User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


COVID-19 death rate was twice as high in cancer patients in NYC study
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
FROM CANCER DISCOVERY
Fountains of Wayne, and a hospitalist’s first day, remembered
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Doctor with a mask: Enhancing communication and empathy
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Case reports illustrate heterogeneity of skin manifestations in COVID patients
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.
Three months of COVID-19 may mean 80,000 missed cancer diagnoses
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.
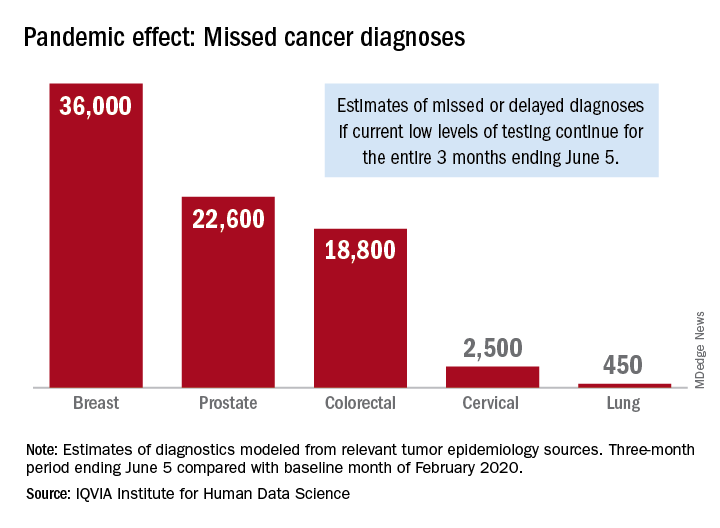
Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
, according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science looking at trends in the United States.

Screening and monitoring tests for breast, prostate, colorectal, cervical, and lung cancer were down 39%-90% in early April, compared with the baseline month of February, according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
These findings are based on data from IQVIA’s medical claims database, which includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data suggest that, at current positivity rates, there could be 36,000 missed or delayed diagnoses of breast cancer during the 3-month period from early March through early June. Estimates for missed diagnoses of the four other cancers analyzed include 450 for lung cancer, 2,500 for cervical cancer, 18,800 for colorectal cancer, and 22,600 for prostate cancer.
The authors project a total of 22 million canceled or delayed tests for the five cancers over the 3-month period ending June 5, based on a comparison of claims data for early April with the February baseline. Catching up on this backlog will be problematic, according to the authors.
“Current excess health care capacity ... would require providers to shift priorities to make time and space in schedules and facilities as well as the cooperation of patients to return to health care providers,” the authors wrote. “Both of these could be further disrupted by economic factors or reintroduction of social distancing in a reemergence of the outbreak.”
The report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
Cancer screening, monitoring down during pandemic
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.
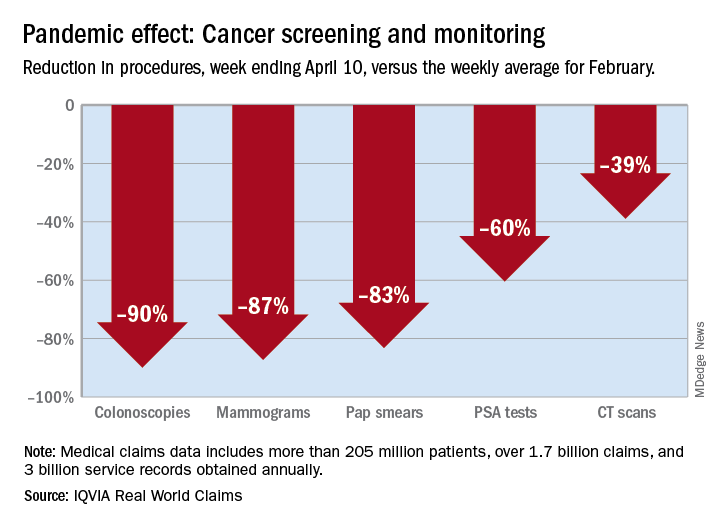
There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
according to a report by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.

There were 90% fewer colonoscopies ordered during the week ending April 10, compared with the weekly average for Feb. 1-28, based on claims data analyzed by IQVIA.
IQVIA’s medical claims database includes more than 205 million patients, over 1.7 billion claims, and 3 billion service records obtained annually.
The data also showed an 87% reduction in mammograms and an 83% reduction in Pap smears during the week ending April 10. Prostate-specific antigen tests for prostate cancer decreased by 60%, and CT scans for lung cancer decreased by 39%.
The smaller decrease in CT scans for lung cancer “may reflect the generally more serious nature of those tumors or be due to concerns about ruling out COVID-related issues in some patients,” according to report authors Murray Aitken and Michael Kleinrock, both of IQVIA.
The report also showed that overall patient interactions with oncologists were down by 20% through April 3, based on medical and pharmacy claims processed since February, but there was variation by tumor type.
The authors noted “little or no disruption” in oncologist visits in March for patients with aggressive tumors or those diagnosed at advanced stages, compared with February. However, for patients with skin cancer or prostate cancer, visit rates were down by 20%-50% in March.
“This may reflect that oncologists who are providing care across multiple tumor types are prioritizing their time and efforts to those patients with more advanced or aggressive tumors,” the authors wrote.
This report was produced by the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science without industry or government funding.
SOURCE: Murray A and Kleinrock M. Shifts in healthcare demand, delivery and care during the COVID-19 era. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. April 2020.
FDA tightens requirements for COVID-19 antibody tests
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration is tightening requirements for companies that develop COVID-19 antibody tests in an effort to combat fraud and better regulate the frenzy of tests coming to market.
The updated policy, announced May 4, requires commercial antibody test developers to apply for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA under a tight time frame and also provides specific performance threshold recommendations for test specificity and sensitivity. The revised requirements follow a March 16 policy that allowed developers to validate their own tests and bring them to market without an agency review. More than 100 coronavirus antibody tests have since entered the market, fueling a congressional investigation into the accuracy of tests.
When the March policy was issued, FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said it was critical for the FDA to provide regulatory flexibility for serology test developers, given the nature of the COVID-19 public health emergency and an understanding that the tests were not meant to be used as the sole basis for COVID-19 diagnosis.
“As FDA has authorized more antibody tests and validation data has become available, including through the capability at [the National Cancer Institute] the careful balancing of risks and benefits has shifted to the approach we have outlined today and our policy update,” Dr. Hahn said during a May 4 press conference.
The new approach requires all commercial manufacturers to submit EUA requests with their validation data within 10 business days from the date they notified the FDA of their validation testing or from the date of the May 4 policy, whichever is later. Additionally, the FDA has provided specific performance threshold recommendations for specificity and sensitivity for all serology test developers.
In a statement released May 4, FDA leaders acknowledged the widespread fraud that is occurring in connection to antibody tests entering the market.
“We unfortunately see unscrupulous actors marketing fraudulent test kits and using the pandemic as an opportunity to take advantage of Americans’ anxiety,” wrote Anand Shah, MD, FDA deputy commissioner for medical and scientific affairs in a joint statement with Jeff E. Shuren, MD, director for the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “Some test developers have falsely claimed their serological tests are FDA approved or authorized. Others have falsely claimed that their tests can diagnose COVID-19 or that they are for at-home testing, which would fall outside of the policies outlined in our March 16 guidance, as well as the updated guidance.”
At the same time, FDA officials said they are aware of a “concerning number” of commercial serology tests that are being inappropriately marketed, including for diagnostic use, or that are performing poorly based on an independent evaluation by the National Institutes of Health, according to the May 4 statement.
In addition to tightening its requirements for test developers, the FDA also is introducing a more streamlined process to support EUA submissions and review. Two voluntary EUA templates for antibody tests are now available – one for commercial manufacturers and one for Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-certified high-complexity labs seeking FDA authorization. The templates will facilitate the preparation and submission of EUA requests and can be used by any interested developer, according to the FDA.
To date, 12 antibody tests have been authorized under an individual EUA, and more than 200 antibody tests are currently the subject of a pre-EUA or EUA review, according to the FDA.
Many unknowns remain about antibody tests and how they might help researchers and clinicians understand and/or potentially treat COVID-19. Antibody tests may be able to provide information on disease prevalence and frequency of asymptomatic infection, as well as identify potential donors of “convalescent plasma,” an approach in which blood plasma containing antibodies from a recovered individual serves as a therapy for an infected patient with severe disease, Dr. Shah wrote in the May 4 statement.
“There are a lot of unanswered questions about this particular issue,” Dr. Hahn said during the press conference. “We need the data because we need to understand this particular aspect of the disease and put it as part of the puzzle around COVID-19.”
FOURIER: Evolocumab follow-up shows no cognitive adverse effects
Treatment with a PCSK9 inhibitor, as well as achieving dramatically lowered cholesterol levels, did not mess with patients’ minds. Results from a cognition self-assessment completed by more than 22,000 patients when they finished participation in the FOURIER pivotal outcomes trial for evolocumab showed no signal of mental harm from either treatment with this PCSK9 inhibitor or from reaching a serum level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) of less than 20 mg/dL.
“We observed that patients treated with evolocumab, as well as those who achieved progressively very low LDL-C at 4 weeks in the FOURIER trial, had similar self-reported cognition in comparison with those receiving placebo and those with higher achieved LDL-C levels,” wrote a team of researchers from the trial in an article published online on May 4 (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]: 2283-93). “These data confirm the neurocognitive safety of intensive LDL-C reduction with evolocumab while reducing recurrent CV [cardiovascular] events in high-risk patients, and suggest that very low achieved LDL-C levels may be safely targeted for high-risk patients.”
The findings added to prior results documenting the cognitive safety of evolocumab (Repatha) from a much smaller FOURIER substudy that involved more intensive testing, the EBBINGHAUS (Evaluating PCSK9 Binding Antibody Influence on Cognitive Health in High Cardiovascular Risk Subjects) study with 1,204 patients drawn from the broader study and tested after a median 19 months on treatment (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[17]: 633-43), as well as reports of neurocognitive safety for the other U.S. approved PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitor, alirocumab (Praluent) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 16;372[16]:1489-99), various statins (J Gen Intern Med. 2015 Mar;30[3]: 348-58), and a third type of LDL-C–lowering agent, ezetimibe (JAMA Cardiol. 2017 May;2[5]:547-55).
Despite this evidence from across several drug classes that all cut LDL-C a long-standing but unsubstantiated belief persists among some that lipid lowering, especially by statins, blunts mental function, misinformation that’s easy to find on the Internet. “I estimate that about 20% of patients prescribed a statin won’t take it because of something they’ve heard” including that statins make you stupid. “It’s hard to undo that,” said Robert P. Giugliano, MD, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and senior author for the new FOURIER study as well as for EBBINGHAUS. The same stigma has not gained nearly as much traction for PCSK9 inhibitors, however, and Dr. Giugliano said he has also recently sensed what may be a downtrend in statin apprehension.
“The information added by this study is very important,” commented Massimo R. Mannarino, MD, an atherosclerotic disease researcher at the University of Perugia (Italy). “The prejudice and misinformation regarding possible side effects of statins among patients and also some physicians unfortunately remains very strong today,” he said in an interview. “My impression is that PCSK9 inhibitors are less affected by this negative bias and are seen as a safer alternative to statins.” Concerns about PCSK9 inhibitors have especially focused on “the possible risks from very low cholesterol levels on the brain.” The evidence from both studies and clinical experience “allows for a very positive opinion about the efficacy and safety of PCSK9 inhibitors, although the long-term effects still require a few more years of observation,” said Dr. Mannarino, who led a review of the evidence that clears this class from links to neurocognitive loss (J Clin Lipid. 2018 Sep 1;12[5]:1123-32).
FOURIER (Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research With PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects With Elevated Risk) randomized 27,564 patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and elevated LDL cholesterol despite maximally tolerated standard treatment. Treatment with evolocumab for a median of 2.2 years resulted in a statistically significant 15% reduction in the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 May 4;376[18]:1713-22), and led to the drug receiving an indication for lowering rates of MI, stroke, and symptom-driven coronary revascularization.
The prespecified substudy reported by Dr. Giugliano and his associates focused on a 23-question, validated, self-assessment survey of cognitive function completed by 22,655 of the FOURIER patients (82%). The more than 4,900 other patients in the study who did not complete the survey had modestly higher prevalence rates of various comorbidities at baseline, and also higher rates of adverse outcomes during follow-up, and in many cases these adverse outcome may have contributed to these patients not being able to complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment. For example, almost a quarter of the patients who did not complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment failed to do so because they had already died.
Overall, the prevalence of patients indicating a cognitive decline was virtually identical among 11,363 patients who had been maintained on evolocumab, with a 3.7% rate, and the 11,292 patients in the placebo group, with a 3.6% rate. When analyzed by achieved level of LDL-C after 4 weeks on treatment, the 2,338 patients with a level below 20 mg/dL had a 3.8% rate of self-reported cognitive loss, compared with a 4.5% rate among 3,613 patients who had an LDL-C level of at least 100 mg/dL when measured 4 weeks into the study.
One of the strengths of the new cognitive analysis is that, although it did not use the more sophisticated assessment tests employed on fewer patients in the EBBINGHAUS substudy, it used the Everyday Cognition scale (Neuropsychiatry. 2008 Jul;22[4]: 531-44). “We asked patients what they have experienced, and in the end that is what’s important, so this adds to the neurocognitive testing,” run in EBBINGHAUS, Dr. Giugliano said in an interview.
“The neurocognitive results in the present study were self-reported, and that might be a limitation, as it is less specific and objective, but it is also a strength, as it could be more sensitive” especially for a “nocebo effect common to all lipid-lowering drugs linked to the bad reputation historically attributed to statins,” Dr. Mannarino said.
Should the new FOURIER data “be interpreted as definitive evidence that intensive LDL-C lowering with PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies has no major harmful cognitive effects, at least over a period of 3 years? The answer appears to be a qualified yes, but with three important caveats,” Jennifer G. Robinson, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Iowa College of Public Health in Iowa City, said in an editorial that accompanied the new report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2294-6). Her three caveats are the missing 18% of patients who never took the end-of-study assessment, the relative paucity of patients at very advanced age in FOURIER, in which patients averaged 62.5 years old, and the exclusion from FOURIER of patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke. Dr. Robinson also cited the 2.2 year median follow-up as leaving unsettled the potential cognitive impact of longer treatment.
In response, Dr. Giugliano noted that the very large size of FOURIER and the 22,655 patients who completed their survey provided substantial numbers of patients to address some of these concerns in robust subgroup analyses. For example, the new report showed no signal of excess cognitive complaints with evolocumab treatment among 1,999 patients who were at least 75 years old when entering the study, or in more than 5,000 patients with a history of cerebrovascular disease at baseline, or in 1,990 patients with a history of a nonstroke neurologic disease. In addition, while he conceded that the 18% of patients not accounted for in the new study placed some limits on generalizability of the findings, he also maintained that this unavoidable failure to collect data from a modest percentage of patients doesn’t scuttle the overarching signal of cognitive safety for most patients. And regarding the duration of treatment monitored, he noted that 5-year follow-up cognitive assessments are planned.
FOURIER was sponsored by Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha). Dr. Giugliano has received personal fees and research support from Amgen and from several other companies. Dr. Mannarino had no disclosures. Dr. Robinson has been a consultant to The Medicines Company, Novartis, and Pfizer, and she has received research funding to her institution from Amgen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Gencer B et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2283-93.
Correction: Dr. Giugliano's name was misspelled in an earlier version of this article.
Treatment with a PCSK9 inhibitor, as well as achieving dramatically lowered cholesterol levels, did not mess with patients’ minds. Results from a cognition self-assessment completed by more than 22,000 patients when they finished participation in the FOURIER pivotal outcomes trial for evolocumab showed no signal of mental harm from either treatment with this PCSK9 inhibitor or from reaching a serum level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) of less than 20 mg/dL.
“We observed that patients treated with evolocumab, as well as those who achieved progressively very low LDL-C at 4 weeks in the FOURIER trial, had similar self-reported cognition in comparison with those receiving placebo and those with higher achieved LDL-C levels,” wrote a team of researchers from the trial in an article published online on May 4 (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]: 2283-93). “These data confirm the neurocognitive safety of intensive LDL-C reduction with evolocumab while reducing recurrent CV [cardiovascular] events in high-risk patients, and suggest that very low achieved LDL-C levels may be safely targeted for high-risk patients.”
The findings added to prior results documenting the cognitive safety of evolocumab (Repatha) from a much smaller FOURIER substudy that involved more intensive testing, the EBBINGHAUS (Evaluating PCSK9 Binding Antibody Influence on Cognitive Health in High Cardiovascular Risk Subjects) study with 1,204 patients drawn from the broader study and tested after a median 19 months on treatment (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[17]: 633-43), as well as reports of neurocognitive safety for the other U.S. approved PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitor, alirocumab (Praluent) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 16;372[16]:1489-99), various statins (J Gen Intern Med. 2015 Mar;30[3]: 348-58), and a third type of LDL-C–lowering agent, ezetimibe (JAMA Cardiol. 2017 May;2[5]:547-55).
Despite this evidence from across several drug classes that all cut LDL-C a long-standing but unsubstantiated belief persists among some that lipid lowering, especially by statins, blunts mental function, misinformation that’s easy to find on the Internet. “I estimate that about 20% of patients prescribed a statin won’t take it because of something they’ve heard” including that statins make you stupid. “It’s hard to undo that,” said Robert P. Giugliano, MD, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and senior author for the new FOURIER study as well as for EBBINGHAUS. The same stigma has not gained nearly as much traction for PCSK9 inhibitors, however, and Dr. Giugliano said he has also recently sensed what may be a downtrend in statin apprehension.
“The information added by this study is very important,” commented Massimo R. Mannarino, MD, an atherosclerotic disease researcher at the University of Perugia (Italy). “The prejudice and misinformation regarding possible side effects of statins among patients and also some physicians unfortunately remains very strong today,” he said in an interview. “My impression is that PCSK9 inhibitors are less affected by this negative bias and are seen as a safer alternative to statins.” Concerns about PCSK9 inhibitors have especially focused on “the possible risks from very low cholesterol levels on the brain.” The evidence from both studies and clinical experience “allows for a very positive opinion about the efficacy and safety of PCSK9 inhibitors, although the long-term effects still require a few more years of observation,” said Dr. Mannarino, who led a review of the evidence that clears this class from links to neurocognitive loss (J Clin Lipid. 2018 Sep 1;12[5]:1123-32).
FOURIER (Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research With PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects With Elevated Risk) randomized 27,564 patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and elevated LDL cholesterol despite maximally tolerated standard treatment. Treatment with evolocumab for a median of 2.2 years resulted in a statistically significant 15% reduction in the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 May 4;376[18]:1713-22), and led to the drug receiving an indication for lowering rates of MI, stroke, and symptom-driven coronary revascularization.
The prespecified substudy reported by Dr. Giugliano and his associates focused on a 23-question, validated, self-assessment survey of cognitive function completed by 22,655 of the FOURIER patients (82%). The more than 4,900 other patients in the study who did not complete the survey had modestly higher prevalence rates of various comorbidities at baseline, and also higher rates of adverse outcomes during follow-up, and in many cases these adverse outcome may have contributed to these patients not being able to complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment. For example, almost a quarter of the patients who did not complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment failed to do so because they had already died.
Overall, the prevalence of patients indicating a cognitive decline was virtually identical among 11,363 patients who had been maintained on evolocumab, with a 3.7% rate, and the 11,292 patients in the placebo group, with a 3.6% rate. When analyzed by achieved level of LDL-C after 4 weeks on treatment, the 2,338 patients with a level below 20 mg/dL had a 3.8% rate of self-reported cognitive loss, compared with a 4.5% rate among 3,613 patients who had an LDL-C level of at least 100 mg/dL when measured 4 weeks into the study.
One of the strengths of the new cognitive analysis is that, although it did not use the more sophisticated assessment tests employed on fewer patients in the EBBINGHAUS substudy, it used the Everyday Cognition scale (Neuropsychiatry. 2008 Jul;22[4]: 531-44). “We asked patients what they have experienced, and in the end that is what’s important, so this adds to the neurocognitive testing,” run in EBBINGHAUS, Dr. Giugliano said in an interview.
“The neurocognitive results in the present study were self-reported, and that might be a limitation, as it is less specific and objective, but it is also a strength, as it could be more sensitive” especially for a “nocebo effect common to all lipid-lowering drugs linked to the bad reputation historically attributed to statins,” Dr. Mannarino said.
Should the new FOURIER data “be interpreted as definitive evidence that intensive LDL-C lowering with PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies has no major harmful cognitive effects, at least over a period of 3 years? The answer appears to be a qualified yes, but with three important caveats,” Jennifer G. Robinson, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Iowa College of Public Health in Iowa City, said in an editorial that accompanied the new report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2294-6). Her three caveats are the missing 18% of patients who never took the end-of-study assessment, the relative paucity of patients at very advanced age in FOURIER, in which patients averaged 62.5 years old, and the exclusion from FOURIER of patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke. Dr. Robinson also cited the 2.2 year median follow-up as leaving unsettled the potential cognitive impact of longer treatment.
In response, Dr. Giugliano noted that the very large size of FOURIER and the 22,655 patients who completed their survey provided substantial numbers of patients to address some of these concerns in robust subgroup analyses. For example, the new report showed no signal of excess cognitive complaints with evolocumab treatment among 1,999 patients who were at least 75 years old when entering the study, or in more than 5,000 patients with a history of cerebrovascular disease at baseline, or in 1,990 patients with a history of a nonstroke neurologic disease. In addition, while he conceded that the 18% of patients not accounted for in the new study placed some limits on generalizability of the findings, he also maintained that this unavoidable failure to collect data from a modest percentage of patients doesn’t scuttle the overarching signal of cognitive safety for most patients. And regarding the duration of treatment monitored, he noted that 5-year follow-up cognitive assessments are planned.
FOURIER was sponsored by Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha). Dr. Giugliano has received personal fees and research support from Amgen and from several other companies. Dr. Mannarino had no disclosures. Dr. Robinson has been a consultant to The Medicines Company, Novartis, and Pfizer, and she has received research funding to her institution from Amgen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Gencer B et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2283-93.
Correction: Dr. Giugliano's name was misspelled in an earlier version of this article.
Treatment with a PCSK9 inhibitor, as well as achieving dramatically lowered cholesterol levels, did not mess with patients’ minds. Results from a cognition self-assessment completed by more than 22,000 patients when they finished participation in the FOURIER pivotal outcomes trial for evolocumab showed no signal of mental harm from either treatment with this PCSK9 inhibitor or from reaching a serum level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) of less than 20 mg/dL.
“We observed that patients treated with evolocumab, as well as those who achieved progressively very low LDL-C at 4 weeks in the FOURIER trial, had similar self-reported cognition in comparison with those receiving placebo and those with higher achieved LDL-C levels,” wrote a team of researchers from the trial in an article published online on May 4 (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]: 2283-93). “These data confirm the neurocognitive safety of intensive LDL-C reduction with evolocumab while reducing recurrent CV [cardiovascular] events in high-risk patients, and suggest that very low achieved LDL-C levels may be safely targeted for high-risk patients.”
The findings added to prior results documenting the cognitive safety of evolocumab (Repatha) from a much smaller FOURIER substudy that involved more intensive testing, the EBBINGHAUS (Evaluating PCSK9 Binding Antibody Influence on Cognitive Health in High Cardiovascular Risk Subjects) study with 1,204 patients drawn from the broader study and tested after a median 19 months on treatment (N Engl J Med. 2017 Aug 17;377[17]: 633-43), as well as reports of neurocognitive safety for the other U.S. approved PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9) inhibitor, alirocumab (Praluent) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 16;372[16]:1489-99), various statins (J Gen Intern Med. 2015 Mar;30[3]: 348-58), and a third type of LDL-C–lowering agent, ezetimibe (JAMA Cardiol. 2017 May;2[5]:547-55).
Despite this evidence from across several drug classes that all cut LDL-C a long-standing but unsubstantiated belief persists among some that lipid lowering, especially by statins, blunts mental function, misinformation that’s easy to find on the Internet. “I estimate that about 20% of patients prescribed a statin won’t take it because of something they’ve heard” including that statins make you stupid. “It’s hard to undo that,” said Robert P. Giugliano, MD, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and senior author for the new FOURIER study as well as for EBBINGHAUS. The same stigma has not gained nearly as much traction for PCSK9 inhibitors, however, and Dr. Giugliano said he has also recently sensed what may be a downtrend in statin apprehension.
“The information added by this study is very important,” commented Massimo R. Mannarino, MD, an atherosclerotic disease researcher at the University of Perugia (Italy). “The prejudice and misinformation regarding possible side effects of statins among patients and also some physicians unfortunately remains very strong today,” he said in an interview. “My impression is that PCSK9 inhibitors are less affected by this negative bias and are seen as a safer alternative to statins.” Concerns about PCSK9 inhibitors have especially focused on “the possible risks from very low cholesterol levels on the brain.” The evidence from both studies and clinical experience “allows for a very positive opinion about the efficacy and safety of PCSK9 inhibitors, although the long-term effects still require a few more years of observation,” said Dr. Mannarino, who led a review of the evidence that clears this class from links to neurocognitive loss (J Clin Lipid. 2018 Sep 1;12[5]:1123-32).
FOURIER (Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research With PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects With Elevated Risk) randomized 27,564 patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and elevated LDL cholesterol despite maximally tolerated standard treatment. Treatment with evolocumab for a median of 2.2 years resulted in a statistically significant 15% reduction in the study’s primary efficacy endpoint, compared with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 May 4;376[18]:1713-22), and led to the drug receiving an indication for lowering rates of MI, stroke, and symptom-driven coronary revascularization.
The prespecified substudy reported by Dr. Giugliano and his associates focused on a 23-question, validated, self-assessment survey of cognitive function completed by 22,655 of the FOURIER patients (82%). The more than 4,900 other patients in the study who did not complete the survey had modestly higher prevalence rates of various comorbidities at baseline, and also higher rates of adverse outcomes during follow-up, and in many cases these adverse outcome may have contributed to these patients not being able to complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment. For example, almost a quarter of the patients who did not complete their end-of-study cognitive assessment failed to do so because they had already died.
Overall, the prevalence of patients indicating a cognitive decline was virtually identical among 11,363 patients who had been maintained on evolocumab, with a 3.7% rate, and the 11,292 patients in the placebo group, with a 3.6% rate. When analyzed by achieved level of LDL-C after 4 weeks on treatment, the 2,338 patients with a level below 20 mg/dL had a 3.8% rate of self-reported cognitive loss, compared with a 4.5% rate among 3,613 patients who had an LDL-C level of at least 100 mg/dL when measured 4 weeks into the study.
One of the strengths of the new cognitive analysis is that, although it did not use the more sophisticated assessment tests employed on fewer patients in the EBBINGHAUS substudy, it used the Everyday Cognition scale (Neuropsychiatry. 2008 Jul;22[4]: 531-44). “We asked patients what they have experienced, and in the end that is what’s important, so this adds to the neurocognitive testing,” run in EBBINGHAUS, Dr. Giugliano said in an interview.
“The neurocognitive results in the present study were self-reported, and that might be a limitation, as it is less specific and objective, but it is also a strength, as it could be more sensitive” especially for a “nocebo effect common to all lipid-lowering drugs linked to the bad reputation historically attributed to statins,” Dr. Mannarino said.
Should the new FOURIER data “be interpreted as definitive evidence that intensive LDL-C lowering with PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies has no major harmful cognitive effects, at least over a period of 3 years? The answer appears to be a qualified yes, but with three important caveats,” Jennifer G. Robinson, MD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Iowa College of Public Health in Iowa City, said in an editorial that accompanied the new report (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2294-6). Her three caveats are the missing 18% of patients who never took the end-of-study assessment, the relative paucity of patients at very advanced age in FOURIER, in which patients averaged 62.5 years old, and the exclusion from FOURIER of patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke. Dr. Robinson also cited the 2.2 year median follow-up as leaving unsettled the potential cognitive impact of longer treatment.
In response, Dr. Giugliano noted that the very large size of FOURIER and the 22,655 patients who completed their survey provided substantial numbers of patients to address some of these concerns in robust subgroup analyses. For example, the new report showed no signal of excess cognitive complaints with evolocumab treatment among 1,999 patients who were at least 75 years old when entering the study, or in more than 5,000 patients with a history of cerebrovascular disease at baseline, or in 1,990 patients with a history of a nonstroke neurologic disease. In addition, while he conceded that the 18% of patients not accounted for in the new study placed some limits on generalizability of the findings, he also maintained that this unavoidable failure to collect data from a modest percentage of patients doesn’t scuttle the overarching signal of cognitive safety for most patients. And regarding the duration of treatment monitored, he noted that 5-year follow-up cognitive assessments are planned.
FOURIER was sponsored by Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha). Dr. Giugliano has received personal fees and research support from Amgen and from several other companies. Dr. Mannarino had no disclosures. Dr. Robinson has been a consultant to The Medicines Company, Novartis, and Pfizer, and she has received research funding to her institution from Amgen and several other companies.
SOURCE: Gencer B et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2283-93.
Correction: Dr. Giugliano's name was misspelled in an earlier version of this article.
FROM JACC
Key clinical point: A cognition survey of a large number of trial participants showed no signal of adverse effects from evolocumab treatment.
Major finding: Survey results showed cognitive compromise in 3.7% of patients on evolocumab and in 3.6% control patients on placebo.
Study details:
Disclosures: FOURIER was sponsored by Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha). Dr. Guigliano has received personal fees and research support from Amgen and from several other companies.
Source: Gencer B et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 12;75[18]:2283-93.
Hydroxychloroquine-triggered QTc-interval prolongations mount in COVID-19 patients
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
The potential for serious arrhythmias from hydroxychloroquine treatment of COVID-19 patients received further documentation from a pair of studies released on May 1, casting further doubt on whether the uncertain benefit from this or related drugs to infected patients is worth the clear risks the agents pose.
A report from 90 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine at one Boston hospital during March-April 2020 identified a significantly prolonged, corrected QT (QTc) interval of at least 500 msec in 18 patients (20%), which included 10 patients whose QTc rose by at least 60 msec above baseline, and a total of 21 patients (23%) having a notable prolongation (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1834). This series included one patient who developed torsades de pointes following treatment with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin, “which to our knowledge has yet to be reported elsewhere in the literature,” the report said.
The second report, from a single center in Lyon, France, included 40 confirmed COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine during 2 weeks in late March, and found that 37 (93%) had some increase in the QTc interval, including 14 patients (36%) with an increase of at least 60 msec, and 7 patients (18%) whose QTc rose to at least 500 msec (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1787). However, none of the 40 patients in this series developed an identified ventricular arrhythmia. All patients in both studies received hydroxychloroquine for at least 1 day, and roughly half the patients in each series also received concurrent azithromycin, another drug that can prolong the QTc interval and that has been frequently used in combination with hydroxychloroquine as an unproven COVID-19 treatment cocktail.
These two reports, as well as prior report from Brazil on COVID-19 patients treated with chloroquine diphosphate (JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3[4]:e208857), “underscore the potential risk associated with widespread use of hydroxychloroquine and the combination of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin in ambulatory patients with known or suspected COVID-19. Understanding whether this risk is worth taking in the absence of evidence of therapeutic efficacy creates a knowledge gap that needs to be addressed,” wrote Robert O. Bonow, MD, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago, and coauthors in an editorial that accompanied the two reports (JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 4;doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782). The editorial cited two recently-begun prospective trials, ORCHID and RECOVERY, that are more systematically assessing the safety and efficacy of hydroxychloroquine treatment in COVID-19 patients.
The findings lend further support to a Safety Communication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on April 24 that reminded clinicians that the Emergency Use Authorization for hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine in COVID-19 patients that the FDA issued on March 28 applied to only certain hospitalized patients or those enrolled in clinical trials. The Safety Communication also said that agency was aware of reports of adverse arrhythmia events when COVID-19 patients received these drugs outside a hospital setting as well as uninfected people who had received one of these drugs for preventing infection.
In addition, leaders of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Rhythm Society on April 10 issued a summary of considerations when using hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin to treat COVID-19 patients, and noted that a way to minimized the risk from these drugs is to withhold them from patients with a QTc interval of 500 msec or greater at baseline (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.016). The summary also highlighted the need for regular ECG monitoring of COVID-19 patients who receive drugs that can prolong the QTc interval, and recommended withdrawing treatment from patients when their QTc exceeds the 500 msec threshold.
None of the authors of the two reports and editorial had relevant commercial disclosures.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
COVID-19: Social distancing with young children
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.
Emma just celebrated her second birthday, and she has been working on the usual things that children start to master at this age: potty training, making friends, exerting her will through both actions and words, and generally enjoying life as the center of attention for both her parents and grandparents. Like everyone else in Maryland, Emma’s life changed suddenly with the coronavirus stay-at-home order that was issued on March 30. There is no more day care and her parents work from home while caring for her. Her grandparents visit, but only outside and only from a distance – there are no more hugs and there is no more sitting in her grandfather’s lap while he reads stories.
One afternoon a few weeks ago, Emma was looking out the window when she saw her friend, Max, walk by with his parents. Before her parents could stop her, Emma bolted out the door, and she and little Max wrapped each other in a tight embrace. Their parents snapped a photo of the smiling toddlers hugging before they separated the children. The photo is adorable, but as all struggle with social distancing, the poignance of two innocent toddlers in a forbidden embrace is a bit heartbreaking.
Everyone who has ever observed children knows that social distancing is not in their nature. Children play, they hug, they wrestle and tackle and poke, and sometimes even bite. And every student of social psychology has been taught about Harry Harlow’s experiments with rhesus macaques who were separated from their mothers and given access to an inanimate object to serve as a surrogate mother. The Harlow studies, while controversial, were revolutionary in demonstrating that early interactions with both a mother and with playmates were essential in the development of normal social relationships.
Regine Galanti, PhD, is a clinical psychologist at Long Island Behavioral Psychology, Cedarhurst, N.Y., who specializes in the treatment of anxiety and behavior problems. With young children she uses parent-child interaction therapy (PCIT) to help build relationships and discipline. Dr. Galanti said: “I don’t think we’re well prepared as a field to answer questions about the long-term effects of social distancing. If you need young children to socially distance, the responsibility has to fall on the adults. It’s important to explain to children what’s going on and to be honest in a developmentally appropriate way.”
Dr. Galanti has noticed that the issues that people had before COVID-19 are exacerbated by the stress of the current situation. What we do know is that young children thrive on structure.”
Tovah P. Klein, PhD, is the author of “How Toddlers Thrive” (Touchstone, 2015) and is the director of the Barnard College Center for Toddler Development in Manhattan. “When this started, we thought we would be closed for a few weeks,” Dr. Klein said. “We wanted to maintain a connection to the children, so we made videos for the parents to show to the kids, just to say ‘We’re still here.’ But as time went on and we realized it was going to be a while, we felt it was important to provide connection, so we launched a virtual program.”
Dr. Klein said that the teachers meet with their classes of 13 2-year-olds over Zoom, and when they first started, she asked the teachers to try to meet for 10 minutes. They are now meeting for 40 minutes twice a week. The children like seeing their teachers in their homes and they like seeing each other. In addition, the teachers make videos to send home and they are currently working on one to demystify masks. “We’re working on normalizing masks and showing children that when you put the mask on, you’re still there underneath.”
The center has existed for 48 years. There have been struggles for some of the children who attend; some of the parents have been hospitalized with the virus, and some work on the front line and so parents may be living away from a child.
“We’ve seen more challenging behaviors during this time, more tantrums, toileting issues, night awakenings, and more fragility. But as the new normal takes hold, things are settling in. Parents have been good about getting new routines and it helps if parents can handle their own stress,” Dr. Klein said. She also pointed out that for parents working at home while caring for their children, this can be particularly difficult on a young child. “The child knows the parent is home, but isn’t spending time with him, and he sees it as a rejection.”
Margaret Adams, MD, is a child psychiatrist in Maryland who works with very young children and their parents. She says that some of the children are thriving with the extra attention from their parents. “I often have seen difficulties with readjustment to the routine of separations to day care after a family vacation of a week, or sometimes even a weekend, even for those young ones who seem to love the social aspects of day care. I think it is likely a big impact will come upon return, depending on the developmental stage of the child,” Dr. Adams noted.
Despite the hardships of the moment, all three experts expressed hopefulness about the future for these children.
“Young children are super-resilient and that’s the blessing of this,” Dr. Galanti said. “I think they will be okay.”
Emma is home for now with her parents, who are expecting another child soon. Her mother notes: “The days are long and balancing work is an impossible challenge, but being with Emma has been a total blessing, and when would I ever have this much time to spend with my kid? She’s at such a fun age – so curious and adventurous – it’s amazing to watch her language and skills progress. I wish we weren’t in the midst of a pandemic, but Emma is definitely the bright spot.”
Dr. Miller is coauthor with Annette Hanson, MD, of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins, both in Baltimore. Dr. Miller has no disclosures.














