User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Eating earlier offers health benefits, studies say
New research suggests there may be better times during the day for eating and fasting.
Eating earlier in the day may help you lose weight, and eating meals within a 10-hour window could improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels, according to two new studies published in Cell Metabolism.
“You have this internal biological clock that makes you better at doing different things at different times of the day,” Courtney Peterson, PhD, an associate professor of nutrition sciences at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told NBC News. Dr. Peterson wasn’t involved with the studies.
“It seems like the best time for your metabolism, in most people, is the mid to late morning,” she said.
In one study, researchers found that eating later in the day made people hungrier during a 24-hour period, as compared with eating the same meals earlier in the day. Combined, the changes may increase the risk for obesity, the study authors found.
In another study, among firefighters as shift workers, researchers found that eating meals within a 10-hour window decreased the size of bad cholesterol particles, which could reduce risk factors for heart disease. The 10-hour eating window also improved blood pressure and blood sugar levels among those with health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
The two new studies confirm findings from previous studies that indicate humans may have an ideal eating window based on the body’s circadian rhythms, which regulate sleep and wake cycles and can affect appetite, metabolism, and blood sugar levels.
In the firefighter study, for instance, the 10-hour window appears to be a “sweet spot” for the body, the authors found. More severe restrictions, as found with many intermittent fasting diets, could be difficult for the body to maintain.
“When we think about 6 or 8 hours, you might see a benefit, but people might not stick to it for a long time,” Satchidananda Panda, PhD, one of the study authors and a professor at the Salk Institute, La Jolla, Calif., told NBC News.
The new studies had small sample sizes, though they offer insight for future research. In the first study, 16 people who were overweight or obese tried two eating plans for 24-hour periods. Some of them began eating an hour after their natural wake-up time, and others waited to begin eating until about 5 hours after waking up. They ate the same meals with the same calories and nutrients.
The researchers measured their hormone levels and found that eating later decreased the levels of leptin, which helps people to feel full. Eating later also doubled the odds that people felt hungry throughout the day. Those in the study who ate later in the day also had more cravings for starchy or salty foods, as well as meat and dairy, which are energy-dense foods.
The research team also found changes in fat tissue, which could lead to a higher chance of building up new fat cells and a lower chance of burning fat. Late eaters burned about 60 fewer calories than early eaters during the day.
“Your body processes calories differently when you eat late in the day. It tips the scale in favor of weight gain and fat gain,” Dr. Peterson said. “From this study, we can get pretty clear recommendations that people shouldn’t skip breakfast.”
The second study followed 137 firefighters in San Diego who ate a Mediterranean diet with fish, vegetables, fruit, and olive oil for 12 weeks. Among those, 70 firefighters ate during a 10-hour window, and the rest ate during a longer window, generally about 13 hours. They logged their meals in an app and wore devices to track blood sugar levels.
In the 10-hour group, most firefighters ate between 8 a.m. or 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. or 7 p.m. The time-restricted eating appeared to be linked with health benefits, such as less harmful cholesterol buildup and reduced heart disease.
Among firefighters with risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure and high blood sugar, the time-restricted eating decreased their blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
The restricted window appears to allow the body to break down toxins and get rid of sodium and other things that can drive up blood pressure and blood sugar, the authors wrote.
During periods of fasting, “organs get some rest from digesting food so they can divert their energy toward repairing cells,” Dr. Panda said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New research suggests there may be better times during the day for eating and fasting.
Eating earlier in the day may help you lose weight, and eating meals within a 10-hour window could improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels, according to two new studies published in Cell Metabolism.
“You have this internal biological clock that makes you better at doing different things at different times of the day,” Courtney Peterson, PhD, an associate professor of nutrition sciences at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told NBC News. Dr. Peterson wasn’t involved with the studies.
“It seems like the best time for your metabolism, in most people, is the mid to late morning,” she said.
In one study, researchers found that eating later in the day made people hungrier during a 24-hour period, as compared with eating the same meals earlier in the day. Combined, the changes may increase the risk for obesity, the study authors found.
In another study, among firefighters as shift workers, researchers found that eating meals within a 10-hour window decreased the size of bad cholesterol particles, which could reduce risk factors for heart disease. The 10-hour eating window also improved blood pressure and blood sugar levels among those with health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
The two new studies confirm findings from previous studies that indicate humans may have an ideal eating window based on the body’s circadian rhythms, which regulate sleep and wake cycles and can affect appetite, metabolism, and blood sugar levels.
In the firefighter study, for instance, the 10-hour window appears to be a “sweet spot” for the body, the authors found. More severe restrictions, as found with many intermittent fasting diets, could be difficult for the body to maintain.
“When we think about 6 or 8 hours, you might see a benefit, but people might not stick to it for a long time,” Satchidananda Panda, PhD, one of the study authors and a professor at the Salk Institute, La Jolla, Calif., told NBC News.
The new studies had small sample sizes, though they offer insight for future research. In the first study, 16 people who were overweight or obese tried two eating plans for 24-hour periods. Some of them began eating an hour after their natural wake-up time, and others waited to begin eating until about 5 hours after waking up. They ate the same meals with the same calories and nutrients.
The researchers measured their hormone levels and found that eating later decreased the levels of leptin, which helps people to feel full. Eating later also doubled the odds that people felt hungry throughout the day. Those in the study who ate later in the day also had more cravings for starchy or salty foods, as well as meat and dairy, which are energy-dense foods.
The research team also found changes in fat tissue, which could lead to a higher chance of building up new fat cells and a lower chance of burning fat. Late eaters burned about 60 fewer calories than early eaters during the day.
“Your body processes calories differently when you eat late in the day. It tips the scale in favor of weight gain and fat gain,” Dr. Peterson said. “From this study, we can get pretty clear recommendations that people shouldn’t skip breakfast.”
The second study followed 137 firefighters in San Diego who ate a Mediterranean diet with fish, vegetables, fruit, and olive oil for 12 weeks. Among those, 70 firefighters ate during a 10-hour window, and the rest ate during a longer window, generally about 13 hours. They logged their meals in an app and wore devices to track blood sugar levels.
In the 10-hour group, most firefighters ate between 8 a.m. or 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. or 7 p.m. The time-restricted eating appeared to be linked with health benefits, such as less harmful cholesterol buildup and reduced heart disease.
Among firefighters with risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure and high blood sugar, the time-restricted eating decreased their blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
The restricted window appears to allow the body to break down toxins and get rid of sodium and other things that can drive up blood pressure and blood sugar, the authors wrote.
During periods of fasting, “organs get some rest from digesting food so they can divert their energy toward repairing cells,” Dr. Panda said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
New research suggests there may be better times during the day for eating and fasting.
Eating earlier in the day may help you lose weight, and eating meals within a 10-hour window could improve blood sugar and cholesterol levels, according to two new studies published in Cell Metabolism.
“You have this internal biological clock that makes you better at doing different things at different times of the day,” Courtney Peterson, PhD, an associate professor of nutrition sciences at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, told NBC News. Dr. Peterson wasn’t involved with the studies.
“It seems like the best time for your metabolism, in most people, is the mid to late morning,” she said.
In one study, researchers found that eating later in the day made people hungrier during a 24-hour period, as compared with eating the same meals earlier in the day. Combined, the changes may increase the risk for obesity, the study authors found.
In another study, among firefighters as shift workers, researchers found that eating meals within a 10-hour window decreased the size of bad cholesterol particles, which could reduce risk factors for heart disease. The 10-hour eating window also improved blood pressure and blood sugar levels among those with health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
The two new studies confirm findings from previous studies that indicate humans may have an ideal eating window based on the body’s circadian rhythms, which regulate sleep and wake cycles and can affect appetite, metabolism, and blood sugar levels.
In the firefighter study, for instance, the 10-hour window appears to be a “sweet spot” for the body, the authors found. More severe restrictions, as found with many intermittent fasting diets, could be difficult for the body to maintain.
“When we think about 6 or 8 hours, you might see a benefit, but people might not stick to it for a long time,” Satchidananda Panda, PhD, one of the study authors and a professor at the Salk Institute, La Jolla, Calif., told NBC News.
The new studies had small sample sizes, though they offer insight for future research. In the first study, 16 people who were overweight or obese tried two eating plans for 24-hour periods. Some of them began eating an hour after their natural wake-up time, and others waited to begin eating until about 5 hours after waking up. They ate the same meals with the same calories and nutrients.
The researchers measured their hormone levels and found that eating later decreased the levels of leptin, which helps people to feel full. Eating later also doubled the odds that people felt hungry throughout the day. Those in the study who ate later in the day also had more cravings for starchy or salty foods, as well as meat and dairy, which are energy-dense foods.
The research team also found changes in fat tissue, which could lead to a higher chance of building up new fat cells and a lower chance of burning fat. Late eaters burned about 60 fewer calories than early eaters during the day.
“Your body processes calories differently when you eat late in the day. It tips the scale in favor of weight gain and fat gain,” Dr. Peterson said. “From this study, we can get pretty clear recommendations that people shouldn’t skip breakfast.”
The second study followed 137 firefighters in San Diego who ate a Mediterranean diet with fish, vegetables, fruit, and olive oil for 12 weeks. Among those, 70 firefighters ate during a 10-hour window, and the rest ate during a longer window, generally about 13 hours. They logged their meals in an app and wore devices to track blood sugar levels.
In the 10-hour group, most firefighters ate between 8 a.m. or 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. or 7 p.m. The time-restricted eating appeared to be linked with health benefits, such as less harmful cholesterol buildup and reduced heart disease.
Among firefighters with risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure and high blood sugar, the time-restricted eating decreased their blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
The restricted window appears to allow the body to break down toxins and get rid of sodium and other things that can drive up blood pressure and blood sugar, the authors wrote.
During periods of fasting, “organs get some rest from digesting food so they can divert their energy toward repairing cells,” Dr. Panda said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM CELL METABOLISM
Is another COVID-19 booster really needed?
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Many countries around the globe are starting to roll out another booster of the COVID-19 vaccine but, with public interest waning and a sense of normalcy firmly installed in our minds, this may prove an ill-fated effort, unless authorities can provide a coherent answer to the question “Is another jab really needed?” (The short answer is a firm “yes,” of course.)
