User login
Discoveries in diabetic embryogenesis
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Many issues surrounding pregnancy care of women with preexisting diabetes remain challenging, especially in light of the relentless increase in maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States and globally. Rising rates of death and severe morbidity in diabetic women have continued despite significant advances in insulin pharmacology and administration technology.
However, despite these advances in glucose monitoring and insulin administration, fetal mortality and childhood morbidity rates continue to climb. This is because critical fetal structural anomalies arise from developmental errors occurring in the embryonic period – between 2 and 13 weeks of gestation – a time when most women with preexisting diabetes are just entering into prenatal care, often with suboptimal glycemic control.
Thus, significant future progress in reducing fetal mortality and childhood disability in infants of diabetic mothers will depend upon effective interventions in the first trimester while embryogenesis and critical organ formation are underway.
In this issue of Ob.Gyn. News, the editor of Master Class in Obstetrics, E. Albert Reece MD, PhD, MBA, steps into the role of coauthor. He and his research colleague Peixin Yang, PhD, present exciting insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying structural birth defects in infants of diabetic mothers – especially cardiac and neural tube defects – and also provide a glimpse into some potentially effective maternal pharmacologic interventions. After appropriate human trials, these interventions could be effectively applied from the time of a positive pregnancy test with potentially dramatic results.
Dr. Reece and Dr. Yang, who lead the Center for the Study of Birth Defects at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, share their impressive accumulation of data from embryos of pregnant diabetic rodents. They demonstrate convincingly that, in first-trimester rodent embryos, maternal hyperglycemia induces excessive apoptosis, which in turn leads to structural defects in critical fetal organs. They further found that maternal hyperglycemia reduces embryonic autophagosomes – the developmentally essential organelles that remove abnormal or damaged cells during embryo formation.
These investigators also identified reactivators of these organelles which, when administered maternally in the first trimester, significantly reduced the incidence of neural tube defects. Thus, for optimal development of diabetes-affected embryos, first-trimester administration of reactivators of autophagy could offer a significant, life-changing intervention in the foreseeable future.
Dr. Moore is professor emeritus of maternal-fetal medicine and chair emeritus in the department of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at UC San Diego Health. He reported no disclosures.
*This story was updated on Nov. 3, 2022.
Bugs, drugs, and the placenta
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
How exquisitely designed is the human body? Despite our efforts to occasionally derail our health and well-being, our bodies come with helpful built-in protective functional barriers. The blood-brain barrier and the placenta are two examples. In basic terms, both restrict the free flow of substances from the systemic circulation and help prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain and the fetus, respectively. The placenta is unique in that it develops along with the fetus and, at delivery, is expelled after having done its work. But what happens when a disease or treatment alters the ability of the placenta to operate as a control gate for the fetus?
In keeping with this column’s title, let’s start with bugs. Based on the 2021 World Malaria Report, malaria continues to strike hardest against pregnant women and children in Africa.1 In 2020 in 33 moderate- and high-transmission African countries, 34% of pregnancies (11.6 million of 33.8 million) were exposed to malaria infection. Malaria infection during pregnancy is associated with adverse birth outcomes, including small for gestational age and preterm birth, which in turn increase the risk for neonatal and childhood mortality.
Malaria is caused by the parasite of the genus Plasmodium and is transmitted by infective female Anopheles mosquitoes. The predominant parasite in sub-Saharan Africa is Plasmodium falciparum. Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable. Once a subject is bitten, the P. falciparum parasite is injected into the human blood stream where it is taken up initially by the liver and subsequently by the erythrocytes of the host which adhere to placental receptors, triggering placental inflammation and subsequent damage. This leads to impaired placental development and function, placental insufficiency, and the adverse birth outcomes identified above.2 In targeting the placenta, this parasite can cause structural and functional placental alterations through infection and inflammation. A recent review by McColl et al. has shown that placental inflammation with or without infection affects the normal function of placental amino acid transporters, leading to similar adverse pregnancy outcomes.3
Moving on to drugs and drug safety in pregnancy, concern generally focuses on exposure during pregnancy that might directly affect the fetus at critical time windows during growth and development. There is a need to understand not only the size of the drug molecules and the degree to which they cross the placenta, but also how those medications may affect the development and function of the placenta itself. New research methods such as the “placenta-on-a-chip” that models the transport of nutrients and drugs allow direct evaluation of placental function.4 Assessing placental function using such tools during drug development will contribute to a better understanding of the safety and efficacy of new medications for use in pregnancy, providing important information at the preclinical phases.5
The placenta is a dynamic organ with metabolic, endocrine, immunologic, and transport functions. Most importantly, it protects a healthy pregnancy. It also provides the advantage of immunologic protection to the fetus when maternal antibodies cross the placenta and provide initial protection until the newborn’s own immune system matures. Using our knowledge of placental alteration models and new research methods such as “placenta-on-a-chip” can help expand our understanding of the role of the placenta in medication safety in pregnancy.
Dr. Hardy is executive director, head of pharmacoepidemiology, at Biohaven Pharmaceuticals. She serves as a member of Council for the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, represents the BDRP on the Coalition to Advance Maternal Therapeutics, and is a member of the North American Board for Amandla Development, South Africa. Dr. Tassinari is a consultant and was formerly employed by Pfizer and the Food and Drug Administration. Dr. Tassinari is a past president of BDRP (formerly the Teratology Society) and currently serves as a member of the External Science Advisory Committee for The Medicines for Malaria Venture and is a member of the Science Advisory Committee for the COVID-19 Vaccines International Pregnancy Exposure Registry.
References
1. World malaria report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021.
2. Chua CLL et al. Front Immunol. 2021;12:621382.
3. McColl ER et al. Drug Metab Dispos. May 2022.
4. Blundeli C et al. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. January;7(2).
5. David AL et al. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2022.
Ivermectin for COVID-19: Final nail in the coffin
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.
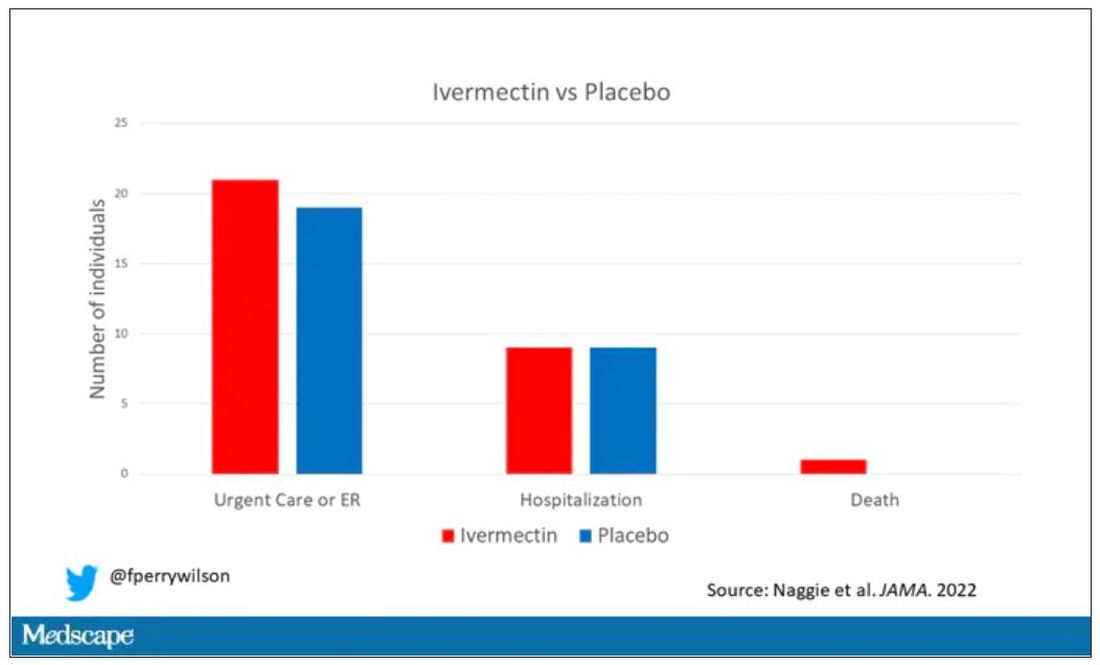
But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How can I keep from losing my mind?
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
A) Thiamine
B) Vitamin E
C) Multivitamin (MV)
D) Keto diet
E) Red wine
FDA-approved therapies for dementia
To date the actual therapies for dementia have been disappointing. Donepezil, the most prescribed medication for the treatment of dementia has a number-needed-to treat (NNT) over 17, and causes frequent side effects. Aducanumab was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but controversy has arisen, as the clinical results were modest, and the price tag will be large – estimated at $30,000-$50,000/year.
Preventive options that may decrease the likelihood of dementia
Patients often ask the question stated above. Regarding how to respond to that question, choice C, MV, has some recent evidence of benefit. Baker and colleagues studied the effect of cocoa extract and multivitamins on cognitive function in the COSMOS-Mind trial.1 A total of 2,262 people were enrolled, and over 90% completed baseline and at least one annual cognitive assessment. Cocoa extract had no impact on global cognition (confidence interval [CI], –.02-.08, P = .28), but MV supplementation did have a statistically significant impact on global cognition (CI, .02-.12, P less than .007).
Vitamin E has been enthusiastically endorsed in the past as a treatment to prevent cognitive decline. The most recent Cochrane review on vitamin E concluded there was no evidence that the alpha-tocopherol form of vitamin E given to people with MCI prevents progression to dementia, or that it improves cognitive function in people with MCI or dementia due to AD.2
Exercise has long been a mainstay of our advice to patients as something they can do to help prevent dementia. Yu and colleagues did a meta-analysis of almost 400 randomized controlled trials and observational studies to grade the evidence on different interventions.3 They gave exercise a grade B for evidence of benefit.
A recent study addressed this issue, and I think it is helpful on quantifying how much exercise is needed. Del Pozo Cruz and colleagues did a prospective population-based cohort study of 78,000 adults aged 40-79, with an average of 6.9 years of follow up.4 The optimal step count was 9,826 steps (hazard ratio [HR], 0.49; 95% CI, 0.39-0.62) and the minimal step count for benefit was 3,826 steps (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.67-0.83).
Modifiable factors
The other major modifiable factors to consider are problems with special senses. Both vision loss and hearing loss have been associated with cognitive impairment.
Shang and colleagues published a meta-analysis of 14 cohort studies addressing vision impairment and cognitive function involving more than 6 million individuals.5 They concluded that vision impairment is associated with an increased risk of both dementia and cognitive impairment in older adults.
Loughrey and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 36 studies addressing hearing loss and cognitive decline.6 They reported that, among cross-sectional studies, a significant association was found for cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR], 2.00; 95% CI, 1.39-2.89) and dementia (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.24-4.72). A similar finding was present in prospective cohort studies with a significant association being found for cognitive impairment (OR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.09-1.36) and dementia (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.02-1.59).
A 25-year prospective, population-based study of patients with hearing loss revealed a difference in the rate of change in MMSE score over the 25-year follow-up between participants with hearing loss not using hearing aids matched with controls who didn’t have hearing loss. Those with untreated hearing loss had more cognitive decline than that of patients without hearing loss.7 The subjects with hearing loss using a hearing aid had no difference in cognitive decline from controls.
Pearl
Several simple and safe interventions may protect our patients from cognitive decline. These include taking a daily multivitamin, walking more than 4,000 steps a day, and optimizing vision and hearing.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at [email protected].
References
1. Baker LD et al. Effects of cocoa extract and a multivitamin on cognitive function: A randomized clinical trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/alz.12767.
2. Farina N et al. Vitamin E for Alzheimer’s dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 18;4(4):CD002854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002854.pub5.
3. Yu JT et al. Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;91(11):1201-9.
4. Del Pozo Cruz B et al. Association of daily step count and intensity with incident dementia in 78,430 adults living in the UK. JAMA Neurol. 2022 Oct 1;79(10):1059-63.
5. Shang X et al. The association between vision impairment and incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-49.
6. Loughrey DG et al. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-26.
7. Amieva H et al. Self-reported hearing loss, hearing aids, and cognitive decline in elderly adults: A 25-year study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2015 Oct;63(10):2099-104.
Asking about gun ownership: A loaded question?
Recently there have been articles and discussions about how involved physicians should be in patient gun ownership.
There are valid points all around. Some of my colleagues, especially those in general practice, feel that they don’t have enough time to add more screening questions on top of those they already have. Others point out that routinely asking about gun ownership is none of our business. A third view I’ve seen is that very few doctors are in a position to teach issues of gun safety.
In my field, with certain patients, I do ask. Namely, the demented.
Anyone with concerning cognitive deficits shouldn’t have access to guns. As their judgment fades and their impulsivity worsens, they often don’t realize right from wrong. They might open fire on family members thinking they’re burglars. Some of them see suspicious people out in the yard that are more likely hallucinations or simply passersby.
In more advanced cases of dementia, patients may not even realize what they’re holding, but that doesn’t make it any less dangerous. Probably more so, since they’re not going to be careful with it.
Another scary issue I sometimes encounter is when patients with dementia find a gun at home – usually one that belonged to a deceased spouse and that family isn’t aware of. No one really knows if it’s working, or loaded, though we have to assume it is. They find it and start carrying it out on walks, pointing it at the mailman who they think is trespassing, etc. Sometimes the police get called. These situations are extremely dangerous for all involved.
It’s pretty easy for someone to get shot under these circumstances. It’s like leaving a gun out and having a toddler find it. They don’t mean any harm, but they’re still just as deadly as someone who does.
These people also have access to knives, which can be equally deadly, but knives aren’t guns. They don’t have the range or hitting power that make firearms so dangerous. It’s a lot easier to disarm an elderly patient with a steak knife if need be.
So, like my colleagues in psychiatry, I ask about guns in certain situations that involve dementia. Are there any guns? If so, are they locked up safely where the person can’t access them?
I’m not making a statement for or against gun ownership here. But I think all of us would agree that
In neurology, that’s a decent chunk of my patients. So for everyone’s safety, I ask them (and, more importantly, their families) about guns.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Recently there have been articles and discussions about how involved physicians should be in patient gun ownership.
There are valid points all around. Some of my colleagues, especially those in general practice, feel that they don’t have enough time to add more screening questions on top of those they already have. Others point out that routinely asking about gun ownership is none of our business. A third view I’ve seen is that very few doctors are in a position to teach issues of gun safety.
In my field, with certain patients, I do ask. Namely, the demented.
Anyone with concerning cognitive deficits shouldn’t have access to guns. As their judgment fades and their impulsivity worsens, they often don’t realize right from wrong. They might open fire on family members thinking they’re burglars. Some of them see suspicious people out in the yard that are more likely hallucinations or simply passersby.
In more advanced cases of dementia, patients may not even realize what they’re holding, but that doesn’t make it any less dangerous. Probably more so, since they’re not going to be careful with it.
Another scary issue I sometimes encounter is when patients with dementia find a gun at home – usually one that belonged to a deceased spouse and that family isn’t aware of. No one really knows if it’s working, or loaded, though we have to assume it is. They find it and start carrying it out on walks, pointing it at the mailman who they think is trespassing, etc. Sometimes the police get called. These situations are extremely dangerous for all involved.
It’s pretty easy for someone to get shot under these circumstances. It’s like leaving a gun out and having a toddler find it. They don’t mean any harm, but they’re still just as deadly as someone who does.
These people also have access to knives, which can be equally deadly, but knives aren’t guns. They don’t have the range or hitting power that make firearms so dangerous. It’s a lot easier to disarm an elderly patient with a steak knife if need be.
So, like my colleagues in psychiatry, I ask about guns in certain situations that involve dementia. Are there any guns? If so, are they locked up safely where the person can’t access them?
I’m not making a statement for or against gun ownership here. But I think all of us would agree that
In neurology, that’s a decent chunk of my patients. So for everyone’s safety, I ask them (and, more importantly, their families) about guns.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Recently there have been articles and discussions about how involved physicians should be in patient gun ownership.
There are valid points all around. Some of my colleagues, especially those in general practice, feel that they don’t have enough time to add more screening questions on top of those they already have. Others point out that routinely asking about gun ownership is none of our business. A third view I’ve seen is that very few doctors are in a position to teach issues of gun safety.
In my field, with certain patients, I do ask. Namely, the demented.
Anyone with concerning cognitive deficits shouldn’t have access to guns. As their judgment fades and their impulsivity worsens, they often don’t realize right from wrong. They might open fire on family members thinking they’re burglars. Some of them see suspicious people out in the yard that are more likely hallucinations or simply passersby.
In more advanced cases of dementia, patients may not even realize what they’re holding, but that doesn’t make it any less dangerous. Probably more so, since they’re not going to be careful with it.
Another scary issue I sometimes encounter is when patients with dementia find a gun at home – usually one that belonged to a deceased spouse and that family isn’t aware of. No one really knows if it’s working, or loaded, though we have to assume it is. They find it and start carrying it out on walks, pointing it at the mailman who they think is trespassing, etc. Sometimes the police get called. These situations are extremely dangerous for all involved.
It’s pretty easy for someone to get shot under these circumstances. It’s like leaving a gun out and having a toddler find it. They don’t mean any harm, but they’re still just as deadly as someone who does.
These people also have access to knives, which can be equally deadly, but knives aren’t guns. They don’t have the range or hitting power that make firearms so dangerous. It’s a lot easier to disarm an elderly patient with a steak knife if need be.
So, like my colleagues in psychiatry, I ask about guns in certain situations that involve dementia. Are there any guns? If so, are they locked up safely where the person can’t access them?
I’m not making a statement for or against gun ownership here. But I think all of us would agree that
In neurology, that’s a decent chunk of my patients. So for everyone’s safety, I ask them (and, more importantly, their families) about guns.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The lives of drug users are more important than stopping drug use
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
One quiet afternoon at a mobile outreach clinic, where I had been working on the West Side of Chicago, a young man without a home to go to, and clothes he kept as clean as he could, came to get a refill of buprenorphine. The drug, which works on the same opioid receptors as heroin, was helping him feel normal. It was also probably helping to keep him alive, as a study found that taking it after an overdose was associated with a one-third reduction in all-cause mortality.
He was still using drugs, but now only a few days a week instead of multiple times a day. He had put on some weight and looked visibly healthier.
I gave him his prescription and thanked him for coming back. As he got up to leave, he turned to our outreach team and said, “Thank you for being here and caring about us. Because a lot of people don’t. They don’t care if we live or die.”
But a lot of people do care and are still failing him and others who use drugs. When I first started treating addictions, I was taught to cut people like him off treatment. We could give patients a medication, but they had to follow the rules, first and foremost to stop using drugs. Keep using, even if you were using less and your health was improving, and I would have to dismiss you from the practice. This was the kind of “tough love” that many doctors have been taught, and are, in many cases, still being taught today. Even though we know that this approach does not work.
For too long, doctors, nurses, caregivers, and the broader American public have favored abstinence only treatment, criminalization, and prohibition. The proof that this approach does not work is in the spectacular overdose crisis we are experiencing in this country, as CDC data documents. While we continue to blame drugs like fentanyl and methamphetamine (and thirty years ago, crack and heroin), we fail to see how our approach contributes to these overdose deaths.
For instance, treating with buprenorphine or methadone was associated with reductions in overdose and serious opioid-related acute care use compared with detox alone. But only one in three centers offer these medications, the gold standard of care. We continue to imprison people who use drugs, even though we have known for 15 years that the risk of overdose is exponentially higher in the first few weeks after people leave prison.
Patients who use opioids safely for decades are also arbitrarily being forced off their prescriptions because too many clinicians equate opioid use with opioid addiction, despite the fact that opioid tapering was associated with increased rates of overdose. And prohibition has led to a change in the drug supply that is now dominated by methamphetamine and fentanyl, substances far more deadly than the ones we demonized and seized decades ago.
We have tried and failed to rid the country of many drugs. We never will. Human beings will seek mind-altering substances, from caffeine to alcohol to hallucinogens. But we can stop the grim massacre of people who use drugs. We have the tools. What we lack is moral clarity.
In lecture after lecture of physicians and medical students, I hear the refrain that patients are not often “ready” for treatment. There’s nothing that doctors can do, they say, if the patient doesn’t want help. Yet they do not examine why that may be. Are we offering the help that they need? Time and again I have seen that if we meet people where they are, we can help virtually anyone.
Tools for fighting the opioid crisis
The reason our policies have failed is because we have not confronted a simple truth: We must care more about saving and improving the lives of people who use drugs than stopping drug use. With that framework, the approach is clear and multifactorial. First, we must make methadone treatment less draconian. Methadone, like buprenorphine, has been associated with a large reduction in all-cause mortality for people who have a history of overdose.
In this country, to access it, however, you must go to a clinic daily for the first 90 days of treatment and jump through hoops that often make it impossible to have a job and accomplish other goals. Other countries have safely moved methadone to primary care offices, and so should we. The other main drug for opioid addiction, buprenorphine, requires a special license to prescribe, even though it is far safer than other opioids that any physician can prescribe. This requirement has been weakened, but it should be removed entirely.
Moreover, the DEA conducts regular audits of buprenorphine prescribers in an effort to prevent diversion, discouraging doctors from prescribing it. This despite the fact that it is almost impossible to overdose on buprenorphine alone, and a study suggests that diversion of buprenorphine is associated with a lower overdose risk in a community by making the medication available to more people who can benefit.
Treatment is not the only way we can help people using drugs. Naloxone, an overdose rescue drug, should be available in every first aid kit and free at pharmacies without a prescription. Clean needles and pipes for people who use can help prevent infections, potentially mitigating the severity of outbreaks. Overdose prevention sites, where people can safely use, should be opened across the country.
We need accessible drug testing so people do not accidentally overdose and so they can know what they are using. We should stop sending people to jail for drug use when we know that it is too often tantamount to a death sentence, and offer effective medical treatment to anyone who is incarcerated.
All these interventions remain controversial within medicine and in the larger culture. If our metric, however, is lives saved and harm avoided, these are sure-fire approaches.
Right now, I am focused on clinical care and changing the culture of medicine, where we have opportunities to help but too often do harm instead. The impact of a shift in mentality would be huge, because we would realize there is no one we cannot help, only millions of people we do not listen to. But this is a national crisis and requires a national response. Until we are clear that our goal should and must be to stem the mounting deaths and harms above all else, we will continue to fail.
Dr. Poorman is board certified in internal medicine and addiction medicine, assistant professor of medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, and provides primary care and addiction services in Chicago. Her views do not necessarily reflect the views of her employer. She has reported no relevant disclosures.
The latest migraine therapies – some you might not know about
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with my very good friend, Dr. Paul Williams. It’s time to talk about headaches. We did a great recent podcast on migraines, Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber. One of the quotes from that episode that stayed with me was when he said, “I tell my patients to think about migraine as an irritable old miser set in their ways, and your brain is set in its ways. It doesn’t like changes in routine. It doesn’t like lack of sleep, it doesn’t like being hungry, it doesn’t like being thirsty, and it doesn’t like changes in the weather.” That’s a reminder of the good, old-fashioned primary care tips for taking care of headache.
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right. Conservative supportive management goes by the wayside because we focus on the medications. But I thought that was a really nice way to start the episode.
Dr. Watto: I asked him about cervicogenic headaches, which I guess you have to diagnose by giving a cervical steroid injection and see if the patient feels better, but he said he doesn’t do this. This is expert opinion territory. He asks his patients with chronic headache about cervical neck pain, because if they have it, he goes after it with physical therapy, which can help with the headaches. I thought that was a great pearl that I hadn’t heard before.
Give the audience a pearl from this great episode.
Dr. Williams: We talked about foundational treatments. We reviewed some of the abortive therapies and over-the-counter products. Some patients do quite well with acetaminophen or NSAIDs. We also talked about triptans, which are the standard medicines that we all know about. You can use those in combination, by the way. Patients can take their triptan with the NSAID that works best for them. They don’t have to be used one at a time, trying one and then trying the other one if the first one doesn’t help. Dr. Weber gave us practical guides in terms of which triptans he favors. He mentioned rizatriptan and naratriptan, which is one that I had not used with any frequency. I’ve seen rizatriptan a fair amount and that one seems to be covered by most insurances. He favors those two triptans.
He also reminded us that even though there is theoretical concern for serotonin toxicity because these are serotonergic and you’ll see these scary pop-ups in your electronic health record, that concern is almost purely theoretical. It hasn’t been borne out. They are really safe medications to use. But do use caution if you have a patient with known cardiovascular disease or cerebrovascular disease. We spent a fair amount of time talking about chest pressure as a common side effect. We also talked about some of the newer agents.
Dr. Watto: I wanted to add something about the triptans. Part of the reason he favors rizatriptan and naratriptan is that they are newer. He thinks they tend to have fewer side effects. But he did mention sumatriptan because it comes in the most different formulations. If patients have severe nausea, there is a subcutaneous version of sumatriptan and also an intranasal version.
The new kids on the block are the CGRP receptor antagonists, and they are available for preventive and abortive therapy. The abortive therapies are probably what people will be seeing most often in primary care – ubrogepant and rimegepant. Patients can take ubrogepant for abortive therapy and then repeat it if necessary. That’s similar to what patients are used to with the triptans. Rimegepant is taken once daily for abortive therapy or every other day as a preventive agent. Those are two of the agents that you might see patients taking. I’ve certainly started to see them.
There are also a whole bunch of monoclonal antibodies that affect the CGRP pathway. Those are given either once a month by subcutaneous injection or once every 3 months, and one is an infusion. They are pretty safe, and the big appeal is that they can be used in patients with cardiovascular disease. He also said that he has some patients who take them because triptans can cause the medication overuse side effect, but the CGRP receptor antagonists don’t. It’s an option for some patients to take the CGRP receptor antagonists on certain days for abortive therapy and then they can take the triptans the rest of the month.
Dr. Weber said that in his practice, these new drugs have really been great, which I can imagine, if you’re a specialist, patients have exhausted many of the typical therapies we offer in primary care.
Paul, bring us home here. What else should we tell the audience about? In primary care, what can we offer these patients?
Dr. Williams: A lot of the stuff we can offer works, by the way. It’s exciting to have fancy new medications to use, but you don’t even necessarily need to get to that point. We have a lot of medications that we can use for migraine prophylaxis, such as the beta-blockers and antihypertensives. Candesartan was a new one to me, an angiotensin receptor blocker that apparently has good evidence for migraine prophylaxis and Dr. Weber swears by it. We talked about some of the antiseizure medications, such as topiramate, which is probably the one with the most comfort in primary care. Some older folks may be using valproic acid or the tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline and nortriptyline) because people with migraine often will have comorbid anxiety or trouble sleeping, so I find that can sometimes be an effective medication or if they have comorbid neuropathic pain.
Another one that was new to me was venlafaxine as migraine prophylaxis. It’s not something I’d heard about before this episode. Certainly, for someone with chronic pain or a mood disorder that’s comorbid with migraines, it may be worth a shot. So there are options that we can exhaust first, and we may actually be doing our specialist friends a favor by trying one or two of these in advance, because then by the time the patient gets to the neurologist, it makes the prior authorization process much easier for the newer, fancier-pants medications that we’re all very excited about.
Dr. Watto: Paul, we’ve teased this fantastic podcast episode filled with so much more great stuff, so people should check out Headache Update: Making Migraines Less Painful with Dr. Kevin Weber.
Until next time, this has been another episode of The Curbsiders, bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole.
The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Criminal profiles of medical murderers
Today’s health care professionals run the very real risk of being sued. This is especially true when a patient dies unexpectedly. But many times, doctors find that they’re defending themselves against very serious charges, such as murder and attempted murder.
In Mexico, a physician can be wrongfully accused of such crimes, as was Azucena Calvillo, MD, last year in Durango. The case drew much media attention, and the accusations were so implausible and ridiculous that the charges were dropped and the case was dismissed.
There are instances in which the authorities create a circuslike atmosphere by making farcical and false accusations against healthcare professionals. Still, there are medical murderers – and these killers are among the most difficult to identify. As John E. Douglas put it, “Medical murderers (physicians, nurses, elder care workers) can have a long list of victims, longer than other kinds of serial killers.” Ted Bundy, one of the most written-about serial killers, confessed to 30 murders. The cases discussed below involve from 60 to 200.
Mr. Douglas was a special agent with the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation. He is the author of Mindhunter, a nonfiction crime book in which he recounts the early days of the FBI’s Behavioral Science Unit and how he and his colleagues began to study the criminal profiles of serial killers. The book has been adapted into a Netflix TV series of the same name.
He is also one of the authors of Crime Classification Manual: A Standard System for Investigating and Classifying Violent Crime. In this book, there are descriptions of criminal profiles of medical murderers.
According to the authors, Each type is associated with a different motive. In the former, the murderers believe that they’re alleviating the patient’s suffering; in the latter, the murderers create a medical emergency so that they can play the hero in what they know will be an unsuccessful attempt to save the patient’s life.
Pseudo-mercy homicide
An example of pseudo-mercy homicide is the infamous case of Harold Shipman, MD, who was convicted of killing 15 people, although an investigation found that more than 200 persons, and possibly as many as 250, died at his hands. In Prescription for Murder: The True Story of Dr. Harold Frederick Shipman, biographer Brian Whittle writes that the general practitioner is England’s (if not the world’s) most prolific serial killer. Dr. Shipman is the only physician in that country’s history to have been convicted of killing his patients.
His modus operandi? Injecting morphine. Most of his victims were elderly women. And though unconfirmed, his youngest victim may have been only 4 years old. It was the death of 81-year-old Kathleen Grundy that led to the physician’s arrest. Her family became extremely suspicious when they learned that her will named Dr. Shipman as the beneficiary of her entire estate.
He always denied being involved in the murders, for which authorities have yet to determine a motive. The speculation is that he enjoyed watching people die. Almost none of the cases attributed to Dr. Shipman involved a critically ill individual with a life-threatening condition. Therefore, his acts were not real acts of mercy. He would make a house call to carry out a routine visit. Once in the patient’s home, he would inject a lethal dose of morphine. Sometimes, relatives and physicians alike would be struck by the strange turn of events.
In 2004, Dr. Shipman committed suicide in prison. His case led to numerous changes to British law with respect to the use of controlled substances, the issuance of death certificates, and the procedure for reporting healthcare staff suspected of engaging in illegal activities. Biographer Whittle concluded, “It is very unlikely that the world will ever see another physician as unrelentingly wicked as Dr. Shipman.”
Pseudo-hero homicide
The pseudo-hero creates serious situations, generally by administering drugs, and then tries to save the patient. Mr. Douglas presents a terrifying case study: Genene Jones, a nurse known as the “Angel of Death.”
Many of Ms. Jones’ colleagues considered her an excellent nurse, an expert at handling unexpected emergencies. If a child died while she was on duty, she would sometimes accompany their body to the morgue. She would even sing children’s songs to their lifeless body. When people started to question the number of deaths that were occurring during her shifts, the staff stood up for Ms. Jones, saying that it was because she took on the most serious cases.
Ms. Jones was found out when a vial of succinylcholine went missing. After it was located, a physician, who had been suspicious of the nurse, noticed that there were two puncture holes in the stopper. None of the staff could offer any explanation. A few days before this event, that same physician had left a healthy 15-month-old girl in Jones’ care. Within a few minutes, the child was showing signs of paralysis and started to have seizures. It appears that Ms. Jones had used succinylcholine to make it appear that the children were sick or were experiencing some sort of emergency so that she could then attempt to save them, and they could die in her arms.
This case highlights the need for mortality review committees and for proper statistical analysis to discern trends in deaths and complications among patients. Genene Jones was convicted of killing the 15-month-old girl and was sentenced to 99 years in prison. Authorities suspect that the nurse was responsible for the deaths of up to 60 children.
A new criminal profile?
Through the podcast and subsequent TV series Dr. Death, many people have come to know of a more recent medical murderer: Christopher Duntsch, MD, PhD. The Texas neurosurgeon killed at least two patients, and his actions left several others with adverse outcomes and serious injuries.
These acts occurred during surgical procedures. Witnesses said that the deaths and injuries were the result of unprecedented, egregious negligence, as though the operations had been performed by someone who had never been trained in the specialty. This is something that resonates very strongly for those who are aware of what’s going on in Mexico, where it’s well known that many physicians who lack specialty training perform operations (mainly cosmetic surgery). No doubt cases such as Dr. Duntsch’s are more frequent in Mexico.
What makes the situation in the United States involving Christopher Duntsch so astonishing is that it resulted from a perfect storm of a physician whom some colleagues described as a “sociopath” and legal loopholes in the country’s healthcare system. Apparently, during his residency, Dr. Duntsch never developed the skills necessary to perform operations. He spent more time carrying out research and engaging in other activities than in participating in the operating room. This is a case that calls into question the way specialists are trained, as it seems that what matters is not how much time they’re spending inside the hospital but what they’re doing and learning there.
Dr. Duntsch’s license was suspended and then permanently revoked. He is currently serving a life sentence. Through the podcast or the TV series, one comes to realize that it’s not easy to catch medical murderers. They are among the most difficult to identify – serial killers who commit numerous homicides before they are captured. Reading about the case of Christopher Duntsch, one might ask, What’s his criminal profile: pseudo-hero? Pseudo-mercy? It is hard to say. Maybe his is a different kind of profile – one that will open a new chapter in the books on medical murderers.
Dr. Sarmiento studied medicine and did his residency in anatomic pathology, internal medicine, and clinical hematology. He went on to study at Central University City Campus Law School, National Autonomous University of Mexico. He now runs a law firm that, among other things, advises physicians on matters of civil liability, administrative processes, and the legal implications of practicing medicine.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.
Today’s health care professionals run the very real risk of being sued. This is especially true when a patient dies unexpectedly. But many times, doctors find that they’re defending themselves against very serious charges, such as murder and attempted murder.
In Mexico, a physician can be wrongfully accused of such crimes, as was Azucena Calvillo, MD, last year in Durango. The case drew much media attention, and the accusations were so implausible and ridiculous that the charges were dropped and the case was dismissed.
There are instances in which the authorities create a circuslike atmosphere by making farcical and false accusations against healthcare professionals. Still, there are medical murderers – and these killers are among the most difficult to identify. As John E. Douglas put it, “Medical murderers (physicians, nurses, elder care workers) can have a long list of victims, longer than other kinds of serial killers.” Ted Bundy, one of the most written-about serial killers, confessed to 30 murders. The cases discussed below involve from 60 to 200.
Mr. Douglas was a special agent with the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation. He is the author of Mindhunter, a nonfiction crime book in which he recounts the early days of the FBI’s Behavioral Science Unit and how he and his colleagues began to study the criminal profiles of serial killers. The book has been adapted into a Netflix TV series of the same name.
He is also one of the authors of Crime Classification Manual: A Standard System for Investigating and Classifying Violent Crime. In this book, there are descriptions of criminal profiles of medical murderers.
According to the authors, Each type is associated with a different motive. In the former, the murderers believe that they’re alleviating the patient’s suffering; in the latter, the murderers create a medical emergency so that they can play the hero in what they know will be an unsuccessful attempt to save the patient’s life.
Pseudo-mercy homicide
An example of pseudo-mercy homicide is the infamous case of Harold Shipman, MD, who was convicted of killing 15 people, although an investigation found that more than 200 persons, and possibly as many as 250, died at his hands. In Prescription for Murder: The True Story of Dr. Harold Frederick Shipman, biographer Brian Whittle writes that the general practitioner is England’s (if not the world’s) most prolific serial killer. Dr. Shipman is the only physician in that country’s history to have been convicted of killing his patients.
His modus operandi? Injecting morphine. Most of his victims were elderly women. And though unconfirmed, his youngest victim may have been only 4 years old. It was the death of 81-year-old Kathleen Grundy that led to the physician’s arrest. Her family became extremely suspicious when they learned that her will named Dr. Shipman as the beneficiary of her entire estate.
He always denied being involved in the murders, for which authorities have yet to determine a motive. The speculation is that he enjoyed watching people die. Almost none of the cases attributed to Dr. Shipman involved a critically ill individual with a life-threatening condition. Therefore, his acts were not real acts of mercy. He would make a house call to carry out a routine visit. Once in the patient’s home, he would inject a lethal dose of morphine. Sometimes, relatives and physicians alike would be struck by the strange turn of events.
In 2004, Dr. Shipman committed suicide in prison. His case led to numerous changes to British law with respect to the use of controlled substances, the issuance of death certificates, and the procedure for reporting healthcare staff suspected of engaging in illegal activities. Biographer Whittle concluded, “It is very unlikely that the world will ever see another physician as unrelentingly wicked as Dr. Shipman.”
Pseudo-hero homicide
The pseudo-hero creates serious situations, generally by administering drugs, and then tries to save the patient. Mr. Douglas presents a terrifying case study: Genene Jones, a nurse known as the “Angel of Death.”
Many of Ms. Jones’ colleagues considered her an excellent nurse, an expert at handling unexpected emergencies. If a child died while she was on duty, she would sometimes accompany their body to the morgue. She would even sing children’s songs to their lifeless body. When people started to question the number of deaths that were occurring during her shifts, the staff stood up for Ms. Jones, saying that it was because she took on the most serious cases.
Ms. Jones was found out when a vial of succinylcholine went missing. After it was located, a physician, who had been suspicious of the nurse, noticed that there were two puncture holes in the stopper. None of the staff could offer any explanation. A few days before this event, that same physician had left a healthy 15-month-old girl in Jones’ care. Within a few minutes, the child was showing signs of paralysis and started to have seizures. It appears that Ms. Jones had used succinylcholine to make it appear that the children were sick or were experiencing some sort of emergency so that she could then attempt to save them, and they could die in her arms.
This case highlights the need for mortality review committees and for proper statistical analysis to discern trends in deaths and complications among patients. Genene Jones was convicted of killing the 15-month-old girl and was sentenced to 99 years in prison. Authorities suspect that the nurse was responsible for the deaths of up to 60 children.
A new criminal profile?
Through the podcast and subsequent TV series Dr. Death, many people have come to know of a more recent medical murderer: Christopher Duntsch, MD, PhD. The Texas neurosurgeon killed at least two patients, and his actions left several others with adverse outcomes and serious injuries.
These acts occurred during surgical procedures. Witnesses said that the deaths and injuries were the result of unprecedented, egregious negligence, as though the operations had been performed by someone who had never been trained in the specialty. This is something that resonates very strongly for those who are aware of what’s going on in Mexico, where it’s well known that many physicians who lack specialty training perform operations (mainly cosmetic surgery). No doubt cases such as Dr. Duntsch’s are more frequent in Mexico.
What makes the situation in the United States involving Christopher Duntsch so astonishing is that it resulted from a perfect storm of a physician whom some colleagues described as a “sociopath” and legal loopholes in the country’s healthcare system. Apparently, during his residency, Dr. Duntsch never developed the skills necessary to perform operations. He spent more time carrying out research and engaging in other activities than in participating in the operating room. This is a case that calls into question the way specialists are trained, as it seems that what matters is not how much time they’re spending inside the hospital but what they’re doing and learning there.
Dr. Duntsch’s license was suspended and then permanently revoked. He is currently serving a life sentence. Through the podcast or the TV series, one comes to realize that it’s not easy to catch medical murderers. They are among the most difficult to identify – serial killers who commit numerous homicides before they are captured. Reading about the case of Christopher Duntsch, one might ask, What’s his criminal profile: pseudo-hero? Pseudo-mercy? It is hard to say. Maybe his is a different kind of profile – one that will open a new chapter in the books on medical murderers.
Dr. Sarmiento studied medicine and did his residency in anatomic pathology, internal medicine, and clinical hematology. He went on to study at Central University City Campus Law School, National Autonomous University of Mexico. He now runs a law firm that, among other things, advises physicians on matters of civil liability, administrative processes, and the legal implications of practicing medicine.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.
Today’s health care professionals run the very real risk of being sued. This is especially true when a patient dies unexpectedly. But many times, doctors find that they’re defending themselves against very serious charges, such as murder and attempted murder.
In Mexico, a physician can be wrongfully accused of such crimes, as was Azucena Calvillo, MD, last year in Durango. The case drew much media attention, and the accusations were so implausible and ridiculous that the charges were dropped and the case was dismissed.
There are instances in which the authorities create a circuslike atmosphere by making farcical and false accusations against healthcare professionals. Still, there are medical murderers – and these killers are among the most difficult to identify. As John E. Douglas put it, “Medical murderers (physicians, nurses, elder care workers) can have a long list of victims, longer than other kinds of serial killers.” Ted Bundy, one of the most written-about serial killers, confessed to 30 murders. The cases discussed below involve from 60 to 200.
Mr. Douglas was a special agent with the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation. He is the author of Mindhunter, a nonfiction crime book in which he recounts the early days of the FBI’s Behavioral Science Unit and how he and his colleagues began to study the criminal profiles of serial killers. The book has been adapted into a Netflix TV series of the same name.
He is also one of the authors of Crime Classification Manual: A Standard System for Investigating and Classifying Violent Crime. In this book, there are descriptions of criminal profiles of medical murderers.
According to the authors, Each type is associated with a different motive. In the former, the murderers believe that they’re alleviating the patient’s suffering; in the latter, the murderers create a medical emergency so that they can play the hero in what they know will be an unsuccessful attempt to save the patient’s life.
Pseudo-mercy homicide
An example of pseudo-mercy homicide is the infamous case of Harold Shipman, MD, who was convicted of killing 15 people, although an investigation found that more than 200 persons, and possibly as many as 250, died at his hands. In Prescription for Murder: The True Story of Dr. Harold Frederick Shipman, biographer Brian Whittle writes that the general practitioner is England’s (if not the world’s) most prolific serial killer. Dr. Shipman is the only physician in that country’s history to have been convicted of killing his patients.
His modus operandi? Injecting morphine. Most of his victims were elderly women. And though unconfirmed, his youngest victim may have been only 4 years old. It was the death of 81-year-old Kathleen Grundy that led to the physician’s arrest. Her family became extremely suspicious when they learned that her will named Dr. Shipman as the beneficiary of her entire estate.
He always denied being involved in the murders, for which authorities have yet to determine a motive. The speculation is that he enjoyed watching people die. Almost none of the cases attributed to Dr. Shipman involved a critically ill individual with a life-threatening condition. Therefore, his acts were not real acts of mercy. He would make a house call to carry out a routine visit. Once in the patient’s home, he would inject a lethal dose of morphine. Sometimes, relatives and physicians alike would be struck by the strange turn of events.
In 2004, Dr. Shipman committed suicide in prison. His case led to numerous changes to British law with respect to the use of controlled substances, the issuance of death certificates, and the procedure for reporting healthcare staff suspected of engaging in illegal activities. Biographer Whittle concluded, “It is very unlikely that the world will ever see another physician as unrelentingly wicked as Dr. Shipman.”
Pseudo-hero homicide
The pseudo-hero creates serious situations, generally by administering drugs, and then tries to save the patient. Mr. Douglas presents a terrifying case study: Genene Jones, a nurse known as the “Angel of Death.”
Many of Ms. Jones’ colleagues considered her an excellent nurse, an expert at handling unexpected emergencies. If a child died while she was on duty, she would sometimes accompany their body to the morgue. She would even sing children’s songs to their lifeless body. When people started to question the number of deaths that were occurring during her shifts, the staff stood up for Ms. Jones, saying that it was because she took on the most serious cases.
Ms. Jones was found out when a vial of succinylcholine went missing. After it was located, a physician, who had been suspicious of the nurse, noticed that there were two puncture holes in the stopper. None of the staff could offer any explanation. A few days before this event, that same physician had left a healthy 15-month-old girl in Jones’ care. Within a few minutes, the child was showing signs of paralysis and started to have seizures. It appears that Ms. Jones had used succinylcholine to make it appear that the children were sick or were experiencing some sort of emergency so that she could then attempt to save them, and they could die in her arms.
This case highlights the need for mortality review committees and for proper statistical analysis to discern trends in deaths and complications among patients. Genene Jones was convicted of killing the 15-month-old girl and was sentenced to 99 years in prison. Authorities suspect that the nurse was responsible for the deaths of up to 60 children.
A new criminal profile?
Through the podcast and subsequent TV series Dr. Death, many people have come to know of a more recent medical murderer: Christopher Duntsch, MD, PhD. The Texas neurosurgeon killed at least two patients, and his actions left several others with adverse outcomes and serious injuries.
These acts occurred during surgical procedures. Witnesses said that the deaths and injuries were the result of unprecedented, egregious negligence, as though the operations had been performed by someone who had never been trained in the specialty. This is something that resonates very strongly for those who are aware of what’s going on in Mexico, where it’s well known that many physicians who lack specialty training perform operations (mainly cosmetic surgery). No doubt cases such as Dr. Duntsch’s are more frequent in Mexico.
What makes the situation in the United States involving Christopher Duntsch so astonishing is that it resulted from a perfect storm of a physician whom some colleagues described as a “sociopath” and legal loopholes in the country’s healthcare system. Apparently, during his residency, Dr. Duntsch never developed the skills necessary to perform operations. He spent more time carrying out research and engaging in other activities than in participating in the operating room. This is a case that calls into question the way specialists are trained, as it seems that what matters is not how much time they’re spending inside the hospital but what they’re doing and learning there.
Dr. Duntsch’s license was suspended and then permanently revoked. He is currently serving a life sentence. Through the podcast or the TV series, one comes to realize that it’s not easy to catch medical murderers. They are among the most difficult to identify – serial killers who commit numerous homicides before they are captured. Reading about the case of Christopher Duntsch, one might ask, What’s his criminal profile: pseudo-hero? Pseudo-mercy? It is hard to say. Maybe his is a different kind of profile – one that will open a new chapter in the books on medical murderers.
Dr. Sarmiento studied medicine and did his residency in anatomic pathology, internal medicine, and clinical hematology. He went on to study at Central University City Campus Law School, National Autonomous University of Mexico. He now runs a law firm that, among other things, advises physicians on matters of civil liability, administrative processes, and the legal implications of practicing medicine.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition.
Caring for the aging transgender patient
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
The elderly transgender population is rapidly expanding and remains significantly overlooked. Although emerging evidence provides some guidance for medical and surgical treatment for transgender youth, there is still a paucity of research directed at the management of gender-diverse elders.
To a large extent, the challenges that transgender elders face are no different from those experienced by the general elder population. Irrespective of gender identity, patients begin to undergo cognitive and physical changes, encounter difficulties with activities of daily living, suffer the loss of social networks and friends, and face end-of-life issues.1 Attributes that contribute to successful aging in the general population include good health, social engagement and support, and having a positive outlook on life.1 Yet, stigma surrounding gender identity and sexual orientation continues to negatively affect elder transgender people.
Many members of the LGBTQIA+ population have higher rates of obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, cardiovascular disease, substance abuse, depression, suicide, and intimate partner violence than the general same-age cohort.2 Compared with lesbian, gay, and bisexual elders of age-matched cohorts, transgender elders have significantly poorer overall physical health, disability, depressive symptoms, and perceived stress.2
Rates of sexually transmitted infections are also rising in the aging general population and increased by 30% between 2014 and 2017.2 There have been no current studies examining these rates in the LGBTQIA+ population. As providers interact more frequently with these patients, it’s not only essential to screen for conditions such as diabetes, lipid disorders, and sexually transmitted infections, but also to evaluate current gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) regimens and order appropriate screening tests.
Hormonal therapy for transfeminine patients should be continued as patients age. One of the biggest concerns providers have in continuing hormone therapy is the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and increasing thromboembolic risk, both of which tend to occur naturally as patients age. Overall, studies on the prevalence of CVD or stroke in gender-diverse individuals indicate an elevated risk independent of GAHT.3 While the overall rates of thromboembolic events are low in transfeminine populations, estrogen therapy does confer an increased risk. However, most transgender women who have experienced cardiac events or stroke were over the age of 50, had one or more CVD risk factors, or were using synthetic estrogens.3
How these studies affect screening is unclear. Current guidelines recommend using tailored risk-based calculators, which take into consideration the patient’s sex assigned at birth, hormone regimen, length of hormone usage, and additional modifiable risk factors, such as diabetes, obesity, and smoking.3 For transfeminine patients who want to continue GAHT but either develop a venous thromboembolism on estrogen or have increased risk for VTE, providers should consider transitioning them to a transdermal application. Patients who stay on GAHT should be counseled accordingly on the heightened risk of VTE recurrence. It is not unreasonable to consider life-long anticoagulation for patients who remain on estrogen therapy after a VTE.4
While exogenous estrogen exposure is one risk factor for the development of breast cancer in cisgender females, the role of GAHT in breast cancer in transgender women is ambiguous. Therefore, breast screening guidelines should follow current recommendations for cisgender female patients with some caveats. The provider must also take into consideration current estrogen dosage, the age at which hormones were initiated, and whether a patient has undergone an augmentation mammaplasty.3
Both estrogen and testosterone play an important role in bone formation and health. Patients who undergo either medical or surgical interventions that alter sex hormone production, such as GAHT, orchiectomy, or androgen blockade, may be at elevated risk for osteoporosis. Providers should take a thorough medical history to determine patients who may be at risk for osteoporosis and treat them accordingly. Overall, GAHT has a positive effect on bone mineral density. Conversely, gonadectomy, particularly if a patient is not taking GAHT, can decrease bone density. Generally, transgender women, like cisgender women, should undergo DEXA scans starting at the age of 65, with earlier screening considered if they have undergone an orchiectomy and are not currently taking GAHT.3
There is no evidence that GAHT or surgery increases the rate of prostate cancer. Providers should note that the prostate is not removed at the time of gender-affirming surgery and that malignancy or benign prostatic hypertrophy can still occur. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that clinicians have a discussion with cisgender men between the ages of 55 and 69 about the risks and benefits of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening.5 For cisgender men aged 70 and older, the USPSTF recommends against PSA-based screening.5 If digital examination of the prostate is warranted for transfeminine patients, the examination is performed through the neovaginal canal.
Caring for elderly transgender patients is complex. Even though evidence guiding the management of elderly transgender patients is improving, there are still not enough definitive long-term data on this dynamic demographic. Like clinical approaches with hormonal or surgical treatments, caring for transgender elders is also multidisciplinary. Providers should be prepared to work with social workers, geriatric care physicians, endocrinologists, surgeons, and other relevant specialists to assist with potential knowledge gaps. The goals for the aging transgender population are the same as those for cisgender patients – preventing preventable diseases and reducing overall mortality so our patients can enjoy their golden years.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. Contact her at [email protected].
References
1. Carroll L. Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2017;40:127-40.
2. Selix NW et al. Clinical care of the aging LGBT population. J Nurse Pract. 2020;16(7):349-54.
3. World Professional Association for Transgender Health. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people. 2022;8th version.
4. Shatzel JJ et al. Am J Hematol. 2017;92(2):204-8.
5. Wolf-Gould CS and Wolf-Gould CH. Primary and preventative care for transgender patients. In: Ferrando CA, ed. Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2020, p. 114-30.
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease guidelines 2022: Management and treatment
In the United States and around the globe, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remains one of the leading causes of death. In addition to new diagnostic guidelines, the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2022 Report, or GOLD report, sets forth recommendations for management and treatment.
According to the GOLD report, initial management of COPD should aim at reducing exposure to risk factors such as smoking or other chemical exposures. In addition to medications, stable COPD patients should be evaluated for inhaler technique, adherence to prescribed therapies, smoking status, and continued exposure to other risk factors. Also, physical activity should be advised and pulmonary rehabilitation should be considered. Spirometry should be performed annually.
These guidelines offer very practical advice but often are difficult to implement in clinical practice. Everyone knows smoking is harmful and quitting provides huge health benefits, not only regarding COPD. However, nicotine is very addictive, and most smokers cannot just quit. Many need smoking cessation aids and counseling. Additionally, some smokers just don’t want to quit. Regarding workplace exposures, it often is not easy for someone just to change their job. Many are afraid to speak because they are afraid of losing their jobs. Everyone, not just patients with COPD, can benefit from increased physical activity, and all doctors know how difficult it is to motivate patients to do this.
The decision to initiate medications should be based on an individual patient’s symptoms and risk of exacerbations. In general, long-acting bronchodilators, including long-acting beta agonists (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA), are preferred except when immediate relief of dyspnea is needed, and then short-acting bronchodilators should be used. Either a single long-acting or dual long-acting bronchodilator can be initiated. If a patient continues to have dyspnea on a single long-acting bronchodilator, treatment should be switched to a dual therapy.
In general, inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are not recommended for stable COPD patients. If a patient has exacerbations despite appropriate treatment with LABAs, an ICS may be added to the LABA, the GOLD guidelines say. Oral corticosteroids are not recommended for long-term use. PDE4 inhibitors should be considered in patents with severe to very severe airflow obstruction, chronic bronchitis, and exacerbations. Macrolide antibiotics, especially azithromycin, can be considered in acute exacerbations. There is no evidence to support the use of antitussives and mucolytics are advised in only certain patients. Inhaled bronchodilators are advised over oral ones and theophylline is recommended when long-acting bronchodilators are unavailable or unaffordable.
In clinical practice, I see many patients treated based on symptomatology with spirometry testing not being done. This may help control many symptoms, but unless my patient has an accurate diagnosis, I won’t know if my patient is receiving the correct treatment.
It is important to keep in mind that COPD is a progressive disease and without appropriate treatment and monitoring, it will just get worse, and this is most likely to be irreversible.
Medications and treatment goals for patients with COPD
Patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency may benefit from the addition of alpha-1 antitrypsin augmentation therapy, the new guidelines say. In patients with severe disease experiencing dyspnea, oral and parental opioids can be considered. Medications that are used to treat primary pulmonary hypertension are not advised to treat pulmonary hypertension secondary to COPD.
The treatment goals of COPD should be to decrease severity of symptoms, reduce the occurrence of exacerbations, and improve exercise tolerance. Peripheral eosinophil counts can be used to guide the use of ICS to prevent exacerbations. However, the best predictor of exacerbations is previous exacerbations. Frequent exacerbations are defined as two or more annually. Additionally, deteriorating airflow is correlated with increased risk of exacerbations, hospitalizations, and death. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) alone lacks precision to predict exacerbations or death.
Vaccines and pulmonary rehabilitation recommended
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization recommend several vaccines for stable patients with COPD. Influenza vaccine was shown to reduce serious complications in COPD patients. Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) reduced the likelihood of COPD exacerbations. The COVID-19 vaccine also has been effective at reducing hospitalizations, in particular ICU admissions, and death in patients with COPD. The CDC also recommends TdaP and Zoster vaccines.
An acute exacerbation of COPD occurs when a patient experiences worsening of respiratory symptoms that requires additional treatment, according to the updated GOLD guidelines. They are usually associated with increased airway inflammation, mucous productions, and trapping of gases. They are often triggered by viral infections, but bacterial and environment factors play a role as well. Less commonly, fungi such as Aspergillus can be observed as well. COPD exacerbations contribute to overall progression of the disease.
In patients with hypoxemia, supplemental oxygen should be titrated to a target O2 saturation of 88%-92%. It is important to follow blood gases to be sure adequate oxygenation is taking place while at the same time avoiding carbon dioxide retention and/or worsening acidosis. In patients with severe exacerbations whose dyspnea does not respond to initial emergency therapy, ICU admission is warranted. Other factors indicating the need for ICU admission include mental status changes, persistent or worsening hypoxemia, severe or worsening respiratory acidosis, the need for mechanical ventilation, and hemodynamic instability. Following an acute exacerbation, steps to prevent further exacerbations should be initiated.
Systemic glucocorticoids are indicated during acute exacerbations. They have been shown to hasten recovery time and improve functioning of the lungs as well as oxygenation. It is recommended to give prednisone 40 mg per day for 5 days. Antibiotics should be used in exacerbations if patients have dyspnea, sputum production, and purulence of the sputum or require mechanical ventilation. The choice of which antibiotic to use should be based on local bacterial resistance.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is an important component of COPD management. It incorporates exercise, education, and self-management aimed to change behavior and improve conditioning. The benefits of rehab have been shown to be considerable. The optimal length is 6-8 weeks. Palliative and end-of-life care are also very important factors to consider when treating COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidelines.
COPD is a very common disease and cause of mortality seen by family physicians. The GOLD report is an extensive document providing very clear guidelines and evidence to support these guidelines in every level of the treatment of COPD patients. As primary care doctors, we are often the first to treat patients with COPD and it is important to know the latest guidelines.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
In the United States and around the globe, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remains one of the leading causes of death. In addition to new diagnostic guidelines, the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2022 Report, or GOLD report, sets forth recommendations for management and treatment.
According to the GOLD report, initial management of COPD should aim at reducing exposure to risk factors such as smoking or other chemical exposures. In addition to medications, stable COPD patients should be evaluated for inhaler technique, adherence to prescribed therapies, smoking status, and continued exposure to other risk factors. Also, physical activity should be advised and pulmonary rehabilitation should be considered. Spirometry should be performed annually.
These guidelines offer very practical advice but often are difficult to implement in clinical practice. Everyone knows smoking is harmful and quitting provides huge health benefits, not only regarding COPD. However, nicotine is very addictive, and most smokers cannot just quit. Many need smoking cessation aids and counseling. Additionally, some smokers just don’t want to quit. Regarding workplace exposures, it often is not easy for someone just to change their job. Many are afraid to speak because they are afraid of losing their jobs. Everyone, not just patients with COPD, can benefit from increased physical activity, and all doctors know how difficult it is to motivate patients to do this.
The decision to initiate medications should be based on an individual patient’s symptoms and risk of exacerbations. In general, long-acting bronchodilators, including long-acting beta agonists (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA), are preferred except when immediate relief of dyspnea is needed, and then short-acting bronchodilators should be used. Either a single long-acting or dual long-acting bronchodilator can be initiated. If a patient continues to have dyspnea on a single long-acting bronchodilator, treatment should be switched to a dual therapy.
In general, inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are not recommended for stable COPD patients. If a patient has exacerbations despite appropriate treatment with LABAs, an ICS may be added to the LABA, the GOLD guidelines say. Oral corticosteroids are not recommended for long-term use. PDE4 inhibitors should be considered in patents with severe to very severe airflow obstruction, chronic bronchitis, and exacerbations. Macrolide antibiotics, especially azithromycin, can be considered in acute exacerbations. There is no evidence to support the use of antitussives and mucolytics are advised in only certain patients. Inhaled bronchodilators are advised over oral ones and theophylline is recommended when long-acting bronchodilators are unavailable or unaffordable.
In clinical practice, I see many patients treated based on symptomatology with spirometry testing not being done. This may help control many symptoms, but unless my patient has an accurate diagnosis, I won’t know if my patient is receiving the correct treatment.
It is important to keep in mind that COPD is a progressive disease and without appropriate treatment and monitoring, it will just get worse, and this is most likely to be irreversible.
Medications and treatment goals for patients with COPD
Patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency may benefit from the addition of alpha-1 antitrypsin augmentation therapy, the new guidelines say. In patients with severe disease experiencing dyspnea, oral and parental opioids can be considered. Medications that are used to treat primary pulmonary hypertension are not advised to treat pulmonary hypertension secondary to COPD.
The treatment goals of COPD should be to decrease severity of symptoms, reduce the occurrence of exacerbations, and improve exercise tolerance. Peripheral eosinophil counts can be used to guide the use of ICS to prevent exacerbations. However, the best predictor of exacerbations is previous exacerbations. Frequent exacerbations are defined as two or more annually. Additionally, deteriorating airflow is correlated with increased risk of exacerbations, hospitalizations, and death. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) alone lacks precision to predict exacerbations or death.
Vaccines and pulmonary rehabilitation recommended
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization recommend several vaccines for stable patients with COPD. Influenza vaccine was shown to reduce serious complications in COPD patients. Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) reduced the likelihood of COPD exacerbations. The COVID-19 vaccine also has been effective at reducing hospitalizations, in particular ICU admissions, and death in patients with COPD. The CDC also recommends TdaP and Zoster vaccines.
An acute exacerbation of COPD occurs when a patient experiences worsening of respiratory symptoms that requires additional treatment, according to the updated GOLD guidelines. They are usually associated with increased airway inflammation, mucous productions, and trapping of gases. They are often triggered by viral infections, but bacterial and environment factors play a role as well. Less commonly, fungi such as Aspergillus can be observed as well. COPD exacerbations contribute to overall progression of the disease.
In patients with hypoxemia, supplemental oxygen should be titrated to a target O2 saturation of 88%-92%. It is important to follow blood gases to be sure adequate oxygenation is taking place while at the same time avoiding carbon dioxide retention and/or worsening acidosis. In patients with severe exacerbations whose dyspnea does not respond to initial emergency therapy, ICU admission is warranted. Other factors indicating the need for ICU admission include mental status changes, persistent or worsening hypoxemia, severe or worsening respiratory acidosis, the need for mechanical ventilation, and hemodynamic instability. Following an acute exacerbation, steps to prevent further exacerbations should be initiated.
Systemic glucocorticoids are indicated during acute exacerbations. They have been shown to hasten recovery time and improve functioning of the lungs as well as oxygenation. It is recommended to give prednisone 40 mg per day for 5 days. Antibiotics should be used in exacerbations if patients have dyspnea, sputum production, and purulence of the sputum or require mechanical ventilation. The choice of which antibiotic to use should be based on local bacterial resistance.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is an important component of COPD management. It incorporates exercise, education, and self-management aimed to change behavior and improve conditioning. The benefits of rehab have been shown to be considerable. The optimal length is 6-8 weeks. Palliative and end-of-life care are also very important factors to consider when treating COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidelines.
COPD is a very common disease and cause of mortality seen by family physicians. The GOLD report is an extensive document providing very clear guidelines and evidence to support these guidelines in every level of the treatment of COPD patients. As primary care doctors, we are often the first to treat patients with COPD and it is important to know the latest guidelines.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].
In the United States and around the globe, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) remains one of the leading causes of death. In addition to new diagnostic guidelines, the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2022 Report, or GOLD report, sets forth recommendations for management and treatment.
According to the GOLD report, initial management of COPD should aim at reducing exposure to risk factors such as smoking or other chemical exposures. In addition to medications, stable COPD patients should be evaluated for inhaler technique, adherence to prescribed therapies, smoking status, and continued exposure to other risk factors. Also, physical activity should be advised and pulmonary rehabilitation should be considered. Spirometry should be performed annually.
These guidelines offer very practical advice but often are difficult to implement in clinical practice. Everyone knows smoking is harmful and quitting provides huge health benefits, not only regarding COPD. However, nicotine is very addictive, and most smokers cannot just quit. Many need smoking cessation aids and counseling. Additionally, some smokers just don’t want to quit. Regarding workplace exposures, it often is not easy for someone just to change their job. Many are afraid to speak because they are afraid of losing their jobs. Everyone, not just patients with COPD, can benefit from increased physical activity, and all doctors know how difficult it is to motivate patients to do this.
The decision to initiate medications should be based on an individual patient’s symptoms and risk of exacerbations. In general, long-acting bronchodilators, including long-acting beta agonists (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA), are preferred except when immediate relief of dyspnea is needed, and then short-acting bronchodilators should be used. Either a single long-acting or dual long-acting bronchodilator can be initiated. If a patient continues to have dyspnea on a single long-acting bronchodilator, treatment should be switched to a dual therapy.
In general, inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are not recommended for stable COPD patients. If a patient has exacerbations despite appropriate treatment with LABAs, an ICS may be added to the LABA, the GOLD guidelines say. Oral corticosteroids are not recommended for long-term use. PDE4 inhibitors should be considered in patents with severe to very severe airflow obstruction, chronic bronchitis, and exacerbations. Macrolide antibiotics, especially azithromycin, can be considered in acute exacerbations. There is no evidence to support the use of antitussives and mucolytics are advised in only certain patients. Inhaled bronchodilators are advised over oral ones and theophylline is recommended when long-acting bronchodilators are unavailable or unaffordable.
In clinical practice, I see many patients treated based on symptomatology with spirometry testing not being done. This may help control many symptoms, but unless my patient has an accurate diagnosis, I won’t know if my patient is receiving the correct treatment.
It is important to keep in mind that COPD is a progressive disease and without appropriate treatment and monitoring, it will just get worse, and this is most likely to be irreversible.
Medications and treatment goals for patients with COPD
Patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency may benefit from the addition of alpha-1 antitrypsin augmentation therapy, the new guidelines say. In patients with severe disease experiencing dyspnea, oral and parental opioids can be considered. Medications that are used to treat primary pulmonary hypertension are not advised to treat pulmonary hypertension secondary to COPD.
The treatment goals of COPD should be to decrease severity of symptoms, reduce the occurrence of exacerbations, and improve exercise tolerance. Peripheral eosinophil counts can be used to guide the use of ICS to prevent exacerbations. However, the best predictor of exacerbations is previous exacerbations. Frequent exacerbations are defined as two or more annually. Additionally, deteriorating airflow is correlated with increased risk of exacerbations, hospitalizations, and death. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) alone lacks precision to predict exacerbations or death.
Vaccines and pulmonary rehabilitation recommended
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization recommend several vaccines for stable patients with COPD. Influenza vaccine was shown to reduce serious complications in COPD patients. Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) reduced the likelihood of COPD exacerbations. The COVID-19 vaccine also has been effective at reducing hospitalizations, in particular ICU admissions, and death in patients with COPD. The CDC also recommends TdaP and Zoster vaccines.
An acute exacerbation of COPD occurs when a patient experiences worsening of respiratory symptoms that requires additional treatment, according to the updated GOLD guidelines. They are usually associated with increased airway inflammation, mucous productions, and trapping of gases. They are often triggered by viral infections, but bacterial and environment factors play a role as well. Less commonly, fungi such as Aspergillus can be observed as well. COPD exacerbations contribute to overall progression of the disease.
In patients with hypoxemia, supplemental oxygen should be titrated to a target O2 saturation of 88%-92%. It is important to follow blood gases to be sure adequate oxygenation is taking place while at the same time avoiding carbon dioxide retention and/or worsening acidosis. In patients with severe exacerbations whose dyspnea does not respond to initial emergency therapy, ICU admission is warranted. Other factors indicating the need for ICU admission include mental status changes, persistent or worsening hypoxemia, severe or worsening respiratory acidosis, the need for mechanical ventilation, and hemodynamic instability. Following an acute exacerbation, steps to prevent further exacerbations should be initiated.
Systemic glucocorticoids are indicated during acute exacerbations. They have been shown to hasten recovery time and improve functioning of the lungs as well as oxygenation. It is recommended to give prednisone 40 mg per day for 5 days. Antibiotics should be used in exacerbations if patients have dyspnea, sputum production, and purulence of the sputum or require mechanical ventilation. The choice of which antibiotic to use should be based on local bacterial resistance.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is an important component of COPD management. It incorporates exercise, education, and self-management aimed to change behavior and improve conditioning. The benefits of rehab have been shown to be considerable. The optimal length is 6-8 weeks. Palliative and end-of-life care are also very important factors to consider when treating COPD patients, according to the GOLD guidelines.
COPD is a very common disease and cause of mortality seen by family physicians. The GOLD report is an extensive document providing very clear guidelines and evidence to support these guidelines in every level of the treatment of COPD patients. As primary care doctors, we are often the first to treat patients with COPD and it is important to know the latest guidelines.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at [email protected].














