User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
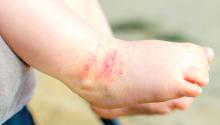
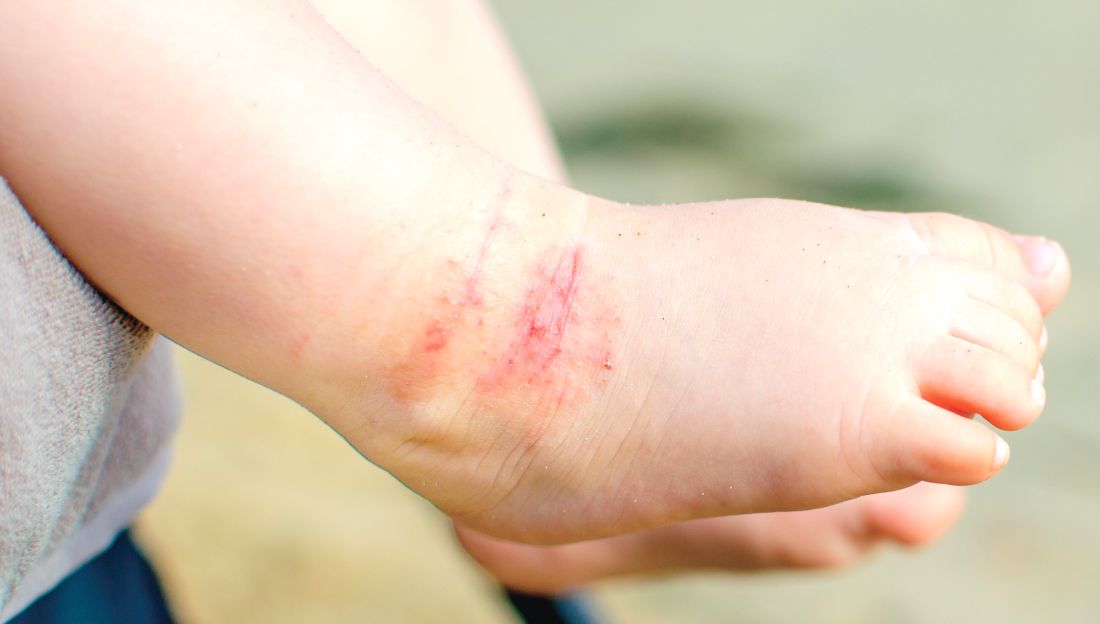
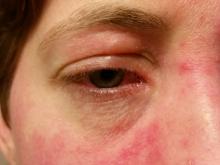
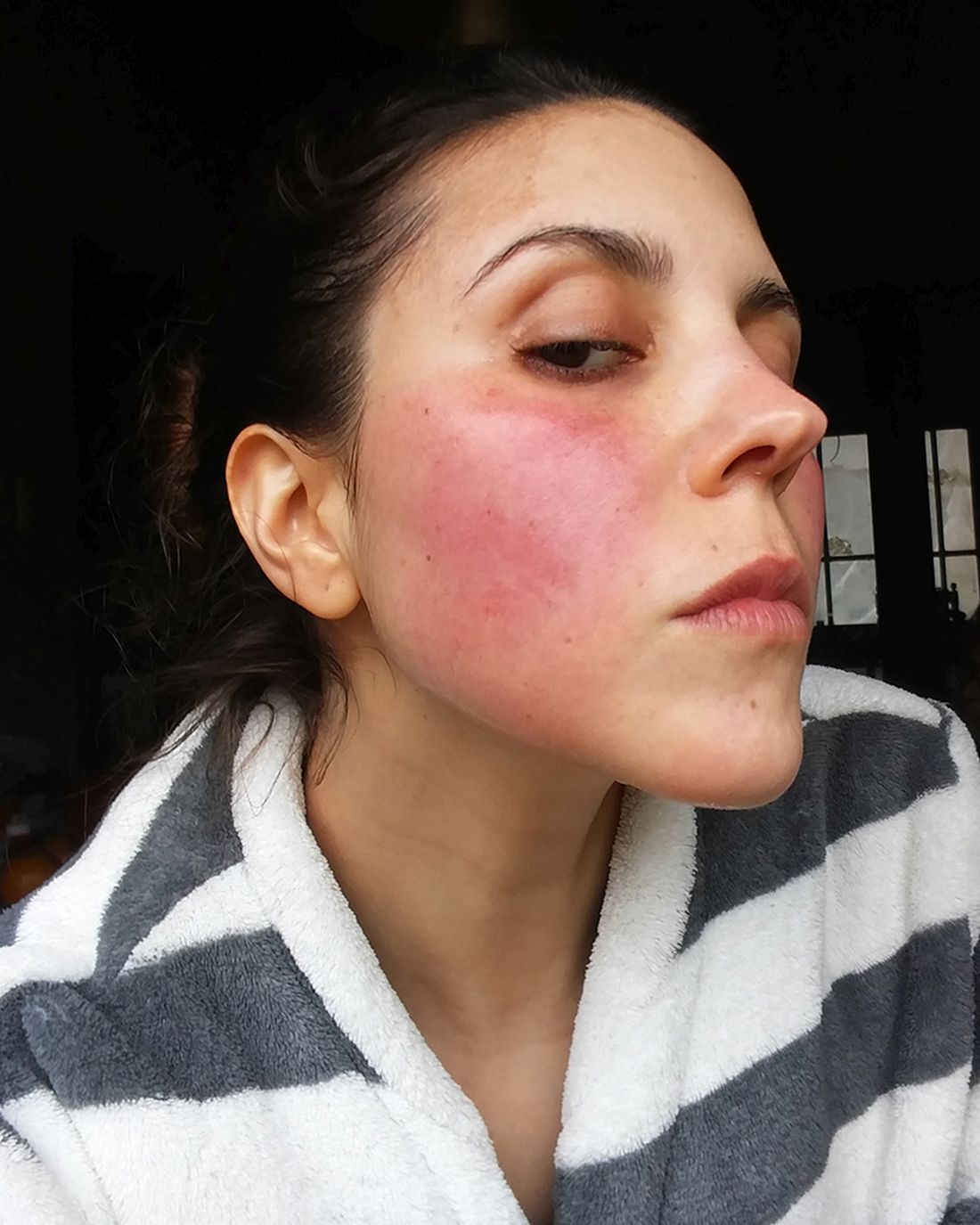
Parental atopic dermatitis, asthma linked to risk of AD in offspring
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
of life, an analysis of a large birth cohort found.
“The prevalence of AD in children has increased dramatically in recent years, and most studies reporting the impact of parental atopic history on AD are based on older data,” wrote the study authors, led by Cathal O’Connor, MD. “Given the recent interest in early intervention to prevent AD and other allergic diseases, enhanced early identification of infants at risk of AD is increasingly important.”
The detailed analysis of AD risk associated with parental atopy in early life “may help to risk stratify infants to optimize early interventions for prevention or early treatment of AD,” they wrote.
The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology.
For the analysis, Dr. O’Connor of the department of pediatrics and child health at University College Cork (Ireland) and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Cork Babies After Scope: Evaluating the Longitudinal Impact Using Neurological and Nutritional Endpoints (BASELINE) Birth Cohort Study.
The study recruited 2,183 healthy first-born babies between August 2009 and October 2011 to examine the effects of environmental factors during pregnancy and infancy on childhood health and development. Skin barrier assessments were performed at birth, 2 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months using a validated open chamber system to measure transepidermal water loss.
Parental atopy was self-reported at 2 months. Parents were asked at 2 months if the infant had an “itchy rash on the face or in the folds of the arms or legs,” as a screening question for AD. Experienced health care personnel used UK Working Party criteria to diagnose AD at 6, 12, and 24 months.
Complete data on AD status was available for 1,505 children in the cohort. Dr. O’Connor and colleagues calculated an overall AD prevalence of 18.6% at 6 months, 15.2% at 12 months, and 16.5% at 24 months.
Overall prevalence of AD was highest at 6 months. The study showed a similar or slightly higher impact of paternal atopy on offspring AD development, compared to maternal atopy.
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of AD were 1.57 at 6 months and 1.66 at 12 months for maternal AD; 1.90 at 6 months and 1.85 at 24 months for paternal AD; 1.76 at 6 months and 1.75 at 12 months for maternal asthma; and 1.70 at 6 months, 1.86 at 12 months, and 1.99 at 24 months for paternal asthma.
“Parental allergic rhinitis was not associated with AD in offspring in the first 2 years, except for maternal rhinitis at 24 months [an adjusted odds ratio of 1.79],” the authors wrote. “The genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, given the key role of aeroallergen sensitization in its pathogenesis, may not be associated with early onset AD, but may have a greater impact in later onset or persistent AD.”
The authors acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was a secondary data analysis, and that parental AD, asthma, and rhinitis were self-reported, “which may reduce reliability and may contribute to the differences seen between the impact of maternal and paternal reported atopy on offspring,” they wrote. “Data on siblings were not captured, as participants in the study were first-born children. Filaggrin mutational analysis was not performed, which would have provided richer detail.”
Kelly M. Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco, who was asked to comment on the work, said that the study confirms the well-known association between parental atopy and the risk of atopy in offspring, which has been shown in several studies dating back decades.
“The authors try to parse risk based on maternal or paternal or biparental history of AD and/or asthma and/or rhinitis, but this type of nuanced analysis when diagnosis is based solely on parental report may be an over-reach,” she said.
“Given that this data supports the association between parental atopy and risk of AD in infants at various time points, the clinically relevant immediate next question is how can we leverage this knowledge to prevent onset of AD in infants at risk?” she said. “To date, interventions such as early introduction of emollients have been evaluated with mixed results.”
A recent Cochrane analysis concluded that, based on available data, skin care interventions such as emollient use during the first year of life in otherwise healthy infants is probably not effective for preventing eczema and may increase risk of skin infection.
“Effects of skin care interventions on risk of asthma are also uncertain,” said Dr. Cordoro, who is also chief of the division of pediatric dermatology at UCSF.
“In sum, this study offers additional data in support of the link between atopy in parents and offspring,” she said. “Understanding how to mitigate risk and prevent atopy requires unraveling of the complex interplay between genetic, environmental, immunologic, microbial and other factors. For now, dermatologists are unable to make broad evidence-based recommendations for otherwise healthy (i.e., with normal skin) but at-risk infants in terms of approaches to skin care that might prevent eczema and asthma.”
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
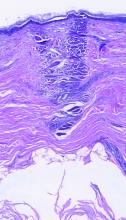
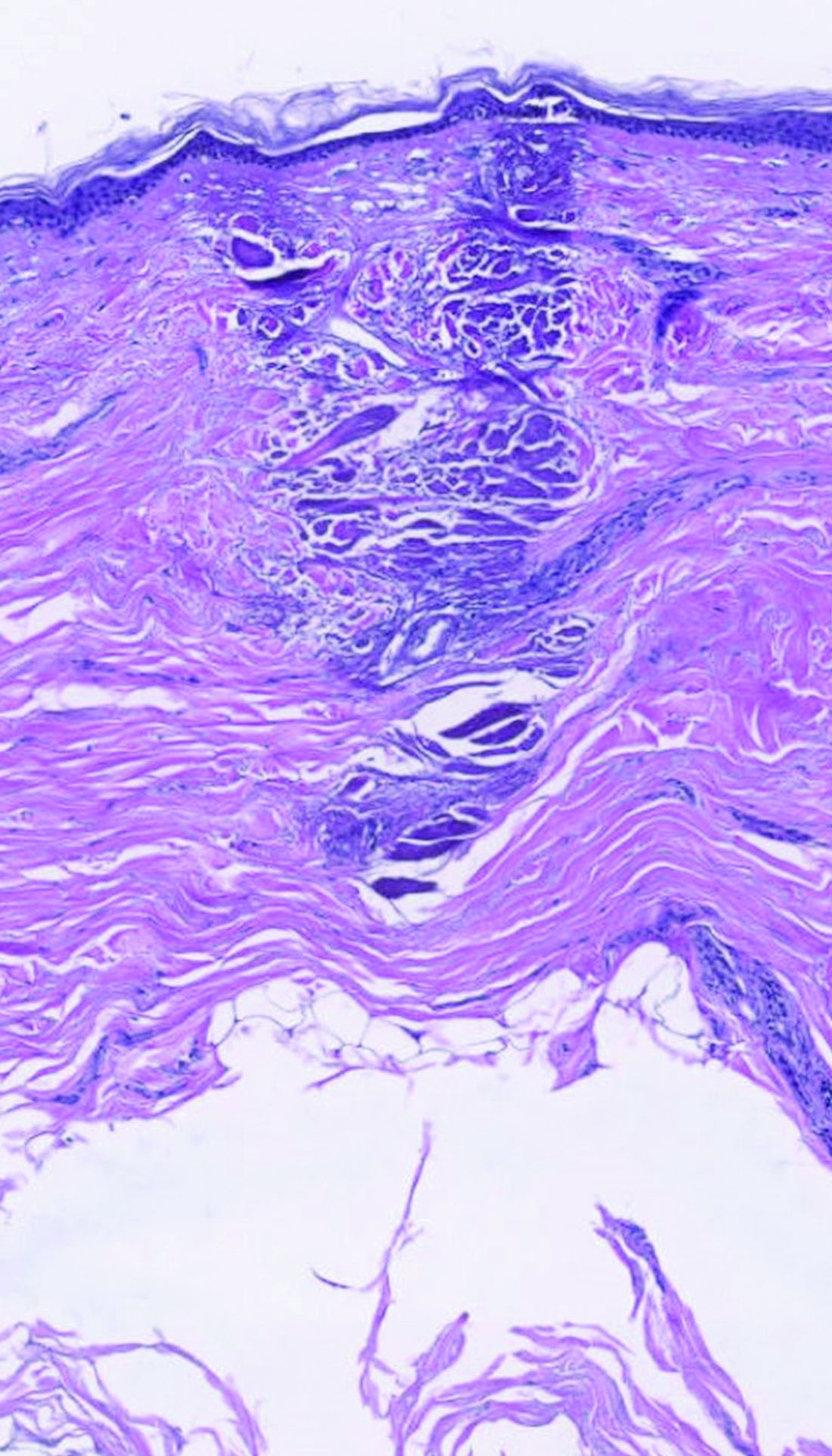
Subset of patients with melanoma have very low mortality risk
Although melanoma is the most serious skin cancer, most patients do have high chances of survival. New research has now identified a subset of patients with early disease who have a very low risk of dying from the disease.
In a cohort of almost 11,600 patients, the overall 7-year rate of death from melanoma was 2.5%, but the risk in a subset of 25% of patients was below 1%. Conversely, the study authors were also able to identify a small subset of high‐risk patients with a greater than 20% risk for death.
and may help to begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis, they note.
“While the topic of very low-risk melanomas has been presented at national and international meetings, there have been no formal discussions to define the classification of ‘melanocytic neoplasms of low malignant potential’ at this time,” first author Megan M. Eguchi, MPH, of the department of medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. “Criteria would need to be established using study designs beyond those available using SEER data.”
She emphasized that currently, they do not propose any change to treatment of these lesions, just a change to the terminology. “A diagnosis of ‘MNLMP’ rather than ‘melanoma’ may potentially alleviate people’s concerns related to prognosis and begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis,” said Ms. Eguchi. The study was recently published online in Cancer.
Even though melanoma is considered to be the most common potentially lethal tumor of the skin, prognosis is often very good for those with T1 tumors, the lowest risk category. Prognostic modeling has been used to predict survival in patients with melanoma and identify prognostic variables, the authors note, with the most prominent attributes being Breslow thickness and ulceration of the primary tumor, which form the basis of the current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system.
There is evidence that the increasing incidence of melanoma is partly due to overdiagnosis, meaning the diagnosis of lesions that will not lead to symptoms or death. The authors write that they were interested in identifying lesions that are currently diagnosed as melanoma but might lack the capacity for metastasis, cases that could potentially be part of the phenomenon of overdiagnosis.
Subsets with low and high risk for death
In the study, Ms. Eguchi and colleagues analyzed information from the United States Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database and identified 11,594 patients who were diagnosed in 2010 and 2011 with stage 1 melanoma that was less than or equal to 1.0 mm in thickness and had not spread to the lymph nodes. Prognostic models for risk for death from melanoma in patients with low-risk melanomas were developed, then the ability of the models to identify very‐low risk subsets of patients with melanoma‐specific survival surpassing that of T1 overall was evaluated.
The median age of the patients was 58 years, the median Breslow thickness was 0.45 mm (interquartile range, 0.30-0.65 mm), and 71% were assigned stage IA. Ulceration was present in 4% of cases, 27% were mitogenic, and 45% were Clark level II, and within this cohort, 292 (2.5%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years. In the training data set, 177 of 7,652 (2.3%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years, and numbers were similar in the testing set (115 of 3,942; 2.9%).
Overall, the investigators identified three large subsets of patients who were in the AJCC seventh edition classification for stage I (“thin”) melanoma, who had a risk for death of approximately less than 1%. This was a marked improvement from the rate of the overall sample. In the simplest model (Model 1A), patients who were younger than 70 years at diagnosis with Clark level II invasion were deemed as very low risk.
In Model 1B, the same initial classification was used, but it was further refined and limited to patients who were either age 43 years or younger or 44-69 years with Breslow thickness less than 0.40 mm. At 10 years postdiagnosis, this subset also showed a less than 1% risk for death from melanoma. The logistic regression model (Model 2) was similar, as it identified about 25% of patients with a predicted risk for death of less than 0.5%, incorporating patient age, sex, mitogenicity, Clark level, and ulceration. Model 2 was also able to further identify a small subset of patients with no deaths.
The logistic regression model was also able to identify a very small subset (0.7% and 0.8%) of patients who had a risk for death that exceeded 20%, which was markedly higher, compared with most patients with T1b tumors.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Eguchi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although melanoma is the most serious skin cancer, most patients do have high chances of survival. New research has now identified a subset of patients with early disease who have a very low risk of dying from the disease.
In a cohort of almost 11,600 patients, the overall 7-year rate of death from melanoma was 2.5%, but the risk in a subset of 25% of patients was below 1%. Conversely, the study authors were also able to identify a small subset of high‐risk patients with a greater than 20% risk for death.
and may help to begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis, they note.
“While the topic of very low-risk melanomas has been presented at national and international meetings, there have been no formal discussions to define the classification of ‘melanocytic neoplasms of low malignant potential’ at this time,” first author Megan M. Eguchi, MPH, of the department of medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. “Criteria would need to be established using study designs beyond those available using SEER data.”
She emphasized that currently, they do not propose any change to treatment of these lesions, just a change to the terminology. “A diagnosis of ‘MNLMP’ rather than ‘melanoma’ may potentially alleviate people’s concerns related to prognosis and begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis,” said Ms. Eguchi. The study was recently published online in Cancer.
Even though melanoma is considered to be the most common potentially lethal tumor of the skin, prognosis is often very good for those with T1 tumors, the lowest risk category. Prognostic modeling has been used to predict survival in patients with melanoma and identify prognostic variables, the authors note, with the most prominent attributes being Breslow thickness and ulceration of the primary tumor, which form the basis of the current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system.
There is evidence that the increasing incidence of melanoma is partly due to overdiagnosis, meaning the diagnosis of lesions that will not lead to symptoms or death. The authors write that they were interested in identifying lesions that are currently diagnosed as melanoma but might lack the capacity for metastasis, cases that could potentially be part of the phenomenon of overdiagnosis.
Subsets with low and high risk for death
In the study, Ms. Eguchi and colleagues analyzed information from the United States Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database and identified 11,594 patients who were diagnosed in 2010 and 2011 with stage 1 melanoma that was less than or equal to 1.0 mm in thickness and had not spread to the lymph nodes. Prognostic models for risk for death from melanoma in patients with low-risk melanomas were developed, then the ability of the models to identify very‐low risk subsets of patients with melanoma‐specific survival surpassing that of T1 overall was evaluated.
The median age of the patients was 58 years, the median Breslow thickness was 0.45 mm (interquartile range, 0.30-0.65 mm), and 71% were assigned stage IA. Ulceration was present in 4% of cases, 27% were mitogenic, and 45% were Clark level II, and within this cohort, 292 (2.5%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years. In the training data set, 177 of 7,652 (2.3%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years, and numbers were similar in the testing set (115 of 3,942; 2.9%).
Overall, the investigators identified three large subsets of patients who were in the AJCC seventh edition classification for stage I (“thin”) melanoma, who had a risk for death of approximately less than 1%. This was a marked improvement from the rate of the overall sample. In the simplest model (Model 1A), patients who were younger than 70 years at diagnosis with Clark level II invasion were deemed as very low risk.
In Model 1B, the same initial classification was used, but it was further refined and limited to patients who were either age 43 years or younger or 44-69 years with Breslow thickness less than 0.40 mm. At 10 years postdiagnosis, this subset also showed a less than 1% risk for death from melanoma. The logistic regression model (Model 2) was similar, as it identified about 25% of patients with a predicted risk for death of less than 0.5%, incorporating patient age, sex, mitogenicity, Clark level, and ulceration. Model 2 was also able to further identify a small subset of patients with no deaths.
The logistic regression model was also able to identify a very small subset (0.7% and 0.8%) of patients who had a risk for death that exceeded 20%, which was markedly higher, compared with most patients with T1b tumors.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Eguchi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although melanoma is the most serious skin cancer, most patients do have high chances of survival. New research has now identified a subset of patients with early disease who have a very low risk of dying from the disease.
In a cohort of almost 11,600 patients, the overall 7-year rate of death from melanoma was 2.5%, but the risk in a subset of 25% of patients was below 1%. Conversely, the study authors were also able to identify a small subset of high‐risk patients with a greater than 20% risk for death.
and may help to begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis, they note.
“While the topic of very low-risk melanomas has been presented at national and international meetings, there have been no formal discussions to define the classification of ‘melanocytic neoplasms of low malignant potential’ at this time,” first author Megan M. Eguchi, MPH, of the department of medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview. “Criteria would need to be established using study designs beyond those available using SEER data.”
She emphasized that currently, they do not propose any change to treatment of these lesions, just a change to the terminology. “A diagnosis of ‘MNLMP’ rather than ‘melanoma’ may potentially alleviate people’s concerns related to prognosis and begin to address the problem of overdiagnosis,” said Ms. Eguchi. The study was recently published online in Cancer.
Even though melanoma is considered to be the most common potentially lethal tumor of the skin, prognosis is often very good for those with T1 tumors, the lowest risk category. Prognostic modeling has been used to predict survival in patients with melanoma and identify prognostic variables, the authors note, with the most prominent attributes being Breslow thickness and ulceration of the primary tumor, which form the basis of the current American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system.
There is evidence that the increasing incidence of melanoma is partly due to overdiagnosis, meaning the diagnosis of lesions that will not lead to symptoms or death. The authors write that they were interested in identifying lesions that are currently diagnosed as melanoma but might lack the capacity for metastasis, cases that could potentially be part of the phenomenon of overdiagnosis.
Subsets with low and high risk for death
In the study, Ms. Eguchi and colleagues analyzed information from the United States Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database and identified 11,594 patients who were diagnosed in 2010 and 2011 with stage 1 melanoma that was less than or equal to 1.0 mm in thickness and had not spread to the lymph nodes. Prognostic models for risk for death from melanoma in patients with low-risk melanomas were developed, then the ability of the models to identify very‐low risk subsets of patients with melanoma‐specific survival surpassing that of T1 overall was evaluated.
The median age of the patients was 58 years, the median Breslow thickness was 0.45 mm (interquartile range, 0.30-0.65 mm), and 71% were assigned stage IA. Ulceration was present in 4% of cases, 27% were mitogenic, and 45% were Clark level II, and within this cohort, 292 (2.5%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years. In the training data set, 177 of 7,652 (2.3%) patients died of melanoma within 7 years, and numbers were similar in the testing set (115 of 3,942; 2.9%).
Overall, the investigators identified three large subsets of patients who were in the AJCC seventh edition classification for stage I (“thin”) melanoma, who had a risk for death of approximately less than 1%. This was a marked improvement from the rate of the overall sample. In the simplest model (Model 1A), patients who were younger than 70 years at diagnosis with Clark level II invasion were deemed as very low risk.
In Model 1B, the same initial classification was used, but it was further refined and limited to patients who were either age 43 years or younger or 44-69 years with Breslow thickness less than 0.40 mm. At 10 years postdiagnosis, this subset also showed a less than 1% risk for death from melanoma. The logistic regression model (Model 2) was similar, as it identified about 25% of patients with a predicted risk for death of less than 0.5%, incorporating patient age, sex, mitogenicity, Clark level, and ulceration. Model 2 was also able to further identify a small subset of patients with no deaths.
The logistic regression model was also able to identify a very small subset (0.7% and 0.8%) of patients who had a risk for death that exceeded 20%, which was markedly higher, compared with most patients with T1b tumors.
This study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Ms. Eguchi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER
Study eyes sunscreens marketed to individuals with skin of color
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
, and more than 40% contain a UV blocker that may create a white cast.
Those are among the findings from a study by Michelle Xiong, a medical student at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and Erin M. Warshaw, MD, of the department of dermatology at Park Nicollet/Health Partners Health Services, Minneapolis, which was published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“There is increasing awareness of the negative effects of ultraviolet (UV) light in individuals with skin of color (SOC), especially in regards to pigmentation disorders induced and/or exacerbated by UV exposure,” the authors wrote. “As a result, there has been a surge in sunscreens marketed to this population. We aimed to characterize cost, marketing claims, and potential allergenic ingredients in sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC.”
Between December 2021 and October 2022, the researchers used the following search terms on Google: “sunscreen” plus “skin of 36 color,” “dark skin,” “brown skin,” “LatinX skin,” and/or “Black skin.” They extracted price, marketing claims, and ingredients from manufacturers’ websites and used 90 allergens contained in the American Contact Dermatitis Society 2020 Core series to identify potential allergens. Next, they combined cross-reactors/synonyms into allergen categories based on ACDS Contact Allergen Management Plan (CAMP) cross-reactor classification. If multiple ingredients in a sunscreen were represented by a single allergen category, it was counted only once. A similar approach was utilized for marketing categories.
A total of 12 sunscreens were included in the analysis: Absolute Joi, Black Girl Sunscreen, Black Girl Sunscreen Make It Matte, Bolden SPF Brightening Moisturizer, Eleven on the Defense Unrivaled Sun Serum, Kinlo Golden Rays Sunscreen, Live Tinted Hueguard 3-in-1 Mineral Sunscreen, Mele Dew The Most Sheer Moisturizer SPF30 Broad Spectrum Sunscreen, Mele No Shade Sunscreen Oil, Specific Beauty Active Radiance Day Moi, Unsun Mineral Sunscreen, and Urban Skin Rx Complexion Protection. Their average cost was $19.30 per ounce (range, $6.33-$50.00) and common marketing claims for these products were “no white cast” (91.7%), being free of an ingredient (83.3%), and “moisturizing” (75%).
Of the 12 sunscreens, 7 (58.3%) contained a chemical sunscreen agent, 5 (41.7%) contained a physical UV blocker, and all contained at least one allergen. The average number of allergens per product was 4.7, most commonly fragrance/botanicals (83.3%), tocopherol (83.3%), sodium benzoates/derivatives (58.3%), and sorbitan sesquiolate/derivatives (58.3%).
“Average cost of sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC was $19.30/oz, much higher than the median price of $3.32/oz reported in a separate study of 65 popular sunscreens,” the study authors wrote. “As many of the sunscreens in our study were sold by smaller businesses, higher prices may be due to higher production costs or a perceived smaller market.”
The authors expressed surprise that five sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC contained a physical UV blocker which may create a white cast. They contacted the manufacturers of these five sunscreens and confirmed that three used micronized formulations. “While ingested/inhaled nanoparticles of titanium dioxide may cause tissue effects, most studies of topical products show excellent safety,” they wrote.
They also noted that the average of 4.7 allergens per product observed in the analysis was similar to the average of 4.9 seen in a separate study of 52 popular sunscreens. “However, that study only included 34 allergens while this study evaluated 90 allergens,” the authors wrote. “Consumers and providers should be aware sunscreens marketed to individuals with SOC may cause allergic contact dermatitis,” they commented.
“It is interesting to see how costly these products are now compared to store bought and general commercially available sunscreens several years ago,” said Lawrence J. Green, clinical professor of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study. “However, to me that is not surprising as products marketed and targeted to specific populations are often priced at a premium. It wasn’t clear to me how many of these specialized online SOC sunscreens are tinted. I wish the authors had compared the cost of tinted sunscreens in general to nontinted sunscreens because tinted ones are more useful for SOC, because when rubbed in, they can readily match SOC and can also offer protection in the visible light spectrum.”
The authors reported having no financial disclosures; the study had no funding source. Dr. Green disclosed that he is a speaker, consultant, or investigator for many pharmaceutical companies.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Pooled safety data analysis of tralokinumab reported
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The most , according to a review published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
These findings underscore the mechanistic elegance of interleukin (IL)-13 inhibition and highlight potential advantages of flexible dosing, according to the study’s lead author, Eric Simpson, MD, MCR. Overall, the pooled analysis of safety data from five phase 2 and 3 trials shows that “blockade of a single cytokine provides excellent short- and long-term safety, which is useful for a severe chronic disease,” said Dr. Simpson, professor of dermatology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland.
Most patients with AD require years of treatment. “So for clinicians to confidently report to patients the low rates of serious adverse events (AEs) and lack of immune suppression side-effect profile is very encouraging for both the provider and patient,” Dr. Simpson said, noting there were no new signals or concerning short-term AEs.
Tralokinumab (Adbry), an IL-13 antagonist administered subcutaneously, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults in December 2021.
Minor differences vs. placebo
In the pooled analysis involving 1,605 patients treated for 16 weeks with tralokinumab and 680 who received placebo, frequency of any AE was 65.7% and 67.2%, respectively. Severe AEs occurred in 4.6% and 6.3% of patients, respectively.
The most common AE overall was AD, which occurred less often in tralokinumab-treated patients (15.4%) than those on placebo (26.2%). Other common AEs that occurred more frequently with tralokinumab included viral upper respiratory tract infections (15.7% vs. 12.2%), upper respiratory tract infections (URTI, 5.6% vs. 4.8%), conjunctivitis (5.4% vs. 1.9%), and injection-site reactions (3.5% vs. 0.3%).
AEs that occurred less often with tralokinumab than placebo included skin infections (3.7% vs. 9.2%, respectively) and infected dermatitis (1.6% vs. 6.4%).
Regarding safety areas of special interest, eye disorders classified as conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or keratitis occurred more commonly with tralokinumab (7.9%) than placebo (3.4%). Most eye disorders were mild or moderate and resolved during the study. During maintenance treatment up to 52 weeks, AE rates mirrored those in the initial treatment period and did not increase with treatment duration.
In fact, Dr. Simpson said, the low rate of AEs that are known to accompany type 2 blockade, such as conjunctivitis, do not increase but rather appear to drop with longer-term use. The fact that skin infections were reduced vs. placebo and decreased over time suggests that long-term IL-13 blockade with tralokinumab positively impacts skin infections, a well-known comorbidity in uncontrolled AD, he added.
Raj Chovatiya, MD, PhD, who was asked to comment on the study, said, “These findings provide additional data supporting the safety and tolerability of tralokinumab and support my personal real-world experience with tralokinumab as a safe and effective biologic therapy for patients with moderate to severe AD.”
Dr. Chovatiya is assistant professor, director of the Center for Eczema and Itch, and medical director of clinical trials at Northwestern University in Chicago.
Four-week dosing
Consistent with ECZTRA 3, the rates of URTIs and conjunctivitis were lower with maintenance dosing 300 mg every 4 weeks, consideration of which is approved for responders weighing less than 220 pounds, vs. 300 mg every 2 weeks. Specifically, 6.7% of patients on every 4-week dosing schedule experienced URTIs, vs. 9.4% on the every 2-week dosing schedule and 7% of those on the every 2-week dosing schedule plus optional topical corticosteroids. Corresponding figures for conjunctivitis were 3%, 5%, and 5.6%, respectively.
“Four-week dosing is a possibility in your patients with a good clinical response at 16 weeks,” Dr. Simpson said. Advantages include improved convenience for patients, he added, and this analysis shows that dosing every 4 weeks may improve tolerability, with a lower rate of conjunctivitis.
Although it is difficult to directly compare review data to other studies, said Dr. Chovatiya, findings also suggest that tralokinumab may be associated with reduced infections and conjunctivitis compared with other advanced AD therapies. Head-to-head trials and real-world studies are needed to better understand comparative safety, he added.
Some patients will lose a degree of response with the 4-week dosing schedule, Dr. Simpson said. In ECZTRA 1 and 2, 55.9% of patients who achieved investigator global assessment (IGA) scores of 0 or 1 after 16 weeks of dosing every 2 weeks maintained this response level through week 52, vs. 42.4% of responders who switched from dosing every 2 weeks to every 4 weeks after week 16. But according to data that Dr. Simpson recently presented, 95% of patients switched to monthly dosing who relapsed and returned to dosing every 2 weeks regained their original response level within approximately 4 weeks.
In his personal practice, Dr. Simpson has prescribed tralokinumab for patients with AD for up to a year. However, he and fellow investigators have been following much larger populations for more than 2 years and are planning additional publications. “Safety data will continue to accrue” said Dr. Simpson, “but I don’t expect any surprises.”
The clinical trials were sponsored by MedImmune (phase 2b) and LEO Pharma ( ECZTRA phase 3 trials), which also sponsored the review. Dr. Simpson reports grants and personal fees from numerous pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Chovatiya has been an advisory board member, consultant, investigator, and speaker for numerous pharmaceutical companies including LEO Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
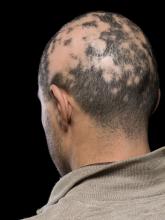
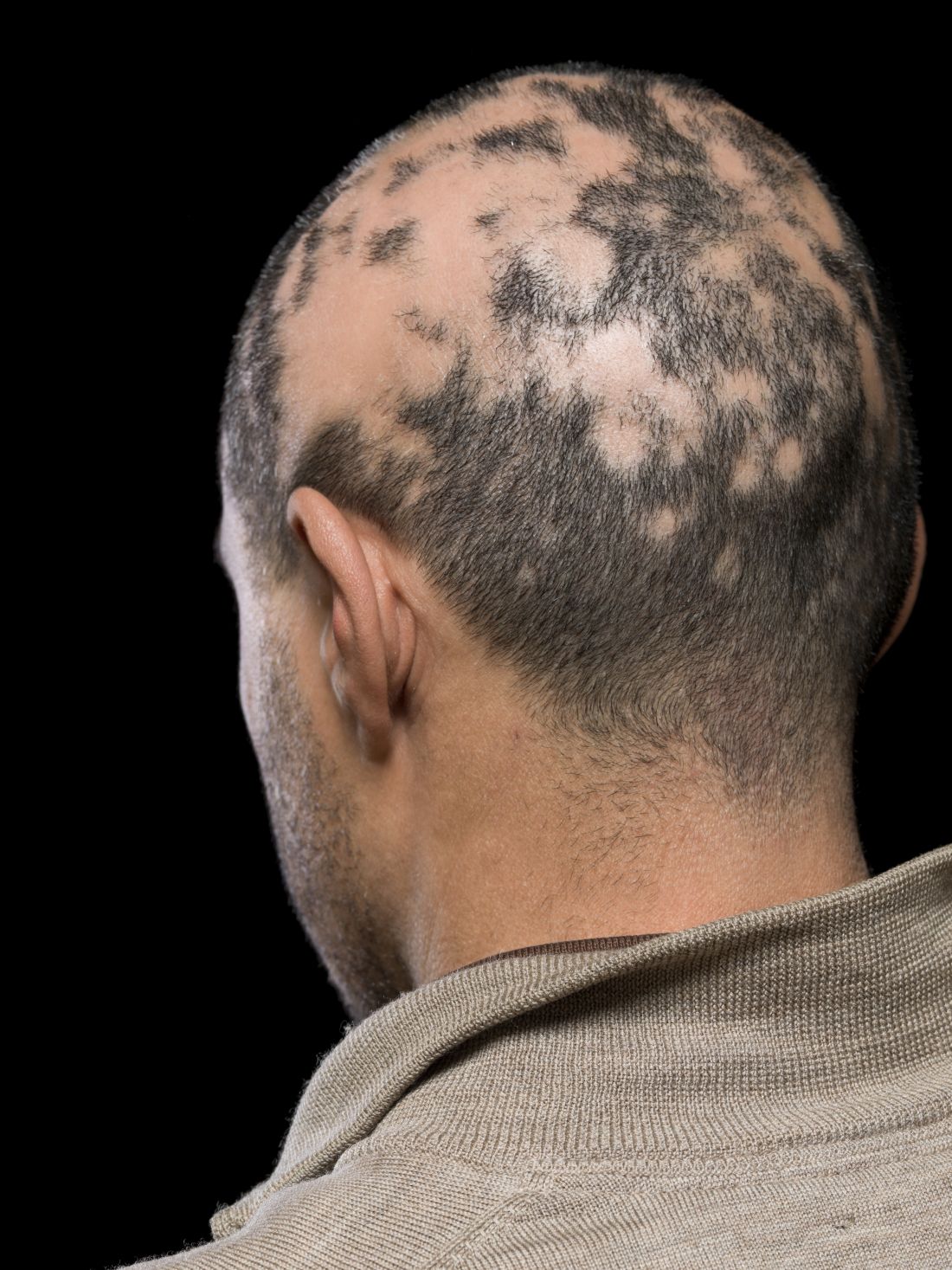
Current alopecia areata options include old and new therapies
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
“Some patients don’t have alopecia, but they have been managed for it,” he said. “Whenever there is an ounce of doubt, take a biopsy,” he advised.
Assessing disease severity in patients with alopecia areata (AA) is especially important as new therapies become available, said Dr. King, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. The Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score has been available since 2004, and remains a useful tool to estimate percent hair loss. The SALT Score divides the scalp into four sections: 18% each for the right and left sides, 40% for the top of the head, and 24% for the back of the head, said Dr. King. However, the SALT Score can be enhanced or modified based on a holistic approach to disease severity that categorizes alopecia as mild (scalp hair loss of 20% or less), moderate (scalp hair loss of 21 to 49%), or severe (scalp hair loss of 50% or more).
For example, if a patient’s hair loss based on SALT Score is mild or moderate, increase the severity by 1 level (from mild to moderate, or moderate to severe) if any of the following conditions apply: Noticeable eyebrow or eyelash involvement, inadequate treatment response after 6 months, diffuse positive hair pull test consistent with rapid progression of AA, or a negative impact on psychosocial functioning because of AA, he said.
Treatment advances
Understanding of the pathogenesis of AA has been slow to evolve, Dr. King noted. “We haven’t been able to shake this concept that people are causing the disease by being depressed,” as noted in the literature from the 1950s.
In 2014, breakthrough research changed the game by identifying the roles of interferon gamma and interleukin 15, Dr. King said. Since then, more research has been conducted on Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors for AA. Dr. King was a coinvestigator on a 2014 case report in which a patient with psoriasis and alopecia universalis experienced regrowth of most of his body hair after 8 months of daily oral tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
However, despite the dramatic results in some patients, “tofacitinib doesn’t always work,” said Dr. King. In his experience, patients for whom tofacitinib didn’t work were those with complete or nearly complete scalp hair loss for more than 10 years.
Approval of baricitinib
Dr. King’s recent work supported the approval in June 2022 of oral baricitinib, a JAK inhibitor, for AA. He reviewed data from his late-breaker abstract presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology in March 2022, where he reported that almost 40% of adults with AA treated with 4 mg of baricitinib daily had significant hair regrowth over 52 weeks.
Two other oral JAK inhibitors in the pipeline for AA are deuruxolitinib and ritlecitinib, which significantly increased the proportion of patients achieving SALT scores of 20 or less, compared with patients on placebo in early clinical trials. Data on both were presented at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
So far, topical JAK inhibitors have not shown success in hair regrowth for AA patients, said Dr. King. Phase 2 studies of both ruxolitinib 1.5% cream and delgocitinib ointment were ineffective for AA.
Emerging role for oral minoxidil
Oral minoxidil has had a recent resurgence as an adjunct therapy to the new JAK inhibitors. A study published in 1987 found that, with oral minoxidil monotherapy, a cosmetic response was seen in 18% of patients with AA, Dr. King said.
In a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Dr. King and colleagues noted that dose escalation is sometimes needed for effective treatment of AA with tofacitinib. They examined the effect of adding oral minoxidil to tofacitinib in patients with severe AA as a way to increase efficacy without increasing tofacitinib dosage. They reviewed data from 12 patients ages 18-51 years who were prescribed 5 mg of tofacitinib twice daily, plus 2.5 mg oral minoxidil daily for women and 2.5 mg of minoxidil twice daily for men; women received a lower dose to minimize the side effect of hypertrichosis.
After 6 months, 67% (eight patients) achieved at least 75% hair regrowth; of those eight patients, seven (58% of the total) had hair regrowth on a twice-daily dose of 5 mg tofacitinib with no need for dose escalation, Dr. King said.
More research is needed, but oral minoxidil may be a useful adjunct treatment for some patients with AA, he added.
During a question and answer session, Dr. King was asked to elaborate on the mechanism of minoxidil in combination with JAK inhibitors. “The truth is that I just don’t know” why the combination works for some patients. However, the majority of patients who succeed with this combination regrow hair by 4 months. “There is something special about that combination.”
Dr. King disclosed serving as a consultant or adviser for AbbVie, AltruBio, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Bioniz, Bristol Myers Squibb, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Horizon, Incyte, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Otsuka, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme, Twi Biotechnology, Viela Bio, and Visterra; serving as a speaker or as a member of the speakers bureau for Incyte, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi Genzyme; and receiving research funding from Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer.
MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Saururus chinensis
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
Also known as Asian or Chinese lizard’s tail (or Sam-baekcho in Korea), Saururus chinensis is an East Asian plant used in traditional medicine for various indications including edema, gonorrhea, jaundice, hypertension, leproma, pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis.1,2 Specifically, Korean traditional medicine practitioners as well as Native Americans and early colonists in what is now the United States used the botanical to treat cancer, edema, rheumatoid arthritis, and other inflammatory conditions.2-4 Modern research has produced evidence supporting the use of this plant in the dermatologic realm. This column focuses on the relevant bench science and possible applications.
Various beneficial effects
In 2008, Yoo et al. found that the ethanol extract of the dried aerial parts of S. chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antinociceptive properties, which they suggested may partially account for the established therapeutic effects of the plant.2 Also, Lee et al. reported in 2012 on the antiproliferative effects against human cancer cell lines of neolignans found in S. chinensis.5
Antioxidant properties have been associated with S. chinensis. In 2014, Kim et al. reported that S. chinensis extract attenuated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated neuroinflammatory response in BV-2 microglia cells, a result that the authors partly ascribed to the antioxidant constituents (particularly quercetin) of the plant.3
Atopic dermatitis
In 2008, Choi et al. determined that the leaves of S. chinensis impeded the formation of atopic dermatitis–like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice caused by repeated application of picryl chloride, potentially by stimulating the Th1 cell response, thus modulating Th1/Th2 imbalance. They concluded that S. chinensis has potential as an adjunct treatment option for atopic dermatitis.6
Anti-inflammatory activity
In 2010, Bae et al. studied the anti-inflammatory properties of sauchinone, a lignan derived from S. chinensis reputed to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective activity,7 using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. They found that the lignan lowered tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha synthesis by inhibiting the c-Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 phosphorylation pathway, accounting for the anti-inflammatory effects of the S. chinensis constituent.8
More recently, Zhang et al. determined that the ethanol extract of S. chinensis leaves impaired proinflammatory gene expression by blocking the TAK1/AP-1 pathway in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. They suggested that such suppression is a significant step in the anti-inflammatory function exhibited by the plant.1
Photoprotection
Park et al. investigated in 2013 the beneficial effects of sauchinone. Specifically, they studied potential photoprotective effects of the lignan against UVB in HaCaT human epidermal keratinocytes. They found that sauchinone (5-40 mcm) conferred significant protection as evaluated by cell viability and a toxicity assay. At 20-40 mcm, sauchinone blocked the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)–1 proteins and decrease of type 1 collagen engendered by UVB exposure. The investigators further discovered that sauchinone diminished the synthesis of reactive oxygen species. Overall, they determined that sauchinone imparted protection by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 MAPK signaling through the activation of oxidative defense enzymes.7
Potential use as a depigmenting agent
In 2009, Seo et al. isolated the lignans manassantin A and B from S. chinensis and determined that these compounds dose-dependently impeded melanin synthesis in alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH)–activated melanoma B16 cells. They also noted that manassantin A suppressed forskolin- or 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX)–induced melanin production and diminished cellular levels of IBMX-inducible tyrosinase protein. The lignan had no effect on the catalytic activity of cell-free tyrosinase, an important enzyme in melanin pigment production. The researchers concluded that their results suggest the potential for S. chinensis to be used to treat hyperpigmentation disorders.9
Two years later Lee et al. found that manassantin A, derived from S. chinensis, steadily suppressed the cAMP elevator IBMX- or dibutyryl cAMP-induced melanin synthesis in B16 cells or in melan-a melanocytes by down-regulating the expression of tyrosinase or the TRP1 gene. The lignan also inhibited microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) induction via the IBMX-activated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) pathway, thus preventing the Ser-133 phosphorylation of CREB. The researchers concluded that this molecular disruption of melanin production suggests the potential for the use of manassantin A as a skin depigmenting agent.10
That same year, another S. chinensis lignan gained interest. Yun et al. investigated the effects of the S. chinensis lignan component saucerneol D on melanin synthesis in cAMP-elevated melanocytes. They found that the lignan efficiently impeded melanin product in B16 melanoma cells stimulated with alpha-MSH or other cAMP elevators. Saucerneol D was also credited with down-regulating alpha-MSH–induced gene expression of tyrosinase at the transcription level in B16 cells, suppressing alpha-MSH–induced phosphorylation of CREB in the cells, and inhibiting MITF induction. The investigators concluded that their results point to the potential of the S. chinensis lignan saucerneol D for the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.11
In 2012, Chang et al. observed that an extract of S. chinensis and one of its constituent lignans, manassantin B, prevented melanosome transport in normal human melanocytes and Melan-a melanocytes, by interrupting the interaction between melanophilin and myosin Va. The investigators concluded that as a substance that can hinder melanosome transport, manassantin B displays potential for use as depigmenting product.12
The following year, Lee et al. studied the effects of S. chinensis extracts on the melanogenesis signaling pathway activated by alpha-MSH, finding dose-dependent inhibition without provoking cytotoxicity in B16F10 cells. Further, the team found evidence that the depigmenting activity exhibited by S. chinensis extracts may occur as a result of MITF and tyrosinase expression stemming from elevated activity of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). They concluded that their results support further examination of S. chinensis for its potential to contribute to skin whitening.5
Conclusion
Multiple lignan constituents in this plant-derived ingredient appear to yield anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, and antitumor properties. Its inhibitory effects on melanin production and its antiaging abilities make it worthy of further study and consideration of inclusion in antiaging skin care products.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in the office and as an e-commerce solution. Write to her at [email protected].
References
1. Zhang J et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114400.
2. Yoo HJ et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):282-6.
3. Kim BW et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:502.
4. Lee DH et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):772-9.
5. Lee YJ et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(8):1361-6.
6. Choi MS et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Jan;31(1):51-6.
7. Park G et al. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(7):1134-9.
8. Bae HB et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Sep;10(9):1022-8.
9. Seo CS et al. Phytother Res. 2009 Nov;23(11):1531-6.
10. Lee HD et al. Exp Dermatol. 2011 Sep;20(9):761-3.
11. Yun JY et al. Arch Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;34(8):1339-45.
12. Chang H et al. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012 Nov;25(6):765-72.
NRS grants target rosacea’s underlying mechanisms
Two new , according to an announcement by the NRS.
As part of the NRS research grants program, the organization recently awarded $10,000 to Emanual Maverakis, MD, professor of dermatology, University of California, Davis, and research fellow Samantha Herbert, MSPH. Their project will characterize rosacea pathophysiology using single-cell RNA sequencing. This novel analytical technique provides specific information on the signals expressed by different cell types and will help researchers better understand the role each subtype may play in rosacea, along with how these cells interact with each other, according to the NRS press release. New knowledge in the foregoing areas may fuel development of better therapies, the release added.
The NRS awarded its second new-research grant to Arisa Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and associate professor of dermatology, University of California, San Diego. She was awarded $5,000 to examine whether laser therapy affects the skin microbiome, the complex ecosystem of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside on the skin. Studies have detected significant differences – such as higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermidis and lower levels of Cutibacterium acnes – in the microbiome of skin with rosacea compared with healthy skin. Dr. Ortiz’s research also will probe how blood vessels, which laser therapy often target, contribute to the rosacea disease process.
The NRS also renewed its support of an ongoing study led by Sezen Karakus, MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology at the Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute, Baltimore. She is studying the role of the ocular-surface microbiome in rosacea pathogenesis. Because ocular rosacea can lead to vision-threatening corneal complications, Dr. Karakus said in the press release, identifying microorganisms present on the ocular surface may spur development of targeted treatment strategies.
A second ongoing study for which the NRS renewed funding is investigating whether certain intracellular signals recently found to be elevated in rosacea lesions may drive skin inflammation, which may be a root cause of rosacea. Emmanuel Contassot, PhD, project leader in the dermatology department at the University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland, is leading the study.
To date, the NRS research grants program has awarded more than $1.6 million to research designed to further elucidate potential causes and other key aspects of rosacea with the goal of advancing treatment, prevention, or potential cure of rosacea.
For interested researchers, the deadline to submit proposals for next year’s grants is June 16, 2023. Forms and instructions are available through the research grants section of the NRS website or by contacting the NRS at 4619 N. Ravenswood Ave., Suite 103, Chicago, IL 60640; 888-662-5874; or [email protected].
Two new , according to an announcement by the NRS.
As part of the NRS research grants program, the organization recently awarded $10,000 to Emanual Maverakis, MD, professor of dermatology, University of California, Davis, and research fellow Samantha Herbert, MSPH. Their project will characterize rosacea pathophysiology using single-cell RNA sequencing. This novel analytical technique provides specific information on the signals expressed by different cell types and will help researchers better understand the role each subtype may play in rosacea, along with how these cells interact with each other, according to the NRS press release. New knowledge in the foregoing areas may fuel development of better therapies, the release added.
The NRS awarded its second new-research grant to Arisa Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and associate professor of dermatology, University of California, San Diego. She was awarded $5,000 to examine whether laser therapy affects the skin microbiome, the complex ecosystem of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside on the skin. Studies have detected significant differences – such as higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermidis and lower levels of Cutibacterium acnes – in the microbiome of skin with rosacea compared with healthy skin. Dr. Ortiz’s research also will probe how blood vessels, which laser therapy often target, contribute to the rosacea disease process.
The NRS also renewed its support of an ongoing study led by Sezen Karakus, MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology at the Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute, Baltimore. She is studying the role of the ocular-surface microbiome in rosacea pathogenesis. Because ocular rosacea can lead to vision-threatening corneal complications, Dr. Karakus said in the press release, identifying microorganisms present on the ocular surface may spur development of targeted treatment strategies.
A second ongoing study for which the NRS renewed funding is investigating whether certain intracellular signals recently found to be elevated in rosacea lesions may drive skin inflammation, which may be a root cause of rosacea. Emmanuel Contassot, PhD, project leader in the dermatology department at the University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland, is leading the study.
To date, the NRS research grants program has awarded more than $1.6 million to research designed to further elucidate potential causes and other key aspects of rosacea with the goal of advancing treatment, prevention, or potential cure of rosacea.
For interested researchers, the deadline to submit proposals for next year’s grants is June 16, 2023. Forms and instructions are available through the research grants section of the NRS website or by contacting the NRS at 4619 N. Ravenswood Ave., Suite 103, Chicago, IL 60640; 888-662-5874; or [email protected].
Two new , according to an announcement by the NRS.
As part of the NRS research grants program, the organization recently awarded $10,000 to Emanual Maverakis, MD, professor of dermatology, University of California, Davis, and research fellow Samantha Herbert, MSPH. Their project will characterize rosacea pathophysiology using single-cell RNA sequencing. This novel analytical technique provides specific information on the signals expressed by different cell types and will help researchers better understand the role each subtype may play in rosacea, along with how these cells interact with each other, according to the NRS press release. New knowledge in the foregoing areas may fuel development of better therapies, the release added.
The NRS awarded its second new-research grant to Arisa Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and associate professor of dermatology, University of California, San Diego. She was awarded $5,000 to examine whether laser therapy affects the skin microbiome, the complex ecosystem of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside on the skin. Studies have detected significant differences – such as higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermidis and lower levels of Cutibacterium acnes – in the microbiome of skin with rosacea compared with healthy skin. Dr. Ortiz’s research also will probe how blood vessels, which laser therapy often target, contribute to the rosacea disease process.
The NRS also renewed its support of an ongoing study led by Sezen Karakus, MD, assistant professor of ophthalmology at the Johns Hopkins Wilmer Eye Institute, Baltimore. She is studying the role of the ocular-surface microbiome in rosacea pathogenesis. Because ocular rosacea can lead to vision-threatening corneal complications, Dr. Karakus said in the press release, identifying microorganisms present on the ocular surface may spur development of targeted treatment strategies.
A second ongoing study for which the NRS renewed funding is investigating whether certain intracellular signals recently found to be elevated in rosacea lesions may drive skin inflammation, which may be a root cause of rosacea. Emmanuel Contassot, PhD, project leader in the dermatology department at the University Hospital of Basel, Switzerland, is leading the study.
To date, the NRS research grants program has awarded more than $1.6 million to research designed to further elucidate potential causes and other key aspects of rosacea with the goal of advancing treatment, prevention, or potential cure of rosacea.
For interested researchers, the deadline to submit proposals for next year’s grants is June 16, 2023. Forms and instructions are available through the research grants section of the NRS website or by contacting the NRS at 4619 N. Ravenswood Ave., Suite 103, Chicago, IL 60640; 888-662-5874; or [email protected].
New Year’s resolutions
I can’t presume to know what issues need addressing in your practice, but I do know the ones I get asked about most often, so I can offer some suggestions that might provide inspiration:
1. Keep your website up to date. Check it now, then make a note to check it regularly. Most people find their physicians online these days, and you don’t want them finding a year-old presentation with outdated photos, personnel, services, and rates. Keep your site current, or hire someone to do it for you.
2. Be an authoritative presence on social media. Like it or not, you should be on Facebook, Twitter (at least for now), Instagram, TikTok – wherever your patients congregate. Medical topics are popular search categories, and they are searching for expert advice. You are the expert. There is a ton of medical misinformation online, and it needs to be countered with accurate, factual data from bona fide experts.
3. Follow colleagues. No need to reinvent the wheel; many physicians have already developed large online followings. Track some of them down, follow them yourself, and use them as inspiration for your own online contributions. Your specialty society probably maintains a presence on Instagram and other sites as well, and they are a good source of topics and tips.
4. Post frequently. We all have a finite amount of time, but a few brief posts per week on various social media platforms will attract more attention, and garner more followers than an occasional long treatise. Add relevant hashtags to get more reach and engagement.
5. Participate in trends. When a topic is getting thousands of views, it a trending topic. Post on trending topics, and if you know the trend’s original authors, tag them. That will increase your audience, and the compliment might be reciprocated in the future.
6. Google yourself. You might be surprised by what you find. Being aware of what is being said about you online is a necessary exercise to maintain a healthy online reputation. The good reviews are ego builders, but it’s the bad reviews that you can learn from. They will help you identify your negative personality traits and motivate you to eliminate them.
7. Encrypt your mobile devices. The biggest HIPAA vulnerability in many practices is laptops and tablets carrying confidential patient information; losing one could be a disaster. Encryption software is cheap and readily available, and a lost or stolen mobile device will probably not be treated as a HIPAA breach if it is properly encrypted.
8. Back up your data. Now is an excellent time to verify that the information on your office and personal computers is being backed up – locally and online – on a regular schedule. Don’t wait until something crashes.
9. Keep a closer eye on your office finances. Most physicians delegate the bookkeeping, and that’s fine. But ignoring the financial side completely creates an atmosphere that facilitates embezzlement. Set aside a couple of hours each month to review the books personally. And make sure your employees know you’re doing it.
10. Make sure your long-range financial planning is on track. I’ve said this before, but it can’t be repeated too often. Economic conditions change all the time. Once a year, you should sit down with your accountant and lawyer and make sure your investments are well-diversified and all other aspects of your finances – budgets, credit ratings, insurance coverage, tax situations, college savings, estate plans, retirement accounts – are in the best shape possible.
11. Pay down your debt. Another oldie but goodie. Debt can destroy the best laid retirement plans. If you carry significant debt, set up a plan to pay it off as soon as you can.
12. Take more vacations. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.” If you’ve been working too much, this is the year to start spending more time enjoying your life, your friends and family, and the world. As John Lennon said, “Life is what happens to you while you’re busy making other plans.”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I can’t presume to know what issues need addressing in your practice, but I do know the ones I get asked about most often, so I can offer some suggestions that might provide inspiration:
1. Keep your website up to date. Check it now, then make a note to check it regularly. Most people find their physicians online these days, and you don’t want them finding a year-old presentation with outdated photos, personnel, services, and rates. Keep your site current, or hire someone to do it for you.
2. Be an authoritative presence on social media. Like it or not, you should be on Facebook, Twitter (at least for now), Instagram, TikTok – wherever your patients congregate. Medical topics are popular search categories, and they are searching for expert advice. You are the expert. There is a ton of medical misinformation online, and it needs to be countered with accurate, factual data from bona fide experts.
3. Follow colleagues. No need to reinvent the wheel; many physicians have already developed large online followings. Track some of them down, follow them yourself, and use them as inspiration for your own online contributions. Your specialty society probably maintains a presence on Instagram and other sites as well, and they are a good source of topics and tips.
4. Post frequently. We all have a finite amount of time, but a few brief posts per week on various social media platforms will attract more attention, and garner more followers than an occasional long treatise. Add relevant hashtags to get more reach and engagement.
5. Participate in trends. When a topic is getting thousands of views, it a trending topic. Post on trending topics, and if you know the trend’s original authors, tag them. That will increase your audience, and the compliment might be reciprocated in the future.
6. Google yourself. You might be surprised by what you find. Being aware of what is being said about you online is a necessary exercise to maintain a healthy online reputation. The good reviews are ego builders, but it’s the bad reviews that you can learn from. They will help you identify your negative personality traits and motivate you to eliminate them.
7. Encrypt your mobile devices. The biggest HIPAA vulnerability in many practices is laptops and tablets carrying confidential patient information; losing one could be a disaster. Encryption software is cheap and readily available, and a lost or stolen mobile device will probably not be treated as a HIPAA breach if it is properly encrypted.
8. Back up your data. Now is an excellent time to verify that the information on your office and personal computers is being backed up – locally and online – on a regular schedule. Don’t wait until something crashes.
9. Keep a closer eye on your office finances. Most physicians delegate the bookkeeping, and that’s fine. But ignoring the financial side completely creates an atmosphere that facilitates embezzlement. Set aside a couple of hours each month to review the books personally. And make sure your employees know you’re doing it.
10. Make sure your long-range financial planning is on track. I’ve said this before, but it can’t be repeated too often. Economic conditions change all the time. Once a year, you should sit down with your accountant and lawyer and make sure your investments are well-diversified and all other aspects of your finances – budgets, credit ratings, insurance coverage, tax situations, college savings, estate plans, retirement accounts – are in the best shape possible.
11. Pay down your debt. Another oldie but goodie. Debt can destroy the best laid retirement plans. If you carry significant debt, set up a plan to pay it off as soon as you can.
12. Take more vacations. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.” If you’ve been working too much, this is the year to start spending more time enjoying your life, your friends and family, and the world. As John Lennon said, “Life is what happens to you while you’re busy making other plans.”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I can’t presume to know what issues need addressing in your practice, but I do know the ones I get asked about most often, so I can offer some suggestions that might provide inspiration:
1. Keep your website up to date. Check it now, then make a note to check it regularly. Most people find their physicians online these days, and you don’t want them finding a year-old presentation with outdated photos, personnel, services, and rates. Keep your site current, or hire someone to do it for you.
2. Be an authoritative presence on social media. Like it or not, you should be on Facebook, Twitter (at least for now), Instagram, TikTok – wherever your patients congregate. Medical topics are popular search categories, and they are searching for expert advice. You are the expert. There is a ton of medical misinformation online, and it needs to be countered with accurate, factual data from bona fide experts.
3. Follow colleagues. No need to reinvent the wheel; many physicians have already developed large online followings. Track some of them down, follow them yourself, and use them as inspiration for your own online contributions. Your specialty society probably maintains a presence on Instagram and other sites as well, and they are a good source of topics and tips.
4. Post frequently. We all have a finite amount of time, but a few brief posts per week on various social media platforms will attract more attention, and garner more followers than an occasional long treatise. Add relevant hashtags to get more reach and engagement.
5. Participate in trends. When a topic is getting thousands of views, it a trending topic. Post on trending topics, and if you know the trend’s original authors, tag them. That will increase your audience, and the compliment might be reciprocated in the future.
6. Google yourself. You might be surprised by what you find. Being aware of what is being said about you online is a necessary exercise to maintain a healthy online reputation. The good reviews are ego builders, but it’s the bad reviews that you can learn from. They will help you identify your negative personality traits and motivate you to eliminate them.
7. Encrypt your mobile devices. The biggest HIPAA vulnerability in many practices is laptops and tablets carrying confidential patient information; losing one could be a disaster. Encryption software is cheap and readily available, and a lost or stolen mobile device will probably not be treated as a HIPAA breach if it is properly encrypted.
8. Back up your data. Now is an excellent time to verify that the information on your office and personal computers is being backed up – locally and online – on a regular schedule. Don’t wait until something crashes.
9. Keep a closer eye on your office finances. Most physicians delegate the bookkeeping, and that’s fine. But ignoring the financial side completely creates an atmosphere that facilitates embezzlement. Set aside a couple of hours each month to review the books personally. And make sure your employees know you’re doing it.
10. Make sure your long-range financial planning is on track. I’ve said this before, but it can’t be repeated too often. Economic conditions change all the time. Once a year, you should sit down with your accountant and lawyer and make sure your investments are well-diversified and all other aspects of your finances – budgets, credit ratings, insurance coverage, tax situations, college savings, estate plans, retirement accounts – are in the best shape possible.
11. Pay down your debt. Another oldie but goodie. Debt can destroy the best laid retirement plans. If you carry significant debt, set up a plan to pay it off as soon as you can.
12. Take more vacations. Remember Eastern’s First Law: Your last words will NOT be, “I wish I had spent more time in the office.” If you’ve been working too much, this is the year to start spending more time enjoying your life, your friends and family, and the world. As John Lennon said, “Life is what happens to you while you’re busy making other plans.”
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
Novel platform harnesses 3D laser technology for skin treatments
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
in all skin types, according to speakers at a virtual course on laser and aesthetic skin therapy.
The products feature “focal point technology,” which pairs 3D laser targeting with an integrated high-resolution imaging system (IntelliView), to help the user guide treatments at selectable depths. They have been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for use in skin resurfacing procedures, and to treat benign pigmented lesions of the skin, including hyperpigmentation, and were created by Dieter Manstein, MD, PhD, Rox Anderson, MD, and Henry Chan, MD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, and Irina Erenburg, PhD, CEO of AVAVA, the company that markets the products.
dermally focused treatment with Focal Point Technology. The coagulation zone, in dark purple, shows a deep conical lesion that extends 1.3 mm deep with significant epidermal sparing.
At the meeting, Mathew M. Avram, MD, JD, director of the Massachusetts General Hospital Dermatology Laser & Cosmetic Center, described focal point technology as an adjustable intradermally focused laser platform guided by real-time visual mapping to ensure the precise dose and depth of energy as the user performs treatments. “This is the key for rejuvenation,” he said. “You can go to different depths of the skin. You can be superficial for dyschromia and maybe a little bit different for wrinkles. If you want to treat scars, you go a little bit deeper. Coagulation occurs at these different depths.”
The collimated beam from conventional lasers affects all tissue in its path. The laser beam from the AVAVA product, however, creates a cone-shaped profile of injury in the dermis that minimizes the area of epidermal damage, making it safe in skin of color, according to Dr. Avram. “The beam comes to a focal point in the dermis at the depth that you want it to,” he explained during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “That’s where the energy is going to focus and it bypasses the dermal/epidermal junction, which traditional fractional lasers cannot. What’s interesting about this platform is that you have a wavelength for skin rejuvenation, then you have wavelengths for pigment, which allows you to treat conditions like melasma at different depths.”
The AVAVA high-speed IntelliView imaging system features 10-micron resolution, “so you get exquisite imaging that can help guide your treatments,” he said. It also features image acquisition and storage with artificial intelligence algorithm interrogation and the ability to personalize treatments to the patient’s specific skin type. Commercial availability is expected in the first half of 2023, Dr. Avram said.
In a separate presentation, New York-based cosmetic dermatologist Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who has been involved in clinical trials of AVAVA’s focal point technology, said that patients “feel less pain and have less down time than we saw previously with other nonablative, fractional technologies.”
Downtime involves “just some mild redness,” he said, adding that he is encouraged by early results seen to date, and that “there appears to be some unique capabilities that will be borne out as the clinical studies progress.”
Dr. Avram disclosed that he has received consulting fees from Allergan, Galderma, and Revelle. He is an investigator for Endo and holds ownership and/or shareholder interest in Cytrellis and La Jolla NanoMedical. Dr. Geronemus disclosed having financial relationships with numerous device and pharmaceutical companies.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE
Rosacea and the gut: Looking into SIBO
, according to speakers at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“SIBO is definitely something we test for and treat,” Raja Sivamani, MD, said in an interview after the meeting. Dr. Sivamani practices as an integrative dermatologist at the Pacific Skin Institute in Sacramento and is the director of clinical research at the institute’s research unit, Integrative Skin Science and Research. He led a panel discussion on rosacea and acne at the meeting.
Associations between SIBO and several dermatologic conditions, including systemic sclerosis, have been reported, but the strongest evidence to date involves rosacea. “There’s associative epidemiological evidence showing higher rates of SIBO among those with rosacea, and there are prospective studies” showing clearance of rosacea in patients treated for SIBO, said Dr. Sivamani, also adjunct associate professor of clinical dermatology at the University of California, Davis.
Studies are small, but are “well done and well-designed,” he said in the interview. “Do we need more studies? Absolutely. But what we have now is compelling [enough] for us to take a look at it.”
Findings of rosacea clearance
SIBO’s believed contribution to the pathophysiology of rosacea is part of the increasingly described gut microbiome-skin axis. SIBO has been recognized as a medical phenomenon for many decades and has been defined as an excessive bacterial load in the small bowel that causes gastrointestinal symptoms, according to the 2020 American College of Gastroenterology clinical guideline on SIBO.
Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO overlap with the cardinal symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): abdominal pain; diarrhea, constipation, or both; bloating; and flatulence. SIBO can be diagnosed with several validated carbohydrate substrate (glucose or lactulose)–based breath tests that measure hydrogen and/or methane.
Hydrogen-positive breath tests suggest bacterial overgrowth, and methane-positive breath tests suggest small intestinal methanogen overgrowth. Methane is increasingly important and recognized, the AGA guideline says, though it creates a “nomenclature problem in the SIBO framework” because methanogens are not bacteria, the authors note.
In conventional practice, SIBO is typically treated with antibiotics such as rifaximin, and often with short-term dietary modification as well. Integrative medicine typically considers the use of supplements and botanicals in addition to or instead of antibiotics, as well as dietary change and increasingly, a close look at SIBO risk factors to prevent recurrence, Dr. Sivamani said. (His research unit is currently studying the use of herbal protocols as an alternative to antibiotics in patients with SIBO and dermatologic conditions.)
During a presentation on rosacea at the meeting, Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research, a dermatology treatment and research center in San Diego, said that currently available breath tests for SIBO “are very interesting tools for understanding what may be happening in the gut” and that the “rifaximin data are good.”
He referred to a study reported in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showing that patients with rosacea were significantly more likely to have SIBO (41.7% of 48 patients vs. 5.0% of 40 controls; P < .001), and that 64.5% of rosacea patients who completed treatment with rifaximin had remission of rosacea at a 3-year follow-up.
An earlier crossover study is also notable, he said. This study enrolled 113 consecutive patients with rosacea and 60 age- and sex-matched controls, and randomized those with SIBO (52 of the 113 with rosacea vs. 3 of the 60 controls) to rifaximin or placebo. Rosacea cleared in 20 of the 28 patients in the rifaximin group and greatly improved in 6 of the 28. Of 20 patients in the placebo group, rosacea remained unchanged in 18 and worsened in 2. When patients in the placebo group were switched to rifaximin, SIBO was eradicated in 17 of the 20, and rosacea completely resolved in 15 of those patients, Dr. Bhatia said.
In his view, it will take more time, greater awareness of the rosacea-SIBO link, and a willingness “to take chances” for more dermatologists to consider SIBO during rosacea care. “Breath tests are not something used in the [typical dermatology] clinic right now, but they may make their way in,” he said at the meeting.
In a follow-up interview, Dr. Bhatia emphasized that “it’s really a question of uptake, which always takes a while” and of willingness to “think through the disease from another angle ... especially in patients who are recalcitrant.”
Treatment
Dr. Sivamani said in the interview that a third type of SIBO – hydrogen sulfide–dominant SIBO – is now documented and worth considering when glucose and lactulose breath tests are negative in patients with rosacea who have gastrointestinal symptoms.
The use of breath tests to objectively diagnose SIBO is always best, Dr. Sivamani said, but he will consider empiric therapy in some patients. “I always tell patients [about] the benefits of testing, but if they can’t get the test covered or are unable to pay for the test, and they have symptoms consistent with SIBO, I’m okay doing a trial with therapy,” he said.
Rifaximin, one of the suggested antibiotics listed in the AGA guideline, is a nonabsorbable antibiotic that is FDA-approved for IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D); it has been shown to not negatively affect the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
However, herbals are also an attractive option – alone or in combination with rifaximin or other antibiotics – speakers at the meeting said. In a multicenter retrospective chart review led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, herbal therapies were at least as effective as rifaximin for treating SIBO, with similar safety profiles. The response rate for normalizing breath hydrogen testing in patients with SIBO was 46% for herbal therapies and 34% for rifaximin.
Dietary change is also part of treatment, with the reduction of fermentable carbohydrates – often through the Low FODMAP Diet and Specific Carbohydrate Diet – being the dominant theme in dietary intervention for SIBO, according to the AGA guideline.
“There are definitely some food choices you can shift,” said Dr. Sivamani. “I’ll work with patients on FODMAP, though it’s hard to sustain over the long-term and can induce psychological issues. You have to provide other options.”
Dr. Sivamani works with patients on using “a restrictive diet for a short amount of time, with the gradual reintroduction of foods to see [what] foods are and aren’t [causing] flares.” He also works to identify and eliminate risk factors and predisposing factors for SIBO so that recurrence will be less likely.
“SIBO is definitely an entity that is not on the fringes anymore ... it adds to inflammation in the body ... and if you have an inflamed gut, there’s a domino effect that will lead to inflammation elsewhere,” Dr. Sivamani said.
“You want to know, do your patients have SIBO? What subset do they have? Do they have risk factors you can eliminate?” he said. “And then what therapies will you use – pharmaceuticals, supplements and botanicals, or a combination? And finally, what will you do with diet?”
Dr. Bhatia disclosed he has affiliations with Abbvie, Almirall, Arcutis, Arena, Biofrontera, BMS, BI, Brickell, Dermavant, EPI Health, Ferndale, Galderma, Genentech, InCyte, ISDIN, Johnson & Johnson, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho, Pfizer, Proctor & Gamble, Regeneron, Sanofi, Stemline, SunPharma, and Verrica. Dr. Sivamani did not provide a disclosure statement.
, according to speakers at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“SIBO is definitely something we test for and treat,” Raja Sivamani, MD, said in an interview after the meeting. Dr. Sivamani practices as an integrative dermatologist at the Pacific Skin Institute in Sacramento and is the director of clinical research at the institute’s research unit, Integrative Skin Science and Research. He led a panel discussion on rosacea and acne at the meeting.
Associations between SIBO and several dermatologic conditions, including systemic sclerosis, have been reported, but the strongest evidence to date involves rosacea. “There’s associative epidemiological evidence showing higher rates of SIBO among those with rosacea, and there are prospective studies” showing clearance of rosacea in patients treated for SIBO, said Dr. Sivamani, also adjunct associate professor of clinical dermatology at the University of California, Davis.
Studies are small, but are “well done and well-designed,” he said in the interview. “Do we need more studies? Absolutely. But what we have now is compelling [enough] for us to take a look at it.”
Findings of rosacea clearance
SIBO’s believed contribution to the pathophysiology of rosacea is part of the increasingly described gut microbiome-skin axis. SIBO has been recognized as a medical phenomenon for many decades and has been defined as an excessive bacterial load in the small bowel that causes gastrointestinal symptoms, according to the 2020 American College of Gastroenterology clinical guideline on SIBO.
Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO overlap with the cardinal symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): abdominal pain; diarrhea, constipation, or both; bloating; and flatulence. SIBO can be diagnosed with several validated carbohydrate substrate (glucose or lactulose)–based breath tests that measure hydrogen and/or methane.
Hydrogen-positive breath tests suggest bacterial overgrowth, and methane-positive breath tests suggest small intestinal methanogen overgrowth. Methane is increasingly important and recognized, the AGA guideline says, though it creates a “nomenclature problem in the SIBO framework” because methanogens are not bacteria, the authors note.
In conventional practice, SIBO is typically treated with antibiotics such as rifaximin, and often with short-term dietary modification as well. Integrative medicine typically considers the use of supplements and botanicals in addition to or instead of antibiotics, as well as dietary change and increasingly, a close look at SIBO risk factors to prevent recurrence, Dr. Sivamani said. (His research unit is currently studying the use of herbal protocols as an alternative to antibiotics in patients with SIBO and dermatologic conditions.)
