User login
Love them or hate them, masks in schools work
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
On March 26, 2022, Hawaii became the last state in the United States to lift its indoor mask mandate. By the time the current school year started, there were essentially no public school mask mandates either.
Whether you viewed the mask as an emblem of stalwart defiance against a rampaging virus, or a scarlet letter emblematic of the overreaches of public policy, you probably aren’t seeing them much anymore.
And yet, the debate about masks still rages. Who was right, who was wrong? Who trusted science, and what does the science even say? If we brought our country into marriage counseling, would we be told it is time to move on? To look forward, not backward? To plan for our bright future together?
Perhaps. But this question isn’t really moot just because masks have largely disappeared in the United States. Variants may emerge that lead to more infection waves – and other pandemics may occur in the future. And so I think it is important to discuss a study that, with quite rigorous analysis, attempts to answer the following question: Did masking in schools lower students’ and teachers’ risk of COVID?
We are talking about this study, appearing in the New England Journal of Medicine. The short version goes like this.
Researchers had access to two important sources of data. One – an accounting of all the teachers and students (more than 300,000 of them) in 79 public, noncharter school districts in Eastern Massachusetts who tested positive for COVID every week. Two – the date that each of those school districts lifted their mask mandates or (in the case of two districts) didn’t.
Right away, I’m sure you’re thinking of potential issues. Districts that kept masks even when the statewide ban was lifted are likely quite a bit different from districts that dropped masks right away. You’re right, of course – hold on to that thought; we’ll get there.
But first – the big question – would districts that kept their masks on longer do better when it comes to the rate of COVID infection?
When everyone was masking, COVID case rates were pretty similar. Statewide mandates are lifted in late February – and most school districts remove their mandates within a few weeks – the black line are the two districts (Boston and Chelsea) where mask mandates remained in place.
Prior to the mask mandate lifting, you see very similar COVID rates in districts that would eventually remove the mandate and those that would not, with a bit of noise around the initial Omicron wave which saw just a huge amount of people get infected.
And then, after the mandate was lifted, separation. Districts that held on to masks longer had lower rates of COVID infection.
In all, over the 15-weeks of the study, there were roughly 12,000 extra cases of COVID in the mask-free school districts, which corresponds to about 35% of the total COVID burden during that time. And, yes, kids do well with COVID – on average. But 12,000 extra cases is enough to translate into a significant number of important clinical outcomes – think hospitalizations and post-COVID syndromes. And of course, maybe most importantly, missed school days. Positive kids were not allowed in class no matter what district they were in.
Okay – I promised we’d address confounders. This was not a cluster-randomized trial, where some school districts had their mandates removed based on the vicissitudes of a virtual coin flip, as much as many of us would have been interested to see that. The decision to remove masks was up to the various school boards – and they had a lot of pressure on them from many different directions. But all we need to worry about is whether any of those things that pressure a school board to keep masks on would ALSO lead to fewer COVID cases. That’s how confounders work, and how you can get false results in a study like this.
And yes – districts that kept the masks on longer were different than those who took them right off. But check out how they were different.
The districts that kept masks on longer had more low-income students. More Black and Latino students. More students per classroom. These are all risk factors that increase the risk of COVID infection. In other words, the confounding here goes in the opposite direction of the results. If anything, these factors should make you more certain that masking works.
The authors also adjusted for other factors – the community transmission of COVID-19, vaccination rates, school district sizes, and so on. No major change in the results.
One concern I addressed to Dr. Ellie Murray, the biostatistician on the study – could districts that removed masks simply have been testing more to compensate, leading to increased capturing of cases?
If anything, the schools that kept masks on were testing more than the schools that took them off – again that would tend to imply that the results are even stronger than what was reported.
Is this a perfect study? Of course not – it’s one study, it’s from one state. And the relatively large effects from keeping masks on for one or 2 weeks require us to really embrace the concept of exponential growth of infections, but, if COVID has taught us anything, it is that small changes in initial conditions can have pretty big effects.
My daughter, who goes to a public school here in Connecticut, unmasked, was home with COVID this past week. She’s fine. But you know what? She missed a week of school. I worked from home to be with her – though I didn’t test positive. And that is a real cost to both of us that I think we need to consider when we consider the value of masks. Yes, they’re annoying – but if they keep kids in school, might they be worth it? Perhaps not for now, as cases aren’t surging. But in the future, be it a particularly concerning variant, or a whole new pandemic, we should not discount the simple, cheap, and apparently beneficial act of wearing masks to decrease transmission.
Dr. Perry Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The body of evidence for Paxlovid therapy
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dear Colleagues,
We have a mismatch. The evidence supporting treatment for Paxlovid is compelling for people aged 60 or over, but the older patients in the United States are much less likely to be treated. Not only was there a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of high-risk patients which showed 89% reduction of hospitalizations and deaths (median age, 45), but there have been multiple real-world effectiveness studies subsequently published that have partitioned the benefit for age 65 or older, such as the ones from Israel and Hong Kong (age 60+). Overall, the real-world effectiveness in the first month after treatment is at least as good, if not better, than in the high-risk randomized trial.
We’re doing the current survey to find out, but the most likely reasons include (1) lack of confidence of benefit; (2) medication interactions; and (3) concerns over rebound.
Let me address each of these briefly. The lack of confidence in benefit stems from the fact that the initial high-risk trial was in unvaccinated individuals. That concern can now be put aside because all of the several real-world studies confirming the protective benefit against hospitalizations and deaths are in people who have been vaccinated, and a significant proportion received booster shots.
The potential medication interactions due to the ritonavir component of the Paxlovid drug combination, attributable to its cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition, have been unduly emphasized. There are many drug-interaction checkers for Paxlovid, but this one from the University of Liverpool is user friendly, color- and icon-coded, and shows that the vast majority of interactions can be sidestepped by discontinuing the medication of concern for the length of the Paxlovid treatment, 5 days. The simple chart is provided in my recent substack newsletter.
As far as rebound, this problem has unfortunately been exaggerated because of lack of prospective systematic studies and appreciation that a positive test of clinical symptom rebound can occur without Paxlovid. There are soon to be multiple reports that the incidence of Paxlovid rebound is fairly low, in the range of 10%. That concern should not be a reason to withhold treatment.
Now the plot thickens. A new preprint report from the Veterans Health Administration, the largest health care system in the United States, looks at 90-day outcomes of about 9,000 Paxlovid-treated patients and approximately 47,000 controls. Not only was there a 26% reduction in long COVID, but of the breakdown of 12 organs/systems and symptoms, 10 of 12 were significantly reduced with Paxlovid, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and neurocognitive impairment. There was also a 48% reduction in death and a 30% reduction in hospitalizations after the first 30 days. I have reviewed all of these data and put them in context in a recent newsletter. A key point is that the magnitude of benefit was unaffected by vaccination or booster status, or prior COVID infections, or unvaccinated status. Also, it was the same for men and women, as well as for age > 70 and age < 60. These findings all emphasize a new reason to be using Paxlovid therapy, and if replicated, Paxlovid may even be indicated for younger patients (who are at low risk for hospitalizations and deaths but at increased risk for long COVID).
In summary, for older patients, we should be thinking of why we should be using Paxlovid rather than the reason not to treat. We’ll be interested in the survey results to understand the mismatch better, and we look forward to your ideas and feedback to make better use of this treatment for the people who need it the most.
Sincerely yours, Eric J. Topol, MD
Dr. Topol reports no conflicts of interest with Pfizer; he receives no honoraria or speaker fees, does not serve in an advisory role, and has no financial association with the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Which exercise is best for bone health?
An 18-year-old woman with Crohn’s disease (diagnosed 3 years ago) came to my office for advice regarding management of osteoporosis. Her bone density was low for her age, and she had three low-impact fractures of her long bones in the preceding 4 years.
Loss of weight after the onset of Crohn’s disease, subsequent loss of periods, inflammation associated with her underlying diagnosis, and early treatment with glucocorticoids (known to have deleterious effects on bone) were believed to have caused osteoporosis in this young woman.
A few months previously, she was switched to a medication that doesn’t impair bone health and glucocorticoids were discontinued; her weight began to improve, and her Crohn’s disease was now in remission. Her menses had resumed about 3 months before her visit to my clinic after a prolonged period without periods. She was on calcium and vitamin D supplements, with normal levels of vitamin D.
Many factors determine bone health including (but not limited to) genetics, nutritional status, exercise activity (with mechanical loading of bones), macro- and micronutrient intake, hormonal status, chronic inflammation and other disease states, and medication use.
Exercise certainly has beneficial effects on bone. Bone-loading activities increase bone formation through the activation of certain cells in bone called osteocytes, which serve as mechanosensors and sense bone loading. Osteocytes make a hormone called sclerostin, which typically inhibits bone formation. When osteocytes sense bone-loading activities, sclerostin secretion reduces, allowing for increased bone formation.
Consistent with this, investigators in Canada have demonstrated greater increases in bone density and strength in schoolchildren who engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity, particularly bone-loading exercise, during the school day, compared with those who don’t (J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Mar;22[3]:434-46; J Bone Miner Res. 2017 Jul;32[7]:1525-36). In females, normal levels of estrogen seem necessary for osteocytes to bring about these effects after bone-loading activities. This is probably one of several reasons why athletes who lose their periods (indicative of low estrogen levels) and develop low bone density with an increased risk for fracture even when they are still at a normal weight (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jun 1;103[6]:2392-402; Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Aug;47[8]:1577-86).
One concern around prescribing bone-loading activity or exercise to persons with osteoporosis is whether it would increase the risk for fracture from the impact on fragile bone. The extent of bone loading safe for fragile bone can be difficult to determine. Furthermore, excessive exercise may worsen bone health by causing weight loss or loss of periods in women. Very careful monitoring may be necessary to ensure that energy balance is maintained. Therefore, the nature and volume of exercise should be discussed with one’s doctor or physical therapist as well as a dietitian (if the patient is seeing one).
In patients with osteoporosis, high-impact activities such as jumping; repetitive impact activities such as running or jogging; and bending and twisting activities such as touching one’s toes, golf, tennis, and bowling aren’t recommended because they increase the risk for fracture. Even yoga poses should be discussed, because some may increase the risk for compression fractures of the vertebrae in the spine.
Strength and resistance training are generally believed to be good for bones. Strength training involves activities that build muscle strength and mass. Resistance training builds muscle strength, mass, and endurance by making muscles work against some form of resistance. Such activities include weight training with free weights or weight machines, use of resistance bands, and use of one’s own body to strengthen major muscle groups (such as through push-ups, squats, lunges, and gluteus maximus extension).
Some amount of weight-bearing aerobic training is also recommended, including walking, low-impact aerobics, the elliptical, and stair-climbing. Non–weight-bearing activities, such as swimming and cycling, typically don’t contribute to improving bone density.
In older individuals with osteoporosis, agility exercises are particularly useful to reduce the fall risk (J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004 May;52[5]:657-65; CMAJ. 2002 Oct 29;167[9]:997-1004). These can be structured to improve hand-eye coordination, foot-eye coordination, static and dynamic balance, and reaction time. Agility exercises with resistance training help improve bone density in older women.
An optimal exercise regimen includes a combination of strength and resistance training; weight-bearing aerobic training; and exercises that build flexibility, stability, and balance. A doctor, physical therapist, or trainer with expertise in the right combination of exercises should be consulted to ensure optimal effects on bone and general health.
In those at risk for overexercising to the point that they start to lose weight or lose their periods, and certainly in all women with disordered eating patterns, a dietitian should be part of the decision team to ensure that energy balance is maintained. In this group, particularly in very-low-weight women with eating disorders, exercise activity is often limited until they reach a healthier weight, and ideally after their menses resume.
For my patient with Crohn’s disease, I recommended that she see a physical therapist and a dietitian for guidance about a graded increase in exercise activity and an exercise regimen that would work best for her. I assess her bone density annually using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Her bone density has gradually improved with the combination of weight gain, resumption of menses, medications for Crohn’s disease that do not affect bone deleteriously, remission of Crohn’s disease, and her exercise regimen.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology at Mass General Hospital for Children and professor in the department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She reported conflicts of interest with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An 18-year-old woman with Crohn’s disease (diagnosed 3 years ago) came to my office for advice regarding management of osteoporosis. Her bone density was low for her age, and she had three low-impact fractures of her long bones in the preceding 4 years.
Loss of weight after the onset of Crohn’s disease, subsequent loss of periods, inflammation associated with her underlying diagnosis, and early treatment with glucocorticoids (known to have deleterious effects on bone) were believed to have caused osteoporosis in this young woman.
A few months previously, she was switched to a medication that doesn’t impair bone health and glucocorticoids were discontinued; her weight began to improve, and her Crohn’s disease was now in remission. Her menses had resumed about 3 months before her visit to my clinic after a prolonged period without periods. She was on calcium and vitamin D supplements, with normal levels of vitamin D.
Many factors determine bone health including (but not limited to) genetics, nutritional status, exercise activity (with mechanical loading of bones), macro- and micronutrient intake, hormonal status, chronic inflammation and other disease states, and medication use.
Exercise certainly has beneficial effects on bone. Bone-loading activities increase bone formation through the activation of certain cells in bone called osteocytes, which serve as mechanosensors and sense bone loading. Osteocytes make a hormone called sclerostin, which typically inhibits bone formation. When osteocytes sense bone-loading activities, sclerostin secretion reduces, allowing for increased bone formation.
Consistent with this, investigators in Canada have demonstrated greater increases in bone density and strength in schoolchildren who engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity, particularly bone-loading exercise, during the school day, compared with those who don’t (J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Mar;22[3]:434-46; J Bone Miner Res. 2017 Jul;32[7]:1525-36). In females, normal levels of estrogen seem necessary for osteocytes to bring about these effects after bone-loading activities. This is probably one of several reasons why athletes who lose their periods (indicative of low estrogen levels) and develop low bone density with an increased risk for fracture even when they are still at a normal weight (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jun 1;103[6]:2392-402; Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Aug;47[8]:1577-86).
One concern around prescribing bone-loading activity or exercise to persons with osteoporosis is whether it would increase the risk for fracture from the impact on fragile bone. The extent of bone loading safe for fragile bone can be difficult to determine. Furthermore, excessive exercise may worsen bone health by causing weight loss or loss of periods in women. Very careful monitoring may be necessary to ensure that energy balance is maintained. Therefore, the nature and volume of exercise should be discussed with one’s doctor or physical therapist as well as a dietitian (if the patient is seeing one).
In patients with osteoporosis, high-impact activities such as jumping; repetitive impact activities such as running or jogging; and bending and twisting activities such as touching one’s toes, golf, tennis, and bowling aren’t recommended because they increase the risk for fracture. Even yoga poses should be discussed, because some may increase the risk for compression fractures of the vertebrae in the spine.
Strength and resistance training are generally believed to be good for bones. Strength training involves activities that build muscle strength and mass. Resistance training builds muscle strength, mass, and endurance by making muscles work against some form of resistance. Such activities include weight training with free weights or weight machines, use of resistance bands, and use of one’s own body to strengthen major muscle groups (such as through push-ups, squats, lunges, and gluteus maximus extension).
Some amount of weight-bearing aerobic training is also recommended, including walking, low-impact aerobics, the elliptical, and stair-climbing. Non–weight-bearing activities, such as swimming and cycling, typically don’t contribute to improving bone density.
In older individuals with osteoporosis, agility exercises are particularly useful to reduce the fall risk (J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004 May;52[5]:657-65; CMAJ. 2002 Oct 29;167[9]:997-1004). These can be structured to improve hand-eye coordination, foot-eye coordination, static and dynamic balance, and reaction time. Agility exercises with resistance training help improve bone density in older women.
An optimal exercise regimen includes a combination of strength and resistance training; weight-bearing aerobic training; and exercises that build flexibility, stability, and balance. A doctor, physical therapist, or trainer with expertise in the right combination of exercises should be consulted to ensure optimal effects on bone and general health.
In those at risk for overexercising to the point that they start to lose weight or lose their periods, and certainly in all women with disordered eating patterns, a dietitian should be part of the decision team to ensure that energy balance is maintained. In this group, particularly in very-low-weight women with eating disorders, exercise activity is often limited until they reach a healthier weight, and ideally after their menses resume.
For my patient with Crohn’s disease, I recommended that she see a physical therapist and a dietitian for guidance about a graded increase in exercise activity and an exercise regimen that would work best for her. I assess her bone density annually using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Her bone density has gradually improved with the combination of weight gain, resumption of menses, medications for Crohn’s disease that do not affect bone deleteriously, remission of Crohn’s disease, and her exercise regimen.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology at Mass General Hospital for Children and professor in the department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She reported conflicts of interest with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An 18-year-old woman with Crohn’s disease (diagnosed 3 years ago) came to my office for advice regarding management of osteoporosis. Her bone density was low for her age, and she had three low-impact fractures of her long bones in the preceding 4 years.
Loss of weight after the onset of Crohn’s disease, subsequent loss of periods, inflammation associated with her underlying diagnosis, and early treatment with glucocorticoids (known to have deleterious effects on bone) were believed to have caused osteoporosis in this young woman.
A few months previously, she was switched to a medication that doesn’t impair bone health and glucocorticoids were discontinued; her weight began to improve, and her Crohn’s disease was now in remission. Her menses had resumed about 3 months before her visit to my clinic after a prolonged period without periods. She was on calcium and vitamin D supplements, with normal levels of vitamin D.
