatment. The Joint Commission said it supports recommendations already made by the Federation of State Medical Boards and the American Medical Association to limit inquiries on licensing applications to conditions that currently impair a clinician’s ability to perform their job.
Also supporting these efforts is the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation, created in honor of an emergency physician who died by suicide in April amid the pandemic.
Lorna Breen, MD, had been working intensely in the response to the pandemic. During one shift, she covered two EDs in Manhattan at locations 5 miles apart, according to a backgrounder on the foundation’s web site.
At an ACEP press conference this week, Dr. Breen’s brother-in-law, J. Corey Feist, JD, MBA, cofounder of the foundation, noted that some states’ licensing applications for physicians include questions that fall outside of the boundaries of the Americans With Disabilities Act. He cited an analysis of state medical boards’ initial licensing questions published in 2018 in the Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
In many cases, states have posed questions that extend beyond an assessment of a physician’s current ability to care for patients, creating a needless hurdle to seeking care, wrote the paper’s lead author, Carol North, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
“Over the years, many medical licensure boards have asked applicants intrusive questions about whether they have any psychiatric history. This has created a major problem for applicants, and unfortunately this has discouraged many of those who need psychiatric treatment from seeking it because of fear of the questions,” Dr. North and colleagues noted. They cited Ohio as an example of a state that had overhauled its approach to questioning to bring it in compliance with the ADA.
Ohio previously required applicants to answer lengthy questions about their mental health, including:
- Within the last 10 years, have you been diagnosed with or have you been treated for bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Have you, since attaining the age of eighteen or within the last 10 years, whichever period is shorter, been admitted to a hospital or other facility for the treatment of bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, paranoia, or any other psychotic disorder?
- Do you have, or have you been diagnosed as having, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?
In the new version, the single question reads: “In the past 5 years, have you been diagnosed as having, or been hospitalized for, a medical condition which in any way impairs or limits your ability to practice medicine with reasonable skill and safety?”
Other states such as New York pose no mental health questions on applications for licensure.
Still, even when states have nondiscriminatory laws, physicians may not be aware of them, said Mr. Feist at an ACEP press conference. In addition to his work with the foundation, Mr. Feist is the CEO of the University of Virginia Physicians Group.
He said his sister-in-law Dr. Breen may have worried without cause about potential consequences of seeking psychiatric treatment during the pandemic. In addition, physicians in need of psychiatric care may worry about encountering hitches with medical organizations and insurers.
“This stigma and this fear of professional action on your license or your credentialing or privileging is pervasive throughout the industry,” he said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Consensus guidelines address inpatient diabetes technology
A new consensus statement offers detailed guidelines for inpatient use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and automated insulin delivery (AID) systems.
Aimed at clinicians, researchers, and hospital administrators, the open-access document was recently published by a multidisciplinary international panel of 24 experts in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.
The statement includes 77 separate recommendations under five headings: 1) continued use of CGM by patients already using them at home, 2) initiation of CGM in hospital, 3) continuation of AID systems in hospital by patients already using them at home, 4) logistics and hands-on care of hospitalized patients using CGM and AID systems, and 5) data management of CGM and AID systems in hospital.
“This is the most comprehensive and up-to-date guideline on the use of diabetes technology in the hospital now,” lead author Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, told Medscape Medical News in an interview.
“Overall, most experts believe that CGM and AID have the potential to overcome the current limitations of glycemic monitoring in the hospital to improve patient outcomes, but we need research – first to get the approval and second to get widespread use,” said Galindo, medical chair of the hospital diabetes taskforce at Emory Healthcare System, Atlanta.
“COVID-19 changed everything”
The guideline is an update of a 2017 statement on hospital use of CGM. The new guideline adds AID systems (sometimes referred to as an artificial pancreas), which combines a CGM and insulin pump and uses an algorithm to guide insulin delivery, and is the first to be developed during the COVID-19 era.
The update had been planned prior to the pandemic, but the actual panel meeting took place in April 2020, after the US Food and Drug Administration allowed inpatient use of CGM despite lack of official approval.
“COVID-19 changed everything. ... We had to be more specific about how to implement CGM in these patients. The standard of care is hourly point-of-care glucose monitoring in the [ICU], and at least every 4 hours outside the ICU. With limited [personal protective equipment] and the burden on nursing it was unachievable,” Galindo explained.
In June 2020, Galindo and other guideline authors developed a COVID-19–specific document (also open-access), which goes more into detail about CGM and how to implement in-hospital use during the pandemic.
The current consensus guideline “provides a high-level review of the evidence by experts,” Galindo added.
Recommendations cover different technologies and hospital settings
The panel “strongly” advises that hospital providers consult with an inpatient diabetes team, if available, to help manage patients already using CGM prior to admission. Among other recommendations, they list several situations in which CGM data should not be relied upon for management decisions, including severe hyper- or hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or in patients with skin infections near the sensor site.
The panel also call for more research into outcomes for CGM continuation in the hospital and optimal implementation of both CGM and point-of-care glucose testing. For hospitals, strong recommendations include developing standard CGM data reports and workflows, as well as policies for CGM use.
Galindo pointed out: “A lot of hospitals have policies on that, but there aren’t many studies. It’s just that patients like it and it’s very hard to take it away from patients when they’re doing well.”
The section on CGM inpatient initiation is where COVID-19 plays the greatest role, which includes just one strong clinical practice recommendation: “Healthcare providers should consider prescribing CGM to reduce the need for frequent nurse contact for point-of-care glucose testing and the use of personal protective equipment for patients on isolation with highly contagious infectious diseases (eg, COVID-19).”
Strong recommendations also include a call for outcomes research and for hospitals to develop CGM protocols and educational tools for staff.
“We can do a study for approval but if administration and hospital policies aren’t there we’re not going to be able to use them,” Galindo noted.
For patients who already use AID systems – either the Medtronic 670G or Tandem Control IQ in the United States – the panel advises assessment to ensure the AID system is the most appropriate inpatient treatment, and the development of an alternative plan for diabetes management, if necessary. They also strongly recommend research in this area, and for hospitals to develop protocols for use of AID systems in various clinical situations.
Most detailed guidance addresses logistics and data management
Most of the strong recommendations regarding logistics are aimed at nursing staff, including receiving training in use of CGM and AID systems, confirming patient capacity, inspection of devices, and understanding when to administer a point-of-care glucose test.
Again, the panel calls for more data and for hospitals to develop policies and protocols for ensuring safe CGM and AID systems use, and when to avoid use.
Finally, they make one strong clinical recommendation regarding data management: “Healthcare providers should develop a set of core data elements and definitions for CGM data for inclusion in common data models and the electronic health record.”
That’s followed by a long list of relevant recommendations for research in the area, and for hospitals to integrate CGM and AID system data into their EHR systems.
This last area has proven particularly challenging, Galindo said. “Right now we do four point-of-care glucoses a day, and that goes right into the EHR, but with CGM it’s much more than that. How do we get all those data into the EHR and interpret it? Many steps need to be taken into consideration.”
Studies are being conducted in order to fulfill requirements for FDA approval of inpatient CGM use, he said, with data on implementation and inpatient AID system use to follow.
“More data will be available, triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the use of technology in the hospital goes beyond COVID-19,” he said
Galindo has reported receiving unrestricted research support to Emory for investigator-initiated studies from Novo Nordisk and Dexcom, and consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Valeritas. He is partially supported by research grants from the NIH/NIDDK.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement offers detailed guidelines for inpatient use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and automated insulin delivery (AID) systems.
Aimed at clinicians, researchers, and hospital administrators, the open-access document was recently published by a multidisciplinary international panel of 24 experts in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.
The statement includes 77 separate recommendations under five headings: 1) continued use of CGM by patients already using them at home, 2) initiation of CGM in hospital, 3) continuation of AID systems in hospital by patients already using them at home, 4) logistics and hands-on care of hospitalized patients using CGM and AID systems, and 5) data management of CGM and AID systems in hospital.
“This is the most comprehensive and up-to-date guideline on the use of diabetes technology in the hospital now,” lead author Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, told Medscape Medical News in an interview.
“Overall, most experts believe that CGM and AID have the potential to overcome the current limitations of glycemic monitoring in the hospital to improve patient outcomes, but we need research – first to get the approval and second to get widespread use,” said Galindo, medical chair of the hospital diabetes taskforce at Emory Healthcare System, Atlanta.
“COVID-19 changed everything”
The guideline is an update of a 2017 statement on hospital use of CGM. The new guideline adds AID systems (sometimes referred to as an artificial pancreas), which combines a CGM and insulin pump and uses an algorithm to guide insulin delivery, and is the first to be developed during the COVID-19 era.
The update had been planned prior to the pandemic, but the actual panel meeting took place in April 2020, after the US Food and Drug Administration allowed inpatient use of CGM despite lack of official approval.
“COVID-19 changed everything. ... We had to be more specific about how to implement CGM in these patients. The standard of care is hourly point-of-care glucose monitoring in the [ICU], and at least every 4 hours outside the ICU. With limited [personal protective equipment] and the burden on nursing it was unachievable,” Galindo explained.
In June 2020, Galindo and other guideline authors developed a COVID-19–specific document (also open-access), which goes more into detail about CGM and how to implement in-hospital use during the pandemic.
The current consensus guideline “provides a high-level review of the evidence by experts,” Galindo added.
Recommendations cover different technologies and hospital settings
The panel “strongly” advises that hospital providers consult with an inpatient diabetes team, if available, to help manage patients already using CGM prior to admission. Among other recommendations, they list several situations in which CGM data should not be relied upon for management decisions, including severe hyper- or hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or in patients with skin infections near the sensor site.
The panel also call for more research into outcomes for CGM continuation in the hospital and optimal implementation of both CGM and point-of-care glucose testing. For hospitals, strong recommendations include developing standard CGM data reports and workflows, as well as policies for CGM use.
Galindo pointed out: “A lot of hospitals have policies on that, but there aren’t many studies. It’s just that patients like it and it’s very hard to take it away from patients when they’re doing well.”
The section on CGM inpatient initiation is where COVID-19 plays the greatest role, which includes just one strong clinical practice recommendation: “Healthcare providers should consider prescribing CGM to reduce the need for frequent nurse contact for point-of-care glucose testing and the use of personal protective equipment for patients on isolation with highly contagious infectious diseases (eg, COVID-19).”
Strong recommendations also include a call for outcomes research and for hospitals to develop CGM protocols and educational tools for staff.
“We can do a study for approval but if administration and hospital policies aren’t there we’re not going to be able to use them,” Galindo noted.
For patients who already use AID systems – either the Medtronic 670G or Tandem Control IQ in the United States – the panel advises assessment to ensure the AID system is the most appropriate inpatient treatment, and the development of an alternative plan for diabetes management, if necessary. They also strongly recommend research in this area, and for hospitals to develop protocols for use of AID systems in various clinical situations.
Most detailed guidance addresses logistics and data management
Most of the strong recommendations regarding logistics are aimed at nursing staff, including receiving training in use of CGM and AID systems, confirming patient capacity, inspection of devices, and understanding when to administer a point-of-care glucose test.
Again, the panel calls for more data and for hospitals to develop policies and protocols for ensuring safe CGM and AID systems use, and when to avoid use.
Finally, they make one strong clinical recommendation regarding data management: “Healthcare providers should develop a set of core data elements and definitions for CGM data for inclusion in common data models and the electronic health record.”
That’s followed by a long list of relevant recommendations for research in the area, and for hospitals to integrate CGM and AID system data into their EHR systems.
This last area has proven particularly challenging, Galindo said. “Right now we do four point-of-care glucoses a day, and that goes right into the EHR, but with CGM it’s much more than that. How do we get all those data into the EHR and interpret it? Many steps need to be taken into consideration.”
Studies are being conducted in order to fulfill requirements for FDA approval of inpatient CGM use, he said, with data on implementation and inpatient AID system use to follow.
“More data will be available, triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the use of technology in the hospital goes beyond COVID-19,” he said
Galindo has reported receiving unrestricted research support to Emory for investigator-initiated studies from Novo Nordisk and Dexcom, and consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Valeritas. He is partially supported by research grants from the NIH/NIDDK.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new consensus statement offers detailed guidelines for inpatient use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and automated insulin delivery (AID) systems.
Aimed at clinicians, researchers, and hospital administrators, the open-access document was recently published by a multidisciplinary international panel of 24 experts in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.
The statement includes 77 separate recommendations under five headings: 1) continued use of CGM by patients already using them at home, 2) initiation of CGM in hospital, 3) continuation of AID systems in hospital by patients already using them at home, 4) logistics and hands-on care of hospitalized patients using CGM and AID systems, and 5) data management of CGM and AID systems in hospital.
“This is the most comprehensive and up-to-date guideline on the use of diabetes technology in the hospital now,” lead author Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, told Medscape Medical News in an interview.
“Overall, most experts believe that CGM and AID have the potential to overcome the current limitations of glycemic monitoring in the hospital to improve patient outcomes, but we need research – first to get the approval and second to get widespread use,” said Galindo, medical chair of the hospital diabetes taskforce at Emory Healthcare System, Atlanta.
“COVID-19 changed everything”
The guideline is an update of a 2017 statement on hospital use of CGM. The new guideline adds AID systems (sometimes referred to as an artificial pancreas), which combines a CGM and insulin pump and uses an algorithm to guide insulin delivery, and is the first to be developed during the COVID-19 era.
The update had been planned prior to the pandemic, but the actual panel meeting took place in April 2020, after the US Food and Drug Administration allowed inpatient use of CGM despite lack of official approval.
“COVID-19 changed everything. ... We had to be more specific about how to implement CGM in these patients. The standard of care is hourly point-of-care glucose monitoring in the [ICU], and at least every 4 hours outside the ICU. With limited [personal protective equipment] and the burden on nursing it was unachievable,” Galindo explained.
In June 2020, Galindo and other guideline authors developed a COVID-19–specific document (also open-access), which goes more into detail about CGM and how to implement in-hospital use during the pandemic.
The current consensus guideline “provides a high-level review of the evidence by experts,” Galindo added.
Recommendations cover different technologies and hospital settings
The panel “strongly” advises that hospital providers consult with an inpatient diabetes team, if available, to help manage patients already using CGM prior to admission. Among other recommendations, they list several situations in which CGM data should not be relied upon for management decisions, including severe hyper- or hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or in patients with skin infections near the sensor site.
The panel also call for more research into outcomes for CGM continuation in the hospital and optimal implementation of both CGM and point-of-care glucose testing. For hospitals, strong recommendations include developing standard CGM data reports and workflows, as well as policies for CGM use.
Galindo pointed out: “A lot of hospitals have policies on that, but there aren’t many studies. It’s just that patients like it and it’s very hard to take it away from patients when they’re doing well.”
The section on CGM inpatient initiation is where COVID-19 plays the greatest role, which includes just one strong clinical practice recommendation: “Healthcare providers should consider prescribing CGM to reduce the need for frequent nurse contact for point-of-care glucose testing and the use of personal protective equipment for patients on isolation with highly contagious infectious diseases (eg, COVID-19).”
Strong recommendations also include a call for outcomes research and for hospitals to develop CGM protocols and educational tools for staff.
“We can do a study for approval but if administration and hospital policies aren’t there we’re not going to be able to use them,” Galindo noted.
For patients who already use AID systems – either the Medtronic 670G or Tandem Control IQ in the United States – the panel advises assessment to ensure the AID system is the most appropriate inpatient treatment, and the development of an alternative plan for diabetes management, if necessary. They also strongly recommend research in this area, and for hospitals to develop protocols for use of AID systems in various clinical situations.
Most detailed guidance addresses logistics and data management
Most of the strong recommendations regarding logistics are aimed at nursing staff, including receiving training in use of CGM and AID systems, confirming patient capacity, inspection of devices, and understanding when to administer a point-of-care glucose test.
Again, the panel calls for more data and for hospitals to develop policies and protocols for ensuring safe CGM and AID systems use, and when to avoid use.
Finally, they make one strong clinical recommendation regarding data management: “Healthcare providers should develop a set of core data elements and definitions for CGM data for inclusion in common data models and the electronic health record.”
That’s followed by a long list of relevant recommendations for research in the area, and for hospitals to integrate CGM and AID system data into their EHR systems.
This last area has proven particularly challenging, Galindo said. “Right now we do four point-of-care glucoses a day, and that goes right into the EHR, but with CGM it’s much more than that. How do we get all those data into the EHR and interpret it? Many steps need to be taken into consideration.”
Studies are being conducted in order to fulfill requirements for FDA approval of inpatient CGM use, he said, with data on implementation and inpatient AID system use to follow.
“More data will be available, triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the use of technology in the hospital goes beyond COVID-19,” he said
Galindo has reported receiving unrestricted research support to Emory for investigator-initiated studies from Novo Nordisk and Dexcom, and consulting fees from Abbott Diabetes Care, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Valeritas. He is partially supported by research grants from the NIH/NIDDK.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ACC expert consensus on post-TAVR arrhythmias
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) has released a new Expert Consensus Decision Pathway (ECDP) on the management of conduction disturbances after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The document provides guidance to clinicians in identifying and managing this common complication of TAVR, covering the pre-TAVR, periprocedural and post-TAVR periods.
“Conduction disturbances after TAVR are common and there is currently heterogeneity in how they’re managed, ranging from a casual observational approach to invasive electrophysiological studies and preemptive pacemaker implantation,” said writing committee chair Scott Lilly, MD, PhD, from the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center in Columbus.
“We felt this kind of collaborative effort to review what little research there is on this topic and come to [an] expert consensus was long overdue,” he added.
The document was published online Oct. 21 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Lilly stressed in an interview that this effort is an ECDP and not a guideline “because there is not data out there to solidly stand on and say, ‘This is the way we should do things.’ “
His hope is that this document will generate more discussion on this topic and spur some (probably National Institutes of Health–sponsored) clinical trials to better guide practice.
Not uncommon and not decreasing
Complete heart block requiring permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation is seen in about 15% of patients within 30 days after TAVR. While this is a clear indication for PPM, there is no consensus on the management of less severe conduction disturbances such as new bundle branch or transient complete atrioventricular (AV) heart block.
Unlike the rates of bleeding, vascular injury, and stroke, which have decreased over time, the rates of in-hospital PPM implantation after TAVR have not changed significantly since commercialization in 2012. This is a concern because TAVR is increasingly used in younger, lower-risk patients.
“The pacemaker rate really hasn’t improved at a clip we would like to see if it was going to be a durable technology,” Dr. Lilly said.
Consensus regarding a reasonable strategy to manage cardiac conduction disturbances after TAVR has been elusive. This is a result of several things: a dearth of adequately powered, randomized controlled trials; the often transient nature of the conduction disturbances; evolving technologies; and the interplay of cardiology subspecialties involved.
The 2013 European Society of Cardiology guidelines address pacing post-TAVR, but do not provide in-depth discussion on the topic. This is the first effort sponsored by a cardiovascular society in the United States to review the existing data and experience and propose evidence-based expert guidance.
Pre-TAVR assessment
Pre-TAVR assessment should consider the patient’s risk for postprocedure conduction disturbances, the authors said. Since bradyarrythmias and aortic stenosis may present similarly (fatigue, lightheadedness, and syncope being hallmarks of both), a careful history is needed to determine if bradyarrhythmia is present.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) or ambulatory rhythm monitoring may identify baseline conduction abnormalities and help predict the need for post-TAVR PPM.
“In this section, we underscored some of the literature that has raised awareness about the presence of preexisting arrhythmias in TAVR patients and suggest that monitoring in selected patients before the procedure is reasonable, particularly those presenting with syncope or lightheadedness,” said Dr. Lilly.
Intraprocedural management
On the day of the procedure, patients determined to have elevated risk for complete AV heart block require careful perioperative ECG and hemodynamic monitoring. Regardless of preexisting risk, said the authors that all patients should be monitored on a telemetry unit during the procedure with ability to do emergency pacing if necessary.
“In the periprocedural section, we address the role of electrophysiological studies for identifying patients at high-risk of subsequent heart block,” said Dr. Lilly. “That’s a practice that’s occurring at a number of centers, but the data out there is insufficient to establish it as a pacemaker indication. Routine EP testing for patients deemed at risk for conduction disturbances after TAVR is not guideline-based and more research is needed.”
The document also outlines the effects of medications and anesthesia on postprocedure conduction abnormalities.
Post-TAVR management
The authors define post-TAVR management as continuing through 30-days after discharge.
The ECDP carefully outlines which patients can be discharged without monitoring and those for whom outpatient monitoring can be considered.
“If I’m going to pick one thing from this section, it’s the monitoring piece. A lot of patients that have a conduction disturbance right after TAVR – but you’re not sure if it’s going to progress and require a pacemaker – might stay in the hospital for an extended time waiting to see if the heart holds up,” reported Dr. Lilly.
“But a number of centers are now discharging people at 1 or 2 days, which begs the question: What do you do with these folks? Our group has published data showing that 30-day monitoring in select patients is a safe approach,” said Dr. Lilly.
There are shortcomings, however, in existing data, and recommendations will likely change as more data are collected, he explained.
As well, there remains uncertainty in how conduction block should be managed after TAVR, and clinical judgment is “foundational” in this, wrote the authors.
“This document is meant to help programs deal with these situations right now, acknowledging full and well, that really good randomized clinical data is not available,” said Dr. Lilly.
Dr. Lilly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The work of the writing committee was supported exclusively by the American College of Cardiology without commercial support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) has released a new Expert Consensus Decision Pathway (ECDP) on the management of conduction disturbances after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The document provides guidance to clinicians in identifying and managing this common complication of TAVR, covering the pre-TAVR, periprocedural and post-TAVR periods.
“Conduction disturbances after TAVR are common and there is currently heterogeneity in how they’re managed, ranging from a casual observational approach to invasive electrophysiological studies and preemptive pacemaker implantation,” said writing committee chair Scott Lilly, MD, PhD, from the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center in Columbus.
“We felt this kind of collaborative effort to review what little research there is on this topic and come to [an] expert consensus was long overdue,” he added.
The document was published online Oct. 21 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Lilly stressed in an interview that this effort is an ECDP and not a guideline “because there is not data out there to solidly stand on and say, ‘This is the way we should do things.’ “
His hope is that this document will generate more discussion on this topic and spur some (probably National Institutes of Health–sponsored) clinical trials to better guide practice.
Not uncommon and not decreasing
Complete heart block requiring permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation is seen in about 15% of patients within 30 days after TAVR. While this is a clear indication for PPM, there is no consensus on the management of less severe conduction disturbances such as new bundle branch or transient complete atrioventricular (AV) heart block.
Unlike the rates of bleeding, vascular injury, and stroke, which have decreased over time, the rates of in-hospital PPM implantation after TAVR have not changed significantly since commercialization in 2012. This is a concern because TAVR is increasingly used in younger, lower-risk patients.
“The pacemaker rate really hasn’t improved at a clip we would like to see if it was going to be a durable technology,” Dr. Lilly said.
Consensus regarding a reasonable strategy to manage cardiac conduction disturbances after TAVR has been elusive. This is a result of several things: a dearth of adequately powered, randomized controlled trials; the often transient nature of the conduction disturbances; evolving technologies; and the interplay of cardiology subspecialties involved.
The 2013 European Society of Cardiology guidelines address pacing post-TAVR, but do not provide in-depth discussion on the topic. This is the first effort sponsored by a cardiovascular society in the United States to review the existing data and experience and propose evidence-based expert guidance.
Pre-TAVR assessment
Pre-TAVR assessment should consider the patient’s risk for postprocedure conduction disturbances, the authors said. Since bradyarrythmias and aortic stenosis may present similarly (fatigue, lightheadedness, and syncope being hallmarks of both), a careful history is needed to determine if bradyarrhythmia is present.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) or ambulatory rhythm monitoring may identify baseline conduction abnormalities and help predict the need for post-TAVR PPM.
“In this section, we underscored some of the literature that has raised awareness about the presence of preexisting arrhythmias in TAVR patients and suggest that monitoring in selected patients before the procedure is reasonable, particularly those presenting with syncope or lightheadedness,” said Dr. Lilly.
Intraprocedural management
On the day of the procedure, patients determined to have elevated risk for complete AV heart block require careful perioperative ECG and hemodynamic monitoring. Regardless of preexisting risk, said the authors that all patients should be monitored on a telemetry unit during the procedure with ability to do emergency pacing if necessary.
“In the periprocedural section, we address the role of electrophysiological studies for identifying patients at high-risk of subsequent heart block,” said Dr. Lilly. “That’s a practice that’s occurring at a number of centers, but the data out there is insufficient to establish it as a pacemaker indication. Routine EP testing for patients deemed at risk for conduction disturbances after TAVR is not guideline-based and more research is needed.”
The document also outlines the effects of medications and anesthesia on postprocedure conduction abnormalities.
Post-TAVR management
The authors define post-TAVR management as continuing through 30-days after discharge.
The ECDP carefully outlines which patients can be discharged without monitoring and those for whom outpatient monitoring can be considered.
“If I’m going to pick one thing from this section, it’s the monitoring piece. A lot of patients that have a conduction disturbance right after TAVR – but you’re not sure if it’s going to progress and require a pacemaker – might stay in the hospital for an extended time waiting to see if the heart holds up,” reported Dr. Lilly.
“But a number of centers are now discharging people at 1 or 2 days, which begs the question: What do you do with these folks? Our group has published data showing that 30-day monitoring in select patients is a safe approach,” said Dr. Lilly.
There are shortcomings, however, in existing data, and recommendations will likely change as more data are collected, he explained.
As well, there remains uncertainty in how conduction block should be managed after TAVR, and clinical judgment is “foundational” in this, wrote the authors.
“This document is meant to help programs deal with these situations right now, acknowledging full and well, that really good randomized clinical data is not available,” said Dr. Lilly.
Dr. Lilly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The work of the writing committee was supported exclusively by the American College of Cardiology without commercial support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) has released a new Expert Consensus Decision Pathway (ECDP) on the management of conduction disturbances after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
The document provides guidance to clinicians in identifying and managing this common complication of TAVR, covering the pre-TAVR, periprocedural and post-TAVR periods.
“Conduction disturbances after TAVR are common and there is currently heterogeneity in how they’re managed, ranging from a casual observational approach to invasive electrophysiological studies and preemptive pacemaker implantation,” said writing committee chair Scott Lilly, MD, PhD, from the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center in Columbus.
“We felt this kind of collaborative effort to review what little research there is on this topic and come to [an] expert consensus was long overdue,” he added.