In what we could call the “chronic” phase of the pandemic, most countries have now settled for a certain number of daily cases and a (relatively low) number of complications and deaths. It’s the vaccines that have afforded us this peace of mind, lest we forget. But they are different to other vaccines that we are more familiar with, such as the MMR that we get as kids and then forget about for the rest of our lives. As good as the different COVID-19 vaccines are, they never came with the promise of generating lifelong antibodies. We knew early on that the immunity they provide slowly wanes with time. That doesn’t mean that those who have their vaccination records up to date (which included a booster probably earlier in 2022) are suddenly exposed. Data suggest that although people several months past their last booster would now be more prone to getting reinfected, the protection against severe disease still hangs around 85%. In other words, their chances of ending up in the hospital are low.
Why worry, then, about further boosting the immune system? The same studies show that an additional jab would increase this percentage up to 99%. Is this roughly 10% improvement really worth another worldwide vaccination campaign? Well, this is a numbers game, after all. The current form of the virus is extremely infectious, and the Northern Hemisphere is heading toward the cold months of the year, which we have seen in past years increases COVID-19 contagions, as you would expect from any airborne virus. Thus, it’s easy to expect a new peak in the number of cases, especially considering that we are not going to apply any of the usual restrictions to prevent this. In these conditions, extending the safety net to a further 10% of the population would substantially reduce the total number of victims. It seems like a good investment of resources.
We can be more surgical about it and direct this new vaccination campaign to the population most likely to end up in the hospital. People with concomitant pathologies are at the top of the list, but it’s also an age issue. On the basis of different studies of the most common ages of admission, the cutoff point for the booster varies from country to country, with the lowest being 50 and in other cases hovering around 65 years of age. Given the safety of these vaccines, if we can afford it, the wider we cast the net, the better, but at least we should make every effort to fully vaccinate the higher age brackets.
The final question is which vaccine to give. There are confounding studies about the importance of switching to Omicron-specific jabs, which are finally available. Although this seems like a good idea, since Omicron infections elicit a more effective range of antibodies and new variants seem to better escape our defenses, recent studies suggest that there actually may not be so much difference with the old formula.
The conclusion? This regimen of yearly boosters for some may be the scenario for the upcoming years, similar to what we already do for the flu, so we should get used to it.
Dr. Macip is associate professor, department of molecular and cellular biology, University of Leicester (England). He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Salt pills for patients with acute decompensated heart failure?
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.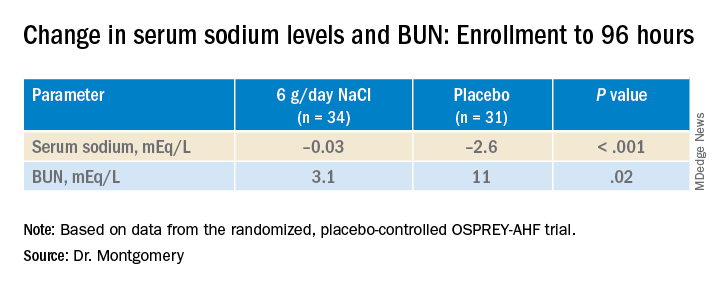
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Restriction of dietary salt to alleviate or prevent volume overload in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is common hospital practice, but without a solid evidence base. A trial testing whether taking salt pills might have benefits for patients with ADHF undergoing intensive diuresis, therefore, may seem a bit counterintuitive.
In just such a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, the approach made no difference to weight loss on diuresis, a proxy for volume reduction, or to serum creatinine levels in ADHF patients receiving high-dose intravenous diuretic therapy.
The patients consumed the extra salt during their intravenous therapy in the form of tablets providing 6 g sodium chloride daily on top of their hospital-provided, low-sodium meals.
During that time, serum sodium levels remained stable for the 34 patients assigned to the salt tablets but dropped significantly in the 31 given placebo pills.
They lost about the same weight, averages of 4 kg and 4.6 kg (8.8-10 lb), respectively, and their urine output was also similar. Patients who took the salt tablets showed less of an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) at both 96 hours and at discharge.
The findings “challenge the routine practice of sodium chloride restriction in acute heart failure, something done thousands of times a day, millions of times a year,” Robert A. Montgomery, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said when presenting the study at the annual scientific meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The trial, called OSPREY-AHF (Oral Sodium to Preserve Renal Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure), also may encourage a shift in ADHF management from a preoccupation with salt restriction to focus more on fighting fluid retention.
OSPREY-HF took on “an established practice that doesn’t have much high-quality evidentiary support,” one guided primarily by consensus and observational data, Montgomery said in an interview.
There are also potential downsides to dietary sodium restriction, including some that may complicate or block ADHF therapies.
“Low-sodium diets can be associated with decreased caloric intake and nutritional quality,” Dr. Montgomery observed. And observational studies suggest that “patients who are on a low sodium diet can develop increased neurohormonal activation. The kidney is not sensing salt, and so starts ramping up the hormones,” which promotes diuretic resistance.
But emerging evidence also suggests “that giving sodium chloride in the form of hypertonic saline can help patients who are diuretic resistant.” The intervention, which appears to attenuate the neurohormonal activation associated with high-dose intravenous diuretics, Dr. Montgomery noted, helped inspire the design of OSPREY-AHF.
Edema consists of “a gallon of water and a pinch of salt, so we really should stop being so salt-centric and think much more about water as the problem in decompensated heart failure,” said John G.F. Cleland, MD, PhD, during the question-and-answer period after Montgomery’s presentation. Dr. Cleland, of the University of Glasgow Institute of Health and Wellbeing, is not connected to OSPREY-AHF.
“I think that maybe we overinterpret how important salt is” as a focus of volume management in ADHF, offered David Lanfear, MD, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, who is also not part of the study.
OSPREY-AHF was well conducted but applies to a “very specific” clinical setting, Dr. Lanfear said in an interview. “These people are getting aggressive diuresis, a big dose and continuous infusion. It’s not everybody that has heart failure.”
Although the study was small, “I think it will fuel interest in this area and, probably, further investigation,” he said. The trial on its own won’t change practice, “but it will raise some eyebrows.”
The trial included patients with ADHF who have been “admitted to a cardiovascular medicine floor, not the intensive care unit” and were receiving at least 10 mg per hour of furosemide. It excluded any who were “hypernatremic or severely hyponatremic,” said Dr. Montgomery when presenting the study. They were required to have an initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of at least 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
The patients were randomly assigned double blind at a single center to receive tablets providing 2 g sodium chloride or placebo pills – 34 and 31 patients, respectively – three times daily during intravenous diuresis.
At 96 hours, the two groups showed no difference in change in creatinine levels or change in weight, both primary endpoints. Nor did they differ in urine output or change in eGFR. But serum sodium levels fell further, and BUN levels went up more in those given placebo.
The two groups showed no differences in hospital length of stay, use of renal replacement therapy at 90 days, ICU time during the index hospitalization, 30-day readmission, or 90-day mortality – although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, Dr. Montgomery reported.
"We have patients who complain about their sodium-restricted diet, we have patients that have cachexia, who have a lot of complaints about provider-ordered meals and recommendations,” Dr. Montgomery explained in an interview.
Clinicians provide education and invest a lot of effort into getting patients with heart failure to start and maintain a low-sodium diet, he said. “But a low-sodium diet, in prior studies – and our study adds to this – is not a lever that actually seems to positively or adversely affect patients.”
Dr. Montgomery pointed to the recently published SODIUM-HF trial comparing low-sodium and unrestricted-sodium diets in outpatients with heart failure. It saw no clinical benefit from the low-sodium intervention.
Until studies show, potentially, that sodium restriction in hospitalized patients with heart failure makes a clinical difference, Dr. Montgomery said, “I’d say we should invest our time in things that we know are the most helpful, like getting them on guideline-directed medical therapy, when instead we spend an enormous amount of time counseling on and enforcing dietary restriction.”
Support for this study was provided by Cleveland Clinic Heart Vascular and Thoracic Institute’s Wilson Grant and Kaufman Center for Heart Failure Treatment and Recovery Grant. Dr. Lanfear disclosed research support from SomaLogic and Lilly; consulting for Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Martin Pharmaceuticals, and Amgen; and serving on advisory panels for Illumina and Cytokinetics. Dr. Montgomery and Dr. Cleland disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HFSA 2022
Newer drugs not cost effective for first-line diabetes therapy
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To be cost effective, compared with metformin, for initial therapy for type 2 diabetes, prices for a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor or a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist would have to fall by at least 70% and at least 90%, respectively, according to estimates.
The study, modeled on U.S. patients, by Jin G. Choi, MD, and colleagues, was published online Oct. 3 in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The researchers simulated the lifetime incidence, prevalence, mortality, and costs associated with three different first-line treatment strategies – metformin, an SGLT2 inhibitor, or a GLP-1 agonist – in U.S. patients with untreated type 2 diabetes.
Compared with patients who received initial treatment with metformin, those who received one of the newer drugs had 4.4% to 5.2% lower lifetime rates of congestive heart failure, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
However, to be cost-effective at under $150,000 per quality-adjusted life-years (QALY), SGLT2 inhibitors would need to cost less than $5 a day ($1,800 a year), and GLP-1 agonists would have to cost less than $6 a day ($2,100 a year), a lot less than now.
Knowing how expensive these drugs are, “I am not surprised” that the model predicts that the price would have to drop so much to make them cost-effective, compared with first-line treatment with metformin, senior author Neda Laiteerapong, MD, said in an interview.
“But I am disappointed,” she said, because these drugs are very effective, and if the prices were lower, more people could benefit.
“In the interest of improving access to high-quality care in the United States, our study results indicate the need to reduce SGLT2 inhibitor and GLP-1 receptor agonist medication costs substantially for patients with type 2 [diabetes] to improve health outcomes and prevent exacerbating diabetes health disparities,” the researchers conclude.
One way that the newer drugs might be more widely affordable is if the government became involved, possibly by passing a law similar to the Affordable Insulin Now Act, speculated Dr. Laiteerapong, who is associate director at the Center for Chronic Disease Research and Policy, University of Chicago.
‘Current prices too high to encourage first-line adoption’
Guidelines recommend the use of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists as second-line therapies for patients with type 2 diabetes, but it has not been clear if clinical benefits would outweigh costs for use as first-line therapies.
“Although clinical trials have demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of these newer drugs, they are hundreds of times more expensive than other ... diabetes drugs,” the researchers note.
On the other hand, costs may fall in the coming years when these new drugs come off-patent.
The current study was designed to help inform future clinical guidelines.
The researchers created a population simulation model based on the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study, Outcomes Model version 2 (UKPDS OM2) for diabetes-related complications and mortality, with added information about hypoglycemic events, quality of life, and U.S. costs.
The researchers also identified a nationally representative sample of people who would be eligible to start first-line diabetes therapy when their A1c reached 7% for the model.
Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (2013-2016), the researchers identified about 7.3 million U.S. adults aged 18 and older with self-reported diabetes or an A1c greater than 6.5% with no reported use of diabetes medications.
Patients were an average age of 55, and 55% were women. They had had diabetes for an average of 4.2 years, and 36% had a history of diabetes complications.
The model projected that patients would have an improved life expectancy of 3.0 and 3.4 months from first-line SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists, respectively, compared with initial therapy with metformin due to reduced rates of macrovascular disease.
“However, the current drug costs would be too high to encourage their adoption as first-line for usual clinical practice,” the researchers report.
‘Disparities could remain for decades’
Generic SGLT2 inhibitors could enter the marketplace shortly, because one of two dapagliflozin patents expired in October 2020 and approval for generic alternatives has been sought from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Dr. Choi and colleagues note.
However, it could still take decades for medication prices to drop low enough to become affordable, the group cautions. For example, a generic GLP-1 agonist became available in 2017, but costs remain high.
“Without external incentives,” the group writes, “limited access to these drug classes will likely persist (for example, due to higher copays or requirements for prior authorizations), as will further diabetes disparities – for decades into the future – because of differential access to care due to insurance (for example, private vs. public), which often tracks race and ethnicity.”
The study was supported by the American Diabetes Association. Dr. Choi was supported by a National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging grant. Dr. Laiteerapong and other co-authors are members of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Chicago Center for Diabetes Translation Research at the University of Chicago. Dr. Choi and Dr. Laiteerapong have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
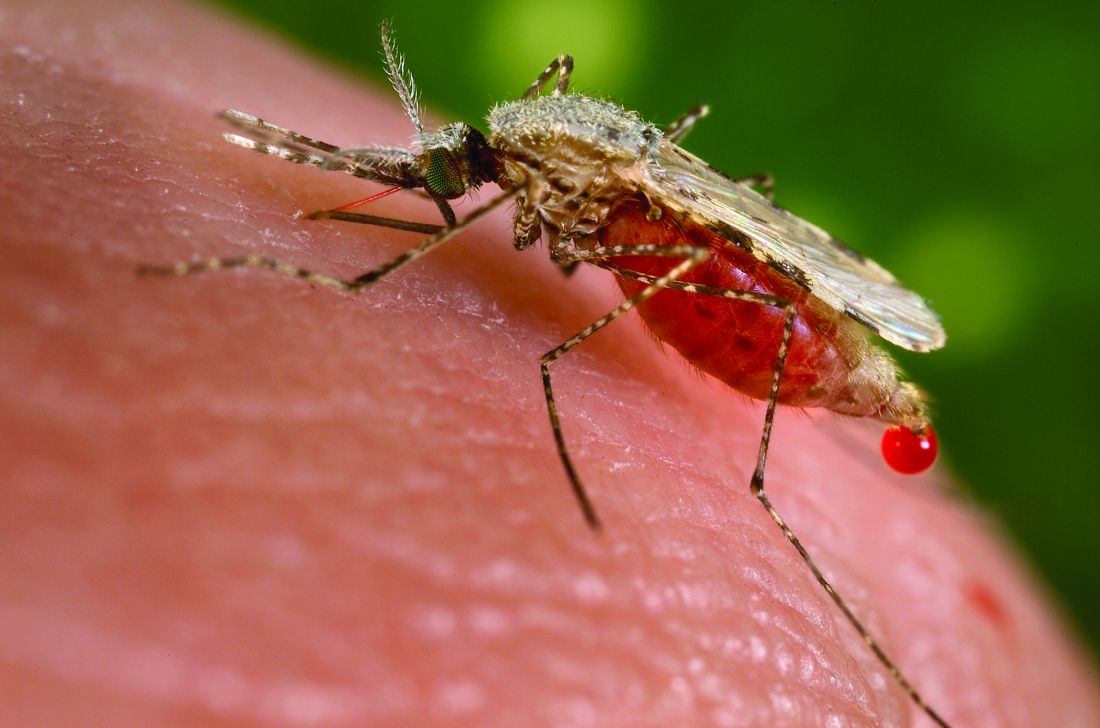
Malaria vaccine gets special delivery by tiny health personnel
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Don’t like needles? Have we got a vaccine for you
Here’s a quick question: How do you turn the most annoying thing ever into something positive?
No, we’re not talking about politicians this time. No, not Elon Musk, either. Infomercials? Guess again. Humidity? Nope, even more annoying than that.
Give up? The most annoying thing ever is mosquitoes. This time, however, NPR reports that mosquitoes have been used to deliver a vaccine for the very disease they’ve been transmitting to their human food sources all these years.
In a recent proof-of-concept trial, investigators used CRISPR technology to genetically modify malaria-causing Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites, which just happen to live in the salivary glands of Anopheles mosquitoes. And since the Plasmodium parasites are already in the mosquitoes, it made sense to use the buzzy little critters as the delivery device for the vaccine.
More sense than a syringe, you ask? Have you ever tried to poke a syringe into the salivary gland of a mosquito? No, we thought not. Well, we can tell you from experience that it’s really, really hard. Never mind how we know. We just do.
The 14 study volunteers – who were paid $4,100 for their participation – were first exposed to hundreds of mosquitoes carrying the altered Plasmodium parasites. Then, to test the vaccine, they were exposed to mosquitoes that had actual, malaria-carrying Plasmodium. Half of the subjects got malaria, so the vaccine was only 50% effective, meaning there’s still work to do.
Meanwhile, the scientists here at LOTMEco are all over this mosquito-delivery business, working on a vaccine to prevent Elon Musk. Plan B involves some sort of really big swatter.
Climate change: Sleeping your life away
It’s no secret that climate change is raising the temperature on everything. You may think you’re getting relief when the sun goes down, but in some places it’s still hot. A new survey conducted in central Japan shows how bad it can be and how higher nighttime temperatures can have a serious impact on people’s health.
That online survey, the Sleep Quality Index for Daily Sleep, enabled the investigators to correlate sleep quality with daily temperature for 1,284 adults in 2011 and 2012 who completed the survey over 10 days.
Not only was there a significant difference in sleep disturbance among younger men (higher) versus older men, but the prevalence of sleep disturbance went up when the daytime temperature was above 24.8° C. They also found that disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), which measure time lost through premature death and time lived in certain conditions that put one’s health at risk, were 81.8 years for the city of Nagoya (population, 2.2 million) in 2012.
The damage to health from sleep disorders caused by daily temperatures higher than 25° C “is comparable to that of heatstroke and must be addressed,” lead author Tomohiko Ihara of the University of Tokyo said in a written statement.
The researchers hope that this information will help sway legislators to consider the impact of higher nighttime temperatures and that it can be used to provide guidance for better sleep. The solution for now? Sleep with the air conditioner on. Your energy bill might increase, but just think about those DALYs. If using the AC lowers DALYs and increases time lived, then we say it’s worth it.
Maybe it would have been a dragon WITH cancer
If you ask a random person on the street to tell you all they know about the country of Wales, they’ll probably mention two things: One, the contorted collection of jumbled-up letters that is the Welsh language (looking at you, Llanfairpwllgwyngyllgogerychwyrndrobwllllantysiliogogogoch) and, two, the association with dragons. The Welsh flag even has a dragon on it.
With that in mind, take a guess as to what sort of statue art dealer Simon Wingett wanted to build in the Welsh town of Wrexham. No, not a monument to the second-longest place name in the world. Try again. His dragon would not be some piddly little thing either; he wanted a virtual kaiju overlooking the town, with the whole statue to stand about 60 meters high. That’s taller than the original 1954 Godzilla.
Artistic masterpieces may sell for frankly insane prices, but art dealers themselves are not the wealthiest of individuals, so Mr. Wingett needed money to fund his dragon-based dream. Lucky for him, he also happened to be the manager of a cancer charity – initially set up by Mr. Wingett’s father, who had throat cancer – which nominally aimed to provide equipment and resources to cancer patients in the Wrexham area.
Yes, this is going precisely where you think it’s going. From 2011 to 2018, when the charity closed, Mr. Wingett used the charity’s donations to fund his dragon statue – which never actually got built, by the way – to the tune of over 400,000 pounds. Of course, Mr. Wingett came under scrutiny when people started to notice that his cancer charity hadn’t actually done anything charitable since 2011, and he was recently banned by the Welsh High Court from serving as trustee of any charity for 10 years. Oh no, tragedy and horror! Truly a punishment worse than death itself.
Okay fine, he also has to pay back 117,000 pounds to actual legitimate cancer charities. The astute mathematicians out there may notice that 117,000 is a lot less than 400,000. But it’s just as the old saying goes: One-quarter of crime doesn’t pay. You can keep three-quarters of it, though, that’s completely fine.
Retinal imaging can predict cardiovascular mortality
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
according to a new study using data from the UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)–Norfolk study.
The researchers, from St. George’s University of London, Cambridge University, Kingston University, Moorfields Eye Hospital, and University College London, developed a method of artificial intelligence (AI)–enabled imaging of the retina’s vascular network that could accurately predict CVD and death, without the need for blood tests or blood pressure measurement.
The system “paves the way for a highly effective, noninvasive screening test for people at medium to high risk of circulatory disease that doesn’t have to be done in a clinic,” they said. “In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.” Optometry specialists welcomed the prospect and hailed it as “an exciting development.”
Retinal vessels give an accurate early indicator of CVD
The study, published online in the British Journal of Ophthalmology, was based on previous research showing that the width of retinal arterioles and venules seen on retinal imaging may provide an accurate early indicator of CVD, whereas current risk prediction frameworks aren’t always reliable in identifying people who will go on to develop or die of circulatory diseases.
The researchers developed a fully automated AI-enabled algorithm, called Quantitative Analysis of Retinal vessels Topology and Size (QUARTZ), to assess the potential of retinal vasculature imaging plus known risk factors to predict vascular health and death. They applied QUARTZ to retinal images from 88,052 UK Biobank participants aged 40-69 years, looking specifically at the width, vessel area, and degree of tortuosity of the retinal microvasculature, to develop prediction models for stroke, heart attack, and death from circulatory disease.
They then applied these models to the retinal images of 7,411 participants, aged 48-92 years, in the EPIC-Norfolk study. They then compared the performance of QUARTZ with the widely used Framingham Risk Scores framework.
The participants in the two studies were tracked for an average of 7.7 and 9.1 years, respectively, during which time there were 327 circulatory disease deaths among 64,144 UK Biobank participants (average age, 56.8 years) and 201 circulatory deaths among 5,862 EPIC-Norfolk participants (average age, 67.6 years).
Vessel characteristics important predictors of CVD mortality
Results from the QUARTZ models showed that in all participants, arteriolar and venular width, venular tortuosity, and width variation were important predictors of circulatory disease death. In addition, in women, but not in men, arteriolar and venular area were separate factors that contributed to risk prediction.
Overall, the predictive models, based on age, smoking, and medical history (antihypertensive or cholesterol lowering medication, diabetes, and history of stroke or MI) as well as retinal vasculature, captured between half and two-thirds of circulatory disease deaths in those most at risk, the authors said.
Compared with Framingham Risk Scores (FRS), the retinal vasculature (RV) models captured about 5% more cases of stroke in UK Biobank men, 8% more cases in UK Biobank women, and 3% more cases among EPIC-Norfolk men most at risk, but nearly 2% fewer cases among EPIC-Norfolk women. However, the team said that, while adding RV to FRS resulted in only marginal changes in prediction of stroke or MI, a simpler noninvasive risk score based on age, sex, smoking status, medical history, and RV “yielded comparable performance to FRS, without the need for blood sampling or BP measurement.”
Vasculometry low cost, noninvasive and with high street availability
They concluded: “Retinal imaging is established within clinic and hospital eye care and in optometric practices in the U.S. and U.K. AI-enabled vasculometry risk prediction is fully automated, low cost, noninvasive and has the potential for reaching a higher proportion of the population in the community because of “high street” availability and because blood sampling or sphygmomanometry are not needed.
“[Retinal vasculature] is a microvascular marker, hence offers better prediction for circulatory mortality and stroke, compared with MI, which is more macrovascular, except perhaps in women.
“In the general population it could be used as a noncontact form of systemic vascular health check, to triage those at medium-high risk of circulatory mortality for further clinical risk assessment and appropriate intervention.”
In the United Kingdom, for example, it could be included in the primary care NHS Health Check for those aged 41-74 years, they suggested. In addition, “high street” retinal scanning could directly feed into primary medical services and help achieve greater screening coverage for older age groups, who are likely to attend an optometric practice for visual correction, especially with the onset of presbyopia. “This would offer a novel approach to identify those at high risk of circulatory mortality, which is not currently screened for,” the team said.
Test could help to identify high-risk individuals
In a linked editorial, Ify Mordi, MD, and Emanuele Trucco, MD, of the University of Dundee (Scotland), said that CVD remains a significant cause of mortality and morbidity and the most common cause of death worldwide, accounting for a quarter of all U.K. deaths – and its burden is increasing. “Identification of individuals at high risk is particularly important,” they said, but current clinical risk scores to identify those at risk “are unfortunately not perfect,” so miss some of those who might benefit from preventative therapy.
“The retina is the only location that allows non-invasive direct visualisation of the vasculature, potentially providing a rich source of information.” In the new study, the measurements derived with the software tool, QUARTZ, were significantly associated with CVD, they said, with similar predictive performance to the Framingham clinical risk score.
“The results strengthen the evidence from several similar studies that the retina can be a useful and potentially disruptive source of information for CVD risk in personalised medicine.” However, a number of questions remain about how this knowledge could be integrated into clinical care, including who would conduct such a retinal screening program and who would act on the findings?
The editorial concluded: “What is now needed is for ophthalmologists, cardiologists, primary care physicians, and computer scientists to work together to design studies to determine whether using this information improves clinical outcome, and, if so, to work with regulatory bodies, scientific societies and healthcare systems to optimize clinical work flows and enable practical implementation in routine practice.”
‘Exciting development that could improve outcomes’
Asked to comment, Farah Topia, clinical and regulatory adviser at the Association of Optometrists, said: “This is an exciting development that could improve outcomes for many patients by enabling earlier detection of serious health risks. Patients attend optometric practice for a variety of reasons and this interaction could be used to a greater extent to help detect disease earlier. With optometrists available on every High Street, in the heart of communities, it’s an element of primary care that can be accessed quickly and easily, and optometrists are also already trained to have health and lifestyle discussion with patients.”
She added: “Retinal photographs are regularly taken when patients visit an optometrist, so being able to further enhance this process using AI is exciting.
“We look forward to seeing how this area develops and how optometrists can work together with other healthcare sectors to improve patient outcomes and ease the burden the NHS currently faces.”
The study was funded by the Medical Research Council Population and Systems Medicine Board and the British Heart Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape UK.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
Temper tantrums, bullying colleagues: How to avert physician misbehavior?
Daniel Freedman, DO, a pediatric neurologist in Austin, Tex., remembers being flabbergasted when a surgeon threw an instrument across the room in medical school.
“I remember thinking, ‘I can’t believe people actually do this, a grown man in his 50s having a temper tantrum,’” Dr. Freedman said in an interview. But it certainly wasn’t the last time he witnessed bad behavior by one of his peers.
The results of Medscape’s recent report, Physicians Behaving Badly: Stress and Hardship Trigger Misconduct, suggest he has plenty of company. More than 4 in 10 respondents (41%) observed inappropriate behavior in the workplace in 2022, an uptick from 35% in 2021, according to the report, which polled more than 1,500 physicians about inappropriate behavior on and off the clock.
Of course, 38% of respondents have not seen any instances of misbehavior; and many of the instances that were seen were mild or infrequent. Additionally, instances of bad behavior have declined significantly over the past 5 years.
Dr. Freedman said he learned a lesson from his mentor and program director during training that has stuck with him throughout his career. “If you couldn’t act that way at any job, whether at McDonald’s or any other possible place, you shouldn’t act that way in medicine.” But he recognizes one limitation of that advice. “A lot of the people that behave badly may not have ever worked in a different environment before,” he said.
“They only perceive that they’re at the top of the food chain, so they can behave badly without repercussions.”
What Dr. Freedman described is formally called disruptive physician behavior, one of several categories of inappropriate behavior in medicine, according to Charles Samenow, MD, MPH, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University, Washington, who has studied this phenomenon for years.
“Disruptive physician behavior compromises the safety of the workplace,” Dr. Samenow explained. The behavior can occur at work, outside of work, or on social media. It can hinder operations, threaten patient and staff safety, and affect workplace morale.
“The question is trying to understand where that bad behavior is coming from and the impact of that bad behavior,” Dr. Samenow said in an interview.
One reason is fairly simple: doctors are human, and humans have a wide range of behavior. Plus, as the Medscape survey showed,
Self-selecting traits become an Achilles heel
“Any human put in a position of power over other humans has the potential to be disruptive, harass, etc, if they have certain personality traits,” said David Gorski, MD, a professor of surgery at Wayne State University, Detroit. That jibes with Dr. Samenow’s research.
Classic disruptive behavior isn’t usually associated with depression, mania, psychosis, or similar characteristics, Dr. Samenow explained. Rather, it tends to be personality driven. “Physicians are not immune to the normal problems every human being faces,” he said.
In the Medscape report, physicians cited personal arrogance as one of the leading reasons physicians engaged in inappropriate behavior (56%), followed closely by personal problems outside of work (52%), a social shift in accepting more casual behavior (50%), and job-related stress (46%). (Respondents could choose more than one answer).
One factor contributing to misbehavior that Dr. Samenow has consistently identified in his research is a history of adverse childhood experiences or family dysfunction: People who grew up in homes with physical or verbal abuse learned anger as a coping skill instead of positive, assertive communication. It’s likely that some physicians, as well as the overall population, learned anger as a coping skill for that reason.
How to help avert disruptive behavior in medical settings
Dr. Samenow said that coaching is a “wonderful tool” in teaching the interpersonal skills that medical school often doesn’t address.
In some case, interventions can be very helpful. For example, programs that teach effective communication strategies and teamwork through a combination of culturally sensitive dialectical and cognitive-behavioral therapy and other modalities have been successful, Dr. Samenow said. Although they are more about treating an illness than addressing “misbehavior,” programs for substance use that have been developed by and for doctors are very effective, too.
Fewer resources are available, however, for addressing racism, classism, misogyny, and other forms of bigotry, Dr. Samenow noted. “There’s implicit bias training, but not at the level of what exists for disruptive physicians and those with addiction. “That’s an area we need to work on.” Racist language was the third most commonly observed bad behavior cited in the Medscape survey, behind only bullying of staff and mocking or disparaging of patients. It was reported frequently outside of work as well.
The Medscape report found an increase in observed behavior at work and on social media, although it’s hard to determine prevalence trends over time, Dr. Samenow said. “The tolerance for this behavior has really gone down,” likely leading to more reporting, he said, and more systems for reporting bad behavior exist today than in the past.
However, Dr. Freedman said inadequate regulation, disciplinary action, and follow-through remain a problem.
“There are lots of limitations to our reporting system and to our follow-through with those reports,” including hospitals that, whether for fear of litigation or other reasons, allow physicians to quietly resign and move to another institution, even with positive recommendations, Dr. Freedman said.
Indeed, only a third of observed misbehavior in the Medscape report resulted in disciplinary action. Half the respondents believed a verbal warning was a necessary consequence, followed by a conversation from management and being reported to a supervisor or human resources. Though only 10% thought a report to the medical board was warranted, it likely depends on the offense and its frequency.
“I think going from paternalism to more patient-centered care and having patients involved in those conversations is a nice shift that makes doctors more human and relatable, and hopefully makes the public more forgiving, that we’re going to make mistakes and nobody’s perfect,” Freedman said. But he added that physicians should be held accountable when a mistake or two becomes a pattern.
Misinformation is professional misconduct
Sufficient accountability is especially absent, these doctors said, for a subset of professional misconduct: spreading misinformation.
While more “conventional” bad behaviors include fraud, dishonesty, abuse of underlings, and incompetence, bad behavior should also include “selling quackery and antivaccine misinformation, the way some doctors did with various nostrums for COVID-19,” said Dr. Gorski, who frequently blogs about doctors’ spreading misinformation.
Taylor Nichols, MD, an emergency medicine physician based in Sacramento, cites the desire for attention and clout as motivations. “Saying things that are wildly, provably false is professional misconduct,” Nichols said. He distinguished such statements from scientific, academic, or clinical disagreement that is necessary within medicine.
Yet there’s been a “long tradition of looking the other way or letting people with fancy titles get away with saying nonsense just because they’re respected,” Jonathan Howard, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and neurology at New York University said in an interview.
“We have a duty to be trusted members of the community,” Dr. Howard said. “People listen when we say things, and we have an obligation to try to be accurate and humble and as honest as possible and admit mistakes when we inevitably make them.”
That extends to social media, which Dr. Nichols said has magnified the problem of promoting quackery and misinformation. He thinks medical boards and professional credentialing bodies should pay attention to what’s happening in the public conversation and understand that our professional responsibility extends beyond the walls of the hospital or clinic. Physicians must represent themselves professionally and uphold the standards that the profession expects.
On the one hand, Medscape respondents agreed: 70% said one doctor’s misbehavior taints the whole profession. Yet, at the same time, 58% of respondents believed physicians should be able to “keep their private lives private” in 2022. But that’s not the reality of the profession when the lines between private life and behavior away from work get blurred, Dr. Samenow said.
“The way a physician behaves in public represents you,” he said. “What happens in Vegas doesn’t always stay in Vegas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daniel Freedman, DO, a pediatric neurologist in Austin, Tex., remembers being flabbergasted when a surgeon threw an instrument across the room in medical school.
“I remember thinking, ‘I can’t believe people actually do this, a grown man in his 50s having a temper tantrum,’” Dr. Freedman said in an interview. But it certainly wasn’t the last time he witnessed bad behavior by one of his peers.
The results of Medscape’s recent report, Physicians Behaving Badly: Stress and Hardship Trigger Misconduct, suggest he has plenty of company. More than 4 in 10 respondents (41%) observed inappropriate behavior in the workplace in 2022, an uptick from 35% in 2021, according to the report, which polled more than 1,500 physicians about inappropriate behavior on and off the clock.
Of course, 38% of respondents have not seen any instances of misbehavior; and many of the instances that were seen were mild or infrequent. Additionally, instances of bad behavior have declined significantly over the past 5 years.
Dr. Freedman said he learned a lesson from his mentor and program director during training that has stuck with him throughout his career. “If you couldn’t act that way at any job, whether at McDonald’s or any other possible place, you shouldn’t act that way in medicine.” But he recognizes one limitation of that advice. “A lot of the people that behave badly may not have ever worked in a different environment before,” he said.
“They only perceive that they’re at the top of the food chain, so they can behave badly without repercussions.”
What Dr. Freedman described is formally called disruptive physician behavior, one of several categories of inappropriate behavior in medicine, according to Charles Samenow, MD, MPH, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University, Washington, who has studied this phenomenon for years.
“Disruptive physician behavior compromises the safety of the workplace,” Dr. Samenow explained. The behavior can occur at work, outside of work, or on social media. It can hinder operations, threaten patient and staff safety, and affect workplace morale.
“The question is trying to understand where that bad behavior is coming from and the impact of that bad behavior,” Dr. Samenow said in an interview.
One reason is fairly simple: doctors are human, and humans have a wide range of behavior. Plus, as the Medscape survey showed,
Self-selecting traits become an Achilles heel
“Any human put in a position of power over other humans has the potential to be disruptive, harass, etc, if they have certain personality traits,” said David Gorski, MD, a professor of surgery at Wayne State University, Detroit. That jibes with Dr. Samenow’s research.
Classic disruptive behavior isn’t usually associated with depression, mania, psychosis, or similar characteristics, Dr. Samenow explained. Rather, it tends to be personality driven. “Physicians are not immune to the normal problems every human being faces,” he said.
In the Medscape report, physicians cited personal arrogance as one of the leading reasons physicians engaged in inappropriate behavior (56%), followed closely by personal problems outside of work (52%), a social shift in accepting more casual behavior (50%), and job-related stress (46%). (Respondents could choose more than one answer).
One factor contributing to misbehavior that Dr. Samenow has consistently identified in his research is a history of adverse childhood experiences or family dysfunction: People who grew up in homes with physical or verbal abuse learned anger as a coping skill instead of positive, assertive communication. It’s likely that some physicians, as well as the overall population, learned anger as a coping skill for that reason.
How to help avert disruptive behavior in medical settings
Dr. Samenow said that coaching is a “wonderful tool” in teaching the interpersonal skills that medical school often doesn’t address.
In some case, interventions can be very helpful. For example, programs that teach effective communication strategies and teamwork through a combination of culturally sensitive dialectical and cognitive-behavioral therapy and other modalities have been successful, Dr. Samenow said. Although they are more about treating an illness than addressing “misbehavior,” programs for substance use that have been developed by and for doctors are very effective, too.
Fewer resources are available, however, for addressing racism, classism, misogyny, and other forms of bigotry, Dr. Samenow noted. “There’s implicit bias training, but not at the level of what exists for disruptive physicians and those with addiction. “That’s an area we need to work on.” Racist language was the third most commonly observed bad behavior cited in the Medscape survey, behind only bullying of staff and mocking or disparaging of patients. It was reported frequently outside of work as well.
The Medscape report found an increase in observed behavior at work and on social media, although it’s hard to determine prevalence trends over time, Dr. Samenow said. “The tolerance for this behavior has really gone down,” likely leading to more reporting, he said, and more systems for reporting bad behavior exist today than in the past.
However, Dr. Freedman said inadequate regulation, disciplinary action, and follow-through remain a problem.
“There are lots of limitations to our reporting system and to our follow-through with those reports,” including hospitals that, whether for fear of litigation or other reasons, allow physicians to quietly resign and move to another institution, even with positive recommendations, Dr. Freedman said.
Indeed, only a third of observed misbehavior in the Medscape report resulted in disciplinary action. Half the respondents believed a verbal warning was a necessary consequence, followed by a conversation from management and being reported to a supervisor or human resources. Though only 10% thought a report to the medical board was warranted, it likely depends on the offense and its frequency.
“I think going from paternalism to more patient-centered care and having patients involved in those conversations is a nice shift that makes doctors more human and relatable, and hopefully makes the public more forgiving, that we’re going to make mistakes and nobody’s perfect,” Freedman said. But he added that physicians should be held accountable when a mistake or two becomes a pattern.
Misinformation is professional misconduct
Sufficient accountability is especially absent, these doctors said, for a subset of professional misconduct: spreading misinformation.
While more “conventional” bad behaviors include fraud, dishonesty, abuse of underlings, and incompetence, bad behavior should also include “selling quackery and antivaccine misinformation, the way some doctors did with various nostrums for COVID-19,” said Dr. Gorski, who frequently blogs about doctors’ spreading misinformation.
Taylor Nichols, MD, an emergency medicine physician based in Sacramento, cites the desire for attention and clout as motivations. “Saying things that are wildly, provably false is professional misconduct,” Nichols said. He distinguished such statements from scientific, academic, or clinical disagreement that is necessary within medicine.
Yet there’s been a “long tradition of looking the other way or letting people with fancy titles get away with saying nonsense just because they’re respected,” Jonathan Howard, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and neurology at New York University said in an interview.
“We have a duty to be trusted members of the community,” Dr. Howard said. “People listen when we say things, and we have an obligation to try to be accurate and humble and as honest as possible and admit mistakes when we inevitably make them.”
That extends to social media, which Dr. Nichols said has magnified the problem of promoting quackery and misinformation. He thinks medical boards and professional credentialing bodies should pay attention to what’s happening in the public conversation and understand that our professional responsibility extends beyond the walls of the hospital or clinic. Physicians must represent themselves professionally and uphold the standards that the profession expects.
On the one hand, Medscape respondents agreed: 70% said one doctor’s misbehavior taints the whole profession. Yet, at the same time, 58% of respondents believed physicians should be able to “keep their private lives private” in 2022. But that’s not the reality of the profession when the lines between private life and behavior away from work get blurred, Dr. Samenow said.
“The way a physician behaves in public represents you,” he said. “What happens in Vegas doesn’t always stay in Vegas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Daniel Freedman, DO, a pediatric neurologist in Austin, Tex., remembers being flabbergasted when a surgeon threw an instrument across the room in medical school.
“I remember thinking, ‘I can’t believe people actually do this, a grown man in his 50s having a temper tantrum,’” Dr. Freedman said in an interview. But it certainly wasn’t the last time he witnessed bad behavior by one of his peers.
The results of Medscape’s recent report, Physicians Behaving Badly: Stress and Hardship Trigger Misconduct, suggest he has plenty of company. More than 4 in 10 respondents (41%) observed inappropriate behavior in the workplace in 2022, an uptick from 35% in 2021, according to the report, which polled more than 1,500 physicians about inappropriate behavior on and off the clock.
Of course, 38% of respondents have not seen any instances of misbehavior; and many of the instances that were seen were mild or infrequent. Additionally, instances of bad behavior have declined significantly over the past 5 years.
Dr. Freedman said he learned a lesson from his mentor and program director during training that has stuck with him throughout his career. “If you couldn’t act that way at any job, whether at McDonald’s or any other possible place, you shouldn’t act that way in medicine.” But he recognizes one limitation of that advice. “A lot of the people that behave badly may not have ever worked in a different environment before,” he said.
“They only perceive that they’re at the top of the food chain, so they can behave badly without repercussions.”
What Dr. Freedman described is formally called disruptive physician behavior, one of several categories of inappropriate behavior in medicine, according to Charles Samenow, MD, MPH, an associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at George Washington University, Washington, who has studied this phenomenon for years.
“Disruptive physician behavior compromises the safety of the workplace,” Dr. Samenow explained. The behavior can occur at work, outside of work, or on social media. It can hinder operations, threaten patient and staff safety, and affect workplace morale.
“The question is trying to understand where that bad behavior is coming from and the impact of that bad behavior,” Dr. Samenow said in an interview.
One reason is fairly simple: doctors are human, and humans have a wide range of behavior. Plus, as the Medscape survey showed,
Self-selecting traits become an Achilles heel
“Any human put in a position of power over other humans has the potential to be disruptive, harass, etc, if they have certain personality traits,” said David Gorski, MD, a professor of surgery at Wayne State University, Detroit. That jibes with Dr. Samenow’s research.
Classic disruptive behavior isn’t usually associated with depression, mania, psychosis, or similar characteristics, Dr. Samenow explained. Rather, it tends to be personality driven. “Physicians are not immune to the normal problems every human being faces,” he said.
In the Medscape report, physicians cited personal arrogance as one of the leading reasons physicians engaged in inappropriate behavior (56%), followed closely by personal problems outside of work (52%), a social shift in accepting more casual behavior (50%), and job-related stress (46%). (Respondents could choose more than one answer).
One factor contributing to misbehavior that Dr. Samenow has consistently identified in his research is a history of adverse childhood experiences or family dysfunction: People who grew up in homes with physical or verbal abuse learned anger as a coping skill instead of positive, assertive communication. It’s likely that some physicians, as well as the overall population, learned anger as a coping skill for that reason.
How to help avert disruptive behavior in medical settings
Dr. Samenow said that coaching is a “wonderful tool” in teaching the interpersonal skills that medical school often doesn’t address.
In some case, interventions can be very helpful. For example, programs that teach effective communication strategies and teamwork through a combination of culturally sensitive dialectical and cognitive-behavioral therapy and other modalities have been successful, Dr. Samenow said. Although they are more about treating an illness than addressing “misbehavior,” programs for substance use that have been developed by and for doctors are very effective, too.
Fewer resources are available, however, for addressing racism, classism, misogyny, and other forms of bigotry, Dr. Samenow noted. “There’s implicit bias training, but not at the level of what exists for disruptive physicians and those with addiction. “That’s an area we need to work on.” Racist language was the third most commonly observed bad behavior cited in the Medscape survey, behind only bullying of staff and mocking or disparaging of patients. It was reported frequently outside of work as well.
The Medscape report found an increase in observed behavior at work and on social media, although it’s hard to determine prevalence trends over time, Dr. Samenow said. “The tolerance for this behavior has really gone down,” likely leading to more reporting, he said, and more systems for reporting bad behavior exist today than in the past.
However, Dr. Freedman said inadequate regulation, disciplinary action, and follow-through remain a problem.
“There are lots of limitations to our reporting system and to our follow-through with those reports,” including hospitals that, whether for fear of litigation or other reasons, allow physicians to quietly resign and move to another institution, even with positive recommendations, Dr. Freedman said.
Indeed, only a third of observed misbehavior in the Medscape report resulted in disciplinary action. Half the respondents believed a verbal warning was a necessary consequence, followed by a conversation from management and being reported to a supervisor or human resources. Though only 10% thought a report to the medical board was warranted, it likely depends on the offense and its frequency.
“I think going from paternalism to more patient-centered care and having patients involved in those conversations is a nice shift that makes doctors more human and relatable, and hopefully makes the public more forgiving, that we’re going to make mistakes and nobody’s perfect,” Freedman said. But he added that physicians should be held accountable when a mistake or two becomes a pattern.
Misinformation is professional misconduct
Sufficient accountability is especially absent, these doctors said, for a subset of professional misconduct: spreading misinformation.
While more “conventional” bad behaviors include fraud, dishonesty, abuse of underlings, and incompetence, bad behavior should also include “selling quackery and antivaccine misinformation, the way some doctors did with various nostrums for COVID-19,” said Dr. Gorski, who frequently blogs about doctors’ spreading misinformation.
Taylor Nichols, MD, an emergency medicine physician based in Sacramento, cites the desire for attention and clout as motivations. “Saying things that are wildly, provably false is professional misconduct,” Nichols said. He distinguished such statements from scientific, academic, or clinical disagreement that is necessary within medicine.
Yet there’s been a “long tradition of looking the other way or letting people with fancy titles get away with saying nonsense just because they’re respected,” Jonathan Howard, MD, an associate professor of psychiatry and neurology at New York University said in an interview.
“We have a duty to be trusted members of the community,” Dr. Howard said. “People listen when we say things, and we have an obligation to try to be accurate and humble and as honest as possible and admit mistakes when we inevitably make them.”
That extends to social media, which Dr. Nichols said has magnified the problem of promoting quackery and misinformation. He thinks medical boards and professional credentialing bodies should pay attention to what’s happening in the public conversation and understand that our professional responsibility extends beyond the walls of the hospital or clinic. Physicians must represent themselves professionally and uphold the standards that the profession expects.
On the one hand, Medscape respondents agreed: 70% said one doctor’s misbehavior taints the whole profession. Yet, at the same time, 58% of respondents believed physicians should be able to “keep their private lives private” in 2022. But that’s not the reality of the profession when the lines between private life and behavior away from work get blurred, Dr. Samenow said.
“The way a physician behaves in public represents you,” he said. “What happens in Vegas doesn’t always stay in Vegas.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Food insecurity a growing problem for many with CVD
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of Americans with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have limited or uncertain access to food, results of a new study suggest.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) representing more than 300 million American adults found that, overall, 38.1% of people with cardiovascular disease were food insecure in 2017-2019.
Twenty years earlier, that rate was 16.3%.
“What really stood out from our study is how frequent food insecurity is among people with cardiovascular disease, compared to those without cardiovascular disease,” lead author, Eric J. Brandt, MD, MHS, a cardiologist at the University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
“We believe that the relationship between food insecurity and cardiovascular disease is bidirectional. Food insecurity puts people at risk for cardiovascular disease, which then makes them vulnerable to events like myocardial infarction or stroke, which in turn may make them less able to work, thereby worsening their financial situation and increasing their vulnerability to food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt said.
For the analysis, Dr. Brandt and his team used an analytic sample of 57,517 adults to represent 312 million non-institutionalized adults in the United States.
Overall, 6,770 individuals (11.8%) in the analytic sample reported food insecurity.
Food insecurity was more prevalent among Hispanic people (n = 1,938, 24.0%) and non-Hispanic Black people (n = 1,202, 18.2%), compared with non-Hispanic Asian people (n = 100, 8.0%), and non-Hispanic White people (n = 3,221, 8.5%).
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the sample was 7.9% (n = 4,527).
Hypertension was the most prevalent CVD risk factor, reported in 49.6% of the sample. This was followed by obesity in 33.2%, dyslipidemia in 30.8%, and diabetes in 11.2%.
The findings were published online in JAMA Cardiology.
“All cardiovascular disease and cardiometabolic diseases except coronary artery disease were more prevalent among those with food insecurity,” Dr. Brandt noted.
“The results of our study are especially timely, as the White House just hosted its first conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health in over 50 years. Food insecurity is a focus of that conference. In the last few years, especially in relation to the pandemic, there has been expansion of some of the federal programs to prevent food insecurity. I would like to see a continued effort to solve this,” he said.
Dr. Brandt added that he hopes clinicians will be more cognizant of the problem of food insecurity and other social determinants of health when they see their patients.
“If someone is not going to be able to afford the food on their table, they’re probably not going to pay for their medications. Recognizing these social determinants in the clinical setting and helping our patients access local resources may address the underlying factors contributing to heart disease,” he said.
Uphill battle
Johanna Contreras, MD, advanced heart failure and transplant cardiologist at the Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, treats food insecure cardiovascular patients in her practice and tries to educate them about good nutrition. But it is an uphill battle.
“A lot of my patients live in the South Bronx. They have hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and there are no grocery stores where they can buy fresh vegetables. I talk to them about eating healthy. They tell me it’s impossible. The stores only have pre-packaged foods. So even in the South Bronx, even though it is in New York, it is very hard to get fresh food. And when it is available, it is very expensive,” Dr. Contreras told this news organization.
“Fresh pineapples can cost $8. A fast-food burger costs $3. So that is what they buy: It’s what they can afford. Even the store managers don’t want to stock fresh produce because it can spoil. They open stores, like Whole Foods, but in the more affluent neighborhoods. They should open one in poor neighborhoods,” she said.
Dr. Contreras says she spends much of her time educating her patients about good nutrition. She asks them to keep a food diary and analyzes the results at each visit.
“I look at what they eat, and I try to see how I can use this information in a good way. I advise them to use frozen foods, and avoid canned, because it is a lot healthier. I am pragmatic, because I know that if I tell my patients to eat salmon, for example, they aren’t going to be able to afford it, if they can even access it.”
She also informs them about relatively healthy fast-food choices.
“I tell them to order 100% fruit juice, water, or milk when they go to McDonalds or other fast-food places. So I think this study is very important. Food insecurity is a very important component of cardiovascular disease, and unfortunately, minority communities are where this occurs.”
Dr. Brandt and Dr. Contreras report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Similar transplant outcomes with hearts donated after circulatory death
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) is associated with short-term clinical outcomes similar to those of hearts donated after brain death (DBD), except for transient posttransplant right heart dysfunction, a single-center analysis suggests.
The right-heart dysfunction resolved by 3 weeks post transplant, and recipient mortality was similar for those receiving DCD and DBD, which is considered standard of care (SOC).
Furthermore, the median waiting list time was significantly shorter for DCD recipients than for SOC recipients (17 vs. 70 days).
The authors suggest that use of DCD hearts could expand the donor pool by as much as 30%.
“Now that we and others have demonstrated the safety of this technique, I believe it is our obligation as a transplant community to use these organs and not allow them to be wasted,” David A. D’Alessandro, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, told this news organization.
“I will caution that DCD heart transplantation is labor intensive, and there is a learning curve which can potentially put patients at risk,” he added. “It is vitally important, therefore, that we learn from each other’s experiences to flatten this curve.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Similar outcomes
Dr. D’Alessandro and colleagues compared the hemodynamic and clinical profiles of 47 DCD hearts with 166 SOC hearts implanted at Massachusetts General Hospital between 2016 and 2022. DCD hearts were maintained with use of a proprietary warm perfusion circuit organ care system (OCS, TransMedics).