During a presentation on rosacea at the meeting, Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research, a dermatology treatment and research center in San Diego, said that currently available breath tests for SIBO “are very interesting tools for understanding what may be happening in the gut” and that the “rifaximin data are good.”
He referred to a study reported in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showing that patients with rosacea were significantly more likely to have SIBO (41.7% of 48 patients vs. 5.0% of 40 controls; P < .001), and that 64.5% of rosacea patients who completed treatment with rifaximin had remission of rosacea at a 3-year follow-up.
An earlier crossover study is also notable, he said. This study enrolled 113 consecutive patients with rosacea and 60 age- and sex-matched controls, and randomized those with SIBO (52 of the 113 with rosacea vs. 3 of the 60 controls) to rifaximin or placebo. Rosacea cleared in 20 of the 28 patients in the rifaximin group and greatly improved in 6 of the 28. Of 20 patients in the placebo group, rosacea remained unchanged in 18 and worsened in 2. When patients in the placebo group were switched to rifaximin, SIBO was eradicated in 17 of the 20, and rosacea completely resolved in 15 of those patients, Dr. Bhatia said.
In his view, it will take more time, greater awareness of the rosacea-SIBO link, and a willingness “to take chances” for more dermatologists to consider SIBO during rosacea care. “Breath tests are not something used in the [typical dermatology] clinic right now, but they may make their way in,” he said at the meeting.
In a follow-up interview, Dr. Bhatia emphasized that “it’s really a question of uptake, which always takes a while” and of willingness to “think through the disease from another angle ... especially in patients who are recalcitrant.”
Treatment
Dr. Sivamani said in the interview that a third type of SIBO – hydrogen sulfide–dominant SIBO – is now documented and worth considering when glucose and lactulose breath tests are negative in patients with rosacea who have gastrointestinal symptoms.
The use of breath tests to objectively diagnose SIBO is always best, Dr. Sivamani said, but he will consider empiric therapy in some patients. “I always tell patients [about] the benefits of testing, but if they can’t get the test covered or are unable to pay for the test, and they have symptoms consistent with SIBO, I’m okay doing a trial with therapy,” he said.
Rifaximin, one of the suggested antibiotics listed in the AGA guideline, is a nonabsorbable antibiotic that is FDA-approved for IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D); it has been shown to not negatively affect the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
However, herbals are also an attractive option – alone or in combination with rifaximin or other antibiotics – speakers at the meeting said. In a multicenter retrospective chart review led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, herbal therapies were at least as effective as rifaximin for treating SIBO, with similar safety profiles. The response rate for normalizing breath hydrogen testing in patients with SIBO was 46% for herbal therapies and 34% for rifaximin.
Dietary change is also part of treatment, with the reduction of fermentable carbohydrates – often through the Low FODMAP Diet and Specific Carbohydrate Diet – being the dominant theme in dietary intervention for SIBO, according to the AGA guideline.
“There are definitely some food choices you can shift,” said Dr. Sivamani. “I’ll work with patients on FODMAP, though it’s hard to sustain over the long-term and can induce psychological issues. You have to provide other options.”
Dr. Sivamani works with patients on using “a restrictive diet for a short amount of time, with the gradual reintroduction of foods to see [what] foods are and aren’t [causing] flares.” He also works to identify and eliminate risk factors and predisposing factors for SIBO so that recurrence will be less likely.
“SIBO is definitely an entity that is not on the fringes anymore ... it adds to inflammation in the body ... and if you have an inflamed gut, there’s a domino effect that will lead to inflammation elsewhere,” Dr. Sivamani said.
“You want to know, do your patients have SIBO? What subset do they have? Do they have risk factors you can eliminate?” he said. “And then what therapies will you use – pharmaceuticals, supplements and botanicals, or a combination? And finally, what will you do with diet?”
Dr. Bhatia disclosed he has affiliations with Abbvie, Almirall, Arcutis, Arena, Biofrontera, BMS, BI, Brickell, Dermavant, EPI Health, Ferndale, Galderma, Genentech, InCyte, ISDIN, Johnson & Johnson, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho, Pfizer, Proctor & Gamble, Regeneron, Sanofi, Stemline, SunPharma, and Verrica. Dr. Sivamani did not provide a disclosure statement.
, according to speakers at the annual Integrative Dermatology Symposium.
“SIBO is definitely something we test for and treat,” Raja Sivamani, MD, said in an interview after the meeting. Dr. Sivamani practices as an integrative dermatologist at the Pacific Skin Institute in Sacramento and is the director of clinical research at the institute’s research unit, Integrative Skin Science and Research. He led a panel discussion on rosacea and acne at the meeting.
Associations between SIBO and several dermatologic conditions, including systemic sclerosis, have been reported, but the strongest evidence to date involves rosacea. “There’s associative epidemiological evidence showing higher rates of SIBO among those with rosacea, and there are prospective studies” showing clearance of rosacea in patients treated for SIBO, said Dr. Sivamani, also adjunct associate professor of clinical dermatology at the University of California, Davis.
Studies are small, but are “well done and well-designed,” he said in the interview. “Do we need more studies? Absolutely. But what we have now is compelling [enough] for us to take a look at it.”
Findings of rosacea clearance
SIBO’s believed contribution to the pathophysiology of rosacea is part of the increasingly described gut microbiome-skin axis. SIBO has been recognized as a medical phenomenon for many decades and has been defined as an excessive bacterial load in the small bowel that causes gastrointestinal symptoms, according to the 2020 American College of Gastroenterology clinical guideline on SIBO.
Symptoms commonly associated with SIBO overlap with the cardinal symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): abdominal pain; diarrhea, constipation, or both; bloating; and flatulence. SIBO can be diagnosed with several validated carbohydrate substrate (glucose or lactulose)–based breath tests that measure hydrogen and/or methane.
Hydrogen-positive breath tests suggest bacterial overgrowth, and methane-positive breath tests suggest small intestinal methanogen overgrowth. Methane is increasingly important and recognized, the AGA guideline says, though it creates a “nomenclature problem in the SIBO framework” because methanogens are not bacteria, the authors note.
In conventional practice, SIBO is typically treated with antibiotics such as rifaximin, and often with short-term dietary modification as well. Integrative medicine typically considers the use of supplements and botanicals in addition to or instead of antibiotics, as well as dietary change and increasingly, a close look at SIBO risk factors to prevent recurrence, Dr. Sivamani said. (His research unit is currently studying the use of herbal protocols as an alternative to antibiotics in patients with SIBO and dermatologic conditions.)
During a presentation on rosacea at the meeting, Neal Bhatia, MD, director of clinical dermatology at Therapeutics Clinical Research, a dermatology treatment and research center in San Diego, said that currently available breath tests for SIBO “are very interesting tools for understanding what may be happening in the gut” and that the “rifaximin data are good.”
He referred to a study reported in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology showing that patients with rosacea were significantly more likely to have SIBO (41.7% of 48 patients vs. 5.0% of 40 controls; P < .001), and that 64.5% of rosacea patients who completed treatment with rifaximin had remission of rosacea at a 3-year follow-up.
An earlier crossover study is also notable, he said. This study enrolled 113 consecutive patients with rosacea and 60 age- and sex-matched controls, and randomized those with SIBO (52 of the 113 with rosacea vs. 3 of the 60 controls) to rifaximin or placebo. Rosacea cleared in 20 of the 28 patients in the rifaximin group and greatly improved in 6 of the 28. Of 20 patients in the placebo group, rosacea remained unchanged in 18 and worsened in 2. When patients in the placebo group were switched to rifaximin, SIBO was eradicated in 17 of the 20, and rosacea completely resolved in 15 of those patients, Dr. Bhatia said.
In his view, it will take more time, greater awareness of the rosacea-SIBO link, and a willingness “to take chances” for more dermatologists to consider SIBO during rosacea care. “Breath tests are not something used in the [typical dermatology] clinic right now, but they may make their way in,” he said at the meeting.
In a follow-up interview, Dr. Bhatia emphasized that “it’s really a question of uptake, which always takes a while” and of willingness to “think through the disease from another angle ... especially in patients who are recalcitrant.”
Treatment
Dr. Sivamani said in the interview that a third type of SIBO – hydrogen sulfide–dominant SIBO – is now documented and worth considering when glucose and lactulose breath tests are negative in patients with rosacea who have gastrointestinal symptoms.
The use of breath tests to objectively diagnose SIBO is always best, Dr. Sivamani said, but he will consider empiric therapy in some patients. “I always tell patients [about] the benefits of testing, but if they can’t get the test covered or are unable to pay for the test, and they have symptoms consistent with SIBO, I’m okay doing a trial with therapy,” he said.
Rifaximin, one of the suggested antibiotics listed in the AGA guideline, is a nonabsorbable antibiotic that is FDA-approved for IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D); it has been shown to not negatively affect the growth of beneficial bacteria in the colon.
However, herbals are also an attractive option – alone or in combination with rifaximin or other antibiotics – speakers at the meeting said. In a multicenter retrospective chart review led by investigators at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, herbal therapies were at least as effective as rifaximin for treating SIBO, with similar safety profiles. The response rate for normalizing breath hydrogen testing in patients with SIBO was 46% for herbal therapies and 34% for rifaximin.
Dietary change is also part of treatment, with the reduction of fermentable carbohydrates – often through the Low FODMAP Diet and Specific Carbohydrate Diet – being the dominant theme in dietary intervention for SIBO, according to the AGA guideline.
“There are definitely some food choices you can shift,” said Dr. Sivamani. “I’ll work with patients on FODMAP, though it’s hard to sustain over the long-term and can induce psychological issues. You have to provide other options.”
Dr. Sivamani works with patients on using “a restrictive diet for a short amount of time, with the gradual reintroduction of foods to see [what] foods are and aren’t [causing] flares.” He also works to identify and eliminate risk factors and predisposing factors for SIBO so that recurrence will be less likely.
“SIBO is definitely an entity that is not on the fringes anymore ... it adds to inflammation in the body ... and if you have an inflamed gut, there’s a domino effect that will lead to inflammation elsewhere,” Dr. Sivamani said.
“You want to know, do your patients have SIBO? What subset do they have? Do they have risk factors you can eliminate?” he said. “And then what therapies will you use – pharmaceuticals, supplements and botanicals, or a combination? And finally, what will you do with diet?”
Dr. Bhatia disclosed he has affiliations with Abbvie, Almirall, Arcutis, Arena, Biofrontera, BMS, BI, Brickell, Dermavant, EPI Health, Ferndale, Galderma, Genentech, InCyte, ISDIN, Johnson & Johnson, LaRoche-Posay, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho, Pfizer, Proctor & Gamble, Regeneron, Sanofi, Stemline, SunPharma, and Verrica. Dr. Sivamani did not provide a disclosure statement.
REPORTING FROM IDS 2022