User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Cutaneous clues linked to COVID-19 coagulation risk
, new evidence suggests.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine NewYork–Presbyterian Medical Center in New York linked livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions to a greater likelihood for occlusive vascular disease associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a small case series.
These skin signs could augment coagulation assays in this patient population. “Physicians should consider a hematology consult for potential anticoagulation in patients with these skin presentations and severe COVID-19,” senior author Joanna Harp, MD, said in an interview.
“Physicians should also consider D-dimer, fibrinogen, coagulation studies, and a skin biopsy given that there are other diagnoses on the differential as well.”
The research letter was published online on Aug. 5 in JAMA Dermatology.
The findings build on multiple previous reports of skin manifestations associated with COVID-19, including a study of 375 patients in Spain. Among people with suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, senior author of the Spanish research, Ignacio Garcia-Doval, MD, PhD, also observed livedoid and necrotic skin eruptions more commonly in severe disease.
“I think that this case series [from Harp and colleagues] confirms the findings of our previous paper – that patients with livedoid or necrotic lesions have a worse prognosis, as these are markers of vascular occlusion,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Harp and colleagues reported their observations with four patients aged 40-80 years. Each had severe COVID-19 with acute respiratory distress syndrome and required intubation. Treating clinicians requested a dermatology consult to assess acral fixed livedo racemosa and retiform purpura presentations.
D-dimer levels exceeded 3 mcg/mL in each case. All four patients had a suspected pulmonary embolism within 1-5 days of the dermatologic findings. Prophylactic anticoagulation at admission was changed to therapeutic anticoagulation because of increasing D-dimer levels and the suspected thrombotic events.
“I think that the paper is interesting because it shows the associated histopathological findings and has important clinical implications due to the association with pulmonary embolism,” said Dr. Garcia-Doval, a researcher at the Spanish Academy of Dermatology in Madrid. “These patients should probably be anticoagulated.”
Skin biopsy results
Punch biopsies revealed pauci-inflammatory thrombogenic vasculopathy involving capillaries, venules, arterioles, or small arteries.
Livedo racemosa skin findings point to partial occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels, whereas retiform purpura indicate full occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels.
An inability to confirm the exact timing of the onset of the skin rash was a limitation of the study.
“The findings suggest that clinicians caring for patients with COVID-19 should be aware of livedoid and purpuric rashes as potential manifestations of an underlying hypercoagulable state,” the authors noted. “If these skin findings are identified, a skin biopsy should be considered because the result may guide anticoagulation management.”
Observations during an outbreak
The researchers observed these cases between March 13 and April 3, during the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak in New York.
“We did see additional cases since our study period. However, it has decreased significantly with the falling number of COVID-19 cases in the city,” said Dr. Harp, a dermatologist at NewYork–Presbyterian.
Another contributing factor in the drop in cases was “implementation of earlier, more aggressive anticoagulation in many of these patients at our institution,” she added.
The investigators plan to continue the research. “We are working on a more formalized study,” lead author Caren Droesch, MD, said in an interview.
“But given very low patient numbers in our area we have not started recruiting patients,” said Dr. Droesch, a resident at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork–Presbyterian at the time of the study. She is now a dermatologist at Mass General Brigham in Wellesley, Mass.
Consider a dermatology consult
“This is a small case series of four patients, but mirrors what we have seen at our institution and what others have reported about individual patients around the world,” Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. “The skin, like many other organ systems, can be affected by thrombotic events within the setting of COVID-19 disease.”
As in the current study, Dr. Fernandez observed skin manifestations in people with severe COVID-19 with elevated D-dimer levels. These patients typically require mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit, he added.
“As these authors point out, it is important for all clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients to look for these rashes,” said Dr. Fernandez, who coauthored a report on skin manifestations in this patient population. “We also agree that clinicians should have a low threshold for consulting dermatology. A skin biopsy is minimally invasive and can be important in confirming or refuting that such rashes are truly reflective of thrombotic vasculopathy.”
Dr. Harp, Dr. Droesch and Dr. Garcia-Doval have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fernandez received funding from the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative at Case Western Reserve University to study skin manifestations of COVID-19.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, new evidence suggests.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine NewYork–Presbyterian Medical Center in New York linked livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions to a greater likelihood for occlusive vascular disease associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a small case series.
These skin signs could augment coagulation assays in this patient population. “Physicians should consider a hematology consult for potential anticoagulation in patients with these skin presentations and severe COVID-19,” senior author Joanna Harp, MD, said in an interview.
“Physicians should also consider D-dimer, fibrinogen, coagulation studies, and a skin biopsy given that there are other diagnoses on the differential as well.”
The research letter was published online on Aug. 5 in JAMA Dermatology.
The findings build on multiple previous reports of skin manifestations associated with COVID-19, including a study of 375 patients in Spain. Among people with suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, senior author of the Spanish research, Ignacio Garcia-Doval, MD, PhD, also observed livedoid and necrotic skin eruptions more commonly in severe disease.
“I think that this case series [from Harp and colleagues] confirms the findings of our previous paper – that patients with livedoid or necrotic lesions have a worse prognosis, as these are markers of vascular occlusion,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Harp and colleagues reported their observations with four patients aged 40-80 years. Each had severe COVID-19 with acute respiratory distress syndrome and required intubation. Treating clinicians requested a dermatology consult to assess acral fixed livedo racemosa and retiform purpura presentations.
D-dimer levels exceeded 3 mcg/mL in each case. All four patients had a suspected pulmonary embolism within 1-5 days of the dermatologic findings. Prophylactic anticoagulation at admission was changed to therapeutic anticoagulation because of increasing D-dimer levels and the suspected thrombotic events.
“I think that the paper is interesting because it shows the associated histopathological findings and has important clinical implications due to the association with pulmonary embolism,” said Dr. Garcia-Doval, a researcher at the Spanish Academy of Dermatology in Madrid. “These patients should probably be anticoagulated.”
Skin biopsy results
Punch biopsies revealed pauci-inflammatory thrombogenic vasculopathy involving capillaries, venules, arterioles, or small arteries.
Livedo racemosa skin findings point to partial occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels, whereas retiform purpura indicate full occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels.
An inability to confirm the exact timing of the onset of the skin rash was a limitation of the study.
“The findings suggest that clinicians caring for patients with COVID-19 should be aware of livedoid and purpuric rashes as potential manifestations of an underlying hypercoagulable state,” the authors noted. “If these skin findings are identified, a skin biopsy should be considered because the result may guide anticoagulation management.”
Observations during an outbreak
The researchers observed these cases between March 13 and April 3, during the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak in New York.
“We did see additional cases since our study period. However, it has decreased significantly with the falling number of COVID-19 cases in the city,” said Dr. Harp, a dermatologist at NewYork–Presbyterian.
Another contributing factor in the drop in cases was “implementation of earlier, more aggressive anticoagulation in many of these patients at our institution,” she added.
The investigators plan to continue the research. “We are working on a more formalized study,” lead author Caren Droesch, MD, said in an interview.
“But given very low patient numbers in our area we have not started recruiting patients,” said Dr. Droesch, a resident at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork–Presbyterian at the time of the study. She is now a dermatologist at Mass General Brigham in Wellesley, Mass.
Consider a dermatology consult
“This is a small case series of four patients, but mirrors what we have seen at our institution and what others have reported about individual patients around the world,” Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. “The skin, like many other organ systems, can be affected by thrombotic events within the setting of COVID-19 disease.”
As in the current study, Dr. Fernandez observed skin manifestations in people with severe COVID-19 with elevated D-dimer levels. These patients typically require mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit, he added.
“As these authors point out, it is important for all clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients to look for these rashes,” said Dr. Fernandez, who coauthored a report on skin manifestations in this patient population. “We also agree that clinicians should have a low threshold for consulting dermatology. A skin biopsy is minimally invasive and can be important in confirming or refuting that such rashes are truly reflective of thrombotic vasculopathy.”
Dr. Harp, Dr. Droesch and Dr. Garcia-Doval have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fernandez received funding from the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative at Case Western Reserve University to study skin manifestations of COVID-19.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, new evidence suggests.
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine NewYork–Presbyterian Medical Center in New York linked livedoid and purpuric skin eruptions to a greater likelihood for occlusive vascular disease associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a small case series.
These skin signs could augment coagulation assays in this patient population. “Physicians should consider a hematology consult for potential anticoagulation in patients with these skin presentations and severe COVID-19,” senior author Joanna Harp, MD, said in an interview.
“Physicians should also consider D-dimer, fibrinogen, coagulation studies, and a skin biopsy given that there are other diagnoses on the differential as well.”
The research letter was published online on Aug. 5 in JAMA Dermatology.
The findings build on multiple previous reports of skin manifestations associated with COVID-19, including a study of 375 patients in Spain. Among people with suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, senior author of the Spanish research, Ignacio Garcia-Doval, MD, PhD, also observed livedoid and necrotic skin eruptions more commonly in severe disease.
“I think that this case series [from Harp and colleagues] confirms the findings of our previous paper – that patients with livedoid or necrotic lesions have a worse prognosis, as these are markers of vascular occlusion,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Harp and colleagues reported their observations with four patients aged 40-80 years. Each had severe COVID-19 with acute respiratory distress syndrome and required intubation. Treating clinicians requested a dermatology consult to assess acral fixed livedo racemosa and retiform purpura presentations.
D-dimer levels exceeded 3 mcg/mL in each case. All four patients had a suspected pulmonary embolism within 1-5 days of the dermatologic findings. Prophylactic anticoagulation at admission was changed to therapeutic anticoagulation because of increasing D-dimer levels and the suspected thrombotic events.
“I think that the paper is interesting because it shows the associated histopathological findings and has important clinical implications due to the association with pulmonary embolism,” said Dr. Garcia-Doval, a researcher at the Spanish Academy of Dermatology in Madrid. “These patients should probably be anticoagulated.”
Skin biopsy results
Punch biopsies revealed pauci-inflammatory thrombogenic vasculopathy involving capillaries, venules, arterioles, or small arteries.
Livedo racemosa skin findings point to partial occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels, whereas retiform purpura indicate full occlusion of cutaneous blood vessels.
An inability to confirm the exact timing of the onset of the skin rash was a limitation of the study.
“The findings suggest that clinicians caring for patients with COVID-19 should be aware of livedoid and purpuric rashes as potential manifestations of an underlying hypercoagulable state,” the authors noted. “If these skin findings are identified, a skin biopsy should be considered because the result may guide anticoagulation management.”
Observations during an outbreak
The researchers observed these cases between March 13 and April 3, during the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak in New York.
“We did see additional cases since our study period. However, it has decreased significantly with the falling number of COVID-19 cases in the city,” said Dr. Harp, a dermatologist at NewYork–Presbyterian.
Another contributing factor in the drop in cases was “implementation of earlier, more aggressive anticoagulation in many of these patients at our institution,” she added.
The investigators plan to continue the research. “We are working on a more formalized study,” lead author Caren Droesch, MD, said in an interview.
“But given very low patient numbers in our area we have not started recruiting patients,” said Dr. Droesch, a resident at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork–Presbyterian at the time of the study. She is now a dermatologist at Mass General Brigham in Wellesley, Mass.
Consider a dermatology consult
“This is a small case series of four patients, but mirrors what we have seen at our institution and what others have reported about individual patients around the world,” Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview. “The skin, like many other organ systems, can be affected by thrombotic events within the setting of COVID-19 disease.”
As in the current study, Dr. Fernandez observed skin manifestations in people with severe COVID-19 with elevated D-dimer levels. These patients typically require mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit, he added.
“As these authors point out, it is important for all clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients to look for these rashes,” said Dr. Fernandez, who coauthored a report on skin manifestations in this patient population. “We also agree that clinicians should have a low threshold for consulting dermatology. A skin biopsy is minimally invasive and can be important in confirming or refuting that such rashes are truly reflective of thrombotic vasculopathy.”
Dr. Harp, Dr. Droesch and Dr. Garcia-Doval have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fernandez received funding from the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative at Case Western Reserve University to study skin manifestations of COVID-19.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Cognitive impairment in 9/11 responders tied to brain atrophy
, suggest results from the first structural neuroimaging study conducted in this population. The study clarifies that a neurodegenerative condition is present in first responders who experience cognitive impairment in midlife, which “is incredibly important to know,” said lead author Sean Clouston, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in Alzheimer’s and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring.
Brain atrophy in midlife
During the 9/11 attack and in its aftermath, WTC responders were exposed to a range of inhaled neurotoxicants, as well as extreme psychosocial stressors. A growing number of WTC responders who are now in their 50s and early 60s are experiencing early cognitive impairment.
Using MRI, the investigators examined cortical thickness (CTX), a surrogate marker for neurodegeneration, in 99 mostly male WTC responders; 48 had cognitive impairment, and 51 did not. The age range of the participants was 45 to 65 years, a range during which cortical atrophy is uncommon in the general population, the researchers noted.
Compared with cognitively normal responders, those with cognitive impairment were found to have reductions in CTX across the whole brain and across 21 of 34 cortical regions, including frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
In both cognitively impaired and cognitively unimpaired WTC responders, CTX was reduced in the entorhinal and temporal cortices compared with normative data, but reductions were greater with cognitive impairment. Posttraumatic distress disorder (PTSD) status was not predictive of a reduction in CTX across groups.
Dr. Clouston said the level of reduction in CTX in many responders is similar to that commonly found in patients with dementia and may reflect early-stage dementia occurring in midlife.
Limitations of the study include the small sample size, the cross-sectional design, the unique nature of the exposure, and a lack of a non-WTC external control group.
‘Illuminating’ study
Keith N. Fargo, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, called the findings “interesting and illuminating” but cautioned that it is not possible to show cause and effect with this type of study.
“We also don’t know when cortical thinning might have started or how quickly it might be progressing,” Dr. Fargo said in an interview.
He noted that the pattern of cortical thinning is “somewhat consistent with what we see among people who live with high levels of air pollution, which is an emerging risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.”
The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care added air pollution to its list of modifiable risk factors for dementia, which was recently updated.
Clinicians “need to be aware that their middle-aged 9/11 first responders are at a higher risk level for cognitive impairment, as well as PTSD and depression,” Dr. Fargo said.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Clouston and Dr. Fargo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggest results from the first structural neuroimaging study conducted in this population. The study clarifies that a neurodegenerative condition is present in first responders who experience cognitive impairment in midlife, which “is incredibly important to know,” said lead author Sean Clouston, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in Alzheimer’s and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring.
Brain atrophy in midlife
During the 9/11 attack and in its aftermath, WTC responders were exposed to a range of inhaled neurotoxicants, as well as extreme psychosocial stressors. A growing number of WTC responders who are now in their 50s and early 60s are experiencing early cognitive impairment.
Using MRI, the investigators examined cortical thickness (CTX), a surrogate marker for neurodegeneration, in 99 mostly male WTC responders; 48 had cognitive impairment, and 51 did not. The age range of the participants was 45 to 65 years, a range during which cortical atrophy is uncommon in the general population, the researchers noted.
Compared with cognitively normal responders, those with cognitive impairment were found to have reductions in CTX across the whole brain and across 21 of 34 cortical regions, including frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
In both cognitively impaired and cognitively unimpaired WTC responders, CTX was reduced in the entorhinal and temporal cortices compared with normative data, but reductions were greater with cognitive impairment. Posttraumatic distress disorder (PTSD) status was not predictive of a reduction in CTX across groups.
Dr. Clouston said the level of reduction in CTX in many responders is similar to that commonly found in patients with dementia and may reflect early-stage dementia occurring in midlife.
Limitations of the study include the small sample size, the cross-sectional design, the unique nature of the exposure, and a lack of a non-WTC external control group.
‘Illuminating’ study
Keith N. Fargo, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, called the findings “interesting and illuminating” but cautioned that it is not possible to show cause and effect with this type of study.
“We also don’t know when cortical thinning might have started or how quickly it might be progressing,” Dr. Fargo said in an interview.
He noted that the pattern of cortical thinning is “somewhat consistent with what we see among people who live with high levels of air pollution, which is an emerging risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.”
The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care added air pollution to its list of modifiable risk factors for dementia, which was recently updated.
Clinicians “need to be aware that their middle-aged 9/11 first responders are at a higher risk level for cognitive impairment, as well as PTSD and depression,” Dr. Fargo said.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Clouston and Dr. Fargo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
, suggest results from the first structural neuroimaging study conducted in this population. The study clarifies that a neurodegenerative condition is present in first responders who experience cognitive impairment in midlife, which “is incredibly important to know,” said lead author Sean Clouston, PhD, of Stony Brook (N.Y.) University.
The findings were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in Alzheimer’s and Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment and Disease Monitoring.
Brain atrophy in midlife
During the 9/11 attack and in its aftermath, WTC responders were exposed to a range of inhaled neurotoxicants, as well as extreme psychosocial stressors. A growing number of WTC responders who are now in their 50s and early 60s are experiencing early cognitive impairment.
Using MRI, the investigators examined cortical thickness (CTX), a surrogate marker for neurodegeneration, in 99 mostly male WTC responders; 48 had cognitive impairment, and 51 did not. The age range of the participants was 45 to 65 years, a range during which cortical atrophy is uncommon in the general population, the researchers noted.
Compared with cognitively normal responders, those with cognitive impairment were found to have reductions in CTX across the whole brain and across 21 of 34 cortical regions, including frontal, temporal, and occipital lobes.
In both cognitively impaired and cognitively unimpaired WTC responders, CTX was reduced in the entorhinal and temporal cortices compared with normative data, but reductions were greater with cognitive impairment. Posttraumatic distress disorder (PTSD) status was not predictive of a reduction in CTX across groups.
Dr. Clouston said the level of reduction in CTX in many responders is similar to that commonly found in patients with dementia and may reflect early-stage dementia occurring in midlife.
Limitations of the study include the small sample size, the cross-sectional design, the unique nature of the exposure, and a lack of a non-WTC external control group.
‘Illuminating’ study
Keith N. Fargo, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, called the findings “interesting and illuminating” but cautioned that it is not possible to show cause and effect with this type of study.
“We also don’t know when cortical thinning might have started or how quickly it might be progressing,” Dr. Fargo said in an interview.
He noted that the pattern of cortical thinning is “somewhat consistent with what we see among people who live with high levels of air pollution, which is an emerging risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias.”
The Lancet Commission on Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care added air pollution to its list of modifiable risk factors for dementia, which was recently updated.
Clinicians “need to be aware that their middle-aged 9/11 first responders are at a higher risk level for cognitive impairment, as well as PTSD and depression,” Dr. Fargo said.
The study was funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Clouston and Dr. Fargo have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAIC 2020
When you see something ...
Over the last several decades science has fallen off this country’s radar screen. Yes, STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) has recently had a brief moment in the spotlight as a buzzword de jour. But the critical importance of careful and systematic investigation into the world around us using observation and trial and error is a tough sell to a large segment of our population.
The COVID-19 pandemic is providing an excellent opportunity for science and medicine to showcase their star qualities. Of course some people in leadership positions persist in disregarding the value of scientific investigation. But I get the feeling that the fear generated by the pandemic is creating some converts among many previous science skeptics. This gathering enthusiasm among the general population is a predictably slow process because that’s the way science works. It often doesn’t provide quick answers. And it is difficult for the nonscientist to see the beauty in the reality that the things we thought were true 2 months ago are likely to be proven wrong today as more observations accumulate.
A recent New York Times article examines the career of one such unscrupulous physician/scientist whose recent exploits threaten to undo much of the positive image the pandemic has cast on science (“The Doctor Behind the Disputed Covid Data,” by Ellen Gabler and Roni Caryn Rabin, The New York Times, July 27, 2020). The subject of the article is the physician who was responsible for providing some of the large data sets on which several papers were published about the apparent ineffectiveness and danger of using hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients. The authenticity of the data sets recently has been seriously questioned, and the articles have been retracted by the journals in which they had appeared.
Based on numerous interviews with coworkers, the Times reporters present a strong case that this individual’s long history of unreliability make his association with allegedly fraudulent data set not surprising but maybe even predictable. At one point in his training, there appears to have been serious questions about advancing the physician to the next level. Despite these concerns, he was allowed to continue and complete his specialty training. It is of note that in his last year of clinical practice, the physician became the subject of three serious malpractice claims that question his competence.
I suspect that some of you have crossed paths with physicians whose competence and/or moral character you found concerning. Were they peers? Were you the individual’s supervisor or was he or she your mentor? How did you respond? Did anyone respond at all?
There has been a lot written and said in recent months about how and when to respond to respond to sexual harassment in the workplace. But I don’t recall reading any articles that discuss how one should respond to incompetence. Of course competency can be a relative term, but in most cases significant incompetence is hard to miss because it tends to be repeated.
It is easy for the airports and subway systems to post signs that say “If you see something say something.” It’s a different story for hospitals and medical schools that may have systems in place for reporting and following up on poor practice. But my sense is that there are too many cases that slip through the cracks.
This is another example of a problem for which I don’t have a solution. However, if this column prompts just one of you who sees something to say something then I have had a good day.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Over the last several decades science has fallen off this country’s radar screen. Yes, STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) has recently had a brief moment in the spotlight as a buzzword de jour. But the critical importance of careful and systematic investigation into the world around us using observation and trial and error is a tough sell to a large segment of our population.
The COVID-19 pandemic is providing an excellent opportunity for science and medicine to showcase their star qualities. Of course some people in leadership positions persist in disregarding the value of scientific investigation. But I get the feeling that the fear generated by the pandemic is creating some converts among many previous science skeptics. This gathering enthusiasm among the general population is a predictably slow process because that’s the way science works. It often doesn’t provide quick answers. And it is difficult for the nonscientist to see the beauty in the reality that the things we thought were true 2 months ago are likely to be proven wrong today as more observations accumulate.
A recent New York Times article examines the career of one such unscrupulous physician/scientist whose recent exploits threaten to undo much of the positive image the pandemic has cast on science (“The Doctor Behind the Disputed Covid Data,” by Ellen Gabler and Roni Caryn Rabin, The New York Times, July 27, 2020). The subject of the article is the physician who was responsible for providing some of the large data sets on which several papers were published about the apparent ineffectiveness and danger of using hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients. The authenticity of the data sets recently has been seriously questioned, and the articles have been retracted by the journals in which they had appeared.
Based on numerous interviews with coworkers, the Times reporters present a strong case that this individual’s long history of unreliability make his association with allegedly fraudulent data set not surprising but maybe even predictable. At one point in his training, there appears to have been serious questions about advancing the physician to the next level. Despite these concerns, he was allowed to continue and complete his specialty training. It is of note that in his last year of clinical practice, the physician became the subject of three serious malpractice claims that question his competence.
I suspect that some of you have crossed paths with physicians whose competence and/or moral character you found concerning. Were they peers? Were you the individual’s supervisor or was he or she your mentor? How did you respond? Did anyone respond at all?
There has been a lot written and said in recent months about how and when to respond to respond to sexual harassment in the workplace. But I don’t recall reading any articles that discuss how one should respond to incompetence. Of course competency can be a relative term, but in most cases significant incompetence is hard to miss because it tends to be repeated.
It is easy for the airports and subway systems to post signs that say “If you see something say something.” It’s a different story for hospitals and medical schools that may have systems in place for reporting and following up on poor practice. But my sense is that there are too many cases that slip through the cracks.
This is another example of a problem for which I don’t have a solution. However, if this column prompts just one of you who sees something to say something then I have had a good day.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
Over the last several decades science has fallen off this country’s radar screen. Yes, STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) has recently had a brief moment in the spotlight as a buzzword de jour. But the critical importance of careful and systematic investigation into the world around us using observation and trial and error is a tough sell to a large segment of our population.
The COVID-19 pandemic is providing an excellent opportunity for science and medicine to showcase their star qualities. Of course some people in leadership positions persist in disregarding the value of scientific investigation. But I get the feeling that the fear generated by the pandemic is creating some converts among many previous science skeptics. This gathering enthusiasm among the general population is a predictably slow process because that’s the way science works. It often doesn’t provide quick answers. And it is difficult for the nonscientist to see the beauty in the reality that the things we thought were true 2 months ago are likely to be proven wrong today as more observations accumulate.
A recent New York Times article examines the career of one such unscrupulous physician/scientist whose recent exploits threaten to undo much of the positive image the pandemic has cast on science (“The Doctor Behind the Disputed Covid Data,” by Ellen Gabler and Roni Caryn Rabin, The New York Times, July 27, 2020). The subject of the article is the physician who was responsible for providing some of the large data sets on which several papers were published about the apparent ineffectiveness and danger of using hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 patients. The authenticity of the data sets recently has been seriously questioned, and the articles have been retracted by the journals in which they had appeared.
Based on numerous interviews with coworkers, the Times reporters present a strong case that this individual’s long history of unreliability make his association with allegedly fraudulent data set not surprising but maybe even predictable. At one point in his training, there appears to have been serious questions about advancing the physician to the next level. Despite these concerns, he was allowed to continue and complete his specialty training. It is of note that in his last year of clinical practice, the physician became the subject of three serious malpractice claims that question his competence.
I suspect that some of you have crossed paths with physicians whose competence and/or moral character you found concerning. Were they peers? Were you the individual’s supervisor or was he or she your mentor? How did you respond? Did anyone respond at all?
There has been a lot written and said in recent months about how and when to respond to respond to sexual harassment in the workplace. But I don’t recall reading any articles that discuss how one should respond to incompetence. Of course competency can be a relative term, but in most cases significant incompetence is hard to miss because it tends to be repeated.
It is easy for the airports and subway systems to post signs that say “If you see something say something.” It’s a different story for hospitals and medical schools that may have systems in place for reporting and following up on poor practice. But my sense is that there are too many cases that slip through the cracks.
This is another example of a problem for which I don’t have a solution. However, if this column prompts just one of you who sees something to say something then I have had a good day.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
AHA on cannabis: No evidence of heart benefits, but potential harms
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
Evidence for a link between cannabis use and cardiovascular health remains unsupported, and the potential risks outweigh any potential benefits, according to a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.
The increased legalization of cannabis and cannabis products in the United States has driven medical professionals to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cannabis in relation to health conditions, wrote Robert L. Page II, PharmD, of the University of Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues.
In a statement published in Circulation, the researchers noted that although cannabis has been shown to relieve pain and other symptoms in certain conditions, clinicians in the United States have been limited from studying its health effects because of federal law restrictions. “Cannabis remains a schedule I controlled substance, deeming no accepted medical use, a high potential for abuse, and an unacceptable safety profile,” the researchers wrote.
The statement addresses issues with the use of cannabis by individuals with cardiovascular disease or those at increased risk. Observational studies have shown no cardiovascular benefits associated with cannabis, the writers noted. The most common chemicals in cannabis include THC (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Some research has shown associations between CBD cardiovascular features including lower blood pressure and reduced inflammation, the writers noted. However, THC, the component of cannabis associated with a “high” or intoxication, has been associated with heart rhythm abnormalities. The writers cited data suggesting an increased risk of heart attacks, atrial fibrillation and heart failure, although more research is needed.
The statement outlines common cannabis formulations including plant-based, extracts, crystalline forms, edible products, and tinctures. In addition, the statement notes that synthetic cannabis products are marketed and used in the United States without subject to regulation.
“Over the past 5 years, we have seen a surge in cannabis use, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic here in Colorado, especially among adolescents and young adults,” Dr. Page said in an interview. Because of the surge, health care practitioners need to familiarize themselves with not only the benefits, but risks associated with cannabis use regardless of the formulation,” he said. As heart disease remains a leading cause of death in the United States, understanding the cardiovascular risks associated with cannabis is crucial at this time.
Dr. Page noted that popular attitudes about cannabis could pose risks to users’ cardiovascular health. “One leading misconception about cannabis is because it is ‘natural’ it must be safe,” Dr. Page said. “As with all medications, cannabis has side effects, some of which can be cardiovascular in nature,” he said. “Significant drug-drug interactions can occur as CBD and THC, both found in cannabis, inhibit CYP3A4, which metabolizes a large number of medications used to treat many cardiovascular conditions,” he noted.
“Unfortunately, much of the published data is observational in nature due to the federal restrictions on cannabis as a schedule I drug,” said Dr. Page. “Nonetheless, safety signals have emerged regarding cannabis use and adverse cardiovascular outcomes, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. Carefully designed prospective short- and long-term studies regarding cannabis use and cardiovascular safety are needed,” he emphasized.
Areas in particular need of additional research include the cardiovascular effects of cannabis in several vulnerable populations such as adolescents, older adults, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and those with underlying cardiovascular disease, said Dr. Page.
“Nonetheless, based on the safety signals described within this Clinical Science Statement, an open discussion regarding the risks of using cannabis needs to occur between patient and health care providers,” he said. “Furthermore, patients must be transparent regarding their cannabis use with their cardiologist and primary care provider. The cannabis story will continue to evolve and is a rapidly moving/changing target,” he said.
“Whether cannabis use is a definitive risk factor for cardiovascular disease as with tobacco use is still unknown, and both acute and long-term studies are desperately needed to address this issue,” he said.
Dr. Page had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Page et al. Circulation. 2020 Aug 5. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000883.
FROM CIRCULATION
Exploring cannabis use by older adults
Older Americans – people aged 65 or older – make up 15% of the U.S. population, according to the Census Bureau. By the end of this decade, or the year 2030, this proportion will increase to 21% – and all “baby boomers,” those born between 1946 and 1964, will be older than 65.1 Those demographic developments are occurring alongside a change in societal, legal, and public attitudes on cannabis.
Liberalization of cannabis laws across the United States allows for ever easier access to medicinal and recreational cannabis. Traditionally, cannabis use, its effects, and related considerations in the adolescent and young adult populations have commanded significant research attention. Cannabis use in older adults, however, is not as well studied.2 An exploration of trends in cannabis use by older adults and potential impact in terms of health is timely and important.
According to data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, cannabis use in adults aged 65 years and older appears to have been increasing steadily over the past 2 decades. Use among this group rose from 0.4% in 2006 and 2007, to 2.9% in 2015 and 2016.2 And, most recently, use climbed from 3.7% in 2017 to 4.2% in 2018.2
Cannabis use also has risen among other adults. For those aged 50-64, cannabis use increased from 2.8% in 2006-2007 to 4.8% in 2012-2013.2,3 Meanwhile, from 2015 to 2016, that number increased to 9.0%.3,4
Past-year cannabis use in the groups of those aged 50-64 and those aged 65 and older appears to be higher in individuals with mental health problems, alcohol use disorder, and nicotine dependence.5,6 Being male and being unmarried appear to be correlated with past-year cannabis use. Multimorbidity does not appear to be associated with past-year cannabis use. Those using cannabis tend to be long-term users and have first use at a much younger age, typically before age 21.
Older adults use cannabis for both recreational and perceived medical benefits. Arthritis, chronic back pain, anxiety, depression, relaxation, stress reduction, and enhancement in terms of creativity are all purported reasons for use. However, there is limited to no evidence for the efficacy of cannabis in helping with those conditions and purposes. Clinical trials have shown that cannabis can be beneficial in managing pain and nausea, but those trials have not been conducted in older adults.7,8
There is a real risk of cannabis use having a negative impact on the health of older adults. To begin with, the cannabis consumed today is significantly higher in potency than the cannabis that baby boomers were introduced to in their youth. The higher potency, combined with an age-related decline in function experienced by some older adults, makes them vulnerable to its known side effects, such as anxiety, dry mouth, tachycardia, high blood pressure, palpitations, wheezing, confusion, and dizziness.
Cannabis use is reported to bring a fourfold increase in cardiac events within the first hour of ingestion.9 Cognitive decline and memory impairment are well known adverse effects of cannabis use. Research has shown significant self-reported cognitive decline in older adults in relation to cannabis use.Cannabis metabolites are known to have an effect on cytochrome P450 enzymes, affecting the metabolism of medication, and increasing the susceptibility of older adults who use cannabis to adverse effects of polypharmacy. Finally, as research on emergency department visits by older adults shows, cannabis use can increase the risk of injury among this cohort.
As in the United States, cannabis use among older adults in Canada has increased significantly. The percentage of older adults who use cannabis in the Canadian province of Ontario, for example, reportedly doubled from 2005 to 2015. In response to this increase, and in anticipation of a rise in problematic use of cannabis and cannabis use disorder in older adults, the Canadian Coalition for Seniors’ Mental Health (through financial support from Substance Use and Addictions Program of Health Canada) has created guidelines on the prevention, assessment, and management of cannabis use disorder in older adults.
In the absence of a set of guidelines specific to the United States, the recommendations made by the coalition should be helpful in the care of older Americans. Among other recommendations, the guidelines highlight the needs for primary care physicians to build a better knowledge base around the use of cannabis in older adults, to screen older adults for cannabis use, and to educate older adults and their families about the risk of cannabis use.9
Cannabis use is increasingly popular among older adults10 for both medicinal and recreational purposes. Research and data supporting its medical benefits are limited, and the potential of harm from its use among older adults is present and significant. Importantly, many older adults who use marijuana have co-occurring mental health issues and substance use disorder(s).
Often, our older patients learn about benefits and harms of cannabis from friends and the Internet rather than from physicians and other clinicians.9 We must do our part to make sure that older patients understand the potential negative health impact that cannabis can have on their health. Physicians should screen older adults for marijuana use. Building a better knowledge base around changing trends and views in/on the use and accessibility of cannabis will help physicians better address cannabis use in older adults.
Mr. Kaleka is a medical student in the class of 2021 at Central Michigan University College of Medicine, Mount Pleasant. He has no disclosures. Mr. Kaleka would like to thank his mentor, Furhut Janssen, DO, for her continued guidance and support in research on mental health in vulnerable populations.
References
1. Vespa J et al. Demographic turning points for the United States: Population projections for 2020 to 2060. Current Population Reports. Washington: U.S. Census Bureau. 2020 Feb.
2. Han BH et al. Addiction. 2016 Oct 21. doi: 10.1111/add.13670.
3. Han BH and Palamar JJ. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Oct;191:374-81.
4. Han BH and Palamar JJ. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 4;180(4):609-11.
5. Choi NG et al. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2018;44(2):215-23.
6. Reynolds IR et al. J Am Griatr Soc. 2018 Nov;66(11):2167-71.
7. Ahmed AIA et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Feb;62(2):410-1.
8. Lum HD et al. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;5:2333721419843707.
9. Bertram JR et al. Can Geriatr J. 2020 Mar;23(1):135-42.
10. Baumbusch J and Yip IS. Clin Gerontol. 2020 Mar 29;1-7.
Older Americans – people aged 65 or older – make up 15% of the U.S. population, according to the Census Bureau. By the end of this decade, or the year 2030, this proportion will increase to 21% – and all “baby boomers,” those born between 1946 and 1964, will be older than 65.1 Those demographic developments are occurring alongside a change in societal, legal, and public attitudes on cannabis.
Liberalization of cannabis laws across the United States allows for ever easier access to medicinal and recreational cannabis. Traditionally, cannabis use, its effects, and related considerations in the adolescent and young adult populations have commanded significant research attention. Cannabis use in older adults, however, is not as well studied.2 An exploration of trends in cannabis use by older adults and potential impact in terms of health is timely and important.
According to data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, cannabis use in adults aged 65 years and older appears to have been increasing steadily over the past 2 decades. Use among this group rose from 0.4% in 2006 and 2007, to 2.9% in 2015 and 2016.2 And, most recently, use climbed from 3.7% in 2017 to 4.2% in 2018.2
Cannabis use also has risen among other adults. For those aged 50-64, cannabis use increased from 2.8% in 2006-2007 to 4.8% in 2012-2013.2,3 Meanwhile, from 2015 to 2016, that number increased to 9.0%.3,4
Past-year cannabis use in the groups of those aged 50-64 and those aged 65 and older appears to be higher in individuals with mental health problems, alcohol use disorder, and nicotine dependence.5,6 Being male and being unmarried appear to be correlated with past-year cannabis use. Multimorbidity does not appear to be associated with past-year cannabis use. Those using cannabis tend to be long-term users and have first use at a much younger age, typically before age 21.
Older adults use cannabis for both recreational and perceived medical benefits. Arthritis, chronic back pain, anxiety, depression, relaxation, stress reduction, and enhancement in terms of creativity are all purported reasons for use. However, there is limited to no evidence for the efficacy of cannabis in helping with those conditions and purposes. Clinical trials have shown that cannabis can be beneficial in managing pain and nausea, but those trials have not been conducted in older adults.7,8
There is a real risk of cannabis use having a negative impact on the health of older adults. To begin with, the cannabis consumed today is significantly higher in potency than the cannabis that baby boomers were introduced to in their youth. The higher potency, combined with an age-related decline in function experienced by some older adults, makes them vulnerable to its known side effects, such as anxiety, dry mouth, tachycardia, high blood pressure, palpitations, wheezing, confusion, and dizziness.
Cannabis use is reported to bring a fourfold increase in cardiac events within the first hour of ingestion.9 Cognitive decline and memory impairment are well known adverse effects of cannabis use. Research has shown significant self-reported cognitive decline in older adults in relation to cannabis use.Cannabis metabolites are known to have an effect on cytochrome P450 enzymes, affecting the metabolism of medication, and increasing the susceptibility of older adults who use cannabis to adverse effects of polypharmacy. Finally, as research on emergency department visits by older adults shows, cannabis use can increase the risk of injury among this cohort.
As in the United States, cannabis use among older adults in Canada has increased significantly. The percentage of older adults who use cannabis in the Canadian province of Ontario, for example, reportedly doubled from 2005 to 2015. In response to this increase, and in anticipation of a rise in problematic use of cannabis and cannabis use disorder in older adults, the Canadian Coalition for Seniors’ Mental Health (through financial support from Substance Use and Addictions Program of Health Canada) has created guidelines on the prevention, assessment, and management of cannabis use disorder in older adults.
In the absence of a set of guidelines specific to the United States, the recommendations made by the coalition should be helpful in the care of older Americans. Among other recommendations, the guidelines highlight the needs for primary care physicians to build a better knowledge base around the use of cannabis in older adults, to screen older adults for cannabis use, and to educate older adults and their families about the risk of cannabis use.9
Cannabis use is increasingly popular among older adults10 for both medicinal and recreational purposes. Research and data supporting its medical benefits are limited, and the potential of harm from its use among older adults is present and significant. Importantly, many older adults who use marijuana have co-occurring mental health issues and substance use disorder(s).
Often, our older patients learn about benefits and harms of cannabis from friends and the Internet rather than from physicians and other clinicians.9 We must do our part to make sure that older patients understand the potential negative health impact that cannabis can have on their health. Physicians should screen older adults for marijuana use. Building a better knowledge base around changing trends and views in/on the use and accessibility of cannabis will help physicians better address cannabis use in older adults.
Mr. Kaleka is a medical student in the class of 2021 at Central Michigan University College of Medicine, Mount Pleasant. He has no disclosures. Mr. Kaleka would like to thank his mentor, Furhut Janssen, DO, for her continued guidance and support in research on mental health in vulnerable populations.
References
1. Vespa J et al. Demographic turning points for the United States: Population projections for 2020 to 2060. Current Population Reports. Washington: U.S. Census Bureau. 2020 Feb.
2. Han BH et al. Addiction. 2016 Oct 21. doi: 10.1111/add.13670.
3. Han BH and Palamar JJ. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Oct;191:374-81.
4. Han BH and Palamar JJ. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 4;180(4):609-11.
5. Choi NG et al. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2018;44(2):215-23.
6. Reynolds IR et al. J Am Griatr Soc. 2018 Nov;66(11):2167-71.
7. Ahmed AIA et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Feb;62(2):410-1.
8. Lum HD et al. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;5:2333721419843707.
9. Bertram JR et al. Can Geriatr J. 2020 Mar;23(1):135-42.
10. Baumbusch J and Yip IS. Clin Gerontol. 2020 Mar 29;1-7.
Older Americans – people aged 65 or older – make up 15% of the U.S. population, according to the Census Bureau. By the end of this decade, or the year 2030, this proportion will increase to 21% – and all “baby boomers,” those born between 1946 and 1964, will be older than 65.1 Those demographic developments are occurring alongside a change in societal, legal, and public attitudes on cannabis.
Liberalization of cannabis laws across the United States allows for ever easier access to medicinal and recreational cannabis. Traditionally, cannabis use, its effects, and related considerations in the adolescent and young adult populations have commanded significant research attention. Cannabis use in older adults, however, is not as well studied.2 An exploration of trends in cannabis use by older adults and potential impact in terms of health is timely and important.
According to data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, cannabis use in adults aged 65 years and older appears to have been increasing steadily over the past 2 decades. Use among this group rose from 0.4% in 2006 and 2007, to 2.9% in 2015 and 2016.2 And, most recently, use climbed from 3.7% in 2017 to 4.2% in 2018.2
Cannabis use also has risen among other adults. For those aged 50-64, cannabis use increased from 2.8% in 2006-2007 to 4.8% in 2012-2013.2,3 Meanwhile, from 2015 to 2016, that number increased to 9.0%.3,4
Past-year cannabis use in the groups of those aged 50-64 and those aged 65 and older appears to be higher in individuals with mental health problems, alcohol use disorder, and nicotine dependence.5,6 Being male and being unmarried appear to be correlated with past-year cannabis use. Multimorbidity does not appear to be associated with past-year cannabis use. Those using cannabis tend to be long-term users and have first use at a much younger age, typically before age 21.
Older adults use cannabis for both recreational and perceived medical benefits. Arthritis, chronic back pain, anxiety, depression, relaxation, stress reduction, and enhancement in terms of creativity are all purported reasons for use. However, there is limited to no evidence for the efficacy of cannabis in helping with those conditions and purposes. Clinical trials have shown that cannabis can be beneficial in managing pain and nausea, but those trials have not been conducted in older adults.7,8
There is a real risk of cannabis use having a negative impact on the health of older adults. To begin with, the cannabis consumed today is significantly higher in potency than the cannabis that baby boomers were introduced to in their youth. The higher potency, combined with an age-related decline in function experienced by some older adults, makes them vulnerable to its known side effects, such as anxiety, dry mouth, tachycardia, high blood pressure, palpitations, wheezing, confusion, and dizziness.
Cannabis use is reported to bring a fourfold increase in cardiac events within the first hour of ingestion.9 Cognitive decline and memory impairment are well known adverse effects of cannabis use. Research has shown significant self-reported cognitive decline in older adults in relation to cannabis use.Cannabis metabolites are known to have an effect on cytochrome P450 enzymes, affecting the metabolism of medication, and increasing the susceptibility of older adults who use cannabis to adverse effects of polypharmacy. Finally, as research on emergency department visits by older adults shows, cannabis use can increase the risk of injury among this cohort.
As in the United States, cannabis use among older adults in Canada has increased significantly. The percentage of older adults who use cannabis in the Canadian province of Ontario, for example, reportedly doubled from 2005 to 2015. In response to this increase, and in anticipation of a rise in problematic use of cannabis and cannabis use disorder in older adults, the Canadian Coalition for Seniors’ Mental Health (through financial support from Substance Use and Addictions Program of Health Canada) has created guidelines on the prevention, assessment, and management of cannabis use disorder in older adults.
In the absence of a set of guidelines specific to the United States, the recommendations made by the coalition should be helpful in the care of older Americans. Among other recommendations, the guidelines highlight the needs for primary care physicians to build a better knowledge base around the use of cannabis in older adults, to screen older adults for cannabis use, and to educate older adults and their families about the risk of cannabis use.9
Cannabis use is increasingly popular among older adults10 for both medicinal and recreational purposes. Research and data supporting its medical benefits are limited, and the potential of harm from its use among older adults is present and significant. Importantly, many older adults who use marijuana have co-occurring mental health issues and substance use disorder(s).
Often, our older patients learn about benefits and harms of cannabis from friends and the Internet rather than from physicians and other clinicians.9 We must do our part to make sure that older patients understand the potential negative health impact that cannabis can have on their health. Physicians should screen older adults for marijuana use. Building a better knowledge base around changing trends and views in/on the use and accessibility of cannabis will help physicians better address cannabis use in older adults.
Mr. Kaleka is a medical student in the class of 2021 at Central Michigan University College of Medicine, Mount Pleasant. He has no disclosures. Mr. Kaleka would like to thank his mentor, Furhut Janssen, DO, for her continued guidance and support in research on mental health in vulnerable populations.
References
1. Vespa J et al. Demographic turning points for the United States: Population projections for 2020 to 2060. Current Population Reports. Washington: U.S. Census Bureau. 2020 Feb.
2. Han BH et al. Addiction. 2016 Oct 21. doi: 10.1111/add.13670.
3. Han BH and Palamar JJ. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Oct;191:374-81.
4. Han BH and Palamar JJ. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Feb 4;180(4):609-11.
5. Choi NG et al. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2018;44(2):215-23.
6. Reynolds IR et al. J Am Griatr Soc. 2018 Nov;66(11):2167-71.
7. Ahmed AIA et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014 Feb;62(2):410-1.
8. Lum HD et al. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;5:2333721419843707.
9. Bertram JR et al. Can Geriatr J. 2020 Mar;23(1):135-42.
10. Baumbusch J and Yip IS. Clin Gerontol. 2020 Mar 29;1-7.
Value of palliative care shines clearly in a crisis
Hospitalists have played a key role
For some palliative care professionals, the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in viral hot spots like New York City, represents a “moment” that could lead to greater awareness of what this service offers to seriously ill patients in a crisis.
They say it has provided an opportunity to show what palliative care teams can contribute to the difficult circumstances of patients with severe symptoms, isolated and alone in quarantined hospitals, with poor survival rates, perhaps sedated for extended stays on scarce ventilators – and for their family members, who are able to visit them only virtually via telephone or tablet.
But it has also highlighted gaps – including insufficient staffing for some palliative care teams. Hospitalists and other clinicians in the hospital need to learn the basics of primary palliative care, such as how to communicate bad news, initiate goals of care conversations, and address common symptoms of serious illness, such as pain. That way, they could shoulder more of the demand for this kind of care when palliative care specialists are in short supply.
Hospitalists, some of whom also have pursued a specialization in palliative care, have played key roles in clarifying and redefining the new role for palliative care, whom it is meant for, and who should provide it. Central to this new role is the greater use of telemedicine – for talking to hospitalized patients without increasing viral exposure, for linking up with family members who can’t visit their loved ones in the hospital, and for helping frontline hospital staff who need a palliative care consultation – or just a chance to debrief on what they are seeing.
A pandemic wake-up call
Elizabeth Gundersen, MD, FHM, FAAHPM, director of the hospice and palliative medicine fellowship program at the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) in Boca Raton, practiced hospital medicine for 10 years before pursuing a fellowship in hospice and palliative medicine and working as an academic palliative medicine physician. She calls the pandemic a wake-up call for gaps in care and all the things that weren’t working well in the health care system.
“Now we are seeing more clearly what’s lacking – or broken – and what we will carry forward from this experience into the post-COVID world,” she said. Some hospitalists do palliative care very well, and others don’t feel as comfortable in having these difficult conversations with patients. But in the uncertain course of the virus they get thrust into it.
Although FAU’s associated hospitals were not as inundated with COVID-19 patients in the early weeks of the pandemic as were other regions, the volume of other patients plummeted, Dr. Gundersen said, adding that “there’s still been incredible intensity and worry about the virus. For me, the basic role of palliative care hasn’t changed, and the phrase I have always used when introducing myself – ‘we’re an extra layer of support for the patient and family’ – still holds true,” she said.
“I try to make it clear to people that palliative care is not synonymous with end-of-life care. We don’t want people to think that a palliative care referral implies imminent death. The goal is not to get more people to have a do not attempt resuscitation (DNAR) order, but to determine the patient and family’s treatment goals and whether a DNAR order fits those goals.”
The tough conversations
Dr. Gundersen is cochair of SHM’s Palliative Care Special Interest Group, along with Rab Razzak, MD, clinical director of palliative medicine at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, one of the hospitals affiliated with Case Western University in Cleveland. (Connect with them on Twitter: @Top_Gundersen and @rabrazzak.)
Dr. Razzak also transitioned from hospital medicine to palliative medicine 10 years ago. “As a hospitalist, I enjoyed the tough conversations and bringing the human element into my health care interactions,” he explained. “To me, palliative care is a philosophy of care that puts the person we call the patient at the center of the interaction, while we try to figure out how to best care for them as a person.”
When the pandemic hit, University Hospitals made 20 ICU beds available for COVID-19 patients, Dr. Razzak said. This unit has since been full but not overflowing, while overall hospital census went down. The palliative care team at the hospital includes four inpatient doctors, nurse practitioners, and a chaplain, as well as an outpatient team primarily focused on oncology.
“In some settings, palliative care has been at the forefront of difficult conversations, when things aren’t going well for the patient and there’s much uncertainty,” Dr. Razzak said. The interface between hospital medicine and palliative care can be complementary, he added. “We talk about primary palliative care, which we want every discipline to be able to do – lead meaningful conversations, help manage symptoms.”
The take-home message for hospitalists, he said, is to get training in how to have these discussions, using such resources as VitalTalk (https://www.vitaltalk.org/), a nonprofit organization that disseminates education in communication skills for difficult conversations, and the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. “Once you’ve mastered the conversation, it will get easier. But ask for help when you need it, and learn how to know when you need it.”
Dr. Gundersen added that hospital medicine groups and palliative care teams could reach out to each other and talk about what they did in the crisis and how they can work together in the future. She recommends frequent ongoing support and collaboration that could range from formal conferences or training sessions to informal team interactions, perhaps with sandwiches in the doctor’s lounge – provided that there’s room for social distancing. She has recently started giving talks in the community and grand rounds presentations in hospitals about palliative care.
Other approaches and applications
In New York City, the initial epicenter for the pandemic in the United States, the adult palliative care service of Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) experienced a sevenfold increase in consultation requests at the apex of the crisis, said its director, Craig Blinderman, MD. That demand was impossible to meet with existing staff. So Dr. Blinderman and colleagues established a virtual consultation model, recruiting and deploying volunteer out-of-state palliative care specialists to staff it.
An eight-bed palliative care unit was opened at CUMC for COVID-19 patients whose surrogates had opted not to initiate or continue intubation or life-sustaining treatments. This helped to relieve some of the pressures on the ICUs while making it possible for in-person visits to the hospice unit by families – in full PPE. Palliative care staff were embedded in various units in the hospital.
A palliative care response team composed of a hospice and palliative medicine fellow and four psychiatry residents or fellows, based in the emergency department and with supervision from the palliative care team, provided time-critical goals of care conversations with families using telemedicine – and a forum for listening to their suffering. Dr. Blinderman and colleagues also have found time to write up their experience for medical journals.1,2
There’s no reason to think that hospitalists, with a little basic training, couldn’t be having these same goals of care conversations, Dr. Blinderman said. “But the fact that hospitalists, at the pandemic’s peak, along with ICU doctors, were seeing an unprecedented magnitude of dying on a daily basis generated a lot of moral distress for them.”
Palliative care professionals, because they engage with these issues in a different way, may be somewhat better equipped to deal with the sheer emotional demands when so many are dying, as at the peak of the surge in New York. “We don’t see dying as a failure on our part but an opportunity to relieve suffering,” Dr. Blinderman said. And the palliative care field also emphasizes the importance of self-care for its practitioners.
“How do we meet the incredible palliative care needs in the epicenter of a pandemic? That question also applies to other kinds of crises we could imagine, for example, climate-related disasters,” Dr. Blinderman said. “What lessons have we learned about the value of palliative care and how to start incorporating it more integrally into the delivery of hospital care? Here we showed that we could work collaboratively with our colleagues at other major medical centers, bringing together their expertise to help us when we didn’t have the bandwidth to meet the demand,” he said.
Scripts can help
“Also, it won’t make sense to just go back to normal (after the crisis fades),” Dr. Blinderman said. “We need to take a close look at how our society is functioning in the wake of the pandemic and the ways the health care system has failed us. We have learned that we’re all interconnected and we need to work together to serve our communities – locally and nationally – applying basic distributive justice.”
Could there be, for example, a national infrastructure for mobilizing and deploying palliative care resources to areas of greatest need, similar to what was done in New York?
At Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, a number of palliative care clinicians at the system’s hospitals worked together to develop scripts designed to help other clinicians start goals of care conversations with patients and families, for use in the hospital as well as in outpatient primary care and other settings, with results integrated into the system’s electronic health record.
Front-line clinicians may not have the time to ask for formal consults from palliative care because of high volume and rapidly changing patient status, explained Eytan Szmuilowicz, MD, director of the section of palliative medicine at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Or they may not have access to specialty-level palliative care in their settings.
The scripts are aimed at primary care, emergency physicians, and hospitalists needing to consider critical care placement or attempted resuscitation and to ICU clinicians helping families make decisions about life-sustaining treatments. They also can help facilitate advance care planning discussions. An example is “CALMER,” a six-step mnemonic guide to promote goals of care discussions with hospitalized patients. For more information on these scripts, contact Dr. Szmuilowicz: [email protected].
Eerily quiet
The COVID-19 crisis has been quite a whirlwind for hospital medicine, said Jeanie Youngwerth, MD, a hospitalist and program director of the palliative care service at the University of Colorado in Denver, which was a significant viral hotspot early on.
“When it first started, things seemed to change almost overnight – starting on Friday, March 13. People had to take action right away to develop work flows and the technology to allow us to see as many patients as possible,” she said. By the time Monday came, it was a whole new ballgame.
Dr. Youngwerth and two colleagues worked quickly to develop inpatient telemedicine capacity where none existed. “We knew we would not be going into patients’ rooms, but most of our team showed up in the hospital to work with the primary care teams. Our job was to see what we could do that actually made a difference,” she said.
“The hospital became a very strange place. You’d walk down the hallway and it was eerily quiet. Everybody you came across was being so nice to each other.” Televisits became a powerful way to bring the human connection back to medical care.
“What we learned from families was that they were thirsting to have some kind of connection with their loved one, and to be able to talk about their loved one and who they were as a person,” she said. “We’d contact the family through video visits and then, when the family meeting ended, the nurse would bring an iPad into the patient’s room so the family could see their loved one on a ventilator. They would immediately start communicating with their loved one, praying aloud, singing, playing music. It would make a huge difference for the family – and for the staff.”
References
1. Nakagawa S et al. Pandemic palliative care consultations spanning state and institutional borders. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16643.
2. Lee J Abrukin L, Flores S. Early intervention of palliative care in the emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2713.
Hospitalists have played a key role
Hospitalists have played a key role
For some palliative care professionals, the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in viral hot spots like New York City, represents a “moment” that could lead to greater awareness of what this service offers to seriously ill patients in a crisis.
They say it has provided an opportunity to show what palliative care teams can contribute to the difficult circumstances of patients with severe symptoms, isolated and alone in quarantined hospitals, with poor survival rates, perhaps sedated for extended stays on scarce ventilators – and for their family members, who are able to visit them only virtually via telephone or tablet.
But it has also highlighted gaps – including insufficient staffing for some palliative care teams. Hospitalists and other clinicians in the hospital need to learn the basics of primary palliative care, such as how to communicate bad news, initiate goals of care conversations, and address common symptoms of serious illness, such as pain. That way, they could shoulder more of the demand for this kind of care when palliative care specialists are in short supply.
Hospitalists, some of whom also have pursued a specialization in palliative care, have played key roles in clarifying and redefining the new role for palliative care, whom it is meant for, and who should provide it. Central to this new role is the greater use of telemedicine – for talking to hospitalized patients without increasing viral exposure, for linking up with family members who can’t visit their loved ones in the hospital, and for helping frontline hospital staff who need a palliative care consultation – or just a chance to debrief on what they are seeing.
A pandemic wake-up call
Elizabeth Gundersen, MD, FHM, FAAHPM, director of the hospice and palliative medicine fellowship program at the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) in Boca Raton, practiced hospital medicine for 10 years before pursuing a fellowship in hospice and palliative medicine and working as an academic palliative medicine physician. She calls the pandemic a wake-up call for gaps in care and all the things that weren’t working well in the health care system.
“Now we are seeing more clearly what’s lacking – or broken – and what we will carry forward from this experience into the post-COVID world,” she said. Some hospitalists do palliative care very well, and others don’t feel as comfortable in having these difficult conversations with patients. But in the uncertain course of the virus they get thrust into it.
Although FAU’s associated hospitals were not as inundated with COVID-19 patients in the early weeks of the pandemic as were other regions, the volume of other patients plummeted, Dr. Gundersen said, adding that “there’s still been incredible intensity and worry about the virus. For me, the basic role of palliative care hasn’t changed, and the phrase I have always used when introducing myself – ‘we’re an extra layer of support for the patient and family’ – still holds true,” she said.
“I try to make it clear to people that palliative care is not synonymous with end-of-life care. We don’t want people to think that a palliative care referral implies imminent death. The goal is not to get more people to have a do not attempt resuscitation (DNAR) order, but to determine the patient and family’s treatment goals and whether a DNAR order fits those goals.”
The tough conversations
Dr. Gundersen is cochair of SHM’s Palliative Care Special Interest Group, along with Rab Razzak, MD, clinical director of palliative medicine at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, one of the hospitals affiliated with Case Western University in Cleveland. (Connect with them on Twitter: @Top_Gundersen and @rabrazzak.)
Dr. Razzak also transitioned from hospital medicine to palliative medicine 10 years ago. “As a hospitalist, I enjoyed the tough conversations and bringing the human element into my health care interactions,” he explained. “To me, palliative care is a philosophy of care that puts the person we call the patient at the center of the interaction, while we try to figure out how to best care for them as a person.”
When the pandemic hit, University Hospitals made 20 ICU beds available for COVID-19 patients, Dr. Razzak said. This unit has since been full but not overflowing, while overall hospital census went down. The palliative care team at the hospital includes four inpatient doctors, nurse practitioners, and a chaplain, as well as an outpatient team primarily focused on oncology.
“In some settings, palliative care has been at the forefront of difficult conversations, when things aren’t going well for the patient and there’s much uncertainty,” Dr. Razzak said. The interface between hospital medicine and palliative care can be complementary, he added. “We talk about primary palliative care, which we want every discipline to be able to do – lead meaningful conversations, help manage symptoms.”
The take-home message for hospitalists, he said, is to get training in how to have these discussions, using such resources as VitalTalk (https://www.vitaltalk.org/), a nonprofit organization that disseminates education in communication skills for difficult conversations, and the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. “Once you’ve mastered the conversation, it will get easier. But ask for help when you need it, and learn how to know when you need it.”
Dr. Gundersen added that hospital medicine groups and palliative care teams could reach out to each other and talk about what they did in the crisis and how they can work together in the future. She recommends frequent ongoing support and collaboration that could range from formal conferences or training sessions to informal team interactions, perhaps with sandwiches in the doctor’s lounge – provided that there’s room for social distancing. She has recently started giving talks in the community and grand rounds presentations in hospitals about palliative care.
Other approaches and applications
In New York City, the initial epicenter for the pandemic in the United States, the adult palliative care service of Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) experienced a sevenfold increase in consultation requests at the apex of the crisis, said its director, Craig Blinderman, MD. That demand was impossible to meet with existing staff. So Dr. Blinderman and colleagues established a virtual consultation model, recruiting and deploying volunteer out-of-state palliative care specialists to staff it.
An eight-bed palliative care unit was opened at CUMC for COVID-19 patients whose surrogates had opted not to initiate or continue intubation or life-sustaining treatments. This helped to relieve some of the pressures on the ICUs while making it possible for in-person visits to the hospice unit by families – in full PPE. Palliative care staff were embedded in various units in the hospital.
A palliative care response team composed of a hospice and palliative medicine fellow and four psychiatry residents or fellows, based in the emergency department and with supervision from the palliative care team, provided time-critical goals of care conversations with families using telemedicine – and a forum for listening to their suffering. Dr. Blinderman and colleagues also have found time to write up their experience for medical journals.1,2
There’s no reason to think that hospitalists, with a little basic training, couldn’t be having these same goals of care conversations, Dr. Blinderman said. “But the fact that hospitalists, at the pandemic’s peak, along with ICU doctors, were seeing an unprecedented magnitude of dying on a daily basis generated a lot of moral distress for them.”
Palliative care professionals, because they engage with these issues in a different way, may be somewhat better equipped to deal with the sheer emotional demands when so many are dying, as at the peak of the surge in New York. “We don’t see dying as a failure on our part but an opportunity to relieve suffering,” Dr. Blinderman said. And the palliative care field also emphasizes the importance of self-care for its practitioners.
“How do we meet the incredible palliative care needs in the epicenter of a pandemic? That question also applies to other kinds of crises we could imagine, for example, climate-related disasters,” Dr. Blinderman said. “What lessons have we learned about the value of palliative care and how to start incorporating it more integrally into the delivery of hospital care? Here we showed that we could work collaboratively with our colleagues at other major medical centers, bringing together their expertise to help us when we didn’t have the bandwidth to meet the demand,” he said.
Scripts can help
“Also, it won’t make sense to just go back to normal (after the crisis fades),” Dr. Blinderman said. “We need to take a close look at how our society is functioning in the wake of the pandemic and the ways the health care system has failed us. We have learned that we’re all interconnected and we need to work together to serve our communities – locally and nationally – applying basic distributive justice.”
Could there be, for example, a national infrastructure for mobilizing and deploying palliative care resources to areas of greatest need, similar to what was done in New York?
At Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, a number of palliative care clinicians at the system’s hospitals worked together to develop scripts designed to help other clinicians start goals of care conversations with patients and families, for use in the hospital as well as in outpatient primary care and other settings, with results integrated into the system’s electronic health record.
Front-line clinicians may not have the time to ask for formal consults from palliative care because of high volume and rapidly changing patient status, explained Eytan Szmuilowicz, MD, director of the section of palliative medicine at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Or they may not have access to specialty-level palliative care in their settings.
The scripts are aimed at primary care, emergency physicians, and hospitalists needing to consider critical care placement or attempted resuscitation and to ICU clinicians helping families make decisions about life-sustaining treatments. They also can help facilitate advance care planning discussions. An example is “CALMER,” a six-step mnemonic guide to promote goals of care discussions with hospitalized patients. For more information on these scripts, contact Dr. Szmuilowicz: [email protected].
Eerily quiet
The COVID-19 crisis has been quite a whirlwind for hospital medicine, said Jeanie Youngwerth, MD, a hospitalist and program director of the palliative care service at the University of Colorado in Denver, which was a significant viral hotspot early on.
“When it first started, things seemed to change almost overnight – starting on Friday, March 13. People had to take action right away to develop work flows and the technology to allow us to see as many patients as possible,” she said. By the time Monday came, it was a whole new ballgame.
Dr. Youngwerth and two colleagues worked quickly to develop inpatient telemedicine capacity where none existed. “We knew we would not be going into patients’ rooms, but most of our team showed up in the hospital to work with the primary care teams. Our job was to see what we could do that actually made a difference,” she said.
“The hospital became a very strange place. You’d walk down the hallway and it was eerily quiet. Everybody you came across was being so nice to each other.” Televisits became a powerful way to bring the human connection back to medical care.
“What we learned from families was that they were thirsting to have some kind of connection with their loved one, and to be able to talk about their loved one and who they were as a person,” she said. “We’d contact the family through video visits and then, when the family meeting ended, the nurse would bring an iPad into the patient’s room so the family could see their loved one on a ventilator. They would immediately start communicating with their loved one, praying aloud, singing, playing music. It would make a huge difference for the family – and for the staff.”
References
1. Nakagawa S et al. Pandemic palliative care consultations spanning state and institutional borders. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16643.
2. Lee J Abrukin L, Flores S. Early intervention of palliative care in the emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2713.
For some palliative care professionals, the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in viral hot spots like New York City, represents a “moment” that could lead to greater awareness of what this service offers to seriously ill patients in a crisis.
They say it has provided an opportunity to show what palliative care teams can contribute to the difficult circumstances of patients with severe symptoms, isolated and alone in quarantined hospitals, with poor survival rates, perhaps sedated for extended stays on scarce ventilators – and for their family members, who are able to visit them only virtually via telephone or tablet.
But it has also highlighted gaps – including insufficient staffing for some palliative care teams. Hospitalists and other clinicians in the hospital need to learn the basics of primary palliative care, such as how to communicate bad news, initiate goals of care conversations, and address common symptoms of serious illness, such as pain. That way, they could shoulder more of the demand for this kind of care when palliative care specialists are in short supply.
Hospitalists, some of whom also have pursued a specialization in palliative care, have played key roles in clarifying and redefining the new role for palliative care, whom it is meant for, and who should provide it. Central to this new role is the greater use of telemedicine – for talking to hospitalized patients without increasing viral exposure, for linking up with family members who can’t visit their loved ones in the hospital, and for helping frontline hospital staff who need a palliative care consultation – or just a chance to debrief on what they are seeing.
A pandemic wake-up call
Elizabeth Gundersen, MD, FHM, FAAHPM, director of the hospice and palliative medicine fellowship program at the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) in Boca Raton, practiced hospital medicine for 10 years before pursuing a fellowship in hospice and palliative medicine and working as an academic palliative medicine physician. She calls the pandemic a wake-up call for gaps in care and all the things that weren’t working well in the health care system.
“Now we are seeing more clearly what’s lacking – or broken – and what we will carry forward from this experience into the post-COVID world,” she said. Some hospitalists do palliative care very well, and others don’t feel as comfortable in having these difficult conversations with patients. But in the uncertain course of the virus they get thrust into it.
Although FAU’s associated hospitals were not as inundated with COVID-19 patients in the early weeks of the pandemic as were other regions, the volume of other patients plummeted, Dr. Gundersen said, adding that “there’s still been incredible intensity and worry about the virus. For me, the basic role of palliative care hasn’t changed, and the phrase I have always used when introducing myself – ‘we’re an extra layer of support for the patient and family’ – still holds true,” she said.
“I try to make it clear to people that palliative care is not synonymous with end-of-life care. We don’t want people to think that a palliative care referral implies imminent death. The goal is not to get more people to have a do not attempt resuscitation (DNAR) order, but to determine the patient and family’s treatment goals and whether a DNAR order fits those goals.”
The tough conversations
Dr. Gundersen is cochair of SHM’s Palliative Care Special Interest Group, along with Rab Razzak, MD, clinical director of palliative medicine at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, one of the hospitals affiliated with Case Western University in Cleveland. (Connect with them on Twitter: @Top_Gundersen and @rabrazzak.)
Dr. Razzak also transitioned from hospital medicine to palliative medicine 10 years ago. “As a hospitalist, I enjoyed the tough conversations and bringing the human element into my health care interactions,” he explained. “To me, palliative care is a philosophy of care that puts the person we call the patient at the center of the interaction, while we try to figure out how to best care for them as a person.”
When the pandemic hit, University Hospitals made 20 ICU beds available for COVID-19 patients, Dr. Razzak said. This unit has since been full but not overflowing, while overall hospital census went down. The palliative care team at the hospital includes four inpatient doctors, nurse practitioners, and a chaplain, as well as an outpatient team primarily focused on oncology.
“In some settings, palliative care has been at the forefront of difficult conversations, when things aren’t going well for the patient and there’s much uncertainty,” Dr. Razzak said. The interface between hospital medicine and palliative care can be complementary, he added. “We talk about primary palliative care, which we want every discipline to be able to do – lead meaningful conversations, help manage symptoms.”
The take-home message for hospitalists, he said, is to get training in how to have these discussions, using such resources as VitalTalk (https://www.vitaltalk.org/), a nonprofit organization that disseminates education in communication skills for difficult conversations, and the Center to Advance Palliative Care (www.capc.org) at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. “Once you’ve mastered the conversation, it will get easier. But ask for help when you need it, and learn how to know when you need it.”
Dr. Gundersen added that hospital medicine groups and palliative care teams could reach out to each other and talk about what they did in the crisis and how they can work together in the future. She recommends frequent ongoing support and collaboration that could range from formal conferences or training sessions to informal team interactions, perhaps with sandwiches in the doctor’s lounge – provided that there’s room for social distancing. She has recently started giving talks in the community and grand rounds presentations in hospitals about palliative care.
Other approaches and applications
In New York City, the initial epicenter for the pandemic in the United States, the adult palliative care service of Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) experienced a sevenfold increase in consultation requests at the apex of the crisis, said its director, Craig Blinderman, MD. That demand was impossible to meet with existing staff. So Dr. Blinderman and colleagues established a virtual consultation model, recruiting and deploying volunteer out-of-state palliative care specialists to staff it.
An eight-bed palliative care unit was opened at CUMC for COVID-19 patients whose surrogates had opted not to initiate or continue intubation or life-sustaining treatments. This helped to relieve some of the pressures on the ICUs while making it possible for in-person visits to the hospice unit by families – in full PPE. Palliative care staff were embedded in various units in the hospital.
A palliative care response team composed of a hospice and palliative medicine fellow and four psychiatry residents or fellows, based in the emergency department and with supervision from the palliative care team, provided time-critical goals of care conversations with families using telemedicine – and a forum for listening to their suffering. Dr. Blinderman and colleagues also have found time to write up their experience for medical journals.1,2
There’s no reason to think that hospitalists, with a little basic training, couldn’t be having these same goals of care conversations, Dr. Blinderman said. “But the fact that hospitalists, at the pandemic’s peak, along with ICU doctors, were seeing an unprecedented magnitude of dying on a daily basis generated a lot of moral distress for them.”
Palliative care professionals, because they engage with these issues in a different way, may be somewhat better equipped to deal with the sheer emotional demands when so many are dying, as at the peak of the surge in New York. “We don’t see dying as a failure on our part but an opportunity to relieve suffering,” Dr. Blinderman said. And the palliative care field also emphasizes the importance of self-care for its practitioners.
“How do we meet the incredible palliative care needs in the epicenter of a pandemic? That question also applies to other kinds of crises we could imagine, for example, climate-related disasters,” Dr. Blinderman said. “What lessons have we learned about the value of palliative care and how to start incorporating it more integrally into the delivery of hospital care? Here we showed that we could work collaboratively with our colleagues at other major medical centers, bringing together their expertise to help us when we didn’t have the bandwidth to meet the demand,” he said.
Scripts can help
“Also, it won’t make sense to just go back to normal (after the crisis fades),” Dr. Blinderman said. “We need to take a close look at how our society is functioning in the wake of the pandemic and the ways the health care system has failed us. We have learned that we’re all interconnected and we need to work together to serve our communities – locally and nationally – applying basic distributive justice.”
Could there be, for example, a national infrastructure for mobilizing and deploying palliative care resources to areas of greatest need, similar to what was done in New York?
At Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, a number of palliative care clinicians at the system’s hospitals worked together to develop scripts designed to help other clinicians start goals of care conversations with patients and families, for use in the hospital as well as in outpatient primary care and other settings, with results integrated into the system’s electronic health record.
Front-line clinicians may not have the time to ask for formal consults from palliative care because of high volume and rapidly changing patient status, explained Eytan Szmuilowicz, MD, director of the section of palliative medicine at Northwestern Memorial Hospital. Or they may not have access to specialty-level palliative care in their settings.
The scripts are aimed at primary care, emergency physicians, and hospitalists needing to consider critical care placement or attempted resuscitation and to ICU clinicians helping families make decisions about life-sustaining treatments. They also can help facilitate advance care planning discussions. An example is “CALMER,” a six-step mnemonic guide to promote goals of care discussions with hospitalized patients. For more information on these scripts, contact Dr. Szmuilowicz: [email protected].
Eerily quiet
The COVID-19 crisis has been quite a whirlwind for hospital medicine, said Jeanie Youngwerth, MD, a hospitalist and program director of the palliative care service at the University of Colorado in Denver, which was a significant viral hotspot early on.
“When it first started, things seemed to change almost overnight – starting on Friday, March 13. People had to take action right away to develop work flows and the technology to allow us to see as many patients as possible,” she said. By the time Monday came, it was a whole new ballgame.
Dr. Youngwerth and two colleagues worked quickly to develop inpatient telemedicine capacity where none existed. “We knew we would not be going into patients’ rooms, but most of our team showed up in the hospital to work with the primary care teams. Our job was to see what we could do that actually made a difference,” she said.
“The hospital became a very strange place. You’d walk down the hallway and it was eerily quiet. Everybody you came across was being so nice to each other.” Televisits became a powerful way to bring the human connection back to medical care.
“What we learned from families was that they were thirsting to have some kind of connection with their loved one, and to be able to talk about their loved one and who they were as a person,” she said. “We’d contact the family through video visits and then, when the family meeting ended, the nurse would bring an iPad into the patient’s room so the family could see their loved one on a ventilator. They would immediately start communicating with their loved one, praying aloud, singing, playing music. It would make a huge difference for the family – and for the staff.”
References
1. Nakagawa S et al. Pandemic palliative care consultations spanning state and institutional borders. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16643.
2. Lee J Abrukin L, Flores S. Early intervention of palliative care in the emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Jun 5. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.2713.
A doctor conquers his demons
Adam B. Hill, MD, is home on a “staycation” this week. Today, he took a 3-hour nap. I know this because I follow Dr. Hill on Twitter, where he has an active feed, a lot of posts, retweets, and more than 20,000 followers.
I also know from Twitter that he is married and has three young children, that he was once suicidal, and has been treated for major depression and alcoholism. As a palliative care doctor, Dr. Hill was required by his state medical board to blow into a breathalyzer several times a day for 5 years – something he felt quite shamed by – and while I’ve never met him, I felt just a little bit proud of this stranger when he was released from the medical board’s oversight.
Dr. Hill’s memoir, “Long Walk Out of the Woods: A Physician’s Story of Addiction, Depression, Hope, and Recovery” (Central Recovery Press, 2019) is the culmination of his efforts to use his difficulties as a way of offering hope and connection to anyone who struggled as he has, or to anyone who has struggled at all. Like his Twitter feed, it is a display of vulnerability and gratitude by someone who has been through dark times then returned to conquer his monsters.
He begins by setting the stage for us. “My name is Adam,” he announces in the preface. He tells us his various titles: human being, husband, father, physician, recovering alcoholic, and psychiatric patient. “In the midst of these struggles, working in modern medicine fractured my identity, stole my authenticity, and left me a shell of the person I wanted to be.”
We learn that he tried to buy a gun, but there was a waiting period and he could not purchase the firearm. Instead, he walked into the woods to drink himself to death, with sleeping pills as an add-on – obviously, he didn’t die, and his journey back from his failed suicidal mission is the meat of the book.
Dr. Hill was a quiet and timid child, and he was bullied at school in a way that has lingered on. He struggles with perfectionism and with a sense of never quite belonging. He was a good student, and later a competitive tennis player who was destined for a regional competition until he broke his ankle after drinking just days before the competition. He did well in college, felt more accepted, and went on to medical school after getting in from the wait list. He went on to do a pediatrics residency, and he and his wife moved from Indiana to North Carolina so he could do a hematology oncology fellowship. It was toward the end of his 2-year fellowship when he tried to purchase a gun, then walked into those woods.
His wife called, asked him to come to dinner, and he left the woods before he’d overdosed. After a meeting with his wife, parents, and sister, he returned to psychiatric care, restarted antidepressants, went to Alcoholics Anonymous, and told his employer that he had a problem. This admission started a distressing series of events, including years of being monitored by state medical boards and being labeled an “impaired physician.”
This is the only thing I didn’t like about Dr. Hill’s memoir: As open as he is about his emotional life, there were pieces missing with respect to what actually happened. At this point, I was befuddled as to why he self-reported his difficulties, and it wasn’t until he talked about starting a second fellowship in palliative care in his home state of Indiana that I could fill in some missing pieces. Dr. Hill and his wife purchased a house, and in November, he started his fellowship. The timing was off from the usual start in July, and I realized that perhaps he had gone to an inpatient setting for a number of months – his disclosure to his employer was voluntary, but his treatment likely interfered with his training and couldn’t be hidden. What else transpired he hints at: bottles hidden, driving while intoxicated, a nurse who gave him IV hydration when he came to work with a hangover.
From here, Dr. Hill’s story becomes every doctor’s nightmare. Settled into his new house and weeks into his fellowship, he is called in and fired: His application for a medical license in Indiana has been denied because of his addiction history. He met with a friend of his father’s who worked in a large pediatrics practice. The meeting went well, but the group felt he was too much of a malpractice risk.
He now needs to pay his mortgage and student loans, so he takes a position in Oklahoma with the Indian Health Service. He’s 700 miles from home, living alone in a hotel room, feeling like the work is beneath him, and the chapter is titled “Exile.” His new boss greets him with, “Listen, we all had our own stories that led us here.” Surprisingly, he likes the work and feels supported. If only it weren’t for all that loneliness, and not surprisingly, he relapses despite the mandated breathalyzer. Six beers later, and Dr. Hill is off to Chicago for a rehab program, then back to Oklahoma to finish off his stint.
What happens next is the second time I wondered about the plot of his life: Through “connections and concession,” he returns to Indiana for the palliative care fellowship, and goes on to work at Riley Children’s Hospital.
When a colleague unexpectedly dies from suicide, Dr. Hill tells others that he, too, once entertained suicidal thoughts. The story from here gets better and better: – to conquer their shame, to share their stories, to feel less alone. He and his wife become parents, he remains sober and healthy, and therapy leads him to a place of self-discovery and success.
Intertwined with telling his story, Dr. Hill takes on some of the institutional issues surrounding addiction and mental illness. He feels shamed and punished by the state medical board that mandates the terms of his medical license. Any physician who reads this book will think twice about revealing a diagnosis of depression or substance use disorder. It’s not a new idea that to protect the public, medical boards should ask about current impairments, not a past history or conditions that have been successfully treated. They should encourage treatment, not punish those who seek care.
Dr. Hill writes about how helpful it has been to allow himself to be vulnerable in the aftermath:
In my experience, the more vulnerability I show, the more opportunities I have to connect to other people. I learned the hard way that when I hide my true self from others, I spiral toward shame. Conversely, when I bury my shame, I begin to accept myself as a beautifully flawed human being, and my perspective on the world reflects that. A turn of the vulnerability dial has opened up connections to other people, while turning away pity, judgment, fear, and shame. Meanwhile, when I am to create spaces for vulnerability, permission is granted to have open and honest conversations about mental health conditions on a larger scale. But I would never have learned these lessons without having been humbled by this disease.
Perhaps the thing I liked best about Dr. Hill’s memoir is that he proposes some solutions. He talks about the importance of fighting stigma, how he finds it everywhere, and how the medical field equates mental illnesses with weakness, thereby perpetuating a self-deprecating cycle in those who have them.
In palliative care, there is an acronym – SPIKES (Set up, Perception, Invitation, Knowledge, Explore emotions, and Summary) that provides guidelines for how to deliver bad news to a family. Dr. Hill suggests using this format to discuss mental health and addictions with patients, colleagues, students. He talks about having “Compassion Rounds” to provide a safe space for his colleagues to talk about their emotional reactions to treating very ill children. And he talks about providing mental health care for trainees as an “opt out” – he schedules all his residents for a counseling session – they can cancel without repercussion, but this serves to “normalize” seeking care. I love the idea that each resident might have someone they’ve met with at least once whom they can call if the going gets rough. “As a result,” Dr. Hill writes, “once secretive conversations about attending counseling happen openly, and the physicians actually feel more comfortable going.”
Adam Hill’s memoir is short, it’s an engaging read, his openness is refreshing, and his plea to let doctors be human beings with human problems is so needed in medicine today. Thank you, Adam.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatry Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Adam B. Hill, MD, is home on a “staycation” this week. Today, he took a 3-hour nap. I know this because I follow Dr. Hill on Twitter, where he has an active feed, a lot of posts, retweets, and more than 20,000 followers.
I also know from Twitter that he is married and has three young children, that he was once suicidal, and has been treated for major depression and alcoholism. As a palliative care doctor, Dr. Hill was required by his state medical board to blow into a breathalyzer several times a day for 5 years – something he felt quite shamed by – and while I’ve never met him, I felt just a little bit proud of this stranger when he was released from the medical board’s oversight.
Dr. Hill’s memoir, “Long Walk Out of the Woods: A Physician’s Story of Addiction, Depression, Hope, and Recovery” (Central Recovery Press, 2019) is the culmination of his efforts to use his difficulties as a way of offering hope and connection to anyone who struggled as he has, or to anyone who has struggled at all. Like his Twitter feed, it is a display of vulnerability and gratitude by someone who has been through dark times then returned to conquer his monsters.
He begins by setting the stage for us. “My name is Adam,” he announces in the preface. He tells us his various titles: human being, husband, father, physician, recovering alcoholic, and psychiatric patient. “In the midst of these struggles, working in modern medicine fractured my identity, stole my authenticity, and left me a shell of the person I wanted to be.”
We learn that he tried to buy a gun, but there was a waiting period and he could not purchase the firearm. Instead, he walked into the woods to drink himself to death, with sleeping pills as an add-on – obviously, he didn’t die, and his journey back from his failed suicidal mission is the meat of the book.
Dr. Hill was a quiet and timid child, and he was bullied at school in a way that has lingered on. He struggles with perfectionism and with a sense of never quite belonging. He was a good student, and later a competitive tennis player who was destined for a regional competition until he broke his ankle after drinking just days before the competition. He did well in college, felt more accepted, and went on to medical school after getting in from the wait list. He went on to do a pediatrics residency, and he and his wife moved from Indiana to North Carolina so he could do a hematology oncology fellowship. It was toward the end of his 2-year fellowship when he tried to purchase a gun, then walked into those woods.
His wife called, asked him to come to dinner, and he left the woods before he’d overdosed. After a meeting with his wife, parents, and sister, he returned to psychiatric care, restarted antidepressants, went to Alcoholics Anonymous, and told his employer that he had a problem. This admission started a distressing series of events, including years of being monitored by state medical boards and being labeled an “impaired physician.”
This is the only thing I didn’t like about Dr. Hill’s memoir: As open as he is about his emotional life, there were pieces missing with respect to what actually happened. At this point, I was befuddled as to why he self-reported his difficulties, and it wasn’t until he talked about starting a second fellowship in palliative care in his home state of Indiana that I could fill in some missing pieces. Dr. Hill and his wife purchased a house, and in November, he started his fellowship. The timing was off from the usual start in July, and I realized that perhaps he had gone to an inpatient setting for a number of months – his disclosure to his employer was voluntary, but his treatment likely interfered with his training and couldn’t be hidden. What else transpired he hints at: bottles hidden, driving while intoxicated, a nurse who gave him IV hydration when he came to work with a hangover.
From here, Dr. Hill’s story becomes every doctor’s nightmare. Settled into his new house and weeks into his fellowship, he is called in and fired: His application for a medical license in Indiana has been denied because of his addiction history. He met with a friend of his father’s who worked in a large pediatrics practice. The meeting went well, but the group felt he was too much of a malpractice risk.
He now needs to pay his mortgage and student loans, so he takes a position in Oklahoma with the Indian Health Service. He’s 700 miles from home, living alone in a hotel room, feeling like the work is beneath him, and the chapter is titled “Exile.” His new boss greets him with, “Listen, we all had our own stories that led us here.” Surprisingly, he likes the work and feels supported. If only it weren’t for all that loneliness, and not surprisingly, he relapses despite the mandated breathalyzer. Six beers later, and Dr. Hill is off to Chicago for a rehab program, then back to Oklahoma to finish off his stint.
What happens next is the second time I wondered about the plot of his life: Through “connections and concession,” he returns to Indiana for the palliative care fellowship, and goes on to work at Riley Children’s Hospital.
When a colleague unexpectedly dies from suicide, Dr. Hill tells others that he, too, once entertained suicidal thoughts. The story from here gets better and better: – to conquer their shame, to share their stories, to feel less alone. He and his wife become parents, he remains sober and healthy, and therapy leads him to a place of self-discovery and success.
Intertwined with telling his story, Dr. Hill takes on some of the institutional issues surrounding addiction and mental illness. He feels shamed and punished by the state medical board that mandates the terms of his medical license. Any physician who reads this book will think twice about revealing a diagnosis of depression or substance use disorder. It’s not a new idea that to protect the public, medical boards should ask about current impairments, not a past history or conditions that have been successfully treated. They should encourage treatment, not punish those who seek care.
Dr. Hill writes about how helpful it has been to allow himself to be vulnerable in the aftermath:
In my experience, the more vulnerability I show, the more opportunities I have to connect to other people. I learned the hard way that when I hide my true self from others, I spiral toward shame. Conversely, when I bury my shame, I begin to accept myself as a beautifully flawed human being, and my perspective on the world reflects that. A turn of the vulnerability dial has opened up connections to other people, while turning away pity, judgment, fear, and shame. Meanwhile, when I am to create spaces for vulnerability, permission is granted to have open and honest conversations about mental health conditions on a larger scale. But I would never have learned these lessons without having been humbled by this disease.
Perhaps the thing I liked best about Dr. Hill’s memoir is that he proposes some solutions. He talks about the importance of fighting stigma, how he finds it everywhere, and how the medical field equates mental illnesses with weakness, thereby perpetuating a self-deprecating cycle in those who have them.
In palliative care, there is an acronym – SPIKES (Set up, Perception, Invitation, Knowledge, Explore emotions, and Summary) that provides guidelines for how to deliver bad news to a family. Dr. Hill suggests using this format to discuss mental health and addictions with patients, colleagues, students. He talks about having “Compassion Rounds” to provide a safe space for his colleagues to talk about their emotional reactions to treating very ill children. And he talks about providing mental health care for trainees as an “opt out” – he schedules all his residents for a counseling session – they can cancel without repercussion, but this serves to “normalize” seeking care. I love the idea that each resident might have someone they’ve met with at least once whom they can call if the going gets rough. “As a result,” Dr. Hill writes, “once secretive conversations about attending counseling happen openly, and the physicians actually feel more comfortable going.”
Adam Hill’s memoir is short, it’s an engaging read, his openness is refreshing, and his plea to let doctors be human beings with human problems is so needed in medicine today. Thank you, Adam.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatry Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Adam B. Hill, MD, is home on a “staycation” this week. Today, he took a 3-hour nap. I know this because I follow Dr. Hill on Twitter, where he has an active feed, a lot of posts, retweets, and more than 20,000 followers.
I also know from Twitter that he is married and has three young children, that he was once suicidal, and has been treated for major depression and alcoholism. As a palliative care doctor, Dr. Hill was required by his state medical board to blow into a breathalyzer several times a day for 5 years – something he felt quite shamed by – and while I’ve never met him, I felt just a little bit proud of this stranger when he was released from the medical board’s oversight.
Dr. Hill’s memoir, “Long Walk Out of the Woods: A Physician’s Story of Addiction, Depression, Hope, and Recovery” (Central Recovery Press, 2019) is the culmination of his efforts to use his difficulties as a way of offering hope and connection to anyone who struggled as he has, or to anyone who has struggled at all. Like his Twitter feed, it is a display of vulnerability and gratitude by someone who has been through dark times then returned to conquer his monsters.
He begins by setting the stage for us. “My name is Adam,” he announces in the preface. He tells us his various titles: human being, husband, father, physician, recovering alcoholic, and psychiatric patient. “In the midst of these struggles, working in modern medicine fractured my identity, stole my authenticity, and left me a shell of the person I wanted to be.”
We learn that he tried to buy a gun, but there was a waiting period and he could not purchase the firearm. Instead, he walked into the woods to drink himself to death, with sleeping pills as an add-on – obviously, he didn’t die, and his journey back from his failed suicidal mission is the meat of the book.
Dr. Hill was a quiet and timid child, and he was bullied at school in a way that has lingered on. He struggles with perfectionism and with a sense of never quite belonging. He was a good student, and later a competitive tennis player who was destined for a regional competition until he broke his ankle after drinking just days before the competition. He did well in college, felt more accepted, and went on to medical school after getting in from the wait list. He went on to do a pediatrics residency, and he and his wife moved from Indiana to North Carolina so he could do a hematology oncology fellowship. It was toward the end of his 2-year fellowship when he tried to purchase a gun, then walked into those woods.
His wife called, asked him to come to dinner, and he left the woods before he’d overdosed. After a meeting with his wife, parents, and sister, he returned to psychiatric care, restarted antidepressants, went to Alcoholics Anonymous, and told his employer that he had a problem. This admission started a distressing series of events, including years of being monitored by state medical boards and being labeled an “impaired physician.”
This is the only thing I didn’t like about Dr. Hill’s memoir: As open as he is about his emotional life, there were pieces missing with respect to what actually happened. At this point, I was befuddled as to why he self-reported his difficulties, and it wasn’t until he talked about starting a second fellowship in palliative care in his home state of Indiana that I could fill in some missing pieces. Dr. Hill and his wife purchased a house, and in November, he started his fellowship. The timing was off from the usual start in July, and I realized that perhaps he had gone to an inpatient setting for a number of months – his disclosure to his employer was voluntary, but his treatment likely interfered with his training and couldn’t be hidden. What else transpired he hints at: bottles hidden, driving while intoxicated, a nurse who gave him IV hydration when he came to work with a hangover.
From here, Dr. Hill’s story becomes every doctor’s nightmare. Settled into his new house and weeks into his fellowship, he is called in and fired: His application for a medical license in Indiana has been denied because of his addiction history. He met with a friend of his father’s who worked in a large pediatrics practice. The meeting went well, but the group felt he was too much of a malpractice risk.
He now needs to pay his mortgage and student loans, so he takes a position in Oklahoma with the Indian Health Service. He’s 700 miles from home, living alone in a hotel room, feeling like the work is beneath him, and the chapter is titled “Exile.” His new boss greets him with, “Listen, we all had our own stories that led us here.” Surprisingly, he likes the work and feels supported. If only it weren’t for all that loneliness, and not surprisingly, he relapses despite the mandated breathalyzer. Six beers later, and Dr. Hill is off to Chicago for a rehab program, then back to Oklahoma to finish off his stint.
What happens next is the second time I wondered about the plot of his life: Through “connections and concession,” he returns to Indiana for the palliative care fellowship, and goes on to work at Riley Children’s Hospital.
When a colleague unexpectedly dies from suicide, Dr. Hill tells others that he, too, once entertained suicidal thoughts. The story from here gets better and better: – to conquer their shame, to share their stories, to feel less alone. He and his wife become parents, he remains sober and healthy, and therapy leads him to a place of self-discovery and success.
Intertwined with telling his story, Dr. Hill takes on some of the institutional issues surrounding addiction and mental illness. He feels shamed and punished by the state medical board that mandates the terms of his medical license. Any physician who reads this book will think twice about revealing a diagnosis of depression or substance use disorder. It’s not a new idea that to protect the public, medical boards should ask about current impairments, not a past history or conditions that have been successfully treated. They should encourage treatment, not punish those who seek care.
Dr. Hill writes about how helpful it has been to allow himself to be vulnerable in the aftermath:
In my experience, the more vulnerability I show, the more opportunities I have to connect to other people. I learned the hard way that when I hide my true self from others, I spiral toward shame. Conversely, when I bury my shame, I begin to accept myself as a beautifully flawed human being, and my perspective on the world reflects that. A turn of the vulnerability dial has opened up connections to other people, while turning away pity, judgment, fear, and shame. Meanwhile, when I am to create spaces for vulnerability, permission is granted to have open and honest conversations about mental health conditions on a larger scale. But I would never have learned these lessons without having been humbled by this disease.
Perhaps the thing I liked best about Dr. Hill’s memoir is that he proposes some solutions. He talks about the importance of fighting stigma, how he finds it everywhere, and how the medical field equates mental illnesses with weakness, thereby perpetuating a self-deprecating cycle in those who have them.
In palliative care, there is an acronym – SPIKES (Set up, Perception, Invitation, Knowledge, Explore emotions, and Summary) that provides guidelines for how to deliver bad news to a family. Dr. Hill suggests using this format to discuss mental health and addictions with patients, colleagues, students. He talks about having “Compassion Rounds” to provide a safe space for his colleagues to talk about their emotional reactions to treating very ill children. And he talks about providing mental health care for trainees as an “opt out” – he schedules all his residents for a counseling session – they can cancel without repercussion, but this serves to “normalize” seeking care. I love the idea that each resident might have someone they’ve met with at least once whom they can call if the going gets rough. “As a result,” Dr. Hill writes, “once secretive conversations about attending counseling happen openly, and the physicians actually feel more comfortable going.”
Adam Hill’s memoir is short, it’s an engaging read, his openness is refreshing, and his plea to let doctors be human beings with human problems is so needed in medicine today. Thank you, Adam.
Dr. Miller is coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatry Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Addiction specialist charged in $681 million treatment fraud case
The federal government has charged a Florida addiction medicine specialist in what it says was a scheme to defraud Medicare and private insurers, charging them roughly $681 million over about a decade for lab tests, office visits, therapy sessions, and other services that were either unnecessary or never delivered.
The Department of Justice and the Attorney for the Southern District of Florida are prosecuting Michael Ligotti, DO, 46, saying that he preyed on individuals seeking substance abuse treatment. They have yet to issue a formal indictment.
“The substance abuse treatment fraud allegedly perpetrated by the defendant sacrificed the genuine care of vulnerable patients at a time when they urgently needed a trusted health care provider,” U.S. Attorney Ariana Fajardo Orshan, Southern District of Florida, said in a statement.
“Health care providers who allow greed to take precedence over their Hippocratic Oath and participate in these schemes are criminals and will be held accountable for their unscrupulous conduct,” she added.
Dr. Ligotti was charged July 31. The prosecutors were seeking to detain him until trial. However, a judge approved his bond today and he is free on bond, according to Ligotti’s attorney, Ben Curtis.
“As is always the case with any criminal matter, the burden of proof rests entirely with the government,” Mr. Curtis said in an interview.
“In this instance, we do not believe the US Department of Justice’s claims – and that is exactly what they are at this point, just one-sided claims – will reconcile with actual evidence at a future trial,” he said.
Mr. Curtis added that Dr. Ligotti “looks forward to establishing his innocence.”
Unnecessary urine tests
The government alleges that Dr. Ligotti played a central role in a scheme in which Medicare and private insurers paid about $121 million to cover some $680 million in charges from 2011 to 2020.
According to the prosecutors, Dr. Ligotti received a fee for becoming a “purported” medical director of about 50 addiction treatment facilities and sober homes – and that he issued 136 separate standing orders for medically unnecessary urinalysis (UA) tests.
The labs allegedly paid occasional kickbacks to the facilities and homes, and those facilities in turn were required to have their patients treated by Dr. Ligotti’s clinic, Whole Health, which is based in Delray Beach, Fla.
This allowed Dr. Ligotti to “bill hundreds of millions of dollars in additional fraudulent treatments, including unnecessary and expensive UAs, costly blood tests, nonexistent therapy sessions, office visits, and other unnecessary services, regardless of whether such treatment and testing were medically necessary and/or actually provided,” alleges the government.
Urine tests have been exploited before by addiction treatment clinics as a revenue generator. Kaiser Health News reported in 2017 that a single nurse practitioner at one pain clinic in Tennessee generated $1 million in billings to Medicare for drug-related urine tests in a single year.
Also in 2017, The New York Times reported that a single patient had been billed $260,000 for urine tests by his treatment center.
The federal government alleges that Dr. Ligotti also “billed for psychiatric services and therapy sessions that never happened, and that he and his staff were not qualified to conduct.”
In addition, they assert that Dr. Ligotti improperly prescribed controlled substances, including large quantities of buprenorphine/Suboxone, often exceeding the number of patients he was legally authorized to treat or giving it to patients who did not require the medications.
Dr. Ligotti may not be practicing any longer. His clinic’s website features a message that the practice will be closed as of Aug. 7.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has charged a Florida addiction medicine specialist in what it says was a scheme to defraud Medicare and private insurers, charging them roughly $681 million over about a decade for lab tests, office visits, therapy sessions, and other services that were either unnecessary or never delivered.
The Department of Justice and the Attorney for the Southern District of Florida are prosecuting Michael Ligotti, DO, 46, saying that he preyed on individuals seeking substance abuse treatment. They have yet to issue a formal indictment.
“The substance abuse treatment fraud allegedly perpetrated by the defendant sacrificed the genuine care of vulnerable patients at a time when they urgently needed a trusted health care provider,” U.S. Attorney Ariana Fajardo Orshan, Southern District of Florida, said in a statement.
“Health care providers who allow greed to take precedence over their Hippocratic Oath and participate in these schemes are criminals and will be held accountable for their unscrupulous conduct,” she added.
Dr. Ligotti was charged July 31. The prosecutors were seeking to detain him until trial. However, a judge approved his bond today and he is free on bond, according to Ligotti’s attorney, Ben Curtis.
“As is always the case with any criminal matter, the burden of proof rests entirely with the government,” Mr. Curtis said in an interview.
“In this instance, we do not believe the US Department of Justice’s claims – and that is exactly what they are at this point, just one-sided claims – will reconcile with actual evidence at a future trial,” he said.
Mr. Curtis added that Dr. Ligotti “looks forward to establishing his innocence.”
Unnecessary urine tests
The government alleges that Dr. Ligotti played a central role in a scheme in which Medicare and private insurers paid about $121 million to cover some $680 million in charges from 2011 to 2020.
According to the prosecutors, Dr. Ligotti received a fee for becoming a “purported” medical director of about 50 addiction treatment facilities and sober homes – and that he issued 136 separate standing orders for medically unnecessary urinalysis (UA) tests.
The labs allegedly paid occasional kickbacks to the facilities and homes, and those facilities in turn were required to have their patients treated by Dr. Ligotti’s clinic, Whole Health, which is based in Delray Beach, Fla.
This allowed Dr. Ligotti to “bill hundreds of millions of dollars in additional fraudulent treatments, including unnecessary and expensive UAs, costly blood tests, nonexistent therapy sessions, office visits, and other unnecessary services, regardless of whether such treatment and testing were medically necessary and/or actually provided,” alleges the government.
Urine tests have been exploited before by addiction treatment clinics as a revenue generator. Kaiser Health News reported in 2017 that a single nurse practitioner at one pain clinic in Tennessee generated $1 million in billings to Medicare for drug-related urine tests in a single year.
Also in 2017, The New York Times reported that a single patient had been billed $260,000 for urine tests by his treatment center.
The federal government alleges that Dr. Ligotti also “billed for psychiatric services and therapy sessions that never happened, and that he and his staff were not qualified to conduct.”
In addition, they assert that Dr. Ligotti improperly prescribed controlled substances, including large quantities of buprenorphine/Suboxone, often exceeding the number of patients he was legally authorized to treat or giving it to patients who did not require the medications.
Dr. Ligotti may not be practicing any longer. His clinic’s website features a message that the practice will be closed as of Aug. 7.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has charged a Florida addiction medicine specialist in what it says was a scheme to defraud Medicare and private insurers, charging them roughly $681 million over about a decade for lab tests, office visits, therapy sessions, and other services that were either unnecessary or never delivered.
The Department of Justice and the Attorney for the Southern District of Florida are prosecuting Michael Ligotti, DO, 46, saying that he preyed on individuals seeking substance abuse treatment. They have yet to issue a formal indictment.
“The substance abuse treatment fraud allegedly perpetrated by the defendant sacrificed the genuine care of vulnerable patients at a time when they urgently needed a trusted health care provider,” U.S. Attorney Ariana Fajardo Orshan, Southern District of Florida, said in a statement.
“Health care providers who allow greed to take precedence over their Hippocratic Oath and participate in these schemes are criminals and will be held accountable for their unscrupulous conduct,” she added.
Dr. Ligotti was charged July 31. The prosecutors were seeking to detain him until trial. However, a judge approved his bond today and he is free on bond, according to Ligotti’s attorney, Ben Curtis.
“As is always the case with any criminal matter, the burden of proof rests entirely with the government,” Mr. Curtis said in an interview.
“In this instance, we do not believe the US Department of Justice’s claims – and that is exactly what they are at this point, just one-sided claims – will reconcile with actual evidence at a future trial,” he said.
Mr. Curtis added that Dr. Ligotti “looks forward to establishing his innocence.”
Unnecessary urine tests
The government alleges that Dr. Ligotti played a central role in a scheme in which Medicare and private insurers paid about $121 million to cover some $680 million in charges from 2011 to 2020.
According to the prosecutors, Dr. Ligotti received a fee for becoming a “purported” medical director of about 50 addiction treatment facilities and sober homes – and that he issued 136 separate standing orders for medically unnecessary urinalysis (UA) tests.
The labs allegedly paid occasional kickbacks to the facilities and homes, and those facilities in turn were required to have their patients treated by Dr. Ligotti’s clinic, Whole Health, which is based in Delray Beach, Fla.
This allowed Dr. Ligotti to “bill hundreds of millions of dollars in additional fraudulent treatments, including unnecessary and expensive UAs, costly blood tests, nonexistent therapy sessions, office visits, and other unnecessary services, regardless of whether such treatment and testing were medically necessary and/or actually provided,” alleges the government.
Urine tests have been exploited before by addiction treatment clinics as a revenue generator. Kaiser Health News reported in 2017 that a single nurse practitioner at one pain clinic in Tennessee generated $1 million in billings to Medicare for drug-related urine tests in a single year.
Also in 2017, The New York Times reported that a single patient had been billed $260,000 for urine tests by his treatment center.
The federal government alleges that Dr. Ligotti also “billed for psychiatric services and therapy sessions that never happened, and that he and his staff were not qualified to conduct.”
In addition, they assert that Dr. Ligotti improperly prescribed controlled substances, including large quantities of buprenorphine/Suboxone, often exceeding the number of patients he was legally authorized to treat or giving it to patients who did not require the medications.
Dr. Ligotti may not be practicing any longer. His clinic’s website features a message that the practice will be closed as of Aug. 7.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The best and worst states for health care in 2020
according to the personal finance website WalletHub.
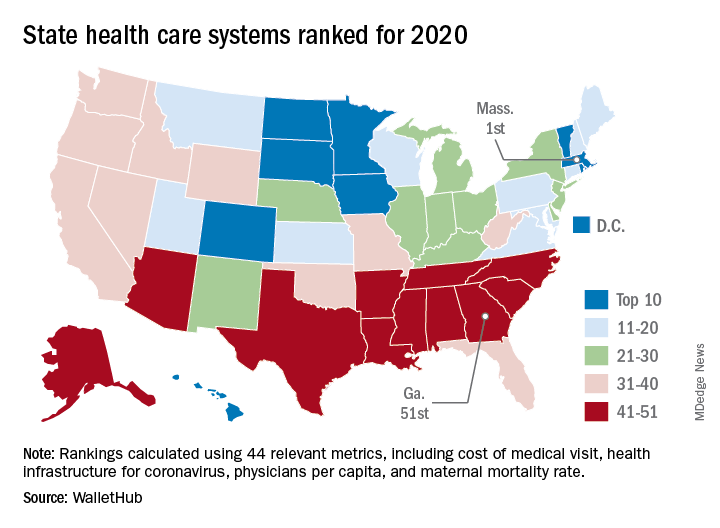
The Bay State finds itself at the top of the company’s annual ranking of state health care systems this year after finishing second in 2019 to Minnesota, which is now ranked second. Rhode Island is third this year, followed by Washington, D.C., and North Dakota, WalletHub reported Aug. 3.
The inclusion of Washington, D.C., allowed Georgia to finish 51st out of 50 states, just below the quartet of Louisiana (50th), Alabama (49th), North Carolina (48th), and Mississippi (47th). Alaska, which occupied the bottom spot in 2019, moved up to 42nd this year, the analysis showed.
The rankings are based on 44 (up from 43 last year) metrics that are grouped into three broad categories: cost (6 metrics), access (24 metrics), and outcomes (14 metrics). The one new measure added for 2020? That would be health infrastructure for coronavirus, which is itself based on a different WalletHub ranking.
Massachusetts’ top finish this year was driven by strong showings in such metrics as average monthly insurance premium (first), physicians per capita (second), insured children (first) and adults (first), and infant mortality rate (fourth). The state was 1st overall in outcomes and 4th in access but only 20th in cost, the company said.
Positive signs among the lowest-ranked states include Louisiana’s 18th-place finish in access, ahead of such top 10 states as Iowa and Hawaii, and Mississippi’s 17th in cost, which is higher than four of the states in the top 10, including Massachusetts, WalletHub said in the report.
Data for the analysis came from 22 different sources, including the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American Telemedicine Association.
according to the personal finance website WalletHub.

The Bay State finds itself at the top of the company’s annual ranking of state health care systems this year after finishing second in 2019 to Minnesota, which is now ranked second. Rhode Island is third this year, followed by Washington, D.C., and North Dakota, WalletHub reported Aug. 3.
The inclusion of Washington, D.C., allowed Georgia to finish 51st out of 50 states, just below the quartet of Louisiana (50th), Alabama (49th), North Carolina (48th), and Mississippi (47th). Alaska, which occupied the bottom spot in 2019, moved up to 42nd this year, the analysis showed.
The rankings are based on 44 (up from 43 last year) metrics that are grouped into three broad categories: cost (6 metrics), access (24 metrics), and outcomes (14 metrics). The one new measure added for 2020? That would be health infrastructure for coronavirus, which is itself based on a different WalletHub ranking.
Massachusetts’ top finish this year was driven by strong showings in such metrics as average monthly insurance premium (first), physicians per capita (second), insured children (first) and adults (first), and infant mortality rate (fourth). The state was 1st overall in outcomes and 4th in access but only 20th in cost, the company said.
Positive signs among the lowest-ranked states include Louisiana’s 18th-place finish in access, ahead of such top 10 states as Iowa and Hawaii, and Mississippi’s 17th in cost, which is higher than four of the states in the top 10, including Massachusetts, WalletHub said in the report.
Data for the analysis came from 22 different sources, including the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American Telemedicine Association.
according to the personal finance website WalletHub.

The Bay State finds itself at the top of the company’s annual ranking of state health care systems this year after finishing second in 2019 to Minnesota, which is now ranked second. Rhode Island is third this year, followed by Washington, D.C., and North Dakota, WalletHub reported Aug. 3.
The inclusion of Washington, D.C., allowed Georgia to finish 51st out of 50 states, just below the quartet of Louisiana (50th), Alabama (49th), North Carolina (48th), and Mississippi (47th). Alaska, which occupied the bottom spot in 2019, moved up to 42nd this year, the analysis showed.
The rankings are based on 44 (up from 43 last year) metrics that are grouped into three broad categories: cost (6 metrics), access (24 metrics), and outcomes (14 metrics). The one new measure added for 2020? That would be health infrastructure for coronavirus, which is itself based on a different WalletHub ranking.
Massachusetts’ top finish this year was driven by strong showings in such metrics as average monthly insurance premium (first), physicians per capita (second), insured children (first) and adults (first), and infant mortality rate (fourth). The state was 1st overall in outcomes and 4th in access but only 20th in cost, the company said.
Positive signs among the lowest-ranked states include Louisiana’s 18th-place finish in access, ahead of such top 10 states as Iowa and Hawaii, and Mississippi’s 17th in cost, which is higher than four of the states in the top 10, including Massachusetts, WalletHub said in the report.
Data for the analysis came from 22 different sources, including the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Association of American Medical Colleges, and the American Telemedicine Association.
FDA okays new indication for esketamine nasal spray
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the supplemental new drug application for esketamine nasal spray (Spravato, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) to treat depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and acute suicidal ideation or behavior.
The FDA approved esketamine nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression in March 2019, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
– which evaluated the efficacy and safety of the nasal spray in addition to a comprehensive standard of care in adults with MDD who had active suicidal ideation with intent.
The standard of care included initial hospitalization, a newly initiated or optimized oral antidepressant, and twice-weekly treatment visits for 4 weeks. During that time, patients received esketamine nasal spray 84 mg or placebo nasal spray.
Results from the trials showed that the active treatment significantly reduced depressive symptoms within 24 hours, with some patients starting to respond as early as 4 hours after the first dose.
“Traditional oral antidepressants need weeks or more to take effect, so the availability of a medicine that can begin providing relief within a day is potentially life changing,” Theresa Nguyen, chief program officer at Mental Health America, said in a company news release.
“The clinical trials supporting this new indication provide compelling evidence that esketamine may offer clinicians a new way to provide support to patients quickly in the midst of an urgent depressive episode and help set them on the path to remission,” Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program, New Haven, Conn., and esketamine clinical trial investigator, said in the same release.
A full course of treatment for MDD with acute suicidal ideation or behavior is twice weekly for 4 weeks, “after which evidence of therapeutic benefit should be evaluated to determine need for continued treatment,” the company said.
Because of the risk for serious adverse events, including sedation and dissociation, and the potential for abuse or misuse, esketamine nasal spray is only available through a restricted distribution system – the Spravato Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS).
The patient self-administers esketamine nasal spray only in REMS-certified health care settings. Patients are not permitted to take the drug home.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the supplemental new drug application for esketamine nasal spray (Spravato, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) to treat depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and acute suicidal ideation or behavior.
The FDA approved esketamine nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression in March 2019, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
– which evaluated the efficacy and safety of the nasal spray in addition to a comprehensive standard of care in adults with MDD who had active suicidal ideation with intent.
The standard of care included initial hospitalization, a newly initiated or optimized oral antidepressant, and twice-weekly treatment visits for 4 weeks. During that time, patients received esketamine nasal spray 84 mg or placebo nasal spray.
Results from the trials showed that the active treatment significantly reduced depressive symptoms within 24 hours, with some patients starting to respond as early as 4 hours after the first dose.
“Traditional oral antidepressants need weeks or more to take effect, so the availability of a medicine that can begin providing relief within a day is potentially life changing,” Theresa Nguyen, chief program officer at Mental Health America, said in a company news release.
“The clinical trials supporting this new indication provide compelling evidence that esketamine may offer clinicians a new way to provide support to patients quickly in the midst of an urgent depressive episode and help set them on the path to remission,” Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program, New Haven, Conn., and esketamine clinical trial investigator, said in the same release.
A full course of treatment for MDD with acute suicidal ideation or behavior is twice weekly for 4 weeks, “after which evidence of therapeutic benefit should be evaluated to determine need for continued treatment,” the company said.
Because of the risk for serious adverse events, including sedation and dissociation, and the potential for abuse or misuse, esketamine nasal spray is only available through a restricted distribution system – the Spravato Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS).
The patient self-administers esketamine nasal spray only in REMS-certified health care settings. Patients are not permitted to take the drug home.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the supplemental new drug application for esketamine nasal spray (Spravato, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) to treat depressive symptoms in adults with major depressive disorder (MDD) and acute suicidal ideation or behavior.
The FDA approved esketamine nasal spray for treatment-resistant depression in March 2019, as reported by Medscape Medical News.
– which evaluated the efficacy and safety of the nasal spray in addition to a comprehensive standard of care in adults with MDD who had active suicidal ideation with intent.
The standard of care included initial hospitalization, a newly initiated or optimized oral antidepressant, and twice-weekly treatment visits for 4 weeks. During that time, patients received esketamine nasal spray 84 mg or placebo nasal spray.
Results from the trials showed that the active treatment significantly reduced depressive symptoms within 24 hours, with some patients starting to respond as early as 4 hours after the first dose.
“Traditional oral antidepressants need weeks or more to take effect, so the availability of a medicine that can begin providing relief within a day is potentially life changing,” Theresa Nguyen, chief program officer at Mental Health America, said in a company news release.
“The clinical trials supporting this new indication provide compelling evidence that esketamine may offer clinicians a new way to provide support to patients quickly in the midst of an urgent depressive episode and help set them on the path to remission,” Gerard Sanacora, MD, PhD, director of the Yale Depression Research Program, New Haven, Conn., and esketamine clinical trial investigator, said in the same release.
A full course of treatment for MDD with acute suicidal ideation or behavior is twice weekly for 4 weeks, “after which evidence of therapeutic benefit should be evaluated to determine need for continued treatment,” the company said.
Because of the risk for serious adverse events, including sedation and dissociation, and the potential for abuse or misuse, esketamine nasal spray is only available through a restricted distribution system – the Spravato Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS).
The patient self-administers esketamine nasal spray only in REMS-certified health care settings. Patients are not permitted to take the drug home.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.




















