User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Get free masks at grocery stores and pharmacies starting Jan. 28
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another winter for our discontent
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
We’re dying to tell you about fatigability
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Monotherapy or one-two punch against EGFR-mutant NSCLC?
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
It is indisputable that patients with newly diagnosed advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) bearing mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway may benefit from targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) directed against EGFR.
What’s less clear is whether monotherapy with an EGFR TKI or combination therapy with a TKI and chemotherapy, immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or other targeted agents is the preferred frontline strategy.
NSCLC guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, for example, recommend that patients with EFGR mutations such as exon 19 deletion, discovered prior to first-line systemic therapy, should preferably received osimertinib (Tagrisso) or another TKI, such as erlotinib (Tarceva), afatinib (Gilotrif), gefitinib (Iressa) or dacomitinib (Vizimpro), or erlotinib with a VEGF inhibitor. For patients with EGFR mutations identified during first-line systemic therapy, NCCN recommends complete systemic therapy or interrupting it, followed by osimertinib as the preferred agent, or another TKI with or without a VEGF inhibitors.
Similarly, guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology and Ontario Health recommend osimertinib monotherapy as a preferred first-line option for patients with L858R/exon 19 deletion EGFR mutations. Alternatives for patients for whom osimertinib is not available include gefitinib plus platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy with maintenance pemetrexed, monotherapy with dacomitinib, or other targeted agents with or without VEGF inhibitors.
Combination or go it alone?
The guidelines are largely mute on the question of chemotherapy in this population, primarily because they have not caught up to clinical trial evidence, said Paul Wheatley-Price, MBChB, FRCP, MD, from the University of Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
“There is recent data that looks quite promising on combining EGFR inhibitors with either chemotherapy or antiangiogenic drugs, but it’s too soon, I think, and while the trials are promising, there are still too many question marks over it to make it into the guidelines,” he said in an interview.
The question of frontline combinations vs. monotherapy in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC was the subject of a recent “controversies in thoracic oncology” feature in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, with Dr. Wheatley-Price and University of Ottawa colleague Sara Moore, MD, FRCPC, arguing that combining EGFR TKIs with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or antiangiogenic monoclonal antibodies targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor has been shown consistently to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and in some cases overall survival (OS).
“There is a consistent drop-off in patients who receive second-line therapy, highlighting the importance of using combination therapy in the first-line setting to ensure patients will be exposed to multiple available therapies that may prolong survival. Chemotherapy-based combinations lead to improved response rates which may be especially helpful in patients with a significant burden of disease,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, compared with patients with wild-type EGFR, patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC had a doubling of response rates to chemotherapy with a platinum-based doublet in the IPASS trial, suggesting that EGFR-mutated tumors may be more chemosensitive.
Promising trials, old drug
“Chemotherapy and EGFR TKIs may have a synergistic effect through combined reduction in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)–mediated angiogenesis, and with EGFR TKIs counteracting chemotherapy-induced up-regulation of downstream EGFR signaling,” they wrote.
The authors cited two studies, one from Japan, and one from India, both of which showed significant improvements in response rates, PFS, and OS with the combination of gefitinib plus carboplatin and pemetrexed chemotherapy with pemetrexed maintenance vs. carboplatin alone,
“Now of course we don’t use gefitinib as our first-line treatment. In Canada and the United States, we use osimertinib, so certainly the chemotherapy/TKI combination, while it looks quite promising, was compared to an old control arm,” Dr. Wheatley-Price said.
He noted that the phase 3 FLAURA2 trial, currently underway, will address the question of whether adding osimertinib to a chemotherapy doublet with pemetrexed plus either carboplatin or cisplatin can improve PFS in patients with EGFR-positive locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC, compared with osimertinib alone.
The authors acknowledged that chemotherapy adds toxicities, compared with the use of TKI monotherapy, but added that, “even with the use of first-line osimertinib monotherapy, patients may still be exposed to chemotherapy with later lines of treatment. Therefore, combination therapy does not expose patients to new toxicity, it simply changes when they will be exposed to that toxicity during their treatment course.”
VEGF plus EGFR
Adding a VEGF-targeted monoclonal antibody or TKI to and EGFR TKI has shown consistent PFS benefits in the NEJ026, ARTEMIS, RELAY, and ACTIVE trials, Dr. Moore and Dr. Wheatley-Price noted.
“In all four trials, resistance testing at the time of progression revealed similar rates of T790M mutation in both arms, highlighting the potential role of optimizing the sequence of therapy with use of second-line osimertinib among those with a T790M resistance mutation,” they wrote.
All four trials also showed higher rates of adverse events in the combination arms, but most, except for hypertension, were low grade, and in the RELAY trial the added toxicities did not significantly affect patient quality of life, they said.
Monotherapy advocated
Although in agreement that the combination of gefitinib and chemotherapy has both PFS and OS benefits compared with monotherapy alone, “these combinations are not applicable to real-life practice given their use of first-generation EGFR TKIs rather than third-generation EGFR TKI osimertinib,” wrote Sophie Stock-Martineau, MD, FRCPC from Hôpital Maisonneuve-Rosemont and the University of Montreal, and Frances A. Shepherd, MD, FRCPC from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre in Toronto, in an article touting EGFR monotherapy.
They stated that until the results of FLAURA2 are available “osimertinib alone remains the current standard first-line therapy in metastatic EGFRm+ NSCLC.”
“The addition of an antiangiogenic agent to an EGFR TKI mildly prolongs PFS; however, it does not yet translate into survival benefit. Not only does it add more toxicity to patients, but it also adds cost, which is far from negligible,” they wrote.
Dr. Stock-Martineau and Dr. Shepherd also noted that two phase 2 trials comparing afatinib with the EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) showed no PFS or OS benefits in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated NSCLC and were terminated for lack of efficacy.
In addition, clinical trials of combinations of EGFR TKIs with immune checkpoint inhibitors or MET inhibitors have failed to date to demonstrate survival benefits, the authors said.
“No trials have yet revealed PFS or OS benefit with osimertinib combinations. Adding virtually all agents to EGFR TKIs has been associated with more toxicity to patients and a significant financial burden to the health care system. Combinations could potentially also worsen quality of life given their heightened toxicity profiles. Therefore, single-agent EGFR TKI, such as osimertinib, remains for now the standard of care in the first-line setting for advanced EGFRm+ NSCLC,” they concluded.
No funding sources for the articles were reported. All authors declared no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM JOURNAL OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY
35% of employers to proceed with vaccine mandate, poll shows
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Omicron survives longer on plastic, skin than other COVID variants
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Presence of autoantibodies most predictive of long COVID in study
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
Other significant early predictors of prolonged COVID symptoms – which the researchers called postacute sequelae – were having type 2 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 RNAemia, and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) viremia, Yapeng Su, PhD, of the Institute for Systems Biology (ISB) in Seattle, and colleagues wrote in Cell.
Having EBV viremia suggested that latent EBV has been reactivated, the authors noted.
“The most important postacute sequelae [that is conditions that are consequences of a disease] of COVID is the presence of autoantibodies,” James R. Heath, PhD, president of ISB and a bioengineering professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview. “It’s about two times more important than the others.”
Dr. Heath and coauthors said early detection of this and other variables could prompt earlier aggressive treatment in patients susceptible to long COVID and ward off lingering symptoms.
“These predictive measures of long COVID can also help to better inform patients of their possible disease course,” study coauthor Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB, said in an interview. “We were also able to partially resolve the immunological underpinnings of some postacute sequelae of COVID in a way that suggested potential therapies, and the timing of those therapies.”
For example, he continued, the use of antivirals very early in the infectious course may mitigate the later development of long COVID. “This will, of course, have to be explored in an appropriately designed clinical trial.
“We also identified biomarkers of certain types of long COVID, such as neurological sequelae. Those biomarkers can help define the condition, which is a first step towards developing treatments.”
Study findings
With COVID patients monitored for 2 or 3 months, the study findings of the international “multiomic profiling” analysis include:
- Subclinical patient autoantibodies that reduce anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies suggest there is immune dysregulation during COVID-19 infection.
- Reactivation of latent other viruses during initial infection may be contributing to long COVID.
- Gastrointestinal postacute sequelae of COVID presents with a unique postacute expansion of cytotoxic T cells.
- SARS-CoV-2–specific and cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed unique dynamics during recovery from infection.
According to the authors, as many as 69% of COVID-19 patients suffer from long COVID – a range of new, recurrent, or ongoing problems 4 or more weeks following initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These may include memory loss, gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, anosmia, and shortness of breath.
Long COVID has been associated with acute disease severity, and is suspected to be related to autoimmune factors and unresolved viral fragments, according to the paper.
Research methods
The international study did a deep and detailed dive into multiple molecular markers of long COVID. It enrolled 209 COVID-19 patients with varying degrees of disease severity and matched them to 457 healthy controls. The researchers’ goal was to identify discrete and quantifiable long COVID factors and guide possible preemptive treatment.
Patients were assessed at three time points: at initial diagnosis, during the acute disease phase about a week later, and again 2 to 3 months post onset of symptoms after recovery from the acute phase of COVID. At the third assessment, some patients had lingering symptoms such as fatigue (52% ), cough (25%), and loss of taste or sense of smell (18%).
Blood draws were analyzed for autoantibodies and SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies, global plasma proteomic and metabolomic profiles, and single-cell multiomic characterizations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Each blood draw was paired with nasal-swab and plasma measurements of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and the data sets were integrated with electronic health records and self-reported patient symptoms to guide the interpretation of the molecular signatures of long COVID.
Author conclusions
The authors found an association between T2 hyperinflammation and long COVID–anticipating autoantibodies. This association further implies that hyperinflammation-controlling therapies in the acute stage of COVID may influence whether a patient experiences long COVID. “However, the detailed timing and context of these therapies matter, and, thus, future well-controlled studies will be needed to test these and other therapeutic implications,” Dr. Su and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, the negative correlations between anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG and certain autoantibodies may suggest that patients with elevated autoantibody levels are more susceptible to breakthrough infections, the authors said.
“Many patients with high autoantibodies simultaneously have low protective antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and that’s going to make them more susceptible to breakthrough infections,” Mr. Chen explained.*
“Detectability of most [long COVID-19 factors] at COVID diagnosis emphasizes the importance of early disease measurements for understanding emergent chronic conditions and suggests [long COVID] treatment strategies,” they wrote.
According to Mr. Chen, there are clear similarities in underlying immunobiology between patients with COVID autoantibodies and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
“These findings are also helping us frame our thinking around other chronic autoimmune conditions, such as postacute Lyme syndrome, for example,” said Dr. Heath.
The bottom line, said Mr. Chen, is that measuring early long COVID indicators may result in preventive treatments. “An example is the cortisol deficiency we see in certain long COVID patients. There are known treatments such as cortisol replacement therapy that should be explored for this group.”
Outside expert’s take on findings
Commenting on the study, Sherry Hsiang-Yi Chou, MD, who was not involved in the research, called the study a very important first step in understanding the path of this complex phenomenon and perhaps other conditions with long-term side effects.
“The researchers have done huge amount of innovative scientific work. They’ve shown the DNA signature of how our bodies respond to this disease,” said Dr. Chou, who is chief of the division of neurocritical care at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
“This type of research will help us scientifically understand and differentiate the various syndromes within long COVID. It will help identify who’s at risk for different aspects of this syndrome and lead to following them for longer periods in clinical trials,” she added.
The authors acknowledged that lengthier studies in larger cohorts were needed to see which patients will develop long-term chronic postacute sequelae of COVID.
This research was supported by the Wilke Family Foundation, the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Merck, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority. Other support came from the National Institutes of Health, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Saint John’s Cancer Center, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. Dr. Heath is a cofounder of Pact Pharma. He and several coauthors disclosed various ties to multiple private-sector companies. Mr. Chen and Dr. Chou had no competing interests.
*Correction, 1/28: An earlier version of this story misidentified Daniel G. Chen, an undergraduate researcher at ISB.
FROM CELL
USPSTF says evidence still lacking for AFib screening in asymptomatic patients
The guidance is similar to the task force’s 2018 statement on screening for AFib with electrocardiography in asymptomatic adults 65 years or older, but lowers the inclusion age to adults 50 years or older.
“This 2021 evidence review included searching for evidence on additional screening methods such as automated blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, and consumer devices such as smartwatches and smartphone apps. However, even with this expanded scope, the USPSTF did not find evidence to recommend for or against screening for AF,” the task force states.
The prevalence of increases in age from less than 0.2% in adults younger than 55 years to about 10% in those 85 years or older, the group says. The prevalence is higher in men than in women, but it is uncertain if it differs by race and ethnicity.
Although AFib substantially increases the risk for stroke, the stroke risk associated with subclinical AFib, particularly that of shorter duration lasting less than 24 hours or of lower burden, as might be detected by some screening approaches, is “uncertain,” the task force adds.
The updated recommendations were published online in JAMA, along with a separate evidence report and editorial.
The task force reviewed 26 studies in 113,784 patients, including 12 new to the update.
Studies showed that systematic screening detected significantly more AFib than no screening or pulse palpation (absolute difference, 1.0%-4.8% over up to 12 months). In two of the trials, however, only 10.7% and 44.5% of participants actually received the screening test.
The review included three randomized trials of screening vs. no screening that reported on health outcomes, but only one, STROKESTOP, was powered for health outcomes. It found a significantly lower risk for the primary composite endpoint of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, system embolism, bleeding leading to hospitalization, and all-cause mortality with twice-daily intermittent single-lead ECG monitoring for 14 days, compared with no screening. However, there were no significant differences in any of the individual outcomes of the composite endpoint.
“Additionally, and probably the most important thing to appreciate for the STROKESTOP study is that it has several limitations,” task force member Gbenga Ogedegbe, MD, MPH, of New York University told this news organization. The intervention was not masked, and outcomes weren’t centrally adjudicated.
Further, “about 11% of patients in the trial had a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), stroke, or embolism and the population that we’re looking at within the task force are people without symptoms or history of stroke or ischemic attack,” he said. “That’s the fundamental difference here. So those limitations make it difficult to say that STROKESTOP actually has benefit.”
Notably absent from the review was the recent LOOP study, which found no significant benefit on outcomes with continuous monitoring with an implantable loop recorder (ILR) over usual care in older adults.
While it “offers some context for this issue,” it was not eligible for inclusion because 25% of the population had a prior history of stroke, TIA, or embolism and “because this screening approach may not be feasible for primary care settings,” lead author of the Evidence Report Leila Kahwati, MD, MPH, from RTI International’s Social and Health Organizational Research and Evaluation Program and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, explained in an email.
Treatment with warfarin (mean, 1.5 years) was associated with a lower risk for ischemic stroke (relative risk, 0.32) and all-cause mortality (relative risk, 0.68), while direct oral anticoagulants were associated with a lower incidence of stroke (adjusted odds ratio range, 0.32-0.44). Patients had an increased risk for major bleeding with both warfarin (pooled relative risk, 1.8) and direct-acting oral anticoagulants (odds ratio, 1.38-2.21), but confidence intervals did not exclude a null effect.
The USPSTF found no trials that reported on the benefits of anticoagulation therapy in screen-detected patients.
In an accompanying editorial Philip Greenland, MD, points out that the task force’s conclusion differs from the 2020 European Society of Cardiology AFib guideline, which endorses opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse palpation or ECG rhythm strip in patients 65 years or older (class I recommendation) and advises that clinicians consider systematic ECG screening to detect AFib in people 75 years or older, or those at high risk for stroke (class IIa).
To possibly resolve whether screening for AFib in asymptomatic patients is justified, “future trials may need to consider enrolling only higher risk patients and identifying those with AF of longer duration,” said Dr. Greenland, JAMA editor and professor of preventive medicine and medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
“One important point raised by the LOOP trial is whether there is a threshold for AF duration that is most strongly associated with stroke risk and therefore most likely to benefit from anticoagulation,” he writes. Indeed, the LOOP authors themselves questioned whether the trial’s short AFib duration of 6 minutes may have led to many low-risk patients being diagnosed and treated.
“Additionally, trials need to recognize the need for longer monitoring periods (preferably continuous), and perhaps novel wearables will allow long-term monitoring, with accurate interpretation of the ECG and long-term adherence,” Dr. Greenland said.
In a related editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health Louisville, Ky., and Andrew Foy, MD, Pennsylvania State University, Hershey, point out that continuous ILR monitoring in the LOOP trial found threefold more AFib and led to 2.7-fold higher rates of oral anticoagulation use, compared with standard care. Yet, there was no statistically significant difference in stroke reduction, and the 20% relative reduction in thromboembolic complications in the screened group was offset by a 26% relative increase in major bleeding.
“Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of the AF screening trials is that as the tools for screening improve, from a single 12-lead ECG to 14-day recordings and then the always-on ILR, more AF is detected and more [oral anticoagulant] is used, yet there is little demonstrable improvement in outcomes,” Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Foy write.
The editorialists also point to the potential for rhythm monitoring to lead to misdiagnosis and downstream cascades of care. “If you assume a 2% AF prevalence, even a device with 98% specificity will misdiagnose approximately 2000 individuals for every million screened.”
Dr. Mandrola told this news organization that the “greatest value” of these reports on AF screening and the critical appraisal of them is as an exercise in thinking about the limits of screening for disease. As James Maxwell Glover Wilson and Gunner Jungner wrote in their 1968 textbook, “Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease”: “in theory, screening is an admirable method of combating disease … [but] in practice, there are snags.”
“It would be good for the public to understand these snags…because they also apply to cancer, coronary calcium testing, and vascular screening as well,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Asked whether it’s possible to put the genie back in the bottle now that every other patient in clinic may have an ECG on their wrist, Dr. Ogedegbe said, “if a patient has no history of stroke or TIA and is 50 years or older, really, monitoring with these devices for AFib, there’s no evidence for or against doing that. Ultimately, the clinician has got to use their clinical judgment in talking to these patients.”
A related editorial in JAMA Cardiology suggests that, to be effective, the movement toward consumer-based screening must first show that such an approach improves outcomes and must deal with the paradox that those at highest risk for AFib and AFib-related stroke may be the least likely to own these technologies unless supported by the healthcare system.
“In addition, appropriate care pathways for confirming the diagnosis and, if necessary, initiating appropriate treatment in individuals with positive findings will need to be established,” Rod Passman, MD, Northwestern University, and Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, University of Sydney, Australia, say. “It will also be critical to ensure that device costs and variable technological literacy do not create barriers to making screening accessible to all those at risk.”
Finally, in a related editorial in JAMA Network Open Matthew Kalscheur, MD, and Zachary D. Goldberger, MD, both from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, say the potential benefits of early AFib detection should extend beyond stroke prevention.
“Patients identified with AF likely would benefit from targeted management of modifiable risk factors that contribute to AF, including obesity, hypertension, alcohol use, sleep apnea, smoking, and diabetes,” they write.
All members of the USPSTF receive travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings. Dr. Ogedegbe has a study included in the Evidence-based Practice Center report for this topic. Dr. Kahwati reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Greenland reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health and from the American Heart Association. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to this news organization. Dr. Foy, Dr. Kalscheur, and Dr. Goldberger reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The guidance is similar to the task force’s 2018 statement on screening for AFib with electrocardiography in asymptomatic adults 65 years or older, but lowers the inclusion age to adults 50 years or older.
“This 2021 evidence review included searching for evidence on additional screening methods such as automated blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, and consumer devices such as smartwatches and smartphone apps. However, even with this expanded scope, the USPSTF did not find evidence to recommend for or against screening for AF,” the task force states.
The prevalence of increases in age from less than 0.2% in adults younger than 55 years to about 10% in those 85 years or older, the group says. The prevalence is higher in men than in women, but it is uncertain if it differs by race and ethnicity.
Although AFib substantially increases the risk for stroke, the stroke risk associated with subclinical AFib, particularly that of shorter duration lasting less than 24 hours or of lower burden, as might be detected by some screening approaches, is “uncertain,” the task force adds.
The updated recommendations were published online in JAMA, along with a separate evidence report and editorial.
The task force reviewed 26 studies in 113,784 patients, including 12 new to the update.
Studies showed that systematic screening detected significantly more AFib than no screening or pulse palpation (absolute difference, 1.0%-4.8% over up to 12 months). In two of the trials, however, only 10.7% and 44.5% of participants actually received the screening test.
The review included three randomized trials of screening vs. no screening that reported on health outcomes, but only one, STROKESTOP, was powered for health outcomes. It found a significantly lower risk for the primary composite endpoint of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, system embolism, bleeding leading to hospitalization, and all-cause mortality with twice-daily intermittent single-lead ECG monitoring for 14 days, compared with no screening. However, there were no significant differences in any of the individual outcomes of the composite endpoint.
“Additionally, and probably the most important thing to appreciate for the STROKESTOP study is that it has several limitations,” task force member Gbenga Ogedegbe, MD, MPH, of New York University told this news organization. The intervention was not masked, and outcomes weren’t centrally adjudicated.
Further, “about 11% of patients in the trial had a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), stroke, or embolism and the population that we’re looking at within the task force are people without symptoms or history of stroke or ischemic attack,” he said. “That’s the fundamental difference here. So those limitations make it difficult to say that STROKESTOP actually has benefit.”
Notably absent from the review was the recent LOOP study, which found no significant benefit on outcomes with continuous monitoring with an implantable loop recorder (ILR) over usual care in older adults.
While it “offers some context for this issue,” it was not eligible for inclusion because 25% of the population had a prior history of stroke, TIA, or embolism and “because this screening approach may not be feasible for primary care settings,” lead author of the Evidence Report Leila Kahwati, MD, MPH, from RTI International’s Social and Health Organizational Research and Evaluation Program and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, explained in an email.
Treatment with warfarin (mean, 1.5 years) was associated with a lower risk for ischemic stroke (relative risk, 0.32) and all-cause mortality (relative risk, 0.68), while direct oral anticoagulants were associated with a lower incidence of stroke (adjusted odds ratio range, 0.32-0.44). Patients had an increased risk for major bleeding with both warfarin (pooled relative risk, 1.8) and direct-acting oral anticoagulants (odds ratio, 1.38-2.21), but confidence intervals did not exclude a null effect.
The USPSTF found no trials that reported on the benefits of anticoagulation therapy in screen-detected patients.
In an accompanying editorial Philip Greenland, MD, points out that the task force’s conclusion differs from the 2020 European Society of Cardiology AFib guideline, which endorses opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse palpation or ECG rhythm strip in patients 65 years or older (class I recommendation) and advises that clinicians consider systematic ECG screening to detect AFib in people 75 years or older, or those at high risk for stroke (class IIa).
To possibly resolve whether screening for AFib in asymptomatic patients is justified, “future trials may need to consider enrolling only higher risk patients and identifying those with AF of longer duration,” said Dr. Greenland, JAMA editor and professor of preventive medicine and medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
“One important point raised by the LOOP trial is whether there is a threshold for AF duration that is most strongly associated with stroke risk and therefore most likely to benefit from anticoagulation,” he writes. Indeed, the LOOP authors themselves questioned whether the trial’s short AFib duration of 6 minutes may have led to many low-risk patients being diagnosed and treated.
“Additionally, trials need to recognize the need for longer monitoring periods (preferably continuous), and perhaps novel wearables will allow long-term monitoring, with accurate interpretation of the ECG and long-term adherence,” Dr. Greenland said.
In a related editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health Louisville, Ky., and Andrew Foy, MD, Pennsylvania State University, Hershey, point out that continuous ILR monitoring in the LOOP trial found threefold more AFib and led to 2.7-fold higher rates of oral anticoagulation use, compared with standard care. Yet, there was no statistically significant difference in stroke reduction, and the 20% relative reduction in thromboembolic complications in the screened group was offset by a 26% relative increase in major bleeding.
“Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of the AF screening trials is that as the tools for screening improve, from a single 12-lead ECG to 14-day recordings and then the always-on ILR, more AF is detected and more [oral anticoagulant] is used, yet there is little demonstrable improvement in outcomes,” Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Foy write.
The editorialists also point to the potential for rhythm monitoring to lead to misdiagnosis and downstream cascades of care. “If you assume a 2% AF prevalence, even a device with 98% specificity will misdiagnose approximately 2000 individuals for every million screened.”
Dr. Mandrola told this news organization that the “greatest value” of these reports on AF screening and the critical appraisal of them is as an exercise in thinking about the limits of screening for disease. As James Maxwell Glover Wilson and Gunner Jungner wrote in their 1968 textbook, “Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease”: “in theory, screening is an admirable method of combating disease … [but] in practice, there are snags.”
“It would be good for the public to understand these snags…because they also apply to cancer, coronary calcium testing, and vascular screening as well,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Asked whether it’s possible to put the genie back in the bottle now that every other patient in clinic may have an ECG on their wrist, Dr. Ogedegbe said, “if a patient has no history of stroke or TIA and is 50 years or older, really, monitoring with these devices for AFib, there’s no evidence for or against doing that. Ultimately, the clinician has got to use their clinical judgment in talking to these patients.”
A related editorial in JAMA Cardiology suggests that, to be effective, the movement toward consumer-based screening must first show that such an approach improves outcomes and must deal with the paradox that those at highest risk for AFib and AFib-related stroke may be the least likely to own these technologies unless supported by the healthcare system.
“In addition, appropriate care pathways for confirming the diagnosis and, if necessary, initiating appropriate treatment in individuals with positive findings will need to be established,” Rod Passman, MD, Northwestern University, and Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, University of Sydney, Australia, say. “It will also be critical to ensure that device costs and variable technological literacy do not create barriers to making screening accessible to all those at risk.”
Finally, in a related editorial in JAMA Network Open Matthew Kalscheur, MD, and Zachary D. Goldberger, MD, both from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, say the potential benefits of early AFib detection should extend beyond stroke prevention.
“Patients identified with AF likely would benefit from targeted management of modifiable risk factors that contribute to AF, including obesity, hypertension, alcohol use, sleep apnea, smoking, and diabetes,” they write.
All members of the USPSTF receive travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings. Dr. Ogedegbe has a study included in the Evidence-based Practice Center report for this topic. Dr. Kahwati reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Greenland reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health and from the American Heart Association. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to this news organization. Dr. Foy, Dr. Kalscheur, and Dr. Goldberger reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The guidance is similar to the task force’s 2018 statement on screening for AFib with electrocardiography in asymptomatic adults 65 years or older, but lowers the inclusion age to adults 50 years or older.
“This 2021 evidence review included searching for evidence on additional screening methods such as automated blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, and consumer devices such as smartwatches and smartphone apps. However, even with this expanded scope, the USPSTF did not find evidence to recommend for or against screening for AF,” the task force states.
The prevalence of increases in age from less than 0.2% in adults younger than 55 years to about 10% in those 85 years or older, the group says. The prevalence is higher in men than in women, but it is uncertain if it differs by race and ethnicity.
Although AFib substantially increases the risk for stroke, the stroke risk associated with subclinical AFib, particularly that of shorter duration lasting less than 24 hours or of lower burden, as might be detected by some screening approaches, is “uncertain,” the task force adds.
The updated recommendations were published online in JAMA, along with a separate evidence report and editorial.
The task force reviewed 26 studies in 113,784 patients, including 12 new to the update.
Studies showed that systematic screening detected significantly more AFib than no screening or pulse palpation (absolute difference, 1.0%-4.8% over up to 12 months). In two of the trials, however, only 10.7% and 44.5% of participants actually received the screening test.
The review included three randomized trials of screening vs. no screening that reported on health outcomes, but only one, STROKESTOP, was powered for health outcomes. It found a significantly lower risk for the primary composite endpoint of ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, system embolism, bleeding leading to hospitalization, and all-cause mortality with twice-daily intermittent single-lead ECG monitoring for 14 days, compared with no screening. However, there were no significant differences in any of the individual outcomes of the composite endpoint.
“Additionally, and probably the most important thing to appreciate for the STROKESTOP study is that it has several limitations,” task force member Gbenga Ogedegbe, MD, MPH, of New York University told this news organization. The intervention was not masked, and outcomes weren’t centrally adjudicated.
Further, “about 11% of patients in the trial had a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA), stroke, or embolism and the population that we’re looking at within the task force are people without symptoms or history of stroke or ischemic attack,” he said. “That’s the fundamental difference here. So those limitations make it difficult to say that STROKESTOP actually has benefit.”
Notably absent from the review was the recent LOOP study, which found no significant benefit on outcomes with continuous monitoring with an implantable loop recorder (ILR) over usual care in older adults.
While it “offers some context for this issue,” it was not eligible for inclusion because 25% of the population had a prior history of stroke, TIA, or embolism and “because this screening approach may not be feasible for primary care settings,” lead author of the Evidence Report Leila Kahwati, MD, MPH, from RTI International’s Social and Health Organizational Research and Evaluation Program and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, explained in an email.
Treatment with warfarin (mean, 1.5 years) was associated with a lower risk for ischemic stroke (relative risk, 0.32) and all-cause mortality (relative risk, 0.68), while direct oral anticoagulants were associated with a lower incidence of stroke (adjusted odds ratio range, 0.32-0.44). Patients had an increased risk for major bleeding with both warfarin (pooled relative risk, 1.8) and direct-acting oral anticoagulants (odds ratio, 1.38-2.21), but confidence intervals did not exclude a null effect.
The USPSTF found no trials that reported on the benefits of anticoagulation therapy in screen-detected patients.
In an accompanying editorial Philip Greenland, MD, points out that the task force’s conclusion differs from the 2020 European Society of Cardiology AFib guideline, which endorses opportunistic screening for AFib by pulse palpation or ECG rhythm strip in patients 65 years or older (class I recommendation) and advises that clinicians consider systematic ECG screening to detect AFib in people 75 years or older, or those at high risk for stroke (class IIa).
To possibly resolve whether screening for AFib in asymptomatic patients is justified, “future trials may need to consider enrolling only higher risk patients and identifying those with AF of longer duration,” said Dr. Greenland, JAMA editor and professor of preventive medicine and medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
“One important point raised by the LOOP trial is whether there is a threshold for AF duration that is most strongly associated with stroke risk and therefore most likely to benefit from anticoagulation,” he writes. Indeed, the LOOP authors themselves questioned whether the trial’s short AFib duration of 6 minutes may have led to many low-risk patients being diagnosed and treated.
“Additionally, trials need to recognize the need for longer monitoring periods (preferably continuous), and perhaps novel wearables will allow long-term monitoring, with accurate interpretation of the ECG and long-term adherence,” Dr. Greenland said.
In a related editorial in JAMA Internal Medicine, John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health Louisville, Ky., and Andrew Foy, MD, Pennsylvania State University, Hershey, point out that continuous ILR monitoring in the LOOP trial found threefold more AFib and led to 2.7-fold higher rates of oral anticoagulation use, compared with standard care. Yet, there was no statistically significant difference in stroke reduction, and the 20% relative reduction in thromboembolic complications in the screened group was offset by a 26% relative increase in major bleeding.
“Perhaps the most remarkable aspect of the AF screening trials is that as the tools for screening improve, from a single 12-lead ECG to 14-day recordings and then the always-on ILR, more AF is detected and more [oral anticoagulant] is used, yet there is little demonstrable improvement in outcomes,” Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Foy write.
The editorialists also point to the potential for rhythm monitoring to lead to misdiagnosis and downstream cascades of care. “If you assume a 2% AF prevalence, even a device with 98% specificity will misdiagnose approximately 2000 individuals for every million screened.”
Dr. Mandrola told this news organization that the “greatest value” of these reports on AF screening and the critical appraisal of them is as an exercise in thinking about the limits of screening for disease. As James Maxwell Glover Wilson and Gunner Jungner wrote in their 1968 textbook, “Principles and Practice of Screening for Disease”: “in theory, screening is an admirable method of combating disease … [but] in practice, there are snags.”
“It would be good for the public to understand these snags…because they also apply to cancer, coronary calcium testing, and vascular screening as well,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Asked whether it’s possible to put the genie back in the bottle now that every other patient in clinic may have an ECG on their wrist, Dr. Ogedegbe said, “if a patient has no history of stroke or TIA and is 50 years or older, really, monitoring with these devices for AFib, there’s no evidence for or against doing that. Ultimately, the clinician has got to use their clinical judgment in talking to these patients.”
A related editorial in JAMA Cardiology suggests that, to be effective, the movement toward consumer-based screening must first show that such an approach improves outcomes and must deal with the paradox that those at highest risk for AFib and AFib-related stroke may be the least likely to own these technologies unless supported by the healthcare system.
“In addition, appropriate care pathways for confirming the diagnosis and, if necessary, initiating appropriate treatment in individuals with positive findings will need to be established,” Rod Passman, MD, Northwestern University, and Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, University of Sydney, Australia, say. “It will also be critical to ensure that device costs and variable technological literacy do not create barriers to making screening accessible to all those at risk.”
Finally, in a related editorial in JAMA Network Open Matthew Kalscheur, MD, and Zachary D. Goldberger, MD, both from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, say the potential benefits of early AFib detection should extend beyond stroke prevention.
“Patients identified with AF likely would benefit from targeted management of modifiable risk factors that contribute to AF, including obesity, hypertension, alcohol use, sleep apnea, smoking, and diabetes,” they write.
All members of the USPSTF receive travel reimbursement and an honorarium for participating in USPSTF meetings. Dr. Ogedegbe has a study included in the Evidence-based Practice Center report for this topic. Dr. Kahwati reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest. Dr. Greenland reported receiving research grants from the National Institutes of Health and from the American Heart Association. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to this news organization. Dr. Foy, Dr. Kalscheur, and Dr. Goldberger reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should we always offer CPR?
Some details have been changed to protect the patient’s identity.
The first thing I noticed about Mr. Barry as I entered the intensive care unit was his left foot: Half of it was black, shriveled, and gangrenous, jutting out from under the white blanket. The soft rays of the morning sun illuminated his gaunt, unshaven, hollow cheeks. Sedated on propofol, with a green endotracheal tube sticking out of his chapped lips, he looked frail. His nurse, Becky, had just cleaned him after he passed tarry, maroon-colored stool. As she turned him over, I saw that the skin over his tailbone was broken. He had a large decubitus ulcer, the edges of which were now dried and black. The Foley bag, hanging next to his bed, was empty; there had been no urine for several hours now.
No one knew much about Mr. Barry. I don’t mean his current medical status – I mean what he did in life, who he loved, whether he had kids, what he valued. All we knew was that he was 83 years old and lived alone. No prior records in our system. No advanced directives. No information on any family. One of his neighbors called 911 after he was not seen for at least 10 days. Emergency medical services found Mr. Barry in bed, nearly lifeless. In the emergency room, he was noted to be in shock, with a dangerously low blood pressure. He was dry as a bone with markedly elevated sodium levels. His laboratory makers for kidney and liver function were deranged. He was admitted to the medical ICU with a diagnosis of hypovolemic shock and/or septic shock with multiorgan dysfunction. With 48 hours of supportive management with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, he did not improve. Blood cultures were positive for gram-positive cocci. The doses for medications used to maintain the blood pressure increased steadily. He also developed gastrointestinal bleeding.
Futile vs. potentially inappropriate
I was called for a cardiology consult because he had transient ST elevation in inferolateral leads on the monitor. Given his clinical scenario, the likelihood of type 1 myocardial infarction from plaque rupture was low; the ST elevations were probably related to vasospasm from increasing pressor requirement. Diagnostic cardiac catheterization showed clean coronary arteries. Continuous renal replacement therapy was soon started. Given Mr Barry’s multiorgan dysfunction and extremely poor prognosis, I recommended making all efforts to find his family or surrogate decision-maker to discuss goals of care or having a two-physician sign-off to place a DNR order.
Despite all efforts, we could not trace the family. We physicians vary individually on how we define value as related to life. We also vary on the degree of uncertainty about prognostication that we are comfortable with. This is one of the reasons the term “futility” is controversial and there is a push to use “potentially inappropriate” instead. The primary team had a different threshold for placing a DNR order and did not do it. That night, after I left the hospital, Mr Barry had a PEA (pulseless electrical activity) arrest and was resuscitated after 10 minutes of CPR. The next day, I noticed his bruised chest. He was on multiple medications to support his blood pressure.
My patient and a Hemingway protagonist
Whether by coincidence or irony, I started reading Ernest Hemingway’s short story “The Snows of Kilimanjaro” the same day that I met Mr. Barry. He reminded me of the story’s protagonist, Harry, lying on the cot with a gangrenous leg, waiting to die. Harry could sense death approaching. He reminisced about his past. All he wanted was to drink his “whiskey-soda.” “Darling, don’t drink that. We have to do everything we can,” his wife said. “You do it. I am tired,” Harry said, and continued to drink his whiskey-soda.
Mr. Barry looked tired. Tired of life? I can’t say with certainty. However, if I had to guess, the medical team’s heroics meant nothing to him. Unfortunately, he was not awake like Harry and could not do what he wished. I wondered what snippets of his life flashed before him as he lay on his bed at home for days. Did he want to have a whiskey-soda before dying? But we are not letting him die. Not easily anyway. We have to do everything we can: medications, coronary angiogram, dialysis, multiple rounds of CPR. Why?
In this country, we need permission to forgo CPR. If there are no advanced directives or next of kin available to discuss end-of-life care, performing CPR is the default status for all hospitalized patients, irrespective of the underlying severity of the illness. A unilateral DNR order written by a physician in good conscience (in a medically futile situation), but to which the patient has not consented, is generally invalid in most U.S. states. If health directives are not available, CPR will be administered on the presumption that the patient would want us to “do everything we can.” The medicolegal consequences and fear of not administering CPR is more profound than being found wrong and defying a patient’s wishes against CPR.
In patients with outside-hospital cardiac arrest, especially if related to ventricular fibrillation, early bystander CPR improves the survival rate. Hence, it makes sense for first responders and paramedics to administer CPR as the default option, focusing on the technique, rather than thinking about its utility based on the patient’s underlying comorbidities.
In the inpatient setting, however, physicians have enough information to comprehensively evaluate the patient. In a cohort of 5,690 critically ill ICU patients, obtained from a U.S. registry, the rate of survival to discharge after inpatient cardiac arrest is very low at 12.5%. Chronic health conditions, malignancy, end-stage renal disease, multiorgan dysfunction, need for vasopressor support, prior CPR, initial rhythm of asystole, or PEA advanced age were all associated with a less than 10% survival rate after CPR.
Dying is a process. Administering CPR to a dying patient is of little to no value. For Mr. Barry, it resulted in a bruised chest and broken ribs. James R. Jude, MD, one of the pioneers of closed chest compression, or modern-day CPR, wrote in 1965 that “resuscitation of the dying patient with irreparable damage to lungs, heart, kidneys, brain or any other vital system of the body has no medical, ethical, or moral justification. The techniques described in this monograph were designed to resuscitate the victim of acute insult, whether be it from drowning, electrical shock, untoward effect of drugs, anesthetic accident, heart block, acute myocardial infarction, or surgery.”
Yet, doctors continue to provide futile treatments at end of life for a variety of reasons: concerns about medico-legal risks, discomfort or inexperience with death and dying, uncertainty in prognostication, family requests, and organizational barriers such as lack of palliative services that can help lead end-of-life care discussions. Despite knowing that CPR has little benefit in critically ill patients with terminal illness and multiorgan dysfunction, we often ask the patient and their surrogate decision-makers: “If your heart stops, do you want us to restore your heart by pressing on the chest and giving electric shocks?” The very act of asking the question implies that CPR may be beneficial. We often do not go over the risks or offer an opinion on whether CPR should be performed. We take a neutral stance.
Anoxic brain injury, pain from broken ribs, and low likelihood of survival to discharge with acceptable neurologic recovery are rarely discussed in detail. Laypeople may overestimate the chances of survival after CPR and they may not comprehend that it does not reverse the dying process in patients with a terminal illness. When you ask about CPR, most families hear: “Do you want your loved one to live?” and the answer is nearly always “Yes.” We then administer CPR, thinking that we are respecting the patient’s autonomy in the medical decision-making process. However, in end-of-life care, elderly patients or surrogates may not fully understand the complexities involved or the outcomes of CPR. So, are we truly respecting their autonomy?
When to offer CPR?
In 2011, Billings and Krakauer, palliative care specialists from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, suggested that we focus on understanding our patient’s values and goals of care, and then decide whether to offer CPR, rather than taking a neutral stance. With this approach, we continue to respect the patient’s autonomy and also affirm our responsibility in providing care consistent with medical reality. We need to have the humility to accept that death is inevitable.
It has been 10 years since a group of physicians from Columbia University Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, MGH, and Boston Children’s Hospital proposed changes to how we determine resuscitation status. Instead of assuming that CPR is always wanted, they suggested three distinct approaches: consider CPR when the benefits versus risks are uncertain, and the patient is not end stage; recommend against CPR when there is a low likelihood of benefit and high likelihood of harm (e.g., patients with anoxic brain injury, advanced incurable cancer, or end-stage multiorgan dysfunction); and do not offer CPR to patients who will die imminently and have no chance of surviving CPR (e.g., patients with multiorgan dysfunction, increasing pressor requirements, and those who are actively dying without a single immediately reversible cause). I agree with their proposal.
Mr. Barry was actively dying. Unfortunately, we had neither his advanced directives nor access to family members or surrogates to discuss values and goals of care. Given the futility of administering CPR again, and based on our humanitarian principles, a moral and ethical responsibility to ensure a peaceful dying process, I and another ICU attending placed the DNR order. He passed away, peacefully, within a few hours.
That evening, as I was sitting on my porch reading the last page of “The Snows of Kilimanjaro,” my phone pinged. It was an email asking me to complete the final attestation for the death certificate. I imagined that Mr. Barry knew where he was going. He probably had his own special place – something beautiful and majestic, great and tall, dazzlingly white in the hot sun, like the snow-capped mountain of Kilimanjaro that Harry saw at the time of his death.
Dr. Mallidi is a general cardiologist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, UCSF. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some details have been changed to protect the patient’s identity.
The first thing I noticed about Mr. Barry as I entered the intensive care unit was his left foot: Half of it was black, shriveled, and gangrenous, jutting out from under the white blanket. The soft rays of the morning sun illuminated his gaunt, unshaven, hollow cheeks. Sedated on propofol, with a green endotracheal tube sticking out of his chapped lips, he looked frail. His nurse, Becky, had just cleaned him after he passed tarry, maroon-colored stool. As she turned him over, I saw that the skin over his tailbone was broken. He had a large decubitus ulcer, the edges of which were now dried and black. The Foley bag, hanging next to his bed, was empty; there had been no urine for several hours now.
No one knew much about Mr. Barry. I don’t mean his current medical status – I mean what he did in life, who he loved, whether he had kids, what he valued. All we knew was that he was 83 years old and lived alone. No prior records in our system. No advanced directives. No information on any family. One of his neighbors called 911 after he was not seen for at least 10 days. Emergency medical services found Mr. Barry in bed, nearly lifeless. In the emergency room, he was noted to be in shock, with a dangerously low blood pressure. He was dry as a bone with markedly elevated sodium levels. His laboratory makers for kidney and liver function were deranged. He was admitted to the medical ICU with a diagnosis of hypovolemic shock and/or septic shock with multiorgan dysfunction. With 48 hours of supportive management with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, he did not improve. Blood cultures were positive for gram-positive cocci. The doses for medications used to maintain the blood pressure increased steadily. He also developed gastrointestinal bleeding.
Futile vs. potentially inappropriate
I was called for a cardiology consult because he had transient ST elevation in inferolateral leads on the monitor. Given his clinical scenario, the likelihood of type 1 myocardial infarction from plaque rupture was low; the ST elevations were probably related to vasospasm from increasing pressor requirement. Diagnostic cardiac catheterization showed clean coronary arteries. Continuous renal replacement therapy was soon started. Given Mr Barry’s multiorgan dysfunction and extremely poor prognosis, I recommended making all efforts to find his family or surrogate decision-maker to discuss goals of care or having a two-physician sign-off to place a DNR order.
Despite all efforts, we could not trace the family. We physicians vary individually on how we define value as related to life. We also vary on the degree of uncertainty about prognostication that we are comfortable with. This is one of the reasons the term “futility” is controversial and there is a push to use “potentially inappropriate” instead. The primary team had a different threshold for placing a DNR order and did not do it. That night, after I left the hospital, Mr Barry had a PEA (pulseless electrical activity) arrest and was resuscitated after 10 minutes of CPR. The next day, I noticed his bruised chest. He was on multiple medications to support his blood pressure.
My patient and a Hemingway protagonist
Whether by coincidence or irony, I started reading Ernest Hemingway’s short story “The Snows of Kilimanjaro” the same day that I met Mr. Barry. He reminded me of the story’s protagonist, Harry, lying on the cot with a gangrenous leg, waiting to die. Harry could sense death approaching. He reminisced about his past. All he wanted was to drink his “whiskey-soda.” “Darling, don’t drink that. We have to do everything we can,” his wife said. “You do it. I am tired,” Harry said, and continued to drink his whiskey-soda.
Mr. Barry looked tired. Tired of life? I can’t say with certainty. However, if I had to guess, the medical team’s heroics meant nothing to him. Unfortunately, he was not awake like Harry and could not do what he wished. I wondered what snippets of his life flashed before him as he lay on his bed at home for days. Did he want to have a whiskey-soda before dying? But we are not letting him die. Not easily anyway. We have to do everything we can: medications, coronary angiogram, dialysis, multiple rounds of CPR. Why?
In this country, we need permission to forgo CPR. If there are no advanced directives or next of kin available to discuss end-of-life care, performing CPR is the default status for all hospitalized patients, irrespective of the underlying severity of the illness. A unilateral DNR order written by a physician in good conscience (in a medically futile situation), but to which the patient has not consented, is generally invalid in most U.S. states. If health directives are not available, CPR will be administered on the presumption that the patient would want us to “do everything we can.” The medicolegal consequences and fear of not administering CPR is more profound than being found wrong and defying a patient’s wishes against CPR.
In patients with outside-hospital cardiac arrest, especially if related to ventricular fibrillation, early bystander CPR improves the survival rate. Hence, it makes sense for first responders and paramedics to administer CPR as the default option, focusing on the technique, rather than thinking about its utility based on the patient’s underlying comorbidities.
In the inpatient setting, however, physicians have enough information to comprehensively evaluate the patient. In a cohort of 5,690 critically ill ICU patients, obtained from a U.S. registry, the rate of survival to discharge after inpatient cardiac arrest is very low at 12.5%. Chronic health conditions, malignancy, end-stage renal disease, multiorgan dysfunction, need for vasopressor support, prior CPR, initial rhythm of asystole, or PEA advanced age were all associated with a less than 10% survival rate after CPR.
Dying is a process. Administering CPR to a dying patient is of little to no value. For Mr. Barry, it resulted in a bruised chest and broken ribs. James R. Jude, MD, one of the pioneers of closed chest compression, or modern-day CPR, wrote in 1965 that “resuscitation of the dying patient with irreparable damage to lungs, heart, kidneys, brain or any other vital system of the body has no medical, ethical, or moral justification. The techniques described in this monograph were designed to resuscitate the victim of acute insult, whether be it from drowning, electrical shock, untoward effect of drugs, anesthetic accident, heart block, acute myocardial infarction, or surgery.”
Yet, doctors continue to provide futile treatments at end of life for a variety of reasons: concerns about medico-legal risks, discomfort or inexperience with death and dying, uncertainty in prognostication, family requests, and organizational barriers such as lack of palliative services that can help lead end-of-life care discussions. Despite knowing that CPR has little benefit in critically ill patients with terminal illness and multiorgan dysfunction, we often ask the patient and their surrogate decision-makers: “If your heart stops, do you want us to restore your heart by pressing on the chest and giving electric shocks?” The very act of asking the question implies that CPR may be beneficial. We often do not go over the risks or offer an opinion on whether CPR should be performed. We take a neutral stance.
Anoxic brain injury, pain from broken ribs, and low likelihood of survival to discharge with acceptable neurologic recovery are rarely discussed in detail. Laypeople may overestimate the chances of survival after CPR and they may not comprehend that it does not reverse the dying process in patients with a terminal illness. When you ask about CPR, most families hear: “Do you want your loved one to live?” and the answer is nearly always “Yes.” We then administer CPR, thinking that we are respecting the patient’s autonomy in the medical decision-making process. However, in end-of-life care, elderly patients or surrogates may not fully understand the complexities involved or the outcomes of CPR. So, are we truly respecting their autonomy?
When to offer CPR?
In 2011, Billings and Krakauer, palliative care specialists from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, suggested that we focus on understanding our patient’s values and goals of care, and then decide whether to offer CPR, rather than taking a neutral stance. With this approach, we continue to respect the patient’s autonomy and also affirm our responsibility in providing care consistent with medical reality. We need to have the humility to accept that death is inevitable.
It has been 10 years since a group of physicians from Columbia University Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, MGH, and Boston Children’s Hospital proposed changes to how we determine resuscitation status. Instead of assuming that CPR is always wanted, they suggested three distinct approaches: consider CPR when the benefits versus risks are uncertain, and the patient is not end stage; recommend against CPR when there is a low likelihood of benefit and high likelihood of harm (e.g., patients with anoxic brain injury, advanced incurable cancer, or end-stage multiorgan dysfunction); and do not offer CPR to patients who will die imminently and have no chance of surviving CPR (e.g., patients with multiorgan dysfunction, increasing pressor requirements, and those who are actively dying without a single immediately reversible cause). I agree with their proposal.
Mr. Barry was actively dying. Unfortunately, we had neither his advanced directives nor access to family members or surrogates to discuss values and goals of care. Given the futility of administering CPR again, and based on our humanitarian principles, a moral and ethical responsibility to ensure a peaceful dying process, I and another ICU attending placed the DNR order. He passed away, peacefully, within a few hours.
That evening, as I was sitting on my porch reading the last page of “The Snows of Kilimanjaro,” my phone pinged. It was an email asking me to complete the final attestation for the death certificate. I imagined that Mr. Barry knew where he was going. He probably had his own special place – something beautiful and majestic, great and tall, dazzlingly white in the hot sun, like the snow-capped mountain of Kilimanjaro that Harry saw at the time of his death.
Dr. Mallidi is a general cardiologist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, UCSF. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Some details have been changed to protect the patient’s identity.
The first thing I noticed about Mr. Barry as I entered the intensive care unit was his left foot: Half of it was black, shriveled, and gangrenous, jutting out from under the white blanket. The soft rays of the morning sun illuminated his gaunt, unshaven, hollow cheeks. Sedated on propofol, with a green endotracheal tube sticking out of his chapped lips, he looked frail. His nurse, Becky, had just cleaned him after he passed tarry, maroon-colored stool. As she turned him over, I saw that the skin over his tailbone was broken. He had a large decubitus ulcer, the edges of which were now dried and black. The Foley bag, hanging next to his bed, was empty; there had been no urine for several hours now.
No one knew much about Mr. Barry. I don’t mean his current medical status – I mean what he did in life, who he loved, whether he had kids, what he valued. All we knew was that he was 83 years old and lived alone. No prior records in our system. No advanced directives. No information on any family. One of his neighbors called 911 after he was not seen for at least 10 days. Emergency medical services found Mr. Barry in bed, nearly lifeless. In the emergency room, he was noted to be in shock, with a dangerously low blood pressure. He was dry as a bone with markedly elevated sodium levels. His laboratory makers for kidney and liver function were deranged. He was admitted to the medical ICU with a diagnosis of hypovolemic shock and/or septic shock with multiorgan dysfunction. With 48 hours of supportive management with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, he did not improve. Blood cultures were positive for gram-positive cocci. The doses for medications used to maintain the blood pressure increased steadily. He also developed gastrointestinal bleeding.
Futile vs. potentially inappropriate
I was called for a cardiology consult because he had transient ST elevation in inferolateral leads on the monitor. Given his clinical scenario, the likelihood of type 1 myocardial infarction from plaque rupture was low; the ST elevations were probably related to vasospasm from increasing pressor requirement. Diagnostic cardiac catheterization showed clean coronary arteries. Continuous renal replacement therapy was soon started. Given Mr Barry’s multiorgan dysfunction and extremely poor prognosis, I recommended making all efforts to find his family or surrogate decision-maker to discuss goals of care or having a two-physician sign-off to place a DNR order.
Despite all efforts, we could not trace the family. We physicians vary individually on how we define value as related to life. We also vary on the degree of uncertainty about prognostication that we are comfortable with. This is one of the reasons the term “futility” is controversial and there is a push to use “potentially inappropriate” instead. The primary team had a different threshold for placing a DNR order and did not do it. That night, after I left the hospital, Mr Barry had a PEA (pulseless electrical activity) arrest and was resuscitated after 10 minutes of CPR. The next day, I noticed his bruised chest. He was on multiple medications to support his blood pressure.
My patient and a Hemingway protagonist
Whether by coincidence or irony, I started reading Ernest Hemingway’s short story “The Snows of Kilimanjaro” the same day that I met Mr. Barry. He reminded me of the story’s protagonist, Harry, lying on the cot with a gangrenous leg, waiting to die. Harry could sense death approaching. He reminisced about his past. All he wanted was to drink his “whiskey-soda.” “Darling, don’t drink that. We have to do everything we can,” his wife said. “You do it. I am tired,” Harry said, and continued to drink his whiskey-soda.
Mr. Barry looked tired. Tired of life? I can’t say with certainty. However, if I had to guess, the medical team’s heroics meant nothing to him. Unfortunately, he was not awake like Harry and could not do what he wished. I wondered what snippets of his life flashed before him as he lay on his bed at home for days. Did he want to have a whiskey-soda before dying? But we are not letting him die. Not easily anyway. We have to do everything we can: medications, coronary angiogram, dialysis, multiple rounds of CPR. Why?
In this country, we need permission to forgo CPR. If there are no advanced directives or next of kin available to discuss end-of-life care, performing CPR is the default status for all hospitalized patients, irrespective of the underlying severity of the illness. A unilateral DNR order written by a physician in good conscience (in a medically futile situation), but to which the patient has not consented, is generally invalid in most U.S. states. If health directives are not available, CPR will be administered on the presumption that the patient would want us to “do everything we can.” The medicolegal consequences and fear of not administering CPR is more profound than being found wrong and defying a patient’s wishes against CPR.
In patients with outside-hospital cardiac arrest, especially if related to ventricular fibrillation, early bystander CPR improves the survival rate. Hence, it makes sense for first responders and paramedics to administer CPR as the default option, focusing on the technique, rather than thinking about its utility based on the patient’s underlying comorbidities.
In the inpatient setting, however, physicians have enough information to comprehensively evaluate the patient. In a cohort of 5,690 critically ill ICU patients, obtained from a U.S. registry, the rate of survival to discharge after inpatient cardiac arrest is very low at 12.5%. Chronic health conditions, malignancy, end-stage renal disease, multiorgan dysfunction, need for vasopressor support, prior CPR, initial rhythm of asystole, or PEA advanced age were all associated with a less than 10% survival rate after CPR.
Dying is a process. Administering CPR to a dying patient is of little to no value. For Mr. Barry, it resulted in a bruised chest and broken ribs. James R. Jude, MD, one of the pioneers of closed chest compression, or modern-day CPR, wrote in 1965 that “resuscitation of the dying patient with irreparable damage to lungs, heart, kidneys, brain or any other vital system of the body has no medical, ethical, or moral justification. The techniques described in this monograph were designed to resuscitate the victim of acute insult, whether be it from drowning, electrical shock, untoward effect of drugs, anesthetic accident, heart block, acute myocardial infarction, or surgery.”
Yet, doctors continue to provide futile treatments at end of life for a variety of reasons: concerns about medico-legal risks, discomfort or inexperience with death and dying, uncertainty in prognostication, family requests, and organizational barriers such as lack of palliative services that can help lead end-of-life care discussions. Despite knowing that CPR has little benefit in critically ill patients with terminal illness and multiorgan dysfunction, we often ask the patient and their surrogate decision-makers: “If your heart stops, do you want us to restore your heart by pressing on the chest and giving electric shocks?” The very act of asking the question implies that CPR may be beneficial. We often do not go over the risks or offer an opinion on whether CPR should be performed. We take a neutral stance.
Anoxic brain injury, pain from broken ribs, and low likelihood of survival to discharge with acceptable neurologic recovery are rarely discussed in detail. Laypeople may overestimate the chances of survival after CPR and they may not comprehend that it does not reverse the dying process in patients with a terminal illness. When you ask about CPR, most families hear: “Do you want your loved one to live?” and the answer is nearly always “Yes.” We then administer CPR, thinking that we are respecting the patient’s autonomy in the medical decision-making process. However, in end-of-life care, elderly patients or surrogates may not fully understand the complexities involved or the outcomes of CPR. So, are we truly respecting their autonomy?
When to offer CPR?
In 2011, Billings and Krakauer, palliative care specialists from Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, suggested that we focus on understanding our patient’s values and goals of care, and then decide whether to offer CPR, rather than taking a neutral stance. With this approach, we continue to respect the patient’s autonomy and also affirm our responsibility in providing care consistent with medical reality. We need to have the humility to accept that death is inevitable.
It has been 10 years since a group of physicians from Columbia University Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, MGH, and Boston Children’s Hospital proposed changes to how we determine resuscitation status. Instead of assuming that CPR is always wanted, they suggested three distinct approaches: consider CPR when the benefits versus risks are uncertain, and the patient is not end stage; recommend against CPR when there is a low likelihood of benefit and high likelihood of harm (e.g., patients with anoxic brain injury, advanced incurable cancer, or end-stage multiorgan dysfunction); and do not offer CPR to patients who will die imminently and have no chance of surviving CPR (e.g., patients with multiorgan dysfunction, increasing pressor requirements, and those who are actively dying without a single immediately reversible cause). I agree with their proposal.
Mr. Barry was actively dying. Unfortunately, we had neither his advanced directives nor access to family members or surrogates to discuss values and goals of care. Given the futility of administering CPR again, and based on our humanitarian principles, a moral and ethical responsibility to ensure a peaceful dying process, I and another ICU attending placed the DNR order. He passed away, peacefully, within a few hours.
That evening, as I was sitting on my porch reading the last page of “The Snows of Kilimanjaro,” my phone pinged. It was an email asking me to complete the final attestation for the death certificate. I imagined that Mr. Barry knew where he was going. He probably had his own special place – something beautiful and majestic, great and tall, dazzlingly white in the hot sun, like the snow-capped mountain of Kilimanjaro that Harry saw at the time of his death.
Dr. Mallidi is a general cardiologist at Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, UCSF. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: United States passes 10 million total cases
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.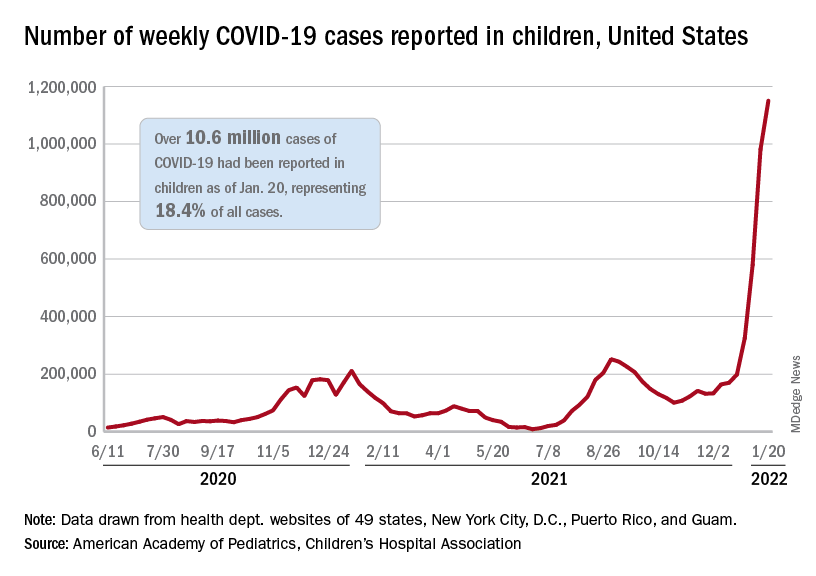
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.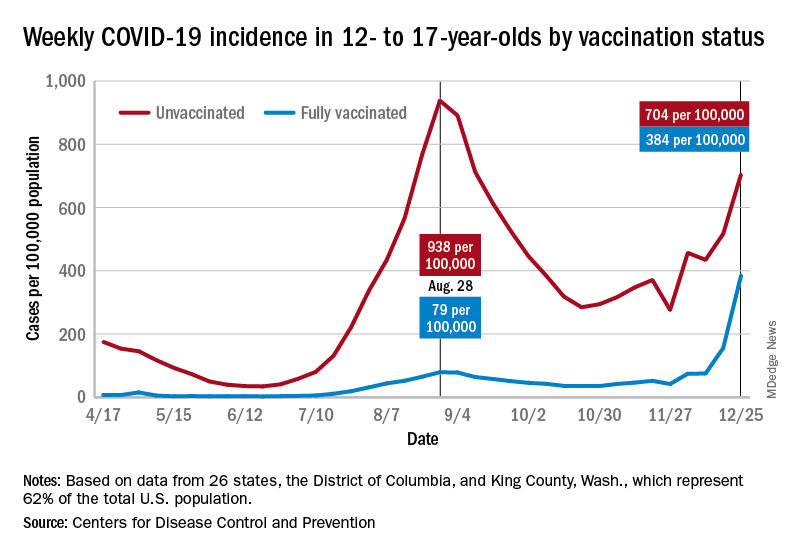
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children topped 1 million for the first time as the cumulative count surpassed 10 million since the start of the pandemic, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report. Those 10.6 million child cases represent 18.4% of all cases, and the latest 1.15 million represented 25.5% of all cases for the week.
Regionally, the South had the most cases with over 380,000 for the week of Jan. 14-20, while the West was next with close to 350,000, followed by the Midwest and then the East. Among the states, the largest percent increases – on the order of 30% – came in New England (Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Vermont), as well as Virginia and California, the AAP and CHA said.
Examining all those cases by vaccination status shows an obvious difference between the Omicron and Delta variants: The fully vaccinated have been hit much harder than before. For the week ending Dec. 25, 2021, the incidence of COVID-19 in children aged 12-17 years was 704 per 100,000 among those were unvaccinated and 384 per 100,000 in those who were fully vaccinated. During the Delta surge in the summer of 2021, the peak rates were 938 (unvaccinated) and 79 (vaccinated), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
Hospitalizations are also at record levels, but two separate CDC databases seem to show a decline in child admissions over the last available week or so of data, which follows the trend among all ages. The peak among children aged 0-17 years came on Jan. 15, when the rate of new admissions reached 1.25 per 100,000, based on reporting to the CDC from 5,265 hospitals nationwide.
The second database, the COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network (COVID-NET), indicates that children aged 0-4 years had the highest admission rate, 14.5 per 100,000, for the week ending Jan. 8, compared with 5.5 per 100,000 for 12- to 17-year-olds and 2.3 per 100,000 for those aged 5-11 years. COVID-NET covers almost 100 counties in 10 states, along with 4 entire states, and represents about 10% of the U.S. population.
Vaccinations rose briefly in late December and into January to meet the Omicron surge, but the numbers for the latest week show a return to their earlier levels. In children aged 5-11 years, new vaccinations went from 381,000 for the week of Dec. 20-26 to 524,000 for Jan. 3-9, but fell to just 260,000 during Jan. 17-23. The response was a little later for those aged 12-17, with the big week coming Jan. 10-16, but there was still a 38% drop for Jan. 17-23, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
Currently, 29.3% of all 5- to 11-year-olds have received at least one dose of the COVID vaccine, and an even 20.0% are fully vaccinated. For children aged 12-17, the corresponding figures are 65.8% and 55.1%, the CDC said.
Statewide vaccination rates vary from Vermont’s high of 61% for those aged 5-11 to 12% for Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, while Hawaii has the highest rate for 12- to 17-year-olds at 92% and Wyoming has the lowest at 39%, the AAP reported.