Many factors determine bone health including (but not limited to) genetics, nutritional status, exercise activity (with mechanical loading of bones), macro- and micronutrient intake, hormonal status, chronic inflammation and other disease states, and medication use.
Exercise certainly has beneficial effects on bone. Bone-loading activities increase bone formation through the activation of certain cells in bone called osteocytes, which serve as mechanosensors and sense bone loading. Osteocytes make a hormone called sclerostin, which typically inhibits bone formation. When osteocytes sense bone-loading activities, sclerostin secretion reduces, allowing for increased bone formation.
Consistent with this, investigators in Canada have demonstrated greater increases in bone density and strength in schoolchildren who engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity, particularly bone-loading exercise, during the school day, compared with those who don’t (J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Mar;22[3]:434-46; J Bone Miner Res. 2017 Jul;32[7]:1525-36). In females, normal levels of estrogen seem necessary for osteocytes to bring about these effects after bone-loading activities. This is probably one of several reasons why athletes who lose their periods (indicative of low estrogen levels) and develop low bone density with an increased risk for fracture even when they are still at a normal weight (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jun 1;103[6]:2392-402; Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Aug;47[8]:1577-86).
One concern around prescribing bone-loading activity or exercise to persons with osteoporosis is whether it would increase the risk for fracture from the impact on fragile bone. The extent of bone loading safe for fragile bone can be difficult to determine. Furthermore, excessive exercise may worsen bone health by causing weight loss or loss of periods in women. Very careful monitoring may be necessary to ensure that energy balance is maintained. Therefore, the nature and volume of exercise should be discussed with one’s doctor or physical therapist as well as a dietitian (if the patient is seeing one).
In patients with osteoporosis, high-impact activities such as jumping; repetitive impact activities such as running or jogging; and bending and twisting activities such as touching one’s toes, golf, tennis, and bowling aren’t recommended because they increase the risk for fracture. Even yoga poses should be discussed, because some may increase the risk for compression fractures of the vertebrae in the spine.
Strength and resistance training are generally believed to be good for bones. Strength training involves activities that build muscle strength and mass. Resistance training builds muscle strength, mass, and endurance by making muscles work against some form of resistance. Such activities include weight training with free weights or weight machines, use of resistance bands, and use of one’s own body to strengthen major muscle groups (such as through push-ups, squats, lunges, and gluteus maximus extension).
Some amount of weight-bearing aerobic training is also recommended, including walking, low-impact aerobics, the elliptical, and stair-climbing. Non–weight-bearing activities, such as swimming and cycling, typically don’t contribute to improving bone density.
In older individuals with osteoporosis, agility exercises are particularly useful to reduce the fall risk (J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004 May;52[5]:657-65; CMAJ. 2002 Oct 29;167[9]:997-1004). These can be structured to improve hand-eye coordination, foot-eye coordination, static and dynamic balance, and reaction time. Agility exercises with resistance training help improve bone density in older women.
An optimal exercise regimen includes a combination of strength and resistance training; weight-bearing aerobic training; and exercises that build flexibility, stability, and balance. A doctor, physical therapist, or trainer with expertise in the right combination of exercises should be consulted to ensure optimal effects on bone and general health.
In those at risk for overexercising to the point that they start to lose weight or lose their periods, and certainly in all women with disordered eating patterns, a dietitian should be part of the decision team to ensure that energy balance is maintained. In this group, particularly in very-low-weight women with eating disorders, exercise activity is often limited until they reach a healthier weight, and ideally after their menses resume.
For my patient with Crohn’s disease, I recommended that she see a physical therapist and a dietitian for guidance about a graded increase in exercise activity and an exercise regimen that would work best for her. I assess her bone density annually using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Her bone density has gradually improved with the combination of weight gain, resumption of menses, medications for Crohn’s disease that do not affect bone deleteriously, remission of Crohn’s disease, and her exercise regimen.
Dr. Misra is chief of the division of pediatric endocrinology at Mass General Hospital for Children and professor in the department of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston. She reported conflicts of interest with AbbVie, Sanofi, and Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
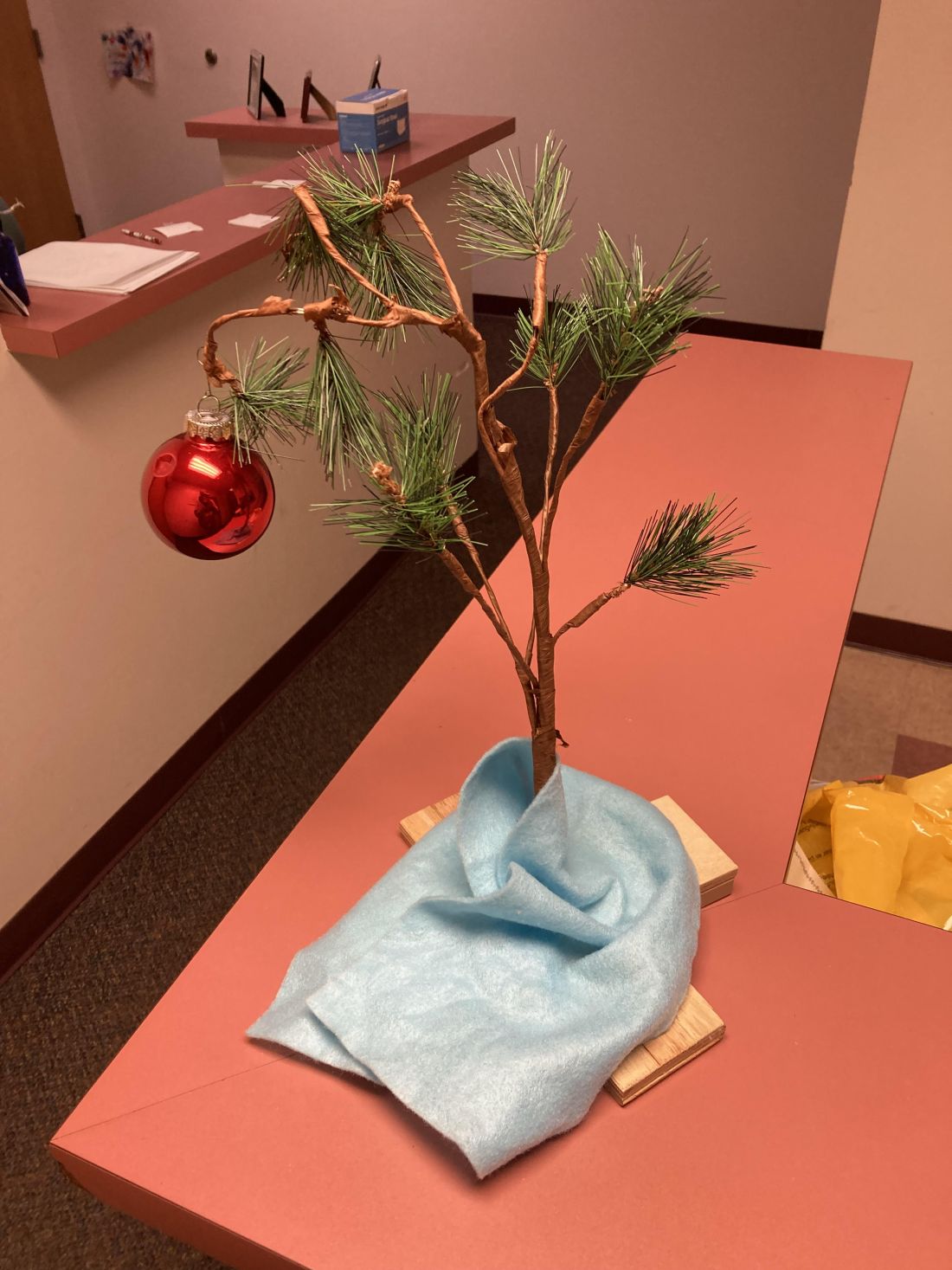
The Charlie Brown tree
I put a Christmas tree up early in November.
It’s not like it’s a real tree, or even a fancy one. For that matter, I’m Jewish.
Growing up in the 1970s one thing that could be relied on every year was the Charlie Brown Christmas special. It never changed. By age 5 you knew most of the lines, and loved the highlight when Charlie Brown brings home the saddest-looking tree ever, which collapses when he puts a single bauble on it.
Years ago, my kids gave me a Charlie Brown tree as a gift. It even plays the late Vince Guaraldi’s immortal Peanuts theme when you push a button. I forgot about it for a few years, then discovered it, and immediately brought it to my office.
I’m not a fan of holiday creep, where they move up earlier in the year, so I used to put it up after Thanksgiving. But we close the office 2-3 weeks later for the rest of the year. I like the tree, my staff likes the tree, and my patients like the tree, so I just started putting it up in early November so we can enjoy it for a month.
It’s whimsical and brings back memories of innocence, childhood, and (of course) Peanuts. It sets a cheerful tone when you see it there. Very few of my patients can resist pressing the button and playing the music as they go by.
The start of a new year is a relatively arbitrary date, chosen long ago. But its approach is always a reminder that life goes on. We continue our trips around the sun. Good times and bad times come and go, but time never stops.
In bad years the tree reminds me that it’s coming to an end, and to look toward the next. In good years it reminds me that it’s time to be ready for the surprises of the coming one.
In mid-December, after the patients are done for the last day of the year, I quietly put it away. It’s a vaguely somber moment, but at the same time I’m glad to know I now have 2-3 weeks of home time. It mostly involves working at my desk and returning phone calls, but there’s also time to relax with my kids, do jigsaw puzzles, and enjoy the Phoenix winter weather as a break before the next round starts.
To those who disagree with my choice of decoration or its timing, I simply respond: “Good grief!”
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I put a Christmas tree up early in November.
It’s not like it’s a real tree, or even a fancy one. For that matter, I’m Jewish.
Growing up in the 1970s one thing that could be relied on every year was the Charlie Brown Christmas special. It never changed. By age 5 you knew most of the lines, and loved the highlight when Charlie Brown brings home the saddest-looking tree ever, which collapses when he puts a single bauble on it.
Years ago, my kids gave me a Charlie Brown tree as a gift. It even plays the late Vince Guaraldi’s immortal Peanuts theme when you push a button. I forgot about it for a few years, then discovered it, and immediately brought it to my office.
I’m not a fan of holiday creep, where they move up earlier in the year, so I used to put it up after Thanksgiving. But we close the office 2-3 weeks later for the rest of the year. I like the tree, my staff likes the tree, and my patients like the tree, so I just started putting it up in early November so we can enjoy it for a month.
It’s whimsical and brings back memories of innocence, childhood, and (of course) Peanuts. It sets a cheerful tone when you see it there. Very few of my patients can resist pressing the button and playing the music as they go by.
The start of a new year is a relatively arbitrary date, chosen long ago. But its approach is always a reminder that life goes on. We continue our trips around the sun. Good times and bad times come and go, but time never stops.
In bad years the tree reminds me that it’s coming to an end, and to look toward the next. In good years it reminds me that it’s time to be ready for the surprises of the coming one.
In mid-December, after the patients are done for the last day of the year, I quietly put it away. It’s a vaguely somber moment, but at the same time I’m glad to know I now have 2-3 weeks of home time. It mostly involves working at my desk and returning phone calls, but there’s also time to relax with my kids, do jigsaw puzzles, and enjoy the Phoenix winter weather as a break before the next round starts.
To those who disagree with my choice of decoration or its timing, I simply respond: “Good grief!”
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
I put a Christmas tree up early in November.
It’s not like it’s a real tree, or even a fancy one. For that matter, I’m Jewish.
Growing up in the 1970s one thing that could be relied on every year was the Charlie Brown Christmas special. It never changed. By age 5 you knew most of the lines, and loved the highlight when Charlie Brown brings home the saddest-looking tree ever, which collapses when he puts a single bauble on it.
Years ago, my kids gave me a Charlie Brown tree as a gift. It even plays the late Vince Guaraldi’s immortal Peanuts theme when you push a button. I forgot about it for a few years, then discovered it, and immediately brought it to my office.
I’m not a fan of holiday creep, where they move up earlier in the year, so I used to put it up after Thanksgiving. But we close the office 2-3 weeks later for the rest of the year. I like the tree, my staff likes the tree, and my patients like the tree, so I just started putting it up in early November so we can enjoy it for a month.
It’s whimsical and brings back memories of innocence, childhood, and (of course) Peanuts. It sets a cheerful tone when you see it there. Very few of my patients can resist pressing the button and playing the music as they go by.
The start of a new year is a relatively arbitrary date, chosen long ago. But its approach is always a reminder that life goes on. We continue our trips around the sun. Good times and bad times come and go, but time never stops.
In bad years the tree reminds me that it’s coming to an end, and to look toward the next. In good years it reminds me that it’s time to be ready for the surprises of the coming one.
In mid-December, after the patients are done for the last day of the year, I quietly put it away. It’s a vaguely somber moment, but at the same time I’m glad to know I now have 2-3 weeks of home time. It mostly involves working at my desk and returning phone calls, but there’s also time to relax with my kids, do jigsaw puzzles, and enjoy the Phoenix winter weather as a break before the next round starts.
To those who disagree with my choice of decoration or its timing, I simply respond: “Good grief!”
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A new ultrabrief screening scale for pediatric OCD
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) affects 1-2% of the population. The disorder is characterized by recurrent intrusive unwanted thoughts (obsessions) that cause significant distress and anxiety, and behavioral or mental rituals (compulsions) that are performed to reduce distress stemming from obsessions. OCD may onset at any time in life, but most commonly begins in childhood or in early adulthood.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with exposure and response prevention is an empirically based and highly effective treatment for OCD. However, most youth with OCD do not receive any treatment, which is related to a shortage of mental health care providers with expertise in assessment and treatment of the disorder, and misdiagnosis of the disorder is all too prevalent.
Aside from the subjective emotional toll associated with OCD, individuals living with this disorder frequently experience interpersonal, academic, and vocational impairments. Nevertheless, OCD is often overlooked or misdiagnosed. This may be more pronounced in youth with OCD, particularly in primary health care settings and large nonspecialized medical institutions. In fact, research indicates that pediatric OCD is often underrecognized even among mental health professionals. This situation is not new, and in fact the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom stated that there is an urgent need to develop brief reliable screeners for OCD nearly 20 years ago.
Although there were several attempts to develop brief screening scales for adults and youth with OCD, none of them were found to be suitable for use as rapid screening tools in nonspecialized settings. One of the primary reasons is that OCD is associated with different “themes” or dimensions. For example, a child with OCD may engage in cleaning rituals because the context (or dimension) of their obsessions is contamination concerns. Another child with OCD, who may suffer from similar overall symptom severity, may primarily engage in checking rituals which are related with obsessions associated with fear of being responsible for harm. Therefore, one child with OCD may score very high on items assessing one dimension (e.g., contamination concerns), but very low on another dimension (e.g., harm obsessions).
This results in a known challenge in the assessment and psychometrics of self-report (as opposed to clinician administered) measures of OCD. Secondly, development of such measures requires very large carefully screened samples of individuals with OCD, with other disorders, and those without a known psychological disorder – which may be more challenging than requiring adult participants.
To accomplish this, we harmonized data from several sites that included three samples of carefully screened youths with OCD, with other disorders, and without known disorders who completed multiple self-report questionnaires, including the 21-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV).
Utilizing psychometric analyses including factor analyses, invariance analyses, and item response theory methodologies, we were able to develop an ultrabrief measure extracted from the OCI-CV: the 5-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV-5). This very brief self-report measure was found to have very good psychometric properties including a sensitive and specific clinical cutoff score. Youth who score at or above the cutoff score are nearly 21 times more likely to meet criteria for OCD.
This measure corresponds to a need to rapidly screen for OCD in children in nonspecialized settings, including community mental health clinics, primary care settings, and pediatric treatment facilities. However, it is important to note it is not a diagnostic measure. The measure is intended to identify youth who should be referred to a mental health care professional to conduct a diagnostic interview.
Dr. Abramovitch is a clinical psychologist and neuropsychologist based in Austin, Tex., and an associate professor at Texas State University. Dr. Abramowitz is professor and director of clinical training in the Anxiety and Stress Lab at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. McKay is professor of psychology at Fordham University, Bronx, N.Y.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) affects 1-2% of the population. The disorder is characterized by recurrent intrusive unwanted thoughts (obsessions) that cause significant distress and anxiety, and behavioral or mental rituals (compulsions) that are performed to reduce distress stemming from obsessions. OCD may onset at any time in life, but most commonly begins in childhood or in early adulthood.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with exposure and response prevention is an empirically based and highly effective treatment for OCD. However, most youth with OCD do not receive any treatment, which is related to a shortage of mental health care providers with expertise in assessment and treatment of the disorder, and misdiagnosis of the disorder is all too prevalent.
Aside from the subjective emotional toll associated with OCD, individuals living with this disorder frequently experience interpersonal, academic, and vocational impairments. Nevertheless, OCD is often overlooked or misdiagnosed. This may be more pronounced in youth with OCD, particularly in primary health care settings and large nonspecialized medical institutions. In fact, research indicates that pediatric OCD is often underrecognized even among mental health professionals. This situation is not new, and in fact the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom stated that there is an urgent need to develop brief reliable screeners for OCD nearly 20 years ago.
Although there were several attempts to develop brief screening scales for adults and youth with OCD, none of them were found to be suitable for use as rapid screening tools in nonspecialized settings. One of the primary reasons is that OCD is associated with different “themes” or dimensions. For example, a child with OCD may engage in cleaning rituals because the context (or dimension) of their obsessions is contamination concerns. Another child with OCD, who may suffer from similar overall symptom severity, may primarily engage in checking rituals which are related with obsessions associated with fear of being responsible for harm. Therefore, one child with OCD may score very high on items assessing one dimension (e.g., contamination concerns), but very low on another dimension (e.g., harm obsessions).
This results in a known challenge in the assessment and psychometrics of self-report (as opposed to clinician administered) measures of OCD. Secondly, development of such measures requires very large carefully screened samples of individuals with OCD, with other disorders, and those without a known psychological disorder – which may be more challenging than requiring adult participants.
To accomplish this, we harmonized data from several sites that included three samples of carefully screened youths with OCD, with other disorders, and without known disorders who completed multiple self-report questionnaires, including the 21-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV).
Utilizing psychometric analyses including factor analyses, invariance analyses, and item response theory methodologies, we were able to develop an ultrabrief measure extracted from the OCI-CV: the 5-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV-5). This very brief self-report measure was found to have very good psychometric properties including a sensitive and specific clinical cutoff score. Youth who score at or above the cutoff score are nearly 21 times more likely to meet criteria for OCD.
This measure corresponds to a need to rapidly screen for OCD in children in nonspecialized settings, including community mental health clinics, primary care settings, and pediatric treatment facilities. However, it is important to note it is not a diagnostic measure. The measure is intended to identify youth who should be referred to a mental health care professional to conduct a diagnostic interview.
Dr. Abramovitch is a clinical psychologist and neuropsychologist based in Austin, Tex., and an associate professor at Texas State University. Dr. Abramowitz is professor and director of clinical training in the Anxiety and Stress Lab at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. McKay is professor of psychology at Fordham University, Bronx, N.Y.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) affects 1-2% of the population. The disorder is characterized by recurrent intrusive unwanted thoughts (obsessions) that cause significant distress and anxiety, and behavioral or mental rituals (compulsions) that are performed to reduce distress stemming from obsessions. OCD may onset at any time in life, but most commonly begins in childhood or in early adulthood.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) with exposure and response prevention is an empirically based and highly effective treatment for OCD. However, most youth with OCD do not receive any treatment, which is related to a shortage of mental health care providers with expertise in assessment and treatment of the disorder, and misdiagnosis of the disorder is all too prevalent.
Aside from the subjective emotional toll associated with OCD, individuals living with this disorder frequently experience interpersonal, academic, and vocational impairments. Nevertheless, OCD is often overlooked or misdiagnosed. This may be more pronounced in youth with OCD, particularly in primary health care settings and large nonspecialized medical institutions. In fact, research indicates that pediatric OCD is often underrecognized even among mental health professionals. This situation is not new, and in fact the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom stated that there is an urgent need to develop brief reliable screeners for OCD nearly 20 years ago.
Although there were several attempts to develop brief screening scales for adults and youth with OCD, none of them were found to be suitable for use as rapid screening tools in nonspecialized settings. One of the primary reasons is that OCD is associated with different “themes” or dimensions. For example, a child with OCD may engage in cleaning rituals because the context (or dimension) of their obsessions is contamination concerns. Another child with OCD, who may suffer from similar overall symptom severity, may primarily engage in checking rituals which are related with obsessions associated with fear of being responsible for harm. Therefore, one child with OCD may score very high on items assessing one dimension (e.g., contamination concerns), but very low on another dimension (e.g., harm obsessions).
This results in a known challenge in the assessment and psychometrics of self-report (as opposed to clinician administered) measures of OCD. Secondly, development of such measures requires very large carefully screened samples of individuals with OCD, with other disorders, and those without a known psychological disorder – which may be more challenging than requiring adult participants.
To accomplish this, we harmonized data from several sites that included three samples of carefully screened youths with OCD, with other disorders, and without known disorders who completed multiple self-report questionnaires, including the 21-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV).
Utilizing psychometric analyses including factor analyses, invariance analyses, and item response theory methodologies, we were able to develop an ultrabrief measure extracted from the OCI-CV: the 5-item Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory – Child Version (OCI-CV-5). This very brief self-report measure was found to have very good psychometric properties including a sensitive and specific clinical cutoff score. Youth who score at or above the cutoff score are nearly 21 times more likely to meet criteria for OCD.
This measure corresponds to a need to rapidly screen for OCD in children in nonspecialized settings, including community mental health clinics, primary care settings, and pediatric treatment facilities. However, it is important to note it is not a diagnostic measure. The measure is intended to identify youth who should be referred to a mental health care professional to conduct a diagnostic interview.
Dr. Abramovitch is a clinical psychologist and neuropsychologist based in Austin, Tex., and an associate professor at Texas State University. Dr. Abramowitz is professor and director of clinical training in the Anxiety and Stress Lab at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. McKay is professor of psychology at Fordham University, Bronx, N.Y.
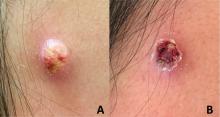
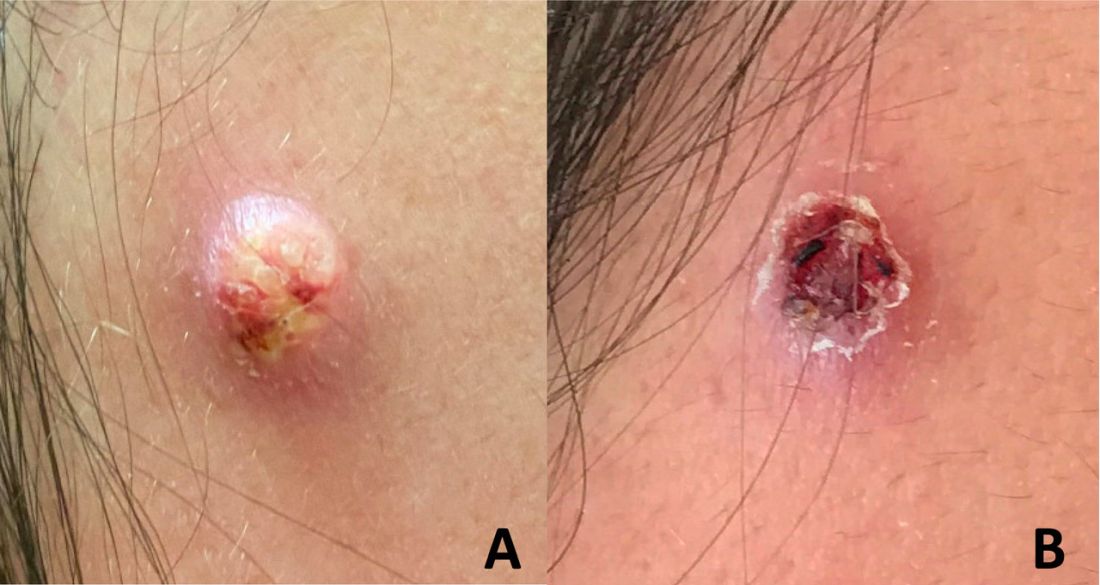
An adolescent male presents with an eroded bump on the temple
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
The correct answer is (D), molluscum contagiosum. Upon surgical excision, the pathology indicated the lesion was consistent with molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign skin disorder caused by a pox virus and is frequently seen in children. This disease is transmitted primarily through direct skin contact with an infected individual.1 Contaminated fomites have been suggested as another source of infection.2 The typical lesion appears dome-shaped, round, and pinkish-purple in color.1 The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months and is typically self-limited in immunocompetent hosts; however, in immunocompromised persons, molluscum contagiosum lesions may present atypically such that they are larger in size and/or resemble malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma (for single lesions), or other infectious diseases, such as cryptococcosis and histoplasmosis (for more numerous lesions).3,4 A giant atypical molluscum contagiosum is rarely seen in healthy individuals.
What’s on the differential?
The recent episode of bleeding raises concern for other neoplastic processes of the skin including squamous cell carcinoma or basal cell carcinoma as well as cutaneous metastatic rhabdoid tumor, given the patient’s history.
Eruptive keratoacanthomas are also reported in patients taking nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, which the patient has received for treatment of his recurrent metastatic rhabdoid tumor.5 More common entities such as a pyogenic granuloma or verruca are also included on the differential. The initial presentation of the lesion, however, is more consistent with the pearly umbilicated papules associated with molluscum contagiosum.
Comments from Dr. Eichenfield
This is a very hard diagnosis to make with the clinical findings and history.
Molluscum contagiosum infections are common, but with this patient’s medical history, biopsy and excision with pathologic examination was an appropriate approach to make a certain diagnosis.
Ms. Moyal is a research associate in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego.
References
1. Brown J et al. Int J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;45(2):93-9.
2. Hanson D and Diven DG. Dermatol Online J. 2003 Mar;9(2).
3. Badri T and Gandhi GR. Molluscum contagiosum. 2022. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing.
4. Schwartz JJ and Myskowski PL. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Oct 1;27(4):583-8.
5. Antonov NK et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Apr 5;5(4):342-5.
Will Congress step up to save primary care?
Primary care and family physicians operate on the front lines of health care, working tirelessly to serve patients and their families. However, many primary care practices are operating on tight margins and cannot sustain additional financial hits. As we continue to navigate a pandemic that has altered our health care landscape, we traveled to Capitol Hill to urge Congress to act on two critical issues: Medicare payment reform and streamlining administrative burden for physicians.
The current Medicare system for compensating physicians jeopardizes access to primary care. Family physicians, along with other primary care clinicians, are facing significant cuts in payments and rising inflation that threaten our ability to care for patients.
Each of us has experienced the effects of this pincer in devastating ways – from the independent clinicians who have been forced to sell their practices to hospitals or large health systems, to the physicians who are retiring early, leaving their practices, or even closing them because they can’t afford to keep their doors open.
Practices also struggle to cover the rising costs of staff wages, leasing space, and purchasing supplies and equipment, leaving little room for innovation or investments to transition into new payment models. Meanwhile, hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, ambulatory surgery centers, and other Medicare providers receive annual payment increases to account for rising costs.
Insufficient Medicare payments also challenge practices that serve many publicly insured patients. If practices cannot cover their expenses, they may be forced to turn away new Medicare and Medicaid patients – something that goes against the core tenets of our health care system.
Fortunately, we have some solutions. We’re asking Congress to pass the Supporting Medicare Providers Act of 2022, which calls for a 4.42% positive adjustment to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) conversion factor for 2023 to offset the statutory reduction triggered by budget neutrality rules.
We also are calling on lawmakers to end the statutory freeze on annual updates to the MPFS and enact a positive annual update to the conversion factor based on the Medicare Economic Index. This critical relief would stave off the most immediate cuts while giving us more time to work with Congress on comprehensive reforms to the Medicare physician payment system.
As many practices struggle to operate, burnout among primary care physicians has also increased, with research showing that 66% of primary care physicians reported frequent burnout symptoms in 2021. Streamlining prior authorizations – a cumbersome process that requires physicians to obtain preapproval for treatments or tests before providing care to patients, and can risk patients’ access to timely care – is one way to reduce burden and alleviate burnout.
According to the American Medical Association, 82% of physicians report that prior authorization can lead to patients abandoning care, and 93% believe that prior authorization delays access to necessary care.
All of us have had patients whose care has been affected by these delays, including difficulty in getting necessary medications filled or having medical procedures postponed. Moreover, primary care physicians and their staff spend hours each week completing paperwork and communicating with insurers to ensure that their patients can access the treatments and services they need.
That is why we’re urging the Senate to pass the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, which would streamline the prior authorization process in the Medicare Advantage program.
As family physicians, we are in a unique position to help improve our patients’ health and their quality of life. But we can’t do this alone. We need the support of policy makers to make patient health and primary care a national priority.
Dr. Iroku-Malize is a family physician in Long Island, New York, and President of the American Academy of Family Physicians. Dr. Ransone is a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair, immediate past president of the AAFP. Dr. Furr is a family physician in Jackson, Ala., and President-elect of the AAFP. They reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care and family physicians operate on the front lines of health care, working tirelessly to serve patients and their families. However, many primary care practices are operating on tight margins and cannot sustain additional financial hits. As we continue to navigate a pandemic that has altered our health care landscape, we traveled to Capitol Hill to urge Congress to act on two critical issues: Medicare payment reform and streamlining administrative burden for physicians.
The current Medicare system for compensating physicians jeopardizes access to primary care. Family physicians, along with other primary care clinicians, are facing significant cuts in payments and rising inflation that threaten our ability to care for patients.
Each of us has experienced the effects of this pincer in devastating ways – from the independent clinicians who have been forced to sell their practices to hospitals or large health systems, to the physicians who are retiring early, leaving their practices, or even closing them because they can’t afford to keep their doors open.
Practices also struggle to cover the rising costs of staff wages, leasing space, and purchasing supplies and equipment, leaving little room for innovation or investments to transition into new payment models. Meanwhile, hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, ambulatory surgery centers, and other Medicare providers receive annual payment increases to account for rising costs.
Insufficient Medicare payments also challenge practices that serve many publicly insured patients. If practices cannot cover their expenses, they may be forced to turn away new Medicare and Medicaid patients – something that goes against the core tenets of our health care system.
Fortunately, we have some solutions. We’re asking Congress to pass the Supporting Medicare Providers Act of 2022, which calls for a 4.42% positive adjustment to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) conversion factor for 2023 to offset the statutory reduction triggered by budget neutrality rules.
We also are calling on lawmakers to end the statutory freeze on annual updates to the MPFS and enact a positive annual update to the conversion factor based on the Medicare Economic Index. This critical relief would stave off the most immediate cuts while giving us more time to work with Congress on comprehensive reforms to the Medicare physician payment system.
As many practices struggle to operate, burnout among primary care physicians has also increased, with research showing that 66% of primary care physicians reported frequent burnout symptoms in 2021. Streamlining prior authorizations – a cumbersome process that requires physicians to obtain preapproval for treatments or tests before providing care to patients, and can risk patients’ access to timely care – is one way to reduce burden and alleviate burnout.
According to the American Medical Association, 82% of physicians report that prior authorization can lead to patients abandoning care, and 93% believe that prior authorization delays access to necessary care.
All of us have had patients whose care has been affected by these delays, including difficulty in getting necessary medications filled or having medical procedures postponed. Moreover, primary care physicians and their staff spend hours each week completing paperwork and communicating with insurers to ensure that their patients can access the treatments and services they need.
That is why we’re urging the Senate to pass the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, which would streamline the prior authorization process in the Medicare Advantage program.
As family physicians, we are in a unique position to help improve our patients’ health and their quality of life. But we can’t do this alone. We need the support of policy makers to make patient health and primary care a national priority.
Dr. Iroku-Malize is a family physician in Long Island, New York, and President of the American Academy of Family Physicians. Dr. Ransone is a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair, immediate past president of the AAFP. Dr. Furr is a family physician in Jackson, Ala., and President-elect of the AAFP. They reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care and family physicians operate on the front lines of health care, working tirelessly to serve patients and their families. However, many primary care practices are operating on tight margins and cannot sustain additional financial hits. As we continue to navigate a pandemic that has altered our health care landscape, we traveled to Capitol Hill to urge Congress to act on two critical issues: Medicare payment reform and streamlining administrative burden for physicians.
The current Medicare system for compensating physicians jeopardizes access to primary care. Family physicians, along with other primary care clinicians, are facing significant cuts in payments and rising inflation that threaten our ability to care for patients.
Each of us has experienced the effects of this pincer in devastating ways – from the independent clinicians who have been forced to sell their practices to hospitals or large health systems, to the physicians who are retiring early, leaving their practices, or even closing them because they can’t afford to keep their doors open.
Practices also struggle to cover the rising costs of staff wages, leasing space, and purchasing supplies and equipment, leaving little room for innovation or investments to transition into new payment models. Meanwhile, hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, ambulatory surgery centers, and other Medicare providers receive annual payment increases to account for rising costs.
Insufficient Medicare payments also challenge practices that serve many publicly insured patients. If practices cannot cover their expenses, they may be forced to turn away new Medicare and Medicaid patients – something that goes against the core tenets of our health care system.
Fortunately, we have some solutions. We’re asking Congress to pass the Supporting Medicare Providers Act of 2022, which calls for a 4.42% positive adjustment to the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) conversion factor for 2023 to offset the statutory reduction triggered by budget neutrality rules.
We also are calling on lawmakers to end the statutory freeze on annual updates to the MPFS and enact a positive annual update to the conversion factor based on the Medicare Economic Index. This critical relief would stave off the most immediate cuts while giving us more time to work with Congress on comprehensive reforms to the Medicare physician payment system.
As many practices struggle to operate, burnout among primary care physicians has also increased, with research showing that 66% of primary care physicians reported frequent burnout symptoms in 2021. Streamlining prior authorizations – a cumbersome process that requires physicians to obtain preapproval for treatments or tests before providing care to patients, and can risk patients’ access to timely care – is one way to reduce burden and alleviate burnout.
According to the American Medical Association, 82% of physicians report that prior authorization can lead to patients abandoning care, and 93% believe that prior authorization delays access to necessary care.
All of us have had patients whose care has been affected by these delays, including difficulty in getting necessary medications filled or having medical procedures postponed. Moreover, primary care physicians and their staff spend hours each week completing paperwork and communicating with insurers to ensure that their patients can access the treatments and services they need.
That is why we’re urging the Senate to pass the Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act, which would streamline the prior authorization process in the Medicare Advantage program.
As family physicians, we are in a unique position to help improve our patients’ health and their quality of life. But we can’t do this alone. We need the support of policy makers to make patient health and primary care a national priority.
Dr. Iroku-Malize is a family physician in Long Island, New York, and President of the American Academy of Family Physicians. Dr. Ransone is a family physician in Deltaville, Va., and board chair, immediate past president of the AAFP. Dr. Furr is a family physician in Jackson, Ala., and President-elect of the AAFP. They reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More children should be getting flu vaccines
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at [email protected].
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at [email protected].
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
Cold and flu season came early in 2022.
On Nov. 4, 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued a Health Alert Network Health Advisory about early, elevated respiratory disease incidence caused by multiple viruses other than SARS-CoV-2.
Interseasonal spread of respiratory syncytial virus has continued in 2022, with RSV-associated hospitalizations increasing in the late spring and continuing throughout the summer and into the fall. In October, some regions of the country were seeing RSV activity near the peak seasonal levels typically observed in December and January.
Cases of severe respiratory infection in children who tested positive for rhinovirus or enterovirus spiked in August; further testing confirmed the presence of EV-D68 in some children. Rhinovirus and enterovirus continue to circulate and are isolated in hospitalized children with respiratory illness.
In some parts of the country, influenza cases have rapidly increased ahead of what we normally anticipate. According to preliminary estimates from the CDC, between Oct. 1 and Oct. 22, 880,000 people were sickened with flu, 420,000 people visited a health care provider for flu illness, and 6,900 people were hospitalized for flu. The cumulative hospitalization rate is higher than observed at this time of year in every previous flu season since 2010-2011. Hospitalization rates are highest in children aged 0-4 years and adults 65 years and older.
Of course, this report came as no surprise to pediatric health care providers. Many children’s hospitals had been operating at or over capacity for weeks. While a systematic assessment of the surge on children’s hospitals has not been published, anecdotally, hospitals from around the country have described record emergency department visits and inpatient census numbers. Some have set up tents or other temporary facilities to see ambulatory patients and have canceled elective surgeries because of a lack of beds.
There is no quick or easy solution to stem the tide of RSV-related or enterovirus/rhinovirus admissions, but many flu-related hospitalizations are vaccine preventable. Unfortunately, too few children are receiving influenza vaccine. As of the week ending Oct. 15, only about 22.1% of eligible children had been immunized. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the CDC recommend that all children are vaccinated, preferably by the end of October so they have time to develop immunity before influenza starts circulating. As it stands now, the majority of the nation’s children are facing a flu season without the benefits of vaccine.
There is still time to take steps to prevent this flu season from becoming one of the worst in recent memory. A strong provider recommendation for influenza vaccine is consistently associated with higher rates of vaccine acceptance. We need to recommend influenza vaccine to all eligible patients at every visit and in every setting. It will help if we can say it like we mean it. Some of us are tired of debating the merits of COVID-19 vaccine with families and may be leery of additional debates about flu. Some of us may just be tired, as many practices have already expanded office hours to care for the influx of kids with respiratory illness. On the heels of two atypical flu seasons, a few of us may be quietly complacent about the importance of flu vaccines for children.
Anyone in need of a little motivation should check out a paper recently published in Clinical Infectious Diseases that reinforces the value of flu vaccine, even in a year when there is a poor match between the vaccine and circulating viruses.
The 2019-2020 flu season was a bad flu season for children. Two antigenically drifted influenza viruses predominated and cases of influenza soared, resulting in the largest influenza epidemic in children in the United States since 1992. Pediatric Intensive Care Influenza Study investigators used a test-negative design to estimate the effectiveness of influenza vaccine in preventing critical and life-threatening influenza in children during that season. The good news: vaccination reduced the risk of critical influenza by 78% against H1N1pdm09 viruses that were well-matched to vaccine and by 47% against mismatched viruses. Vaccination was estimated to be 75% protective against antigenically drifted B-Victoria viruses. Overall vaccine effectiveness against critical illness from any influenza virus was 63% (95% confidence interval, 38%-78%).
While it might be tempting to attribute suboptimal immunization rates to vaccine hesitancy, ready availability remains an issue for some families. We need to eliminate barriers to access. While the AAP continues to emphasize immunization in the medical home, especially for the youngest infants, the 2022 policy statement suggests that vaccinating children in schools, pharmacies, and other nontraditional settings could improve immunization rates. To the extent feasible, we need to work with partners to support community-based initiatives and promote these to families who struggle to make it into the office.
Improving access is just one potential way to reduce health disparities related to influenza and influenza vaccination. Over 10 influenza seasons, higher rates of influenza-associated hospitalizations and intensive care unit admissions were observed in Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native people. These disparities were highest in children aged younger than 4 years and influenza-associated in-hospital deaths were three- to fourfold higher in Black, Hispanic, and Asian/Pacific Islander children, compared with White children. The reason for the disparities isn’t completely clear but increasing immunization rates may be part of the solution. During the 2020-2021 influenza season, flu immunization rates in Black children (51.6%) were lower than those seen in White (57.4%) and Hispanic children (58.9%).
The AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023, highlight a variety of evidence-based strategies to increase influenza immunization rates. These may provide a little inspiration for clinicians looking to try a new approach. If you wish to share your experience with increasing influenza immunization rates in your practice setting, please email me at [email protected].
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital, also in Louisville. She is a member of the AAP’s Committee on Infectious Diseases and one of the lead authors of the AAP’s Recommendations for Prevention and Control of Influenza in Children, 2022–2023. The opinions expressed in this article are her own. Dr. Bryant discloses that she has served as an investigator on clinical trials funded by Pfizer, Enanta, and Gilead.
With a little help from your friends
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Case: You are talking with one of your teenage patients, who has a history of significant suicidal ideation and an aborted attempt, and you ask her if there is someone she can talk with if she is feeling suicidal. “I call a friend,” she says. “That’s the only thing that works when I’m feeling bad.”
During difficult times, it is important to have a repertoire of coping skills to address stress, tension, frustration, anxiety, anger, sadness, and to help avoid dangerous behaviors. It is also important to have someone to talk to. For many youth, talking with friends is their preferred coping skill and contact when struggling with intense feelings.
This is hardly surprising. Peer relations are central to adolescent development. The ongoing individuation-separation process means that adolescents are peeling away from the family and into a community of their peers, where they figure out who they are through social interactions in subtle and complex ways. Adolescents are often profoundly immersed in the world of their peers; they often spend more time with their peers in educational and social settings than with their parents or other adults; and their connections with peers are often pleasurable, engaging, supportive, and intense. It is natural that they would want to communicate with their peers during stressful times.
At the same time, they may also want to avoid talking with adults. They may identify adult figures with authority, expectations, and control. So much adolescent psychic suffering and so many mental health crises involve shame, guilt, and fear, and are associated with romance, love, disappointment, and trauma – all of which may be difficult to share with parents and adult figures.
Adults also struggle with these kinds of conversations. Even benign attempts at comforting the youth (“Don’t worry, it’ll get better,” “Everyone feels this way sometimes”) can be seen as invalidating. And in stressful times, a difficult conversation can be ignited by the fuel of adult anxieties about the independence and autonomy of the child that is coming, which can make charged conversations all the more inflammatory.
Reaching out to peers during stressful times is therefore developmentally appropriate and often feels far more comfortable, validating, and sympathetic.
One of the most important things we can do is to help kids understand when, how, and why they can support each other – and when they cannot. Whether we like it or not, for many youth, peers are peer mental health counselors. They have shared vocabularies and can share experiences in the mental health care system. In addition to relying on their peers, a great many youth we work with also see themselves as supports to their peers, so it’s not just a one-way street.
So we talk with them frankly about when, how, and why talking with their friends can be an effective way of getting through a hard time and when, how, and why they need to reach out to an adult.
Recognizing how positive peer support can be, we ask them to identify problems with it. Kids often recognize the drawbacks of relying on their peers for support. They can see how it can be a burden to their friends. They often acknowledge that their friends may be experts in some aspects of their lives but not in others. For example, they can have shared stressors in school, can have similar understandings of the drama in their lives, and can relate to each other’s worlds, but will also not necessarily know what to do if a situation becomes dangerous.
The youth also tend to understand that the stakes in these conversations are high. We have seen peer groups suffer terribly when the youth have felt responsible – and even been the last preceding contact – in bad or even fatal outcomes.
We need to open up conversations about different forms of communication: when teens need understanding, compassion, patience; when they need a good understanding of local, cultural contexts, and a sense of support without anxieties and stressors; and when they need support and adult capacities and connections to solve problems. We can help them understand how to access people – both peers and adults – but also discuss responsibility: who you are responsible for, how you cannot be responsible alone for your friends’ mental health, how they cannot be responsible for yours, and who can be responsible for you.
To this end, we validate the importance of peers and ask more specifically when the adolescent thinks it is helpful to contact peers and when they think it would not be helpful. Having teens explain the difference may help them identify the right times to connect with peers or adults.
We can then talk about how to understand that there are different kinds of crisis: the kind where comfort, understanding, and support from friends can alleviate the crisis, and times when it is imperative to involve adults.
We can then identify which adults in their lives they can contact and how they would do so, both in terms of method of communication (texting an older sister, speaking in person with a parent, calling a therapist) and what they could say.
Then comes a more difficult step. We help them think about how to identify adults whom they do not know: how to contact a hotline or go to an emergency room or call 911. It is important not just to provide the numbers or address, but to help them run through a brief script so they know what to say and would be comfortable saying in their own words (but effectively saying, “I really need to speak with someone right now, I’m not safe.”)
Helping youth understand the advantages and disadvantages of reaching out to peers, and when and how to reach out to adults, can be a constructive conversation. It is a chance not only to speak with and hear about a youth’s life and relationships but also a chance to give them a stronger and safer support network.
Dr. Henderson is a psychiatrist who treats children and adolescents at NYU Langone Health, New York.
Do scare tactics work?
I suspect that you have heard about or maybe read the recent Associated Press story reporting that four daycare workers in Hamilton, Miss., have been charged with felony child abuse for intentionally scaring the children “who didn’t clean up or act good” by wearing a Halloween mask and yelling in their faces. I can have some sympathy for those among us who choose to spend their days tending a flock of sometimes unruly and mischievous toddlers and preschoolers. But, I think one would be hard pressed to find very many adults who would condone the strategy of these misguided daycare providers. Not surprisingly, the parents of some of these children describe their children as traumatized and having disordered sleep.
The news report of this incident in Mississippi doesn’t tell us if these daycare providers had used this tactic in the past. One wonders whether they had found less dramatic verbal threats just weren’t as effective as they had hoped and so decided to go all out.
How effective is fear in changing behavior? Certainly, we have all experienced situations in which a frightening experience has caused us to avoid places, people, and activities. But, is a fear-focused strategy one that health care providers should include in their quiver as we try to mold patient behavior? As luck would have it, 2 weeks before this news story broke I encountered a global study from 84 countries that sought to answer this question (Affect Sci. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1007/s42761-022-00128-3).
Using the WHO four-point advice about COVID prevention (stay home/avoid shops/use face covering/isolate if exposed) as a model the researchers around the world reviewed the responses of 16,000 individuals. They found that there was no difference in the effectiveness of the message whether it was framed as a negative (“you have so much to lose”) or a positive (“you have so much to gain”). However, investigators observed that the negatively framed presentations generated significantly more anxiety in the respondents. The authors of the paper conclude that if there is no significant difference in the effectiveness, why would we chose a negatively framed presentation that is likely to generate anxiety that we know is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. From a purely public health perspective, it doesn’t make sense and is counterproductive.
I guess if we look back to the old carrot and stick metaphor we shouldn’t be surprised by the findings in this paper. If one’s only goal is to get a group of young preschoolers to behave by scaring the b’geezes out of them with a mask or a threat of bodily punishment, then go for it. Scare tactics will probably work just as well as offering a well-chosen reward system. However, the devil is in the side effects. It’s the same argument that I give to parents who argue that spanking works. Of course it does, but it has a narrow margin for safety and can set up ripples of negative side effects that can destroy healthy parent-child relationships.
The bottom line of this story is the sad truth that somewhere along the line someone failed to effectively train these four daycare workers. But, do we as health care providers need to rethink our training? Have we forgotten our commitment to “First do no harm?” As we craft our messaging have we thought enough about the potential side effects of our attempts at scaring the public into following our suggestions?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that you have heard about or maybe read the recent Associated Press story reporting that four daycare workers in Hamilton, Miss., have been charged with felony child abuse for intentionally scaring the children “who didn’t clean up or act good” by wearing a Halloween mask and yelling in their faces. I can have some sympathy for those among us who choose to spend their days tending a flock of sometimes unruly and mischievous toddlers and preschoolers. But, I think one would be hard pressed to find very many adults who would condone the strategy of these misguided daycare providers. Not surprisingly, the parents of some of these children describe their children as traumatized and having disordered sleep.
The news report of this incident in Mississippi doesn’t tell us if these daycare providers had used this tactic in the past. One wonders whether they had found less dramatic verbal threats just weren’t as effective as they had hoped and so decided to go all out.
How effective is fear in changing behavior? Certainly, we have all experienced situations in which a frightening experience has caused us to avoid places, people, and activities. But, is a fear-focused strategy one that health care providers should include in their quiver as we try to mold patient behavior? As luck would have it, 2 weeks before this news story broke I encountered a global study from 84 countries that sought to answer this question (Affect Sci. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1007/s42761-022-00128-3).
Using the WHO four-point advice about COVID prevention (stay home/avoid shops/use face covering/isolate if exposed) as a model the researchers around the world reviewed the responses of 16,000 individuals. They found that there was no difference in the effectiveness of the message whether it was framed as a negative (“you have so much to lose”) or a positive (“you have so much to gain”). However, investigators observed that the negatively framed presentations generated significantly more anxiety in the respondents. The authors of the paper conclude that if there is no significant difference in the effectiveness, why would we chose a negatively framed presentation that is likely to generate anxiety that we know is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. From a purely public health perspective, it doesn’t make sense and is counterproductive.
I guess if we look back to the old carrot and stick metaphor we shouldn’t be surprised by the findings in this paper. If one’s only goal is to get a group of young preschoolers to behave by scaring the b’geezes out of them with a mask or a threat of bodily punishment, then go for it. Scare tactics will probably work just as well as offering a well-chosen reward system. However, the devil is in the side effects. It’s the same argument that I give to parents who argue that spanking works. Of course it does, but it has a narrow margin for safety and can set up ripples of negative side effects that can destroy healthy parent-child relationships.
The bottom line of this story is the sad truth that somewhere along the line someone failed to effectively train these four daycare workers. But, do we as health care providers need to rethink our training? Have we forgotten our commitment to “First do no harm?” As we craft our messaging have we thought enough about the potential side effects of our attempts at scaring the public into following our suggestions?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I suspect that you have heard about or maybe read the recent Associated Press story reporting that four daycare workers in Hamilton, Miss., have been charged with felony child abuse for intentionally scaring the children “who didn’t clean up or act good” by wearing a Halloween mask and yelling in their faces. I can have some sympathy for those among us who choose to spend their days tending a flock of sometimes unruly and mischievous toddlers and preschoolers. But, I think one would be hard pressed to find very many adults who would condone the strategy of these misguided daycare providers. Not surprisingly, the parents of some of these children describe their children as traumatized and having disordered sleep.
The news report of this incident in Mississippi doesn’t tell us if these daycare providers had used this tactic in the past. One wonders whether they had found less dramatic verbal threats just weren’t as effective as they had hoped and so decided to go all out.
How effective is fear in changing behavior? Certainly, we have all experienced situations in which a frightening experience has caused us to avoid places, people, and activities. But, is a fear-focused strategy one that health care providers should include in their quiver as we try to mold patient behavior? As luck would have it, 2 weeks before this news story broke I encountered a global study from 84 countries that sought to answer this question (Affect Sci. 2022 Sep. doi: 10.1007/s42761-022-00128-3).
Using the WHO four-point advice about COVID prevention (stay home/avoid shops/use face covering/isolate if exposed) as a model the researchers around the world reviewed the responses of 16,000 individuals. They found that there was no difference in the effectiveness of the message whether it was framed as a negative (“you have so much to lose”) or a positive (“you have so much to gain”). However, investigators observed that the negatively framed presentations generated significantly more anxiety in the respondents. The authors of the paper conclude that if there is no significant difference in the effectiveness, why would we chose a negatively framed presentation that is likely to generate anxiety that we know is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. From a purely public health perspective, it doesn’t make sense and is counterproductive.
I guess if we look back to the old carrot and stick metaphor we shouldn’t be surprised by the findings in this paper. If one’s only goal is to get a group of young preschoolers to behave by scaring the b’geezes out of them with a mask or a threat of bodily punishment, then go for it. Scare tactics will probably work just as well as offering a well-chosen reward system. However, the devil is in the side effects. It’s the same argument that I give to parents who argue that spanking works. Of course it does, but it has a narrow margin for safety and can set up ripples of negative side effects that can destroy healthy parent-child relationships.
The bottom line of this story is the sad truth that somewhere along the line someone failed to effectively train these four daycare workers. But, do we as health care providers need to rethink our training? Have we forgotten our commitment to “First do no harm?” As we craft our messaging have we thought enough about the potential side effects of our attempts at scaring the public into following our suggestions?
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].