User login
Clinical Endocrinology News is an independent news source that provides endocrinologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the endocrinologist's practice. Specialty topics include Diabetes, Lipid & Metabolic Disorders Menopause, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Pediatric Endocrinology, Pituitary, Thyroid & Adrenal Disorders, and Reproductive Endocrinology. Featured content includes Commentaries, Implementin Health Reform, Law & Medicine, and In the Loop, the blog of Clinical Endocrinology News. Clinical Endocrinology News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
addict
addicted
addicting
addiction
adult sites
alcohol
antibody
ass
attorney
audit
auditor
babies
babpa
baby
ban
banned
banning
best
bisexual
bitch
bleach
blog
blow job
bondage
boobs
booty
buy
cannabis
certificate
certification
certified
cheap
cheapest
class action
cocaine
cock
counterfeit drug
crack
crap
crime
criminal
cunt
curable
cure
dangerous
dangers
dead
deadly
death
defend
defended
depedent
dependence
dependent
detergent
dick
die
dildo
drug abuse
drug recall
dying
fag
fake
fatal
fatalities
fatality
free
fuck
gangs
gingivitis
guns
hardcore
herbal
herbs
heroin
herpes
home remedies
homo
horny
hypersensitivity
hypoglycemia treatment
illegal drug use
illegal use of prescription
incest
infant
infants
job
ketoacidosis
kill
killer
killing
kinky
law suit
lawsuit
lawyer
lesbian
marijuana
medicine for hypoglycemia
murder
naked
natural
newborn
nigger
noise
nude
nudity
orgy
over the counter
overdosage
overdose
overdosed
overdosing
penis
pimp
pistol
porn
porno
pornographic
pornography
prison
profanity
purchase
purchasing
pussy
queer
rape
rapist
recall
recreational drug
rob
robberies
sale
sales
sex
sexual
shit
shoot
slut
slutty
stole
stolen
store
sue
suicidal
suicide
supplements
supply company
theft
thief
thieves
tit
toddler
toddlers
toxic
toxin
tragedy
treating dka
treating hypoglycemia
treatment for hypoglycemia
vagina
violence
whore
withdrawal
without prescription
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-imn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Irregular sleep tied to markers of atherosclerosis
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Physicians and clinicians should be required to get flu shots: Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Therapy app cut A1c, drug intensification in T2D
An investigational smartphone app that delivers cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to people with type 2 diabetes led to a significant 10 percentage point cut in the incidence of antihyperglycemic-drug intensification during 6 months’ follow-up, when compared with a control phone app, in the CBT app’s pivotal trial with 669 randomized patients.
Previously reported results from this trial, called BT-001, showed that people randomized to use the CBT app had a significant average 0.4 percentage point reduction in hemoglobin A1c, compared with controls, after 90 days for the trial’s primary endpoint, and a significant 0.29 percentage point reduction in A1c, compared with controls, after 180 days.
The new finding, that these incremental drops in A1c occurred while the control patients also received significantly more intensification of their antihyperglycemic medication, provides further evidence for the efficacy of the CBT app, said Marc P. Bonaca, MD, in a press conference organized by the American College of Cardiology in advance of its upcoming joint scientific sessions.
The CBT app “significantly reduced A1c despite less intensification of antihyperglycemic therapy,” noted Dr. Bonaca, a vascular medicine specialist and executive director of CPC Clinical Research, an academic research organization created by and affiliated with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Based on positive safety and efficacy findings from the primary-endpoint phase of the BT-001 trial, reported in Diabetes Care, the company developing the CBT app, Better Therapeutics, said in a statement that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration accepted the company’s application for de novo classification and marketing approval of the app, also called BT-001. If the agency grants this classification and marketing approval, the company plans to sell the app on a prescription basis for use by people with type 2 diabetes.
CBT app gives patients problem-solving skills
CBT gives people with type 2 diabetes a way to better understand their unhelpful behaviors and motivations and teaches them problem-solving skills. Providing this counseling via an app addresses the challenge of making the intervention scalable to a broad range of patients, Dr. Bonaca explained.
“Clinicians are frustrated by trying to produce behavioral change” in patients. The BT-001 app “provides a new avenue to treatment,” an approach that clinicians have been “very receptive” to using “once they understand the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “The effect at 90 days was very similar to what a drug would do. It’s not just drugs any more” for treating people with type 2 diabetes, he declared.
“CBT is an empirically supported psychotherapy for a variety of emotional disorders, and it has been adapted to target specific emotional distress in the context of chronic illness,” commented Amit Shapira, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston who has not been involved in the BT-001 studies. A CBT protocol designed for diabetes, CBT for Adherence and Depression “has been shown to have a positive impact on depression symptoms and glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Shapira noted in an interview.
“Once a physician explains this [CBT] app and patients understand how to use it, then patients will be happy to use it,” commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, who moderated the press conference. “We may see an explosion of apps like this one, designed to help better control” other chronic disorders, such as elevated blood pressure or abnormal lipid levels, Dr. Grapsa predicted. “I’m very optimistic that these apps have a great future in health care.”
Forty percent relative cut in new antihyperglycemic drug use
The BT-001 study randomized 669 adults with smartphone access and type 2 diabetes at any of six U.S. sites. The enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 11 years, and an A1c of 7%-10.9% with an average level of 8.2%. Participants had to be on a stable medication regimen for at least 3 months but not using prandial insulin, and their treatment regimens could undergo adjustment during the trial. At baseline, each subject was on an average of 2.1 antihyperglycemic medications, including 90% on metformin and 42% on a sulfonylurea.
The new results reported by Dr. Bonaca showed that, during follow-up, people using the app had a 14.4% rate of antihyperglycemic drug intensification compared with a 24.4% rate among the controls, a roughly 40% relative decrease in new antihyperglycemic medication use. In addition, among those using insulin at baseline, 3.8% of controls increased their insulin dose, compared with 1.5% of those using the CBT app, while insulin doses decreased in 0.9% of the control subjects and in 2.2% of those using the BT-001 app.
Further study findings, first reported by Dr. Bonaca at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in late 2022, also showed a clear dose-response pattern for the CBT app: the more CBT lessons a person completed, the greater their reduction in A1c over 180 days of app use. People who used the app fewer than 10 times had an average reduction from baseline in their A1c of less than 0.1 percentage points. Among those who used the app 10-20 times (a subgroup with roughly one-third of the people randomized to app use), average A1c reduction increased to about 0.4 percentage points, and among those who used the app more than 20 times (also about one-third of the intervention group), the average A1c reduction from baseline was about 0.6 percentage points.
“It would be interesting to learn more about the adults who engaged with the app” and had a higher use rate “to provide more targeted care” with the app to people who match the profiles of those who were more likely to use the app during the trial, said Dr. Shapira.
This “clear” dose-response relationship “was one of the most exciting findings. It helps validate the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “We’re now modeling which patients were the most engaged” with using the app, and “looking at ways to increase app engagement.”
Better Therapeutics also announced, in December 2022, results from a separate, uncontrolled study of a similar CBT app in 19 people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The findings showed that use of the tested app linked with an average 16% drop from baseline in liver fat content as measured by MRI, as well as other improvements in markers of hepatic function. The company said in a statement that based on these findings it planned to apply for breakthrough-device designation with the FDA for use of a liver-specific CBT app in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The BT-001 trial was sponsored by Better Therapeutics, the company developing the app. CPC Clinical Research receives research and consulting funding from numerous companies. Dr. Bonaca has been a consultant to Audentes, and is a stockholder of Medtronic and Pfizer. Dr. Shapira and Dr. Grapsa had no disclosures.
An investigational smartphone app that delivers cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to people with type 2 diabetes led to a significant 10 percentage point cut in the incidence of antihyperglycemic-drug intensification during 6 months’ follow-up, when compared with a control phone app, in the CBT app’s pivotal trial with 669 randomized patients.
Previously reported results from this trial, called BT-001, showed that people randomized to use the CBT app had a significant average 0.4 percentage point reduction in hemoglobin A1c, compared with controls, after 90 days for the trial’s primary endpoint, and a significant 0.29 percentage point reduction in A1c, compared with controls, after 180 days.
The new finding, that these incremental drops in A1c occurred while the control patients also received significantly more intensification of their antihyperglycemic medication, provides further evidence for the efficacy of the CBT app, said Marc P. Bonaca, MD, in a press conference organized by the American College of Cardiology in advance of its upcoming joint scientific sessions.
The CBT app “significantly reduced A1c despite less intensification of antihyperglycemic therapy,” noted Dr. Bonaca, a vascular medicine specialist and executive director of CPC Clinical Research, an academic research organization created by and affiliated with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Based on positive safety and efficacy findings from the primary-endpoint phase of the BT-001 trial, reported in Diabetes Care, the company developing the CBT app, Better Therapeutics, said in a statement that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration accepted the company’s application for de novo classification and marketing approval of the app, also called BT-001. If the agency grants this classification and marketing approval, the company plans to sell the app on a prescription basis for use by people with type 2 diabetes.
CBT app gives patients problem-solving skills
CBT gives people with type 2 diabetes a way to better understand their unhelpful behaviors and motivations and teaches them problem-solving skills. Providing this counseling via an app addresses the challenge of making the intervention scalable to a broad range of patients, Dr. Bonaca explained.
“Clinicians are frustrated by trying to produce behavioral change” in patients. The BT-001 app “provides a new avenue to treatment,” an approach that clinicians have been “very receptive” to using “once they understand the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “The effect at 90 days was very similar to what a drug would do. It’s not just drugs any more” for treating people with type 2 diabetes, he declared.
“CBT is an empirically supported psychotherapy for a variety of emotional disorders, and it has been adapted to target specific emotional distress in the context of chronic illness,” commented Amit Shapira, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston who has not been involved in the BT-001 studies. A CBT protocol designed for diabetes, CBT for Adherence and Depression “has been shown to have a positive impact on depression symptoms and glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Shapira noted in an interview.
“Once a physician explains this [CBT] app and patients understand how to use it, then patients will be happy to use it,” commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, who moderated the press conference. “We may see an explosion of apps like this one, designed to help better control” other chronic disorders, such as elevated blood pressure or abnormal lipid levels, Dr. Grapsa predicted. “I’m very optimistic that these apps have a great future in health care.”
Forty percent relative cut in new antihyperglycemic drug use
The BT-001 study randomized 669 adults with smartphone access and type 2 diabetes at any of six U.S. sites. The enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 11 years, and an A1c of 7%-10.9% with an average level of 8.2%. Participants had to be on a stable medication regimen for at least 3 months but not using prandial insulin, and their treatment regimens could undergo adjustment during the trial. At baseline, each subject was on an average of 2.1 antihyperglycemic medications, including 90% on metformin and 42% on a sulfonylurea.
The new results reported by Dr. Bonaca showed that, during follow-up, people using the app had a 14.4% rate of antihyperglycemic drug intensification compared with a 24.4% rate among the controls, a roughly 40% relative decrease in new antihyperglycemic medication use. In addition, among those using insulin at baseline, 3.8% of controls increased their insulin dose, compared with 1.5% of those using the CBT app, while insulin doses decreased in 0.9% of the control subjects and in 2.2% of those using the BT-001 app.
Further study findings, first reported by Dr. Bonaca at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in late 2022, also showed a clear dose-response pattern for the CBT app: the more CBT lessons a person completed, the greater their reduction in A1c over 180 days of app use. People who used the app fewer than 10 times had an average reduction from baseline in their A1c of less than 0.1 percentage points. Among those who used the app 10-20 times (a subgroup with roughly one-third of the people randomized to app use), average A1c reduction increased to about 0.4 percentage points, and among those who used the app more than 20 times (also about one-third of the intervention group), the average A1c reduction from baseline was about 0.6 percentage points.
“It would be interesting to learn more about the adults who engaged with the app” and had a higher use rate “to provide more targeted care” with the app to people who match the profiles of those who were more likely to use the app during the trial, said Dr. Shapira.
This “clear” dose-response relationship “was one of the most exciting findings. It helps validate the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “We’re now modeling which patients were the most engaged” with using the app, and “looking at ways to increase app engagement.”
Better Therapeutics also announced, in December 2022, results from a separate, uncontrolled study of a similar CBT app in 19 people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The findings showed that use of the tested app linked with an average 16% drop from baseline in liver fat content as measured by MRI, as well as other improvements in markers of hepatic function. The company said in a statement that based on these findings it planned to apply for breakthrough-device designation with the FDA for use of a liver-specific CBT app in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The BT-001 trial was sponsored by Better Therapeutics, the company developing the app. CPC Clinical Research receives research and consulting funding from numerous companies. Dr. Bonaca has been a consultant to Audentes, and is a stockholder of Medtronic and Pfizer. Dr. Shapira and Dr. Grapsa had no disclosures.
An investigational smartphone app that delivers cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to people with type 2 diabetes led to a significant 10 percentage point cut in the incidence of antihyperglycemic-drug intensification during 6 months’ follow-up, when compared with a control phone app, in the CBT app’s pivotal trial with 669 randomized patients.
Previously reported results from this trial, called BT-001, showed that people randomized to use the CBT app had a significant average 0.4 percentage point reduction in hemoglobin A1c, compared with controls, after 90 days for the trial’s primary endpoint, and a significant 0.29 percentage point reduction in A1c, compared with controls, after 180 days.
The new finding, that these incremental drops in A1c occurred while the control patients also received significantly more intensification of their antihyperglycemic medication, provides further evidence for the efficacy of the CBT app, said Marc P. Bonaca, MD, in a press conference organized by the American College of Cardiology in advance of its upcoming joint scientific sessions.
The CBT app “significantly reduced A1c despite less intensification of antihyperglycemic therapy,” noted Dr. Bonaca, a vascular medicine specialist and executive director of CPC Clinical Research, an academic research organization created by and affiliated with the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Based on positive safety and efficacy findings from the primary-endpoint phase of the BT-001 trial, reported in Diabetes Care, the company developing the CBT app, Better Therapeutics, said in a statement that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration accepted the company’s application for de novo classification and marketing approval of the app, also called BT-001. If the agency grants this classification and marketing approval, the company plans to sell the app on a prescription basis for use by people with type 2 diabetes.
CBT app gives patients problem-solving skills
CBT gives people with type 2 diabetes a way to better understand their unhelpful behaviors and motivations and teaches them problem-solving skills. Providing this counseling via an app addresses the challenge of making the intervention scalable to a broad range of patients, Dr. Bonaca explained.
“Clinicians are frustrated by trying to produce behavioral change” in patients. The BT-001 app “provides a new avenue to treatment,” an approach that clinicians have been “very receptive” to using “once they understand the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “The effect at 90 days was very similar to what a drug would do. It’s not just drugs any more” for treating people with type 2 diabetes, he declared.
“CBT is an empirically supported psychotherapy for a variety of emotional disorders, and it has been adapted to target specific emotional distress in the context of chronic illness,” commented Amit Shapira, PhD, a clinical psychologist at the Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston who has not been involved in the BT-001 studies. A CBT protocol designed for diabetes, CBT for Adherence and Depression “has been shown to have a positive impact on depression symptoms and glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Shapira noted in an interview.
“Once a physician explains this [CBT] app and patients understand how to use it, then patients will be happy to use it,” commented Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, a cardiologist at St. Thomas Hospital in London, who moderated the press conference. “We may see an explosion of apps like this one, designed to help better control” other chronic disorders, such as elevated blood pressure or abnormal lipid levels, Dr. Grapsa predicted. “I’m very optimistic that these apps have a great future in health care.”
Forty percent relative cut in new antihyperglycemic drug use
The BT-001 study randomized 669 adults with smartphone access and type 2 diabetes at any of six U.S. sites. The enrolled patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 11 years, and an A1c of 7%-10.9% with an average level of 8.2%. Participants had to be on a stable medication regimen for at least 3 months but not using prandial insulin, and their treatment regimens could undergo adjustment during the trial. At baseline, each subject was on an average of 2.1 antihyperglycemic medications, including 90% on metformin and 42% on a sulfonylurea.
The new results reported by Dr. Bonaca showed that, during follow-up, people using the app had a 14.4% rate of antihyperglycemic drug intensification compared with a 24.4% rate among the controls, a roughly 40% relative decrease in new antihyperglycemic medication use. In addition, among those using insulin at baseline, 3.8% of controls increased their insulin dose, compared with 1.5% of those using the CBT app, while insulin doses decreased in 0.9% of the control subjects and in 2.2% of those using the BT-001 app.
Further study findings, first reported by Dr. Bonaca at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in late 2022, also showed a clear dose-response pattern for the CBT app: the more CBT lessons a person completed, the greater their reduction in A1c over 180 days of app use. People who used the app fewer than 10 times had an average reduction from baseline in their A1c of less than 0.1 percentage points. Among those who used the app 10-20 times (a subgroup with roughly one-third of the people randomized to app use), average A1c reduction increased to about 0.4 percentage points, and among those who used the app more than 20 times (also about one-third of the intervention group), the average A1c reduction from baseline was about 0.6 percentage points.
“It would be interesting to learn more about the adults who engaged with the app” and had a higher use rate “to provide more targeted care” with the app to people who match the profiles of those who were more likely to use the app during the trial, said Dr. Shapira.
This “clear” dose-response relationship “was one of the most exciting findings. It helps validate the mechanism,” Dr. Bonaca said during the press conference. “We’re now modeling which patients were the most engaged” with using the app, and “looking at ways to increase app engagement.”
Better Therapeutics also announced, in December 2022, results from a separate, uncontrolled study of a similar CBT app in 19 people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The findings showed that use of the tested app linked with an average 16% drop from baseline in liver fat content as measured by MRI, as well as other improvements in markers of hepatic function. The company said in a statement that based on these findings it planned to apply for breakthrough-device designation with the FDA for use of a liver-specific CBT app in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
The BT-001 trial was sponsored by Better Therapeutics, the company developing the app. CPC Clinical Research receives research and consulting funding from numerous companies. Dr. Bonaca has been a consultant to Audentes, and is a stockholder of Medtronic and Pfizer. Dr. Shapira and Dr. Grapsa had no disclosures.
FROM ACC 2023
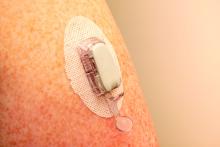
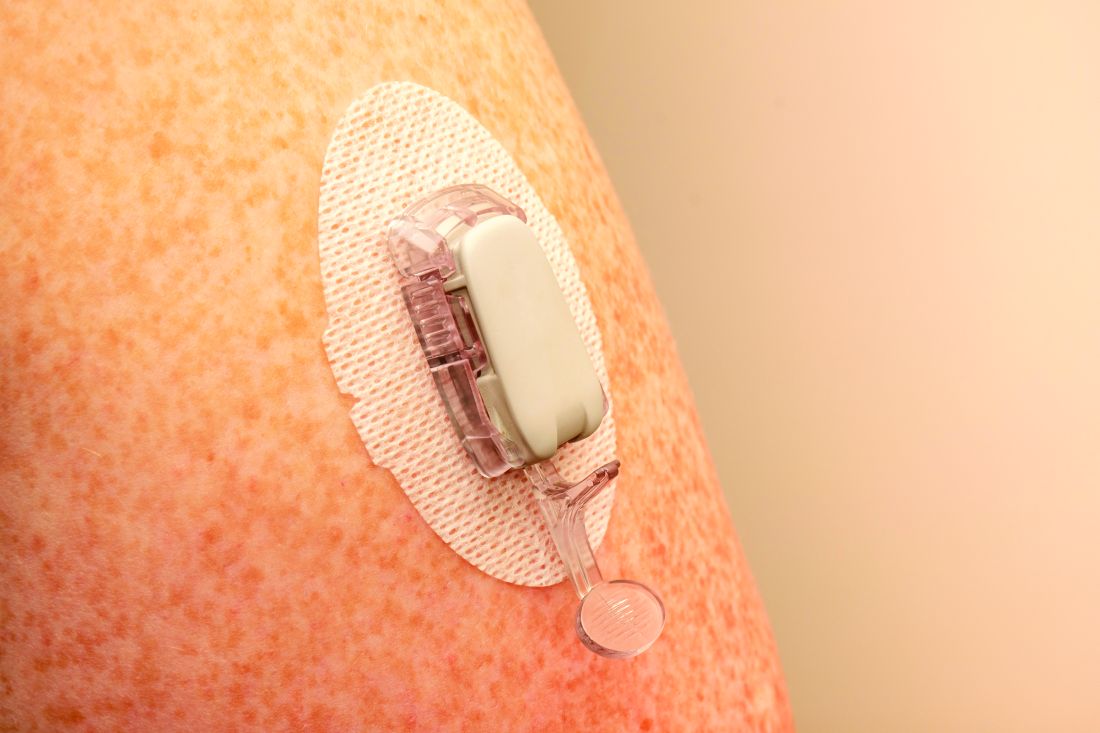
Real-time CGM plus insulin pump best for type 1 diabetes
Youth with type 1 diabetes who use real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) and an insulin pump spend more time in target glucose range than do those using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) and/or multiple daily insulin injections, new data show.
In the multinational cohort study of more than 4,500 people younger than age 21 with type 1 diabetes, those using rtCGM and pumps also spent less time above and below glucose targets and had fewer severe adverse events – either severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – compared with injections and isCGM.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by Klemen Dovc, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of pediatric endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolic diseases, University Children’s Hospital, Ljubljana, Slovenia, and colleagues.
“These results underscore the synergistic effect of advanced diabetes technologies that should be more readily available to youths with type 1 diabetes for further improvement of diabetes-related clinical outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Moreover, Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “Clinicians should be aware that there may be differences in effectiveness between different types of devices, and that choosing the right device for each individual may be important for achieving optimal outcomes.”
Real-time CGM + insulin pump = highest time in range
The researchers explained that two modalities of CGM are broadly available: rtCGM, which continuously displays glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid (usually at intervals of 1-5 minutes) on a dedicated receiver or other portable device, such as a smartphone, and provides various adjustable alarms, and isCGM, which displays data on demand when the transmitter is scanned using either a dedicated reader or smartphone-based application.
rtCGMs include devices from Dexcom and Medtronic. The isCGM, or “flash,” generally refers to the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
The study included individuals younger than 21 years from 34 centers in 21 countries in the SWEET registry, a worldwide network of diabetes care centers for youth, between Jan. 1, 2016, and Dec. 31, 2021.
The researchers didn’t report which particular devices were used in the trial, rather they just divided patients into four groups: 850 used isCGM with a pump, 1,231 used isCGM with multiple daily injections, 2,252 used rtCGM with a pump, and 886 used rtCGM with insulin injections.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes duration, and body mass index standard deviation score, rtCGM plus insulin pump was the most likely group to achieve the recommended greater than 70% time in target glycemic range (70-180 mg/dL), with 36.2% achieving it, followed by rtCGM plus injections, at 20.9%, and isCGM plus injections, at 12.5%. Those using isCGM with an insulin pump were the least likely to achieve time in range, at just 11.3%.
Similar trends were seen for the recommended goal of less than 4% of time spent below range (< 70 mg/dL) and less than 25% of time spent above range (> 180 mg/dL). Those using rtCGM with a pump had the highest proportions achieving both of those goals, 73.1% and 32.5%, respectively.
The use of rtCGM, with or without a pump, was associated with lower rates of severe hypoglycemia (2.5% and 2.0%, respectively) than isCGM with or without a pump (5.5% and 5.2%, respectively).
Similarly, the proportion experiencing at least one DKA episode varied from 1.4% for rtCGM plus insulin pump and 0.7% for rtCGM plus injections to 3.0% for isCGM plus pump and 1.5% isCGM plus injections.
Study looked at older technology but results still reflect benefit
Among the rtCGM plus insulin pump group were 264 participants (5% of the total study population) recorded in the database as using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, also known as the artificial pancreas, although this is likely an undercount as the presence of communication between the two devices was not automatically recorded, Dr. Dovc explained.
Those individuals recorded as using AIDs had a higher unadjusted time in range compared with non-AID users (66.3% vs. 59.0%) and lower time above range (30.1% vs. 37.0%) but didn’t differ in time below range (2.9% vs. 3.0%).
Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “While automated systems are becoming more common, there are still many individuals who do not have access to glucose-responsive devices.” Reasons include lack of reimbursement, or decisions not to use them, he said.
But, he added, “Despite the low reported numbers of AID users, results achieved in the pump with real-time CGM [group] are admirable and approaching recommended consensus targets with a clinically meaningful difference towards all other treatment modalities. As our findings may not be directly applicable to all participants using automated systems, they may still provide useful insights into the factors that influence glycemic control.”
Similarly, the intermittently scanned CGMs used by most in the study, and particularly in the earlier period, didn’t have low- or high-glucose alarms as do later versions. And an even more recent version also doesn’t require scanning either, so is essentially also “real-time.”
Dr. Dovc noted, “in the first half of our observational period only first generation of intermittently-scanned CGM was generally available, and we can speculate that only a small proportion started to use second generation towards the end of our observational period. The exact number of second-generation users was not available in this analysis.”
He acknowledged that because the study was observational and not randomized, patient choice of device could have influenced the outcomes.
“For example, participants who choose to use a more expensive device may have more resources or support available to them, which could influence their ability to manage their diabetes effectively. Additionally, individuals who choose to use a particular device may be more motivated or engaged in their diabetes care, which could also impact their outcomes. It would be important for future studies to explore the impact of device selection on device effectiveness and to control for this potential confounding factor in the analysis.”
This study was supported by the international Better Control in Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes: Working to Create Centers of Reference (SWEET) corporate members, including Abbott Laboratories, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Insulet, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Sanofi, and the Slovenian National Research Agency. Dr. Dovc disclosed ties with Abbott Laboratories, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer. He served as a member of the European Commission Expert Panel for Medical Devices for Endocrinology and Diabetes.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Youth with type 1 diabetes who use real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) and an insulin pump spend more time in target glucose range than do those using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) and/or multiple daily insulin injections, new data show.
In the multinational cohort study of more than 4,500 people younger than age 21 with type 1 diabetes, those using rtCGM and pumps also spent less time above and below glucose targets and had fewer severe adverse events – either severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – compared with injections and isCGM.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by Klemen Dovc, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of pediatric endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolic diseases, University Children’s Hospital, Ljubljana, Slovenia, and colleagues.
“These results underscore the synergistic effect of advanced diabetes technologies that should be more readily available to youths with type 1 diabetes for further improvement of diabetes-related clinical outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Moreover, Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “Clinicians should be aware that there may be differences in effectiveness between different types of devices, and that choosing the right device for each individual may be important for achieving optimal outcomes.”
Real-time CGM + insulin pump = highest time in range
The researchers explained that two modalities of CGM are broadly available: rtCGM, which continuously displays glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid (usually at intervals of 1-5 minutes) on a dedicated receiver or other portable device, such as a smartphone, and provides various adjustable alarms, and isCGM, which displays data on demand when the transmitter is scanned using either a dedicated reader or smartphone-based application.
rtCGMs include devices from Dexcom and Medtronic. The isCGM, or “flash,” generally refers to the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
The study included individuals younger than 21 years from 34 centers in 21 countries in the SWEET registry, a worldwide network of diabetes care centers for youth, between Jan. 1, 2016, and Dec. 31, 2021.
The researchers didn’t report which particular devices were used in the trial, rather they just divided patients into four groups: 850 used isCGM with a pump, 1,231 used isCGM with multiple daily injections, 2,252 used rtCGM with a pump, and 886 used rtCGM with insulin injections.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes duration, and body mass index standard deviation score, rtCGM plus insulin pump was the most likely group to achieve the recommended greater than 70% time in target glycemic range (70-180 mg/dL), with 36.2% achieving it, followed by rtCGM plus injections, at 20.9%, and isCGM plus injections, at 12.5%. Those using isCGM with an insulin pump were the least likely to achieve time in range, at just 11.3%.
Similar trends were seen for the recommended goal of less than 4% of time spent below range (< 70 mg/dL) and less than 25% of time spent above range (> 180 mg/dL). Those using rtCGM with a pump had the highest proportions achieving both of those goals, 73.1% and 32.5%, respectively.
The use of rtCGM, with or without a pump, was associated with lower rates of severe hypoglycemia (2.5% and 2.0%, respectively) than isCGM with or without a pump (5.5% and 5.2%, respectively).
Similarly, the proportion experiencing at least one DKA episode varied from 1.4% for rtCGM plus insulin pump and 0.7% for rtCGM plus injections to 3.0% for isCGM plus pump and 1.5% isCGM plus injections.
Study looked at older technology but results still reflect benefit
Among the rtCGM plus insulin pump group were 264 participants (5% of the total study population) recorded in the database as using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, also known as the artificial pancreas, although this is likely an undercount as the presence of communication between the two devices was not automatically recorded, Dr. Dovc explained.
Those individuals recorded as using AIDs had a higher unadjusted time in range compared with non-AID users (66.3% vs. 59.0%) and lower time above range (30.1% vs. 37.0%) but didn’t differ in time below range (2.9% vs. 3.0%).
Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “While automated systems are becoming more common, there are still many individuals who do not have access to glucose-responsive devices.” Reasons include lack of reimbursement, or decisions not to use them, he said.
But, he added, “Despite the low reported numbers of AID users, results achieved in the pump with real-time CGM [group] are admirable and approaching recommended consensus targets with a clinically meaningful difference towards all other treatment modalities. As our findings may not be directly applicable to all participants using automated systems, they may still provide useful insights into the factors that influence glycemic control.”
Similarly, the intermittently scanned CGMs used by most in the study, and particularly in the earlier period, didn’t have low- or high-glucose alarms as do later versions. And an even more recent version also doesn’t require scanning either, so is essentially also “real-time.”
Dr. Dovc noted, “in the first half of our observational period only first generation of intermittently-scanned CGM was generally available, and we can speculate that only a small proportion started to use second generation towards the end of our observational period. The exact number of second-generation users was not available in this analysis.”
He acknowledged that because the study was observational and not randomized, patient choice of device could have influenced the outcomes.
“For example, participants who choose to use a more expensive device may have more resources or support available to them, which could influence their ability to manage their diabetes effectively. Additionally, individuals who choose to use a particular device may be more motivated or engaged in their diabetes care, which could also impact their outcomes. It would be important for future studies to explore the impact of device selection on device effectiveness and to control for this potential confounding factor in the analysis.”
This study was supported by the international Better Control in Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes: Working to Create Centers of Reference (SWEET) corporate members, including Abbott Laboratories, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Insulet, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Sanofi, and the Slovenian National Research Agency. Dr. Dovc disclosed ties with Abbott Laboratories, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer. He served as a member of the European Commission Expert Panel for Medical Devices for Endocrinology and Diabetes.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Youth with type 1 diabetes who use real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) and an insulin pump spend more time in target glucose range than do those using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) and/or multiple daily insulin injections, new data show.
In the multinational cohort study of more than 4,500 people younger than age 21 with type 1 diabetes, those using rtCGM and pumps also spent less time above and below glucose targets and had fewer severe adverse events – either severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – compared with injections and isCGM.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open by Klemen Dovc, MD, PhD, assistant professor in the department of pediatric endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolic diseases, University Children’s Hospital, Ljubljana, Slovenia, and colleagues.
“These results underscore the synergistic effect of advanced diabetes technologies that should be more readily available to youths with type 1 diabetes for further improvement of diabetes-related clinical outcomes,” the authors wrote.
Moreover, Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “Clinicians should be aware that there may be differences in effectiveness between different types of devices, and that choosing the right device for each individual may be important for achieving optimal outcomes.”
Real-time CGM + insulin pump = highest time in range
The researchers explained that two modalities of CGM are broadly available: rtCGM, which continuously displays glucose concentration in the interstitial fluid (usually at intervals of 1-5 minutes) on a dedicated receiver or other portable device, such as a smartphone, and provides various adjustable alarms, and isCGM, which displays data on demand when the transmitter is scanned using either a dedicated reader or smartphone-based application.
rtCGMs include devices from Dexcom and Medtronic. The isCGM, or “flash,” generally refers to the Abbott FreeStyle Libre.
The study included individuals younger than 21 years from 34 centers in 21 countries in the SWEET registry, a worldwide network of diabetes care centers for youth, between Jan. 1, 2016, and Dec. 31, 2021.
The researchers didn’t report which particular devices were used in the trial, rather they just divided patients into four groups: 850 used isCGM with a pump, 1,231 used isCGM with multiple daily injections, 2,252 used rtCGM with a pump, and 886 used rtCGM with insulin injections.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes duration, and body mass index standard deviation score, rtCGM plus insulin pump was the most likely group to achieve the recommended greater than 70% time in target glycemic range (70-180 mg/dL), with 36.2% achieving it, followed by rtCGM plus injections, at 20.9%, and isCGM plus injections, at 12.5%. Those using isCGM with an insulin pump were the least likely to achieve time in range, at just 11.3%.
Similar trends were seen for the recommended goal of less than 4% of time spent below range (< 70 mg/dL) and less than 25% of time spent above range (> 180 mg/dL). Those using rtCGM with a pump had the highest proportions achieving both of those goals, 73.1% and 32.5%, respectively.
The use of rtCGM, with or without a pump, was associated with lower rates of severe hypoglycemia (2.5% and 2.0%, respectively) than isCGM with or without a pump (5.5% and 5.2%, respectively).
Similarly, the proportion experiencing at least one DKA episode varied from 1.4% for rtCGM plus insulin pump and 0.7% for rtCGM plus injections to 3.0% for isCGM plus pump and 1.5% isCGM plus injections.
Study looked at older technology but results still reflect benefit
Among the rtCGM plus insulin pump group were 264 participants (5% of the total study population) recorded in the database as using automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, also known as the artificial pancreas, although this is likely an undercount as the presence of communication between the two devices was not automatically recorded, Dr. Dovc explained.
Those individuals recorded as using AIDs had a higher unadjusted time in range compared with non-AID users (66.3% vs. 59.0%) and lower time above range (30.1% vs. 37.0%) but didn’t differ in time below range (2.9% vs. 3.0%).
Dr. Dovc told this news organization: “While automated systems are becoming more common, there are still many individuals who do not have access to glucose-responsive devices.” Reasons include lack of reimbursement, or decisions not to use them, he said.
But, he added, “Despite the low reported numbers of AID users, results achieved in the pump with real-time CGM [group] are admirable and approaching recommended consensus targets with a clinically meaningful difference towards all other treatment modalities. As our findings may not be directly applicable to all participants using automated systems, they may still provide useful insights into the factors that influence glycemic control.”
Similarly, the intermittently scanned CGMs used by most in the study, and particularly in the earlier period, didn’t have low- or high-glucose alarms as do later versions. And an even more recent version also doesn’t require scanning either, so is essentially also “real-time.”
Dr. Dovc noted, “in the first half of our observational period only first generation of intermittently-scanned CGM was generally available, and we can speculate that only a small proportion started to use second generation towards the end of our observational period. The exact number of second-generation users was not available in this analysis.”
He acknowledged that because the study was observational and not randomized, patient choice of device could have influenced the outcomes.
“For example, participants who choose to use a more expensive device may have more resources or support available to them, which could influence their ability to manage their diabetes effectively. Additionally, individuals who choose to use a particular device may be more motivated or engaged in their diabetes care, which could also impact their outcomes. It would be important for future studies to explore the impact of device selection on device effectiveness and to control for this potential confounding factor in the analysis.”
This study was supported by the international Better Control in Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes: Working to Create Centers of Reference (SWEET) corporate members, including Abbott Laboratories, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Insulet, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Sanofi, and the Slovenian National Research Agency. Dr. Dovc disclosed ties with Abbott Laboratories, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer. He served as a member of the European Commission Expert Panel for Medical Devices for Endocrinology and Diabetes.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
How spirituality guides these three doctors
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whether you’re spiritual, religious – or neither – the Medscape Physician Lifestyle & Happiness Report 2023 asked if you have a religious or spiritual belief. Turns out 69% of physicians shared that they have a spiritual or religious practice.
Tapping into the universe
Nick Shamie, MD, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at University of California, Los Angeles, says the constant challenges of making life-and-death decisions offer an opportunity to check in with a higher power.
“Sometimes when I’m going into a tough surgery or have a tough situation, I pause and think about how this isn’t about me and the situation I’m in,” says Dr. Shamie, whose family is Muslim. “It’s about the whole universe. I feel like someone, or some being, is looking over my shoulders, and if my intentions are good, I’ll be fine. The person I’m going to take care of will be fine. That’s how I use my faith.”
Having a belief in something greater than herself also fuels Jill Carnahan, MD, a family medicine physician and functional medicine expert in Boulder, Colo.
“This is key for me as a physician,” says Dr. Carnahan, author of “Unexpected: Finding Resilience Through Functional Medicine, Science, and Faith.” “I urge physicians to think about their source of strength. That’s not necessarily even religious. It could be meditation or being in nature.”
Dr. Carnahan likes to share with patients that there are lessons that can come from being ill – whether treating ill patients or struggling with one’s own illness.
“I like to teach this idea of illness as a teacher,” says Dr. Carnahan, who has Crohn’s disease and is a cancer survivor. “This is tough, but what you’re saying here is that there is meaning or purpose to this experience. It brings awareness to your life that may not have been there before.”
Often illness is our body’s way of getting our attention that our life, relationships, or work needs adjustment. Illness can be a reminder to make changes. “For example, a diagnosis of autoimmunity may be a reminder to take better care of ourselves, or a diagnosis of cancer may cause us to get out of an unhealthy relationship or change jobs to do something more fulfilling, as we have increased awareness of the brevity of life.”
When patients are affected by illness, pain, reduced functionality, and even imminent death, understanding the experience is difficult, and finding any purpose in it may seem impossible. Still, studies show that those who find meaning in the experience cope better with their illness.
Finding that meaning may be a strong driver of survival and may be positively related to hope, belief, and happiness.
Spirituality supports patients
Even if you’re not religious yourself, it can be helpful to support a patient who opts to pray before an arduous procedure, says Sharyar Baradaran, DDS, a periodontist specializing in gum surgery in Beverly Hills, Calif.
“I’ve had patients who go into meditation mode, or they say a prayer before I start surgery,” he says. “I take that opportunity to connect. In that instance, we hold hands. I want them to know that I understand what they’re going through and how they’re trying to find the courage to undergo surgery.”
When Dr. Shamie was a child, his father described religion as embodying the basic tenet of being good to others. “I’ve taken that to heart,” he says. “All religions, all faiths have that as a central premise.”
These doctors agree that when you take the time to stop and hold a patient’s hand, bow your head during their prayer, or acknowledge or speak for a few moments about their faith, especially during a health crisis, surgery, or challenging diagnosis, patients appreciate it and develop an even deeper connection with you.
Dr. Baradaran believes spirituality can play an important role in how health care providers care for patients. Though it may not be widely discussed or reported, and physicians may find little time and space to address patients’ spiritual needs, there is growing sensitivity regarding spirituality in health care. One study found that while physicians understand its importance, nurses are more apt to integrate spirituality into practice.
“No matter the religion, if you’re spiritual, it means you’re listening and being respectful,” says Dr. Baradaran, who is Jewish. “There are times that I’m not familiar with the prayers my patients are saying, but I always take them in, absorb them, and respect them. This allows me to have a deeper connection with them, which is wonderful.”
Dr. Shamie says that he turns to his faith in good times as well as tough ones.
“I see a lot of people who are dealing with very difficult situations, and it’s not their choice to be in this position,” he says. “At those moments, I think to myself how fortunate I am that I’m not experiencing what this individual or family is going through. I do thank God at that time. I appreciate the life I have, and when I witness hardships, it resets my appreciation.”
For Dr. Carnahan, faith is about becoming comfortable with the inevitable uncertainty of life. It’s also about finding ways to tap into the day’s stresses.
“As physicians, we’re workaholics, and one in four of us are burnt out,” she says. “One solution that really works is to step back from the day-to-day grind and find time to pray or meditate or be in nature.”
There are times when a tragedy occurs, and despite your most intense efforts, a patient may die. Those experiences can be crushing to a physician. However, to guide you through the loss of a patient or the daily juggles of managing your practice, Dr. Carnahan suggests finding time every morning to focus on the day ahead and how you connect with the universe.
“I take 15 minutes in the morning and think about how I will bring love to the world,” she says. “If you look for the miracles and the good and the unexpected, that gratitude shift allows your mind to be transformed by what’s happening. It’s often in those moments that you’ll realize again why you went into medicine in the first place.”
Doctors without faith
So, what does this mean if you’re among the 25% of physicians in the Medscape report who do not have a religious or spiritual leaning and aren’t apt to be spiritually minded when it comes to your patients? An article on KevinMD.com points out that atheist physicians are often in the closet about their atheism because they usually bow their heads or keep a respectful silence when a patient or their family offers a prayer request before surgery or a prayer of thanks after a procedure.
The retired atheist physician who wrote the piece reminds us that nonreligious doctors are good people with a high moral compass who may not believe in an afterlife. However, that means they try to make their patients’ quality of life the best they can.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Zero tolerance for patient bias: Too harsh? Clinicians respond
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If a patient refuses care from a health care practitioner because of their race or sex, should their request be accommodated?
In a recent blog on Medscape titled “No, You Can’t See a Different Doctor: We Need Zero Tolerance of Patient Bias,” Cleveland Francis Jr., MD, argued no.
Dr. Francis, who is Black, is a recently retired cardiologist who practiced for 50 years. He is currently Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Advisor at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Falls Church, Va.
When Francis was a medical student and was preparing to take a patient’s history and perform a medical exam, the patient refused and requested a “White doctor,” he recounted.
“I can remember the hurt and embarrassment as if it were yesterday,” he wrote.
The blog, especially the title, drew strong reactions. Close to 500 readers weighed in.
“The title of my blog sounds harsh,” Dr. Francis said, “but in reality, a simple conversation with the patient usually resolves these issues. The difference is that in the old days, there was utter silence, and the wishes of the patient would be granted”
Health care practitioners “should expect to be treated with respect,” he concluded his blog.
Readers agreed on that point, but they debated whether being uncomfortable with a health care practitioner of a different sex or race always constituted “patient bias.”
Some noted that difficulty understanding a practitioner’s accent, for example, is a legitimate reason for asking for another clinician.
Accents and understanding
“If I am struggling to understand you because your accent is too thick or ... because hearing aids can only do so much, I need to ask for someone else,” a reader commented.
Another chimed in: “My elderly parents changed PCPs frequently during the final years of their lives, mainly due to language barriers encountered with foreign-born providers. Due to progressive hearing loss, they simply couldn’t understand them.”
“It is important to remember that there is a Patient Bill of Rights,” she noted, “the first part of which states, ‘You have the right to safe, considerate, and respectful care, provided in a manner consistent with your beliefs.’ ”
A former charge nurse added: “If a request for change was substantive (poor communication, perceived incompetence, trauma history, etc.), I would move mountains to accommodate it, but IMHO [in my humble opinion], the belief in honoring patient preference doesn’t necessarily need to include rearranging the world in order to accommodate racism, sexism, etc.”
Bias against female doctors, male nurses
Many commenters described how they gladly traded when a patient requested a practitioner of the opposite sex.
A female hospitalist related how she contacted the senior male doctor working with her to arrange a patient trade, adding, “I do agree that racial discrimination ought to be discouraged.”
Similarly, a male ICU RN commented: “Over 13 years, I have had a handful of female (usually older) patients request a female nurse. I have always strived to make this happen.”
However, an older woman related how at first she “had some bias against a male nurse touching me and also felt self-conscious,” she said. “So, I tried to relax ... and let him do his job. He was one of the most compassionate, kind, and sensitive nurses I’ve ever had.”
“I think in some cases,” she noted, “some women have had a history of some sort of abuse by a male, whether it’s sexual or psychological,” but in other cases, “it’s often just a personal preference, not a bias.”
A physician assistant (PA) who worked in a rural ED recounted how “there was only one physician and one PA on at any given evening/night shift, both usually White males.”
“Sometimes, you just have to cope as best you can with whomever is available, and in doing so,” he said, “they might just end up being pleasantly surprised.”
Don’t take it personally, move on
“If a patient doesn’t want to see me for whatever reason, then I would rather not treat them,” was a common sentiment.
Patients “should feel comfortable with their provider even if it’s with someone other than myself,” a reader wrote.
A female physician chimed in: “I frequently have older male patients refuse to see me. ... While this is irritating on several levels, I recognize that it is the patient’s choice, sigh, and move on to the next patient.”
“There are many more patients who specifically ask to see me, so I don’t waste my time and energy on being bothered by those who refuse.”
Similarly, a female mental health provider and sometimes patient wrote: “If any patient tells me that they prefer a male ... or someone of a particular race or religion or whatever, I don’t take it personally.”
A female Hispanic doctor chimed in: “Honestly, if a patient does not want to see me due to my race, I’m OK with that. Patients need to feel comfortable with me for the relationship to be therapeutic and effective,” she said.
“Forcing the patient to see me is adding injury to insult to ME! Not to mention increase[d] workload since that patient will take [so] much more time.”
Similarly, an Asian American doctor commented: “There are people who choose not to see me because of my ethnicity. However, I strongly believe that it should always be the patient’s preference. Whatever the reason, do not force the patient to see you in the name of Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, or whatever hurts your feeling. Let the patient go.”
Patient bias vs. patient preference
A physician referring to Dr. Francis’s experience suggested that “perhaps there was an opportunity to explore this misconception directly with the patient. If not, your supervising senior resident or attending should have been informed and brought into the process and conversation.”
“If/when I were rejected by a patient for whatever reason,” another physician commented, “I would gracefully accede, and hope that my colleague would tactfully point out to the patient their error.”
“Having a nurse ask the patient ... what they need style-wise (keeping race, gender, etc., out of it) might help identify whether or not the underlying issue(s) are based on style/needs mismatch match rather than bias,” a reader suggested.
A health care worker commented: “We generally assure patients that we are professionals and think nothing of situations that they might find uncomfortable, but don’t realize that our comfort does not translate to theirs.”
Maybe a different strategy is needed
“Having been the target of bias many times,” a reader said, “I understand the pain that is inflicted. Unfortunately, a patient bias policy, while a good idea, will not prevent patient bias. This is a much larger societal problem. But we can at least tell patients that it is not okay. On the other hand, I would not want to be the provider for a patient who was biased against me and held me in disdain.”
“I do not like Zero Tolerance policies ever. They are too absolute,” another reader commented. “Sometimes, there are reasons and we do have to listen to our patients for why. ... I do not think a policy of zero tolerance will fix the problem of racism.”
“Instead of trying to educate the general public about how not to be jerks,” another reader suggested, “perhaps it would be easier to provide elective classes for doctors and employees who believe themselves to be at-risk for discrimination, providing them with a ‘toolkit’ of strategies for responding to discrimination in the moment, processing it emotionally later on, and reporting the most egregious events through designated channels.”
Another commenter agreed and wrote that, “While we as doctors need and deserve protection, we are also called to act with compassion. So, rather than ask the system for ‘zero-tolerance’ in either direction, we could encourage our health systems to provide education, support, and mediation to any party who feels or fears that they are not being well served. Such a model would include support for physicians who have been the victims of bias and hurt.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A purple warrior rises in the battle against diabetes
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
One-eyed, one-horned, flying purple veggie eater
Big Fruits and Vegetables is at it again. You notice how they’re always like “Oh, vegetables are good for your health,” and “Eating fruits every day makes you live longer,” but come on. It’s a marketing ploy, leading us astray from our personal savior, McDonald’s.
Just look at this latest bit of research: According to researchers from Finland, eating purple vegetables can protect against diabetes. Considering nearly 40 million Americans have diabetes (and nearly 100 million have prediabetes), anything to reduce the incidence of diabetes (people with diabetes account for one-fourth of every dollar spent in U.S. health care) would be beneficial. So, let’s humor the fruits and veggies people this time and hear them out.
It all comes down to a chemical called anthocyanin, which is a pigment that gives fruits and vegetables such as blueberries, radishes, and red cabbages their purplish color. Anthocyanin also has probiotic and anti-inflammatory effects, meaning it can help improve intestinal lining health and regulate glucose and lipid metabolic pathways. Obviously, good things if you want to avoid diabetes.
The investigators also found that, while standard anthocyanin was beneficial, acylated anthocyanin (which has an acyl group added to the sugar molecules of anthocyanin) is really what you want to go for. The acylated version, found in abundance in purple potatoes, purple carrots, radishes, and red cabbages, is tougher to digest, but the positive effects it has in the body are enhanced over the standard version.
Now, this all a compelling bit of research, but at the end of the day, you’re still eating fruits and vegetables, and we are red-blooded Americans here. We don’t do healthy foods. Although, if you were to dye our burgers with anthocyanin and make them purple, you’d have our attention. Purple is our favorite color.
Manuka honey better as building material than antibiotic
Milk, according to the old saying, builds strong bones, but when it comes to patients with bone loss caused by various medical reasons, researchers found that manuka honey, produced only in New Zealand and some parts of Australia, may also do the job. They soaked collagen scaffolds used for bone implants in various concentrations of the honey and found that 5% led to higher mineral formation and osteoprotegerin production, which suggests increased bone production.
But, and this is a pretty big one, the other half of the study – testing manuka honey’s ability to ward off bacteria – wasn’t so successful. Bone implants, apparently, count for almost half of all hospital-acquired infections, which obviously can put a damper on the healing process. The hope was that a biomaterial would be more effective than something like metal in lessening bacteria formation. Nope.
When the researchers soaked paper disks in honey and added them to cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, none of the various concentrations stopped bacterial growth in the scaffolding, even when they added antibiotics.
The sticky conclusion, you could say, is more bitter than sweet.
It may sound like Korn, but can it play ‘Freak on a Leash’?
Like all right-thinking Americans, we love corn, corn-based products, and almost corn. Corn on the cob grilled in the husk? Mmm. Plus, we’re big fans of the band Korn. Also, we once had a reporter here named Tim Kirn. And don’t even get us started with Karn. Best Family Feud host ever.
But what about Quorn? Oh sure, the fungi-based meat alternative is full of yummy mycoprotein, but can it prevent colorectal cancer? Can we add Quorn to our favorites list? Let’s see what Science has to say.
Researchers at Northumbria University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, fed a group of 20 men some meat (240 g/day) for 2 weeks – hopefully, they were allowed to eat some other food as well – and then gave them the same amount of Quorn, excuse us, fungi-derived mycoprotein equivalents, for 2 more weeks, with a 4-week washout period in between.
Levels of cancer-causing chemicals known as genotoxins fell significantly in the mycoprotein phase but rose during the meat phase. The mycoprotein diet also improved gut health “by increasing the abundance of protective bacteria such as Lactobacilli, Roseburia, and Akkermansia, which are associated with offering protection against chemically induced tumours, inflammation and bowel cancer,” they said in a statement from the university.
The meat phase, on the other hand, resulted in an increase in “gut bacteria linked with issues such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, weight gain and other negative health outcomes,” they noted.
Science, then, seems to approve of Quorn, and that’s good enough for us. We’re adding Quorn to our diet, starting with a fungi-derived mycoproteinburger tonight while we’re watching the Cornell Big Red take the court against their archrivals, the Big Green of Dartmouth College. GO RED!
Physician group staffing down, expenses up, new reports show
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician groups saw staff-to-physician ratios decline even as their workforce expenses rose between 2019 and 2021, according to recent reports from the American Medical Group Association (AMGA) and the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA).
As patients started to return to doctors’ offices as the pandemic eased in 2021, physician groups found it increasingly difficult to recruit and retain lower-level clinicians, including medical assistants and LPNs, officials from both associations told this news organization. Many clinics had to raise their pay scales to be competitive with employers in other fields, and some had to hire higher-priced RNs to keep their practices running.
The AMGA report was based largely on data from groups of over 500 physicians, mostly affiliated with health systems. According to a news release accompanying the report, the ratio between full-time equivalent (FTE) clinic staff and health care professionals in direct patient care dropped by 11.3% between 2019 and 2021. The ratio of medical assistants (MAs) to clinicians declined by a greater percentage.
In the MGMA report, which represented about 4,000 practices ranging from very small (two doctors) to very large groups, total support staff per FTE primary-care physician dropped by 18% from 2019 to 2021 in independent groups and by 13% in hospital-affiliated groups. The ratios decreased by smaller amounts in surgical practices.
In contrast, nonsurgical specialty groups under both types of ownership saw their staffing ratios rise slightly.
Although it’s unclear why medical specialties increased their staff while other types of specialties lost employees, Ron Holder, MHA, chief operating officer of MGMA, said that some specialists may have opened more ancillary facilities and hired new employees to recoup revenue lost during the pandemic.
Expenses rise sharply
The AMGA report found that staffing expenses for the surveyed groups increased by 15% between 2019 and 2021.
“We saw a decrease in staff and an increase in expenses during that time period, and there are a few reasons for that,” Rose Wagner, RN, chief operating officer of AMGA, said. “Groups increased salaries to maintain staff. We also saw lower-paid staff find other jobs outside of health care. For example, medical assistants and receptionists could find jobs outside of health care that paid more. [Open positions] got back-filled with other higher paid staff, such as RNs, doing lower skilled jobs.”
Mr. Holder added that rising wages in other sectors made leaving physician groups more attractive for employees.
“Three years ago, there weren’t many positions in a medical practice where you were competing with Chick-fil-A or Taco Bell,” he said. In Denver, where Mr. Holder is based, “every restaurant in town is now advertising $17-$19 [hourly] starting pay just to do fast food. That causes practices to either lose employees or pay more for the employees they have. So that raises per-employee expense significantly,” he said.
Mr. Holder noted that inflation also has driven up wages as employees demand higher pay to keep up with the cost of living.
Unusual exodus of employees
Fred Horton, MHA, president of AMGA Consulting, said he has never seen so many people leaving health care for other occupations.
Some exits resulted from practices laying people off early in the pandemic, but most staff members who left practices were seeking higher pay, he said. In addition, Ms. Wagner noted, some staff members didn’t want to be exposed to COVID at work.
“There was an exodus from health care that was different from what we’d experienced in the past,” Mr. Horton added. “It’s still extremely challenging to get up to the staffing levels that are appropriate.”
Mr. Holder, however, said that the situation is slowly improving. “Health care is fairly recession-proof, because people need it. So when you see companies in other industries closing shop or reducing their head count, that actually helps health care recruiting in some jobs. And people are coming back to the workplace who previously were worried about COVID or didn’t want to get the vaccine.”
Paying more for nurses
In 2021, groups adopted a variety of tactics to adapt to the pandemic and respond to patient demand, the AMGA survey shows. Forty percent of system-affiliated groups and 18% of independent practices changed registered nurses’ responsibilities, in many cases having them do the work of medical assistants who were in short supply.
Some practices hired RNs, who have historically been utilized less by primary care than by surgical specialties, Mr. Holder noted. Other clinics paid temp agencies to supply nurses at a steep cost.
“When you’re short staffed, you end up paying more overtime, you end up paying temporary agencies at higher dollars, and you hire higher skilled people to do lower-skilled work,” Ms. Wagner said.
Meanwhile, many physician groups tried to cope with the physician shortage by bringing on more advanced practice clinicians (APCs), including nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Seventy percent of the AMGA groups used this strategy, the report revealed.
“The use of APCs has been steadily increasing as groups try to adopt a lower-cost care model in the midst of a nationwide physician shortage,” Ms. Wagner said in the press release.
Changes in patient care
About half of the groups in the AMGA survey said they changed their staff structure to allow APCs to carry their own patient panels. Although most of these clinicians were probably under physician supervision, nearly half of the states now allow NPs to practice autonomously.
Mr. Horton cautioned that APCs can’t fully substitute for physicians and require the same support staff that doctors do if they have their own panels. In primary care groups, Mr. Holder noted, the average salary of an APC “is continuing to rise, and there isn’t a huge difference between what they and doctors make.”
Nevertheless, he added, “there are more NPs and PAs being added to the marketplace all the time, whereas [physician] residency programs aren’t really growing. There are caps on the number of residency positions, and some physicians are retiring. So the clock is ticking to the point where someday doctors will be grossly outnumbered by NPs.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors and their families tend to ignore medical guidelines
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a study by economic professors from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; Stanford (Calif.) University; and the George Gund Professor of Economics and Business Administration at Harvard University, Boston.
What to know
- Doctors’ medical knowledge may influence them and their families to often ignore medical advice while the rest of the population adheres to general medication guidelines.
- Of the 63 guidelines used in the study, doctors and their families followed the standards less than a third of the time.
- The difference in adherence to guidelines between experts and nonexperts is largest with respect to antibiotics, in which doctors and their families are 5.2 percentage points less in compliance than everyone else.
- Doctors could be more likely to prescribe broader-spectrum antibiotics for themselves and their families, whereas most patients receive more narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
- Many members of the general public don’t understand medical guidelines, finding them too complex to follow, and many people don’t trust their doctors.
This is a summary of the article, “A Taste of Their Own Medicine: Guideline Adherence and Access to Expertise,” published in the American Economic Review: Insights on December 13, 2022. The full article can be found on aeaweb.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Docs with one paid malpractice claim are four times more likely to have another
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this retrospective case-control study, law and public health researchers from Georgetown University, the National Opinion Research Center, the University of Colorado, and Northwestern University analyzed paid malpractice claims for all licensed U.S. physicians.
The findings suggest that a single malpractice claim may not be a random stroke of bad luck but instead holds some predictive power into the risk for future paid claims.
“A four times increase in risk is huge, particularly since we observe a similar increase in both high-risk and lower-risk specialties,” David Hyman, JD, MD, professor of health law and policy at Georgetown University, Washington, and lead researcher on the study, told this news organization. “There are surely some false positives, but there must be lots of actual negligence too, or we would not see these results.”
For the 881,876 physicians analyzed, researchers looked at malpractice claims paid during two 5-year periods: 2009-2013 and 2014-2018. Nearly 96% of physicians had no paid malpractice claims between 2009 and 2013; 3% had one, and less than 1% had multiple claims. The proportion of physicians with paid claims between 2014 and 2018 was similar.
Compared with physicians with no 2009-2013 claims, a physician with just one paid claim in that time period had a 3.7 times higher risk for a future paid claim. Physicians with two paid claims were nearly 7 times more likely to have a future paid claim, and those with three or more paid claims were more than 11 times more likely to have one.
Approximately 3% of physicians with no paid claims between 2009 and 2013 had a future paid claim, growing to 12.4% of those with one paid claim during that time.
The study’s findings may have implications for medical licensing boards and hospitals granting staff privileges.
“After some number of paid claims, there should be an official response” from these entities, such as a hands-on assessment of technical skills or assignment of a peer mentor, said Dr. Hyman, who is also coauthor of a book titled “Medical Malpractice Litigation: How It Works, Why Tort Reform Hasn’t Helped.” A graduated set of interventions, whether voluntary or mandatory, can reduce future claim risk and patient harm, Dr. Hyman added.
Interventions may include error avoidance and post-error communication training, counseling to improve bedside skills, and encouragement to move into nonclinical practice. Either way, Dr. Hyman says a nuanced intervention strategy would be a welcome shift away from the current “all or nothing approach” that too often ends in the revocation of a physician’s medical license.
Although there are strategies to proactively identify physicians with excess risk for malpractice claims and implement preventive measures – like Vanderbilt University’s Patient Advocacy Reporting System, for example – most hospitals and physician groups fail to initiate even informal interventions after a malpractice settlement or verdict, which is a missed opportunity, Dr. Hyman said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA