User login
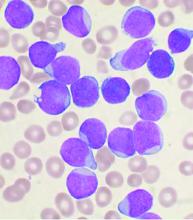
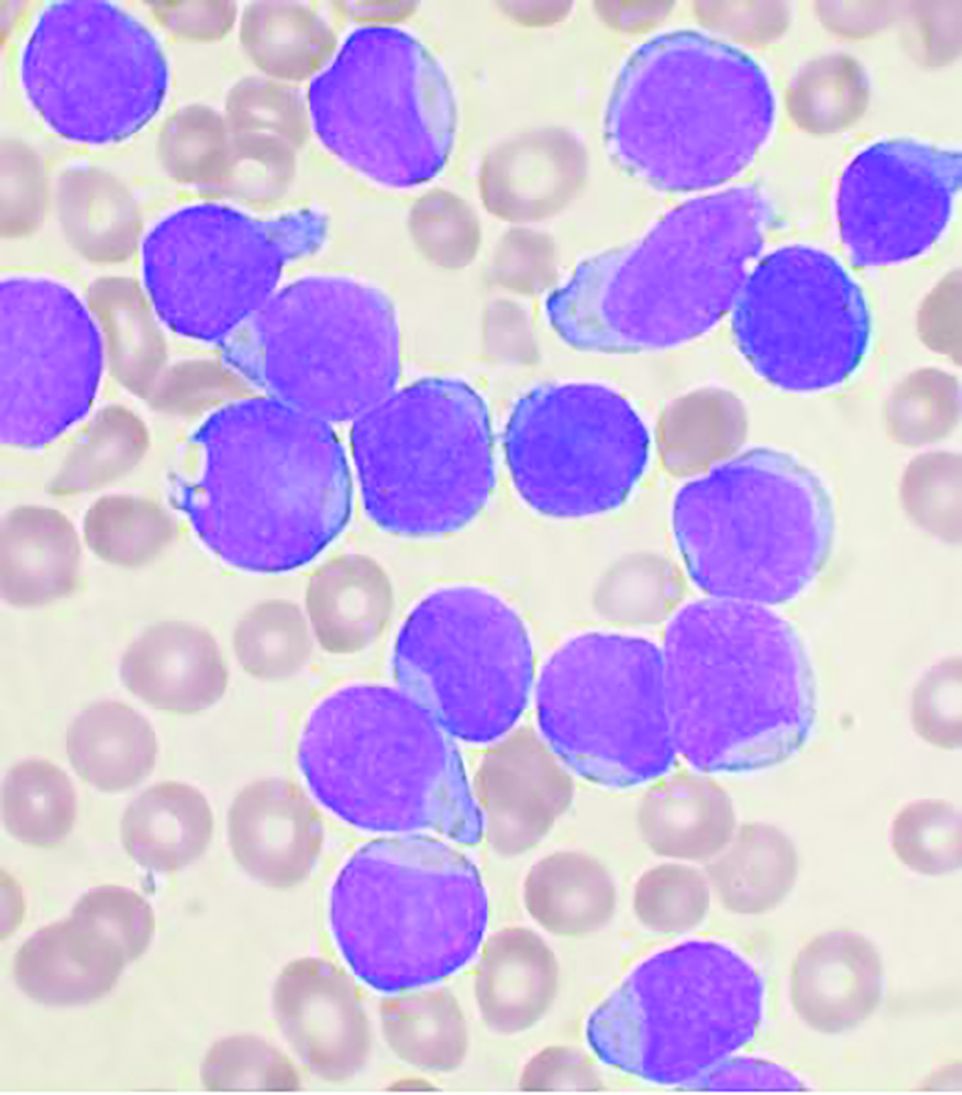
CDC: 20% of people in the U.S. are infected with an STD
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
Among the more than 320 million people in the United States, there was a prevalence estimate of 67.6 million sexually transmitted infections at the time of assessment in 2018, according to the results of an epidemiologic study using multiple data sources, including the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
In addition, almost half of the incident STIs occurred in the 15- to 24-year age bracket, according to a report published online in Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Researchers estimated the combined number of prevalent and incident infections of eight STIs in the United States in 2018: chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, syphilis, genital herpes (caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 [HSV-2]), human papillomavirus (HPV), sexually transmitted hepatitis B virus (HBV), and sexually transmitted HIV.
The estimated incidences of these STIs in this update, the first since 2008, were made using more recent data and improved estimation methods to provide updated STI prevalence and incidence estimates for 2018, both overall and by disease. “Having a combined estimate is crucial for policy purposes to illustrate the importance of STIs in the United States,” according to Kristen M. Kreisel, PhD, an epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, division of STD prevention, and colleagues.
The number of prevalent and incident infections were obtained by multiplying each STI’s updated per capita estimates by the 2018 full resident population estimates from the American Community Survey.
Detailed results
Chlamydia. The prevalence of chlamydia was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. There were an estimated 2.4 million prevalent urogenital chlamydial infections among persons aged 15-39 years in 2018; 1.1 and 1.3 million infections among men and women, respectively. Individuals aged 15-24 years comprised 56.7% and 75.8% of all infections in men and women respectively.
Gonorrhea. The prevalence of gonorrhea was estimated using ordinary differential equation based modeling. The number of prevalent urogenital gonococcal infections in 2018 among 15- to 39-year-olds was 209,000 overall; 50,000 in men and 155,000 in women. Of these, 113,000 (54.1%) occurred in 15- to 24-year-olds.
Trichomoniasis. The prevalence of trichomoniasis was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, which was then used to create a modeled prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. The number of prevalent Trichomonas infections among 15- to 59-year-olds was 2.6 million, with 470,000 in men and 2.1 million in women. Persons aged 15-24 years comprised 15.6% of all prevalent infections, according to the authors.
Syphilis. The number of estimated prevalent syphilitic infections (all stages) among 14- to 49-year-old persons in 2018 was 156,000, with infections in men comprising 71.8% of all infections. Infections in both men and women aged 14-24 years accounted for about 25% of all infections, with 36,000 total prevalent syphilitic infections among 14- to 24-year-olds in 2018.
Genital herpes. The prevalence of genital herpes (caused by HSV-2) was estimated using 2015-2018 NHANES data, according to the authors. In persons aged 15-49 years in 2018, there were 18.6 million prevalent HSV-2 infections; 6.4 million among men and 12.2 million among women. Infections in 15- to 24-year-olds comprised 7.1% of all prevalent HSV-2 infections.
HPV. The prevalence of HPV was estimated using 2013-2016 NHANES data, which was assumed to reflect stable prevalence in 2018, according to the authors. Among 15- to 59-year-olds, the estimated number of persons, men, and women infected with one or more disease-associated HPV types in 2018 was 42.5, 23.4, and 19.2 million, respectively, with an estimated 9.0 million (21%) 15- to 24-year-olds infected,
HBV. NHANES 2013-2018 data were used to estimate the prevalence of sexually transmitted chronic HBV infections in 2018, according to the authors. The estimated number of infections among persons aged 15 years and older in 2018 was 103,000 (51,000 men and 52,000 women). There small sample size of individuals aged 15-24 years in the NHANES database made it impossible to obtain an accurate estimate for this group, according to the authors.
HIV. Data from the National HIV Surveillance System were used to estimate the prevalence and incidence of sexually transmitted HIV infections for persons aged 13 years and older in 2018. A total of 984,000 individuals aged 13 years and older were estimated to be living with sexually transmitted HIV at the end of 2018, according to the authors. Nearly 80% were men. In the 13- to 24-year-old age bracket, there were an estimated 45,400 living with sexually transmitted HIV.
Billions in costs
Commenting on the study by the CDC researchers, Raul Romaguera, acting director for CDC’s division of STD prevention, stated in a press release: “There are significant human and financial costs associated with these infections, and we know from other studies that cuts in STI prevention efforts result in higher costs down the road. Preventing STIs could save billions in medical costs, but more importantly, prevention would improve the health and lives of millions of people.”
“About 20% of the total U.S. population had an STI at a given point in 2018, while nearly half of all incident infections occurred in people aged 15-24 years. Focusing STI prevention efforts on the 15- to 24-year-old population may be key to lowering the STI burden in the U.S.,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no disclosures.
FROM SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
First monthly injectable HIV treatment approved by FDA
Cabenuva (cabotegravir and rilpivirine, a once-per-month injectable formulation) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a complete regimen for treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults. It is intended to replace current antiretroviral regimens in those patients who are virologically suppressed with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either of the two component drugs.
Cabenuva is the first FDA-approved monthly injectable, complete regimen for HIV-infected adults, according to the agency’s announcement.
In addition, the FDA-approved Vocabria (cabotegravir, tablet formulation), a preparatory treatment intended to be taken in combination with oral rilpivirine (Edurant) for 1 month prior to starting treatment with Cabenuva to ensure the medications are well tolerated before switching to the extended-release injectable formulation. The FDA granted the approval of Cabenuva and Vocabria to ViiV Healthcare.
Cabotegravir is as an integrase strand transfer inhibitor that blocks HIV integrase by attaching to the active integrase site and inhibiting retroviral DNA integration, which is necessary in order for HIV to replicate. In contrast, rilpivirine acts as a diarylpyrimidine nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of HIV-1.
Approval of Cabenuva was based upon two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials in 1,182 HIV-infected adults who were virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL) before initiation of treatment with Cabenuva. The two pivotal phase three clinical studies were: Antiretroviral Therapy as Long-Acting Suppression (ATLAS; NCT02951052) and First Long-Acting Injectable Regimen (FLAIR; NCT02938520). Patients in both trials continued to show virologic suppression at the conclusion of each study, and no clinically relevant change from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was observed, according to the FDA announcement.
Adverse reactions with Cabenuva included injection-site reactions, fever, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. The FDA warned that Cabenuva should not be used if there is a known previous hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine, or in patients who are not virally suppressed (HIV-1 RNA greater than 50 copies/mL).
Cabenuva and Vocabria were granted Fast Track and Priority Review designation by the FDA. Prescribing information for Cabenuva is available on the ViiV Healthcare website.
Cabenuva (cabotegravir and rilpivirine, a once-per-month injectable formulation) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a complete regimen for treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults. It is intended to replace current antiretroviral regimens in those patients who are virologically suppressed with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either of the two component drugs.
Cabenuva is the first FDA-approved monthly injectable, complete regimen for HIV-infected adults, according to the agency’s announcement.
In addition, the FDA-approved Vocabria (cabotegravir, tablet formulation), a preparatory treatment intended to be taken in combination with oral rilpivirine (Edurant) for 1 month prior to starting treatment with Cabenuva to ensure the medications are well tolerated before switching to the extended-release injectable formulation. The FDA granted the approval of Cabenuva and Vocabria to ViiV Healthcare.
Cabotegravir is as an integrase strand transfer inhibitor that blocks HIV integrase by attaching to the active integrase site and inhibiting retroviral DNA integration, which is necessary in order for HIV to replicate. In contrast, rilpivirine acts as a diarylpyrimidine nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of HIV-1.
Approval of Cabenuva was based upon two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials in 1,182 HIV-infected adults who were virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL) before initiation of treatment with Cabenuva. The two pivotal phase three clinical studies were: Antiretroviral Therapy as Long-Acting Suppression (ATLAS; NCT02951052) and First Long-Acting Injectable Regimen (FLAIR; NCT02938520). Patients in both trials continued to show virologic suppression at the conclusion of each study, and no clinically relevant change from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was observed, according to the FDA announcement.
Adverse reactions with Cabenuva included injection-site reactions, fever, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. The FDA warned that Cabenuva should not be used if there is a known previous hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine, or in patients who are not virally suppressed (HIV-1 RNA greater than 50 copies/mL).
Cabenuva and Vocabria were granted Fast Track and Priority Review designation by the FDA. Prescribing information for Cabenuva is available on the ViiV Healthcare website.
Cabenuva (cabotegravir and rilpivirine, a once-per-month injectable formulation) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a complete regimen for treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults. It is intended to replace current antiretroviral regimens in those patients who are virologically suppressed with no history of treatment failure and with no known or suspected resistance to either of the two component drugs.
Cabenuva is the first FDA-approved monthly injectable, complete regimen for HIV-infected adults, according to the agency’s announcement.
In addition, the FDA-approved Vocabria (cabotegravir, tablet formulation), a preparatory treatment intended to be taken in combination with oral rilpivirine (Edurant) for 1 month prior to starting treatment with Cabenuva to ensure the medications are well tolerated before switching to the extended-release injectable formulation. The FDA granted the approval of Cabenuva and Vocabria to ViiV Healthcare.
Cabotegravir is as an integrase strand transfer inhibitor that blocks HIV integrase by attaching to the active integrase site and inhibiting retroviral DNA integration, which is necessary in order for HIV to replicate. In contrast, rilpivirine acts as a diarylpyrimidine nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of HIV-1.
Approval of Cabenuva was based upon two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials in 1,182 HIV-infected adults who were virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies/mL) before initiation of treatment with Cabenuva. The two pivotal phase three clinical studies were: Antiretroviral Therapy as Long-Acting Suppression (ATLAS; NCT02951052) and First Long-Acting Injectable Regimen (FLAIR; NCT02938520). Patients in both trials continued to show virologic suppression at the conclusion of each study, and no clinically relevant change from baseline in CD4+ cell counts was observed, according to the FDA announcement.
Adverse reactions with Cabenuva included injection-site reactions, fever, fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, sleep disorders, dizziness, and rash. The FDA warned that Cabenuva should not be used if there is a known previous hypersensitivity reaction to cabotegravir or rilpivirine, or in patients who are not virally suppressed (HIV-1 RNA greater than 50 copies/mL).
Cabenuva and Vocabria were granted Fast Track and Priority Review designation by the FDA. Prescribing information for Cabenuva is available on the ViiV Healthcare website.
NEWS FROM THE FDA
Global Ebola vaccine stockpile established
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
The International Coordinating Group (ICG) on Vaccine Provision announced the establishment of a global Ebola vaccine stockpile initiative.
The ICG, which was established in 1997, is made up of the World Health Organization, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and Médecins Sans Frontières.
The stockpile was created in order to make the single-dose Ebola vaccine (rVSV∆G-ZEBOV-GP, live; trade name Everbo) rapidly available at the start of the next Ebola outbreak anywhere in the world. The vaccine was developed and is marketed by Merck Sharp & Dohme, with financial support from the United States.
The stockpile, which is maintained in Switzerland and managed by UNICEF, is designed to be readily deployed to other countries whenever there is an outbreak. The ICG will be the decision-making body for the vaccine’s allocation and release, as is also the case with previously created stockpiles of cholera, meningitis, and yellow fever vaccines.
“The decision to allocate the vaccine will be made within 48 hours of receiving a request from a country; vaccines will be made available together with ultra-cold chain packaging by the manufacturer for shipment to countries within 48 hours of the decision. The targeted overall delivery time from the stockpile to countries is 7 days,” according to the WHO press release.
Currently 6,890 doses are available for outbreak response, with further quantities to be delivered into the stockpile throughout 2021 and beyond. Initial use of the vaccine will be directed to health care and frontline workers. It is expected that it will take 2-3 years to reach the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization–recommended level of 500,000 doses for the stockpile of Ebola vaccines.
Allo-HSCT improves disease-free, but not overall survival in adults with ALL, compared with ped-inspired chemo
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (AHSCT) improved disease-free survival (DFS), compared with pediatric-inspired Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM-95) chemotherapy in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to the results of retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. However, overall survival (OS) was not significantly different between the two groups, as reported by Elifcan Aladag, MD, of the Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey, and colleagues.
Despite this, “AHSCT is recommended for all patients with suitable donors, but the risk of transplant-related mortality should be kept in mind,” according to the researchers.
The multicenter study compared two different treatment approaches (BFM-95 chemotherapy regimen and AHSCT). The BFM-95 chemotherapy group comprised 47 newly diagnosed ALL patients. The transplant cohort comprised 83 patients with ALL in first complete remission who received AHSCT from fully matched human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical siblings. Thirty-five of the AHSCT patients (42.1%) received chemotherapy at least until the M stage of the BFM-95 protocol.
The primary endpoints of the study were OS and duration of DFS. OS was defined from the day of starting BFM-95 chemotherapy until death from any cause, and DFS was calculated from the date of complete remission until the date of first relapse or death from any cause, whichever occurred first, according to the authors.
Study results
The median OS was 68 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 46 months in patients treated only with BFM-95 (P = .3). Two- and 5-year OS rates were 78% and 60% , respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 69% and 64% in the BFM-95 group (P = .06 and .13, respectively).
The median DFS was 36.6 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 28 months in patients treated with BFM-95 (P = .033). Two- and 5-year DFS rates were 68.5% and 57%, respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 63% and 38% respectively, in the BFM-95 group (P = .12 and .029, respectively).
Mortality in the BFM-95 group was the result of sepsis due to infections (fungal infection in two patients, resistant bacterial infections in four patients). In the AHSCT group, respectively, three and seven patients died of graft-versus-host disease and bacterial infections (with fungal infections in four patients and resistant bacterial infections in three patients), according to the researchers.
“In our study, no 2-year OS and DFS difference was observed in any treatment group; however, a significant difference occurred in 5-year DFS in favor of AHSCT. This may be due to transplant-related mortality in the first 2 years, which led to no statistically significant difference,” the authors stated.
“In order to further elucidate the role of AHSCT when pediatric-derived regimens are used for the treatment of adult lymphoblastic leukemia, higher-powered randomized prospective studies are needed,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (AHSCT) improved disease-free survival (DFS), compared with pediatric-inspired Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM-95) chemotherapy in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to the results of retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. However, overall survival (OS) was not significantly different between the two groups, as reported by Elifcan Aladag, MD, of the Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey, and colleagues.
Despite this, “AHSCT is recommended for all patients with suitable donors, but the risk of transplant-related mortality should be kept in mind,” according to the researchers.
The multicenter study compared two different treatment approaches (BFM-95 chemotherapy regimen and AHSCT). The BFM-95 chemotherapy group comprised 47 newly diagnosed ALL patients. The transplant cohort comprised 83 patients with ALL in first complete remission who received AHSCT from fully matched human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical siblings. Thirty-five of the AHSCT patients (42.1%) received chemotherapy at least until the M stage of the BFM-95 protocol.
The primary endpoints of the study were OS and duration of DFS. OS was defined from the day of starting BFM-95 chemotherapy until death from any cause, and DFS was calculated from the date of complete remission until the date of first relapse or death from any cause, whichever occurred first, according to the authors.
Study results
The median OS was 68 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 46 months in patients treated only with BFM-95 (P = .3). Two- and 5-year OS rates were 78% and 60% , respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 69% and 64% in the BFM-95 group (P = .06 and .13, respectively).
The median DFS was 36.6 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 28 months in patients treated with BFM-95 (P = .033). Two- and 5-year DFS rates were 68.5% and 57%, respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 63% and 38% respectively, in the BFM-95 group (P = .12 and .029, respectively).
Mortality in the BFM-95 group was the result of sepsis due to infections (fungal infection in two patients, resistant bacterial infections in four patients). In the AHSCT group, respectively, three and seven patients died of graft-versus-host disease and bacterial infections (with fungal infections in four patients and resistant bacterial infections in three patients), according to the researchers.
“In our study, no 2-year OS and DFS difference was observed in any treatment group; however, a significant difference occurred in 5-year DFS in favor of AHSCT. This may be due to transplant-related mortality in the first 2 years, which led to no statistically significant difference,” the authors stated.
“In order to further elucidate the role of AHSCT when pediatric-derived regimens are used for the treatment of adult lymphoblastic leukemia, higher-powered randomized prospective studies are needed,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (AHSCT) improved disease-free survival (DFS), compared with pediatric-inspired Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM-95) chemotherapy in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to the results of retrospective study published in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia. However, overall survival (OS) was not significantly different between the two groups, as reported by Elifcan Aladag, MD, of the Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine, Ankara, Turkey, and colleagues.
Despite this, “AHSCT is recommended for all patients with suitable donors, but the risk of transplant-related mortality should be kept in mind,” according to the researchers.
The multicenter study compared two different treatment approaches (BFM-95 chemotherapy regimen and AHSCT). The BFM-95 chemotherapy group comprised 47 newly diagnosed ALL patients. The transplant cohort comprised 83 patients with ALL in first complete remission who received AHSCT from fully matched human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical siblings. Thirty-five of the AHSCT patients (42.1%) received chemotherapy at least until the M stage of the BFM-95 protocol.
The primary endpoints of the study were OS and duration of DFS. OS was defined from the day of starting BFM-95 chemotherapy until death from any cause, and DFS was calculated from the date of complete remission until the date of first relapse or death from any cause, whichever occurred first, according to the authors.
Study results
The median OS was 68 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 46 months in patients treated only with BFM-95 (P = .3). Two- and 5-year OS rates were 78% and 60% , respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 69% and 64% in the BFM-95 group (P = .06 and .13, respectively).
The median DFS was 36.6 months in patients who underwent AHSCT and 28 months in patients treated with BFM-95 (P = .033). Two- and 5-year DFS rates were 68.5% and 57%, respectively, in the AHSCT group, and 63% and 38% respectively, in the BFM-95 group (P = .12 and .029, respectively).
Mortality in the BFM-95 group was the result of sepsis due to infections (fungal infection in two patients, resistant bacterial infections in four patients). In the AHSCT group, respectively, three and seven patients died of graft-versus-host disease and bacterial infections (with fungal infections in four patients and resistant bacterial infections in three patients), according to the researchers.
“In our study, no 2-year OS and DFS difference was observed in any treatment group; however, a significant difference occurred in 5-year DFS in favor of AHSCT. This may be due to transplant-related mortality in the first 2 years, which led to no statistically significant difference,” the authors stated.
“In order to further elucidate the role of AHSCT when pediatric-derived regimens are used for the treatment of adult lymphoblastic leukemia, higher-powered randomized prospective studies are needed,” they concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Eliminating hepatitis by 2030: HHS releases new strategic plan
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
Eliminating hepatitis by 2030: HHS releases new strategic plan
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
In an effort to counteract alarming trends in rising hepatitis infections, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has developed and released its Viral Hepatitis National Strategic Plan 2021-2025, which aims to eliminate viral hepatitis infection in the United States by 2030.
An estimated 3.3 million people in the United States were chronically infected with hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) as of 2016. In addition, the country “is currently facing unprecedented hepatitis A (HAV) outbreaks, while progress in preventing hepatitis B has stalled, and hepatitis C rates nearly tripled from 2011 to 2018,” according to the HHS.
The new plan, “A Roadmap to Elimination for the United States,” builds upon previous initiatives the HHS has made to tackle the diseases and was coordinated by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health through the Office of Infectious Disease and HIV/AIDS Policy.
The plan focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, which have the largest impact on the health of the nation, according to the HHS. The plan addresses populations with the highest burden of viral hepatitis based on nationwide data so that resources can be focused there to achieve the greatest impact. Persons who inject drugs are a priority population for all three hepatitis viruses. HAV efforts will also include a focus on the homeless population. HBV efforts will also focus on Asian and Pacific Islander and the Black, non-Hispanic populations, while HCV efforts will include a focus on Black, non-Hispanic people, people born during 1945-1965, people with HIV, and the American Indian/Alaska Native population.
Goal-setting
There are five main goals outlined in the plan, according to the HHS:
- Prevent new hepatitis infections.
- Improve hepatitis-related health outcomes of people with viral hepatitis.
- Reduce hepatitis-related disparities and health inequities.
- Improve hepatitis surveillance and data use.
- Achieve integrated, coordinated efforts that address the viral hepatitis epidemics among all partners and stakeholders.
“The United States will be a place where new viral hepatitis infections are prevented, every person knows their status, and every person with viral hepatitis has high-quality health care and treatment and lives free from stigma and discrimination. This vision includes all people, regardless of age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, ethnicity, religion, disability, geographic location, or socioeconomic circumstance,” according to the HHS vision statement.
NEWS FROM HHS
Mortality risks rise with age, infections, but not inhibitor status in persons with non-severe hemophilia A
However, even though inhibitors, which can develop from factor VIII (FVIII) hemophilia therapy, were detected at an earlier age than previously reported, their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality according to the report published in Blood Advances (2020;4[19]:4739-47).
The researchers assessed 6,624 individuals born between 1920 and 2018 (5,694 [86.0%] men and 930 women) with NSHA from the ATHNdataset, according to Ming Y. Lim, MBBCH, MS, of the division of hematology and hematologic malignancies, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
Demographically, the proportion of Black participants in the ATHNdataset was lower at 8.2%, than the 11.6% found in U.S. hemophilia population as a whole. A total of 77.3% (n = 5,122) had documented exposure to FVIII concentrates, 8.4% (n = 555) had no documented exposure, and information was unknown for the remaining 14.3%.
Causes of mortality
The researchers found that inhibitors occurred at an early age of 13 years with a prevalence of 2.6%, compared with the commonly reported median age of about 30 years for inhibitor development, but their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality, according to the authors. Instead, they found that mortality rates in the NSHA cohort were influenced by age, male sex, and hepatitis C and HIV infections.
The researchers speculated that the earlier age of inhibitor development may be due to the fact of the increased availability of FVIII concentrates over time, and that they may have been used more often from 2010 to 2018, compared with previously reported INSIGHT study (1980-2011).
In a multivariable analysis, men with NSHA were found to have 2.6 times the risk of death. Mortality risk increased twofold with each additional decade of age. Persons with hepatitis C had twice the risk of death and persons with HIV had almost four times the risk, compared with persons without these conditions.
The most common primary cause of death was malignancy (20.0%). The observed number of deaths from liver disease in the NSHA cohort was almost five times the expected death rate at 14%. Hemophilia-related deaths were 5.9%.
“Continued monitoring of persons with NSHA by comprehensive care visits at HTC should occur annually to address hemophilia-related issues and other age-related comorbidities, in collaboration with the primary care physician and other subspecialists. Importantly, we found that in the NSHA cohort, the development of inhibitors occurred at an earlier age than previously reported. This highlights the importance of routine monitoring for inhibitors in the NSHA population, regardless of age, especially if they have recently received intense factor replacement therapy,” the researchers concluded.
Ms. Lim reported no conflicts. Other authors reported research and consulting funding from a variety of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Lim MY et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(19):4739-47.
However, even though inhibitors, which can develop from factor VIII (FVIII) hemophilia therapy, were detected at an earlier age than previously reported, their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality according to the report published in Blood Advances (2020;4[19]:4739-47).
The researchers assessed 6,624 individuals born between 1920 and 2018 (5,694 [86.0%] men and 930 women) with NSHA from the ATHNdataset, according to Ming Y. Lim, MBBCH, MS, of the division of hematology and hematologic malignancies, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
Demographically, the proportion of Black participants in the ATHNdataset was lower at 8.2%, than the 11.6% found in U.S. hemophilia population as a whole. A total of 77.3% (n = 5,122) had documented exposure to FVIII concentrates, 8.4% (n = 555) had no documented exposure, and information was unknown for the remaining 14.3%.
Causes of mortality
The researchers found that inhibitors occurred at an early age of 13 years with a prevalence of 2.6%, compared with the commonly reported median age of about 30 years for inhibitor development, but their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality, according to the authors. Instead, they found that mortality rates in the NSHA cohort were influenced by age, male sex, and hepatitis C and HIV infections.
The researchers speculated that the earlier age of inhibitor development may be due to the fact of the increased availability of FVIII concentrates over time, and that they may have been used more often from 2010 to 2018, compared with previously reported INSIGHT study (1980-2011).
In a multivariable analysis, men with NSHA were found to have 2.6 times the risk of death. Mortality risk increased twofold with each additional decade of age. Persons with hepatitis C had twice the risk of death and persons with HIV had almost four times the risk, compared with persons without these conditions.
The most common primary cause of death was malignancy (20.0%). The observed number of deaths from liver disease in the NSHA cohort was almost five times the expected death rate at 14%. Hemophilia-related deaths were 5.9%.
“Continued monitoring of persons with NSHA by comprehensive care visits at HTC should occur annually to address hemophilia-related issues and other age-related comorbidities, in collaboration with the primary care physician and other subspecialists. Importantly, we found that in the NSHA cohort, the development of inhibitors occurred at an earlier age than previously reported. This highlights the importance of routine monitoring for inhibitors in the NSHA population, regardless of age, especially if they have recently received intense factor replacement therapy,” the researchers concluded.
Ms. Lim reported no conflicts. Other authors reported research and consulting funding from a variety of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Lim MY et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(19):4739-47.
However, even though inhibitors, which can develop from factor VIII (FVIII) hemophilia therapy, were detected at an earlier age than previously reported, their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality according to the report published in Blood Advances (2020;4[19]:4739-47).
The researchers assessed 6,624 individuals born between 1920 and 2018 (5,694 [86.0%] men and 930 women) with NSHA from the ATHNdataset, according to Ming Y. Lim, MBBCH, MS, of the division of hematology and hematologic malignancies, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues.
Demographically, the proportion of Black participants in the ATHNdataset was lower at 8.2%, than the 11.6% found in U.S. hemophilia population as a whole. A total of 77.3% (n = 5,122) had documented exposure to FVIII concentrates, 8.4% (n = 555) had no documented exposure, and information was unknown for the remaining 14.3%.
Causes of mortality
The researchers found that inhibitors occurred at an early age of 13 years with a prevalence of 2.6%, compared with the commonly reported median age of about 30 years for inhibitor development, but their presence was not associated with an increased risk of mortality, according to the authors. Instead, they found that mortality rates in the NSHA cohort were influenced by age, male sex, and hepatitis C and HIV infections.
The researchers speculated that the earlier age of inhibitor development may be due to the fact of the increased availability of FVIII concentrates over time, and that they may have been used more often from 2010 to 2018, compared with previously reported INSIGHT study (1980-2011).
In a multivariable analysis, men with NSHA were found to have 2.6 times the risk of death. Mortality risk increased twofold with each additional decade of age. Persons with hepatitis C had twice the risk of death and persons with HIV had almost four times the risk, compared with persons without these conditions.
The most common primary cause of death was malignancy (20.0%). The observed number of deaths from liver disease in the NSHA cohort was almost five times the expected death rate at 14%. Hemophilia-related deaths were 5.9%.
“Continued monitoring of persons with NSHA by comprehensive care visits at HTC should occur annually to address hemophilia-related issues and other age-related comorbidities, in collaboration with the primary care physician and other subspecialists. Importantly, we found that in the NSHA cohort, the development of inhibitors occurred at an earlier age than previously reported. This highlights the importance of routine monitoring for inhibitors in the NSHA population, regardless of age, especially if they have recently received intense factor replacement therapy,” the researchers concluded.
Ms. Lim reported no conflicts. Other authors reported research and consulting funding from a variety of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
SOURCE: Lim MY et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(19):4739-47.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Study shows no link between race and mortality in clear cell RCC
The issue of race and survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has been debated in the literature.
Some studies have shown worse survival for Black patients, while others have suggested that Black race is instead a stand-in for social determinants, including access to care.
New research suggests that Black race is not correlated with increased mortality from ccRCC. These results were published in Urology.
“Despite well documented racial biases and race-specific outcomes in the health care landscape, our study found race was not associated with 5-year cause-specific survival from ccRCC,” wrote investigator Dhaval Jivanji, a medical student at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues.
In their retrospective study, the investigators examined 5-year survival in ccRCC patients, comparing results across races. The team used data from the Surveillance Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, which collects cancer data from 13 states using population-based cancer registries. They extracted data on demographics, prevalence, and mortality, in relation to ccRCC.
A total of 8,421 subjects with ccRCC were included in the analysis, which covered the years 2007-2015. The primary outcome was 5-year survival, defined as cause-specific mortality up to the first 60 months from time of cancer diagnosis.
In addition to race, variables included in the statistical model were age (18-50, 51-60, 61-70,71-80, >80), sex (male/female), SEER Summary tumor staging (localized, regionalized, distant), insurance status (uninsured, insured, insured not specific, Medicaid), and marital status (single, married/partner, separated/divorced/widowed).
Demographic determinism
In the adjusted analysis, the researchers found no association between race and 5-year cause-specific survival in patients with ccRCC.
The hazard ratios for death were 0.96 for Black patients, 1.01 for American Indian/Alaska Native patients, and 0.99 for Asian/Pacific Islander patients, with White patients as the comparator.
In terms of the other covariates studied, the researchers found that older age (>50 years) and the presence of regional or distant tumors were associated with an increased hazard of death, while female sex and having insurance were associated with a decreased hazard of death.
“Our study found that age, tumor stage, and insurance status are significantly associated with 5-year cause-specific survival. Future studies will benefit from complete assessment of other demographic factors, including income, medical comorbidities, and access to care. These are negative predictors, and [their] potential impact on overall survival should be considered by the clinician in treatment and management plans for RCC patients,” the researchers concluded.
In an editorial commentary published within the main article, Paul Russo, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, stated: “Investigations such as this utilizing the SEER registries provide a 30,000-foot demographic view of some disease elements but lack important granularity, such as tumor size and grade, family income, critical medical comorbidities, and patient access to hospitals with surgical and medical oncologic expertise.”
Dr. Russo said it is well known that disparate access to diagnosis, surgical intervention, and expert treatment have an impact on survival.
He went on to ask: “Could African Americans have had superior outcomes if the data was controlled for these important variables? As urologic surgeons, we must join the greater medical community in understanding the root causes leading to structural racial and economic disparities, inequities in access to care, and the profound negative impact these disparities have on health outcomes in general and cancer outcomes specifically.”
The authors did not disclose funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jivanji D et al. Urology. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.10.055.
The issue of race and survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has been debated in the literature.
Some studies have shown worse survival for Black patients, while others have suggested that Black race is instead a stand-in for social determinants, including access to care.
New research suggests that Black race is not correlated with increased mortality from ccRCC. These results were published in Urology.
“Despite well documented racial biases and race-specific outcomes in the health care landscape, our study found race was not associated with 5-year cause-specific survival from ccRCC,” wrote investigator Dhaval Jivanji, a medical student at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues.
In their retrospective study, the investigators examined 5-year survival in ccRCC patients, comparing results across races. The team used data from the Surveillance Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, which collects cancer data from 13 states using population-based cancer registries. They extracted data on demographics, prevalence, and mortality, in relation to ccRCC.
A total of 8,421 subjects with ccRCC were included in the analysis, which covered the years 2007-2015. The primary outcome was 5-year survival, defined as cause-specific mortality up to the first 60 months from time of cancer diagnosis.
In addition to race, variables included in the statistical model were age (18-50, 51-60, 61-70,71-80, >80), sex (male/female), SEER Summary tumor staging (localized, regionalized, distant), insurance status (uninsured, insured, insured not specific, Medicaid), and marital status (single, married/partner, separated/divorced/widowed).
Demographic determinism
In the adjusted analysis, the researchers found no association between race and 5-year cause-specific survival in patients with ccRCC.
The hazard ratios for death were 0.96 for Black patients, 1.01 for American Indian/Alaska Native patients, and 0.99 for Asian/Pacific Islander patients, with White patients as the comparator.
In terms of the other covariates studied, the researchers found that older age (>50 years) and the presence of regional or distant tumors were associated with an increased hazard of death, while female sex and having insurance were associated with a decreased hazard of death.
“Our study found that age, tumor stage, and insurance status are significantly associated with 5-year cause-specific survival. Future studies will benefit from complete assessment of other demographic factors, including income, medical comorbidities, and access to care. These are negative predictors, and [their] potential impact on overall survival should be considered by the clinician in treatment and management plans for RCC patients,” the researchers concluded.
In an editorial commentary published within the main article, Paul Russo, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, stated: “Investigations such as this utilizing the SEER registries provide a 30,000-foot demographic view of some disease elements but lack important granularity, such as tumor size and grade, family income, critical medical comorbidities, and patient access to hospitals with surgical and medical oncologic expertise.”
Dr. Russo said it is well known that disparate access to diagnosis, surgical intervention, and expert treatment have an impact on survival.
He went on to ask: “Could African Americans have had superior outcomes if the data was controlled for these important variables? As urologic surgeons, we must join the greater medical community in understanding the root causes leading to structural racial and economic disparities, inequities in access to care, and the profound negative impact these disparities have on health outcomes in general and cancer outcomes specifically.”
The authors did not disclose funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jivanji D et al. Urology. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.10.055.
The issue of race and survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) has been debated in the literature.
Some studies have shown worse survival for Black patients, while others have suggested that Black race is instead a stand-in for social determinants, including access to care.
New research suggests that Black race is not correlated with increased mortality from ccRCC. These results were published in Urology.
“Despite well documented racial biases and race-specific outcomes in the health care landscape, our study found race was not associated with 5-year cause-specific survival from ccRCC,” wrote investigator Dhaval Jivanji, a medical student at Florida International University, Miami, and colleagues.
In their retrospective study, the investigators examined 5-year survival in ccRCC patients, comparing results across races. The team used data from the Surveillance Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database, which collects cancer data from 13 states using population-based cancer registries. They extracted data on demographics, prevalence, and mortality, in relation to ccRCC.
A total of 8,421 subjects with ccRCC were included in the analysis, which covered the years 2007-2015. The primary outcome was 5-year survival, defined as cause-specific mortality up to the first 60 months from time of cancer diagnosis.
In addition to race, variables included in the statistical model were age (18-50, 51-60, 61-70,71-80, >80), sex (male/female), SEER Summary tumor staging (localized, regionalized, distant), insurance status (uninsured, insured, insured not specific, Medicaid), and marital status (single, married/partner, separated/divorced/widowed).
Demographic determinism
In the adjusted analysis, the researchers found no association between race and 5-year cause-specific survival in patients with ccRCC.
The hazard ratios for death were 0.96 for Black patients, 1.01 for American Indian/Alaska Native patients, and 0.99 for Asian/Pacific Islander patients, with White patients as the comparator.
In terms of the other covariates studied, the researchers found that older age (>50 years) and the presence of regional or distant tumors were associated with an increased hazard of death, while female sex and having insurance were associated with a decreased hazard of death.
“Our study found that age, tumor stage, and insurance status are significantly associated with 5-year cause-specific survival. Future studies will benefit from complete assessment of other demographic factors, including income, medical comorbidities, and access to care. These are negative predictors, and [their] potential impact on overall survival should be considered by the clinician in treatment and management plans for RCC patients,” the researchers concluded.
In an editorial commentary published within the main article, Paul Russo, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, stated: “Investigations such as this utilizing the SEER registries provide a 30,000-foot demographic view of some disease elements but lack important granularity, such as tumor size and grade, family income, critical medical comorbidities, and patient access to hospitals with surgical and medical oncologic expertise.”
Dr. Russo said it is well known that disparate access to diagnosis, surgical intervention, and expert treatment have an impact on survival.
He went on to ask: “Could African Americans have had superior outcomes if the data was controlled for these important variables? As urologic surgeons, we must join the greater medical community in understanding the root causes leading to structural racial and economic disparities, inequities in access to care, and the profound negative impact these disparities have on health outcomes in general and cancer outcomes specifically.”
The authors did not disclose funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jivanji D et al. Urology. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.10.055.
FROM UROLOGY
‘Excellent short-term outcomes’ seen in HCV+ liver transplants to HCV– recipients
Liver transplantation using hepatitis C virus (HCV)-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in “excellent short-term outcomes,” according to the results of a prospective, multicenter study reported in the Journal of Hepatology.
A total of 34 HCV– liver transplantation recipients received grafts from HCV+ donors (20 HCV viremic and 14 nonviremic) from January 2018 to September 2019, according to Bashar Aqel, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz., and colleagues.
Seven of the grafts were obtained from donation after cardiac death (DCD). Six recipients underwent simultaneous liver/kidney (SLK) transplant, and four patients were repeat liver transplants.
Sustained viral response
None of the recipients of an HCV nonviremic graft developed HCV viremia. However, all 20 patients who received HCV viremic grafts had HCV viremia confirmed within 3 days after liver transplant. Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment was started at the median time of 27.5 days in these patients.
All 20 patients successfully completed the treatment and achieved a sustained viral response. In addition, the DAA treatment was well tolerated with minimal adverse events, according to the researchers.
However, one patient died, having developed HCV-related acute membranous nephropathy that resulted in end-stage kidney disease. In addition, a recipient of an HCV nonviremic graft died with acute myocardial infarction 610 days post liver transplant, the authors reported.
“This multicenter study demonstrated LT [liver transplantation] using HCV-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in acceptable short-term outcomes even with the use of DCD grafts and expansion into SLK or repeat LT. However, a careful ongoing assessment regarding patient and graft selection, complications, and the timing of treatment is required,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded in part by the McIver Estate Young Investigator Benefactor Award. The authors reported they had no potential conflicts.
SOURCE: Aqel B et al. J Hepatol. 2020, Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.005.
Liver transplantation using hepatitis C virus (HCV)-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in “excellent short-term outcomes,” according to the results of a prospective, multicenter study reported in the Journal of Hepatology.
A total of 34 HCV– liver transplantation recipients received grafts from HCV+ donors (20 HCV viremic and 14 nonviremic) from January 2018 to September 2019, according to Bashar Aqel, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz., and colleagues.
Seven of the grafts were obtained from donation after cardiac death (DCD). Six recipients underwent simultaneous liver/kidney (SLK) transplant, and four patients were repeat liver transplants.
Sustained viral response
None of the recipients of an HCV nonviremic graft developed HCV viremia. However, all 20 patients who received HCV viremic grafts had HCV viremia confirmed within 3 days after liver transplant. Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment was started at the median time of 27.5 days in these patients.
All 20 patients successfully completed the treatment and achieved a sustained viral response. In addition, the DAA treatment was well tolerated with minimal adverse events, according to the researchers.
However, one patient died, having developed HCV-related acute membranous nephropathy that resulted in end-stage kidney disease. In addition, a recipient of an HCV nonviremic graft died with acute myocardial infarction 610 days post liver transplant, the authors reported.
“This multicenter study demonstrated LT [liver transplantation] using HCV-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in acceptable short-term outcomes even with the use of DCD grafts and expansion into SLK or repeat LT. However, a careful ongoing assessment regarding patient and graft selection, complications, and the timing of treatment is required,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded in part by the McIver Estate Young Investigator Benefactor Award. The authors reported they had no potential conflicts.
SOURCE: Aqel B et al. J Hepatol. 2020, Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.005.
Liver transplantation using hepatitis C virus (HCV)-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in “excellent short-term outcomes,” according to the results of a prospective, multicenter study reported in the Journal of Hepatology.
A total of 34 HCV– liver transplantation recipients received grafts from HCV+ donors (20 HCV viremic and 14 nonviremic) from January 2018 to September 2019, according to Bashar Aqel, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, Ariz., and colleagues.
Seven of the grafts were obtained from donation after cardiac death (DCD). Six recipients underwent simultaneous liver/kidney (SLK) transplant, and four patients were repeat liver transplants.
Sustained viral response
None of the recipients of an HCV nonviremic graft developed HCV viremia. However, all 20 patients who received HCV viremic grafts had HCV viremia confirmed within 3 days after liver transplant. Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment was started at the median time of 27.5 days in these patients.
All 20 patients successfully completed the treatment and achieved a sustained viral response. In addition, the DAA treatment was well tolerated with minimal adverse events, according to the researchers.
However, one patient died, having developed HCV-related acute membranous nephropathy that resulted in end-stage kidney disease. In addition, a recipient of an HCV nonviremic graft died with acute myocardial infarction 610 days post liver transplant, the authors reported.
“This multicenter study demonstrated LT [liver transplantation] using HCV-seropositive grafts to HCV-seronegative recipients resulted in acceptable short-term outcomes even with the use of DCD grafts and expansion into SLK or repeat LT. However, a careful ongoing assessment regarding patient and graft selection, complications, and the timing of treatment is required,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded in part by the McIver Estate Young Investigator Benefactor Award. The authors reported they had no potential conflicts.
SOURCE: Aqel B et al. J Hepatol. 2020, Nov 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.005.
FROM JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY
Circulating miRNA could be a potential biomarker for early diagnosis of MM
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) could be a potential noninvasive biomarker for early diagnosis of multiple myeloma (MM), according to the results of a meta-analysis published online in the Journal of Bone Oncology.
In recent years, because of the rise of the miRNA technique, many scholars have studied its value in the diagnosis of MM, and have obtained good but inconsistent results, according to Shuai-Shuai Gao, of the Xi’an (China) Daxing Hospital, and colleagues. For this reason, they conducted the meta-analysis in order to more clearly determine the role of miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM. The meta-analysis ultimately assessed 32 studies from 15 articles comprising 2,053 MM patients and 1,118 healthy controls.
All the included studies involved newly diagnosed MM patients and healthy controls; the obtained miRNA was derived from serum or plasma specimens; and the report contained relevant statistics such as sensitivity, specificity, and area-under-the-curve values.
High sensitivity and specificity
The researchers found that the overall sensitivity and specificity of using miRNAs for the diagnosis of MM were 0.81 and 0.85, respectively. In addition, the overall positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve were 5.5, 0.22, 25 and 0.90, respectively.
A subgroup analysis showed that the down-regulation of miRNA clusters with larger samples size of plasma type could carry out a better diagnostic accuracy of MM patients, according to the authors.
“[Circulating miRNAs] not only had high sensitivity and strong specificity, but also had noninvasive and no radiation risks. It is worth continuing to optimize its practicality. In the future, multicenter, more rigorous, and high-quality case-control studies are still needed in clinical practice to improve the efficacy of circulating miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM,” the researchers concluded.
The study did not receive any outside funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Gao S-S et al. J Bone Oncol. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2020.100327.
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) could be a potential noninvasive biomarker for early diagnosis of multiple myeloma (MM), according to the results of a meta-analysis published online in the Journal of Bone Oncology.
In recent years, because of the rise of the miRNA technique, many scholars have studied its value in the diagnosis of MM, and have obtained good but inconsistent results, according to Shuai-Shuai Gao, of the Xi’an (China) Daxing Hospital, and colleagues. For this reason, they conducted the meta-analysis in order to more clearly determine the role of miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM. The meta-analysis ultimately assessed 32 studies from 15 articles comprising 2,053 MM patients and 1,118 healthy controls.
All the included studies involved newly diagnosed MM patients and healthy controls; the obtained miRNA was derived from serum or plasma specimens; and the report contained relevant statistics such as sensitivity, specificity, and area-under-the-curve values.
High sensitivity and specificity
The researchers found that the overall sensitivity and specificity of using miRNAs for the diagnosis of MM were 0.81 and 0.85, respectively. In addition, the overall positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve were 5.5, 0.22, 25 and 0.90, respectively.
A subgroup analysis showed that the down-regulation of miRNA clusters with larger samples size of plasma type could carry out a better diagnostic accuracy of MM patients, according to the authors.
“[Circulating miRNAs] not only had high sensitivity and strong specificity, but also had noninvasive and no radiation risks. It is worth continuing to optimize its practicality. In the future, multicenter, more rigorous, and high-quality case-control studies are still needed in clinical practice to improve the efficacy of circulating miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM,” the researchers concluded.
The study did not receive any outside funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Gao S-S et al. J Bone Oncol. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2020.100327.
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) could be a potential noninvasive biomarker for early diagnosis of multiple myeloma (MM), according to the results of a meta-analysis published online in the Journal of Bone Oncology.
In recent years, because of the rise of the miRNA technique, many scholars have studied its value in the diagnosis of MM, and have obtained good but inconsistent results, according to Shuai-Shuai Gao, of the Xi’an (China) Daxing Hospital, and colleagues. For this reason, they conducted the meta-analysis in order to more clearly determine the role of miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM. The meta-analysis ultimately assessed 32 studies from 15 articles comprising 2,053 MM patients and 1,118 healthy controls.
All the included studies involved newly diagnosed MM patients and healthy controls; the obtained miRNA was derived from serum or plasma specimens; and the report contained relevant statistics such as sensitivity, specificity, and area-under-the-curve values.
High sensitivity and specificity
The researchers found that the overall sensitivity and specificity of using miRNAs for the diagnosis of MM were 0.81 and 0.85, respectively. In addition, the overall positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under the curve were 5.5, 0.22, 25 and 0.90, respectively.
A subgroup analysis showed that the down-regulation of miRNA clusters with larger samples size of plasma type could carry out a better diagnostic accuracy of MM patients, according to the authors.
“[Circulating miRNAs] not only had high sensitivity and strong specificity, but also had noninvasive and no radiation risks. It is worth continuing to optimize its practicality. In the future, multicenter, more rigorous, and high-quality case-control studies are still needed in clinical practice to improve the efficacy of circulating miRNA in the early diagnosis of MM,” the researchers concluded.
The study did not receive any outside funding and the researchers reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Gao S-S et al. J Bone Oncol. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2020.100327.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF BONE ONCOLOGY