User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
Enoxaparin-Induced Hemorrhagic Bullae at Sites of Trauma and Endothelial Pathology
To the Editor:
A 67-year-old man with diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital for exacerbation of congestive heart failure and atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response. He subsequently developed a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction and was started on subcutaneous enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily. On day 9 of hospitalization, small “blood blisters” on the legs were noted by the nurse, and dermatology was consulted.
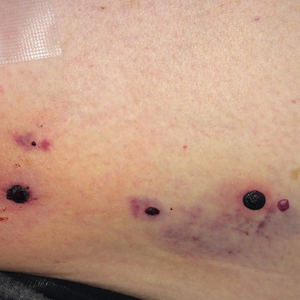
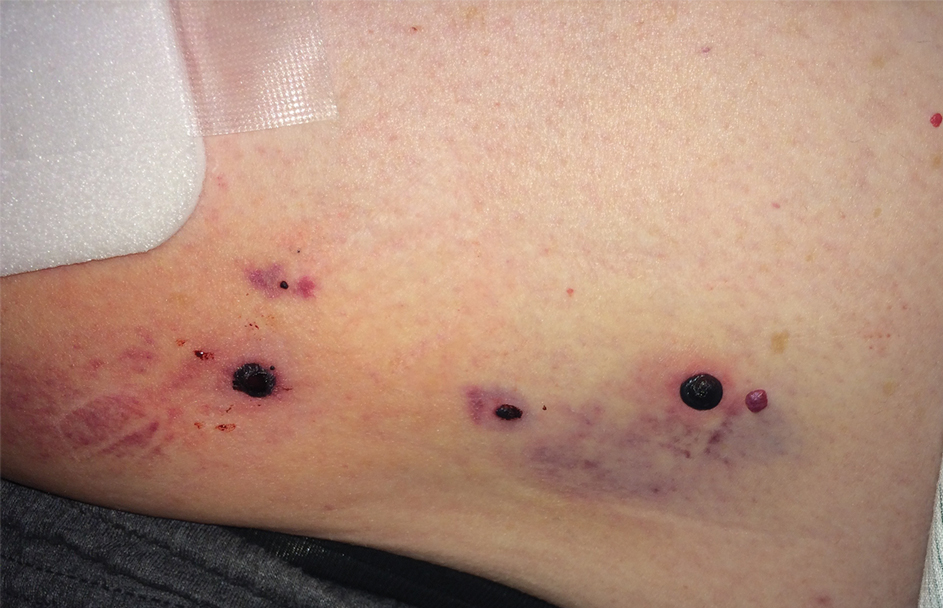
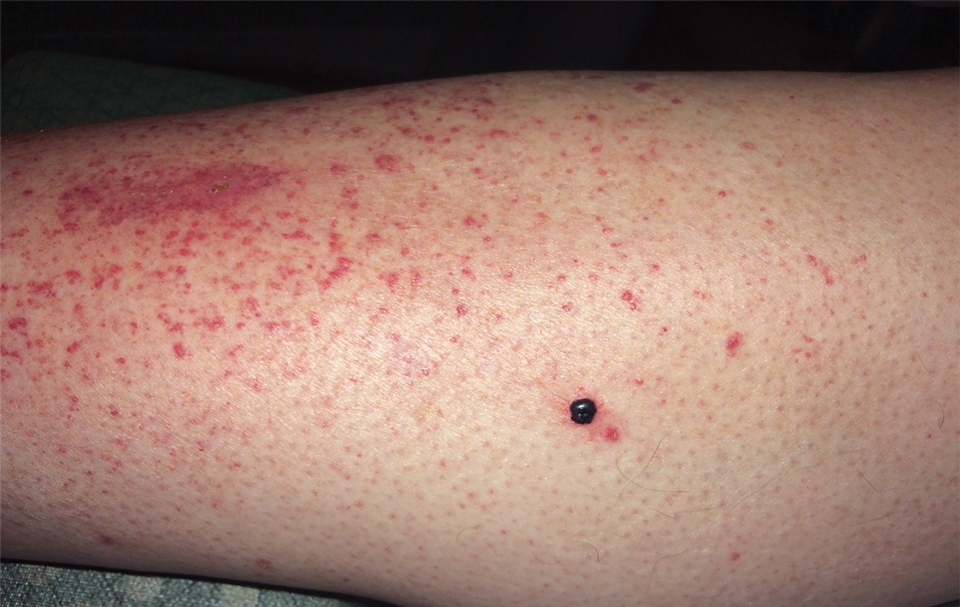
Physical examination revealed tense hemorrhagic bullae with erythematous haloes scattered over the arms and legs and to a lesser extent on the trunk. The bullae were most concentrated at the surrounding subcutaneous injection sites of insulin and enoxaparin with secondary bruising (Figure 1). The lesions also were present on the legs, where pitting edema and capillaritis also were appreciated (Figure 2).
Laboratory workup for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia was negative. A diagnosis of enoxaparin-associated hemorrhagic bullae was made. Biopsy was recommended, but the patient declined based on anecdotal reports that the bullae typically self-resolve.
The enoxaparin was discontinued 7 days after the dermatology consultation, and the patient was transitioned to apixaban. A review of the medical record during the dermatology consultation revealed he had been on aspirin (81–385 mg/d) for 13 years prior to admission and had received prophylactic enoxaparin (40 mg/d) while hospitalized 2 and 7 years prior to the current episode of hemorrhagic bullae.
The patient declined outpatient dermatology follow-up; however, his cardiologist noted that the skin lesions had resolved at a 3-week postdischarge appointment. Approximately 5 months after discharge, the patient was re-treated by the cardiologist with enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily for 3 days to bridge to warfarin after he developed a deep vein thrombosis while taking apixaban. He did not develop hemorrhagic bullae upon retreatment with enoxaparin.
Heparin-induced hemorrhagic bullous dermatosis (HBD) has been associated with administration of both unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin.1 The condition typically develops 5 to 21 days after initiation of heparin as asymptomatic, purple-to-black bullae, sometimes with an erythematous halo.2,3 The arms and legs are the most common location, but the exact pathogenesis of the lesions remains unknown.3,4 Most cases resolve within weeks of discontinuing heparin, although some reports have suggested that discontinuation is unnecessary.3,4
Histopathologic analysis shows intraepidermal or subepidermal bullae with red blood cells and fibrin in the absence of vasculitis and intravascular thrombi.1,4 Immunofluorescence studies are negative.3 In a comprehensive review of HBD, the investigators hypothesized that the pathogenesis may be related to noninflammatory to pauci-inflammatory activation of basement membrane zone proteases or possibly epithelial or endothelial fragility in conjunction with trauma that causes disruption of the vascular endothelium (eg, subcutaneous injections, vasculitis).4
Our case is of particular interest because the bullae were strikingly limited to sites of subcutaneous injection and surrounding areas along with coexistent endothelial pathology on the lower legs (capillaritis and pitting edema). These clinical observations support trauma from the injections and altered endothelia as pathogenetic factors in HBD.
Of interest, our patient had 2 prior hospitalizations during which he received prophylactic enoxaparin and did not develop hemorrhagic bullae. Furthermore, repeat exposure to therapeutic dosing of enoxaparin with a shorter duration did not result in recurrence of HBD. This suggests that heparin dosing and duration of therapy also might be involved in the development of HBD.
Our hope is that future reports of HBD will address the presence or absence of coexistent cutaneous pathology, such as edema, stasis dermatitis, bruising, and capillaritis, along with heparin dosing, duration, and prior exposure to heparin treatment so that risk factors and pathogenesis can be further investigated. We also agree with Snow et al4 that HBD should be included as an outcome in future trials of heparin therapy.
- Komforti MK, Bressler ES, Selim MA, et al. A rare cutaneous manifestation of hemorrhagic bullae to low-molecular-weight heparin and fondaparinux: report of two cases: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:104-106. doi:10.1111/cup.12821
- Peña ZG, Suszko JW, Morrison LH. Hemorrhagic bullae in a 73-year-old man. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:871-872. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.3364a
- Gouveia AI, Lopes L, Soares-Almeida L, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis induced by enoxaparin. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016;35:160-162. doi:10.3109/15569527.2015.1041033
- Snow SC, Pearson DR, Fathi R, et al. Heparin‐induced haemorrhagic bullous dermatosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:393-398. doi:10.1111/ced.13327
To the Editor:
A 67-year-old man with diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital for exacerbation of congestive heart failure and atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response. He subsequently developed a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction and was started on subcutaneous enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily. On day 9 of hospitalization, small “blood blisters” on the legs were noted by the nurse, and dermatology was consulted.
Physical examination revealed tense hemorrhagic bullae with erythematous haloes scattered over the arms and legs and to a lesser extent on the trunk. The bullae were most concentrated at the surrounding subcutaneous injection sites of insulin and enoxaparin with secondary bruising (Figure 1). The lesions also were present on the legs, where pitting edema and capillaritis also were appreciated (Figure 2).

Laboratory workup for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia was negative. A diagnosis of enoxaparin-associated hemorrhagic bullae was made. Biopsy was recommended, but the patient declined based on anecdotal reports that the bullae typically self-resolve.

The enoxaparin was discontinued 7 days after the dermatology consultation, and the patient was transitioned to apixaban. A review of the medical record during the dermatology consultation revealed he had been on aspirin (81–385 mg/d) for 13 years prior to admission and had received prophylactic enoxaparin (40 mg/d) while hospitalized 2 and 7 years prior to the current episode of hemorrhagic bullae.
The patient declined outpatient dermatology follow-up; however, his cardiologist noted that the skin lesions had resolved at a 3-week postdischarge appointment. Approximately 5 months after discharge, the patient was re-treated by the cardiologist with enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily for 3 days to bridge to warfarin after he developed a deep vein thrombosis while taking apixaban. He did not develop hemorrhagic bullae upon retreatment with enoxaparin.
Heparin-induced hemorrhagic bullous dermatosis (HBD) has been associated with administration of both unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin.1 The condition typically develops 5 to 21 days after initiation of heparin as asymptomatic, purple-to-black bullae, sometimes with an erythematous halo.2,3 The arms and legs are the most common location, but the exact pathogenesis of the lesions remains unknown.3,4 Most cases resolve within weeks of discontinuing heparin, although some reports have suggested that discontinuation is unnecessary.3,4
Histopathologic analysis shows intraepidermal or subepidermal bullae with red blood cells and fibrin in the absence of vasculitis and intravascular thrombi.1,4 Immunofluorescence studies are negative.3 In a comprehensive review of HBD, the investigators hypothesized that the pathogenesis may be related to noninflammatory to pauci-inflammatory activation of basement membrane zone proteases or possibly epithelial or endothelial fragility in conjunction with trauma that causes disruption of the vascular endothelium (eg, subcutaneous injections, vasculitis).4
Our case is of particular interest because the bullae were strikingly limited to sites of subcutaneous injection and surrounding areas along with coexistent endothelial pathology on the lower legs (capillaritis and pitting edema). These clinical observations support trauma from the injections and altered endothelia as pathogenetic factors in HBD.
Of interest, our patient had 2 prior hospitalizations during which he received prophylactic enoxaparin and did not develop hemorrhagic bullae. Furthermore, repeat exposure to therapeutic dosing of enoxaparin with a shorter duration did not result in recurrence of HBD. This suggests that heparin dosing and duration of therapy also might be involved in the development of HBD.
Our hope is that future reports of HBD will address the presence or absence of coexistent cutaneous pathology, such as edema, stasis dermatitis, bruising, and capillaritis, along with heparin dosing, duration, and prior exposure to heparin treatment so that risk factors and pathogenesis can be further investigated. We also agree with Snow et al4 that HBD should be included as an outcome in future trials of heparin therapy.
To the Editor:
A 67-year-old man with diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital for exacerbation of congestive heart failure and atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response. He subsequently developed a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction and was started on subcutaneous enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily. On day 9 of hospitalization, small “blood blisters” on the legs were noted by the nurse, and dermatology was consulted.
Physical examination revealed tense hemorrhagic bullae with erythematous haloes scattered over the arms and legs and to a lesser extent on the trunk. The bullae were most concentrated at the surrounding subcutaneous injection sites of insulin and enoxaparin with secondary bruising (Figure 1). The lesions also were present on the legs, where pitting edema and capillaritis also were appreciated (Figure 2).

Laboratory workup for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia was negative. A diagnosis of enoxaparin-associated hemorrhagic bullae was made. Biopsy was recommended, but the patient declined based on anecdotal reports that the bullae typically self-resolve.

The enoxaparin was discontinued 7 days after the dermatology consultation, and the patient was transitioned to apixaban. A review of the medical record during the dermatology consultation revealed he had been on aspirin (81–385 mg/d) for 13 years prior to admission and had received prophylactic enoxaparin (40 mg/d) while hospitalized 2 and 7 years prior to the current episode of hemorrhagic bullae.
The patient declined outpatient dermatology follow-up; however, his cardiologist noted that the skin lesions had resolved at a 3-week postdischarge appointment. Approximately 5 months after discharge, the patient was re-treated by the cardiologist with enoxaparin 110 mg twice daily for 3 days to bridge to warfarin after he developed a deep vein thrombosis while taking apixaban. He did not develop hemorrhagic bullae upon retreatment with enoxaparin.
Heparin-induced hemorrhagic bullous dermatosis (HBD) has been associated with administration of both unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin.1 The condition typically develops 5 to 21 days after initiation of heparin as asymptomatic, purple-to-black bullae, sometimes with an erythematous halo.2,3 The arms and legs are the most common location, but the exact pathogenesis of the lesions remains unknown.3,4 Most cases resolve within weeks of discontinuing heparin, although some reports have suggested that discontinuation is unnecessary.3,4
Histopathologic analysis shows intraepidermal or subepidermal bullae with red blood cells and fibrin in the absence of vasculitis and intravascular thrombi.1,4 Immunofluorescence studies are negative.3 In a comprehensive review of HBD, the investigators hypothesized that the pathogenesis may be related to noninflammatory to pauci-inflammatory activation of basement membrane zone proteases or possibly epithelial or endothelial fragility in conjunction with trauma that causes disruption of the vascular endothelium (eg, subcutaneous injections, vasculitis).4
Our case is of particular interest because the bullae were strikingly limited to sites of subcutaneous injection and surrounding areas along with coexistent endothelial pathology on the lower legs (capillaritis and pitting edema). These clinical observations support trauma from the injections and altered endothelia as pathogenetic factors in HBD.
Of interest, our patient had 2 prior hospitalizations during which he received prophylactic enoxaparin and did not develop hemorrhagic bullae. Furthermore, repeat exposure to therapeutic dosing of enoxaparin with a shorter duration did not result in recurrence of HBD. This suggests that heparin dosing and duration of therapy also might be involved in the development of HBD.
Our hope is that future reports of HBD will address the presence or absence of coexistent cutaneous pathology, such as edema, stasis dermatitis, bruising, and capillaritis, along with heparin dosing, duration, and prior exposure to heparin treatment so that risk factors and pathogenesis can be further investigated. We also agree with Snow et al4 that HBD should be included as an outcome in future trials of heparin therapy.
- Komforti MK, Bressler ES, Selim MA, et al. A rare cutaneous manifestation of hemorrhagic bullae to low-molecular-weight heparin and fondaparinux: report of two cases: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:104-106. doi:10.1111/cup.12821
- Peña ZG, Suszko JW, Morrison LH. Hemorrhagic bullae in a 73-year-old man. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:871-872. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.3364a
- Gouveia AI, Lopes L, Soares-Almeida L, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis induced by enoxaparin. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016;35:160-162. doi:10.3109/15569527.2015.1041033
- Snow SC, Pearson DR, Fathi R, et al. Heparin‐induced haemorrhagic bullous dermatosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:393-398. doi:10.1111/ced.13327
- Komforti MK, Bressler ES, Selim MA, et al. A rare cutaneous manifestation of hemorrhagic bullae to low-molecular-weight heparin and fondaparinux: report of two cases: letter to the editor. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:104-106. doi:10.1111/cup.12821
- Peña ZG, Suszko JW, Morrison LH. Hemorrhagic bullae in a 73-year-old man. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:871-872. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2013.3364a
- Gouveia AI, Lopes L, Soares-Almeida L, et al. Bullous hemorrhagic dermatosis induced by enoxaparin. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016;35:160-162. doi:10.3109/15569527.2015.1041033
- Snow SC, Pearson DR, Fathi R, et al. Heparin‐induced haemorrhagic bullous dermatosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018;43:393-398. doi:10.1111/ced.13327
Granulomatous Facial Dermatoses
Cutaneous granulomatous diseases encompass many entities that are skin-limited or systemic. The prototypical cutaneous granuloma is a painless, rounded, well-defined, red-pink or flesh-colored papule1 and is smooth, owing to minimal epidermal involvement. Examples of conditions that present with such lesions include granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (GPD), granulomatous rosacea (GR), lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and papular sarcoidosis. These entities commonly are seen on the face and can be a source of distress to patients when they are extensive. Several reports have raised the possibility that these conditions lie on a spectrum.2-4 We present 2 cases of patients with facial papular granulomas, discuss potential causes of the lesions, review historical aspects from the literature, and highlight the challenges that these lesions can pose to the clinician.
Case Reports
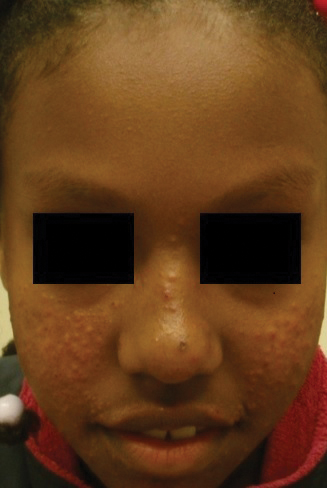
Patient 1—A 10-year-old Ethiopian girl with a history of atopic dermatitis presented with a facial rash of 4 months’ duration. Her pediatrician initially treated the rash as pityriasis alba and prescribed hydrocortisone cream. Two months into treatment, the patient developed an otherwise asymptomatic, unilateral, papular dermatosis on the right cheek. She subsequently was switched to treatment with benzoyl peroxide and topical clindamycin, which she had been using for 2 months with no improvement at the time of the current presentation. The lesions then spread bilaterally and periorally.
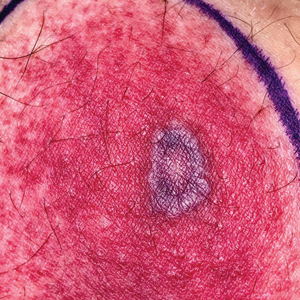
At the current presentation, physical examination demonstrated fine, diffuse, follicular-based, flesh-colored papules over both cheeks, the right side of the nose, and the perioral region (Figure 1). A biopsy of a papular lesion from the right cheek revealed well-formed, noncaseating granulomas in the superficial and mid dermis with an associated lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 2). No organisms were identified on acid-fast, Fite, or periodic acid–Schiff staining. A tuberculin skin test was negative. A chest radiograph showed small calcified hilar lymph nodes bilaterally. Pulmonary function tests were unremarkable. Calcium and angiotensin-converting enzyme levels were normal.
The patient denied any fever, chills, hemoptysis, cough, dyspnea, lymphadenopathy, scleral or conjunctival pain or erythema, visual disturbances, or arthralgias. Hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily was started with minimal improvement after 5 months. Methotrexate 20 mg once weekly was then added. Topical fluocinonide 0.05% also was started at this time, as the patient had required several prednisone tapers over the past 3 months for symptomatic relief. The lesions improved minimally after 5 more months of treatment, at which time she had developed inflammatory papules, pustules, and open comedones in the same areas as well as the glabella.
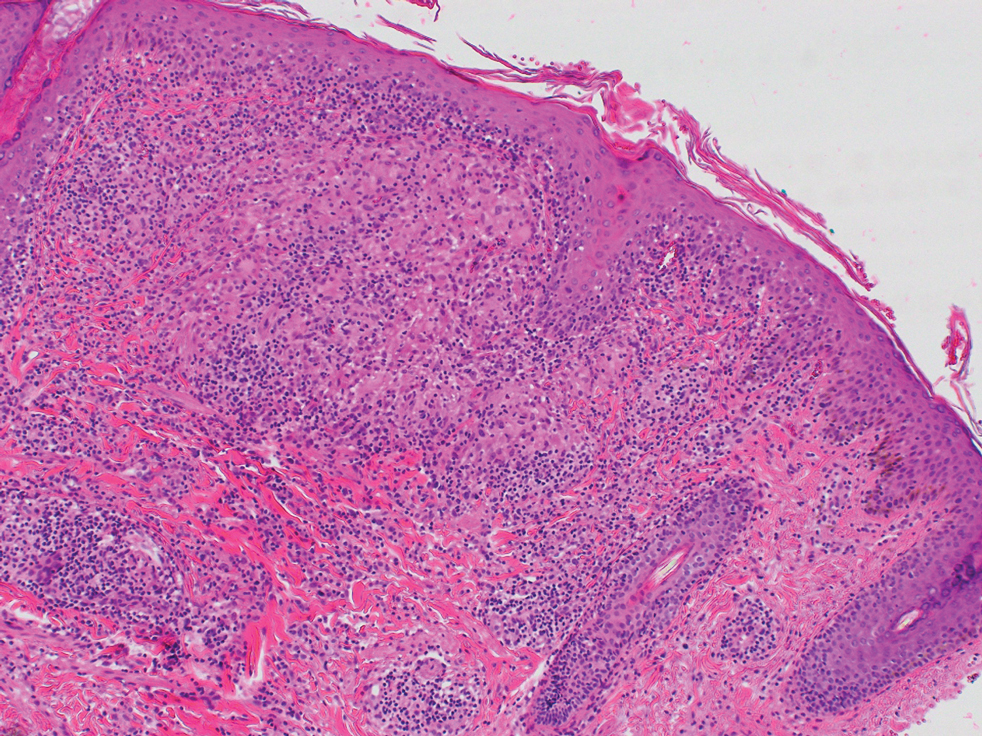
Repeat biopsy of a papular lesion demonstrated noncaseating granulomas and an associated chronic lymphocytic infiltrate in a follicular and perifollicular distribution (Figure 3). Biopsy of a pustule demonstrated acute Demodex folliculitis. Fluocinonide was stopped, and anti-mite therapy with ivermectin, permethrin cream 5%, and selenium sulfide lotion 2.5% was started, with good response from the pustular lesions.
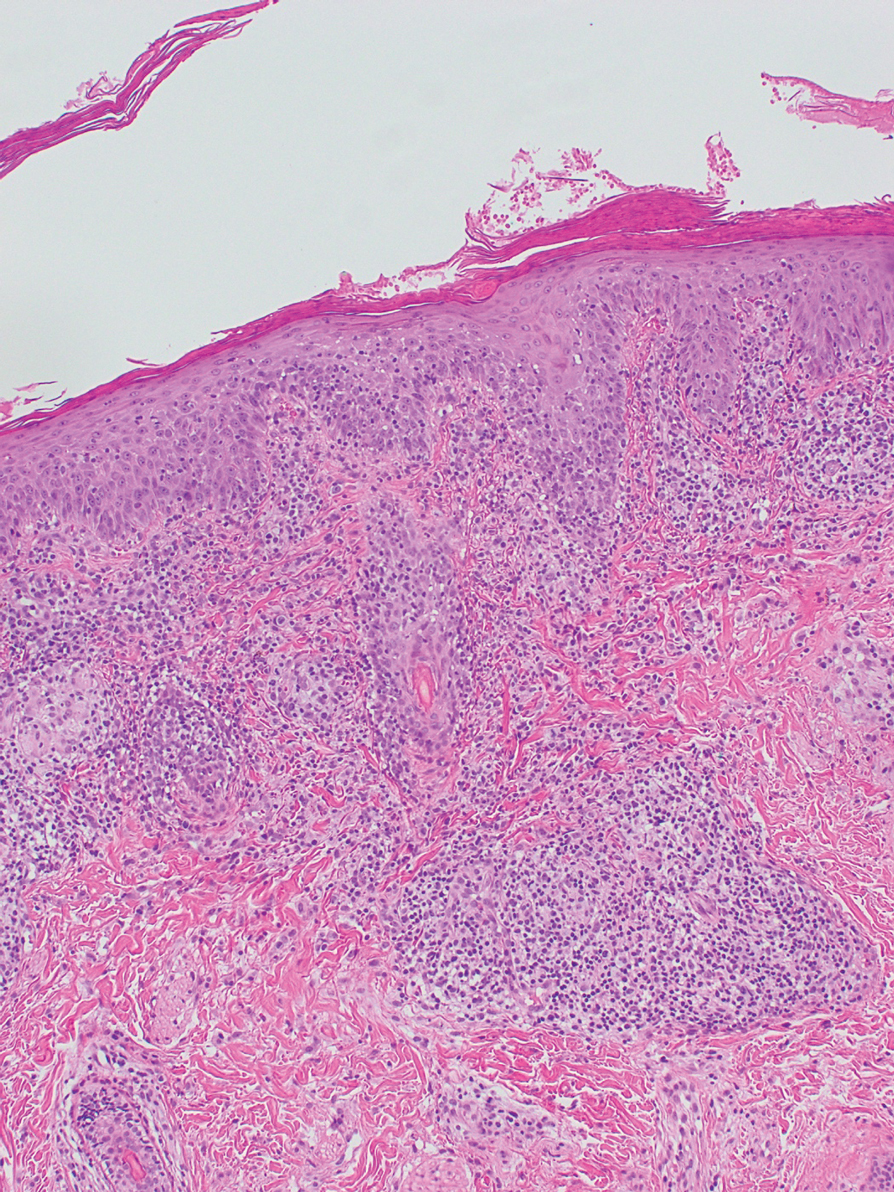
The patient continued taking methotrexate 20 mg once weekly during this time, with improvement in the papular lesions. She discontinued methotrexate after 12 months with complete resolution. At follow-up 12 months after stopping the methotrexate (roughly 2 years after initial presentation), she showed sustained resolution, with small pitted scars on both cheeks and the nasal tip.
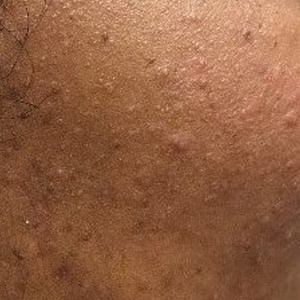
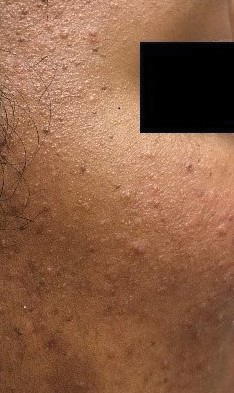
Patient 2—A 33-year-old Ethiopian woman presented with a facial rash of 15 years’ duration. The lesions had been accumulating slowly and were asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed multiple follicular-based, flesh-colored, and erythematous papules on the cheeks, chin, perioral area, and forehead (Figure 4). There were no pustules or telangiectasias. Treatment with tretinoin cream 0.05% for 6 months offered minimal relief.
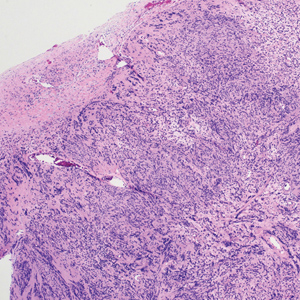
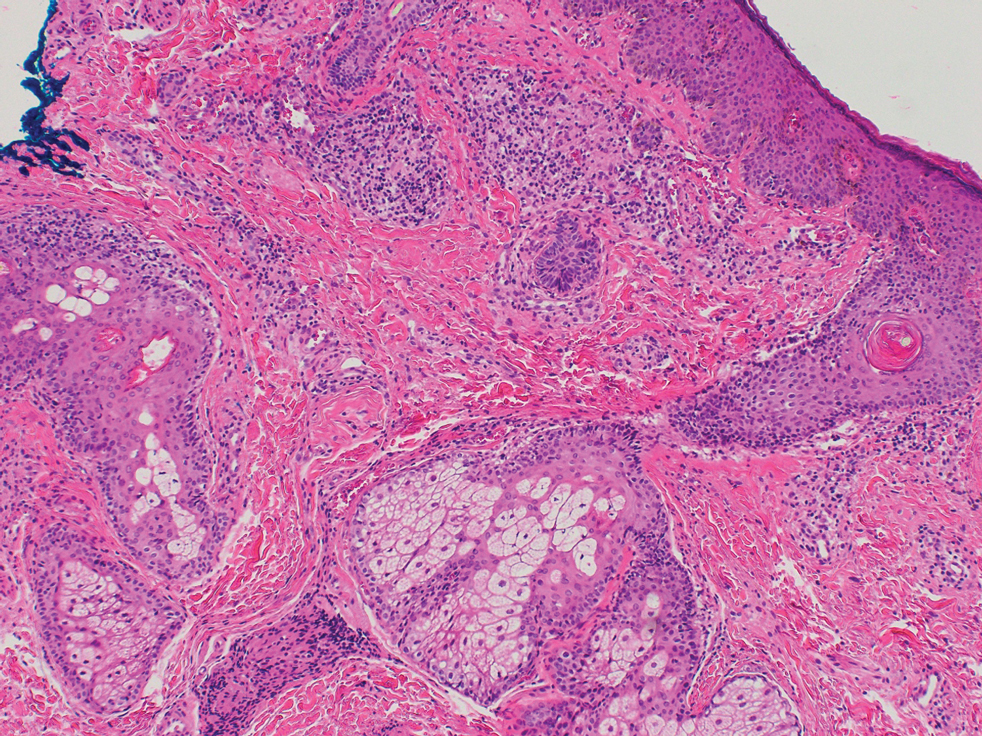
Biopsy of a papule from the left mandible showed superficial vascular telangiectasias, noncaseating granulomas comprising epithelioid histiocytes and lymphocytes in the superficial dermis, and a perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 5). No organisms were identified on Fite or Gomori methenamine silver staining.
Comment
The first step in differentiating cutaneous granulomatous lesions should be to distinguish infectious from noninfectious causes.1 Noninfectious cutaneous granulomas can appear nearly anywhere; however, certain processes have a predilection for the face, including GPD, GR, LMDF, and papular sarcoidosis.5-7 These conditions generally present with papular granulomas with features as described above.
Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis—In 1970, Gianotti and colleagues8 briefly described the first possible cases of GPD in 5 children. The eruption comprised numerous yellow, dome-shaped papules in a mostly perioral distribution. Tuberculin and the Kveim tests were nonreactive; histopathology was described as sarcoid-type and not necessarily follicular or perifollicular.8 In 1974, Marten et al9 described 22 Afro-Caribbean children with flesh-colored, papular eruptions on the face that did not show histologic granulomatous changes but were morphologically similar to the reports by Gianotti et al.8 By 1989, Frieden and colleagues10 described this facial eruption as “granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children”. Additionally, the investigators observed granulomatous infiltrates in a perifollicular distribution and suggested follicular disruption as a possible cause. It was clear from the case discussions that these eruptions were not uncommonly diagnosed as papular sarcoidosis.10 The following year, Williams et al11 reported 5 cases of similar papular eruptions in 5 Afro-Caribbean children, coining the term facial Afro-Caribbean eruption.11 Knautz and Lesher12 referred to this entity as “childhood GPD” in 1996 to avoid limiting the diagnosis to Afro-Caribbean patients and to a perioral distribution; this is the most popular current terminology.12 Since then, reports of extrafacial involvement and disease in adults have been published.13,14
Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis often is seen in the perinasal, periocular, and perioral regions of the face.2 It is associated with topical steroid exposure.5 Histologically, noncaseating granulomas around the upper half of undisrupted hair follicles with a lymphocytic infiltrate are typical.13 Treatment should begin with cessation of any topical steroids; first-line agents are oral tetracycline or macrolide antibiotics.5 These agents can be used alone or in combination with topical erythromycin, metronidazole, or sulfur-based lotions.13 Rarely, GPD presents extrafacially.13 Even so, it usually resolves within 2 weeks to 6 months, especially with therapy; scarring is unusual.5,13,15
Granulomatous Rosacea—A report in the early 20th century described patients with tuberculoid granulomas resembling papular rosacea; the initial belief was that this finding represented a rosacealike tuberculid eruption.5 However, this belief was questioned by Snapp,16 among others, who demonstrated near universal lack of reactivity to tuberculin among 20 of these patients in 1949; more recent evidence has substantiated these findings.17 Still, Snapp16 postulated that these rosacealike granulomatous lesions were distinct from classic rosacea because they lacked vascular symptoms and pustules and were recalcitrant to rosacea treatment modalities.
In 1970, Mullanax and colleagues18 introduced the term granulomatous rosacea, reiterating that this entity was not tuberculous. They documented papulopustular lesions as well as telangiectasias, raising the possibility that GR does overlap with acne rosacea. More recent studies have established the current theory that GR is a histologic variant of acne rosacea because, in addition to typical granulomatous papules, its microscopic features can be seen across subtypes of acne rosacea.19,20
Various causes have been proposed for GR. Demodex mites have been reported in association with GR for nearly 30 years.19,20 In the past 10 years, molecular studies have started to define the role of metalloproteinases, UV radiation, and cutaneous peptides in the pathogenesis of acne rosacea and GR.21,22
Granulomatous rosacea typically is seen in middle-aged women.20,23 Hallmarks of rosacea, such as facial erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, pustules, and rhinophyma, are not always present in GR.5,20,23 Lesions usually are distributed around the central face, although extension to the cheeks, total facial involvement, and extrafacial lesions are possible.5,20 Histologically, perifollicular and follicular-based noncaseating granulomas with dilatation of the dermal papillary vasculature are seen.17,23 As a whole, rosacea is comparatively uncommon in dark-skinned patients; when it does occur, GR is a frequent presentation.24
First-line treatment for GR is tetracycline antibiotics.5 Unresponsive cases have been treated—largely anecdotally—with topical modalities (eg, metronidazole, steroids, immunomodulators), systemic agents (eg, dapsone, erythromycin, isotretinoin), and other therapies.5 Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a chronic course.5,23
Lupus Miliaris Disseminatus Faciei—Classic LMDF demonstrates caseating perifollicular granulomas histologically.6,17,25 Lesions tend to appear on the central face, particularly the eyelids, and can be seen extrafacially.3,6,25,26 Although LMDF originally was categorized as a tuberculid eruption, this no longer is thought to be the case.27 It is now regarded by some as a variant of GR25; however, LMDF responds poorly to tetracyclines, is more common in males, and lacks rosacealike vascular abnormalities, leading some to question this association.3,6,17 In the past 20 years, some have proposed renaming LMDF to better reflect its clinical course and to consider it independent of tuberculosis and GR.28 It usually resolves spontaneously after 1 to 3 years, leaving pitted scars.3,6
Papular Sarcoidosis—The first potential documented case of sarcoidosis was by Hutchinson29 in 1869 in a patient seen in London. The author labeled purple plaques on the index patient’s legs and hands as “livid papillary psoriasis.” In 1889, Besnier30 described a patient with violaceous swellings on the nose, ears, and fingers, which he called “lupus pernio”; his contemporary, Tenneson,31 published a case of lupus pernio and described its histologic profile as comprising epithelioid cells and giant cells. It was not until 1899 that the term sarkoid was used to describe these cutaneous lesions by Boeck,32 who thought they were reminiscent of sarcoma. In 1915, Kuznitsky and Bittorf33 described a patient with cutaneous lesions histologically consistent with Boeck’s sarkoid but additionally with hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary infiltrates. Around 1916 or 1917, Schaumann34 described patients with cutaneous lesions and additionally with involvement of pulmonary, osseous, hepatosplenic, and tonsillar tissue. These reports are among the first to recognize the multisystemic nature of sarcoidosis. The first possible case of childhood sarcoidosis might have been reported by Osler35 in the United States in 1898.
In the past century or so, an ongoing effort by researchers has focused on identifying etiologic triggers for sarcoidosis. Microbial agents have been considered in this role, with Mycobacterium and Propionibacterium organisms the most intensively studied; the possibility that foreign material contributes to the formation of granulomas also has been raised.36 Current models of the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis involve an interplay between the immune system in genetically predisposed patients and an infection that leads to a hyperimmune type 1 T–helper cell response that clears the infection but not antigens generated by the microbes and the acute host response, including proteins such as serum amyloid A and vimentin.36,37 These antigens aggregate and serve as a nidus for granuloma formation and maintenance long after infection has resolved.
Cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, plaques, and lupus pernio, as well as lesions arising within scars or tattoos, with many less common presentations.7,38 Papular sarcoidosis is common on the face but also can involve the extremities.4,7 Strictly, at least 2 organ systems must be involved to diagnose sarcoidosis, but this is debatable.4,7 Among 41 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis, 24 (58.5%) had systemic disease; cutaneous lesions were the presenting sign in 87.5% (21/24) of patients.38 Histologic analysis, regardless of the lesion, usually shows noncaseating so-called “naked” granulomas, which have minimal lymphocytic infiltrate associated with the epithelioid histiocytes.38,39 Perifollicular granulomas are possible but unusual.40
Treatment depends on the extent of cutaneous and systemic involvement. Pharmacotherapeutic modalities include topical steroids, immunomodulators, and retinoids; systemic immunomodulators and immunosuppressants; and biologic agents.7 Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis, particularly the papular variant, usually is associated with acute disease lasting less than 2 years, with resolution of skin lesions.7,38 That said, a recent report suggested that cutaneous sarcoidosis can progress to multisystemic disease as long as 7 years after the initial diagnosis.41
Clinical and Histologic Overlap—Despite this categorization of noninfectious facial granulomatous conditions, each has some clinical and histologic overlap with the others, which must be considered when encountering a granulomatous facial dermatosis. Both GPD and GR tend to present with lesions near the eyes, mouth, and nose, although GR can extend to lateral aspects of the face, below the mandible, and the forehead and has different demographic features.15,20,23 Granulomas in both GPD and GR generally are noncaseating and form in a follicular or perifollicular distribution within the dermis.2,15,23 Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei and GR share a similar facial distribution in some cases.17,20 Even papular cutaneous sarcoidosis has masqueraded as GR clinically and histologically.4
Diagnostic and Treatment Difficulty—Our cases illustrate the range of difficulty in evaluating and managing patients with facial papular granulomas. On one hand, our adult patient’s clinical and histologic findings were highly consistent with GR; on the other hand, our younger patient had clinicopathologic features of both sarcoidosis and GPD at varying times. Both conditions are more common in dark-skinned patients.11,42
Juvenile sarcoidosis is comparatively rare, with a reported annual incidence of 0.22 to 0.27 for every 100,000 children younger than 15 years; however, juvenile sarcoidosis commonly presents around 8 to 15 years of age.43
It is unusual for sarcoid granulomas to be isolated to the skin, much less to the face.4,7,43,44 Patient 1 initially presented in this manner and lacked convincing laboratory or radiographic evidence of systemic sarcoidosis. Bilateral hilar calcifications in sarcoidosis are more typical among adults after 5 to 20 years; there were no signs or symptoms of active infection that could account for the pulmonary and cutaneous lesions.45
The presence of perifollicular granulomas with associated lymphocytic infiltrates on repeat biopsy, coupled with the use of topical steroids, made it difficult to rule out a contribution by GPD to her clinical course. That her lesions resolved with pitted scarring while she was taking methotrexate and after topical steroids had been stopped could be the result of successful management or spontaneous resolution of her dermatosis; both papular sarcoidosis and GPD tend to have a self-limited course.7,13
Conclusion
We present 2 cases of papular facial granulomas in patients with similar skin types who had different clinical courses. Evaluation of such lesions remains challenging given the similarity between specific entities that present in this manner. Certainly, it is reasonable to consider a spectrum upon which all of these conditions fall, in light of the findings of these cases and those reported previously.
- Beretta-Piccoli BT, Mainetti C, Peeters M-A, et al. Cutaneous granulomatosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54:131-146. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8666-8
- Lucas CR, Korman NJ, Gilliam AC. Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis: a variant of granulomatous rosacea in children? J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:115-118. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.07088
- van de Scheur MR, van der Waal RIF, Starink TM. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei: a distinctive rosacea-like syndrome and not a granulomatous form of rosacea. Dermatology. 2003;206:120-123. doi:10.1159/000068457
- Simonart T, Lowy M, Rasquin F, et al. Overlap of sarcoidosis and rosacea. Dermatology. 1997;194:416-418. doi:10.1159/000246165
- Lee GL, Zirwas MJ. Granulomatous rosacea and periorificial dermatitis: controversies and review of management. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:447-455. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.009
- Michaels JD, Cook-Norris RH, Lehman JS, et al. Adult with papular eruption of the central aspect of the face. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:410-412. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.06.039
- Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;38:685-702. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2015.08.010
- Gianotti F, Ermacora E, Benelli MG, et al. Particulière dermatite peri-orale infantile. observations sur 5 cas. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:341.
- Marten RH, Presbury DG, Adamson JE, et al. An unusual papular and acneiform facial eruption in the negro child. Br J Dermatol. 1974;91:435-438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb13083.x
- Frieden IJ, Prose NS, Fletcher V, et al. Granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:369-373.
- Williams HC, Ashworth J, Pembroke AC, et al. FACE—facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1990;15:163-166. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.1990.tb02063.x
- Knautz MA, Lesher JL Jr. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:131-134. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1996.tb01419.x
- Urbatsch AJ, Frieden I, Williams ML, et al. Extrafacial and generalized granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1354-1358. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.10.1354
- Vincenzi C, Parente G, Tosti A. Perioral granulomatous dermatitis: two cases treated with clarithromycin. J Dermatol Treat. 2000;11:57-61.
- Kim YJ, Shin JW, Lee JS, et al. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:386-388. doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.3.386
- Snapp RH. Lewandowsky’s rosacea-like eruption; a clinical study. J Invest Dermatol. 1949;13:175-190. doi:10.1038/jid.1949.86
- Chougule A, Chatterjee D, Sethi S, et al. Granulomatous rosacea versus lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—2 faces of facial granulomatous disorder: a clinicohistological and molecular study. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:819-823. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001243
- Mullanax MG, Kierland RR. Granulomatous rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:206-211.
- Sánchez JL, Berlingeri-Ramos AC, Dueño DV. Granulomatous rosacea. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:6-9. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815bc191
- Helm KF, Menz J, Gibson LE, et al. A clinical and histopathologic study of granulomatous rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1038-1043. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70304-k
- Kanada KN, Nakatsuji T, Gallo RL. Doxycycline indirectly inhibits proteolytic activation of tryptic kallikrein-related peptidases and activation of cathelicidin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1435-1442. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.14
- Jang YH, Sim JH, Kang HY, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases in the granulomatous rosacea compared with the non-granulomatous rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:544-548. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03825.x
- Khokhar O, Khachemoune A. A case of granulomatous rosacea: sorting granulomatous rosacea from other granulomatous diseases that affect the face. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:6.
- Rosen T, Stone MS. Acne rosacea in blacks. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:70-73. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70173-x
- Adams AK, Davis JL, Davis MDP, et al. What is your diagnosis? granulomatous rosacea (lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei, acne agminata). Cutis. 2008;82:103-112.
- Shitara A. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:542-544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1984.tb04206.x
- Hodak E, Trattner A, Feuerman H, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not detectable in active lesions by polymerase chain reaction. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:614-619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1997.tb03797.x
- Skowron F, Causeret AS, Pabion C, et al. F.I.GU.R.E.: facial idiopathic granulomas with regressive evolution. Dermatology. 2000;201:287-289. doi:10.1159/000051539
- Hutchinson J. Case of livid papillary psoriasis. In: London J, Churchill A, eds. Illustrations of Clinical Surgery. J&A Churchill; 1877:42-43.
- Besnier E. Lupus pernio of the face [in French]. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:33-36.
- Tenneson H. Lupus pernio. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:333-336.
- Boeck C. Multiple benign sarkoid of the skin [in Norwegian]. Norsk Mag Laegevidensk. 1899;14:1321-1334.
- Kuznitsky E, Bittorf A. Sarkoid mit beteiligung innerer organe. Münch Med Wochenschr. 1915;62:1349-1353.
- Schaumann J. Etude sur le lupus pernio et ses rapports avec les sarcoides et la tuberculose. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr. 1916-1917;6:357-373.
- Osler W. On chronic symmetrical enlargement of the salivary and lacrimal glands. Am J Med Sci. 1898;115:27-30.
- Chen ES, Moller DR. Etiologies of sarcoidosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49:6-18. doi:10.1007/s12016-015-8481-z
- Eberhardt C, Thillai M, Parker R, et al. Proteomic analysis of Kveim reagent identifies targets of cellular immunity in sarcoidosis. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0170285. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170285
- Esteves TC, Aparicio G, Ferrer B, et al. Prognostic value of skin lesions in sarcoidosis: clinical and histopathological clues. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:556-562. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2666
- Cardoso JC, Cravo M, Reis JP, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: a histopathological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:678-682. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03153.x
- Mangas C, Fernández-Figueras M-T, Fité E, et al. Clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 32 cases of specific cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:772-777. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00563.x
- García-Colmenero L, Sánchez-Schmidt JM, Barranco C, et al. The natural history of cutaneous sarcoidosis. clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 40 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:178-184. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14218
- Shetty AK, Gedalia A. Childhood sarcoidosis: a rare but fascinating disorder. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2008;6:16. doi:10.1186/1546-0096-6-16
- Milman N, Hoffmann AL, Byg KE. Sarcoidosis in children. epidemiology in Danes, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Acta Paediatr. 1998;87:871-878. doi:10.1080/08035259875001366244. A, H, Yapıcı I. Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:220.
- Scadding JG. The late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Postgrad Med J. 1970;46:530-536. doi:10.1136/pgmj.46.538.530
Cutaneous granulomatous diseases encompass many entities that are skin-limited or systemic. The prototypical cutaneous granuloma is a painless, rounded, well-defined, red-pink or flesh-colored papule1 and is smooth, owing to minimal epidermal involvement. Examples of conditions that present with such lesions include granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (GPD), granulomatous rosacea (GR), lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and papular sarcoidosis. These entities commonly are seen on the face and can be a source of distress to patients when they are extensive. Several reports have raised the possibility that these conditions lie on a spectrum.2-4 We present 2 cases of patients with facial papular granulomas, discuss potential causes of the lesions, review historical aspects from the literature, and highlight the challenges that these lesions can pose to the clinician.
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 10-year-old Ethiopian girl with a history of atopic dermatitis presented with a facial rash of 4 months’ duration. Her pediatrician initially treated the rash as pityriasis alba and prescribed hydrocortisone cream. Two months into treatment, the patient developed an otherwise asymptomatic, unilateral, papular dermatosis on the right cheek. She subsequently was switched to treatment with benzoyl peroxide and topical clindamycin, which she had been using for 2 months with no improvement at the time of the current presentation. The lesions then spread bilaterally and periorally.
At the current presentation, physical examination demonstrated fine, diffuse, follicular-based, flesh-colored papules over both cheeks, the right side of the nose, and the perioral region (Figure 1). A biopsy of a papular lesion from the right cheek revealed well-formed, noncaseating granulomas in the superficial and mid dermis with an associated lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 2). No organisms were identified on acid-fast, Fite, or periodic acid–Schiff staining. A tuberculin skin test was negative. A chest radiograph showed small calcified hilar lymph nodes bilaterally. Pulmonary function tests were unremarkable. Calcium and angiotensin-converting enzyme levels were normal.

The patient denied any fever, chills, hemoptysis, cough, dyspnea, lymphadenopathy, scleral or conjunctival pain or erythema, visual disturbances, or arthralgias. Hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily was started with minimal improvement after 5 months. Methotrexate 20 mg once weekly was then added. Topical fluocinonide 0.05% also was started at this time, as the patient had required several prednisone tapers over the past 3 months for symptomatic relief. The lesions improved minimally after 5 more months of treatment, at which time she had developed inflammatory papules, pustules, and open comedones in the same areas as well as the glabella.

Repeat biopsy of a papular lesion demonstrated noncaseating granulomas and an associated chronic lymphocytic infiltrate in a follicular and perifollicular distribution (Figure 3). Biopsy of a pustule demonstrated acute Demodex folliculitis. Fluocinonide was stopped, and anti-mite therapy with ivermectin, permethrin cream 5%, and selenium sulfide lotion 2.5% was started, with good response from the pustular lesions.

The patient continued taking methotrexate 20 mg once weekly during this time, with improvement in the papular lesions. She discontinued methotrexate after 12 months with complete resolution. At follow-up 12 months after stopping the methotrexate (roughly 2 years after initial presentation), she showed sustained resolution, with small pitted scars on both cheeks and the nasal tip.
Patient 2—A 33-year-old Ethiopian woman presented with a facial rash of 15 years’ duration. The lesions had been accumulating slowly and were asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed multiple follicular-based, flesh-colored, and erythematous papules on the cheeks, chin, perioral area, and forehead (Figure 4). There were no pustules or telangiectasias. Treatment with tretinoin cream 0.05% for 6 months offered minimal relief.

Biopsy of a papule from the left mandible showed superficial vascular telangiectasias, noncaseating granulomas comprising epithelioid histiocytes and lymphocytes in the superficial dermis, and a perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 5). No organisms were identified on Fite or Gomori methenamine silver staining.

Comment
The first step in differentiating cutaneous granulomatous lesions should be to distinguish infectious from noninfectious causes.1 Noninfectious cutaneous granulomas can appear nearly anywhere; however, certain processes have a predilection for the face, including GPD, GR, LMDF, and papular sarcoidosis.5-7 These conditions generally present with papular granulomas with features as described above.
Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis—In 1970, Gianotti and colleagues8 briefly described the first possible cases of GPD in 5 children. The eruption comprised numerous yellow, dome-shaped papules in a mostly perioral distribution. Tuberculin and the Kveim tests were nonreactive; histopathology was described as sarcoid-type and not necessarily follicular or perifollicular.8 In 1974, Marten et al9 described 22 Afro-Caribbean children with flesh-colored, papular eruptions on the face that did not show histologic granulomatous changes but were morphologically similar to the reports by Gianotti et al.8 By 1989, Frieden and colleagues10 described this facial eruption as “granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children”. Additionally, the investigators observed granulomatous infiltrates in a perifollicular distribution and suggested follicular disruption as a possible cause. It was clear from the case discussions that these eruptions were not uncommonly diagnosed as papular sarcoidosis.10 The following year, Williams et al11 reported 5 cases of similar papular eruptions in 5 Afro-Caribbean children, coining the term facial Afro-Caribbean eruption.11 Knautz and Lesher12 referred to this entity as “childhood GPD” in 1996 to avoid limiting the diagnosis to Afro-Caribbean patients and to a perioral distribution; this is the most popular current terminology.12 Since then, reports of extrafacial involvement and disease in adults have been published.13,14
Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis often is seen in the perinasal, periocular, and perioral regions of the face.2 It is associated with topical steroid exposure.5 Histologically, noncaseating granulomas around the upper half of undisrupted hair follicles with a lymphocytic infiltrate are typical.13 Treatment should begin with cessation of any topical steroids; first-line agents are oral tetracycline or macrolide antibiotics.5 These agents can be used alone or in combination with topical erythromycin, metronidazole, or sulfur-based lotions.13 Rarely, GPD presents extrafacially.13 Even so, it usually resolves within 2 weeks to 6 months, especially with therapy; scarring is unusual.5,13,15
Granulomatous Rosacea—A report in the early 20th century described patients with tuberculoid granulomas resembling papular rosacea; the initial belief was that this finding represented a rosacealike tuberculid eruption.5 However, this belief was questioned by Snapp,16 among others, who demonstrated near universal lack of reactivity to tuberculin among 20 of these patients in 1949; more recent evidence has substantiated these findings.17 Still, Snapp16 postulated that these rosacealike granulomatous lesions were distinct from classic rosacea because they lacked vascular symptoms and pustules and were recalcitrant to rosacea treatment modalities.
In 1970, Mullanax and colleagues18 introduced the term granulomatous rosacea, reiterating that this entity was not tuberculous. They documented papulopustular lesions as well as telangiectasias, raising the possibility that GR does overlap with acne rosacea. More recent studies have established the current theory that GR is a histologic variant of acne rosacea because, in addition to typical granulomatous papules, its microscopic features can be seen across subtypes of acne rosacea.19,20
Various causes have been proposed for GR. Demodex mites have been reported in association with GR for nearly 30 years.19,20 In the past 10 years, molecular studies have started to define the role of metalloproteinases, UV radiation, and cutaneous peptides in the pathogenesis of acne rosacea and GR.21,22
Granulomatous rosacea typically is seen in middle-aged women.20,23 Hallmarks of rosacea, such as facial erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, pustules, and rhinophyma, are not always present in GR.5,20,23 Lesions usually are distributed around the central face, although extension to the cheeks, total facial involvement, and extrafacial lesions are possible.5,20 Histologically, perifollicular and follicular-based noncaseating granulomas with dilatation of the dermal papillary vasculature are seen.17,23 As a whole, rosacea is comparatively uncommon in dark-skinned patients; when it does occur, GR is a frequent presentation.24
First-line treatment for GR is tetracycline antibiotics.5 Unresponsive cases have been treated—largely anecdotally—with topical modalities (eg, metronidazole, steroids, immunomodulators), systemic agents (eg, dapsone, erythromycin, isotretinoin), and other therapies.5 Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a chronic course.5,23
Lupus Miliaris Disseminatus Faciei—Classic LMDF demonstrates caseating perifollicular granulomas histologically.6,17,25 Lesions tend to appear on the central face, particularly the eyelids, and can be seen extrafacially.3,6,25,26 Although LMDF originally was categorized as a tuberculid eruption, this no longer is thought to be the case.27 It is now regarded by some as a variant of GR25; however, LMDF responds poorly to tetracyclines, is more common in males, and lacks rosacealike vascular abnormalities, leading some to question this association.3,6,17 In the past 20 years, some have proposed renaming LMDF to better reflect its clinical course and to consider it independent of tuberculosis and GR.28 It usually resolves spontaneously after 1 to 3 years, leaving pitted scars.3,6
Papular Sarcoidosis—The first potential documented case of sarcoidosis was by Hutchinson29 in 1869 in a patient seen in London. The author labeled purple plaques on the index patient’s legs and hands as “livid papillary psoriasis.” In 1889, Besnier30 described a patient with violaceous swellings on the nose, ears, and fingers, which he called “lupus pernio”; his contemporary, Tenneson,31 published a case of lupus pernio and described its histologic profile as comprising epithelioid cells and giant cells. It was not until 1899 that the term sarkoid was used to describe these cutaneous lesions by Boeck,32 who thought they were reminiscent of sarcoma. In 1915, Kuznitsky and Bittorf33 described a patient with cutaneous lesions histologically consistent with Boeck’s sarkoid but additionally with hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary infiltrates. Around 1916 or 1917, Schaumann34 described patients with cutaneous lesions and additionally with involvement of pulmonary, osseous, hepatosplenic, and tonsillar tissue. These reports are among the first to recognize the multisystemic nature of sarcoidosis. The first possible case of childhood sarcoidosis might have been reported by Osler35 in the United States in 1898.
In the past century or so, an ongoing effort by researchers has focused on identifying etiologic triggers for sarcoidosis. Microbial agents have been considered in this role, with Mycobacterium and Propionibacterium organisms the most intensively studied; the possibility that foreign material contributes to the formation of granulomas also has been raised.36 Current models of the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis involve an interplay between the immune system in genetically predisposed patients and an infection that leads to a hyperimmune type 1 T–helper cell response that clears the infection but not antigens generated by the microbes and the acute host response, including proteins such as serum amyloid A and vimentin.36,37 These antigens aggregate and serve as a nidus for granuloma formation and maintenance long after infection has resolved.
Cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, plaques, and lupus pernio, as well as lesions arising within scars or tattoos, with many less common presentations.7,38 Papular sarcoidosis is common on the face but also can involve the extremities.4,7 Strictly, at least 2 organ systems must be involved to diagnose sarcoidosis, but this is debatable.4,7 Among 41 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis, 24 (58.5%) had systemic disease; cutaneous lesions were the presenting sign in 87.5% (21/24) of patients.38 Histologic analysis, regardless of the lesion, usually shows noncaseating so-called “naked” granulomas, which have minimal lymphocytic infiltrate associated with the epithelioid histiocytes.38,39 Perifollicular granulomas are possible but unusual.40
Treatment depends on the extent of cutaneous and systemic involvement. Pharmacotherapeutic modalities include topical steroids, immunomodulators, and retinoids; systemic immunomodulators and immunosuppressants; and biologic agents.7 Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis, particularly the papular variant, usually is associated with acute disease lasting less than 2 years, with resolution of skin lesions.7,38 That said, a recent report suggested that cutaneous sarcoidosis can progress to multisystemic disease as long as 7 years after the initial diagnosis.41
Clinical and Histologic Overlap—Despite this categorization of noninfectious facial granulomatous conditions, each has some clinical and histologic overlap with the others, which must be considered when encountering a granulomatous facial dermatosis. Both GPD and GR tend to present with lesions near the eyes, mouth, and nose, although GR can extend to lateral aspects of the face, below the mandible, and the forehead and has different demographic features.15,20,23 Granulomas in both GPD and GR generally are noncaseating and form in a follicular or perifollicular distribution within the dermis.2,15,23 Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei and GR share a similar facial distribution in some cases.17,20 Even papular cutaneous sarcoidosis has masqueraded as GR clinically and histologically.4
Diagnostic and Treatment Difficulty—Our cases illustrate the range of difficulty in evaluating and managing patients with facial papular granulomas. On one hand, our adult patient’s clinical and histologic findings were highly consistent with GR; on the other hand, our younger patient had clinicopathologic features of both sarcoidosis and GPD at varying times. Both conditions are more common in dark-skinned patients.11,42
Juvenile sarcoidosis is comparatively rare, with a reported annual incidence of 0.22 to 0.27 for every 100,000 children younger than 15 years; however, juvenile sarcoidosis commonly presents around 8 to 15 years of age.43
It is unusual for sarcoid granulomas to be isolated to the skin, much less to the face.4,7,43,44 Patient 1 initially presented in this manner and lacked convincing laboratory or radiographic evidence of systemic sarcoidosis. Bilateral hilar calcifications in sarcoidosis are more typical among adults after 5 to 20 years; there were no signs or symptoms of active infection that could account for the pulmonary and cutaneous lesions.45
The presence of perifollicular granulomas with associated lymphocytic infiltrates on repeat biopsy, coupled with the use of topical steroids, made it difficult to rule out a contribution by GPD to her clinical course. That her lesions resolved with pitted scarring while she was taking methotrexate and after topical steroids had been stopped could be the result of successful management or spontaneous resolution of her dermatosis; both papular sarcoidosis and GPD tend to have a self-limited course.7,13
Conclusion
We present 2 cases of papular facial granulomas in patients with similar skin types who had different clinical courses. Evaluation of such lesions remains challenging given the similarity between specific entities that present in this manner. Certainly, it is reasonable to consider a spectrum upon which all of these conditions fall, in light of the findings of these cases and those reported previously.
Cutaneous granulomatous diseases encompass many entities that are skin-limited or systemic. The prototypical cutaneous granuloma is a painless, rounded, well-defined, red-pink or flesh-colored papule1 and is smooth, owing to minimal epidermal involvement. Examples of conditions that present with such lesions include granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (GPD), granulomatous rosacea (GR), lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei (LMDF), and papular sarcoidosis. These entities commonly are seen on the face and can be a source of distress to patients when they are extensive. Several reports have raised the possibility that these conditions lie on a spectrum.2-4 We present 2 cases of patients with facial papular granulomas, discuss potential causes of the lesions, review historical aspects from the literature, and highlight the challenges that these lesions can pose to the clinician.
Case Reports
Patient 1—A 10-year-old Ethiopian girl with a history of atopic dermatitis presented with a facial rash of 4 months’ duration. Her pediatrician initially treated the rash as pityriasis alba and prescribed hydrocortisone cream. Two months into treatment, the patient developed an otherwise asymptomatic, unilateral, papular dermatosis on the right cheek. She subsequently was switched to treatment with benzoyl peroxide and topical clindamycin, which she had been using for 2 months with no improvement at the time of the current presentation. The lesions then spread bilaterally and periorally.
At the current presentation, physical examination demonstrated fine, diffuse, follicular-based, flesh-colored papules over both cheeks, the right side of the nose, and the perioral region (Figure 1). A biopsy of a papular lesion from the right cheek revealed well-formed, noncaseating granulomas in the superficial and mid dermis with an associated lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 2). No organisms were identified on acid-fast, Fite, or periodic acid–Schiff staining. A tuberculin skin test was negative. A chest radiograph showed small calcified hilar lymph nodes bilaterally. Pulmonary function tests were unremarkable. Calcium and angiotensin-converting enzyme levels were normal.

The patient denied any fever, chills, hemoptysis, cough, dyspnea, lymphadenopathy, scleral or conjunctival pain or erythema, visual disturbances, or arthralgias. Hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily was started with minimal improvement after 5 months. Methotrexate 20 mg once weekly was then added. Topical fluocinonide 0.05% also was started at this time, as the patient had required several prednisone tapers over the past 3 months for symptomatic relief. The lesions improved minimally after 5 more months of treatment, at which time she had developed inflammatory papules, pustules, and open comedones in the same areas as well as the glabella.

Repeat biopsy of a papular lesion demonstrated noncaseating granulomas and an associated chronic lymphocytic infiltrate in a follicular and perifollicular distribution (Figure 3). Biopsy of a pustule demonstrated acute Demodex folliculitis. Fluocinonide was stopped, and anti-mite therapy with ivermectin, permethrin cream 5%, and selenium sulfide lotion 2.5% was started, with good response from the pustular lesions.

The patient continued taking methotrexate 20 mg once weekly during this time, with improvement in the papular lesions. She discontinued methotrexate after 12 months with complete resolution. At follow-up 12 months after stopping the methotrexate (roughly 2 years after initial presentation), she showed sustained resolution, with small pitted scars on both cheeks and the nasal tip.
Patient 2—A 33-year-old Ethiopian woman presented with a facial rash of 15 years’ duration. The lesions had been accumulating slowly and were asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed multiple follicular-based, flesh-colored, and erythematous papules on the cheeks, chin, perioral area, and forehead (Figure 4). There were no pustules or telangiectasias. Treatment with tretinoin cream 0.05% for 6 months offered minimal relief.

Biopsy of a papule from the left mandible showed superficial vascular telangiectasias, noncaseating granulomas comprising epithelioid histiocytes and lymphocytes in the superficial dermis, and a perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure 5). No organisms were identified on Fite or Gomori methenamine silver staining.

Comment
The first step in differentiating cutaneous granulomatous lesions should be to distinguish infectious from noninfectious causes.1 Noninfectious cutaneous granulomas can appear nearly anywhere; however, certain processes have a predilection for the face, including GPD, GR, LMDF, and papular sarcoidosis.5-7 These conditions generally present with papular granulomas with features as described above.
Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis—In 1970, Gianotti and colleagues8 briefly described the first possible cases of GPD in 5 children. The eruption comprised numerous yellow, dome-shaped papules in a mostly perioral distribution. Tuberculin and the Kveim tests were nonreactive; histopathology was described as sarcoid-type and not necessarily follicular or perifollicular.8 In 1974, Marten et al9 described 22 Afro-Caribbean children with flesh-colored, papular eruptions on the face that did not show histologic granulomatous changes but were morphologically similar to the reports by Gianotti et al.8 By 1989, Frieden and colleagues10 described this facial eruption as “granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children”. Additionally, the investigators observed granulomatous infiltrates in a perifollicular distribution and suggested follicular disruption as a possible cause. It was clear from the case discussions that these eruptions were not uncommonly diagnosed as papular sarcoidosis.10 The following year, Williams et al11 reported 5 cases of similar papular eruptions in 5 Afro-Caribbean children, coining the term facial Afro-Caribbean eruption.11 Knautz and Lesher12 referred to this entity as “childhood GPD” in 1996 to avoid limiting the diagnosis to Afro-Caribbean patients and to a perioral distribution; this is the most popular current terminology.12 Since then, reports of extrafacial involvement and disease in adults have been published.13,14
Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis often is seen in the perinasal, periocular, and perioral regions of the face.2 It is associated with topical steroid exposure.5 Histologically, noncaseating granulomas around the upper half of undisrupted hair follicles with a lymphocytic infiltrate are typical.13 Treatment should begin with cessation of any topical steroids; first-line agents are oral tetracycline or macrolide antibiotics.5 These agents can be used alone or in combination with topical erythromycin, metronidazole, or sulfur-based lotions.13 Rarely, GPD presents extrafacially.13 Even so, it usually resolves within 2 weeks to 6 months, especially with therapy; scarring is unusual.5,13,15
Granulomatous Rosacea—A report in the early 20th century described patients with tuberculoid granulomas resembling papular rosacea; the initial belief was that this finding represented a rosacealike tuberculid eruption.5 However, this belief was questioned by Snapp,16 among others, who demonstrated near universal lack of reactivity to tuberculin among 20 of these patients in 1949; more recent evidence has substantiated these findings.17 Still, Snapp16 postulated that these rosacealike granulomatous lesions were distinct from classic rosacea because they lacked vascular symptoms and pustules and were recalcitrant to rosacea treatment modalities.
In 1970, Mullanax and colleagues18 introduced the term granulomatous rosacea, reiterating that this entity was not tuberculous. They documented papulopustular lesions as well as telangiectasias, raising the possibility that GR does overlap with acne rosacea. More recent studies have established the current theory that GR is a histologic variant of acne rosacea because, in addition to typical granulomatous papules, its microscopic features can be seen across subtypes of acne rosacea.19,20
Various causes have been proposed for GR. Demodex mites have been reported in association with GR for nearly 30 years.19,20 In the past 10 years, molecular studies have started to define the role of metalloproteinases, UV radiation, and cutaneous peptides in the pathogenesis of acne rosacea and GR.21,22
Granulomatous rosacea typically is seen in middle-aged women.20,23 Hallmarks of rosacea, such as facial erythema, flushing, telangiectasias, pustules, and rhinophyma, are not always present in GR.5,20,23 Lesions usually are distributed around the central face, although extension to the cheeks, total facial involvement, and extrafacial lesions are possible.5,20 Histologically, perifollicular and follicular-based noncaseating granulomas with dilatation of the dermal papillary vasculature are seen.17,23 As a whole, rosacea is comparatively uncommon in dark-skinned patients; when it does occur, GR is a frequent presentation.24
First-line treatment for GR is tetracycline antibiotics.5 Unresponsive cases have been treated—largely anecdotally—with topical modalities (eg, metronidazole, steroids, immunomodulators), systemic agents (eg, dapsone, erythromycin, isotretinoin), and other therapies.5 Granulomatous rosacea tends to have a chronic course.5,23
Lupus Miliaris Disseminatus Faciei—Classic LMDF demonstrates caseating perifollicular granulomas histologically.6,17,25 Lesions tend to appear on the central face, particularly the eyelids, and can be seen extrafacially.3,6,25,26 Although LMDF originally was categorized as a tuberculid eruption, this no longer is thought to be the case.27 It is now regarded by some as a variant of GR25; however, LMDF responds poorly to tetracyclines, is more common in males, and lacks rosacealike vascular abnormalities, leading some to question this association.3,6,17 In the past 20 years, some have proposed renaming LMDF to better reflect its clinical course and to consider it independent of tuberculosis and GR.28 It usually resolves spontaneously after 1 to 3 years, leaving pitted scars.3,6
Papular Sarcoidosis—The first potential documented case of sarcoidosis was by Hutchinson29 in 1869 in a patient seen in London. The author labeled purple plaques on the index patient’s legs and hands as “livid papillary psoriasis.” In 1889, Besnier30 described a patient with violaceous swellings on the nose, ears, and fingers, which he called “lupus pernio”; his contemporary, Tenneson,31 published a case of lupus pernio and described its histologic profile as comprising epithelioid cells and giant cells. It was not until 1899 that the term sarkoid was used to describe these cutaneous lesions by Boeck,32 who thought they were reminiscent of sarcoma. In 1915, Kuznitsky and Bittorf33 described a patient with cutaneous lesions histologically consistent with Boeck’s sarkoid but additionally with hilar lymphadenopathy and pulmonary infiltrates. Around 1916 or 1917, Schaumann34 described patients with cutaneous lesions and additionally with involvement of pulmonary, osseous, hepatosplenic, and tonsillar tissue. These reports are among the first to recognize the multisystemic nature of sarcoidosis. The first possible case of childhood sarcoidosis might have been reported by Osler35 in the United States in 1898.
In the past century or so, an ongoing effort by researchers has focused on identifying etiologic triggers for sarcoidosis. Microbial agents have been considered in this role, with Mycobacterium and Propionibacterium organisms the most intensively studied; the possibility that foreign material contributes to the formation of granulomas also has been raised.36 Current models of the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis involve an interplay between the immune system in genetically predisposed patients and an infection that leads to a hyperimmune type 1 T–helper cell response that clears the infection but not antigens generated by the microbes and the acute host response, including proteins such as serum amyloid A and vimentin.36,37 These antigens aggregate and serve as a nidus for granuloma formation and maintenance long after infection has resolved.
Cutaneous lesions of sarcoidosis include macules, papules, plaques, and lupus pernio, as well as lesions arising within scars or tattoos, with many less common presentations.7,38 Papular sarcoidosis is common on the face but also can involve the extremities.4,7 Strictly, at least 2 organ systems must be involved to diagnose sarcoidosis, but this is debatable.4,7 Among 41 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis, 24 (58.5%) had systemic disease; cutaneous lesions were the presenting sign in 87.5% (21/24) of patients.38 Histologic analysis, regardless of the lesion, usually shows noncaseating so-called “naked” granulomas, which have minimal lymphocytic infiltrate associated with the epithelioid histiocytes.38,39 Perifollicular granulomas are possible but unusual.40
Treatment depends on the extent of cutaneous and systemic involvement. Pharmacotherapeutic modalities include topical steroids, immunomodulators, and retinoids; systemic immunomodulators and immunosuppressants; and biologic agents.7 Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis, particularly the papular variant, usually is associated with acute disease lasting less than 2 years, with resolution of skin lesions.7,38 That said, a recent report suggested that cutaneous sarcoidosis can progress to multisystemic disease as long as 7 years after the initial diagnosis.41
Clinical and Histologic Overlap—Despite this categorization of noninfectious facial granulomatous conditions, each has some clinical and histologic overlap with the others, which must be considered when encountering a granulomatous facial dermatosis. Both GPD and GR tend to present with lesions near the eyes, mouth, and nose, although GR can extend to lateral aspects of the face, below the mandible, and the forehead and has different demographic features.15,20,23 Granulomas in both GPD and GR generally are noncaseating and form in a follicular or perifollicular distribution within the dermis.2,15,23 Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei and GR share a similar facial distribution in some cases.17,20 Even papular cutaneous sarcoidosis has masqueraded as GR clinically and histologically.4
Diagnostic and Treatment Difficulty—Our cases illustrate the range of difficulty in evaluating and managing patients with facial papular granulomas. On one hand, our adult patient’s clinical and histologic findings were highly consistent with GR; on the other hand, our younger patient had clinicopathologic features of both sarcoidosis and GPD at varying times. Both conditions are more common in dark-skinned patients.11,42
Juvenile sarcoidosis is comparatively rare, with a reported annual incidence of 0.22 to 0.27 for every 100,000 children younger than 15 years; however, juvenile sarcoidosis commonly presents around 8 to 15 years of age.43
It is unusual for sarcoid granulomas to be isolated to the skin, much less to the face.4,7,43,44 Patient 1 initially presented in this manner and lacked convincing laboratory or radiographic evidence of systemic sarcoidosis. Bilateral hilar calcifications in sarcoidosis are more typical among adults after 5 to 20 years; there were no signs or symptoms of active infection that could account for the pulmonary and cutaneous lesions.45
The presence of perifollicular granulomas with associated lymphocytic infiltrates on repeat biopsy, coupled with the use of topical steroids, made it difficult to rule out a contribution by GPD to her clinical course. That her lesions resolved with pitted scarring while she was taking methotrexate and after topical steroids had been stopped could be the result of successful management or spontaneous resolution of her dermatosis; both papular sarcoidosis and GPD tend to have a self-limited course.7,13
Conclusion
We present 2 cases of papular facial granulomas in patients with similar skin types who had different clinical courses. Evaluation of such lesions remains challenging given the similarity between specific entities that present in this manner. Certainly, it is reasonable to consider a spectrum upon which all of these conditions fall, in light of the findings of these cases and those reported previously.
- Beretta-Piccoli BT, Mainetti C, Peeters M-A, et al. Cutaneous granulomatosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54:131-146. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8666-8
- Lucas CR, Korman NJ, Gilliam AC. Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis: a variant of granulomatous rosacea in children? J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:115-118. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.07088
- van de Scheur MR, van der Waal RIF, Starink TM. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei: a distinctive rosacea-like syndrome and not a granulomatous form of rosacea. Dermatology. 2003;206:120-123. doi:10.1159/000068457
- Simonart T, Lowy M, Rasquin F, et al. Overlap of sarcoidosis and rosacea. Dermatology. 1997;194:416-418. doi:10.1159/000246165
- Lee GL, Zirwas MJ. Granulomatous rosacea and periorificial dermatitis: controversies and review of management. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:447-455. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.009
- Michaels JD, Cook-Norris RH, Lehman JS, et al. Adult with papular eruption of the central aspect of the face. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:410-412. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.06.039
- Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;38:685-702. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2015.08.010
- Gianotti F, Ermacora E, Benelli MG, et al. Particulière dermatite peri-orale infantile. observations sur 5 cas. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:341.
- Marten RH, Presbury DG, Adamson JE, et al. An unusual papular and acneiform facial eruption in the negro child. Br J Dermatol. 1974;91:435-438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb13083.x
- Frieden IJ, Prose NS, Fletcher V, et al. Granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:369-373.
- Williams HC, Ashworth J, Pembroke AC, et al. FACE—facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1990;15:163-166. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.1990.tb02063.x
- Knautz MA, Lesher JL Jr. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:131-134. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1996.tb01419.x
- Urbatsch AJ, Frieden I, Williams ML, et al. Extrafacial and generalized granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1354-1358. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.10.1354
- Vincenzi C, Parente G, Tosti A. Perioral granulomatous dermatitis: two cases treated with clarithromycin. J Dermatol Treat. 2000;11:57-61.
- Kim YJ, Shin JW, Lee JS, et al. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:386-388. doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.3.386
- Snapp RH. Lewandowsky’s rosacea-like eruption; a clinical study. J Invest Dermatol. 1949;13:175-190. doi:10.1038/jid.1949.86
- Chougule A, Chatterjee D, Sethi S, et al. Granulomatous rosacea versus lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—2 faces of facial granulomatous disorder: a clinicohistological and molecular study. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:819-823. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001243
- Mullanax MG, Kierland RR. Granulomatous rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:206-211.
- Sánchez JL, Berlingeri-Ramos AC, Dueño DV. Granulomatous rosacea. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:6-9. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815bc191
- Helm KF, Menz J, Gibson LE, et al. A clinical and histopathologic study of granulomatous rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1038-1043. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70304-k
- Kanada KN, Nakatsuji T, Gallo RL. Doxycycline indirectly inhibits proteolytic activation of tryptic kallikrein-related peptidases and activation of cathelicidin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1435-1442. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.14
- Jang YH, Sim JH, Kang HY, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases in the granulomatous rosacea compared with the non-granulomatous rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:544-548. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03825.x
- Khokhar O, Khachemoune A. A case of granulomatous rosacea: sorting granulomatous rosacea from other granulomatous diseases that affect the face. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:6.
- Rosen T, Stone MS. Acne rosacea in blacks. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:70-73. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70173-x
- Adams AK, Davis JL, Davis MDP, et al. What is your diagnosis? granulomatous rosacea (lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei, acne agminata). Cutis. 2008;82:103-112.
- Shitara A. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:542-544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1984.tb04206.x
- Hodak E, Trattner A, Feuerman H, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not detectable in active lesions by polymerase chain reaction. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:614-619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1997.tb03797.x
- Skowron F, Causeret AS, Pabion C, et al. F.I.GU.R.E.: facial idiopathic granulomas with regressive evolution. Dermatology. 2000;201:287-289. doi:10.1159/000051539
- Hutchinson J. Case of livid papillary psoriasis. In: London J, Churchill A, eds. Illustrations of Clinical Surgery. J&A Churchill; 1877:42-43.
- Besnier E. Lupus pernio of the face [in French]. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:33-36.
- Tenneson H. Lupus pernio. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:333-336.
- Boeck C. Multiple benign sarkoid of the skin [in Norwegian]. Norsk Mag Laegevidensk. 1899;14:1321-1334.
- Kuznitsky E, Bittorf A. Sarkoid mit beteiligung innerer organe. Münch Med Wochenschr. 1915;62:1349-1353.
- Schaumann J. Etude sur le lupus pernio et ses rapports avec les sarcoides et la tuberculose. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr. 1916-1917;6:357-373.
- Osler W. On chronic symmetrical enlargement of the salivary and lacrimal glands. Am J Med Sci. 1898;115:27-30.
- Chen ES, Moller DR. Etiologies of sarcoidosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49:6-18. doi:10.1007/s12016-015-8481-z
- Eberhardt C, Thillai M, Parker R, et al. Proteomic analysis of Kveim reagent identifies targets of cellular immunity in sarcoidosis. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0170285. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170285
- Esteves TC, Aparicio G, Ferrer B, et al. Prognostic value of skin lesions in sarcoidosis: clinical and histopathological clues. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:556-562. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2666
- Cardoso JC, Cravo M, Reis JP, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: a histopathological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:678-682. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03153.x
- Mangas C, Fernández-Figueras M-T, Fité E, et al. Clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 32 cases of specific cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:772-777. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00563.x
- García-Colmenero L, Sánchez-Schmidt JM, Barranco C, et al. The natural history of cutaneous sarcoidosis. clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 40 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:178-184. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14218
- Shetty AK, Gedalia A. Childhood sarcoidosis: a rare but fascinating disorder. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2008;6:16. doi:10.1186/1546-0096-6-16
- Milman N, Hoffmann AL, Byg KE. Sarcoidosis in children. epidemiology in Danes, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Acta Paediatr. 1998;87:871-878. doi:10.1080/08035259875001366244. A, H, Yapıcı I. Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:220.
- Scadding JG. The late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Postgrad Med J. 1970;46:530-536. doi:10.1136/pgmj.46.538.530
- Beretta-Piccoli BT, Mainetti C, Peeters M-A, et al. Cutaneous granulomatosis: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54:131-146. doi:10.1007/s12016-017-8666-8
- Lucas CR, Korman NJ, Gilliam AC. Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis: a variant of granulomatous rosacea in children? J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:115-118. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.07088
- van de Scheur MR, van der Waal RIF, Starink TM. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei: a distinctive rosacea-like syndrome and not a granulomatous form of rosacea. Dermatology. 2003;206:120-123. doi:10.1159/000068457
- Simonart T, Lowy M, Rasquin F, et al. Overlap of sarcoidosis and rosacea. Dermatology. 1997;194:416-418. doi:10.1159/000246165
- Lee GL, Zirwas MJ. Granulomatous rosacea and periorificial dermatitis: controversies and review of management. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:447-455. doi:10.1016/j.det.2015.03.009
- Michaels JD, Cook-Norris RH, Lehman JS, et al. Adult with papular eruption of the central aspect of the face. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:410-412. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.06.039
- Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015;38:685-702. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2015.08.010
- Gianotti F, Ermacora E, Benelli MG, et al. Particulière dermatite peri-orale infantile. observations sur 5 cas. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:341.
- Marten RH, Presbury DG, Adamson JE, et al. An unusual papular and acneiform facial eruption in the negro child. Br J Dermatol. 1974;91:435-438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb13083.x
- Frieden IJ, Prose NS, Fletcher V, et al. Granulomatous perioral dermatitis in children. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:369-373.
- Williams HC, Ashworth J, Pembroke AC, et al. FACE—facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1990;15:163-166. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.1990.tb02063.x
- Knautz MA, Lesher JL Jr. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 1996;13:131-134. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1996.tb01419.x
- Urbatsch AJ, Frieden I, Williams ML, et al. Extrafacial and generalized granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1354-1358. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.10.1354
- Vincenzi C, Parente G, Tosti A. Perioral granulomatous dermatitis: two cases treated with clarithromycin. J Dermatol Treat. 2000;11:57-61.
- Kim YJ, Shin JW, Lee JS, et al. Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:386-388. doi:10.5021/ad.2011.23.3.386
- Snapp RH. Lewandowsky’s rosacea-like eruption; a clinical study. J Invest Dermatol. 1949;13:175-190. doi:10.1038/jid.1949.86
- Chougule A, Chatterjee D, Sethi S, et al. Granulomatous rosacea versus lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—2 faces of facial granulomatous disorder: a clinicohistological and molecular study. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:819-823. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000001243
- Mullanax MG, Kierland RR. Granulomatous rosacea. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:206-211.
- Sánchez JL, Berlingeri-Ramos AC, Dueño DV. Granulomatous rosacea. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:6-9. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815bc191
- Helm KF, Menz J, Gibson LE, et al. A clinical and histopathologic study of granulomatous rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1038-1043. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70304-k
- Kanada KN, Nakatsuji T, Gallo RL. Doxycycline indirectly inhibits proteolytic activation of tryptic kallikrein-related peptidases and activation of cathelicidin. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1435-1442. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.14
- Jang YH, Sim JH, Kang HY, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of matrix metalloproteinases in the granulomatous rosacea compared with the non-granulomatous rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:544-548. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03825.x
- Khokhar O, Khachemoune A. A case of granulomatous rosacea: sorting granulomatous rosacea from other granulomatous diseases that affect the face. Dermatol Online J. 2004;10:6.
- Rosen T, Stone MS. Acne rosacea in blacks. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;17:70-73. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70173-x
- Adams AK, Davis JL, Davis MDP, et al. What is your diagnosis? granulomatous rosacea (lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei, acne agminata). Cutis. 2008;82:103-112.
- Shitara A. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei. Int J Dermatol. 1984;23:542-544. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362.1984.tb04206.x
- Hodak E, Trattner A, Feuerman H, et al. Lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei—the DNA of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not detectable in active lesions by polymerase chain reaction. Br J Dermatol. 1997;137:614-619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1997.tb03797.x
- Skowron F, Causeret AS, Pabion C, et al. F.I.GU.R.E.: facial idiopathic granulomas with regressive evolution. Dermatology. 2000;201:287-289. doi:10.1159/000051539
- Hutchinson J. Case of livid papillary psoriasis. In: London J, Churchill A, eds. Illustrations of Clinical Surgery. J&A Churchill; 1877:42-43.
- Besnier E. Lupus pernio of the face [in French]. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:33-36.
- Tenneson H. Lupus pernio. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr (Paris). 1889;10:333-336.
- Boeck C. Multiple benign sarkoid of the skin [in Norwegian]. Norsk Mag Laegevidensk. 1899;14:1321-1334.
- Kuznitsky E, Bittorf A. Sarkoid mit beteiligung innerer organe. Münch Med Wochenschr. 1915;62:1349-1353.
- Schaumann J. Etude sur le lupus pernio et ses rapports avec les sarcoides et la tuberculose. Ann Dermatol Syphiligr. 1916-1917;6:357-373.
- Osler W. On chronic symmetrical enlargement of the salivary and lacrimal glands. Am J Med Sci. 1898;115:27-30.
- Chen ES, Moller DR. Etiologies of sarcoidosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49:6-18. doi:10.1007/s12016-015-8481-z
- Eberhardt C, Thillai M, Parker R, et al. Proteomic analysis of Kveim reagent identifies targets of cellular immunity in sarcoidosis. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0170285. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170285
- Esteves TC, Aparicio G, Ferrer B, et al. Prognostic value of skin lesions in sarcoidosis: clinical and histopathological clues. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:556-562. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2666
- Cardoso JC, Cravo M, Reis JP, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis: a histopathological study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:678-682. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03153.x
- Mangas C, Fernández-Figueras M-T, Fité E, et al. Clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 32 cases of specific cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:772-777. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00563.x
- García-Colmenero L, Sánchez-Schmidt JM, Barranco C, et al. The natural history of cutaneous sarcoidosis. clinical spectrum and histological analysis of 40 cases. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:178-184. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14218
- Shetty AK, Gedalia A. Childhood sarcoidosis: a rare but fascinating disorder. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2008;6:16. doi:10.1186/1546-0096-6-16
- Milman N, Hoffmann AL, Byg KE. Sarcoidosis in children. epidemiology in Danes, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Acta Paediatr. 1998;87:871-878. doi:10.1080/08035259875001366244. A, H, Yapıcı I. Isolated cutaneous sarcoidosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:220.
- Scadding JG. The late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Postgrad Med J. 1970;46:530-536. doi:10.1136/pgmj.46.538.530
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should be aware that noninfectious granulomatous dermatosis of the face can be caused by granulomatous periorificial dermatitis, granulomatous rosacea, lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei, and papular sarcoidosis.
- These conditions lie on a spectrum, suggested by their historical description and clinical and histological features.
- Because their clinical courses can vary considerably from patient to patient, a thorough effort should be made to differentiate these conditions.
Flesh-Colored Papule in the Nose of a Child
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).
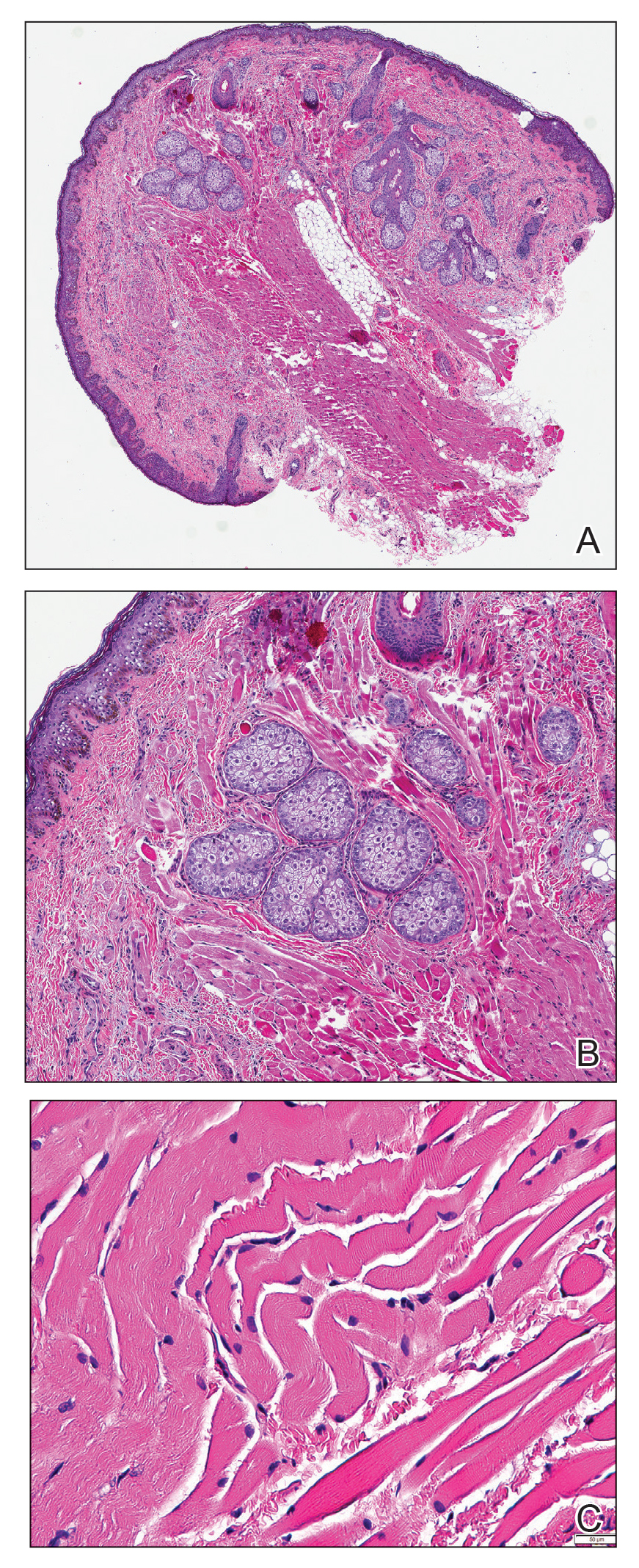
Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).

Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
The Diagnosis: Striated Muscle Hamartoma
Histopathologic evaluation revealed a dome-shaped papule with a center composed of mature striated muscle bundles, vellus hairs, sebaceous lobules, and nerve twigs (Figure) consistent with a diagnosis of striated muscle hamartoma (SMH).

Striated muscle hamartoma was first described in 1986 by Hendrick et al1 with 2 cases in neonates. Biopsies of the lesions taken from the upper lip and sternum showed a characteristic histology consisting of dermal striated muscle fibers and nerve bundles in the central core of the papules associated with a marked number of adnexa. In 1989, the diagnosis of rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma was described, which showed similar findings.2 Cases reported since these entities were discovered have used the terms striated muscle hamartoma and rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma interchangeably.3
Most commonly found on the head and neck, SMH has now been observed in diverse locations including the sternum, hallux, vagina, and oral cavity.1-15 Many reported cases describe lesions around or in the nose.4,7,8 Multiple congenital anomalies have been described alongside SMH and may be associated with this entity including amniotic bands, cleft lip and palate, coloboma, and Delleman syndrome.1,3,4 Almost all of the lesions present as a sessile or pedunculated papule, polyp, nodule, or plaque measuring from 0.3 cm up to 4.9 cm and typically are present since birth.3,5,15 However, there are a few cases of lesions presenting in adults with no prior history.5,6,15
Microscopically, SMH is defined by a dermal lesion with a core comprised of mature skeletal muscle admixed with adipose tissue, adnexa, nerve bundles, and fibrovascular tissue.1 There are other entities that should be considered before making the diagnosis of SMH. Other hamartomas such as accessory tragus, connective tissue nevus, fibrous hamartoma of infancy, and nevus lipomatosis may present similarly; however, these lesions classically lack skeletal muscle. Benign triton tumors, or neuromuscular hamartomas, are rare lesions composed of skeletal muscle and abundant, intimately associated neural tissue. Neuromuscular hamartomas frequently involve large nerves.16 Rhabdomyomas also should be considered. Adult rhabdomyomas are composed of eosinophilic polygonal cells with granular cytoplasm and occasional cross-striations. Fetal rhabdomyomas have multiple histologic types and are defined by a variable myxoid stroma, eosinophilic spindled cells, and rhabdomyocytes in various stages of maturity. Genital rhabdomyomas histopathologically appear similar to fetal rhabdomyomas but are confined to the genital region. The skeletal muscle present in rhabdomyomas typically is less differentiated.17 TMature skeletal bundles should be a dominant component of the lesion before diagnosing SMH.
Typically presenting as congenital lesions in the head and neck region, papules with a dermal core of mature skeletal muscle associated with adnexa and nerve twigs should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of SMH or rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. These lesions are benign and usually are cured with complete excision.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
- Hendrick SJ, Sanchez RL, Blackwell SJ, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma: description of two cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:153-157.
- Mills AE. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989;1:58-63.
- Rosenberg AS, Kirk J, Morgan MB. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: an unusual dermal entity with a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:238-243.
- Sánchez RL, Raimer SS. Clinical and histologic features of striated muscle hamartoma: possible relationship to Delleman’s syndrome. J Cutan Pathol. 1994;21:40-46.
- Chang CP, Chen GS. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma: a plaque-type variant in an adult. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2005;21:185-188.
- Harris MA, Dutton JJ, Proia AD. Striated muscle hamartoma of the eyelid in an adult woman. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;24:492-494.
- Nakanishi H, Hashimoto I, Takiwaki H, et al. Striated muscle hamartoma of the nostril. J Dermatol. 1995;22:504-507.
- Farris PE, Manning S, Veatch F. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994;16:73-75.
- Grilli R, Escalonilla P, Soriano ML, et al. The so-called striated muscle hamartoma is a hamartoma of cutaneous adnexa and mesenchyme, but not of striated muscle. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:390.
- Sampat K, Cheesman E, Siminas S. Perianal rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99:E193-E195.
- Brinster NK, Farmer ER. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting on a digit. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:61-63.
- Han SH, Song HJ, Hong WK, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of the vagina. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009;26:753-755.
- De la Sotta P, Salomone C, González S. Rhabdomyomatous (mesenchymal) hamartoma of the tongue: report of a case. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:58-59.
- Magro G, Di Benedetto A, Sanges G, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma of oral cavity: an unusual location for such a rare lesion. Virchows Arch. 2005;446:346-347.
- Wang Y, Zhao H, Yue X, et al. Rhabdomyomatous mesenchymal hamartoma presenting as a big subcutaneous mass on the neck: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:410.
- Amita K, Shankar SV, Nischal KC, et al. Benign triton tumor: a rare entity in head and neck region. Korean J Pathol. 2013;47:74-76.
- Walsh S, Hurt M. Cutaneous fetal rhabdomyoma: a case report and historical review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008;32:485-491.
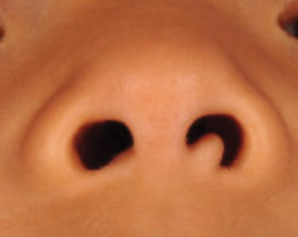
A 4-year-old girl presented to our clinic with an asymptomatic flesh-colored papule in the left nostril. The lesion had been present since birth and grew in relation to the patient with no rapid changes. There had been no pigmentation changes and no bleeding, pain, or itching. The patient’s birth and developmental history were normal. Physical examination revealed a singular, 10×5-mm, flesh-colored, pedunculated mass on the left nasal sill. There were no additional lesions present. An excisional biopsy was performed and submitted for pathologic diagnosis.
Tender Annular Plaque on the Thigh
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
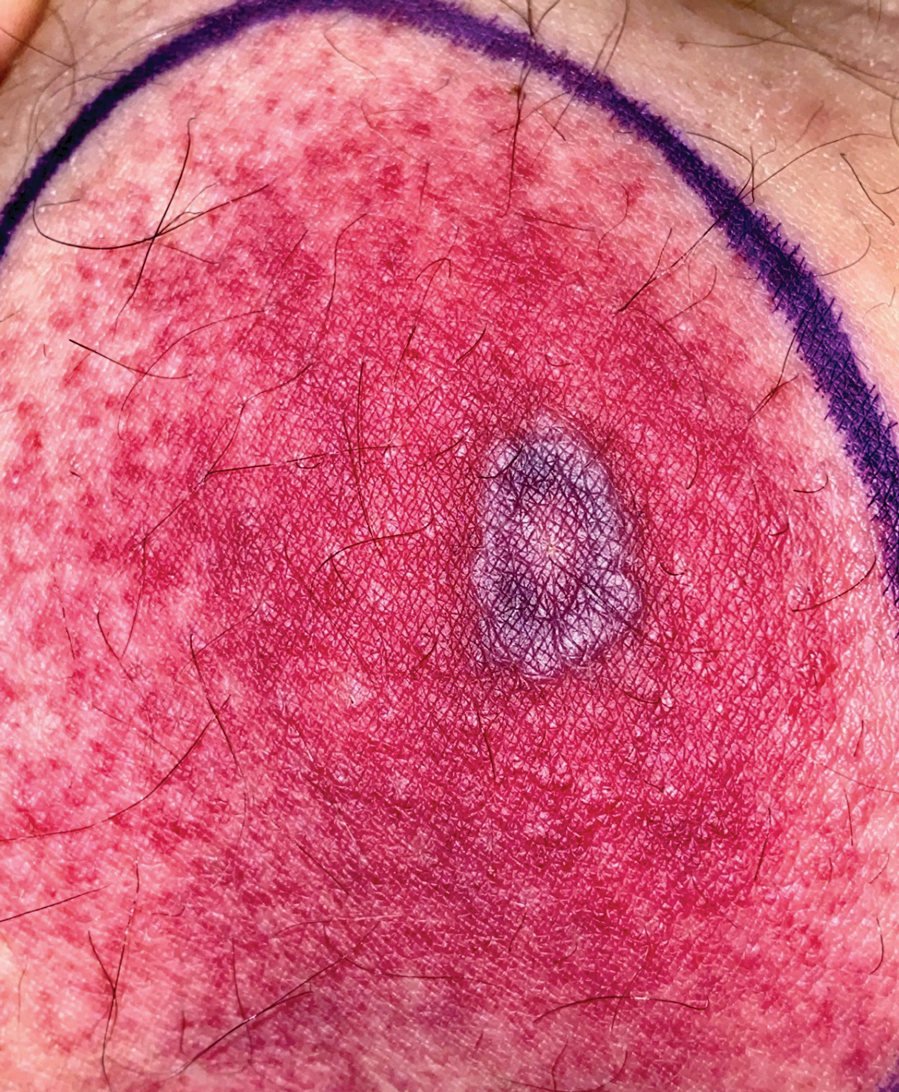
A 58-year-old man who was receiving gilteritinib therapy for relapsed acute myeloid leukemia presented to the emergency department with a painful, rapidly enlarging lesion on the right medial thigh of 2 days’ duration that was accompanied by fever (temperature, 39.2 °C) and body aches. Physical examination revealed a tender annular plaque with a dark violaceous halo overlying a larger area of erythema and induration. Laboratory evaluation revealed a white blood cell count of 600/μL (reference range, 4500–11,000/μL) and an absolute neutrophil count of 200/μL (reference range, 1800–7000/μL). A biopsy was performed.
Soft Nodule on the Forearm
The Diagnosis: Schwannoma
Schwannoma, also known as neurilemmoma, is a benign encapsulated neoplasm of the peripheral nerve sheath that presents as a subcutaneous nodule.1 It also may present in the retroperitoneum, mediastinum, and viscera (eg, gastrointestinal tract, bone, upper respiratory tract, lymph nodes). It may occur as multiple lesions when associated with certain syndromes. It usually is an asymptomatic indolent tumor with neurologic symptoms, such as pain and tenderness, in the lesions that are deeper, larger, or closer in proximity to nearby structures.2,3
Histologically, a schwannoma is encapsulated by the perineurium of the nerve bundle from which it originates (quiz image [top]). The tumor consists of hypercellular (Antoni type A) and hypocellular (Antoni type B) areas. Antoni type A areas consist of tightly packed, spindleshaped cells with elongated wavy nuclei and indistinct cytoplasmic borders. These nuclei tend to align into parallel rows with intervening anuclear zones forming Verocay bodies (quiz image [bottom]).4 Verocay bodies are not seen in all schwannomas, and similar formations may be seen in other tumors as well. Solitary circumscribed neuromas also have Verocay bodies, whereas dermatofibromas and leiomyomas have Verocay-like bodies. Antoni type B areas have scattered spindled or ovoid cells in an edematous or myxoid matrix interspersed with inflammatory cells such as lymphocytes and histiocytes. Vessels with thick hyalinized walls are a helpful feature in diagnosis.2 Schwann cells of a schwannoma stain diffusely positive with S-100 protein. The capsule stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen due to the presence of perineurial cells.2
The morphologic variants of this entity include conventional (common, solitary), cellular, plexiform, ancient, melanotic, epithelioid, pseudoglandular, neuroblastomalike, and microcystic/reticular schwannomas. There are additional variants that are associated with genetic syndromes, such as multiple cutaneous plexiform schwannomas linked with neurofibromatosis type 2, psammomatous melanotic schwannoma presenting in Carney complex, schwannomatosis, and segmental schwannomatosis (a distinct form of neurofibromatosis characterized by multiple schwannomas localized to one limb). Either presentation may have alteration or deletion of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene, NF2, on chromosome 22.2,5
Nodular fasciitis is a benign tumor of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts that usually arises in the subcutaneous tissues. It most commonly occurs in the upper extremities, trunk, head, and neck. It presents as a single, often painful, rapidly growing, subcutaneous nodule. Histologically, lesions mostly are well circumscribed yet unencapsulated, in contrast to schwannomas. They may be hypocellular or hypercellular and are composed of uniform spindle cells with a feathery or fascicular (tissue culture–like) appearance in a loose, myxoid to collagenous stroma. There may be foci of hemorrhage and conspicuous mitoses but not atypical figures (Figure 1). Immunohistochemically, the cells stain positively for smooth muscle actin and negatively for S-100 protein, which sets it apart from a schwannoma. Most cases contain fusion genes, with myosin heavy chain 9 ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, MYH9-USP6, being the most common fusion product.6
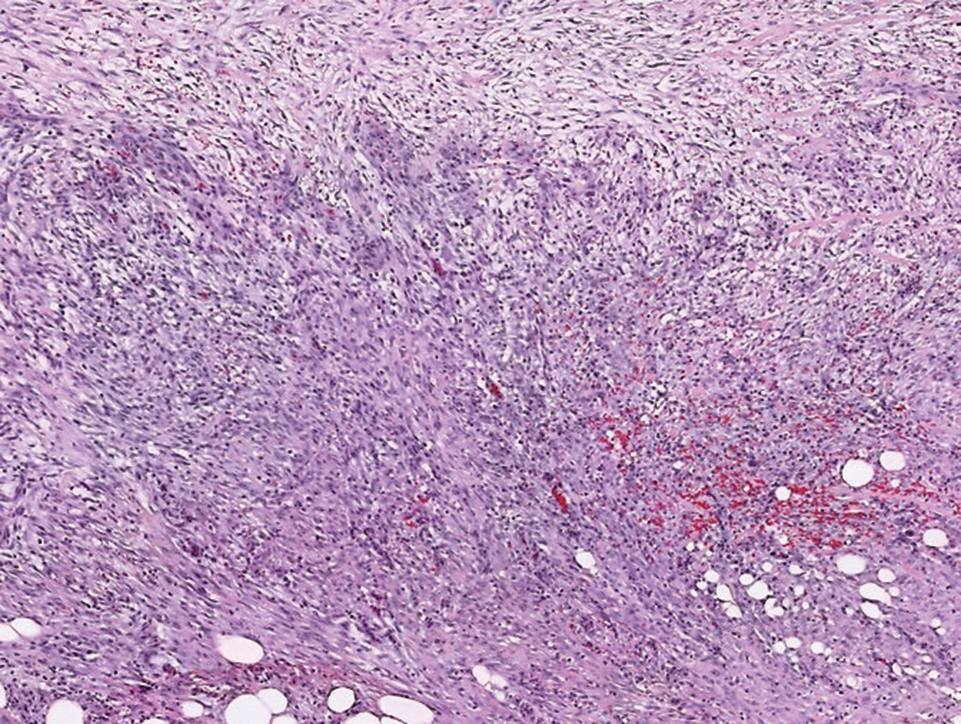
Solitary circumscribed neuroma (palisaded encapsulated neuroma) is a benign, usually solitary dermal lesion. It most commonly occurs in middle-aged to elderly adults as a small (<1 cm), firm, flesh-colored to pink papule on the face (ie, cheeks, nose, nasolabial folds) and less commonly in the oral and acral regions and on the eyelids and penis. The lesion usually is unilobular; however, other growth patterns such as plexiform, multilobular, and fungating variants have been identified. Histologically, it is a well-circumscribed nodule with a thin capsule of perineurium that is composed of interlacing bundles of Schwann cells with a characteristic clefting artifact (Figure 2). Cells have wavy dark nuclei with scant cytoplasm that occasionally form palisades or Verocay bodies causing these lesions to be confused with schwannomas. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positively with S-100 protein, and the perineurium stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen, Claudin-1, and Glut-1. Neurofilament protein stains axons throughout neuromas, whereas in schwannoma, the expression often is limited to entrapped axons at the periphery of the tumor.7
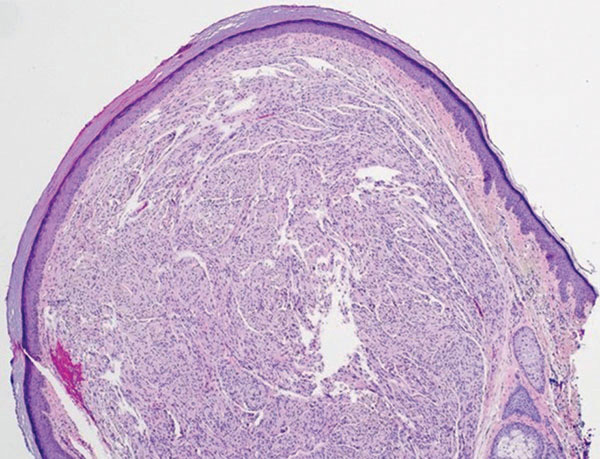
Angioleiomyoma is an uncommon, benign, smooth muscle neoplasm of the skin and subcutaneous tissue that originates from vascular smooth muscle. It most commonly presents in adult females aged 30 to 60 years, with a predilection for the lower limbs. These tumors typically are solitary, slow growing, and less than 2 cm in diameter and may be painful upon compression. Similar to schwannoma, angioleiomyoma is an encapsulated lesion composed of interlacing, uniform, smooth muscle bundles distributed around vessels (Figure 3). Smooth muscle cells have oval- or cigar-shaped nuclei with a small perinuclear vacuole of glycogen. Immunohistochemically, there is strong diffuse staining for smooth muscle actin and h-caldesmon. Recurrence after excision is rare.2,8
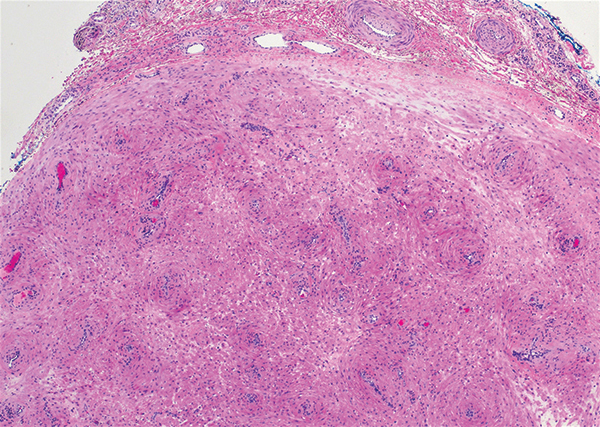
Neurofibroma is a common, mostly sporadic, benign tumor of nerve sheath origin. The solitary type may be localized (well circumscribed, unencapsulated) or diffuse. The presence of multiple, deep, and plexiform lesions is associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease) that is caused by germline mutations in the NF1 gene. Histologically, the tumor is composed of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineurial cells, and nerve axons within an extracellular myxoid to collagenous matrix (Figure 4). The diffuse type is an ill-defined proliferation that entraps adnexal structures. The plexiform type is defined by multinodular serpentine fascicles. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positive for S-100 protein and SOX10 (SRY-Box Transcription Factor 10). Epithelial membrane antigen stains admixed perineurial cells. Neurofilament protein highlights intratumoral axons, which generally are not found throughout schwannomas. Transformation to a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor occurs in up to 10% of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1, usually in plexiform neurofibromas, and is characterized by increased cellularity, atypia, mitotic activity, and necrosis.9
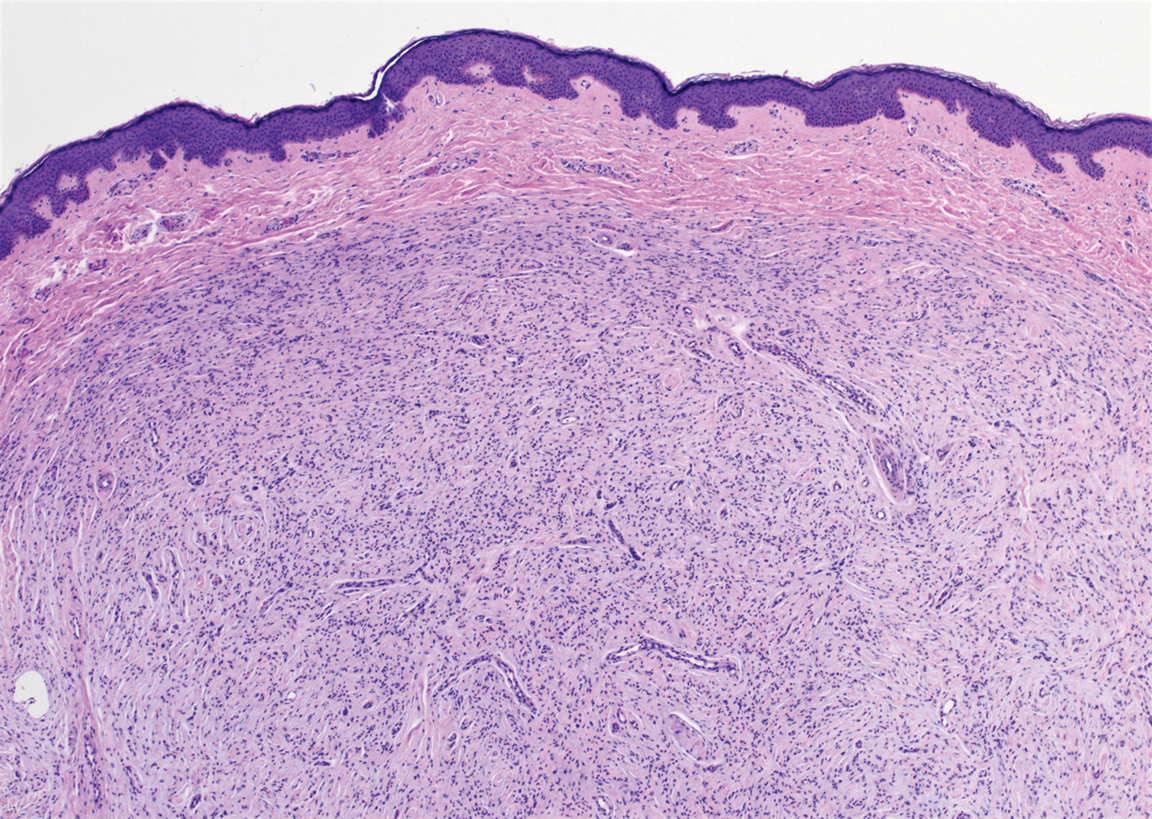
- Ritter SE, Elston DM. Cutaneous schwannoma of the foot. Cutis. 2001;67:127-129.
- Calonje E, Damaskou V, Lazar AJ. Connective tissue tumors. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 5th ed. Vol 2. Elsevier Saunders; 2020:1698-1894.
- Knight DM, Birch R, Pringle J. Benign solitary schwannomas: a review of 234 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:382-387.
- Lespi PJ, Smit R. Verocay body—prominent cutaneous leiomyoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:110-111.
- Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM. The pathobiologic spectrum of schwannomas. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:925-934.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Leblebici C, Savli TC, Yeni B, et al. Palisaded encapsulated (solitary circumscribed) neuroma: a review of 30 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2019;27:506-514.
- Yeung CM, Moore L, Lans J, et al. Angioleiomyoma of the hand: a case series and review of the literature. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020; 8:373-377.
- Skovronsky DM, Oberholtzer JC. Pathologic classification of peripheral nerve tumors. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2004;15:157-166.
The Diagnosis: Schwannoma
Schwannoma, also known as neurilemmoma, is a benign encapsulated neoplasm of the peripheral nerve sheath that presents as a subcutaneous nodule.1 It also may present in the retroperitoneum, mediastinum, and viscera (eg, gastrointestinal tract, bone, upper respiratory tract, lymph nodes). It may occur as multiple lesions when associated with certain syndromes. It usually is an asymptomatic indolent tumor with neurologic symptoms, such as pain and tenderness, in the lesions that are deeper, larger, or closer in proximity to nearby structures.2,3
Histologically, a schwannoma is encapsulated by the perineurium of the nerve bundle from which it originates (quiz image [top]). The tumor consists of hypercellular (Antoni type A) and hypocellular (Antoni type B) areas. Antoni type A areas consist of tightly packed, spindleshaped cells with elongated wavy nuclei and indistinct cytoplasmic borders. These nuclei tend to align into parallel rows with intervening anuclear zones forming Verocay bodies (quiz image [bottom]).4 Verocay bodies are not seen in all schwannomas, and similar formations may be seen in other tumors as well. Solitary circumscribed neuromas also have Verocay bodies, whereas dermatofibromas and leiomyomas have Verocay-like bodies. Antoni type B areas have scattered spindled or ovoid cells in an edematous or myxoid matrix interspersed with inflammatory cells such as lymphocytes and histiocytes. Vessels with thick hyalinized walls are a helpful feature in diagnosis.2 Schwann cells of a schwannoma stain diffusely positive with S-100 protein. The capsule stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen due to the presence of perineurial cells.2
The morphologic variants of this entity include conventional (common, solitary), cellular, plexiform, ancient, melanotic, epithelioid, pseudoglandular, neuroblastomalike, and microcystic/reticular schwannomas. There are additional variants that are associated with genetic syndromes, such as multiple cutaneous plexiform schwannomas linked with neurofibromatosis type 2, psammomatous melanotic schwannoma presenting in Carney complex, schwannomatosis, and segmental schwannomatosis (a distinct form of neurofibromatosis characterized by multiple schwannomas localized to one limb). Either presentation may have alteration or deletion of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene, NF2, on chromosome 22.2,5
Nodular fasciitis is a benign tumor of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts that usually arises in the subcutaneous tissues. It most commonly occurs in the upper extremities, trunk, head, and neck. It presents as a single, often painful, rapidly growing, subcutaneous nodule. Histologically, lesions mostly are well circumscribed yet unencapsulated, in contrast to schwannomas. They may be hypocellular or hypercellular and are composed of uniform spindle cells with a feathery or fascicular (tissue culture–like) appearance in a loose, myxoid to collagenous stroma. There may be foci of hemorrhage and conspicuous mitoses but not atypical figures (Figure 1). Immunohistochemically, the cells stain positively for smooth muscle actin and negatively for S-100 protein, which sets it apart from a schwannoma. Most cases contain fusion genes, with myosin heavy chain 9 ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, MYH9-USP6, being the most common fusion product.6

Solitary circumscribed neuroma (palisaded encapsulated neuroma) is a benign, usually solitary dermal lesion. It most commonly occurs in middle-aged to elderly adults as a small (<1 cm), firm, flesh-colored to pink papule on the face (ie, cheeks, nose, nasolabial folds) and less commonly in the oral and acral regions and on the eyelids and penis. The lesion usually is unilobular; however, other growth patterns such as plexiform, multilobular, and fungating variants have been identified. Histologically, it is a well-circumscribed nodule with a thin capsule of perineurium that is composed of interlacing bundles of Schwann cells with a characteristic clefting artifact (Figure 2). Cells have wavy dark nuclei with scant cytoplasm that occasionally form palisades or Verocay bodies causing these lesions to be confused with schwannomas. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positively with S-100 protein, and the perineurium stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen, Claudin-1, and Glut-1. Neurofilament protein stains axons throughout neuromas, whereas in schwannoma, the expression often is limited to entrapped axons at the periphery of the tumor.7

Angioleiomyoma is an uncommon, benign, smooth muscle neoplasm of the skin and subcutaneous tissue that originates from vascular smooth muscle. It most commonly presents in adult females aged 30 to 60 years, with a predilection for the lower limbs. These tumors typically are solitary, slow growing, and less than 2 cm in diameter and may be painful upon compression. Similar to schwannoma, angioleiomyoma is an encapsulated lesion composed of interlacing, uniform, smooth muscle bundles distributed around vessels (Figure 3). Smooth muscle cells have oval- or cigar-shaped nuclei with a small perinuclear vacuole of glycogen. Immunohistochemically, there is strong diffuse staining for smooth muscle actin and h-caldesmon. Recurrence after excision is rare.2,8

Neurofibroma is a common, mostly sporadic, benign tumor of nerve sheath origin. The solitary type may be localized (well circumscribed, unencapsulated) or diffuse. The presence of multiple, deep, and plexiform lesions is associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease) that is caused by germline mutations in the NF1 gene. Histologically, the tumor is composed of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineurial cells, and nerve axons within an extracellular myxoid to collagenous matrix (Figure 4). The diffuse type is an ill-defined proliferation that entraps adnexal structures. The plexiform type is defined by multinodular serpentine fascicles. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positive for S-100 protein and SOX10 (SRY-Box Transcription Factor 10). Epithelial membrane antigen stains admixed perineurial cells. Neurofilament protein highlights intratumoral axons, which generally are not found throughout schwannomas. Transformation to a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor occurs in up to 10% of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1, usually in plexiform neurofibromas, and is characterized by increased cellularity, atypia, mitotic activity, and necrosis.9

The Diagnosis: Schwannoma
Schwannoma, also known as neurilemmoma, is a benign encapsulated neoplasm of the peripheral nerve sheath that presents as a subcutaneous nodule.1 It also may present in the retroperitoneum, mediastinum, and viscera (eg, gastrointestinal tract, bone, upper respiratory tract, lymph nodes). It may occur as multiple lesions when associated with certain syndromes. It usually is an asymptomatic indolent tumor with neurologic symptoms, such as pain and tenderness, in the lesions that are deeper, larger, or closer in proximity to nearby structures.2,3
Histologically, a schwannoma is encapsulated by the perineurium of the nerve bundle from which it originates (quiz image [top]). The tumor consists of hypercellular (Antoni type A) and hypocellular (Antoni type B) areas. Antoni type A areas consist of tightly packed, spindleshaped cells with elongated wavy nuclei and indistinct cytoplasmic borders. These nuclei tend to align into parallel rows with intervening anuclear zones forming Verocay bodies (quiz image [bottom]).4 Verocay bodies are not seen in all schwannomas, and similar formations may be seen in other tumors as well. Solitary circumscribed neuromas also have Verocay bodies, whereas dermatofibromas and leiomyomas have Verocay-like bodies. Antoni type B areas have scattered spindled or ovoid cells in an edematous or myxoid matrix interspersed with inflammatory cells such as lymphocytes and histiocytes. Vessels with thick hyalinized walls are a helpful feature in diagnosis.2 Schwann cells of a schwannoma stain diffusely positive with S-100 protein. The capsule stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen due to the presence of perineurial cells.2
The morphologic variants of this entity include conventional (common, solitary), cellular, plexiform, ancient, melanotic, epithelioid, pseudoglandular, neuroblastomalike, and microcystic/reticular schwannomas. There are additional variants that are associated with genetic syndromes, such as multiple cutaneous plexiform schwannomas linked with neurofibromatosis type 2, psammomatous melanotic schwannoma presenting in Carney complex, schwannomatosis, and segmental schwannomatosis (a distinct form of neurofibromatosis characterized by multiple schwannomas localized to one limb). Either presentation may have alteration or deletion of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene, NF2, on chromosome 22.2,5
Nodular fasciitis is a benign tumor of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts that usually arises in the subcutaneous tissues. It most commonly occurs in the upper extremities, trunk, head, and neck. It presents as a single, often painful, rapidly growing, subcutaneous nodule. Histologically, lesions mostly are well circumscribed yet unencapsulated, in contrast to schwannomas. They may be hypocellular or hypercellular and are composed of uniform spindle cells with a feathery or fascicular (tissue culture–like) appearance in a loose, myxoid to collagenous stroma. There may be foci of hemorrhage and conspicuous mitoses but not atypical figures (Figure 1). Immunohistochemically, the cells stain positively for smooth muscle actin and negatively for S-100 protein, which sets it apart from a schwannoma. Most cases contain fusion genes, with myosin heavy chain 9 ubiquitin-specific peptidase 6, MYH9-USP6, being the most common fusion product.6

Solitary circumscribed neuroma (palisaded encapsulated neuroma) is a benign, usually solitary dermal lesion. It most commonly occurs in middle-aged to elderly adults as a small (<1 cm), firm, flesh-colored to pink papule on the face (ie, cheeks, nose, nasolabial folds) and less commonly in the oral and acral regions and on the eyelids and penis. The lesion usually is unilobular; however, other growth patterns such as plexiform, multilobular, and fungating variants have been identified. Histologically, it is a well-circumscribed nodule with a thin capsule of perineurium that is composed of interlacing bundles of Schwann cells with a characteristic clefting artifact (Figure 2). Cells have wavy dark nuclei with scant cytoplasm that occasionally form palisades or Verocay bodies causing these lesions to be confused with schwannomas. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positively with S-100 protein, and the perineurium stains positively with epithelial membrane antigen, Claudin-1, and Glut-1. Neurofilament protein stains axons throughout neuromas, whereas in schwannoma, the expression often is limited to entrapped axons at the periphery of the tumor.7

Angioleiomyoma is an uncommon, benign, smooth muscle neoplasm of the skin and subcutaneous tissue that originates from vascular smooth muscle. It most commonly presents in adult females aged 30 to 60 years, with a predilection for the lower limbs. These tumors typically are solitary, slow growing, and less than 2 cm in diameter and may be painful upon compression. Similar to schwannoma, angioleiomyoma is an encapsulated lesion composed of interlacing, uniform, smooth muscle bundles distributed around vessels (Figure 3). Smooth muscle cells have oval- or cigar-shaped nuclei with a small perinuclear vacuole of glycogen. Immunohistochemically, there is strong diffuse staining for smooth muscle actin and h-caldesmon. Recurrence after excision is rare.2,8

Neurofibroma is a common, mostly sporadic, benign tumor of nerve sheath origin. The solitary type may be localized (well circumscribed, unencapsulated) or diffuse. The presence of multiple, deep, and plexiform lesions is associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (von Recklinghausen disease) that is caused by germline mutations in the NF1 gene. Histologically, the tumor is composed of Schwann cells, fibroblasts, perineurial cells, and nerve axons within an extracellular myxoid to collagenous matrix (Figure 4). The diffuse type is an ill-defined proliferation that entraps adnexal structures. The plexiform type is defined by multinodular serpentine fascicles. Immunohistochemically, the Schwann cells stain positive for S-100 protein and SOX10 (SRY-Box Transcription Factor 10). Epithelial membrane antigen stains admixed perineurial cells. Neurofilament protein highlights intratumoral axons, which generally are not found throughout schwannomas. Transformation to a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor occurs in up to 10% of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1, usually in plexiform neurofibromas, and is characterized by increased cellularity, atypia, mitotic activity, and necrosis.9

- Ritter SE, Elston DM. Cutaneous schwannoma of the foot. Cutis. 2001;67:127-129.
- Calonje E, Damaskou V, Lazar AJ. Connective tissue tumors. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 5th ed. Vol 2. Elsevier Saunders; 2020:1698-1894.
- Knight DM, Birch R, Pringle J. Benign solitary schwannomas: a review of 234 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:382-387.
- Lespi PJ, Smit R. Verocay body—prominent cutaneous leiomyoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:110-111.
- Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM. The pathobiologic spectrum of schwannomas. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:925-934.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Leblebici C, Savli TC, Yeni B, et al. Palisaded encapsulated (solitary circumscribed) neuroma: a review of 30 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2019;27:506-514.
- Yeung CM, Moore L, Lans J, et al. Angioleiomyoma of the hand: a case series and review of the literature. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020; 8:373-377.
- Skovronsky DM, Oberholtzer JC. Pathologic classification of peripheral nerve tumors. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2004;15:157-166.
- Ritter SE, Elston DM. Cutaneous schwannoma of the foot. Cutis. 2001;67:127-129.
- Calonje E, Damaskou V, Lazar AJ. Connective tissue tumors. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin. 5th ed. Vol 2. Elsevier Saunders; 2020:1698-1894.
- Knight DM, Birch R, Pringle J. Benign solitary schwannomas: a review of 234 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:382-387.
- Lespi PJ, Smit R. Verocay body—prominent cutaneous leiomyoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 1999;21:110-111.
- Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM. The pathobiologic spectrum of schwannomas. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18:925-934.
- Erickson-Johnson MR, Chou MM, Evers BR, et al. Nodular fasciitis: a novel model of transient neoplasia induced by MYH9-USP6 gene fusion. Lab Invest. 2011;91:1427-1433.
- Leblebici C, Savli TC, Yeni B, et al. Palisaded encapsulated (solitary circumscribed) neuroma: a review of 30 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2019;27:506-514.
- Yeung CM, Moore L, Lans J, et al. Angioleiomyoma of the hand: a case series and review of the literature. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020; 8:373-377.
- Skovronsky DM, Oberholtzer JC. Pathologic classification of peripheral nerve tumors. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2004;15:157-166.

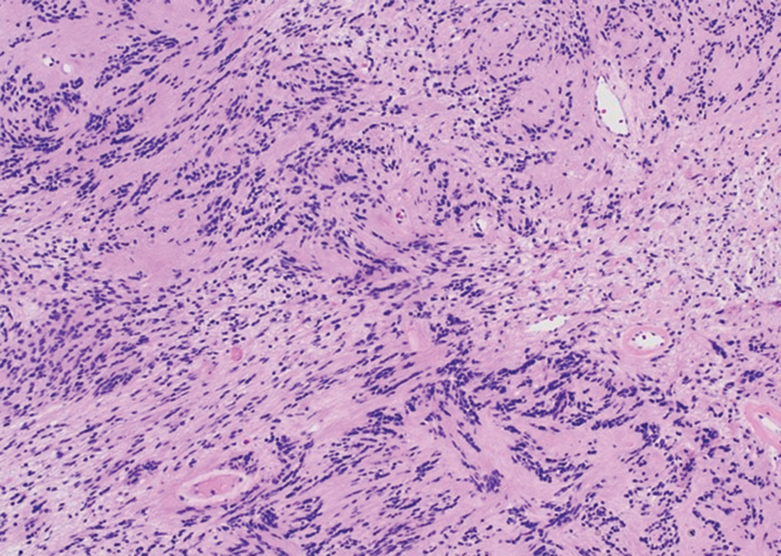
A 54-year-old woman presented with an enlarging mass on the right volar forearm. Physical examination revealed a 1-cm, soft, mobile, subcutaneous nodule. Excision revealed tan-pink, indurated, fibrous, nodular tissue.
Product News October 2021
Opzelura FDA Approved for Atopic Dermatitis Incyte
Corporation announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream 1.5% for the short-term and noncontinuous chronic treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Opzelura is formulated with ruxolitinib, a selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 inhibitor, to target key cytokine signals believed to contribute to itch and inflammation. For more information, visit www.opzelurahcp.com/.
Twyneo FDA Approved for Acne Vulgaris
Sol-Gel Technologies, Ltd, announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Twyneo (tretinoin 0.1% /benzoyl peroxide 3%) cream for the treatment of acne vulgaris in adult and pediatric patients 9 years and older. Tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide are widely prescribed separately for acne vulgaris; however, benzoyl peroxide causes degradation of the tretinoin molecule, thereby potentially reducing its effectiveness if used at the same time or combined in the same formulation. The formulation of Twyneo uses silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures to separately microencapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the 2 active ingredients in the cream. For more information, visit www.sol-gel.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Opzelura FDA Approved for Atopic Dermatitis Incyte
Corporation announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream 1.5% for the short-term and noncontinuous chronic treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Opzelura is formulated with ruxolitinib, a selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 inhibitor, to target key cytokine signals believed to contribute to itch and inflammation. For more information, visit www.opzelurahcp.com/.
Twyneo FDA Approved for Acne Vulgaris
Sol-Gel Technologies, Ltd, announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Twyneo (tretinoin 0.1% /benzoyl peroxide 3%) cream for the treatment of acne vulgaris in adult and pediatric patients 9 years and older. Tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide are widely prescribed separately for acne vulgaris; however, benzoyl peroxide causes degradation of the tretinoin molecule, thereby potentially reducing its effectiveness if used at the same time or combined in the same formulation. The formulation of Twyneo uses silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures to separately microencapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the 2 active ingredients in the cream. For more information, visit www.sol-gel.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Opzelura FDA Approved for Atopic Dermatitis Incyte
Corporation announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream 1.5% for the short-term and noncontinuous chronic treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis (AD) in nonimmunocompromised patients 12 years and older whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Opzelura is formulated with ruxolitinib, a selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 inhibitor, to target key cytokine signals believed to contribute to itch and inflammation. For more information, visit www.opzelurahcp.com/.
Twyneo FDA Approved for Acne Vulgaris
Sol-Gel Technologies, Ltd, announces US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of Twyneo (tretinoin 0.1% /benzoyl peroxide 3%) cream for the treatment of acne vulgaris in adult and pediatric patients 9 years and older. Tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide are widely prescribed separately for acne vulgaris; however, benzoyl peroxide causes degradation of the tretinoin molecule, thereby potentially reducing its effectiveness if used at the same time or combined in the same formulation. The formulation of Twyneo uses silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures to separately microencapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the 2 active ingredients in the cream. For more information, visit www.sol-gel.com.
If you would like your product included in Product News, please email a press release to the Editorial Office at [email protected].
Underrepresented Minority Students Applying to Dermatology Residency in the COVID-19 Era: Challenges and Considerations
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
The COVID-19 pandemic has markedly changed the dermatology residency application process. As medical students head into this application cycle, the impacts of systemic racism and deeply rooted structural barriers continue to be exacerbated for students who identify as an underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine—historically defined as those who self-identify as Hispanic or Latinx; Black or African American; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander. The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) defines URMs as racial and ethnic populations that are underrepresented in medicine relative to their numbers in the general population.1 Although these groups account for approximately 34% of the population of the United States, they constitute only 11% of the country’s physician workforce.2,3
Of the total physician workforce in the United States, Black and African American physicians account for 5% of practicing physicians; Hispanic physicians, 5.8%; American Indian and Alaska Native physicians, 0.3%; and Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander physicians, 0.1%.2 In competitive medical specialties, the disproportionality of these numbers compared to our current demographics in the United States as shown above is even more staggering. In 2018, for example, 10% of practicing dermatologists identified as female URM physicians; 6%, as male URM physicians.2 In this article, we discuss some of the challenges and considerations for URM students applying to dermatology residency in the era of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Barriers for URM Students in Dermatology
Multiple studies have attempted to identify some of the barriers faced by URM students in medicine that might explain the lack of diversity in competitive specialties. Vasquez and colleagues4 identified 4 major factors that play a role in dermatology: lack of equitable resources, lack of support, financial limitations, and the lack of group identity. More than half of URM students surveyed (1) identified lack of support as a barrier and (2) reported having been encouraged to seek a specialty more reflective of their community.4
Soliman et al5 reported that URM barriers in dermatology extend to include lack of diversity in the field, socioeconomic factors, lack of mentorship, and a negative perception of minority students by residency programs. Dermatology is the second least diverse specialty in medicine after orthopedic surgery, which, in and of itself, might further discourage URM students from applying to dermatology.5
With the minimal exposure that URM students have to the field of dermatology, the lack of pipeline programs, and reports that URMs often are encouraged to pursue primary care, the current diversity deficiency in dermatology comes as no surprise. In addition, the substantial disadvantage for URM students is perpetuated by the traditional highly selective process that favors grades, board scores, and honor society status over holistic assessment of the individual student and their unique experiences and potential for contribution.
Looking Beyond Test Scores
The US Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) traditionally has been used to select dermatology residency applicants, with high cutoff scores often excluding outstanding URM students. Research has suggested that the use of USMLE examination test scores for residency recruitment lacks validity because it has poor predictability of residency performance.6 Although the USMLE Step 1 examination is transitioning to pass/fail scoring, applicants for the next cycle will still have a 3-digit numerical score.
We strongly recommend that dermatology programs transition from emphasizing scores of residency candidates to reviewing each candidate holistically. The AAMC defines “holistic review” as a “flexible, individualized way of assessing an applicant’s capabilities, by which balanced consideration is given to experiences, attributes, competencies, and academic or scholarly metrics and, when considered in combination, how the individual might contribute value to the institution’s mission.”7 Furthermore, we recommend that dermatology residency programs have multiple faculty members review each application, including a representative of the diversity, inclusion, and equity committee.
Applying to Residency in the COVID-19 Virtual Environment
In the COVID-19 era, dermatology externship opportunities that would have allowed URM students to work directly with potential residency programs, showcase their abilities, and network have been limited. Virtual residency interviews could make it more challenging to evaluate candidates, especially URM students from less prestigious programs or unusual socioeconomic backgrounds, or with lower board scores. In addition, virtual interviews can more easily become one-dimensional, depriving URM students of the opportunity to gauge their personal fit in a specific dermatology residency program and its community. Questions and concerns of URM students might include: Will I be appropriately supported and mentored? Will my cultural preferences, religion, sexual preference, hairstyle, and beliefs be accepted? Can I advocate for minorities and support antiracism and diversity and inclusion initiatives? To that end, we recommend that dermatology programs continue to host virtual meet-and-greet events for potential students to meet faculty and learn more about the program. In addition, programs should consider having current residents interact virtually with candidates to allow students to better understand the culture of the department and residents’ experiences as trainees in such an environment. For URM students, this is highly important because diversity, inclusion, and antiracism policies and initiatives might not be explicitly available on the institution’s website or residency information page.
Organizations Championing Diversity
Recently, multiple dermatology societies and organizations have been emphasizing the need for diversity and inclusion as well as promoting holistic application review. The American Academy of Dermatology pioneered the Diversity Champion Workshop in 2019 and continues to offer the Diversity Mentorship program, connecting URM students to mentors nationally. The Skin of Color Society offers yearly grants and awards to medical students to develop mentorship and research, and recently hosted webinars to guide medical students and residency programs on diversity and inclusion, residency application and review, and COVID-19 virtual interviews. Other national societies, such as the Student National Medical Association and Latino Medical Student Association, have been promoting workshops and interview mentoring for URM students, including dermatology-specific events. Although it is estimated that more than 90% of medical schools in the United States already perform holistic application review and that such review has been adopted by many dermatology programs nationwide, data regarding dermatology residency programs’ implementation of holistic application review are lacking.8
In addition, we encourage continuation of the proposed coordinated interview invite release from the Association of Professors of Dermatology, which was implemented in the 2020-2021 cycle. In light of the recent AAMC letter9 on the maldistribution of interview invitations to highest-tier applicants, coordination of interview release dates and other similar initiatives to prevent programs from offering more invites than their available slots and improve transparency about interview days are needed. Furthermore, continuing to offer optional virtual interviews for applicants in future cycles could make the process less cost-prohibitive for many URM students.4,5
Final Thoughts
Dermatology residency programs must intentionally guard against falling back to traditional standards of assessment as the only means of student evaluation, especially in this virtual era. It is our responsibility to remove artificial barriers that continue to stall progress in diversity, inclusion, equity, and belonging in dermatology.
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
- Underrepresented in medicine definition. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/what-we-do/mission-areas/diversity-inclusion/underrepresented-in-medicine
- Diversity in medicine: facts and figures 2019. table 13. practice specialty, males by race/ethnicity, 2018. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/table-13-practice-specialty-males-race/ethnicity-2018 1B
- US Census Bureau. Quick facts: United States. Updated July 1, 2019. Accessed September 20, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219
- Vasquez R, Jeong H, Florez-Pollack S, et al. What are the barriers faced by underrepresented minorities applying to dermatology? a qualitative cross-sectional study of applicants applying to a large dermatology residency program. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1770-1773. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.067
- Soliman YS, Rzepecki AK, Guzman AK, et al. Understanding perceived barriers of minority medical students pursuing a career in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:252-254. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4813
- Williams C, Kwan B, Pereira A, et al. A call to improve conditions for conducting holistic review in graduate medical education recruitment. MedEdPublish. 2019;8:6. https://doi.org/10.15694/mep.2019.000076.1
- Holistic principles in resident selection: an introduction. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/system/files/2020-08/aa-member-capacity-building-holistic-review-transcript-activities-GME-081420.pdf
- Luke J, Cornelius L, Lim H. Dermatology resident selection: shifting toward holistic review? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;84:1208-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.025
- Open letter on residency interviews from Alison Whelan, MD, AAMC Chief Medical Education Officer. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Published December 18, 2020. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://www.aamc.org/media/50291/download
Practice Points
- Dermatology remains one of the least diverse medical specialties.
- Underrepresented minority (URM) in medicine residency applicants might be negatively affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The implementation of holistic review, diversity and inclusion initiatives, and virtual opportunities might mitigate some of the barriers faced by URM applicants.
Duration of Adalimumab Therapy in Hidradenitis Suppurativa With and Without Oral Immunosuppressants
To the Editor:
The tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab is the only US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Although 50.6% of patients fulfilled Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response criteria with adalimumab at 12 weeks, many responders were not satisfied with their disease control, and secondary loss of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response fulfillment occurred in 15.9% of patients within approximately 3 years.1 Without other US Food and Drug Administration–approved HS treatments, some dermatologists have combined adalimumab with methotrexate (MTX) and/or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to attempt to increase the duration of satisfactory disease control while on adalimumab. Combining tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors with oral immunosuppressants is a well-established approach in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease; however, to the best of our knowledge, this approach has not been studied for HS.2,3
To assess whether there is a role for combining adalimumab with MTX and/or MMF in the treatment of HS, we performed a single-institution retrospective chart review at the University of Connecticut Department of Dermatology to determine whether patients receiving combination therapy stayed on adalimumab longer than those who received adalimumab monotherapy. All patients receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS with at least 1 follow-up visit 3 or more months after treatment initiation were included. Duration of treatment with adalimumab was defined as the length of time between initiation and termination of adalimumab, regardless of flares, adverse events, or addition of adjuvant therapy that occurred during this time span. Because standardized rating scales measuring the severity of HS at this time are not recorded routinely at our institution, treatment duration with adalimumab was used as a surrogate for measuring therapeutic success. Additionally, treatment duration is a meaningful end point, as patients with HS may require indefinite treatment. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS. Patients were excluded if they were lost to follow-up or had received adalimumab for less than 6 months, as data suggest that biologics do not reach peak effect for up to 6 months in HS.4
We identified 116 eligible patients with HS, 32 of whom received combination therapy. Five patients received 40 mg of adalimumab every other week, and 111 patients received 40 mg of adalimumab each week. Patients receiving oral immunosuppressants were more likely to be male and as likely to be biologic naïve compared to patients on monotherapy (Table). The average weekly dose of MTX was 14.63 mg, and the average daily dose of MMF was 1000 mg. The average number of days between starting adalimumab and starting an oral immunosuppressant was 114.5 (SD, 217; median, 0) days. Reasons for discontinuation of adalimumab included insufficient response, noncompliance, dislike of injections, adverse events, fear of adverse events, other medical issues unrelated to HS, and insurance coverage issues. Patients who ended treatment with adalimumab owing to insurance coverage issues were still included in our study because insurance coverage remains a major determinant of treatment choice in HS and is relevant to the dynamics of medical decision-making.
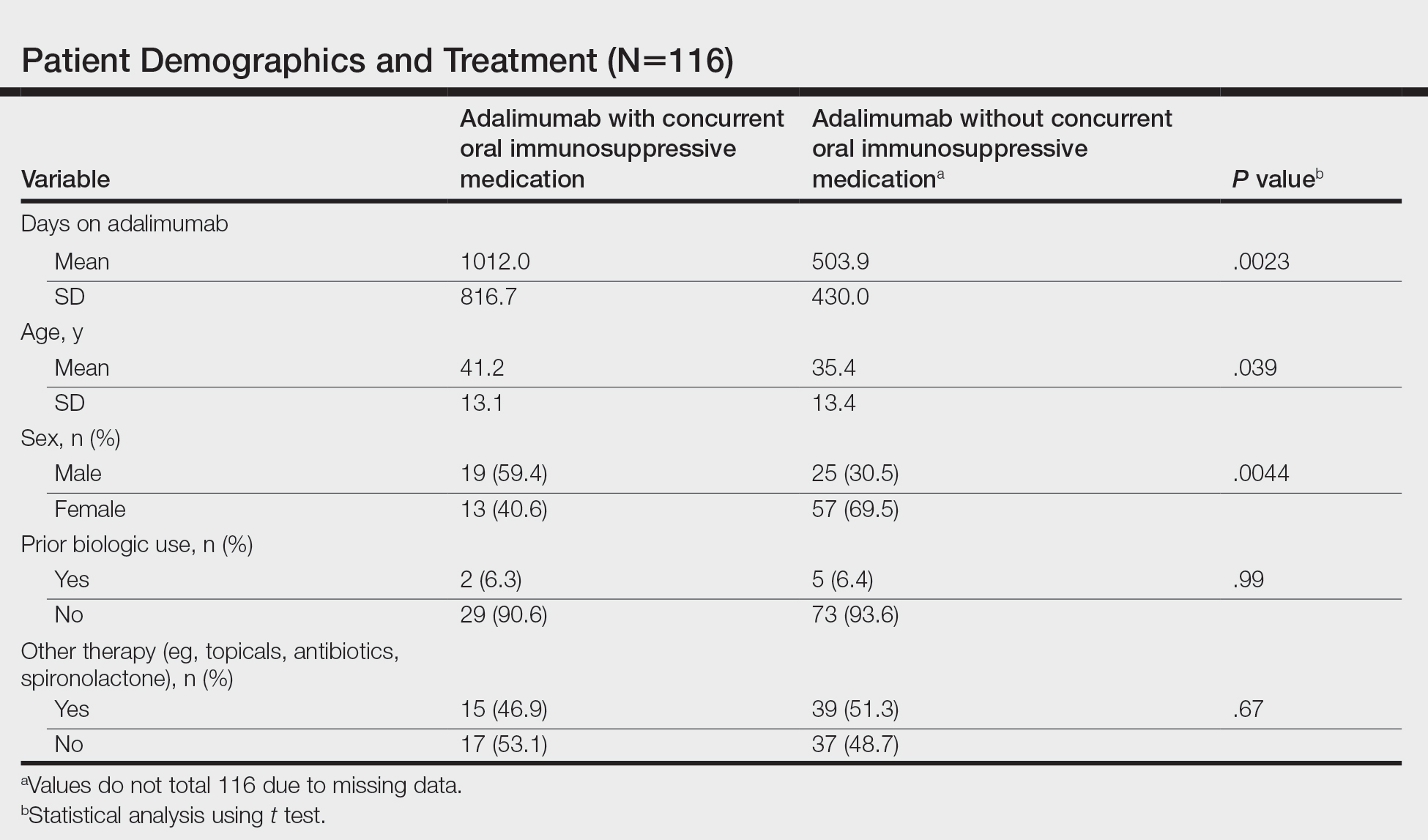
Statistical analysis was conducted on all patients inclusive of any reason for discontinuation to avoid bias in the calculation of treatment duration. Cox regression analysis was conducted for all independent variables and was noncontributory. Kaplan-Meier methodology was used to assess the duration of treatment of adalimumab with and without concomitant oral immunosuppressants, and quartile survival times were calculated. Quartile survival time is the time point after adalimumab initiation at which 25% of patients have discontinued adalimumab. We chose quartile survival time instead of average treatment duration to adequately power this study, given our small patient pool.
Although patients receiving adalimumab with oral immunosuppressants had a longer quartile treatment duration (450 days; 95% CI, 185-1800) than the group without oral immunosuppressants (360 days; 95% CI, 200-700), neither MTX nor MMF was shown to significantly prolong duration of therapy with adalimumab (log-rank test: P=.12). Additionally, patients receiving combination therapy were just as likely to discontinue adalimumab as those on monotherapy (χ2 test: P=.93). Patients who took both MTX and MMF at different times did show a statistically significant increase in adalimumab quartile treatment duration (1710 days; 95% CI, 1620 [upper limit not calculable]), but this is likely because these patients were kept on adalimumab while trialing adjunctive medications.
The results of our study indicate that MTX and MMF do not prolong duration of adalimumab therapy, which suggests that adalimumab combination therapy with MTX and MMF may not improve HS more than adalimumab alone, and/or partial responders to adalimumab monotherapy are unlikely to be converted to satisfactory responders with the addition of oral immunosuppressants. Limitations of our study include that it was retrospective, used treatment duration as a surrogate for objective efficacy measures, and relied on a single-institution data source. Additionally, owing to our small sample size, we were unable to account for certain potential confounders, including patient weight and insurance status. Future controlled prospective studies using objective end points are needed to further elucidate whether oral immunosuppressants have a role as an adjunct in the treatment of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Okun MM, Prens EP, et al. Long-term adalimumab efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: 3-year results of a phase 3 open-label extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:60-69.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.040
- Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1029-1072. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.057
- Sultan KS, Berkowitz JC, Khan S. Combination therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2017;8:103-113. doi:10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i2.103
- Prussick L, Rothstein B, Joshipura D, et al. Open-label, investigator-initiated, single-site exploratory trial evaluating secukinumab, an anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, for patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:609-611.
To the Editor:
The tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab is the only US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Although 50.6% of patients fulfilled Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response criteria with adalimumab at 12 weeks, many responders were not satisfied with their disease control, and secondary loss of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response fulfillment occurred in 15.9% of patients within approximately 3 years.1 Without other US Food and Drug Administration–approved HS treatments, some dermatologists have combined adalimumab with methotrexate (MTX) and/or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to attempt to increase the duration of satisfactory disease control while on adalimumab. Combining tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors with oral immunosuppressants is a well-established approach in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease; however, to the best of our knowledge, this approach has not been studied for HS.2,3
To assess whether there is a role for combining adalimumab with MTX and/or MMF in the treatment of HS, we performed a single-institution retrospective chart review at the University of Connecticut Department of Dermatology to determine whether patients receiving combination therapy stayed on adalimumab longer than those who received adalimumab monotherapy. All patients receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS with at least 1 follow-up visit 3 or more months after treatment initiation were included. Duration of treatment with adalimumab was defined as the length of time between initiation and termination of adalimumab, regardless of flares, adverse events, or addition of adjuvant therapy that occurred during this time span. Because standardized rating scales measuring the severity of HS at this time are not recorded routinely at our institution, treatment duration with adalimumab was used as a surrogate for measuring therapeutic success. Additionally, treatment duration is a meaningful end point, as patients with HS may require indefinite treatment. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS. Patients were excluded if they were lost to follow-up or had received adalimumab for less than 6 months, as data suggest that biologics do not reach peak effect for up to 6 months in HS.4
We identified 116 eligible patients with HS, 32 of whom received combination therapy. Five patients received 40 mg of adalimumab every other week, and 111 patients received 40 mg of adalimumab each week. Patients receiving oral immunosuppressants were more likely to be male and as likely to be biologic naïve compared to patients on monotherapy (Table). The average weekly dose of MTX was 14.63 mg, and the average daily dose of MMF was 1000 mg. The average number of days between starting adalimumab and starting an oral immunosuppressant was 114.5 (SD, 217; median, 0) days. Reasons for discontinuation of adalimumab included insufficient response, noncompliance, dislike of injections, adverse events, fear of adverse events, other medical issues unrelated to HS, and insurance coverage issues. Patients who ended treatment with adalimumab owing to insurance coverage issues were still included in our study because insurance coverage remains a major determinant of treatment choice in HS and is relevant to the dynamics of medical decision-making.

Statistical analysis was conducted on all patients inclusive of any reason for discontinuation to avoid bias in the calculation of treatment duration. Cox regression analysis was conducted for all independent variables and was noncontributory. Kaplan-Meier methodology was used to assess the duration of treatment of adalimumab with and without concomitant oral immunosuppressants, and quartile survival times were calculated. Quartile survival time is the time point after adalimumab initiation at which 25% of patients have discontinued adalimumab. We chose quartile survival time instead of average treatment duration to adequately power this study, given our small patient pool.
Although patients receiving adalimumab with oral immunosuppressants had a longer quartile treatment duration (450 days; 95% CI, 185-1800) than the group without oral immunosuppressants (360 days; 95% CI, 200-700), neither MTX nor MMF was shown to significantly prolong duration of therapy with adalimumab (log-rank test: P=.12). Additionally, patients receiving combination therapy were just as likely to discontinue adalimumab as those on monotherapy (χ2 test: P=.93). Patients who took both MTX and MMF at different times did show a statistically significant increase in adalimumab quartile treatment duration (1710 days; 95% CI, 1620 [upper limit not calculable]), but this is likely because these patients were kept on adalimumab while trialing adjunctive medications.
The results of our study indicate that MTX and MMF do not prolong duration of adalimumab therapy, which suggests that adalimumab combination therapy with MTX and MMF may not improve HS more than adalimumab alone, and/or partial responders to adalimumab monotherapy are unlikely to be converted to satisfactory responders with the addition of oral immunosuppressants. Limitations of our study include that it was retrospective, used treatment duration as a surrogate for objective efficacy measures, and relied on a single-institution data source. Additionally, owing to our small sample size, we were unable to account for certain potential confounders, including patient weight and insurance status. Future controlled prospective studies using objective end points are needed to further elucidate whether oral immunosuppressants have a role as an adjunct in the treatment of HS.
To the Editor:
The tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor adalimumab is the only US Food and Drug Administration–approved treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Although 50.6% of patients fulfilled Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response criteria with adalimumab at 12 weeks, many responders were not satisfied with their disease control, and secondary loss of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response fulfillment occurred in 15.9% of patients within approximately 3 years.1 Without other US Food and Drug Administration–approved HS treatments, some dermatologists have combined adalimumab with methotrexate (MTX) and/or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to attempt to increase the duration of satisfactory disease control while on adalimumab. Combining tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors with oral immunosuppressants is a well-established approach in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease; however, to the best of our knowledge, this approach has not been studied for HS.2,3
To assess whether there is a role for combining adalimumab with MTX and/or MMF in the treatment of HS, we performed a single-institution retrospective chart review at the University of Connecticut Department of Dermatology to determine whether patients receiving combination therapy stayed on adalimumab longer than those who received adalimumab monotherapy. All patients receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS with at least 1 follow-up visit 3 or more months after treatment initiation were included. Duration of treatment with adalimumab was defined as the length of time between initiation and termination of adalimumab, regardless of flares, adverse events, or addition of adjuvant therapy that occurred during this time span. Because standardized rating scales measuring the severity of HS at this time are not recorded routinely at our institution, treatment duration with adalimumab was used as a surrogate for measuring therapeutic success. Additionally, treatment duration is a meaningful end point, as patients with HS may require indefinite treatment. Patients were eligible for inclusion if they were receiving adalimumab for the treatment of HS. Patients were excluded if they were lost to follow-up or had received adalimumab for less than 6 months, as data suggest that biologics do not reach peak effect for up to 6 months in HS.4
We identified 116 eligible patients with HS, 32 of whom received combination therapy. Five patients received 40 mg of adalimumab every other week, and 111 patients received 40 mg of adalimumab each week. Patients receiving oral immunosuppressants were more likely to be male and as likely to be biologic naïve compared to patients on monotherapy (Table). The average weekly dose of MTX was 14.63 mg, and the average daily dose of MMF was 1000 mg. The average number of days between starting adalimumab and starting an oral immunosuppressant was 114.5 (SD, 217; median, 0) days. Reasons for discontinuation of adalimumab included insufficient response, noncompliance, dislike of injections, adverse events, fear of adverse events, other medical issues unrelated to HS, and insurance coverage issues. Patients who ended treatment with adalimumab owing to insurance coverage issues were still included in our study because insurance coverage remains a major determinant of treatment choice in HS and is relevant to the dynamics of medical decision-making.

Statistical analysis was conducted on all patients inclusive of any reason for discontinuation to avoid bias in the calculation of treatment duration. Cox regression analysis was conducted for all independent variables and was noncontributory. Kaplan-Meier methodology was used to assess the duration of treatment of adalimumab with and without concomitant oral immunosuppressants, and quartile survival times were calculated. Quartile survival time is the time point after adalimumab initiation at which 25% of patients have discontinued adalimumab. We chose quartile survival time instead of average treatment duration to adequately power this study, given our small patient pool.
Although patients receiving adalimumab with oral immunosuppressants had a longer quartile treatment duration (450 days; 95% CI, 185-1800) than the group without oral immunosuppressants (360 days; 95% CI, 200-700), neither MTX nor MMF was shown to significantly prolong duration of therapy with adalimumab (log-rank test: P=.12). Additionally, patients receiving combination therapy were just as likely to discontinue adalimumab as those on monotherapy (χ2 test: P=.93). Patients who took both MTX and MMF at different times did show a statistically significant increase in adalimumab quartile treatment duration (1710 days; 95% CI, 1620 [upper limit not calculable]), but this is likely because these patients were kept on adalimumab while trialing adjunctive medications.
The results of our study indicate that MTX and MMF do not prolong duration of adalimumab therapy, which suggests that adalimumab combination therapy with MTX and MMF may not improve HS more than adalimumab alone, and/or partial responders to adalimumab monotherapy are unlikely to be converted to satisfactory responders with the addition of oral immunosuppressants. Limitations of our study include that it was retrospective, used treatment duration as a surrogate for objective efficacy measures, and relied on a single-institution data source. Additionally, owing to our small sample size, we were unable to account for certain potential confounders, including patient weight and insurance status. Future controlled prospective studies using objective end points are needed to further elucidate whether oral immunosuppressants have a role as an adjunct in the treatment of HS.
- Zouboulis CC, Okun MM, Prens EP, et al. Long-term adalimumab efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: 3-year results of a phase 3 open-label extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:60-69.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.040
- Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1029-1072. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.057
- Sultan KS, Berkowitz JC, Khan S. Combination therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2017;8:103-113. doi:10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i2.103
- Prussick L, Rothstein B, Joshipura D, et al. Open-label, investigator-initiated, single-site exploratory trial evaluating secukinumab, an anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, for patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:609-611.
- Zouboulis CC, Okun MM, Prens EP, et al. Long-term adalimumab efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: 3-year results of a phase 3 open-label extension study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:60-69.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.040
- Menter A, Strober BE, Kaplan DH, et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1029-1072. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.057
- Sultan KS, Berkowitz JC, Khan S. Combination therapy for inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2017;8:103-113. doi:10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i2.103
- Prussick L, Rothstein B, Joshipura D, et al. Open-label, investigator-initiated, single-site exploratory trial evaluating secukinumab, an anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, for patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:609-611.
Practice Points
- Adalimumab is the only medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), yet many patients on adalimumab do not achieve satisfactory results. New treatment options are in demand for patients affected by HS.
- Although combining tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors with oral immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and mycophenolate mofetil appears to be beneficial in treating other conditions such as psoriasis, these treatments may not have as great a benefit for patients with HS.
Mineral Oil Scabies Preparation From Under the Fingernail
Practice Gap
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite is a microscopic organism that causes scabies in the human host. The scabies mite is highly transmissible, making scabies a common disease in heavily populated areas. The mite survives by burrowing into the epidermis, where it feeds, lays eggs, and defecates.1
The rash in the host represents an allergic reaction to the body of the scabies mite, producing symptoms such as intense itching, rash, and erosions of the skin. The scabies rash tends to occur in warm and occluded areas of the body such as the hands, axillae, groin, buttocks, and feet.1,2
Delaying treatment of scabies can be hazardous because of the risk of rapid spread from one person to another. This rapid spread can be debilitating in specific populations, such as the immunocompromised, elderly, and disabled.
Mineral oil preparation is the classic method used to identify scabies (Figure 1). This method relies on obtaining mites by applying mineral oil to the skin and using a 15-mm blade to scrape off layers of the affected skin. The scraped material is spread onto a microscope slide with mineral oil, a coverslip is applied, and the specimen is analyzed by direct microscopy. This method proves only as effective as knowing where the few mites are located.
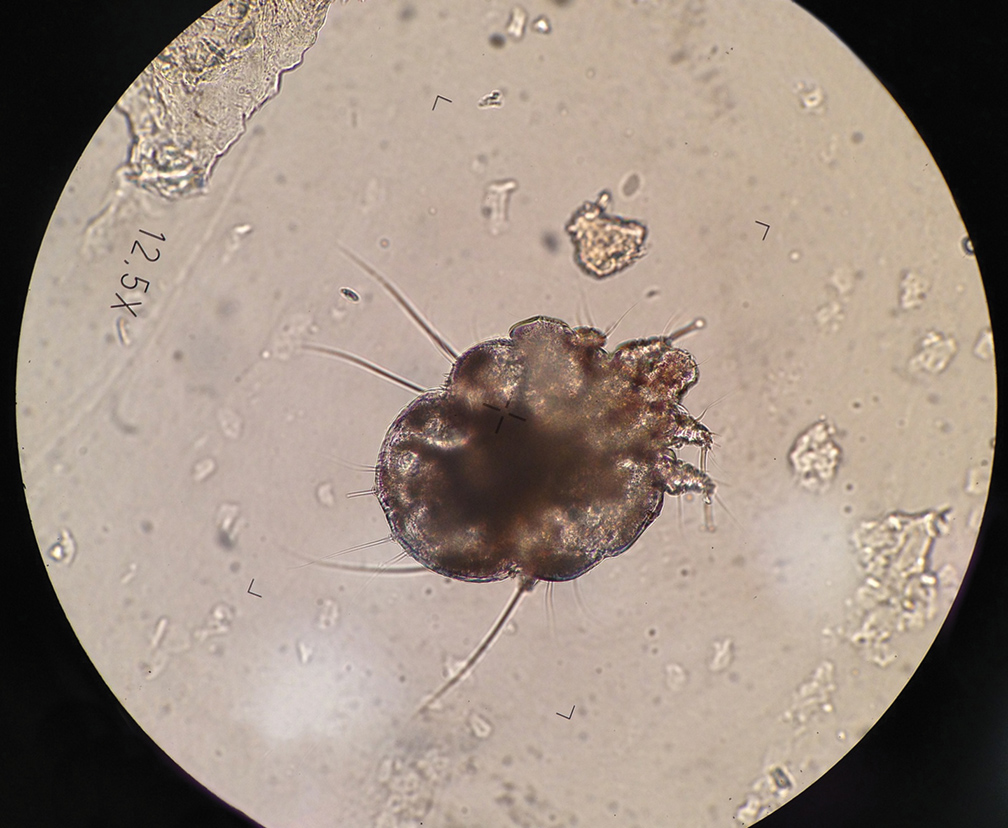
At any time, only 10 to 12 mites live on a human host.3 Therefore, it can be challenging to obtain a mite for diagnosis because the location of the skin mites may be unknown. Dermoscopy can be used to locate burrows and other signs of S scabiei. With a dermatoscope, the scabies mite can be identified by the so-called delta-wing jet sign.4
However, dermoscopy is not always successful because extensive hemorrhagic crusting and erosions of the skin secondary to constant scratching can obscure the appearance of burrows and mites. Because patients are constantly scratching areas of irritation, it is possible that S scabiei can be located under the fingernail of the dominant hand.
The Technique
To address this practice gap, a mineral oil scabies preparation can be performed by scraping under the fingernail plate at the level of the hyponychium. Mites might accumulate underneath the fingernails of the dominant hand when patients scratch the area of the skin where S scabiei mites are burrowing and reproducing.
A convenient and painless way to obtain a mineral oil scabies preparation from under the fingernail is to use the tip of a disposable hyfrecator, readily available in most dermatology practices for use in electrosurgery (Figure 2). Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip for the mineral oil preparation would be done without attachment to the full apparatus.
The hyponychium of the fingernail is prepared with mineral oil, which aids in collecting and suspending the material obtained from under the nail plate. Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip, material from underneath the fingernail is removed using a gentle sweeping motion (Figure 3). The specimen is then analyzed under the microscope similar to a routine mineral oil scabies preparation. This method can be utilized by health care providers for easy and painless diagnosis of scabies.
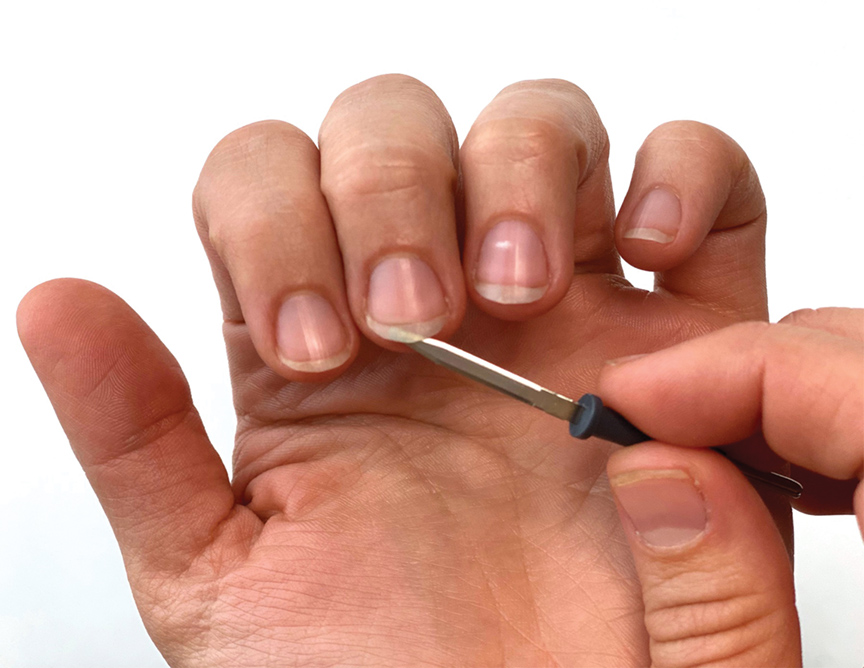

Practice Implications
Use of a blunt hyfrecator tip to extract S scabiei from underneath the fingernail plate can be used for efficient diagnosis of scabies. This technique can be implemented in any clinic where blunt-tip hyfrecator electrodes are available. Using a gentle sweeping motion, the blunt-tip hyfrecator allows the provider to extract material from under the fingernail for diagnosis. The material obtained is used to prepare a mineral oil scabies preparation for direct microscopic analysis.
This technique can diagnose scabies efficiently, and treatment can be initiated promptly. Use of a disposable blunt-tip hyfrecator for scabies extraction is a novel technique that can be added to the armamentarium of tools to diagnose scabies, which includes traditional mineral oil preparation and dermoscopy.
- Banerji A; Canadian Paediatric Society, First Nations, Inuit and Métis Health Committee. Scabies. Paediatr Child Health. 2015;20:395-402. doi:10.1093/pch/20.7.395
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Mellanby K. The development of symptoms, parasitic infection and immunity in human scabies. Parasitology. 1944;35:197-206. doi:10.1017/S0031182000021612
- Fox G. Diagnosis of scabies by dermoscopy [published online February 2, 2009]. BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0279. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0279
Practice Gap
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite is a microscopic organism that causes scabies in the human host. The scabies mite is highly transmissible, making scabies a common disease in heavily populated areas. The mite survives by burrowing into the epidermis, where it feeds, lays eggs, and defecates.1
The rash in the host represents an allergic reaction to the body of the scabies mite, producing symptoms such as intense itching, rash, and erosions of the skin. The scabies rash tends to occur in warm and occluded areas of the body such as the hands, axillae, groin, buttocks, and feet.1,2
Delaying treatment of scabies can be hazardous because of the risk of rapid spread from one person to another. This rapid spread can be debilitating in specific populations, such as the immunocompromised, elderly, and disabled.
Mineral oil preparation is the classic method used to identify scabies (Figure 1). This method relies on obtaining mites by applying mineral oil to the skin and using a 15-mm blade to scrape off layers of the affected skin. The scraped material is spread onto a microscope slide with mineral oil, a coverslip is applied, and the specimen is analyzed by direct microscopy. This method proves only as effective as knowing where the few mites are located.

At any time, only 10 to 12 mites live on a human host.3 Therefore, it can be challenging to obtain a mite for diagnosis because the location of the skin mites may be unknown. Dermoscopy can be used to locate burrows and other signs of S scabiei. With a dermatoscope, the scabies mite can be identified by the so-called delta-wing jet sign.4
However, dermoscopy is not always successful because extensive hemorrhagic crusting and erosions of the skin secondary to constant scratching can obscure the appearance of burrows and mites. Because patients are constantly scratching areas of irritation, it is possible that S scabiei can be located under the fingernail of the dominant hand.
The Technique
To address this practice gap, a mineral oil scabies preparation can be performed by scraping under the fingernail plate at the level of the hyponychium. Mites might accumulate underneath the fingernails of the dominant hand when patients scratch the area of the skin where S scabiei mites are burrowing and reproducing.
A convenient and painless way to obtain a mineral oil scabies preparation from under the fingernail is to use the tip of a disposable hyfrecator, readily available in most dermatology practices for use in electrosurgery (Figure 2). Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip for the mineral oil preparation would be done without attachment to the full apparatus.

The hyponychium of the fingernail is prepared with mineral oil, which aids in collecting and suspending the material obtained from under the nail plate. Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip, material from underneath the fingernail is removed using a gentle sweeping motion (Figure 3). The specimen is then analyzed under the microscope similar to a routine mineral oil scabies preparation. This method can be utilized by health care providers for easy and painless diagnosis of scabies.

Practice Implications
Use of a blunt hyfrecator tip to extract S scabiei from underneath the fingernail plate can be used for efficient diagnosis of scabies. This technique can be implemented in any clinic where blunt-tip hyfrecator electrodes are available. Using a gentle sweeping motion, the blunt-tip hyfrecator allows the provider to extract material from under the fingernail for diagnosis. The material obtained is used to prepare a mineral oil scabies preparation for direct microscopic analysis.
This technique can diagnose scabies efficiently, and treatment can be initiated promptly. Use of a disposable blunt-tip hyfrecator for scabies extraction is a novel technique that can be added to the armamentarium of tools to diagnose scabies, which includes traditional mineral oil preparation and dermoscopy.
Practice Gap
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite is a microscopic organism that causes scabies in the human host. The scabies mite is highly transmissible, making scabies a common disease in heavily populated areas. The mite survives by burrowing into the epidermis, where it feeds, lays eggs, and defecates.1
The rash in the host represents an allergic reaction to the body of the scabies mite, producing symptoms such as intense itching, rash, and erosions of the skin. The scabies rash tends to occur in warm and occluded areas of the body such as the hands, axillae, groin, buttocks, and feet.1,2
Delaying treatment of scabies can be hazardous because of the risk of rapid spread from one person to another. This rapid spread can be debilitating in specific populations, such as the immunocompromised, elderly, and disabled.
Mineral oil preparation is the classic method used to identify scabies (Figure 1). This method relies on obtaining mites by applying mineral oil to the skin and using a 15-mm blade to scrape off layers of the affected skin. The scraped material is spread onto a microscope slide with mineral oil, a coverslip is applied, and the specimen is analyzed by direct microscopy. This method proves only as effective as knowing where the few mites are located.

At any time, only 10 to 12 mites live on a human host.3 Therefore, it can be challenging to obtain a mite for diagnosis because the location of the skin mites may be unknown. Dermoscopy can be used to locate burrows and other signs of S scabiei. With a dermatoscope, the scabies mite can be identified by the so-called delta-wing jet sign.4
However, dermoscopy is not always successful because extensive hemorrhagic crusting and erosions of the skin secondary to constant scratching can obscure the appearance of burrows and mites. Because patients are constantly scratching areas of irritation, it is possible that S scabiei can be located under the fingernail of the dominant hand.
The Technique
To address this practice gap, a mineral oil scabies preparation can be performed by scraping under the fingernail plate at the level of the hyponychium. Mites might accumulate underneath the fingernails of the dominant hand when patients scratch the area of the skin where S scabiei mites are burrowing and reproducing.
A convenient and painless way to obtain a mineral oil scabies preparation from under the fingernail is to use the tip of a disposable hyfrecator, readily available in most dermatology practices for use in electrosurgery (Figure 2). Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip for the mineral oil preparation would be done without attachment to the full apparatus.

The hyponychium of the fingernail is prepared with mineral oil, which aids in collecting and suspending the material obtained from under the nail plate. Using the blunt end of the hyfrecator tip, material from underneath the fingernail is removed using a gentle sweeping motion (Figure 3). The specimen is then analyzed under the microscope similar to a routine mineral oil scabies preparation. This method can be utilized by health care providers for easy and painless diagnosis of scabies.

Practice Implications
Use of a blunt hyfrecator tip to extract S scabiei from underneath the fingernail plate can be used for efficient diagnosis of scabies. This technique can be implemented in any clinic where blunt-tip hyfrecator electrodes are available. Using a gentle sweeping motion, the blunt-tip hyfrecator allows the provider to extract material from under the fingernail for diagnosis. The material obtained is used to prepare a mineral oil scabies preparation for direct microscopic analysis.
This technique can diagnose scabies efficiently, and treatment can be initiated promptly. Use of a disposable blunt-tip hyfrecator for scabies extraction is a novel technique that can be added to the armamentarium of tools to diagnose scabies, which includes traditional mineral oil preparation and dermoscopy.
- Banerji A; Canadian Paediatric Society, First Nations, Inuit and Métis Health Committee. Scabies. Paediatr Child Health. 2015;20:395-402. doi:10.1093/pch/20.7.395
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Mellanby K. The development of symptoms, parasitic infection and immunity in human scabies. Parasitology. 1944;35:197-206. doi:10.1017/S0031182000021612
- Fox G. Diagnosis of scabies by dermoscopy [published online February 2, 2009]. BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0279. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0279
- Banerji A; Canadian Paediatric Society, First Nations, Inuit and Métis Health Committee. Scabies. Paediatr Child Health. 2015;20:395-402. doi:10.1093/pch/20.7.395
- Johnston G, Sladden M. Scabies: diagnosis and treatment. BMJ. 2005;331:619-622. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7517.619
- Mellanby K. The development of symptoms, parasitic infection and immunity in human scabies. Parasitology. 1944;35:197-206. doi:10.1017/S0031182000021612
- Fox G. Diagnosis of scabies by dermoscopy [published online February 2, 2009]. BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009:bcr06.2008.0279. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0279
Cutaneous Manifestations and Clinical Disparities in Patients Without Housing
More than half a million individuals are without housing (NWH) on any given night in the United States, as estimated by the US Department of Housing and Urban Development. 1 Lack of hygiene, increased risk of infection and infestation due to living conditions, and barriers to health care put these individuals at increased risk for disease. 2 Skin disease, including fungal infection and acne, are within the top 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide and can cause major psychologic impairment, yet dermatologic concerns and clinical outcomes in NWH patients have not been well characterized. 2-5 Further, because this vulnerable demographic tends to be underinsured, they frequently present to the emergency department (ED) for management of disease. 1,6 Survey of common concerns in NWH patients is of utility to consulting dermatologists and nondermatologist providers in the ED, who can familiarize themselves with management of diseases they are more likely to encounter. Few studies examine dermatologic conditions in the ED, and a thorough literature review indicates none have included homelessness as a variable. 6,7 Additionally, comparison with a matched control group of patients with housing (WH) is limited. 5,8 We present one of the largest comparisons of cutaneous disease in NWH vs WH patients in a single hospital system to elucidate the types of cutaneous disease that motivate patients to seek care, the location of skin disease, and differences in clinical care.
Methods
A retrospective medical record review of patients seen for an inclusive list of dermatologic diagnoses in the ED or while admitted at University Medical Center New Orleans, Louisiana (UMC), between January 1, 2018, and April 21, 2020, was conducted. This study was qualified as exempt from the institutional review board by Louisiana State University because it proposed zero risk to the patients and remained completely anonymous. Eight hundred forty-two total medical records were reviewed (NWH, 421; WH, 421)(Table 1). Patients with housing were matched based on self-identified race and ethnicity, sex, and age. Disease categories were constructed based on fundamental pathophysiology adapted from Dermatology9: infectious, noninfectious inflammatory, neoplasm, trauma and wounds, drug-related eruptions, vascular, pruritic, pigmented, bullous, neuropsychiatric, and other. Other included unspecified eruptions as well as miscellaneous lesions such as calluses. The current chief concern, anatomic location, and configuration were recorded, as well as biopsied lesions and outpatient referrals or inpatient consultations to dermatology or other specialties, including wound care, infectious disease, podiatry, and surgery. χ2 analysis was used to analyze significance of cutaneous categories, body location, and referrals. Groups smaller than 5 defaulted to the Fisher exact test.

Results
The total diagnoses (including both chief concerns and secondary diagnoses) are shown in Table 2. Chief concerns were more frequently cutaneous or dermatologic for WH (NWH, 209; WH, 307; P<.001). In both groups, cutaneous infectious etiologies were more likely to be a patient’s presenting chief concern (58% NWH, P=.002; 42% WH, P<.001). Noninfectious inflammatory etiologies and pigmented lesions were more likely to be secondary diagnoses with an unrelated noncutaneous concern; noninfectious inflammatory etiologies were only 16% of the total cutaneous chief concerns (11% NWH, P=.04; 20% WH, P=.03), and no pigmented lesions were chief concerns.
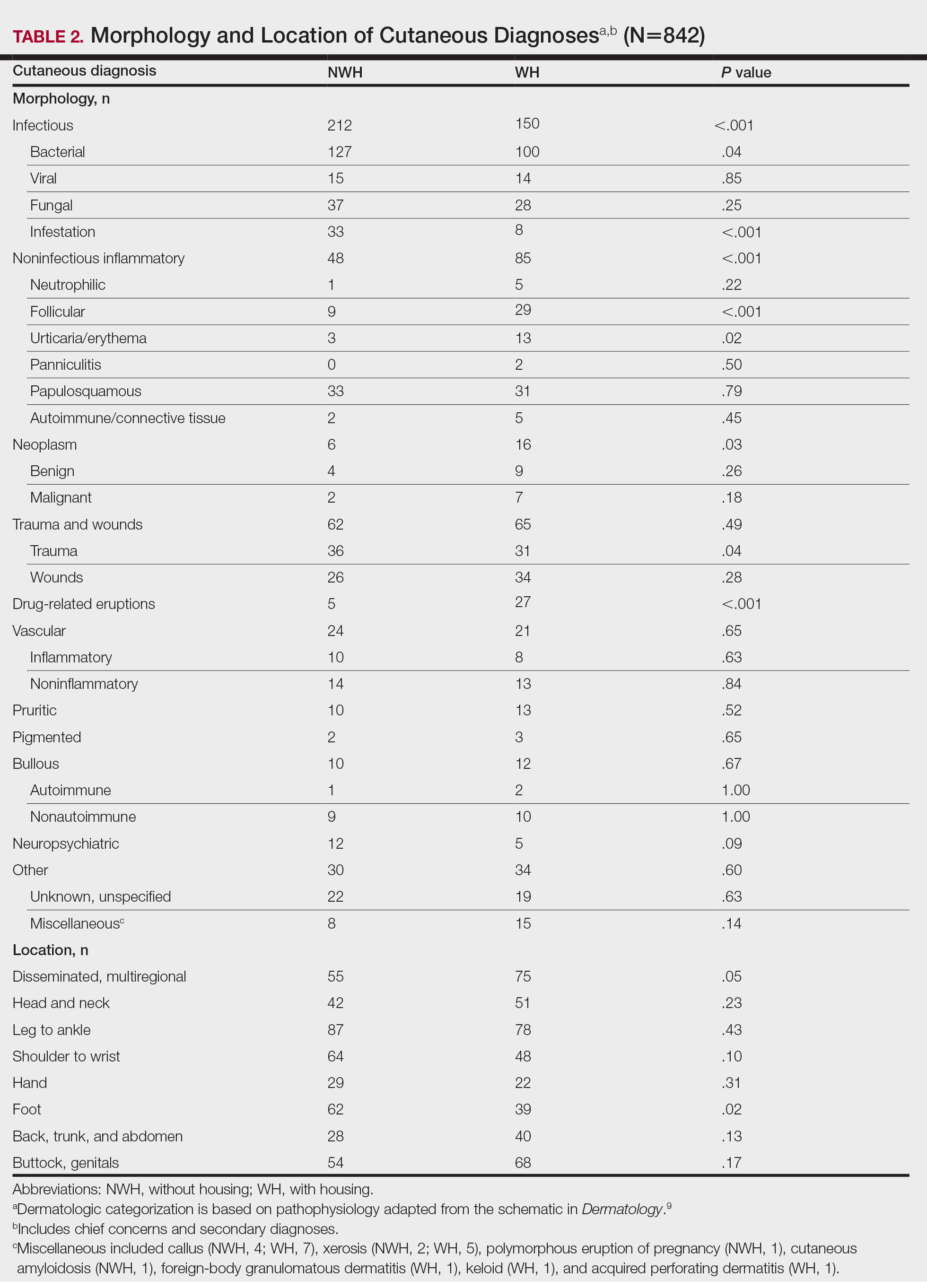
Infection was the most common chief concern, though NWH patients presented with significantly more infectious concerns (NWH, 212; WH, 150; P<.001), particularly infestations (NWH, 33; WH, 8; P<.001) and bacterial etiologies (NWH, 127; WH, 100; P=.04). The majority of bacterial etiologies were either an abscess or cellulitis (NWH, 106; WH, 83), though infected chronic wounds were categorized as bacterial infection when treated definitively as such (eg, in the case of sacral ulcers causing osteomyelitis)(NWH, 21; WH, 17). Of note, infectious etiology was associated with intravenous drug use (IVDU) in both NWH and WH patients. Of 184 NWH who reported IVDU, 127 had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Similarly, 43 of 56 total WH patients who reported IVDU had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Infestation (within the infectious category) included scabies (NWH, 20; WH, 3) and insect or arthropod bites (NWH, 12; WH, 5). Two NWH patients also presented with swelling of the lower extremities and were subsequently diagnosed with maggot infestations. Fungal and viral etiologies were not significantly increased in either group; however, NWH did have a higher incidence of tinea pedis (NWH, 14; WH, 4; P=.03).
More neoplasms (NWH, 6; WH, 16; P=.03), noninfectious inflammatory eruptions (NWH, 48; WH, 85; P<.001), and cutaneous drug eruptions (NWH, 5; WH, 27; P<.001) were reported in WH patients. There was no significant difference in benign vs malignant neoplastic processes between groups. More noninfectious inflammatory eruptions in WH were specifically driven by a markedly increased incidence of follicular (NWH, 9; WH, 29; P<.001) and urticarial/erythematous (NWH, 3; WH, 13; P=.02) lesions. Follicular etiologies included acne (NWH, 1; WH, 6; P=.12), folliculitis (NWH, 5; WH, 2; P=.45), hidradenitis suppurativa (NWH, 2; WH, 11; P=.02), and pilonidal and sebaceous cysts (NWH, 1; WH, 10; P=.01). Allergic urticaria dominated the urticarial/erythematous category (NWH, 3; WH, 11; P=.06), though there were 2 WH presentations of diffuse erythema and skin peeling.
Another substantial proportion of cutaneous etiologies were due to trauma or chronic wounds. Significantly more traumatic injuries presented in NWH patients vs WH patients (36 vs 31; P=.04). Trauma included human or dog bites (NWH, 5; WH, 4), sunburns (NWH, 3; WH, 0), other burns (NWH, 11; WH, 13), abrasions and lacerations (NWH, 16; WH, 3; P=.004), and foreign bodies (NWH, 1; WH, 1). Wounds consisted of chronic wounds such as those due to diabetes mellitus (foot ulcers) or immobility (sacral ulcers); numbers were similar between groups.
Looking at location, NWH patients had more pathology on the feet (NWH, 62; WH, 39; P=.02), whereas WH patients had more disseminated multiregional concerns (NWH, 55; WH, 75; P=.05). No one body location was notably more likely to warrant a chief concern.
For clinical outcomes, more WH patients received a consultation of any kind (NWH, 171; WH, 217; P<.001), consultation to dermatology (NWH, 49; WH, 87; P<.001), and consultation to surgery (NWH, 64; WH, 110; P<.001)(Table 3 and Figure). More outpatient referrals to dermatology were made for WH patients (NWH, 61; WH, 82; P=.05). Notably, NWH patients presented for 80% fewer hospital follow-up appointments (NWH, 11; WH, 55; P<.001). It is essential to note that these findings were not affected by self-reported race or ethnicity. Results remained significant when broken into cohorts consisting of patients with and without skin of color.
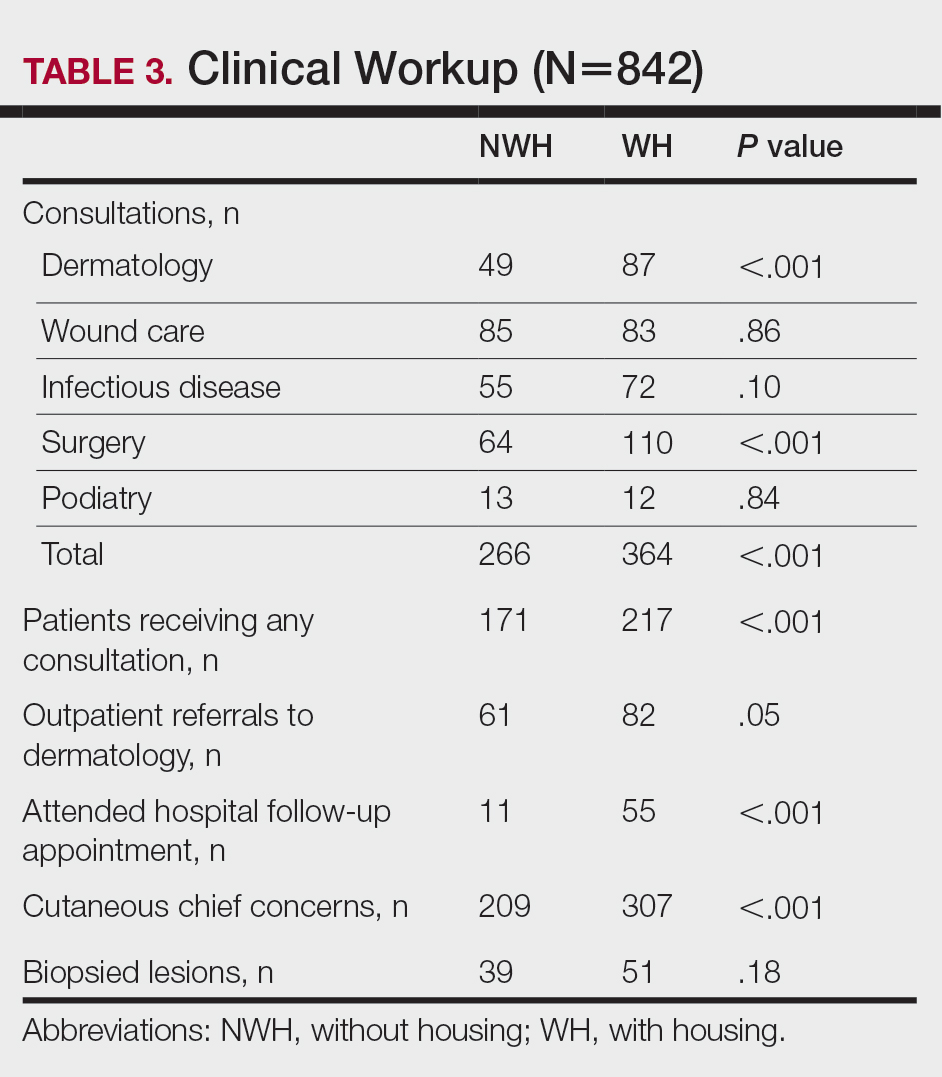
Comment
Cutaneous Concerns in NWH Patients—Although cutaneous disease has been reported to disproportionately affect NWH patients,10 in our cohort, NWH patients had fewer cutaneous chief concerns than WH patients. However, without comparing with all patients entering the ED at UMC, we cannot make a statement on this claim. We do present a few reasons why NWH patients do not have more cutaneous concerns. First, they may wait to present with cutaneous disease until it becomes more severe (eg, until chronic wounds have progressed to infections). Second, as discussed in depth by Hollestein and Nijsten,3 dermatologic disease may be a major contributor to the overall count of disability-adjusted life years but may play a minor role in individual disability. Therefore, skin disease often is considered less important on an individual basis, despite substantial psychosocial burden, leading to further stigmatization of this vulnerable population and discouraged care-seeking behavior, particularly for noninfectious inflammatory eruptions, which were notably more present in WH individuals. Third, fewer dermatologic lesions were reported on NWH patients, which may explain why all 3 WH pigmented lesions were diagnosed after presentation with a noncutaneous concern (eg, headache, anemia, nausea).
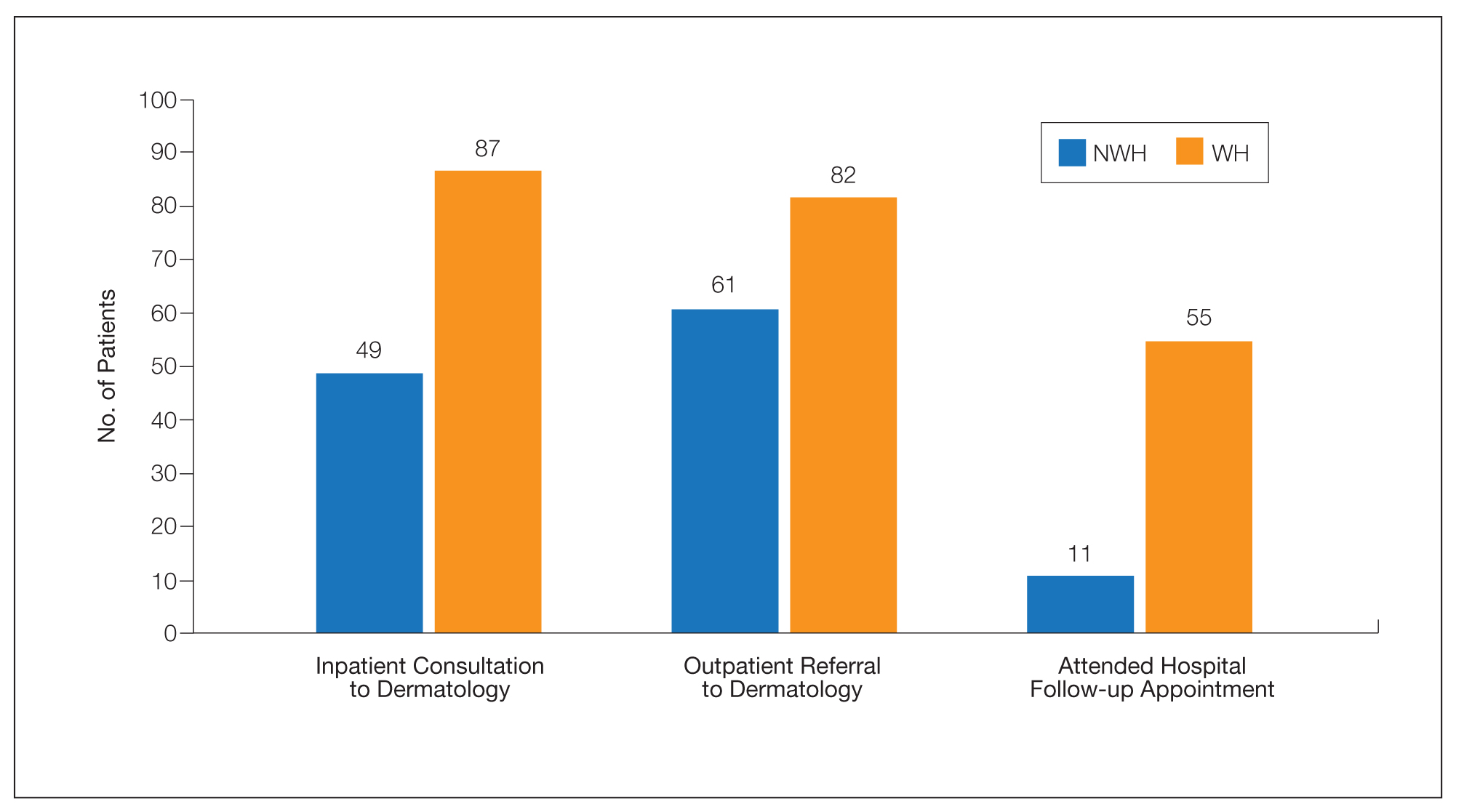
Infectious Cutaneous Diagnoses—The increased presentation of infectious etiologies, especially bacterial, is linked to the increased numbers of IVDUs reported in NWH individuals as well as increased exposure and decreased access to basic hygienic supplies. Intravenous drug use acted as an effect modifier of infectious etiology diagnoses, playing a major role in both NWH and WH cohorts. Although Black and Hispanic individuals as well as individuals with low socioeconomic status have increased proportions of skin cancer, there are inadequate data on the prevalence in NWH individuals.4 We found no increase in malignant dermatologic processes in NWH individuals; however, this may be secondary to inadequate screening with a total body skin examination.
Clinical Workup of NWH Patients—Because most NWH individuals present to the ED to receive care, their care compared with WH patients should be considered. In this cohort, WH patients received a less extensive clinical workup. They received almost half as many dermatologic consultations and fewer outpatient referrals to dermatology. Major communication barriers may affect NWH presentation to follow-up, which was drastically lower than WH individuals, as scheduling typically occurs well after discharge from the ED or inpatient unit. We suggest a few alterations to improve dermatologic care for NWH individuals:
• Consider inpatient consultation for serious dermatologic conditions—even if chronic—to improve disease control, considering that many barriers inhibit follow-up in clinic.
• Involve outreach teams, such as the Assertive Community Treatment teams, that assist individuals by delivering medicine for psychiatric disorders, conducting total-body skin examinations, assisting with wound care, providing basic skin barrier creams or medicaments, and carrying information regarding outpatient follow-up.
• Educate ED providers on the most common skin concerns, especially those that fall within the noninfectious inflammatory category, such as hidradenitis suppurativa, which could easily be misdiagnosed as an abscess.
Future Directions—Owing to limitations of a retrospective cohort study, we present several opportunities for further research on this vulnerable population. The severity of disease, especially infectious etiologies, should be graded to determine if NWH patients truly present later in the disease course. The duration and quality of housing for NWH patients could be categorized based on living conditions (eg, on the street vs in a shelter). Although the findings of our NWH cohort presenting to the ED at UMC provide helpful insight into dermatologic disease, these findings may be disparate from those conducted at other locations in the United States. University Medical Center provides care to mostly subsidized insurance plans in a racially diverse community. Improved outcomes for the NWH individuals living in New Orleans start with obtaining a greater understanding of their diseases and where disparities exist that can be bridged with better care.
Acknowledgment—The dataset generated during this study and used for analysis is not publicly available to protect public health information but is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- Fazel S, Geddes JR, Kushel M. The health of homeless people in high-income countries: descriptive epidemiology, health consequences, and clinical and policy recommendations. Lancet. 2014;384:1529-1540. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61132-6
- Contag C, Lowenstein SE, Jain S, et al. Survey of symptomatic dermatologic disease in homeless patients at a shelter-based clinic. Our Dermatol Online. 2017;8:133-137. doi:10.7241/ourd.20172.37
- Hollestein LM, Nijsten T. An insight into the global burden of skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1499-1501. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.513
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Mackelprang JL, Graves JM, Rivara FP. Homeless in America: injuries treated in US emergency departments, 2007-2011. Int J Inj Contr Saf Promot. 2014;21:289-297. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.371
- Chen CL, Fitzpatrick L, Kamel H. Who uses the emergency department for dermatologic care? a statewide analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:308-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.013
- Stratigos AJ, Stern R, Gonzalez E, et al. Prevalence of skin disease in a cohort of shelter-based homeless men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:197-202. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70048-4
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Badiaga S, Menard A, Tissot Dupont H, et al. Prevalence of skin infections in sheltered homeless. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:382-386.
More than half a million individuals are without housing (NWH) on any given night in the United States, as estimated by the US Department of Housing and Urban Development. 1 Lack of hygiene, increased risk of infection and infestation due to living conditions, and barriers to health care put these individuals at increased risk for disease. 2 Skin disease, including fungal infection and acne, are within the top 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide and can cause major psychologic impairment, yet dermatologic concerns and clinical outcomes in NWH patients have not been well characterized. 2-5 Further, because this vulnerable demographic tends to be underinsured, they frequently present to the emergency department (ED) for management of disease. 1,6 Survey of common concerns in NWH patients is of utility to consulting dermatologists and nondermatologist providers in the ED, who can familiarize themselves with management of diseases they are more likely to encounter. Few studies examine dermatologic conditions in the ED, and a thorough literature review indicates none have included homelessness as a variable. 6,7 Additionally, comparison with a matched control group of patients with housing (WH) is limited. 5,8 We present one of the largest comparisons of cutaneous disease in NWH vs WH patients in a single hospital system to elucidate the types of cutaneous disease that motivate patients to seek care, the location of skin disease, and differences in clinical care.
Methods
A retrospective medical record review of patients seen for an inclusive list of dermatologic diagnoses in the ED or while admitted at University Medical Center New Orleans, Louisiana (UMC), between January 1, 2018, and April 21, 2020, was conducted. This study was qualified as exempt from the institutional review board by Louisiana State University because it proposed zero risk to the patients and remained completely anonymous. Eight hundred forty-two total medical records were reviewed (NWH, 421; WH, 421)(Table 1). Patients with housing were matched based on self-identified race and ethnicity, sex, and age. Disease categories were constructed based on fundamental pathophysiology adapted from Dermatology9: infectious, noninfectious inflammatory, neoplasm, trauma and wounds, drug-related eruptions, vascular, pruritic, pigmented, bullous, neuropsychiatric, and other. Other included unspecified eruptions as well as miscellaneous lesions such as calluses. The current chief concern, anatomic location, and configuration were recorded, as well as biopsied lesions and outpatient referrals or inpatient consultations to dermatology or other specialties, including wound care, infectious disease, podiatry, and surgery. χ2 analysis was used to analyze significance of cutaneous categories, body location, and referrals. Groups smaller than 5 defaulted to the Fisher exact test.

