User login
Profile of respiratory bacteria in children younger than 6 months
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
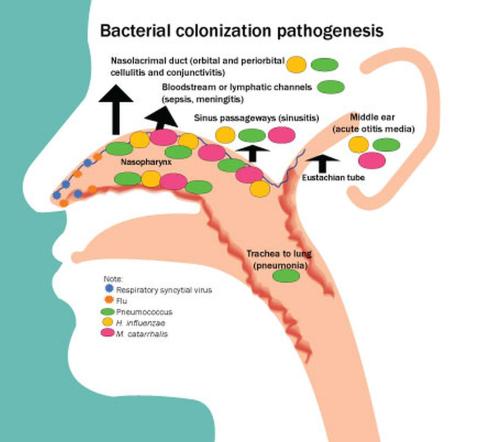
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
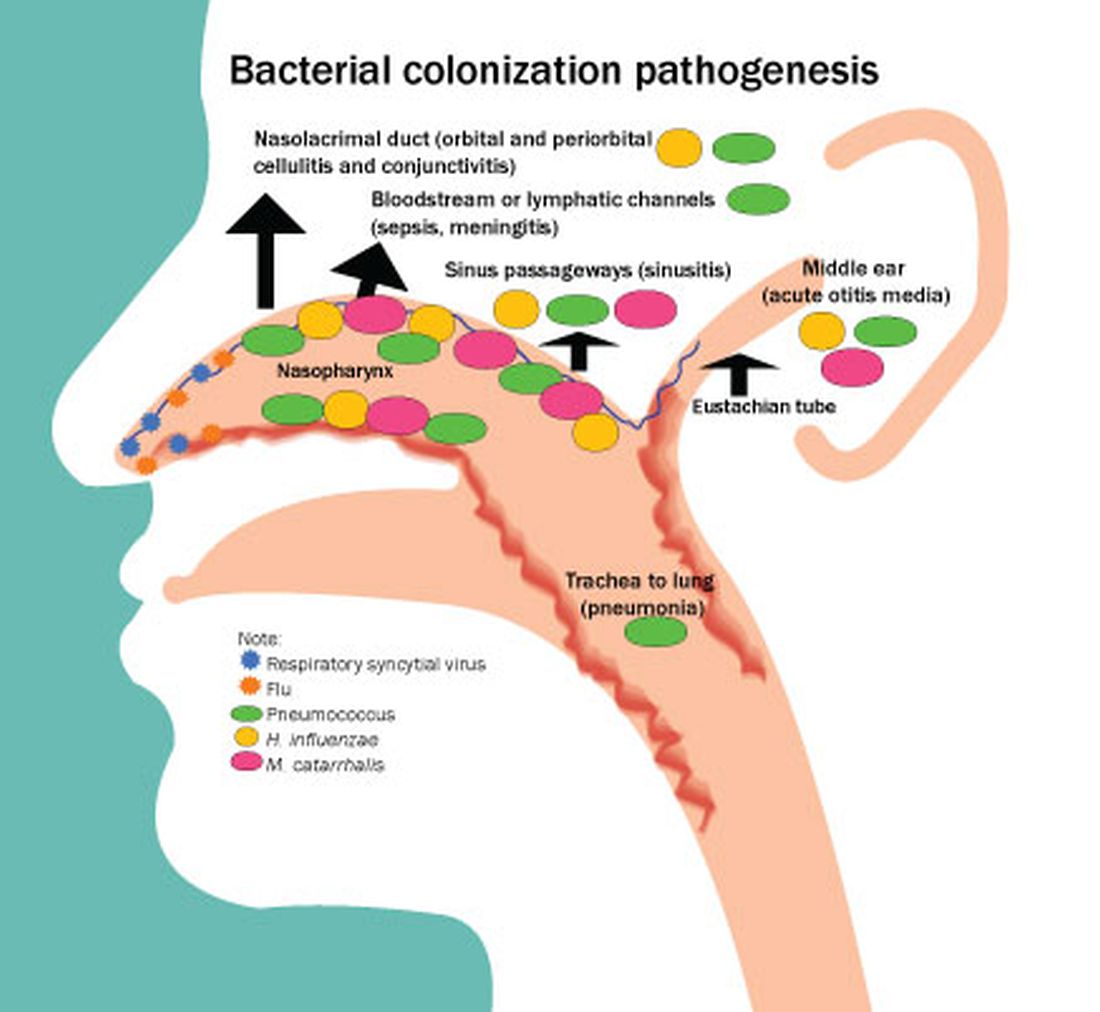
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
Wildfire smoke and air quality: How long could health effects last?
People with moderate to severe asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and other risk factors are used to checking air quality warnings before heading outside. But this situation is anything but typical.
Even people not normally at risk can have burning eyes, a runny nose, and a hard time breathing. These are among the symptoms to watch for as health effects of wildfire smoke. Special considerations should be made for people with heart disease, lung disease, and other conditions that put them at increased risk. Those affected can also have trouble sleeping, anxiety, and ongoing mental health issues.
The smoke will stick around the next few days, possibly clearing out early next week when the winds change direction, Weather Channel meteorologist Ari Sarsalari predicted June 8. But that doesn’t mean any physical or mental health effects will clear up as quickly.
“We are seeing dramatic increases in air pollution, and we are seeing increases in patients coming to the ED and the hospital. We expect that this will increase in the days ahead,” said Meredith McCormack, MD, MHS, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association.
“The air quality in our area – Baltimore – and other surrounding areas is not healthy for anyone,” said Dr. McCormack, who specializes in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
How serious are the health warnings?
Residents of California might be more familiar with the hazards of wildfire smoke, but this is a novel experience for many people along the East Coast. Air quality advisories are popping up on cellphones for people living in Boston, New York, and as far south as Northern Virginia. What should the estimated 75 million to 128 million affected Americans do?
We asked experts to weigh in on when it’s safe or not safe to spend time outside, when to seek medical help, and the best ways for people to protect themselves.
“It’s important to stay indoors and close all windows to reduce exposure to smoke from wildfires. It’s also essential to stay away from any windows that may not have a good seal, in order to minimize any potential exposure to smoke,” said Robert Glatter, MD, editor at large for Medscape Emergency Medicine and an emergency medicine doctor at Lenox Hill Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Dr. Glatter noted that placing moist towels under doors and sealing leaking windows can help.
Monitor your symptoms, and contact your doctor or go to urgent care, Dr. McCormack advised, if you see any increase in concerning symptoms. These include shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, or wheezing. Also make sure you take recommended medications and have enough on hand, she said.
Fine particles, big concerns
The weather is warming in many parts of the country, and that can mean air conditioning. Adding a MERV 13 filter to a central air conditioning system could reduce exposure to wildfire smoke. Using a portable indoor air purifier with a HEPA filter also can help people without central air conditioning. The filter can help remove small particles in the air but must be replaced regularly.
Smoke from wildfires contains multiple toxins, including heavy metals, carcinogens, and fine particulate matter (PM) under 2.5 microns. Dr. Glatter explained that these particles are about 100 times thinner than a human hair. Because of their size, they can embed deeper into the airways in the lungs and trigger chronic inflammation.
“This has also been linked to increased rates of lung cancer and brain tumors,” he said, based on a 2022 study in Canada.
The effects of smoke from wildfires can continue for many years. After the 2014 Hazelwood coal mine fire, emergency department visits for respiratory conditions and cardiovascular complaints remained higher for up to 2-5 years later, Dr. Glatter said. Again, large quantities of fine particulate matter in the smoke, less than 2.5 microns (PM 2.5), was to blame.
Exposure to smoke from wildfires during pregnancy has also been linked to abnormal fetal growth, preterm birth, as well as low birth weight, a January 2023 preprint on MedRxiv suggested.
Time to wear a mask again?
A properly fitted N95 mask will be the best approach to lessen exposure to smoke from wildfires, “but by itself cannot eliminate all of the risk,” Dr. Glatter said. Surgical masks can add minimal protection, and cloth masks will not provide any significant protection against the damaging effects of smoke from wildfires.
KN95 masks tend to be more comfortable to wear than N95s. But leakage often occurs that can make this type of protection less effective, Dr. Glatter said.
“Masks are important if you need to go outdoors,” Dr. McCormack said. Also, if you’re traveling by car, set the air conditioning system to recirculate to filter the air inside the vehicle, she recommended.
What does that number mean?
The federal government monitors air quality nationwide. In case you’re unfamiliar, the U.S. Air Quality Index includes a color-coded scale for ozone levels and particle pollution, the main concern from wildfire smoke. The lowest risk is the Green or satisfactory air quality category, where air pollution poses little or no risk, with an Index number from 0 to 50.
The index gets progressively more serious, from Yellow for moderate risk (51-100) up to a Maroon category, a hazardous range of 300 or higher on the index. When a Maroon advisory is issued, it means an emergency health warning where “everyone is more likely to be affected.”
How do you know if your outside air is polluted? Your local Air Quality Index (AQI) from the EPA can help. It’s a scale of 0 to 500, and the greater the number, the more harmful pollution in the air. It has six levels: good, moderate, unhealthy for sensitive groups, unhealthy, very unhealthy, and hazardous. You can find it at AirNow.gov.
New York is under an air quality alert until midnight Friday with a current “unhealthy” Index report of 200. The city recorded its worst-ever air quality on Wednesday. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation warns that fine particulate levels – small particles that can enter a person’s lungs – are the biggest concern.
AirNow.gov warns that western New England down to Washington has air quality in the three worst categories – ranging from unhealthy to very unhealthy and hazardous. The ten worst locations on the U.S. Air Quality Index as of 10 a.m. ET on June 8 include the Wilmington, Del., area with an Index of 241, or “very unhealthy.”
Other “very unhealthy” locations have the following Index readings:
- 244: Suburban Washington/Maryland.
- 252: Southern coastal New Jersey.
- 252: Kent County, Del.
- 270: Philadelphia.
- 291: Greater New Castle County, Del.
- 293: Northern Virginia.
- 293: Metropolitan Washington.
These two locations are in the “hazardous” or health emergency warning category:
- 309: Lehigh Valley, Pa.
- 399: Susquehanna Valley, Pa.
To check an air quality advisory in your area, enter your ZIP code at AirNow.gov.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People with moderate to severe asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and other risk factors are used to checking air quality warnings before heading outside. But this situation is anything but typical.
Even people not normally at risk can have burning eyes, a runny nose, and a hard time breathing. These are among the symptoms to watch for as health effects of wildfire smoke. Special considerations should be made for people with heart disease, lung disease, and other conditions that put them at increased risk. Those affected can also have trouble sleeping, anxiety, and ongoing mental health issues.
The smoke will stick around the next few days, possibly clearing out early next week when the winds change direction, Weather Channel meteorologist Ari Sarsalari predicted June 8. But that doesn’t mean any physical or mental health effects will clear up as quickly.
“We are seeing dramatic increases in air pollution, and we are seeing increases in patients coming to the ED and the hospital. We expect that this will increase in the days ahead,” said Meredith McCormack, MD, MHS, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association.
“The air quality in our area – Baltimore – and other surrounding areas is not healthy for anyone,” said Dr. McCormack, who specializes in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
How serious are the health warnings?
Residents of California might be more familiar with the hazards of wildfire smoke, but this is a novel experience for many people along the East Coast. Air quality advisories are popping up on cellphones for people living in Boston, New York, and as far south as Northern Virginia. What should the estimated 75 million to 128 million affected Americans do?
We asked experts to weigh in on when it’s safe or not safe to spend time outside, when to seek medical help, and the best ways for people to protect themselves.
“It’s important to stay indoors and close all windows to reduce exposure to smoke from wildfires. It’s also essential to stay away from any windows that may not have a good seal, in order to minimize any potential exposure to smoke,” said Robert Glatter, MD, editor at large for Medscape Emergency Medicine and an emergency medicine doctor at Lenox Hill Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Dr. Glatter noted that placing moist towels under doors and sealing leaking windows can help.
Monitor your symptoms, and contact your doctor or go to urgent care, Dr. McCormack advised, if you see any increase in concerning symptoms. These include shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, or wheezing. Also make sure you take recommended medications and have enough on hand, she said.
Fine particles, big concerns
The weather is warming in many parts of the country, and that can mean air conditioning. Adding a MERV 13 filter to a central air conditioning system could reduce exposure to wildfire smoke. Using a portable indoor air purifier with a HEPA filter also can help people without central air conditioning. The filter can help remove small particles in the air but must be replaced regularly.
Smoke from wildfires contains multiple toxins, including heavy metals, carcinogens, and fine particulate matter (PM) under 2.5 microns. Dr. Glatter explained that these particles are about 100 times thinner than a human hair. Because of their size, they can embed deeper into the airways in the lungs and trigger chronic inflammation.
“This has also been linked to increased rates of lung cancer and brain tumors,” he said, based on a 2022 study in Canada.
The effects of smoke from wildfires can continue for many years. After the 2014 Hazelwood coal mine fire, emergency department visits for respiratory conditions and cardiovascular complaints remained higher for up to 2-5 years later, Dr. Glatter said. Again, large quantities of fine particulate matter in the smoke, less than 2.5 microns (PM 2.5), was to blame.
Exposure to smoke from wildfires during pregnancy has also been linked to abnormal fetal growth, preterm birth, as well as low birth weight, a January 2023 preprint on MedRxiv suggested.
Time to wear a mask again?
A properly fitted N95 mask will be the best approach to lessen exposure to smoke from wildfires, “but by itself cannot eliminate all of the risk,” Dr. Glatter said. Surgical masks can add minimal protection, and cloth masks will not provide any significant protection against the damaging effects of smoke from wildfires.
KN95 masks tend to be more comfortable to wear than N95s. But leakage often occurs that can make this type of protection less effective, Dr. Glatter said.
“Masks are important if you need to go outdoors,” Dr. McCormack said. Also, if you’re traveling by car, set the air conditioning system to recirculate to filter the air inside the vehicle, she recommended.
What does that number mean?
The federal government monitors air quality nationwide. In case you’re unfamiliar, the U.S. Air Quality Index includes a color-coded scale for ozone levels and particle pollution, the main concern from wildfire smoke. The lowest risk is the Green or satisfactory air quality category, where air pollution poses little or no risk, with an Index number from 0 to 50.
The index gets progressively more serious, from Yellow for moderate risk (51-100) up to a Maroon category, a hazardous range of 300 or higher on the index. When a Maroon advisory is issued, it means an emergency health warning where “everyone is more likely to be affected.”
How do you know if your outside air is polluted? Your local Air Quality Index (AQI) from the EPA can help. It’s a scale of 0 to 500, and the greater the number, the more harmful pollution in the air. It has six levels: good, moderate, unhealthy for sensitive groups, unhealthy, very unhealthy, and hazardous. You can find it at AirNow.gov.
New York is under an air quality alert until midnight Friday with a current “unhealthy” Index report of 200. The city recorded its worst-ever air quality on Wednesday. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation warns that fine particulate levels – small particles that can enter a person’s lungs – are the biggest concern.
AirNow.gov warns that western New England down to Washington has air quality in the three worst categories – ranging from unhealthy to very unhealthy and hazardous. The ten worst locations on the U.S. Air Quality Index as of 10 a.m. ET on June 8 include the Wilmington, Del., area with an Index of 241, or “very unhealthy.”
Other “very unhealthy” locations have the following Index readings:
- 244: Suburban Washington/Maryland.
- 252: Southern coastal New Jersey.
- 252: Kent County, Del.
- 270: Philadelphia.
- 291: Greater New Castle County, Del.
- 293: Northern Virginia.
- 293: Metropolitan Washington.
These two locations are in the “hazardous” or health emergency warning category:
- 309: Lehigh Valley, Pa.
- 399: Susquehanna Valley, Pa.
To check an air quality advisory in your area, enter your ZIP code at AirNow.gov.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People with moderate to severe asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and other risk factors are used to checking air quality warnings before heading outside. But this situation is anything but typical.
Even people not normally at risk can have burning eyes, a runny nose, and a hard time breathing. These are among the symptoms to watch for as health effects of wildfire smoke. Special considerations should be made for people with heart disease, lung disease, and other conditions that put them at increased risk. Those affected can also have trouble sleeping, anxiety, and ongoing mental health issues.
The smoke will stick around the next few days, possibly clearing out early next week when the winds change direction, Weather Channel meteorologist Ari Sarsalari predicted June 8. But that doesn’t mean any physical or mental health effects will clear up as quickly.
“We are seeing dramatic increases in air pollution, and we are seeing increases in patients coming to the ED and the hospital. We expect that this will increase in the days ahead,” said Meredith McCormack, MD, MHS, a volunteer medical spokesperson for the American Lung Association.
“The air quality in our area – Baltimore – and other surrounding areas is not healthy for anyone,” said Dr. McCormack, who specializes in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
How serious are the health warnings?
Residents of California might be more familiar with the hazards of wildfire smoke, but this is a novel experience for many people along the East Coast. Air quality advisories are popping up on cellphones for people living in Boston, New York, and as far south as Northern Virginia. What should the estimated 75 million to 128 million affected Americans do?
We asked experts to weigh in on when it’s safe or not safe to spend time outside, when to seek medical help, and the best ways for people to protect themselves.
“It’s important to stay indoors and close all windows to reduce exposure to smoke from wildfires. It’s also essential to stay away from any windows that may not have a good seal, in order to minimize any potential exposure to smoke,” said Robert Glatter, MD, editor at large for Medscape Emergency Medicine and an emergency medicine doctor at Lenox Hill Hospital/Northwell Health in New York.
Dr. Glatter noted that placing moist towels under doors and sealing leaking windows can help.
Monitor your symptoms, and contact your doctor or go to urgent care, Dr. McCormack advised, if you see any increase in concerning symptoms. These include shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, or wheezing. Also make sure you take recommended medications and have enough on hand, she said.
Fine particles, big concerns
The weather is warming in many parts of the country, and that can mean air conditioning. Adding a MERV 13 filter to a central air conditioning system could reduce exposure to wildfire smoke. Using a portable indoor air purifier with a HEPA filter also can help people without central air conditioning. The filter can help remove small particles in the air but must be replaced regularly.
Smoke from wildfires contains multiple toxins, including heavy metals, carcinogens, and fine particulate matter (PM) under 2.5 microns. Dr. Glatter explained that these particles are about 100 times thinner than a human hair. Because of their size, they can embed deeper into the airways in the lungs and trigger chronic inflammation.
“This has also been linked to increased rates of lung cancer and brain tumors,” he said, based on a 2022 study in Canada.
The effects of smoke from wildfires can continue for many years. After the 2014 Hazelwood coal mine fire, emergency department visits for respiratory conditions and cardiovascular complaints remained higher for up to 2-5 years later, Dr. Glatter said. Again, large quantities of fine particulate matter in the smoke, less than 2.5 microns (PM 2.5), was to blame.
Exposure to smoke from wildfires during pregnancy has also been linked to abnormal fetal growth, preterm birth, as well as low birth weight, a January 2023 preprint on MedRxiv suggested.
Time to wear a mask again?
A properly fitted N95 mask will be the best approach to lessen exposure to smoke from wildfires, “but by itself cannot eliminate all of the risk,” Dr. Glatter said. Surgical masks can add minimal protection, and cloth masks will not provide any significant protection against the damaging effects of smoke from wildfires.
KN95 masks tend to be more comfortable to wear than N95s. But leakage often occurs that can make this type of protection less effective, Dr. Glatter said.
“Masks are important if you need to go outdoors,” Dr. McCormack said. Also, if you’re traveling by car, set the air conditioning system to recirculate to filter the air inside the vehicle, she recommended.
What does that number mean?
The federal government monitors air quality nationwide. In case you’re unfamiliar, the U.S. Air Quality Index includes a color-coded scale for ozone levels and particle pollution, the main concern from wildfire smoke. The lowest risk is the Green or satisfactory air quality category, where air pollution poses little or no risk, with an Index number from 0 to 50.
The index gets progressively more serious, from Yellow for moderate risk (51-100) up to a Maroon category, a hazardous range of 300 or higher on the index. When a Maroon advisory is issued, it means an emergency health warning where “everyone is more likely to be affected.”
How do you know if your outside air is polluted? Your local Air Quality Index (AQI) from the EPA can help. It’s a scale of 0 to 500, and the greater the number, the more harmful pollution in the air. It has six levels: good, moderate, unhealthy for sensitive groups, unhealthy, very unhealthy, and hazardous. You can find it at AirNow.gov.
New York is under an air quality alert until midnight Friday with a current “unhealthy” Index report of 200. The city recorded its worst-ever air quality on Wednesday. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation warns that fine particulate levels – small particles that can enter a person’s lungs – are the biggest concern.
AirNow.gov warns that western New England down to Washington has air quality in the three worst categories – ranging from unhealthy to very unhealthy and hazardous. The ten worst locations on the U.S. Air Quality Index as of 10 a.m. ET on June 8 include the Wilmington, Del., area with an Index of 241, or “very unhealthy.”
Other “very unhealthy” locations have the following Index readings:
- 244: Suburban Washington/Maryland.
- 252: Southern coastal New Jersey.
- 252: Kent County, Del.
- 270: Philadelphia.
- 291: Greater New Castle County, Del.
- 293: Northern Virginia.
- 293: Metropolitan Washington.
These two locations are in the “hazardous” or health emergency warning category:
- 309: Lehigh Valley, Pa.
- 399: Susquehanna Valley, Pa.
To check an air quality advisory in your area, enter your ZIP code at AirNow.gov.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Antibiotics for acute exacerbation of COPD: It’s still controversial
In late 2021, the Rome Proposal for diagnosing acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) and grading their severity was published. The 2023 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Report has adopted the Rome Proposal criteria. Given that an endorsement by GOLD is tantamount to acceptance by clinicians, researchers, and policymakers alike, I guess we’re all using them now.
Anyone who’s ever cared for patients with COPD knows that treatment and reduction of exacerbations is how we improve outcomes. AECOPD are associated with considerable morbidity, greater health care utilization and costs, and a long-term decline in lung function. While we hope our pharmacotherapies improve symptoms, we know they reduce AECOPD. If our pharmacotherapies have any impact on mortality, it’s probably via AECOPD prevention.
Since antibiotic indications are tied to severity, using the Rome Proposal criteria may affect management in unpredictable ways. As such, it’s worth reviewing the data on antibiotics for AECOPD.
What do the data reveal?
To start, it’s important to note that GOLD doesn’t equate having an AECOPD with needing an antibiotic. I myself have conflated the diagnosis with the indication and thereby overprescribed. The bar for diagnosis is quite low. In previous GOLD summaries, any “change in respiratory symptoms” would warrant the AECOPD label. Although the Rome Proposal definition is more specific, it leaves room for liberal interpretation. It’s likely to have a greater effect on research than on clinical practice. My guess is that AECOPD prevalence doesn’t change.
The antibiotic hurdle is slightly higher than that for diagnosis but is equally open to interpretation. In part, that’s related to the inherent subjectivity of judging symptoms, sputum production, and changes in color, but it’s also because the data are so poor. The meta-analyses that have been used to establish the indications include fewer than 1000 patients spread across 10 to 11 trials. Thus, the individual trials are small, and the sample size remains nominal even after adding them together. The addition of antibiotics – and it doesn’t seem to matter which class, type, or duration – will decrease mortality and hospital length of stay. One study says these effects are limited to inpatients while the other does not. After reading GOLD 2013, GOLD 2023, and both the meta-analyses they used to support their recommendations, I’m still not sure who benefits. Do you have to be hospitalized? Is some sort of ventilatory support required? Does C-reactive protein help or not?
In accordance with the classic Anthonisen criteria, GOLD relies on sputum volume and color as evidence of a bacterial infection. Soon after GOLD 2023 was published, a meta-analysis found that sputum color isn’t particularly accurate for detecting bacterial infection. Because it doesn’t seem to matter which antibiotic class is used, I always thought we were using antibiotics for their magical, pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects anyway. I didn’t think the presence of an actual bacterial infection was important. If I saw an infiltrate on chest x-ray, I’d change my diagnosis from AECOPD to community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and switch to CAP coverage. I’ve been doing this so long that I swear it’s in a guideline somewhere, though admittedly I couldn’t find said guideline while reading for this piece.
Key takeaways
In summary, I believe that the guidance reflects the data, which is muddy. The Rome Proposal should be seen as just that – a framework for moving forward with AECOPD classification and antibiotic indications that will need to be refined over time as better data become available. In fact, they allow for a more objective, point-of-care assessment of severity that can be validated and tied to antibiotic benefits. The Rome criteria aren’t evidence-based; they’re a necessary first step toward creating the evidence.
In the meantime, if your AECOPD patients are hospitalized, they probably warrant an antibiotic. If they’re not, sputum changes may be a reasonable surrogate for a bacterial infection. Considerable uncertainty remains.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is a professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In late 2021, the Rome Proposal for diagnosing acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) and grading their severity was published. The 2023 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Report has adopted the Rome Proposal criteria. Given that an endorsement by GOLD is tantamount to acceptance by clinicians, researchers, and policymakers alike, I guess we’re all using them now.
Anyone who’s ever cared for patients with COPD knows that treatment and reduction of exacerbations is how we improve outcomes. AECOPD are associated with considerable morbidity, greater health care utilization and costs, and a long-term decline in lung function. While we hope our pharmacotherapies improve symptoms, we know they reduce AECOPD. If our pharmacotherapies have any impact on mortality, it’s probably via AECOPD prevention.
Since antibiotic indications are tied to severity, using the Rome Proposal criteria may affect management in unpredictable ways. As such, it’s worth reviewing the data on antibiotics for AECOPD.
What do the data reveal?
To start, it’s important to note that GOLD doesn’t equate having an AECOPD with needing an antibiotic. I myself have conflated the diagnosis with the indication and thereby overprescribed. The bar for diagnosis is quite low. In previous GOLD summaries, any “change in respiratory symptoms” would warrant the AECOPD label. Although the Rome Proposal definition is more specific, it leaves room for liberal interpretation. It’s likely to have a greater effect on research than on clinical practice. My guess is that AECOPD prevalence doesn’t change.
The antibiotic hurdle is slightly higher than that for diagnosis but is equally open to interpretation. In part, that’s related to the inherent subjectivity of judging symptoms, sputum production, and changes in color, but it’s also because the data are so poor. The meta-analyses that have been used to establish the indications include fewer than 1000 patients spread across 10 to 11 trials. Thus, the individual trials are small, and the sample size remains nominal even after adding them together. The addition of antibiotics – and it doesn’t seem to matter which class, type, or duration – will decrease mortality and hospital length of stay. One study says these effects are limited to inpatients while the other does not. After reading GOLD 2013, GOLD 2023, and both the meta-analyses they used to support their recommendations, I’m still not sure who benefits. Do you have to be hospitalized? Is some sort of ventilatory support required? Does C-reactive protein help or not?
In accordance with the classic Anthonisen criteria, GOLD relies on sputum volume and color as evidence of a bacterial infection. Soon after GOLD 2023 was published, a meta-analysis found that sputum color isn’t particularly accurate for detecting bacterial infection. Because it doesn’t seem to matter which antibiotic class is used, I always thought we were using antibiotics for their magical, pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects anyway. I didn’t think the presence of an actual bacterial infection was important. If I saw an infiltrate on chest x-ray, I’d change my diagnosis from AECOPD to community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and switch to CAP coverage. I’ve been doing this so long that I swear it’s in a guideline somewhere, though admittedly I couldn’t find said guideline while reading for this piece.
Key takeaways
In summary, I believe that the guidance reflects the data, which is muddy. The Rome Proposal should be seen as just that – a framework for moving forward with AECOPD classification and antibiotic indications that will need to be refined over time as better data become available. In fact, they allow for a more objective, point-of-care assessment of severity that can be validated and tied to antibiotic benefits. The Rome criteria aren’t evidence-based; they’re a necessary first step toward creating the evidence.
In the meantime, if your AECOPD patients are hospitalized, they probably warrant an antibiotic. If they’re not, sputum changes may be a reasonable surrogate for a bacterial infection. Considerable uncertainty remains.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is a professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In late 2021, the Rome Proposal for diagnosing acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) and grading their severity was published. The 2023 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) Report has adopted the Rome Proposal criteria. Given that an endorsement by GOLD is tantamount to acceptance by clinicians, researchers, and policymakers alike, I guess we’re all using them now.
Anyone who’s ever cared for patients with COPD knows that treatment and reduction of exacerbations is how we improve outcomes. AECOPD are associated with considerable morbidity, greater health care utilization and costs, and a long-term decline in lung function. While we hope our pharmacotherapies improve symptoms, we know they reduce AECOPD. If our pharmacotherapies have any impact on mortality, it’s probably via AECOPD prevention.
Since antibiotic indications are tied to severity, using the Rome Proposal criteria may affect management in unpredictable ways. As such, it’s worth reviewing the data on antibiotics for AECOPD.
What do the data reveal?
To start, it’s important to note that GOLD doesn’t equate having an AECOPD with needing an antibiotic. I myself have conflated the diagnosis with the indication and thereby overprescribed. The bar for diagnosis is quite low. In previous GOLD summaries, any “change in respiratory symptoms” would warrant the AECOPD label. Although the Rome Proposal definition is more specific, it leaves room for liberal interpretation. It’s likely to have a greater effect on research than on clinical practice. My guess is that AECOPD prevalence doesn’t change.
The antibiotic hurdle is slightly higher than that for diagnosis but is equally open to interpretation. In part, that’s related to the inherent subjectivity of judging symptoms, sputum production, and changes in color, but it’s also because the data are so poor. The meta-analyses that have been used to establish the indications include fewer than 1000 patients spread across 10 to 11 trials. Thus, the individual trials are small, and the sample size remains nominal even after adding them together. The addition of antibiotics – and it doesn’t seem to matter which class, type, or duration – will decrease mortality and hospital length of stay. One study says these effects are limited to inpatients while the other does not. After reading GOLD 2013, GOLD 2023, and both the meta-analyses they used to support their recommendations, I’m still not sure who benefits. Do you have to be hospitalized? Is some sort of ventilatory support required? Does C-reactive protein help or not?
In accordance with the classic Anthonisen criteria, GOLD relies on sputum volume and color as evidence of a bacterial infection. Soon after GOLD 2023 was published, a meta-analysis found that sputum color isn’t particularly accurate for detecting bacterial infection. Because it doesn’t seem to matter which antibiotic class is used, I always thought we were using antibiotics for their magical, pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects anyway. I didn’t think the presence of an actual bacterial infection was important. If I saw an infiltrate on chest x-ray, I’d change my diagnosis from AECOPD to community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and switch to CAP coverage. I’ve been doing this so long that I swear it’s in a guideline somewhere, though admittedly I couldn’t find said guideline while reading for this piece.
Key takeaways
In summary, I believe that the guidance reflects the data, which is muddy. The Rome Proposal should be seen as just that – a framework for moving forward with AECOPD classification and antibiotic indications that will need to be refined over time as better data become available. In fact, they allow for a more objective, point-of-care assessment of severity that can be validated and tied to antibiotic benefits. The Rome criteria aren’t evidence-based; they’re a necessary first step toward creating the evidence.
In the meantime, if your AECOPD patients are hospitalized, they probably warrant an antibiotic. If they’re not, sputum changes may be a reasonable surrogate for a bacterial infection. Considerable uncertainty remains.
Aaron B. Holley, MD, is a professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University in Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He reported conflicts of interest with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The enemy of carcinogenic fumes is my friendly begonia
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
Sowing the seeds of cancer prevention
Are you looking to add to your quality of life, even though pets are not your speed? Might we suggest something with lower maintenance? Something a little greener?
Indoor plants can purify the air that comes from outside. Researchers at the University of Technology Sydney, in partnership with the plantscaping company Ambius, showed that a “green wall” made up of mixed indoor plants was able to suck up 97% of “the most toxic compounds” from the air in just 8 hours. We’re talking about lung-irritating, headache-inducing, cancer risk–boosting compounds from gasoline fumes, including benzene.
Public health initiatives often strive to reduce cardiovascular and obesity risks, but breathing seems pretty important too. According to the World Health Organization, household air pollution is responsible for about 2.5 million global premature deaths each year. And since 2020 we’ve become accustomed to spending more time inside and at home.
“This new research proves that plants should not just be seen as ‘nice to have,’ but rather a crucial part of every workplace wellness plan,” Ambius General Manager Johan Hodgson said in statement released by the university.
So don’t spend hundreds of dollars on a fancy air filtration system when a wall of plants can do that for next to nothing. Find what works for you and your space and become a plant parent today! Your lungs will thank you.
But officer, I had to swerve to miss the duodenal ampulla
Tiny video capsule endoscopes have been around for many years, but they have one big weakness: The ingestible cameras’ journey through the GI tract is passively driven by gravity and the natural movement of the body, so they often miss potential problem areas.
Not anymore. That flaw has been addressed by medical technology company AnX Robotica, which has taken endoscopy to the next level by adding that wondrous directional control device of the modern electronic age, a joystick.
The new system “uses an external magnet and hand-held video game style joysticks to move the capsule in three dimensions,” which allows physicians to “remotely drive a miniature video capsule to all regions of the stomach to visualize and photograph potential problem areas,” according to Andrew C. Meltzer, MD, of George Washington University and associates, who conducted a pilot study funded by AnX Robotica.
The video capsule provided a 95% rate of visualization in the stomachs of 40 patients who were examined at a medical office building by an emergency medicine physician who had no previous specialty training in endoscopy. “Capsules were driven by the ER physician and then the study reports were reviewed by an attending gastroenterologist who was physically off site,” the investigators said in a written statement.
The capsule operator did receive some additional training, and development of artificial intelligence to self-drive the capsule is in the works, but for now, we’re talking about a device controlled by a human using a joystick. And we all know that 50-year-olds are not especially known for their joystick skills. For that we need real experts. Yup, we need to put those joystick-controlled capsule endoscopes in the hands of teenage gamers. Who wants to go first?
Maybe AI isn’t ready for the big time after all
“How long before some intrepid stockholder says: ‘Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?’ ” Those words appeared on LOTME but a month ago. After all, the AI is supposed to be smarter and more empathetic than a doctor. And did we mention it’s free? Or at least extremely cheap. Cheaper than, say, a group of recently unionized health care workers.
In early May, the paid employees manning the National Eating Disorders Association emergency hotline voted to unionize, as they felt overwhelmed and underpaid. Apparently, paying six people an extra few thousand a year was too much for NEDA’s leadership, as they decided a few weeks later to fire those workers, fully closing down the hotline. Instead of talking to a real person, people “calling in” for support would be met with Tessa, a wellness chatbot that would hopefully guide them through their crisis. Key word, hopefully.
In perhaps the least surprising twist of the year, NEDA was forced to walk back its decision about a week after its initial announcement. It all started with a viral Instagram post from a woman who called in and received the following advice from Tessa: Lose 1-2 pounds a week, count calories and work for a 500- to 1,000-calorie deficit, weigh herself weekly, and restrict her diet. Unfortunately, all of these suggestions were things that led to the development of the woman’s eating disorder.
Naturally, NEDA responded in good grace, accusing the woman of lying. A NEDA vice president even left some nasty comments on the post, but hastily deleted them a day later when NEDA announced it was shutting down Tessa “until further notice for a complete investigation.” NEDA’s CEO insisted they hadn’t seen that behavior from Tessa before, calling it a “bug” and insisting the bot would only be down temporarily until the triggers causing the bug were fixed.
In the aftermath, several doctors and psychologists chimed in, terming the rush to automate human roles dangerous and risky. After all, much of what makes these hotlines effective is the volunteers speaking from their own experience. An unsupervised bot doesn’t seem to have what it takes to deal with a mental health crisis, but we’re betting that Tessa will be back. As a wise cephalopod once said: Nobody gives a care about the fate of labor as long as they can get their instant gratification.
You can’t spell existential without s-t-e-n-t
This week, we’re including a special “bonus” item that, to be honest, has nothing to do with stents. That’s why our editor is making us call this a “bonus” (and making us use quote marks, too): It doesn’t really have anything to do with stents or health care or those who practice health care. Actually, his exact words were, “You can’t just give the readers someone else’s ****ing list and expect to get paid for it.” Did we mention that he looks like Jack Nicklaus but acts like BoJack Horseman?
Anywaaay, we’re pretty sure that the list in question – “America’s Top 10 Most Googled Existential Questions” – says something about the human condition, just not about stents:
1. Why is the sky blue?
2. What do dreams mean?
3. What is the meaning of life?
4. Why am I so tired?
5. Who am I?
6. What is love?
7. Is a hot dog a sandwich?
8. What came first, the chicken or the egg?
9. What should I do?
10. Do animals have souls?
ILD risk elevated in RA, PsA after starting biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs
MILAN – Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who are using biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) have fivefold higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than does the general population, according to the first study to explore risk of ILD in this particular patient group.
The study also found 10-fold higher risk of ILD in patients with RA who were starting a b/tsDMARD, compared with the general population, while the addition of methotrexate did not appear to be associated with increased risk for ILD in either RA nor PsA.
Sella Aarrestad Provan, MD, of the Center for Treatment of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases at Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, presented the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Explaining the motivation for the study, Dr. Aarrestad Provan said that, in RA, methotrexate’s role in ILD development remained unclear, while some small studies linked b/tsDMARDs with risk for ILD. “In PsA, very few studies have explored the risk of ILD, and no systematic studies have looked at ILD risk factors in this disease.”
The researchers analyzed patient data from hospital and death registries across five Nordic countries (Denmark, Norway, Finland, Iceland, and Sweden) and compared them with general population controls. They calculated risk ratios for people who developed ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD (with or without methotrexate).
A total of 37,010 patients with RA, 12,341 with PsA, and 569,451 members of the general population were included in the analysis, with respective disease durations of 10 and 8.9 years. Methotrexate was used along with b/tsDMARDs in 49% of patients with RA and 41% with PsA, and most patients were already on methotrexate when b/tsDMARDs were started. The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor etanercept (Enbrel) was the most commonly used b/tsDMARD in both RA and PsA, followed by infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) and adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars).
The incidence of ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD was 0.8% in patients with RA, 0.2% with PsA, and 0.1% in the general population, and these findings generated hazard ratios of 10.1 (95% confidence interval, 8.6-11.9) for RA and 5.0 (95% CI, 3.4-7.4) for PsA, compared with the general population as reference.
When the risk for ILD was explored according to methotrexate use in RA patients, “there was no signal of increased risk across patients using methotrexate,” Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported. When risk of ILD was explored according to b/tsDMARD use in RA patients, a signal of increased risk was observed with rituximab, she noted, “but upon adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities, this association was no longer significant, but was still numerically increased.”
Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, vice principal, professor of rheumatology, and head of the College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences at the University of Glasgow, remarked that he “loves results that are unexpected” and thanked the researcher for such an “important study.”
“For years, we’ve been interested in the potential for DMARDs to impact interstitial lung disease, with potential that drugs could make it worse, or better,” he said. “This study is wonderful and novel because first of all, there hasn’t, until now, been a direct comparison between RA and PsA in quite this way, and secondly, we haven’t really assessed whether there is a drug-related risk in PsA. Note that drug related does not necessarily imply causality.”
Regarding mechanisms, Dr. McInnes added that “epidemiologic studies suggest that PsA often coexists with the presence of cardiometabolic syndrome and obesity, which has a higher prevalence in PsA than in RA. Obesity is also related to ILD. As such, it begs the question of whether cardiometabolic, diabetes, or obesity-related features may give us a clue as to what is going on in these PsA patients.”
The research was supported by NordForsk and FOREUM. Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported serving as a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis and receiving grant/research support from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. McInnes declared no disclosures relevant to this study.
MILAN – Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who are using biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) have fivefold higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than does the general population, according to the first study to explore risk of ILD in this particular patient group.
The study also found 10-fold higher risk of ILD in patients with RA who were starting a b/tsDMARD, compared with the general population, while the addition of methotrexate did not appear to be associated with increased risk for ILD in either RA nor PsA.
Sella Aarrestad Provan, MD, of the Center for Treatment of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases at Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, presented the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Explaining the motivation for the study, Dr. Aarrestad Provan said that, in RA, methotrexate’s role in ILD development remained unclear, while some small studies linked b/tsDMARDs with risk for ILD. “In PsA, very few studies have explored the risk of ILD, and no systematic studies have looked at ILD risk factors in this disease.”
The researchers analyzed patient data from hospital and death registries across five Nordic countries (Denmark, Norway, Finland, Iceland, and Sweden) and compared them with general population controls. They calculated risk ratios for people who developed ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD (with or without methotrexate).
A total of 37,010 patients with RA, 12,341 with PsA, and 569,451 members of the general population were included in the analysis, with respective disease durations of 10 and 8.9 years. Methotrexate was used along with b/tsDMARDs in 49% of patients with RA and 41% with PsA, and most patients were already on methotrexate when b/tsDMARDs were started. The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor etanercept (Enbrel) was the most commonly used b/tsDMARD in both RA and PsA, followed by infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) and adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars).
The incidence of ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD was 0.8% in patients with RA, 0.2% with PsA, and 0.1% in the general population, and these findings generated hazard ratios of 10.1 (95% confidence interval, 8.6-11.9) for RA and 5.0 (95% CI, 3.4-7.4) for PsA, compared with the general population as reference.
When the risk for ILD was explored according to methotrexate use in RA patients, “there was no signal of increased risk across patients using methotrexate,” Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported. When risk of ILD was explored according to b/tsDMARD use in RA patients, a signal of increased risk was observed with rituximab, she noted, “but upon adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities, this association was no longer significant, but was still numerically increased.”
Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, vice principal, professor of rheumatology, and head of the College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences at the University of Glasgow, remarked that he “loves results that are unexpected” and thanked the researcher for such an “important study.”
“For years, we’ve been interested in the potential for DMARDs to impact interstitial lung disease, with potential that drugs could make it worse, or better,” he said. “This study is wonderful and novel because first of all, there hasn’t, until now, been a direct comparison between RA and PsA in quite this way, and secondly, we haven’t really assessed whether there is a drug-related risk in PsA. Note that drug related does not necessarily imply causality.”
Regarding mechanisms, Dr. McInnes added that “epidemiologic studies suggest that PsA often coexists with the presence of cardiometabolic syndrome and obesity, which has a higher prevalence in PsA than in RA. Obesity is also related to ILD. As such, it begs the question of whether cardiometabolic, diabetes, or obesity-related features may give us a clue as to what is going on in these PsA patients.”
The research was supported by NordForsk and FOREUM. Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported serving as a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis and receiving grant/research support from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. McInnes declared no disclosures relevant to this study.
MILAN – Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who are using biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) have fivefold higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than does the general population, according to the first study to explore risk of ILD in this particular patient group.
The study also found 10-fold higher risk of ILD in patients with RA who were starting a b/tsDMARD, compared with the general population, while the addition of methotrexate did not appear to be associated with increased risk for ILD in either RA nor PsA.
Sella Aarrestad Provan, MD, of the Center for Treatment of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases at Diakonhjemmet Hospital, Oslo, presented the results at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Explaining the motivation for the study, Dr. Aarrestad Provan said that, in RA, methotrexate’s role in ILD development remained unclear, while some small studies linked b/tsDMARDs with risk for ILD. “In PsA, very few studies have explored the risk of ILD, and no systematic studies have looked at ILD risk factors in this disease.”
The researchers analyzed patient data from hospital and death registries across five Nordic countries (Denmark, Norway, Finland, Iceland, and Sweden) and compared them with general population controls. They calculated risk ratios for people who developed ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD (with or without methotrexate).
A total of 37,010 patients with RA, 12,341 with PsA, and 569,451 members of the general population were included in the analysis, with respective disease durations of 10 and 8.9 years. Methotrexate was used along with b/tsDMARDs in 49% of patients with RA and 41% with PsA, and most patients were already on methotrexate when b/tsDMARDs were started. The tumor necrosis factor inhibitor etanercept (Enbrel) was the most commonly used b/tsDMARD in both RA and PsA, followed by infliximab (Remicade and biosimilars) and adalimumab (Humira and biosimilars).
The incidence of ILD within 5 years of starting a b/tsDMARD was 0.8% in patients with RA, 0.2% with PsA, and 0.1% in the general population, and these findings generated hazard ratios of 10.1 (95% confidence interval, 8.6-11.9) for RA and 5.0 (95% CI, 3.4-7.4) for PsA, compared with the general population as reference.
When the risk for ILD was explored according to methotrexate use in RA patients, “there was no signal of increased risk across patients using methotrexate,” Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported. When risk of ILD was explored according to b/tsDMARD use in RA patients, a signal of increased risk was observed with rituximab, she noted, “but upon adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities, this association was no longer significant, but was still numerically increased.”
Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, vice principal, professor of rheumatology, and head of the College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences at the University of Glasgow, remarked that he “loves results that are unexpected” and thanked the researcher for such an “important study.”
“For years, we’ve been interested in the potential for DMARDs to impact interstitial lung disease, with potential that drugs could make it worse, or better,” he said. “This study is wonderful and novel because first of all, there hasn’t, until now, been a direct comparison between RA and PsA in quite this way, and secondly, we haven’t really assessed whether there is a drug-related risk in PsA. Note that drug related does not necessarily imply causality.”
Regarding mechanisms, Dr. McInnes added that “epidemiologic studies suggest that PsA often coexists with the presence of cardiometabolic syndrome and obesity, which has a higher prevalence in PsA than in RA. Obesity is also related to ILD. As such, it begs the question of whether cardiometabolic, diabetes, or obesity-related features may give us a clue as to what is going on in these PsA patients.”
The research was supported by NordForsk and FOREUM. Dr. Aarrestad Provan reported serving as a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Novartis and receiving grant/research support from Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. McInnes declared no disclosures relevant to this study.
AT EULAR 2023
Endobronchial valves: Sustained improvement in emphysema
WASHINGTON – based on data from 174 individuals.
One-way endobronchial valves demonstrated benefits for patients with severe emphysema over a 12-month period in the EMPROVE trial, according to Gerard J. Criner, MD, of Temple University, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Five-year results from the EMPROVE study were presented in a poster session at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
The initial EMPROVE trial demonstrated safety and efficacy of the Spiration Valve System (SVS) over 12 months. However, data on the long-term benefits of one-way endobronchial values are limited, the researchers wrote.
The valve was designed for use in selected areas of the bronchial airways and features a flexible umbrella that allows air and mucus to clear from treated airways while blocking inspired air flow to areas of the lungs affected by disease, the researchers explained in the poster.
Dr. Criner and colleagues assessed 172 patients who were randomly assigned to treatment with a one-way valve system (113 patients) or a control group (59 patients).
Participants were evaluated at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, then annually for 5 years.
The primary efficacy outcome was lung function, measured by forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1). At five years, the FEV1 values improved by 0.1098 liters in the treatment group (P < .001). Treated patients and controls experienced decreased FEV1 at a rate of 0.0440 liters per year from baseline, a significant difference (P < .001). Assuming a steady rate of disease progression, “the treatment group gained approximately 2.5 years of FEV1 improvement immediately following SVS treatment, which was maintained, compared to controls,” the researchers noted in their abstract.
Serious adverse events were assessed from 6 months to 5 years (352.7 patient-years) for treated patients and from 6 months to 2 years (72.9 patient-years) for controls.
Overall, 210 SAEs occurred in the treatment group and 35 occurred in controls, for rates of 0.60 and 0.48, respectively (P = .201). The most common SAEs in the treatment and control groups were COPD exacerbations, pneumothorax, and death.
The results suggest that the FEV1 improvements seen in patients with severe emphysema after one-way endobronchial value placement compared with usual care are enduring after 5 years, with no significant changes in safety, the researchers concluded.
The original EMPROVE study was supported by Olympus Respiratory America, a part of Olympus Corporation and the developer of the Spiration Valve System. Results of the original study were published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Criner is associate editor of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. His participation complies with American Thoracic Society requirements for recusal from review and decisions for authored works.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – based on data from 174 individuals.
One-way endobronchial valves demonstrated benefits for patients with severe emphysema over a 12-month period in the EMPROVE trial, according to Gerard J. Criner, MD, of Temple University, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Five-year results from the EMPROVE study were presented in a poster session at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
The initial EMPROVE trial demonstrated safety and efficacy of the Spiration Valve System (SVS) over 12 months. However, data on the long-term benefits of one-way endobronchial values are limited, the researchers wrote.
The valve was designed for use in selected areas of the bronchial airways and features a flexible umbrella that allows air and mucus to clear from treated airways while blocking inspired air flow to areas of the lungs affected by disease, the researchers explained in the poster.
Dr. Criner and colleagues assessed 172 patients who were randomly assigned to treatment with a one-way valve system (113 patients) or a control group (59 patients).
Participants were evaluated at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, then annually for 5 years.
The primary efficacy outcome was lung function, measured by forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1). At five years, the FEV1 values improved by 0.1098 liters in the treatment group (P < .001). Treated patients and controls experienced decreased FEV1 at a rate of 0.0440 liters per year from baseline, a significant difference (P < .001). Assuming a steady rate of disease progression, “the treatment group gained approximately 2.5 years of FEV1 improvement immediately following SVS treatment, which was maintained, compared to controls,” the researchers noted in their abstract.
Serious adverse events were assessed from 6 months to 5 years (352.7 patient-years) for treated patients and from 6 months to 2 years (72.9 patient-years) for controls.
Overall, 210 SAEs occurred in the treatment group and 35 occurred in controls, for rates of 0.60 and 0.48, respectively (P = .201). The most common SAEs in the treatment and control groups were COPD exacerbations, pneumothorax, and death.
The results suggest that the FEV1 improvements seen in patients with severe emphysema after one-way endobronchial value placement compared with usual care are enduring after 5 years, with no significant changes in safety, the researchers concluded.
The original EMPROVE study was supported by Olympus Respiratory America, a part of Olympus Corporation and the developer of the Spiration Valve System. Results of the original study were published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Criner is associate editor of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. His participation complies with American Thoracic Society requirements for recusal from review and decisions for authored works.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – based on data from 174 individuals.
One-way endobronchial valves demonstrated benefits for patients with severe emphysema over a 12-month period in the EMPROVE trial, according to Gerard J. Criner, MD, of Temple University, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Five-year results from the EMPROVE study were presented in a poster session at the American Thoracic Society’s international conference.
The initial EMPROVE trial demonstrated safety and efficacy of the Spiration Valve System (SVS) over 12 months. However, data on the long-term benefits of one-way endobronchial values are limited, the researchers wrote.
The valve was designed for use in selected areas of the bronchial airways and features a flexible umbrella that allows air and mucus to clear from treated airways while blocking inspired air flow to areas of the lungs affected by disease, the researchers explained in the poster.
Dr. Criner and colleagues assessed 172 patients who were randomly assigned to treatment with a one-way valve system (113 patients) or a control group (59 patients).
Participants were evaluated at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, then annually for 5 years.
The primary efficacy outcome was lung function, measured by forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1). At five years, the FEV1 values improved by 0.1098 liters in the treatment group (P < .001). Treated patients and controls experienced decreased FEV1 at a rate of 0.0440 liters per year from baseline, a significant difference (P < .001). Assuming a steady rate of disease progression, “the treatment group gained approximately 2.5 years of FEV1 improvement immediately following SVS treatment, which was maintained, compared to controls,” the researchers noted in their abstract.
Serious adverse events were assessed from 6 months to 5 years (352.7 patient-years) for treated patients and from 6 months to 2 years (72.9 patient-years) for controls.
Overall, 210 SAEs occurred in the treatment group and 35 occurred in controls, for rates of 0.60 and 0.48, respectively (P = .201). The most common SAEs in the treatment and control groups were COPD exacerbations, pneumothorax, and death.
The results suggest that the FEV1 improvements seen in patients with severe emphysema after one-way endobronchial value placement compared with usual care are enduring after 5 years, with no significant changes in safety, the researchers concluded.
The original EMPROVE study was supported by Olympus Respiratory America, a part of Olympus Corporation and the developer of the Spiration Valve System. Results of the original study were published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Dr. Criner is associate editor of the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. His participation complies with American Thoracic Society requirements for recusal from review and decisions for authored works.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ATS 2023
Fatigue is a monster for patients with pulmonary disease
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Study of hospitalizations in Canada quantifies benefit of COVID-19 vaccine to reduce death, ICU admissions
A cohort study of more than 1.5 million hospital admissions in Canada through the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic has quantified the benefit of vaccinations. Unvaccinated patients were found to be up to 15 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than fully vaccinated patients.
Investigators analyzed 1.513 million admissions at 155 hospitals across Canada from March 15, 2020, to May 28, 2022. The study included 51,679 adult admissions and 4,035 pediatric admissions for COVID-19. Although the share of COVID-19 admissions increased in the fifth and sixth waves, from Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022 – after the full vaccine rollout – to 7.73% from 2.47% in the previous four waves, the proportion of adults admitted to the intensive care unit was significantly lower, at 8.7% versus 21.8% (odds ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.32-0.36).
“The good thing about waves five and six was we were able to show the COVID cases tended to be less severe, but on the other hand, because the disease in the community was so much higher, the demands on the health care system were much higher than the previous waves,” study author Charles Frenette, MD, director of infection prevention and control at McGill University, Montreal, and chair of the study’s adult subgroup, said in an interview. “But here we were able to show the benefit of vaccinations, particularly the boosting dose, in protecting against those severe outcomes.”
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, used the Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program database, which collects hospital data across Canada. It was activated in March 2020 to collect details on all COVID-19 admissions, co-author Nisha Thampi, MD, chair of the study’s pediatric subgroup, told this news organization.
“We’re now over 3 years into the pandemic, and CNISP continues to monitor COVID-19 as well as other pathogens in near real time,” said Dr. Thampi, an associate professor and infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario.
“That’s a particular strength of this surveillance program as well. We would see this data on a biweekly basis, and that allows for [us] to implement timely protection and action.”
Tracing trends over six waves
The study tracked COVID-19 hospitalizations during six waves. The first lasted from March 15 to August 31, 2020, and the second lasted from Sept. 1, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021. The wild-type variant was dominant during both waves. The third wave lasted from March 1 to June 30, 2021, and was marked by the mixed Alpha, Beta, and Gamma variants. The fourth wave lasted from July 1 to Dec. 25, 2021, when the Alpha variant was dominant. The Omicron variant dominated during waves five (Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022) and six (March 20 to May 28, 2022).
Hospitalizations reached a peak of 14,461 in wave five. ICU admissions, however, peaked at 2,164 during wave four, and all-cause deaths peaked at 1,663 during wave two.
The investigators also analyzed how unvaccinated patients fared, compared with the fully vaccinated and the fully vaccinated-plus (that is, patients with one or more additional doses). During waves five and six, unvaccinated patients were 4.3 times more likely to end up in the ICU than fully vaccinated patients and were 12.2 times more likely than fully vaccinated-plus patients. Likewise, the rate for all-cause in-hospital death for unvaccinated patients was 3.9 times greater than that for fully vaccinated patients and 15.1 times greater than that for fully vaccinated-plus patients.
The effect of vaccines emerged in waves three and four, said Dr. Frenette. “We started to see really, really significant protection and benefit from the vaccine, not only in incidence of admission but also in the incidence of complications of ICU care, ventilation, and mortality.”
Results for pediatric patients were similar to those for adults, Dr. Thampi noted. During waves five and six, overall admissions peaked, but the share of ICU admissions decreased to 9.4% from 18.1%, which was the rate during the previous four waves (OR, 0.47).
“What’s important is how pediatric hospitalizations changed over the course of the various waves,” said Dr. Thampi.
“Where we saw the highest admissions during the early Omicron dominance, we actually had the lowest numbers of hospitalizations with death and admissions into ICUs.”
Doing more with the data
David Fisman, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, said, “This is a study that shows us how tremendously dramatic the effects of the COVID-19 vaccine were in terms of saving lives during the pandemic.” Dr. Fisman was not involved in the study.
But CNISP, which receives funding from Public Health Agency of Canada, could do more with the data it collects to better protect the public from COVID-19 and other nosocomial infections, Dr. Fisman said.
“The first problematic thing about this paper is that Canadians are paying for a surveillance system that looks at risks of acquiring infections, including COVID-19 infections, in the hospital, but that data is not fed back to the people paying for its production,” he said.
“So, Canadians don’t have the ability to really understand in real time how much risk they’re experiencing via going to the hospital for some other reason.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Frenette and Dr. Thampi report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fisman has disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Seqirus, Merck, the Ontario Nurses Association, and the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cohort study of more than 1.5 million hospital admissions in Canada through the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic has quantified the benefit of vaccinations. Unvaccinated patients were found to be up to 15 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than fully vaccinated patients.
Investigators analyzed 1.513 million admissions at 155 hospitals across Canada from March 15, 2020, to May 28, 2022. The study included 51,679 adult admissions and 4,035 pediatric admissions for COVID-19. Although the share of COVID-19 admissions increased in the fifth and sixth waves, from Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022 – after the full vaccine rollout – to 7.73% from 2.47% in the previous four waves, the proportion of adults admitted to the intensive care unit was significantly lower, at 8.7% versus 21.8% (odds ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.32-0.36).
“The good thing about waves five and six was we were able to show the COVID cases tended to be less severe, but on the other hand, because the disease in the community was so much higher, the demands on the health care system were much higher than the previous waves,” study author Charles Frenette, MD, director of infection prevention and control at McGill University, Montreal, and chair of the study’s adult subgroup, said in an interview. “But here we were able to show the benefit of vaccinations, particularly the boosting dose, in protecting against those severe outcomes.”
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, used the Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program database, which collects hospital data across Canada. It was activated in March 2020 to collect details on all COVID-19 admissions, co-author Nisha Thampi, MD, chair of the study’s pediatric subgroup, told this news organization.
“We’re now over 3 years into the pandemic, and CNISP continues to monitor COVID-19 as well as other pathogens in near real time,” said Dr. Thampi, an associate professor and infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario.
“That’s a particular strength of this surveillance program as well. We would see this data on a biweekly basis, and that allows for [us] to implement timely protection and action.”
Tracing trends over six waves
The study tracked COVID-19 hospitalizations during six waves. The first lasted from March 15 to August 31, 2020, and the second lasted from Sept. 1, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021. The wild-type variant was dominant during both waves. The third wave lasted from March 1 to June 30, 2021, and was marked by the mixed Alpha, Beta, and Gamma variants. The fourth wave lasted from July 1 to Dec. 25, 2021, when the Alpha variant was dominant. The Omicron variant dominated during waves five (Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022) and six (March 20 to May 28, 2022).
Hospitalizations reached a peak of 14,461 in wave five. ICU admissions, however, peaked at 2,164 during wave four, and all-cause deaths peaked at 1,663 during wave two.
The investigators also analyzed how unvaccinated patients fared, compared with the fully vaccinated and the fully vaccinated-plus (that is, patients with one or more additional doses). During waves five and six, unvaccinated patients were 4.3 times more likely to end up in the ICU than fully vaccinated patients and were 12.2 times more likely than fully vaccinated-plus patients. Likewise, the rate for all-cause in-hospital death for unvaccinated patients was 3.9 times greater than that for fully vaccinated patients and 15.1 times greater than that for fully vaccinated-plus patients.
The effect of vaccines emerged in waves three and four, said Dr. Frenette. “We started to see really, really significant protection and benefit from the vaccine, not only in incidence of admission but also in the incidence of complications of ICU care, ventilation, and mortality.”
Results for pediatric patients were similar to those for adults, Dr. Thampi noted. During waves five and six, overall admissions peaked, but the share of ICU admissions decreased to 9.4% from 18.1%, which was the rate during the previous four waves (OR, 0.47).
“What’s important is how pediatric hospitalizations changed over the course of the various waves,” said Dr. Thampi.
“Where we saw the highest admissions during the early Omicron dominance, we actually had the lowest numbers of hospitalizations with death and admissions into ICUs.”
Doing more with the data
David Fisman, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, said, “This is a study that shows us how tremendously dramatic the effects of the COVID-19 vaccine were in terms of saving lives during the pandemic.” Dr. Fisman was not involved in the study.
But CNISP, which receives funding from Public Health Agency of Canada, could do more with the data it collects to better protect the public from COVID-19 and other nosocomial infections, Dr. Fisman said.
“The first problematic thing about this paper is that Canadians are paying for a surveillance system that looks at risks of acquiring infections, including COVID-19 infections, in the hospital, but that data is not fed back to the people paying for its production,” he said.
“So, Canadians don’t have the ability to really understand in real time how much risk they’re experiencing via going to the hospital for some other reason.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Frenette and Dr. Thampi report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fisman has disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Seqirus, Merck, the Ontario Nurses Association, and the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cohort study of more than 1.5 million hospital admissions in Canada through the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic has quantified the benefit of vaccinations. Unvaccinated patients were found to be up to 15 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than fully vaccinated patients.
Investigators analyzed 1.513 million admissions at 155 hospitals across Canada from March 15, 2020, to May 28, 2022. The study included 51,679 adult admissions and 4,035 pediatric admissions for COVID-19. Although the share of COVID-19 admissions increased in the fifth and sixth waves, from Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022 – after the full vaccine rollout – to 7.73% from 2.47% in the previous four waves, the proportion of adults admitted to the intensive care unit was significantly lower, at 8.7% versus 21.8% (odds ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.32-0.36).
“The good thing about waves five and six was we were able to show the COVID cases tended to be less severe, but on the other hand, because the disease in the community was so much higher, the demands on the health care system were much higher than the previous waves,” study author Charles Frenette, MD, director of infection prevention and control at McGill University, Montreal, and chair of the study’s adult subgroup, said in an interview. “But here we were able to show the benefit of vaccinations, particularly the boosting dose, in protecting against those severe outcomes.”
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, used the Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program database, which collects hospital data across Canada. It was activated in March 2020 to collect details on all COVID-19 admissions, co-author Nisha Thampi, MD, chair of the study’s pediatric subgroup, told this news organization.
“We’re now over 3 years into the pandemic, and CNISP continues to monitor COVID-19 as well as other pathogens in near real time,” said Dr. Thampi, an associate professor and infectious disease specialist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario.
“That’s a particular strength of this surveillance program as well. We would see this data on a biweekly basis, and that allows for [us] to implement timely protection and action.”
Tracing trends over six waves
The study tracked COVID-19 hospitalizations during six waves. The first lasted from March 15 to August 31, 2020, and the second lasted from Sept. 1, 2020, to Feb. 28, 2021. The wild-type variant was dominant during both waves. The third wave lasted from March 1 to June 30, 2021, and was marked by the mixed Alpha, Beta, and Gamma variants. The fourth wave lasted from July 1 to Dec. 25, 2021, when the Alpha variant was dominant. The Omicron variant dominated during waves five (Dec. 26, 2021, to March 19, 2022) and six (March 20 to May 28, 2022).
Hospitalizations reached a peak of 14,461 in wave five. ICU admissions, however, peaked at 2,164 during wave four, and all-cause deaths peaked at 1,663 during wave two.
The investigators also analyzed how unvaccinated patients fared, compared with the fully vaccinated and the fully vaccinated-plus (that is, patients with one or more additional doses). During waves five and six, unvaccinated patients were 4.3 times more likely to end up in the ICU than fully vaccinated patients and were 12.2 times more likely than fully vaccinated-plus patients. Likewise, the rate for all-cause in-hospital death for unvaccinated patients was 3.9 times greater than that for fully vaccinated patients and 15.1 times greater than that for fully vaccinated-plus patients.
The effect of vaccines emerged in waves three and four, said Dr. Frenette. “We started to see really, really significant protection and benefit from the vaccine, not only in incidence of admission but also in the incidence of complications of ICU care, ventilation, and mortality.”
Results for pediatric patients were similar to those for adults, Dr. Thampi noted. During waves five and six, overall admissions peaked, but the share of ICU admissions decreased to 9.4% from 18.1%, which was the rate during the previous four waves (OR, 0.47).
“What’s important is how pediatric hospitalizations changed over the course of the various waves,” said Dr. Thampi.
“Where we saw the highest admissions during the early Omicron dominance, we actually had the lowest numbers of hospitalizations with death and admissions into ICUs.”
Doing more with the data
David Fisman, MD, MPH, a professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, said, “This is a study that shows us how tremendously dramatic the effects of the COVID-19 vaccine were in terms of saving lives during the pandemic.” Dr. Fisman was not involved in the study.
But CNISP, which receives funding from Public Health Agency of Canada, could do more with the data it collects to better protect the public from COVID-19 and other nosocomial infections, Dr. Fisman said.
“The first problematic thing about this paper is that Canadians are paying for a surveillance system that looks at risks of acquiring infections, including COVID-19 infections, in the hospital, but that data is not fed back to the people paying for its production,” he said.
“So, Canadians don’t have the ability to really understand in real time how much risk they’re experiencing via going to the hospital for some other reason.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Frenette and Dr. Thampi report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fisman has disclosed financial relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Seqirus, Merck, the Ontario Nurses Association, and the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helmet interface for ventilation likely superior in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure
For adults with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF), treatment using a helmet interface is likely superior to a face mask interface, according to a systematic review of recent randomized controlled trials examining different noninvasive oxygenation strategies for AHRF treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the benefits of optimizing noninvasive strategies to avoid unnecessary intubation. Intubation may be avoided in patients with AHRF through noninvasive oxygenation strategies, including high flow nasal cannula (HFNC), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and noninvasive bilevel ventilation, noted Tyler Pitre, MD, department of medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. CPAP and bilevel ventilation can be delivered through different interfaces, most commonly face mask or helmet. While research has shown noninvasive strategies to be associated with reductions in risk for invasive mechanical ventilation, mortality assessments and analyses comparing specific modalities (i.e., CPAP vs. bilevel ventilation) have been limited. The incremental reduction in diaphragmatic effort and improved gas exchange demonstrated for bilevel ventilation compared with CPAP in COPD patients suggests that responses in AHRF may differ for CPAP and bilevel ventilation, state Dr. Pitre and colleagues. On the other hand, the increased drive pressure of bilevel ventilation may compound patient self-induced lung injury with concomitant lung inflammation and need for prolonged respiratory support. New evidence from several large, high quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in COVID-19-related AHRF offered an opportunity to reassess comparative efficacies, the researchers noted.
The retrospective study encompassed RCTs with all types of AHRF, including COVID-19 related, with a total of 7,046 patients whose median age was 59.4 years (61.4% were males). Thirty of the 36 RCTs reported on mortality (6,114 patients and 1,539 deaths). The study’s analysis showed with moderate certainty that helmet CPAP reduces mortality (231 fewer deaths per 1,000 [95% confidence interval (CI), 126-273]) while the 63 fewer deaths per 1,000 (95% CI, 15-102) indicated with low certainty that HFNC may reduce mortality compared with standard oxygen therapy (SOT). The analysis showed also that face mask bilevel (36 fewer deaths per 1,000 [84.0 fewer to 24.0 more]) and helmet bilevel ventilation (129.0 fewer deaths per 1,000 [195.0 to 24.0 fewer]) may reduce death compared with SOT (all low certainty). The mortality benefit for face mask CPAP compared with SOT was uncertain (very low certainty) (9 fewer deaths per 1,000 [81 fewer deaths to 84 more]). For helmet CPAP vs. HFNC ventilation, the mortality benefit had moderate certainty (198.1 fewer events per 1,000 [95% CI, 69.75-248.31].
Mechanical ventilation and ICU duration
The authors found that HFNC probably reduces the need for invasive mechanical ventilation (103.5 fewer events per 1,000 [40.5-157.5 fewer]; moderate certainty). Helmet bilevel ventilation and helmet CPAP may reduce the duration of ICU stay compared with SOT (both low certainty) at (4.84 days fewer [95% CI 2.33 to 16 7.36 days fewer]) and (1.74 days fewer [95% CI 4.49 fewer to 1.01 more]), respectively. Also, SOT may be more comfortable than face mask noninvasive ventilation (NIV) and no different in comfort compared with HFNC (both low certainty).
“Helmet noninvasive ventilation interfaces is probably effective in acute hypoxic respiratory failure and is superior to face mask interfaces. All modalities including HFNC probably reduce the risk of need for invasive mechanical ventilation,” the researchers wrote.
“This meta-analysis shows that helmet noninvasive ventilation is effective in reducing death, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation based on a moderate certainty of evidence,” Shyamsunder Subramanian, MD, chief, division of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine, Sutter Health, Tracy, Calif., said in an interview. “It is premature based on the results of this meta-analysis to conclude that guideline changes are needed. Use of helmet based ventilation remains limited in scope. We need appropriately designed prospective trials across multiple centers to get sufficient rigor of scientific evidence before any change in guidelines or practice recommendations can be formulated about the appropriate use of helmet NIV in acute respiratory failure.”
The researchers cited the relative heterogeneity of the population included in this analysis as a study limitation.
Dr. Pitre and Dr. Subramanian disclosed that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
For adults with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF), treatment using a helmet interface is likely superior to a face mask interface, according to a systematic review of recent randomized controlled trials examining different noninvasive oxygenation strategies for AHRF treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the benefits of optimizing noninvasive strategies to avoid unnecessary intubation. Intubation may be avoided in patients with AHRF through noninvasive oxygenation strategies, including high flow nasal cannula (HFNC), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and noninvasive bilevel ventilation, noted Tyler Pitre, MD, department of medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. CPAP and bilevel ventilation can be delivered through different interfaces, most commonly face mask or helmet. While research has shown noninvasive strategies to be associated with reductions in risk for invasive mechanical ventilation, mortality assessments and analyses comparing specific modalities (i.e., CPAP vs. bilevel ventilation) have been limited. The incremental reduction in diaphragmatic effort and improved gas exchange demonstrated for bilevel ventilation compared with CPAP in COPD patients suggests that responses in AHRF may differ for CPAP and bilevel ventilation, state Dr. Pitre and colleagues. On the other hand, the increased drive pressure of bilevel ventilation may compound patient self-induced lung injury with concomitant lung inflammation and need for prolonged respiratory support. New evidence from several large, high quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in COVID-19-related AHRF offered an opportunity to reassess comparative efficacies, the researchers noted.
The retrospective study encompassed RCTs with all types of AHRF, including COVID-19 related, with a total of 7,046 patients whose median age was 59.4 years (61.4% were males). Thirty of the 36 RCTs reported on mortality (6,114 patients and 1,539 deaths). The study’s analysis showed with moderate certainty that helmet CPAP reduces mortality (231 fewer deaths per 1,000 [95% confidence interval (CI), 126-273]) while the 63 fewer deaths per 1,000 (95% CI, 15-102) indicated with low certainty that HFNC may reduce mortality compared with standard oxygen therapy (SOT). The analysis showed also that face mask bilevel (36 fewer deaths per 1,000 [84.0 fewer to 24.0 more]) and helmet bilevel ventilation (129.0 fewer deaths per 1,000 [195.0 to 24.0 fewer]) may reduce death compared with SOT (all low certainty). The mortality benefit for face mask CPAP compared with SOT was uncertain (very low certainty) (9 fewer deaths per 1,000 [81 fewer deaths to 84 more]). For helmet CPAP vs. HFNC ventilation, the mortality benefit had moderate certainty (198.1 fewer events per 1,000 [95% CI, 69.75-248.31].
Mechanical ventilation and ICU duration
The authors found that HFNC probably reduces the need for invasive mechanical ventilation (103.5 fewer events per 1,000 [40.5-157.5 fewer]; moderate certainty). Helmet bilevel ventilation and helmet CPAP may reduce the duration of ICU stay compared with SOT (both low certainty) at (4.84 days fewer [95% CI 2.33 to 16 7.36 days fewer]) and (1.74 days fewer [95% CI 4.49 fewer to 1.01 more]), respectively. Also, SOT may be more comfortable than face mask noninvasive ventilation (NIV) and no different in comfort compared with HFNC (both low certainty).
“Helmet noninvasive ventilation interfaces is probably effective in acute hypoxic respiratory failure and is superior to face mask interfaces. All modalities including HFNC probably reduce the risk of need for invasive mechanical ventilation,” the researchers wrote.
“This meta-analysis shows that helmet noninvasive ventilation is effective in reducing death, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation based on a moderate certainty of evidence,” Shyamsunder Subramanian, MD, chief, division of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine, Sutter Health, Tracy, Calif., said in an interview. “It is premature based on the results of this meta-analysis to conclude that guideline changes are needed. Use of helmet based ventilation remains limited in scope. We need appropriately designed prospective trials across multiple centers to get sufficient rigor of scientific evidence before any change in guidelines or practice recommendations can be formulated about the appropriate use of helmet NIV in acute respiratory failure.”
The researchers cited the relative heterogeneity of the population included in this analysis as a study limitation.
Dr. Pitre and Dr. Subramanian disclosed that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
For adults with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF), treatment using a helmet interface is likely superior to a face mask interface, according to a systematic review of recent randomized controlled trials examining different noninvasive oxygenation strategies for AHRF treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the benefits of optimizing noninvasive strategies to avoid unnecessary intubation. Intubation may be avoided in patients with AHRF through noninvasive oxygenation strategies, including high flow nasal cannula (HFNC), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and noninvasive bilevel ventilation, noted Tyler Pitre, MD, department of medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., and colleagues. CPAP and bilevel ventilation can be delivered through different interfaces, most commonly face mask or helmet. While research has shown noninvasive strategies to be associated with reductions in risk for invasive mechanical ventilation, mortality assessments and analyses comparing specific modalities (i.e., CPAP vs. bilevel ventilation) have been limited. The incremental reduction in diaphragmatic effort and improved gas exchange demonstrated for bilevel ventilation compared with CPAP in COPD patients suggests that responses in AHRF may differ for CPAP and bilevel ventilation, state Dr. Pitre and colleagues. On the other hand, the increased drive pressure of bilevel ventilation may compound patient self-induced lung injury with concomitant lung inflammation and need for prolonged respiratory support. New evidence from several large, high quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in COVID-19-related AHRF offered an opportunity to reassess comparative efficacies, the researchers noted.
The retrospective study encompassed RCTs with all types of AHRF, including COVID-19 related, with a total of 7,046 patients whose median age was 59.4 years (61.4% were males). Thirty of the 36 RCTs reported on mortality (6,114 patients and 1,539 deaths). The study’s analysis showed with moderate certainty that helmet CPAP reduces mortality (231 fewer deaths per 1,000 [95% confidence interval (CI), 126-273]) while the 63 fewer deaths per 1,000 (95% CI, 15-102) indicated with low certainty that HFNC may reduce mortality compared with standard oxygen therapy (SOT). The analysis showed also that face mask bilevel (36 fewer deaths per 1,000 [84.0 fewer to 24.0 more]) and helmet bilevel ventilation (129.0 fewer deaths per 1,000 [195.0 to 24.0 fewer]) may reduce death compared with SOT (all low certainty). The mortality benefit for face mask CPAP compared with SOT was uncertain (very low certainty) (9 fewer deaths per 1,000 [81 fewer deaths to 84 more]). For helmet CPAP vs. HFNC ventilation, the mortality benefit had moderate certainty (198.1 fewer events per 1,000 [95% CI, 69.75-248.31].
Mechanical ventilation and ICU duration
The authors found that HFNC probably reduces the need for invasive mechanical ventilation (103.5 fewer events per 1,000 [40.5-157.5 fewer]; moderate certainty). Helmet bilevel ventilation and helmet CPAP may reduce the duration of ICU stay compared with SOT (both low certainty) at (4.84 days fewer [95% CI 2.33 to 16 7.36 days fewer]) and (1.74 days fewer [95% CI 4.49 fewer to 1.01 more]), respectively. Also, SOT may be more comfortable than face mask noninvasive ventilation (NIV) and no different in comfort compared with HFNC (both low certainty).
“Helmet noninvasive ventilation interfaces is probably effective in acute hypoxic respiratory failure and is superior to face mask interfaces. All modalities including HFNC probably reduce the risk of need for invasive mechanical ventilation,” the researchers wrote.
“This meta-analysis shows that helmet noninvasive ventilation is effective in reducing death, and need for invasive mechanical ventilation based on a moderate certainty of evidence,” Shyamsunder Subramanian, MD, chief, division of pulmonary critical care and sleep medicine, Sutter Health, Tracy, Calif., said in an interview. “It is premature based on the results of this meta-analysis to conclude that guideline changes are needed. Use of helmet based ventilation remains limited in scope. We need appropriately designed prospective trials across multiple centers to get sufficient rigor of scientific evidence before any change in guidelines or practice recommendations can be formulated about the appropriate use of helmet NIV in acute respiratory failure.”
The researchers cited the relative heterogeneity of the population included in this analysis as a study limitation.
Dr. Pitre and Dr. Subramanian disclosed that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM CHEST
General, abdominal obesity linked to chronic respiratory illness
A recent Swedish study found that both abdominal and general obesity were independently associated with respiratory illnesses, including asthma and self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Relationships between respiratory conditions with characterized obesity types in adults were assessed using self-report surveys from participants originally enrolled in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS) investigating asthma, allergy, and risk factors. The Respiratory Health in Northern Europe (RHINE) III provides a second follow-up substudy of ECRHS focused on two forms of obesity associated with respiratory illnesses.
Obesity is a characteristic risk factor linked to respiratory ailments such as asthma and COPD. High body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) provide quantitative measurements for defining conditions of comprehensive general and abdominal obesity, respectively.
Although both types of obesity have been associated with asthma incidence, studies on their independent impact on this disease have been limited. Previous reports on abdominal obesity associated with asthma have been inconsistent when considering sexes in the analysis. Additionally, COPD and related outcomes differed between abdominal and general obesity, indicating a need to discover whether self-reported WC abdominal obesity and BMI-based general obesity are independently associated with respiratory symptoms, early- and late-onset asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, rhinitis, and sex, Marta A. Kisiel, MD, PhD, of the department of environmental and occupational medicine, Uppsala University, Sweden, and colleagues write.
In a prospective study published in the journal Respiratory Medicine, the researchers report on a cross-sectional investigation of responses to a questionnaire similar to one utilized 10 years earlier in the RHINE II study. Questions required simple yes/no responses that covered asthma, respiratory symptoms, allergic rhinitis, chronic bronchitis, and COPD. Additional requested information included age of asthma onset, potential confounding variables of age, smoking, physical activity, and highest education level, weight and height for BMI calculation, and WC measurement with instructions and a provided tape measure.
The population of the RHINE III study conducted from 2010 to 2012 was composed of 12,290 participants (53% response frequency) obtained from a total of seven research centers located in five northern European countries. Obesity categorization classified 1,837 (6.7%) participants as generally obese based on a high BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 and 4,261 (34.7%) as abdominally obese by WC measurements of ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women. Of the 4,261 total participants, 1,669 met both general and abdominal obesity criteria. Mean age was in the low 50s range and the obese population consisted of more women than men.
Simple linear regression revealed that BMI and WC were highly correlated, and both were associated with tested respiratory conditions when adjusted for confounding variables. Differences with respect to WC and BMI were independently associated with most of the examined respiratory conditions when WC was adjusted for BMI and vice versa. Neither early-onset asthma nor allergic rhinitis were associated with WC, BMI, or abdominal or general obesity.
An independent association of abdominal obesity (with or without general obesity) was found to occur with respiratory symptoms, asthma, late-onset asthma, and chronic bronchitis.
After adjusting for abdominal obesity, general obesity showed an independent and significant association with respiratory symptoms, asthma, adult-onset asthma, and COPD. An analysis stratified by sex indicated a significant association of abdominal and general obesity with asthma in women presented as an odds ratio of 1.56 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.87) and 1.95 (95% CI, 1.56-2.43), respectively, compared with men, with an OR of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.97-3.17) and 1.28 (95% CI, 0.97-1.68), respectively. The association of abdominal and general obesity with COPD was also stronger in women, compared with men.
The researchers conclude that “both general and abdominal obesity [were], independent of each other, associated with respiratory symptoms in adults.” There is also a distinct difference between women and men for the association of self-reported asthma and COPD with abdominal and general obesity.
The large randomly selected sample size of participants from research centers located in five northern European countries was considered a major strength of this study as it permitted simultaneous adjustment for multiple potential confounders. Several limitations were acknowledged, including absence of data on obstructive respiratory disease severity, WC measurements not being performed by trained staff, and self-reported height and weight measurements.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent Swedish study found that both abdominal and general obesity were independently associated with respiratory illnesses, including asthma and self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Relationships between respiratory conditions with characterized obesity types in adults were assessed using self-report surveys from participants originally enrolled in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS) investigating asthma, allergy, and risk factors. The Respiratory Health in Northern Europe (RHINE) III provides a second follow-up substudy of ECRHS focused on two forms of obesity associated with respiratory illnesses.
Obesity is a characteristic risk factor linked to respiratory ailments such as asthma and COPD. High body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) provide quantitative measurements for defining conditions of comprehensive general and abdominal obesity, respectively.
Although both types of obesity have been associated with asthma incidence, studies on their independent impact on this disease have been limited. Previous reports on abdominal obesity associated with asthma have been inconsistent when considering sexes in the analysis. Additionally, COPD and related outcomes differed between abdominal and general obesity, indicating a need to discover whether self-reported WC abdominal obesity and BMI-based general obesity are independently associated with respiratory symptoms, early- and late-onset asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, rhinitis, and sex, Marta A. Kisiel, MD, PhD, of the department of environmental and occupational medicine, Uppsala University, Sweden, and colleagues write.
In a prospective study published in the journal Respiratory Medicine, the researchers report on a cross-sectional investigation of responses to a questionnaire similar to one utilized 10 years earlier in the RHINE II study. Questions required simple yes/no responses that covered asthma, respiratory symptoms, allergic rhinitis, chronic bronchitis, and COPD. Additional requested information included age of asthma onset, potential confounding variables of age, smoking, physical activity, and highest education level, weight and height for BMI calculation, and WC measurement with instructions and a provided tape measure.
The population of the RHINE III study conducted from 2010 to 2012 was composed of 12,290 participants (53% response frequency) obtained from a total of seven research centers located in five northern European countries. Obesity categorization classified 1,837 (6.7%) participants as generally obese based on a high BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 and 4,261 (34.7%) as abdominally obese by WC measurements of ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women. Of the 4,261 total participants, 1,669 met both general and abdominal obesity criteria. Mean age was in the low 50s range and the obese population consisted of more women than men.
Simple linear regression revealed that BMI and WC were highly correlated, and both were associated with tested respiratory conditions when adjusted for confounding variables. Differences with respect to WC and BMI were independently associated with most of the examined respiratory conditions when WC was adjusted for BMI and vice versa. Neither early-onset asthma nor allergic rhinitis were associated with WC, BMI, or abdominal or general obesity.
An independent association of abdominal obesity (with or without general obesity) was found to occur with respiratory symptoms, asthma, late-onset asthma, and chronic bronchitis.
After adjusting for abdominal obesity, general obesity showed an independent and significant association with respiratory symptoms, asthma, adult-onset asthma, and COPD. An analysis stratified by sex indicated a significant association of abdominal and general obesity with asthma in women presented as an odds ratio of 1.56 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.87) and 1.95 (95% CI, 1.56-2.43), respectively, compared with men, with an OR of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.97-3.17) and 1.28 (95% CI, 0.97-1.68), respectively. The association of abdominal and general obesity with COPD was also stronger in women, compared with men.
The researchers conclude that “both general and abdominal obesity [were], independent of each other, associated with respiratory symptoms in adults.” There is also a distinct difference between women and men for the association of self-reported asthma and COPD with abdominal and general obesity.
The large randomly selected sample size of participants from research centers located in five northern European countries was considered a major strength of this study as it permitted simultaneous adjustment for multiple potential confounders. Several limitations were acknowledged, including absence of data on obstructive respiratory disease severity, WC measurements not being performed by trained staff, and self-reported height and weight measurements.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent Swedish study found that both abdominal and general obesity were independently associated with respiratory illnesses, including asthma and self-reported chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Relationships between respiratory conditions with characterized obesity types in adults were assessed using self-report surveys from participants originally enrolled in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS) investigating asthma, allergy, and risk factors. The Respiratory Health in Northern Europe (RHINE) III provides a second follow-up substudy of ECRHS focused on two forms of obesity associated with respiratory illnesses.
Obesity is a characteristic risk factor linked to respiratory ailments such as asthma and COPD. High body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) provide quantitative measurements for defining conditions of comprehensive general and abdominal obesity, respectively.
Although both types of obesity have been associated with asthma incidence, studies on their independent impact on this disease have been limited. Previous reports on abdominal obesity associated with asthma have been inconsistent when considering sexes in the analysis. Additionally, COPD and related outcomes differed between abdominal and general obesity, indicating a need to discover whether self-reported WC abdominal obesity and BMI-based general obesity are independently associated with respiratory symptoms, early- and late-onset asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, rhinitis, and sex, Marta A. Kisiel, MD, PhD, of the department of environmental and occupational medicine, Uppsala University, Sweden, and colleagues write.
In a prospective study published in the journal Respiratory Medicine, the researchers report on a cross-sectional investigation of responses to a questionnaire similar to one utilized 10 years earlier in the RHINE II study. Questions required simple yes/no responses that covered asthma, respiratory symptoms, allergic rhinitis, chronic bronchitis, and COPD. Additional requested information included age of asthma onset, potential confounding variables of age, smoking, physical activity, and highest education level, weight and height for BMI calculation, and WC measurement with instructions and a provided tape measure.
The population of the RHINE III study conducted from 2010 to 2012 was composed of 12,290 participants (53% response frequency) obtained from a total of seven research centers located in five northern European countries. Obesity categorization classified 1,837 (6.7%) participants as generally obese based on a high BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 and 4,261 (34.7%) as abdominally obese by WC measurements of ≥ 102 cm for men and ≥ 88 cm for women. Of the 4,261 total participants, 1,669 met both general and abdominal obesity criteria. Mean age was in the low 50s range and the obese population consisted of more women than men.
Simple linear regression revealed that BMI and WC were highly correlated, and both were associated with tested respiratory conditions when adjusted for confounding variables. Differences with respect to WC and BMI were independently associated with most of the examined respiratory conditions when WC was adjusted for BMI and vice versa. Neither early-onset asthma nor allergic rhinitis were associated with WC, BMI, or abdominal or general obesity.
An independent association of abdominal obesity (with or without general obesity) was found to occur with respiratory symptoms, asthma, late-onset asthma, and chronic bronchitis.
After adjusting for abdominal obesity, general obesity showed an independent and significant association with respiratory symptoms, asthma, adult-onset asthma, and COPD. An analysis stratified by sex indicated a significant association of abdominal and general obesity with asthma in women presented as an odds ratio of 1.56 (95% confidence interval, 1.30-1.87) and 1.95 (95% CI, 1.56-2.43), respectively, compared with men, with an OR of 1.22 (95% CI, 0.97-3.17) and 1.28 (95% CI, 0.97-1.68), respectively. The association of abdominal and general obesity with COPD was also stronger in women, compared with men.
The researchers conclude that “both general and abdominal obesity [were], independent of each other, associated with respiratory symptoms in adults.” There is also a distinct difference between women and men for the association of self-reported asthma and COPD with abdominal and general obesity.
The large randomly selected sample size of participants from research centers located in five northern European countries was considered a major strength of this study as it permitted simultaneous adjustment for multiple potential confounders. Several limitations were acknowledged, including absence of data on obstructive respiratory disease severity, WC measurements not being performed by trained staff, and self-reported height and weight measurements.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.