Baseline characteristics were similar between the groups, except the DCD heart recipients were younger (mean age, 55 vs. 59); they were less likely to be an inpatient at the time of transplant (26% vs. 49%); and they had lower pulmonary vascular resistance (1.73 WU vs. 2.26 WU).
The median time from DCD consent to transplant was significantly shorter than for SOC hearts (17 vs. 70 days). However, there was a higher, though not statistically significant, incidence of severe primary graft dysfunction at 24 hours post transplant with DCD (10.6% vs. SOC 3.6%), leading five DCD recipients (10.6%) and nine SOC recipients (5.4%) to receive venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Right heart function was significantly impaired in DCD vs. SOC recipients 1 week post transplant, with higher median right atrial pressure (10 mm Hg vs. 7 mm Hg); higher right atrial pressure to pulmonary capillary wedge pressure ratio (0.64 vs. 0.57); and lower pulmonary arterial pulsatility index (1.66 vs. 2.52).
However, by 3 weeks post transplant, right heart function was similar between the groups, as was mortality at 30 days (0 vs. 2%) and 1 year (3% vs. 8%).
Furthermore, hospital length of stay following transplant, intensive care unit length of stay, ICU readmissions, and 30-day readmissions were similar between the groups.
“We and others will continue to push the boundaries of this technique to understand if we can safely extend the warm ischemic time, which could make additional organs available,” Dr. D’Alessandro said. “We will also be exploring additional ways to monitor and assess organ health and viability ex situ and potential avenues of treatment which could repair and optimize organ function.
“A successful DCD heart transplant program requires institutional and team commitment,” he added, “and there are clinical nuances which should be appreciated to minimize patient risks associated with the obligate learning curve.”
Ulrich P. Jorde, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center in New York, author of a related editorial, concluded that heart donation after circulatory death “promises significant expansion of the donor pool and will lead to many lives saved” and that “the current investigation is a timely and important contribution to this effort”.
However, he noted, “it must be acknowledged that donation after cardiac death has evoked significant controversy regarding the ethics of this approach,” particularly when using a technique called normothermic regional perfusion (NRP), in which, after declaration of death and ligation of cerebral vessels, the heart is resuscitated in situ using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, as opposed to the proprietary warm perfusion OCS used in this study.
“Central to this discussion is the definition of death and its irreversibility,” Dr. Jorde noted. “In contrast to DBD, where brain death protocols are well established and accepted by societies across the globe, DCD protocol rules, e.g., standoff times after complete cessation of circulation, continue to vary even within national jurisdictions. Such variability and incomplete standardization of practice is particularly important when the organ is resuscitated in situ using normothermic regional perfusion.
“The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation has recently provided a framework within which donation after cardiac death, with or without the use of NRP, can be conducted to comply with ethical and legal norms and regulations, acknowledging that such norms and regulations may differ between societies,” he wrote. “To advance the field, and to ensure ongoing trust in the transplantation system, it is of critical importance that such discussions are held publicly and transparently.”
More ‘dry runs’
“Donor heart allographs are safe for our patients with heart failure if procured and transplanted in an organized and protocolized manner,” Philip J. Spencer, MD, a cardiovascular and transplant surgeon at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., told this news organization. “As the techniques are adopted globally, our patients will benefit.”
Nevertheless, like Dr. D’Alessandro, he noted that procurement of DCD hearts is more labor intensive. “A program and its patients must be willing to accept a higher number of ‘dry runs,’ which occurs when the team is sent for an organ and the donor does not progress to circulatory death in a time and manner appropriate for safe organ recovery.
“There is no doubt that being open to these organs will increase the patient’s chances of receiving a donor heart in a shorter period of time,” he said. “However, the experience of a dry run, or multiple, can be emotionally and financially stressful for the patient and the program.”
No commercial funding or relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Bariatric surgery may up risk for epilepsy
Analyzing health records, investigators compared almost 17,000 patients who had undergone bariatric surgery with more than 620,000 individuals with obesity who had not undergone the surgery.
During a minimum 3-year follow-up period, the surgery group had a 45% higher risk of developing epilepsy than the nonsurgery group. Moreover, patients who had a stroke after their bariatric surgery were 14 times more likely to develop epilepsy than those who did not have a stroke.
“When considering having bariatric surgery, people should talk to their doctors about the benefits and risks,” senior investigator Jorge Burneo, MD, professor of neurology, biostatistics, and epidemiology and endowed chair in epilepsy at Western University, London, told this news organization.
“While there are many health benefits of weight loss, our findings suggest that epilepsy is a long-term risk of bariatric surgery for weight loss,” Dr. Burneo said.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Unrecognized risk factor?
Bariatric surgery has become more common as global rates of obesity have increased. The surgery has been shown to reduce the risk for serious obesity-related conditions, the researchers note.
However, “in addition to the positive outcomes of bariatric surgery, several long-term neurological complications have also been identified,” they write.
One previous study reported increased epilepsy risk following gastric bypass. Those findings “suggest that bariatric surgery may be an unrecognized epilepsy risk factor; however, this possible association has not been thoroughly explored,” write the investigators.
Dr. Burneo said he conducted the study because he has seen patients with epilepsy in his clinic who were “without risk factors, with normal MRIs, who shared the history of having bariatric surgery before the development of epilepsy.”
The researchers’ primary objective was to “assess whether epilepsy risk is elevated following bariatric surgery for weight loss relative to a nonsurgical cohort of patients who are obese,” he noted.
The study used linked administrative health databases in Ontario, Canada. Patients were accrued from July 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2016, and were followed until Dec. 31, 2019. The analysis included 639,472 participants, 2.7% of whom had undergone bariatric surgery.
The “exposed” cohort consisted of all Ontario residents aged 18 years or older who had undergone bariatric surgery during the 6-year period (n = 16,958; 65.1% women; mean age, 47.4 years), while the “unexposed” cohort consisted of patients hospitalized with a diagnosis of obesity who had not undergone bariatric surgery (n = 622,514; 62.8% women; mean age, 47.6 years).
Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, epilepsy risk factors, prior brain surgery, psychiatric disorders, or drug or alcohol abuse/dependence were excluded from the analysis.
The researchers collected data on patients’ sociodemographic characteristics at the index date, as well as Charlson Comorbidity Index scores during the 2 years prior to index, and data regarding several specific comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, sleep apnea, depression/anxiety, and cardiovascular factors.
The exposed and unexposed cohorts were followed for a median period of 5.8 and 5.9 person-years, respectively.
‘Unclear’ mechanisms
Before weighting, 0.4% of participants in the exposed cohort (n = 73) developed epilepsy, versus 0.2% of participants in the unexposed cohort (n = 1,260) by the end of the follow-up period.
In the weighted cohorts, there were 50.1 epilepsy diagnoses per 100,000 person-years, versus 34.1 per 100,000 person-years (rate difference, 16 per 100,000 person-years).
The multivariable analysis of the weighted cohort showed the hazard ratio for epilepsy cases that were associated with bariatric surgery was 1.45 (95% confidence interval, 1.35-1.56), after adjusting for sleep apnea and including stroke as a time-varying covariate.
Having a stroke during the follow-up period increased epilepsy 14-fold in the exposed cohort (HR, 14.03; 95% CI, 4.25-46.25).
The investigators note that they were unable to measure obesity status or body mass index throughout the study and that some obesity-related comorbidities “may affect epilepsy risk.”
In addition, Dr. Burneo reported that the study did not investigate potential causes and mechanisms of the association between bariatric surgery and epilepsy risk.
Hypotheses “include potential nutritional deficiencies, receipt of general anesthesia, or other unclear causes,” he said.
“Future research should investigate epilepsy as a potential long-term complication of bariatric surgery, exploring the possible effects of this procedure,” Dr. Burneo added.
Risk-benefit discussion
In a comment, Jacqueline French, MD, professor of neurology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of NYU’s Epilepsy Study Consortium, said she was “not 100% surprised by the findings” because she has seen in her clinical practice “a number of patients who developed epilepsy after bariatric surgery or had a history of bariatric surgery at the time they developed epilepsy.”
On the other hand, she has also seen patients who did not have a history of bariatric surgery and who developed epilepsy.
“I’m unable to tell if there is an association, although I’ve had it at the back of my head as a thought and wondered about it,” said Dr. French, who is also the chief medical and innovation officer at the Epilepsy Foundation. She was not involved with the study.
She noted that possible mechanisms underlying the association are that gastric bypass surgery leads to a “significant alteration” in nutrient absorption. Moreover, “we now know that the microbiome is associated with epilepsy” and that changes occur in the gut microbiome after bariatric surgery, Dr. French said.
There are two take-home messages for practicing clinicians, she added.
“Although the risk [of developing epilepsy] is very low, it should be presented as part of the risks and benefits to patients considering bariatric surgery,” she said.
“It’s equally important to follow up on the potential differences in these patients who go on to develop epilepsy following bariatric surgery,” said Dr. French. “Is there a certain metabolic profile or some nutrient previously absorbed that now is not absorbed that might predispose people to risk?”
This would be “enormously important to know because it might not just pertain to these people but to a whole other cohort of people who develop epilepsy,” Dr. French concluded.
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care and by the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. Dr. Burneo holds the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. The other investigators and Dr. French have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Analyzing health records, investigators compared almost 17,000 patients who had undergone bariatric surgery with more than 620,000 individuals with obesity who had not undergone the surgery.
During a minimum 3-year follow-up period, the surgery group had a 45% higher risk of developing epilepsy than the nonsurgery group. Moreover, patients who had a stroke after their bariatric surgery were 14 times more likely to develop epilepsy than those who did not have a stroke.
“When considering having bariatric surgery, people should talk to their doctors about the benefits and risks,” senior investigator Jorge Burneo, MD, professor of neurology, biostatistics, and epidemiology and endowed chair in epilepsy at Western University, London, told this news organization.
“While there are many health benefits of weight loss, our findings suggest that epilepsy is a long-term risk of bariatric surgery for weight loss,” Dr. Burneo said.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Unrecognized risk factor?
Bariatric surgery has become more common as global rates of obesity have increased. The surgery has been shown to reduce the risk for serious obesity-related conditions, the researchers note.
However, “in addition to the positive outcomes of bariatric surgery, several long-term neurological complications have also been identified,” they write.
One previous study reported increased epilepsy risk following gastric bypass. Those findings “suggest that bariatric surgery may be an unrecognized epilepsy risk factor; however, this possible association has not been thoroughly explored,” write the investigators.
Dr. Burneo said he conducted the study because he has seen patients with epilepsy in his clinic who were “without risk factors, with normal MRIs, who shared the history of having bariatric surgery before the development of epilepsy.”
The researchers’ primary objective was to “assess whether epilepsy risk is elevated following bariatric surgery for weight loss relative to a nonsurgical cohort of patients who are obese,” he noted.
The study used linked administrative health databases in Ontario, Canada. Patients were accrued from July 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2016, and were followed until Dec. 31, 2019. The analysis included 639,472 participants, 2.7% of whom had undergone bariatric surgery.
The “exposed” cohort consisted of all Ontario residents aged 18 years or older who had undergone bariatric surgery during the 6-year period (n = 16,958; 65.1% women; mean age, 47.4 years), while the “unexposed” cohort consisted of patients hospitalized with a diagnosis of obesity who had not undergone bariatric surgery (n = 622,514; 62.8% women; mean age, 47.6 years).
Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, epilepsy risk factors, prior brain surgery, psychiatric disorders, or drug or alcohol abuse/dependence were excluded from the analysis.
The researchers collected data on patients’ sociodemographic characteristics at the index date, as well as Charlson Comorbidity Index scores during the 2 years prior to index, and data regarding several specific comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, sleep apnea, depression/anxiety, and cardiovascular factors.
The exposed and unexposed cohorts were followed for a median period of 5.8 and 5.9 person-years, respectively.
‘Unclear’ mechanisms
Before weighting, 0.4% of participants in the exposed cohort (n = 73) developed epilepsy, versus 0.2% of participants in the unexposed cohort (n = 1,260) by the end of the follow-up period.
In the weighted cohorts, there were 50.1 epilepsy diagnoses per 100,000 person-years, versus 34.1 per 100,000 person-years (rate difference, 16 per 100,000 person-years).
The multivariable analysis of the weighted cohort showed the hazard ratio for epilepsy cases that were associated with bariatric surgery was 1.45 (95% confidence interval, 1.35-1.56), after adjusting for sleep apnea and including stroke as a time-varying covariate.
Having a stroke during the follow-up period increased epilepsy 14-fold in the exposed cohort (HR, 14.03; 95% CI, 4.25-46.25).
The investigators note that they were unable to measure obesity status or body mass index throughout the study and that some obesity-related comorbidities “may affect epilepsy risk.”
In addition, Dr. Burneo reported that the study did not investigate potential causes and mechanisms of the association between bariatric surgery and epilepsy risk.
Hypotheses “include potential nutritional deficiencies, receipt of general anesthesia, or other unclear causes,” he said.
“Future research should investigate epilepsy as a potential long-term complication of bariatric surgery, exploring the possible effects of this procedure,” Dr. Burneo added.
Risk-benefit discussion
In a comment, Jacqueline French, MD, professor of neurology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of NYU’s Epilepsy Study Consortium, said she was “not 100% surprised by the findings” because she has seen in her clinical practice “a number of patients who developed epilepsy after bariatric surgery or had a history of bariatric surgery at the time they developed epilepsy.”
On the other hand, she has also seen patients who did not have a history of bariatric surgery and who developed epilepsy.
“I’m unable to tell if there is an association, although I’ve had it at the back of my head as a thought and wondered about it,” said Dr. French, who is also the chief medical and innovation officer at the Epilepsy Foundation. She was not involved with the study.
She noted that possible mechanisms underlying the association are that gastric bypass surgery leads to a “significant alteration” in nutrient absorption. Moreover, “we now know that the microbiome is associated with epilepsy” and that changes occur in the gut microbiome after bariatric surgery, Dr. French said.
There are two take-home messages for practicing clinicians, she added.
“Although the risk [of developing epilepsy] is very low, it should be presented as part of the risks and benefits to patients considering bariatric surgery,” she said.
“It’s equally important to follow up on the potential differences in these patients who go on to develop epilepsy following bariatric surgery,” said Dr. French. “Is there a certain metabolic profile or some nutrient previously absorbed that now is not absorbed that might predispose people to risk?”
This would be “enormously important to know because it might not just pertain to these people but to a whole other cohort of people who develop epilepsy,” Dr. French concluded.
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care and by the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. Dr. Burneo holds the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. The other investigators and Dr. French have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Analyzing health records, investigators compared almost 17,000 patients who had undergone bariatric surgery with more than 620,000 individuals with obesity who had not undergone the surgery.
During a minimum 3-year follow-up period, the surgery group had a 45% higher risk of developing epilepsy than the nonsurgery group. Moreover, patients who had a stroke after their bariatric surgery were 14 times more likely to develop epilepsy than those who did not have a stroke.
“When considering having bariatric surgery, people should talk to their doctors about the benefits and risks,” senior investigator Jorge Burneo, MD, professor of neurology, biostatistics, and epidemiology and endowed chair in epilepsy at Western University, London, told this news organization.
“While there are many health benefits of weight loss, our findings suggest that epilepsy is a long-term risk of bariatric surgery for weight loss,” Dr. Burneo said.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Unrecognized risk factor?
Bariatric surgery has become more common as global rates of obesity have increased. The surgery has been shown to reduce the risk for serious obesity-related conditions, the researchers note.
However, “in addition to the positive outcomes of bariatric surgery, several long-term neurological complications have also been identified,” they write.
One previous study reported increased epilepsy risk following gastric bypass. Those findings “suggest that bariatric surgery may be an unrecognized epilepsy risk factor; however, this possible association has not been thoroughly explored,” write the investigators.
Dr. Burneo said he conducted the study because he has seen patients with epilepsy in his clinic who were “without risk factors, with normal MRIs, who shared the history of having bariatric surgery before the development of epilepsy.”
The researchers’ primary objective was to “assess whether epilepsy risk is elevated following bariatric surgery for weight loss relative to a nonsurgical cohort of patients who are obese,” he noted.
The study used linked administrative health databases in Ontario, Canada. Patients were accrued from July 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2016, and were followed until Dec. 31, 2019. The analysis included 639,472 participants, 2.7% of whom had undergone bariatric surgery.
The “exposed” cohort consisted of all Ontario residents aged 18 years or older who had undergone bariatric surgery during the 6-year period (n = 16,958; 65.1% women; mean age, 47.4 years), while the “unexposed” cohort consisted of patients hospitalized with a diagnosis of obesity who had not undergone bariatric surgery (n = 622,514; 62.8% women; mean age, 47.6 years).
Patients with a history of seizures, epilepsy, epilepsy risk factors, prior brain surgery, psychiatric disorders, or drug or alcohol abuse/dependence were excluded from the analysis.
The researchers collected data on patients’ sociodemographic characteristics at the index date, as well as Charlson Comorbidity Index scores during the 2 years prior to index, and data regarding several specific comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, sleep apnea, depression/anxiety, and cardiovascular factors.
The exposed and unexposed cohorts were followed for a median period of 5.8 and 5.9 person-years, respectively.
‘Unclear’ mechanisms
Before weighting, 0.4% of participants in the exposed cohort (n = 73) developed epilepsy, versus 0.2% of participants in the unexposed cohort (n = 1,260) by the end of the follow-up period.
In the weighted cohorts, there were 50.1 epilepsy diagnoses per 100,000 person-years, versus 34.1 per 100,000 person-years (rate difference, 16 per 100,000 person-years).
The multivariable analysis of the weighted cohort showed the hazard ratio for epilepsy cases that were associated with bariatric surgery was 1.45 (95% confidence interval, 1.35-1.56), after adjusting for sleep apnea and including stroke as a time-varying covariate.
Having a stroke during the follow-up period increased epilepsy 14-fold in the exposed cohort (HR, 14.03; 95% CI, 4.25-46.25).
The investigators note that they were unable to measure obesity status or body mass index throughout the study and that some obesity-related comorbidities “may affect epilepsy risk.”
In addition, Dr. Burneo reported that the study did not investigate potential causes and mechanisms of the association between bariatric surgery and epilepsy risk.
Hypotheses “include potential nutritional deficiencies, receipt of general anesthesia, or other unclear causes,” he said.
“Future research should investigate epilepsy as a potential long-term complication of bariatric surgery, exploring the possible effects of this procedure,” Dr. Burneo added.
Risk-benefit discussion
In a comment, Jacqueline French, MD, professor of neurology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, and director of NYU’s Epilepsy Study Consortium, said she was “not 100% surprised by the findings” because she has seen in her clinical practice “a number of patients who developed epilepsy after bariatric surgery or had a history of bariatric surgery at the time they developed epilepsy.”
On the other hand, she has also seen patients who did not have a history of bariatric surgery and who developed epilepsy.
“I’m unable to tell if there is an association, although I’ve had it at the back of my head as a thought and wondered about it,” said Dr. French, who is also the chief medical and innovation officer at the Epilepsy Foundation. She was not involved with the study.
She noted that possible mechanisms underlying the association are that gastric bypass surgery leads to a “significant alteration” in nutrient absorption. Moreover, “we now know that the microbiome is associated with epilepsy” and that changes occur in the gut microbiome after bariatric surgery, Dr. French said.
There are two take-home messages for practicing clinicians, she added.
“Although the risk [of developing epilepsy] is very low, it should be presented as part of the risks and benefits to patients considering bariatric surgery,” she said.
“It’s equally important to follow up on the potential differences in these patients who go on to develop epilepsy following bariatric surgery,” said Dr. French. “Is there a certain metabolic profile or some nutrient previously absorbed that now is not absorbed that might predispose people to risk?”
This would be “enormously important to know because it might not just pertain to these people but to a whole other cohort of people who develop epilepsy,” Dr. French concluded.
The study was funded by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care and by the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. Dr. Burneo holds the Jack Cowin Endowed Chair in Epilepsy Research at Western University. The other investigators and Dr. French have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY