User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Children and COVID: New cases and hospital admissions skyrocket
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.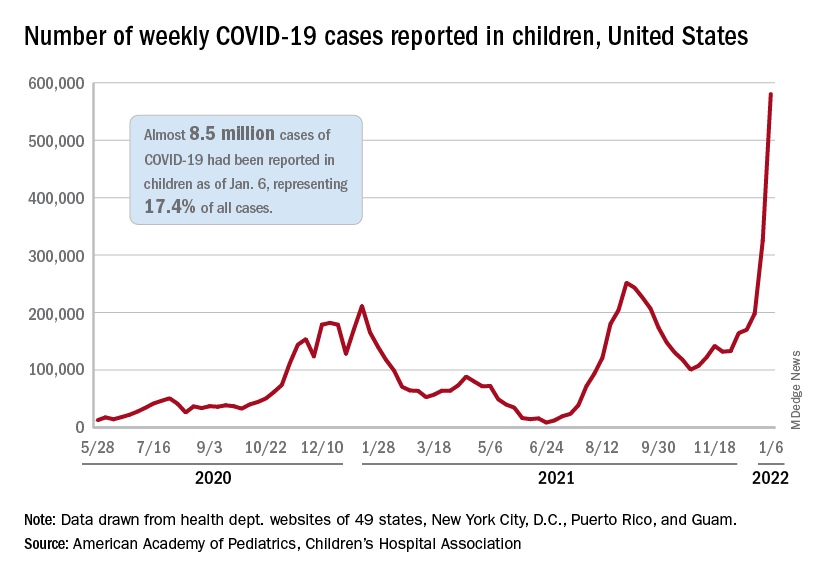
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The total for the week of Dec. 31 to Jan. 6 – the highest since the pandemic began – was an increase of 78% over the previous week (325,000) and 192% higher than just 2 weeks before (199,000), the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report. No region of the country was spared, as all four saw at least 50,000 more cases than the week before, but the increase was largest in the West and smallest in the Midwest.
“Nearly 8.5 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic; nearly 11% of these cases have been added in the past 2 weeks,” the AAP said.
The situation is the same for hospitalizations. On Dec. 15, the daily rate of new admissions for children aged 0-17 years was 0.26 per 100,000, and by Jan. 7 it had more than quadrupled to 1.15 per 100,000, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported. Before Omicron, the highest rate was 0.47 per 100,000 on Sept. 4, 2021.
The number of children occupying inpatient beds who had laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 went from 2,343 on Jan. 2 to 3,476 on Jan. 9, a jump of more than 48% in just 1 week. Texas had more hospitalized children (392) than any other state on Jan. 9, with California (339) and New York (313) the only other states over 300, according to data from the Department of Health & Human Services.
For vaccinations. however, the situation is definitely not the same. The number of children added to the ranks of those with at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine was down in early 2022 (Jan. 3-9) for both 5- to 11-year-olds (–8.2%) and 16- to 17-year-olds (–12.2%) but higher among those aged 12-15 (12.2%), compared with the previous week (Dec. 27 to Jan. 2), the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Cumulative figures show that 26.3% of all children aged 5-11 had received at least one dose of vaccine and 17.2% were fully vaccinated as of Jan. 10, compared with 62.2% and 52.0% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 68.5% and 58.1% of those aged 16-17. Altogether, over 23.8 million children in those three age groups have received at least one dose and almost 18.6 million are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
U.S. reports record-breaking 1.35 million new COVID cases in a day
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The United States reported 1.35 million new COVID-19 cases on Jan. 10, logging the highest daily total for any country in the world during the pandemic.
The United States set the previous record of 1 million cases on Jan. 3. (A large number of cases are reported on Mondays, since many states don’t provide updates over the weekend, according to Reuters.)
Still, the 7-day average for new cases has surpassed 700,000, tripling in 2 weeks as the contagious Omicron variant continues to spread across the country.
The daily record of new cases came a day after the United States crossed the grim milestone of 60 million COVID-19 cases during the pandemic, according to the latest data from Johns Hopkins University. More than 11 million new cases were reported in the past 28 days, with 5 million reported since Jan. 2.
Globally, more than 310 million cases have been reported, resulting in nearly 5.5 million COVID-19 deaths. Almost 40 million cases have been confirmed worldwide during the past month, with the United States accounting for 28% of those.
Texas became the second state to report more than 5 million cases since the pandemic began, behind California’s total of 6 million cases. Florida has reported more than 4.6 million, while New York has reported more than 4.1 million.
The United States has also hit an all-time high for hospitalizations, with nearly 146,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, according to the latest data from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The previous record was 142,000 hospitalizations in January 2021.
Jan. 11’s hospitalizations are more than twice as many as 2 weeks ago, according to CNN. About 78% of inpatient beds are in use nationwide, and 21% are being used for COVID-19 patients.
Deaths are averaging about 1,700 per day, Reuters reported, which is up from 1,400 in recent days but not much higher than earlier this winter. The peak average was 3,400 daily deaths in mid-January 2021.
The surging numbers of cases and hospitalizations across the country are straining hospitals. On Jan. 10, Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam declared a state of emergency after the number of intensive care unit hospitalizations more than doubled since Dec. 1, CNN reported. The order allows hospitals to expand bed capacity, use telehealth options, and be more flexible with staffing.
Texas is hiring at least 2,700 medical staff to help with the surge, CNN reported, and Kentucky has mobilized the National Guard to provide support.
“Omicron continues to burn through the commonwealth, growing at levels we have never seen before. Omicron is significantly more contagious than even the Delta variant,” Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear said during a news briefing Jan. 10.
Kentucky reported its highest weekly total of cases last week and has its highest rate of positive tests, at 26%. Mr. Beshear said the state is down to 134 available adult ICU beds.
“If it spreads at the rate we are seeing, it is certainly going to fill up our hospitals,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Health issues in women midlife linked with health decline at 65
Having specific health issues, including depressive symptoms and cardiovascular disease, as a middle-aged woman was associated with experiencing clinically important declines in health later in life, a new study finds.
The most predictive parameters of poorer health at age 65 were cardiovascular disease, clinically significant depressive symptoms, and current smoking. Osteoarthritis, lower education level, and higher body mass index (BMI) also were associated with poorer health status 10 years on, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH and colleagues wrote in their observational study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
Determining a patient’s score on a health-related quality of life measure based on these variables might be useful in clinical practice to recognize midlife patients at increased risk for later health deterioration, Dr. Solomon, of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a statement. This measure is called the Short Form 36 (SF-36), and the researchers specifically focused on the physical component summary score (PCS) of this measure. The SF-36 is similar to the Framingham 10-year coronary heart disease risk prediction score, according to Dr. Solomon, who is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Based on their risk scores, women could preemptively target modifiable risk factors before they enter old age, the investigators wrote.
“Age 55-65 may be a critical decade. A person’s health and factors during this period may set them on a path for their later adult years,” Dr. Solomon said in a statement. “The good news is that a large proportion of women at midlife are very stable and will not go on to experience declines. But being able to identify women at higher risk could help lead to interventions targeted to them.”
Study details
The study included a cohort of 1,091 women drawn from the 3,302-participant Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN), a racially and ethnically diverse group enrolled from six U.S. sites at or immediately before transition to menopause and followed for 10 years from age 55 to 65. The study sample, consisting of 24.6% Black, 24% Japanese or Chinese, and 51.9% White, had a median baseline age of 54.8 years and median BMI of 27 kg/m2 at entry. The median baseline PCS score was 53.1 (interquartile range, 46.8-56.7).
Over 10 years, 206 (18.9%) of the women in the study experienced clinically important declines of at least 8 points in baseline characteristics at around age 55. The following were significantly associated with these declines:
- Having a higher BMI.
- Having osteoarthritis.
- Having a lower educational level.
- Being a current smoker.
- Having clinically significant depressive symptoms.
- Having cardiovascular disease.
- Having better (or higher) physical health and function score on the PCS.
The association between a higher PCS score and a greater decline might seem like an anomaly, Dr. Solomon said in an interview, but one interpretation of this finding is that women with higher or better scores at baseline have further to fall once other risk factors take effect.
With data analyzed from October 2020 to March 2021, the median 10-year change in PCS was –1.02 points, but 206 women experienced declines of 8 points or more.
Those with health declines were more likely to be Black and less likely to be Japanese. They were also more likely to have other comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, and osteoporosis, and to report less physical activity.
Scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation, outside expert said
Commenting on the findings, Margaret J. Nachtigall, MD, a clinical associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at New York University Langone Health, cautioned that a generalized scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation of women at midlife.
“I assess women around age 55 on a daily basis for health risk factors going forward. And while a number such as BMI can be helpful, I worry that reliance on a score could miss treating the individual,” Dr. Nachtigall said an interview. For instance, one woman might have a high BMI owing to greater muscle mass, which is heavy, while another may have a lower BMI but more fat-related weight, as well as exacerbating conditions such as hypertension that would elevate her risk. “You have to make the calculation for each person.”
Dr. Nachtigall, who was not involved in the SWAN analysis, noted, however, that a big-data scoring system might be a useful adjunct to individual patient evaluation in that “it would make physicians look at all these many risk factors to identify those prone to decline.”
Study includes racially diverse population
According to the authors, while other studies have identified similar and other risk factors such as poor sleep, most have not included such a racially diverse population and have focused on women already in their senior years when the window of opportunity may already have closed.
“As a clinician and epidemiologist, I often think about the window of opportunity at midlife, when people are vital, engaged, and resilient,” said Dr. Solomon in the statement. “If we can identify risk factors and determine who is at risk, we may be able to find interventions that can stave off health declines and help put people on a better health trajectory.”
Eric M. Ascher, DO, who practices family medicine at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and was not involved in the SWAN research, agreed with Dr. Solomon.
“Doctors who treat chronic conditions often meet patients when they are already suffering from a medical problem,” he said in an interview. “It is key to decrease your risk factors before it is too late.”
Dr. Ascher added that many primary care providers already rely heavily on scoring systems when determining level of risk and type of intervention. “Any additional risk factor-scoring systems that are easy to implement and will prevent chronic diseases would be something providers would want to use with their patients.”
Detailed analyses of larger at-risk populations are needed to validate these risk factors and identify others, the authors said.
SWAN is supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the National Institutes of Heath’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Solomon reported financial ties to Amgen, AbbVie and Moderna, UpToDate, and Arthritis & Rheumatology; as well as serving on the board of directors for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and an advisory committee for the Food and Drug Administration outside of this work. Dr. Nachtigall and Dr. Ascher disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to their comments.
Having specific health issues, including depressive symptoms and cardiovascular disease, as a middle-aged woman was associated with experiencing clinically important declines in health later in life, a new study finds.
The most predictive parameters of poorer health at age 65 were cardiovascular disease, clinically significant depressive symptoms, and current smoking. Osteoarthritis, lower education level, and higher body mass index (BMI) also were associated with poorer health status 10 years on, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH and colleagues wrote in their observational study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
Determining a patient’s score on a health-related quality of life measure based on these variables might be useful in clinical practice to recognize midlife patients at increased risk for later health deterioration, Dr. Solomon, of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a statement. This measure is called the Short Form 36 (SF-36), and the researchers specifically focused on the physical component summary score (PCS) of this measure. The SF-36 is similar to the Framingham 10-year coronary heart disease risk prediction score, according to Dr. Solomon, who is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Based on their risk scores, women could preemptively target modifiable risk factors before they enter old age, the investigators wrote.
“Age 55-65 may be a critical decade. A person’s health and factors during this period may set them on a path for their later adult years,” Dr. Solomon said in a statement. “The good news is that a large proportion of women at midlife are very stable and will not go on to experience declines. But being able to identify women at higher risk could help lead to interventions targeted to them.”
Study details
The study included a cohort of 1,091 women drawn from the 3,302-participant Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN), a racially and ethnically diverse group enrolled from six U.S. sites at or immediately before transition to menopause and followed for 10 years from age 55 to 65. The study sample, consisting of 24.6% Black, 24% Japanese or Chinese, and 51.9% White, had a median baseline age of 54.8 years and median BMI of 27 kg/m2 at entry. The median baseline PCS score was 53.1 (interquartile range, 46.8-56.7).
Over 10 years, 206 (18.9%) of the women in the study experienced clinically important declines of at least 8 points in baseline characteristics at around age 55. The following were significantly associated with these declines:
- Having a higher BMI.
- Having osteoarthritis.
- Having a lower educational level.
- Being a current smoker.
- Having clinically significant depressive symptoms.
- Having cardiovascular disease.
- Having better (or higher) physical health and function score on the PCS.
The association between a higher PCS score and a greater decline might seem like an anomaly, Dr. Solomon said in an interview, but one interpretation of this finding is that women with higher or better scores at baseline have further to fall once other risk factors take effect.
With data analyzed from October 2020 to March 2021, the median 10-year change in PCS was –1.02 points, but 206 women experienced declines of 8 points or more.
Those with health declines were more likely to be Black and less likely to be Japanese. They were also more likely to have other comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, and osteoporosis, and to report less physical activity.
Scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation, outside expert said
Commenting on the findings, Margaret J. Nachtigall, MD, a clinical associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at New York University Langone Health, cautioned that a generalized scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation of women at midlife.
“I assess women around age 55 on a daily basis for health risk factors going forward. And while a number such as BMI can be helpful, I worry that reliance on a score could miss treating the individual,” Dr. Nachtigall said an interview. For instance, one woman might have a high BMI owing to greater muscle mass, which is heavy, while another may have a lower BMI but more fat-related weight, as well as exacerbating conditions such as hypertension that would elevate her risk. “You have to make the calculation for each person.”
Dr. Nachtigall, who was not involved in the SWAN analysis, noted, however, that a big-data scoring system might be a useful adjunct to individual patient evaluation in that “it would make physicians look at all these many risk factors to identify those prone to decline.”
Study includes racially diverse population
According to the authors, while other studies have identified similar and other risk factors such as poor sleep, most have not included such a racially diverse population and have focused on women already in their senior years when the window of opportunity may already have closed.
“As a clinician and epidemiologist, I often think about the window of opportunity at midlife, when people are vital, engaged, and resilient,” said Dr. Solomon in the statement. “If we can identify risk factors and determine who is at risk, we may be able to find interventions that can stave off health declines and help put people on a better health trajectory.”
Eric M. Ascher, DO, who practices family medicine at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and was not involved in the SWAN research, agreed with Dr. Solomon.
“Doctors who treat chronic conditions often meet patients when they are already suffering from a medical problem,” he said in an interview. “It is key to decrease your risk factors before it is too late.”
Dr. Ascher added that many primary care providers already rely heavily on scoring systems when determining level of risk and type of intervention. “Any additional risk factor-scoring systems that are easy to implement and will prevent chronic diseases would be something providers would want to use with their patients.”
Detailed analyses of larger at-risk populations are needed to validate these risk factors and identify others, the authors said.
SWAN is supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the National Institutes of Heath’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Solomon reported financial ties to Amgen, AbbVie and Moderna, UpToDate, and Arthritis & Rheumatology; as well as serving on the board of directors for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and an advisory committee for the Food and Drug Administration outside of this work. Dr. Nachtigall and Dr. Ascher disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to their comments.
Having specific health issues, including depressive symptoms and cardiovascular disease, as a middle-aged woman was associated with experiencing clinically important declines in health later in life, a new study finds.
The most predictive parameters of poorer health at age 65 were cardiovascular disease, clinically significant depressive symptoms, and current smoking. Osteoarthritis, lower education level, and higher body mass index (BMI) also were associated with poorer health status 10 years on, Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH and colleagues wrote in their observational study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
Determining a patient’s score on a health-related quality of life measure based on these variables might be useful in clinical practice to recognize midlife patients at increased risk for later health deterioration, Dr. Solomon, of the division of rheumatology, inflammation, and immunity at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in a statement. This measure is called the Short Form 36 (SF-36), and the researchers specifically focused on the physical component summary score (PCS) of this measure. The SF-36 is similar to the Framingham 10-year coronary heart disease risk prediction score, according to Dr. Solomon, who is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Based on their risk scores, women could preemptively target modifiable risk factors before they enter old age, the investigators wrote.
“Age 55-65 may be a critical decade. A person’s health and factors during this period may set them on a path for their later adult years,” Dr. Solomon said in a statement. “The good news is that a large proportion of women at midlife are very stable and will not go on to experience declines. But being able to identify women at higher risk could help lead to interventions targeted to them.”
Study details
The study included a cohort of 1,091 women drawn from the 3,302-participant Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN), a racially and ethnically diverse group enrolled from six U.S. sites at or immediately before transition to menopause and followed for 10 years from age 55 to 65. The study sample, consisting of 24.6% Black, 24% Japanese or Chinese, and 51.9% White, had a median baseline age of 54.8 years and median BMI of 27 kg/m2 at entry. The median baseline PCS score was 53.1 (interquartile range, 46.8-56.7).
Over 10 years, 206 (18.9%) of the women in the study experienced clinically important declines of at least 8 points in baseline characteristics at around age 55. The following were significantly associated with these declines:
- Having a higher BMI.
- Having osteoarthritis.
- Having a lower educational level.
- Being a current smoker.
- Having clinically significant depressive symptoms.
- Having cardiovascular disease.
- Having better (or higher) physical health and function score on the PCS.
The association between a higher PCS score and a greater decline might seem like an anomaly, Dr. Solomon said in an interview, but one interpretation of this finding is that women with higher or better scores at baseline have further to fall once other risk factors take effect.
With data analyzed from October 2020 to March 2021, the median 10-year change in PCS was –1.02 points, but 206 women experienced declines of 8 points or more.
Those with health declines were more likely to be Black and less likely to be Japanese. They were also more likely to have other comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, and osteoporosis, and to report less physical activity.
Scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation, outside expert said
Commenting on the findings, Margaret J. Nachtigall, MD, a clinical associate professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at New York University Langone Health, cautioned that a generalized scoring system should not replace individualized evaluation of women at midlife.
“I assess women around age 55 on a daily basis for health risk factors going forward. And while a number such as BMI can be helpful, I worry that reliance on a score could miss treating the individual,” Dr. Nachtigall said an interview. For instance, one woman might have a high BMI owing to greater muscle mass, which is heavy, while another may have a lower BMI but more fat-related weight, as well as exacerbating conditions such as hypertension that would elevate her risk. “You have to make the calculation for each person.”
Dr. Nachtigall, who was not involved in the SWAN analysis, noted, however, that a big-data scoring system might be a useful adjunct to individual patient evaluation in that “it would make physicians look at all these many risk factors to identify those prone to decline.”
Study includes racially diverse population
According to the authors, while other studies have identified similar and other risk factors such as poor sleep, most have not included such a racially diverse population and have focused on women already in their senior years when the window of opportunity may already have closed.
“As a clinician and epidemiologist, I often think about the window of opportunity at midlife, when people are vital, engaged, and resilient,” said Dr. Solomon in the statement. “If we can identify risk factors and determine who is at risk, we may be able to find interventions that can stave off health declines and help put people on a better health trajectory.”
Eric M. Ascher, DO, who practices family medicine at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York and was not involved in the SWAN research, agreed with Dr. Solomon.
“Doctors who treat chronic conditions often meet patients when they are already suffering from a medical problem,” he said in an interview. “It is key to decrease your risk factors before it is too late.”
Dr. Ascher added that many primary care providers already rely heavily on scoring systems when determining level of risk and type of intervention. “Any additional risk factor-scoring systems that are easy to implement and will prevent chronic diseases would be something providers would want to use with their patients.”
