User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Sputum markers may predict remission in eosinophilic asthma
for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. The finding was based on data from 52 individuals.
Although IL-5 therapies have been shown to be effective for improving asthma, patients’ responses vary, write Catherine Moermans, PhD, of Liège University, Belgium, and colleagues.
Biotherapies targeting IL-5 allow a tangible improvement of asthma. However, all patients do not respond the same way to these treatments, and reliable biomarkers for predicting treatment response are lacking, they say.
In an observational study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 52 adults with severe asthma who began anti–IL-5 treatment at a single center. The primary outcome was remission of asthma.
Remission was defined as meeting all of the following criteria 1 year after therapy: no chronic treatment with oral corticosteroids; no exacerbation; asthma control questionnaire scores lower than 1.5 and/or asthma test greater than 19; forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of at least 80% predicted; and/or improvement of FEV1 equal to or larger than 10%, and a blood eosinophil count lower than 300 cells/mL.
Prior to treatment, the researchers measured eosinophil peroxidase (EPX), immunoglobulin E (IgE), IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-25, IL-33, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), and eotaxin-1 levels in the sputum of each patient.
At follow-up, 11 patients met the criteria for remission. These patients had significantly higher sputum eosinophil counts, sputum macrophage counts, and lymphocyte counts at baseline, compared with those not in remission (P = .006, P = .02, and P = .04, respectively). Sputum neutrophil percentage levels were significantly lower in patients whose asthma was in remission, compared with those whose asthma was not in remission (P = .007).
At the protein level, remission patients also showed higher baseline levels of sputum eotaxin-1, TSLP, IL-5, EPX, and IgE protein, compared with patients who did not achieve remission (P = .046, P = .04, P = .002, P = .001, and P = .006, respectively).
Overall, EPX and IL-5 measures showed the best combination of sensitivity and specificity, as well as the best area under the curve, the researchers write.
Patients in remission were significantly more likely to be men (8 of 11 patients), a finding that reflected previous studies, the researchers write. The finding of eosinophilic inflammation associated with stronger response to anti–IL-5 therapy also reflected previous studies, but the current study showed that “with a comparable blood eosinophil level at baseline before biotherapy, the response can be highly variable.”
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size and the lack of a formal definition of remission. Other research needs include an analysis based on nonresponse or suboptimal response predictors, the researchers note.
The results suggest that sputum type 2 markers are potential predictors of remission after anti–IL-5 treatment in adults with severe eosinophilic asthma, although the results must be validated in a larger, multicenter cohort, they conclude.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. Several coauthors have relationships with these companies. Dr. Moermans has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. The finding was based on data from 52 individuals.
Although IL-5 therapies have been shown to be effective for improving asthma, patients’ responses vary, write Catherine Moermans, PhD, of Liège University, Belgium, and colleagues.
Biotherapies targeting IL-5 allow a tangible improvement of asthma. However, all patients do not respond the same way to these treatments, and reliable biomarkers for predicting treatment response are lacking, they say.
In an observational study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 52 adults with severe asthma who began anti–IL-5 treatment at a single center. The primary outcome was remission of asthma.
Remission was defined as meeting all of the following criteria 1 year after therapy: no chronic treatment with oral corticosteroids; no exacerbation; asthma control questionnaire scores lower than 1.5 and/or asthma test greater than 19; forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of at least 80% predicted; and/or improvement of FEV1 equal to or larger than 10%, and a blood eosinophil count lower than 300 cells/mL.
Prior to treatment, the researchers measured eosinophil peroxidase (EPX), immunoglobulin E (IgE), IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-25, IL-33, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), and eotaxin-1 levels in the sputum of each patient.
At follow-up, 11 patients met the criteria for remission. These patients had significantly higher sputum eosinophil counts, sputum macrophage counts, and lymphocyte counts at baseline, compared with those not in remission (P = .006, P = .02, and P = .04, respectively). Sputum neutrophil percentage levels were significantly lower in patients whose asthma was in remission, compared with those whose asthma was not in remission (P = .007).
At the protein level, remission patients also showed higher baseline levels of sputum eotaxin-1, TSLP, IL-5, EPX, and IgE protein, compared with patients who did not achieve remission (P = .046, P = .04, P = .002, P = .001, and P = .006, respectively).
Overall, EPX and IL-5 measures showed the best combination of sensitivity and specificity, as well as the best area under the curve, the researchers write.
Patients in remission were significantly more likely to be men (8 of 11 patients), a finding that reflected previous studies, the researchers write. The finding of eosinophilic inflammation associated with stronger response to anti–IL-5 therapy also reflected previous studies, but the current study showed that “with a comparable blood eosinophil level at baseline before biotherapy, the response can be highly variable.”
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size and the lack of a formal definition of remission. Other research needs include an analysis based on nonresponse or suboptimal response predictors, the researchers note.
The results suggest that sputum type 2 markers are potential predictors of remission after anti–IL-5 treatment in adults with severe eosinophilic asthma, although the results must be validated in a larger, multicenter cohort, they conclude.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. Several coauthors have relationships with these companies. Dr. Moermans has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. The finding was based on data from 52 individuals.
Although IL-5 therapies have been shown to be effective for improving asthma, patients’ responses vary, write Catherine Moermans, PhD, of Liège University, Belgium, and colleagues.
Biotherapies targeting IL-5 allow a tangible improvement of asthma. However, all patients do not respond the same way to these treatments, and reliable biomarkers for predicting treatment response are lacking, they say.
In an observational study published in the journal Chest, the researchers recruited 52 adults with severe asthma who began anti–IL-5 treatment at a single center. The primary outcome was remission of asthma.
Remission was defined as meeting all of the following criteria 1 year after therapy: no chronic treatment with oral corticosteroids; no exacerbation; asthma control questionnaire scores lower than 1.5 and/or asthma test greater than 19; forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) of at least 80% predicted; and/or improvement of FEV1 equal to or larger than 10%, and a blood eosinophil count lower than 300 cells/mL.
Prior to treatment, the researchers measured eosinophil peroxidase (EPX), immunoglobulin E (IgE), IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-25, IL-33, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), and eotaxin-1 levels in the sputum of each patient.
At follow-up, 11 patients met the criteria for remission. These patients had significantly higher sputum eosinophil counts, sputum macrophage counts, and lymphocyte counts at baseline, compared with those not in remission (P = .006, P = .02, and P = .04, respectively). Sputum neutrophil percentage levels were significantly lower in patients whose asthma was in remission, compared with those whose asthma was not in remission (P = .007).
At the protein level, remission patients also showed higher baseline levels of sputum eotaxin-1, TSLP, IL-5, EPX, and IgE protein, compared with patients who did not achieve remission (P = .046, P = .04, P = .002, P = .001, and P = .006, respectively).
Overall, EPX and IL-5 measures showed the best combination of sensitivity and specificity, as well as the best area under the curve, the researchers write.
Patients in remission were significantly more likely to be men (8 of 11 patients), a finding that reflected previous studies, the researchers write. The finding of eosinophilic inflammation associated with stronger response to anti–IL-5 therapy also reflected previous studies, but the current study showed that “with a comparable blood eosinophil level at baseline before biotherapy, the response can be highly variable.”
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the small sample size and the lack of a formal definition of remission. Other research needs include an analysis based on nonresponse or suboptimal response predictors, the researchers note.
The results suggest that sputum type 2 markers are potential predictors of remission after anti–IL-5 treatment in adults with severe eosinophilic asthma, although the results must be validated in a larger, multicenter cohort, they conclude.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. Several coauthors have relationships with these companies. Dr. Moermans has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Beware risk of sedatives for respiratory patients
Both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be challenging to diagnose, and medication-driven episodes of sedation or hypoventilation are often overlooked as causes of acute exacerbations in these conditions, according to a letter published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
write Christos V. Chalitsios, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
The authors note that exacerbations are the main complications of both asthma and COPD, and stress the importance of identifying causes and preventive strategies.
Sedatives such as opioids have been shown to depress respiratory drive, reduce muscle tone, and increase the risk of pneumonia, they write. The authors also propose that the risk of sedative-induced aspiration or hypoventilation would be associated with medications including pregabalin, gabapentin, and amitriptyline.
Other mechanisms may be involved in the association between sedatives and exacerbations in asthma and COPD. For example, sedative medications can suppress coughing, which may promote airway mucous compaction and possible infection, the authors write.
Most research involving prevention of asthma and COPD exacerbations has not addressed the potential impact of sedatives taken for reasons outside of obstructive lung disease, the authors say.
“Although the risk of sedation and hypoventilation events are known to be increased by opioids and antipsychotic drugs, there has not been a systematic assessment of commonly prescribed medications with potential respiratory side-effects, including gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin,” they write.
Polypharmacy is increasingly common and results in many patients with asthma or COPD presenting for treatment of acute exacerbations while on a combination of gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline, and opioids, the authors note; “however, there is little data or disease-specific guidance on how best to manage this problem, which often starts with a prescription in primary care,” they write. Simply stopping sedatives is not an option for many patients given the addictive nature of these drugs and the unlikely resolution of the condition for which the drugs were prescribed, the authors say. However, “cautious dose reduction” of sedatives is possible once patients understand the reason, they add.
Clinicians may be able to suggest reduced doses and alternative treatments to patients with asthma and COPD while highlighting the risk of respiratory depression and polypharmacy – “potentially reducing the number of exacerbations of obstructive lung disease,” the authors conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be challenging to diagnose, and medication-driven episodes of sedation or hypoventilation are often overlooked as causes of acute exacerbations in these conditions, according to a letter published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
write Christos V. Chalitsios, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
The authors note that exacerbations are the main complications of both asthma and COPD, and stress the importance of identifying causes and preventive strategies.
Sedatives such as opioids have been shown to depress respiratory drive, reduce muscle tone, and increase the risk of pneumonia, they write. The authors also propose that the risk of sedative-induced aspiration or hypoventilation would be associated with medications including pregabalin, gabapentin, and amitriptyline.
Other mechanisms may be involved in the association between sedatives and exacerbations in asthma and COPD. For example, sedative medications can suppress coughing, which may promote airway mucous compaction and possible infection, the authors write.
Most research involving prevention of asthma and COPD exacerbations has not addressed the potential impact of sedatives taken for reasons outside of obstructive lung disease, the authors say.
“Although the risk of sedation and hypoventilation events are known to be increased by opioids and antipsychotic drugs, there has not been a systematic assessment of commonly prescribed medications with potential respiratory side-effects, including gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin,” they write.
Polypharmacy is increasingly common and results in many patients with asthma or COPD presenting for treatment of acute exacerbations while on a combination of gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline, and opioids, the authors note; “however, there is little data or disease-specific guidance on how best to manage this problem, which often starts with a prescription in primary care,” they write. Simply stopping sedatives is not an option for many patients given the addictive nature of these drugs and the unlikely resolution of the condition for which the drugs were prescribed, the authors say. However, “cautious dose reduction” of sedatives is possible once patients understand the reason, they add.
Clinicians may be able to suggest reduced doses and alternative treatments to patients with asthma and COPD while highlighting the risk of respiratory depression and polypharmacy – “potentially reducing the number of exacerbations of obstructive lung disease,” the authors conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Both asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be challenging to diagnose, and medication-driven episodes of sedation or hypoventilation are often overlooked as causes of acute exacerbations in these conditions, according to a letter published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
write Christos V. Chalitsios, PhD, of the University of Nottingham, England, and colleagues.
The authors note that exacerbations are the main complications of both asthma and COPD, and stress the importance of identifying causes and preventive strategies.
Sedatives such as opioids have been shown to depress respiratory drive, reduce muscle tone, and increase the risk of pneumonia, they write. The authors also propose that the risk of sedative-induced aspiration or hypoventilation would be associated with medications including pregabalin, gabapentin, and amitriptyline.
Other mechanisms may be involved in the association between sedatives and exacerbations in asthma and COPD. For example, sedative medications can suppress coughing, which may promote airway mucous compaction and possible infection, the authors write.
Most research involving prevention of asthma and COPD exacerbations has not addressed the potential impact of sedatives taken for reasons outside of obstructive lung disease, the authors say.
“Although the risk of sedation and hypoventilation events are known to be increased by opioids and antipsychotic drugs, there has not been a systematic assessment of commonly prescribed medications with potential respiratory side-effects, including gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin,” they write.
Polypharmacy is increasingly common and results in many patients with asthma or COPD presenting for treatment of acute exacerbations while on a combination of gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline, and opioids, the authors note; “however, there is little data or disease-specific guidance on how best to manage this problem, which often starts with a prescription in primary care,” they write. Simply stopping sedatives is not an option for many patients given the addictive nature of these drugs and the unlikely resolution of the condition for which the drugs were prescribed, the authors say. However, “cautious dose reduction” of sedatives is possible once patients understand the reason, they add.
Clinicians may be able to suggest reduced doses and alternative treatments to patients with asthma and COPD while highlighting the risk of respiratory depression and polypharmacy – “potentially reducing the number of exacerbations of obstructive lung disease,” the authors conclude.
The study received no outside funding. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Is cellular senescence related to post–COVID-19 syndrome?
Proinflammatory elements mediated through metabolic pathways related to obesity and increased cellular senescence in CD57 expression in CD8+ T cells are associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), according to a Mexican study. The researchers followed a Mexican cohort of 102 patients 3 months and 6 months after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study’s principal investigator was Diana Gómez-Martín, MD, PhD, of the department of immunology and rheumatology at the Salvador Zubirán National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition, Mexico City. She told this news organization that follow-up of the patients began with the objective of understanding the determinative clinical, genetic, metabolic, and immunological factors in the progression of the acute disease. However, clinical aspects associated with PASC developed in the selected cohort. As a result, the study was extended, and the clinical, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in this single-center Mexican cohort were evaluated 3 months 6 months after the onset of infection.
Dr. Gómez-Martín explained that the immune senescence in CD57 of CD8+ T cells is one of the best-known findings of the present study. If it is confirmed in future studies, it could have important implications. “Its main implication is the possibility of better understanding the physiopathology of the clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19, potentially being used for early detection and to provide follow-up aimed at patients, in addition to eventually developing targeted therapeutic strategies, such as immunometabolism regulation, in certain populations.”
Patients with PASC
The study was conducted from August 2020 to August 2021. Investigators recruited 102 patients (median age, 50.5 years; 55% were women) at the Mexico City Temporary Unit with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Of the patients, 44% had mild or moderate COVID-19, 30% had severe cases, and 26% of patients had critical cases. The most frequent comorbidities were obesity (44%), hypertension (24%), and type 2 diabetes (24%). The authors used a questionnaire to assess the presence of symptoms during follow-up. They analyzed immunologic variables at the time of recruitment, as well as levels of cytokines, immunoglobulin G against SARS-CoV-2, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) at 1, 3, and 6 months. At 6 months’ follow-up, 12.7% of the cohort had symptoms compatible with PASC, which was defined for the study as the presence and report of three or more symptoms at 6 months’ follow-up.
As in similar studies, the authors found that female gender, remaining in intensive care, and having had more symptoms and greater titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during the acute infection were associated with the development of clinical aspects associated with PASC. Patients who had the disease at 6 months had increased serum levels of interleukin-1 alpha (6.21 pg/mL vs. 2.21 pg/mL), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (55.08 pg/mL vs. 14.68 pg/mL), and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (2,309.40 pg/mL vs. 780 pg/mL). Also, there was a trend toward an increase in serum concentration of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
Patients whose condition met the definition of persistent PASC had increased expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (42,714 arbitrary units vs. 28,506) 6 months after the acute infection. The authors reported that there was no association between the persistence of PASC and the baseline amount of NETs, TRIM63, and anticellular antibodies. Nor was there an association between PASC and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at baseline and 1 month after COVID-19 diagnosis. Nonetheless, patients with persistent PASC had higher titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgGs 3 months after the onset of COVID-19.
On the basis of previous data, the researchers aimed to construct a preliminary explanatory model to address the clinical and immunologic features associated with persistent PASC 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the univariate analysis, the variables associated with the diagnosis of persistent PASC were the serum levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (odds ratio, 1.01), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (OR, 1.13), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (OR, 1.00), interleukin-6 (OR, 1.03), the expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (OR, 1.00), and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG at 1 month (OR, 1.45).
, such as obesity, greater levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 in peripheral blood, greater expression of the senescence CD57 marker in CD8+ T lymphocytes, and persistent symptoms at 3 months.
Using these parameters to construct a predictive model after 3 months, the authors found a sensitivity of 97.7%, specificity of 53.8%, positive predictive value of 93.5%, and a negative predictive value of 77.7% for the diagnosis of clinical aspects associated with PASC at 6 months.
Interpreting CD57
One of the researchers who participated in the study was Luis Martínez-Juárez, MD, MPH, DrPH. He is on the operative solutions team at the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Martínez-Juárez pointed out that one of the contributions of this study was that it specifically examined the Mexican population. He noted that “according to the findings, obesity is not only a comorbidity associated with more severe progressions during acute COVID-19 disease, but also, through inflammation parameters, such as interleukin-6, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, it’s involved in the development of clinical aspects related to postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín added that finding proinflammatory and obesity parameters in the patients could potentially support the hypothesis of the persistence of virus fragments in adipose tissue as possibly involved in clinical aspects associated with PASC, as some groups have reported in the medical literature.
Angélica Cuapio, MD, DrMed, an immunologist and senior investigator at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, who did not participate in the study, said in an interview that the authors’ findings on the sustained increase of the CD57 marker in CD8+ lymphocytes are of notable interest. They may be associated with senescence states or cellular aging or with a stage of chronic viral infections. Therefore, Dr. Cuapio argued, it would have been valuable to include cellular markers of the innate system, such as natural killer cells, since in various infections, an increase in CD57 in lymphocytes is accompanied by an almost proportional increase of this marker in natural killer cells.
“This information would help to determine more accurately if we are talking about a cellular senescence or more about a chronic infection in persistent COVID-19.” The finding is important, but future research is needed in this developing field.
Dr. Cuapio pointed out that the authors found an interesting elevation in interleukin-1 alpha in patients with clinical aspects associated with PASC in a clinically well-characterized population in Mexico. “It is possible that this is a specific marker either of a specific population or location, or this could be an association with a humoral response. Despite the fact that this finding is new and unclear, it is worth investigating. This study is of great value for the scientific community because it’s one more piece in the complex puzzle of clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín noted that the main limitations of the study consist of its single-center design and the small patient sample. Dr. Martínez-Juárez added that the study did not consider reinfections. In future studies, it would be ideal to integrate other molecular assessments associated with various hypotheses of the physiopathology of clinical aspects associated with PASC, such as microbiota alteration, coagulation anomalies, endothelial damage, and dysfunctional neurologic signaling.
The study was supported and funded by the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Gómez-Martín, Dr. Martínez-Juárez, and Dr. Cuapio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Proinflammatory elements mediated through metabolic pathways related to obesity and increased cellular senescence in CD57 expression in CD8+ T cells are associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), according to a Mexican study. The researchers followed a Mexican cohort of 102 patients 3 months and 6 months after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study’s principal investigator was Diana Gómez-Martín, MD, PhD, of the department of immunology and rheumatology at the Salvador Zubirán National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition, Mexico City. She told this news organization that follow-up of the patients began with the objective of understanding the determinative clinical, genetic, metabolic, and immunological factors in the progression of the acute disease. However, clinical aspects associated with PASC developed in the selected cohort. As a result, the study was extended, and the clinical, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in this single-center Mexican cohort were evaluated 3 months 6 months after the onset of infection.
Dr. Gómez-Martín explained that the immune senescence in CD57 of CD8+ T cells is one of the best-known findings of the present study. If it is confirmed in future studies, it could have important implications. “Its main implication is the possibility of better understanding the physiopathology of the clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19, potentially being used for early detection and to provide follow-up aimed at patients, in addition to eventually developing targeted therapeutic strategies, such as immunometabolism regulation, in certain populations.”
Patients with PASC
The study was conducted from August 2020 to August 2021. Investigators recruited 102 patients (median age, 50.5 years; 55% were women) at the Mexico City Temporary Unit with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Of the patients, 44% had mild or moderate COVID-19, 30% had severe cases, and 26% of patients had critical cases. The most frequent comorbidities were obesity (44%), hypertension (24%), and type 2 diabetes (24%). The authors used a questionnaire to assess the presence of symptoms during follow-up. They analyzed immunologic variables at the time of recruitment, as well as levels of cytokines, immunoglobulin G against SARS-CoV-2, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) at 1, 3, and 6 months. At 6 months’ follow-up, 12.7% of the cohort had symptoms compatible with PASC, which was defined for the study as the presence and report of three or more symptoms at 6 months’ follow-up.
As in similar studies, the authors found that female gender, remaining in intensive care, and having had more symptoms and greater titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during the acute infection were associated with the development of clinical aspects associated with PASC. Patients who had the disease at 6 months had increased serum levels of interleukin-1 alpha (6.21 pg/mL vs. 2.21 pg/mL), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (55.08 pg/mL vs. 14.68 pg/mL), and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (2,309.40 pg/mL vs. 780 pg/mL). Also, there was a trend toward an increase in serum concentration of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
Patients whose condition met the definition of persistent PASC had increased expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (42,714 arbitrary units vs. 28,506) 6 months after the acute infection. The authors reported that there was no association between the persistence of PASC and the baseline amount of NETs, TRIM63, and anticellular antibodies. Nor was there an association between PASC and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at baseline and 1 month after COVID-19 diagnosis. Nonetheless, patients with persistent PASC had higher titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgGs 3 months after the onset of COVID-19.
On the basis of previous data, the researchers aimed to construct a preliminary explanatory model to address the clinical and immunologic features associated with persistent PASC 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the univariate analysis, the variables associated with the diagnosis of persistent PASC were the serum levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (odds ratio, 1.01), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (OR, 1.13), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (OR, 1.00), interleukin-6 (OR, 1.03), the expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (OR, 1.00), and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG at 1 month (OR, 1.45).
, such as obesity, greater levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 in peripheral blood, greater expression of the senescence CD57 marker in CD8+ T lymphocytes, and persistent symptoms at 3 months.
Using these parameters to construct a predictive model after 3 months, the authors found a sensitivity of 97.7%, specificity of 53.8%, positive predictive value of 93.5%, and a negative predictive value of 77.7% for the diagnosis of clinical aspects associated with PASC at 6 months.
Interpreting CD57
One of the researchers who participated in the study was Luis Martínez-Juárez, MD, MPH, DrPH. He is on the operative solutions team at the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Martínez-Juárez pointed out that one of the contributions of this study was that it specifically examined the Mexican population. He noted that “according to the findings, obesity is not only a comorbidity associated with more severe progressions during acute COVID-19 disease, but also, through inflammation parameters, such as interleukin-6, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, it’s involved in the development of clinical aspects related to postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín added that finding proinflammatory and obesity parameters in the patients could potentially support the hypothesis of the persistence of virus fragments in adipose tissue as possibly involved in clinical aspects associated with PASC, as some groups have reported in the medical literature.
Angélica Cuapio, MD, DrMed, an immunologist and senior investigator at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, who did not participate in the study, said in an interview that the authors’ findings on the sustained increase of the CD57 marker in CD8+ lymphocytes are of notable interest. They may be associated with senescence states or cellular aging or with a stage of chronic viral infections. Therefore, Dr. Cuapio argued, it would have been valuable to include cellular markers of the innate system, such as natural killer cells, since in various infections, an increase in CD57 in lymphocytes is accompanied by an almost proportional increase of this marker in natural killer cells.
“This information would help to determine more accurately if we are talking about a cellular senescence or more about a chronic infection in persistent COVID-19.” The finding is important, but future research is needed in this developing field.
Dr. Cuapio pointed out that the authors found an interesting elevation in interleukin-1 alpha in patients with clinical aspects associated with PASC in a clinically well-characterized population in Mexico. “It is possible that this is a specific marker either of a specific population or location, or this could be an association with a humoral response. Despite the fact that this finding is new and unclear, it is worth investigating. This study is of great value for the scientific community because it’s one more piece in the complex puzzle of clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín noted that the main limitations of the study consist of its single-center design and the small patient sample. Dr. Martínez-Juárez added that the study did not consider reinfections. In future studies, it would be ideal to integrate other molecular assessments associated with various hypotheses of the physiopathology of clinical aspects associated with PASC, such as microbiota alteration, coagulation anomalies, endothelial damage, and dysfunctional neurologic signaling.
The study was supported and funded by the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Gómez-Martín, Dr. Martínez-Juárez, and Dr. Cuapio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Proinflammatory elements mediated through metabolic pathways related to obesity and increased cellular senescence in CD57 expression in CD8+ T cells are associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), according to a Mexican study. The researchers followed a Mexican cohort of 102 patients 3 months and 6 months after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study’s principal investigator was Diana Gómez-Martín, MD, PhD, of the department of immunology and rheumatology at the Salvador Zubirán National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition, Mexico City. She told this news organization that follow-up of the patients began with the objective of understanding the determinative clinical, genetic, metabolic, and immunological factors in the progression of the acute disease. However, clinical aspects associated with PASC developed in the selected cohort. As a result, the study was extended, and the clinical, metabolic, and immunologic conditions in this single-center Mexican cohort were evaluated 3 months 6 months after the onset of infection.
Dr. Gómez-Martín explained that the immune senescence in CD57 of CD8+ T cells is one of the best-known findings of the present study. If it is confirmed in future studies, it could have important implications. “Its main implication is the possibility of better understanding the physiopathology of the clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19, potentially being used for early detection and to provide follow-up aimed at patients, in addition to eventually developing targeted therapeutic strategies, such as immunometabolism regulation, in certain populations.”
Patients with PASC
The study was conducted from August 2020 to August 2021. Investigators recruited 102 patients (median age, 50.5 years; 55% were women) at the Mexico City Temporary Unit with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Of the patients, 44% had mild or moderate COVID-19, 30% had severe cases, and 26% of patients had critical cases. The most frequent comorbidities were obesity (44%), hypertension (24%), and type 2 diabetes (24%). The authors used a questionnaire to assess the presence of symptoms during follow-up. They analyzed immunologic variables at the time of recruitment, as well as levels of cytokines, immunoglobulin G against SARS-CoV-2, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) at 1, 3, and 6 months. At 6 months’ follow-up, 12.7% of the cohort had symptoms compatible with PASC, which was defined for the study as the presence and report of three or more symptoms at 6 months’ follow-up.
As in similar studies, the authors found that female gender, remaining in intensive care, and having had more symptoms and greater titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies during the acute infection were associated with the development of clinical aspects associated with PASC. Patients who had the disease at 6 months had increased serum levels of interleukin-1 alpha (6.21 pg/mL vs. 2.21 pg/mL), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (55.08 pg/mL vs. 14.68 pg/mL), and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (2,309.40 pg/mL vs. 780 pg/mL). Also, there was a trend toward an increase in serum concentration of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
Patients whose condition met the definition of persistent PASC had increased expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (42,714 arbitrary units vs. 28,506) 6 months after the acute infection. The authors reported that there was no association between the persistence of PASC and the baseline amount of NETs, TRIM63, and anticellular antibodies. Nor was there an association between PASC and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at baseline and 1 month after COVID-19 diagnosis. Nonetheless, patients with persistent PASC had higher titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgGs 3 months after the onset of COVID-19.
On the basis of previous data, the researchers aimed to construct a preliminary explanatory model to address the clinical and immunologic features associated with persistent PASC 6 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the univariate analysis, the variables associated with the diagnosis of persistent PASC were the serum levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (odds ratio, 1.01), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (OR, 1.13), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (OR, 1.00), interleukin-6 (OR, 1.03), the expression of CD57 in CD8+ T cells (OR, 1.00), and the titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG at 1 month (OR, 1.45).
, such as obesity, greater levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha and interferon gamma-induced protein 10 in peripheral blood, greater expression of the senescence CD57 marker in CD8+ T lymphocytes, and persistent symptoms at 3 months.
Using these parameters to construct a predictive model after 3 months, the authors found a sensitivity of 97.7%, specificity of 53.8%, positive predictive value of 93.5%, and a negative predictive value of 77.7% for the diagnosis of clinical aspects associated with PASC at 6 months.
Interpreting CD57
One of the researchers who participated in the study was Luis Martínez-Juárez, MD, MPH, DrPH. He is on the operative solutions team at the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Martínez-Juárez pointed out that one of the contributions of this study was that it specifically examined the Mexican population. He noted that “according to the findings, obesity is not only a comorbidity associated with more severe progressions during acute COVID-19 disease, but also, through inflammation parameters, such as interleukin-6, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, it’s involved in the development of clinical aspects related to postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín added that finding proinflammatory and obesity parameters in the patients could potentially support the hypothesis of the persistence of virus fragments in adipose tissue as possibly involved in clinical aspects associated with PASC, as some groups have reported in the medical literature.
Angélica Cuapio, MD, DrMed, an immunologist and senior investigator at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, who did not participate in the study, said in an interview that the authors’ findings on the sustained increase of the CD57 marker in CD8+ lymphocytes are of notable interest. They may be associated with senescence states or cellular aging or with a stage of chronic viral infections. Therefore, Dr. Cuapio argued, it would have been valuable to include cellular markers of the innate system, such as natural killer cells, since in various infections, an increase in CD57 in lymphocytes is accompanied by an almost proportional increase of this marker in natural killer cells.
“This information would help to determine more accurately if we are talking about a cellular senescence or more about a chronic infection in persistent COVID-19.” The finding is important, but future research is needed in this developing field.
Dr. Cuapio pointed out that the authors found an interesting elevation in interleukin-1 alpha in patients with clinical aspects associated with PASC in a clinically well-characterized population in Mexico. “It is possible that this is a specific marker either of a specific population or location, or this could be an association with a humoral response. Despite the fact that this finding is new and unclear, it is worth investigating. This study is of great value for the scientific community because it’s one more piece in the complex puzzle of clinical aspects associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19.”
Dr. Gómez-Martín noted that the main limitations of the study consist of its single-center design and the small patient sample. Dr. Martínez-Juárez added that the study did not consider reinfections. In future studies, it would be ideal to integrate other molecular assessments associated with various hypotheses of the physiopathology of clinical aspects associated with PASC, such as microbiota alteration, coagulation anomalies, endothelial damage, and dysfunctional neurologic signaling.
The study was supported and funded by the Carlos Slim Foundation. Dr. Gómez-Martín, Dr. Martínez-Juárez, and Dr. Cuapio have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
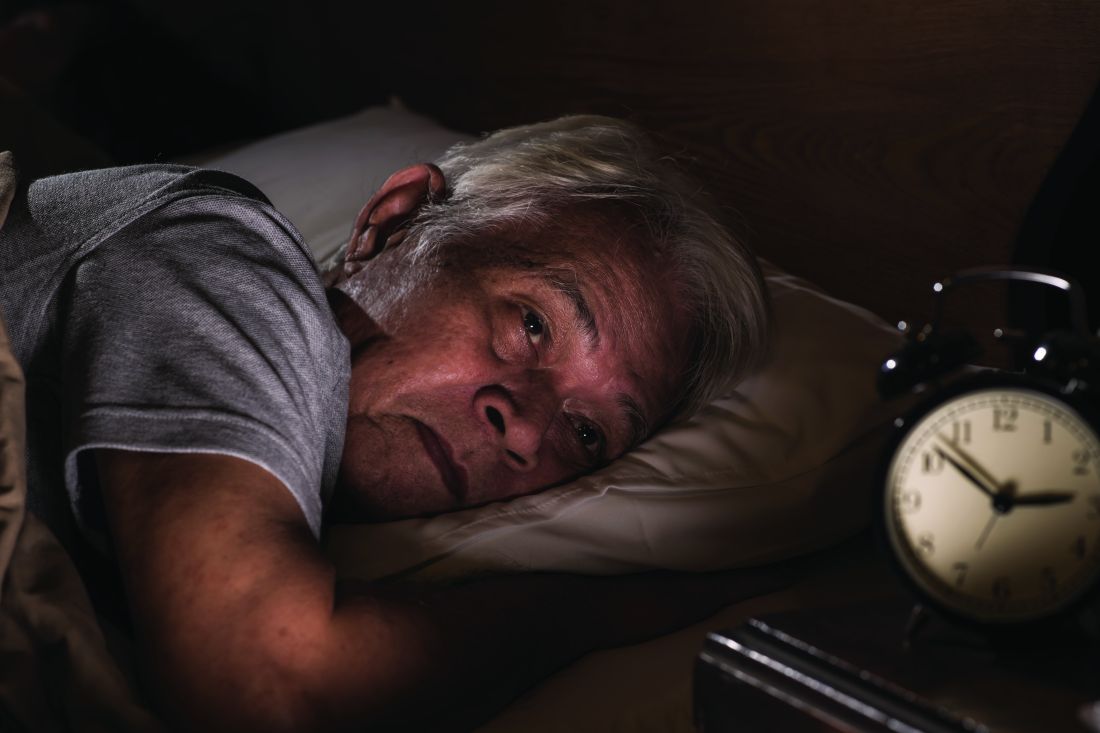
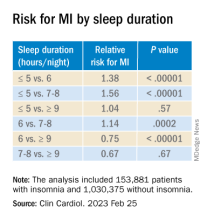
Insomnia, short sleep linked to greater risk for MI
Insomnia – difficulty falling or staying asleep – was associated with a 69% greater risk of having a myocardial infarction than among adults without insomnia, according to new research.
Those who slept 5 or fewer hours per night had the highest risk for MI, and those with both diabetes and insomnia had double the risk for MI, compared with patients without these comorbidities.
The findings are from a meta-analysis of studies in more than 1 million patients, almost all without prior MI who were, on average, in their early 50s and followed for 9 years.
Yomna E. Dean, a medical student at Alexandria (Egypt) University, reported these results in a press briefing, and the study was simultaneously published in Clinical Cardiology. It will be presented at the upcoming at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Insomnia and ]at least] 5 hours of sleep are highly associated with increased incidence of MI, an association comparable to that of other MI risk factors and as such, it should be considered as a risk factor for MI and to be incorporated into MI prevention guidelines,” the researchers concluded.
“We believe that [insomnia] should be screened and patients should be educated about the importance of sleep because nowadays insomnia is no longer a disease – sleep deprivation could also be a life choice,” Ms, Dean told a press conference prior to the meeting.
“Clinicians must educate the patients about the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy heart and encourage proper sleep hygiene,” Ms. Dean reiterated in an email. “And if a patient still has insomnia, other methods should be considered such as cognitive-behavior[al] therapy for insomnia [CBT-I].”
Adds to growing evidence
This study does not allow any conclusion about whether treating insomnia will reduce heart attack risk, Jennifer L. Martin, PhD, president of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, noted in a comment. Nor does it report the diversity of study participants, since insomnia is also a health equity issue, she noted, and insomnia symptoms and comorbidities were self-reported.
However, this analysis “adds to the growing evidence that poor quality or insufficient sleep is associated with poor health,” said Dr. Martin, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this research.
The study reinforces the recommendation from the American Heart Association, which includes “Get Healthy Sleep” as one of “Life’s Essential 8” for heart health, Dr. Martin noted.
“Particularly in primary care where disease prevention and health promotion are important, clinicians should be asking all patients about their sleep – just like they ask about diet and exercise – as a key aspect of maintaining heart health,” she said.
Advice about basic sleep hygiene advice is a first step, she noted.
When improved sleep hygiene is not enough to address chronic insomnia, the AASM’s clinical practice guidelines and the guidelines of the Department of Veterans Affairs/Department of Defense, recommend first-line treatment with CBT-I, typically offered by a sleep specialist or mental health clinician.
Similarly, the American College of Physicians suggests that sleeping pills should be reserved for short-term use in patients who may not benefit sufficiently from CBT-I.
Sleeping too little, too much, equally harmful
“Studies have found that insomnia and subsequent sleep deprivation puts the body under stress,” Ms. Dean said. “This triggers cortisol release which could accelerate atherosclerosis,” and increase risk of MI.
For this analysis, the researchers identified nine observational studies, published from 1998 to 2019, with data on incident MI in adults who had insomnia.
The diagnosis of insomnia was based on ICD diagnostic codes or on the DSM‐5, which defines insomnia as the presence of any of the following three symptoms: difficulty initiating sleep, difficulty maintaining sleep, or early morning awakening with inability to return to sleep. Patients with sleep apnea were excluded.
The studies were in populations in China, Germany, Norway, Taiwan, United Kingdom, and United States, in 1.1 million adults aged 18 and older. The patients had a mean age of 52 years and 13% had insomnia.
During follow-up, 2,406 of 153,881 patients with insomnia, and 12,398 of 1,030,375 patients without insomnia had an MI.
In the pooled analysis, patients with insomnia had a significantly increased risk of MI (relative risk, 1.69; P < .00001), after adjusting for age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Sleeping 5 hours or less was associated with a greater risk for MI than sleeping 6 hours, or 7-8 hours, but sleeping 9 hours or more was just as harmful.
Patients who had difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep – two symptoms of insomnia – had a 13% increased risk for MI compared with other patients (RR, 1.13; P = .003).
However, patients who had nonrestorative sleep and daytime dysfunction despite adequate sleep – which is common – did not have an increased risk of MI, compared with other patients (RR, 1.06; P = .46).
Women with insomnia had a 2.24-fold greater risk for MI than other women, whereas men with insomnia had a 2.03-fold greater risk for MI than other men.
Patients with insomnia had a greater risk for MI than those without insomnia in subgroups based on patients’ age (< 65 and > 65), follow up duration (≤ 5 years and > 5 years), and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia).
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Insomnia – difficulty falling or staying asleep – was associated with a 69% greater risk of having a myocardial infarction than among adults without insomnia, according to new research.
Those who slept 5 or fewer hours per night had the highest risk for MI, and those with both diabetes and insomnia had double the risk for MI, compared with patients without these comorbidities.
The findings are from a meta-analysis of studies in more than 1 million patients, almost all without prior MI who were, on average, in their early 50s and followed for 9 years.
Yomna E. Dean, a medical student at Alexandria (Egypt) University, reported these results in a press briefing, and the study was simultaneously published in Clinical Cardiology. It will be presented at the upcoming at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Insomnia and ]at least] 5 hours of sleep are highly associated with increased incidence of MI, an association comparable to that of other MI risk factors and as such, it should be considered as a risk factor for MI and to be incorporated into MI prevention guidelines,” the researchers concluded.
“We believe that [insomnia] should be screened and patients should be educated about the importance of sleep because nowadays insomnia is no longer a disease – sleep deprivation could also be a life choice,” Ms, Dean told a press conference prior to the meeting.
“Clinicians must educate the patients about the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy heart and encourage proper sleep hygiene,” Ms. Dean reiterated in an email. “And if a patient still has insomnia, other methods should be considered such as cognitive-behavior[al] therapy for insomnia [CBT-I].”
Adds to growing evidence
This study does not allow any conclusion about whether treating insomnia will reduce heart attack risk, Jennifer L. Martin, PhD, president of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, noted in a comment. Nor does it report the diversity of study participants, since insomnia is also a health equity issue, she noted, and insomnia symptoms and comorbidities were self-reported.
However, this analysis “adds to the growing evidence that poor quality or insufficient sleep is associated with poor health,” said Dr. Martin, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this research.
The study reinforces the recommendation from the American Heart Association, which includes “Get Healthy Sleep” as one of “Life’s Essential 8” for heart health, Dr. Martin noted.
“Particularly in primary care where disease prevention and health promotion are important, clinicians should be asking all patients about their sleep – just like they ask about diet and exercise – as a key aspect of maintaining heart health,” she said.
Advice about basic sleep hygiene advice is a first step, she noted.
When improved sleep hygiene is not enough to address chronic insomnia, the AASM’s clinical practice guidelines and the guidelines of the Department of Veterans Affairs/Department of Defense, recommend first-line treatment with CBT-I, typically offered by a sleep specialist or mental health clinician.
Similarly, the American College of Physicians suggests that sleeping pills should be reserved for short-term use in patients who may not benefit sufficiently from CBT-I.
Sleeping too little, too much, equally harmful
“Studies have found that insomnia and subsequent sleep deprivation puts the body under stress,” Ms. Dean said. “This triggers cortisol release which could accelerate atherosclerosis,” and increase risk of MI.
For this analysis, the researchers identified nine observational studies, published from 1998 to 2019, with data on incident MI in adults who had insomnia.
The diagnosis of insomnia was based on ICD diagnostic codes or on the DSM‐5, which defines insomnia as the presence of any of the following three symptoms: difficulty initiating sleep, difficulty maintaining sleep, or early morning awakening with inability to return to sleep. Patients with sleep apnea were excluded.
The studies were in populations in China, Germany, Norway, Taiwan, United Kingdom, and United States, in 1.1 million adults aged 18 and older. The patients had a mean age of 52 years and 13% had insomnia.
During follow-up, 2,406 of 153,881 patients with insomnia, and 12,398 of 1,030,375 patients without insomnia had an MI.
In the pooled analysis, patients with insomnia had a significantly increased risk of MI (relative risk, 1.69; P < .00001), after adjusting for age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Sleeping 5 hours or less was associated with a greater risk for MI than sleeping 6 hours, or 7-8 hours, but sleeping 9 hours or more was just as harmful.
Patients who had difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep – two symptoms of insomnia – had a 13% increased risk for MI compared with other patients (RR, 1.13; P = .003).
However, patients who had nonrestorative sleep and daytime dysfunction despite adequate sleep – which is common – did not have an increased risk of MI, compared with other patients (RR, 1.06; P = .46).
Women with insomnia had a 2.24-fold greater risk for MI than other women, whereas men with insomnia had a 2.03-fold greater risk for MI than other men.
Patients with insomnia had a greater risk for MI than those without insomnia in subgroups based on patients’ age (< 65 and > 65), follow up duration (≤ 5 years and > 5 years), and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia).
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Insomnia – difficulty falling or staying asleep – was associated with a 69% greater risk of having a myocardial infarction than among adults without insomnia, according to new research.
Those who slept 5 or fewer hours per night had the highest risk for MI, and those with both diabetes and insomnia had double the risk for MI, compared with patients without these comorbidities.
The findings are from a meta-analysis of studies in more than 1 million patients, almost all without prior MI who were, on average, in their early 50s and followed for 9 years.
Yomna E. Dean, a medical student at Alexandria (Egypt) University, reported these results in a press briefing, and the study was simultaneously published in Clinical Cardiology. It will be presented at the upcoming at the annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology.
“Insomnia and ]at least] 5 hours of sleep are highly associated with increased incidence of MI, an association comparable to that of other MI risk factors and as such, it should be considered as a risk factor for MI and to be incorporated into MI prevention guidelines,” the researchers concluded.
“We believe that [insomnia] should be screened and patients should be educated about the importance of sleep because nowadays insomnia is no longer a disease – sleep deprivation could also be a life choice,” Ms, Dean told a press conference prior to the meeting.
“Clinicians must educate the patients about the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy heart and encourage proper sleep hygiene,” Ms. Dean reiterated in an email. “And if a patient still has insomnia, other methods should be considered such as cognitive-behavior[al] therapy for insomnia [CBT-I].”
Adds to growing evidence
This study does not allow any conclusion about whether treating insomnia will reduce heart attack risk, Jennifer L. Martin, PhD, president of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, noted in a comment. Nor does it report the diversity of study participants, since insomnia is also a health equity issue, she noted, and insomnia symptoms and comorbidities were self-reported.
However, this analysis “adds to the growing evidence that poor quality or insufficient sleep is associated with poor health,” said Dr. Martin, professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, who was not involved with this research.
The study reinforces the recommendation from the American Heart Association, which includes “Get Healthy Sleep” as one of “Life’s Essential 8” for heart health, Dr. Martin noted.
“Particularly in primary care where disease prevention and health promotion are important, clinicians should be asking all patients about their sleep – just like they ask about diet and exercise – as a key aspect of maintaining heart health,” she said.
Advice about basic sleep hygiene advice is a first step, she noted.
When improved sleep hygiene is not enough to address chronic insomnia, the AASM’s clinical practice guidelines and the guidelines of the Department of Veterans Affairs/Department of Defense, recommend first-line treatment with CBT-I, typically offered by a sleep specialist or mental health clinician.
Similarly, the American College of Physicians suggests that sleeping pills should be reserved for short-term use in patients who may not benefit sufficiently from CBT-I.
Sleeping too little, too much, equally harmful
“Studies have found that insomnia and subsequent sleep deprivation puts the body under stress,” Ms. Dean said. “This triggers cortisol release which could accelerate atherosclerosis,” and increase risk of MI.
For this analysis, the researchers identified nine observational studies, published from 1998 to 2019, with data on incident MI in adults who had insomnia.
The diagnosis of insomnia was based on ICD diagnostic codes or on the DSM‐5, which defines insomnia as the presence of any of the following three symptoms: difficulty initiating sleep, difficulty maintaining sleep, or early morning awakening with inability to return to sleep. Patients with sleep apnea were excluded.
The studies were in populations in China, Germany, Norway, Taiwan, United Kingdom, and United States, in 1.1 million adults aged 18 and older. The patients had a mean age of 52 years and 13% had insomnia.
During follow-up, 2,406 of 153,881 patients with insomnia, and 12,398 of 1,030,375 patients without insomnia had an MI.
In the pooled analysis, patients with insomnia had a significantly increased risk of MI (relative risk, 1.69; P < .00001), after adjusting for age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Sleeping 5 hours or less was associated with a greater risk for MI than sleeping 6 hours, or 7-8 hours, but sleeping 9 hours or more was just as harmful.
Patients who had difficulty initiating and maintaining sleep – two symptoms of insomnia – had a 13% increased risk for MI compared with other patients (RR, 1.13; P = .003).
However, patients who had nonrestorative sleep and daytime dysfunction despite adequate sleep – which is common – did not have an increased risk of MI, compared with other patients (RR, 1.06; P = .46).
Women with insomnia had a 2.24-fold greater risk for MI than other women, whereas men with insomnia had a 2.03-fold greater risk for MI than other men.
Patients with insomnia had a greater risk for MI than those without insomnia in subgroups based on patients’ age (< 65 and > 65), follow up duration (≤ 5 years and > 5 years), and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia).
The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023
Myths about smoking, diet, alcohol, and cancer persist
FRANCE – Conducted every 5 years since 2005, the Cancer Survey documents the knowledge, perceptions, and way of life of the French people in relation to cancer. The researchers analyzed responses to telephone interviews of a representative sample of almost 5,000 individuals aged 15-85 years.
This study shows how thinking has changed over time and how difficult it is to alter preconceived notions.
Is cancer hereditary?
The report shows that 67.7% of respondents believe that cancer is a hereditary disease. Respondents were asked to explain their answer. “Data show that medical practices for cancer treatment substantiate this belief [that cancer is hereditary],” wrote the authors of the report.
“Indeed, health care professionals almost systematically ask questions about family history of breast cancer and, when a family member has been diagnosed with cancer, medical monitoring of other family members is often sought out, thus reinforcing the belief that cancer is hereditary,” they said.
Furthermore, there seems to be confusion regarding the role of genes in the development of cancer. A person can inherit cancer-predisposing genes, not cancer itself. The authors highlighted their concern that this confusion may “lead people to think that prevention measures are unnecessary because cancer is inherited.”
Misconceptions about smoking
About 41% of smokers think that the length of time one has been smoking is the biggest determining factor for developing cancer; 58.1% think the number of cigarettes smoked per day has a bigger impact.
Experts at InCA and SPF put the debate to rest, stating that prolonged exposure to carcinogenic substances is far more toxic. As for the danger threshold concerning the number of cigarettes smoked per day, respondents believed this to be 9.2 cigarettes per day, on average. They believed that the danger threshold for the number of years as an active smoker is 13.4, on average.
“The [survey] respondents clearly understand that smoking carries a risk, but many smokers think that light smoking or smoking for a short period of time doesn’t carry any risks.” Yet it is understood that even occasional tobacco consumption increases mortality.
This was not the only misconception regarding smoking and its relationship with cancer. About 34% of survey respondents agreed with the following statement: “Smoking doesn’t cause cancer unless you’re a heavy smoker and have smoked for a long time.” Furthermore, 43.3% agreed with the statement, “Pollution is more likely to cause cancer than smoking,” 54.6% think that “exercising cleans your lungs of tobacco,” and 61.6% think that “a smoker can prevent developing cancer caused by smoking if they know to quit on time.”
Overweight and obesity
Although diet and excess weight represent the third and fourth biggest avoidable cancer risk factors, after smoking and alcohol, only 30% of survey respondents knew of this link.
“Among the causes of cancer known and cited by respondents without prompting, excessive weight and obesity were mentioned only 100 times out of 12,558 responses,” highlighted the authors of the report. The explanation put forward by the authors is that discourse about diet has been more focused on diet as a protective health factor, especially in preventing cardiovascular diseases. “The link between cancer and diet is less prominent in the public space,” they noted.
Breastfeeding and cancer
About 63% of survey respondents, which for the first time included both women and men, believe that breastfeeding does not affect mothers’ risk of breast cancer, but this is a misconception. And almost 1 in 3 respondents said that breastfeeding provides health benefits for the mother.
Artificial UV rays
Exposure to UV rays, whether of natural or artificial origin, is a major risk factor for skin cancer. However, 1 in 5 people (20.9%) think that a session in a tanning bed is less harmful than sun exposure.
Daily stress
Regarding psychological factors linked to cancer, the authors noted that risk factors not supported by scientific evidence were, ironically, cited more often by respondents than proven risk factors. There is a real knowledge gap between scientific data and the beliefs of the French people. For example, “working at night” is largely not seen as a risk factor, but data show that it presents a clear risk. However, “not being able to express one’s feelings,” “having been weakened by traumatic experiences,” and “being exposed to the stress of modern life” are seen as risk factors of cancer, without any scientific evidence.
Cigarettes and e-cigarettes
About 53% of respondents agreed that “e-cigarettes are just as harmful or more harmful than traditional cigarettes.” Nicotine and the flavors in e-cigarettes are largely perceived as “very” or “extremely” harmful to the health of a person. However, the authors note that “no published study on nicotine substitutes has shown harmful effects on the health of a person, let alone determined it a risk factor for cancer. The nicotine doses in e-cigarettes are similar to traditional nicotine substitutes, and no cytotoxic effect of nicotine in its inhaled form has been found.” There seems to be confusion between dependence and risk of cancer.
Alcohol consumption
Eight of 10 respondents believe that “some people can drink a lot of alcohol all their life without ever getting cancer,” which goes against the scientific literature. The authors of the report state that the negative effects of alcohol on health seem poorly understood. Although alcohol is the second biggest cause of cancer, only a third of survey respondents cited it without having been prompted as one of the main causes of cancer. And 23.5% even think that “in terms of decreasing your risk of cancer, it’s better to drink a little wine than to drink no wine at all.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FRANCE – Conducted every 5 years since 2005, the Cancer Survey documents the knowledge, perceptions, and way of life of the French people in relation to cancer. The researchers analyzed responses to telephone interviews of a representative sample of almost 5,000 individuals aged 15-85 years.
This study shows how thinking has changed over time and how difficult it is to alter preconceived notions.
Is cancer hereditary?
The report shows that 67.7% of respondents believe that cancer is a hereditary disease. Respondents were asked to explain their answer. “Data show that medical practices for cancer treatment substantiate this belief [that cancer is hereditary],” wrote the authors of the report.
“Indeed, health care professionals almost systematically ask questions about family history of breast cancer and, when a family member has been diagnosed with cancer, medical monitoring of other family members is often sought out, thus reinforcing the belief that cancer is hereditary,” they said.
Furthermore, there seems to be confusion regarding the role of genes in the development of cancer. A person can inherit cancer-predisposing genes, not cancer itself. The authors highlighted their concern that this confusion may “lead people to think that prevention measures are unnecessary because cancer is inherited.”
Misconceptions about smoking
About 41% of smokers think that the length of time one has been smoking is the biggest determining factor for developing cancer; 58.1% think the number of cigarettes smoked per day has a bigger impact.
Experts at InCA and SPF put the debate to rest, stating that prolonged exposure to carcinogenic substances is far more toxic. As for the danger threshold concerning the number of cigarettes smoked per day, respondents believed this to be 9.2 cigarettes per day, on average. They believed that the danger threshold for the number of years as an active smoker is 13.4, on average.
“The [survey] respondents clearly understand that smoking carries a risk, but many smokers think that light smoking or smoking for a short period of time doesn’t carry any risks.” Yet it is understood that even occasional tobacco consumption increases mortality.
This was not the only misconception regarding smoking and its relationship with cancer. About 34% of survey respondents agreed with the following statement: “Smoking doesn’t cause cancer unless you’re a heavy smoker and have smoked for a long time.” Furthermore, 43.3% agreed with the statement, “Pollution is more likely to cause cancer than smoking,” 54.6% think that “exercising cleans your lungs of tobacco,” and 61.6% think that “a smoker can prevent developing cancer caused by smoking if they know to quit on time.”
Overweight and obesity
Although diet and excess weight represent the third and fourth biggest avoidable cancer risk factors, after smoking and alcohol, only 30% of survey respondents knew of this link.
“Among the causes of cancer known and cited by respondents without prompting, excessive weight and obesity were mentioned only 100 times out of 12,558 responses,” highlighted the authors of the report. The explanation put forward by the authors is that discourse about diet has been more focused on diet as a protective health factor, especially in preventing cardiovascular diseases. “The link between cancer and diet is less prominent in the public space,” they noted.
Breastfeeding and cancer
About 63% of survey respondents, which for the first time included both women and men, believe that breastfeeding does not affect mothers’ risk of breast cancer, but this is a misconception. And almost 1 in 3 respondents said that breastfeeding provides health benefits for the mother.
Artificial UV rays
Exposure to UV rays, whether of natural or artificial origin, is a major risk factor for skin cancer. However, 1 in 5 people (20.9%) think that a session in a tanning bed is less harmful than sun exposure.
Daily stress
Regarding psychological factors linked to cancer, the authors noted that risk factors not supported by scientific evidence were, ironically, cited more often by respondents than proven risk factors. There is a real knowledge gap between scientific data and the beliefs of the French people. For example, “working at night” is largely not seen as a risk factor, but data show that it presents a clear risk. However, “not being able to express one’s feelings,” “having been weakened by traumatic experiences,” and “being exposed to the stress of modern life” are seen as risk factors of cancer, without any scientific evidence.
Cigarettes and e-cigarettes
About 53% of respondents agreed that “e-cigarettes are just as harmful or more harmful than traditional cigarettes.” Nicotine and the flavors in e-cigarettes are largely perceived as “very” or “extremely” harmful to the health of a person. However, the authors note that “no published study on nicotine substitutes has shown harmful effects on the health of a person, let alone determined it a risk factor for cancer. The nicotine doses in e-cigarettes are similar to traditional nicotine substitutes, and no cytotoxic effect of nicotine in its inhaled form has been found.” There seems to be confusion between dependence and risk of cancer.
Alcohol consumption
Eight of 10 respondents believe that “some people can drink a lot of alcohol all their life without ever getting cancer,” which goes against the scientific literature. The authors of the report state that the negative effects of alcohol on health seem poorly understood. Although alcohol is the second biggest cause of cancer, only a third of survey respondents cited it without having been prompted as one of the main causes of cancer. And 23.5% even think that “in terms of decreasing your risk of cancer, it’s better to drink a little wine than to drink no wine at all.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FRANCE – Conducted every 5 years since 2005, the Cancer Survey documents the knowledge, perceptions, and way of life of the French people in relation to cancer. The researchers analyzed responses to telephone interviews of a representative sample of almost 5,000 individuals aged 15-85 years.
This study shows how thinking has changed over time and how difficult it is to alter preconceived notions.
Is cancer hereditary?
The report shows that 67.7% of respondents believe that cancer is a hereditary disease. Respondents were asked to explain their answer. “Data show that medical practices for cancer treatment substantiate this belief [that cancer is hereditary],” wrote the authors of the report.
“Indeed, health care professionals almost systematically ask questions about family history of breast cancer and, when a family member has been diagnosed with cancer, medical monitoring of other family members is often sought out, thus reinforcing the belief that cancer is hereditary,” they said.
Furthermore, there seems to be confusion regarding the role of genes in the development of cancer. A person can inherit cancer-predisposing genes, not cancer itself. The authors highlighted their concern that this confusion may “lead people to think that prevention measures are unnecessary because cancer is inherited.”
Misconceptions about smoking
About 41% of smokers think that the length of time one has been smoking is the biggest determining factor for developing cancer; 58.1% think the number of cigarettes smoked per day has a bigger impact.
Experts at InCA and SPF put the debate to rest, stating that prolonged exposure to carcinogenic substances is far more toxic. As for the danger threshold concerning the number of cigarettes smoked per day, respondents believed this to be 9.2 cigarettes per day, on average. They believed that the danger threshold for the number of years as an active smoker is 13.4, on average.
“The [survey] respondents clearly understand that smoking carries a risk, but many smokers think that light smoking or smoking for a short period of time doesn’t carry any risks.” Yet it is understood that even occasional tobacco consumption increases mortality.
This was not the only misconception regarding smoking and its relationship with cancer. About 34% of survey respondents agreed with the following statement: “Smoking doesn’t cause cancer unless you’re a heavy smoker and have smoked for a long time.” Furthermore, 43.3% agreed with the statement, “Pollution is more likely to cause cancer than smoking,” 54.6% think that “exercising cleans your lungs of tobacco,” and 61.6% think that “a smoker can prevent developing cancer caused by smoking if they know to quit on time.”
Overweight and obesity
Although diet and excess weight represent the third and fourth biggest avoidable cancer risk factors, after smoking and alcohol, only 30% of survey respondents knew of this link.
“Among the causes of cancer known and cited by respondents without prompting, excessive weight and obesity were mentioned only 100 times out of 12,558 responses,” highlighted the authors of the report. The explanation put forward by the authors is that discourse about diet has been more focused on diet as a protective health factor, especially in preventing cardiovascular diseases. “The link between cancer and diet is less prominent in the public space,” they noted.
Breastfeeding and cancer
About 63% of survey respondents, which for the first time included both women and men, believe that breastfeeding does not affect mothers’ risk of breast cancer, but this is a misconception. And almost 1 in 3 respondents said that breastfeeding provides health benefits for the mother.
Artificial UV rays
Exposure to UV rays, whether of natural or artificial origin, is a major risk factor for skin cancer. However, 1 in 5 people (20.9%) think that a session in a tanning bed is less harmful than sun exposure.
Daily stress
Regarding psychological factors linked to cancer, the authors noted that risk factors not supported by scientific evidence were, ironically, cited more often by respondents than proven risk factors. There is a real knowledge gap between scientific data and the beliefs of the French people. For example, “working at night” is largely not seen as a risk factor, but data show that it presents a clear risk. However, “not being able to express one’s feelings,” “having been weakened by traumatic experiences,” and “being exposed to the stress of modern life” are seen as risk factors of cancer, without any scientific evidence.
Cigarettes and e-cigarettes
About 53% of respondents agreed that “e-cigarettes are just as harmful or more harmful than traditional cigarettes.” Nicotine and the flavors in e-cigarettes are largely perceived as “very” or “extremely” harmful to the health of a person. However, the authors note that “no published study on nicotine substitutes has shown harmful effects on the health of a person, let alone determined it a risk factor for cancer. The nicotine doses in e-cigarettes are similar to traditional nicotine substitutes, and no cytotoxic effect of nicotine in its inhaled form has been found.” There seems to be confusion between dependence and risk of cancer.
Alcohol consumption
Eight of 10 respondents believe that “some people can drink a lot of alcohol all their life without ever getting cancer,” which goes against the scientific literature. The authors of the report state that the negative effects of alcohol on health seem poorly understood. Although alcohol is the second biggest cause of cancer, only a third of survey respondents cited it without having been prompted as one of the main causes of cancer. And 23.5% even think that “in terms of decreasing your risk of cancer, it’s better to drink a little wine than to drink no wine at all.”
This article was translated from the Medscape French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician pleads guilty to 52 counts in opioid scheme
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Jeffrey B. Sutton, DO, a neuromuscular medicine specialist, pled guilty on January 30 in federal court to 31 counts of illegally prescribing opioids and other controlled substances, 1 count of illegally distributing controlled substances, and 20 counts of health care fraud.
Prosecutors said Dr. Sutton admitted that he ignored warnings from prescription drug management organizations, insurers, and state authorities that he was prescribing excessively high dosages of opioids.
Dr. Sutton also admitted to ignoring patient requests to lower dosages and that he also ignored signs that patients were selling prescribed medications or otherwise engaging in illicit activity, including violations of a “pain management agreement” that he required them to sign.
The fraud counts pertained to Dr. Sutton billing Medicare, Medicaid, and other insurers for medically unnecessary visits that he required of patients so that he could prescribe inappropriate or unnecessary opioids.
In the charging document shared with this news organization, prosecutors said Dr. Sutton had sex with at least three patients, including during office visits and outside of the office. Occasionally, the physician would give opioids or other controlled substances – often benzodiazepines – to these patients, without a prescription or valid medical need.
Dr. Sutton escalated the dosage for one of those patients, even as the subjective pain score did not improve and when the patient’s urine tests showed the presence of THC and buprenorphine, but not any of the prescribed medications.
Another patient came to Dr. Sutton in 2007 with a warning that she had a history of “narcotic-seeking” behavior and diagnoses of depression, anxiety, paranoid schizophrenia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The patient was hospitalized in 2018 for complications from benzodiazepine use (prescribed by Dr. Sutton). She weighed 80 pounds at the time. Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe benzodiazepines and extreme doses of opioids – in excess of 2,000 morphine equivalent dose – “despite recognizing and documenting repeated instances of noncompliance with treatment for psychiatric conditions, and despite the known contraindications of long-term opioid use for patients with these mental illnesses,” according to the charging document.
Dr. Sutton continued to prescribe opioids despite two hospitalizations for overdoses, more than 20 failed urine drug screens that showed presence of illicit drugs such as cocaine, and documented excessive use of alprazolam (Xanax) and methadone.
The physician surrendered his Drug Enforcement Administration Certificate of Registration of Controlled Substances Privileges in February 2022 “as an indication of your good faith in desiring to remedy any incorrect or unlawful practices on your part,” according to a letter to Dr. Sutton from the State Medical Board of Ohio. In that September 2022 letter, the Board notified Dr. Sutton of its intention to possibly suspend or revoke his license.
Dr. Sutton did not request a hearing, and the Board permanently revoked his medical license on January 16.
The court will sentence Dr. Sutton on May 23, according to a report by WFMJ.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Toxic chemicals we consume without knowing it
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Life expectancy is falling precipitously. Three-fourths of Americans are overweight or obese, half have diabetes or prediabetes, and a majority are metabolically unhealthy. Furthermore, the rates of allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases are rising at rates of 3%-9% per year in the West, far faster than the speed of genetic change in this population.
Of course, diet and lifestyle are major factors behind such trends, but a grossly underappreciated driver in what ails us is the role of environmental toxins and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In years past, these factors have largely evaded the traditional Western medical establishment; however, mounting evidence now supports their significance in fertility, metabolic health, and cancer.
Although several industrial chemicals and toxins have been identified as carcinogens and have subsequently been regulated, many more remain persistent in the environment and continue to be freely used. It is therefore incumbent upon both the general public and clinicians to be knowledgeable about these exposures. Here, we review some of the most common exposures and the substantial health risks associated with them, along with some general guidance around best practices for how to minimize exposure.
Microplastics
“Microplastics” is a term used to describe small fragments or particles of plastic breakdown or microbeads from household or personal care products, measuring less than 5 mm in length.
Plastic waste is accumulating at alarming and devastating proportions – by 2050, it is estimated that by weight, there will be more plastic than fish in the oceans. That translates into hundreds of thousands of tons of microplastics and trillions of these particles in the seas. A recent study demonstrated that microplastics were present in the bloodstream in the majority of 22 otherwise healthy participants.
Since the 1950s, plastic exposure has been shown to promote tumorigenesis in animal studies, and in vitro studies have demonstrated the toxicity of microplastics at the cellular level. However, it is not well known whether the plastic itself is toxic or if it simply serves as a carrier for other environmental toxins to bioaccumulate.
According to Tasha Stoiber, a senior scientist at the Environmental Working Group, “Microplastics have been widely detected in fish and seafood, as well as other products like bottled water, beer, honey, and tap water.” The EWG states there are no formal advisories on fish consumption to avoid exposure to microplastics at the moment.
Pressure also is mounting for a ban on microbeads in personal care products.
Until such bans are put in place, it is advised to avoid single-use plastics, favor reusable tote bags for grocery shopping rather than plastic bags, and opt for loose leaf tea or paper tea bags rather than mesh-based alternatives.
Phthalates
Phthalates are chemicals used to make plastics soft and durable, as well as to bind fragrances. They are commonly found in household items such as vinyl (for example, flooring, shower curtains) and fragrances, air fresheners, and perfumes.
Phthalates are known hormone-disrupting chemicals, exposure to which has been associated with abnormal sexual and brain development in children, as well as lower levels of testosterone in men. Exposures are thought to occur via inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact; however, fasting studies demonstrate that a majority of exposure is probably food related.
To avoid phthalate exposures, recommendations include avoiding polyvinyl chloride plastics (particularly food containers, plastic wrap, and children’s toys), which are identifiable by the recycle code number 3, as well as air fresheners and fragranced products.
The EWG’s Skin Deep database provides an important resource on phthalate-free personal care products.
Despite pressure from consumer advocacy groups, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not yet banned phthalates in food packaging.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
BPA is a chemical additive used to make clear and hard polycarbonate plastics, as well as epoxy and thermal papers. BPA is one of the highest-volume chemicals, with roughly 6 billion pounds produced each year. BPA is traditionally found in many clear plastic bottles and sippy cups, as well as in the lining of canned foods.
Structurally, BPA acts as an estrogen mimetic and has been associated with cardiovascular disease, obesity, and male sexual dysfunction. Since 2012, BPA has been banned in sippy cups and baby bottles, but there is some debate as to whether its replacements (bisphenol S and bisphenol F) are any safer; they appear to have similar hormonal effects as BPA.
As with phthalates, the majority of ingestion is thought to be food related. BPA has been found in more than 90% of a representative study population in the United States.
Guidance advises avoiding polycarbonate plastics (identifiable with the recycling code number 7), as well as avoiding handling thermal papers such as tickets and receipts, if possible. Food and beverages should be stored in glass or stainless steel. If plastic must be used, opt for polycarbonate- and polyvinyl chloride–free plastics, and food and beverages should never be reheated in plastic containers or wrapping. Canned foods should ideally be avoided, particularly canned tunas and condensed soups. If canned products are bought, they should ideally be BPA free.
Dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Dioxins are mainly the byproducts of industrial practices; they are released after incineration, trash burning, and fires. PCBs, which are somewhat structurally related to dioxins, were previously found in products such as flame retardants and coolants. Dioxins and PCBs are often grouped in the same category under the umbrella term “persistent organic pollutants” because they break down slowly and remain in the environment even after emissions have been curbed.
Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, perhaps the best-known dioxin, is a known carcinogen. Dioxins also have been associated with a host of health implications in development, immunity, and reproductive and endocrine systems. Higher levels of PCB exposure have also been associated with an increased risk for mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Notably, dioxin emissions have been reduced by 90% since the 1980s, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has banned the use of PCBs in industrial manufacturing since 1979. However, environmental dioxins and PCBs still enter the food chain and accumulate in fat.
The best ways to avoid exposures are through limiting meat, fish, and dairy consumption and trimming the skin and fat from meats. The level of dioxins and PCBs found in meat, eggs, fish, and dairy are approximately 5-10 times higher than they are in plant-based foods. Research has shown that farmed salmon is likely to be the most PCB-contaminated protein source in the U.S. diet; however, newer forms of land-based and sustainable aquaculture probably avoid this exposure.
Pesticides
The growth of modern monoculture agriculture in the United States over the past century has coincided with a dramatic surge in the use of industrial pesticides. In fact, over 90% of the U.S. population have pesticides in their urine and blood, regardless of where they live. Exposures are thought to be food related.
Approximately 1 billion pounds of pesticides are used annually in the United States, including nearly 300 million pounds of glyphosate, which has been identified as a probable carcinogen by European agencies. The EPA has not yet reached this conclusion, although the matter is currently being litigated.
A large European prospective cohort trial demonstrated a lower risk for cancer in those with a greater frequency of self-reported organic food consumption. In addition to cancer risk, relatively elevated blood levels of a pesticide known as beta-hexachlorocyclohexane (B-HCH) are associated with higher all-cause mortality. Also, exposure to DDE – a metabolite of DDT, a chlorinated pesticide heavily used in the 1940s-1960s that still persists in the environment today – has been shown to increase the risk for Alzheimer’s-type dementia as well as overall cognitive decline.
Because these chlorinated pesticides are often fat soluble, they seem to accumulate in animal products. Therefore, people consuming a vegetarian diet have been found to have lower levels of B-HCH. This has led to the recommendation that consumers of produce should favor organic over conventional, if possible. Here too, the EWG provides an important resource to consumers in the form of shopper guides regarding pesticides in produce.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
PFAS are a group of fluorinated compounds discovered in the 1930s. Their chemical composition includes a durable carbon-fluoride bond, giving them a persistence within the environment that has led to their being referred to as “forever chemicals.”
PFAS have been detected in the blood of 98% of Americans, and in the rainwater of locations as far afield as Tibet and Antarctica. Even low levels of exposure have been associated with an increased risk for cancer, liver disease, low birth weight, and hormonal disruption.
The properties of PFAS also make them both durable at very high heat and water repellent. Notoriously, the chemical was used by 3M to make Scotchgard for carpets and fabrics and by Dupont to make Teflon for nonstick coating of pots and pans. Although perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was removed from nonstick cookware in 2013, PFAS – a family of thousands of synthetic compounds – remain common in fast-food packaging, water- and stain-repellent clothing, firefighting foam, and personal care products. PFAS are released into the environment during the breakdown of these consumer and industrial products, as well as from dumping from waste facilities.
Alarmingly, the EWG notes that up to 200 million Americans may be exposed to PFAS in their drinking water. In March 2021, the EPA announced that they will be regulating PFAS in drinking water; however, the regulations have not been finalized. Currently, it is up to individual states to test for its presence in the water. The EWG has compiled a map of all known PFAS contamination sites.
To avoid or prevent exposures from PFAS, recommendations include filtering tap water with either reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters, as well as avoiding fast food and carry-out food, if possible, and consumer products labeled as “water resistant,” “stain-resistant,” and “nonstick.”
In a testament to how harmful these chemicals are, the EPA recently revised their lifetime health advisories for PFAS, such as PFOA, to 0.004 parts per trillion, which is more than 10,000 times smaller than the previous limit of 70 parts per trillion. The EPA also has proposed formally designating certain PFAS chemicals as “hazardous substances.”
Dr. Goel, clinical assistant professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Irregular sleep tied to markers of atherosclerosis
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
a new report suggests.
In particular, variation in sleep duration of more than 2 hours per night in the same week was tied to higher rates of atherosclerosis.
“Poor sleep is linked with several cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes,” lead author Kelsie M. Full, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said in an interview.
“Overall, we found that participants who slept varying amounts of hours throughout the week (meaning that one night they slept less, one night they slept more) were more likely to have atherosclerosis than participants who slept about the same amount of time each night,” she said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Analyzing associations
Dr. Full and colleagues examined data from 2032 participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Sleep Ancillary Study, which included adults aged between 45 and 84 years in six U.S. communities who completed 7-day wrist actigraphy assessment and kept a sleep diary between 2010 and 2013.
For subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease, participants underwent assessments of coronary artery calcium, carotid plaque presence, carotid intima-media thickness, and ankle-brachial index.
The research team assessed sleep duration, or the total number of minutes of sleep in a night, and sleep timing regularity, which was determined on the basis of the time someone initially fell asleep each night. They adjusted for cardiovascular disease risk factors and sleep characteristics, such as obstructive sleep apnea, sleep duration, and sleep fragmentation.
The average age of the participants was 68.6 years, and 53.6% were women. About 37.9% identified as White, 27.6% as Black or African American, 23.4% as Hispanic American, and 11.1% as Chinese American.
During the 7-day period, about 38% of participants experienced a change in sleep duration of more than 90 minutes, and 18% experienced a sleep duration change of more than 120 minutes. Those who had irregular sleep were more likely to be non-White, current smokers, have lower average annual incomes, have work shift schedules or did not work, and have a higher average body mass index.
For the study, sleep duration irregularity was defined as a standard deviation of more than 120 minutes. Those participants who had a greater degree of sleep irregularity were more likely to have high coronary artery calcium burden than those whose sleep duration was more more regular, defined as an SD of 60 minutes or less (> 300; prevalence ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.71), as well as abnormal ankle-brachial index (< 0.9, prevalence ratio, 1.75;95% CI, 1.03-2.95).
Further, those with irregular sleep timing (SD > 90 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden (prevalence ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.07-1.82) in comparison with those with more regular sleep timing (SD < 30 minutes).
“The biggest surprise to me was that 30% of the participants in the study had total sleep times that varied by more than 90 minutes over the course of the week,” Dr. Full said. “This is consistent with prior studies that suggest that a large proportion of the general public have irregular sleep patterns, not just shift workers.”
Investigating next steps
In additional analyses, Dr. Full and colleagues found that sleep duration regularity continued to be associated with high coronary artery calcium burden and abnormal ankle-brachial index when accounting for severe obstructive sleep apnea, average nightly sleep duration, and average sleep fragmentation.
Notably, when sleep duration was added, all participants with more irregular sleep durations (SD > 60 minutes) were more likely to have a high coronary artery calcium burden, compared with those with regular sleep durations (SD < 60 minutes). The results remained when participants who reported shift work, including night shift work, were excluded.
Additional studies are needed to understand the mechanisms, the study authors wrote. Night-to-night variability in sleep duration and sleep timing can cause desynchronization in the sleep-wake timing and circadian disruption.
“A key issue highlighted in this study is that sleep irregularity itself, independent of how much sleep people were getting, was related to heart health. Sleep is a naturally recurring phenomenon, and maintaining regularity helps provide stability and predictability to the body,” Michael Grandner, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and director of the sleep and health research program at the University of Arizona, Tucson, said in an interview.
Dr. Grandner, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched sleep irregularity and associations with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and many other adverse outcomes.
“When people have very irregular sleep schedules, it may make it harder for the body to optimally make good use of the sleep it is getting, since it such a moving target,” he said. “The unique angle here is the ability to focus on regularity of sleep.”
The study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health. One author received grants and consulting fees from pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the research. The other authors and Dr. Grandner disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Physicians and clinicians should be required to get flu shots: Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hi. I’m Art Caplan. I’m at the Division of Medical Ethics at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, where I’m the director.
I’ve long believed that every health care institution – nursing homes, hospitals, clinics, home care, hospice – should require flu shots for all doctors and all nurses because it is the easiest, cheapest, and most ethical way to protect the workforce, who you need to be in there when flu outbreaks take place, and to protect patients against getting the flu when they come into hospital settings and get exposed to health care workers who may have the flu already but don’t know it.
In a recent poll, I was happy to see that the majority of physicians surveyed agreed with me: 65% said they supported mandatory flu vaccination in hospitals and only 23% said they did not. I think flu vaccination is something that has already been shown to be useful and important, not only in stopping people from getting the flu but also in making sure that they don’t get as sick when they get the flu.
Just like COVID-19 vaccination, it doesn’t always prevent somebody from getting infected, but if you get it, it keeps you from winding up sick at home, or worse – from dying and winding up in the morgue. Flu kills many, many people every year. We don’t want that to happen. A flu vaccine will really help prevent deaths, help prevent the number of symptoms that somebody gets, and will get people back to work. The benefits are pretty clear.
Does the flu vaccine work equally well every year? It does not. Some years, the strains that are picked for the vaccine don’t match the ones that circulate, and we don’t get as much protection as we hoped for. I think the safety side is so strong that it’s worth making the investment and the effort to promote mandatory flu vaccination.
Can you opt out on religious grounds? Well, some hospitals permit that at New York University. You have to go before a committee and make a case that your exemption on religious grounds is based on an authentic set of beliefs that are deeply held, and not just something you thought up the day before flu vaccine requirements went into effect.
There may be room for some exemptions – obviously, for health reasons. If people think that the flu vaccine is dangerous to them and can get a physician to agree and sign off that they are not appropriate to vaccinate, okay.
On the other hand, if you’re working with an especially vulnerable population – newborns, people who are immunosuppressed – then I think you’ve got to be vaccinated and you shouldn’t be working around people who are at huge risk of getting the flu if you refuse to be vaccinated or, for that matter, can’t be vaccinated.
Would I extend these mandates? Yes, I would. I’d extend them to COVID-19 vaccination and to measles vaccination. I think physicians and nurses should be good role models. They should get vaccinated. We know that the best available evidence says that vaccination for infectious disease is safe. It is really the best thing we can do to combat a variety of diseases such as the flu and COVID-19.
It seems to me that, in addition, the data that are out there in terms of risks from flu and COVID-19 – deaths in places like nursing homes – are overwhelming about the importance of trying to get staff vaccinated so they don’t bring flu into an institutionalized population. This is similar for prison health and many other settings where people are kept close together and staff may move from place to place, rotating from institution to institution, spreading infectious disease.
I’m going to go with the poll. Let’s keep pushing for health care workers to do the right thing and to be good role models. Let’s get everybody a flu vaccination. Let’s extend it to a COVID-19 vaccination and its boosters.
Let’s try to show the nation that health care is going to be guided by good science, a duty to one’s own health, and a duty to one’s patients. It shouldn’t be political. It should be based on what works best for the interests of health care providers and those they care for.
I’m Art Caplan at the New York University Grossman School of Medicine. Thanks for watching.
Dr. Caplan has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position). Serves as a contributing author and advisor for Medscape. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Advanced imaging technology could help predict lung cancer progression after surgery
, according to new data.
The technology, known as highly multiplexed imaging mass cytometry (IMC), can provide cellular-level detail of the tumor immune microenvironment, which may allow clinicians to identify patients who need additional treatment, as well as those who don’t.
“It is well known that the frequency of certain cell populations within the tumor microenvironment correlates with clinical outcomes. These observations help us understand the biology underlying cancer progression,” senior author Logan Walsh, PhD, assistant professor of human genetics and the Rosalind Goodman Chair in Lung Cancer Research at McGill University’s Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Institute, Montreal, said in an interview.
“We wanted to test whether using completely unbiased AI could find and use the spatial topography of the tumor microenvironment from IMC data to predict clinical outcomes,” he said. “It turns out the answer is yes! AI can predict clinical outcomes when combined with IMC with extremely high accuracy from a single 1-mm2 tumor core.”
The study was published on in Nature.
The immune landscape
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in Canada, surpassing breast, colon, and prostate cancer deaths combined, the study authors write.
Lung adenocarcinoma, a non–small cell lung cancer, is the most common subtype and is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. The tumor immune microenvironment influences disease progression and therapy response, the authors write. Understanding the spatial landscape of the microenvironment could provide insight into disease progression, therapeutic vulnerabilities, and biomarkers of response to existing treatments.
In a collaborative study, Dr. Walsh and colleagues from McGill University and Université Laval profiled the cellular composition and spatial organization of the tumor immune microenvironment in tumors from 416 patients with lung adenocarcinoma across five histologic patterns. They used IMC to assess at samples from the universities’ biobanks that patients had provided for research purposes.
The research team detected more than 1.6 million cells, which allowed spatial analysis of immune lineages and activation states with distinct clinical correlates, including survival. They used a supervised lineage assignment approach to classify 14 distinct immune cell populations, along with tumor cells and endothelial cells.
High-grade solid tumors had the greatest immune infiltrate (44.6%), compared with micropapillary (37%), acinar (39.7%), papillary (32.8%), and lepidic architectures (32.7%). Macrophages were the most frequent cell population in the tumor immune microenvironment, representing 12.3% of total cells and 34.1% of immune cells.
The prevalence of CD163+ macrophages was strongly correlated with FOXP3+ immunoregulatory T cells in the solid pattern. This relationship was less pronounced in low-grade lepidic and papillary architectures. This finding could suggest an interplay between macrophage and T-cell populations in the tumor immune microenvironment across lung adenocarcinoma patterns.
Using a deep neural network model, the researchers also analyzed the relationship between immune populations and clinical or pathologic variables by examining the frequency of individual cell types as a percentage of total cells in each image. Each image was cross-referenced with clinical data from patients, including sex, age, body mass index, smoking status, stage, progression, survival, and histologic subtype.
Overall, the researchers found that various clinical outcomes, including cancer progression, could be predicted with high accuracy using a single 1-mm2 tumor core. For instance, they could predict progression in stage IA and IB resected lung cancer with 95.9% accuracy.
Additional applications
“We were not surprised that AI was able to predict clinical outcomes, but we were surprised that it was able to do so with such high accuracy and precision,” said Dr. Walsh. “We were also surprised to learn that our predictions were equally accurate using only six-plex data, compared with 35-plex. This hinted to us that we could potentially scale down the number of markers to a practical number that would be amenable to technologies available in routine pathology labs.”
Dr. Walsh and colleagues are now validating the predictive tool using a lower-plex technology. In addition, they are investigating the immune landscapes of primary and metastatic brain tumors.
“This study is important, as it helps us to understand and appreciate the biological and mechanistic factors that may influence treatment outcomes. Our standard clinical predictors for predicting risk of recurrence and probability of response to therapy are not optimal,” Yee Ung, MD, an associate professor of radiation oncology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, said in an interview.
Dr. Ung, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched noninvasive hypoxia imaging and targeting in lung cancer. Ideally, he said, future studies should incorporate the use of noninvasive imaging predictive factors, in addition to the tumor immune microenvironment and clinical factors, to predict outcomes and provide personalized treatment.
“As we begin to investigate and understand more about cancer biology down to the cellular and molecular level, we need to strategically use AI methodologies in the processing and analysis of data,” he said.
The study was supported by the McGill Interdisciplinary Initiative in Infection and Immunity, the Brain Tumour Funders’ Collaborative, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Ung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
The technology, known as highly multiplexed imaging mass cytometry (IMC), can provide cellular-level detail of the tumor immune microenvironment, which may allow clinicians to identify patients who need additional treatment, as well as those who don’t.
“It is well known that the frequency of certain cell populations within the tumor microenvironment correlates with clinical outcomes. These observations help us understand the biology underlying cancer progression,” senior author Logan Walsh, PhD, assistant professor of human genetics and the Rosalind Goodman Chair in Lung Cancer Research at McGill University’s Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Institute, Montreal, said in an interview.
“We wanted to test whether using completely unbiased AI could find and use the spatial topography of the tumor microenvironment from IMC data to predict clinical outcomes,” he said. “It turns out the answer is yes! AI can predict clinical outcomes when combined with IMC with extremely high accuracy from a single 1-mm2 tumor core.”
The study was published on in Nature.
The immune landscape
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in Canada, surpassing breast, colon, and prostate cancer deaths combined, the study authors write.
Lung adenocarcinoma, a non–small cell lung cancer, is the most common subtype and is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. The tumor immune microenvironment influences disease progression and therapy response, the authors write. Understanding the spatial landscape of the microenvironment could provide insight into disease progression, therapeutic vulnerabilities, and biomarkers of response to existing treatments.
In a collaborative study, Dr. Walsh and colleagues from McGill University and Université Laval profiled the cellular composition and spatial organization of the tumor immune microenvironment in tumors from 416 patients with lung adenocarcinoma across five histologic patterns. They used IMC to assess at samples from the universities’ biobanks that patients had provided for research purposes.
The research team detected more than 1.6 million cells, which allowed spatial analysis of immune lineages and activation states with distinct clinical correlates, including survival. They used a supervised lineage assignment approach to classify 14 distinct immune cell populations, along with tumor cells and endothelial cells.
High-grade solid tumors had the greatest immune infiltrate (44.6%), compared with micropapillary (37%), acinar (39.7%), papillary (32.8%), and lepidic architectures (32.7%). Macrophages were the most frequent cell population in the tumor immune microenvironment, representing 12.3% of total cells and 34.1% of immune cells.
The prevalence of CD163+ macrophages was strongly correlated with FOXP3+ immunoregulatory T cells in the solid pattern. This relationship was less pronounced in low-grade lepidic and papillary architectures. This finding could suggest an interplay between macrophage and T-cell populations in the tumor immune microenvironment across lung adenocarcinoma patterns.
Using a deep neural network model, the researchers also analyzed the relationship between immune populations and clinical or pathologic variables by examining the frequency of individual cell types as a percentage of total cells in each image. Each image was cross-referenced with clinical data from patients, including sex, age, body mass index, smoking status, stage, progression, survival, and histologic subtype.
Overall, the researchers found that various clinical outcomes, including cancer progression, could be predicted with high accuracy using a single 1-mm2 tumor core. For instance, they could predict progression in stage IA and IB resected lung cancer with 95.9% accuracy.
Additional applications
“We were not surprised that AI was able to predict clinical outcomes, but we were surprised that it was able to do so with such high accuracy and precision,” said Dr. Walsh. “We were also surprised to learn that our predictions were equally accurate using only six-plex data, compared with 35-plex. This hinted to us that we could potentially scale down the number of markers to a practical number that would be amenable to technologies available in routine pathology labs.”
Dr. Walsh and colleagues are now validating the predictive tool using a lower-plex technology. In addition, they are investigating the immune landscapes of primary and metastatic brain tumors.
“This study is important, as it helps us to understand and appreciate the biological and mechanistic factors that may influence treatment outcomes. Our standard clinical predictors for predicting risk of recurrence and probability of response to therapy are not optimal,” Yee Ung, MD, an associate professor of radiation oncology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, said in an interview.
Dr. Ung, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched noninvasive hypoxia imaging and targeting in lung cancer. Ideally, he said, future studies should incorporate the use of noninvasive imaging predictive factors, in addition to the tumor immune microenvironment and clinical factors, to predict outcomes and provide personalized treatment.
“As we begin to investigate and understand more about cancer biology down to the cellular and molecular level, we need to strategically use AI methodologies in the processing and analysis of data,” he said.
The study was supported by the McGill Interdisciplinary Initiative in Infection and Immunity, the Brain Tumour Funders’ Collaborative, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Ung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
The technology, known as highly multiplexed imaging mass cytometry (IMC), can provide cellular-level detail of the tumor immune microenvironment, which may allow clinicians to identify patients who need additional treatment, as well as those who don’t.
“It is well known that the frequency of certain cell populations within the tumor microenvironment correlates with clinical outcomes. These observations help us understand the biology underlying cancer progression,” senior author Logan Walsh, PhD, assistant professor of human genetics and the Rosalind Goodman Chair in Lung Cancer Research at McGill University’s Rosalind and Morris Goodman Cancer Institute, Montreal, said in an interview.
“We wanted to test whether using completely unbiased AI could find and use the spatial topography of the tumor microenvironment from IMC data to predict clinical outcomes,” he said. “It turns out the answer is yes! AI can predict clinical outcomes when combined with IMC with extremely high accuracy from a single 1-mm2 tumor core.”
The study was published on in Nature.
The immune landscape
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in Canada, surpassing breast, colon, and prostate cancer deaths combined, the study authors write.
Lung adenocarcinoma, a non–small cell lung cancer, is the most common subtype and is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. The tumor immune microenvironment influences disease progression and therapy response, the authors write. Understanding the spatial landscape of the microenvironment could provide insight into disease progression, therapeutic vulnerabilities, and biomarkers of response to existing treatments.
In a collaborative study, Dr. Walsh and colleagues from McGill University and Université Laval profiled the cellular composition and spatial organization of the tumor immune microenvironment in tumors from 416 patients with lung adenocarcinoma across five histologic patterns. They used IMC to assess at samples from the universities’ biobanks that patients had provided for research purposes.
The research team detected more than 1.6 million cells, which allowed spatial analysis of immune lineages and activation states with distinct clinical correlates, including survival. They used a supervised lineage assignment approach to classify 14 distinct immune cell populations, along with tumor cells and endothelial cells.
High-grade solid tumors had the greatest immune infiltrate (44.6%), compared with micropapillary (37%), acinar (39.7%), papillary (32.8%), and lepidic architectures (32.7%). Macrophages were the most frequent cell population in the tumor immune microenvironment, representing 12.3% of total cells and 34.1% of immune cells.
The prevalence of CD163+ macrophages was strongly correlated with FOXP3+ immunoregulatory T cells in the solid pattern. This relationship was less pronounced in low-grade lepidic and papillary architectures. This finding could suggest an interplay between macrophage and T-cell populations in the tumor immune microenvironment across lung adenocarcinoma patterns.
Using a deep neural network model, the researchers also analyzed the relationship between immune populations and clinical or pathologic variables by examining the frequency of individual cell types as a percentage of total cells in each image. Each image was cross-referenced with clinical data from patients, including sex, age, body mass index, smoking status, stage, progression, survival, and histologic subtype.
Overall, the researchers found that various clinical outcomes, including cancer progression, could be predicted with high accuracy using a single 1-mm2 tumor core. For instance, they could predict progression in stage IA and IB resected lung cancer with 95.9% accuracy.
Additional applications
“We were not surprised that AI was able to predict clinical outcomes, but we were surprised that it was able to do so with such high accuracy and precision,” said Dr. Walsh. “We were also surprised to learn that our predictions were equally accurate using only six-plex data, compared with 35-plex. This hinted to us that we could potentially scale down the number of markers to a practical number that would be amenable to technologies available in routine pathology labs.”
Dr. Walsh and colleagues are now validating the predictive tool using a lower-plex technology. In addition, they are investigating the immune landscapes of primary and metastatic brain tumors.
“This study is important, as it helps us to understand and appreciate the biological and mechanistic factors that may influence treatment outcomes. Our standard clinical predictors for predicting risk of recurrence and probability of response to therapy are not optimal,” Yee Ung, MD, an associate professor of radiation oncology at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, said in an interview.
Dr. Ung, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched noninvasive hypoxia imaging and targeting in lung cancer. Ideally, he said, future studies should incorporate the use of noninvasive imaging predictive factors, in addition to the tumor immune microenvironment and clinical factors, to predict outcomes and provide personalized treatment.
“As we begin to investigate and understand more about cancer biology down to the cellular and molecular level, we need to strategically use AI methodologies in the processing and analysis of data,” he said.
The study was supported by the McGill Interdisciplinary Initiative in Infection and Immunity, the Brain Tumour Funders’ Collaborative, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation. Dr. Walsh and Dr. Ung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE