User login
Mobile Medical Apps for Patient Education: A Graded Review of Available Dermatology Apps
According to industry estimates, roughly 64% of US adults were smartphone users in 2015.1 Smartphones enable users to utilize mobile applications (apps) that can perform a variety of functions in many categories, including business, music, photography, entertainment, education, social networking, travel, and lifestyle. The widespread adoption and use of mobile apps has implications for medical practice. Mobile apps have the capability to serve as information sources for patients, educational tools for students, and diagnostic aids for physicians.2 Consequently, a number of medical and health care–oriented apps have already been developed3 and are increasingly utilized by patients and providers.4
Given its visual nature, dermatology is particularly amenable to the integration of mobile medical apps. A study by Brewer et al5 identified more than 229 dermatology-related apps in categories ranging from general dermatology reference, self-surveillance and diagnosis, disease guides, educational aids, sunscreen and UV recommendations, and teledermatology. Patients served as the target audience and principal consumers of more than half of these dermatology apps.5
Mobile medical and health care apps demonstrate great potential for serving as valuable information sources for patients with dermatologic conditions; however, the content, functions, accuracy, and educational value of dermatology mobile apps are not well characterized, making it difficult for patients and health care providers to select and recommend appropriate apps.6 In this study, we created a rubric to objectively grade 44 publicly available mobile dermatology apps with the primary focus of patient education.
Methods
We conducted a search of dermatology-related educational mobile apps that were publicly available via the App Store (Apple Inc) from January 2016 to November 2016. (The pricing, availability, and other features of these apps may have changed since the study period.) The following search terms were used: dermatology, dermoscopy, melanoma, skin cancer, psoriasis, rosacea, acne, eczema, dermal fillers, and Mohs surgery. We excluded apps that were not in English; had a solely commercial focus; were mobile textbooks or scientific journals; were used to provide teledermatology services with no educational purpose; were solely focused on homeopathic, alternative, and/or complementary medicine; or were intended primarily as a reference for students or health care professionals. Our search yielded 44 apps with patient education as a primary objective. The apps were divided into 6 categories based on their focus: general dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer.
Each app was reviewed using a quantified grading rubric developed by the researchers. In a prior evaluation, Handel7 reviewed 35 health and wellness mobile apps utilizing the categories of ease of use, reliability, quality, scope of information, and aesthetics.4 These criteria were modified and adapted for the purposes of this study, and a 4-point scale was applied to each criterion. The final criteria were (1) educational objectives, (2) content, (3) accuracy, (4) design, and (5) conflict of interest. The quantified grading rubric is described in Table 1.
Results
The possible range of scores based on the grading rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 8 to 19 (Table 2). The 44 reviewed apps were categorized by topic as acne, cosmetic dermatology, eczema, general dermatology, psoriasis, or skin cancer. A sample of 15 apps selected to represent the distribution of scores and their grading on the rubric are presented in Table 3.
Comment
The number of dermatology-related apps available to mobile users continues to grow at an increasing rate.8 The apps vary in many aspects, including their purpose, scope, intended audience, and goals of the app publisher. In turn, more individuals are turning to mobile apps for medical information,4 especially in dermatology, thus it is necessary to create a systematic way to evaluate the quality and utility of each app to assist users in making informed decisions about which apps will best meet their needs in the midst of a wide array of choices.
For the purpose of this study, an objective rubric was created that can be used to evaluate the quality of medical apps for patient education in dermatology. An app’s adequacy and usefulness for patient education was thought to depend on 3 possible score ranges into which the app could fall based on the grading rubric. An app with a total score in the range of 5 to 10 was not thought to be useful and may even be detrimental to patients. An app with a total score in the range of 11 to 15 may be used for patient education with some reservations based on shortcomings for certain criteria. An app with a score in the range of 16 to 20 was thought to be valuable and adequate for patient education. For example, the How to Treat Acne app received a total score of 8 and therefore would not be recommended to patients based on the grading rubric used in this study. This particular app provided sparse and sometimes inaccurate information, had a confusing user interface, and contained many obstructive advertisements. In contrast, the Eczema Doc app received a total score of 19, which indicates a quality app deemed to be useful for patient information based on the established rubric. This app met all the objectives that it advertised, contained accurate information with verified citation of sources, and was very easy for users to navigate.
Of the 44 graded apps, only 9 (20.5%) received scores in the highest range of 16 to 20, which indicates a need for improvements in mobile dermatology apps intended for patient education. Adopting the grading rubric developed in this study as a standard in the creation of medical apps could have beneficial implications in disseminating accurate, safe, unbiased, and easy-to-understand information to patients.
- Smith A. U.S. smartphone use in 2015. Pew Research Center website. http://www.pewinternet.org/2015/04/01/us-smartphone-use-in-2015. Published April 1, 2015. Accessed August 29, 2017.
- Nilsen W, Kumar S, Shar A, et al. Advancing the science of mHealth. J Health Commun. 2012;17(suppl 1):5-10.
- West DM. How mobile devices are transforming healthcare issues in technology innovation. Issues Technol Innov. 2012;18:1-14.
- Boudreaux ED, Waring ME, Hayes RB, et al. Evaluating and selecting mobile health apps: strategies for healthcare providers and healthcare organizations. Transl Behav Med. 2014;4:363-371.
- Brewer AC, Endly DC, Henley J, et al. Mobile applications in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1300-1304.
- Cummings E, Borycki E, Roehrer E. Issues and considerations for healthcare consumers using mobile applications. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2013;183:227-231.
- Handel MJ. mHealth (mobile health)-using apps for health and wellness. Explore. 2011;7:256-261.
- Boulos MN, Brewer AC, Karimkhani C, et al. Mobile medical and health apps: state of the art, concerns, regulatory control and certification. Online J Public Health Inform. 2014;5:229.
According to industry estimates, roughly 64% of US adults were smartphone users in 2015.1 Smartphones enable users to utilize mobile applications (apps) that can perform a variety of functions in many categories, including business, music, photography, entertainment, education, social networking, travel, and lifestyle. The widespread adoption and use of mobile apps has implications for medical practice. Mobile apps have the capability to serve as information sources for patients, educational tools for students, and diagnostic aids for physicians.2 Consequently, a number of medical and health care–oriented apps have already been developed3 and are increasingly utilized by patients and providers.4
Given its visual nature, dermatology is particularly amenable to the integration of mobile medical apps. A study by Brewer et al5 identified more than 229 dermatology-related apps in categories ranging from general dermatology reference, self-surveillance and diagnosis, disease guides, educational aids, sunscreen and UV recommendations, and teledermatology. Patients served as the target audience and principal consumers of more than half of these dermatology apps.5
Mobile medical and health care apps demonstrate great potential for serving as valuable information sources for patients with dermatologic conditions; however, the content, functions, accuracy, and educational value of dermatology mobile apps are not well characterized, making it difficult for patients and health care providers to select and recommend appropriate apps.6 In this study, we created a rubric to objectively grade 44 publicly available mobile dermatology apps with the primary focus of patient education.
Methods
We conducted a search of dermatology-related educational mobile apps that were publicly available via the App Store (Apple Inc) from January 2016 to November 2016. (The pricing, availability, and other features of these apps may have changed since the study period.) The following search terms were used: dermatology, dermoscopy, melanoma, skin cancer, psoriasis, rosacea, acne, eczema, dermal fillers, and Mohs surgery. We excluded apps that were not in English; had a solely commercial focus; were mobile textbooks or scientific journals; were used to provide teledermatology services with no educational purpose; were solely focused on homeopathic, alternative, and/or complementary medicine; or were intended primarily as a reference for students or health care professionals. Our search yielded 44 apps with patient education as a primary objective. The apps were divided into 6 categories based on their focus: general dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer.
Each app was reviewed using a quantified grading rubric developed by the researchers. In a prior evaluation, Handel7 reviewed 35 health and wellness mobile apps utilizing the categories of ease of use, reliability, quality, scope of information, and aesthetics.4 These criteria were modified and adapted for the purposes of this study, and a 4-point scale was applied to each criterion. The final criteria were (1) educational objectives, (2) content, (3) accuracy, (4) design, and (5) conflict of interest. The quantified grading rubric is described in Table 1.
Results
The possible range of scores based on the grading rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 8 to 19 (Table 2). The 44 reviewed apps were categorized by topic as acne, cosmetic dermatology, eczema, general dermatology, psoriasis, or skin cancer. A sample of 15 apps selected to represent the distribution of scores and their grading on the rubric are presented in Table 3.
Comment
The number of dermatology-related apps available to mobile users continues to grow at an increasing rate.8 The apps vary in many aspects, including their purpose, scope, intended audience, and goals of the app publisher. In turn, more individuals are turning to mobile apps for medical information,4 especially in dermatology, thus it is necessary to create a systematic way to evaluate the quality and utility of each app to assist users in making informed decisions about which apps will best meet their needs in the midst of a wide array of choices.
For the purpose of this study, an objective rubric was created that can be used to evaluate the quality of medical apps for patient education in dermatology. An app’s adequacy and usefulness for patient education was thought to depend on 3 possible score ranges into which the app could fall based on the grading rubric. An app with a total score in the range of 5 to 10 was not thought to be useful and may even be detrimental to patients. An app with a total score in the range of 11 to 15 may be used for patient education with some reservations based on shortcomings for certain criteria. An app with a score in the range of 16 to 20 was thought to be valuable and adequate for patient education. For example, the How to Treat Acne app received a total score of 8 and therefore would not be recommended to patients based on the grading rubric used in this study. This particular app provided sparse and sometimes inaccurate information, had a confusing user interface, and contained many obstructive advertisements. In contrast, the Eczema Doc app received a total score of 19, which indicates a quality app deemed to be useful for patient information based on the established rubric. This app met all the objectives that it advertised, contained accurate information with verified citation of sources, and was very easy for users to navigate.
Of the 44 graded apps, only 9 (20.5%) received scores in the highest range of 16 to 20, which indicates a need for improvements in mobile dermatology apps intended for patient education. Adopting the grading rubric developed in this study as a standard in the creation of medical apps could have beneficial implications in disseminating accurate, safe, unbiased, and easy-to-understand information to patients.
According to industry estimates, roughly 64% of US adults were smartphone users in 2015.1 Smartphones enable users to utilize mobile applications (apps) that can perform a variety of functions in many categories, including business, music, photography, entertainment, education, social networking, travel, and lifestyle. The widespread adoption and use of mobile apps has implications for medical practice. Mobile apps have the capability to serve as information sources for patients, educational tools for students, and diagnostic aids for physicians.2 Consequently, a number of medical and health care–oriented apps have already been developed3 and are increasingly utilized by patients and providers.4
Given its visual nature, dermatology is particularly amenable to the integration of mobile medical apps. A study by Brewer et al5 identified more than 229 dermatology-related apps in categories ranging from general dermatology reference, self-surveillance and diagnosis, disease guides, educational aids, sunscreen and UV recommendations, and teledermatology. Patients served as the target audience and principal consumers of more than half of these dermatology apps.5
Mobile medical and health care apps demonstrate great potential for serving as valuable information sources for patients with dermatologic conditions; however, the content, functions, accuracy, and educational value of dermatology mobile apps are not well characterized, making it difficult for patients and health care providers to select and recommend appropriate apps.6 In this study, we created a rubric to objectively grade 44 publicly available mobile dermatology apps with the primary focus of patient education.
Methods
We conducted a search of dermatology-related educational mobile apps that were publicly available via the App Store (Apple Inc) from January 2016 to November 2016. (The pricing, availability, and other features of these apps may have changed since the study period.) The following search terms were used: dermatology, dermoscopy, melanoma, skin cancer, psoriasis, rosacea, acne, eczema, dermal fillers, and Mohs surgery. We excluded apps that were not in English; had a solely commercial focus; were mobile textbooks or scientific journals; were used to provide teledermatology services with no educational purpose; were solely focused on homeopathic, alternative, and/or complementary medicine; or were intended primarily as a reference for students or health care professionals. Our search yielded 44 apps with patient education as a primary objective. The apps were divided into 6 categories based on their focus: general dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer.
Each app was reviewed using a quantified grading rubric developed by the researchers. In a prior evaluation, Handel7 reviewed 35 health and wellness mobile apps utilizing the categories of ease of use, reliability, quality, scope of information, and aesthetics.4 These criteria were modified and adapted for the purposes of this study, and a 4-point scale was applied to each criterion. The final criteria were (1) educational objectives, (2) content, (3) accuracy, (4) design, and (5) conflict of interest. The quantified grading rubric is described in Table 1.
Results
The possible range of scores based on the grading rubric was 5 to 20. The actual range of scores was 8 to 19 (Table 2). The 44 reviewed apps were categorized by topic as acne, cosmetic dermatology, eczema, general dermatology, psoriasis, or skin cancer. A sample of 15 apps selected to represent the distribution of scores and their grading on the rubric are presented in Table 3.
Comment
The number of dermatology-related apps available to mobile users continues to grow at an increasing rate.8 The apps vary in many aspects, including their purpose, scope, intended audience, and goals of the app publisher. In turn, more individuals are turning to mobile apps for medical information,4 especially in dermatology, thus it is necessary to create a systematic way to evaluate the quality and utility of each app to assist users in making informed decisions about which apps will best meet their needs in the midst of a wide array of choices.
For the purpose of this study, an objective rubric was created that can be used to evaluate the quality of medical apps for patient education in dermatology. An app’s adequacy and usefulness for patient education was thought to depend on 3 possible score ranges into which the app could fall based on the grading rubric. An app with a total score in the range of 5 to 10 was not thought to be useful and may even be detrimental to patients. An app with a total score in the range of 11 to 15 may be used for patient education with some reservations based on shortcomings for certain criteria. An app with a score in the range of 16 to 20 was thought to be valuable and adequate for patient education. For example, the How to Treat Acne app received a total score of 8 and therefore would not be recommended to patients based on the grading rubric used in this study. This particular app provided sparse and sometimes inaccurate information, had a confusing user interface, and contained many obstructive advertisements. In contrast, the Eczema Doc app received a total score of 19, which indicates a quality app deemed to be useful for patient information based on the established rubric. This app met all the objectives that it advertised, contained accurate information with verified citation of sources, and was very easy for users to navigate.
Of the 44 graded apps, only 9 (20.5%) received scores in the highest range of 16 to 20, which indicates a need for improvements in mobile dermatology apps intended for patient education. Adopting the grading rubric developed in this study as a standard in the creation of medical apps could have beneficial implications in disseminating accurate, safe, unbiased, and easy-to-understand information to patients.
- Smith A. U.S. smartphone use in 2015. Pew Research Center website. http://www.pewinternet.org/2015/04/01/us-smartphone-use-in-2015. Published April 1, 2015. Accessed August 29, 2017.
- Nilsen W, Kumar S, Shar A, et al. Advancing the science of mHealth. J Health Commun. 2012;17(suppl 1):5-10.
- West DM. How mobile devices are transforming healthcare issues in technology innovation. Issues Technol Innov. 2012;18:1-14.
- Boudreaux ED, Waring ME, Hayes RB, et al. Evaluating and selecting mobile health apps: strategies for healthcare providers and healthcare organizations. Transl Behav Med. 2014;4:363-371.
- Brewer AC, Endly DC, Henley J, et al. Mobile applications in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1300-1304.
- Cummings E, Borycki E, Roehrer E. Issues and considerations for healthcare consumers using mobile applications. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2013;183:227-231.
- Handel MJ. mHealth (mobile health)-using apps for health and wellness. Explore. 2011;7:256-261.
- Boulos MN, Brewer AC, Karimkhani C, et al. Mobile medical and health apps: state of the art, concerns, regulatory control and certification. Online J Public Health Inform. 2014;5:229.
- Smith A. U.S. smartphone use in 2015. Pew Research Center website. http://www.pewinternet.org/2015/04/01/us-smartphone-use-in-2015. Published April 1, 2015. Accessed August 29, 2017.
- Nilsen W, Kumar S, Shar A, et al. Advancing the science of mHealth. J Health Commun. 2012;17(suppl 1):5-10.
- West DM. How mobile devices are transforming healthcare issues in technology innovation. Issues Technol Innov. 2012;18:1-14.
- Boudreaux ED, Waring ME, Hayes RB, et al. Evaluating and selecting mobile health apps: strategies for healthcare providers and healthcare organizations. Transl Behav Med. 2014;4:363-371.
- Brewer AC, Endly DC, Henley J, et al. Mobile applications in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:1300-1304.
- Cummings E, Borycki E, Roehrer E. Issues and considerations for healthcare consumers using mobile applications. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2013;183:227-231.
- Handel MJ. mHealth (mobile health)-using apps for health and wellness. Explore. 2011;7:256-261.
- Boulos MN, Brewer AC, Karimkhani C, et al. Mobile medical and health apps: state of the art, concerns, regulatory control and certification. Online J Public Health Inform. 2014;5:229.
Practice Points
- Mobile dermatology apps for educational purposes should be objectively reviewed before being used by patients.
- In our study, only 9 (20.5%) of the 44 dermatology apps evaluated were considered adequate for patient information based on our grading criteria.
Complete Remission of Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma in a Patient With Severe Psoriasis
To the Editor:
A 69-year-old white man presented with a skin lesion on the back of 1 to 2 weeks’ duration. The patient stated he was unaware of it, but his wife had recently noticed the new spot. He denied any bleeding, pain, pruritus, or other associated symptoms with the lesion. He also denied any prior treatment to the area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for severe psoriasis involving more than 80% body surface area, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, coronary artery disease, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic keratoses. He had been on multiple treatment regimens over the last 20 years for control of psoriasis including topical corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA and UVB phototherapy, gold injections, acitretin, prednisone, efalizumab, ustekinumab, and alefacept upon evaluation of this new skin lesion. Utilization of immunosuppressive agents also provided an additional benefit of controlling the patient’s inflammatory arthritic disease.