Detailed analyses of larger at-risk populations are needed to validate these risk factors and identify others, the authors said.
SWAN is supported by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the National Institutes of Heath’s Office of Research on Women’s Health. Dr. Solomon reported financial ties to Amgen, AbbVie and Moderna, UpToDate, and Arthritis & Rheumatology; as well as serving on the board of directors for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance and an advisory committee for the Food and Drug Administration outside of this work. Dr. Nachtigall and Dr. Ascher disclosed no conflicts of interest with regard to their comments.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
CDC: More kids hospitalized with COVID since pandemic began
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hospital admissions of U.S. children younger than 5 – the only group ineligible for vaccination – have reached their peak since the start of the pandemic, according to new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said the higher numbers show the importance of vaccination for all eligible groups.
“This is the highest number of pediatric hospitalizations we’ve seen throughout the pandemic, which we said about Delta until now,” she said at a CDC briefing Friday. “This very well may be that there are just more cases out there, and our children are more vulnerable when they have more cases surrounding them.”
Despite the skyrocketing admissions, hospitalizations are still relatively low for children, she said. The hospitalization rate for children under 5 is 4 in 100,000, and it’s about 1 in 100,000 in children 5-17.
Dr. Walensky said not all children are being hospitalized for COVID-19 – some are admitted for unrelated issues and test positive but don’t have symptoms.
“We are still learning more about the severity of Omicron in children,” she said, noting that just over 50% of children 12-18 are fully vaccinated, while only 16% of those ages 5-11 are fully vaccinated.
Friday’s teleconference was the first CDC briefing in several months and comes on the heels of recent guideline updates for testing and isolation that have left the American public dumbfounded. When asked why the briefing was held, Dr. Walensky said there had been interest in hearing more from the CDC, saying, “I anticipate this will be the first of many briefings.”
She also defended the confusing guideline changes, saying, “We’re in an unprecedented time with the speed of Omicron cases rising. … This is hard, and I am committed to continuing to improve as we learn more about the science and communicate that to you.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Heavy snoring in early pregnancy linked to increased insulin resistance
Severe maternal sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a known risk factor for gestational diabetes, which is commonly diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
Now, a new study suggests that increases in insulin resistance, a precursor for gestational diabetes, may take place as early as the first trimester of pregnancy in women with risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), such as overweight and habitual snoring.
This finding could potentially provide physicians with a window of opportunity to improve outcomes by screening at-risk women early in pregnancy or even prior to conception, Laura Sanapo, MD, assistant professor of medicine (research) at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote in Sleep.
“Further studies are needed to investigate the association and its impact on the development of gestational diabetes, and to establish whether early-gestation or pregestational treatment of SDB would improve glucose metabolic outcomes in pregnancy,” they wrote.
”What this paper demonstrates is that the changes that predate gestational diabetes are seen much earlier in pregnancy,” senior study author Ghada Bourjeily, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University, said in an interview. Women should be screened for SDB rather than insulin resistance in early pregnancy since continuous positive airway pressure therapy (CPAP) is a highly effective intervention.
Waiting until midpregnancy to screen for OSA “is too late to make significant changes in the care of these women,” said Dr. Bourjeily, who is also director of research and training at the Women’s Medicine Collaborative at The Miriam Hospital in Providence, R.I. “By the time you diagnose gestational diabetes, the cat is out of the bag.”
For the study, women with early singleton pregnancies and risk factors for OSA such as habitual snoring and a median body mass index (BMI) of at least 27 kg/m2 were recruited from two prospective clinical trial studies enriched for OSA positivity. Women with a history of pregestational diabetes and those using CPAP or receiving chronic steroid therapy were excluded from the current study.
A total of 192 study participants underwent in-home sleep study (HSAT) and homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) between 11 and 15 gestational weeks, respectively. The association between continuous measures of SDB as a respiratory-event index as well as oxygen-desaturation index and glucose metabolism parameters such as insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were analyzed after adjusting for gestational age, maternal age, BMI, ethnicity, race, and parity.
In all, 61 women (32%) were diagnosed with OSA based on respiratory event index values greater than or equal to five events per hour. These participants were more likely to be older, to have a high BMI, and to be multipara, compared with women who didn’t have a diagnosis of OSA. Women with a diagnosis of OSA exhibited higher glucose and C-peptide values and a higher degree of insulin resistance, compared with women without OSA, the researchers found. An increase of 0.3 in HOMA-IR related to maternal SDB in early pregnancy may significantly affect glucose metabolism.
Although the findings of the current study cannot be extrapolated to women who don’t have overweight or obesity, some women with normal-range BMI (18.5-24.9) are also at increased risk of glucose metabolism changes, Dr. Bourjeily pointed out. This includes those of Southeast Asian descent. “We found that the association of SDB parameters with insulin resistance was actually happening independently of BMI and other factors.”
Ideally, screening for SDB would begin prior to pregnancy, Dr. Bourjeily said. A BMI greater than 25 should be taken into account and patients asked if they snore and if so, whether it’s loud enough to wake their partner. They should also be asked about experiencing daytime sleepiness.
“Based on these answers, especially in women screened prior to pregnancy, there will be time to make the diagnosis of sleep apnea and get the patient on CPAP,” Dr. Bourjeily said.
“This is an interesting study and one of the rare ones looking at early pregnancy and some of the mechanisms that could possibly be contributing to gestational diabetes,” commented Grenye O’Malley, MD, assistant professor in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and bone disease at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. O’Malley was not involved in the study.
“It confirms our suspicions that there’s probably a lot of things happening earlier in pregnancy before a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. It also confirms that some of the mechanisms are probably very similar to those involved in the association between disordered sleep and the development of type 2 diabetes.”
However, it’s too early to determine whether screening for SDB and the use of CPAP will prevent glycemic changes, Dr. O’Malley said in an interview. “Whenever we screen, we ask whether we have an intervention that changes outcomes and we don’t know that yet.”
Some of the symptoms of SDB are also common in early pregnancy, such as a BMI greater than 25 and daytime sleepiness, Dr. O’Malley pointed out. It was unclear whether the study participants had a propensity to develop type 2 diabetes or whether they were at risk of gestational diabetes.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute for Child Health; and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bourjeily and colleagues, as well as Dr. O’Malley, reported having no potential financial conflicts of interest.
Severe maternal sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a known risk factor for gestational diabetes, which is commonly diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
Now, a new study suggests that increases in insulin resistance, a precursor for gestational diabetes, may take place as early as the first trimester of pregnancy in women with risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), such as overweight and habitual snoring.
This finding could potentially provide physicians with a window of opportunity to improve outcomes by screening at-risk women early in pregnancy or even prior to conception, Laura Sanapo, MD, assistant professor of medicine (research) at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote in Sleep.
“Further studies are needed to investigate the association and its impact on the development of gestational diabetes, and to establish whether early-gestation or pregestational treatment of SDB would improve glucose metabolic outcomes in pregnancy,” they wrote.
”What this paper demonstrates is that the changes that predate gestational diabetes are seen much earlier in pregnancy,” senior study author Ghada Bourjeily, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University, said in an interview. Women should be screened for SDB rather than insulin resistance in early pregnancy since continuous positive airway pressure therapy (CPAP) is a highly effective intervention.
Waiting until midpregnancy to screen for OSA “is too late to make significant changes in the care of these women,” said Dr. Bourjeily, who is also director of research and training at the Women’s Medicine Collaborative at The Miriam Hospital in Providence, R.I. “By the time you diagnose gestational diabetes, the cat is out of the bag.”
For the study, women with early singleton pregnancies and risk factors for OSA such as habitual snoring and a median body mass index (BMI) of at least 27 kg/m2 were recruited from two prospective clinical trial studies enriched for OSA positivity. Women with a history of pregestational diabetes and those using CPAP or receiving chronic steroid therapy were excluded from the current study.
A total of 192 study participants underwent in-home sleep study (HSAT) and homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) between 11 and 15 gestational weeks, respectively. The association between continuous measures of SDB as a respiratory-event index as well as oxygen-desaturation index and glucose metabolism parameters such as insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were analyzed after adjusting for gestational age, maternal age, BMI, ethnicity, race, and parity.
In all, 61 women (32%) were diagnosed with OSA based on respiratory event index values greater than or equal to five events per hour. These participants were more likely to be older, to have a high BMI, and to be multipara, compared with women who didn’t have a diagnosis of OSA. Women with a diagnosis of OSA exhibited higher glucose and C-peptide values and a higher degree of insulin resistance, compared with women without OSA, the researchers found. An increase of 0.3 in HOMA-IR related to maternal SDB in early pregnancy may significantly affect glucose metabolism.
Although the findings of the current study cannot be extrapolated to women who don’t have overweight or obesity, some women with normal-range BMI (18.5-24.9) are also at increased risk of glucose metabolism changes, Dr. Bourjeily pointed out. This includes those of Southeast Asian descent. “We found that the association of SDB parameters with insulin resistance was actually happening independently of BMI and other factors.”
Ideally, screening for SDB would begin prior to pregnancy, Dr. Bourjeily said. A BMI greater than 25 should be taken into account and patients asked if they snore and if so, whether it’s loud enough to wake their partner. They should also be asked about experiencing daytime sleepiness.
“Based on these answers, especially in women screened prior to pregnancy, there will be time to make the diagnosis of sleep apnea and get the patient on CPAP,” Dr. Bourjeily said.
“This is an interesting study and one of the rare ones looking at early pregnancy and some of the mechanisms that could possibly be contributing to gestational diabetes,” commented Grenye O’Malley, MD, assistant professor in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and bone disease at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. O’Malley was not involved in the study.
“It confirms our suspicions that there’s probably a lot of things happening earlier in pregnancy before a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. It also confirms that some of the mechanisms are probably very similar to those involved in the association between disordered sleep and the development of type 2 diabetes.”
However, it’s too early to determine whether screening for SDB and the use of CPAP will prevent glycemic changes, Dr. O’Malley said in an interview. “Whenever we screen, we ask whether we have an intervention that changes outcomes and we don’t know that yet.”
Some of the symptoms of SDB are also common in early pregnancy, such as a BMI greater than 25 and daytime sleepiness, Dr. O’Malley pointed out. It was unclear whether the study participants had a propensity to develop type 2 diabetes or whether they were at risk of gestational diabetes.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute for Child Health; and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bourjeily and colleagues, as well as Dr. O’Malley, reported having no potential financial conflicts of interest.
Severe maternal sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a known risk factor for gestational diabetes, which is commonly diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
Now, a new study suggests that increases in insulin resistance, a precursor for gestational diabetes, may take place as early as the first trimester of pregnancy in women with risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), such as overweight and habitual snoring.
This finding could potentially provide physicians with a window of opportunity to improve outcomes by screening at-risk women early in pregnancy or even prior to conception, Laura Sanapo, MD, assistant professor of medicine (research) at Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote in Sleep.
“Further studies are needed to investigate the association and its impact on the development of gestational diabetes, and to establish whether early-gestation or pregestational treatment of SDB would improve glucose metabolic outcomes in pregnancy,” they wrote.
”What this paper demonstrates is that the changes that predate gestational diabetes are seen much earlier in pregnancy,” senior study author Ghada Bourjeily, MD, professor of medicine at Brown University, said in an interview. Women should be screened for SDB rather than insulin resistance in early pregnancy since continuous positive airway pressure therapy (CPAP) is a highly effective intervention.
Waiting until midpregnancy to screen for OSA “is too late to make significant changes in the care of these women,” said Dr. Bourjeily, who is also director of research and training at the Women’s Medicine Collaborative at The Miriam Hospital in Providence, R.I. “By the time you diagnose gestational diabetes, the cat is out of the bag.”
For the study, women with early singleton pregnancies and risk factors for OSA such as habitual snoring and a median body mass index (BMI) of at least 27 kg/m2 were recruited from two prospective clinical trial studies enriched for OSA positivity. Women with a history of pregestational diabetes and those using CPAP or receiving chronic steroid therapy were excluded from the current study.
A total of 192 study participants underwent in-home sleep study (HSAT) and homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) between 11 and 15 gestational weeks, respectively. The association between continuous measures of SDB as a respiratory-event index as well as oxygen-desaturation index and glucose metabolism parameters such as insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were analyzed after adjusting for gestational age, maternal age, BMI, ethnicity, race, and parity.
In all, 61 women (32%) were diagnosed with OSA based on respiratory event index values greater than or equal to five events per hour. These participants were more likely to be older, to have a high BMI, and to be multipara, compared with women who didn’t have a diagnosis of OSA. Women with a diagnosis of OSA exhibited higher glucose and C-peptide values and a higher degree of insulin resistance, compared with women without OSA, the researchers found. An increase of 0.3 in HOMA-IR related to maternal SDB in early pregnancy may significantly affect glucose metabolism.
Although the findings of the current study cannot be extrapolated to women who don’t have overweight or obesity, some women with normal-range BMI (18.5-24.9) are also at increased risk of glucose metabolism changes, Dr. Bourjeily pointed out. This includes those of Southeast Asian descent. “We found that the association of SDB parameters with insulin resistance was actually happening independently of BMI and other factors.”
Ideally, screening for SDB would begin prior to pregnancy, Dr. Bourjeily said. A BMI greater than 25 should be taken into account and patients asked if they snore and if so, whether it’s loud enough to wake their partner. They should also be asked about experiencing daytime sleepiness.
“Based on these answers, especially in women screened prior to pregnancy, there will be time to make the diagnosis of sleep apnea and get the patient on CPAP,” Dr. Bourjeily said.
“This is an interesting study and one of the rare ones looking at early pregnancy and some of the mechanisms that could possibly be contributing to gestational diabetes,” commented Grenye O’Malley, MD, assistant professor in the division of endocrinology, diabetes, and bone disease at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Dr. O’Malley was not involved in the study.
“It confirms our suspicions that there’s probably a lot of things happening earlier in pregnancy before a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. It also confirms that some of the mechanisms are probably very similar to those involved in the association between disordered sleep and the development of type 2 diabetes.”
However, it’s too early to determine whether screening for SDB and the use of CPAP will prevent glycemic changes, Dr. O’Malley said in an interview. “Whenever we screen, we ask whether we have an intervention that changes outcomes and we don’t know that yet.”
Some of the symptoms of SDB are also common in early pregnancy, such as a BMI greater than 25 and daytime sleepiness, Dr. O’Malley pointed out. It was unclear whether the study participants had a propensity to develop type 2 diabetes or whether they were at risk of gestational diabetes.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the National Institute for Child Health; and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences. Dr. Bourjeily and colleagues, as well as Dr. O’Malley, reported having no potential financial conflicts of interest.
FROM SLEEP
Pig heart successfully transplanted to man
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Palliative care specialists seek greater role in lung disease
Mrs. S.’s long-term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) prognosis was grim, and she faced a harder time getting through each day. But neither she nor her primary care physician was willing to embrace strategies other than drugs.
“She felt guilty for continuing to smoke, but also expressed a need to smoke to help her deal with her husband’s cancer and eventual death,” recalled Georgia Narsavage, PhD, RN, ANP-BC, professor emerita of nursing at West Virginia University. “Her primary care physician was reluctant to introduce any treatment other than medications because her family was resistant to facing ‘mother dying.’ ”
But things changed when Mrs. S. was referred to a palliative-care clinical nurse specialist following a hospitalization. “The goal of palliative care is to support quality of life by relieving symptoms and decreasing suffering. She was assisted to improve functioning overall, and home support services were provided,” Dr. Narsavage said. “They allowed her to live at home relatively pain free with decreased dyspnea for 3 more years until her transition to hospice care a few months before death.
It wasn’t quite a happy ending. But it was a happier ending, and one that palliative care (PC) advocates hope will become more common in pulmonary care. They’re working to convince colleagues that PC is neither another word for hospice nor a sign that anyone is giving up on a patient.
Underutilized but beneficial
“Palliative care is underutilized in patients with chronic pulmonary disease, and it’s a missed opportunity to potentially alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life,” said Hilary DuBrock, MD, an internist and critical care pulmonologist with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Chest physicians should know that it’s important to recognize your limitations in addressing all aspects of a chronic disease, and it’s OK to ask for help from a specialty multidisciplinary team of palliative care providers.”
Statistics back up Dr. DuBrock’s perspective about how PC isn’t common in pulmonary care. A 2017 study examined 181,689 U.S. adult patients who had COPD, received oxygen at home, and were hospitalized for exacerbations from 2006-2012. Just 1.7% received PC, although the number grew over the study period.
Another study published in 2017 examined 3,166 patients over the same period with end-stage idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) who were on ventilators. The use of PC is group rose from 2.3% in 2006 to 21.6% in 2012.
More recently, a 2020 meta-analysis examined 19 studies and found that patients with lung cancer were much more likely to receive PC than were those with COPD (odds ratio (OR) = 9.59, P < .001, for hospital-based PC and OR = 8.79, P < .001, for home-based PC).
Patients with lung cancer vs. COPD were also less likely to receive invasive ventilation (OR = .26, P < .001), noninvasive ventilation (OR = .63, P = .009) or CPR (OR = .29, P < .001) or die at a nursing home/long-term care facility (OR = .32, P < .001).
Other studies support PC in COPD: Research in Europe has linked PC in COPD to fewer in-hospital deaths and lower end-of-life expenses. A Canadian study also linked PC to fewer in-hospital deaths in COPD.
Dr. DuBrock said she believes there are a couple reasons why PC isn’t more widely accepted in pulmonology. “There has been little evidence in chronic pulmonary disease regarding the role of PC, and there is a lack of standardized guidelines to help clinicians determine appropriate timing and patient selection for referral,” she said. “There is also a reluctance to refer patients to palliative care since some may think that referral implies that they are giving up on their patients.”
In fact, she said, “if appropriately explained and discussed with patients, PC does not necessarily need to imply to patients that you are giving up on them, but rather that you care enough about them to try to find novel ways to improve their quality of life and relieve their symptoms. Additionally, palliative care can be provided alongside ongoing medical care and treatment of their chronic lung disease.”
More than standard care
Another obstacle comes from pulmonologists who claim PC isn’t necessary because they’re handling patient care themselves, said University of Alabama at Birmingham critical care pulmonologist Anand S. Iyer, MD. “They’ll say: ‘I do palliative care, I palliate their breathing. I treat breathlessness and cough, that’s what I do.’ ”
But these symptoms only brush the surface of patient needs, he said. “I don’t think that the average pulmonologist goes beyond that to comprehensive symptom assessment and management of a whole host of symptoms beyond those limited to the lungs – depression, anxiety, fatigue, malnutrition.”
On that latter front, he said, pulmonologists “are really good at having end-of-life conversations at the end of life. We do that every day in the ICU.” Advocates for PC, he said, “want to push that to the clinic a year or two earlier.”
Timing and use of PC
When should pulmonologists call in a PC team? Specialists recommend early consultations, even right after a pulmonary disease is diagnosed. “When a pulmonologist diagnoses a condition as a serious illness – especially chronic pulmonary disease – a consultation with a palliative care physician or advanced practice registered nurse” can help assess the need for care and the best time to introduce palliative care to the patient and family “to provide relief and enhance quality of life,” West Virginia University’s Dr. Narsavage said. “Initial diagnosis is not too early to think about the trajectory.
Dr. Iyer agreed that early PC consultation is key. “We’re talking about comprehensive support for the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families. It can grow as needs of patients become more severe.”
For her part, Dr. DuBrock urged colleagues to focus on patient experiences. “The exact timing of when to refer patients with pulmonary disease is not well established,” she said. “Thus, it’s important to take cues from our patients. If they are experiencing significant symptom burden or impaired quality of life or having difficulty coping with their lung disease, then it may be helpful to call in palliative care to address these issues alongside education and discussion with the patient about the role of palliative care to address their unmet needs.”
As an example, Dr. DuBrock spoke of one of her own patients who has pulmonary hypertension (PH), connective tissue disease, and interstitial lung disease. “Her hypertension was relatively well controlled, but she was still quite symptomatic as well as depressed and having difficulty sleeping. I struggled with wanting to help her feel better but I also recognized that more PH therapy wasn’t necessarily the answer,” Dr. Dubrock said. “After some discussions, I referred her to palliative care, and they were extremely helpful with addressing her symptoms with a combination of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapy and also addressing some of her underlying concerns and fears regarding her prognosis and issues related to advance-care planning. Social work was also helpful with addressing some of her financial concerns. I continue to see her on regular basis and treat her PH, but her overall quality of life, sleep, and mood have improved substantially.”
First steps
According to specialists, the first step in the PC process with patients is to make sure they understand their conditions, their prognoses, and the role of palliative care itself.
Kathleen Oare Lindell, PhD, RN, associate professor of nursing at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who specializes in PC in pulmonary disease, remembers taking the histories of patients with grim prognoses and “their look on their face was like, ‘I just have a common cold.’ ” In other cases, she said, patients may fear they’ll die immediately when they have 3-5 years to live.
Dr. Lindell, who has worked at a specialty center for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), emphasized the importance of speaking in layperson terms that patients understand, such as referring to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as “unknown lung scarring.” She also said it’s crucial to be up front about their prognoses.
As for patient understanding of PC, she said, “people think it’s hospice that they’re giving. Palliative care is neither. Instead, it helps to address symptom management, I always tell patients, ‘You’ll be scared, you’ll have a cough. There are medicines and nonpharmacological therapies [that can help], and that’s what palliative care does.’ ”
Keith Swetz, MD, an internist and palliative care specialist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, agreed that a concise discussion of prognosis is vital. “What do they know about their illness, and what do they understand about what will happen when things get worse?” he said.
“With pulmonary disease, they may be looking at months to years punctuated with a lot of ICU admissions, trips to the hospital, symptom burden, and decline in function. Some will want aggressive treatment and say they’re fine being in the hospital, while others will say being comfortable at home is more important.”
Dr. Swetz’s patients commonly have COPD, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, or PH, and some may have concurrent heart failure. While their prognoses may be poor, he said, discussion about their wishes probably aren’t happening outside of the PC setting.
Or if they are happening, he said, they’re lower quality, boiling down complicated care questions to “Do you want us to do everything yes, or no?
“A lot of it has to do with time,” he said. “Clinicians are busy, they might have a full ICU or pulmonary clinic with 15 minutes to see patients. Sitting down and talking about these things isn’t something that’s prioritized or fits into the work stream very well, and often it hasn’t been reimbursed.”
There typically aren’t insurance hassles regarding referrals for PC, Dr. Iyer said, although finding available specialists may be challenging. A 2019 study projected a wave of retirements of older PC physicians over the next few years, and the ratio of patients to PC specialists may not return to 2019 levels for decades. Rural areas are especially shorthanded. But telehealth may improve access, Dr. Iyer said.
What’s next? Specialists are trying to pin down guidelines for when PC consultation is appropriate in pulmonary disease.
Triggers to PC
Dr. Iyer, Dr. Lindell and others authored a 2021 report in the journal CHEST that offers guidance about triggers for PC consultation. The authors cited four “levers” or triggers that are important: worsening lung function, severe symptoms or high burden of care needs, poor prognosis, and frequent severe exacerbations.
“The overall point here is that integrating palliative care into COPD practice isn’t an on-off switch; rather, it should be based upon multiple factors and can evolve over time,” they wrote.
They noted that, “patients with COPD accept palliative care as early as moderate COPD (FEV1 < 80%), so patients may be ready sooner than clinicians think.”
They added that, “if prognosis is such a concern that a clinician is considering referral for lung transplant evaluation, then concurrent referral to specialist palliative care should be routine practice.
Finally, frequent severe exacerbations, i.e. those that require hospitalization or an emergency room visit, carry a high risk for posthospitalization mortality and are ideal inflection points in the illness trajectory of COPD.”
In the big picture, the authors contend, “palliative care should be integrated early and concurrently with COPD-directed therapies, and its intensity should increase over time as symptoms, needs, and exacerbations worsen approaching EOL [end of life].”
None of the interviewees or other authors reported having any relevant conflicts for this story.
Mrs. S.’s long-term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) prognosis was grim, and she faced a harder time getting through each day. But neither she nor her primary care physician was willing to embrace strategies other than drugs.
“She felt guilty for continuing to smoke, but also expressed a need to smoke to help her deal with her husband’s cancer and eventual death,” recalled Georgia Narsavage, PhD, RN, ANP-BC, professor emerita of nursing at West Virginia University. “Her primary care physician was reluctant to introduce any treatment other than medications because her family was resistant to facing ‘mother dying.’ ”
But things changed when Mrs. S. was referred to a palliative-care clinical nurse specialist following a hospitalization. “The goal of palliative care is to support quality of life by relieving symptoms and decreasing suffering. She was assisted to improve functioning overall, and home support services were provided,” Dr. Narsavage said. “They allowed her to live at home relatively pain free with decreased dyspnea for 3 more years until her transition to hospice care a few months before death.
It wasn’t quite a happy ending. But it was a happier ending, and one that palliative care (PC) advocates hope will become more common in pulmonary care. They’re working to convince colleagues that PC is neither another word for hospice nor a sign that anyone is giving up on a patient.
Underutilized but beneficial
“Palliative care is underutilized in patients with chronic pulmonary disease, and it’s a missed opportunity to potentially alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life,” said Hilary DuBrock, MD, an internist and critical care pulmonologist with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Chest physicians should know that it’s important to recognize your limitations in addressing all aspects of a chronic disease, and it’s OK to ask for help from a specialty multidisciplinary team of palliative care providers.”
Statistics back up Dr. DuBrock’s perspective about how PC isn’t common in pulmonary care. A 2017 study examined 181,689 U.S. adult patients who had COPD, received oxygen at home, and were hospitalized for exacerbations from 2006-2012. Just 1.7% received PC, although the number grew over the study period.
Another study published in 2017 examined 3,166 patients over the same period with end-stage idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) who were on ventilators. The use of PC is group rose from 2.3% in 2006 to 21.6% in 2012.
More recently, a 2020 meta-analysis examined 19 studies and found that patients with lung cancer were much more likely to receive PC than were those with COPD (odds ratio (OR) = 9.59, P < .001, for hospital-based PC and OR = 8.79, P < .001, for home-based PC).
Patients with lung cancer vs. COPD were also less likely to receive invasive ventilation (OR = .26, P < .001), noninvasive ventilation (OR = .63, P = .009) or CPR (OR = .29, P < .001) or die at a nursing home/long-term care facility (OR = .32, P < .001).
Other studies support PC in COPD: Research in Europe has linked PC in COPD to fewer in-hospital deaths and lower end-of-life expenses. A Canadian study also linked PC to fewer in-hospital deaths in COPD.
Dr. DuBrock said she believes there are a couple reasons why PC isn’t more widely accepted in pulmonology. “There has been little evidence in chronic pulmonary disease regarding the role of PC, and there is a lack of standardized guidelines to help clinicians determine appropriate timing and patient selection for referral,” she said. “There is also a reluctance to refer patients to palliative care since some may think that referral implies that they are giving up on their patients.”
In fact, she said, “if appropriately explained and discussed with patients, PC does not necessarily need to imply to patients that you are giving up on them, but rather that you care enough about them to try to find novel ways to improve their quality of life and relieve their symptoms. Additionally, palliative care can be provided alongside ongoing medical care and treatment of their chronic lung disease.”
More than standard care
Another obstacle comes from pulmonologists who claim PC isn’t necessary because they’re handling patient care themselves, said University of Alabama at Birmingham critical care pulmonologist Anand S. Iyer, MD. “They’ll say: ‘I do palliative care, I palliate their breathing. I treat breathlessness and cough, that’s what I do.’ ”
But these symptoms only brush the surface of patient needs, he said. “I don’t think that the average pulmonologist goes beyond that to comprehensive symptom assessment and management of a whole host of symptoms beyond those limited to the lungs – depression, anxiety, fatigue, malnutrition.”
On that latter front, he said, pulmonologists “are really good at having end-of-life conversations at the end of life. We do that every day in the ICU.” Advocates for PC, he said, “want to push that to the clinic a year or two earlier.”
Timing and use of PC
When should pulmonologists call in a PC team? Specialists recommend early consultations, even right after a pulmonary disease is diagnosed. “When a pulmonologist diagnoses a condition as a serious illness – especially chronic pulmonary disease – a consultation with a palliative care physician or advanced practice registered nurse” can help assess the need for care and the best time to introduce palliative care to the patient and family “to provide relief and enhance quality of life,” West Virginia University’s Dr. Narsavage said. “Initial diagnosis is not too early to think about the trajectory.
Dr. Iyer agreed that early PC consultation is key. “We’re talking about comprehensive support for the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families. It can grow as needs of patients become more severe.”
For her part, Dr. DuBrock urged colleagues to focus on patient experiences. “The exact timing of when to refer patients with pulmonary disease is not well established,” she said. “Thus, it’s important to take cues from our patients. If they are experiencing significant symptom burden or impaired quality of life or having difficulty coping with their lung disease, then it may be helpful to call in palliative care to address these issues alongside education and discussion with the patient about the role of palliative care to address their unmet needs.”
As an example, Dr. DuBrock spoke of one of her own patients who has pulmonary hypertension (PH), connective tissue disease, and interstitial lung disease. “Her hypertension was relatively well controlled, but she was still quite symptomatic as well as depressed and having difficulty sleeping. I struggled with wanting to help her feel better but I also recognized that more PH therapy wasn’t necessarily the answer,” Dr. Dubrock said. “After some discussions, I referred her to palliative care, and they were extremely helpful with addressing her symptoms with a combination of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapy and also addressing some of her underlying concerns and fears regarding her prognosis and issues related to advance-care planning. Social work was also helpful with addressing some of her financial concerns. I continue to see her on regular basis and treat her PH, but her overall quality of life, sleep, and mood have improved substantially.”
First steps
According to specialists, the first step in the PC process with patients is to make sure they understand their conditions, their prognoses, and the role of palliative care itself.
Kathleen Oare Lindell, PhD, RN, associate professor of nursing at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who specializes in PC in pulmonary disease, remembers taking the histories of patients with grim prognoses and “their look on their face was like, ‘I just have a common cold.’ ” In other cases, she said, patients may fear they’ll die immediately when they have 3-5 years to live.
Dr. Lindell, who has worked at a specialty center for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), emphasized the importance of speaking in layperson terms that patients understand, such as referring to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as “unknown lung scarring.” She also said it’s crucial to be up front about their prognoses.
As for patient understanding of PC, she said, “people think it’s hospice that they’re giving. Palliative care is neither. Instead, it helps to address symptom management, I always tell patients, ‘You’ll be scared, you’ll have a cough. There are medicines and nonpharmacological therapies [that can help], and that’s what palliative care does.’ ”
Keith Swetz, MD, an internist and palliative care specialist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, agreed that a concise discussion of prognosis is vital. “What do they know about their illness, and what do they understand about what will happen when things get worse?” he said.
“With pulmonary disease, they may be looking at months to years punctuated with a lot of ICU admissions, trips to the hospital, symptom burden, and decline in function. Some will want aggressive treatment and say they’re fine being in the hospital, while others will say being comfortable at home is more important.”
Dr. Swetz’s patients commonly have COPD, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, or PH, and some may have concurrent heart failure. While their prognoses may be poor, he said, discussion about their wishes probably aren’t happening outside of the PC setting.
Or if they are happening, he said, they’re lower quality, boiling down complicated care questions to “Do you want us to do everything yes, or no?
“A lot of it has to do with time,” he said. “Clinicians are busy, they might have a full ICU or pulmonary clinic with 15 minutes to see patients. Sitting down and talking about these things isn’t something that’s prioritized or fits into the work stream very well, and often it hasn’t been reimbursed.”
There typically aren’t insurance hassles regarding referrals for PC, Dr. Iyer said, although finding available specialists may be challenging. A 2019 study projected a wave of retirements of older PC physicians over the next few years, and the ratio of patients to PC specialists may not return to 2019 levels for decades. Rural areas are especially shorthanded. But telehealth may improve access, Dr. Iyer said.
What’s next? Specialists are trying to pin down guidelines for when PC consultation is appropriate in pulmonary disease.
Triggers to PC
Dr. Iyer, Dr. Lindell and others authored a 2021 report in the journal CHEST that offers guidance about triggers for PC consultation. The authors cited four “levers” or triggers that are important: worsening lung function, severe symptoms or high burden of care needs, poor prognosis, and frequent severe exacerbations.
“The overall point here is that integrating palliative care into COPD practice isn’t an on-off switch; rather, it should be based upon multiple factors and can evolve over time,” they wrote.
They noted that, “patients with COPD accept palliative care as early as moderate COPD (FEV1 < 80%), so patients may be ready sooner than clinicians think.”
They added that, “if prognosis is such a concern that a clinician is considering referral for lung transplant evaluation, then concurrent referral to specialist palliative care should be routine practice.
Finally, frequent severe exacerbations, i.e. those that require hospitalization or an emergency room visit, carry a high risk for posthospitalization mortality and are ideal inflection points in the illness trajectory of COPD.”
In the big picture, the authors contend, “palliative care should be integrated early and concurrently with COPD-directed therapies, and its intensity should increase over time as symptoms, needs, and exacerbations worsen approaching EOL [end of life].”
None of the interviewees or other authors reported having any relevant conflicts for this story.
Mrs. S.’s long-term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) prognosis was grim, and she faced a harder time getting through each day. But neither she nor her primary care physician was willing to embrace strategies other than drugs.
“She felt guilty for continuing to smoke, but also expressed a need to smoke to help her deal with her husband’s cancer and eventual death,” recalled Georgia Narsavage, PhD, RN, ANP-BC, professor emerita of nursing at West Virginia University. “Her primary care physician was reluctant to introduce any treatment other than medications because her family was resistant to facing ‘mother dying.’ ”
But things changed when Mrs. S. was referred to a palliative-care clinical nurse specialist following a hospitalization. “The goal of palliative care is to support quality of life by relieving symptoms and decreasing suffering. She was assisted to improve functioning overall, and home support services were provided,” Dr. Narsavage said. “They allowed her to live at home relatively pain free with decreased dyspnea for 3 more years until her transition to hospice care a few months before death.
It wasn’t quite a happy ending. But it was a happier ending, and one that palliative care (PC) advocates hope will become more common in pulmonary care. They’re working to convince colleagues that PC is neither another word for hospice nor a sign that anyone is giving up on a patient.
Underutilized but beneficial
“Palliative care is underutilized in patients with chronic pulmonary disease, and it’s a missed opportunity to potentially alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life,” said Hilary DuBrock, MD, an internist and critical care pulmonologist with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Chest physicians should know that it’s important to recognize your limitations in addressing all aspects of a chronic disease, and it’s OK to ask for help from a specialty multidisciplinary team of palliative care providers.”
Statistics back up Dr. DuBrock’s perspective about how PC isn’t common in pulmonary care. A 2017 study examined 181,689 U.S. adult patients who had COPD, received oxygen at home, and were hospitalized for exacerbations from 2006-2012. Just 1.7% received PC, although the number grew over the study period.
Another study published in 2017 examined 3,166 patients over the same period with end-stage idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) who were on ventilators. The use of PC is group rose from 2.3% in 2006 to 21.6% in 2012.
More recently, a 2020 meta-analysis examined 19 studies and found that patients with lung cancer were much more likely to receive PC than were those with COPD (odds ratio (OR) = 9.59, P < .001, for hospital-based PC and OR = 8.79, P < .001, for home-based PC).
Patients with lung cancer vs. COPD were also less likely to receive invasive ventilation (OR = .26, P < .001), noninvasive ventilation (OR = .63, P = .009) or CPR (OR = .29, P < .001) or die at a nursing home/long-term care facility (OR = .32, P < .001).
Other studies support PC in COPD: Research in Europe has linked PC in COPD to fewer in-hospital deaths and lower end-of-life expenses. A Canadian study also linked PC to fewer in-hospital deaths in COPD.
Dr. DuBrock said she believes there are a couple reasons why PC isn’t more widely accepted in pulmonology. “There has been little evidence in chronic pulmonary disease regarding the role of PC, and there is a lack of standardized guidelines to help clinicians determine appropriate timing and patient selection for referral,” she said. “There is also a reluctance to refer patients to palliative care since some may think that referral implies that they are giving up on their patients.”
In fact, she said, “if appropriately explained and discussed with patients, PC does not necessarily need to imply to patients that you are giving up on them, but rather that you care enough about them to try to find novel ways to improve their quality of life and relieve their symptoms. Additionally, palliative care can be provided alongside ongoing medical care and treatment of their chronic lung disease.”
More than standard care
Another obstacle comes from pulmonologists who claim PC isn’t necessary because they’re handling patient care themselves, said University of Alabama at Birmingham critical care pulmonologist Anand S. Iyer, MD. “They’ll say: ‘I do palliative care, I palliate their breathing. I treat breathlessness and cough, that’s what I do.’ ”
But these symptoms only brush the surface of patient needs, he said. “I don’t think that the average pulmonologist goes beyond that to comprehensive symptom assessment and management of a whole host of symptoms beyond those limited to the lungs – depression, anxiety, fatigue, malnutrition.”
On that latter front, he said, pulmonologists “are really good at having end-of-life conversations at the end of life. We do that every day in the ICU.” Advocates for PC, he said, “want to push that to the clinic a year or two earlier.”
Timing and use of PC
When should pulmonologists call in a PC team? Specialists recommend early consultations, even right after a pulmonary disease is diagnosed. “When a pulmonologist diagnoses a condition as a serious illness – especially chronic pulmonary disease – a consultation with a palliative care physician or advanced practice registered nurse” can help assess the need for care and the best time to introduce palliative care to the patient and family “to provide relief and enhance quality of life,” West Virginia University’s Dr. Narsavage said. “Initial diagnosis is not too early to think about the trajectory.
Dr. Iyer agreed that early PC consultation is key. “We’re talking about comprehensive support for the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families. It can grow as needs of patients become more severe.”
For her part, Dr. DuBrock urged colleagues to focus on patient experiences. “The exact timing of when to refer patients with pulmonary disease is not well established,” she said. “Thus, it’s important to take cues from our patients. If they are experiencing significant symptom burden or impaired quality of life or having difficulty coping with their lung disease, then it may be helpful to call in palliative care to address these issues alongside education and discussion with the patient about the role of palliative care to address their unmet needs.”
As an example, Dr. DuBrock spoke of one of her own patients who has pulmonary hypertension (PH), connective tissue disease, and interstitial lung disease. “Her hypertension was relatively well controlled, but she was still quite symptomatic as well as depressed and having difficulty sleeping. I struggled with wanting to help her feel better but I also recognized that more PH therapy wasn’t necessarily the answer,” Dr. Dubrock said. “After some discussions, I referred her to palliative care, and they were extremely helpful with addressing her symptoms with a combination of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapy and also addressing some of her underlying concerns and fears regarding her prognosis and issues related to advance-care planning. Social work was also helpful with addressing some of her financial concerns. I continue to see her on regular basis and treat her PH, but her overall quality of life, sleep, and mood have improved substantially.”
First steps
According to specialists, the first step in the PC process with patients is to make sure they understand their conditions, their prognoses, and the role of palliative care itself.
Kathleen Oare Lindell, PhD, RN, associate professor of nursing at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, who specializes in PC in pulmonary disease, remembers taking the histories of patients with grim prognoses and “their look on their face was like, ‘I just have a common cold.’ ” In other cases, she said, patients may fear they’ll die immediately when they have 3-5 years to live.
Dr. Lindell, who has worked at a specialty center for patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), emphasized the importance of speaking in layperson terms that patients understand, such as referring to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as “unknown lung scarring.” She also said it’s crucial to be up front about their prognoses.
As for patient understanding of PC, she said, “people think it’s hospice that they’re giving. Palliative care is neither. Instead, it helps to address symptom management, I always tell patients, ‘You’ll be scared, you’ll have a cough. There are medicines and nonpharmacological therapies [that can help], and that’s what palliative care does.’ ”
Keith Swetz, MD, an internist and palliative care specialist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, agreed that a concise discussion of prognosis is vital. “What do they know about their illness, and what do they understand about what will happen when things get worse?” he said.
“With pulmonary disease, they may be looking at months to years punctuated with a lot of ICU admissions, trips to the hospital, symptom burden, and decline in function. Some will want aggressive treatment and say they’re fine being in the hospital, while others will say being comfortable at home is more important.”
Dr. Swetz’s patients commonly have COPD, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, or PH, and some may have concurrent heart failure. While their prognoses may be poor, he said, discussion about their wishes probably aren’t happening outside of the PC setting.
Or if they are happening, he said, they’re lower quality, boiling down complicated care questions to “Do you want us to do everything yes, or no?
“A lot of it has to do with time,” he said. “Clinicians are busy, they might have a full ICU or pulmonary clinic with 15 minutes to see patients. Sitting down and talking about these things isn’t something that’s prioritized or fits into the work stream very well, and often it hasn’t been reimbursed.”
There typically aren’t insurance hassles regarding referrals for PC, Dr. Iyer said, although finding available specialists may be challenging. A 2019 study projected a wave of retirements of older PC physicians over the next few years, and the ratio of patients to PC specialists may not return to 2019 levels for decades. Rural areas are especially shorthanded. But telehealth may improve access, Dr. Iyer said.
What’s next? Specialists are trying to pin down guidelines for when PC consultation is appropriate in pulmonary disease.
Triggers to PC
Dr. Iyer, Dr. Lindell and others authored a 2021 report in the journal CHEST that offers guidance about triggers for PC consultation. The authors cited four “levers” or triggers that are important: worsening lung function, severe symptoms or high burden of care needs, poor prognosis, and frequent severe exacerbations.
“The overall point here is that integrating palliative care into COPD practice isn’t an on-off switch; rather, it should be based upon multiple factors and can evolve over time,” they wrote.
They noted that, “patients with COPD accept palliative care as early as moderate COPD (FEV1 < 80%), so patients may be ready sooner than clinicians think.”
They added that, “if prognosis is such a concern that a clinician is considering referral for lung transplant evaluation, then concurrent referral to specialist palliative care should be routine practice.
Finally, frequent severe exacerbations, i.e. those that require hospitalization or an emergency room visit, carry a high risk for posthospitalization mortality and are ideal inflection points in the illness trajectory of COPD.”
In the big picture, the authors contend, “palliative care should be integrated early and concurrently with COPD-directed therapies, and its intensity should increase over time as symptoms, needs, and exacerbations worsen approaching EOL [end of life].”
None of the interviewees or other authors reported having any relevant conflicts for this story.
COVID-vaccine myocarditis: Rare, mild, and usually in young men
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of myocarditis after immunization with mRNA-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 raised concerns when it came to light in early 2021. But as report after report showed such cases to be rare and usually mild and self-limited, focus has turned to the “how and why.”
The mechanism linking the BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) and especially mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines to the occurrence of myocarditis is unclear for now, but one potential driver may be tied to a peculiarity that became apparent early: It occurs overwhelmingly in younger males, from 16 to perhaps 40 or 50 years of age. Excess risk has not been consistently seen among women, girls, and older men.
That observation has led to speculation that higher testosterone levels in adolescent boys and young men may somehow promote the adverse vaccine effect, whereas greater levels of estrogen among girls and women in the same age range may be cardioprotective.
Unlikely, brief, and ‘benign’
“Most of the myocarditis is benign, by which I mean that maybe the patients are admitted due to chest pain, but without reduction in ventricular function,” Enrico Ammirati, MD, PhD, a myocarditis expert at De Gasperis Cardio Center and Transplant Center, Niguarda Hospital, Milan, said in an interview.
In a Nov. 14 address on this topic at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, Dror Mevorach, MD, described the typical case presentation as “mild” and one that clears in fairly short order based on resolution of “clinical symptoms, inflammatory markers and troponin decline, EKG normalization, echo normalization, and a relatively short length of hospital stay.”
Dr. Mevorach, of Hadassah Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, subsequently published the findings in a report in the New England Journal of Medicine that described 136 confirmed myocarditis cases among more than 5 million people in Israel immunized with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Myocarditis was considered “mild” in 129 cases, or 95%.
And the risk is tiny, compared with myocarditis from infection by SARS-CoV-2, not to mention the possibility of nasty clinical COVID-19 complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary embolism, Dr. Mevorach observed.
Many other reports agree that the incidence is minimal, especially given the rewards of vaccination. In a separate NEJM publication in September 2021 – from Noam Barda, MD, Clalit (Israel) Research Institute, and colleagues on 1.7 million people in that country, about half unvaccinated and half given the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine – there were an estimated 2.7 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 vaccinated persons. There were also 11 cases of myocarditis per 100,000 persons who were positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
And in a recent case series of vaccinated people aged 16 or older, the myocarditis rate after a first or second Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna injection was estimated at 1 or fewer per 100,000. The corresponding estimate was 4 such cases per 100,000 after a positive SARS-CoV-2 test among the same population, notes a report published Dec.14, 2021, in Nature Medicine.
In general, “the risk of any kind of cardiac injury is vastly lower with a vaccine than it is with the actual viral infection,” Leslie T. Cooper Jr., MD, a myocarditis expert and clinical trialist at the Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, Fla., said in an interview. With the mRNA-based vaccines, “we do not have any conceivable danger signal that would outweigh the benefit of vaccination.”
Males of a certain age
Evidence that such myocarditis predominates in young adult men and adolescent boys, especially following a second vaccine dose, is remarkably consistent.
The risk was elevated only among mRNA-based vaccine recipients who were younger than 40 in the recent Nature Medicine analysis. Among that group, estimates after a second dose numbered fewer than 1 case per 100,000 for Pfizer-BioNTech and 1.5 per 100,000 for Moderna.
In a third analysis from Israel – also in NEJM, from Guy Witberg, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, and colleagues, based on 2.5 million people aged 16 and older with at least one Pfizer-BioNTech injection – 2.1 cases per 100,000 were estimated overall, but the number rose to 10.7 per 100,000 among those aged 16-29 years.
In Dr. Mevorach’s NEJM report, estimates after a second Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose were 1 per 26,000 males versus 1 in 218,000 females, compared with 1 myocarditis case in 10,857 persons among “the general unvaccinated population.”
Most recipients of a first vaccine dose were younger than 50, and 16- to 29-year-olds accounted for most who completed two doses, noted Dr. Mevorach. Younger males bore the brunt of any myocarditis: the estimated prevalence after a second dose among males aged 16-19 was 1 per 6,637, compared with 1 per 99,853 females in the same age range, the group reported.
In the BMJ report, based on about 5 million people 12 years of age or older in Denmark, the estimated rates of myocarditis or pericarditis associated with Moderna immunization were 2 per 100,000 among women but 6.3 per 100,000 for men. The incidence and sex difference was much lower among those getting the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine: 1.3 per 100,000 and 1.5 per 100,000 in women and men, respectively.
Sex hormones may be key
The predominance of vaccine-associated myocarditis among adolescent and young adult males is probably more about the myocarditis itself than the vaccines, observed Biykem Bozkurt, MD, PhD, who has been studying COVID-related myocarditis at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston.
Male sex historically is associated in both epidemiologic studies and experimental models with a greater propensity for most any form of myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said in an interview. Given that males aged 16-19 or so appear to be at highest risk of myocarditis as a complication of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, the mechanism may well be related to sex hormones.
“Therefore, testosterone is implicated as a player in their higher risk of inflammation and injury and lack of adaptive response in terms of healing, and in terms of prevention of injury,” Dr. Bozkurt said. For its part, estrogen inhibits proinflammatory processes and, in particular, “blunts cell-mediated immune responses.”
“We don’t know the mechanism, but a theory that attributes a protective role to estrogen, or a risk associated with testosterone, is reasonable. It makes sense, at least based on epidemiological data,” Dr. Ammirati agreed. Still, “we do not have any direct evidence in human beings.”
Sex-associated differences in experimental myocarditis have been reported in the journals for at least 70 years, but “the testosterone literature and the estrogen literature have not been evaluated in detail in vaccine-associated myocarditis,” Dr. Cooper said.
Most myocarditis in the laboratory is viral, Dr. Cooper observed, and “the links between testosterone, viruses, and inflammation have been pretty well worked out, I would say, if you’re a mouse. If you’re a human, I think it’s still a bit uncertain.”
Were it to apply in humans, greater testosterone levels might independently promote myocarditis, “and if estrogen is cardioprotective, it would be another mechanism,” Dr. Cooper said. “That would translate to slight male predominance in most kinds of myocarditis.”
In males, compared with females, “the heart can be more vulnerable to events such as arrhythmias or to immune-mediated phenomena. So, probably there is also higher vulnerability to myocarditis in men,” Dr. Ammirati noted.
Male predominance in vaccine-related myocarditis is provocative, so it’s worth considering whether testosterone is part of the mechanism as well as the possibility of estrogen cardioprotection, Dr. Ammirati said. But given limitations of the animal models, “we don’t really have robust data to support any part of that.”
Although myocarditis is in some way immune mediated, “and hormones can modulate the response,” the mechanism has to be more than just sex hormones, he said. “They probably cannot explain the specificity for the heart. It’s not a systemic response, it’s an organ-specific response.”
Modulation of immune responses
Details about the immune processes underlying mRNA-vaccine myocarditis, hormone modulated or not, have been elusive. The complication doesn’t resemble serum sickness, nor does it seem to be a reaction to infection by other cardiotropic viruses, such as coxsackie virus B, a cause of viral myocarditis, Dr. Bozkurt said. The latter had been a compelling possibility because such hypersensitivity to smallpox vaccination is well recognized.
“We don’t know the mechanism, that’s the short answer. But there are many hypotheses,” she said. One candidate widely proposed in the literature: autoantibodies driven by molecular mimicry between the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein targeted by the mRNA vaccines and a structurally similar myocardial protein, possibly alpha-myosin, noted Dr. Bozkurt and colleagues in a recent publication.
But elevations in specific “antiheart antibodies” have not been documented in recipients of the two mRNA-based vaccines, said Dr. Cooper. “So, I would say that – although molecular mimicry is a well-established mechanism of, for example, rheumatic carditis after a streptococcal A infection – that has not been demonstrated yet for COVID-19 mRNA vaccination–related myocarditis.”
“We probably won’t know, ever, with a huge level of certainty, the exact mechanisms,” Dr. Cooper added. There is no animal model for vaccine-induced myocarditis, and “We’re still talking very, very small numbers of patients. The vast majority of them recover,” and so don’t generally provide mechanistic clues.
Prospects for younger children
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 has now been authorized by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for kids as young as 5-11 years, using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Experience so far suggests the immunization is safe in that age group with negligible risk of myocarditis or other complications. But with prospects of possible authorization in children younger than 5, should myocarditis be a concern for them?
Probably not, if the complication is driven primarily by sex hormones, Dr. Cooper proposed. “One would predict that before puberty you would have a lower – much, much lower – rate of myocarditis in males than you would in the 16- to 19-year-old range, and that it would be roughly equal to females.” Dr. Ammirati and Dr. Bozkurt largely agreed.
It remains to be seen whether the vaccine-related myocarditis risk applies to children younger than 12, “but I doubt it. I think it’s going to be puberty-related,” Dr. Bozkurt said. Still, “I don’t want to hypothesize without data.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black-owned hospice seeks to bring greater ease in dying to Black families
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
This time, it didn’t take much persuading for Mary Murphy to embrace home hospice. When her mother was dying from Alzheimer’s disease in 2020, she had been reluctant until she saw what a help it was. So when her husband, Willie, neared the end of his life, she embraced hospice again.
The Murphys’ house in a leafy Nashville, Tenn., neighborhood is their happy place – full of their treasures.
“He’s good to me – buys me anything I want,” she said, as she pulled a milky glass vase out of a floor-to-ceiling cabinet with mirrored shelves.
Willie bought Mary the display case to help her to show off the trinkets she picks up at estate sales.
Down the hall, Willie was lying in their bed, now unable to speak. His heart was giving out.
“You gonna wake up for a minute?” she asked, cradling his head. She patted his back while he cleared his throat. “Cough it out.”
Heart and Soul Hospice is owned and operated by people who share the same cultural background as the patients they aim to serve.
In their application to obtain a certificate of need in Tennessee, the hospice owners made it clear they are Black and intend to serve everyone but will focus on African Americans, who are currently underserved. Tennessee data shows that in Nashville just 19% of hospice patients are Black, although they make up 27% of the capital city’s population.
Though the area already had numerous hospice agencies, regulators granted Heart and Soul permission to operate, based primarily on the value of educating an underserved group.
In Ms. Murphy’s first hospice experience, her mother had been living with dementia for decades. Still, Ms. Murphy had concerns about transitioning her mother to hospice. She felt as if she was giving up on her mom.
“My first thought was death,” she said.
National data shows that Black Medicare patients and their families are not making the move to comfort care as often as white patients are. Roughly 41% of Black Medicare beneficiaries who died in 2019 were enrolled in hospice, compared with 54% of White patients, according to data compiled annually by the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization.
Ms. Murphy’s mother survived nearly 3 years on hospice. The benefit is meant for those in the final 6 months of life, but predicting when the end will come is difficult, especially in cases of dementia. Hospice provides palliative care for the dying and support for caregivers for a long as the process lasts.
Ms. Murphy did most of the caregiving – which can be overwhelming – but hospice helped with a few baths a week, medication in the mail and any medical equipment they needed.
And most important to Ms. Murphy was the emotional support, which came mostly from her hospice nurse.
“Wasn’t no doctor going to come here, hold my hand, stay here until the funeral home came for her,” she said about the day her mother died.
Last year, on the day after Thanksgiving, Willie Murphy died. And the same hospice nurse was at the Murphy home within minutes. She’d already stopped by that morning to check on him and returned as soon as Mary called and told her he wasn’t breathing.
“If you don’t feel like: ‘Oh my God, thank God I have hospice,’ if you can’t say that, then we’re doing something wrong,” said Keisha Mason, Heart and Soul’s director of nursing.
Ms. Mason, like Ms. Murphy, is Black and said that in her view there’s nothing fundamental keeping Black patients from using hospice except learning what the service can offer and that it’s basically free to patients – paid for by Medicare, Medicaid, and most private health plans.
“I say to them, ‘If you see a bill, then call us, because you should not,’” she said.
As Ms. Mason helped launch this new hospice agency, she began using new language, calling hospice more than a Medicare benefit. She describes it as an entitlement.
“Just as you are entitled to unemployment, as you are entitled to Social Security, you are entitled to a hospice benefit,” she said.
The investors in Heart and Soul include David Turner, owner of CNS Hospice in Detroit; Nashville pastor the Rev. Sandy McClain; and André Lee, a former hospital administrator on the campus of Meharry Medical College, a historically Black institution in Nashville.
Mr. Lee and Mr. Turner also started a Black-focused hospice agency in Michigan and have plans to replicate the model in other states.
More families need to consider home hospice as an alternative for end-of-life care, Mr. Lee said. Nursing homes are pricey. And even with Medicare, a hospital bill can be hefty.
“You’ll go in there and they’ll eat you alive,” he said. “I hate to say [something] bad about hospitals, but it’s true.”
Hospice research hasn’t come up with clear reasons to explain the gap between White and Black families’ use of the benefit. Some experts speculate it’s related to spiritual beliefs and widespread mistrust in the medical system because of decades of discrimination.
The hospice industry’s national trade group, the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, released a diversity and inclusion toolkit and a guide to reaching more Black patients. It recommends connecting with influential DJs, partnering with Black pastors and simply hiring more Black nurses.
Bridging the gap is not overly complicated, Mr. Lee said.
“A lot of hospices don’t employ enough Black people,” he said. “We all feel comfortable when you see someone over there that looks like you.”
Well-established hospice agencies have attempted to minimize barriers with their own diversity initiatives. Michelle Drayton of Visiting Nurse Service of New York said her large agency has met with ministers who counsel families dealing with failing health.
“Many of them did not fully understand what hospice was,” she said. “They had many of the same sort of misperceptions.”
Every hospice company, whether it’s an upstart or one of the nation’s oldest, can promote end-of-life education and ease care disparities, Ms. Drayton said. “We’re not just handing out a brochure,” she added.
This story is part of a partnership that includes Nashville Public Radio, NPR, and KHN. KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
At-risk Americans become eligible for fourth COVID shot this week
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention endorsed a third dose of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines for moderately and severely immunocompromised people on Aug. 13, which is considered part of their first immunization series rather than a booster shot.
In October, the CDC said moderately and severely immunocompromised people could receive a booster shot, or a fourth dose of the vaccine , 6 months after their third dose.
But the CDC last week shortened the timeline to 5 months for a booster shot of the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines. That means immunocompromised people could begin signing up for a fourth shot later this week, the New York Times reported.
About 2.7% of U.S. adults, or about 7 million adults, are considered immunocompromised, according to the CDC. They’re more likely to contract severe COVID-19, have a higher risk for long COVID, have lower antibody levels after vaccination, and develop serious breakthrough infections. About 40% of hospitalized breakthrough cases are among immunocompromised people.
According to CDC guidance, people are considered to be “moderately or severely immunocompromised” if they have:
- Active cancer treatment for tumors or cancers of the blood
- Had an organ transplant and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Had a stem cell transplant in the last 2 years and are taking medicine to suppress the immune system
- Advanced or untreated HIV infection
- Moderate or severe primary immunodeficiency, such as DiGeorge syndrome or Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Active treatment with high-dose corticosteroids or other drugs that suppress the immune response
So far, only moderately and severely immunocompromised Americans are eligible for a fourth shot. Israel has begun offering fourth doses to high-risk groups, including older adults, but the Biden administration hasn’t yet said whether the United States will follow, the Times reported.
Overall, the focus remains on getting third shots to Americans who are eligible for boosters, Rochelle Walensky, MD, the CDC director, told reporters Jan. 7. U.S. officials will remain in touch with Israel to follow their data on fourth shots.
“We will be following our own data carefully as well, to see how these boosters are working in terms of waning effectiveness, not just for infection but, importantly, for severe disease,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .