User login
At what age do ObGyns recommend their patients begin cervical cancer screening?
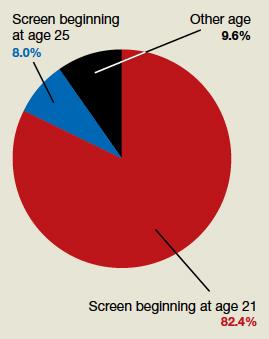
In their peer-to-peer interview, “Cervical cancer: A path to eradication,” (OBG Manag. May 2022;34:30-34.) David G. Mutch, MD, and Warner Huh, MD, discussed the varying guidelines for cervical cancer screening. Dr. Huh pointed out that the 2020 guidelines for the American Cancer Society recommend cervical cancer screening to begin at age 25 years, although the current guidelines for the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists continue to recommend age 21. He noted that “the rate of cervical cancer is extremely low under age 25, and other countries like the United Kingdom already” screen beginning at age 25. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask: “Guidelines vary on what age to begin screening for cervical cancer. What age do you typically recommend for patients?”
A total of 187 readers cast their vote:
82.4% (154 readers) said age 21
8.0% (15 readers) said age 25
9.6% (18 readers) said other age
In their peer-to-peer interview, “Cervical cancer: A path to eradication,” (OBG Manag. May 2022;34:30-34.) David G. Mutch, MD, and Warner Huh, MD, discussed the varying guidelines for cervical cancer screening. Dr. Huh pointed out that the 2020 guidelines for the American Cancer Society recommend cervical cancer screening to begin at age 25 years, although the current guidelines for the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists continue to recommend age 21. He noted that “the rate of cervical cancer is extremely low under age 25, and other countries like the United Kingdom already” screen beginning at age 25. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask: “Guidelines vary on what age to begin screening for cervical cancer. What age do you typically recommend for patients?”
A total of 187 readers cast their vote:
82.4% (154 readers) said age 21
8.0% (15 readers) said age 25
9.6% (18 readers) said other age
In their peer-to-peer interview, “Cervical cancer: A path to eradication,” (OBG Manag. May 2022;34:30-34.) David G. Mutch, MD, and Warner Huh, MD, discussed the varying guidelines for cervical cancer screening. Dr. Huh pointed out that the 2020 guidelines for the American Cancer Society recommend cervical cancer screening to begin at age 25 years, although the current guidelines for the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists continue to recommend age 21. He noted that “the rate of cervical cancer is extremely low under age 25, and other countries like the United Kingdom already” screen beginning at age 25. OBG Management followed up with a poll for readers to ask: “Guidelines vary on what age to begin screening for cervical cancer. What age do you typically recommend for patients?”
A total of 187 readers cast their vote:
82.4% (154 readers) said age 21
8.0% (15 readers) said age 25
9.6% (18 readers) said other age
Implementation of a Virtual Huddle to Support Patient Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic challenged hospital medicine teams to care for patients with complex respiratory needs, comply with evolving protocols, and remain abreast of new therapies.1,2 Pulmonary and critical care medicine (PCCM) faculty grappled with similar issues, acknowledging that their critical care expertise could be beneficial outside of the intensive care unit (ICU). Clinical pharmacists managed the procurement, allocation, and monitoring of complex (and sometimes limited) pharmacologic therapies. Although strategies used by health care systems to prepare and restructure for COVID-19 are reported, processes to enhance multidisciplinary care are limited.3,4 Therefore, we developed the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program using video conference to support hospital medicine teams caring for patients with COVID-19 and high disease severity.
Program Description
The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) in Houston, Texas, is a 349-bed, level 1A federal health care facility serving more than 113,000 veterans in southeast Texas.5 The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program took place over a 4-week period from July 6 to August 2, 2020. By the end of the 4-week period, there was a decline in the number of COVID patient admissions and thus the need for the huddle. Participation in the huddle also declined, likely reflecting the end of the surge and an increase in knowledge about COVID management acquired by the teams. Each COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation session consisted of at least 1 member from each hospital medicine team, 1 to 2 PCCM faculty members, and 1 to 2 clinical pharmacy specialists (Figure). The consultation team members included 4 PCCM faculty members and 2 clinical pharmacy specialists. The internal medicine (IM) participants included 10 ward teams with a total of 20 interns (PGY1), 12 upper-level residents (PGY2 and PGY 3), and 10 attending physicians.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program was a daily (including weekends) video conference. The hospital medicine team members joined the huddle from team workrooms, using webcams supplied by the MEDVAMC information technology department. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation team members joined remotely. Each hospital medicine team joined the huddle at a pre-assigned 15- to 30-minute time allotment, which varied based on patient volume. Participation in the huddle was mandatory for the first week and became optional thereafter. This was in recognition of the steep learning curve and provided the teams both basic knowledge of COVID management and a shared understanding of when a multidisciplinary consultation would be critical. Mandatory daily participation was challenging due to the pressures of patient volume during the surge.
COVID-19 patients with high disease severity were discussed during huddles based on specific criteria: all newly admitted COVID-19 patients, patients requiring step-down level of care, those with increasing oxygen requirements, and/or patients requiring authorization of remdesivir therapy, which required clinical pharmacy authorization at MEDVAMC. The hospital medicine teams reported the patients’ oxygen requirements, comorbid medical conditions, current and prior therapies, fluid status, and relevant laboratory values. A dashboard using the Premier Inc. TheraDoc clinical decision support system was developed to display patient vital signs, laboratory values, and medications. The PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists listened to inpatient medicine teams presentations and used the dashboard and radiographic images to formulate clinical decisions. Discussion of a patient at the huddle did not preclude in-person consultation at any time.
Tele-Huddles were not recorded, and all protected health information discussed was accessed through the electronic health record using a secure network. Data on length of the meeting, number of patients discussed, and management decisions were recorded daily in a spreadsheet. At the end of the 4-week surge, participants in the program completed a survey, which assessed participant demographics, prior experience with COVID-19, and satisfaction with the program based on a series of agree/disagree questions.
Program Metrics
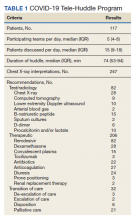
During the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program 4-week evaluation period, 323 encounters were discussed with 117 unique patients with COVID-19. A median (IQR) of 5 (4-8) hospital medicine teams discussed 15 (9-18) patients. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program lasted a median (IQR) 74 (53-94) minutes. A mean (SD) 27% (13) of patients with COVID-19 admitted to the acute care services were discussed.
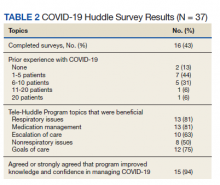
The multidisciplinary team provided 247 chest X-ray interpretations, 82 diagnostic recommendations, 206 therapeutic recommendations, and 32 transition of care recommendations (Table 1). A total of 55 (47%) patients were given remdesivir with first dose authorized by clinical pharmacy and given within a median (IQR) 6 (3-10) hours after the order was placed. Oxygen therapy, including titration and de-escalation of high-flow nasal cannula and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV), was used for 26 (22.2%) patients. Additional interventions included the review of imaging, the assessment of volume status to guide diuretic recommendations, and the discussion of goals of care.
Of the participating IM trainees and attendings, 16 of 37 (43%) completed the user survey (Table 2). Prior experience with COVID-19 patients varied, with 7 of 16 respondents indicating experience with ≥ 5 patients with COVID-19 prior to the intervention period. Respondents believed that the huddle was helpful in management of respiratory issues (13 of 16), management of medications (13 of 16), escalation of care to ICU (10 of 16), and management of nonrespiratory issues (8 of 16) and goals of care (12 of 16). Fifteen of 16 participants strongly agreed or agreed that the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program improved their knowledge and confidence in managing patients. One participant commented, “Getting interdisciplinary help on COVID patients has really helped our team feel confident in our decisions about some of these very complex patients.” Another respondent commented, “Reliability was very helpful for planning how to discuss updates with our patients rather than the formal consultative process.”
Discussion
During the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems have been challenged to manage a large volume of patients, often with high disease severity, in non-ICU settings. This surge in cases has placed strain on hospital medicine teams. There is a subset of patients with COVID-19 with high disease severity that may be managed safely by hospital medicine teams, provided the accessibility and support of consultants, such as PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists.
Huddles are defined as functional groups of people focused on enhancing communication and care coordination to benefit patient safety. While often brief in nature, huddles can encompass a variety of structures, agendas, and outcome measures.6,7 We implemented a modified huddle using video conferencing to provide important aspects of critical care for patients with COVID-19. Face-to-face evaluation of about 15 patients each day would have strained an already burdened PCCM faculty who were providing additional critical care services as part of the surge response. Conversion of in-person consultations to the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for mitigation of COVID-19 transmission risk for additional clinicians, conservation of personal protective equipment, and more effective communication between acute inpatient practitioners and clinical services. The huddle model expedited the authorization and delivery of therapeutics, including remdesivir, which was prescribed for many patients discussed. Clinical pharmacists provided a review of all medications with input on escalation, de-escalation, dosing, drug-drug interactions, and emergency use authorization therapies.
Our experience resonates with previously described advantages of a huddle model, including the reliability of the consultation, empowerment for all members with a de-emphasis on hierarchy and accountability expected by all.8 The huddle provided situational awareness about patients that may require escalation of care to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Assistance with these transitions of care was highly appreciated by the hospital medicine teams who voiced that these decisions were quite challenging. COVID-19 patients at risk for decompensation were referred for in-person consultation and follow-up if required.
addition, the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for a safe and dependable venue for IM trainees and attending physicians to voice questions and concerns about their patients. We observed the development of a shared mental model among all huddle participants, in the face of a steep learning curve on the management of patients with complex respiratory needs. This was reflected in the survey: Most respondents reported improved knowledge and confidence in managing these patients. Situational awareness that arose from the huddle provided the PCCM faculty the opportunity to guide the inpatient ward teams on next steps whether it be escalation to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Facilitation of transitions of care were voiced as challenging decisions faced by the inpatient ward teams, and there was appreciation for additional support from the PCCM faculty in making these difficult decisions.
Challenges and Opportunities
This was a single-center experience caring for veterans. Challenges with having virtual huddles during the COVID-19 surge involved both time for the health care practitioners and technology. This was recognized early by the educational leaders at our facility, and headsets and cameras were purchased for the team rooms and made available as quickly as possible. Another limitation was the unpredictability and variability of patient volume for specific teams that sometimes would affect the efficiency of the huddle. The number of teams who attended the COVID-19 huddle was highest for the first 2 weeks (maximum of 9 teams) but declined to a nadir of 3 at the end of the month. This reflected the increase in knowledge about COVID-19 and respiratory disease that the teams acquired initially as well as a decline in COVID-19 patient admissions over those weeks.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program model also can be expanded to include other frontline clinicians, including nurses and respiratory therapists. For example, case management huddles were performed in a similar way during the COVID-19 surge to allow for efficient and effective multidisciplinary conversations about patients
Conclusions
Given the rise of telemedicine and availability of video conferencing services, virtual huddles can be implemented in institutions with appropriate staff and remote access to health records. Multidisciplinary consultation services using video conferencing can serve as an adjunct to the traditional, in-person consultation service model for patients with complex needs.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all of the Baylor Internal Medicine house staff and internal medicine attendings who participated in our huddle and more importantly, cared for our veterans during this COVID-19 surge.
1. Heymann DL, Shindo N; WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards. COVID-19: what is next for public health?. Lancet. 2020;395(10224):542-545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3
2. Dichter JR, Kanter RK, Dries D, et al; Task Force for Mass Critical Care. System-level planning, coordination, and communication: care of the critically ill and injured during pandemics and disasters: CHEST consensus statement. Chest. 2014;146(suppl 4):e87S-e102S. doi:10.1378/chest.14-0738
3. Chowdhury JM, Patel M, Zheng M, Abramian O, Criner GJ. Mobilization and preparation of a large urban academic center during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020;17(8):922-925. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-259PS
4. Uppal A, Silvestri DM, Siegler M, et al. Critical care and emergency department response at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1443-1449. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00901
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center- Houston, Texas. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.houston.va.gov/about
6. Provost SM, Lanham HJ, Leykum LK, McDaniel RR Jr, Pugh J. Health care huddles: managing complexity to achieve high reliability. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(1):2-12. doi:10.1097/HMR.0000000000000009
7. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
8. Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22(11):899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
The COVID-19 pandemic challenged hospital medicine teams to care for patients with complex respiratory needs, comply with evolving protocols, and remain abreast of new therapies.1,2 Pulmonary and critical care medicine (PCCM) faculty grappled with similar issues, acknowledging that their critical care expertise could be beneficial outside of the intensive care unit (ICU). Clinical pharmacists managed the procurement, allocation, and monitoring of complex (and sometimes limited) pharmacologic therapies. Although strategies used by health care systems to prepare and restructure for COVID-19 are reported, processes to enhance multidisciplinary care are limited.3,4 Therefore, we developed the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program using video conference to support hospital medicine teams caring for patients with COVID-19 and high disease severity.
Program Description
The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) in Houston, Texas, is a 349-bed, level 1A federal health care facility serving more than 113,000 veterans in southeast Texas.5 The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program took place over a 4-week period from July 6 to August 2, 2020. By the end of the 4-week period, there was a decline in the number of COVID patient admissions and thus the need for the huddle. Participation in the huddle also declined, likely reflecting the end of the surge and an increase in knowledge about COVID management acquired by the teams. Each COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation session consisted of at least 1 member from each hospital medicine team, 1 to 2 PCCM faculty members, and 1 to 2 clinical pharmacy specialists (Figure). The consultation team members included 4 PCCM faculty members and 2 clinical pharmacy specialists. The internal medicine (IM) participants included 10 ward teams with a total of 20 interns (PGY1), 12 upper-level residents (PGY2 and PGY 3), and 10 attending physicians.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program was a daily (including weekends) video conference. The hospital medicine team members joined the huddle from team workrooms, using webcams supplied by the MEDVAMC information technology department. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation team members joined remotely. Each hospital medicine team joined the huddle at a pre-assigned 15- to 30-minute time allotment, which varied based on patient volume. Participation in the huddle was mandatory for the first week and became optional thereafter. This was in recognition of the steep learning curve and provided the teams both basic knowledge of COVID management and a shared understanding of when a multidisciplinary consultation would be critical. Mandatory daily participation was challenging due to the pressures of patient volume during the surge.
COVID-19 patients with high disease severity were discussed during huddles based on specific criteria: all newly admitted COVID-19 patients, patients requiring step-down level of care, those with increasing oxygen requirements, and/or patients requiring authorization of remdesivir therapy, which required clinical pharmacy authorization at MEDVAMC. The hospital medicine teams reported the patients’ oxygen requirements, comorbid medical conditions, current and prior therapies, fluid status, and relevant laboratory values. A dashboard using the Premier Inc. TheraDoc clinical decision support system was developed to display patient vital signs, laboratory values, and medications. The PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists listened to inpatient medicine teams presentations and used the dashboard and radiographic images to formulate clinical decisions. Discussion of a patient at the huddle did not preclude in-person consultation at any time.
Tele-Huddles were not recorded, and all protected health information discussed was accessed through the electronic health record using a secure network. Data on length of the meeting, number of patients discussed, and management decisions were recorded daily in a spreadsheet. At the end of the 4-week surge, participants in the program completed a survey, which assessed participant demographics, prior experience with COVID-19, and satisfaction with the program based on a series of agree/disagree questions.
Program Metrics
During the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program 4-week evaluation period, 323 encounters were discussed with 117 unique patients with COVID-19. A median (IQR) of 5 (4-8) hospital medicine teams discussed 15 (9-18) patients. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program lasted a median (IQR) 74 (53-94) minutes. A mean (SD) 27% (13) of patients with COVID-19 admitted to the acute care services were discussed.
The multidisciplinary team provided 247 chest X-ray interpretations, 82 diagnostic recommendations, 206 therapeutic recommendations, and 32 transition of care recommendations (Table 1). A total of 55 (47%) patients were given remdesivir with first dose authorized by clinical pharmacy and given within a median (IQR) 6 (3-10) hours after the order was placed. Oxygen therapy, including titration and de-escalation of high-flow nasal cannula and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV), was used for 26 (22.2%) patients. Additional interventions included the review of imaging, the assessment of volume status to guide diuretic recommendations, and the discussion of goals of care.
Of the participating IM trainees and attendings, 16 of 37 (43%) completed the user survey (Table 2). Prior experience with COVID-19 patients varied, with 7 of 16 respondents indicating experience with ≥ 5 patients with COVID-19 prior to the intervention period. Respondents believed that the huddle was helpful in management of respiratory issues (13 of 16), management of medications (13 of 16), escalation of care to ICU (10 of 16), and management of nonrespiratory issues (8 of 16) and goals of care (12 of 16). Fifteen of 16 participants strongly agreed or agreed that the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program improved their knowledge and confidence in managing patients. One participant commented, “Getting interdisciplinary help on COVID patients has really helped our team feel confident in our decisions about some of these very complex patients.” Another respondent commented, “Reliability was very helpful for planning how to discuss updates with our patients rather than the formal consultative process.”
Discussion
During the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems have been challenged to manage a large volume of patients, often with high disease severity, in non-ICU settings. This surge in cases has placed strain on hospital medicine teams. There is a subset of patients with COVID-19 with high disease severity that may be managed safely by hospital medicine teams, provided the accessibility and support of consultants, such as PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists.
Huddles are defined as functional groups of people focused on enhancing communication and care coordination to benefit patient safety. While often brief in nature, huddles can encompass a variety of structures, agendas, and outcome measures.6,7 We implemented a modified huddle using video conferencing to provide important aspects of critical care for patients with COVID-19. Face-to-face evaluation of about 15 patients each day would have strained an already burdened PCCM faculty who were providing additional critical care services as part of the surge response. Conversion of in-person consultations to the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for mitigation of COVID-19 transmission risk for additional clinicians, conservation of personal protective equipment, and more effective communication between acute inpatient practitioners and clinical services. The huddle model expedited the authorization and delivery of therapeutics, including remdesivir, which was prescribed for many patients discussed. Clinical pharmacists provided a review of all medications with input on escalation, de-escalation, dosing, drug-drug interactions, and emergency use authorization therapies.
Our experience resonates with previously described advantages of a huddle model, including the reliability of the consultation, empowerment for all members with a de-emphasis on hierarchy and accountability expected by all.8 The huddle provided situational awareness about patients that may require escalation of care to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Assistance with these transitions of care was highly appreciated by the hospital medicine teams who voiced that these decisions were quite challenging. COVID-19 patients at risk for decompensation were referred for in-person consultation and follow-up if required.
addition, the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for a safe and dependable venue for IM trainees and attending physicians to voice questions and concerns about their patients. We observed the development of a shared mental model among all huddle participants, in the face of a steep learning curve on the management of patients with complex respiratory needs. This was reflected in the survey: Most respondents reported improved knowledge and confidence in managing these patients. Situational awareness that arose from the huddle provided the PCCM faculty the opportunity to guide the inpatient ward teams on next steps whether it be escalation to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Facilitation of transitions of care were voiced as challenging decisions faced by the inpatient ward teams, and there was appreciation for additional support from the PCCM faculty in making these difficult decisions.
Challenges and Opportunities
This was a single-center experience caring for veterans. Challenges with having virtual huddles during the COVID-19 surge involved both time for the health care practitioners and technology. This was recognized early by the educational leaders at our facility, and headsets and cameras were purchased for the team rooms and made available as quickly as possible. Another limitation was the unpredictability and variability of patient volume for specific teams that sometimes would affect the efficiency of the huddle. The number of teams who attended the COVID-19 huddle was highest for the first 2 weeks (maximum of 9 teams) but declined to a nadir of 3 at the end of the month. This reflected the increase in knowledge about COVID-19 and respiratory disease that the teams acquired initially as well as a decline in COVID-19 patient admissions over those weeks.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program model also can be expanded to include other frontline clinicians, including nurses and respiratory therapists. For example, case management huddles were performed in a similar way during the COVID-19 surge to allow for efficient and effective multidisciplinary conversations about patients
Conclusions
Given the rise of telemedicine and availability of video conferencing services, virtual huddles can be implemented in institutions with appropriate staff and remote access to health records. Multidisciplinary consultation services using video conferencing can serve as an adjunct to the traditional, in-person consultation service model for patients with complex needs.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all of the Baylor Internal Medicine house staff and internal medicine attendings who participated in our huddle and more importantly, cared for our veterans during this COVID-19 surge.
The COVID-19 pandemic challenged hospital medicine teams to care for patients with complex respiratory needs, comply with evolving protocols, and remain abreast of new therapies.1,2 Pulmonary and critical care medicine (PCCM) faculty grappled with similar issues, acknowledging that their critical care expertise could be beneficial outside of the intensive care unit (ICU). Clinical pharmacists managed the procurement, allocation, and monitoring of complex (and sometimes limited) pharmacologic therapies. Although strategies used by health care systems to prepare and restructure for COVID-19 are reported, processes to enhance multidisciplinary care are limited.3,4 Therefore, we developed the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program using video conference to support hospital medicine teams caring for patients with COVID-19 and high disease severity.
Program Description
The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) in Houston, Texas, is a 349-bed, level 1A federal health care facility serving more than 113,000 veterans in southeast Texas.5 The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program took place over a 4-week period from July 6 to August 2, 2020. By the end of the 4-week period, there was a decline in the number of COVID patient admissions and thus the need for the huddle. Participation in the huddle also declined, likely reflecting the end of the surge and an increase in knowledge about COVID management acquired by the teams. Each COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation session consisted of at least 1 member from each hospital medicine team, 1 to 2 PCCM faculty members, and 1 to 2 clinical pharmacy specialists (Figure). The consultation team members included 4 PCCM faculty members and 2 clinical pharmacy specialists. The internal medicine (IM) participants included 10 ward teams with a total of 20 interns (PGY1), 12 upper-level residents (PGY2 and PGY 3), and 10 attending physicians.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program was a daily (including weekends) video conference. The hospital medicine team members joined the huddle from team workrooms, using webcams supplied by the MEDVAMC information technology department. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program consultation team members joined remotely. Each hospital medicine team joined the huddle at a pre-assigned 15- to 30-minute time allotment, which varied based on patient volume. Participation in the huddle was mandatory for the first week and became optional thereafter. This was in recognition of the steep learning curve and provided the teams both basic knowledge of COVID management and a shared understanding of when a multidisciplinary consultation would be critical. Mandatory daily participation was challenging due to the pressures of patient volume during the surge.
COVID-19 patients with high disease severity were discussed during huddles based on specific criteria: all newly admitted COVID-19 patients, patients requiring step-down level of care, those with increasing oxygen requirements, and/or patients requiring authorization of remdesivir therapy, which required clinical pharmacy authorization at MEDVAMC. The hospital medicine teams reported the patients’ oxygen requirements, comorbid medical conditions, current and prior therapies, fluid status, and relevant laboratory values. A dashboard using the Premier Inc. TheraDoc clinical decision support system was developed to display patient vital signs, laboratory values, and medications. The PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists listened to inpatient medicine teams presentations and used the dashboard and radiographic images to formulate clinical decisions. Discussion of a patient at the huddle did not preclude in-person consultation at any time.
Tele-Huddles were not recorded, and all protected health information discussed was accessed through the electronic health record using a secure network. Data on length of the meeting, number of patients discussed, and management decisions were recorded daily in a spreadsheet. At the end of the 4-week surge, participants in the program completed a survey, which assessed participant demographics, prior experience with COVID-19, and satisfaction with the program based on a series of agree/disagree questions.
Program Metrics
During the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program 4-week evaluation period, 323 encounters were discussed with 117 unique patients with COVID-19. A median (IQR) of 5 (4-8) hospital medicine teams discussed 15 (9-18) patients. The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program lasted a median (IQR) 74 (53-94) minutes. A mean (SD) 27% (13) of patients with COVID-19 admitted to the acute care services were discussed.
The multidisciplinary team provided 247 chest X-ray interpretations, 82 diagnostic recommendations, 206 therapeutic recommendations, and 32 transition of care recommendations (Table 1). A total of 55 (47%) patients were given remdesivir with first dose authorized by clinical pharmacy and given within a median (IQR) 6 (3-10) hours after the order was placed. Oxygen therapy, including titration and de-escalation of high-flow nasal cannula and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV), was used for 26 (22.2%) patients. Additional interventions included the review of imaging, the assessment of volume status to guide diuretic recommendations, and the discussion of goals of care.
Of the participating IM trainees and attendings, 16 of 37 (43%) completed the user survey (Table 2). Prior experience with COVID-19 patients varied, with 7 of 16 respondents indicating experience with ≥ 5 patients with COVID-19 prior to the intervention period. Respondents believed that the huddle was helpful in management of respiratory issues (13 of 16), management of medications (13 of 16), escalation of care to ICU (10 of 16), and management of nonrespiratory issues (8 of 16) and goals of care (12 of 16). Fifteen of 16 participants strongly agreed or agreed that the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program improved their knowledge and confidence in managing patients. One participant commented, “Getting interdisciplinary help on COVID patients has really helped our team feel confident in our decisions about some of these very complex patients.” Another respondent commented, “Reliability was very helpful for planning how to discuss updates with our patients rather than the formal consultative process.”
Discussion
During the unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems have been challenged to manage a large volume of patients, often with high disease severity, in non-ICU settings. This surge in cases has placed strain on hospital medicine teams. There is a subset of patients with COVID-19 with high disease severity that may be managed safely by hospital medicine teams, provided the accessibility and support of consultants, such as PCCM faculty and clinical pharmacists.
Huddles are defined as functional groups of people focused on enhancing communication and care coordination to benefit patient safety. While often brief in nature, huddles can encompass a variety of structures, agendas, and outcome measures.6,7 We implemented a modified huddle using video conferencing to provide important aspects of critical care for patients with COVID-19. Face-to-face evaluation of about 15 patients each day would have strained an already burdened PCCM faculty who were providing additional critical care services as part of the surge response. Conversion of in-person consultations to the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for mitigation of COVID-19 transmission risk for additional clinicians, conservation of personal protective equipment, and more effective communication between acute inpatient practitioners and clinical services. The huddle model expedited the authorization and delivery of therapeutics, including remdesivir, which was prescribed for many patients discussed. Clinical pharmacists provided a review of all medications with input on escalation, de-escalation, dosing, drug-drug interactions, and emergency use authorization therapies.
Our experience resonates with previously described advantages of a huddle model, including the reliability of the consultation, empowerment for all members with a de-emphasis on hierarchy and accountability expected by all.8 The huddle provided situational awareness about patients that may require escalation of care to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Assistance with these transitions of care was highly appreciated by the hospital medicine teams who voiced that these decisions were quite challenging. COVID-19 patients at risk for decompensation were referred for in-person consultation and follow-up if required.
addition, the COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program allowed for a safe and dependable venue for IM trainees and attending physicians to voice questions and concerns about their patients. We observed the development of a shared mental model among all huddle participants, in the face of a steep learning curve on the management of patients with complex respiratory needs. This was reflected in the survey: Most respondents reported improved knowledge and confidence in managing these patients. Situational awareness that arose from the huddle provided the PCCM faculty the opportunity to guide the inpatient ward teams on next steps whether it be escalation to the ICU and/or further goals of care conversations. Facilitation of transitions of care were voiced as challenging decisions faced by the inpatient ward teams, and there was appreciation for additional support from the PCCM faculty in making these difficult decisions.
Challenges and Opportunities
This was a single-center experience caring for veterans. Challenges with having virtual huddles during the COVID-19 surge involved both time for the health care practitioners and technology. This was recognized early by the educational leaders at our facility, and headsets and cameras were purchased for the team rooms and made available as quickly as possible. Another limitation was the unpredictability and variability of patient volume for specific teams that sometimes would affect the efficiency of the huddle. The number of teams who attended the COVID-19 huddle was highest for the first 2 weeks (maximum of 9 teams) but declined to a nadir of 3 at the end of the month. This reflected the increase in knowledge about COVID-19 and respiratory disease that the teams acquired initially as well as a decline in COVID-19 patient admissions over those weeks.
The COVID-19 Tele-Huddle Program model also can be expanded to include other frontline clinicians, including nurses and respiratory therapists. For example, case management huddles were performed in a similar way during the COVID-19 surge to allow for efficient and effective multidisciplinary conversations about patients
Conclusions
Given the rise of telemedicine and availability of video conferencing services, virtual huddles can be implemented in institutions with appropriate staff and remote access to health records. Multidisciplinary consultation services using video conferencing can serve as an adjunct to the traditional, in-person consultation service model for patients with complex needs.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all of the Baylor Internal Medicine house staff and internal medicine attendings who participated in our huddle and more importantly, cared for our veterans during this COVID-19 surge.
1. Heymann DL, Shindo N; WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards. COVID-19: what is next for public health?. Lancet. 2020;395(10224):542-545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3
2. Dichter JR, Kanter RK, Dries D, et al; Task Force for Mass Critical Care. System-level planning, coordination, and communication: care of the critically ill and injured during pandemics and disasters: CHEST consensus statement. Chest. 2014;146(suppl 4):e87S-e102S. doi:10.1378/chest.14-0738
3. Chowdhury JM, Patel M, Zheng M, Abramian O, Criner GJ. Mobilization and preparation of a large urban academic center during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020;17(8):922-925. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-259PS
4. Uppal A, Silvestri DM, Siegler M, et al. Critical care and emergency department response at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1443-1449. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00901
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center- Houston, Texas. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.houston.va.gov/about
6. Provost SM, Lanham HJ, Leykum LK, McDaniel RR Jr, Pugh J. Health care huddles: managing complexity to achieve high reliability. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(1):2-12. doi:10.1097/HMR.0000000000000009
7. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
8. Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22(11):899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
1. Heymann DL, Shindo N; WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards. COVID-19: what is next for public health?. Lancet. 2020;395(10224):542-545. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30374-3
2. Dichter JR, Kanter RK, Dries D, et al; Task Force for Mass Critical Care. System-level planning, coordination, and communication: care of the critically ill and injured during pandemics and disasters: CHEST consensus statement. Chest. 2014;146(suppl 4):e87S-e102S. doi:10.1378/chest.14-0738
3. Chowdhury JM, Patel M, Zheng M, Abramian O, Criner GJ. Mobilization and preparation of a large urban academic center during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020;17(8):922-925. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-259PS
4. Uppal A, Silvestri DM, Siegler M, et al. Critical care and emergency department response at the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic. Health Aff (Millwood). 2020;39(8):1443-1449. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2020.00901
5. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center- Houston, Texas. Accessed December 10, 2020. https://www.houston.va.gov/about
6. Provost SM, Lanham HJ, Leykum LK, McDaniel RR Jr, Pugh J. Health care huddles: managing complexity to achieve high reliability. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(1):2-12. doi:10.1097/HMR.0000000000000009
7. Franklin BJ, Gandhi TK, Bates DW, et al. Impact of multidisciplinary team huddles on patient safety: a systematic review and proposed taxonomy. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29(10):1-2. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2019-009911
8. Goldenhar LM, Brady PW, Sutcliffe KM, Muething SE. Huddling for high reliability and situation awareness. BMJ Qual Saf. 2013;22(11):899-906. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2012-001467
Postprandial Right Upper Quadrant Abdominal Pain
A 53-year-old male patient presented to the emergency department following a primary care office visit with sudden onset right upper quadrant abdominal pain that persisted for 3 weeks, worsening over the last 2 days. The abdominal pain worsened after eating or drinking and mildly improved with omeprazole. Associated symptoms included intermittent fever, night sweats, fatigue, and bloating since onset without vomiting or diarrhea. He reported a “complicated” cholecystectomy at an outside facility 6 months prior and that his “gallbladder was adhered to his duodenum,” though outside records were not available. Additional medical history included diverticulosis with prior flares of diverticulitis but no recent flares or treatments. His home medications included acetaminophen, naproxen, intranasal fluticasone, omeprazole, gabapentin, baclofen, trazodone, and antihistamines. He reported no tobacco or illicit drug use and stated he consumed a 6 pack of beer every 6 weeks.
Initial vital signs in the emergency department demonstrated an afebrile oral temperature with unremarkable blood pressure and pulse. He was alert and oriented and did not appear in significant acute distress. Physical examination of the abdomen demonstrated a nondistended abdomen, normal active bowel sounds in all 4 quadrants, and mild right upper and lower quadrant tenderness to soft and deep palpation with release.
Significant laboratory values included elevated C-reactive protein of 44.1 mg/L and mild leukocytosis of 11.1 K/µL (reference range, 4.00-10.60 K/µL). The basic metabolic panel, liver-associated enzymes, and lipase levels were within normal limits.
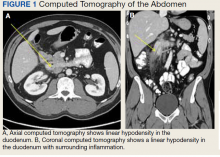
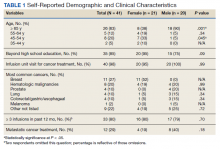
The initial imaging study was a computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and IV contrast. The radiology report depicted a thin, needle-like hypodense foreign body approximately 8 cm in length in the proximal duodenum, slightly protruding extraluminally, and at least a moderate amount of surrounding inflammation without abscess or free air (Figure 1).
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?
Our Diagnosis
Based on the clinical history of postprandial abdominal pain with prior cholecystectomy and leukocytosis, the initial differential diagnosis included peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux, or delayed sequela of the cholecystectomy 6 months prior. Although suspicion remained for possible delayed postoperative complications from the cholecystectomy, ultrasound and hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan were not pursued based on CT imaging findings. The needle-like hypodensity in the duodenum with surrounding inflammation visualized on CT was concerning for an unidentified penetrating foreign body with a possible retroperitoneal microperforation.
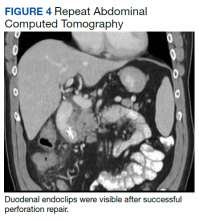
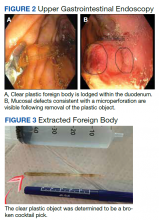
After these imaging findings were relayed from Radiology to the Gastroenterology Service, the patient underwent an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy to further evaluate the duodenum. Inspection revealed mild gastritis and a linear, clear piece of plastic with both ends firmly lodged within the mucosa from the distal duodenal bulb to the second portion of the duodenum; a significant mucosal defect of the bowel wall was visualized after careful extraction of the foreign body (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with a small duodenal perforation, which was sealed endoscopically with 2 endoclips. The extracted piece of plastic was examined and determined to be a broken cocktail pick (Figure 3). During discussion with the patient postprocedure, he stated that he ingested several olive martinis (which were served with cocktail picks) approximately 3 weeks prior to presentation and did not recall ingesting the cocktail pick. A repeat abdominal CT following the endoscopy demonstrated no leak or free air from the site of the repaired duodenal perforation (Figure 4). The patient avoided surgery and was permitted to resume a liquid diet prior to discharge.
Discussion
Foreign body ingestion in adults is most commonly unintentional with fish bones being the most common culprit.1 In unintentional instances of foreign body ingestion, many patients are not aware of the event, with dentures posing a significant well-known risk factor due to lack of palatal sensory feedback.2 Most ingested foreign bodies pass uninhibited through the GI tract without complications. However, less than 1% of ingested foreign bodies cause potentially life-threatening GI perforations.3
The risk of GI perforation due to foreign body ingestion is greatest with elongated, sharp objects, such as needles, bones, toothpicks, and cocktail picks. These objects tend to lodge at areas of narrowing or angulation, such as the appendix, ileocecal region, or as in this case, the duodenum.3 Passage of a foreign body through the duodenum is more likely to be inhibited if the object is longer than 6 cm and with a diameter > 2.5 cm.4 Signs of duodenal perforation are often subtle compared with jejunal or ileal perforations. Patients are commonly afebrile with normal white blood cell counts and are more likely to have chronic symptoms for > 3 days before the appropriate diagnosis of foreign body ingestion is made.1 Duodenal perforations may be more stable clinically compared with distal GI perforations in part due to the retroperitoneal location with relatively fewer bacteria present intraluminally. GI perforations may not occur acutely during passage of the foreign body but can present weeks, months, or even years later.5 Delayed onset of symptoms may happen when the foreign body becomes lodged and only partially perforates the bowel wall, resulting in a chronic inflammatory process. Other possible complications include fistulization and abscess formation from migrating linear sharp objects through the bowel wall, which is most observed with toothpicks and cocktail picks, specifically.5
Foreign bodies identified on plain radiographs commonly include radiopaque objects, such as glass, metallic objects, most animal bones and some fish bones, and some medications. However, radiolucent objects, such as toothpicks and cocktail picks, wood, plastic, most fish bones, and most medicines, often will not appear on radiographs. The diagnosis of ingested foreign body can therefore easily be delayed or overlooked on plain radiographs due to ingestion of radiolucent objects or lack of adequate patient history. A high index of suspicion is needed in such instances. The modality of choice for identifying GI perforation due to ingested foreign objects is CT.5 All of these commonly missed materials on radiographs will be visible on CT with variable densities. As an added benefit, CT also may reveal ingested objects not visualized on radiographs and show ancillary signs of perforation, such as extraluminal free air, localized inflammation, and fluid collections or abscess surrounding a segment of thickened bowel.5
Most ingested foreign bodies will pass through the GI system and can be managed with careful observation alone. However, upper endoscopy is emergently indicated in 3 scenarios of foreign body ingestion: (1) complete occlusion of the esophagus with salivary pooling due to risk of aspiration; (2) ingestion of batteries due to toxic substances; and (3) ingestion of sharp or pointed foreign bodies due to risk of perforation.4 Overall, endoscopic intervention is required in 20% of cases and surgical intervention remains rare at 1%.4 In the case of this patient, an emergent upper endoscopy was needed due to suspected duodenal perforation.
Treatment of duodenal perforations due to foreign bodies may involve conservative, surgical, or endoscopic management. Contained, small perforations in a stable patient may be treated conservatively with IV fluids, antibiotics, and proton pump inhibitors as they self-seal with omentum if the foreign body has passed.6 Retained duodenal foreign bodies pose a risk of persistent perforation or fistulization and must be removed. Anterior duodenal perforations pose a risk of peritonitis, whereas posterior duodenal perforations, although retroperitoneal and sparing the peritoneal cavity, may result in localized abscess formation necessitating foreign body removal. Endoscopic clipping is a modernized, less invasive way to close GI perforations. Through-the-scope clips (TTSCs) can close luminal defects < 2 cm in size.7 Defects > 1 cm may be repaired with combined TTSCs and endoloop or omental patching. Over-the-scope clips can close full thickness defects up to 2 to 3 cm with the advantage of being able to close leaks and fistulas involving inflamed or indurated tissue.7
Conclusions
Intestinal perforations related to foreign body ingestion are a rare complication occurring in < 1% of patients. Although most ingested foreign objects will pass through the GI tract, elongated or sharp objects pose a risk for perforation. In many cases, a history of foreign body ingestion is not obtained, and a high index of suspicion is required. Duodenal perforations due to foreign body ingestion should be included in the differential among the more common diagnoses of peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, and gallbladder disease in the setting of postprandial right upper quadrant abdominal pain. CT is the best modality for identifying foreign bodies, including objects that may be missed on plain radiographs.
1. Goh BK, Chow PK, Quah HM, et al. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract secondary to ingestion of foreign bodies. World J Surg. 2006;(30)372-377. doi:10.1007/s00268-005-0490-2
2. Bunker PG. The role of dentistry in problems of foreign body in the air and food passage. J Am Dent Assoc. 1962;(64):782-787. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.1962.0160
3. Hunter TB, Taljanovic MS. Foreign bodies. Radiographics. 2003;23(3):731-757. doi:10.1148/rg.233025137
4. Ambe P, Weber SA, Schauer M, Knoefel WT. Swallowed foreign bodies in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012;109(50):869-875. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2012.0869
5. Kuzmich S, Burke CJ, Harvey CJ, et al. Perforation of gastrointestinal tract by poorly conspicuous ingested foreign bodies: radiological diagnosis. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1050):20150086. doi:10.1259/bjr.20150086
6. Hill AG. Management of perforated duodenal ulcer. In: Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA, eds. Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Zuckschwerdt; 2001.
7. Rogalski P, Daniluk J, Baniukiewicz A, Wroblewski E, Dabrowski A. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(37):10542-10552. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10542
A 53-year-old male patient presented to the emergency department following a primary care office visit with sudden onset right upper quadrant abdominal pain that persisted for 3 weeks, worsening over the last 2 days. The abdominal pain worsened after eating or drinking and mildly improved with omeprazole. Associated symptoms included intermittent fever, night sweats, fatigue, and bloating since onset without vomiting or diarrhea. He reported a “complicated” cholecystectomy at an outside facility 6 months prior and that his “gallbladder was adhered to his duodenum,” though outside records were not available. Additional medical history included diverticulosis with prior flares of diverticulitis but no recent flares or treatments. His home medications included acetaminophen, naproxen, intranasal fluticasone, omeprazole, gabapentin, baclofen, trazodone, and antihistamines. He reported no tobacco or illicit drug use and stated he consumed a 6 pack of beer every 6 weeks.
Initial vital signs in the emergency department demonstrated an afebrile oral temperature with unremarkable blood pressure and pulse. He was alert and oriented and did not appear in significant acute distress. Physical examination of the abdomen demonstrated a nondistended abdomen, normal active bowel sounds in all 4 quadrants, and mild right upper and lower quadrant tenderness to soft and deep palpation with release.
Significant laboratory values included elevated C-reactive protein of 44.1 mg/L and mild leukocytosis of 11.1 K/µL (reference range, 4.00-10.60 K/µL). The basic metabolic panel, liver-associated enzymes, and lipase levels were within normal limits.
The initial imaging study was a computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and IV contrast. The radiology report depicted a thin, needle-like hypodense foreign body approximately 8 cm in length in the proximal duodenum, slightly protruding extraluminally, and at least a moderate amount of surrounding inflammation without abscess or free air (Figure 1).
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?
Our Diagnosis
Based on the clinical history of postprandial abdominal pain with prior cholecystectomy and leukocytosis, the initial differential diagnosis included peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux, or delayed sequela of the cholecystectomy 6 months prior. Although suspicion remained for possible delayed postoperative complications from the cholecystectomy, ultrasound and hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan were not pursued based on CT imaging findings. The needle-like hypodensity in the duodenum with surrounding inflammation visualized on CT was concerning for an unidentified penetrating foreign body with a possible retroperitoneal microperforation.
After these imaging findings were relayed from Radiology to the Gastroenterology Service, the patient underwent an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy to further evaluate the duodenum. Inspection revealed mild gastritis and a linear, clear piece of plastic with both ends firmly lodged within the mucosa from the distal duodenal bulb to the second portion of the duodenum; a significant mucosal defect of the bowel wall was visualized after careful extraction of the foreign body (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with a small duodenal perforation, which was sealed endoscopically with 2 endoclips. The extracted piece of plastic was examined and determined to be a broken cocktail pick (Figure 3). During discussion with the patient postprocedure, he stated that he ingested several olive martinis (which were served with cocktail picks) approximately 3 weeks prior to presentation and did not recall ingesting the cocktail pick. A repeat abdominal CT following the endoscopy demonstrated no leak or free air from the site of the repaired duodenal perforation (Figure 4). The patient avoided surgery and was permitted to resume a liquid diet prior to discharge.
Discussion
Foreign body ingestion in adults is most commonly unintentional with fish bones being the most common culprit.1 In unintentional instances of foreign body ingestion, many patients are not aware of the event, with dentures posing a significant well-known risk factor due to lack of palatal sensory feedback.2 Most ingested foreign bodies pass uninhibited through the GI tract without complications. However, less than 1% of ingested foreign bodies cause potentially life-threatening GI perforations.3
The risk of GI perforation due to foreign body ingestion is greatest with elongated, sharp objects, such as needles, bones, toothpicks, and cocktail picks. These objects tend to lodge at areas of narrowing or angulation, such as the appendix, ileocecal region, or as in this case, the duodenum.3 Passage of a foreign body through the duodenum is more likely to be inhibited if the object is longer than 6 cm and with a diameter > 2.5 cm.4 Signs of duodenal perforation are often subtle compared with jejunal or ileal perforations. Patients are commonly afebrile with normal white blood cell counts and are more likely to have chronic symptoms for > 3 days before the appropriate diagnosis of foreign body ingestion is made.1 Duodenal perforations may be more stable clinically compared with distal GI perforations in part due to the retroperitoneal location with relatively fewer bacteria present intraluminally. GI perforations may not occur acutely during passage of the foreign body but can present weeks, months, or even years later.5 Delayed onset of symptoms may happen when the foreign body becomes lodged and only partially perforates the bowel wall, resulting in a chronic inflammatory process. Other possible complications include fistulization and abscess formation from migrating linear sharp objects through the bowel wall, which is most observed with toothpicks and cocktail picks, specifically.5
Foreign bodies identified on plain radiographs commonly include radiopaque objects, such as glass, metallic objects, most animal bones and some fish bones, and some medications. However, radiolucent objects, such as toothpicks and cocktail picks, wood, plastic, most fish bones, and most medicines, often will not appear on radiographs. The diagnosis of ingested foreign body can therefore easily be delayed or overlooked on plain radiographs due to ingestion of radiolucent objects or lack of adequate patient history. A high index of suspicion is needed in such instances. The modality of choice for identifying GI perforation due to ingested foreign objects is CT.5 All of these commonly missed materials on radiographs will be visible on CT with variable densities. As an added benefit, CT also may reveal ingested objects not visualized on radiographs and show ancillary signs of perforation, such as extraluminal free air, localized inflammation, and fluid collections or abscess surrounding a segment of thickened bowel.5
Most ingested foreign bodies will pass through the GI system and can be managed with careful observation alone. However, upper endoscopy is emergently indicated in 3 scenarios of foreign body ingestion: (1) complete occlusion of the esophagus with salivary pooling due to risk of aspiration; (2) ingestion of batteries due to toxic substances; and (3) ingestion of sharp or pointed foreign bodies due to risk of perforation.4 Overall, endoscopic intervention is required in 20% of cases and surgical intervention remains rare at 1%.4 In the case of this patient, an emergent upper endoscopy was needed due to suspected duodenal perforation.
Treatment of duodenal perforations due to foreign bodies may involve conservative, surgical, or endoscopic management. Contained, small perforations in a stable patient may be treated conservatively with IV fluids, antibiotics, and proton pump inhibitors as they self-seal with omentum if the foreign body has passed.6 Retained duodenal foreign bodies pose a risk of persistent perforation or fistulization and must be removed. Anterior duodenal perforations pose a risk of peritonitis, whereas posterior duodenal perforations, although retroperitoneal and sparing the peritoneal cavity, may result in localized abscess formation necessitating foreign body removal. Endoscopic clipping is a modernized, less invasive way to close GI perforations. Through-the-scope clips (TTSCs) can close luminal defects < 2 cm in size.7 Defects > 1 cm may be repaired with combined TTSCs and endoloop or omental patching. Over-the-scope clips can close full thickness defects up to 2 to 3 cm with the advantage of being able to close leaks and fistulas involving inflamed or indurated tissue.7
Conclusions
Intestinal perforations related to foreign body ingestion are a rare complication occurring in < 1% of patients. Although most ingested foreign objects will pass through the GI tract, elongated or sharp objects pose a risk for perforation. In many cases, a history of foreign body ingestion is not obtained, and a high index of suspicion is required. Duodenal perforations due to foreign body ingestion should be included in the differential among the more common diagnoses of peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, and gallbladder disease in the setting of postprandial right upper quadrant abdominal pain. CT is the best modality for identifying foreign bodies, including objects that may be missed on plain radiographs.
A 53-year-old male patient presented to the emergency department following a primary care office visit with sudden onset right upper quadrant abdominal pain that persisted for 3 weeks, worsening over the last 2 days. The abdominal pain worsened after eating or drinking and mildly improved with omeprazole. Associated symptoms included intermittent fever, night sweats, fatigue, and bloating since onset without vomiting or diarrhea. He reported a “complicated” cholecystectomy at an outside facility 6 months prior and that his “gallbladder was adhered to his duodenum,” though outside records were not available. Additional medical history included diverticulosis with prior flares of diverticulitis but no recent flares or treatments. His home medications included acetaminophen, naproxen, intranasal fluticasone, omeprazole, gabapentin, baclofen, trazodone, and antihistamines. He reported no tobacco or illicit drug use and stated he consumed a 6 pack of beer every 6 weeks.
Initial vital signs in the emergency department demonstrated an afebrile oral temperature with unremarkable blood pressure and pulse. He was alert and oriented and did not appear in significant acute distress. Physical examination of the abdomen demonstrated a nondistended abdomen, normal active bowel sounds in all 4 quadrants, and mild right upper and lower quadrant tenderness to soft and deep palpation with release.
Significant laboratory values included elevated C-reactive protein of 44.1 mg/L and mild leukocytosis of 11.1 K/µL (reference range, 4.00-10.60 K/µL). The basic metabolic panel, liver-associated enzymes, and lipase levels were within normal limits.
The initial imaging study was a computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with oral and IV contrast. The radiology report depicted a thin, needle-like hypodense foreign body approximately 8 cm in length in the proximal duodenum, slightly protruding extraluminally, and at least a moderate amount of surrounding inflammation without abscess or free air (Figure 1).
- What is your diagnosis?
- How would you treat this patient?
Our Diagnosis
Based on the clinical history of postprandial abdominal pain with prior cholecystectomy and leukocytosis, the initial differential diagnosis included peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux, or delayed sequela of the cholecystectomy 6 months prior. Although suspicion remained for possible delayed postoperative complications from the cholecystectomy, ultrasound and hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan were not pursued based on CT imaging findings. The needle-like hypodensity in the duodenum with surrounding inflammation visualized on CT was concerning for an unidentified penetrating foreign body with a possible retroperitoneal microperforation.
After these imaging findings were relayed from Radiology to the Gastroenterology Service, the patient underwent an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy to further evaluate the duodenum. Inspection revealed mild gastritis and a linear, clear piece of plastic with both ends firmly lodged within the mucosa from the distal duodenal bulb to the second portion of the duodenum; a significant mucosal defect of the bowel wall was visualized after careful extraction of the foreign body (Figure 2). The patient was diagnosed with a small duodenal perforation, which was sealed endoscopically with 2 endoclips. The extracted piece of plastic was examined and determined to be a broken cocktail pick (Figure 3). During discussion with the patient postprocedure, he stated that he ingested several olive martinis (which were served with cocktail picks) approximately 3 weeks prior to presentation and did not recall ingesting the cocktail pick. A repeat abdominal CT following the endoscopy demonstrated no leak or free air from the site of the repaired duodenal perforation (Figure 4). The patient avoided surgery and was permitted to resume a liquid diet prior to discharge.
Discussion
Foreign body ingestion in adults is most commonly unintentional with fish bones being the most common culprit.1 In unintentional instances of foreign body ingestion, many patients are not aware of the event, with dentures posing a significant well-known risk factor due to lack of palatal sensory feedback.2 Most ingested foreign bodies pass uninhibited through the GI tract without complications. However, less than 1% of ingested foreign bodies cause potentially life-threatening GI perforations.3
The risk of GI perforation due to foreign body ingestion is greatest with elongated, sharp objects, such as needles, bones, toothpicks, and cocktail picks. These objects tend to lodge at areas of narrowing or angulation, such as the appendix, ileocecal region, or as in this case, the duodenum.3 Passage of a foreign body through the duodenum is more likely to be inhibited if the object is longer than 6 cm and with a diameter > 2.5 cm.4 Signs of duodenal perforation are often subtle compared with jejunal or ileal perforations. Patients are commonly afebrile with normal white blood cell counts and are more likely to have chronic symptoms for > 3 days before the appropriate diagnosis of foreign body ingestion is made.1 Duodenal perforations may be more stable clinically compared with distal GI perforations in part due to the retroperitoneal location with relatively fewer bacteria present intraluminally. GI perforations may not occur acutely during passage of the foreign body but can present weeks, months, or even years later.5 Delayed onset of symptoms may happen when the foreign body becomes lodged and only partially perforates the bowel wall, resulting in a chronic inflammatory process. Other possible complications include fistulization and abscess formation from migrating linear sharp objects through the bowel wall, which is most observed with toothpicks and cocktail picks, specifically.5
Foreign bodies identified on plain radiographs commonly include radiopaque objects, such as glass, metallic objects, most animal bones and some fish bones, and some medications. However, radiolucent objects, such as toothpicks and cocktail picks, wood, plastic, most fish bones, and most medicines, often will not appear on radiographs. The diagnosis of ingested foreign body can therefore easily be delayed or overlooked on plain radiographs due to ingestion of radiolucent objects or lack of adequate patient history. A high index of suspicion is needed in such instances. The modality of choice for identifying GI perforation due to ingested foreign objects is CT.5 All of these commonly missed materials on radiographs will be visible on CT with variable densities. As an added benefit, CT also may reveal ingested objects not visualized on radiographs and show ancillary signs of perforation, such as extraluminal free air, localized inflammation, and fluid collections or abscess surrounding a segment of thickened bowel.5
Most ingested foreign bodies will pass through the GI system and can be managed with careful observation alone. However, upper endoscopy is emergently indicated in 3 scenarios of foreign body ingestion: (1) complete occlusion of the esophagus with salivary pooling due to risk of aspiration; (2) ingestion of batteries due to toxic substances; and (3) ingestion of sharp or pointed foreign bodies due to risk of perforation.4 Overall, endoscopic intervention is required in 20% of cases and surgical intervention remains rare at 1%.4 In the case of this patient, an emergent upper endoscopy was needed due to suspected duodenal perforation.
Treatment of duodenal perforations due to foreign bodies may involve conservative, surgical, or endoscopic management. Contained, small perforations in a stable patient may be treated conservatively with IV fluids, antibiotics, and proton pump inhibitors as they self-seal with omentum if the foreign body has passed.6 Retained duodenal foreign bodies pose a risk of persistent perforation or fistulization and must be removed. Anterior duodenal perforations pose a risk of peritonitis, whereas posterior duodenal perforations, although retroperitoneal and sparing the peritoneal cavity, may result in localized abscess formation necessitating foreign body removal. Endoscopic clipping is a modernized, less invasive way to close GI perforations. Through-the-scope clips (TTSCs) can close luminal defects < 2 cm in size.7 Defects > 1 cm may be repaired with combined TTSCs and endoloop or omental patching. Over-the-scope clips can close full thickness defects up to 2 to 3 cm with the advantage of being able to close leaks and fistulas involving inflamed or indurated tissue.7
Conclusions
Intestinal perforations related to foreign body ingestion are a rare complication occurring in < 1% of patients. Although most ingested foreign objects will pass through the GI tract, elongated or sharp objects pose a risk for perforation. In many cases, a history of foreign body ingestion is not obtained, and a high index of suspicion is required. Duodenal perforations due to foreign body ingestion should be included in the differential among the more common diagnoses of peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, and gallbladder disease in the setting of postprandial right upper quadrant abdominal pain. CT is the best modality for identifying foreign bodies, including objects that may be missed on plain radiographs.
1. Goh BK, Chow PK, Quah HM, et al. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract secondary to ingestion of foreign bodies. World J Surg. 2006;(30)372-377. doi:10.1007/s00268-005-0490-2
2. Bunker PG. The role of dentistry in problems of foreign body in the air and food passage. J Am Dent Assoc. 1962;(64):782-787. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.1962.0160
3. Hunter TB, Taljanovic MS. Foreign bodies. Radiographics. 2003;23(3):731-757. doi:10.1148/rg.233025137
4. Ambe P, Weber SA, Schauer M, Knoefel WT. Swallowed foreign bodies in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012;109(50):869-875. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2012.0869
5. Kuzmich S, Burke CJ, Harvey CJ, et al. Perforation of gastrointestinal tract by poorly conspicuous ingested foreign bodies: radiological diagnosis. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1050):20150086. doi:10.1259/bjr.20150086
6. Hill AG. Management of perforated duodenal ulcer. In: Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA, eds. Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Zuckschwerdt; 2001.
7. Rogalski P, Daniluk J, Baniukiewicz A, Wroblewski E, Dabrowski A. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(37):10542-10552. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10542
1. Goh BK, Chow PK, Quah HM, et al. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract secondary to ingestion of foreign bodies. World J Surg. 2006;(30)372-377. doi:10.1007/s00268-005-0490-2
2. Bunker PG. The role of dentistry in problems of foreign body in the air and food passage. J Am Dent Assoc. 1962;(64):782-787. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.1962.0160
3. Hunter TB, Taljanovic MS. Foreign bodies. Radiographics. 2003;23(3):731-757. doi:10.1148/rg.233025137
4. Ambe P, Weber SA, Schauer M, Knoefel WT. Swallowed foreign bodies in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2012;109(50):869-875. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2012.0869
5. Kuzmich S, Burke CJ, Harvey CJ, et al. Perforation of gastrointestinal tract by poorly conspicuous ingested foreign bodies: radiological diagnosis. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1050):20150086. doi:10.1259/bjr.20150086
6. Hill AG. Management of perforated duodenal ulcer. In: Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA, eds. Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Zuckschwerdt; 2001.
7. Rogalski P, Daniluk J, Baniukiewicz A, Wroblewski E, Dabrowski A. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal perforations, leaks and fistulas. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(37):10542-10552. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10542
Call for Neurology Papers
Federal Practitioner invites VA, DoD, and PHS health care professionals and researchers to contribute to a future special issue on neurology. Topics of interest include epilepsy, headache and migraine, COVID-19 and neurology, Alzheimer and dementia, MS, and other neurological disorders.
Interested authors should submit an abstract to [email protected] with the subject line “Neurology Special Issue” for consideration. Once the editorial team confirms the article is eligible for consideration, authors will be asked to submit their manuscript in full through Editorial Manager.
Federal Practitioner never charges authors or readers. All submissions undergo a double-blinded peer review before publication. Accepted manuscripts are always available for free online at www.mdedge.com/fedprac and on PubMed Central.
Federal Practitioner welcomes original research, commentaries, clinical reviews, program profiles, case reports, and other evidence-based articles. The updated and complete submission guidelines, including details about the style and format, can be found here:
Federal Practitioner invites VA, DoD, and PHS health care professionals and researchers to contribute to a future special issue on neurology. Topics of interest include epilepsy, headache and migraine, COVID-19 and neurology, Alzheimer and dementia, MS, and other neurological disorders.
Interested authors should submit an abstract to [email protected] with the subject line “Neurology Special Issue” for consideration. Once the editorial team confirms the article is eligible for consideration, authors will be asked to submit their manuscript in full through Editorial Manager.
Federal Practitioner never charges authors or readers. All submissions undergo a double-blinded peer review before publication. Accepted manuscripts are always available for free online at www.mdedge.com/fedprac and on PubMed Central.
Federal Practitioner welcomes original research, commentaries, clinical reviews, program profiles, case reports, and other evidence-based articles. The updated and complete submission guidelines, including details about the style and format, can be found here:
Federal Practitioner invites VA, DoD, and PHS health care professionals and researchers to contribute to a future special issue on neurology. Topics of interest include epilepsy, headache and migraine, COVID-19 and neurology, Alzheimer and dementia, MS, and other neurological disorders.
Interested authors should submit an abstract to [email protected] with the subject line “Neurology Special Issue” for consideration. Once the editorial team confirms the article is eligible for consideration, authors will be asked to submit their manuscript in full through Editorial Manager.
Federal Practitioner never charges authors or readers. All submissions undergo a double-blinded peer review before publication. Accepted manuscripts are always available for free online at www.mdedge.com/fedprac and on PubMed Central.
Federal Practitioner welcomes original research, commentaries, clinical reviews, program profiles, case reports, and other evidence-based articles. The updated and complete submission guidelines, including details about the style and format, can be found here:
In Memoriam: John Hickner, MD, MSc
We are deeply saddened by the recent death of our friend and colleague, John Hickner. Although we are grieving, we consider ourselves fortunate to have had John in our lives and to be able to share a few of his many accomplishments and attributes. Anyone who knew John knew that he had many gifts. But above all, John was kind, generous, and thoughtful. Val, John’s wife of 48 years, and their family were at the center of John’s world. Everything John did was a reflection of his love for his family.
John was a small-town family physician, and this guided virtually all of his professional endeavors. He was a member of the faculty for the Michigan State University Department of Family Medicine in Escanaba, in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. While in the Upper Peninsula, he helped establish 2 practice-based research networks: the statewide Michigan Research Network (MiRNet) and the regional Upper Peninsula Research Network (UPRNet). If you ever had the chance to attend the UPRNet meetings, you would have observed the entire practice staff included in planning research activities, sharing, and troubleshooting common practice hiccups. At the end of those meetings, John would conclude by reading a children’s story such as Goodnight Moon or play a song on his guitar and then give a final thoughtful message.
In 1999, John worked with the American Academy of Family Physicians to create the National Research Network, now composed of more than 870 practices and nearly 2400 members. His own interests in respiratory infections, stemming from his experiences with his own children, led to work with the North American Respiratory Infection Study Group and with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
John’s interests in practice-based research paralleled his interests in evidence-based medicine, largely as a way to translate research into daily practice. This focus on evidence guided much of his work as Editor-in-Chief for The Journal of Family Practice, a title he held for a decade. He also worked with state Academies of Family Physicians for more than a decade to create a new conference series centered on short, practical clinical topics and based completely on summaries of recent research. Any listener of the Primary Care Update podcasts could hear his thoughtful questioning of current research and his wise approach to its integration into practice.
John was more than a thoughtful and kind clinician, an outstanding educator, and a gifted researcher; he was a natural leader. John had the capacity to understand the systems in which he worked and was able to skillfully guide teams to improve those systems. He served as the Chair of Family Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic and then at the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC), and mentored many faculty, residents, and students during his time at those institutions.
After retiring from UIC, John and Val moved back to Escanaba. At his retirement dinner, his children (Michael, Laura, Zach, Anna, and Olivia) gifted him a beautiful maple acoustic guitar with which he then serenaded the attendees. John was an avid tennis player and often would tell us he would have to skip meeting us for dinner while away at a conference because he had found a tennis opponent! Most of all, he loved to set out on his 35-foot sailboat on Big Bay de Noc or on Green Bay. We have fond memories of the days spent sailing with John and hope that he has found fair winds and following seas.
Henry C. Barry, MD, MS
Mark Ebell, MD, MS
Kate Rowland, MD, MS, FAAFP
We are deeply saddened by the recent death of our friend and colleague, John Hickner. Although we are grieving, we consider ourselves fortunate to have had John in our lives and to be able to share a few of his many accomplishments and attributes. Anyone who knew John knew that he had many gifts. But above all, John was kind, generous, and thoughtful. Val, John’s wife of 48 years, and their family were at the center of John’s world. Everything John did was a reflection of his love for his family.
John was a small-town family physician, and this guided virtually all of his professional endeavors. He was a member of the faculty for the Michigan State University Department of Family Medicine in Escanaba, in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. While in the Upper Peninsula, he helped establish 2 practice-based research networks: the statewide Michigan Research Network (MiRNet) and the regional Upper Peninsula Research Network (UPRNet). If you ever had the chance to attend the UPRNet meetings, you would have observed the entire practice staff included in planning research activities, sharing, and troubleshooting common practice hiccups. At the end of those meetings, John would conclude by reading a children’s story such as Goodnight Moon or play a song on his guitar and then give a final thoughtful message.
In 1999, John worked with the American Academy of Family Physicians to create the National Research Network, now composed of more than 870 practices and nearly 2400 members. His own interests in respiratory infections, stemming from his experiences with his own children, led to work with the North American Respiratory Infection Study Group and with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
John’s interests in practice-based research paralleled his interests in evidence-based medicine, largely as a way to translate research into daily practice. This focus on evidence guided much of his work as Editor-in-Chief for The Journal of Family Practice, a title he held for a decade. He also worked with state Academies of Family Physicians for more than a decade to create a new conference series centered on short, practical clinical topics and based completely on summaries of recent research. Any listener of the Primary Care Update podcasts could hear his thoughtful questioning of current research and his wise approach to its integration into practice.
John was more than a thoughtful and kind clinician, an outstanding educator, and a gifted researcher; he was a natural leader. John had the capacity to understand the systems in which he worked and was able to skillfully guide teams to improve those systems. He served as the Chair of Family Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic and then at the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC), and mentored many faculty, residents, and students during his time at those institutions.
After retiring from UIC, John and Val moved back to Escanaba. At his retirement dinner, his children (Michael, Laura, Zach, Anna, and Olivia) gifted him a beautiful maple acoustic guitar with which he then serenaded the attendees. John was an avid tennis player and often would tell us he would have to skip meeting us for dinner while away at a conference because he had found a tennis opponent! Most of all, he loved to set out on his 35-foot sailboat on Big Bay de Noc or on Green Bay. We have fond memories of the days spent sailing with John and hope that he has found fair winds and following seas.
Henry C. Barry, MD, MS
Mark Ebell, MD, MS
Kate Rowland, MD, MS, FAAFP
We are deeply saddened by the recent death of our friend and colleague, John Hickner. Although we are grieving, we consider ourselves fortunate to have had John in our lives and to be able to share a few of his many accomplishments and attributes. Anyone who knew John knew that he had many gifts. But above all, John was kind, generous, and thoughtful. Val, John’s wife of 48 years, and their family were at the center of John’s world. Everything John did was a reflection of his love for his family.
John was a small-town family physician, and this guided virtually all of his professional endeavors. He was a member of the faculty for the Michigan State University Department of Family Medicine in Escanaba, in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. While in the Upper Peninsula, he helped establish 2 practice-based research networks: the statewide Michigan Research Network (MiRNet) and the regional Upper Peninsula Research Network (UPRNet). If you ever had the chance to attend the UPRNet meetings, you would have observed the entire practice staff included in planning research activities, sharing, and troubleshooting common practice hiccups. At the end of those meetings, John would conclude by reading a children’s story such as Goodnight Moon or play a song on his guitar and then give a final thoughtful message.
In 1999, John worked with the American Academy of Family Physicians to create the National Research Network, now composed of more than 870 practices and nearly 2400 members. His own interests in respiratory infections, stemming from his experiences with his own children, led to work with the North American Respiratory Infection Study Group and with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
John’s interests in practice-based research paralleled his interests in evidence-based medicine, largely as a way to translate research into daily practice. This focus on evidence guided much of his work as Editor-in-Chief for The Journal of Family Practice, a title he held for a decade. He also worked with state Academies of Family Physicians for more than a decade to create a new conference series centered on short, practical clinical topics and based completely on summaries of recent research. Any listener of the Primary Care Update podcasts could hear his thoughtful questioning of current research and his wise approach to its integration into practice.
John was more than a thoughtful and kind clinician, an outstanding educator, and a gifted researcher; he was a natural leader. John had the capacity to understand the systems in which he worked and was able to skillfully guide teams to improve those systems. He served as the Chair of Family Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic and then at the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC), and mentored many faculty, residents, and students during his time at those institutions.
After retiring from UIC, John and Val moved back to Escanaba. At his retirement dinner, his children (Michael, Laura, Zach, Anna, and Olivia) gifted him a beautiful maple acoustic guitar with which he then serenaded the attendees. John was an avid tennis player and often would tell us he would have to skip meeting us for dinner while away at a conference because he had found a tennis opponent! Most of all, he loved to set out on his 35-foot sailboat on Big Bay de Noc or on Green Bay. We have fond memories of the days spent sailing with John and hope that he has found fair winds and following seas.
Henry C. Barry, MD, MS
Mark Ebell, MD, MS
Kate Rowland, MD, MS, FAAFP
Pink Nodule Behind the Ear
The Diagnosis: Acanthoma Fissuratum
Acanthoma fissuratum is a skin lesion that results from consistent pressure, typically from ill-fitting eyeglass frames.1 The chronic irritation leads to collagen deposition and inflammation that gradually creates the lesion. Many patients never seek care, making incidence figures undeterminable.2 It usually presents as a firm, tender, flesh-colored or pink nodule or plaque with a central indentation from where the frame rests. This indentation splits the lesion in half and classically gives the appearance of a coffee bean.1 The repeated minor trauma at this point of contact also may lead to centralized ulceration, which further blurs the diagnosis to include basal cell carcinoma (BCC).3,4 Although the postauricular groove is the most cited location, lesions also may occur at other contact points of the glasses, such as the lateral aspect of the bridge of the nose and the superior auricular sulcus.5 Acanthoma fissuratum is not limited to the external head. Other etiologies of local trauma and pressure have led to its diagnosis in the upper labioalveolar fold, posterior fourchette of the vulva, penis, and external auditory canal.6-9
The diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum mainly is clinical; however, due to its similar appearance to BCC and other lesions, a biopsy can be taken to support the diagnosis; a biopsy was not performed in our patient. The main features seen on histopathology include acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, variable parakeratosis, and perivascular nonspecific inflammatory infiltration. The epidermis may reflect the macroscopic frame indentation with central attenuation of the epidermis, which potentially is filled with inflammatory cells or keratin.5
Treatment normally encompasses removing the illfitting frames or fixing the fit, which gradually leads to reduction of the lesion.4,5 This occurred in our patient, who changed eyeglasses and saw an 80% resolution of the lesion in 8 months. Such improvement after removal of a trauma-inducing stimulus would not be seen in malignancies (eg, BCC, squamous cell carcinoma [SCC]), keloids, or cylindromas. If the granulation tissue does not regress or recurs, other potential treatments include excision, intralesional corticosteroids, and electrosurgery.5
Basal cell carcinoma is a common nonmelanoma skin cancer that most often presents on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck, especially the cheeks, nasolabial folds, and forehead. Although the nodular subtype may clinically appear similar to acanthoma fissuratum, it more typically presents as a pearly papule or nodule with a sharp border, small telangiectases, and potential ulceration.10 Squamous cell carcinoma is another common nonmelanoma skin cancer that often arises in sun-exposed areas, which can include the postauricular area. Although the lesion can be associated with chronic wounds and also can grow vertically, SCC typically has a scalier and more hyperkeratotic surface that can ulcerate.1 A cylindroma is a benign sweat gland tumor that most commonly presents on the head and neck (also known as the turban tumor), though it can develop on the ear. It appears as solitary or multiple nodules that often are flesh colored, red, or blue with a shiny surface.1 Cylindromas are not known to be associated with chronic local trauma or irritation,11 such as wearing ill-fitting eyeglasses. Unlike acanthoma fissuratum, the treatment of cylindromas, BCC, and SCC most often involves excision.1 A keloid presents as a flesh-colored, red, or purple exophytic plaque that is composed of dense dermal tissue and progressively forms after local trauma. Although keloids can spontaneously develop, they commonly form on the ears in susceptible individuals after skin excisions including prior keloid removal, piercings, repairment of auricular traumas, or infections.1 The patient’s coffee bean–like lesion that coincided with wearing new eyeglasses better fits the diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum than a keloid. Additionally, keloids typically do not regress without treatment. Keloid treatment consists of intralesional steroid injections, occlusive silicone dressings, compression, cryotherapy, radiation, and excisional surgery.1
- Sand M, Sand D, Brors D, et al. Cutaneous lesions of the external ear. Head Face Med. 2008;4. doi:10.1186/1746-160X-4-2
- Orengo I, Robbins K, Marsch A. Pathology of the ear. Semin Plast Surg. 2011;25:279-287. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1288920
- Ramroop S. Successful treatment of acanthoma fissuratum with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide. Clin Case Rep. 2020;8:702-703. doi:10.1002/ccr3.2708
- Delaney TJ, Stewart TW. Granuloma fissuratum. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:373-375. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14235.x
- Deshpande NS, Sen A, Vasudevan B, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum: lest we forget. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:141-143. doi:10.4103/2229- 5178.202267
- Surron RL Jr. A fissured granulomatous lesion of the upper labioalveolar fold. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1932;26:425. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1932.01450030423004
- Kennedy CM, Dewdney S, Galask RP. Vulvar granuloma fissuratum: a description of fissuring of the posterior fourchette and the repair. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:1018-1023. doi:10.1097/01. AOG.0000158863.70819.53
- Lee JL, Lee YB, Cho BK, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum on the penis. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:382-384. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.04903.x
- Gonzalez SA, Moore AGN. Acanthoma fissuratum of the outer auditory canal from a hearing aid. J Cutan Pathol. 1989;16:304.
- Fania L, Didona D, Morese R, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: from pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines. 2020;8:449. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8110449
- Chauhan DS, Guruprasad Y. Dermal cylindroma of the scalp. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2012;3:59-61. doi:10.4103/0975-5950.102163
The Diagnosis: Acanthoma Fissuratum
Acanthoma fissuratum is a skin lesion that results from consistent pressure, typically from ill-fitting eyeglass frames.1 The chronic irritation leads to collagen deposition and inflammation that gradually creates the lesion. Many patients never seek care, making incidence figures undeterminable.2 It usually presents as a firm, tender, flesh-colored or pink nodule or plaque with a central indentation from where the frame rests. This indentation splits the lesion in half and classically gives the appearance of a coffee bean.1 The repeated minor trauma at this point of contact also may lead to centralized ulceration, which further blurs the diagnosis to include basal cell carcinoma (BCC).3,4 Although the postauricular groove is the most cited location, lesions also may occur at other contact points of the glasses, such as the lateral aspect of the bridge of the nose and the superior auricular sulcus.5 Acanthoma fissuratum is not limited to the external head. Other etiologies of local trauma and pressure have led to its diagnosis in the upper labioalveolar fold, posterior fourchette of the vulva, penis, and external auditory canal.6-9
The diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum mainly is clinical; however, due to its similar appearance to BCC and other lesions, a biopsy can be taken to support the diagnosis; a biopsy was not performed in our patient. The main features seen on histopathology include acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, variable parakeratosis, and perivascular nonspecific inflammatory infiltration. The epidermis may reflect the macroscopic frame indentation with central attenuation of the epidermis, which potentially is filled with inflammatory cells or keratin.5
Treatment normally encompasses removing the illfitting frames or fixing the fit, which gradually leads to reduction of the lesion.4,5 This occurred in our patient, who changed eyeglasses and saw an 80% resolution of the lesion in 8 months. Such improvement after removal of a trauma-inducing stimulus would not be seen in malignancies (eg, BCC, squamous cell carcinoma [SCC]), keloids, or cylindromas. If the granulation tissue does not regress or recurs, other potential treatments include excision, intralesional corticosteroids, and electrosurgery.5
Basal cell carcinoma is a common nonmelanoma skin cancer that most often presents on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck, especially the cheeks, nasolabial folds, and forehead. Although the nodular subtype may clinically appear similar to acanthoma fissuratum, it more typically presents as a pearly papule or nodule with a sharp border, small telangiectases, and potential ulceration.10 Squamous cell carcinoma is another common nonmelanoma skin cancer that often arises in sun-exposed areas, which can include the postauricular area. Although the lesion can be associated with chronic wounds and also can grow vertically, SCC typically has a scalier and more hyperkeratotic surface that can ulcerate.1 A cylindroma is a benign sweat gland tumor that most commonly presents on the head and neck (also known as the turban tumor), though it can develop on the ear. It appears as solitary or multiple nodules that often are flesh colored, red, or blue with a shiny surface.1 Cylindromas are not known to be associated with chronic local trauma or irritation,11 such as wearing ill-fitting eyeglasses. Unlike acanthoma fissuratum, the treatment of cylindromas, BCC, and SCC most often involves excision.1 A keloid presents as a flesh-colored, red, or purple exophytic plaque that is composed of dense dermal tissue and progressively forms after local trauma. Although keloids can spontaneously develop, they commonly form on the ears in susceptible individuals after skin excisions including prior keloid removal, piercings, repairment of auricular traumas, or infections.1 The patient’s coffee bean–like lesion that coincided with wearing new eyeglasses better fits the diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum than a keloid. Additionally, keloids typically do not regress without treatment. Keloid treatment consists of intralesional steroid injections, occlusive silicone dressings, compression, cryotherapy, radiation, and excisional surgery.1
The Diagnosis: Acanthoma Fissuratum
Acanthoma fissuratum is a skin lesion that results from consistent pressure, typically from ill-fitting eyeglass frames.1 The chronic irritation leads to collagen deposition and inflammation that gradually creates the lesion. Many patients never seek care, making incidence figures undeterminable.2 It usually presents as a firm, tender, flesh-colored or pink nodule or plaque with a central indentation from where the frame rests. This indentation splits the lesion in half and classically gives the appearance of a coffee bean.1 The repeated minor trauma at this point of contact also may lead to centralized ulceration, which further blurs the diagnosis to include basal cell carcinoma (BCC).3,4 Although the postauricular groove is the most cited location, lesions also may occur at other contact points of the glasses, such as the lateral aspect of the bridge of the nose and the superior auricular sulcus.5 Acanthoma fissuratum is not limited to the external head. Other etiologies of local trauma and pressure have led to its diagnosis in the upper labioalveolar fold, posterior fourchette of the vulva, penis, and external auditory canal.6-9
The diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum mainly is clinical; however, due to its similar appearance to BCC and other lesions, a biopsy can be taken to support the diagnosis; a biopsy was not performed in our patient. The main features seen on histopathology include acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, variable parakeratosis, and perivascular nonspecific inflammatory infiltration. The epidermis may reflect the macroscopic frame indentation with central attenuation of the epidermis, which potentially is filled with inflammatory cells or keratin.5
Treatment normally encompasses removing the illfitting frames or fixing the fit, which gradually leads to reduction of the lesion.4,5 This occurred in our patient, who changed eyeglasses and saw an 80% resolution of the lesion in 8 months. Such improvement after removal of a trauma-inducing stimulus would not be seen in malignancies (eg, BCC, squamous cell carcinoma [SCC]), keloids, or cylindromas. If the granulation tissue does not regress or recurs, other potential treatments include excision, intralesional corticosteroids, and electrosurgery.5
Basal cell carcinoma is a common nonmelanoma skin cancer that most often presents on the sun-exposed areas of the head and neck, especially the cheeks, nasolabial folds, and forehead. Although the nodular subtype may clinically appear similar to acanthoma fissuratum, it more typically presents as a pearly papule or nodule with a sharp border, small telangiectases, and potential ulceration.10 Squamous cell carcinoma is another common nonmelanoma skin cancer that often arises in sun-exposed areas, which can include the postauricular area. Although the lesion can be associated with chronic wounds and also can grow vertically, SCC typically has a scalier and more hyperkeratotic surface that can ulcerate.1 A cylindroma is a benign sweat gland tumor that most commonly presents on the head and neck (also known as the turban tumor), though it can develop on the ear. It appears as solitary or multiple nodules that often are flesh colored, red, or blue with a shiny surface.1 Cylindromas are not known to be associated with chronic local trauma or irritation,11 such as wearing ill-fitting eyeglasses. Unlike acanthoma fissuratum, the treatment of cylindromas, BCC, and SCC most often involves excision.1 A keloid presents as a flesh-colored, red, or purple exophytic plaque that is composed of dense dermal tissue and progressively forms after local trauma. Although keloids can spontaneously develop, they commonly form on the ears in susceptible individuals after skin excisions including prior keloid removal, piercings, repairment of auricular traumas, or infections.1 The patient’s coffee bean–like lesion that coincided with wearing new eyeglasses better fits the diagnosis of acanthoma fissuratum than a keloid. Additionally, keloids typically do not regress without treatment. Keloid treatment consists of intralesional steroid injections, occlusive silicone dressings, compression, cryotherapy, radiation, and excisional surgery.1
- Sand M, Sand D, Brors D, et al. Cutaneous lesions of the external ear. Head Face Med. 2008;4. doi:10.1186/1746-160X-4-2
- Orengo I, Robbins K, Marsch A. Pathology of the ear. Semin Plast Surg. 2011;25:279-287. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1288920
- Ramroop S. Successful treatment of acanthoma fissuratum with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide. Clin Case Rep. 2020;8:702-703. doi:10.1002/ccr3.2708
- Delaney TJ, Stewart TW. Granuloma fissuratum. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:373-375. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14235.x
- Deshpande NS, Sen A, Vasudevan B, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum: lest we forget. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:141-143. doi:10.4103/2229- 5178.202267
- Surron RL Jr. A fissured granulomatous lesion of the upper labioalveolar fold. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1932;26:425. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1932.01450030423004
- Kennedy CM, Dewdney S, Galask RP. Vulvar granuloma fissuratum: a description of fissuring of the posterior fourchette and the repair. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:1018-1023. doi:10.1097/01. AOG.0000158863.70819.53
- Lee JL, Lee YB, Cho BK, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum on the penis. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:382-384. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.04903.x
- Gonzalez SA, Moore AGN. Acanthoma fissuratum of the outer auditory canal from a hearing aid. J Cutan Pathol. 1989;16:304.
- Fania L, Didona D, Morese R, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: from pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines. 2020;8:449. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8110449
- Chauhan DS, Guruprasad Y. Dermal cylindroma of the scalp. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2012;3:59-61. doi:10.4103/0975-5950.102163
- Sand M, Sand D, Brors D, et al. Cutaneous lesions of the external ear. Head Face Med. 2008;4. doi:10.1186/1746-160X-4-2
- Orengo I, Robbins K, Marsch A. Pathology of the ear. Semin Plast Surg. 2011;25:279-287. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1288920
- Ramroop S. Successful treatment of acanthoma fissuratum with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide. Clin Case Rep. 2020;8:702-703. doi:10.1002/ccr3.2708
- Delaney TJ, Stewart TW. Granuloma fissuratum. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:373-375. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14235.x
- Deshpande NS, Sen A, Vasudevan B, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum: lest we forget. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017;8:141-143. doi:10.4103/2229- 5178.202267
- Surron RL Jr. A fissured granulomatous lesion of the upper labioalveolar fold. Arch Dermatol Syph. 1932;26:425. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1932.01450030423004
- Kennedy CM, Dewdney S, Galask RP. Vulvar granuloma fissuratum: a description of fissuring of the posterior fourchette and the repair. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:1018-1023. doi:10.1097/01. AOG.0000158863.70819.53
- Lee JL, Lee YB, Cho BK, et al. Acanthoma fissuratum on the penis. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:382-384. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.04903.x
- Gonzalez SA, Moore AGN. Acanthoma fissuratum of the outer auditory canal from a hearing aid. J Cutan Pathol. 1989;16:304.
- Fania L, Didona D, Morese R, et al. Basal cell carcinoma: from pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines. 2020;8:449. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8110449
- Chauhan DS, Guruprasad Y. Dermal cylindroma of the scalp. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2012;3:59-61. doi:10.4103/0975-5950.102163
A 62-year-old man presented to the dermatology office with a 1.5-cm, pink, rubbery nodule behind the left ear that sometimes was tender. He stated that the lesion gradually grew in size over the last 2 years, and it developed after he was fitted for new glasses.
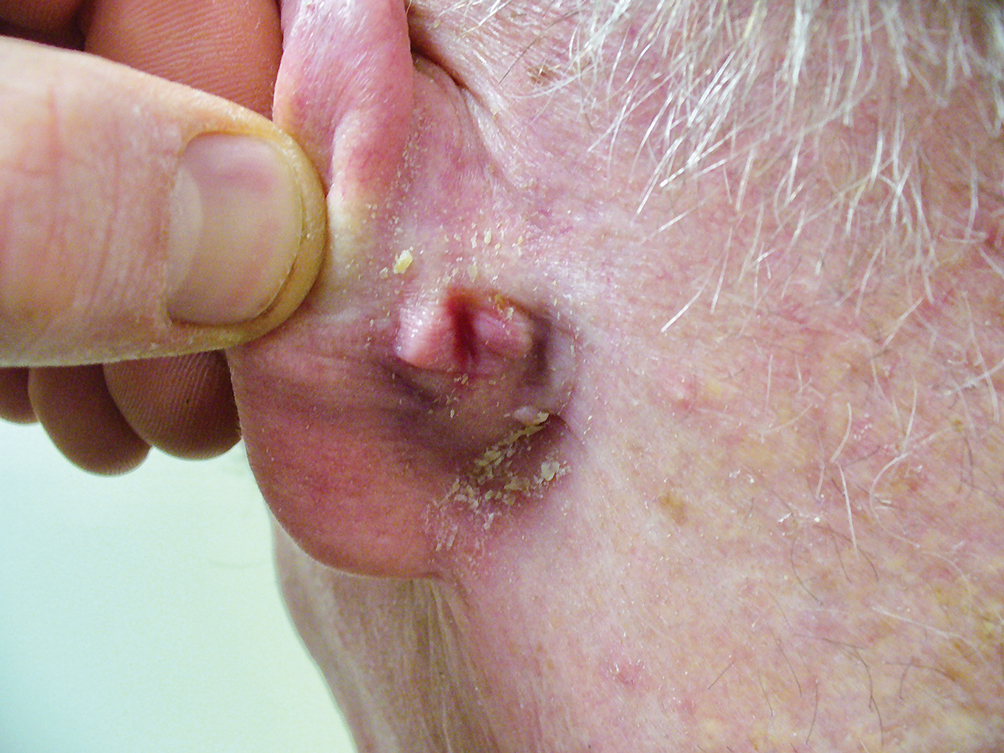
Parameters of Scratch Pleasurability in the Management of Pruritic Conditions
To the Editor:
The itch-scratch cycle refers to the sequence created when a pruritic skin condition leads to scratching and skin barrier disruption, ultimately facilitating secondary skin changes and neural activation that prolongs pruritus. In patients with pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle often can run unrestrained, with patients unaware of their scratching habits. Understanding what drives a patient to scratch, such as the pleasure gained from scratching, may be beneficial for dermatologists combating a patient’s scratching habits. The earliest documented attempts to understand the mechanism of an itch were made in Greece around the fifth century, but the pathophysiology of this sensation still is not fully understood. The Latin term pruritus refers to itching, irritation, or sexual excitement, while the Greek term knêsmos and related words also denote itch in an irritating or pleasurable sense.1 This paradoxical duality of irritation and pleasure is a phenomenon all too well understood by those affected with pruritic symptoms.
Although there are many measured characteristics of an itch, the pleasure granted from scratching an itch rarely is addressed. Understanding the factors influencing the pleasurability of scratching could help improve management and outcomes of patients’ pruritic conditions.
Pruritus is associated with a wide array of etiologies including dermatologic, infectious, metabolic, and autoimmune, but unanimously it evokes a strong desire to scratch. Scratching an itch often yields temporary relief from the irritation by dispensing a complex sensory concoction between pleasure and pain.2 The neurobiology behind this pleasure phenomenon is inconclusive. Some hypotheses point to how scratching-induced pleasure may be derived from the deactivation or inhibition of the unpleasant sensation of an itch in the central nervous system, the stimulation of the reward signals in the C-fiber system in the peripheral nervous system, the release of pruritis-inhibiting prostaglandin D2, or a combination of these pathways. Levels of sensation and pleasure induced from itch attenuation by scratching even vary based on anatomic location. One study demonstrated that, when compared to the forearms, the ankles and back perceived baseline induced itch most intensely, but no significant difference in perceived itch intensity was found between the ankles and back. Additionally, scratching an itchy back or ankle notably induced more pleasure when compared to the forearms, but there was no significant difference in scratching pleasurability between the ankle and back.3
Although there are adequate questionnaires and scales (eg, ItchyQoL,4 Skindex-16, Skindex-29) to quantify the severity of pruritus and its effects on a patient’s quality of life, these measurements do not assess the pleasure yielded from scratching, the impact of scratch pleasure on the patient experience, or the effect of scratch pleasure on the disease state.4 It appears that there are inadequate assessment tools to define factors associated with the pleasurability of scratching. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scratching pleasure scale and pruritus pleasure questionnaire yielded scarce results measuring patient perspectives on scratching-associated pleasure. A pertinent study performed by O’Neill et al5 compared the differences in itch characteristics between patients with psoriasis and those with atopic dermatitis using a web-based questionnaire featuring a numerical pleasure scale (ranging from −5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) on an 11-point Likert scale. The questionnaire sought to measure the effects of scratching during a typical episode of itch within the past 2 weeks. Scratching was found pleasurable in both groups of patients.5 Another web-based questionnaire that characterized pleasurability in scratching a typical episode of itch in individuals with atopic dermatitis using a −5 to +5 Likert scale (−5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) found that most participants perceived scratching as pleasurable and that there was a positive correlation between itch intensity and scratch pleasurability.6 Both of these studies quantified that scratching an itch is pleasurable, a correlation that may not come as a surprise. This direct correlation suggests that a more detailed analysis of this scratch pleasure could be beneficial in the management of pruritic conditions.
Treating the underlying cause of an itch is key to inhibiting the sensation; in some cases, anti-itch medications must be used. Current medications have limited effects on itch relief, but an expanding understanding of itch pathophysiology through clinical and laboratory research in the fields of dermatology, immunology, and neurology is paving the way for promising new therapeutic medications.7-11 In a review of the literature, Sanders and Akiyama12 elucidated the influence of stress and anxiety in scratching an itch and the way in which both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic (ie, psychological and educational interventions) may be used to help break the itch-scratch cycle. Possible techniques include habit-reversal training, relaxation therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy.13 Understanding patient perspectives on the pleasure yielded from scratching an itch and the disease factors that influence this pleasure seeking are paramount to reducing patient scratching. In understanding the pleasurability of scratching in pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle and its accompanying deleterious effects (eg, stress, anxiety, pain, infection, secondary skin changes) can be broken.
The pleasure yielded from scratching an itch is a component of patient scratching habits that should be analyzed and quantified to reduce itch in pruritic conditions, mitigate damaging consequences of scratching, and improve the quality of life of patients with pruritic conditions. Furthermore, this understanding may help guide clinicians in management, such as counseling patients on the itch-scratch cycle and deciding which forthcoming medications could ameliorate a patient’s pruritic symptoms.
- Weisshaar E, Grüll V, König A, et al. The symptom of itch in medical history: highlights through the centuries. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1385-1394.
- Lavery MJ, Kinney MO, Mochizuki H, et al. Pruritus: an overview. what drives people to scratch an itch? Ulster Med J. 2016;85:164-173.
- Bin Saif GA, Papoiu ADP, Banari L, et al. The pleasurability of scratching an itch: a psychophysical and topographical assessment. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:981-985.
- Desai NS, Poindexter GB, Monthrope YM, et al. A pilot quality-of-life instrument for pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:234-244.
- O’Neill JL, Chan YH, Rapp SR, et al. Differences in itch characteristics between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients: results of a web-based questionnaire. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:537-540.
- Dawn A, Papoiu ADP, Chan YH, et al. Itch characteristics in atopic dermatitis: results of a web-based questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:642-644.
- Yosipovitch G, Rosen JD, Hashimoto T. Itch: from mechanism to (novel) therapeutic approaches. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:1375-1390.
- Yosipovitch G, Misery L, Proksch E, et al. Skin barrier damage and itch: review of mechanisms, topical management and future directions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:1201-1209.
- Dong X, Dong X. Peripheral and central mechanisms of itch. Neuron. 2018;98:482-494.
- Lerner EA. Pathophysiology of itch. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:175-177.
- Cevikbas F, Lerner EA. Physiology and pathophysiology of itch. Physiol Rev. 2020;100:945-982.
- Sanders KM, Akiyama T. The vicious cycle of itch and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;87:17-26.
- Sanders KM, Nattkemper LA, Yosipovitch G. Advances in understanding itching and scratching: a new era of targeted treatments [published online August 22, 2016]. F1000Res. doi:10.12688/f1000research.8659.
To the Editor:
The itch-scratch cycle refers to the sequence created when a pruritic skin condition leads to scratching and skin barrier disruption, ultimately facilitating secondary skin changes and neural activation that prolongs pruritus. In patients with pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle often can run unrestrained, with patients unaware of their scratching habits. Understanding what drives a patient to scratch, such as the pleasure gained from scratching, may be beneficial for dermatologists combating a patient’s scratching habits. The earliest documented attempts to understand the mechanism of an itch were made in Greece around the fifth century, but the pathophysiology of this sensation still is not fully understood. The Latin term pruritus refers to itching, irritation, or sexual excitement, while the Greek term knêsmos and related words also denote itch in an irritating or pleasurable sense.1 This paradoxical duality of irritation and pleasure is a phenomenon all too well understood by those affected with pruritic symptoms.
Although there are many measured characteristics of an itch, the pleasure granted from scratching an itch rarely is addressed. Understanding the factors influencing the pleasurability of scratching could help improve management and outcomes of patients’ pruritic conditions.
Pruritus is associated with a wide array of etiologies including dermatologic, infectious, metabolic, and autoimmune, but unanimously it evokes a strong desire to scratch. Scratching an itch often yields temporary relief from the irritation by dispensing a complex sensory concoction between pleasure and pain.2 The neurobiology behind this pleasure phenomenon is inconclusive. Some hypotheses point to how scratching-induced pleasure may be derived from the deactivation or inhibition of the unpleasant sensation of an itch in the central nervous system, the stimulation of the reward signals in the C-fiber system in the peripheral nervous system, the release of pruritis-inhibiting prostaglandin D2, or a combination of these pathways. Levels of sensation and pleasure induced from itch attenuation by scratching even vary based on anatomic location. One study demonstrated that, when compared to the forearms, the ankles and back perceived baseline induced itch most intensely, but no significant difference in perceived itch intensity was found between the ankles and back. Additionally, scratching an itchy back or ankle notably induced more pleasure when compared to the forearms, but there was no significant difference in scratching pleasurability between the ankle and back.3
Although there are adequate questionnaires and scales (eg, ItchyQoL,4 Skindex-16, Skindex-29) to quantify the severity of pruritus and its effects on a patient’s quality of life, these measurements do not assess the pleasure yielded from scratching, the impact of scratch pleasure on the patient experience, or the effect of scratch pleasure on the disease state.4 It appears that there are inadequate assessment tools to define factors associated with the pleasurability of scratching. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scratching pleasure scale and pruritus pleasure questionnaire yielded scarce results measuring patient perspectives on scratching-associated pleasure. A pertinent study performed by O’Neill et al5 compared the differences in itch characteristics between patients with psoriasis and those with atopic dermatitis using a web-based questionnaire featuring a numerical pleasure scale (ranging from −5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) on an 11-point Likert scale. The questionnaire sought to measure the effects of scratching during a typical episode of itch within the past 2 weeks. Scratching was found pleasurable in both groups of patients.5 Another web-based questionnaire that characterized pleasurability in scratching a typical episode of itch in individuals with atopic dermatitis using a −5 to +5 Likert scale (−5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) found that most participants perceived scratching as pleasurable and that there was a positive correlation between itch intensity and scratch pleasurability.6 Both of these studies quantified that scratching an itch is pleasurable, a correlation that may not come as a surprise. This direct correlation suggests that a more detailed analysis of this scratch pleasure could be beneficial in the management of pruritic conditions.
Treating the underlying cause of an itch is key to inhibiting the sensation; in some cases, anti-itch medications must be used. Current medications have limited effects on itch relief, but an expanding understanding of itch pathophysiology through clinical and laboratory research in the fields of dermatology, immunology, and neurology is paving the way for promising new therapeutic medications.7-11 In a review of the literature, Sanders and Akiyama12 elucidated the influence of stress and anxiety in scratching an itch and the way in which both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic (ie, psychological and educational interventions) may be used to help break the itch-scratch cycle. Possible techniques include habit-reversal training, relaxation therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy.13 Understanding patient perspectives on the pleasure yielded from scratching an itch and the disease factors that influence this pleasure seeking are paramount to reducing patient scratching. In understanding the pleasurability of scratching in pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle and its accompanying deleterious effects (eg, stress, anxiety, pain, infection, secondary skin changes) can be broken.
The pleasure yielded from scratching an itch is a component of patient scratching habits that should be analyzed and quantified to reduce itch in pruritic conditions, mitigate damaging consequences of scratching, and improve the quality of life of patients with pruritic conditions. Furthermore, this understanding may help guide clinicians in management, such as counseling patients on the itch-scratch cycle and deciding which forthcoming medications could ameliorate a patient’s pruritic symptoms.
To the Editor:
The itch-scratch cycle refers to the sequence created when a pruritic skin condition leads to scratching and skin barrier disruption, ultimately facilitating secondary skin changes and neural activation that prolongs pruritus. In patients with pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle often can run unrestrained, with patients unaware of their scratching habits. Understanding what drives a patient to scratch, such as the pleasure gained from scratching, may be beneficial for dermatologists combating a patient’s scratching habits. The earliest documented attempts to understand the mechanism of an itch were made in Greece around the fifth century, but the pathophysiology of this sensation still is not fully understood. The Latin term pruritus refers to itching, irritation, or sexual excitement, while the Greek term knêsmos and related words also denote itch in an irritating or pleasurable sense.1 This paradoxical duality of irritation and pleasure is a phenomenon all too well understood by those affected with pruritic symptoms.
Although there are many measured characteristics of an itch, the pleasure granted from scratching an itch rarely is addressed. Understanding the factors influencing the pleasurability of scratching could help improve management and outcomes of patients’ pruritic conditions.
Pruritus is associated with a wide array of etiologies including dermatologic, infectious, metabolic, and autoimmune, but unanimously it evokes a strong desire to scratch. Scratching an itch often yields temporary relief from the irritation by dispensing a complex sensory concoction between pleasure and pain.2 The neurobiology behind this pleasure phenomenon is inconclusive. Some hypotheses point to how scratching-induced pleasure may be derived from the deactivation or inhibition of the unpleasant sensation of an itch in the central nervous system, the stimulation of the reward signals in the C-fiber system in the peripheral nervous system, the release of pruritis-inhibiting prostaglandin D2, or a combination of these pathways. Levels of sensation and pleasure induced from itch attenuation by scratching even vary based on anatomic location. One study demonstrated that, when compared to the forearms, the ankles and back perceived baseline induced itch most intensely, but no significant difference in perceived itch intensity was found between the ankles and back. Additionally, scratching an itchy back or ankle notably induced more pleasure when compared to the forearms, but there was no significant difference in scratching pleasurability between the ankle and back.3
Although there are adequate questionnaires and scales (eg, ItchyQoL,4 Skindex-16, Skindex-29) to quantify the severity of pruritus and its effects on a patient’s quality of life, these measurements do not assess the pleasure yielded from scratching, the impact of scratch pleasure on the patient experience, or the effect of scratch pleasure on the disease state.4 It appears that there are inadequate assessment tools to define factors associated with the pleasurability of scratching. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms scratching pleasure scale and pruritus pleasure questionnaire yielded scarce results measuring patient perspectives on scratching-associated pleasure. A pertinent study performed by O’Neill et al5 compared the differences in itch characteristics between patients with psoriasis and those with atopic dermatitis using a web-based questionnaire featuring a numerical pleasure scale (ranging from −5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) on an 11-point Likert scale. The questionnaire sought to measure the effects of scratching during a typical episode of itch within the past 2 weeks. Scratching was found pleasurable in both groups of patients.5 Another web-based questionnaire that characterized pleasurability in scratching a typical episode of itch in individuals with atopic dermatitis using a −5 to +5 Likert scale (−5 [highly unpleasurable] to +5 [highly pleasurable]) found that most participants perceived scratching as pleasurable and that there was a positive correlation between itch intensity and scratch pleasurability.6 Both of these studies quantified that scratching an itch is pleasurable, a correlation that may not come as a surprise. This direct correlation suggests that a more detailed analysis of this scratch pleasure could be beneficial in the management of pruritic conditions.
Treating the underlying cause of an itch is key to inhibiting the sensation; in some cases, anti-itch medications must be used. Current medications have limited effects on itch relief, but an expanding understanding of itch pathophysiology through clinical and laboratory research in the fields of dermatology, immunology, and neurology is paving the way for promising new therapeutic medications.7-11 In a review of the literature, Sanders and Akiyama12 elucidated the influence of stress and anxiety in scratching an itch and the way in which both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic (ie, psychological and educational interventions) may be used to help break the itch-scratch cycle. Possible techniques include habit-reversal training, relaxation therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy.13 Understanding patient perspectives on the pleasure yielded from scratching an itch and the disease factors that influence this pleasure seeking are paramount to reducing patient scratching. In understanding the pleasurability of scratching in pruritic conditions, the itch-scratch cycle and its accompanying deleterious effects (eg, stress, anxiety, pain, infection, secondary skin changes) can be broken.
The pleasure yielded from scratching an itch is a component of patient scratching habits that should be analyzed and quantified to reduce itch in pruritic conditions, mitigate damaging consequences of scratching, and improve the quality of life of patients with pruritic conditions. Furthermore, this understanding may help guide clinicians in management, such as counseling patients on the itch-scratch cycle and deciding which forthcoming medications could ameliorate a patient’s pruritic symptoms.
- Weisshaar E, Grüll V, König A, et al. The symptom of itch in medical history: highlights through the centuries. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1385-1394.
- Lavery MJ, Kinney MO, Mochizuki H, et al. Pruritus: an overview. what drives people to scratch an itch? Ulster Med J. 2016;85:164-173.
- Bin Saif GA, Papoiu ADP, Banari L, et al. The pleasurability of scratching an itch: a psychophysical and topographical assessment. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:981-985.
- Desai NS, Poindexter GB, Monthrope YM, et al. A pilot quality-of-life instrument for pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:234-244.
- O’Neill JL, Chan YH, Rapp SR, et al. Differences in itch characteristics between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients: results of a web-based questionnaire. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:537-540.
- Dawn A, Papoiu ADP, Chan YH, et al. Itch characteristics in atopic dermatitis: results of a web-based questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:642-644.
- Yosipovitch G, Rosen JD, Hashimoto T. Itch: from mechanism to (novel) therapeutic approaches. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:1375-1390.
- Yosipovitch G, Misery L, Proksch E, et al. Skin barrier damage and itch: review of mechanisms, topical management and future directions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:1201-1209.
- Dong X, Dong X. Peripheral and central mechanisms of itch. Neuron. 2018;98:482-494.
- Lerner EA. Pathophysiology of itch. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:175-177.
- Cevikbas F, Lerner EA. Physiology and pathophysiology of itch. Physiol Rev. 2020;100:945-982.
- Sanders KM, Akiyama T. The vicious cycle of itch and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;87:17-26.
- Sanders KM, Nattkemper LA, Yosipovitch G. Advances in understanding itching and scratching: a new era of targeted treatments [published online August 22, 2016]. F1000Res. doi:10.12688/f1000research.8659.
- Weisshaar E, Grüll V, König A, et al. The symptom of itch in medical history: highlights through the centuries. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:1385-1394.
- Lavery MJ, Kinney MO, Mochizuki H, et al. Pruritus: an overview. what drives people to scratch an itch? Ulster Med J. 2016;85:164-173.
- Bin Saif GA, Papoiu ADP, Banari L, et al. The pleasurability of scratching an itch: a psychophysical and topographical assessment. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:981-985.
- Desai NS, Poindexter GB, Monthrope YM, et al. A pilot quality-of-life instrument for pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:234-244.
- O’Neill JL, Chan YH, Rapp SR, et al. Differences in itch characteristics between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients: results of a web-based questionnaire. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:537-540.
- Dawn A, Papoiu ADP, Chan YH, et al. Itch characteristics in atopic dermatitis: results of a web-based questionnaire. Br J Dermatol. 2009;160:642-644.
- Yosipovitch G, Rosen JD, Hashimoto T. Itch: from mechanism to (novel) therapeutic approaches. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:1375-1390.
- Yosipovitch G, Misery L, Proksch E, et al. Skin barrier damage and itch: review of mechanisms, topical management and future directions. Acta Derm Venereol. 2019;99:1201-1209.
- Dong X, Dong X. Peripheral and central mechanisms of itch. Neuron. 2018;98:482-494.
- Lerner EA. Pathophysiology of itch. Dermatol Clin. 2018;36:175-177.
- Cevikbas F, Lerner EA. Physiology and pathophysiology of itch. Physiol Rev. 2020;100:945-982.
- Sanders KM, Akiyama T. The vicious cycle of itch and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018;87:17-26.
- Sanders KM, Nattkemper LA, Yosipovitch G. Advances in understanding itching and scratching: a new era of targeted treatments [published online August 22, 2016]. F1000Res. doi:10.12688/f1000research.8659.
Practice Points
- In individuals with pruritic skin conditions, the itch-scratch cycle can have damaging consequences such as anxiety, infection, and secondary skin changes.
- Understanding the pleasurability of scratching in pruritic skin conditions allows providers to help patients break the itch-scratch cycle and improve quality of life.
Multiple Eruptive Dermatofibromas Associated With Down Syndrome
To the Editor:
Dermatofibromas (also known as fibrous histiocytomas) are benign fibrous nodules that most often arise as solitary lesions on the lower extremities. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas (MEDFs) are uncommon and have been defined as more than 15 in number1 or 5 to 8 dermatofibromas appearing within 4 months.2 They have been reported in association with a number of conditions of immune dysregulation such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, HIV infection, and leukemia.3 Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas also have been described in patients with Down syndrome (DS).4-7 We report a case of MEDFs in a patient with DS and review the literature on the association between MEDFs and DS.
A 38-year-old woman with DS, hidradenitis suppurativa, and hypothyroidism presented with multiple cutaneous lesions developing over the last year. The lesions continued to increase in number but were otherwise asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed approximately 20 rubbery, pink-tan papules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter that were scattered along the trunk (Figure, A), arms, and legs (Figure, B).
The patient had no known history of immunosuppression or rheumatologic disease and was otherwise healthy. Basic laboratory tests including a complete blood cell count and antinuclear antibody titer were within reference range. The lesions were clinically consistent with dermatofibromas, but due to their increasing number within a short period of time, a biopsy of a representative lesion was performed to confirm the diagnosis.
The exact incidence of MEDFs is unknown, but they are rare, with one review finding only 50 cases reported from 1960 to 2002.8 They are increasingly recognized as a sign of potential immune dysregulation. Approximately 56% to 70% of cases are seen in patients with an underlying disease state; 80% are immune mediated.8,9 Interestingly, DS has long been associated with notable immune dysfunction,10,11 with evidence suggesting that trisomy 21 may result in widespread changes in gene expression that can lead to interferon activation.12
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms dermatofibroma and Down, dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, eruptive dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, and multiple dermatofibroma and Down syndrome revealed 6 cases of MEDFs in patients with DS that have been reported since 2005.4-7 An additional report by Honda et al13 described a patient with DS who developed 7 dermatofibromas, but no time frame of development was specified. We reviewed the characteristics of 8 patients with DS with MEDFs, which included our patient (Table). The average age at time of presentation was 39 years (median age, 40 years). Six patients (75%) were female and 2 (25%) were male. Dermatofibromas were reported to appear over the course of months to years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis (treated with methotrexate),6 thyroid disorders (ie, Graves disease),6 hypercholesterolemia,6 hidradenitis suppurativa, long-standing mild lymphopenia (1.4×109/L [reference range, 1.5−4.0×109/L]),4 and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia13 treated 15 years before the appearance of dermatofibromas.
Many dermatologic conditions have been reported at increased rates in individuals with DS, including seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia areata, syringomas, elastosis perforans serpiginosa, cutis marmorata, xerosis, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis.14,15 Although drawing conclusions about associations between MEDFs and DS is limited by our small sample size, we have reported this case and reviewed existing cases of MEDFs in DS to highlight a potential association that may be underrecognized or underreported. More evidence is needed to determine the strength of the association between MEDFs and DS, but dermatologists should be aware that MEDFs may be an additional skin finding associated with DS that is related to the syndrome’s immune dysregulation.
- Baraf CS, Shapiro L. Multiple histiocytomas: report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:588-590.
- Ammirati CT, Mann C, Hornstra IK. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in three men with HIV infection. Dermatology. 1997;4:344-348.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Lamb RC, Gangopadhyay M, MacDonald A. Multiple dermatofibromas in Down syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E274-E275.
- Monteagudo B, Álvarez-Fernández JC, Iglesias B, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with Down’s syndrome [article in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2005;96:199.
- Monteagudo B, Suárez-Amor O, Cabanillas M, et al. Down syndrome: another cause of immunosuppression associated with multiple eruptive dermatofibroma? [article in Spanish]. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:15.
- Tanaka M, Hoashi T, Serizawa N, et al. Multiple unilaterally localized dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2017;44:1074-1076.
- Niiyama S, Katsuoka K, Happle R, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:241-244.
- Her Y, Ku SH, Kim KH. A case of multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a healthy adult. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:539-540.
- Bertotto A, Arcangeli C, Crupi S, et al. T cell response to anti-CD3 antibody in Down’s syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1987;62:1148-1151.
- Kusters MA, Verstegen RH, Gemen EF, et al. Intrinsic defect of the immune system in children with Down syndrome: a review. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;156:189-193.
- Sullivan KD, Evans D, Pandey A, et al. Trisomy 21 causes changes in the circulating proteome indicative of chronic inflammation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14818.
- Honda M, Tomimura S, de Vega S, et al. Multiple dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2016;43:346-348.
- Daneshpazhooh M, Nazemi TM, Bigdeloo L, et al. Mucocutaneous findings in 100 children with Down syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:317-320.
- Madan V, Williams J, Lear JT. Dermatological manifestations of Down’s syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:623-629.
To the Editor:
Dermatofibromas (also known as fibrous histiocytomas) are benign fibrous nodules that most often arise as solitary lesions on the lower extremities. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas (MEDFs) are uncommon and have been defined as more than 15 in number1 or 5 to 8 dermatofibromas appearing within 4 months.2 They have been reported in association with a number of conditions of immune dysregulation such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, HIV infection, and leukemia.3 Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas also have been described in patients with Down syndrome (DS).4-7 We report a case of MEDFs in a patient with DS and review the literature on the association between MEDFs and DS.
A 38-year-old woman with DS, hidradenitis suppurativa, and hypothyroidism presented with multiple cutaneous lesions developing over the last year. The lesions continued to increase in number but were otherwise asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed approximately 20 rubbery, pink-tan papules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter that were scattered along the trunk (Figure, A), arms, and legs (Figure, B).

The patient had no known history of immunosuppression or rheumatologic disease and was otherwise healthy. Basic laboratory tests including a complete blood cell count and antinuclear antibody titer were within reference range. The lesions were clinically consistent with dermatofibromas, but due to their increasing number within a short period of time, a biopsy of a representative lesion was performed to confirm the diagnosis.
The exact incidence of MEDFs is unknown, but they are rare, with one review finding only 50 cases reported from 1960 to 2002.8 They are increasingly recognized as a sign of potential immune dysregulation. Approximately 56% to 70% of cases are seen in patients with an underlying disease state; 80% are immune mediated.8,9 Interestingly, DS has long been associated with notable immune dysfunction,10,11 with evidence suggesting that trisomy 21 may result in widespread changes in gene expression that can lead to interferon activation.12
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms dermatofibroma and Down, dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, eruptive dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, and multiple dermatofibroma and Down syndrome revealed 6 cases of MEDFs in patients with DS that have been reported since 2005.4-7 An additional report by Honda et al13 described a patient with DS who developed 7 dermatofibromas, but no time frame of development was specified. We reviewed the characteristics of 8 patients with DS with MEDFs, which included our patient (Table). The average age at time of presentation was 39 years (median age, 40 years). Six patients (75%) were female and 2 (25%) were male. Dermatofibromas were reported to appear over the course of months to years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis (treated with methotrexate),6 thyroid disorders (ie, Graves disease),6 hypercholesterolemia,6 hidradenitis suppurativa, long-standing mild lymphopenia (1.4×109/L [reference range, 1.5−4.0×109/L]),4 and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia13 treated 15 years before the appearance of dermatofibromas.

Many dermatologic conditions have been reported at increased rates in individuals with DS, including seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia areata, syringomas, elastosis perforans serpiginosa, cutis marmorata, xerosis, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis.14,15 Although drawing conclusions about associations between MEDFs and DS is limited by our small sample size, we have reported this case and reviewed existing cases of MEDFs in DS to highlight a potential association that may be underrecognized or underreported. More evidence is needed to determine the strength of the association between MEDFs and DS, but dermatologists should be aware that MEDFs may be an additional skin finding associated with DS that is related to the syndrome’s immune dysregulation.
To the Editor:
Dermatofibromas (also known as fibrous histiocytomas) are benign fibrous nodules that most often arise as solitary lesions on the lower extremities. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas (MEDFs) are uncommon and have been defined as more than 15 in number1 or 5 to 8 dermatofibromas appearing within 4 months.2 They have been reported in association with a number of conditions of immune dysregulation such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, HIV infection, and leukemia.3 Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas also have been described in patients with Down syndrome (DS).4-7 We report a case of MEDFs in a patient with DS and review the literature on the association between MEDFs and DS.
A 38-year-old woman with DS, hidradenitis suppurativa, and hypothyroidism presented with multiple cutaneous lesions developing over the last year. The lesions continued to increase in number but were otherwise asymptomatic. Physical examination revealed approximately 20 rubbery, pink-tan papules measuring less than 1 cm in diameter that were scattered along the trunk (Figure, A), arms, and legs (Figure, B).

The patient had no known history of immunosuppression or rheumatologic disease and was otherwise healthy. Basic laboratory tests including a complete blood cell count and antinuclear antibody titer were within reference range. The lesions were clinically consistent with dermatofibromas, but due to their increasing number within a short period of time, a biopsy of a representative lesion was performed to confirm the diagnosis.
The exact incidence of MEDFs is unknown, but they are rare, with one review finding only 50 cases reported from 1960 to 2002.8 They are increasingly recognized as a sign of potential immune dysregulation. Approximately 56% to 70% of cases are seen in patients with an underlying disease state; 80% are immune mediated.8,9 Interestingly, DS has long been associated with notable immune dysfunction,10,11 with evidence suggesting that trisomy 21 may result in widespread changes in gene expression that can lead to interferon activation.12
A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms dermatofibroma and Down, dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, eruptive dermatofibroma and Down syndrome, and multiple dermatofibroma and Down syndrome revealed 6 cases of MEDFs in patients with DS that have been reported since 2005.4-7 An additional report by Honda et al13 described a patient with DS who developed 7 dermatofibromas, but no time frame of development was specified. We reviewed the characteristics of 8 patients with DS with MEDFs, which included our patient (Table). The average age at time of presentation was 39 years (median age, 40 years). Six patients (75%) were female and 2 (25%) were male. Dermatofibromas were reported to appear over the course of months to years. Comorbidities included psoriatic arthritis (treated with methotrexate),6 thyroid disorders (ie, Graves disease),6 hypercholesterolemia,6 hidradenitis suppurativa, long-standing mild lymphopenia (1.4×109/L [reference range, 1.5−4.0×109/L]),4 and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia13 treated 15 years before the appearance of dermatofibromas.

Many dermatologic conditions have been reported at increased rates in individuals with DS, including seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia areata, syringomas, elastosis perforans serpiginosa, cutis marmorata, xerosis, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis.14,15 Although drawing conclusions about associations between MEDFs and DS is limited by our small sample size, we have reported this case and reviewed existing cases of MEDFs in DS to highlight a potential association that may be underrecognized or underreported. More evidence is needed to determine the strength of the association between MEDFs and DS, but dermatologists should be aware that MEDFs may be an additional skin finding associated with DS that is related to the syndrome’s immune dysregulation.
- Baraf CS, Shapiro L. Multiple histiocytomas: report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:588-590.
- Ammirati CT, Mann C, Hornstra IK. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in three men with HIV infection. Dermatology. 1997;4:344-348.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Lamb RC, Gangopadhyay M, MacDonald A. Multiple dermatofibromas in Down syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E274-E275.
- Monteagudo B, Álvarez-Fernández JC, Iglesias B, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with Down’s syndrome [article in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2005;96:199.
- Monteagudo B, Suárez-Amor O, Cabanillas M, et al. Down syndrome: another cause of immunosuppression associated with multiple eruptive dermatofibroma? [article in Spanish]. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:15.
- Tanaka M, Hoashi T, Serizawa N, et al. Multiple unilaterally localized dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2017;44:1074-1076.
- Niiyama S, Katsuoka K, Happle R, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:241-244.
- Her Y, Ku SH, Kim KH. A case of multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a healthy adult. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:539-540.
- Bertotto A, Arcangeli C, Crupi S, et al. T cell response to anti-CD3 antibody in Down’s syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1987;62:1148-1151.
- Kusters MA, Verstegen RH, Gemen EF, et al. Intrinsic defect of the immune system in children with Down syndrome: a review. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;156:189-193.
- Sullivan KD, Evans D, Pandey A, et al. Trisomy 21 causes changes in the circulating proteome indicative of chronic inflammation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14818.
- Honda M, Tomimura S, de Vega S, et al. Multiple dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2016;43:346-348.
- Daneshpazhooh M, Nazemi TM, Bigdeloo L, et al. Mucocutaneous findings in 100 children with Down syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:317-320.
- Madan V, Williams J, Lear JT. Dermatological manifestations of Down’s syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:623-629.
- Baraf CS, Shapiro L. Multiple histiocytomas: report of a case. Arch Dermatol. 1970;101:588-590.
- Ammirati CT, Mann C, Hornstra IK. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in three men with HIV infection. Dermatology. 1997;4:344-348.
- Zaccaria E, Rebora A, Rongioletti F. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas and immunosuppression: report of two cases and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:723-727.
- Lamb RC, Gangopadhyay M, MacDonald A. Multiple dermatofibromas in Down syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:E274-E275.
- Monteagudo B, Álvarez-Fernández JC, Iglesias B, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a patient with Down’s syndrome [article in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2005;96:199.
- Monteagudo B, Suárez-Amor O, Cabanillas M, et al. Down syndrome: another cause of immunosuppression associated with multiple eruptive dermatofibroma? [article in Spanish]. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:15.
- Tanaka M, Hoashi T, Serizawa N, et al. Multiple unilaterally localized dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2017;44:1074-1076.
- Niiyama S, Katsuoka K, Happle R, et al. Multiple eruptive dermatofibromas: a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol. 2002;82:241-244.
- Her Y, Ku SH, Kim KH. A case of multiple eruptive dermatofibromas in a healthy adult. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:539-540.
- Bertotto A, Arcangeli C, Crupi S, et al. T cell response to anti-CD3 antibody in Down’s syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1987;62:1148-1151.
- Kusters MA, Verstegen RH, Gemen EF, et al. Intrinsic defect of the immune system in children with Down syndrome: a review. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;156:189-193.
- Sullivan KD, Evans D, Pandey A, et al. Trisomy 21 causes changes in the circulating proteome indicative of chronic inflammation. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14818.
- Honda M, Tomimura S, de Vega S, et al. Multiple dermatofibromas in a patient with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2016;43:346-348.
- Daneshpazhooh M, Nazemi TM, Bigdeloo L, et al. Mucocutaneous findings in 100 children with Down syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007;24:317-320.
- Madan V, Williams J, Lear JT. Dermatological manifestations of Down’s syndrome. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:623-629.
Practice Points
- Although dermatofibromas are common and benign skin lesions, multiple eruptive dermatofibromas have been associated with a number of underlying conditions, particularly those associated with immune dysregulation.
- The immune dysregulation reported in Down syndrome may explain the appearance of multiple dermatofibromas.
Commentary: Appropriate Downstaging and TACE in HCC, September 2022
Liver transplantation has the opportunity to cure both localized HCC as well as underlying liver cirrhosis. Donor organ shortage has led to the implementation of the Milan criteria as a way to identify patients whose tumor burden is low enough to predict a good outcome. Downstaging liver cancer to fit within Milan criteria has been controversial.
Tabrizian and colleagues undertook a retrospective cohort analysis of 2645 adult patients with HCC who underwent liver transplant. Out of those, 2122 patients always had disease that was within the Milan criteria, 341 patients had HCC that was downstaged to fit within the Milan criteria, and 182 patients had HCC that was outside the Milan criteria at the time of liver transplantation. The authors report that the 10-year post-transplant survival and recurrence rates were 61.5% and 13.3%, respectively, in those always within the Milan criteria, 52.1% and 20.6% among those whose disease was downstaged, and 43.3% and 41.1% in those whose disease was never downstaged. Characteristics that predicted recurrence after downstaging were tumor size > 7 cm at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR] 2.62; 95% CI 1.20-5.75; P = .02), more than three tumors at diagnosis (OR 2.34; 95% CI 1.22-4.50; P = .01), and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) response ≥ 20 ng/mL with < 50% improvement from maximum AFP before transplantation (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.14-3.46; P = .02). Additionally, patients with recurrent tumors that were surgically resected had improved 5-year post-recurrence survival (31.6% vs 7.3%; P < .001). The conclusion was that the national downstaging policies were valid and should continue.
For patients who have unresectable HCC, systemic therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Peng and colleagues reported the results of the LAUNCH phase 3 clinical trial that randomized patients to receive lenvatinib alone or lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Out of 338 patients, 170 received lenvatinib plus TACE. Unsurprisingly, the response rate was higher with the combination (54.1% vs 25.0%; P < .001); however, so was the median overall survival (17.8 vs 11.5 months; hazard ratio 0.45; P < .001), and median progression-free survival (10.6 vs 6.4 months; hazard ratio 0.43; P < .001). The investigators concluded that the addition of TACE to lenvatinib had manageable toxicities, improved clinical outcomes, and could be used as a potential first-line treatment for some patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, in patients whose HCC progressed after a single TACE treatment, the question remains whether repeated TACE is worthwhile. Zhao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the outcomes of 94 patients who underwent at least one TACE. Of these, 28 (29.8%) had a response to the first TACE, and these patients tended to have a longer OS compared with nonresponders (36.7 vs 21.5 months; P = .071). Of the 43 initial nonresponders who underwent a second TACE, 15 of 43 (34.9%) achieved a response and had an improved median overall survival (47.8 v. 13.6 months; P = .01), suggesting that repeat TACE may offer a benefit to some patients, even after no response to the initial treatment.
Liver transplantation has the opportunity to cure both localized HCC as well as underlying liver cirrhosis. Donor organ shortage has led to the implementation of the Milan criteria as a way to identify patients whose tumor burden is low enough to predict a good outcome. Downstaging liver cancer to fit within Milan criteria has been controversial.
Tabrizian and colleagues undertook a retrospective cohort analysis of 2645 adult patients with HCC who underwent liver transplant. Out of those, 2122 patients always had disease that was within the Milan criteria, 341 patients had HCC that was downstaged to fit within the Milan criteria, and 182 patients had HCC that was outside the Milan criteria at the time of liver transplantation. The authors report that the 10-year post-transplant survival and recurrence rates were 61.5% and 13.3%, respectively, in those always within the Milan criteria, 52.1% and 20.6% among those whose disease was downstaged, and 43.3% and 41.1% in those whose disease was never downstaged. Characteristics that predicted recurrence after downstaging were tumor size > 7 cm at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR] 2.62; 95% CI 1.20-5.75; P = .02), more than three tumors at diagnosis (OR 2.34; 95% CI 1.22-4.50; P = .01), and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) response ≥ 20 ng/mL with < 50% improvement from maximum AFP before transplantation (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.14-3.46; P = .02). Additionally, patients with recurrent tumors that were surgically resected had improved 5-year post-recurrence survival (31.6% vs 7.3%; P < .001). The conclusion was that the national downstaging policies were valid and should continue.
For patients who have unresectable HCC, systemic therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Peng and colleagues reported the results of the LAUNCH phase 3 clinical trial that randomized patients to receive lenvatinib alone or lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Out of 338 patients, 170 received lenvatinib plus TACE. Unsurprisingly, the response rate was higher with the combination (54.1% vs 25.0%; P < .001); however, so was the median overall survival (17.8 vs 11.5 months; hazard ratio 0.45; P < .001), and median progression-free survival (10.6 vs 6.4 months; hazard ratio 0.43; P < .001). The investigators concluded that the addition of TACE to lenvatinib had manageable toxicities, improved clinical outcomes, and could be used as a potential first-line treatment for some patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, in patients whose HCC progressed after a single TACE treatment, the question remains whether repeated TACE is worthwhile. Zhao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the outcomes of 94 patients who underwent at least one TACE. Of these, 28 (29.8%) had a response to the first TACE, and these patients tended to have a longer OS compared with nonresponders (36.7 vs 21.5 months; P = .071). Of the 43 initial nonresponders who underwent a second TACE, 15 of 43 (34.9%) achieved a response and had an improved median overall survival (47.8 v. 13.6 months; P = .01), suggesting that repeat TACE may offer a benefit to some patients, even after no response to the initial treatment.
Liver transplantation has the opportunity to cure both localized HCC as well as underlying liver cirrhosis. Donor organ shortage has led to the implementation of the Milan criteria as a way to identify patients whose tumor burden is low enough to predict a good outcome. Downstaging liver cancer to fit within Milan criteria has been controversial.
Tabrizian and colleagues undertook a retrospective cohort analysis of 2645 adult patients with HCC who underwent liver transplant. Out of those, 2122 patients always had disease that was within the Milan criteria, 341 patients had HCC that was downstaged to fit within the Milan criteria, and 182 patients had HCC that was outside the Milan criteria at the time of liver transplantation. The authors report that the 10-year post-transplant survival and recurrence rates were 61.5% and 13.3%, respectively, in those always within the Milan criteria, 52.1% and 20.6% among those whose disease was downstaged, and 43.3% and 41.1% in those whose disease was never downstaged. Characteristics that predicted recurrence after downstaging were tumor size > 7 cm at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR] 2.62; 95% CI 1.20-5.75; P = .02), more than three tumors at diagnosis (OR 2.34; 95% CI 1.22-4.50; P = .01), and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) response ≥ 20 ng/mL with < 50% improvement from maximum AFP before transplantation (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.14-3.46; P = .02). Additionally, patients with recurrent tumors that were surgically resected had improved 5-year post-recurrence survival (31.6% vs 7.3%; P < .001). The conclusion was that the national downstaging policies were valid and should continue.
For patients who have unresectable HCC, systemic therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Peng and colleagues reported the results of the LAUNCH phase 3 clinical trial that randomized patients to receive lenvatinib alone or lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Out of 338 patients, 170 received lenvatinib plus TACE. Unsurprisingly, the response rate was higher with the combination (54.1% vs 25.0%; P < .001); however, so was the median overall survival (17.8 vs 11.5 months; hazard ratio 0.45; P < .001), and median progression-free survival (10.6 vs 6.4 months; hazard ratio 0.43; P < .001). The investigators concluded that the addition of TACE to lenvatinib had manageable toxicities, improved clinical outcomes, and could be used as a potential first-line treatment for some patients with unresectable HCC.
Finally, in patients whose HCC progressed after a single TACE treatment, the question remains whether repeated TACE is worthwhile. Zhao and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the outcomes of 94 patients who underwent at least one TACE. Of these, 28 (29.8%) had a response to the first TACE, and these patients tended to have a longer OS compared with nonresponders (36.7 vs 21.5 months; P = .071). Of the 43 initial nonresponders who underwent a second TACE, 15 of 43 (34.9%) achieved a response and had an improved median overall survival (47.8 v. 13.6 months; P = .01), suggesting that repeat TACE may offer a benefit to some patients, even after no response to the initial treatment.
Gender and Patient Satisfaction in a Veterans Health Administration Outpatient Chemotherapy Unit
Gender differences in patient satisfaction with medical care have been evaluated in multiple settings; however, studies specific to the unique population of women veterans with cancer are lacking. Women are reported to value privacy, psychosocial support, and communication to a higher degree compared with men.1 Factors affecting satisfaction include the following: discomfort in sharing treatment rooms with the opposite gender, a desire for privacy with treatment and restroom use, anatomic or illness differences, and a personal history of abuse.2-4 Regrettably, up to 1 in 3 women in the United States are victims of sexual trauma in their lifetimes, and up to 1 in 4 women in the military are victims of military sexual trauma. Incidence in both settings is suspected to be higher due to underreporting.5,6
Chemotherapy treatment units are often uniquely designed as an open space, with several patients sharing a treatment area. The design reduces isolation and facilitates quick nurse-patient access during potentially toxic treatments known to have frequent adverse effects. Data suggest that nursing staff prefer open models to facilitate quick patient assessments and interventions as needed; however, patients and families prefer private treatment rooms, especially among women patients or those receiving longer infusions.7
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient population is male predominant, comprised only of 10% female patients.8 Although the proportion of female patients in the VHA is expected to rise annually to about 16% by 2043, the low percentage of female veterans will persist for the foreseeable future.8 This low percentage of female veterans is reflected in the Veterans Affairs Portland Health Care System (VAPHCS) cancer patient population and in the use of the chemotherapy infusion unit, which is used for the ambulatory treatment of veterans undergoing cancer therapy.
The VHA has previously explored gender differences in health care, such as with cardiovascular disease, transgender care, and access to mental health.9-11 However, to the best of our knowledge, no analysis has explored gender differences within the outpatient cancer treatment experience. Patient satisfaction with outpatient cancer care may be magnified in the VHA setting due to the uniquely unequal gender populations, shared treatment space design, and high incidence of sexual abuse among women veterans. Given this, we aimed to identify gender-related preferences in outpatient cancer care in our chemotherapy infusion unit.
In our study, we used the terms male and female to reflect statistical data from the literature or labeled data from the electronic health record (EHR); whereas the terms men and women were used to describe and encompass the cultural implications and context of gender.12
Methods
This study was designated as a quality improvement (QI) project by the VAPHCS research office and Institutional Review Board in accordance with VHA policies.
The VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit is designed with 6 rooms for chemotherapy administration. One room is a large open space with 6 chairs for patients. The other rooms are smaller with glass dividers between the rooms, and 3 chairs inside each for patients. There are 2 private bathrooms, each gender neutral. Direct patient care is provided by physicians, nurse practitioners (NPs), infusion unit nurses, and nurse coordinators. Men represent the majority of hematology and oncology physicians (13 of 20 total: 5 women fellow physicians and 2 women attending physicians), and 2 of 4 NPs. Women represent 10 of 12 infusion unit and cancer coordinator nurses. We used the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) EHR, to create a list of veterans treated at the VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit for a 2-year period (January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2020).
Male and female patient lists were first generated based on CPRS categorization. We identified all female veterans treated in the ambulatory infusion unit during the study period. Male patients were then chosen at random, recording the most recent names for each year until a matched number per year compared with the female cohort was reached. Patients were recorded only once even though they had multiple infusion unit visits. Patients were excluded who were deceased, on hospice care, lost to follow-up, could not be reached by phone, refused to take the survey, had undeliverable email addresses, or lacked internet or email access.
After filing the appropriate request through the VAPHCS Institutional Review Board committee in January 2021, patient records were reviewed for demographics data, contact information, and infusion treatment history. The survey was then conducted over a 2-week period during January and February 2021. Each patient was invited by phone to complete a 25-question anonymous online survey. The survey questions were created from patient-relayed experiences, then modeled into survey questions in a format similar to other patient satisfaction questionnaires described in cancer care and gender differences.2,13,14 The survey included self-identification of gender and was multiple choice for all except 2 questions, which allowed an open-ended response (Appendix). Only 1 answer per question was permitted. Only 1 survey link was sent to each veteran who gave permission for the survey. To protect anonymity for the small patient population, we excluded those identifying as gender nonbinary or transgender.
Statistical Analysis
Patient, disease, and treatment features are separated by male and female cohorts to reflect information from the EHR (Table 1). Survey percentages were calculated to reflect the affirmative response of the question asked (Table 2). Questions with answer options of not important, minimally important, important, or very important were calculated to reflect the sum of any importance in both cohorts. Questions with answer options of never, once, often, or every time were calculated to reflect any occurrence (sum of once, often, or every time) in both patient groups. Questions with answer options of strongly agree, somewhat agree, somewhat disagree, and strongly disagree were calculated to reflect any agreement (somewhat agree and strongly agree summed together) for both groups. Comparisons between cohorts were then conducted using a Fisher exact test. A Welch t test was used to calculate the significance of the continuous variable and overall ranking of the infusion unit experience between groups.
Results
In 2020, 414 individual patients were treated at the VAPAHCS outpatient infusion unit. Of these, 23 (5.6%) were female, and 18 agreed to take the survey. After deceased and duplicate names from 2020 were removed, another 14 eligible 2019 female patients were invited and 6 agreed to participate; 6 eligible 2018 female patients were invited and 4 agreed to take the survey (Figure). Thirty female veterans were sent a survey link and 21 (70%) responses were collected. Twenty-one male 2020 patients were contacted and 18 agreed to take the survey. After removing duplicate names and deceased individuals, 17 of 21 eligible 2019 male patients and 4 of 6 eligible 2018 patients agreed to take the survey. Five additional male veterans declined the online-based survey method. In total, 39 male veterans were reached who agreed to have the survey link emailed, and 20 (51%) total responses were collected.
Most respondents answered all questions in the survey. The most frequently skipped questions included 3 questions that were contingent on a yes answer to a prior question, and 2 openended questions asking for a write-in response. Percentages for female and male respondents were adjusted for number of responses when applicable.
Thirteen (62%) female patients were aged < 65 years, while 18 (90%) of male patients were aged ≥ 65 years. Education beyond high school was reported in 20 female and 15 male respondents. Almost all treatment administered in the infusion unit was for cancer-directed treatment, with only 1 reporting a noncancer treatment (IV iron). The most common malignancy among female patients was breast cancer (n = 11, 52%); for male patients prostate cancer (n = 4, 20%) and hematologic malignancy (n = 4, 20%) were most common. Four (19%) female and 8 (40%) male respondents reported having a metastatic diagnosis. Overall patient satisfaction ranked high with an average score of 9.1 on a 10-point scale. The mean (SD) satisfaction score for female respondents was 1 point lower than that for men: 8.7 (2.2) vs 9.6 (0.6) in men (P = .11).
Eighteen (86%) women reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment compared with 2 (10%) men (P < .001). The sexual abuse assailant was a different gender for 17 of 18 female respondents and of the same gender for both male respondents. Of those with sexual abuse history, 4 women reported feeling uncomfortable around their assailant’s gender vs no men (P = .11), but this difference was not statistically significant. Six women (29%) and 2 (10%) men reported feeling uncomfortable during clinical examinations from comments made by the clinician or during treatment administration (P = .24). Six (29%) women and no men reported that they “felt uncomfortable in the infusion unit by other patients” (P = .02). Six (29%) women and no men reported feeling unable to “voice uncomfortable experiences” to the infusion unit clinician (P = .02).
Ten (48%) women and 6 (30%) men reported emotional support when receiving treatments provided by staff of the same gender (P = .34). Eight (38%) women and 4 (20%) men noted that access to treatment with the same gender was important (P = .31). Six (29%) women and 4 (20%) men indicated that access to a sex or gender-specific restroom was important (P = .72). No gender preferences were identified in the survey questions regarding importance of private treatment room access and level of emotional support when receiving treatment with others of the same malignancy. These relationships were not statistically significant.
In addition, 2 open-ended questions were asked. Seventeen women and 14 men responded. Contact the corresponding author for more information on the questions and responses.
Discussion
Overall patient satisfaction was high among the men and women veterans with cancer who received treatment in our outpatient infusion unit; however, notable gender differences existed. Three items in the survey revealed statistically significant differences in the patient experience between men and women veterans: history of sexual abuse or harassment, uncomfortable feelings among other patients, and discomfort in relaying uncomfortable feelings to a clinician. Other items in the survey did not reach statistical significance; however, we have included discussion of the findings as they may highlight important trends and be of clinical significance.
We suspect differences among genders in patient satisfaction to be related to the high incidence of sexual abuse or harassment history reported by women, much higher at 86% than the one-third to one-fourth incidence rates estimated by the existing literature for civilian or military sexual abuse in women.5,6 These high sexual abuse or harassment rates are present in a majority of women who receive cancer-directed treatment toward a gender-specific breast malignancy, surrounded predominantly among men in a shared treatment space. Together, these factors are likely key reasons behind the differences in satisfaction observed. This sentiment is expressed in our cohort, where one-fifth of women with a sexual abuse or harassment history continue to remain uncomfortable around men, and 29% of women reporting some uncomfortable feelings during their treatment experience compared with none of the men. Additionally, 6 (29%) women vs no men felt uncomfortable in reporting an uncomfortable experience with a clinician; this represents a significant barrier in providing care for these patients.
A key gender preference among women included access to shared treatment rooms with other women and that sharing a treatment space with other women resulted in feeling more emotional support during treatments. Access to gender-specific restrooms was also preferred by women more than men. Key findings in both genders were that about half of men and women valued access to a private treatment room and would derive more emotional support when surrounded by others with the same cancer.
Prior studies on gender and patient satisfaction in general medical care and cancer care have found women value privacy more than men.1-3 Wessels and colleagues performed an analysis of 386 patients with cancer in Europe and found gender to be the strongest influence in patient preferences within cancer care. Specifically, the highest statically significant association in care preferences among women included privacy, support/counseling/rehabilitation access, and decreased wait times.2 These findings were most pronounced in those with breast cancer compared with other malignancy type and highlights that malignancy type and gender predominance impact care satisfaction.
Traditionally a shared treatment space design has been used in outpatient chemotherapy units, similar to the design of the VAPHCS. However, recent data report on the patient preference for a private treatment space, which was especially prominent among women and those receiving longer infusions.7 In another study that evaluated 225 patients with cancer preferences in sharing a treatment space with those of a different sexual orientation or gender identify, differences were found. Both men and women had a similar level of comfort in sharing a treatment room with someone of a different sexual orientation; however, more women reported discomfort in sharing a treatment space with a transgender woman compared with men who felt more comfortable sharing a space with a transgender man.4 We noted a gender preference may be present to explain the difference. Within our cohort, women valued access to treatment with other women and derived more emotional support when with other women; however, we did not inquire about feelings in sharing a treatment space among transgender individuals or differing sexual orientation.
Gender differences for privacy and in shared room preferences may result from the lasting impacts of prior sexual abuse or harassment. A history of sexual abuse negatively impacts later medical care access and use.15 Those veterans who experienced sexual abuse/harrassment reported higher feelings of lack of control, vulnerability, depression, and pursued less medical care.15,16 Within cancer care, these feelings are most pronounced among women with gender-specific malignancies, such as gynecologic cancers or breast cancer. Treatment, screening, and physical examinations by clinicians who are of the same gender as the sexual abuse/harassment assailant can recreate traumatic feelings.15,16
A majority of women (n = 18, 86%) in our cohort reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment and breast malignancy was the most common cancer among women. However women represent just 5.6% of the VAPHCS infusion unit treatment population. This combination of factors may explain the reasons for women veterans’ preference for privacy during treatments, access to gender-specific restrooms, and feeling more emotional support when surrounded by other women. Strategies to help patients with a history of abuse have been described and include discussions from the clinician asking about abuse history, allowing time for the patient to express fears with an examination or test, and training on how to deliver sensitive care for those with trauma.17,18
Quality Improvement
Project In the VAPHCS infusion unit, several low-cost interventions have been undertaken as a result of our survey findings. We presented our survey data to the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, accredited through the national American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer. The committee awarded support for a yearlong QI project, including a formal framework of quarterly multidisciplinary meetings to discuss project updates, challenges, and resources. The QI project centers on education to raise awareness of survey results as well as specific interventions for improvement.
Education efforts have been applied through multiple department-wide emails, in-person education to our chemotherapy unit staff, abstract submission to national oncology conferences, and grand rounds department presentations at VAPHCS and at other VHA-affiliated university programs. Additionally, education to clinicians with specific contact information for psychology and women’s health to support mental health, trauma, and sexual abuse histories has been given to each clinician who cares for veterans in the chemotherapy unit.
We also have implemented a mandatory cancer care navigation consultation for all women veterans who have a new cancer or infusion need. The cancer care navigator has received specialized training in sensitive history-taking and provides women veterans with a direct number to reach the cancer care navigation nurse. Cancer care navigation also provides a continuum of support and referral access for psychosocial needs as indicated between infusion or health care visits. Our hope is that these resources may help offset the sentiment reflected in our cohort of women feeling unable to voice concerns to a clinician.
Other interventions underway include offering designated scheduling time each week to women so they can receive infusions in an area with other women. This may help mitigate the finding that women veterans felt more uncomfortable around other patients during infusion treatments compared with how men felt in the chemotherapy unit. We also have implemented gender-specific restrooms labeled with a sign on each bathroom door so men and women can have access to a designated restroom. Offering private or semiprivate treatment rooms is currently limited by space and capacity; however, these may offer the greatest opportunity to improve patient satisfaction, especially among women veterans. Working with the support of the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, we aim to reevaluate the impact of the education and QI efforts on gender differences and patient satisfaction at completion of the 1-year award.
Limitations
Limitations to our study include the overall small sample size. This is due to the combination of the low number of women treated at VAPHCS and many with advanced cancer who, unfortunately, have a limited overall survival and hinders accrual of a larger sample size. Other limitations included age as a possible confounder in our findings, with women representing a younger demographic compared with men. We did not collect responses on duration of infusion time, which also may impact overall satisfaction and patient experience. We also acknowledge that biologic male or female sex may not correspond to a specific individual’s gender. Use of CPRS to obtain a matched number of male and female patients through random selection relied on labeled data from the EHR. This potentially may have excluded male patients who identify as another gender that would have been captured on the anonymous survey.
Last, we restricted survey responses to online only, which excluded a small percentage who declined this approach.
Conclusions
Our findings may have broad applications to other VHA facilities and other cancer-directed treatment centers where the patient demographic and open shared infusion unit design may be similar. The study also may serve as a model of survey design and implementation from which other centers may consider improving patient satisfaction. We hope these survey results and interventions can provide insight and be used to improve patient satisfaction among all cancer patients at infusion units serving veterans and nonveterans.
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to our cancer patients who took the time to take the survey. We also are very grateful to the VHA infusion unit nurses, staff, nurse practitioners, and physicians who have embraced this project and welcomed any changes that may positively impact treatment of veterans. Also, thank you to Tia Kohs for statistical support and Sophie West for gender discussions. Last, we specifically thank Barbara, for her pursuit of better care for women and for all veterans.
1. Clarke SA, Booth L, Velikova G, Hewison J. Social support: gender differences in cancer patients in the United Kingdom. Cancer Nurs. 2006;29(1):66-72. doi:10.1097/00002820-200601000-00012
2. Wessels H, de Graeff A, Wynia K, et al. Gender-related needs and preferences in cancer care indicate the need for an individualized approach to cancer patients. Oncologist. 2010;15(6):648-655. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0337
3. Hartigan SM, Bonnet K, Chisholm L, et al. Why do women not use the bathroom? Women’s attitudes and beliefs on using public restrooms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):2053. doi:10.3390/ijerph17062053
4. Alexander K, Walters CB, Banerjee SC. Oncology patients’ preferences regarding sexual orientation and gender identity (SOGI) disclosure and room sharing sharing. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103(5):1041-1048. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2019.12.006
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sexual violence. Updated July 5, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/features /sexual-violence/index.html
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Military sexual trauma. Updated May 16, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https:// www.mentalhealth.va.gov/mentalhealth/msthome/index.asp
7. Wang Z, Pukszta M. Private Rooms, Semi-open areas, or open areas for chemotherapy care: perspectives of cancer patients, families, and nursing staff. HERD. 2018;11(3):94- 108. doi:10.1177/1937586718758445
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vetdata /docs/specialreports/women_veterans_2015_final.pdf
9. Driscoll MA, Higgins DM, Seng EK, et al. Trauma, social support, family conflict, and chronic pain in recent service veterans: does gender matter? Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1101- 1111. doi:10.1111/pme.12744
10. Fox AB, Meyer EC, Vogt D. Attitudes about the VA healthcare setting, mental illness, and mental health treatment and their relationship with VA mental health service use among female and male OEF/OIF veterans. Psychol Serv. 2015;12(1):49-58. doi:10.1037/a0038269
11. Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(1):21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
12. Tseng J. Sex, gender, and why the differences matter. Virtual Mentor. 2008;10(7):427-428. doi:10.1001/virtualmentor.2008.10.7.fred1-0807
13. Booij JC, Zegers M, Evers PMPJ, Hendricks M, Delnoij DMJ, Rademakers JJDJM. Improving cancer patient care: development of a generic cancer consumer quality index questionnaire for cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(203). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-203
14. Meropol NJ, Egleston BL, Buzaglo JS, et al. Cancer patient preferences for quality and length of life. Cancer. 2008;113(12):3459-3466. doi:10.1002/cncr.23968 1
5. Schnur JB, Dillon MJ, Goldsmith RE, Montgomery GH. Cancer treatment experiences among survivors of childhood sexual abuse: a qualitative investigation of triggers and reactions to cumulative trauma. Palliat Support Care. 2018;16(6):767-776. doi:10.1017/S147895151700075X
16. Cadman L, Waller J, Ashdown-Barr L, Szarewski A. Barriers to cervical screening in women who have experienced sexual abuse: an exploratory study. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):214-220. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100378
17. Kelly S. The effects of childhood sexual abuse on women’s lives and their attitudes to cervical screening. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):212-213. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100418
18. McCloskey LA, Lichter E, Williams C, Gerber M, Wittenberg E, Ganz M. Assessing intimate partner violence in health care settings leads to women’s receipt of interventions and improved health. Public Health Rep. 2006;121(4):435-444. doi:10.1177/003335490612100412
Gender differences in patient satisfaction with medical care have been evaluated in multiple settings; however, studies specific to the unique population of women veterans with cancer are lacking. Women are reported to value privacy, psychosocial support, and communication to a higher degree compared with men.1 Factors affecting satisfaction include the following: discomfort in sharing treatment rooms with the opposite gender, a desire for privacy with treatment and restroom use, anatomic or illness differences, and a personal history of abuse.2-4 Regrettably, up to 1 in 3 women in the United States are victims of sexual trauma in their lifetimes, and up to 1 in 4 women in the military are victims of military sexual trauma. Incidence in both settings is suspected to be higher due to underreporting.5,6
Chemotherapy treatment units are often uniquely designed as an open space, with several patients sharing a treatment area. The design reduces isolation and facilitates quick nurse-patient access during potentially toxic treatments known to have frequent adverse effects. Data suggest that nursing staff prefer open models to facilitate quick patient assessments and interventions as needed; however, patients and families prefer private treatment rooms, especially among women patients or those receiving longer infusions.7
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient population is male predominant, comprised only of 10% female patients.8 Although the proportion of female patients in the VHA is expected to rise annually to about 16% by 2043, the low percentage of female veterans will persist for the foreseeable future.8 This low percentage of female veterans is reflected in the Veterans Affairs Portland Health Care System (VAPHCS) cancer patient population and in the use of the chemotherapy infusion unit, which is used for the ambulatory treatment of veterans undergoing cancer therapy.
The VHA has previously explored gender differences in health care, such as with cardiovascular disease, transgender care, and access to mental health.9-11 However, to the best of our knowledge, no analysis has explored gender differences within the outpatient cancer treatment experience. Patient satisfaction with outpatient cancer care may be magnified in the VHA setting due to the uniquely unequal gender populations, shared treatment space design, and high incidence of sexual abuse among women veterans. Given this, we aimed to identify gender-related preferences in outpatient cancer care in our chemotherapy infusion unit.
In our study, we used the terms male and female to reflect statistical data from the literature or labeled data from the electronic health record (EHR); whereas the terms men and women were used to describe and encompass the cultural implications and context of gender.12
Methods
This study was designated as a quality improvement (QI) project by the VAPHCS research office and Institutional Review Board in accordance with VHA policies.
The VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit is designed with 6 rooms for chemotherapy administration. One room is a large open space with 6 chairs for patients. The other rooms are smaller with glass dividers between the rooms, and 3 chairs inside each for patients. There are 2 private bathrooms, each gender neutral. Direct patient care is provided by physicians, nurse practitioners (NPs), infusion unit nurses, and nurse coordinators. Men represent the majority of hematology and oncology physicians (13 of 20 total: 5 women fellow physicians and 2 women attending physicians), and 2 of 4 NPs. Women represent 10 of 12 infusion unit and cancer coordinator nurses. We used the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) EHR, to create a list of veterans treated at the VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit for a 2-year period (January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2020).
Male and female patient lists were first generated based on CPRS categorization. We identified all female veterans treated in the ambulatory infusion unit during the study period. Male patients were then chosen at random, recording the most recent names for each year until a matched number per year compared with the female cohort was reached. Patients were recorded only once even though they had multiple infusion unit visits. Patients were excluded who were deceased, on hospice care, lost to follow-up, could not be reached by phone, refused to take the survey, had undeliverable email addresses, or lacked internet or email access.
After filing the appropriate request through the VAPHCS Institutional Review Board committee in January 2021, patient records were reviewed for demographics data, contact information, and infusion treatment history. The survey was then conducted over a 2-week period during January and February 2021. Each patient was invited by phone to complete a 25-question anonymous online survey. The survey questions were created from patient-relayed experiences, then modeled into survey questions in a format similar to other patient satisfaction questionnaires described in cancer care and gender differences.2,13,14 The survey included self-identification of gender and was multiple choice for all except 2 questions, which allowed an open-ended response (Appendix). Only 1 answer per question was permitted. Only 1 survey link was sent to each veteran who gave permission for the survey. To protect anonymity for the small patient population, we excluded those identifying as gender nonbinary or transgender.
Statistical Analysis
Patient, disease, and treatment features are separated by male and female cohorts to reflect information from the EHR (Table 1). Survey percentages were calculated to reflect the affirmative response of the question asked (Table 2). Questions with answer options of not important, minimally important, important, or very important were calculated to reflect the sum of any importance in both cohorts. Questions with answer options of never, once, often, or every time were calculated to reflect any occurrence (sum of once, often, or every time) in both patient groups. Questions with answer options of strongly agree, somewhat agree, somewhat disagree, and strongly disagree were calculated to reflect any agreement (somewhat agree and strongly agree summed together) for both groups. Comparisons between cohorts were then conducted using a Fisher exact test. A Welch t test was used to calculate the significance of the continuous variable and overall ranking of the infusion unit experience between groups.
Results
In 2020, 414 individual patients were treated at the VAPAHCS outpatient infusion unit. Of these, 23 (5.6%) were female, and 18 agreed to take the survey. After deceased and duplicate names from 2020 were removed, another 14 eligible 2019 female patients were invited and 6 agreed to participate; 6 eligible 2018 female patients were invited and 4 agreed to take the survey (Figure). Thirty female veterans were sent a survey link and 21 (70%) responses were collected. Twenty-one male 2020 patients were contacted and 18 agreed to take the survey. After removing duplicate names and deceased individuals, 17 of 21 eligible 2019 male patients and 4 of 6 eligible 2018 patients agreed to take the survey. Five additional male veterans declined the online-based survey method. In total, 39 male veterans were reached who agreed to have the survey link emailed, and 20 (51%) total responses were collected.
Most respondents answered all questions in the survey. The most frequently skipped questions included 3 questions that were contingent on a yes answer to a prior question, and 2 openended questions asking for a write-in response. Percentages for female and male respondents were adjusted for number of responses when applicable.
Thirteen (62%) female patients were aged < 65 years, while 18 (90%) of male patients were aged ≥ 65 years. Education beyond high school was reported in 20 female and 15 male respondents. Almost all treatment administered in the infusion unit was for cancer-directed treatment, with only 1 reporting a noncancer treatment (IV iron). The most common malignancy among female patients was breast cancer (n = 11, 52%); for male patients prostate cancer (n = 4, 20%) and hematologic malignancy (n = 4, 20%) were most common. Four (19%) female and 8 (40%) male respondents reported having a metastatic diagnosis. Overall patient satisfaction ranked high with an average score of 9.1 on a 10-point scale. The mean (SD) satisfaction score for female respondents was 1 point lower than that for men: 8.7 (2.2) vs 9.6 (0.6) in men (P = .11).
Eighteen (86%) women reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment compared with 2 (10%) men (P < .001). The sexual abuse assailant was a different gender for 17 of 18 female respondents and of the same gender for both male respondents. Of those with sexual abuse history, 4 women reported feeling uncomfortable around their assailant’s gender vs no men (P = .11), but this difference was not statistically significant. Six women (29%) and 2 (10%) men reported feeling uncomfortable during clinical examinations from comments made by the clinician or during treatment administration (P = .24). Six (29%) women and no men reported that they “felt uncomfortable in the infusion unit by other patients” (P = .02). Six (29%) women and no men reported feeling unable to “voice uncomfortable experiences” to the infusion unit clinician (P = .02).
Ten (48%) women and 6 (30%) men reported emotional support when receiving treatments provided by staff of the same gender (P = .34). Eight (38%) women and 4 (20%) men noted that access to treatment with the same gender was important (P = .31). Six (29%) women and 4 (20%) men indicated that access to a sex or gender-specific restroom was important (P = .72). No gender preferences were identified in the survey questions regarding importance of private treatment room access and level of emotional support when receiving treatment with others of the same malignancy. These relationships were not statistically significant.
In addition, 2 open-ended questions were asked. Seventeen women and 14 men responded. Contact the corresponding author for more information on the questions and responses.
Discussion
Overall patient satisfaction was high among the men and women veterans with cancer who received treatment in our outpatient infusion unit; however, notable gender differences existed. Three items in the survey revealed statistically significant differences in the patient experience between men and women veterans: history of sexual abuse or harassment, uncomfortable feelings among other patients, and discomfort in relaying uncomfortable feelings to a clinician. Other items in the survey did not reach statistical significance; however, we have included discussion of the findings as they may highlight important trends and be of clinical significance.
We suspect differences among genders in patient satisfaction to be related to the high incidence of sexual abuse or harassment history reported by women, much higher at 86% than the one-third to one-fourth incidence rates estimated by the existing literature for civilian or military sexual abuse in women.5,6 These high sexual abuse or harassment rates are present in a majority of women who receive cancer-directed treatment toward a gender-specific breast malignancy, surrounded predominantly among men in a shared treatment space. Together, these factors are likely key reasons behind the differences in satisfaction observed. This sentiment is expressed in our cohort, where one-fifth of women with a sexual abuse or harassment history continue to remain uncomfortable around men, and 29% of women reporting some uncomfortable feelings during their treatment experience compared with none of the men. Additionally, 6 (29%) women vs no men felt uncomfortable in reporting an uncomfortable experience with a clinician; this represents a significant barrier in providing care for these patients.
A key gender preference among women included access to shared treatment rooms with other women and that sharing a treatment space with other women resulted in feeling more emotional support during treatments. Access to gender-specific restrooms was also preferred by women more than men. Key findings in both genders were that about half of men and women valued access to a private treatment room and would derive more emotional support when surrounded by others with the same cancer.
Prior studies on gender and patient satisfaction in general medical care and cancer care have found women value privacy more than men.1-3 Wessels and colleagues performed an analysis of 386 patients with cancer in Europe and found gender to be the strongest influence in patient preferences within cancer care. Specifically, the highest statically significant association in care preferences among women included privacy, support/counseling/rehabilitation access, and decreased wait times.2 These findings were most pronounced in those with breast cancer compared with other malignancy type and highlights that malignancy type and gender predominance impact care satisfaction.
Traditionally a shared treatment space design has been used in outpatient chemotherapy units, similar to the design of the VAPHCS. However, recent data report on the patient preference for a private treatment space, which was especially prominent among women and those receiving longer infusions.7 In another study that evaluated 225 patients with cancer preferences in sharing a treatment space with those of a different sexual orientation or gender identify, differences were found. Both men and women had a similar level of comfort in sharing a treatment room with someone of a different sexual orientation; however, more women reported discomfort in sharing a treatment space with a transgender woman compared with men who felt more comfortable sharing a space with a transgender man.4 We noted a gender preference may be present to explain the difference. Within our cohort, women valued access to treatment with other women and derived more emotional support when with other women; however, we did not inquire about feelings in sharing a treatment space among transgender individuals or differing sexual orientation.
Gender differences for privacy and in shared room preferences may result from the lasting impacts of prior sexual abuse or harassment. A history of sexual abuse negatively impacts later medical care access and use.15 Those veterans who experienced sexual abuse/harrassment reported higher feelings of lack of control, vulnerability, depression, and pursued less medical care.15,16 Within cancer care, these feelings are most pronounced among women with gender-specific malignancies, such as gynecologic cancers or breast cancer. Treatment, screening, and physical examinations by clinicians who are of the same gender as the sexual abuse/harassment assailant can recreate traumatic feelings.15,16
A majority of women (n = 18, 86%) in our cohort reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment and breast malignancy was the most common cancer among women. However women represent just 5.6% of the VAPHCS infusion unit treatment population. This combination of factors may explain the reasons for women veterans’ preference for privacy during treatments, access to gender-specific restrooms, and feeling more emotional support when surrounded by other women. Strategies to help patients with a history of abuse have been described and include discussions from the clinician asking about abuse history, allowing time for the patient to express fears with an examination or test, and training on how to deliver sensitive care for those with trauma.17,18
Quality Improvement
Project In the VAPHCS infusion unit, several low-cost interventions have been undertaken as a result of our survey findings. We presented our survey data to the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, accredited through the national American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer. The committee awarded support for a yearlong QI project, including a formal framework of quarterly multidisciplinary meetings to discuss project updates, challenges, and resources. The QI project centers on education to raise awareness of survey results as well as specific interventions for improvement.
Education efforts have been applied through multiple department-wide emails, in-person education to our chemotherapy unit staff, abstract submission to national oncology conferences, and grand rounds department presentations at VAPHCS and at other VHA-affiliated university programs. Additionally, education to clinicians with specific contact information for psychology and women’s health to support mental health, trauma, and sexual abuse histories has been given to each clinician who cares for veterans in the chemotherapy unit.
We also have implemented a mandatory cancer care navigation consultation for all women veterans who have a new cancer or infusion need. The cancer care navigator has received specialized training in sensitive history-taking and provides women veterans with a direct number to reach the cancer care navigation nurse. Cancer care navigation also provides a continuum of support and referral access for psychosocial needs as indicated between infusion or health care visits. Our hope is that these resources may help offset the sentiment reflected in our cohort of women feeling unable to voice concerns to a clinician.
Other interventions underway include offering designated scheduling time each week to women so they can receive infusions in an area with other women. This may help mitigate the finding that women veterans felt more uncomfortable around other patients during infusion treatments compared with how men felt in the chemotherapy unit. We also have implemented gender-specific restrooms labeled with a sign on each bathroom door so men and women can have access to a designated restroom. Offering private or semiprivate treatment rooms is currently limited by space and capacity; however, these may offer the greatest opportunity to improve patient satisfaction, especially among women veterans. Working with the support of the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, we aim to reevaluate the impact of the education and QI efforts on gender differences and patient satisfaction at completion of the 1-year award.
Limitations
Limitations to our study include the overall small sample size. This is due to the combination of the low number of women treated at VAPHCS and many with advanced cancer who, unfortunately, have a limited overall survival and hinders accrual of a larger sample size. Other limitations included age as a possible confounder in our findings, with women representing a younger demographic compared with men. We did not collect responses on duration of infusion time, which also may impact overall satisfaction and patient experience. We also acknowledge that biologic male or female sex may not correspond to a specific individual’s gender. Use of CPRS to obtain a matched number of male and female patients through random selection relied on labeled data from the EHR. This potentially may have excluded male patients who identify as another gender that would have been captured on the anonymous survey.
Last, we restricted survey responses to online only, which excluded a small percentage who declined this approach.
Conclusions
Our findings may have broad applications to other VHA facilities and other cancer-directed treatment centers where the patient demographic and open shared infusion unit design may be similar. The study also may serve as a model of survey design and implementation from which other centers may consider improving patient satisfaction. We hope these survey results and interventions can provide insight and be used to improve patient satisfaction among all cancer patients at infusion units serving veterans and nonveterans.
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to our cancer patients who took the time to take the survey. We also are very grateful to the VHA infusion unit nurses, staff, nurse practitioners, and physicians who have embraced this project and welcomed any changes that may positively impact treatment of veterans. Also, thank you to Tia Kohs for statistical support and Sophie West for gender discussions. Last, we specifically thank Barbara, for her pursuit of better care for women and for all veterans.
Gender differences in patient satisfaction with medical care have been evaluated in multiple settings; however, studies specific to the unique population of women veterans with cancer are lacking. Women are reported to value privacy, psychosocial support, and communication to a higher degree compared with men.1 Factors affecting satisfaction include the following: discomfort in sharing treatment rooms with the opposite gender, a desire for privacy with treatment and restroom use, anatomic or illness differences, and a personal history of abuse.2-4 Regrettably, up to 1 in 3 women in the United States are victims of sexual trauma in their lifetimes, and up to 1 in 4 women in the military are victims of military sexual trauma. Incidence in both settings is suspected to be higher due to underreporting.5,6
Chemotherapy treatment units are often uniquely designed as an open space, with several patients sharing a treatment area. The design reduces isolation and facilitates quick nurse-patient access during potentially toxic treatments known to have frequent adverse effects. Data suggest that nursing staff prefer open models to facilitate quick patient assessments and interventions as needed; however, patients and families prefer private treatment rooms, especially among women patients or those receiving longer infusions.7
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patient population is male predominant, comprised only of 10% female patients.8 Although the proportion of female patients in the VHA is expected to rise annually to about 16% by 2043, the low percentage of female veterans will persist for the foreseeable future.8 This low percentage of female veterans is reflected in the Veterans Affairs Portland Health Care System (VAPHCS) cancer patient population and in the use of the chemotherapy infusion unit, which is used for the ambulatory treatment of veterans undergoing cancer therapy.
The VHA has previously explored gender differences in health care, such as with cardiovascular disease, transgender care, and access to mental health.9-11 However, to the best of our knowledge, no analysis has explored gender differences within the outpatient cancer treatment experience. Patient satisfaction with outpatient cancer care may be magnified in the VHA setting due to the uniquely unequal gender populations, shared treatment space design, and high incidence of sexual abuse among women veterans. Given this, we aimed to identify gender-related preferences in outpatient cancer care in our chemotherapy infusion unit.
In our study, we used the terms male and female to reflect statistical data from the literature or labeled data from the electronic health record (EHR); whereas the terms men and women were used to describe and encompass the cultural implications and context of gender.12
Methods
This study was designated as a quality improvement (QI) project by the VAPHCS research office and Institutional Review Board in accordance with VHA policies.
The VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit is designed with 6 rooms for chemotherapy administration. One room is a large open space with 6 chairs for patients. The other rooms are smaller with glass dividers between the rooms, and 3 chairs inside each for patients. There are 2 private bathrooms, each gender neutral. Direct patient care is provided by physicians, nurse practitioners (NPs), infusion unit nurses, and nurse coordinators. Men represent the majority of hematology and oncology physicians (13 of 20 total: 5 women fellow physicians and 2 women attending physicians), and 2 of 4 NPs. Women represent 10 of 12 infusion unit and cancer coordinator nurses. We used the VHA Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) EHR, to create a list of veterans treated at the VAPHCS outpatient chemotherapy infusion unit for a 2-year period (January 1, 2018, to December 31, 2020).
Male and female patient lists were first generated based on CPRS categorization. We identified all female veterans treated in the ambulatory infusion unit during the study period. Male patients were then chosen at random, recording the most recent names for each year until a matched number per year compared with the female cohort was reached. Patients were recorded only once even though they had multiple infusion unit visits. Patients were excluded who were deceased, on hospice care, lost to follow-up, could not be reached by phone, refused to take the survey, had undeliverable email addresses, or lacked internet or email access.
After filing the appropriate request through the VAPHCS Institutional Review Board committee in January 2021, patient records were reviewed for demographics data, contact information, and infusion treatment history. The survey was then conducted over a 2-week period during January and February 2021. Each patient was invited by phone to complete a 25-question anonymous online survey. The survey questions were created from patient-relayed experiences, then modeled into survey questions in a format similar to other patient satisfaction questionnaires described in cancer care and gender differences.2,13,14 The survey included self-identification of gender and was multiple choice for all except 2 questions, which allowed an open-ended response (Appendix). Only 1 answer per question was permitted. Only 1 survey link was sent to each veteran who gave permission for the survey. To protect anonymity for the small patient population, we excluded those identifying as gender nonbinary or transgender.
Statistical Analysis
Patient, disease, and treatment features are separated by male and female cohorts to reflect information from the EHR (Table 1). Survey percentages were calculated to reflect the affirmative response of the question asked (Table 2). Questions with answer options of not important, minimally important, important, or very important were calculated to reflect the sum of any importance in both cohorts. Questions with answer options of never, once, often, or every time were calculated to reflect any occurrence (sum of once, often, or every time) in both patient groups. Questions with answer options of strongly agree, somewhat agree, somewhat disagree, and strongly disagree were calculated to reflect any agreement (somewhat agree and strongly agree summed together) for both groups. Comparisons between cohorts were then conducted using a Fisher exact test. A Welch t test was used to calculate the significance of the continuous variable and overall ranking of the infusion unit experience between groups.
Results
In 2020, 414 individual patients were treated at the VAPAHCS outpatient infusion unit. Of these, 23 (5.6%) were female, and 18 agreed to take the survey. After deceased and duplicate names from 2020 were removed, another 14 eligible 2019 female patients were invited and 6 agreed to participate; 6 eligible 2018 female patients were invited and 4 agreed to take the survey (Figure). Thirty female veterans were sent a survey link and 21 (70%) responses were collected. Twenty-one male 2020 patients were contacted and 18 agreed to take the survey. After removing duplicate names and deceased individuals, 17 of 21 eligible 2019 male patients and 4 of 6 eligible 2018 patients agreed to take the survey. Five additional male veterans declined the online-based survey method. In total, 39 male veterans were reached who agreed to have the survey link emailed, and 20 (51%) total responses were collected.
Most respondents answered all questions in the survey. The most frequently skipped questions included 3 questions that were contingent on a yes answer to a prior question, and 2 openended questions asking for a write-in response. Percentages for female and male respondents were adjusted for number of responses when applicable.
Thirteen (62%) female patients were aged < 65 years, while 18 (90%) of male patients were aged ≥ 65 years. Education beyond high school was reported in 20 female and 15 male respondents. Almost all treatment administered in the infusion unit was for cancer-directed treatment, with only 1 reporting a noncancer treatment (IV iron). The most common malignancy among female patients was breast cancer (n = 11, 52%); for male patients prostate cancer (n = 4, 20%) and hematologic malignancy (n = 4, 20%) were most common. Four (19%) female and 8 (40%) male respondents reported having a metastatic diagnosis. Overall patient satisfaction ranked high with an average score of 9.1 on a 10-point scale. The mean (SD) satisfaction score for female respondents was 1 point lower than that for men: 8.7 (2.2) vs 9.6 (0.6) in men (P = .11).
Eighteen (86%) women reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment compared with 2 (10%) men (P < .001). The sexual abuse assailant was a different gender for 17 of 18 female respondents and of the same gender for both male respondents. Of those with sexual abuse history, 4 women reported feeling uncomfortable around their assailant’s gender vs no men (P = .11), but this difference was not statistically significant. Six women (29%) and 2 (10%) men reported feeling uncomfortable during clinical examinations from comments made by the clinician or during treatment administration (P = .24). Six (29%) women and no men reported that they “felt uncomfortable in the infusion unit by other patients” (P = .02). Six (29%) women and no men reported feeling unable to “voice uncomfortable experiences” to the infusion unit clinician (P = .02).
Ten (48%) women and 6 (30%) men reported emotional support when receiving treatments provided by staff of the same gender (P = .34). Eight (38%) women and 4 (20%) men noted that access to treatment with the same gender was important (P = .31). Six (29%) women and 4 (20%) men indicated that access to a sex or gender-specific restroom was important (P = .72). No gender preferences were identified in the survey questions regarding importance of private treatment room access and level of emotional support when receiving treatment with others of the same malignancy. These relationships were not statistically significant.
In addition, 2 open-ended questions were asked. Seventeen women and 14 men responded. Contact the corresponding author for more information on the questions and responses.
Discussion
Overall patient satisfaction was high among the men and women veterans with cancer who received treatment in our outpatient infusion unit; however, notable gender differences existed. Three items in the survey revealed statistically significant differences in the patient experience between men and women veterans: history of sexual abuse or harassment, uncomfortable feelings among other patients, and discomfort in relaying uncomfortable feelings to a clinician. Other items in the survey did not reach statistical significance; however, we have included discussion of the findings as they may highlight important trends and be of clinical significance.
We suspect differences among genders in patient satisfaction to be related to the high incidence of sexual abuse or harassment history reported by women, much higher at 86% than the one-third to one-fourth incidence rates estimated by the existing literature for civilian or military sexual abuse in women.5,6 These high sexual abuse or harassment rates are present in a majority of women who receive cancer-directed treatment toward a gender-specific breast malignancy, surrounded predominantly among men in a shared treatment space. Together, these factors are likely key reasons behind the differences in satisfaction observed. This sentiment is expressed in our cohort, where one-fifth of women with a sexual abuse or harassment history continue to remain uncomfortable around men, and 29% of women reporting some uncomfortable feelings during their treatment experience compared with none of the men. Additionally, 6 (29%) women vs no men felt uncomfortable in reporting an uncomfortable experience with a clinician; this represents a significant barrier in providing care for these patients.
A key gender preference among women included access to shared treatment rooms with other women and that sharing a treatment space with other women resulted in feeling more emotional support during treatments. Access to gender-specific restrooms was also preferred by women more than men. Key findings in both genders were that about half of men and women valued access to a private treatment room and would derive more emotional support when surrounded by others with the same cancer.
Prior studies on gender and patient satisfaction in general medical care and cancer care have found women value privacy more than men.1-3 Wessels and colleagues performed an analysis of 386 patients with cancer in Europe and found gender to be the strongest influence in patient preferences within cancer care. Specifically, the highest statically significant association in care preferences among women included privacy, support/counseling/rehabilitation access, and decreased wait times.2 These findings were most pronounced in those with breast cancer compared with other malignancy type and highlights that malignancy type and gender predominance impact care satisfaction.
Traditionally a shared treatment space design has been used in outpatient chemotherapy units, similar to the design of the VAPHCS. However, recent data report on the patient preference for a private treatment space, which was especially prominent among women and those receiving longer infusions.7 In another study that evaluated 225 patients with cancer preferences in sharing a treatment space with those of a different sexual orientation or gender identify, differences were found. Both men and women had a similar level of comfort in sharing a treatment room with someone of a different sexual orientation; however, more women reported discomfort in sharing a treatment space with a transgender woman compared with men who felt more comfortable sharing a space with a transgender man.4 We noted a gender preference may be present to explain the difference. Within our cohort, women valued access to treatment with other women and derived more emotional support when with other women; however, we did not inquire about feelings in sharing a treatment space among transgender individuals or differing sexual orientation.
Gender differences for privacy and in shared room preferences may result from the lasting impacts of prior sexual abuse or harassment. A history of sexual abuse negatively impacts later medical care access and use.15 Those veterans who experienced sexual abuse/harrassment reported higher feelings of lack of control, vulnerability, depression, and pursued less medical care.15,16 Within cancer care, these feelings are most pronounced among women with gender-specific malignancies, such as gynecologic cancers or breast cancer. Treatment, screening, and physical examinations by clinicians who are of the same gender as the sexual abuse/harassment assailant can recreate traumatic feelings.15,16
A majority of women (n = 18, 86%) in our cohort reported a history of sexual abuse or harassment and breast malignancy was the most common cancer among women. However women represent just 5.6% of the VAPHCS infusion unit treatment population. This combination of factors may explain the reasons for women veterans’ preference for privacy during treatments, access to gender-specific restrooms, and feeling more emotional support when surrounded by other women. Strategies to help patients with a history of abuse have been described and include discussions from the clinician asking about abuse history, allowing time for the patient to express fears with an examination or test, and training on how to deliver sensitive care for those with trauma.17,18
Quality Improvement
Project In the VAPHCS infusion unit, several low-cost interventions have been undertaken as a result of our survey findings. We presented our survey data to the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, accredited through the national American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer. The committee awarded support for a yearlong QI project, including a formal framework of quarterly multidisciplinary meetings to discuss project updates, challenges, and resources. The QI project centers on education to raise awareness of survey results as well as specific interventions for improvement.
Education efforts have been applied through multiple department-wide emails, in-person education to our chemotherapy unit staff, abstract submission to national oncology conferences, and grand rounds department presentations at VAPHCS and at other VHA-affiliated university programs. Additionally, education to clinicians with specific contact information for psychology and women’s health to support mental health, trauma, and sexual abuse histories has been given to each clinician who cares for veterans in the chemotherapy unit.
We also have implemented a mandatory cancer care navigation consultation for all women veterans who have a new cancer or infusion need. The cancer care navigator has received specialized training in sensitive history-taking and provides women veterans with a direct number to reach the cancer care navigation nurse. Cancer care navigation also provides a continuum of support and referral access for psychosocial needs as indicated between infusion or health care visits. Our hope is that these resources may help offset the sentiment reflected in our cohort of women feeling unable to voice concerns to a clinician.
Other interventions underway include offering designated scheduling time each week to women so they can receive infusions in an area with other women. This may help mitigate the finding that women veterans felt more uncomfortable around other patients during infusion treatments compared with how men felt in the chemotherapy unit. We also have implemented gender-specific restrooms labeled with a sign on each bathroom door so men and women can have access to a designated restroom. Offering private or semiprivate treatment rooms is currently limited by space and capacity; however, these may offer the greatest opportunity to improve patient satisfaction, especially among women veterans. Working with the support of the VAPHCS Cancer Committee, we aim to reevaluate the impact of the education and QI efforts on gender differences and patient satisfaction at completion of the 1-year award.
Limitations
Limitations to our study include the overall small sample size. This is due to the combination of the low number of women treated at VAPHCS and many with advanced cancer who, unfortunately, have a limited overall survival and hinders accrual of a larger sample size. Other limitations included age as a possible confounder in our findings, with women representing a younger demographic compared with men. We did not collect responses on duration of infusion time, which also may impact overall satisfaction and patient experience. We also acknowledge that biologic male or female sex may not correspond to a specific individual’s gender. Use of CPRS to obtain a matched number of male and female patients through random selection relied on labeled data from the EHR. This potentially may have excluded male patients who identify as another gender that would have been captured on the anonymous survey.
Last, we restricted survey responses to online only, which excluded a small percentage who declined this approach.
Conclusions
Our findings may have broad applications to other VHA facilities and other cancer-directed treatment centers where the patient demographic and open shared infusion unit design may be similar. The study also may serve as a model of survey design and implementation from which other centers may consider improving patient satisfaction. We hope these survey results and interventions can provide insight and be used to improve patient satisfaction among all cancer patients at infusion units serving veterans and nonveterans.
Acknowledgments
We are very thankful to our cancer patients who took the time to take the survey. We also are very grateful to the VHA infusion unit nurses, staff, nurse practitioners, and physicians who have embraced this project and welcomed any changes that may positively impact treatment of veterans. Also, thank you to Tia Kohs for statistical support and Sophie West for gender discussions. Last, we specifically thank Barbara, for her pursuit of better care for women and for all veterans.
1. Clarke SA, Booth L, Velikova G, Hewison J. Social support: gender differences in cancer patients in the United Kingdom. Cancer Nurs. 2006;29(1):66-72. doi:10.1097/00002820-200601000-00012
2. Wessels H, de Graeff A, Wynia K, et al. Gender-related needs and preferences in cancer care indicate the need for an individualized approach to cancer patients. Oncologist. 2010;15(6):648-655. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0337
3. Hartigan SM, Bonnet K, Chisholm L, et al. Why do women not use the bathroom? Women’s attitudes and beliefs on using public restrooms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):2053. doi:10.3390/ijerph17062053
4. Alexander K, Walters CB, Banerjee SC. Oncology patients’ preferences regarding sexual orientation and gender identity (SOGI) disclosure and room sharing sharing. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103(5):1041-1048. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2019.12.006
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sexual violence. Updated July 5, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/features /sexual-violence/index.html
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Military sexual trauma. Updated May 16, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https:// www.mentalhealth.va.gov/mentalhealth/msthome/index.asp
7. Wang Z, Pukszta M. Private Rooms, Semi-open areas, or open areas for chemotherapy care: perspectives of cancer patients, families, and nursing staff. HERD. 2018;11(3):94- 108. doi:10.1177/1937586718758445
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vetdata /docs/specialreports/women_veterans_2015_final.pdf
9. Driscoll MA, Higgins DM, Seng EK, et al. Trauma, social support, family conflict, and chronic pain in recent service veterans: does gender matter? Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1101- 1111. doi:10.1111/pme.12744
10. Fox AB, Meyer EC, Vogt D. Attitudes about the VA healthcare setting, mental illness, and mental health treatment and their relationship with VA mental health service use among female and male OEF/OIF veterans. Psychol Serv. 2015;12(1):49-58. doi:10.1037/a0038269
11. Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(1):21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
12. Tseng J. Sex, gender, and why the differences matter. Virtual Mentor. 2008;10(7):427-428. doi:10.1001/virtualmentor.2008.10.7.fred1-0807
13. Booij JC, Zegers M, Evers PMPJ, Hendricks M, Delnoij DMJ, Rademakers JJDJM. Improving cancer patient care: development of a generic cancer consumer quality index questionnaire for cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(203). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-203
14. Meropol NJ, Egleston BL, Buzaglo JS, et al. Cancer patient preferences for quality and length of life. Cancer. 2008;113(12):3459-3466. doi:10.1002/cncr.23968 1
5. Schnur JB, Dillon MJ, Goldsmith RE, Montgomery GH. Cancer treatment experiences among survivors of childhood sexual abuse: a qualitative investigation of triggers and reactions to cumulative trauma. Palliat Support Care. 2018;16(6):767-776. doi:10.1017/S147895151700075X
16. Cadman L, Waller J, Ashdown-Barr L, Szarewski A. Barriers to cervical screening in women who have experienced sexual abuse: an exploratory study. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):214-220. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100378
17. Kelly S. The effects of childhood sexual abuse on women’s lives and their attitudes to cervical screening. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):212-213. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100418
18. McCloskey LA, Lichter E, Williams C, Gerber M, Wittenberg E, Ganz M. Assessing intimate partner violence in health care settings leads to women’s receipt of interventions and improved health. Public Health Rep. 2006;121(4):435-444. doi:10.1177/003335490612100412
1. Clarke SA, Booth L, Velikova G, Hewison J. Social support: gender differences in cancer patients in the United Kingdom. Cancer Nurs. 2006;29(1):66-72. doi:10.1097/00002820-200601000-00012
2. Wessels H, de Graeff A, Wynia K, et al. Gender-related needs and preferences in cancer care indicate the need for an individualized approach to cancer patients. Oncologist. 2010;15(6):648-655. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0337
3. Hartigan SM, Bonnet K, Chisholm L, et al. Why do women not use the bathroom? Women’s attitudes and beliefs on using public restrooms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):2053. doi:10.3390/ijerph17062053
4. Alexander K, Walters CB, Banerjee SC. Oncology patients’ preferences regarding sexual orientation and gender identity (SOGI) disclosure and room sharing sharing. Patient Educ Couns. 2020;103(5):1041-1048. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2019.12.006
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facts about sexual violence. Updated July 5, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/features /sexual-violence/index.html
6. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Military sexual trauma. Updated May 16, 2022. Accessed July 13, 2022. https:// www.mentalhealth.va.gov/mentalhealth/msthome/index.asp
7. Wang Z, Pukszta M. Private Rooms, Semi-open areas, or open areas for chemotherapy care: perspectives of cancer patients, families, and nursing staff. HERD. 2018;11(3):94- 108. doi:10.1177/1937586718758445
8. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. Women veterans report: the past, present, and future of women veterans. Accessed July 13, 2022. https://www.va.gov/vetdata /docs/specialreports/women_veterans_2015_final.pdf
9. Driscoll MA, Higgins DM, Seng EK, et al. Trauma, social support, family conflict, and chronic pain in recent service veterans: does gender matter? Pain Med. 2015;16(6):1101- 1111. doi:10.1111/pme.12744
10. Fox AB, Meyer EC, Vogt D. Attitudes about the VA healthcare setting, mental illness, and mental health treatment and their relationship with VA mental health service use among female and male OEF/OIF veterans. Psychol Serv. 2015;12(1):49-58. doi:10.1037/a0038269
11. Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(1):21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
12. Tseng J. Sex, gender, and why the differences matter. Virtual Mentor. 2008;10(7):427-428. doi:10.1001/virtualmentor.2008.10.7.fred1-0807
13. Booij JC, Zegers M, Evers PMPJ, Hendricks M, Delnoij DMJ, Rademakers JJDJM. Improving cancer patient care: development of a generic cancer consumer quality index questionnaire for cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(203). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-203
14. Meropol NJ, Egleston BL, Buzaglo JS, et al. Cancer patient preferences for quality and length of life. Cancer. 2008;113(12):3459-3466. doi:10.1002/cncr.23968 1
5. Schnur JB, Dillon MJ, Goldsmith RE, Montgomery GH. Cancer treatment experiences among survivors of childhood sexual abuse: a qualitative investigation of triggers and reactions to cumulative trauma. Palliat Support Care. 2018;16(6):767-776. doi:10.1017/S147895151700075X
16. Cadman L, Waller J, Ashdown-Barr L, Szarewski A. Barriers to cervical screening in women who have experienced sexual abuse: an exploratory study. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):214-220. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100378
17. Kelly S. The effects of childhood sexual abuse on women’s lives and their attitudes to cervical screening. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2012;38(4):212-213. doi:10.1136/jfprhc-2012-100418
18. McCloskey LA, Lichter E, Williams C, Gerber M, Wittenberg E, Ganz M. Assessing intimate partner violence in health care settings leads to women’s receipt of interventions and improved health. Public Health Rep. 2006;121(4):435-444. doi:10.1177/003335490612100412