User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Exercise capacity and QOL linked to significant survival benefit with endobronchial valves
according to study results published in Respiratory Medicine. The benefits were independent of reduction in target lobe volume or the presence of a complete lobar atelectasis.
In patients with more severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the usual treatments of smoking cessation, pharmacological therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation aiming for symptom reduction, minimizing the burden of disease, slowing disease progression, and improving exercise tolerance fall short according to Sharyn A. Roodenburg, PhD candidate in the department of pulmonary diseases, University of Groningen (the Netherlands), and colleagues.
Lung volume reduction is generally reserved for patients with COPD that has a predominantly emphysematous phenotype and severely hyperinflated lungs. While both surgical and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) approaches are in use, bronchoscopic approaches are less invasive and incur lower morbidity. When technically feasible, they are generally preferred over open surgery.
BLVR using endobronchial valves (EBV), the most effective and commonly employed technique, has been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve pulmonary function, exercise capacity, and health-related quality of life.
Noting a survival benefit in prior studies among patients with complete lobar atelectasis following treatment, the authors wrote that their own clinical experience has been that significant treatment responses (pulmonary function and/or exercise capacity) observed in patients with a partial lobar atelectasis may also be associated with a survival benefit. Their aim was to evaluate whether pulmonary function, radiological, health-related quality of life, and/or exercise capacity outcome responders to EBV treatment have a survival benefit over nonresponders.
Their analysis included data collected prospectively out of four clinical trials (CHARTIS, STELVIO, IMPACT, and LIBERATE) from June 2008 to Dec. 2020 at the University Medical Center Groningen. Predetermined potential predictors of survival included change in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), change in residual volume (RV), change in RV/total lung capacity (RV/TLC) ratio, change in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), change in total score on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), target lobe volume reduction (TLVR), and presence of complete lobar atelectasis (defined as a TLVR of 100%).
Mean age was 61.3 years among the 428 included patients (68% women). Data on both the 6MWD and SGRQ total score at baseline and 1-year follow-up were available for 252 patients. SGRQ decreased by 8.3 points or more, and 6MWD increased by 26 meters or more over baseline. Among these patients, 113 (45%) were responders on both 6MWD and SGRQ, 49 (19%) patients were responders on 6MWD only, 31 (12%) patients on SGRQ only, and 59 (23%) were nonresponders on both. Survival was significantly worse among nonresponders on 6MWD, SGRQ, or on both. 6MWD and SGRQ response were independent predictors for improved survival time (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.28-0.89; P = .02 and HR, 0.54; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.94; P = .03, respectively). Survival was not significantly affected by the presence of complete lobar atelectasis or pulmonary function improvements.
“Especially in patients with a low FEV1 (< 50% predicted), 6-minute walk distance was found to be a better predictor for mortality than pulmonary function. A possible explanation for why change in 6-minute walk distance is a better predictor for survival after EBV treatment than the change in pulmonary function and hyperinflation might be that the 6-minute walk distance not only reflects the pulmonary limitation of these patients, but also captures the extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD, such as cardiac dysfunction, musculoskeletal disorders, fatigue, and psychological symptoms, all of which can impact survival,” the authors noted
The study received no funding, and the authors did not report any disclosures.
This article was updated 3/30/23.
according to study results published in Respiratory Medicine. The benefits were independent of reduction in target lobe volume or the presence of a complete lobar atelectasis.
In patients with more severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the usual treatments of smoking cessation, pharmacological therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation aiming for symptom reduction, minimizing the burden of disease, slowing disease progression, and improving exercise tolerance fall short according to Sharyn A. Roodenburg, PhD candidate in the department of pulmonary diseases, University of Groningen (the Netherlands), and colleagues.
Lung volume reduction is generally reserved for patients with COPD that has a predominantly emphysematous phenotype and severely hyperinflated lungs. While both surgical and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) approaches are in use, bronchoscopic approaches are less invasive and incur lower morbidity. When technically feasible, they are generally preferred over open surgery.
BLVR using endobronchial valves (EBV), the most effective and commonly employed technique, has been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve pulmonary function, exercise capacity, and health-related quality of life.
Noting a survival benefit in prior studies among patients with complete lobar atelectasis following treatment, the authors wrote that their own clinical experience has been that significant treatment responses (pulmonary function and/or exercise capacity) observed in patients with a partial lobar atelectasis may also be associated with a survival benefit. Their aim was to evaluate whether pulmonary function, radiological, health-related quality of life, and/or exercise capacity outcome responders to EBV treatment have a survival benefit over nonresponders.
Their analysis included data collected prospectively out of four clinical trials (CHARTIS, STELVIO, IMPACT, and LIBERATE) from June 2008 to Dec. 2020 at the University Medical Center Groningen. Predetermined potential predictors of survival included change in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), change in residual volume (RV), change in RV/total lung capacity (RV/TLC) ratio, change in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), change in total score on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), target lobe volume reduction (TLVR), and presence of complete lobar atelectasis (defined as a TLVR of 100%).
Mean age was 61.3 years among the 428 included patients (68% women). Data on both the 6MWD and SGRQ total score at baseline and 1-year follow-up were available for 252 patients. SGRQ decreased by 8.3 points or more, and 6MWD increased by 26 meters or more over baseline. Among these patients, 113 (45%) were responders on both 6MWD and SGRQ, 49 (19%) patients were responders on 6MWD only, 31 (12%) patients on SGRQ only, and 59 (23%) were nonresponders on both. Survival was significantly worse among nonresponders on 6MWD, SGRQ, or on both. 6MWD and SGRQ response were independent predictors for improved survival time (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.28-0.89; P = .02 and HR, 0.54; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.94; P = .03, respectively). Survival was not significantly affected by the presence of complete lobar atelectasis or pulmonary function improvements.
“Especially in patients with a low FEV1 (< 50% predicted), 6-minute walk distance was found to be a better predictor for mortality than pulmonary function. A possible explanation for why change in 6-minute walk distance is a better predictor for survival after EBV treatment than the change in pulmonary function and hyperinflation might be that the 6-minute walk distance not only reflects the pulmonary limitation of these patients, but also captures the extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD, such as cardiac dysfunction, musculoskeletal disorders, fatigue, and psychological symptoms, all of which can impact survival,” the authors noted
The study received no funding, and the authors did not report any disclosures.
This article was updated 3/30/23.
according to study results published in Respiratory Medicine. The benefits were independent of reduction in target lobe volume or the presence of a complete lobar atelectasis.
In patients with more severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the usual treatments of smoking cessation, pharmacological therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation aiming for symptom reduction, minimizing the burden of disease, slowing disease progression, and improving exercise tolerance fall short according to Sharyn A. Roodenburg, PhD candidate in the department of pulmonary diseases, University of Groningen (the Netherlands), and colleagues.
Lung volume reduction is generally reserved for patients with COPD that has a predominantly emphysematous phenotype and severely hyperinflated lungs. While both surgical and bronchoscopic lung volume reduction (BLVR) approaches are in use, bronchoscopic approaches are less invasive and incur lower morbidity. When technically feasible, they are generally preferred over open surgery.
BLVR using endobronchial valves (EBV), the most effective and commonly employed technique, has been shown in randomized controlled trials to improve pulmonary function, exercise capacity, and health-related quality of life.
Noting a survival benefit in prior studies among patients with complete lobar atelectasis following treatment, the authors wrote that their own clinical experience has been that significant treatment responses (pulmonary function and/or exercise capacity) observed in patients with a partial lobar atelectasis may also be associated with a survival benefit. Their aim was to evaluate whether pulmonary function, radiological, health-related quality of life, and/or exercise capacity outcome responders to EBV treatment have a survival benefit over nonresponders.
Their analysis included data collected prospectively out of four clinical trials (CHARTIS, STELVIO, IMPACT, and LIBERATE) from June 2008 to Dec. 2020 at the University Medical Center Groningen. Predetermined potential predictors of survival included change in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), change in residual volume (RV), change in RV/total lung capacity (RV/TLC) ratio, change in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), change in total score on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), target lobe volume reduction (TLVR), and presence of complete lobar atelectasis (defined as a TLVR of 100%).
Mean age was 61.3 years among the 428 included patients (68% women). Data on both the 6MWD and SGRQ total score at baseline and 1-year follow-up were available for 252 patients. SGRQ decreased by 8.3 points or more, and 6MWD increased by 26 meters or more over baseline. Among these patients, 113 (45%) were responders on both 6MWD and SGRQ, 49 (19%) patients were responders on 6MWD only, 31 (12%) patients on SGRQ only, and 59 (23%) were nonresponders on both. Survival was significantly worse among nonresponders on 6MWD, SGRQ, or on both. 6MWD and SGRQ response were independent predictors for improved survival time (hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.28-0.89; P = .02 and HR, 0.54; 95% confidence interval, 0.30-0.94; P = .03, respectively). Survival was not significantly affected by the presence of complete lobar atelectasis or pulmonary function improvements.
“Especially in patients with a low FEV1 (< 50% predicted), 6-minute walk distance was found to be a better predictor for mortality than pulmonary function. A possible explanation for why change in 6-minute walk distance is a better predictor for survival after EBV treatment than the change in pulmonary function and hyperinflation might be that the 6-minute walk distance not only reflects the pulmonary limitation of these patients, but also captures the extrapulmonary manifestations of COPD, such as cardiac dysfunction, musculoskeletal disorders, fatigue, and psychological symptoms, all of which can impact survival,” the authors noted
The study received no funding, and the authors did not report any disclosures.
This article was updated 3/30/23.
FROM RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
Celebrity death finally solved – with locks of hair
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to open this week with a case.
A 56-year-old musician presents with diffuse abdominal pain, cramping, and jaundice. His medical history is notable for years of diffuse abdominal complaints, characterized by disabling bouts of diarrhea.
In addition to the jaundice, this acute illness was accompanied by fever as well as diffuse edema and ascites. The patient underwent several abdominal paracenteses to drain excess fluid. One consulting physician administered alcohol to relieve pain, to little avail.
The patient succumbed to his illness. An autopsy showed diffuse liver injury, as well as papillary necrosis of the kidneys. Notably, the nerves of his auditory canal were noted to be thickened, along with the bony part of the skull, consistent with Paget disease of the bone and explaining, potentially, why the talented musician had gone deaf at such a young age.
An interesting note on social history: The patient had apparently developed some feelings for the niece of that doctor who prescribed alcohol. Her name was Therese, perhaps mistranscribed as Elise, and it seems that he may have written this song for her.
We’re talking about this paper in Current Biology, by Tristan Begg and colleagues, which gives us a look into the very genome of what some would argue is the world’s greatest composer.
The ability to extract DNA from older specimens has transformed the fields of anthropology, archaeology, and history, and now, perhaps, musicology as well.
The researchers identified eight locks of hair in private and public collections, all attributed to the maestro.
Four of the samples had an intact chain of custody from the time the hair was cut. DNA sequencing on these four and an additional one of the eight locks came from the same individual, a male of European heritage.
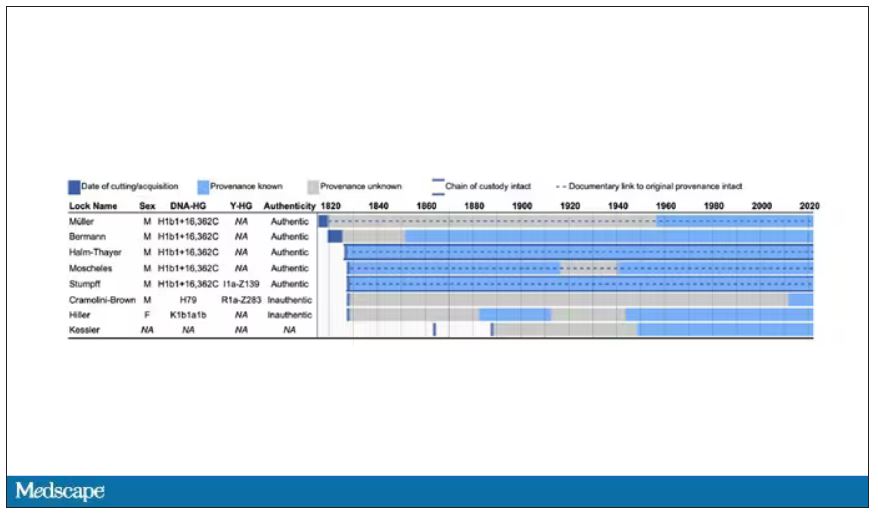
The three locks with less documentation came from three other unrelated individuals. Interestingly, analysis of one of those hair samples – the so-called Hiller Lock – had shown high levels of lead, leading historians to speculate that lead poisoning could account for some of Beethoven’s symptoms.

DNA analysis of that hair reveals it to have come from a woman likely of North African, Middle Eastern, or Jewish ancestry. We can no longer presume that plumbism was involved in Beethoven’s death. Beethoven’s ancestry turns out to be less exotic and maps quite well to ethnic German populations today.
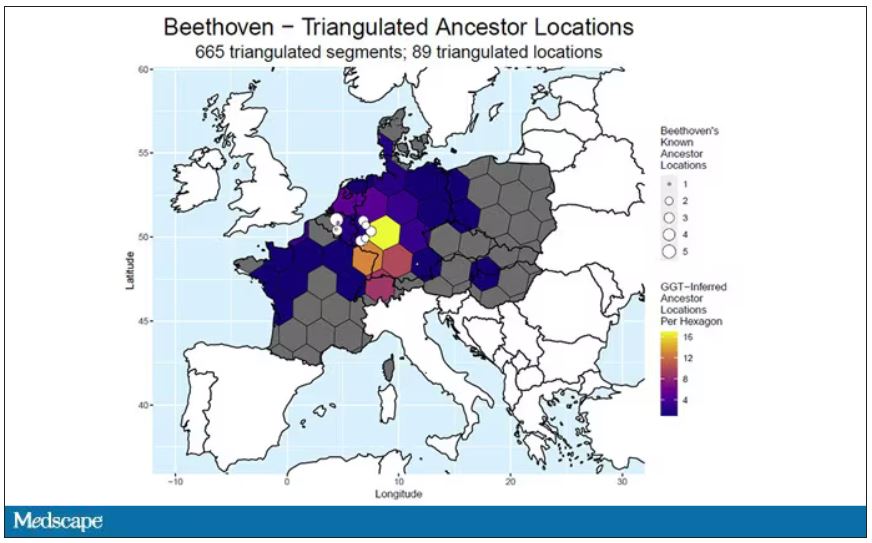
In fact, there are van Beethovens alive as we speak, primarily in Belgium. Genealogic records suggest that these van Beethovens share a common ancestor with the virtuoso composer, a man by the name of Aert van Beethoven.
But the DNA reveals a scandal.
The Y-chromosome that Beethoven inherited was not Aert van Beethoven’s. Questions of Beethoven’s paternity have been raised before, but this evidence strongly suggests an extramarital paternity event, at least in the generations preceding his birth. That’s right – Beethoven may not have been a Beethoven.
With five locks now essentially certain to have come from Beethoven himself, the authors could use DNA analysis to try to explain three significant health problems he experienced throughout his life and death: his hearing loss, his terrible gastrointestinal issues, and his liver failure.
Let’s start with the most disappointing results, explanations for his hearing loss. No genetic cause was forthcoming, though the authors note that they have little to go on in regard to the genetic risk for otosclerosis, to which his hearing loss has often been attributed. Lead poisoning is, of course, possible here, though this report focuses only on genetics – there was no testing for lead – and as I mentioned, the lock that was strongly lead-positive in prior studies is almost certainly inauthentic.
What about his lifelong GI complaints? Some have suggested celiac disease or lactose intolerance as explanations. These can essentially be ruled out by the genetic analysis, which shows no risk alleles for celiac disease and the presence of the lactase-persistence gene which confers the ability to metabolize lactose throughout one’s life. IBS is harder to assess genetically, but for what it’s worth, he scored quite low on a polygenic risk score for the condition, in just the 9th percentile of risk. We should probably be looking elsewhere to explain the GI distress.
The genetic information bore much more fruit in regard to his liver disease. Remember that Beethoven’s autopsy showed cirrhosis. His polygenic risk score for liver cirrhosis puts him in the 96th percentile of risk. He was also heterozygous for two variants that can cause hereditary hemochromatosis. The risk for cirrhosis among those with these variants is increased by the use of alcohol. And historical accounts are quite clear that Beethoven consumed more than his share.
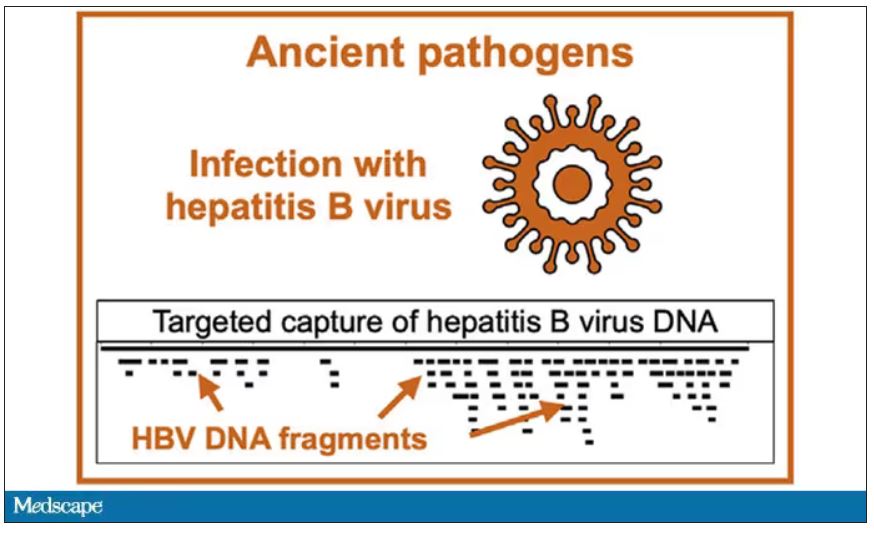
But it wasn’t just Beethoven’s DNA in these hair follicles. Analysis of a follicle from later in his life revealed the unmistakable presence of hepatitis B virus. Endemic in Europe at the time, this was a common cause of liver failure and is likely to have contributed to, if not directly caused, Beethoven’s demise.
It’s hard to read these results and not marvel at the fact that, two centuries after his death, our fascination with Beethoven has led us to probe every corner of his life – his letters, his writings, his medical records, and now his very DNA. What are we actually looking for? Is it relevant to us today what caused his hearing loss? His stomach troubles? Even his death? Will it help any patients in the future? I propose that what we are actually trying to understand is something ineffable: Genius of magnitude that is rarely seen in one or many lifetimes. And our scientific tools, as sharp as they may have become, are still far too blunt to probe the depths of that transcendence.
In any case, friends, no more of these sounds. Let us sing more cheerful songs, more full of joy.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to open this week with a case.
A 56-year-old musician presents with diffuse abdominal pain, cramping, and jaundice. His medical history is notable for years of diffuse abdominal complaints, characterized by disabling bouts of diarrhea.
In addition to the jaundice, this acute illness was accompanied by fever as well as diffuse edema and ascites. The patient underwent several abdominal paracenteses to drain excess fluid. One consulting physician administered alcohol to relieve pain, to little avail.
The patient succumbed to his illness. An autopsy showed diffuse liver injury, as well as papillary necrosis of the kidneys. Notably, the nerves of his auditory canal were noted to be thickened, along with the bony part of the skull, consistent with Paget disease of the bone and explaining, potentially, why the talented musician had gone deaf at such a young age.
An interesting note on social history: The patient had apparently developed some feelings for the niece of that doctor who prescribed alcohol. Her name was Therese, perhaps mistranscribed as Elise, and it seems that he may have written this song for her.
We’re talking about this paper in Current Biology, by Tristan Begg and colleagues, which gives us a look into the very genome of what some would argue is the world’s greatest composer.
The ability to extract DNA from older specimens has transformed the fields of anthropology, archaeology, and history, and now, perhaps, musicology as well.
The researchers identified eight locks of hair in private and public collections, all attributed to the maestro.
Four of the samples had an intact chain of custody from the time the hair was cut. DNA sequencing on these four and an additional one of the eight locks came from the same individual, a male of European heritage.

The three locks with less documentation came from three other unrelated individuals. Interestingly, analysis of one of those hair samples – the so-called Hiller Lock – had shown high levels of lead, leading historians to speculate that lead poisoning could account for some of Beethoven’s symptoms.

DNA analysis of that hair reveals it to have come from a woman likely of North African, Middle Eastern, or Jewish ancestry. We can no longer presume that plumbism was involved in Beethoven’s death. Beethoven’s ancestry turns out to be less exotic and maps quite well to ethnic German populations today.

In fact, there are van Beethovens alive as we speak, primarily in Belgium. Genealogic records suggest that these van Beethovens share a common ancestor with the virtuoso composer, a man by the name of Aert van Beethoven.
But the DNA reveals a scandal.
The Y-chromosome that Beethoven inherited was not Aert van Beethoven’s. Questions of Beethoven’s paternity have been raised before, but this evidence strongly suggests an extramarital paternity event, at least in the generations preceding his birth. That’s right – Beethoven may not have been a Beethoven.
With five locks now essentially certain to have come from Beethoven himself, the authors could use DNA analysis to try to explain three significant health problems he experienced throughout his life and death: his hearing loss, his terrible gastrointestinal issues, and his liver failure.
Let’s start with the most disappointing results, explanations for his hearing loss. No genetic cause was forthcoming, though the authors note that they have little to go on in regard to the genetic risk for otosclerosis, to which his hearing loss has often been attributed. Lead poisoning is, of course, possible here, though this report focuses only on genetics – there was no testing for lead – and as I mentioned, the lock that was strongly lead-positive in prior studies is almost certainly inauthentic.
What about his lifelong GI complaints? Some have suggested celiac disease or lactose intolerance as explanations. These can essentially be ruled out by the genetic analysis, which shows no risk alleles for celiac disease and the presence of the lactase-persistence gene which confers the ability to metabolize lactose throughout one’s life. IBS is harder to assess genetically, but for what it’s worth, he scored quite low on a polygenic risk score for the condition, in just the 9th percentile of risk. We should probably be looking elsewhere to explain the GI distress.
The genetic information bore much more fruit in regard to his liver disease. Remember that Beethoven’s autopsy showed cirrhosis. His polygenic risk score for liver cirrhosis puts him in the 96th percentile of risk. He was also heterozygous for two variants that can cause hereditary hemochromatosis. The risk for cirrhosis among those with these variants is increased by the use of alcohol. And historical accounts are quite clear that Beethoven consumed more than his share.
But it wasn’t just Beethoven’s DNA in these hair follicles. Analysis of a follicle from later in his life revealed the unmistakable presence of hepatitis B virus. Endemic in Europe at the time, this was a common cause of liver failure and is likely to have contributed to, if not directly caused, Beethoven’s demise.

It’s hard to read these results and not marvel at the fact that, two centuries after his death, our fascination with Beethoven has led us to probe every corner of his life – his letters, his writings, his medical records, and now his very DNA. What are we actually looking for? Is it relevant to us today what caused his hearing loss? His stomach troubles? Even his death? Will it help any patients in the future? I propose that what we are actually trying to understand is something ineffable: Genius of magnitude that is rarely seen in one or many lifetimes. And our scientific tools, as sharp as they may have become, are still far too blunt to probe the depths of that transcendence.
In any case, friends, no more of these sounds. Let us sing more cheerful songs, more full of joy.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m going to open this week with a case.
A 56-year-old musician presents with diffuse abdominal pain, cramping, and jaundice. His medical history is notable for years of diffuse abdominal complaints, characterized by disabling bouts of diarrhea.
In addition to the jaundice, this acute illness was accompanied by fever as well as diffuse edema and ascites. The patient underwent several abdominal paracenteses to drain excess fluid. One consulting physician administered alcohol to relieve pain, to little avail.
The patient succumbed to his illness. An autopsy showed diffuse liver injury, as well as papillary necrosis of the kidneys. Notably, the nerves of his auditory canal were noted to be thickened, along with the bony part of the skull, consistent with Paget disease of the bone and explaining, potentially, why the talented musician had gone deaf at such a young age.
An interesting note on social history: The patient had apparently developed some feelings for the niece of that doctor who prescribed alcohol. Her name was Therese, perhaps mistranscribed as Elise, and it seems that he may have written this song for her.
We’re talking about this paper in Current Biology, by Tristan Begg and colleagues, which gives us a look into the very genome of what some would argue is the world’s greatest composer.
The ability to extract DNA from older specimens has transformed the fields of anthropology, archaeology, and history, and now, perhaps, musicology as well.
The researchers identified eight locks of hair in private and public collections, all attributed to the maestro.
Four of the samples had an intact chain of custody from the time the hair was cut. DNA sequencing on these four and an additional one of the eight locks came from the same individual, a male of European heritage.

The three locks with less documentation came from three other unrelated individuals. Interestingly, analysis of one of those hair samples – the so-called Hiller Lock – had shown high levels of lead, leading historians to speculate that lead poisoning could account for some of Beethoven’s symptoms.

DNA analysis of that hair reveals it to have come from a woman likely of North African, Middle Eastern, or Jewish ancestry. We can no longer presume that plumbism was involved in Beethoven’s death. Beethoven’s ancestry turns out to be less exotic and maps quite well to ethnic German populations today.

In fact, there are van Beethovens alive as we speak, primarily in Belgium. Genealogic records suggest that these van Beethovens share a common ancestor with the virtuoso composer, a man by the name of Aert van Beethoven.
But the DNA reveals a scandal.
The Y-chromosome that Beethoven inherited was not Aert van Beethoven’s. Questions of Beethoven’s paternity have been raised before, but this evidence strongly suggests an extramarital paternity event, at least in the generations preceding his birth. That’s right – Beethoven may not have been a Beethoven.
With five locks now essentially certain to have come from Beethoven himself, the authors could use DNA analysis to try to explain three significant health problems he experienced throughout his life and death: his hearing loss, his terrible gastrointestinal issues, and his liver failure.
Let’s start with the most disappointing results, explanations for his hearing loss. No genetic cause was forthcoming, though the authors note that they have little to go on in regard to the genetic risk for otosclerosis, to which his hearing loss has often been attributed. Lead poisoning is, of course, possible here, though this report focuses only on genetics – there was no testing for lead – and as I mentioned, the lock that was strongly lead-positive in prior studies is almost certainly inauthentic.
What about his lifelong GI complaints? Some have suggested celiac disease or lactose intolerance as explanations. These can essentially be ruled out by the genetic analysis, which shows no risk alleles for celiac disease and the presence of the lactase-persistence gene which confers the ability to metabolize lactose throughout one’s life. IBS is harder to assess genetically, but for what it’s worth, he scored quite low on a polygenic risk score for the condition, in just the 9th percentile of risk. We should probably be looking elsewhere to explain the GI distress.
The genetic information bore much more fruit in regard to his liver disease. Remember that Beethoven’s autopsy showed cirrhosis. His polygenic risk score for liver cirrhosis puts him in the 96th percentile of risk. He was also heterozygous for two variants that can cause hereditary hemochromatosis. The risk for cirrhosis among those with these variants is increased by the use of alcohol. And historical accounts are quite clear that Beethoven consumed more than his share.
But it wasn’t just Beethoven’s DNA in these hair follicles. Analysis of a follicle from later in his life revealed the unmistakable presence of hepatitis B virus. Endemic in Europe at the time, this was a common cause of liver failure and is likely to have contributed to, if not directly caused, Beethoven’s demise.

It’s hard to read these results and not marvel at the fact that, two centuries after his death, our fascination with Beethoven has led us to probe every corner of his life – his letters, his writings, his medical records, and now his very DNA. What are we actually looking for? Is it relevant to us today what caused his hearing loss? His stomach troubles? Even his death? Will it help any patients in the future? I propose that what we are actually trying to understand is something ineffable: Genius of magnitude that is rarely seen in one or many lifetimes. And our scientific tools, as sharp as they may have become, are still far too blunt to probe the depths of that transcendence.
In any case, friends, no more of these sounds. Let us sing more cheerful songs, more full of joy.
For Medscape, I’m Perry Wilson.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors – a new weapon against respiratory viruses?
Five different nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors were effective against viral replication of pandemic viruses and seasonal influenza viruses in an ex vivo lung model.
Influenza viruses remain a high cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide as viral mutations outwit vaccine efficacy, Robert Meineke, PhD, of the University of Veterinary Medicine in Hannover, Germany, and colleagues wrote.
“As with previous influenza pandemics and the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, effective vaccines are not readily available at early stages of a pandemic,” they noted. To help manage the limitations of timing and effectiveness of current vaccines, the researchers proposed repurposing nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (NRTKIs) to block seasonal flu and COVID-19 viral replication.
In a study published in iScience, the researchers identified six NRTKIs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that showed in vitro inhibition of both pandemic viruses (H1N1) and seasonal influenza viruses (H3N2). These included defactinib, acalabrutinib, saracatinib, and bosutinib, all of which reduced hPCLS infectivity by approximately 50%. In addition, ibrutinib and bosutinib had the largest impact on viral titers. The antiviral effects of NRTKIs appeared to be independent of multiplicity of infection.
The researchers then tested the NRIKIs on an ex vivo model of human precision-cut lung slices to validate the effects of NRTKIs as antivirals against influenza A viruses (IAVs).