The document was published online Oct. 21 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Lilly stressed in an interview that this effort is an ECDP and not a guideline “because there is not data out there to solidly stand on and say, ‘This is the way we should do things.’ “
His hope is that this document will generate more discussion on this topic and spur some (probably National Institutes of Health–sponsored) clinical trials to better guide practice.
Not uncommon and not decreasing
Complete heart block requiring permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation is seen in about 15% of patients within 30 days after TAVR. While this is a clear indication for PPM, there is no consensus on the management of less severe conduction disturbances such as new bundle branch or transient complete atrioventricular (AV) heart block.
Unlike the rates of bleeding, vascular injury, and stroke, which have decreased over time, the rates of in-hospital PPM implantation after TAVR have not changed significantly since commercialization in 2012. This is a concern because TAVR is increasingly used in younger, lower-risk patients.
“The pacemaker rate really hasn’t improved at a clip we would like to see if it was going to be a durable technology,” Dr. Lilly said.
Consensus regarding a reasonable strategy to manage cardiac conduction disturbances after TAVR has been elusive. This is a result of several things: a dearth of adequately powered, randomized controlled trials; the often transient nature of the conduction disturbances; evolving technologies; and the interplay of cardiology subspecialties involved.
The 2013 European Society of Cardiology guidelines address pacing post-TAVR, but do not provide in-depth discussion on the topic. This is the first effort sponsored by a cardiovascular society in the United States to review the existing data and experience and propose evidence-based expert guidance.
Pre-TAVR assessment
Pre-TAVR assessment should consider the patient’s risk for postprocedure conduction disturbances, the authors said. Since bradyarrythmias and aortic stenosis may present similarly (fatigue, lightheadedness, and syncope being hallmarks of both), a careful history is needed to determine if bradyarrhythmia is present.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) or ambulatory rhythm monitoring may identify baseline conduction abnormalities and help predict the need for post-TAVR PPM.
“In this section, we underscored some of the literature that has raised awareness about the presence of preexisting arrhythmias in TAVR patients and suggest that monitoring in selected patients before the procedure is reasonable, particularly those presenting with syncope or lightheadedness,” said Dr. Lilly.
Intraprocedural management
On the day of the procedure, patients determined to have elevated risk for complete AV heart block require careful perioperative ECG and hemodynamic monitoring. Regardless of preexisting risk, said the authors that all patients should be monitored on a telemetry unit during the procedure with ability to do emergency pacing if necessary.
“In the periprocedural section, we address the role of electrophysiological studies for identifying patients at high-risk of subsequent heart block,” said Dr. Lilly. “That’s a practice that’s occurring at a number of centers, but the data out there is insufficient to establish it as a pacemaker indication. Routine EP testing for patients deemed at risk for conduction disturbances after TAVR is not guideline-based and more research is needed.”
The document also outlines the effects of medications and anesthesia on postprocedure conduction abnormalities.
Post-TAVR management
The authors define post-TAVR management as continuing through 30-days after discharge.
The ECDP carefully outlines which patients can be discharged without monitoring and those for whom outpatient monitoring can be considered.
“If I’m going to pick one thing from this section, it’s the monitoring piece. A lot of patients that have a conduction disturbance right after TAVR – but you’re not sure if it’s going to progress and require a pacemaker – might stay in the hospital for an extended time waiting to see if the heart holds up,” reported Dr. Lilly.
“But a number of centers are now discharging people at 1 or 2 days, which begs the question: What do you do with these folks? Our group has published data showing that 30-day monitoring in select patients is a safe approach,” said Dr. Lilly.
There are shortcomings, however, in existing data, and recommendations will likely change as more data are collected, he explained.
As well, there remains uncertainty in how conduction block should be managed after TAVR, and clinical judgment is “foundational” in this, wrote the authors.
“This document is meant to help programs deal with these situations right now, acknowledging full and well, that really good randomized clinical data is not available,” said Dr. Lilly.
Dr. Lilly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. The work of the writing committee was supported exclusively by the American College of Cardiology without commercial support.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher serum omega-3 tied to better outcome after STEMI
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular consumption of foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids was associated with improved prognosis after ST-segment myocardial infarction (STEMI) in a new observational study.
The prospective study, which involved 944 patients with STEMI who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), showed that plasma levels of fatty acids at the time of the STEMI were inversely associated with both incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and cardiovascular readmissions (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.76 and 0.74 for 1-SD increase; for both, P < .05).
No association was seen for the endpoint of all-cause mortality.
“What we showed is that your consumption of fish and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids before the heart attack impacts your prognosis after the heart attack. It’s a novel approach because it’s not primary prevention or secondary prevention,” said Aleix Sala-Vila, PharmD, PhD, from the Institut Hospital del Mar d’Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) in Barcelona, Spain.
Sala-Vila, co–senior author Antoni Bayés-Genís, MD, PhD, Heart Universitari Germans Trias I Pujol, Barcelona, and first author Iolanda Lázaro, PhD, also from IMIM, reported their findings online Oct. 26 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
It has been established that dietary omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has cardioprotective properties, but observational studies and randomized trials of EPA intake have yielded disparate findings.
This study avoided the usual traps of nutritional epidemiology research – self-reported food diaries and intake questionnaires. For this study, the researchers measured tissue levels of EPA and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) by measuring serum phosphatidylcholine (PC) levels, which reflect dietary intake during the previous 3 or 4 weeks.
This technique, said Sala-Vila, not only provides a more reliable measure of fatty acid intake over time but also avoids measurement errors related to fatty acid content variation.
For example, “The EPA content of a piece of fish eaten in January could be very different from one eaten in June,” explained Sala-Vila.
That said, he acknowledged that this technique, which uses gas chromatography, does not at present have a clear clinical application. “It’s quite difficult just to convert levels of serum-PC EPA into consumption of fatty fish. We feel that the best advice at this point is that given by the American Heart Association to eat two servings of fatty fish a week.”
EPA and ALA: Partners in prevention?
In addition to the findings regarding EPA, the researchers also found that serum-PC ALA was inversely related to all-cause mortality after STEMI (HR, 0.65 for 1-SD increase; P < .05).
A trend was seen for an association between ALA and lower risk for incident MACE (P = .093).
ALA is readily available from inexpensive plant sources (eg, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, soy beans) and has been associated with lower all-cause mortality in high-risk individuals.
This omega-3 fatty acid is often given short shrift in the fatty acid world because of the seven-step enzymatic process needed to convert it into more beneficial forms.
“We know that the conversion of ALA to EPA or DHA [docohexaenoic acid] is marginal, but we decided to include it in the study because we feel that this fatty acid is becoming more important because there are some issues with fish consumption – people are concerned about pollutants and sustainability, and some just don’t like it,” explained Sala-Vila.
“We were shocked to see that the marine-derived and vegetable-derived fatty acids don’t appear to compete, but rather they act synergistically,” said Sala-Villa. The researchers suggested that marine and vegetable omega-3 fatty acids may act as “partners in prevention.”
“We are not metabolically adapted to converting ALA to EPA, but despite this, there is a large body of evidence showing that one way to increase the status of EPA and DHA in our membranes is by eating these sources of fatty acids,” said Sala-Vila.
For almost 20 years, Sala-Vila has been studying how the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 affects disease. Two of his current projects involve studying levels of ALA in red blood cell membranes as a risk factor for ischemic stroke and omega-3 status in individuals with cognitive impairment who are at high risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Applicable to all patients with atherosclerosis
In comments to theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology, Deepak Bhatt, MD, called the study “terrific,” adding that the effort is “as good as it gets” for observational nutrition research.
“I think one has to view these findings in the larger universe of what is really a revolution in omega-3 fatty acid research,” said Bhatt.
This universe, he said, includes a wealth of observational research showing the benefits of omega-3s, two outcome trials – JELIS and REDUCE-IT – that showed the benefits of EPA supplementation, and two imaging studies – EVAPORATE and CHERRY – that showed favorable effects of EPA on the vasculature.
REDUCE-IT, for which Bhatt served as principal investigator, showed that treatment with icosapent ethyl (Vascepa), a high-dose purified form of EPA, led to a 25% relative risk reduction in MACE in an at-risk Western population.
The results, said Bhatt, who co-wrote an editorial that accompanies the current Sala-Vila article, “likely apply to all patients with atherosclerosis or who are at high risk for it” and supports the practice of counseling patients to increase their intake of food rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
The field may be due for a shake-up, he noted. At next month’s American Heart Association meeting, the results of another trial of another prescription-grade EPA/DHA supplement will be presented, and they are expected to be negative.
AstraZeneca announced in January 2020 the early closure of the STRENGTH trial of Epanova after an interim analysis showed a low likelihood of their product demonstrating benefit in the enrolled population.
Epanova is a fish-oil derived mixture of free fatty acids, primarily EPA and DHA. It is approved in the United States and is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride levels in adults with severe (≥500 mg/dL) hypertriglyceridemia. This indication is not affected by the data from the STRENGTH trial, according to a company press release.
Sala-Vila has received grants and support from the California Walnut Commission, including a grant to support part of this study. Bayés-Genís and Bhatt have relationships with a number of companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.