User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Home Insulin Pumps Safe for In-Hospital Pediatric Care
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical guidelines support the use of home insulin pumps in adults hospitalized for noncritical illnesses, but it has been unclear if adult safety data translate to pediatric inpatients.
- The study evaluated if insulin can be safely and precisely delivered using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers in 2738 patients (0.5-25 years old; median age about 16) with insulin-dependent diabetes admitted to non–intensive care units of a tertiary children’s hospital between January 2016 and December 2021.
- Insulin was delivered either using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers or using hospital insulin pumps or subcutaneous injections managed by hospital staff.
- Safety was measured by hyperglycemia (glucose level > 250 mg/dL), hypoglycemia (moderate: glucose level, 45-59 mg/dL or severe: glucose level, < 45 mg/dL), glucose variability, and the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis for each delivery method.
- Results were calculated by the number of days a patient had one or more glucose levels meeting the definition of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and divided by the number of days a patient receive any insulin dose.
TAKEAWAY:
The number of hyperglycemic days was lower in patients using a hospital (15.7%) or a home (27.0%) insulin pump than in those receiving subcutaneous insulin injections (45.2%; P < .001).
At least one moderate hypoglycemic day was noted in patients receiving insulin through subcutaneous injections (5.1%) compared with those receiving it through hospital (3.1%) or home insulin pumps (4.5%; P = .02).
The proportion of days within the desired blood glucose range and glucose variability were similar in patients using hospital or home insulin pumps and worse in patients managed with injections (P < .001).
No patients using home or hospital pumps developed diabetic ketoacidosis, but two cases of diabetic ketoacidosis were noted among patients using injections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Safety is not sacrificed when patients or caregivers use home pumps during pediatric non–intensive care unit admissions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The investigation, led by Jodi Owens, MSN, RN, Division of Endocrinology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, was published along with an invited commentary in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The strategies employed for insulin safety and awareness by the institution may have led to improved rates of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Moreover, the study did not assess changes in glycemic levels during transition in the insulin delivery method. The study was limited to non–intensive care units and hence cannot be generalized to intensive care unit settings or in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. The study did not include patients using hybrid-closed loop insulin pumps.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any source of funding. The authors did not report any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical guidelines support the use of home insulin pumps in adults hospitalized for noncritical illnesses, but it has been unclear if adult safety data translate to pediatric inpatients.
- The study evaluated if insulin can be safely and precisely delivered using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers in 2738 patients (0.5-25 years old; median age about 16) with insulin-dependent diabetes admitted to non–intensive care units of a tertiary children’s hospital between January 2016 and December 2021.
- Insulin was delivered either using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers or using hospital insulin pumps or subcutaneous injections managed by hospital staff.
- Safety was measured by hyperglycemia (glucose level > 250 mg/dL), hypoglycemia (moderate: glucose level, 45-59 mg/dL or severe: glucose level, < 45 mg/dL), glucose variability, and the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis for each delivery method.
- Results were calculated by the number of days a patient had one or more glucose levels meeting the definition of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and divided by the number of days a patient receive any insulin dose.
TAKEAWAY:
The number of hyperglycemic days was lower in patients using a hospital (15.7%) or a home (27.0%) insulin pump than in those receiving subcutaneous insulin injections (45.2%; P < .001).
At least one moderate hypoglycemic day was noted in patients receiving insulin through subcutaneous injections (5.1%) compared with those receiving it through hospital (3.1%) or home insulin pumps (4.5%; P = .02).
The proportion of days within the desired blood glucose range and glucose variability were similar in patients using hospital or home insulin pumps and worse in patients managed with injections (P < .001).
No patients using home or hospital pumps developed diabetic ketoacidosis, but two cases of diabetic ketoacidosis were noted among patients using injections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Safety is not sacrificed when patients or caregivers use home pumps during pediatric non–intensive care unit admissions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The investigation, led by Jodi Owens, MSN, RN, Division of Endocrinology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, was published along with an invited commentary in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The strategies employed for insulin safety and awareness by the institution may have led to improved rates of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Moreover, the study did not assess changes in glycemic levels during transition in the insulin delivery method. The study was limited to non–intensive care units and hence cannot be generalized to intensive care unit settings or in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. The study did not include patients using hybrid-closed loop insulin pumps.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any source of funding. The authors did not report any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical guidelines support the use of home insulin pumps in adults hospitalized for noncritical illnesses, but it has been unclear if adult safety data translate to pediatric inpatients.
- The study evaluated if insulin can be safely and precisely delivered using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers in 2738 patients (0.5-25 years old; median age about 16) with insulin-dependent diabetes admitted to non–intensive care units of a tertiary children’s hospital between January 2016 and December 2021.
- Insulin was delivered either using home insulin pumps managed by patients or caregivers or using hospital insulin pumps or subcutaneous injections managed by hospital staff.
- Safety was measured by hyperglycemia (glucose level > 250 mg/dL), hypoglycemia (moderate: glucose level, 45-59 mg/dL or severe: glucose level, < 45 mg/dL), glucose variability, and the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis for each delivery method.
- Results were calculated by the number of days a patient had one or more glucose levels meeting the definition of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and divided by the number of days a patient receive any insulin dose.
TAKEAWAY:
The number of hyperglycemic days was lower in patients using a hospital (15.7%) or a home (27.0%) insulin pump than in those receiving subcutaneous insulin injections (45.2%; P < .001).
At least one moderate hypoglycemic day was noted in patients receiving insulin through subcutaneous injections (5.1%) compared with those receiving it through hospital (3.1%) or home insulin pumps (4.5%; P = .02).
The proportion of days within the desired blood glucose range and glucose variability were similar in patients using hospital or home insulin pumps and worse in patients managed with injections (P < .001).
No patients using home or hospital pumps developed diabetic ketoacidosis, but two cases of diabetic ketoacidosis were noted among patients using injections.
IN PRACTICE:
“Safety is not sacrificed when patients or caregivers use home pumps during pediatric non–intensive care unit admissions,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The investigation, led by Jodi Owens, MSN, RN, Division of Endocrinology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, was published along with an invited commentary in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The strategies employed for insulin safety and awareness by the institution may have led to improved rates of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Moreover, the study did not assess changes in glycemic levels during transition in the insulin delivery method. The study was limited to non–intensive care units and hence cannot be generalized to intensive care unit settings or in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. The study did not include patients using hybrid-closed loop insulin pumps.
DISCLOSURES:
The study did not disclose any source of funding. The authors did not report any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Organophosphate Esters Increase Thyroid Disease Risk?
TOPLINE:
, bis(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (BCEP) being the main contributor.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have reported that OPEs — used in building materials, electronic products, furniture, and textiles — may interfere with thyroid function, hinting at a possible association of OPEs with thyroid disease.
- Researchers assessed the association between OPE exposure and the risk for thyroid disease using data from the 2011-2014 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey cycle.
- They included 2449 participants (mean age, 46 years; half of whom were women) who had complete values for seven OPE metabolites through urinalysis and completed questionnaires regarding the presence of thyroid disease.
- The seven OPE metabolites assessed in this study were diphenyl phosphate (DPHP), bis(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate, bis(1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate, BCEP, dibutyl phosphate, dibenzyl phosphate, and 2,3,4,5-tetrabromobenzoic acid.
- Several mixed exposure models were used to investigate the associations between the risk for thyroid disease and exposure to individual and mixed OPEs.
TAKEAWAY:
- A history of thyroid disease was self-reported by 228 participants.
- In one model, the risk for thyroid disease was 57% higher in people in the highest vs the lowest tertile of BCEP exposure (P = .005).
- A newer method confirmed the positive association between exposure to mixed OPE metabolites and a higher risk for thyroid disease (odds ratio, 1.03; P = .013), with BCEP (65%) being the main contributing factor, followed by DPHP (35%).
- A model from another new method showed a J-shaped relationship between the risk for thyroid disease and increasing levels of BCEP exposure, in which the risk first dropped but then rose with increasing exposure.
IN PRACTICE:
“The three models in our study provided similar results, with exposure to mixed OPEs having a tendency to increase the risk of thyroid disease and pointing to BCEP as the most significant compound responsible for this trend,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yuxin Lin, from the Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China, and published online in Frontiers in Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design cannot establish a causal relationship between OPE exposure and thyroid disease. The study used unweighted data, which could have limited the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, urine sample measurements were performed only once.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Fujian Natural Science Foundation Program and the Scientific Research Program of High-level Talents of Fujian Medical University. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, bis(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (BCEP) being the main contributor.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have reported that OPEs — used in building materials, electronic products, furniture, and textiles — may interfere with thyroid function, hinting at a possible association of OPEs with thyroid disease.
- Researchers assessed the association between OPE exposure and the risk for thyroid disease using data from the 2011-2014 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey cycle.
- They included 2449 participants (mean age, 46 years; half of whom were women) who had complete values for seven OPE metabolites through urinalysis and completed questionnaires regarding the presence of thyroid disease.
- The seven OPE metabolites assessed in this study were diphenyl phosphate (DPHP), bis(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate, bis(1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate, BCEP, dibutyl phosphate, dibenzyl phosphate, and 2,3,4,5-tetrabromobenzoic acid.
- Several mixed exposure models were used to investigate the associations between the risk for thyroid disease and exposure to individual and mixed OPEs.
TAKEAWAY:
- A history of thyroid disease was self-reported by 228 participants.
- In one model, the risk for thyroid disease was 57% higher in people in the highest vs the lowest tertile of BCEP exposure (P = .005).
- A newer method confirmed the positive association between exposure to mixed OPE metabolites and a higher risk for thyroid disease (odds ratio, 1.03; P = .013), with BCEP (65%) being the main contributing factor, followed by DPHP (35%).
- A model from another new method showed a J-shaped relationship between the risk for thyroid disease and increasing levels of BCEP exposure, in which the risk first dropped but then rose with increasing exposure.
IN PRACTICE:
“The three models in our study provided similar results, with exposure to mixed OPEs having a tendency to increase the risk of thyroid disease and pointing to BCEP as the most significant compound responsible for this trend,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yuxin Lin, from the Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China, and published online in Frontiers in Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design cannot establish a causal relationship between OPE exposure and thyroid disease. The study used unweighted data, which could have limited the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, urine sample measurements were performed only once.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Fujian Natural Science Foundation Program and the Scientific Research Program of High-level Talents of Fujian Medical University. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, bis(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (BCEP) being the main contributor.
METHODOLOGY:
- Prior studies have reported that OPEs — used in building materials, electronic products, furniture, and textiles — may interfere with thyroid function, hinting at a possible association of OPEs with thyroid disease.
- Researchers assessed the association between OPE exposure and the risk for thyroid disease using data from the 2011-2014 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey cycle.
- They included 2449 participants (mean age, 46 years; half of whom were women) who had complete values for seven OPE metabolites through urinalysis and completed questionnaires regarding the presence of thyroid disease.
- The seven OPE metabolites assessed in this study were diphenyl phosphate (DPHP), bis(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate, bis(1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate, BCEP, dibutyl phosphate, dibenzyl phosphate, and 2,3,4,5-tetrabromobenzoic acid.
- Several mixed exposure models were used to investigate the associations between the risk for thyroid disease and exposure to individual and mixed OPEs.
TAKEAWAY:
- A history of thyroid disease was self-reported by 228 participants.
- In one model, the risk for thyroid disease was 57% higher in people in the highest vs the lowest tertile of BCEP exposure (P = .005).
- A newer method confirmed the positive association between exposure to mixed OPE metabolites and a higher risk for thyroid disease (odds ratio, 1.03; P = .013), with BCEP (65%) being the main contributing factor, followed by DPHP (35%).
- A model from another new method showed a J-shaped relationship between the risk for thyroid disease and increasing levels of BCEP exposure, in which the risk first dropped but then rose with increasing exposure.
IN PRACTICE:
“The three models in our study provided similar results, with exposure to mixed OPEs having a tendency to increase the risk of thyroid disease and pointing to BCEP as the most significant compound responsible for this trend,” wrote the authors.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yuxin Lin, from the Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics, School of Public Health, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China, and published online in Frontiers in Endocrinology.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design cannot establish a causal relationship between OPE exposure and thyroid disease. The study used unweighted data, which could have limited the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, urine sample measurements were performed only once.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Fujian Natural Science Foundation Program and the Scientific Research Program of High-level Talents of Fujian Medical University. The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Decoding the Gut-Immune Connection During Pregnancy
TOPLINE:
The anti-inflammatory shift in mid-pregnancy may be linked to changes in gut microbiota, which, in turn, may wield their influence through fecal and plasma metabolites.
METHODOLOGY:
- by unknown mechanisms.
- The study explored the associations between the gut microbiota, fecal and plasma metabolites, and cytokine levels of pregnant women and compared them with those of nonpregnant women.
- The study recruited 30 pregnant women (ages 18-34 years; prepregnancy body mass index [BMI], 18.5-21.9) who conceived naturally with a singleton pregnancy and 15 nonpregnant women of similar age and BMI from the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, between February 2019 and August 2020.
- All participants had not used probiotics or antibiotics in the 6 months prior to participating in the study.
- Fecal and blood samples were collected during or after the 37th week of pregnancy in pregnant women until their labor and on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle in nonpregnant women.
TAKEAWAY:
- Pregnant women had more Actinobacteriota than nonpregnant women (9.15% vs 2.98%, respectively; P = .002) in their gut microbiomes, and the most enriched other microbes showed a negative correlation with pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Pregnant women had differences in 44 fecal and 53 plasma metabolites, with certain enriched metabolites negatively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and certain depleted ones positively correlated.
- Levels of pro-inflammatory plasma cytokines such as interleukins (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12, interferon gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha were reduced, while levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 were elevated in pregnant vs nonpregnant women.
- Researchers identified a total of 46 connections between gut microbes, metabolites, and cytokines, with details suggesting that gut microbes may alter plasma cytokine levels by interacting with host metabolites.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study revealed complicated associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system during pregnancy and identified some specific metabolites which may act as mediators between symbiotic microorganisms and immune homeostasis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ting Huang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, was published online on February 7, 2024, in mSystems.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size of the study may have limited capacity to address errors resulting from individual differences. No causal relationships between gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system response could be confirmed. Researchers were unable to account for the possible effects of confounding variables, such as diet, because of the cross-sectional nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The anti-inflammatory shift in mid-pregnancy may be linked to changes in gut microbiota, which, in turn, may wield their influence through fecal and plasma metabolites.
METHODOLOGY:
- by unknown mechanisms.
- The study explored the associations between the gut microbiota, fecal and plasma metabolites, and cytokine levels of pregnant women and compared them with those of nonpregnant women.
- The study recruited 30 pregnant women (ages 18-34 years; prepregnancy body mass index [BMI], 18.5-21.9) who conceived naturally with a singleton pregnancy and 15 nonpregnant women of similar age and BMI from the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, between February 2019 and August 2020.
- All participants had not used probiotics or antibiotics in the 6 months prior to participating in the study.
- Fecal and blood samples were collected during or after the 37th week of pregnancy in pregnant women until their labor and on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle in nonpregnant women.
TAKEAWAY:
- Pregnant women had more Actinobacteriota than nonpregnant women (9.15% vs 2.98%, respectively; P = .002) in their gut microbiomes, and the most enriched other microbes showed a negative correlation with pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Pregnant women had differences in 44 fecal and 53 plasma metabolites, with certain enriched metabolites negatively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and certain depleted ones positively correlated.
- Levels of pro-inflammatory plasma cytokines such as interleukins (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12, interferon gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha were reduced, while levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 were elevated in pregnant vs nonpregnant women.
- Researchers identified a total of 46 connections between gut microbes, metabolites, and cytokines, with details suggesting that gut microbes may alter plasma cytokine levels by interacting with host metabolites.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study revealed complicated associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system during pregnancy and identified some specific metabolites which may act as mediators between symbiotic microorganisms and immune homeostasis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ting Huang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, was published online on February 7, 2024, in mSystems.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size of the study may have limited capacity to address errors resulting from individual differences. No causal relationships between gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system response could be confirmed. Researchers were unable to account for the possible effects of confounding variables, such as diet, because of the cross-sectional nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The anti-inflammatory shift in mid-pregnancy may be linked to changes in gut microbiota, which, in turn, may wield their influence through fecal and plasma metabolites.
METHODOLOGY:
- by unknown mechanisms.
- The study explored the associations between the gut microbiota, fecal and plasma metabolites, and cytokine levels of pregnant women and compared them with those of nonpregnant women.
- The study recruited 30 pregnant women (ages 18-34 years; prepregnancy body mass index [BMI], 18.5-21.9) who conceived naturally with a singleton pregnancy and 15 nonpregnant women of similar age and BMI from the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, between February 2019 and August 2020.
- All participants had not used probiotics or antibiotics in the 6 months prior to participating in the study.
- Fecal and blood samples were collected during or after the 37th week of pregnancy in pregnant women until their labor and on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle in nonpregnant women.
TAKEAWAY:
- Pregnant women had more Actinobacteriota than nonpregnant women (9.15% vs 2.98%, respectively; P = .002) in their gut microbiomes, and the most enriched other microbes showed a negative correlation with pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Pregnant women had differences in 44 fecal and 53 plasma metabolites, with certain enriched metabolites negatively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and certain depleted ones positively correlated.
- Levels of pro-inflammatory plasma cytokines such as interleukins (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12, interferon gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha were reduced, while levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 were elevated in pregnant vs nonpregnant women.
- Researchers identified a total of 46 connections between gut microbes, metabolites, and cytokines, with details suggesting that gut microbes may alter plasma cytokine levels by interacting with host metabolites.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study revealed complicated associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system during pregnancy and identified some specific metabolites which may act as mediators between symbiotic microorganisms and immune homeostasis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Ting Huang, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, was published online on February 7, 2024, in mSystems.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size of the study may have limited capacity to address errors resulting from individual differences. No causal relationships between gut microbiota, metabolites, and immune system response could be confirmed. Researchers were unable to account for the possible effects of confounding variables, such as diet, because of the cross-sectional nature of this study.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flu Vaccines to Change After COVID Kills Off One Strain of Virus
The flu vaccine currently in use targets two A strains and two B strains. But the Yamagata/B subtype, which was already in decline, has not been detected worldwide since March 2020, the FDA said. Social distancing and other precautions used to avoid COVID apparently finished it off.
In response to that change, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) voted on March 5 to recommend the three-strain flu shot.
VRBPAC recommended the egg-based flu vaccines contain an A/Victoria/4897/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/Thailand/8/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The committee recommended the cell- or recombinant-based flu vaccines contain an A/Wisconsin/67/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus; an A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The move is no surprise. The World Health Organization and FDA experts had been recommending the change since last year.
Jerry Weir, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Viral Products, said companies that make flu vaccines should have the trivalent shot ready for the 2024-2025 flu season.
“Each of the U.S. influenza vaccine manufacturers have submitted updated regulatory files related to a trivalent influenza vaccine, and approval of all the necessary regulatory submissions is on track for 2024-25,” he said during the advisory committee’s meeting, according to CNN.
“FDA anticipates that there will be an adequate and diverse supply of approved trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines for the United States in the coming season,” the agency said.
U.S. flu vaccine manufacturers will still make a four-strain vaccine for distribution to overseas markets, CNN said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The flu vaccine currently in use targets two A strains and two B strains. But the Yamagata/B subtype, which was already in decline, has not been detected worldwide since March 2020, the FDA said. Social distancing and other precautions used to avoid COVID apparently finished it off.
In response to that change, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) voted on March 5 to recommend the three-strain flu shot.
VRBPAC recommended the egg-based flu vaccines contain an A/Victoria/4897/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/Thailand/8/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The committee recommended the cell- or recombinant-based flu vaccines contain an A/Wisconsin/67/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus; an A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The move is no surprise. The World Health Organization and FDA experts had been recommending the change since last year.
Jerry Weir, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Viral Products, said companies that make flu vaccines should have the trivalent shot ready for the 2024-2025 flu season.
“Each of the U.S. influenza vaccine manufacturers have submitted updated regulatory files related to a trivalent influenza vaccine, and approval of all the necessary regulatory submissions is on track for 2024-25,” he said during the advisory committee’s meeting, according to CNN.
“FDA anticipates that there will be an adequate and diverse supply of approved trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines for the United States in the coming season,” the agency said.
U.S. flu vaccine manufacturers will still make a four-strain vaccine for distribution to overseas markets, CNN said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
The flu vaccine currently in use targets two A strains and two B strains. But the Yamagata/B subtype, which was already in decline, has not been detected worldwide since March 2020, the FDA said. Social distancing and other precautions used to avoid COVID apparently finished it off.
In response to that change, the Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) voted on March 5 to recommend the three-strain flu shot.
VRBPAC recommended the egg-based flu vaccines contain an A/Victoria/4897/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus, an A/Thailand/8/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The committee recommended the cell- or recombinant-based flu vaccines contain an A/Wisconsin/67/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus; an A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus; and a B/Austria/1359417/2021 (B/Victoria lineage)-like virus.
The move is no surprise. The World Health Organization and FDA experts had been recommending the change since last year.
Jerry Weir, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Viral Products, said companies that make flu vaccines should have the trivalent shot ready for the 2024-2025 flu season.
“Each of the U.S. influenza vaccine manufacturers have submitted updated regulatory files related to a trivalent influenza vaccine, and approval of all the necessary regulatory submissions is on track for 2024-25,” he said during the advisory committee’s meeting, according to CNN.
“FDA anticipates that there will be an adequate and diverse supply of approved trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines for the United States in the coming season,” the agency said.
U.S. flu vaccine manufacturers will still make a four-strain vaccine for distribution to overseas markets, CNN said.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
How the Change Healthcare Cyberattack Affects Oncology Care
Change Healthcare, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth, took its systems offline after a cyberattack by BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware group.
The American Hospital Association said that this massive interruption is the “most significant cyberattack on the US healthcare system in American history.”
What Is the Change Healthcare Attack?
On February 21, Change Healthcare experienced an outside cybersecurity threat. When it became aware of the issue, the company disconnected its systems to prevent any further issues. Change Healthcare said that it has a “high level” of confidence that the cyberattack did not affect Optum, UnitedHealthcare, and UnitedHealth Group systems, stating it was an isolated attack on Change Healthcare. However, Change Healthcare has not said whether patient information has been compromised.
Who Is Behind the Attack?
In a statement, Change Healthcare announced that BlackCat/ALPHV identified itself to the company, claiming responsibility for the cybercrime. According to the US Department of Justice, BlackCat/ALPHV is the second most prolific ransomware-as-a-service entity in the world, with over 1000 victims of cybercrimes across the globe.
This news organization reached out to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), a component of the US Department of Homeland Security, for comment on whether CISA or other agencies had taken any previous action to stop the group after other attacks.
“CISA is working with our partners and Change Healthcare to support remediation, assist impacted organizations, and share timely information to reduce the likelihood of similar intrusions,” Eric Goldstein, executive assistant director for cybersecurity, responded in a statement.
How Has the Attack Affected Oncology Practices?
Change Healthcare is a technology company that provides services to hospitals and clinics across the country, including pharmacy claims transactions, clinician claims processing, patient access and financial clearance, clinician payments, and prior authorizations.
The Community Oncology Alliance (COA) said that the cyberattack has caused a massive disruption in claims processing. COA also said that practices have reported the disruption of benefits verification for patients, prior authorizations, and financial assistance from the attack.
“It’s impacting pretty much every facet of the practice and practice management,” said Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at COA. “Right now, practices are making do, they’re working around these challenges.”
However, Ferreyros cautioned, continuing to manage these challenges “is absolutely, 100% unsustainable” for oncology practices.
“Very soon you’re going to find practices that are having to make tough decisions about what to do, how are they going to make payroll, are they going to take financial risks on filling prescriptions and treating patients?” he added.
What Are Current Workarounds for Clinicians?
Change Healthcare recommends that clinicians use manual methods such as calling the payer’s provider service line to check patients’ claim status and complete eligibility verification and prior authorizations.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued guidance to Medicare Advantage organizations and Part D sponsors asking them to “remove or relax prior authorization, other utilization management, and timely filing requirements” while systems are offline. The department is also asking Medicare Advantage to offer advance funding to clinicians who have been affected the most.
How Common Are Attacks Like These?
In 2023, a record-setting 725 healthcare security breaches were reported to the Department of Health & Human Services Office for Civil Rights, according to a report from The HIPAA Journal. The number of breachers has increased yearly. Last year, an average of 370,000 healthcare records were breached every day.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Change Healthcare, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth, took its systems offline after a cyberattack by BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware group.
The American Hospital Association said that this massive interruption is the “most significant cyberattack on the US healthcare system in American history.”
What Is the Change Healthcare Attack?
On February 21, Change Healthcare experienced an outside cybersecurity threat. When it became aware of the issue, the company disconnected its systems to prevent any further issues. Change Healthcare said that it has a “high level” of confidence that the cyberattack did not affect Optum, UnitedHealthcare, and UnitedHealth Group systems, stating it was an isolated attack on Change Healthcare. However, Change Healthcare has not said whether patient information has been compromised.
Who Is Behind the Attack?
In a statement, Change Healthcare announced that BlackCat/ALPHV identified itself to the company, claiming responsibility for the cybercrime. According to the US Department of Justice, BlackCat/ALPHV is the second most prolific ransomware-as-a-service entity in the world, with over 1000 victims of cybercrimes across the globe.
This news organization reached out to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), a component of the US Department of Homeland Security, for comment on whether CISA or other agencies had taken any previous action to stop the group after other attacks.
“CISA is working with our partners and Change Healthcare to support remediation, assist impacted organizations, and share timely information to reduce the likelihood of similar intrusions,” Eric Goldstein, executive assistant director for cybersecurity, responded in a statement.
How Has the Attack Affected Oncology Practices?
Change Healthcare is a technology company that provides services to hospitals and clinics across the country, including pharmacy claims transactions, clinician claims processing, patient access and financial clearance, clinician payments, and prior authorizations.
The Community Oncology Alliance (COA) said that the cyberattack has caused a massive disruption in claims processing. COA also said that practices have reported the disruption of benefits verification for patients, prior authorizations, and financial assistance from the attack.
“It’s impacting pretty much every facet of the practice and practice management,” said Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at COA. “Right now, practices are making do, they’re working around these challenges.”
However, Ferreyros cautioned, continuing to manage these challenges “is absolutely, 100% unsustainable” for oncology practices.
“Very soon you’re going to find practices that are having to make tough decisions about what to do, how are they going to make payroll, are they going to take financial risks on filling prescriptions and treating patients?” he added.
What Are Current Workarounds for Clinicians?
Change Healthcare recommends that clinicians use manual methods such as calling the payer’s provider service line to check patients’ claim status and complete eligibility verification and prior authorizations.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued guidance to Medicare Advantage organizations and Part D sponsors asking them to “remove or relax prior authorization, other utilization management, and timely filing requirements” while systems are offline. The department is also asking Medicare Advantage to offer advance funding to clinicians who have been affected the most.
How Common Are Attacks Like These?
In 2023, a record-setting 725 healthcare security breaches were reported to the Department of Health & Human Services Office for Civil Rights, according to a report from The HIPAA Journal. The number of breachers has increased yearly. Last year, an average of 370,000 healthcare records were breached every day.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Change Healthcare, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth, took its systems offline after a cyberattack by BlackCat/ALPHV ransomware group.
The American Hospital Association said that this massive interruption is the “most significant cyberattack on the US healthcare system in American history.”
What Is the Change Healthcare Attack?
On February 21, Change Healthcare experienced an outside cybersecurity threat. When it became aware of the issue, the company disconnected its systems to prevent any further issues. Change Healthcare said that it has a “high level” of confidence that the cyberattack did not affect Optum, UnitedHealthcare, and UnitedHealth Group systems, stating it was an isolated attack on Change Healthcare. However, Change Healthcare has not said whether patient information has been compromised.
Who Is Behind the Attack?
In a statement, Change Healthcare announced that BlackCat/ALPHV identified itself to the company, claiming responsibility for the cybercrime. According to the US Department of Justice, BlackCat/ALPHV is the second most prolific ransomware-as-a-service entity in the world, with over 1000 victims of cybercrimes across the globe.
This news organization reached out to the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), a component of the US Department of Homeland Security, for comment on whether CISA or other agencies had taken any previous action to stop the group after other attacks.
“CISA is working with our partners and Change Healthcare to support remediation, assist impacted organizations, and share timely information to reduce the likelihood of similar intrusions,” Eric Goldstein, executive assistant director for cybersecurity, responded in a statement.
How Has the Attack Affected Oncology Practices?
Change Healthcare is a technology company that provides services to hospitals and clinics across the country, including pharmacy claims transactions, clinician claims processing, patient access and financial clearance, clinician payments, and prior authorizations.
The Community Oncology Alliance (COA) said that the cyberattack has caused a massive disruption in claims processing. COA also said that practices have reported the disruption of benefits verification for patients, prior authorizations, and financial assistance from the attack.
“It’s impacting pretty much every facet of the practice and practice management,” said Nicolas Ferreyros, managing director of policy, advocacy, and communications at COA. “Right now, practices are making do, they’re working around these challenges.”
However, Ferreyros cautioned, continuing to manage these challenges “is absolutely, 100% unsustainable” for oncology practices.
“Very soon you’re going to find practices that are having to make tough decisions about what to do, how are they going to make payroll, are they going to take financial risks on filling prescriptions and treating patients?” he added.
What Are Current Workarounds for Clinicians?
Change Healthcare recommends that clinicians use manual methods such as calling the payer’s provider service line to check patients’ claim status and complete eligibility verification and prior authorizations.
The Department of Health & Human Services has issued guidance to Medicare Advantage organizations and Part D sponsors asking them to “remove or relax prior authorization, other utilization management, and timely filing requirements” while systems are offline. The department is also asking Medicare Advantage to offer advance funding to clinicians who have been affected the most.
How Common Are Attacks Like These?
In 2023, a record-setting 725 healthcare security breaches were reported to the Department of Health & Human Services Office for Civil Rights, according to a report from The HIPAA Journal. The number of breachers has increased yearly. Last year, an average of 370,000 healthcare records were breached every day.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Finds No Increased Cancer Risk With Spironolactone
TOPLINE:
than that of unexposed women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Spironolactone, used off-label for several skin conditions in women, carries a warning about an increased tumor risk associated with high doses in rat models, and its antiandrogen properties have prompted hypotheses about a possible increased risk for breast or gynecologic cancers.
- The researchers reviewed data on 420 women with a history of spironolactone use for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and 3272 women with no spironolactone use at the authors› institution. Their mean age ranged from 42 to 63 years; the majority were White, and 38% were non-White.
- Median spironolactone doses ranged from 25 mg to 225 mg; chart reviews included 5-year follow-up data from the first spironolactone exposure to allow time for tumor development.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 37 of the 420 women exposed to spironolactone developed any tumors, as did 546 of the 3272 with no spironolactone exposure.
- After the researchers controlled for age and race, women exposed to spironolactone were no more likely to develop a malignant tumor than a benign tumor, compared with unexposed women (odds ratio [OR], 0.48, P = .2).
- The risk for breast or uterine cancer was not significantly different in the spironolactone and non-spironolactone groups (OR, 0.95, P > .9).
IN PRACTICE:
“Women taking spironolactone for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and who are at low risk of breast or gynecologic cancers may be counseled to have regular gynecology follow-up, but no more frequently than the general population,” but more studies are needed to evaluate risk over longer periods of time, the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Rachel C. Hill, BS, a student at Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College, was the corresponding author. The study was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the retrospective design, as well as the small number of spironolactone patients analyzed, the short follow-up period, the lack of information about spironolactone courses, and the inability to control for family history of malignancy.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and a grant from the Clinical and Translational Science Center at Weill Cornell Medical College awarded to Ms. Hill. None of the authors had relevant disclosures; Dr. Lipner disclosed serving as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Eli Lilly, Moberg Pharmaceuticals, and BelleTorus Corporation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
than that of unexposed women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Spironolactone, used off-label for several skin conditions in women, carries a warning about an increased tumor risk associated with high doses in rat models, and its antiandrogen properties have prompted hypotheses about a possible increased risk for breast or gynecologic cancers.
- The researchers reviewed data on 420 women with a history of spironolactone use for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and 3272 women with no spironolactone use at the authors› institution. Their mean age ranged from 42 to 63 years; the majority were White, and 38% were non-White.
- Median spironolactone doses ranged from 25 mg to 225 mg; chart reviews included 5-year follow-up data from the first spironolactone exposure to allow time for tumor development.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 37 of the 420 women exposed to spironolactone developed any tumors, as did 546 of the 3272 with no spironolactone exposure.
- After the researchers controlled for age and race, women exposed to spironolactone were no more likely to develop a malignant tumor than a benign tumor, compared with unexposed women (odds ratio [OR], 0.48, P = .2).
- The risk for breast or uterine cancer was not significantly different in the spironolactone and non-spironolactone groups (OR, 0.95, P > .9).
IN PRACTICE:
“Women taking spironolactone for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and who are at low risk of breast or gynecologic cancers may be counseled to have regular gynecology follow-up, but no more frequently than the general population,” but more studies are needed to evaluate risk over longer periods of time, the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Rachel C. Hill, BS, a student at Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College, was the corresponding author. The study was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the retrospective design, as well as the small number of spironolactone patients analyzed, the short follow-up period, the lack of information about spironolactone courses, and the inability to control for family history of malignancy.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and a grant from the Clinical and Translational Science Center at Weill Cornell Medical College awarded to Ms. Hill. None of the authors had relevant disclosures; Dr. Lipner disclosed serving as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Eli Lilly, Moberg Pharmaceuticals, and BelleTorus Corporation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
than that of unexposed women.
METHODOLOGY:
- Spironolactone, used off-label for several skin conditions in women, carries a warning about an increased tumor risk associated with high doses in rat models, and its antiandrogen properties have prompted hypotheses about a possible increased risk for breast or gynecologic cancers.
- The researchers reviewed data on 420 women with a history of spironolactone use for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and 3272 women with no spironolactone use at the authors› institution. Their mean age ranged from 42 to 63 years; the majority were White, and 38% were non-White.
- Median spironolactone doses ranged from 25 mg to 225 mg; chart reviews included 5-year follow-up data from the first spironolactone exposure to allow time for tumor development.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 37 of the 420 women exposed to spironolactone developed any tumors, as did 546 of the 3272 with no spironolactone exposure.
- After the researchers controlled for age and race, women exposed to spironolactone were no more likely to develop a malignant tumor than a benign tumor, compared with unexposed women (odds ratio [OR], 0.48, P = .2).
- The risk for breast or uterine cancer was not significantly different in the spironolactone and non-spironolactone groups (OR, 0.95, P > .9).
IN PRACTICE:
“Women taking spironolactone for acne, hair loss, and hirsutism and who are at low risk of breast or gynecologic cancers may be counseled to have regular gynecology follow-up, but no more frequently than the general population,” but more studies are needed to evaluate risk over longer periods of time, the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Rachel C. Hill, BS, a student at Weill Cornell Medical College, New York City, and Shari R. Lipner, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College, was the corresponding author. The study was published online in The Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The findings were limited by the retrospective design, as well as the small number of spironolactone patients analyzed, the short follow-up period, the lack of information about spironolactone courses, and the inability to control for family history of malignancy.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences and a grant from the Clinical and Translational Science Center at Weill Cornell Medical College awarded to Ms. Hill. None of the authors had relevant disclosures; Dr. Lipner disclosed serving as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics, Eli Lilly, Moberg Pharmaceuticals, and BelleTorus Corporation.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
High-Fiber Gut Microbe Makeover Aids Weight Loss
TOPLINE:
A fiber supplement also found in beans and other foods may lead to weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity in people with excess body weight, partly due to changes in the gut microbiota.
METHODOLOGY:
- In animal studies, resistant starch (RS), a kind of dietary fiber, has shown a potential to reduce body fat along with other metabolic benefits, but human dietary studies of RS have been inconsistent, especially with a high-fat diet.
- Researchers conducted a crossover, randomized trial to study the effect of RS as a dietary supplement on 37 individuals with overweight or obesity (average age, 33.43 years; 15 women; body mass index > 24 or higher waist circumference).
- Participants were fed a similar background diet and either 40 g of RS (high-amylose maize) or an energy-matched placebo starch daily for 8 weeks and then switched between the two in a separate 8-week period.
- The primary outcome was body weight, and the secondary outcomes were visceral and subcutaneous fat mass, waist circumference, lipid profiles, insulin sensitivity, metabolome, and gut microbiome.
- RS’s impact on gut microbiota composition and function was assessed with metagenomics and metabolomics, and RS-modified gut microbiota’s effect on host body fat and glucose was confirmed by transferring from select average participants to mice.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants showed a mean weight loss of 2.8 kg after consuming RS for 8 weeks (P < .001), but there was no significant change in body weight in those on placebo starch.
- RS improved insulin sensitivity in people to a greater extent than placebo starch (P = .025) and showed a greater reduction in fat mass, waist circumference, and other obesity-related outcomes.
- The abundance in the gut of the microbe Bifidobacterium adolescentis increased significantly following RS intervention, an increase that exhibited a strong correlation with decreased BMI, suggesting a role of RS in reducing obesity.
- The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta, were significantly lower in participants who consumed RS than in those who had placebo starch.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study provided an effective dietary recommendation using RS as a supplement (40 g/d with a balanced background diet containing 25%-30% fat), which may help to achieve significant weight loss,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led and corresponded by Huating Li, Shanghai Clinical Center for Diabetes, Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, and University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, and published online in Nature Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was limited by the small sample size and stringent inclusion criteria for participants. The use of database-driven and taxane-based methodology might have led to difficult-to-classify sequences being discarded and strain-level functional diversity being overlooked. The authors also acknowledged the need to validate the findings of this study in larger and more diverse cohorts.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A fiber supplement also found in beans and other foods may lead to weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity in people with excess body weight, partly due to changes in the gut microbiota.
METHODOLOGY:
- In animal studies, resistant starch (RS), a kind of dietary fiber, has shown a potential to reduce body fat along with other metabolic benefits, but human dietary studies of RS have been inconsistent, especially with a high-fat diet.
- Researchers conducted a crossover, randomized trial to study the effect of RS as a dietary supplement on 37 individuals with overweight or obesity (average age, 33.43 years; 15 women; body mass index > 24 or higher waist circumference).
- Participants were fed a similar background diet and either 40 g of RS (high-amylose maize) or an energy-matched placebo starch daily for 8 weeks and then switched between the two in a separate 8-week period.
- The primary outcome was body weight, and the secondary outcomes were visceral and subcutaneous fat mass, waist circumference, lipid profiles, insulin sensitivity, metabolome, and gut microbiome.
- RS’s impact on gut microbiota composition and function was assessed with metagenomics and metabolomics, and RS-modified gut microbiota’s effect on host body fat and glucose was confirmed by transferring from select average participants to mice.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants showed a mean weight loss of 2.8 kg after consuming RS for 8 weeks (P < .001), but there was no significant change in body weight in those on placebo starch.
- RS improved insulin sensitivity in people to a greater extent than placebo starch (P = .025) and showed a greater reduction in fat mass, waist circumference, and other obesity-related outcomes.
- The abundance in the gut of the microbe Bifidobacterium adolescentis increased significantly following RS intervention, an increase that exhibited a strong correlation with decreased BMI, suggesting a role of RS in reducing obesity.
- The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta, were significantly lower in participants who consumed RS than in those who had placebo starch.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study provided an effective dietary recommendation using RS as a supplement (40 g/d with a balanced background diet containing 25%-30% fat), which may help to achieve significant weight loss,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led and corresponded by Huating Li, Shanghai Clinical Center for Diabetes, Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, and University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, and published online in Nature Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was limited by the small sample size and stringent inclusion criteria for participants. The use of database-driven and taxane-based methodology might have led to difficult-to-classify sequences being discarded and strain-level functional diversity being overlooked. The authors also acknowledged the need to validate the findings of this study in larger and more diverse cohorts.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A fiber supplement also found in beans and other foods may lead to weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity in people with excess body weight, partly due to changes in the gut microbiota.
METHODOLOGY:
- In animal studies, resistant starch (RS), a kind of dietary fiber, has shown a potential to reduce body fat along with other metabolic benefits, but human dietary studies of RS have been inconsistent, especially with a high-fat diet.
- Researchers conducted a crossover, randomized trial to study the effect of RS as a dietary supplement on 37 individuals with overweight or obesity (average age, 33.43 years; 15 women; body mass index > 24 or higher waist circumference).
- Participants were fed a similar background diet and either 40 g of RS (high-amylose maize) or an energy-matched placebo starch daily for 8 weeks and then switched between the two in a separate 8-week period.
- The primary outcome was body weight, and the secondary outcomes were visceral and subcutaneous fat mass, waist circumference, lipid profiles, insulin sensitivity, metabolome, and gut microbiome.
- RS’s impact on gut microbiota composition and function was assessed with metagenomics and metabolomics, and RS-modified gut microbiota’s effect on host body fat and glucose was confirmed by transferring from select average participants to mice.
TAKEAWAY:
- Participants showed a mean weight loss of 2.8 kg after consuming RS for 8 weeks (P < .001), but there was no significant change in body weight in those on placebo starch.
- RS improved insulin sensitivity in people to a greater extent than placebo starch (P = .025) and showed a greater reduction in fat mass, waist circumference, and other obesity-related outcomes.
- The abundance in the gut of the microbe Bifidobacterium adolescentis increased significantly following RS intervention, an increase that exhibited a strong correlation with decreased BMI, suggesting a role of RS in reducing obesity.
- The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta, were significantly lower in participants who consumed RS than in those who had placebo starch.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our study provided an effective dietary recommendation using RS as a supplement (40 g/d with a balanced background diet containing 25%-30% fat), which may help to achieve significant weight loss,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led and corresponded by Huating Li, Shanghai Clinical Center for Diabetes, Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China, and University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, and published online in Nature Metabolism.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was limited by the small sample size and stringent inclusion criteria for participants. The use of database-driven and taxane-based methodology might have led to difficult-to-classify sequences being discarded and strain-level functional diversity being overlooked. The authors also acknowledged the need to validate the findings of this study in larger and more diverse cohorts.
DISCLOSURES:
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and other sources. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
No Increase in Autoimmune Risk Seen With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors
TOPLINE:
In patients with type 2 diabetes, there was no difference in risk of developing autoimmune disease if prescribed glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RAs), sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The effect of GLP-1-RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors on autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARD) is understudied, though previous case reports and one study have hinted at increased risk.
- Researchers used administrative health data from 2014 to 2021 to identify 34,400 patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs and 83,500 patients prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors.
- They compared patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs or SGLT2 inhibitors with 68,400 patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors, which previous studies suggest do not increase ARD risk.
- Primary outcome was ARD incidence, defined by diagnostic codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were no significant differences in incident ARDs between the three groups.
- Mean follow-up time was 0.88-1.53 years.
- The hazard ratio (HR) for developing ARDs with GLP-1-RAs exposure was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.66-1.30) compared with DPP-4 inhibitors.
- The HR for developing ARDs with SGLT2 inhibitor exposure was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.76-1.24).
IN PRACTICE:
“Extended longitudinal data are needed to assess risk and benefit with longer-term exposure,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Derin Karacabeyli, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, presented the study in abstract form at the Canadian Rheumatology Association (CRA) 2024 Annual Meeting in Winnipeg on February 29.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, which could have some residual or unmeasured confounding of data. The researchers relied on diagnostic codes and the average follow-up time was short.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with type 2 diabetes, there was no difference in risk of developing autoimmune disease if prescribed glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RAs), sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The effect of GLP-1-RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors on autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARD) is understudied, though previous case reports and one study have hinted at increased risk.
- Researchers used administrative health data from 2014 to 2021 to identify 34,400 patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs and 83,500 patients prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors.
- They compared patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs or SGLT2 inhibitors with 68,400 patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors, which previous studies suggest do not increase ARD risk.
- Primary outcome was ARD incidence, defined by diagnostic codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were no significant differences in incident ARDs between the three groups.
- Mean follow-up time was 0.88-1.53 years.
- The hazard ratio (HR) for developing ARDs with GLP-1-RAs exposure was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.66-1.30) compared with DPP-4 inhibitors.
- The HR for developing ARDs with SGLT2 inhibitor exposure was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.76-1.24).
IN PRACTICE:
“Extended longitudinal data are needed to assess risk and benefit with longer-term exposure,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Derin Karacabeyli, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, presented the study in abstract form at the Canadian Rheumatology Association (CRA) 2024 Annual Meeting in Winnipeg on February 29.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, which could have some residual or unmeasured confounding of data. The researchers relied on diagnostic codes and the average follow-up time was short.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with type 2 diabetes, there was no difference in risk of developing autoimmune disease if prescribed glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RAs), sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors.
METHODOLOGY:
- The effect of GLP-1-RAs and SGLT2 inhibitors on autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARD) is understudied, though previous case reports and one study have hinted at increased risk.
- Researchers used administrative health data from 2014 to 2021 to identify 34,400 patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs and 83,500 patients prescribed SGLT2 inhibitors.
- They compared patients prescribed GLP-1-RAs or SGLT2 inhibitors with 68,400 patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors, which previous studies suggest do not increase ARD risk.
- Primary outcome was ARD incidence, defined by diagnostic codes.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were no significant differences in incident ARDs between the three groups.
- Mean follow-up time was 0.88-1.53 years.
- The hazard ratio (HR) for developing ARDs with GLP-1-RAs exposure was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.66-1.30) compared with DPP-4 inhibitors.
- The HR for developing ARDs with SGLT2 inhibitor exposure was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.76-1.24).
IN PRACTICE:
“Extended longitudinal data are needed to assess risk and benefit with longer-term exposure,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
First author Derin Karacabeyli, MD, of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, presented the study in abstract form at the Canadian Rheumatology Association (CRA) 2024 Annual Meeting in Winnipeg on February 29.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational, which could have some residual or unmeasured confounding of data. The researchers relied on diagnostic codes and the average follow-up time was short.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
First Denosumab Biosimilar Approved in Two Different Formulations
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first biosimilar to denosumab, denosumab-bddz (Wyost/Jubbonti).
The biosimilar was also granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). Sandoz announced the approval on March 5, 2024. The lower dosage of denosumab-bddz, marketed as Jubbonti, was also approved by Health Canada in February.
The FDA approval “is based on robust clinical studies and accompanied by labeling with safety warnings,” according to the press release. Like the reference products Prolia and Xgeva, denosumab-bddz is approved for two indications at separate doses.
Wyost (120-mg/1.7-mL injection) is approved to:
- Prevent skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors
- Treat adults and skeletally mature adolescents with giant cell tumor of bone that is unresectable or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity
- Treat hypercalcemia of cancer that is refractory to bisphosphonate therapy
Jubbonti (60-mg/1-mL injection) is approved to:
- Treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer
- Increase bone mass in women who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
Both doses are contraindicated for hypocalcemia and known clinically significant hypersensitivity to denosumab products. Exposure to denosumab products during pregnancy can cause fetal harm, so women of reproductive potential should be advised to use effective contraception during therapy and for at least 5 months after the last dose of denosumab-bddz.
Sandoz did not provide information on US launch details, citing “ongoing patent litigation around these products.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first biosimilar to denosumab, denosumab-bddz (Wyost/Jubbonti).
The biosimilar was also granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). Sandoz announced the approval on March 5, 2024. The lower dosage of denosumab-bddz, marketed as Jubbonti, was also approved by Health Canada in February.
The FDA approval “is based on robust clinical studies and accompanied by labeling with safety warnings,” according to the press release. Like the reference products Prolia and Xgeva, denosumab-bddz is approved for two indications at separate doses.
Wyost (120-mg/1.7-mL injection) is approved to:
- Prevent skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors
- Treat adults and skeletally mature adolescents with giant cell tumor of bone that is unresectable or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity
- Treat hypercalcemia of cancer that is refractory to bisphosphonate therapy
Jubbonti (60-mg/1-mL injection) is approved to:
- Treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer
- Increase bone mass in women who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
Both doses are contraindicated for hypocalcemia and known clinically significant hypersensitivity to denosumab products. Exposure to denosumab products during pregnancy can cause fetal harm, so women of reproductive potential should be advised to use effective contraception during therapy and for at least 5 months after the last dose of denosumab-bddz.
Sandoz did not provide information on US launch details, citing “ongoing patent litigation around these products.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the first biosimilar to denosumab, denosumab-bddz (Wyost/Jubbonti).
The biosimilar was also granted interchangeability status, which allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). Sandoz announced the approval on March 5, 2024. The lower dosage of denosumab-bddz, marketed as Jubbonti, was also approved by Health Canada in February.
The FDA approval “is based on robust clinical studies and accompanied by labeling with safety warnings,” according to the press release. Like the reference products Prolia and Xgeva, denosumab-bddz is approved for two indications at separate doses.
Wyost (120-mg/1.7-mL injection) is approved to:
- Prevent skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors
- Treat adults and skeletally mature adolescents with giant cell tumor of bone that is unresectable or where surgical resection is likely to result in severe morbidity
- Treat hypercalcemia of cancer that is refractory to bisphosphonate therapy
Jubbonti (60-mg/1-mL injection) is approved to:
- Treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis who are at high risk for fracture
- Treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who are at high risk for fracture
- Increase bone mass in men who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer
- Increase bone mass in women who are at high risk for fracture who are receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer.
Both doses are contraindicated for hypocalcemia and known clinically significant hypersensitivity to denosumab products. Exposure to denosumab products during pregnancy can cause fetal harm, so women of reproductive potential should be advised to use effective contraception during therapy and for at least 5 months after the last dose of denosumab-bddz.
Sandoz did not provide information on US launch details, citing “ongoing patent litigation around these products.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 Is a Very Weird Virus
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.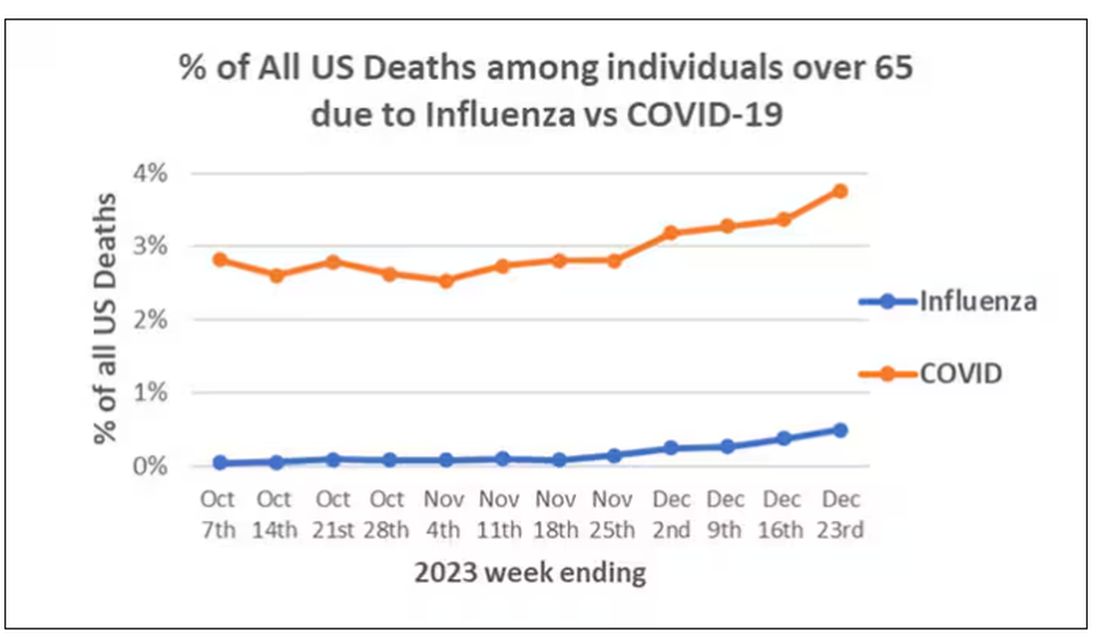
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)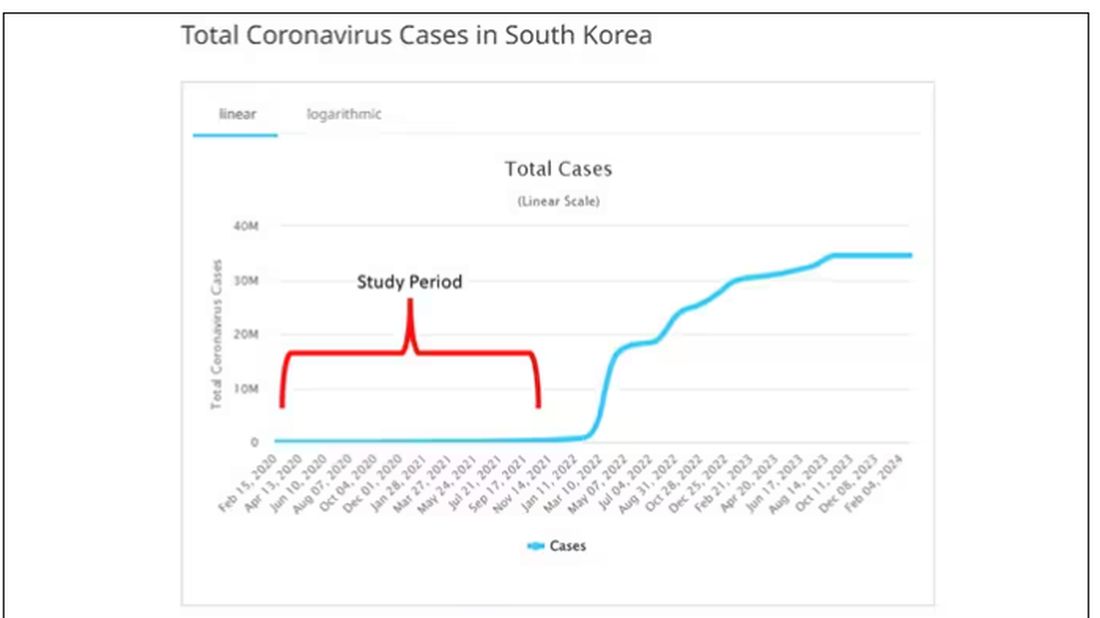
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.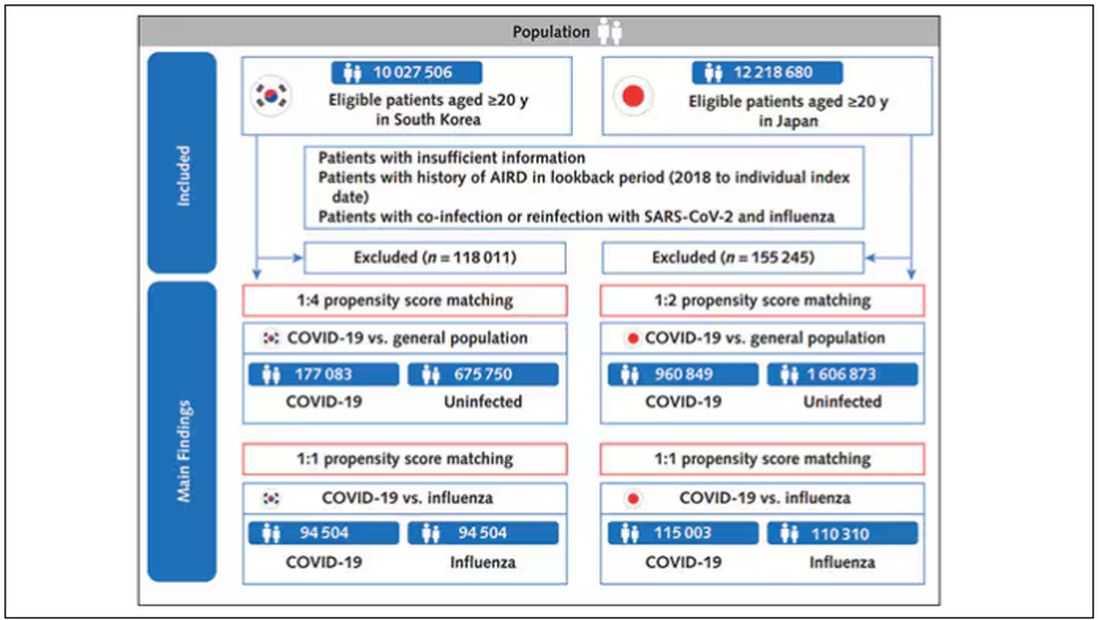
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).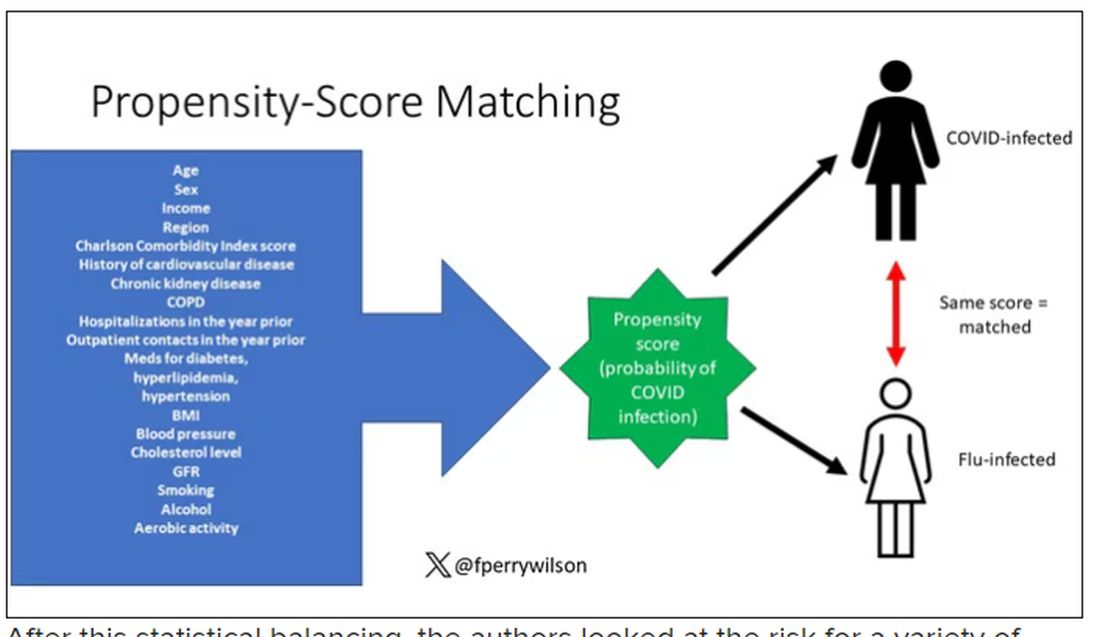
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.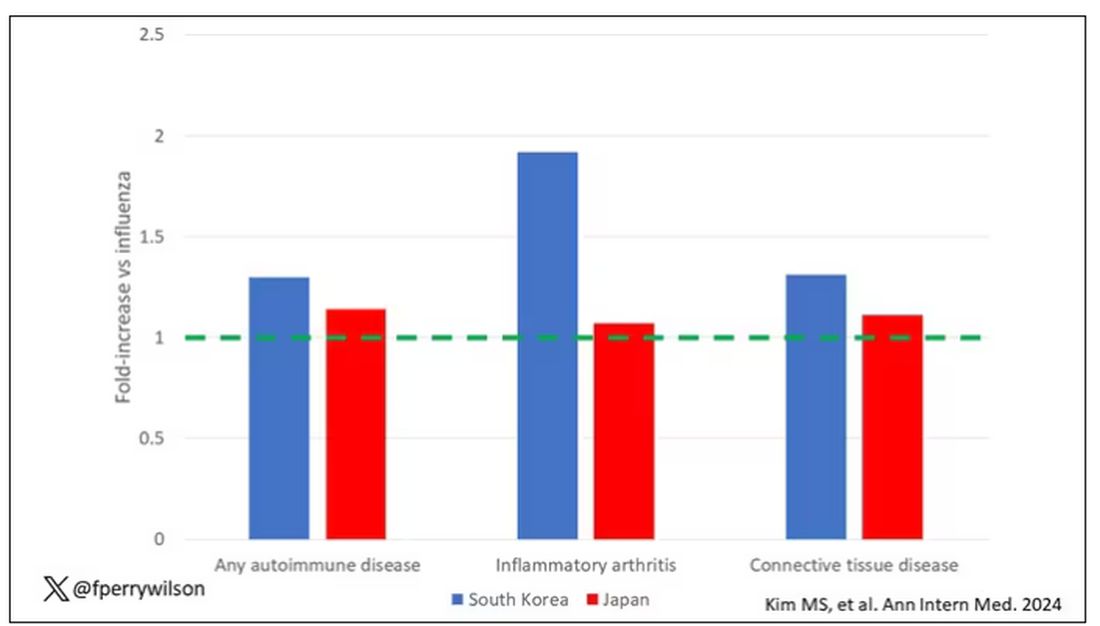
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.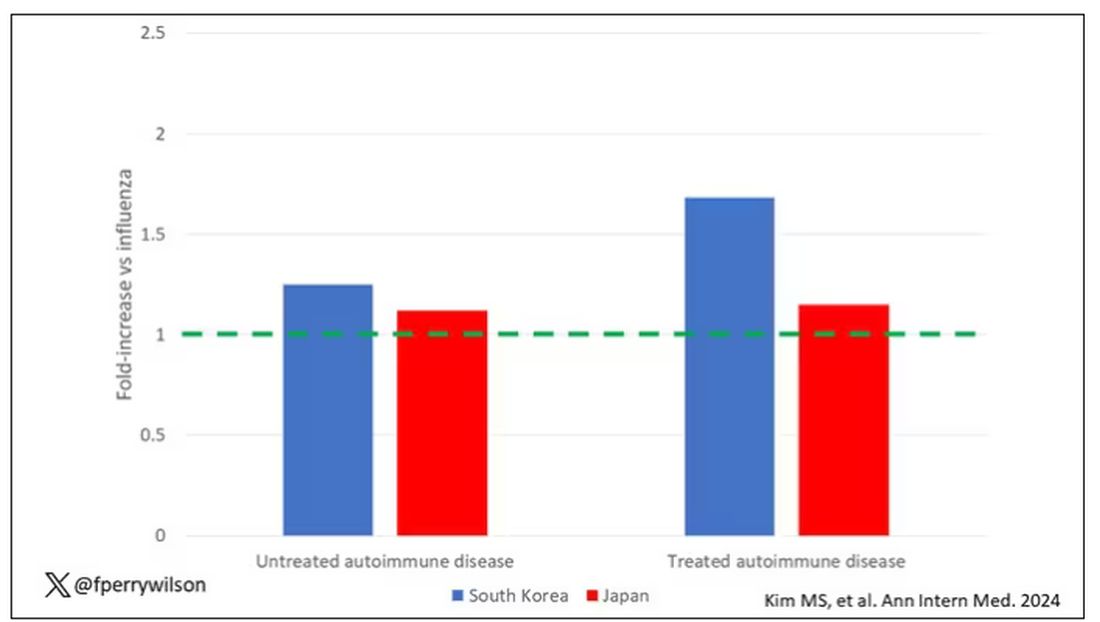
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.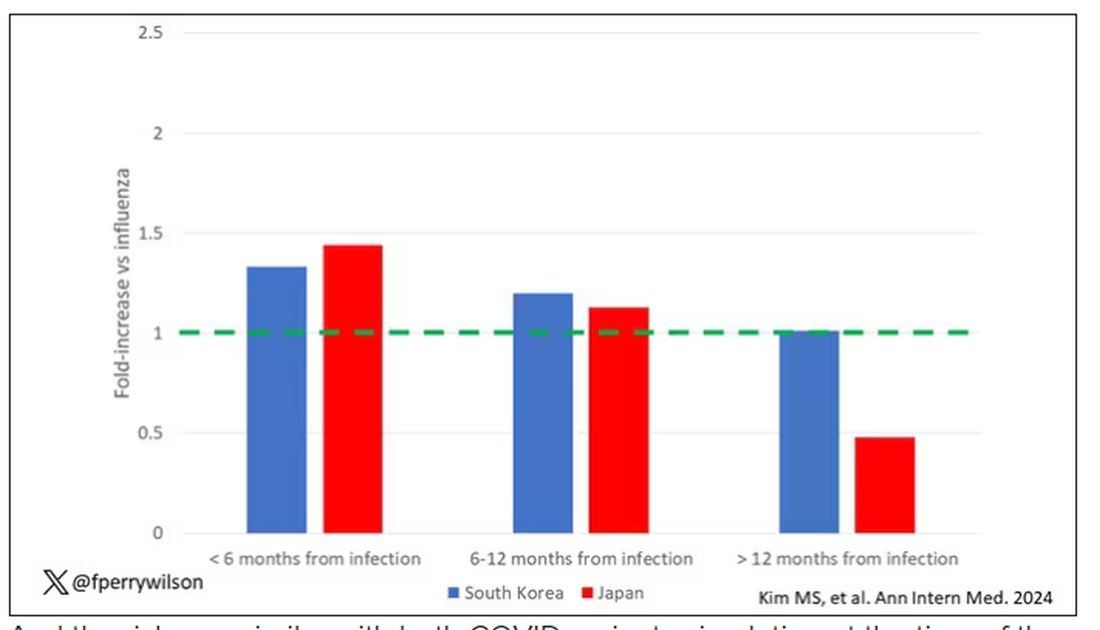
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?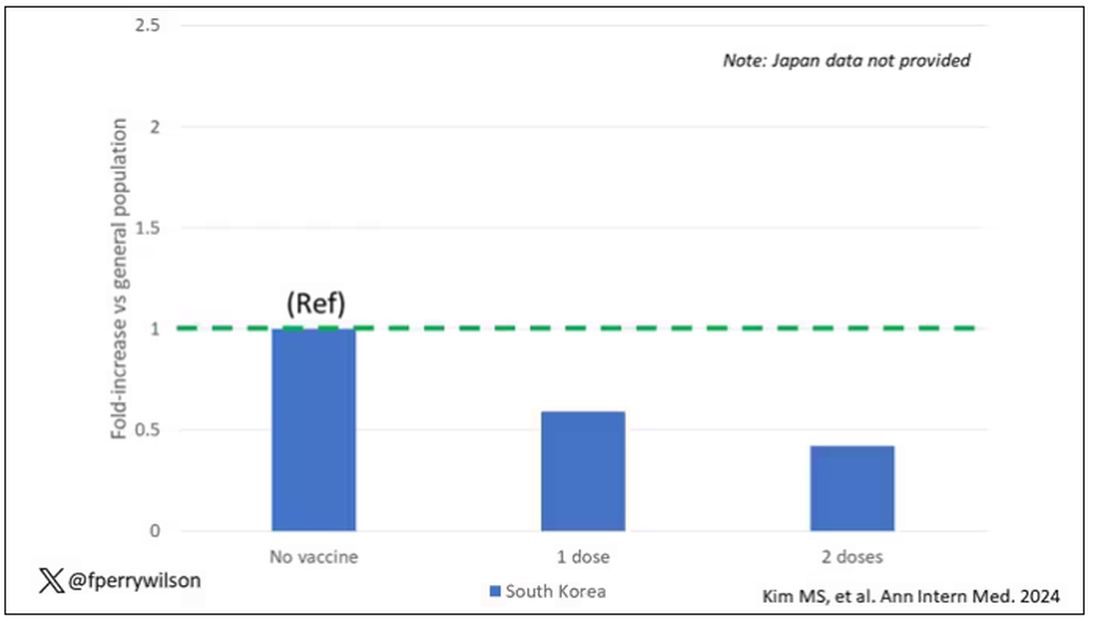
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.