In this model, the highest peak titers were achieved at 48 hpi following infection with virus strains NL09 and NL11. The hPCLS models also showed consistent tolerability to 1x concentrations. “Our cytotoxicity cut-off was 20% of the positive control treatment; none of the NRTKIs surpassed this cutoff at [1x] max,” the researchers wrote.
Five of the six identified NRTKIs were validated in the ex vivo setting. All five reduced viral titers by at least 10-fold to more than 1,000-fold. Of these, ibrutinib, bosutinib, and bosutinib showed a significant effect at all concentrations, while treatments with acalabrutinib and defactinib were significant at 24 hpi and 48 hpi. The NRTKs also showed a high genetic barrier against emerging resistant virus mutations.
The study demonstrates the ability of NRTKIs to target kinases required for replication of IAV, the researchers wrote, and that NRTKIs “represent promising drugs for the development of the next generation of antivirals.”
More research is needed to determine the therapeutic window given that NRTKIs are targeting host factors versus virus-targeted antivirals, but the advantages of NRTKIs include localized delivery that can limit possible cytotoxic effects, and their safety and bioavailability are well established, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of lung tissue mainly from older donors with lung cancer, the researchers noted. However, this population could be considered at increased risk for IAVs and therefore the data are more clinically applicable.
In addition, “because many viruses utilize the same (or related) host kinases to facilitate replication and transmission, our studies have broader implications for the potential use of these SMKIs to treat infections by other viruses,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Five different nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors were effective against viral replication of pandemic viruses and seasonal influenza viruses in an ex vivo lung model.
Influenza viruses remain a high cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide as viral mutations outwit vaccine efficacy, Robert Meineke, PhD, of the University of Veterinary Medicine in Hannover, Germany, and colleagues wrote.
“As with previous influenza pandemics and the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, effective vaccines are not readily available at early stages of a pandemic,” they noted. To help manage the limitations of timing and effectiveness of current vaccines, the researchers proposed repurposing nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (NRTKIs) to block seasonal flu and COVID-19 viral replication.
In a study published in iScience, the researchers identified six NRTKIs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that showed in vitro inhibition of both pandemic viruses (H1N1) and seasonal influenza viruses (H3N2). These included defactinib, acalabrutinib, saracatinib, and bosutinib, all of which reduced hPCLS infectivity by approximately 50%. In addition, ibrutinib and bosutinib had the largest impact on viral titers. The antiviral effects of NRTKIs appeared to be independent of multiplicity of infection.
The researchers then tested the NRIKIs on an ex vivo model of human precision-cut lung slices to validate the effects of NRTKIs as antivirals against influenza A viruses (IAVs).
In this model, the highest peak titers were achieved at 48 hpi following infection with virus strains NL09 and NL11. The hPCLS models also showed consistent tolerability to 1x concentrations. “Our cytotoxicity cut-off was 20% of the positive control treatment; none of the NRTKIs surpassed this cutoff at [1x] max,” the researchers wrote.
Five of the six identified NRTKIs were validated in the ex vivo setting. All five reduced viral titers by at least 10-fold to more than 1,000-fold. Of these, ibrutinib, bosutinib, and bosutinib showed a significant effect at all concentrations, while treatments with acalabrutinib and defactinib were significant at 24 hpi and 48 hpi. The NRTKs also showed a high genetic barrier against emerging resistant virus mutations.
The study demonstrates the ability of NRTKIs to target kinases required for replication of IAV, the researchers wrote, and that NRTKIs “represent promising drugs for the development of the next generation of antivirals.”
More research is needed to determine the therapeutic window given that NRTKIs are targeting host factors versus virus-targeted antivirals, but the advantages of NRTKIs include localized delivery that can limit possible cytotoxic effects, and their safety and bioavailability are well established, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of lung tissue mainly from older donors with lung cancer, the researchers noted. However, this population could be considered at increased risk for IAVs and therefore the data are more clinically applicable.
In addition, “because many viruses utilize the same (or related) host kinases to facilitate replication and transmission, our studies have broader implications for the potential use of these SMKIs to treat infections by other viruses,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Five different nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors were effective against viral replication of pandemic viruses and seasonal influenza viruses in an ex vivo lung model.
Influenza viruses remain a high cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide as viral mutations outwit vaccine efficacy, Robert Meineke, PhD, of the University of Veterinary Medicine in Hannover, Germany, and colleagues wrote.
“As with previous influenza pandemics and the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, effective vaccines are not readily available at early stages of a pandemic,” they noted. To help manage the limitations of timing and effectiveness of current vaccines, the researchers proposed repurposing nonreceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (NRTKIs) to block seasonal flu and COVID-19 viral replication.
In a study published in iScience, the researchers identified six NRTKIs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that showed in vitro inhibition of both pandemic viruses (H1N1) and seasonal influenza viruses (H3N2). These included defactinib, acalabrutinib, saracatinib, and bosutinib, all of which reduced hPCLS infectivity by approximately 50%. In addition, ibrutinib and bosutinib had the largest impact on viral titers. The antiviral effects of NRTKIs appeared to be independent of multiplicity of infection.
The researchers then tested the NRIKIs on an ex vivo model of human precision-cut lung slices to validate the effects of NRTKIs as antivirals against influenza A viruses (IAVs).
In this model, the highest peak titers were achieved at 48 hpi following infection with virus strains NL09 and NL11. The hPCLS models also showed consistent tolerability to 1x concentrations. “Our cytotoxicity cut-off was 20% of the positive control treatment; none of the NRTKIs surpassed this cutoff at [1x] max,” the researchers wrote.
Five of the six identified NRTKIs were validated in the ex vivo setting. All five reduced viral titers by at least 10-fold to more than 1,000-fold. Of these, ibrutinib, bosutinib, and bosutinib showed a significant effect at all concentrations, while treatments with acalabrutinib and defactinib were significant at 24 hpi and 48 hpi. The NRTKs also showed a high genetic barrier against emerging resistant virus mutations.
The study demonstrates the ability of NRTKIs to target kinases required for replication of IAV, the researchers wrote, and that NRTKIs “represent promising drugs for the development of the next generation of antivirals.”
More research is needed to determine the therapeutic window given that NRTKIs are targeting host factors versus virus-targeted antivirals, but the advantages of NRTKIs include localized delivery that can limit possible cytotoxic effects, and their safety and bioavailability are well established, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of lung tissue mainly from older donors with lung cancer, the researchers noted. However, this population could be considered at increased risk for IAVs and therefore the data are more clinically applicable.
In addition, “because many viruses utilize the same (or related) host kinases to facilitate replication and transmission, our studies have broader implications for the potential use of these SMKIs to treat infections by other viruses,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ISCIENCE
Nurse makes millions selling her licensing exam study sheets
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Beggs, 28, sells one-page study sheets or bundles of sheets, sometimes with colorful drawings, conversation bubbles and underlining, that boil down concepts for particular conditions into easy-to-understand language.
The biggest seller on Ms. Beggs’ online marketplace Etsy site, RNExplained, is a bundle of study guides covering eight core nursing classes. The notes range in price from $2 to $150. More than 70,000 customers have bought the $60 bundle, according to the website.
Ms. Beggs’ business developed in a “very unintentional” way when COVID hit with just months left in her nursing program at Mount Saint Mary’s University, Los Angeles, she told this news organization.
Classes had switched to Zoom, and she had no one to study with as she prepared to take her board exams.
“The best way I know how to study is to teach things out loud. But because I had nobody to teach out loud to, I would literally teach them to the wall,” Ms. Beggs said. “I would record myself so I could play it back and teach myself these topics that were hard for me to understand.”
Just for fun, she says, she posted them on TikTok and the responses started flowing in, with followers asking where she was selling the sheets. She now has more than 660,000 TikTok followers and 9 million likes.
Ms. Beggs said that every sheet highlights a condition, and she has made 308 of them.
Traditional classroom lessons typically teach one medical condition in 5-6 pages, Ms. Beggs said. “I go straight to the point.”
One reviewer on Ms. Beggs’ Etsy site appreciated the handwritten notes, calling them “simplified and concise.” Another commented: “Definitely helped me pass my last exam.”
Ms. Beggs says that her notes may seem simple, but each page represents comprehensive research.
“I have to go through not just one source of information to make sure my information is factual,” Ms. Beggs says. “What you teach in California might be a little different than what you teach in Florida. It’s very meticulous. The lab values will be a little different everywhere you go.”
She acknowledges her competition, noting that there are many other study guides for the NCLEX and nursing courses.
Nursing groups weigh in
Dawn Kappel, spokesperson for the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, which oversees NCLEX, said in an interview that “NCSBN has no issue with the current content of Stephanee Beggs’ business venture.”
For many students, the study guides will be helpful, especially for visual learners, said Carole Kenner, PhD, RN, dean and professor in the School of Nursing and Health Sciences at The College of New Jersey.
But for students “who are less confident in their knowledge, I would want to see a lot more in-depth explanation and rationale,” Dr. Kenner said.
“Since the NCLEX is moving to more cased-based scenarios, the next-gen unfolding cases, you really have to understand a lot of the rationale.”
The notes remind Dr. Kenner of traditional flash cards. “I don’t think it will work for all students, but even the fanciest of onsite review courses are useful to everyone,” she said.
‘Not cutting corners’
As an emergency nurse, Ms. Beggs said, “I have the experience as a nurse to show people that what you are learning will be seen in real life.”
“The way I teach my brand is not to take shortcuts. I love to teach to understand rather than teaching to memorize for an exam.”
She said she sees her guides as a supplement to learning, not a replacement.
“It’s not cutting corners,” she says. “I condense a medical condition that could take a very long time to understand and break it into layman’s terms.”
Ms. Beggs said when people hear about the $2 million, they often ask her whether she plans to give up her shifts in the emergency department for the more lucrative venture.
The answer is no, at least not yet.
“Aside from teaching, I genuinely love being at the bedside,” Ms. Beggs said. “I don’t foresee myself leaving that for good for as long as I can handle both.” She acknowledged, though, that her business now takes up most of her time.
“I love everything about both aspects, so it’s hard for me to choose.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The air up there: Oxygen could be a bit overrated
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.
Cases of potentially deadly fungus jump 200%: CDC
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
prompting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to issue a warning to health care facilities about the rising threat.
C. auris is a yeast that spreads easily from touching it on a surface like a countertop. It can also spread from person to person. It isn’t a threat to healthy people, but people in hospitals and nursing homes are at a heightened risk because they might have weakened immune systems or be using invasive medical devices that can introduce the fungus inside their bodies. When C. auris progresses to causing an infection that reaches the brain, blood, or lungs, more than one in three people die.
The worrying increase was detailed in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine. In 2021, cases reached a count of 3,270 with an active infection, and 7,413 cases showed the fungus was present but hadn’t caused an infection. Infection counts were up 95% over the previous year, and the fungus showed up on screenings three times as often. The number of cases resistant to medication also tripled.
The CDC called the figures “alarming,” noting that the fungus was only detected in the United States in 2016.
“The timing of this increase and findings from public health investigations suggest C. auris spread may have worsened due to strain on health care and public health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the CDC explained in a news release.
Another potential reason for the jump could be that screening for C. auris has simply increased and it’s being found more often because it’s being looked for more often. But researchers believe that, even with the increase in testing, the reported counts are underestimated. That’s because even though screening has increased, health care providers still aren’t looking for the presence of the fungus as often as the CDC would like.
“The rapid rise and geographic spread of cases is concerning and emphasizes the need for continued surveillance, expanded lab capacity, quicker diagnostic tests, and adherence to proven infection prevention and control,” said study author Meghan Lyman, MD, a CDC epidemiologist in Atlanta, in a statement.
Cases of C. auris continued to rise in 2022, the CDC said. A map on the agency’s website of reported cases from 2022 shows it was found in more than half of U.S. states, with the highest counts occurring in California, Florida, Illinois, Nevada, New York, and Texas. The fungus is a problem worldwide and is listed among the most threatening treatment-resistant fungi by the World Health Organization.
The study authors concluded that screening capacity for the fungus needs to be expanded nationwide so that when C. auris is detected, measures can be taken to prevent its spread.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
After the Match: Next steps for new residents, unmatched
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical school graduates around the US took to social media after last week's Match Day to share their joy ― or explore their options if they did not match.
Take this post March 19 on Twitter: “I went unmatched this year; looking for research position at any institute for internal medicine.”
including an international medical graduate who matched into his chosen specialty after multiple disappointments.
“I’ve waited for this email for 8 years,” Sahil Bawa, MD, posted on Twitter on March 13. A few days later, when he learned about his residency position, he posted: “I’m beyond grateful. Will be moving to Alabama soon #familymedicine.”
Dr. Bawa, who matched into UAB Medicine Selma (Ala.), graduated from medical school in India in 2014. He said in an interview that he has visited the United States periodically since then to pass medical tests, obtain letters of recommendation, and participate in research.
Over the years he watched his Indian colleagues give up on becoming American doctors, find alternative careers, or resolve to practice in their native country. But he held onto the few success stories he saw on social media. “There were always one to two every year. It kept me going. If they can do it, I can do it.”
International medical graduates (IMGs) like Dr. Bawa applied in record numbers to Match2023, according to the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP), which announced the results on March 13 of its main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP) for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
Overall, 48,156 total applicants registered for the match, which was driven by the increase of non-U.S. IMG applicants and U.S. DO seniors over the past year, NRMP stated in its release. U.S. MD seniors had a match rate of nearly 94%, and U.S. DO seniors, nearly 92%. U.S. IMGs had a match rate of nearly 68%, an “all-time high,” and non-U.S. IMGs, nearly 60%, NRMP stated.
Three specialties that filled all of their 30 or more available positions were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), radiology – diagnostic, and thoracic surgery. Specialties with 30 or more positions that filled with the highest percentage of U.S. MD and DO seniors were plastic surgery (integrated), internal medicine-pediatrics, ob.gyn., and orthopedic surgery.
The number of available primary care positions increased slightly, NRMP reported. Considering “a serious and growing shortage of primary care physicians across the U.S.,” there were 571 more primary care positions than 2022. That’s an increase of about 3% over last year and 17% over the past 5 years. Primary care positions filled at a rate of 94%, which remained steady from 2022.
NRMP also pointed out specialties with increases in the number of positions filled by U.S. MD seniors of more than 10% and 10 positions in the past 5 years: anesthesiology, child neurology, interventional radiology, neurology, pathology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, plastic surgery (integrated), psychiatry, radiology-diagnostic, transitional year, and vascular surgery.
Bryan Carmody, MD, MPH, a pediatric nephrologist known for his medical school commentaries, said in an interview that the most competitive specialties he noted in 2023 were radiology, pathology, and neurology.
“The surgical specialties are always competitive, so it wasn’t a surprise that orthopedics, plastic surgery, and thoracic surgery filled all of their positions. But I was surprised to see diagnostic radiology fill every single one of their positions in the match. And although pathology and neurology aren’t typically considered extremely competitive specialties, they filled over 99% of their positions in the Match this year.”
On Dr. Carmody’s blog about the winners and losers of Match Day, he said that despite the record number of primary care positions offered, family medicine programs suffered. “Only 89% of family medicine programs filled in the Match, and graduating U.S. MD and DO students only filled a little more than half of all the available positions,” he wrote.
For a record number of applicants that match each year, and “the most favorable ratio in the past 2 decades” of applicants-to-positions in 2023, there are still a lot unmatched, Dr. Carmody said. “It’s a tough thing to talk about. The reality is the number of residency positions should be determined by the number of physicians needed.”
One student, Asim Ansari, didn’t match into a traditional residency or through SOAP. It was his fifth attempt. He was serving a transitional-year residency at Merit Health Wesley in Hattiesburg, Miss., and when he didn’t match, he accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City.
He said he was “relieved and excited” to have found a program in his chosen specialty. Still, in 2 years, Mr. Ansari must again try to match into a traditional psychiatry residency.
Meanwhile, Dr. Bawa will prepare for his 3-year residency in Alabama after completing his interim research year in the surgery department at Wayne State University, Detroit, in May.
Despite his years in limbo, Dr. Bawa said, “I have no regrets, no complaints. I am still very happy.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Old-school printer helps scientists quickly spot bacteria in blood
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When a bacterial infection reaches the bloodstream, every second is critical. The person’s life is on the line. Yet blood tests to identify bacteria take hours to days. While waiting, doctors often prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics in hopes of killing whatever bug may be at fault.
Someday soon, that wait time could shrink significantly, allowing health care providers to more quickly zero in on the best antibiotic for each infection – thanks to an innovation from Stanford (Calif.) University that identifies bacteria in seconds.
The cutting-edge method relies on old-school tech: an inkjet printer similar the kind you might have at home – except this one has been modified to print blood instead of ink.
The very small sample size – each drop is two trillionths of a liter, or about a billion times smaller than a raindrop – make spotting bacteria easier. Smaller samples mean fewer cells, so lab techs can more swiftly separate the bacterial spectra from other components, like red blood cells and white blood cells.
To boost efficiency even more, the researchers added gold nanoparticles, which attach to the bacteria, serving like antennas to focus the light. Machine learning – a type of artificial intelligence – helps interpret the spectrum of light and identify which fingerprint goes with which bacteria.
“It kind of wound up being this really interesting historical period where we could put the pieces together from different technologies, including nanophotonics, printing, and artificial intelligence, to help accelerate identification of bacteria in these complex samples,” says study author Jennifer Dionne, PhD, associate professor of materials science and engineering at Stanford.
Compare that to blood culture testing in hospitals, where it takes days for bacterial cells to grow and multiply inside a large machine that looks like a refrigerator. For some bacteria, like the kinds that cause tuberculosis, cultures take weeks.
Then further testing is needed to identify which antibiotics will quell the infection. The new technology from Stanford could accelerate this process, too.
“The promise of our technique is that you don’t need to have a culture of cells to put the antibiotic on top,” says Dr. Dionne. “What we’re finding is that from the Raman scattering, we can use that to identify – even without incubating with antibiotics – which drug the bacteria would respond to, and that’s really exciting.”
If patients can receive the antibiotic best suited for their infection, they will likely have better outcomes.
“Blood cultures can typically take 48-72 hours to come back, and then you base your clinical decisions and adjusting antibiotics based on those blood cultures,” says Richard Watkins, MD, an infectious disease physician and professor of medicine at the Northeastern Ohio Universities, Rootstown. Dr. Watkins was not involved in the study.
“Sometimes, despite your best guess, you’re wrong,” Dr. Watkins says, “and obviously, the patient could have an adverse outcome. So, if you can diagnose the pathogen sooner, that is ideal. Whatever technology enables clinicians to do that is definitely progress and a step forward.”
On a global scale, this technology could help reduce the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which contributes to antimicrobial resistance, an emerging health threat, says Dr. Dionne.
The team is working to develop the technology further into an instrument the size of a shoebox and, with further testing, commercialize the product. That could take a few years.
This technology has potential beyond bloodstream infections, too. It could be used to identify bacteria in other fluids, such as in wastewater or contaminated food.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID can mimic prostate cancer symptoms
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This patient has a strong likelihood of aggressive prostate cancer, right? If that same patient also presents with severe, burning bone pain with no precipitating trauma to the area and rest and over-the-counter painkillers are not helping, you’d think, “check for metastases,” right?
That patient was me in late January 2023.
As a research scientist member of the American Urological Association, I knew enough to know I had to consult my urologist ASAP.
With the above symptoms, I’ll admit I was scared. Fortunately, if that’s the right word, I was no stranger to a rapid, dramatic spike in PSA. In 2021 I was temporarily living in a new city, and I wanted to form a relationship with a good local urologist. The urologist that I was referred to gave me a thorough consultation, including a vigorous digital rectal exam (DRE) and sent me across the street for a blood draw.
To my shock, my PSA had spiked over 2 points, to 9.9 from 7.8 a few months earlier. I freaked. Had my 3-cm tumor burst out into an aggressive cancer? Research on PubMed provided an array of studies showing what could cause PSA to suddenly rise, including a DRE performed 72 hours before the blood draw.1 A week later, my PSA was back down to its normal 7.6.
But in January 2023, I had none of those previously reported experiences that could suddenly trigger a spike in PSA, like a DRE or riding on a thin bicycle seat for a few hours before the lab visit.
The COVID effect
I went back to PubMed and found a new circumstance that could cause a surge in PSA: COVID-19. A recent study2 of 91 men with benign prostatic hypertrophy by researchers in Turkey found that PSA spiked from 0 to 5 points during the COVID infection period and up to 2 points higher 3 months after the infection had cleared. I had tested positive for COVID-19 in mid-December 2022, 4 weeks before my 9.9 PSA reading.
Using Google translate, I communicated with the team in Turkey and found out that the PSA spike can last up to 6 months.
That study helps explain why my PSA dropped over 1.5 points to 8.5 just 2 weeks after the 9.9 reading, with the expectation that it would return to its previous normal of 7.8 within 6 months of infection with SARS-CoV-2. To be safe, my urologist scheduled another PSA test in May, along with an updated multiparametric MRI, which may be followed by an in-bore MRI-guided biopsy of the 3-cm tumor if the mass has enlarged.
COVID-19 pain
What about my burning bone pain in my upper right humerus and right rotator cuff that was not precipitated by trauma or strain? A radiograph found no evidence of metastasis, thank goodness. And my research showed that several studies3 have found that COVID-19 can cause burning musculoskeletal pain, including enthesopathy, which is what I had per the radiology report. So my PSA spike and searing pain were likely consequences of the infection.
To avoid the risk for a gross misdiagnosis after a radical spike in PSA, the informed urologist should ask the patient if he has had COVID-19 in the previous 6 months. Overlooking that question could lead to the wrong diagnostic decisions about a rapid jump in PSA or unexplained bone pain.
References
1. Bossens MM et al. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:682-5.
2. Cinislioglu AE et al. Urology. 2022;159:16-21.
3. Ciaffi J et al. Joint Bone Spine. 2021;88:105158.
Dr. Keller is founder of the Keller Research Institute, Jacksonville, Fla. He reported serving as a research scientist for the American Urological Association, serving on the advisory board of Active Surveillance Patient’s International, and serving on the boards of numerous nonprofit organizations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Depression tied to inflammation and survival in lung cancer
suggests a new study.
The findings underscore the importance of assessing and treating depression in patients with cancer, particularly given the high rate of depression among those with lung cancer versus other types of cancer, the investigators said.
The study involved 186 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), of whom 35% had self-reported moderate to severe depressive symptoms.
Depression was reliably associated with lung-relevant systemic inflammation responses (SIRs), which included neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) score.
These SIRs were prognostic for 2-year OS.
Overall mortality at 2 years was 61%. Higher NLRs and PLRs and lower ALI scores all predicted worse OS (hazard ratio, 1.91, 2.08, and 0.53, respectively).
The findings were published online in PLoS ONE (2023 Feb 24.
“These patients with high levels of depression are at much higher risk for poor outcomes,” but the key finding was that patients with the highest depression levels were driving the relationship, lead author Barbara Andersen, PhD, professor of psychology at Ohio State University, Columbus, stated in a press release.
“It was patients with high depression levels who had strikingly higher inflammation levels, and that is what really drove the correlation we saw,” she explained.
For example, 56% of patients with no depression symptoms or only mild depression symptoms had a PLR above the cutoff for dangerous levels of inflammation, compared with 42% whose PLR was below the cutoff. However, among those with high depression levels, 77% and 23% had a PLR above and below the cutoff, respectively.
“These highly depressed patients were 1.3-3 times more likely to have high inflammation levels, even after controlling for other factors related to inflammation biomarker levels, including demographics and smoking status,” Dr. Andersen noted.
“Depression levels may be as important or even more important than other factors that have been associated with how people fare with lung cancer,” she suggested.
In a previous study, the team controlled for baseline depression and found that “the trajectory of depression from diagnosis through 2 years (18 assessments) predicted NSCLC patients’ survival (HR, 1.09), above and beyond baseline depression, sociodemographics, smoking status, cell type, and receipt of targeted treatments and immunotherapies.”
“Taken together, data support psychological, behavioral, and biologic toxicities of depression capable of influencing treatment response and/or survival,” they wrote.
“The results may help explain why a substantial portion of lung cancer patients fail to respond to new immunotherapy and targeted treatments that have led to significantly longer survival for many people with the disease,” Dr. Andersen said.
The investigators concluded that “intensive study of depression among patients with NSCLC, combined with measures of cell biology, inflammation, and immunity, is needed to extend these findings and discover their mechanisms, with the long-term aim to improve patients’ quality of life, treatment responses, and longevity.”
This study was funded by the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center and Pelotonia through grants to individual authors. Dr. Andersen reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new study.
The findings underscore the importance of assessing and treating depression in patients with cancer, particularly given the high rate of depression among those with lung cancer versus other types of cancer, the investigators said.
The study involved 186 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), of whom 35% had self-reported moderate to severe depressive symptoms.
Depression was reliably associated with lung-relevant systemic inflammation responses (SIRs), which included neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) score.
These SIRs were prognostic for 2-year OS.
Overall mortality at 2 years was 61%. Higher NLRs and PLRs and lower ALI scores all predicted worse OS (hazard ratio, 1.91, 2.08, and 0.53, respectively).
The findings were published online in PLoS ONE (2023 Feb 24.
“These patients with high levels of depression are at much higher risk for poor outcomes,” but the key finding was that patients with the highest depression levels were driving the relationship, lead author Barbara Andersen, PhD, professor of psychology at Ohio State University, Columbus, stated in a press release.
“It was patients with high depression levels who had strikingly higher inflammation levels, and that is what really drove the correlation we saw,” she explained.
For example, 56% of patients with no depression symptoms or only mild depression symptoms had a PLR above the cutoff for dangerous levels of inflammation, compared with 42% whose PLR was below the cutoff. However, among those with high depression levels, 77% and 23% had a PLR above and below the cutoff, respectively.
“These highly depressed patients were 1.3-3 times more likely to have high inflammation levels, even after controlling for other factors related to inflammation biomarker levels, including demographics and smoking status,” Dr. Andersen noted.
“Depression levels may be as important or even more important than other factors that have been associated with how people fare with lung cancer,” she suggested.
In a previous study, the team controlled for baseline depression and found that “the trajectory of depression from diagnosis through 2 years (18 assessments) predicted NSCLC patients’ survival (HR, 1.09), above and beyond baseline depression, sociodemographics, smoking status, cell type, and receipt of targeted treatments and immunotherapies.”
“Taken together, data support psychological, behavioral, and biologic toxicities of depression capable of influencing treatment response and/or survival,” they wrote.
“The results may help explain why a substantial portion of lung cancer patients fail to respond to new immunotherapy and targeted treatments that have led to significantly longer survival for many people with the disease,” Dr. Andersen said.
The investigators concluded that “intensive study of depression among patients with NSCLC, combined with measures of cell biology, inflammation, and immunity, is needed to extend these findings and discover their mechanisms, with the long-term aim to improve patients’ quality of life, treatment responses, and longevity.”
This study was funded by the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center and Pelotonia through grants to individual authors. Dr. Andersen reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new study.
The findings underscore the importance of assessing and treating depression in patients with cancer, particularly given the high rate of depression among those with lung cancer versus other types of cancer, the investigators said.
The study involved 186 patients with newly diagnosed stage IV non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), of whom 35% had self-reported moderate to severe depressive symptoms.
Depression was reliably associated with lung-relevant systemic inflammation responses (SIRs), which included neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) score.
These SIRs were prognostic for 2-year OS.
Overall mortality at 2 years was 61%. Higher NLRs and PLRs and lower ALI scores all predicted worse OS (hazard ratio, 1.91, 2.08, and 0.53, respectively).
The findings were published online in PLoS ONE (2023 Feb 24.
“These patients with high levels of depression are at much higher risk for poor outcomes,” but the key finding was that patients with the highest depression levels were driving the relationship, lead author Barbara Andersen, PhD, professor of psychology at Ohio State University, Columbus, stated in a press release.
“It was patients with high depression levels who had strikingly higher inflammation levels, and that is what really drove the correlation we saw,” she explained.
For example, 56% of patients with no depression symptoms or only mild depression symptoms had a PLR above the cutoff for dangerous levels of inflammation, compared with 42% whose PLR was below the cutoff. However, among those with high depression levels, 77% and 23% had a PLR above and below the cutoff, respectively.
“These highly depressed patients were 1.3-3 times more likely to have high inflammation levels, even after controlling for other factors related to inflammation biomarker levels, including demographics and smoking status,” Dr. Andersen noted.
“Depression levels may be as important or even more important than other factors that have been associated with how people fare with lung cancer,” she suggested.
In a previous study, the team controlled for baseline depression and found that “the trajectory of depression from diagnosis through 2 years (18 assessments) predicted NSCLC patients’ survival (HR, 1.09), above and beyond baseline depression, sociodemographics, smoking status, cell type, and receipt of targeted treatments and immunotherapies.”
“Taken together, data support psychological, behavioral, and biologic toxicities of depression capable of influencing treatment response and/or survival,” they wrote.
“The results may help explain why a substantial portion of lung cancer patients fail to respond to new immunotherapy and targeted treatments that have led to significantly longer survival for many people with the disease,” Dr. Andersen said.
The investigators concluded that “intensive study of depression among patients with NSCLC, combined with measures of cell biology, inflammation, and immunity, is needed to extend these findings and discover their mechanisms, with the long-term aim to improve patients’ quality of life, treatment responses, and longevity.”
This study was funded by the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center and Pelotonia through grants to individual authors. Dr. Andersen reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PLOS ONE