Results
The total diagnoses (including both chief concerns and secondary diagnoses) are shown in Table 2. Chief concerns were more frequently cutaneous or dermatologic for WH (NWH, 209; WH, 307; P<.001). In both groups, cutaneous infectious etiologies were more likely to be a patient’s presenting chief concern (58% NWH, P=.002; 42% WH, P<.001). Noninfectious inflammatory etiologies and pigmented lesions were more likely to be secondary diagnoses with an unrelated noncutaneous concern; noninfectious inflammatory etiologies were only 16% of the total cutaneous chief concerns (11% NWH, P=.04; 20% WH, P=.03), and no pigmented lesions were chief concerns.

Infection was the most common chief concern, though NWH patients presented with significantly more infectious concerns (NWH, 212; WH, 150; P<.001), particularly infestations (NWH, 33; WH, 8; P<.001) and bacterial etiologies (NWH, 127; WH, 100; P=.04). The majority of bacterial etiologies were either an abscess or cellulitis (NWH, 106; WH, 83), though infected chronic wounds were categorized as bacterial infection when treated definitively as such (eg, in the case of sacral ulcers causing osteomyelitis)(NWH, 21; WH, 17). Of note, infectious etiology was associated with intravenous drug use (IVDU) in both NWH and WH patients. Of 184 NWH who reported IVDU, 127 had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Similarly, 43 of 56 total WH patients who reported IVDU had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Infestation (within the infectious category) included scabies (NWH, 20; WH, 3) and insect or arthropod bites (NWH, 12; WH, 5). Two NWH patients also presented with swelling of the lower extremities and were subsequently diagnosed with maggot infestations. Fungal and viral etiologies were not significantly increased in either group; however, NWH did have a higher incidence of tinea pedis (NWH, 14; WH, 4; P=.03).
More neoplasms (NWH, 6; WH, 16; P=.03), noninfectious inflammatory eruptions (NWH, 48; WH, 85; P<.001), and cutaneous drug eruptions (NWH, 5; WH, 27; P<.001) were reported in WH patients. There was no significant difference in benign vs malignant neoplastic processes between groups. More noninfectious inflammatory eruptions in WH were specifically driven by a markedly increased incidence of follicular (NWH, 9; WH, 29; P<.001) and urticarial/erythematous (NWH, 3; WH, 13; P=.02) lesions. Follicular etiologies included acne (NWH, 1; WH, 6; P=.12), folliculitis (NWH, 5; WH, 2; P=.45), hidradenitis suppurativa (NWH, 2; WH, 11; P=.02), and pilonidal and sebaceous cysts (NWH, 1; WH, 10; P=.01). Allergic urticaria dominated the urticarial/erythematous category (NWH, 3; WH, 11; P=.06), though there were 2 WH presentations of diffuse erythema and skin peeling.
Another substantial proportion of cutaneous etiologies were due to trauma or chronic wounds. Significantly more traumatic injuries presented in NWH patients vs WH patients (36 vs 31; P=.04). Trauma included human or dog bites (NWH, 5; WH, 4), sunburns (NWH, 3; WH, 0), other burns (NWH, 11; WH, 13), abrasions and lacerations (NWH, 16; WH, 3; P=.004), and foreign bodies (NWH, 1; WH, 1). Wounds consisted of chronic wounds such as those due to diabetes mellitus (foot ulcers) or immobility (sacral ulcers); numbers were similar between groups.
Looking at location, NWH patients had more pathology on the feet (NWH, 62; WH, 39; P=.02), whereas WH patients had more disseminated multiregional concerns (NWH, 55; WH, 75; P=.05). No one body location was notably more likely to warrant a chief concern.
For clinical outcomes, more WH patients received a consultation of any kind (NWH, 171; WH, 217; P<.001), consultation to dermatology (NWH, 49; WH, 87; P<.001), and consultation to surgery (NWH, 64; WH, 110; P<.001)(Table 3 and Figure). More outpatient referrals to dermatology were made for WH patients (NWH, 61; WH, 82; P=.05). Notably, NWH patients presented for 80% fewer hospital follow-up appointments (NWH, 11; WH, 55; P<.001). It is essential to note that these findings were not affected by self-reported race or ethnicity. Results remained significant when broken into cohorts consisting of patients with and without skin of color.

Comment
Cutaneous Concerns in NWH Patients—Although cutaneous disease has been reported to disproportionately affect NWH patients,10 in our cohort, NWH patients had fewer cutaneous chief concerns than WH patients. However, without comparing with all patients entering the ED at UMC, we cannot make a statement on this claim. We do present a few reasons why NWH patients do not have more cutaneous concerns. First, they may wait to present with cutaneous disease until it becomes more severe (eg, until chronic wounds have progressed to infections). Second, as discussed in depth by Hollestein and Nijsten,3 dermatologic disease may be a major contributor to the overall count of disability-adjusted life years but may play a minor role in individual disability. Therefore, skin disease often is considered less important on an individual basis, despite substantial psychosocial burden, leading to further stigmatization of this vulnerable population and discouraged care-seeking behavior, particularly for noninfectious inflammatory eruptions, which were notably more present in WH individuals. Third, fewer dermatologic lesions were reported on NWH patients, which may explain why all 3 WH pigmented lesions were diagnosed after presentation with a noncutaneous concern (eg, headache, anemia, nausea).

Infectious Cutaneous Diagnoses—The increased presentation of infectious etiologies, especially bacterial, is linked to the increased numbers of IVDUs reported in NWH individuals as well as increased exposure and decreased access to basic hygienic supplies. Intravenous drug use acted as an effect modifier of infectious etiology diagnoses, playing a major role in both NWH and WH cohorts. Although Black and Hispanic individuals as well as individuals with low socioeconomic status have increased proportions of skin cancer, there are inadequate data on the prevalence in NWH individuals.4 We found no increase in malignant dermatologic processes in NWH individuals; however, this may be secondary to inadequate screening with a total body skin examination.
Clinical Workup of NWH Patients—Because most NWH individuals present to the ED to receive care, their care compared with WH patients should be considered. In this cohort, WH patients received a less extensive clinical workup. They received almost half as many dermatologic consultations and fewer outpatient referrals to dermatology. Major communication barriers may affect NWH presentation to follow-up, which was drastically lower than WH individuals, as scheduling typically occurs well after discharge from the ED or inpatient unit. We suggest a few alterations to improve dermatologic care for NWH individuals:
• Consider inpatient consultation for serious dermatologic conditions—even if chronic—to improve disease control, considering that many barriers inhibit follow-up in clinic.
• Involve outreach teams, such as the Assertive Community Treatment teams, that assist individuals by delivering medicine for psychiatric disorders, conducting total-body skin examinations, assisting with wound care, providing basic skin barrier creams or medicaments, and carrying information regarding outpatient follow-up.
• Educate ED providers on the most common skin concerns, especially those that fall within the noninfectious inflammatory category, such as hidradenitis suppurativa, which could easily be misdiagnosed as an abscess.
Future Directions—Owing to limitations of a retrospective cohort study, we present several opportunities for further research on this vulnerable population. The severity of disease, especially infectious etiologies, should be graded to determine if NWH patients truly present later in the disease course. The duration and quality of housing for NWH patients could be categorized based on living conditions (eg, on the street vs in a shelter). Although the findings of our NWH cohort presenting to the ED at UMC provide helpful insight into dermatologic disease, these findings may be disparate from those conducted at other locations in the United States. University Medical Center provides care to mostly subsidized insurance plans in a racially diverse community. Improved outcomes for the NWH individuals living in New Orleans start with obtaining a greater understanding of their diseases and where disparities exist that can be bridged with better care.
Acknowledgment—The dataset generated during this study and used for analysis is not publicly available to protect public health information but is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
More than half a million individuals are without housing (NWH) on any given night in the United States, as estimated by the US Department of Housing and Urban Development. 1 Lack of hygiene, increased risk of infection and infestation due to living conditions, and barriers to health care put these individuals at increased risk for disease. 2 Skin disease, including fungal infection and acne, are within the top 10 most prevalent diseases worldwide and can cause major psychologic impairment, yet dermatologic concerns and clinical outcomes in NWH patients have not been well characterized. 2-5 Further, because this vulnerable demographic tends to be underinsured, they frequently present to the emergency department (ED) for management of disease. 1,6 Survey of common concerns in NWH patients is of utility to consulting dermatologists and nondermatologist providers in the ED, who can familiarize themselves with management of diseases they are more likely to encounter. Few studies examine dermatologic conditions in the ED, and a thorough literature review indicates none have included homelessness as a variable. 6,7 Additionally, comparison with a matched control group of patients with housing (WH) is limited. 5,8 We present one of the largest comparisons of cutaneous disease in NWH vs WH patients in a single hospital system to elucidate the types of cutaneous disease that motivate patients to seek care, the location of skin disease, and differences in clinical care.
Methods
A retrospective medical record review of patients seen for an inclusive list of dermatologic diagnoses in the ED or while admitted at University Medical Center New Orleans, Louisiana (UMC), between January 1, 2018, and April 21, 2020, was conducted. This study was qualified as exempt from the institutional review board by Louisiana State University because it proposed zero risk to the patients and remained completely anonymous. Eight hundred forty-two total medical records were reviewed (NWH, 421; WH, 421)(Table 1). Patients with housing were matched based on self-identified race and ethnicity, sex, and age. Disease categories were constructed based on fundamental pathophysiology adapted from Dermatology9: infectious, noninfectious inflammatory, neoplasm, trauma and wounds, drug-related eruptions, vascular, pruritic, pigmented, bullous, neuropsychiatric, and other. Other included unspecified eruptions as well as miscellaneous lesions such as calluses. The current chief concern, anatomic location, and configuration were recorded, as well as biopsied lesions and outpatient referrals or inpatient consultations to dermatology or other specialties, including wound care, infectious disease, podiatry, and surgery. χ2 analysis was used to analyze significance of cutaneous categories, body location, and referrals. Groups smaller than 5 defaulted to the Fisher exact test.

Results
The total diagnoses (including both chief concerns and secondary diagnoses) are shown in Table 2. Chief concerns were more frequently cutaneous or dermatologic for WH (NWH, 209; WH, 307; P<.001). In both groups, cutaneous infectious etiologies were more likely to be a patient’s presenting chief concern (58% NWH, P=.002; 42% WH, P<.001). Noninfectious inflammatory etiologies and pigmented lesions were more likely to be secondary diagnoses with an unrelated noncutaneous concern; noninfectious inflammatory etiologies were only 16% of the total cutaneous chief concerns (11% NWH, P=.04; 20% WH, P=.03), and no pigmented lesions were chief concerns.

Infection was the most common chief concern, though NWH patients presented with significantly more infectious concerns (NWH, 212; WH, 150; P<.001), particularly infestations (NWH, 33; WH, 8; P<.001) and bacterial etiologies (NWH, 127; WH, 100; P=.04). The majority of bacterial etiologies were either an abscess or cellulitis (NWH, 106; WH, 83), though infected chronic wounds were categorized as bacterial infection when treated definitively as such (eg, in the case of sacral ulcers causing osteomyelitis)(NWH, 21; WH, 17). Of note, infectious etiology was associated with intravenous drug use (IVDU) in both NWH and WH patients. Of 184 NWH who reported IVDU, 127 had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Similarly, 43 of 56 total WH patients who reported IVDU had an infectious diagnosis (P<.001). Infestation (within the infectious category) included scabies (NWH, 20; WH, 3) and insect or arthropod bites (NWH, 12; WH, 5). Two NWH patients also presented with swelling of the lower extremities and were subsequently diagnosed with maggot infestations. Fungal and viral etiologies were not significantly increased in either group; however, NWH did have a higher incidence of tinea pedis (NWH, 14; WH, 4; P=.03).
More neoplasms (NWH, 6; WH, 16; P=.03), noninfectious inflammatory eruptions (NWH, 48; WH, 85; P<.001), and cutaneous drug eruptions (NWH, 5; WH, 27; P<.001) were reported in WH patients. There was no significant difference in benign vs malignant neoplastic processes between groups. More noninfectious inflammatory eruptions in WH were specifically driven by a markedly increased incidence of follicular (NWH, 9; WH, 29; P<.001) and urticarial/erythematous (NWH, 3; WH, 13; P=.02) lesions. Follicular etiologies included acne (NWH, 1; WH, 6; P=.12), folliculitis (NWH, 5; WH, 2; P=.45), hidradenitis suppurativa (NWH, 2; WH, 11; P=.02), and pilonidal and sebaceous cysts (NWH, 1; WH, 10; P=.01). Allergic urticaria dominated the urticarial/erythematous category (NWH, 3; WH, 11; P=.06), though there were 2 WH presentations of diffuse erythema and skin peeling.
Another substantial proportion of cutaneous etiologies were due to trauma or chronic wounds. Significantly more traumatic injuries presented in NWH patients vs WH patients (36 vs 31; P=.04). Trauma included human or dog bites (NWH, 5; WH, 4), sunburns (NWH, 3; WH, 0), other burns (NWH, 11; WH, 13), abrasions and lacerations (NWH, 16; WH, 3; P=.004), and foreign bodies (NWH, 1; WH, 1). Wounds consisted of chronic wounds such as those due to diabetes mellitus (foot ulcers) or immobility (sacral ulcers); numbers were similar between groups.
Looking at location, NWH patients had more pathology on the feet (NWH, 62; WH, 39; P=.02), whereas WH patients had more disseminated multiregional concerns (NWH, 55; WH, 75; P=.05). No one body location was notably more likely to warrant a chief concern.
For clinical outcomes, more WH patients received a consultation of any kind (NWH, 171; WH, 217; P<.001), consultation to dermatology (NWH, 49; WH, 87; P<.001), and consultation to surgery (NWH, 64; WH, 110; P<.001)(Table 3 and Figure). More outpatient referrals to dermatology were made for WH patients (NWH, 61; WH, 82; P=.05). Notably, NWH patients presented for 80% fewer hospital follow-up appointments (NWH, 11; WH, 55; P<.001). It is essential to note that these findings were not affected by self-reported race or ethnicity. Results remained significant when broken into cohorts consisting of patients with and without skin of color.

Comment
Cutaneous Concerns in NWH Patients—Although cutaneous disease has been reported to disproportionately affect NWH patients,10 in our cohort, NWH patients had fewer cutaneous chief concerns than WH patients. However, without comparing with all patients entering the ED at UMC, we cannot make a statement on this claim. We do present a few reasons why NWH patients do not have more cutaneous concerns. First, they may wait to present with cutaneous disease until it becomes more severe (eg, until chronic wounds have progressed to infections). Second, as discussed in depth by Hollestein and Nijsten,3 dermatologic disease may be a major contributor to the overall count of disability-adjusted life years but may play a minor role in individual disability. Therefore, skin disease often is considered less important on an individual basis, despite substantial psychosocial burden, leading to further stigmatization of this vulnerable population and discouraged care-seeking behavior, particularly for noninfectious inflammatory eruptions, which were notably more present in WH individuals. Third, fewer dermatologic lesions were reported on NWH patients, which may explain why all 3 WH pigmented lesions were diagnosed after presentation with a noncutaneous concern (eg, headache, anemia, nausea).

Infectious Cutaneous Diagnoses—The increased presentation of infectious etiologies, especially bacterial, is linked to the increased numbers of IVDUs reported in NWH individuals as well as increased exposure and decreased access to basic hygienic supplies. Intravenous drug use acted as an effect modifier of infectious etiology diagnoses, playing a major role in both NWH and WH cohorts. Although Black and Hispanic individuals as well as individuals with low socioeconomic status have increased proportions of skin cancer, there are inadequate data on the prevalence in NWH individuals.4 We found no increase in malignant dermatologic processes in NWH individuals; however, this may be secondary to inadequate screening with a total body skin examination.
Clinical Workup of NWH Patients—Because most NWH individuals present to the ED to receive care, their care compared with WH patients should be considered. In this cohort, WH patients received a less extensive clinical workup. They received almost half as many dermatologic consultations and fewer outpatient referrals to dermatology. Major communication barriers may affect NWH presentation to follow-up, which was drastically lower than WH individuals, as scheduling typically occurs well after discharge from the ED or inpatient unit. We suggest a few alterations to improve dermatologic care for NWH individuals:
• Consider inpatient consultation for serious dermatologic conditions—even if chronic—to improve disease control, considering that many barriers inhibit follow-up in clinic.
• Involve outreach teams, such as the Assertive Community Treatment teams, that assist individuals by delivering medicine for psychiatric disorders, conducting total-body skin examinations, assisting with wound care, providing basic skin barrier creams or medicaments, and carrying information regarding outpatient follow-up.
• Educate ED providers on the most common skin concerns, especially those that fall within the noninfectious inflammatory category, such as hidradenitis suppurativa, which could easily be misdiagnosed as an abscess.
Future Directions—Owing to limitations of a retrospective cohort study, we present several opportunities for further research on this vulnerable population. The severity of disease, especially infectious etiologies, should be graded to determine if NWH patients truly present later in the disease course. The duration and quality of housing for NWH patients could be categorized based on living conditions (eg, on the street vs in a shelter). Although the findings of our NWH cohort presenting to the ED at UMC provide helpful insight into dermatologic disease, these findings may be disparate from those conducted at other locations in the United States. University Medical Center provides care to mostly subsidized insurance plans in a racially diverse community. Improved outcomes for the NWH individuals living in New Orleans start with obtaining a greater understanding of their diseases and where disparities exist that can be bridged with better care.
Acknowledgment—The dataset generated during this study and used for analysis is not publicly available to protect public health information but is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- Fazel S, Geddes JR, Kushel M. The health of homeless people in high-income countries: descriptive epidemiology, health consequences, and clinical and policy recommendations. Lancet. 2014;384:1529-1540. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61132-6
- Contag C, Lowenstein SE, Jain S, et al. Survey of symptomatic dermatologic disease in homeless patients at a shelter-based clinic. Our Dermatol Online. 2017;8:133-137. doi:10.7241/ourd.20172.37
- Hollestein LM, Nijsten T. An insight into the global burden of skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1499-1501. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.513
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Mackelprang JL, Graves JM, Rivara FP. Homeless in America: injuries treated in US emergency departments, 2007-2011. Int J Inj Contr Saf Promot. 2014;21:289-297. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.371
- Chen CL, Fitzpatrick L, Kamel H. Who uses the emergency department for dermatologic care? a statewide analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:308-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.013
- Stratigos AJ, Stern R, Gonzalez E, et al. Prevalence of skin disease in a cohort of shelter-based homeless men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:197-202. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70048-4
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Badiaga S, Menard A, Tissot Dupont H, et al. Prevalence of skin infections in sheltered homeless. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:382-386.
- Fazel S, Geddes JR, Kushel M. The health of homeless people in high-income countries: descriptive epidemiology, health consequences, and clinical and policy recommendations. Lancet. 2014;384:1529-1540. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61132-6
- Contag C, Lowenstein SE, Jain S, et al. Survey of symptomatic dermatologic disease in homeless patients at a shelter-based clinic. Our Dermatol Online. 2017;8:133-137. doi:10.7241/ourd.20172.37
- Hollestein LM, Nijsten T. An insight into the global burden of skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1499-1501. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.513
- Buster KJ, Stevens EI, Elmets CA. Dermatologic health disparities. Dermatol Clin. 2012;30:53-59. doi:10.1016/j.det.2011.08.002
- Grossberg AL, Carranza D, Lamp K, et al. Dermatologic care in the homeless and underserved populations: observations from the Venice Family Clinic. Cutis. 2012;89:25-32.
- Mackelprang JL, Graves JM, Rivara FP. Homeless in America: injuries treated in US emergency departments, 2007-2011. Int J Inj Contr Saf Promot. 2014;21:289-297. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.371
- Chen CL, Fitzpatrick L, Kamel H. Who uses the emergency department for dermatologic care? a statewide analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:308-313. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2014.03.013
- Stratigos AJ, Stern R, Gonzalez E, et al. Prevalence of skin disease in a cohort of shelter-based homeless men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:197-202. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70048-4
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2012.
- Badiaga S, Menard A, Tissot Dupont H, et al. Prevalence of skin infections in sheltered homeless. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:382-386.
Practice Points
- Dermatologic disease in patients without housing (NWH) is characterized by more infectious concerns and fewer follicular and urticarial noninfectious inflammatory eruptions compared with matched controls of those with housing.
- Patients with housing more frequently presented with cutaneous chief concerns and received more consultations while in the hospital.
- This study uncovered notable pathological and clinical differences in treating dermatologic conditions in NWH patients.