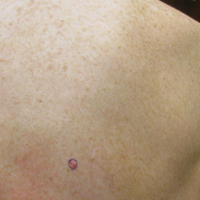
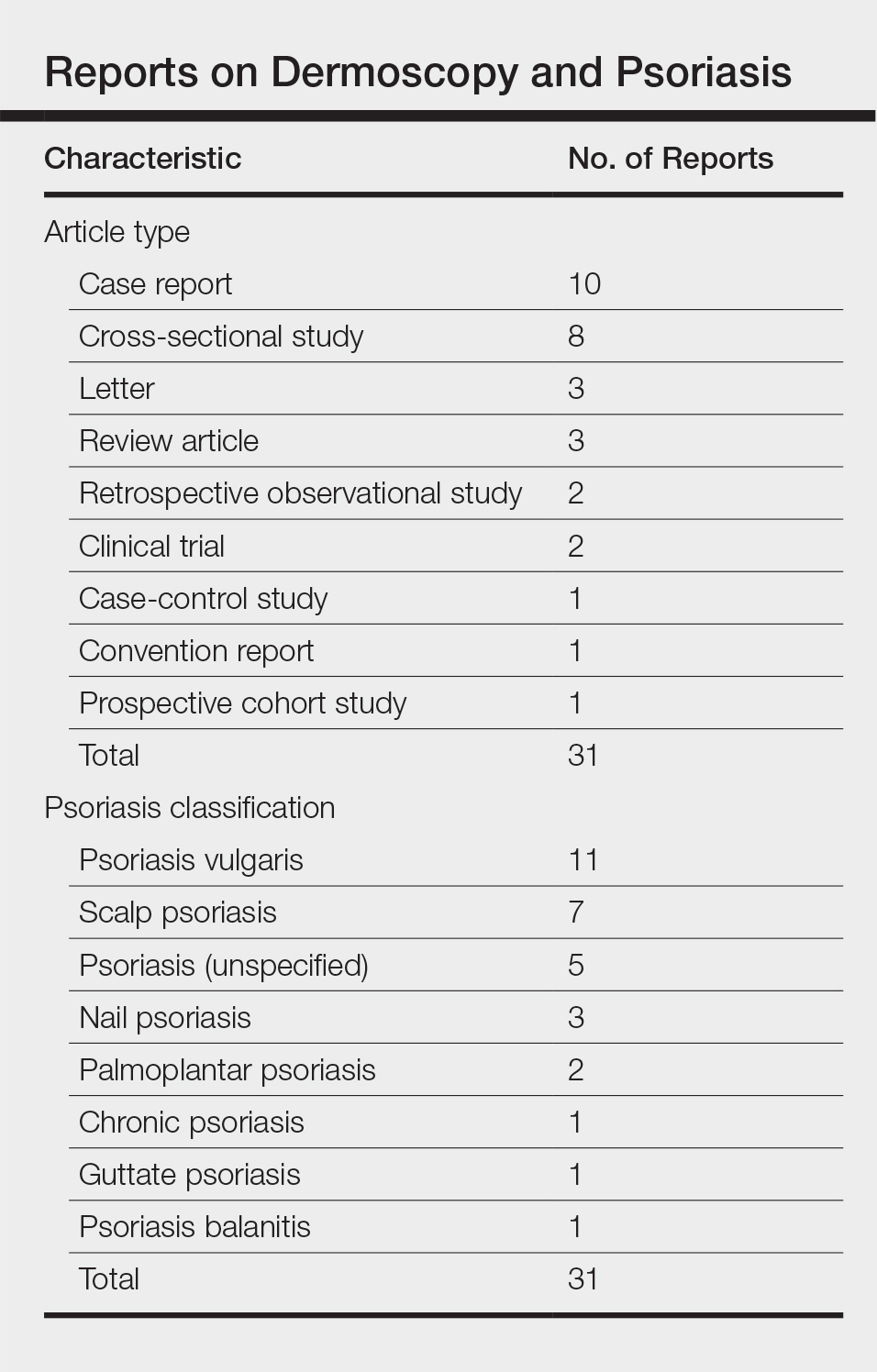
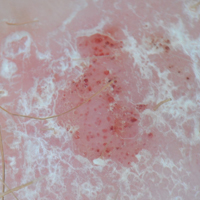
On physical examination a 0.6×0.7-cm, pink to erythematous, pearly papule with superficial telangiectases was noted on the right side of the dorsal thorax (Figure 1). Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with silvery scale and areas of secondary excoriation were noted on the trunk and both legs consistent with the patient’s history of psoriasis.
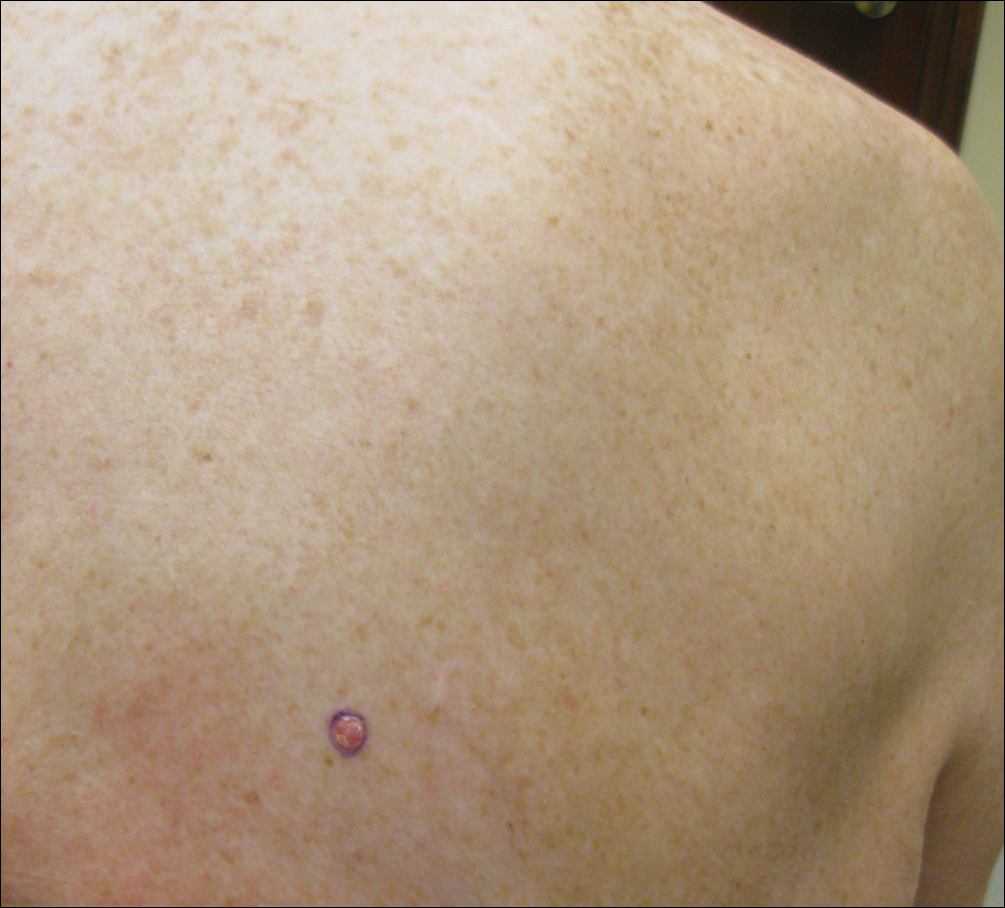
A shave biopsy was performed on the skin lesion on the right side of the dorsal thorax with a suspected clinical diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Two weeks later the patient returned for a discussion of the pathology report, which revealed nodules of basaloid cells with tightly packed vesicular nuclei and scant cytoplasm in sheets within the superficial dermis, as well as areas of nuclear molding, numerous mitotic figures, and areas of focal necrosis (Figure 2). In addition, immunostaining was positive for cytokeratin (CK) 20 antibodies with a characteristic paranuclear dot uptake of the antibody. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). At that time, alefacept was discontinued and he was referred to a tertiary referral center for further evaluation and treatment.
The patient subsequently underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins of the MCC, with intraoperative lymphatic mapping/sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) of the right axillary nodal basin 1 month later, which he tolerated well without any associated complications. Further histopathologic examination revealed the deep, medial, and lateral surgical margins to be negative of residual neoplasm. However, one sentinel lymph node indicated positivity for micrometastatic MCC, consistent with stage IIIA disease progression.
He underwent a second procedure the following month for complete right axillary lymph node dissection. Histopathologic examination of the right axillary contents included 28 lymph nodes, which were negative for carcinoma. He continued to do well without any signs of clinical recurrence or distant metastasis at subsequent follow-up visits.
Approximately 2.5 years after the second procedure, the patient began to develop right upper quadrant abdominal pain of an unclear etiology. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis was performed, revealing areas of calcification and findings consistent with malignant lymphadenopathy. Multiple hepatic lesions also were noted including a 9-cm lesion in the posterior right hepatic lobe. Computed tomography–guided biopsy of the liver lesion was performed and the findings were consistent with metastatic MCC, indicating progression to stage IV disease.
The patient was subsequently started on combination chemotherapeutic treatment with carboplatin and VP-16, with a planned treatment course of 4 to 6 cycles. He was able to complete a total of 6 cycles over a 4-month period, tolerating the treatment regimen fairly well. Follow-up positron emission tomography–computed tomography was within normal limits with no evidence of any hypermetabolic activity noted, indicating a complete radiographic remission of MCC. He was seen approximately 1 month after completion of treatment for clinical follow-up and monthly thereafter.
While on chemotherapy, the patient experienced a notable improvement in the psoriasis and psoriatic joint disease. Upon completion of chemotherapy, he was restarted on the same treatment plan that was utilized prior to surgery including topical corticosteroids, calcitriol, intramuscular steroid injections, and UVB phototherapy, which provided substantial control of psoriasis and arthritic joint disease. The patient later died, likely due to his multiple comorbidities.
Merkel cells are slow-responding mechanoreceptors located within the basal layer of the epidermis and are the source of a rare aggressive cutaneous malignancy.1 Merkel cell carcinoma was first noted in 1972 and termed trabecular carcinoma of the skin, and it accounts for less than 1% of all nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 This primary neuroendocrine carcinoma has remarkable metastatic potential (34%–75%) and can invade regional lymph nodes, as well as distant metastasis most commonly to the liver, lungs, bones, and brain.2 Approximately 25% of patients present with palpable lymphadenopathy and 5% with distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis. This frequency of metastasis at diagnosis as well as the recurrence after treatment contributes to the poor prognosis of MCC. Local recurrence rates have been reported at 25% with lymph node involvement in 52% and metastasis in 34%, with most recurrences occurring within 2 years of diagnosis. Patient mortality is dependent on the aggressiveness of the tumor, with 5-year survival rates of 83.3% without lymph node involvement, 58.3% with lymph node involvement, and 31.3% in those with metastatic disease.4
The tumor classically presents as a red to violaceous, painless nodule with a smooth shiny surface most often on the head and neck region.4-6 Approximately 50% of MCC cases present in the head and neck region, 32% to 38% on the extremities, and 12% to 14% on the trunk.1 This nonspecific presentation may lead to diagnostic uncertainty and a consequent delay in treatment. Definitive diagnosis of MCC is achieved with a skin biopsy and allows for distinction from other clinically similar–appearing neoplasms. Merkel cell carcinoma presents histologically as small round basophilic cells penetrating through the dermis in 3 histologic patterns: the trabecular, intermediate (80% of cases), and small cell type.5 It may be differentiated immunohistochemically from other neoplasms, as it displays CK20 positivity (showing paranuclear dotlike depositions in the cytoplasm or cell membrane) and is negative for CK7. Chromagranin and synaptophysin positivity also may provide further histologic confirmation. In addition, absence of peripheral palisading, retraction artifact, and a fibromyxoid stroma allow for distinction from cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, which may display these features histologically. Other immunohistochemical markers that may be of value include thyroid transcription factor 1, which is typically positive in cutaneous metastasis of neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung; S-100 and human melanoma black 45, which are positive in melanoma; and leukocyte common antigen (CD45), which can be positive in lymphoma. These stains are classically negative in MCC.3
Merkel cell carcinoma is commonly associated with the presence of Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) in tumor specimens, with a prevalence of 70% to 80% in all cases. Merkel cell polyomavirus is a class 2A carcinogen (ie, a probable carcinogen to humans) and is classified among a group of viruses that encode T antigens (ie, an antigen coded by a viral genome associated with transformation of infected cells by tumor viruses), which can lead to initiation of tumorigenesis through interference with cellular tumor suppressing proteins such as p53.5 In addition, several risk factors have been associated with the development of MCC including immunosuppression, older age (>50 years), and UV-exposed fair skin.7 One explanation for this phenomenon is the increase in MCPyV small T antigen transcripts induced by UV irradiation.5 In addition, as with other cancers induced by viruses, host immunity can impede tumor progression and development. Therefore, impairment of normal immune function likely creates a higher risk for MCC development and potential for a worse prognosis.3Although the exact incidence of MCC in immunosuppressed patients appears unclear, chronic immunosuppressive therapy may play a notable role in the pathogenesis of the tumor.3
Although each of these factors was observed in our patient, it also was possible that his associated comorbidities further contributed to disease presentation. In particular, rheumatoid arthritis has been shown to carry an increased risk for the development of MCC.8 In addition, inflammatory monocytes infected with MCPyV, as evidenced in a patient with a history of chronic psoriasis prior to diagnosis of MCC, also may contribute to the pathogenesis of MCC by traveling to inflammatory skin lesions, such as those seen in psoriasis, releasing MCPyV locally and infecting Merkel cells.9 Although MCPyV testing was never performed in our patient, it certainly would be prudent as well as further studies determining the correlation of MCC to these disease processes.
Although regression is rare, multiple cases have documented spontaneous regression of MCC after biopsy of these lesions.4,6,10 The exact mechanism is unclear, but apoptosis induced by T-cell immunity is suspected to play a role. Programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1)–positive cells play a role. The PD-1 receptor is an inhibitory receptor expressed by T cells and in approximately half of tumor-infiltrating cells in MCC. It was found that in a regressed case of MCC there was a notably lower percentage of PD-1 positivity compared to cases with no apparent regression, suggesting that PD-1–positive cells suppress tumor immunity to MCC and that significant reduction in these cells may induce clinical regression.10 Additional investigation would be beneficial to examine the relationship of this phenomenon to tumor regression.
Initial evaluation of these patients should include a meticulous clinical examination with an emphasis on detection of cutaneous, lymph node, and distant metastasis. Due to the risk of metastatic potential, regional lymph node ultrasonography and computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis typically are recommended at baseline. Other imaging modalities may be warranted based on clinical findings.3 Treatment modalities include various approaches, with surgical excision of the primary tumor with more than 1-cm margin to the fascial plane being the primary modality for uncomplicated cases.1,3,7 In addition, SLNB also should be performed at the time of the procedure. In the case of a positive SLNB or suspected regional lymph node involvement upon initial examination, radical regional lymph node dissection also is recommended.3 Although some authorities advocate postsurgical radiation therapy to minimize the risk of local recurrence, there does not appear to be a clear benefit in survival rate.3,5 However, radiation treatment as monotherapy has been advocated in certain instances, particularly in cases of unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates.5,7 Cases of distant metastasis (stage IV disease) may include management with surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy. Although none of these modalities have consistently shown to improve survival, there appears to be up to a 60% response with chemotherapy in these patients.3
Because MCC tends to affect an older population, often with other notable comorbidities, important considerations involving a treatment plan include the cost, side effects, and convenience for patients. The combination of carboplatin and VP-16 (etoposide) was utilized and tolerated well in our patient, and it has been successful in achieving complete radiologic and clinical remission of his metastatic disease. This combination appears to prolong survival in patients with distant metastasis, as compared to those patients not receiving chemotherapy.1 Our patient has since died, but in these high-risk patients, close clinical monitoring is essential to help optimize their prognosis.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that most commonly affects the elderly, immunosuppressed, and those with chronic UV sun damage. An association between the oncogenesis of MCC and infection with MCPyV has been documented, but other underlying diseases also may play a role in this process including rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Although these risk factors were associated with our patient, his history of chronic immunosuppressive therapy for treatment of his psoriasis and inflammatory joint disease likely played a role in the pathogenesis of the tumor and should be an important point of discussion with any patient requiring this type of long-term management for disease control. Our unique clinical case highlights a patient with substantial comorbidities who developed metastatic MCC and achieved complete clinical and radiologic remission after treatment with surgery and chemotherapy.
- Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment [published online March 11, 2015]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
- Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis [published online December 1, 2014]. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
- Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives [published online Dec 31, 2014]. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
- Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging [published online January 30, 2015]. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
- Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy [published online May 14, 2015]. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
- Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature [published online November 13, 2014]. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
- Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
- Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults [published online June 15, 2010]. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
- Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus [published online December 17, 2009]. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
- Fujimoto N, Nakanishi G, Kabuto M, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma showing regression after biopsy: evaluation of programmed cell death 1-positive cells [published online February 24, 2015]. J Dermatol. 2015;42:496-499.
To the Editor:
A 69-year-old white man presented with a skin lesion on the back of 1 to 2 weeks’ duration. The patient stated he was unaware of it, but his wife had recently noticed the new spot. He denied any bleeding, pain, pruritus, or other associated symptoms with the lesion. He also denied any prior treatment to the area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for severe psoriasis involving more than 80% body surface area, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, coronary artery disease, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic keratoses. He had been on multiple treatment regimens over the last 20 years for control of psoriasis including topical corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA and UVB phototherapy, gold injections, acitretin, prednisone, efalizumab, ustekinumab, and alefacept upon evaluation of this new skin lesion. Utilization of immunosuppressive agents also provided an additional benefit of controlling the patient’s inflammatory arthritic disease.
On physical examination a 0.6×0.7-cm, pink to erythematous, pearly papule with superficial telangiectases was noted on the right side of the dorsal thorax (Figure 1). Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with silvery scale and areas of secondary excoriation were noted on the trunk and both legs consistent with the patient’s history of psoriasis.

A shave biopsy was performed on the skin lesion on the right side of the dorsal thorax with a suspected clinical diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Two weeks later the patient returned for a discussion of the pathology report, which revealed nodules of basaloid cells with tightly packed vesicular nuclei and scant cytoplasm in sheets within the superficial dermis, as well as areas of nuclear molding, numerous mitotic figures, and areas of focal necrosis (Figure 2). In addition, immunostaining was positive for cytokeratin (CK) 20 antibodies with a characteristic paranuclear dot uptake of the antibody. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). At that time, alefacept was discontinued and he was referred to a tertiary referral center for further evaluation and treatment.

The patient subsequently underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins of the MCC, with intraoperative lymphatic mapping/sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) of the right axillary nodal basin 1 month later, which he tolerated well without any associated complications. Further histopathologic examination revealed the deep, medial, and lateral surgical margins to be negative of residual neoplasm. However, one sentinel lymph node indicated positivity for micrometastatic MCC, consistent with stage IIIA disease progression.
He underwent a second procedure the following month for complete right axillary lymph node dissection. Histopathologic examination of the right axillary contents included 28 lymph nodes, which were negative for carcinoma. He continued to do well without any signs of clinical recurrence or distant metastasis at subsequent follow-up visits.
Approximately 2.5 years after the second procedure, the patient began to develop right upper quadrant abdominal pain of an unclear etiology. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis was performed, revealing areas of calcification and findings consistent with malignant lymphadenopathy. Multiple hepatic lesions also were noted including a 9-cm lesion in the posterior right hepatic lobe. Computed tomography–guided biopsy of the liver lesion was performed and the findings were consistent with metastatic MCC, indicating progression to stage IV disease.
The patient was subsequently started on combination chemotherapeutic treatment with carboplatin and VP-16, with a planned treatment course of 4 to 6 cycles. He was able to complete a total of 6 cycles over a 4-month period, tolerating the treatment regimen fairly well. Follow-up positron emission tomography–computed tomography was within normal limits with no evidence of any hypermetabolic activity noted, indicating a complete radiographic remission of MCC. He was seen approximately 1 month after completion of treatment for clinical follow-up and monthly thereafter.
While on chemotherapy, the patient experienced a notable improvement in the psoriasis and psoriatic joint disease. Upon completion of chemotherapy, he was restarted on the same treatment plan that was utilized prior to surgery including topical corticosteroids, calcitriol, intramuscular steroid injections, and UVB phototherapy, which provided substantial control of psoriasis and arthritic joint disease. The patient later died, likely due to his multiple comorbidities.
Merkel cells are slow-responding mechanoreceptors located within the basal layer of the epidermis and are the source of a rare aggressive cutaneous malignancy.1 Merkel cell carcinoma was first noted in 1972 and termed trabecular carcinoma of the skin, and it accounts for less than 1% of all nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 This primary neuroendocrine carcinoma has remarkable metastatic potential (34%–75%) and can invade regional lymph nodes, as well as distant metastasis most commonly to the liver, lungs, bones, and brain.2 Approximately 25% of patients present with palpable lymphadenopathy and 5% with distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis. This frequency of metastasis at diagnosis as well as the recurrence after treatment contributes to the poor prognosis of MCC. Local recurrence rates have been reported at 25% with lymph node involvement in 52% and metastasis in 34%, with most recurrences occurring within 2 years of diagnosis. Patient mortality is dependent on the aggressiveness of the tumor, with 5-year survival rates of 83.3% without lymph node involvement, 58.3% with lymph node involvement, and 31.3% in those with metastatic disease.4
The tumor classically presents as a red to violaceous, painless nodule with a smooth shiny surface most often on the head and neck region.4-6 Approximately 50% of MCC cases present in the head and neck region, 32% to 38% on the extremities, and 12% to 14% on the trunk.1 This nonspecific presentation may lead to diagnostic uncertainty and a consequent delay in treatment. Definitive diagnosis of MCC is achieved with a skin biopsy and allows for distinction from other clinically similar–appearing neoplasms. Merkel cell carcinoma presents histologically as small round basophilic cells penetrating through the dermis in 3 histologic patterns: the trabecular, intermediate (80% of cases), and small cell type.5 It may be differentiated immunohistochemically from other neoplasms, as it displays CK20 positivity (showing paranuclear dotlike depositions in the cytoplasm or cell membrane) and is negative for CK7. Chromagranin and synaptophysin positivity also may provide further histologic confirmation. In addition, absence of peripheral palisading, retraction artifact, and a fibromyxoid stroma allow for distinction from cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, which may display these features histologically. Other immunohistochemical markers that may be of value include thyroid transcription factor 1, which is typically positive in cutaneous metastasis of neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung; S-100 and human melanoma black 45, which are positive in melanoma; and leukocyte common antigen (CD45), which can be positive in lymphoma. These stains are classically negative in MCC.3
Merkel cell carcinoma is commonly associated with the presence of Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) in tumor specimens, with a prevalence of 70% to 80% in all cases. Merkel cell polyomavirus is a class 2A carcinogen (ie, a probable carcinogen to humans) and is classified among a group of viruses that encode T antigens (ie, an antigen coded by a viral genome associated with transformation of infected cells by tumor viruses), which can lead to initiation of tumorigenesis through interference with cellular tumor suppressing proteins such as p53.5 In addition, several risk factors have been associated with the development of MCC including immunosuppression, older age (>50 years), and UV-exposed fair skin.7 One explanation for this phenomenon is the increase in MCPyV small T antigen transcripts induced by UV irradiation.5 In addition, as with other cancers induced by viruses, host immunity can impede tumor progression and development. Therefore, impairment of normal immune function likely creates a higher risk for MCC development and potential for a worse prognosis.3Although the exact incidence of MCC in immunosuppressed patients appears unclear, chronic immunosuppressive therapy may play a notable role in the pathogenesis of the tumor.3
Although each of these factors was observed in our patient, it also was possible that his associated comorbidities further contributed to disease presentation. In particular, rheumatoid arthritis has been shown to carry an increased risk for the development of MCC.8 In addition, inflammatory monocytes infected with MCPyV, as evidenced in a patient with a history of chronic psoriasis prior to diagnosis of MCC, also may contribute to the pathogenesis of MCC by traveling to inflammatory skin lesions, such as those seen in psoriasis, releasing MCPyV locally and infecting Merkel cells.9 Although MCPyV testing was never performed in our patient, it certainly would be prudent as well as further studies determining the correlation of MCC to these disease processes.
Although regression is rare, multiple cases have documented spontaneous regression of MCC after biopsy of these lesions.4,6,10 The exact mechanism is unclear, but apoptosis induced by T-cell immunity is suspected to play a role. Programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1)–positive cells play a role. The PD-1 receptor is an inhibitory receptor expressed by T cells and in approximately half of tumor-infiltrating cells in MCC. It was found that in a regressed case of MCC there was a notably lower percentage of PD-1 positivity compared to cases with no apparent regression, suggesting that PD-1–positive cells suppress tumor immunity to MCC and that significant reduction in these cells may induce clinical regression.10 Additional investigation would be beneficial to examine the relationship of this phenomenon to tumor regression.
Initial evaluation of these patients should include a meticulous clinical examination with an emphasis on detection of cutaneous, lymph node, and distant metastasis. Due to the risk of metastatic potential, regional lymph node ultrasonography and computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis typically are recommended at baseline. Other imaging modalities may be warranted based on clinical findings.3 Treatment modalities include various approaches, with surgical excision of the primary tumor with more than 1-cm margin to the fascial plane being the primary modality for uncomplicated cases.1,3,7 In addition, SLNB also should be performed at the time of the procedure. In the case of a positive SLNB or suspected regional lymph node involvement upon initial examination, radical regional lymph node dissection also is recommended.3 Although some authorities advocate postsurgical radiation therapy to minimize the risk of local recurrence, there does not appear to be a clear benefit in survival rate.3,5 However, radiation treatment as monotherapy has been advocated in certain instances, particularly in cases of unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates.5,7 Cases of distant metastasis (stage IV disease) may include management with surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy. Although none of these modalities have consistently shown to improve survival, there appears to be up to a 60% response with chemotherapy in these patients.3
Because MCC tends to affect an older population, often with other notable comorbidities, important considerations involving a treatment plan include the cost, side effects, and convenience for patients. The combination of carboplatin and VP-16 (etoposide) was utilized and tolerated well in our patient, and it has been successful in achieving complete radiologic and clinical remission of his metastatic disease. This combination appears to prolong survival in patients with distant metastasis, as compared to those patients not receiving chemotherapy.1 Our patient has since died, but in these high-risk patients, close clinical monitoring is essential to help optimize their prognosis.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that most commonly affects the elderly, immunosuppressed, and those with chronic UV sun damage. An association between the oncogenesis of MCC and infection with MCPyV has been documented, but other underlying diseases also may play a role in this process including rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Although these risk factors were associated with our patient, his history of chronic immunosuppressive therapy for treatment of his psoriasis and inflammatory joint disease likely played a role in the pathogenesis of the tumor and should be an important point of discussion with any patient requiring this type of long-term management for disease control. Our unique clinical case highlights a patient with substantial comorbidities who developed metastatic MCC and achieved complete clinical and radiologic remission after treatment with surgery and chemotherapy.
To the Editor:
A 69-year-old white man presented with a skin lesion on the back of 1 to 2 weeks’ duration. The patient stated he was unaware of it, but his wife had recently noticed the new spot. He denied any bleeding, pain, pruritus, or other associated symptoms with the lesion. He also denied any prior treatment to the area. The patient’s medical history was remarkable for severe psoriasis involving more than 80% body surface area, psoriatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, coronary artery disease, squamous cell carcinoma, and actinic keratoses. He had been on multiple treatment regimens over the last 20 years for control of psoriasis including topical corticosteroids, psoralen plus UVA and UVB phototherapy, gold injections, acitretin, prednisone, efalizumab, ustekinumab, and alefacept upon evaluation of this new skin lesion. Utilization of immunosuppressive agents also provided an additional benefit of controlling the patient’s inflammatory arthritic disease.
On physical examination a 0.6×0.7-cm, pink to erythematous, pearly papule with superficial telangiectases was noted on the right side of the dorsal thorax (Figure 1). Multiple well-demarcated erythematous plaques with silvery scale and areas of secondary excoriation were noted on the trunk and both legs consistent with the patient’s history of psoriasis.

A shave biopsy was performed on the skin lesion on the right side of the dorsal thorax with a suspected clinical diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Two weeks later the patient returned for a discussion of the pathology report, which revealed nodules of basaloid cells with tightly packed vesicular nuclei and scant cytoplasm in sheets within the superficial dermis, as well as areas of nuclear molding, numerous mitotic figures, and areas of focal necrosis (Figure 2). In addition, immunostaining was positive for cytokeratin (CK) 20 antibodies with a characteristic paranuclear dot uptake of the antibody. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). At that time, alefacept was discontinued and he was referred to a tertiary referral center for further evaluation and treatment.

The patient subsequently underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins of the MCC, with intraoperative lymphatic mapping/sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) of the right axillary nodal basin 1 month later, which he tolerated well without any associated complications. Further histopathologic examination revealed the deep, medial, and lateral surgical margins to be negative of residual neoplasm. However, one sentinel lymph node indicated positivity for micrometastatic MCC, consistent with stage IIIA disease progression.
He underwent a second procedure the following month for complete right axillary lymph node dissection. Histopathologic examination of the right axillary contents included 28 lymph nodes, which were negative for carcinoma. He continued to do well without any signs of clinical recurrence or distant metastasis at subsequent follow-up visits.
Approximately 2.5 years after the second procedure, the patient began to develop right upper quadrant abdominal pain of an unclear etiology. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis was performed, revealing areas of calcification and findings consistent with malignant lymphadenopathy. Multiple hepatic lesions also were noted including a 9-cm lesion in the posterior right hepatic lobe. Computed tomography–guided biopsy of the liver lesion was performed and the findings were consistent with metastatic MCC, indicating progression to stage IV disease.
The patient was subsequently started on combination chemotherapeutic treatment with carboplatin and VP-16, with a planned treatment course of 4 to 6 cycles. He was able to complete a total of 6 cycles over a 4-month period, tolerating the treatment regimen fairly well. Follow-up positron emission tomography–computed tomography was within normal limits with no evidence of any hypermetabolic activity noted, indicating a complete radiographic remission of MCC. He was seen approximately 1 month after completion of treatment for clinical follow-up and monthly thereafter.
While on chemotherapy, the patient experienced a notable improvement in the psoriasis and psoriatic joint disease. Upon completion of chemotherapy, he was restarted on the same treatment plan that was utilized prior to surgery including topical corticosteroids, calcitriol, intramuscular steroid injections, and UVB phototherapy, which provided substantial control of psoriasis and arthritic joint disease. The patient later died, likely due to his multiple comorbidities.
Merkel cells are slow-responding mechanoreceptors located within the basal layer of the epidermis and are the source of a rare aggressive cutaneous malignancy.1 Merkel cell carcinoma was first noted in 1972 and termed trabecular carcinoma of the skin, and it accounts for less than 1% of all nonmelanoma skin cancer.2,3 This primary neuroendocrine carcinoma has remarkable metastatic potential (34%–75%) and can invade regional lymph nodes, as well as distant metastasis most commonly to the liver, lungs, bones, and brain.2 Approximately 25% of patients present with palpable lymphadenopathy and 5% with distant metastasis at the time of diagnosis. This frequency of metastasis at diagnosis as well as the recurrence after treatment contributes to the poor prognosis of MCC. Local recurrence rates have been reported at 25% with lymph node involvement in 52% and metastasis in 34%, with most recurrences occurring within 2 years of diagnosis. Patient mortality is dependent on the aggressiveness of the tumor, with 5-year survival rates of 83.3% without lymph node involvement, 58.3% with lymph node involvement, and 31.3% in those with metastatic disease.4
The tumor classically presents as a red to violaceous, painless nodule with a smooth shiny surface most often on the head and neck region.4-6 Approximately 50% of MCC cases present in the head and neck region, 32% to 38% on the extremities, and 12% to 14% on the trunk.1 This nonspecific presentation may lead to diagnostic uncertainty and a consequent delay in treatment. Definitive diagnosis of MCC is achieved with a skin biopsy and allows for distinction from other clinically similar–appearing neoplasms. Merkel cell carcinoma presents histologically as small round basophilic cells penetrating through the dermis in 3 histologic patterns: the trabecular, intermediate (80% of cases), and small cell type.5 It may be differentiated immunohistochemically from other neoplasms, as it displays CK20 positivity (showing paranuclear dotlike depositions in the cytoplasm or cell membrane) and is negative for CK7. Chromagranin and synaptophysin positivity also may provide further histologic confirmation. In addition, absence of peripheral palisading, retraction artifact, and a fibromyxoid stroma allow for distinction from cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, which may display these features histologically. Other immunohistochemical markers that may be of value include thyroid transcription factor 1, which is typically positive in cutaneous metastasis of neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung; S-100 and human melanoma black 45, which are positive in melanoma; and leukocyte common antigen (CD45), which can be positive in lymphoma. These stains are classically negative in MCC.3
Merkel cell carcinoma is commonly associated with the presence of Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) in tumor specimens, with a prevalence of 70% to 80% in all cases. Merkel cell polyomavirus is a class 2A carcinogen (ie, a probable carcinogen to humans) and is classified among a group of viruses that encode T antigens (ie, an antigen coded by a viral genome associated with transformation of infected cells by tumor viruses), which can lead to initiation of tumorigenesis through interference with cellular tumor suppressing proteins such as p53.5 In addition, several risk factors have been associated with the development of MCC including immunosuppression, older age (>50 years), and UV-exposed fair skin.7 One explanation for this phenomenon is the increase in MCPyV small T antigen transcripts induced by UV irradiation.5 In addition, as with other cancers induced by viruses, host immunity can impede tumor progression and development. Therefore, impairment of normal immune function likely creates a higher risk for MCC development and potential for a worse prognosis.3Although the exact incidence of MCC in immunosuppressed patients appears unclear, chronic immunosuppressive therapy may play a notable role in the pathogenesis of the tumor.3
Although each of these factors was observed in our patient, it also was possible that his associated comorbidities further contributed to disease presentation. In particular, rheumatoid arthritis has been shown to carry an increased risk for the development of MCC.8 In addition, inflammatory monocytes infected with MCPyV, as evidenced in a patient with a history of chronic psoriasis prior to diagnosis of MCC, also may contribute to the pathogenesis of MCC by traveling to inflammatory skin lesions, such as those seen in psoriasis, releasing MCPyV locally and infecting Merkel cells.9 Although MCPyV testing was never performed in our patient, it certainly would be prudent as well as further studies determining the correlation of MCC to these disease processes.
Although regression is rare, multiple cases have documented spontaneous regression of MCC after biopsy of these lesions.4,6,10 The exact mechanism is unclear, but apoptosis induced by T-cell immunity is suspected to play a role. Programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1)–positive cells play a role. The PD-1 receptor is an inhibitory receptor expressed by T cells and in approximately half of tumor-infiltrating cells in MCC. It was found that in a regressed case of MCC there was a notably lower percentage of PD-1 positivity compared to cases with no apparent regression, suggesting that PD-1–positive cells suppress tumor immunity to MCC and that significant reduction in these cells may induce clinical regression.10 Additional investigation would be beneficial to examine the relationship of this phenomenon to tumor regression.
Initial evaluation of these patients should include a meticulous clinical examination with an emphasis on detection of cutaneous, lymph node, and distant metastasis. Due to the risk of metastatic potential, regional lymph node ultrasonography and computed tomography of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis typically are recommended at baseline. Other imaging modalities may be warranted based on clinical findings.3 Treatment modalities include various approaches, with surgical excision of the primary tumor with more than 1-cm margin to the fascial plane being the primary modality for uncomplicated cases.1,3,7 In addition, SLNB also should be performed at the time of the procedure. In the case of a positive SLNB or suspected regional lymph node involvement upon initial examination, radical regional lymph node dissection also is recommended.3 Although some authorities advocate postsurgical radiation therapy to minimize the risk of local recurrence, there does not appear to be a clear benefit in survival rate.3,5 However, radiation treatment as monotherapy has been advocated in certain instances, particularly in cases of unresectable tumors or patients who are poor surgical candidates.5,7 Cases of distant metastasis (stage IV disease) may include management with surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy. Although none of these modalities have consistently shown to improve survival, there appears to be up to a 60% response with chemotherapy in these patients.3
Because MCC tends to affect an older population, often with other notable comorbidities, important considerations involving a treatment plan include the cost, side effects, and convenience for patients. The combination of carboplatin and VP-16 (etoposide) was utilized and tolerated well in our patient, and it has been successful in achieving complete radiologic and clinical remission of his metastatic disease. This combination appears to prolong survival in patients with distant metastasis, as compared to those patients not receiving chemotherapy.1 Our patient has since died, but in these high-risk patients, close clinical monitoring is essential to help optimize their prognosis.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare aggressive cutaneous neoplasm that most commonly affects the elderly, immunosuppressed, and those with chronic UV sun damage. An association between the oncogenesis of MCC and infection with MCPyV has been documented, but other underlying diseases also may play a role in this process including rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Although these risk factors were associated with our patient, his history of chronic immunosuppressive therapy for treatment of his psoriasis and inflammatory joint disease likely played a role in the pathogenesis of the tumor and should be an important point of discussion with any patient requiring this type of long-term management for disease control. Our unique clinical case highlights a patient with substantial comorbidities who developed metastatic MCC and achieved complete clinical and radiologic remission after treatment with surgery and chemotherapy.
- Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment [published online March 11, 2015]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
- Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis [published online December 1, 2014]. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
- Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives [published online Dec 31, 2014]. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
- Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging [published online January 30, 2015]. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
- Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy [published online May 14, 2015]. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
- Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature [published online November 13, 2014]. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
- Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
- Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults [published online June 15, 2010]. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
- Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus [published online December 17, 2009]. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
- Fujimoto N, Nakanishi G, Kabuto M, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma showing regression after biopsy: evaluation of programmed cell death 1-positive cells [published online February 24, 2015]. J Dermatol. 2015;42:496-499.
- Timmer FC, Klop WM, Relyveld GN, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma of the head and neck: emphasizing the risk of undertreatment [published online March 11, 2015]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273:1243-1252.
- Açıkalın A, Paydas¸ S, Güleç ÜK, et al. A unique case of Merkel cell carcinoma with ovarian metastasis [published online December 1, 2014]. Balkan Med J. 2014;31:356-359.
- Samimi M, Gardair C, Nicol JT, et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma: clinical and therapeutic perspectives [published online Dec 31, 2014]. Semin Oncol. 2015;42:347-358.
- Grandhaye M, Teixeira PG, Henrot P, et al. Focus on Merkel cell carcinoma: diagnosis and staging [published online January 30, 2015]. Skeletal Radiol. 2015;44:777-786.
- Chatzinasiou F, Papadavid E, Korkolopoulou P, et al. An unusual case of diffuse Merkel cell carcinoma successfully treated with low dose radiotherapy [published online May 14, 2015]. Dermatol Ther. 2015;28:282-286.
- Pang C, Sharma D, Sankar T. Spontaneous regression of Merkel cell carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature [published online November 13, 2014]. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;7C:104-108.
- Kitamura N, Tomita R, Yamamoto M, et al. Complete remission of Merkel cell carcinoma on the upper lip treated with radiation monotherapy and a literature review of Japanese cases. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:152.
- Lanoy E, Engels EA. Skin cancers associated with autoimmune conditions among elderly adults [published online June 15, 2010]. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:112-114.
- Mertz KD, Junt T, Schmid M, et al. Inflammatory monocytes are a reservoir for Merkel cell polyomavirus [published online December 17, 2009]. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;130:1146-1151.
- Fujimoto N, Nakanishi G, Kabuto M, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma showing regression after biopsy: evaluation of programmed cell death 1-positive cells [published online February 24, 2015]. J Dermatol. 2015;42:496-499.
Practice Points
- Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) has remarkable metastatic potential.
- Initial evaluation of patients with MCC should include clinical examination to detect cutaneous, lymph node, and distant metastasis.
- Risk factors associated with the development of MCC include immunosuppression, older age, and UV-exposed fair skin.
Meta-analysis: Lifestyle changes improve psoriasis
GENEVA – according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented by Ching-Chi Chi, MD, at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A plausible mechanism of benefit exists for these findings: “Fat tissue is known to be an endocrine organ that produces inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor. Reduce the amount of fat tissue and you reduce inflammation,” explained Dr. Chi, professor of dermatology at Chang Gung University in Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Among the key findings in the meta-analysis: Participation in dietary interventions provided obese psoriasis patients with a 66% increased likelihood of achieving a PASI 75 response at week 24, compared with controls, with a number needed to treat of 3. These low-calorie diets were typically rigorous, the dermatologist noted. For example, one entailed a food intake of 1,000 kcal/day or less, while another restricted intake by 500 kcal/day less than a patient’s calculated resting energy expenditure.
Also, participants in the dietary intervention studies averaged a 14.4-point improvement from baseline in Dermatologic Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores at week 24 versus a 2.2-point improvement in controls. Researchers consider a 5-point or greater improvement in the DLQI clinically meaningful.
A combined diet and exercise program resulted in a 45% increased likelihood that obese psoriasis patients would achieve a PASI 50 response at week 16, with a number needed to treat of 7. There was a trend in the active treatment arm for higher PASI 75 and PASI 100 responses than in controls as well, but it wasn’t statistically significant.
The one randomized trial of a walking exercise program coupled with continuous health education demonstrated a significant reduction in the rate of psoriasis flares, compared with controls, over a 3-year period.
In contrast, the studies of educational programs promoting a healthy lifestyle without an associated dietary or physical activity intervention failed to show a reduction in PASI scores.
Dr. Chi reported no financial conflicts of interest regarding his study, which was funded by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
SOURCE: Chi C. EADV 2017.
GENEVA – according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented by Ching-Chi Chi, MD, at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A plausible mechanism of benefit exists for these findings: “Fat tissue is known to be an endocrine organ that produces inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor. Reduce the amount of fat tissue and you reduce inflammation,” explained Dr. Chi, professor of dermatology at Chang Gung University in Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Among the key findings in the meta-analysis: Participation in dietary interventions provided obese psoriasis patients with a 66% increased likelihood of achieving a PASI 75 response at week 24, compared with controls, with a number needed to treat of 3. These low-calorie diets were typically rigorous, the dermatologist noted. For example, one entailed a food intake of 1,000 kcal/day or less, while another restricted intake by 500 kcal/day less than a patient’s calculated resting energy expenditure.
Also, participants in the dietary intervention studies averaged a 14.4-point improvement from baseline in Dermatologic Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores at week 24 versus a 2.2-point improvement in controls. Researchers consider a 5-point or greater improvement in the DLQI clinically meaningful.
A combined diet and exercise program resulted in a 45% increased likelihood that obese psoriasis patients would achieve a PASI 50 response at week 16, with a number needed to treat of 7. There was a trend in the active treatment arm for higher PASI 75 and PASI 100 responses than in controls as well, but it wasn’t statistically significant.
The one randomized trial of a walking exercise program coupled with continuous health education demonstrated a significant reduction in the rate of psoriasis flares, compared with controls, over a 3-year period.
In contrast, the studies of educational programs promoting a healthy lifestyle without an associated dietary or physical activity intervention failed to show a reduction in PASI scores.
Dr. Chi reported no financial conflicts of interest regarding his study, which was funded by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
SOURCE: Chi C. EADV 2017.
GENEVA – according to a systematic review and meta-analysis presented by Ching-Chi Chi, MD, at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A plausible mechanism of benefit exists for these findings: “Fat tissue is known to be an endocrine organ that produces inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor. Reduce the amount of fat tissue and you reduce inflammation,” explained Dr. Chi, professor of dermatology at Chang Gung University in Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Among the key findings in the meta-analysis: Participation in dietary interventions provided obese psoriasis patients with a 66% increased likelihood of achieving a PASI 75 response at week 24, compared with controls, with a number needed to treat of 3. These low-calorie diets were typically rigorous, the dermatologist noted. For example, one entailed a food intake of 1,000 kcal/day or less, while another restricted intake by 500 kcal/day less than a patient’s calculated resting energy expenditure.
Also, participants in the dietary intervention studies averaged a 14.4-point improvement from baseline in Dermatologic Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores at week 24 versus a 2.2-point improvement in controls. Researchers consider a 5-point or greater improvement in the DLQI clinically meaningful.
A combined diet and exercise program resulted in a 45% increased likelihood that obese psoriasis patients would achieve a PASI 50 response at week 16, with a number needed to treat of 7. There was a trend in the active treatment arm for higher PASI 75 and PASI 100 responses than in controls as well, but it wasn’t statistically significant.
The one randomized trial of a walking exercise program coupled with continuous health education demonstrated a significant reduction in the rate of psoriasis flares, compared with controls, over a 3-year period.
In contrast, the studies of educational programs promoting a healthy lifestyle without an associated dietary or physical activity intervention failed to show a reduction in PASI scores.
Dr. Chi reported no financial conflicts of interest regarding his study, which was funded by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
SOURCE: Chi C. EADV 2017.
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Weight loss and exercise reduce psoriasis severity.
Major finding: The number needed to treat with a calorie-restricted diet in order for one additional obese patient with psoriasis on systemic therapy to achieve a PASI 75 response is 3.
Study details: This meta-analysis included 10 randomized, controlled trials totaling 1,163 patients with psoriasis.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Source: Chi C. EADV 2017.
Ixekizumab beats ustekinumab for fingernail psoriasis, hands down
GENEVA – Ixekizumab improved fingernail psoriasis significantly faster and with a higher complete nail clearance rate by week 24 compared with ustekinumab in a head-to-head phase 3b randomized trial, Yves Dutronc, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This is a clinically important finding because – as dermatologists and psoriasis patients well know – nail and skin psoriasis are two different animals.
He presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the randomized, phase 3b, multicenter IXORA-S trial. The study pit the interleukin-17A inhibitor ixekizumab (Taltz) head-to-head against the interleukin 12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara). The primary endpoint, which was the PASI 90 improvement rate, has previously been reported: 73% in the ixekizumab group versus 42% in the ustekinumab group at week 12, and 83% versus 59% at week 24. And ixekizumab’s superior efficacy was achieved with a safety profile similar to that of ustekinumab (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:1014-23).
However, change in PASI score or Investigator’s Global Assessment isn’t informative regarding a patient’s change in nail psoriasis status. This was the impetus for the secondary analysis focused on the IXORA-S subgroup with baseline fingernail psoriasis. For this purpose, Dr. Dutronc and his coinvestigators used as their metric the change over time in the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI) total score, which entails a quadrant-by-quadrant assessment of every fingernail.
By play of chance, the 84 patients randomized to ixekizumab had slightly more severe nail psoriasis at baseline than that of the 105 ustekinumab patients. Their mean baseline NAPSI total score was 28.3, compared with 24.8 for the ustekinumab group. More than one-quarter of patients in the ixekizumab arm had a baseline NAPSI score greater than 43, whereas the top quartile of nail psoriasis severity in the ustekinumab group began with a NAPSI score above 34.
Not surprisingly, not much happened in terms of improvement in nail appearance in the first 12 weeks, since new nail grows slowly. But by week 8 the between-group difference in improvement in NAPSI score had become significant in favor of ixekizumab, with a mean 12.9-point reduction from baseline versus a 5.6-point drop in the ustekinumab group. This difference continued to grow over time, such that at week 24 the ixekizumab had a mean 19.9-point reduction, compared with a 13.2-point decrease for the ustekinumab group.
At week 12, 15.5% of the ixekizumab group and 11.3% of the ustekinumab group had reached complete clearance of their fingernail psoriasis. At week 24, complete clearance had been achieved in 48.8% of the ixekizumab group and 22.9% of patients on ustekinumab.
This is an interim analysis. Final results of the IXORA-S nail psoriasis substudy will be reported at 52 weeks of follow-up.
SOURCE: Dutronc Y. https://eadvgeneva2017.org/
GENEVA – Ixekizumab improved fingernail psoriasis significantly faster and with a higher complete nail clearance rate by week 24 compared with ustekinumab in a head-to-head phase 3b randomized trial, Yves Dutronc, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This is a clinically important finding because – as dermatologists and psoriasis patients well know – nail and skin psoriasis are two different animals.
He presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the randomized, phase 3b, multicenter IXORA-S trial. The study pit the interleukin-17A inhibitor ixekizumab (Taltz) head-to-head against the interleukin 12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara). The primary endpoint, which was the PASI 90 improvement rate, has previously been reported: 73% in the ixekizumab group versus 42% in the ustekinumab group at week 12, and 83% versus 59% at week 24. And ixekizumab’s superior efficacy was achieved with a safety profile similar to that of ustekinumab (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:1014-23).
However, change in PASI score or Investigator’s Global Assessment isn’t informative regarding a patient’s change in nail psoriasis status. This was the impetus for the secondary analysis focused on the IXORA-S subgroup with baseline fingernail psoriasis. For this purpose, Dr. Dutronc and his coinvestigators used as their metric the change over time in the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI) total score, which entails a quadrant-by-quadrant assessment of every fingernail.
By play of chance, the 84 patients randomized to ixekizumab had slightly more severe nail psoriasis at baseline than that of the 105 ustekinumab patients. Their mean baseline NAPSI total score was 28.3, compared with 24.8 for the ustekinumab group. More than one-quarter of patients in the ixekizumab arm had a baseline NAPSI score greater than 43, whereas the top quartile of nail psoriasis severity in the ustekinumab group began with a NAPSI score above 34.
Not surprisingly, not much happened in terms of improvement in nail appearance in the first 12 weeks, since new nail grows slowly. But by week 8 the between-group difference in improvement in NAPSI score had become significant in favor of ixekizumab, with a mean 12.9-point reduction from baseline versus a 5.6-point drop in the ustekinumab group. This difference continued to grow over time, such that at week 24 the ixekizumab had a mean 19.9-point reduction, compared with a 13.2-point decrease for the ustekinumab group.
At week 12, 15.5% of the ixekizumab group and 11.3% of the ustekinumab group had reached complete clearance of their fingernail psoriasis. At week 24, complete clearance had been achieved in 48.8% of the ixekizumab group and 22.9% of patients on ustekinumab.
This is an interim analysis. Final results of the IXORA-S nail psoriasis substudy will be reported at 52 weeks of follow-up.
SOURCE: Dutronc Y. https://eadvgeneva2017.org/
GENEVA – Ixekizumab improved fingernail psoriasis significantly faster and with a higher complete nail clearance rate by week 24 compared with ustekinumab in a head-to-head phase 3b randomized trial, Yves Dutronc, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This is a clinically important finding because – as dermatologists and psoriasis patients well know – nail and skin psoriasis are two different animals.
He presented a prespecified secondary analysis of the randomized, phase 3b, multicenter IXORA-S trial. The study pit the interleukin-17A inhibitor ixekizumab (Taltz) head-to-head against the interleukin 12/23 inhibitor ustekinumab (Stelara). The primary endpoint, which was the PASI 90 improvement rate, has previously been reported: 73% in the ixekizumab group versus 42% in the ustekinumab group at week 12, and 83% versus 59% at week 24. And ixekizumab’s superior efficacy was achieved with a safety profile similar to that of ustekinumab (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:1014-23).
However, change in PASI score or Investigator’s Global Assessment isn’t informative regarding a patient’s change in nail psoriasis status. This was the impetus for the secondary analysis focused on the IXORA-S subgroup with baseline fingernail psoriasis. For this purpose, Dr. Dutronc and his coinvestigators used as their metric the change over time in the Nail Psoriasis Severity Index (NAPSI) total score, which entails a quadrant-by-quadrant assessment of every fingernail.
By play of chance, the 84 patients randomized to ixekizumab had slightly more severe nail psoriasis at baseline than that of the 105 ustekinumab patients. Their mean baseline NAPSI total score was 28.3, compared with 24.8 for the ustekinumab group. More than one-quarter of patients in the ixekizumab arm had a baseline NAPSI score greater than 43, whereas the top quartile of nail psoriasis severity in the ustekinumab group began with a NAPSI score above 34.
Not surprisingly, not much happened in terms of improvement in nail appearance in the first 12 weeks, since new nail grows slowly. But by week 8 the between-group difference in improvement in NAPSI score had become significant in favor of ixekizumab, with a mean 12.9-point reduction from baseline versus a 5.6-point drop in the ustekinumab group. This difference continued to grow over time, such that at week 24 the ixekizumab had a mean 19.9-point reduction, compared with a 13.2-point decrease for the ustekinumab group.
At week 12, 15.5% of the ixekizumab group and 11.3% of the ustekinumab group had reached complete clearance of their fingernail psoriasis. At week 24, complete clearance had been achieved in 48.8% of the ixekizumab group and 22.9% of patients on ustekinumab.
This is an interim analysis. Final results of the IXORA-S nail psoriasis substudy will be reported at 52 weeks of follow-up.
SOURCE: Dutronc Y. https://eadvgeneva2017.org/
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: At week 24, complete clearance of fingernail psoriasis was documented in 49% of patients on ixekizumab and 23% on ustekinumab.
Study details: This secondary analysis of the randomized, multicenter, prospective, phase 3b IXORA-S trial included 189 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis with fingernail involvement.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly and presented by a company employee.
Source: Dutronc Y. https://eadvgeneva2017.org
Pearls in Dermatology: 2017
The Pearls in Dermatology collection consists of our popular pearls from the year in one convenient file. Topics include:
- Nail psoriasis and psoriasis on the hands and feet
- Genital wart treatment
- Isotretinoin for acne
- Cosmeceuticals for rosacea
- Surgical technique with the flexible scalpel blade
Editor’s Commentary provided by Vincent A. DeLeo, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Cutis.
Save this collection, print it, and/or share it with your colleagues. We hope this comprehensive collection will positively impact how you manage patients.
The Pearls in Dermatology collection consists of our popular pearls from the year in one convenient file. Topics include:
- Nail psoriasis and psoriasis on the hands and feet
- Genital wart treatment
- Isotretinoin for acne
- Cosmeceuticals for rosacea
- Surgical technique with the flexible scalpel blade
Editor’s Commentary provided by Vincent A. DeLeo, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Cutis.
Save this collection, print it, and/or share it with your colleagues. We hope this comprehensive collection will positively impact how you manage patients.
The Pearls in Dermatology collection consists of our popular pearls from the year in one convenient file. Topics include:
- Nail psoriasis and psoriasis on the hands and feet
- Genital wart treatment
- Isotretinoin for acne
- Cosmeceuticals for rosacea
- Surgical technique with the flexible scalpel blade
Editor’s Commentary provided by Vincent A. DeLeo, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Cutis.
Save this collection, print it, and/or share it with your colleagues. We hope this comprehensive collection will positively impact how you manage patients.
Mood changes reported in cases of methotrexate use for dermatologic disease
, said Trisha Bhat and Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, both of Washington University, St. Louis.
Neurotoxicity with low-dose methotrexate often has been described when used to treat rheumatologic disease, the investigators said, but not in the dermatologic literature – although CNS symptoms such as dizziness and headache have been described in both.
An 8-year-old girl with psoriasis vulgaris and no prior psychiatric history began weekly subcutaneous methotrexate 12.5 mg (0.23 mg/kg) with folic acid supplementation 6 days per week after failing topical therapy. Her parents noticed severe irritability right away and fluctuating mood changes over the next 2 months. At first, she was angry and unsettled, with depressed mood; her irritability became less frequent later, but she said she wanted to hurt someone else. After stopping methotrexate, her mood returned to normal within 2 weeks.
It is unclear how methotrexate affects mood, but recent evidence suggests that abnormalities in synaptic plasticity are involved in mood changes, and there is evidence that mice treated with methotrexate show changes in synaptic plasticity. Methotrexate also increases extracellular adenosine, which affects neuronal excitability and synaptic plasticity, Ms. Bhat and Dr. Coughlin observed. Methotrexate also affects glucose metabolism in rats, and regional metabolic disturbances occur in a number of psychiatric disorders.
Read more at Pediatric Dermatology (2018 Jan 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.13406).
, said Trisha Bhat and Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, both of Washington University, St. Louis.
Neurotoxicity with low-dose methotrexate often has been described when used to treat rheumatologic disease, the investigators said, but not in the dermatologic literature – although CNS symptoms such as dizziness and headache have been described in both.
An 8-year-old girl with psoriasis vulgaris and no prior psychiatric history began weekly subcutaneous methotrexate 12.5 mg (0.23 mg/kg) with folic acid supplementation 6 days per week after failing topical therapy. Her parents noticed severe irritability right away and fluctuating mood changes over the next 2 months. At first, she was angry and unsettled, with depressed mood; her irritability became less frequent later, but she said she wanted to hurt someone else. After stopping methotrexate, her mood returned to normal within 2 weeks.
It is unclear how methotrexate affects mood, but recent evidence suggests that abnormalities in synaptic plasticity are involved in mood changes, and there is evidence that mice treated with methotrexate show changes in synaptic plasticity. Methotrexate also increases extracellular adenosine, which affects neuronal excitability and synaptic plasticity, Ms. Bhat and Dr. Coughlin observed. Methotrexate also affects glucose metabolism in rats, and regional metabolic disturbances occur in a number of psychiatric disorders.
Read more at Pediatric Dermatology (2018 Jan 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.13406).
, said Trisha Bhat and Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, both of Washington University, St. Louis.
Neurotoxicity with low-dose methotrexate often has been described when used to treat rheumatologic disease, the investigators said, but not in the dermatologic literature – although CNS symptoms such as dizziness and headache have been described in both.
An 8-year-old girl with psoriasis vulgaris and no prior psychiatric history began weekly subcutaneous methotrexate 12.5 mg (0.23 mg/kg) with folic acid supplementation 6 days per week after failing topical therapy. Her parents noticed severe irritability right away and fluctuating mood changes over the next 2 months. At first, she was angry and unsettled, with depressed mood; her irritability became less frequent later, but she said she wanted to hurt someone else. After stopping methotrexate, her mood returned to normal within 2 weeks.
It is unclear how methotrexate affects mood, but recent evidence suggests that abnormalities in synaptic plasticity are involved in mood changes, and there is evidence that mice treated with methotrexate show changes in synaptic plasticity. Methotrexate also increases extracellular adenosine, which affects neuronal excitability and synaptic plasticity, Ms. Bhat and Dr. Coughlin observed. Methotrexate also affects glucose metabolism in rats, and regional metabolic disturbances occur in a number of psychiatric disorders.
Read more at Pediatric Dermatology (2018 Jan 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.13406).
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Prior biologic exposure doesn’t diminish ixekizumab’s efficacy
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
GENEVA – Psoriasis patients switched to ixekizumab after previous exposure to another interleukin-17 inhibitor respond as well as those who are IL-17 antagonist naive, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This finding is of importance in real-world clinical practice because it’s not at all uncommon for psoriasis patients on one biologic to have to switch to another because of insufficient efficacy, side effects, or a change in insurance coverage. Physicians would like to know what sort of responses can be expected to whatever agent they prescribe next.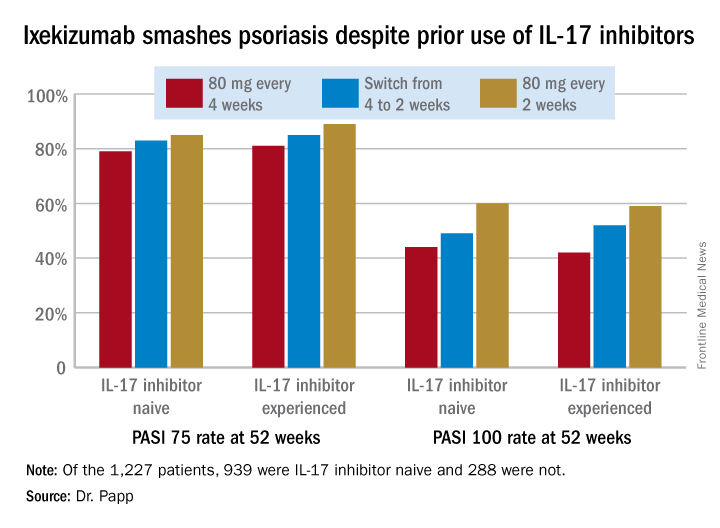
However, that was not a problem in this secondary analysis of a large clinical trial whose primary purpose was to evaluate the relative safety and efficacy of ixekizumab (Taltz) when dosed every 2 weeks versus every 4 weeks.
“I think what we have seen here is a very compelling story: , nor for that matter does it appear to impact safety,” the dermatologist said.
He reported on 1,227 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were randomized to ixekizumab at 80 mg every 2 or 4 weeks following an initial 160 mg loading dose. Among those who started out on ixekizumab every 4 weeks, 306 patients got a per-protocol dose adjustment to biweekly therapy because of an insufficient response to monthly dosing as defined by a Physician’s Global Assessment score of 2 or more on two consecutive office visits during study weeks 12-40.
A total of 939 patients were IL-17 inhibitor naive. The other 288 had previously been on the IL-17 antagonists brodalumab (Siliq) or secukinumab (Cosentyx). The two groups had similar baseline demographics with the exception that the experienced cohort had on average a 22.2-year duration of psoriasis, 3.7 years more than IL-17 antagonist-naive patients.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 52 didn’t differ significantly between the IL-17 inhibitor-naive and -experienced groups. In fact, patients with prior exposure to other IL-17 antagonists showed a consistent trend for slightly higher response rates (see graphic).
It was clear from this analysis that dosing ixekizumab every 2 weeks provides significantly better efficacy than was dosing every 4 weeks, Dr. Papp noted. Yet the approved dosing is 160 mg at week 0, followed by 80 mg at weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12, then 80 mg every 4 weeks.
No new safety issues arose in this study. The only difference between the naive and experienced groups was a lower rate of allergic reactions/hypersensitivity in the experienced group. For example, in patients on ixekizumab every 2 weeks for the entire 52-week study period the incidence of such reactions was 11.5% in the IL-17 antagonist-naive group, compared with 4.1% in the experienced cohort. This isn’t really surprising, according to Dr. Papp.
“Most injection site reactions occur in the newbies,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly. Dr. Papp serves as a consultant and/or adviser to Lilly and numerous other pharmaceutical companies involved in the development of dermatologic therapies.
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
GENEVA – Psoriasis patients switched to ixekizumab after previous exposure to another interleukin-17 inhibitor respond as well as those who are IL-17 antagonist naive, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This finding is of importance in real-world clinical practice because it’s not at all uncommon for psoriasis patients on one biologic to have to switch to another because of insufficient efficacy, side effects, or a change in insurance coverage. Physicians would like to know what sort of responses can be expected to whatever agent they prescribe next.
However, that was not a problem in this secondary analysis of a large clinical trial whose primary purpose was to evaluate the relative safety and efficacy of ixekizumab (Taltz) when dosed every 2 weeks versus every 4 weeks.
“I think what we have seen here is a very compelling story: , nor for that matter does it appear to impact safety,” the dermatologist said.
He reported on 1,227 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were randomized to ixekizumab at 80 mg every 2 or 4 weeks following an initial 160 mg loading dose. Among those who started out on ixekizumab every 4 weeks, 306 patients got a per-protocol dose adjustment to biweekly therapy because of an insufficient response to monthly dosing as defined by a Physician’s Global Assessment score of 2 or more on two consecutive office visits during study weeks 12-40.
A total of 939 patients were IL-17 inhibitor naive. The other 288 had previously been on the IL-17 antagonists brodalumab (Siliq) or secukinumab (Cosentyx). The two groups had similar baseline demographics with the exception that the experienced cohort had on average a 22.2-year duration of psoriasis, 3.7 years more than IL-17 antagonist-naive patients.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 52 didn’t differ significantly between the IL-17 inhibitor-naive and -experienced groups. In fact, patients with prior exposure to other IL-17 antagonists showed a consistent trend for slightly higher response rates (see graphic).
It was clear from this analysis that dosing ixekizumab every 2 weeks provides significantly better efficacy than was dosing every 4 weeks, Dr. Papp noted. Yet the approved dosing is 160 mg at week 0, followed by 80 mg at weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12, then 80 mg every 4 weeks.
No new safety issues arose in this study. The only difference between the naive and experienced groups was a lower rate of allergic reactions/hypersensitivity in the experienced group. For example, in patients on ixekizumab every 2 weeks for the entire 52-week study period the incidence of such reactions was 11.5% in the IL-17 antagonist-naive group, compared with 4.1% in the experienced cohort. This isn’t really surprising, according to Dr. Papp.
“Most injection site reactions occur in the newbies,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly. Dr. Papp serves as a consultant and/or adviser to Lilly and numerous other pharmaceutical companies involved in the development of dermatologic therapies.
REPORTING FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
GENEVA – Psoriasis patients switched to ixekizumab after previous exposure to another interleukin-17 inhibitor respond as well as those who are IL-17 antagonist naive, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
This finding is of importance in real-world clinical practice because it’s not at all uncommon for psoriasis patients on one biologic to have to switch to another because of insufficient efficacy, side effects, or a change in insurance coverage. Physicians would like to know what sort of responses can be expected to whatever agent they prescribe next.
However, that was not a problem in this secondary analysis of a large clinical trial whose primary purpose was to evaluate the relative safety and efficacy of ixekizumab (Taltz) when dosed every 2 weeks versus every 4 weeks.
“I think what we have seen here is a very compelling story: , nor for that matter does it appear to impact safety,” the dermatologist said.
He reported on 1,227 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who were randomized to ixekizumab at 80 mg every 2 or 4 weeks following an initial 160 mg loading dose. Among those who started out on ixekizumab every 4 weeks, 306 patients got a per-protocol dose adjustment to biweekly therapy because of an insufficient response to monthly dosing as defined by a Physician’s Global Assessment score of 2 or more on two consecutive office visits during study weeks 12-40.
A total of 939 patients were IL-17 inhibitor naive. The other 288 had previously been on the IL-17 antagonists brodalumab (Siliq) or secukinumab (Cosentyx). The two groups had similar baseline demographics with the exception that the experienced cohort had on average a 22.2-year duration of psoriasis, 3.7 years more than IL-17 antagonist-naive patients.
In an intent-to-treat analysis, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 75, 90, and 100 responses at week 52 didn’t differ significantly between the IL-17 inhibitor-naive and -experienced groups. In fact, patients with prior exposure to other IL-17 antagonists showed a consistent trend for slightly higher response rates (see graphic).
It was clear from this analysis that dosing ixekizumab every 2 weeks provides significantly better efficacy than was dosing every 4 weeks, Dr. Papp noted. Yet the approved dosing is 160 mg at week 0, followed by 80 mg at weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12, then 80 mg every 4 weeks.
No new safety issues arose in this study. The only difference between the naive and experienced groups was a lower rate of allergic reactions/hypersensitivity in the experienced group. For example, in patients on ixekizumab every 2 weeks for the entire 52-week study period the incidence of such reactions was 11.5% in the IL-17 antagonist-naive group, compared with 4.1% in the experienced cohort. This isn’t really surprising, according to Dr. Papp.
“Most injection site reactions occur in the newbies,” he said.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly. Dr. Papp serves as a consultant and/or adviser to Lilly and numerous other pharmaceutical companies involved in the development of dermatologic therapies.
Scaly Pink Patches: Differentiating Psoriasis From Basal Cell Carcinoma
Dermoscopy increases diagnostic accuracy in the analysis of skin growths.1,2 Recently the use of dermoscopy has broadened to include inflammatory dermatoses and skin infections.3 To substantiate the value of dermoscopy in assessing psoriasis, we performed a systematic review of the literature and briefly reviewed 31 articles. We also report a case that highlights the differences between psoriasis and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) under dermoscopic examination, and we discuss the literature on the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis with an emphasis on the relative sensitivities and specificities of dermoscopic findings for psoriasis and for BCC.
Case Report
A 63-year-old man with psoriasis and a history of BCC presented for follow-up of psoriasis, which was well-controlled on etanercept. The physical examination was remarkable for scaly pink papules scattered on the trunk and extremities. A new larger red-pink patch was located on the left lower back (Figure 1). Dermoscopic evaluation of the new patch revealed shiny white lines and branching blood vessels (Figure 2).
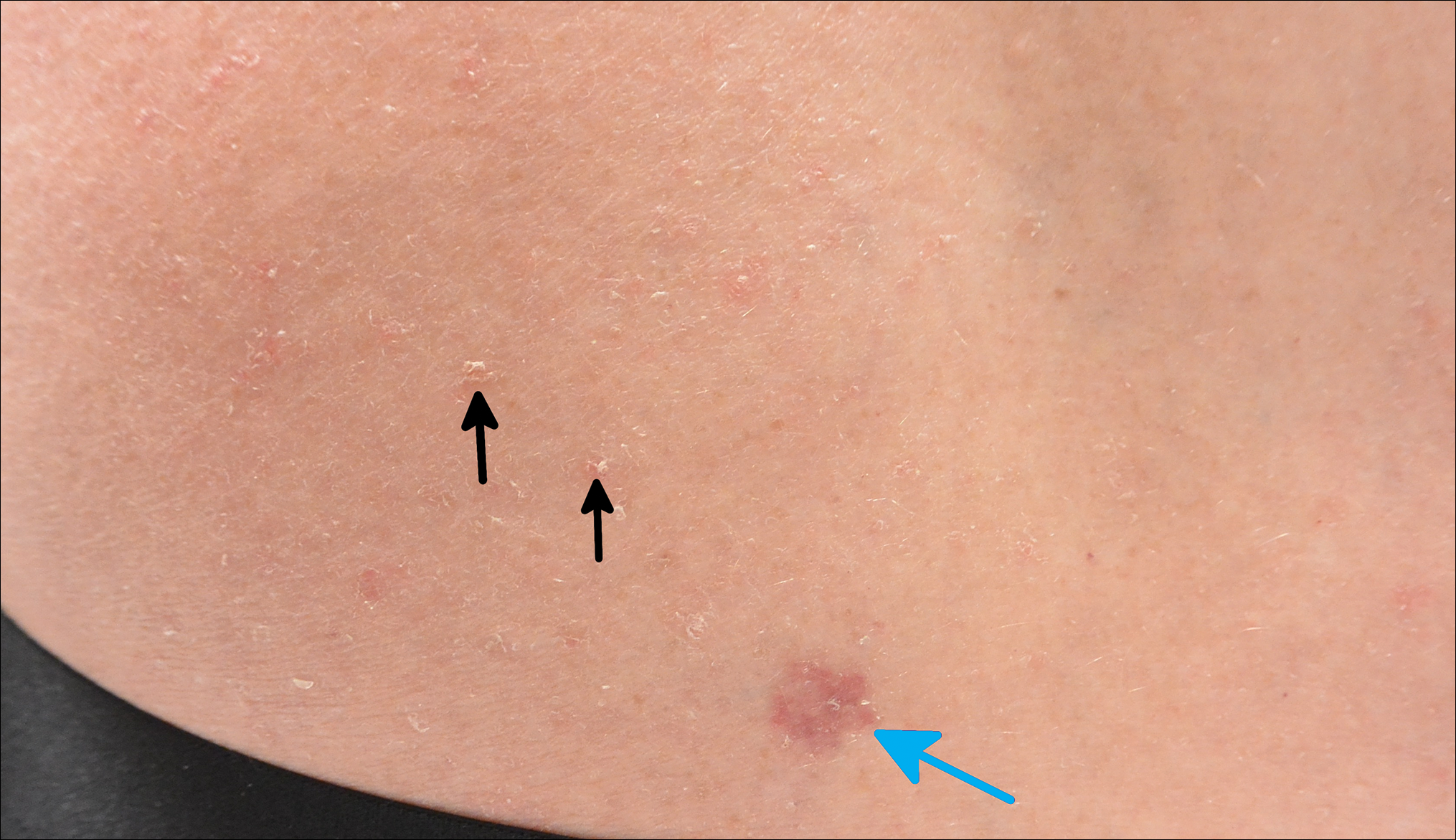
Comment
The clinical morphology of psoriasis and BCC can be similar, and dermoscopy can help in differentiating between the 2 conditions.
Literature Search on Dermoscopy and Psoriasis
We performed a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to review the published literature on dermoscopy and psoriasis. Two reviewers (C.H. and L.C.) searched for psoriasis paired with the terms dermoscopy or dermatoscopy or epiluminescence microscopy. Only English-language articles published between 1996 and 2016 were included in the search. Articles that focused solely on confocal microscopy were excluded. Article titles and abstracts were evaluated and articles that omitted mention of dermoscopy and psoriasis were excluded, yielding a total of 31 articles. Of these articles, only 2 discussed the specificity or sensitivity of the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Most of the articles were case reports and descriptive cross-sectional studies. The reports addressed multiple subtypes of psoriasis, but reports on psoriasis vulgaris and scalp psoriasis were most common (Table). Lallas et al6 provided a comprehensive descriptive review of the main findings on dermoscopy for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions, but it lacked a comparison between psoriasis and BCC or data on the sensitivity and specificity of the findings. Two studies reported sensitivity and specificity values for the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Pan et al5 reported a 98% diagnostic probability of psoriasis if red dots, homogeneous vascular pattern, and a light red background are all present. Additionally, they reported that the presence of 4 of 6 criteria for BCC—scattered vascular pattern, arborizing microvessels, telangiectatic or atypical vessels, milky-pink background, and brown dots⁄globules—yielded a diagnostic probability of 99%.5 Similarly, Lallas et al6 demonstrated that the presence of dotted vessels alone is not sufficient to presume a diagnosis of psoriasis, as this finding can be seen in other inflammatory skin conditions. However, “the combination of regularly distributed dotted vessels over a light red background associated with diffuse white scales was highly predictive of [plaque psoriasis] and allowed a correct diagnosis with 88.0% specificity and 84.9% sensitivity.”4 Figure 3 shows a dermoscopic image of plaque psoriasis that demonstrates these findings. The remaining literature corroborated this evidence, with the most commonly reported dermoscopic findings of psoriasis being red dots, red globules, glomerular vessels (also known as twisted capillary loops), red globular ring
Dermoscopy and BCC
Much has been published on the dermoscopic findings of BCC.5,13-15 The dermoscopic findings of BCC include large blue-gray ovoid nests, leaflike areas, spoke-wheel–like areas, arborizing vessels (telangiectasia), and ulceration.15 Superficial BCC is characterized by short fine or arborizing telangiectasia, shallow erosions, and shiny white areas.15 The positive predictive value of dermoscopy in BCC is as high as 97%.16 Additionally, multiple studies report a sensitivity of 95% to 99%5,13,14 and a specificity of 79% to 99% in the use of dermoscopy for identifying BCC. According to Pan et al,5 the most sensitive finding for BCC is a scattered vascular pattern (97%), while the most specific finding is arborizing microvessels (99%).
Utility of Dermoscopy
Our case of a 63-year-old man with a history of psoriasis and BCC highlights the usefulness of dermoscopy in accurately determining the features of each condition. Additionally, dermoscopy aids in differentiating between psoriasis and squamous cell carcinoma. In contrast to the dotted vessels seen in psoriasis, squamous cell carcinomas often have peripheral hairpin (glomerular) vessels.17
If future reports confirm dermoscopy’s utility in accurately diagnosing psoriasis, fewer biopsies may be needed when evaluating patients with new rashes. Furthermore, dermoscopy may expedite treatment of psoriasis (as it can for malignant conditions) by obviating the wait for pathology results currently needed to initiate systemic treatment. For patients with psoriasis who also have sun-damaged skin, dermoscopy may assist in differentiating pink patches and plaques of psoriasis from skin cancer, such as superficial BCCs, which often have shiny white lines not seen in psoriasis.15
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Vestergaard ME, Macaskill P, Holt PE, et al. Dermoscopy compared with naked eye examination for the diagnosis of primary melanoma: a meta-analysis of studies performed in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:669-676.
- Lallas A, Giacomel J, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: practical tips for the clinician. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:514-526.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Tzellos TG, et al. Accuracy of dermoscopic criteria for the diagnosis of psoriasis, dermatitis, lichen planus and pityriasis rosea. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1198-1205.
- Pan Y, Chamberlain AJ, Bailey M, et al. Dermatoscopy aids in the diagnosis of the solitary red scaly patch or plaque–features distinguishing superficial basal cell carcinoma, intraepidermal carcinoma, and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:268-274.
- Lallas A, Apalla Z, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopic pattern of psoriatic lesions on specific body sites. Dermatology. 2014;228:250-254.
- Almeida MC, Romiti R, Doche I, et al. Psoriatic scarring alopecia. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:29-31.
- Zalaudek I, Argenziano G. Dermoscopy subpatterns of inflammatory skin disorders. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:808.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Hair and scalp dermatoscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1040-1048.
- Vázquez-López F, Zaballos P, Fueyo-Casado A, et al. A dermoscopy subpattern of plaque-type psoriasis: red globular rings. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1612.
- Lacarrubba F, Nasca MR, Micali G. Videodermatoscopy enhances diagnostic capability in psoriatic balanitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1084-1086.
- Liebman TN, Wang SQ. Detection of early basal cell carcinoma with dermoscopy in a patient with psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:12.
- Menzies SW, Westerhoff K, Rabinovitz H, et al. Surface microscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1012-1016.
- Altamura D, Menzies SW, Argenziano G, et al. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:67-75.
- Marghoob AA, Malvehy J, Braun RP, eds. An Atlas of Dermoscopy. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Nelson SA, Scope A, Rishpon A, et al. Accuracy and confidence in the clinical diagnosis of basal cell cancer using dermoscopy and reflex confocal microscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1351-1356.
- Zalaudek I, Kreusch J, Giacomel J, et al. How to diagnose nonpigmented skin tumors: a review of vascular structures seen with dermoscopy: part I. melanocytic skin tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:361-374.
Dermoscopy increases diagnostic accuracy in the analysis of skin growths.1,2 Recently the use of dermoscopy has broadened to include inflammatory dermatoses and skin infections.3 To substantiate the value of dermoscopy in assessing psoriasis, we performed a systematic review of the literature and briefly reviewed 31 articles. We also report a case that highlights the differences between psoriasis and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) under dermoscopic examination, and we discuss the literature on the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis with an emphasis on the relative sensitivities and specificities of dermoscopic findings for psoriasis and for BCC.
Case Report
A 63-year-old man with psoriasis and a history of BCC presented for follow-up of psoriasis, which was well-controlled on etanercept. The physical examination was remarkable for scaly pink papules scattered on the trunk and extremities. A new larger red-pink patch was located on the left lower back (Figure 1). Dermoscopic evaluation of the new patch revealed shiny white lines and branching blood vessels (Figure 2).


Comment
The clinical morphology of psoriasis and BCC can be similar, and dermoscopy can help in differentiating between the 2 conditions.
Literature Search on Dermoscopy and Psoriasis
We performed a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to review the published literature on dermoscopy and psoriasis. Two reviewers (C.H. and L.C.) searched for psoriasis paired with the terms dermoscopy or dermatoscopy or epiluminescence microscopy. Only English-language articles published between 1996 and 2016 were included in the search. Articles that focused solely on confocal microscopy were excluded. Article titles and abstracts were evaluated and articles that omitted mention of dermoscopy and psoriasis were excluded, yielding a total of 31 articles. Of these articles, only 2 discussed the specificity or sensitivity of the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Most of the articles were case reports and descriptive cross-sectional studies. The reports addressed multiple subtypes of psoriasis, but reports on psoriasis vulgaris and scalp psoriasis were most common (Table). Lallas et al6 provided a comprehensive descriptive review of the main findings on dermoscopy for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions, but it lacked a comparison between psoriasis and BCC or data on the sensitivity and specificity of the findings. Two studies reported sensitivity and specificity values for the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Pan et al5 reported a 98% diagnostic probability of psoriasis if red dots, homogeneous vascular pattern, and a light red background are all present. Additionally, they reported that the presence of 4 of 6 criteria for BCC—scattered vascular pattern, arborizing microvessels, telangiectatic or atypical vessels, milky-pink background, and brown dots⁄globules—yielded a diagnostic probability of 99%.5 Similarly, Lallas et al6 demonstrated that the presence of dotted vessels alone is not sufficient to presume a diagnosis of psoriasis, as this finding can be seen in other inflammatory skin conditions. However, “the combination of regularly distributed dotted vessels over a light red background associated with diffuse white scales was highly predictive of [plaque psoriasis] and allowed a correct diagnosis with 88.0% specificity and 84.9% sensitivity.”4 Figure 3 shows a dermoscopic image of plaque psoriasis that demonstrates these findings. The remaining literature corroborated this evidence, with the most commonly reported dermoscopic findings of psoriasis being red dots, red globules, glomerular vessels (also known as twisted capillary loops), red globular ring

Dermoscopy and BCC
Much has been published on the dermoscopic findings of BCC.5,13-15 The dermoscopic findings of BCC include large blue-gray ovoid nests, leaflike areas, spoke-wheel–like areas, arborizing vessels (telangiectasia), and ulceration.15 Superficial BCC is characterized by short fine or arborizing telangiectasia, shallow erosions, and shiny white areas.15 The positive predictive value of dermoscopy in BCC is as high as 97%.16 Additionally, multiple studies report a sensitivity of 95% to 99%5,13,14 and a specificity of 79% to 99% in the use of dermoscopy for identifying BCC. According to Pan et al,5 the most sensitive finding for BCC is a scattered vascular pattern (97%), while the most specific finding is arborizing microvessels (99%).
Utility of Dermoscopy
Our case of a 63-year-old man with a history of psoriasis and BCC highlights the usefulness of dermoscopy in accurately determining the features of each condition. Additionally, dermoscopy aids in differentiating between psoriasis and squamous cell carcinoma. In contrast to the dotted vessels seen in psoriasis, squamous cell carcinomas often have peripheral hairpin (glomerular) vessels.17
If future reports confirm dermoscopy’s utility in accurately diagnosing psoriasis, fewer biopsies may be needed when evaluating patients with new rashes. Furthermore, dermoscopy may expedite treatment of psoriasis (as it can for malignant conditions) by obviating the wait for pathology results currently needed to initiate systemic treatment. For patients with psoriasis who also have sun-damaged skin, dermoscopy may assist in differentiating pink patches and plaques of psoriasis from skin cancer, such as superficial BCCs, which often have shiny white lines not seen in psoriasis.15
Dermoscopy increases diagnostic accuracy in the analysis of skin growths.1,2 Recently the use of dermoscopy has broadened to include inflammatory dermatoses and skin infections.3 To substantiate the value of dermoscopy in assessing psoriasis, we performed a systematic review of the literature and briefly reviewed 31 articles. We also report a case that highlights the differences between psoriasis and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) under dermoscopic examination, and we discuss the literature on the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis with an emphasis on the relative sensitivities and specificities of dermoscopic findings for psoriasis and for BCC.
Case Report
A 63-year-old man with psoriasis and a history of BCC presented for follow-up of psoriasis, which was well-controlled on etanercept. The physical examination was remarkable for scaly pink papules scattered on the trunk and extremities. A new larger red-pink patch was located on the left lower back (Figure 1). Dermoscopic evaluation of the new patch revealed shiny white lines and branching blood vessels (Figure 2).


Comment
The clinical morphology of psoriasis and BCC can be similar, and dermoscopy can help in differentiating between the 2 conditions.
Literature Search on Dermoscopy and Psoriasis
We performed a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to review the published literature on dermoscopy and psoriasis. Two reviewers (C.H. and L.C.) searched for psoriasis paired with the terms dermoscopy or dermatoscopy or epiluminescence microscopy. Only English-language articles published between 1996 and 2016 were included in the search. Articles that focused solely on confocal microscopy were excluded. Article titles and abstracts were evaluated and articles that omitted mention of dermoscopy and psoriasis were excluded, yielding a total of 31 articles. Of these articles, only 2 discussed the specificity or sensitivity of the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Most of the articles were case reports and descriptive cross-sectional studies. The reports addressed multiple subtypes of psoriasis, but reports on psoriasis vulgaris and scalp psoriasis were most common (Table). Lallas et al6 provided a comprehensive descriptive review of the main findings on dermoscopy for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin conditions, but it lacked a comparison between psoriasis and BCC or data on the sensitivity and specificity of the findings. Two studies reported sensitivity and specificity values for the dermoscopic findings of psoriasis.4,5 Pan et al5 reported a 98% diagnostic probability of psoriasis if red dots, homogeneous vascular pattern, and a light red background are all present. Additionally, they reported that the presence of 4 of 6 criteria for BCC—scattered vascular pattern, arborizing microvessels, telangiectatic or atypical vessels, milky-pink background, and brown dots⁄globules—yielded a diagnostic probability of 99%.5 Similarly, Lallas et al6 demonstrated that the presence of dotted vessels alone is not sufficient to presume a diagnosis of psoriasis, as this finding can be seen in other inflammatory skin conditions. However, “the combination of regularly distributed dotted vessels over a light red background associated with diffuse white scales was highly predictive of [plaque psoriasis] and allowed a correct diagnosis with 88.0% specificity and 84.9% sensitivity.”4 Figure 3 shows a dermoscopic image of plaque psoriasis that demonstrates these findings. The remaining literature corroborated this evidence, with the most commonly reported dermoscopic findings of psoriasis being red dots, red globules, glomerular vessels (also known as twisted capillary loops), red globular ring

Dermoscopy and BCC
Much has been published on the dermoscopic findings of BCC.5,13-15 The dermoscopic findings of BCC include large blue-gray ovoid nests, leaflike areas, spoke-wheel–like areas, arborizing vessels (telangiectasia), and ulceration.15 Superficial BCC is characterized by short fine or arborizing telangiectasia, shallow erosions, and shiny white areas.15 The positive predictive value of dermoscopy in BCC is as high as 97%.16 Additionally, multiple studies report a sensitivity of 95% to 99%5,13,14 and a specificity of 79% to 99% in the use of dermoscopy for identifying BCC. According to Pan et al,5 the most sensitive finding for BCC is a scattered vascular pattern (97%), while the most specific finding is arborizing microvessels (99%).
Utility of Dermoscopy
Our case of a 63-year-old man with a history of psoriasis and BCC highlights the usefulness of dermoscopy in accurately determining the features of each condition. Additionally, dermoscopy aids in differentiating between psoriasis and squamous cell carcinoma. In contrast to the dotted vessels seen in psoriasis, squamous cell carcinomas often have peripheral hairpin (glomerular) vessels.17
If future reports confirm dermoscopy’s utility in accurately diagnosing psoriasis, fewer biopsies may be needed when evaluating patients with new rashes. Furthermore, dermoscopy may expedite treatment of psoriasis (as it can for malignant conditions) by obviating the wait for pathology results currently needed to initiate systemic treatment. For patients with psoriasis who also have sun-damaged skin, dermoscopy may assist in differentiating pink patches and plaques of psoriasis from skin cancer, such as superficial BCCs, which often have shiny white lines not seen in psoriasis.15
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Vestergaard ME, Macaskill P, Holt PE, et al. Dermoscopy compared with naked eye examination for the diagnosis of primary melanoma: a meta-analysis of studies performed in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:669-676.
- Lallas A, Giacomel J, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: practical tips for the clinician. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:514-526.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Tzellos TG, et al. Accuracy of dermoscopic criteria for the diagnosis of psoriasis, dermatitis, lichen planus and pityriasis rosea. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1198-1205.
- Pan Y, Chamberlain AJ, Bailey M, et al. Dermatoscopy aids in the diagnosis of the solitary red scaly patch or plaque–features distinguishing superficial basal cell carcinoma, intraepidermal carcinoma, and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:268-274.
- Lallas A, Apalla Z, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopic pattern of psoriatic lesions on specific body sites. Dermatology. 2014;228:250-254.
- Almeida MC, Romiti R, Doche I, et al. Psoriatic scarring alopecia. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:29-31.
- Zalaudek I, Argenziano G. Dermoscopy subpatterns of inflammatory skin disorders. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:808.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Hair and scalp dermatoscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1040-1048.
- Vázquez-López F, Zaballos P, Fueyo-Casado A, et al. A dermoscopy subpattern of plaque-type psoriasis: red globular rings. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1612.
- Lacarrubba F, Nasca MR, Micali G. Videodermatoscopy enhances diagnostic capability in psoriatic balanitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1084-1086.
- Liebman TN, Wang SQ. Detection of early basal cell carcinoma with dermoscopy in a patient with psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:12.
- Menzies SW, Westerhoff K, Rabinovitz H, et al. Surface microscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1012-1016.
- Altamura D, Menzies SW, Argenziano G, et al. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:67-75.
- Marghoob AA, Malvehy J, Braun RP, eds. An Atlas of Dermoscopy. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Nelson SA, Scope A, Rishpon A, et al. Accuracy and confidence in the clinical diagnosis of basal cell cancer using dermoscopy and reflex confocal microscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1351-1356.
- Zalaudek I, Kreusch J, Giacomel J, et al. How to diagnose nonpigmented skin tumors: a review of vascular structures seen with dermoscopy: part I. melanocytic skin tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:361-374.
- Kittler H, Pehamberger H, Wolff K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy. Lancet Oncol. 2002;3:159-165.
- Vestergaard ME, Macaskill P, Holt PE, et al. Dermoscopy compared with naked eye examination for the diagnosis of primary melanoma: a meta-analysis of studies performed in a clinical setting. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:669-676.
- Lallas A, Giacomel J, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopy in general dermatology: practical tips for the clinician. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:514-526.
- Lallas A, Kyrgidis A, Tzellos TG, et al. Accuracy of dermoscopic criteria for the diagnosis of psoriasis, dermatitis, lichen planus and pityriasis rosea. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1198-1205.
- Pan Y, Chamberlain AJ, Bailey M, et al. Dermatoscopy aids in the diagnosis of the solitary red scaly patch or plaque–features distinguishing superficial basal cell carcinoma, intraepidermal carcinoma, and psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:268-274.
- Lallas A, Apalla Z, Argenziano G, et al. Dermoscopic pattern of psoriatic lesions on specific body sites. Dermatology. 2014;228:250-254.
- Almeida MC, Romiti R, Doche I, et al. Psoriatic scarring alopecia. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:29-31.
- Zalaudek I, Argenziano G. Dermoscopy subpatterns of inflammatory skin disorders. Arch Dermatol. 2006;142:808.
- Miteva M, Tosti A. Hair and scalp dermatoscopy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:1040-1048.
- Vázquez-López F, Zaballos P, Fueyo-Casado A, et al. A dermoscopy subpattern of plaque-type psoriasis: red globular rings. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:1612.
- Lacarrubba F, Nasca MR, Micali G. Videodermatoscopy enhances diagnostic capability in psoriatic balanitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:1084-1086.
- Liebman TN, Wang SQ. Detection of early basal cell carcinoma with dermoscopy in a patient with psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 2011;17:12.
- Menzies SW, Westerhoff K, Rabinovitz H, et al. Surface microscopy of pigmented basal cell carcinoma. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:1012-1016.
- Altamura D, Menzies SW, Argenziano G, et al. Dermatoscopy of basal cell carcinoma: morphologic variability of global and local features and accuracy of diagnosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:67-75.
- Marghoob AA, Malvehy J, Braun RP, eds. An Atlas of Dermoscopy. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2012.
- Nelson SA, Scope A, Rishpon A, et al. Accuracy and confidence in the clinical diagnosis of basal cell cancer using dermoscopy and reflex confocal microscopy. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:1351-1356.
- Zalaudek I, Kreusch J, Giacomel J, et al. How to diagnose nonpigmented skin tumors: a review of vascular structures seen with dermoscopy: part I. melanocytic skin tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63:361-374.
Practice Points
- Dermoscopy has been largely utilized for the evaluation of malignant lesions. It also is gaining traction in the evaluation of inflammatory dermatoses.
- Early distinction between basal cell carcinoma and psoriasis is important for both treatment options and health care costs.
Psoriasis Treatment in HIV-Positive Patients: A Systematic Review of Systemic Immunosuppressive Therapies
The prevalence of psoriasis among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–positive patients in the United States is reported to be approximately 1% to 3%, which is similar to the rates reported for the general population.1 Recalcitrant cases of psoriasis in patients with no history of the condition can be the initial manifestation of HIV infection. In patients with preexisting psoriasis, a flare of their disease can be seen following infection, and progression of HIV correlates with worsening psoriasis.2 Psoriatic arthropathy also affects 23% to 50% of HIV-positive patients with psoriasis worldwide, which may be higher than the general population,1 with more severe joint disease.
The management of psoriatic disease in the HIV-positive population is challenging. The current first-line recommendations for treatment include topical therapies, phototherapy, and highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), followed by oral retinoids as second-line agents.3 However, the clinical course of psoriasis in HIV-positive patients often is progressive and refractory2; therefore, these therapies often are inadequate to control both skin and joint manifestations. Most other currently available systemic therapies for psoriatic disease are immunosuppressive, which poses a distinct clinical challenge because HIV-positive patients are already immunocompromised.
There currently are many systemic immunosuppressive agents used for the treatment of psoriatic disease, including oral agents (eg, methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine), as well as newer biologic medications, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, and certolizumab pegol. Golimumab and certolizumab pegol currently are indicated for psoriatic arthritis only. Other newer biologic therapies include ustekinumab, which inhibits IL-12 and IL-23, and secukinumab, which inhibits IL-17A. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the most current literature to explore the efficacy and safety data as they pertain to systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals.
Methods
To investigate the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE (1985-2015) was conducted using the terms psoriasis and HIV and psoriatic arthritis and HIV combined with each of the following systemic immunosuppressive agents: methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, ustekinumab, and secukinumab. Pediatric cases and articles that were not available in the English language were excluded.
For each case, patient demographic information (ie, age, sex), prior failed psoriasis treatments, and history of HAART were documented. The dosing regimen of the systemic agent was noted when different from the US Food and Drug administration–approved dosage for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. The duration of immunosuppressive therapy as well as pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts (when available) were collected. The response to treatment and adverse effects were summarized.
Results
Our review of the literature yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab (Table). There were no reports of the use of hydroxyurea, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, or secukinumab to treat psoriatic disease in this patient population.
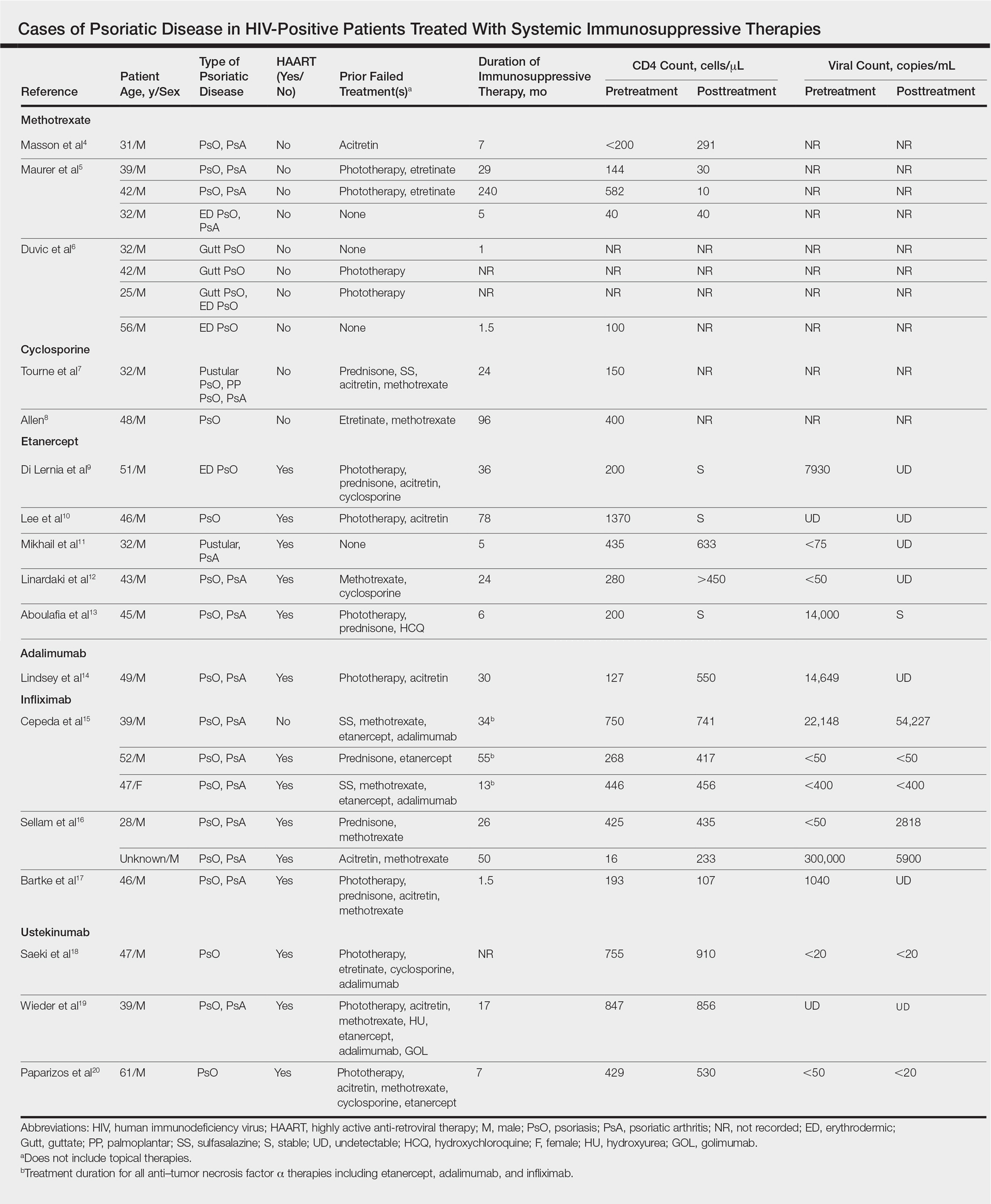
Methotrexate
Eight individual cases of methotrexate used to treat psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients were reported.4-6 Duvic et al6 described 4 patients with psoriatic disease that was treated with methotrexate with varying efficacy. One patient developed toxic encephalopathy, which improved after discontinuation of methotrexate; however, he died 5 months later from pneumocystis pneumonia. In this early study, none of the 4 patients were on antiretroviral therapy for HIV.6
In the cases reported by Masson et al4 and Maurer et al,5 4 patients were treated with a single antiretroviral agent and received appropriate prophylaxis against opportunistic infections. In 1 case, methotrexate was given at a chemotherapeutic dose of 525 mg once weekly for Kaposi sarcoma.4 In 2 of 4 cases, the patients developed pneumocystis pneumonia.4,5
Cyclosporine
There were 2 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with cyclosporine in HIV-positive patients.7,8 Skin and joint manifestations improved rapidly without reports of infection for 27 and 8 years.8 Both patients were treated with one antiretroviral agent.7,8
Etanercept
There were 5 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with etanercept. In all 5 cases the patients were on HAART, and the CD4 count increased or remained stable and viral count became undetectable or remained stable following treatment.9-13 In 2 cases, the patient also had hepatitis C virus, which remained stable throughout the treatment period.9,12 The maximum duration of treatment was 6 years, with only 1 reported adverse event.13 In this case reported by Aboulafia et al,13 the patient experienced recurrent polymicrobial infections, including enterococcal cellulitis, cystitis, and bacteremia, as well as pseudomonas pneumonia and septic arthritis. Therapy was discontinued at 6 months. Four months after discontinuation of etanercept, the patient died from infectious causes.13
Adalimumab
There was 1 case of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. In this case, the patient was on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved substantially after 30 months of treatment.14
Infliximab
Six individual cases of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with infliximab were reported.15-17 In a report by Cepeda et al,15 HIV-positive patients with various rheumatologic diseases were chosen to receive etanercept followed by adalimumab and/or infliximab if clinical improvement was not observed on etanercept. In 3 patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, inadequate response was observed on etanercept. Two of these 3 patients received adalimumab with only partial response. All 3 were treated with infliximab in the end and showed excellent response. One of the patients experienced facial abscess responsive to antibiotics and was continued on infliximab therapy without further complications. In all 6 cases of infliximab therapy, the patients were on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.15
Ustekinumab
There were 3 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with ustekinumab in HIV-positive patients on HAART. CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.18-20
Comment
Currently, all of the systemic immunosuppressive therapies approved for psoriatic disease have a warning by the US Food and Drug Administration for increased risk of serious infection. Given such labels, these therapies are not routinely prescribed for HIV-positive patients who are already immunocompromised; however, many HIV-positive patients have severe psoriatic disease that cannot be adequately treated with first- and second-line therapies including topical agents, phototherapy, or oral retinoids.
Our comprehensive review yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab. Although data are limited to case reports and case series, some trends were observed.
Efficacy
In most of the cases reviewed, the patients had inadequate improvement of psoriatic disease with first- and second-line therapies, which included antiretrovirals alone, topical agents, phototherapy, and oral retinoids. Some cases reported poor response to methotrexate and cyclosporine.4-8 Biologic agents were effective in many such cases.
Safety
Overall, there were 11 cases in which the patient was not on adequate HAART while being treated with systemic immunosuppressive therapy for psoriatic disease.4-8,15 Of them, 3 were associated with serious infection while on methotrexate.5,6 There was only 1 report of serious infection13 of 14 cases in which the patient was on concomitant HAART. In this case, which reported polymicrobial infections and subsequent death of the patient, the infections continued after discontinuing etanercept; thus, the association is unclear. Interestingly, despite multiple infections, the CD4 and viral counts were stable throughout treatment with etanercept.13
From reviewing the 4 total cases5,6,13 of serious infection, HAART appears to be a valuable concomitant treatment during systemic immunosuppressive therapy for HIV-positive patients; however, it does not necessarily prevent serious infections from occurring, and thus the clinician’s diligence in monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection remains important.
CD4 and Viral Counts
Although reports of CD4 and viral counts were not available in earlier studies,4-8 there were 15 cases that reported consistent pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts during treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab.9-20 In all cases, the CD4 count was stable or increased. Similarly, the viral count was stable or decreased. All patients, except 1 by Cepeda et al,15 were on concomitant HAART.9-14,16-20
Although data are limited, treatment of psoriatic disease with biologic agents when used in combination with HAART may have beneficial effects on CD4 and viral counts. Tumor necrosis factor has a role in HIV expression through the action of nuclear factor κβ.21 An increase in TNF levels is shown to be associated with increased viral count, decreased CD4 count, and increased symptoms of HIV progression, such as fever, fatigue, cachexia, and dementia.22 Although more studies are necessary, TNF-α inhibitors may have a positive effect on HIV while simultaneously treating psoriatic disease. Other cytokines (eg, IL-12, IL-23, IL-17) involved in the mechanism of action of other biologic agents (ustekinumab and secukinumab) have not been shown to be directly associated with HIV activity; however, studies have shown that IL-10 has a role in inhibiting HIV-1 replication and inhibits secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α.21 It may be speculated that the inhibition of IL-12 and TNF-α may create a positive feedback effect to increase IL-10, which in turn inhibits HIV replication.
Conclusion
Although there are limited data on the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, a review of 25 individual cases suggest that these treatments are not only required but also are sufficient to treat some of the most resistant cases. It is possible that with adequate concomitant HAART and monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection, the likelihood of serious infection may be low. Furthermore, biologic agents may have a positive effect over other systemic immunosuppressive agents, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, in improving CD4 and viral counts when used in combination with HAART. Although randomized controlled trials are necessary, current biologic therapies such as etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab may be safe viable options as third-line treatment of severe psoriasis in the HIV-positive population.
- Mallon
E, Bunker CB. HIV-associated psoriasis. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2000;14:239-246. - Montaz
eri A, Kanitakis J, Bazex J. Psoriasis and HIV infection. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:475-479. - Menon
K, Van Vorhees AS, Bebo BF, et al; National Psoriasis Foundation. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299. - Masso
n C, Chennebault JM, Leclech C. Is HIV infection contraindication to the use of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis? J Rheumatol. 1995;22:2191. - Maurer
TA, Zackheim HS, Tuffanelli L, et al. The use of methotrexate for treatment of psoriasis in patients with HIV infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:372-375. - Duvic
M, Johnson TM, Rapini RP, et al. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated psoriasis and Reiter’s syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1622-1632. - Tourne
L, Durez P, Van Vooren JP, et al. Alleviation of HIV-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with cyclosporine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:501-502. - Allen
BR. Use of cyclosporine for psoriasis in HIV-positive patient. Lancet. 1992;339:686. - Di Ler
nia V, Zoboli G, Ficarelli E. Long-term management of HIV/hepatitis C virus associated psoriasis with etanercept. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:444. - Lee E
S, Heller MM, Kamangar F, et al. Long-term etanercept use for severe generalized psoriasis in an HIV-infected individual: a case study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:413-414. - Mikha
il M, Weinberg JM, Smith BL. Successful treatment with etanercept of von Zumbusch pustular psoriasis in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:453-456. - Linar
daki G, Katsarou O, Ioannidou P, et al. Effective etanercept treatment for psoriatic arthritis complicating concomitant human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infection. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1353-1355. - Aboul
afia DM, Bundow D, Wilske K, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriatic arthritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75:1093-1098. - Linds
ey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871. - Ceped
a EJ, Williams FM, Ishimori ML, et al. The use of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in HIV-positive individuals with rheumatic disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:710-712. - Sella
m J, Bouvard B, Masson C, et al. Use of infliximab to treat psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74:197-200. - Bartk
e U, Venten I, Kreuter A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with infliximab. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:784-786. - Saeki
H, Ito T, Hayashi M, et al. Successful treatment of ustekinumab in a severe psoriasis patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1653-1655. - Wiede
r S, Routt E, Levitt J, et al. Treatment of refractory psoriasis with ustekinumab in an HIV-positive patient: a case presentation and review of the biologic literature. Psoriasis Forum. 2014;20:96-102. - Papar
izos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399. - Kedzierska K, Crowe SM, Turville S, et al. The influence of cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors on HIV-1 replication in monocytes and macrophages. Rev Med Virol. 2003;13:39-56.
- Emer JJ. Is there a potential role for anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:29-35.
The prevalence of psoriasis among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–positive patients in the United States is reported to be approximately 1% to 3%, which is similar to the rates reported for the general population.1 Recalcitrant cases of psoriasis in patients with no history of the condition can be the initial manifestation of HIV infection. In patients with preexisting psoriasis, a flare of their disease can be seen following infection, and progression of HIV correlates with worsening psoriasis.2 Psoriatic arthropathy also affects 23% to 50% of HIV-positive patients with psoriasis worldwide, which may be higher than the general population,1 with more severe joint disease.
The management of psoriatic disease in the HIV-positive population is challenging. The current first-line recommendations for treatment include topical therapies, phototherapy, and highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), followed by oral retinoids as second-line agents.3 However, the clinical course of psoriasis in HIV-positive patients often is progressive and refractory2; therefore, these therapies often are inadequate to control both skin and joint manifestations. Most other currently available systemic therapies for psoriatic disease are immunosuppressive, which poses a distinct clinical challenge because HIV-positive patients are already immunocompromised.
There currently are many systemic immunosuppressive agents used for the treatment of psoriatic disease, including oral agents (eg, methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine), as well as newer biologic medications, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, and certolizumab pegol. Golimumab and certolizumab pegol currently are indicated for psoriatic arthritis only. Other newer biologic therapies include ustekinumab, which inhibits IL-12 and IL-23, and secukinumab, which inhibits IL-17A. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the most current literature to explore the efficacy and safety data as they pertain to systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals.
Methods
To investigate the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE (1985-2015) was conducted using the terms psoriasis and HIV and psoriatic arthritis and HIV combined with each of the following systemic immunosuppressive agents: methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, ustekinumab, and secukinumab. Pediatric cases and articles that were not available in the English language were excluded.
For each case, patient demographic information (ie, age, sex), prior failed psoriasis treatments, and history of HAART were documented. The dosing regimen of the systemic agent was noted when different from the US Food and Drug administration–approved dosage for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. The duration of immunosuppressive therapy as well as pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts (when available) were collected. The response to treatment and adverse effects were summarized.
Results
Our review of the literature yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab (Table). There were no reports of the use of hydroxyurea, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, or secukinumab to treat psoriatic disease in this patient population.

Methotrexate
Eight individual cases of methotrexate used to treat psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients were reported.4-6 Duvic et al6 described 4 patients with psoriatic disease that was treated with methotrexate with varying efficacy. One patient developed toxic encephalopathy, which improved after discontinuation of methotrexate; however, he died 5 months later from pneumocystis pneumonia. In this early study, none of the 4 patients were on antiretroviral therapy for HIV.6
In the cases reported by Masson et al4 and Maurer et al,5 4 patients were treated with a single antiretroviral agent and received appropriate prophylaxis against opportunistic infections. In 1 case, methotrexate was given at a chemotherapeutic dose of 525 mg once weekly for Kaposi sarcoma.4 In 2 of 4 cases, the patients developed pneumocystis pneumonia.4,5
Cyclosporine
There were 2 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with cyclosporine in HIV-positive patients.7,8 Skin and joint manifestations improved rapidly without reports of infection for 27 and 8 years.8 Both patients were treated with one antiretroviral agent.7,8
Etanercept
There were 5 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with etanercept. In all 5 cases the patients were on HAART, and the CD4 count increased or remained stable and viral count became undetectable or remained stable following treatment.9-13 In 2 cases, the patient also had hepatitis C virus, which remained stable throughout the treatment period.9,12 The maximum duration of treatment was 6 years, with only 1 reported adverse event.13 In this case reported by Aboulafia et al,13 the patient experienced recurrent polymicrobial infections, including enterococcal cellulitis, cystitis, and bacteremia, as well as pseudomonas pneumonia and septic arthritis. Therapy was discontinued at 6 months. Four months after discontinuation of etanercept, the patient died from infectious causes.13
Adalimumab
There was 1 case of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. In this case, the patient was on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved substantially after 30 months of treatment.14
Infliximab
Six individual cases of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with infliximab were reported.15-17 In a report by Cepeda et al,15 HIV-positive patients with various rheumatologic diseases were chosen to receive etanercept followed by adalimumab and/or infliximab if clinical improvement was not observed on etanercept. In 3 patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, inadequate response was observed on etanercept. Two of these 3 patients received adalimumab with only partial response. All 3 were treated with infliximab in the end and showed excellent response. One of the patients experienced facial abscess responsive to antibiotics and was continued on infliximab therapy without further complications. In all 6 cases of infliximab therapy, the patients were on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.15
Ustekinumab
There were 3 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with ustekinumab in HIV-positive patients on HAART. CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.18-20
Comment
Currently, all of the systemic immunosuppressive therapies approved for psoriatic disease have a warning by the US Food and Drug Administration for increased risk of serious infection. Given such labels, these therapies are not routinely prescribed for HIV-positive patients who are already immunocompromised; however, many HIV-positive patients have severe psoriatic disease that cannot be adequately treated with first- and second-line therapies including topical agents, phototherapy, or oral retinoids.
Our comprehensive review yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab. Although data are limited to case reports and case series, some trends were observed.
Efficacy
In most of the cases reviewed, the patients had inadequate improvement of psoriatic disease with first- and second-line therapies, which included antiretrovirals alone, topical agents, phototherapy, and oral retinoids. Some cases reported poor response to methotrexate and cyclosporine.4-8 Biologic agents were effective in many such cases.
Safety
Overall, there were 11 cases in which the patient was not on adequate HAART while being treated with systemic immunosuppressive therapy for psoriatic disease.4-8,15 Of them, 3 were associated with serious infection while on methotrexate.5,6 There was only 1 report of serious infection13 of 14 cases in which the patient was on concomitant HAART. In this case, which reported polymicrobial infections and subsequent death of the patient, the infections continued after discontinuing etanercept; thus, the association is unclear. Interestingly, despite multiple infections, the CD4 and viral counts were stable throughout treatment with etanercept.13
From reviewing the 4 total cases5,6,13 of serious infection, HAART appears to be a valuable concomitant treatment during systemic immunosuppressive therapy for HIV-positive patients; however, it does not necessarily prevent serious infections from occurring, and thus the clinician’s diligence in monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection remains important.
CD4 and Viral Counts
Although reports of CD4 and viral counts were not available in earlier studies,4-8 there were 15 cases that reported consistent pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts during treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab.9-20 In all cases, the CD4 count was stable or increased. Similarly, the viral count was stable or decreased. All patients, except 1 by Cepeda et al,15 were on concomitant HAART.9-14,16-20
Although data are limited, treatment of psoriatic disease with biologic agents when used in combination with HAART may have beneficial effects on CD4 and viral counts. Tumor necrosis factor has a role in HIV expression through the action of nuclear factor κβ.21 An increase in TNF levels is shown to be associated with increased viral count, decreased CD4 count, and increased symptoms of HIV progression, such as fever, fatigue, cachexia, and dementia.22 Although more studies are necessary, TNF-α inhibitors may have a positive effect on HIV while simultaneously treating psoriatic disease. Other cytokines (eg, IL-12, IL-23, IL-17) involved in the mechanism of action of other biologic agents (ustekinumab and secukinumab) have not been shown to be directly associated with HIV activity; however, studies have shown that IL-10 has a role in inhibiting HIV-1 replication and inhibits secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α.21 It may be speculated that the inhibition of IL-12 and TNF-α may create a positive feedback effect to increase IL-10, which in turn inhibits HIV replication.
Conclusion
Although there are limited data on the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, a review of 25 individual cases suggest that these treatments are not only required but also are sufficient to treat some of the most resistant cases. It is possible that with adequate concomitant HAART and monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection, the likelihood of serious infection may be low. Furthermore, biologic agents may have a positive effect over other systemic immunosuppressive agents, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, in improving CD4 and viral counts when used in combination with HAART. Although randomized controlled trials are necessary, current biologic therapies such as etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab may be safe viable options as third-line treatment of severe psoriasis in the HIV-positive population.
The prevalence of psoriasis among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–positive patients in the United States is reported to be approximately 1% to 3%, which is similar to the rates reported for the general population.1 Recalcitrant cases of psoriasis in patients with no history of the condition can be the initial manifestation of HIV infection. In patients with preexisting psoriasis, a flare of their disease can be seen following infection, and progression of HIV correlates with worsening psoriasis.2 Psoriatic arthropathy also affects 23% to 50% of HIV-positive patients with psoriasis worldwide, which may be higher than the general population,1 with more severe joint disease.
The management of psoriatic disease in the HIV-positive population is challenging. The current first-line recommendations for treatment include topical therapies, phototherapy, and highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), followed by oral retinoids as second-line agents.3 However, the clinical course of psoriasis in HIV-positive patients often is progressive and refractory2; therefore, these therapies often are inadequate to control both skin and joint manifestations. Most other currently available systemic therapies for psoriatic disease are immunosuppressive, which poses a distinct clinical challenge because HIV-positive patients are already immunocompromised.
There currently are many systemic immunosuppressive agents used for the treatment of psoriatic disease, including oral agents (eg, methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine), as well as newer biologic medications, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, and certolizumab pegol. Golimumab and certolizumab pegol currently are indicated for psoriatic arthritis only. Other newer biologic therapies include ustekinumab, which inhibits IL-12 and IL-23, and secukinumab, which inhibits IL-17A. The purpose of this systematic review is to evaluate the most current literature to explore the efficacy and safety data as they pertain to systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals.
Methods
To investigate the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for psoriatic disease in HIV-positive individuals, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE (1985-2015) was conducted using the terms psoriasis and HIV and psoriatic arthritis and HIV combined with each of the following systemic immunosuppressive agents: methotrexate, hydroxyurea, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, ustekinumab, and secukinumab. Pediatric cases and articles that were not available in the English language were excluded.
For each case, patient demographic information (ie, age, sex), prior failed psoriasis treatments, and history of HAART were documented. The dosing regimen of the systemic agent was noted when different from the US Food and Drug administration–approved dosage for psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. The duration of immunosuppressive therapy as well as pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts (when available) were collected. The response to treatment and adverse effects were summarized.
Results
Our review of the literature yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab (Table). There were no reports of the use of hydroxyurea, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, or secukinumab to treat psoriatic disease in this patient population.

Methotrexate
Eight individual cases of methotrexate used to treat psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients were reported.4-6 Duvic et al6 described 4 patients with psoriatic disease that was treated with methotrexate with varying efficacy. One patient developed toxic encephalopathy, which improved after discontinuation of methotrexate; however, he died 5 months later from pneumocystis pneumonia. In this early study, none of the 4 patients were on antiretroviral therapy for HIV.6
In the cases reported by Masson et al4 and Maurer et al,5 4 patients were treated with a single antiretroviral agent and received appropriate prophylaxis against opportunistic infections. In 1 case, methotrexate was given at a chemotherapeutic dose of 525 mg once weekly for Kaposi sarcoma.4 In 2 of 4 cases, the patients developed pneumocystis pneumonia.4,5
Cyclosporine
There were 2 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with cyclosporine in HIV-positive patients.7,8 Skin and joint manifestations improved rapidly without reports of infection for 27 and 8 years.8 Both patients were treated with one antiretroviral agent.7,8
Etanercept
There were 5 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with etanercept. In all 5 cases the patients were on HAART, and the CD4 count increased or remained stable and viral count became undetectable or remained stable following treatment.9-13 In 2 cases, the patient also had hepatitis C virus, which remained stable throughout the treatment period.9,12 The maximum duration of treatment was 6 years, with only 1 reported adverse event.13 In this case reported by Aboulafia et al,13 the patient experienced recurrent polymicrobial infections, including enterococcal cellulitis, cystitis, and bacteremia, as well as pseudomonas pneumonia and septic arthritis. Therapy was discontinued at 6 months. Four months after discontinuation of etanercept, the patient died from infectious causes.13
Adalimumab
There was 1 case of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. In this case, the patient was on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved substantially after 30 months of treatment.14
Infliximab
Six individual cases of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with infliximab were reported.15-17 In a report by Cepeda et al,15 HIV-positive patients with various rheumatologic diseases were chosen to receive etanercept followed by adalimumab and/or infliximab if clinical improvement was not observed on etanercept. In 3 patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, inadequate response was observed on etanercept. Two of these 3 patients received adalimumab with only partial response. All 3 were treated with infliximab in the end and showed excellent response. One of the patients experienced facial abscess responsive to antibiotics and was continued on infliximab therapy without further complications. In all 6 cases of infliximab therapy, the patients were on HAART, and CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.15
Ustekinumab
There were 3 case reports of successful treatment of psoriatic disease with ustekinumab in HIV-positive patients on HAART. CD4 and viral counts improved or remained stable.18-20
Comment
Currently, all of the systemic immunosuppressive therapies approved for psoriatic disease have a warning by the US Food and Drug Administration for increased risk of serious infection. Given such labels, these therapies are not routinely prescribed for HIV-positive patients who are already immunocompromised; however, many HIV-positive patients have severe psoriatic disease that cannot be adequately treated with first- and second-line therapies including topical agents, phototherapy, or oral retinoids.
Our comprehensive review yielded a total of 25 reported cases of systemic immunosuppressive therapies used to treat psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients including methotrexate, cyclosporine, etanercept, adalimumab, in-fliximab, and ustekinumab. Although data are limited to case reports and case series, some trends were observed.
Efficacy
In most of the cases reviewed, the patients had inadequate improvement of psoriatic disease with first- and second-line therapies, which included antiretrovirals alone, topical agents, phototherapy, and oral retinoids. Some cases reported poor response to methotrexate and cyclosporine.4-8 Biologic agents were effective in many such cases.
Safety
Overall, there were 11 cases in which the patient was not on adequate HAART while being treated with systemic immunosuppressive therapy for psoriatic disease.4-8,15 Of them, 3 were associated with serious infection while on methotrexate.5,6 There was only 1 report of serious infection13 of 14 cases in which the patient was on concomitant HAART. In this case, which reported polymicrobial infections and subsequent death of the patient, the infections continued after discontinuing etanercept; thus, the association is unclear. Interestingly, despite multiple infections, the CD4 and viral counts were stable throughout treatment with etanercept.13
From reviewing the 4 total cases5,6,13 of serious infection, HAART appears to be a valuable concomitant treatment during systemic immunosuppressive therapy for HIV-positive patients; however, it does not necessarily prevent serious infections from occurring, and thus the clinician’s diligence in monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection remains important.
CD4 and Viral Counts
Although reports of CD4 and viral counts were not available in earlier studies,4-8 there were 15 cases that reported consistent pretreatment and posttreatment CD4 and viral counts during treatment with etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab.9-20 In all cases, the CD4 count was stable or increased. Similarly, the viral count was stable or decreased. All patients, except 1 by Cepeda et al,15 were on concomitant HAART.9-14,16-20
Although data are limited, treatment of psoriatic disease with biologic agents when used in combination with HAART may have beneficial effects on CD4 and viral counts. Tumor necrosis factor has a role in HIV expression through the action of nuclear factor κβ.21 An increase in TNF levels is shown to be associated with increased viral count, decreased CD4 count, and increased symptoms of HIV progression, such as fever, fatigue, cachexia, and dementia.22 Although more studies are necessary, TNF-α inhibitors may have a positive effect on HIV while simultaneously treating psoriatic disease. Other cytokines (eg, IL-12, IL-23, IL-17) involved in the mechanism of action of other biologic agents (ustekinumab and secukinumab) have not been shown to be directly associated with HIV activity; however, studies have shown that IL-10 has a role in inhibiting HIV-1 replication and inhibits secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α.21 It may be speculated that the inhibition of IL-12 and TNF-α may create a positive feedback effect to increase IL-10, which in turn inhibits HIV replication.
Conclusion
Although there are limited data on the efficacy and safety of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in HIV-positive patients, a review of 25 individual cases suggest that these treatments are not only required but also are sufficient to treat some of the most resistant cases. It is possible that with adequate concomitant HAART and monitoring for signs and symptoms of infection, the likelihood of serious infection may be low. Furthermore, biologic agents may have a positive effect over other systemic immunosuppressive agents, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, in improving CD4 and viral counts when used in combination with HAART. Although randomized controlled trials are necessary, current biologic therapies such as etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, and ustekinumab may be safe viable options as third-line treatment of severe psoriasis in the HIV-positive population.
- Mallon
E, Bunker CB. HIV-associated psoriasis. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2000;14:239-246. - Montaz
eri A, Kanitakis J, Bazex J. Psoriasis and HIV infection. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:475-479. - Menon
K, Van Vorhees AS, Bebo BF, et al; National Psoriasis Foundation. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299. - Masso
n C, Chennebault JM, Leclech C. Is HIV infection contraindication to the use of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis? J Rheumatol. 1995;22:2191. - Maurer
TA, Zackheim HS, Tuffanelli L, et al. The use of methotrexate for treatment of psoriasis in patients with HIV infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:372-375. - Duvic
M, Johnson TM, Rapini RP, et al. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated psoriasis and Reiter’s syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1622-1632. - Tourne
L, Durez P, Van Vooren JP, et al. Alleviation of HIV-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with cyclosporine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:501-502. - Allen
BR. Use of cyclosporine for psoriasis in HIV-positive patient. Lancet. 1992;339:686. - Di Ler
nia V, Zoboli G, Ficarelli E. Long-term management of HIV/hepatitis C virus associated psoriasis with etanercept. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:444. - Lee E
S, Heller MM, Kamangar F, et al. Long-term etanercept use for severe generalized psoriasis in an HIV-infected individual: a case study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:413-414. - Mikha
il M, Weinberg JM, Smith BL. Successful treatment with etanercept of von Zumbusch pustular psoriasis in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:453-456. - Linar
daki G, Katsarou O, Ioannidou P, et al. Effective etanercept treatment for psoriatic arthritis complicating concomitant human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infection. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1353-1355. - Aboul
afia DM, Bundow D, Wilske K, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriatic arthritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75:1093-1098. - Linds
ey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871. - Ceped
a EJ, Williams FM, Ishimori ML, et al. The use of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in HIV-positive individuals with rheumatic disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:710-712. - Sella
m J, Bouvard B, Masson C, et al. Use of infliximab to treat psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74:197-200. - Bartk
e U, Venten I, Kreuter A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with infliximab. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:784-786. - Saeki
H, Ito T, Hayashi M, et al. Successful treatment of ustekinumab in a severe psoriasis patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1653-1655. - Wiede
r S, Routt E, Levitt J, et al. Treatment of refractory psoriasis with ustekinumab in an HIV-positive patient: a case presentation and review of the biologic literature. Psoriasis Forum. 2014;20:96-102. - Papar
izos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399. - Kedzierska K, Crowe SM, Turville S, et al. The influence of cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors on HIV-1 replication in monocytes and macrophages. Rev Med Virol. 2003;13:39-56.
- Emer JJ. Is there a potential role for anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:29-35.
- Mallon
E, Bunker CB. HIV-associated psoriasis. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2000;14:239-246. - Montaz
eri A, Kanitakis J, Bazex J. Psoriasis and HIV infection. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:475-479. - Menon
K, Van Vorhees AS, Bebo BF, et al; National Psoriasis Foundation. Psoriasis in patients with HIV infection: from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:291-299. - Masso
n C, Chennebault JM, Leclech C. Is HIV infection contraindication to the use of methotrexate in psoriatic arthritis? J Rheumatol. 1995;22:2191. - Maurer
TA, Zackheim HS, Tuffanelli L, et al. The use of methotrexate for treatment of psoriasis in patients with HIV infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:372-375. - Duvic
M, Johnson TM, Rapini RP, et al. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated psoriasis and Reiter’s syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1987;123:1622-1632. - Tourne
L, Durez P, Van Vooren JP, et al. Alleviation of HIV-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with cyclosporine. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:501-502. - Allen
BR. Use of cyclosporine for psoriasis in HIV-positive patient. Lancet. 1992;339:686. - Di Ler
nia V, Zoboli G, Ficarelli E. Long-term management of HIV/hepatitis C virus associated psoriasis with etanercept. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:444. - Lee E
S, Heller MM, Kamangar F, et al. Long-term etanercept use for severe generalized psoriasis in an HIV-infected individual: a case study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:413-414. - Mikha
il M, Weinberg JM, Smith BL. Successful treatment with etanercept of von Zumbusch pustular psoriasis in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:453-456. - Linar
daki G, Katsarou O, Ioannidou P, et al. Effective etanercept treatment for psoriatic arthritis complicating concomitant human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infection. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:1353-1355. - Aboul
afia DM, Bundow D, Wilske K, et al. Etanercept for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriatic arthritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75:1093-1098. - Linds
ey SF, Weiss J, Lee ES, et al. Treatment of severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis with adalimumab in an HIV-positive patient. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13:869-871. - Ceped
a EJ, Williams FM, Ishimori ML, et al. The use of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in HIV-positive individuals with rheumatic disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:710-712. - Sella
m J, Bouvard B, Masson C, et al. Use of infliximab to treat psoriatic arthritis in HIV-positive patients. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74:197-200. - Bartk
e U, Venten I, Kreuter A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with infliximab. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:784-786. - Saeki
H, Ito T, Hayashi M, et al. Successful treatment of ustekinumab in a severe psoriasis patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:1653-1655. - Wiede
r S, Routt E, Levitt J, et al. Treatment of refractory psoriasis with ustekinumab in an HIV-positive patient: a case presentation and review of the biologic literature. Psoriasis Forum. 2014;20:96-102. - Papar
izos V, Rallis E, Kirsten L, et al. Ustekinumab for the treatment of HIV psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat. 2012;23:398-399. - Kedzierska K, Crowe SM, Turville S, et al. The influence of cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors on HIV-1 replication in monocytes and macrophages. Rev Med Virol. 2003;13:39-56.
- Emer JJ. Is there a potential role for anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with human immunodeficiency virus? J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2009;2:29-35.
Practice Points
- There are limited data on the use of systemic immunosuppressive therapies for the treatment of psoriatic disease in human immunodeficiency virus–positive patients.
- The limited data suggest that biologic therapies may be effective for cases of psoriasis recalcitrant to other systemic agents and may have a positive effect on CD4 and viral counts when used in combination with highly active antiretroviral therapy.
- Further research is needed.
The Clock Is Ticking
Over the last decade we have come to understand the nature of psoriasis as a systemic inflammatory condition rather than as simply a skin disease. With this concept, we have continued to identify systemic comorbidities associated with psoriasis, including cardiovascular risk, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome. As dermatologists, we must serve as the gatekeeper for our patients with psoriasis and help to screen for comorbidities as well as provide appropriate counseling and referral.
Of the potential benefits of novel systemic therapies for psoriasis, the potential for addressing comorbid conditions with these treatments is critically important. Therefore, when I discuss psoriasis treatments, I always review and emphasize the anti-inflammatory effects of these agents. Although we know that psoriasis increases the risk for vascular inflammation and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), it has been unclear if psoriasis duration affects these risks.
Egeberg et al1 utilized 2 resources to understand the effect of psoriasis duration on vascular disease and cardiovascular events: a human imaging study and a population-based study of cardiovascular disease events. In the first part of the study, patients with psoriasis (N=190) underwent fludeoxyglucose F 18 positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Next, MACE risk was examined using nationwide registries (adjusted hazard ratio in patients with psoriasis [n=87,161] vs the general population [n=4,234,793]). In the imaging study, participants had low cardiovascular risk by traditional risk scores. The authors found that vascular inflammation as demonstrated by the imaging system was significantly associated with disease duration (β=.171; P=.002). In the population-based study, psoriasis duration had a strong relationship with MACE risk (1.0% per additional year of psoriasis duration [hazard ratio, 1.010; 95% confidence interval, 1.007-1.013]). The researchers reported that every standard deviation increase in disease duration increased the target-to-background ratio by 2.5%, which translated into an absolute increase of approximately 10% in future adverse events.1
Therefore, the authors concluded that there were negative effects of psoriasis duration on vascular inflammation and MACEs,1 which suggests that the cumulative duration of low-grade chronic inflammation may accelerate vascular disease development and MACEs. The authors therefore noted that providers should consider inquiring about duration of disease to counsel for heightened cardiovascular disease risk in psoriasis patients.1
We have some evidence that therapeutic intervention may be useful. Wu et al2 compared MACE risk in psoriasis patients receiving methotrexate or tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitors.
The findings of these studies are poignant and help to further emphasize the importance of proper identification and treatment of psoriasis and its comorbidities. This information also adds an element of urgency to the way we look at this disease and demonstrates that we must intervene as soon as possible in this process.
- Egeberg A, Skov L, Joshi AA, et al. The relationship between duration of psoriasis, vascular inflammation, and cardiovascular events [published online August 18, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:650.e3-656.e3.
- Wu JJ, Guerin AD, Sundaram M, et al. Cardiovascular event risk assessment in psoriasis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors versus methotrexate [published online October 26, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:81-90.
Over the last decade we have come to understand the nature of psoriasis as a systemic inflammatory condition rather than as simply a skin disease. With this concept, we have continued to identify systemic comorbidities associated with psoriasis, including cardiovascular risk, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome. As dermatologists, we must serve as the gatekeeper for our patients with psoriasis and help to screen for comorbidities as well as provide appropriate counseling and referral.
Of the potential benefits of novel systemic therapies for psoriasis, the potential for addressing comorbid conditions with these treatments is critically important. Therefore, when I discuss psoriasis treatments, I always review and emphasize the anti-inflammatory effects of these agents. Although we know that psoriasis increases the risk for vascular inflammation and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), it has been unclear if psoriasis duration affects these risks.
Egeberg et al1 utilized 2 resources to understand the effect of psoriasis duration on vascular disease and cardiovascular events: a human imaging study and a population-based study of cardiovascular disease events. In the first part of the study, patients with psoriasis (N=190) underwent fludeoxyglucose F 18 positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Next, MACE risk was examined using nationwide registries (adjusted hazard ratio in patients with psoriasis [n=87,161] vs the general population [n=4,234,793]). In the imaging study, participants had low cardiovascular risk by traditional risk scores. The authors found that vascular inflammation as demonstrated by the imaging system was significantly associated with disease duration (β=.171; P=.002). In the population-based study, psoriasis duration had a strong relationship with MACE risk (1.0% per additional year of psoriasis duration [hazard ratio, 1.010; 95% confidence interval, 1.007-1.013]). The researchers reported that every standard deviation increase in disease duration increased the target-to-background ratio by 2.5%, which translated into an absolute increase of approximately 10% in future adverse events.1
Therefore, the authors concluded that there were negative effects of psoriasis duration on vascular inflammation and MACEs,1 which suggests that the cumulative duration of low-grade chronic inflammation may accelerate vascular disease development and MACEs. The authors therefore noted that providers should consider inquiring about duration of disease to counsel for heightened cardiovascular disease risk in psoriasis patients.1
We have some evidence that therapeutic intervention may be useful. Wu et al2 compared MACE risk in psoriasis patients receiving methotrexate or tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitors.
The findings of these studies are poignant and help to further emphasize the importance of proper identification and treatment of psoriasis and its comorbidities. This information also adds an element of urgency to the way we look at this disease and demonstrates that we must intervene as soon as possible in this process.
Over the last decade we have come to understand the nature of psoriasis as a systemic inflammatory condition rather than as simply a skin disease. With this concept, we have continued to identify systemic comorbidities associated with psoriasis, including cardiovascular risk, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome. As dermatologists, we must serve as the gatekeeper for our patients with psoriasis and help to screen for comorbidities as well as provide appropriate counseling and referral.
Of the potential benefits of novel systemic therapies for psoriasis, the potential for addressing comorbid conditions with these treatments is critically important. Therefore, when I discuss psoriasis treatments, I always review and emphasize the anti-inflammatory effects of these agents. Although we know that psoriasis increases the risk for vascular inflammation and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), it has been unclear if psoriasis duration affects these risks.
Egeberg et al1 utilized 2 resources to understand the effect of psoriasis duration on vascular disease and cardiovascular events: a human imaging study and a population-based study of cardiovascular disease events. In the first part of the study, patients with psoriasis (N=190) underwent fludeoxyglucose F 18 positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Next, MACE risk was examined using nationwide registries (adjusted hazard ratio in patients with psoriasis [n=87,161] vs the general population [n=4,234,793]). In the imaging study, participants had low cardiovascular risk by traditional risk scores. The authors found that vascular inflammation as demonstrated by the imaging system was significantly associated with disease duration (β=.171; P=.002). In the population-based study, psoriasis duration had a strong relationship with MACE risk (1.0% per additional year of psoriasis duration [hazard ratio, 1.010; 95% confidence interval, 1.007-1.013]). The researchers reported that every standard deviation increase in disease duration increased the target-to-background ratio by 2.5%, which translated into an absolute increase of approximately 10% in future adverse events.1
Therefore, the authors concluded that there were negative effects of psoriasis duration on vascular inflammation and MACEs,1 which suggests that the cumulative duration of low-grade chronic inflammation may accelerate vascular disease development and MACEs. The authors therefore noted that providers should consider inquiring about duration of disease to counsel for heightened cardiovascular disease risk in psoriasis patients.1
We have some evidence that therapeutic intervention may be useful. Wu et al2 compared MACE risk in psoriasis patients receiving methotrexate or tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) inhibitors.
The findings of these studies are poignant and help to further emphasize the importance of proper identification and treatment of psoriasis and its comorbidities. This information also adds an element of urgency to the way we look at this disease and demonstrates that we must intervene as soon as possible in this process.
- Egeberg A, Skov L, Joshi AA, et al. The relationship between duration of psoriasis, vascular inflammation, and cardiovascular events [published online August 18, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:650.e3-656.e3.
- Wu JJ, Guerin AD, Sundaram M, et al. Cardiovascular event risk assessment in psoriasis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors versus methotrexate [published online October 26, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:81-90.
- Egeberg A, Skov L, Joshi AA, et al. The relationship between duration of psoriasis, vascular inflammation, and cardiovascular events [published online August 18, 2017]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:650.e3-656.e3.
- Wu JJ, Guerin AD, Sundaram M, et al. Cardiovascular event risk assessment in psoriasis patients treated with tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors versus methotrexate [published online October 26, 2016]. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:81-90.
Related Content Online
The Role of Biologic Therapy for Psoriasis in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction