User login
researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend in a Pediatrics special report.
More than 41,000 measles cases and 37 deaths – primarily due to low immunization coverage – were reported in the World Health Organization European Region in the first 6 months of 2018, the highest incidence since the 1990s. Typical case counts since 2010 have ranged from 5,000 to 24,000 in this region, wrote Kristina M. Angelo, DO, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Travelers’ Health Branch in Atlanta, and associates.
France, Italy and Greece – all particularly popular countries for U.S. vacationers to visit – have particularly high numbers of cases, as do Georgia, Russia, Serbia and, comprising the majority of cases, Ukraine. Italy, for example, is the 10th most popular destination worldwide for Americans, with an estimated 2.5 million American visitors in 2015.
“The large number of measles infections in the WHO European Region ... is a global concern because the European continent is the most common travel destination worldwide,” but is not perceived as a place with infectious disease risk. So travelers may not consider the need of a pretravel health consultation, including vaccination, they said.
But they need to, Dr. Angelo and associates state, and health care providers should be vigilant about checking for symptoms of measles among those who have recently returned from overseas. Given how highly contagious measles is, unvaccinated and under vaccinated travelers to Europe are susceptible to infection, as are any people they encounter back in the United States if the travelers come home sick.
Measles was eliminated in the United States in 2000, but that status is in jeopardy, CDC officials recently warned. The number of domestic measles cases has exceeded 1,000 just halfway through 2019, the highest count since 1992, nearly a decade before elimination.
“Avoiding international travel with nonimmune infants and performing early vaccination at 6 to 12 months of age per the ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations if travel is unavoidable are of utmost importance,” Dr. Angelo and colleagues advised. “Other at-risk populations (e.g., immunocompromised individuals and pregnant women), for whom vaccination against the measles virus is contraindicated, may consider alternative destinations or delay travel to measles-endemic destinations or areas with known, ongoing measles outbreaks.”
“Presumptive immunity to measles is defined as 1 or more of the following: birth before 1957, laboratory evidence of immunity or infection, 1 or more doses of a measles containing vaccine administered for preschool-aged children and low-risk adults, or 2 doses of measles vaccine among school-aged children and high-risk adults, including international travelers,” they explained.
In Europe, measles remains endemic in Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, France, Georgia, Germany, Italy, Romania, the Russian Federation, Serbia and the Ukraine, the authors wrote.
“As long as measles remains endemic in other countries, the United States will be challenged by measles importations,” the authors wrote. Yet at least one past study in 2017 revealed a third of U.S. travelers to Europe left the country without being fully vaccinated against measles, most often due to vaccine refusal.
“The reason one-third of travelers to Europe missed an opportunity for measles vaccination remains unclear,” the authors wrote. “It may represent a lack of concern or awareness on the part of travelers and the health care providers about acquiring measles in Europe.”
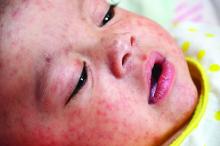
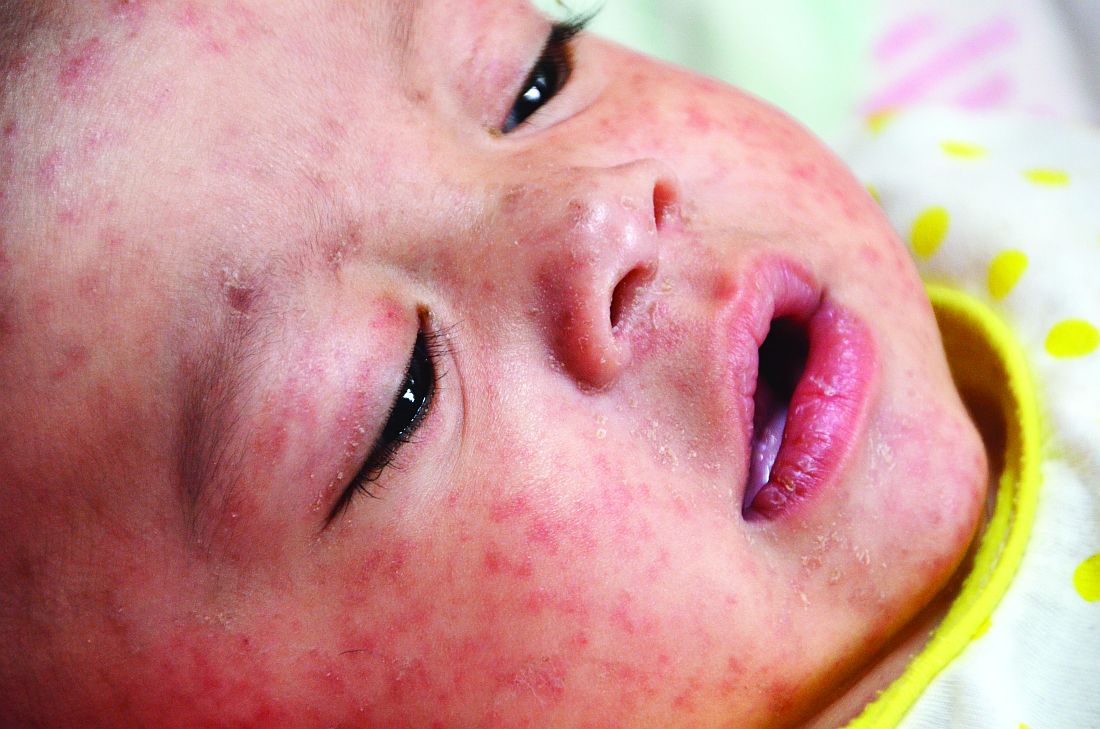
Dr. Angelo and colleagues also emphasized the importance of returning U.S. travelers seeking health care if they have symptoms of measles, including fever and a rash.
Health care providers should ask all patients about recent international travel, they stated. “If measles is suspected, health care providers should isolate travelers immediately, placing them on airborne precautions until day 4 of the rash.” Providers may consider administering immunoglobulin for unvaccinated and undervaccinated travelers and monitor them for 21 days for development of measles symptoms.
The statement was funded by the CDC. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Angelo KM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Jun 17. doi: /10.1542/peds.2019-0414.
researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend in a Pediatrics special report.
More than 41,000 measles cases and 37 deaths – primarily due to low immunization coverage – were reported in the World Health Organization European Region in the first 6 months of 2018, the highest incidence since the 1990s. Typical case counts since 2010 have ranged from 5,000 to 24,000 in this region, wrote Kristina M. Angelo, DO, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Travelers’ Health Branch in Atlanta, and associates.
France, Italy and Greece – all particularly popular countries for U.S. vacationers to visit – have particularly high numbers of cases, as do Georgia, Russia, Serbia and, comprising the majority of cases, Ukraine. Italy, for example, is the 10th most popular destination worldwide for Americans, with an estimated 2.5 million American visitors in 2015.
“The large number of measles infections in the WHO European Region ... is a global concern because the European continent is the most common travel destination worldwide,” but is not perceived as a place with infectious disease risk. So travelers may not consider the need of a pretravel health consultation, including vaccination, they said.
But they need to, Dr. Angelo and associates state, and health care providers should be vigilant about checking for symptoms of measles among those who have recently returned from overseas. Given how highly contagious measles is, unvaccinated and under vaccinated travelers to Europe are susceptible to infection, as are any people they encounter back in the United States if the travelers come home sick.
Measles was eliminated in the United States in 2000, but that status is in jeopardy, CDC officials recently warned. The number of domestic measles cases has exceeded 1,000 just halfway through 2019, the highest count since 1992, nearly a decade before elimination.
“Avoiding international travel with nonimmune infants and performing early vaccination at 6 to 12 months of age per the ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations if travel is unavoidable are of utmost importance,” Dr. Angelo and colleagues advised. “Other at-risk populations (e.g., immunocompromised individuals and pregnant women), for whom vaccination against the measles virus is contraindicated, may consider alternative destinations or delay travel to measles-endemic destinations or areas with known, ongoing measles outbreaks.”
“Presumptive immunity to measles is defined as 1 or more of the following: birth before 1957, laboratory evidence of immunity or infection, 1 or more doses of a measles containing vaccine administered for preschool-aged children and low-risk adults, or 2 doses of measles vaccine among school-aged children and high-risk adults, including international travelers,” they explained.
In Europe, measles remains endemic in Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, France, Georgia, Germany, Italy, Romania, the Russian Federation, Serbia and the Ukraine, the authors wrote.
“As long as measles remains endemic in other countries, the United States will be challenged by measles importations,” the authors wrote. Yet at least one past study in 2017 revealed a third of U.S. travelers to Europe left the country without being fully vaccinated against measles, most often due to vaccine refusal.
“The reason one-third of travelers to Europe missed an opportunity for measles vaccination remains unclear,” the authors wrote. “It may represent a lack of concern or awareness on the part of travelers and the health care providers about acquiring measles in Europe.”
Dr. Angelo and colleagues also emphasized the importance of returning U.S. travelers seeking health care if they have symptoms of measles, including fever and a rash.
Health care providers should ask all patients about recent international travel, they stated. “If measles is suspected, health care providers should isolate travelers immediately, placing them on airborne precautions until day 4 of the rash.” Providers may consider administering immunoglobulin for unvaccinated and undervaccinated travelers and monitor them for 21 days for development of measles symptoms.
The statement was funded by the CDC. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Angelo KM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Jun 17. doi: /10.1542/peds.2019-0414.
researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend in a Pediatrics special report.
More than 41,000 measles cases and 37 deaths – primarily due to low immunization coverage – were reported in the World Health Organization European Region in the first 6 months of 2018, the highest incidence since the 1990s. Typical case counts since 2010 have ranged from 5,000 to 24,000 in this region, wrote Kristina M. Angelo, DO, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Travelers’ Health Branch in Atlanta, and associates.
France, Italy and Greece – all particularly popular countries for U.S. vacationers to visit – have particularly high numbers of cases, as do Georgia, Russia, Serbia and, comprising the majority of cases, Ukraine. Italy, for example, is the 10th most popular destination worldwide for Americans, with an estimated 2.5 million American visitors in 2015.
“The large number of measles infections in the WHO European Region ... is a global concern because the European continent is the most common travel destination worldwide,” but is not perceived as a place with infectious disease risk. So travelers may not consider the need of a pretravel health consultation, including vaccination, they said.
But they need to, Dr. Angelo and associates state, and health care providers should be vigilant about checking for symptoms of measles among those who have recently returned from overseas. Given how highly contagious measles is, unvaccinated and under vaccinated travelers to Europe are susceptible to infection, as are any people they encounter back in the United States if the travelers come home sick.
Measles was eliminated in the United States in 2000, but that status is in jeopardy, CDC officials recently warned. The number of domestic measles cases has exceeded 1,000 just halfway through 2019, the highest count since 1992, nearly a decade before elimination.
“Avoiding international travel with nonimmune infants and performing early vaccination at 6 to 12 months of age per the ACIP [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] recommendations if travel is unavoidable are of utmost importance,” Dr. Angelo and colleagues advised. “Other at-risk populations (e.g., immunocompromised individuals and pregnant women), for whom vaccination against the measles virus is contraindicated, may consider alternative destinations or delay travel to measles-endemic destinations or areas with known, ongoing measles outbreaks.”
“Presumptive immunity to measles is defined as 1 or more of the following: birth before 1957, laboratory evidence of immunity or infection, 1 or more doses of a measles containing vaccine administered for preschool-aged children and low-risk adults, or 2 doses of measles vaccine among school-aged children and high-risk adults, including international travelers,” they explained.
In Europe, measles remains endemic in Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, France, Georgia, Germany, Italy, Romania, the Russian Federation, Serbia and the Ukraine, the authors wrote.
“As long as measles remains endemic in other countries, the United States will be challenged by measles importations,” the authors wrote. Yet at least one past study in 2017 revealed a third of U.S. travelers to Europe left the country without being fully vaccinated against measles, most often due to vaccine refusal.
“The reason one-third of travelers to Europe missed an opportunity for measles vaccination remains unclear,” the authors wrote. “It may represent a lack of concern or awareness on the part of travelers and the health care providers about acquiring measles in Europe.”
Dr. Angelo and colleagues also emphasized the importance of returning U.S. travelers seeking health care if they have symptoms of measles, including fever and a rash.
Health care providers should ask all patients about recent international travel, they stated. “If measles is suspected, health care providers should isolate travelers immediately, placing them on airborne precautions until day 4 of the rash.” Providers may consider administering immunoglobulin for unvaccinated and undervaccinated travelers and monitor them for 21 days for development of measles symptoms.
The statement was funded by the CDC. The authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Angelo KM et al. Pediatrics. 2019 Jun 17. doi: /10.1542/peds.2019-0414.
FROM PEDIATRICS