User login
Must-read acute care medicine articles from 2022
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The five biggest changes in the 2023 adult vaccine schedules
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Sandra Fryhofer. Welcome to Medicine Matters.
It’s a new year, which means a new ACIP adult immunization schedule – a valuable resource collating ACIP’s most up-to-date vaccination recommendations.
Here are this year’s five most important changes:
- COVID vaccines now front and center
- New emphasis on polio vaccination
- Inclusion of some nonvaccine products (such as monoclonal antibody products)
- Pharmacists group has approved the schedule for the first time
- New shared clinical decision-making option for pneumococcal vaccines
The schedule’s organization remains the same. It still has four sections:
- Table 1: vaccinations by age
- Table 2: vaccinations by medical condition and other indications
- The Notes section (alphabetically ordered by vaccine type)
- Appendix listing of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions
But what’s unique this year is that some of the abbreviations have historical implications. The first change is no big surprise in light of what we’ve gone through in the past few years. COVID vaccines are listed first on the cover page by brand name for those authorized and by company name for those still under US emergency use authorization. They’re also listed first on the graphics and in the notes.
COVID and mRNA and protein-based vaccines have now been assigned official abbreviations based on vaccine platform and valency.
- 1vCOV-mRNA: Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech and Spikevax Moderna COVID-19 vaccines
- 2vCOV-mRNA: Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna bivalent COVID-19 vaccines
- 1vCOV-aPS: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine
Also remarkable is the absence of COVID viral vector vaccines on the list. However, the viral vector COVID vaccine (which has been available but is not preferred) does have a CDC website link in the Notes section.
A sad but necessary inclusion was triggered by recent polio cases in New York. Polio was believed to be eradicated, and we thought adults no longer needed to be vaccinated against polio. In the new schedule, the polio vaccine is listed on the cover page but is not included in the tables. Current polio vaccination recommendations are now in the Notes section.
Also of historical significance and something that may set a precedent is the inclusion of nonvaccine products. The value of COVID preexposure prophylaxis with products including monoclonal antibodies (such as Evusheld) for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised is mentioned in the Notes section.
For the first time ever, the schedule has been approved by the American Pharmacists Association, which validates pharmacists as established partners in vaccine administration.
Color-code key
One aspect of the schedule that has not changed is the color-code key:
- Yellow: Recommended if the patient meets the age requirement
- Purple: Indicated for those with additional risk factors or another indication
- Blue: Recommended based on shared clinical decision-making
- Orange: Precaution
- Red: Contraindicated or not recommended; the vaccine should not be administered. Overlays on the red more precisely clarify whether a vaccine is really contraindicated or just not recommended. An asterisk on red means vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated.
- Gray: No recommendation or not applicable
Vaccinations by age
Table 1 lists recommended vaccinations by age. There is one major change. COVID vaccines are on the first row of the graphic, with the need for both a primary series and boosters emphasized on the overlay. The notes have hyperlinks to the most up-to-date COVID vaccination recommendations.
Pneumococcal vaccination. Pneumococcal vaccination is routinely recommended starting at age 65. Current recommendations for those not previously vaccinated have not changed since last year. But on Table 1, the bottom half of the row for those 65 or older is now blue (and that’s new). This new color blue means shared clinical decision-making and applies to people who were previously considered fully vaccinated with the now extinct combination of PCV13 and PPSV23. These patients now have the option of getting a dose of PCV20 five years after completing their PCV13-PPSV23 combo series. This option is blue because the decision is up to you and your patient.
Check the notes for more pneumococcal vaccination details. For example, for those partially vaccinated using lower valency vaccines, there’s an option of substituting PCV20 for PPSV23 to broaden and increase durability of protection.
The pneumococcal vaccination recommendation options are complicated. A new pneumococcal vaccination app can help.
Hepatitis B. For adults under age 60, the color code for the hepatitis B vaccine is yellow, meaning it’s indicated for all. For older patients, the color code is purple. If a patient who is age 60 or older wants the hepatitis B vaccine, they can have it even in the absence of additional risk indications.
Vaccinations by medical condition or other indications
Other than a few minor word changes on the overlay, the only thing that’s new is the COVID vaccine row.
This table is helpful for matching vaccine recommendations with specific medical conditions, including pregnancy, immunocompromise, HIV (with specifics according to CD4 count), asplenia, complement deficiencies, heart disease, lung disease, alcoholism, chronic liver disease, diabetes, health care personnel, and men who have sex with men.
Use this table to dot the i’s and cross the t’s when it comes to vaccination recommendations. For example, take a look at the pregnancy column. Live virus vaccines, including LAIV, MMR, and varicella, are contraindicated and color-coded red. MMR and varicella also have an asterisk, meaning vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated. HPV vaccines are not live virus vaccines, but the overlay says they are not recommended during pregnancy. The asterisk indicates that you can vaccinate after pregnancy.
Vaccine notes
The notes are in alphabetical order, and their organization (routine, special situations, and shared clinical decision-making when indicated) has not changed. They are concise and succinct, but sometimes they’re not enough. That’s why vaccine-specific links to more complete recommendations are so convenient.
Notes for hepatitis B contain nuances on specific dosing for vaccinating patients on dialysis, as well as a reminder that newer hepatitis C vaccines such as Heplisav and PreHevbrio are not recommended during pregnancy due to lack of safety data.
For influenza, everyone 6 months or older still needs yearly flu vaccination with an age- and health-appropriate flu vaccine. But for those aged 65 or older, the notes specify the three vaccine versions now preferred: high-dose, recombinant, or adjuvanted versions. However, if these aren’t available, it’s better to get any flu vaccine than to go without.
Under meningococcal vaccines, the notes for MenACWY and MenB are combined. For MenB, trade names Bexsero and Trumenba are specified because the products are not interchangeable. Booster intervals for those still at risk are different for each vaccine type: every 5 years for MenACWY boosters, and every 2-3 years for boosts of MenB.
The recent polio cases in New York have put polio vaccination in the spotlight. ACIP has now reinstated its Polio Vaccine Work Group. The new schedule lists polio vaccines on the cover page. Current recommendations have been added to the notes section. Routine vaccination for adults is not necessary, at least for now. However, those at increased risk for exposure to polio fall in the special-situation category. For those at increased risk who have completed a polio vaccine series, a single lifetime IPV booster can be given. For those at increased risk who have not completed their polio vaccine series, now would be the time to finish the series.
Appendix
The final step in using the new schedule is checking the appendix and its list of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions.
I hope this review of the new ACIP adult immunization schedule has been helpful. For Medicine Matters, I’m Dr. Sandra Fryhofer.
Dr. Fryhofer is clinical associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. She reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Sandra Fryhofer. Welcome to Medicine Matters.
It’s a new year, which means a new ACIP adult immunization schedule – a valuable resource collating ACIP’s most up-to-date vaccination recommendations.
Here are this year’s five most important changes:
- COVID vaccines now front and center
- New emphasis on polio vaccination
- Inclusion of some nonvaccine products (such as monoclonal antibody products)
- Pharmacists group has approved the schedule for the first time
- New shared clinical decision-making option for pneumococcal vaccines
The schedule’s organization remains the same. It still has four sections:
- Table 1: vaccinations by age
- Table 2: vaccinations by medical condition and other indications
- The Notes section (alphabetically ordered by vaccine type)
- Appendix listing of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions
But what’s unique this year is that some of the abbreviations have historical implications. The first change is no big surprise in light of what we’ve gone through in the past few years. COVID vaccines are listed first on the cover page by brand name for those authorized and by company name for those still under US emergency use authorization. They’re also listed first on the graphics and in the notes.
COVID and mRNA and protein-based vaccines have now been assigned official abbreviations based on vaccine platform and valency.
- 1vCOV-mRNA: Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech and Spikevax Moderna COVID-19 vaccines
- 2vCOV-mRNA: Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna bivalent COVID-19 vaccines
- 1vCOV-aPS: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine
Also remarkable is the absence of COVID viral vector vaccines on the list. However, the viral vector COVID vaccine (which has been available but is not preferred) does have a CDC website link in the Notes section.
A sad but necessary inclusion was triggered by recent polio cases in New York. Polio was believed to be eradicated, and we thought adults no longer needed to be vaccinated against polio. In the new schedule, the polio vaccine is listed on the cover page but is not included in the tables. Current polio vaccination recommendations are now in the Notes section.
Also of historical significance and something that may set a precedent is the inclusion of nonvaccine products. The value of COVID preexposure prophylaxis with products including monoclonal antibodies (such as Evusheld) for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised is mentioned in the Notes section.
For the first time ever, the schedule has been approved by the American Pharmacists Association, which validates pharmacists as established partners in vaccine administration.
Color-code key
One aspect of the schedule that has not changed is the color-code key:
- Yellow: Recommended if the patient meets the age requirement
- Purple: Indicated for those with additional risk factors or another indication
- Blue: Recommended based on shared clinical decision-making
- Orange: Precaution
- Red: Contraindicated or not recommended; the vaccine should not be administered. Overlays on the red more precisely clarify whether a vaccine is really contraindicated or just not recommended. An asterisk on red means vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated.
- Gray: No recommendation or not applicable
Vaccinations by age
Table 1 lists recommended vaccinations by age. There is one major change. COVID vaccines are on the first row of the graphic, with the need for both a primary series and boosters emphasized on the overlay. The notes have hyperlinks to the most up-to-date COVID vaccination recommendations.
Pneumococcal vaccination. Pneumococcal vaccination is routinely recommended starting at age 65. Current recommendations for those not previously vaccinated have not changed since last year. But on Table 1, the bottom half of the row for those 65 or older is now blue (and that’s new). This new color blue means shared clinical decision-making and applies to people who were previously considered fully vaccinated with the now extinct combination of PCV13 and PPSV23. These patients now have the option of getting a dose of PCV20 five years after completing their PCV13-PPSV23 combo series. This option is blue because the decision is up to you and your patient.
Check the notes for more pneumococcal vaccination details. For example, for those partially vaccinated using lower valency vaccines, there’s an option of substituting PCV20 for PPSV23 to broaden and increase durability of protection.
The pneumococcal vaccination recommendation options are complicated. A new pneumococcal vaccination app can help.
Hepatitis B. For adults under age 60, the color code for the hepatitis B vaccine is yellow, meaning it’s indicated for all. For older patients, the color code is purple. If a patient who is age 60 or older wants the hepatitis B vaccine, they can have it even in the absence of additional risk indications.
Vaccinations by medical condition or other indications
Other than a few minor word changes on the overlay, the only thing that’s new is the COVID vaccine row.
This table is helpful for matching vaccine recommendations with specific medical conditions, including pregnancy, immunocompromise, HIV (with specifics according to CD4 count), asplenia, complement deficiencies, heart disease, lung disease, alcoholism, chronic liver disease, diabetes, health care personnel, and men who have sex with men.
Use this table to dot the i’s and cross the t’s when it comes to vaccination recommendations. For example, take a look at the pregnancy column. Live virus vaccines, including LAIV, MMR, and varicella, are contraindicated and color-coded red. MMR and varicella also have an asterisk, meaning vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated. HPV vaccines are not live virus vaccines, but the overlay says they are not recommended during pregnancy. The asterisk indicates that you can vaccinate after pregnancy.
Vaccine notes
The notes are in alphabetical order, and their organization (routine, special situations, and shared clinical decision-making when indicated) has not changed. They are concise and succinct, but sometimes they’re not enough. That’s why vaccine-specific links to more complete recommendations are so convenient.
Notes for hepatitis B contain nuances on specific dosing for vaccinating patients on dialysis, as well as a reminder that newer hepatitis C vaccines such as Heplisav and PreHevbrio are not recommended during pregnancy due to lack of safety data.
For influenza, everyone 6 months or older still needs yearly flu vaccination with an age- and health-appropriate flu vaccine. But for those aged 65 or older, the notes specify the three vaccine versions now preferred: high-dose, recombinant, or adjuvanted versions. However, if these aren’t available, it’s better to get any flu vaccine than to go without.
Under meningococcal vaccines, the notes for MenACWY and MenB are combined. For MenB, trade names Bexsero and Trumenba are specified because the products are not interchangeable. Booster intervals for those still at risk are different for each vaccine type: every 5 years for MenACWY boosters, and every 2-3 years for boosts of MenB.
The recent polio cases in New York have put polio vaccination in the spotlight. ACIP has now reinstated its Polio Vaccine Work Group. The new schedule lists polio vaccines on the cover page. Current recommendations have been added to the notes section. Routine vaccination for adults is not necessary, at least for now. However, those at increased risk for exposure to polio fall in the special-situation category. For those at increased risk who have completed a polio vaccine series, a single lifetime IPV booster can be given. For those at increased risk who have not completed their polio vaccine series, now would be the time to finish the series.
Appendix
The final step in using the new schedule is checking the appendix and its list of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions.
I hope this review of the new ACIP adult immunization schedule has been helpful. For Medicine Matters, I’m Dr. Sandra Fryhofer.
Dr. Fryhofer is clinical associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. She reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Sandra Fryhofer. Welcome to Medicine Matters.
It’s a new year, which means a new ACIP adult immunization schedule – a valuable resource collating ACIP’s most up-to-date vaccination recommendations.
Here are this year’s five most important changes:
- COVID vaccines now front and center
- New emphasis on polio vaccination
- Inclusion of some nonvaccine products (such as monoclonal antibody products)
- Pharmacists group has approved the schedule for the first time
- New shared clinical decision-making option for pneumococcal vaccines
The schedule’s organization remains the same. It still has four sections:
- Table 1: vaccinations by age
- Table 2: vaccinations by medical condition and other indications
- The Notes section (alphabetically ordered by vaccine type)
- Appendix listing of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions
But what’s unique this year is that some of the abbreviations have historical implications. The first change is no big surprise in light of what we’ve gone through in the past few years. COVID vaccines are listed first on the cover page by brand name for those authorized and by company name for those still under US emergency use authorization. They’re also listed first on the graphics and in the notes.
COVID and mRNA and protein-based vaccines have now been assigned official abbreviations based on vaccine platform and valency.
- 1vCOV-mRNA: Comirnaty/Pfizer-BioNTech and Spikevax Moderna COVID-19 vaccines
- 2vCOV-mRNA: Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna bivalent COVID-19 vaccines
- 1vCOV-aPS: Novavax COVID-19 vaccine
Also remarkable is the absence of COVID viral vector vaccines on the list. However, the viral vector COVID vaccine (which has been available but is not preferred) does have a CDC website link in the Notes section.
A sad but necessary inclusion was triggered by recent polio cases in New York. Polio was believed to be eradicated, and we thought adults no longer needed to be vaccinated against polio. In the new schedule, the polio vaccine is listed on the cover page but is not included in the tables. Current polio vaccination recommendations are now in the Notes section.
Also of historical significance and something that may set a precedent is the inclusion of nonvaccine products. The value of COVID preexposure prophylaxis with products including monoclonal antibodies (such as Evusheld) for people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised is mentioned in the Notes section.
For the first time ever, the schedule has been approved by the American Pharmacists Association, which validates pharmacists as established partners in vaccine administration.
Color-code key
One aspect of the schedule that has not changed is the color-code key:
- Yellow: Recommended if the patient meets the age requirement
- Purple: Indicated for those with additional risk factors or another indication
- Blue: Recommended based on shared clinical decision-making
- Orange: Precaution
- Red: Contraindicated or not recommended; the vaccine should not be administered. Overlays on the red more precisely clarify whether a vaccine is really contraindicated or just not recommended. An asterisk on red means vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated.
- Gray: No recommendation or not applicable
Vaccinations by age
Table 1 lists recommended vaccinations by age. There is one major change. COVID vaccines are on the first row of the graphic, with the need for both a primary series and boosters emphasized on the overlay. The notes have hyperlinks to the most up-to-date COVID vaccination recommendations.
Pneumococcal vaccination. Pneumococcal vaccination is routinely recommended starting at age 65. Current recommendations for those not previously vaccinated have not changed since last year. But on Table 1, the bottom half of the row for those 65 or older is now blue (and that’s new). This new color blue means shared clinical decision-making and applies to people who were previously considered fully vaccinated with the now extinct combination of PCV13 and PPSV23. These patients now have the option of getting a dose of PCV20 five years after completing their PCV13-PPSV23 combo series. This option is blue because the decision is up to you and your patient.
Check the notes for more pneumococcal vaccination details. For example, for those partially vaccinated using lower valency vaccines, there’s an option of substituting PCV20 for PPSV23 to broaden and increase durability of protection.
The pneumococcal vaccination recommendation options are complicated. A new pneumococcal vaccination app can help.
Hepatitis B. For adults under age 60, the color code for the hepatitis B vaccine is yellow, meaning it’s indicated for all. For older patients, the color code is purple. If a patient who is age 60 or older wants the hepatitis B vaccine, they can have it even in the absence of additional risk indications.
Vaccinations by medical condition or other indications
Other than a few minor word changes on the overlay, the only thing that’s new is the COVID vaccine row.
This table is helpful for matching vaccine recommendations with specific medical conditions, including pregnancy, immunocompromise, HIV (with specifics according to CD4 count), asplenia, complement deficiencies, heart disease, lung disease, alcoholism, chronic liver disease, diabetes, health care personnel, and men who have sex with men.
Use this table to dot the i’s and cross the t’s when it comes to vaccination recommendations. For example, take a look at the pregnancy column. Live virus vaccines, including LAIV, MMR, and varicella, are contraindicated and color-coded red. MMR and varicella also have an asterisk, meaning vaccinate after pregnancy if indicated. HPV vaccines are not live virus vaccines, but the overlay says they are not recommended during pregnancy. The asterisk indicates that you can vaccinate after pregnancy.
Vaccine notes
The notes are in alphabetical order, and their organization (routine, special situations, and shared clinical decision-making when indicated) has not changed. They are concise and succinct, but sometimes they’re not enough. That’s why vaccine-specific links to more complete recommendations are so convenient.
Notes for hepatitis B contain nuances on specific dosing for vaccinating patients on dialysis, as well as a reminder that newer hepatitis C vaccines such as Heplisav and PreHevbrio are not recommended during pregnancy due to lack of safety data.
For influenza, everyone 6 months or older still needs yearly flu vaccination with an age- and health-appropriate flu vaccine. But for those aged 65 or older, the notes specify the three vaccine versions now preferred: high-dose, recombinant, or adjuvanted versions. However, if these aren’t available, it’s better to get any flu vaccine than to go without.
Under meningococcal vaccines, the notes for MenACWY and MenB are combined. For MenB, trade names Bexsero and Trumenba are specified because the products are not interchangeable. Booster intervals for those still at risk are different for each vaccine type: every 5 years for MenACWY boosters, and every 2-3 years for boosts of MenB.
The recent polio cases in New York have put polio vaccination in the spotlight. ACIP has now reinstated its Polio Vaccine Work Group. The new schedule lists polio vaccines on the cover page. Current recommendations have been added to the notes section. Routine vaccination for adults is not necessary, at least for now. However, those at increased risk for exposure to polio fall in the special-situation category. For those at increased risk who have completed a polio vaccine series, a single lifetime IPV booster can be given. For those at increased risk who have not completed their polio vaccine series, now would be the time to finish the series.
Appendix
The final step in using the new schedule is checking the appendix and its list of vaccine-specific contraindications and precautions.
I hope this review of the new ACIP adult immunization schedule has been helpful. For Medicine Matters, I’m Dr. Sandra Fryhofer.
Dr. Fryhofer is clinical associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. She reported numerous conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new (old) drug joins the COVID fray, and guess what? It works
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
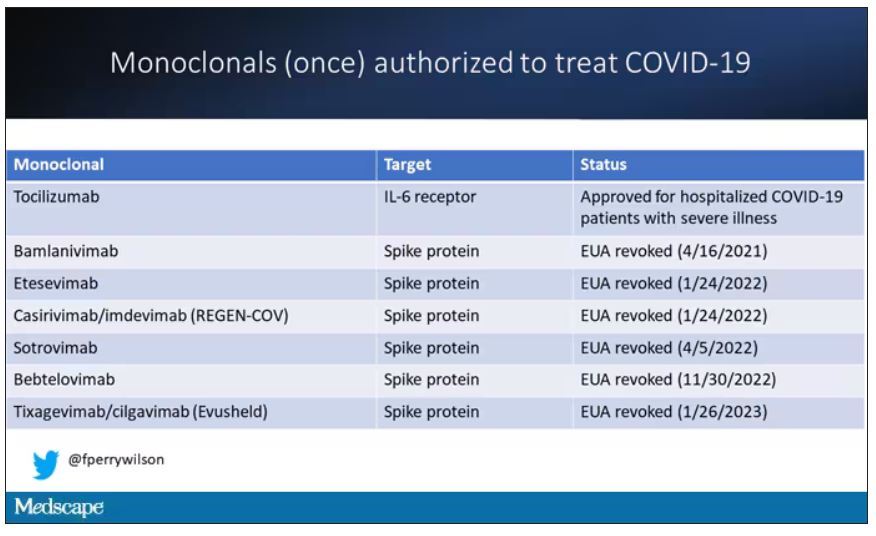
At this point, with the monoclonals found to be essentially useless, we are left with remdesivir with its modest efficacy and Paxlovid, which, for some reason, people don’t seem to be taking.
Part of the reason the monoclonals have failed lately is because of their specificity; they are homogeneous antibodies targeted toward a very specific epitope that may change from variant to variant. We need a broader therapeutic, one that has activity across all variants — maybe even one that has activity against all viruses? We’ve got one. Interferon.
The first mention of interferon as a potential COVID therapy was at the very start of the pandemic, so I’m sort of surprised that the first large, randomized trial is only being reported now in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Before we dig into the results, let’s talk mechanism. This is a trial of interferon-lambda, also known as interleukin-29.
The lambda interferons were only discovered in 2003. They differ from the more familiar interferons only in their cellular receptors; the downstream effects seem quite similar. As opposed to the cellular receptors for interferon alfa, which are widely expressed, the receptors for lambda are restricted to epithelial tissues. This makes it a good choice as a COVID treatment, since the virus also preferentially targets those epithelial cells.
In this study, 1,951 participants from Brazil and Canada, but mostly Brazil, with new COVID infections who were not yet hospitalized were randomized to receive 180 mcg of interferon lambda or placebo.
This was a relatively current COVID trial, as you can see from the participant characteristics. The majority had been vaccinated, and nearly half of the infections were during the Omicron phase of the pandemic.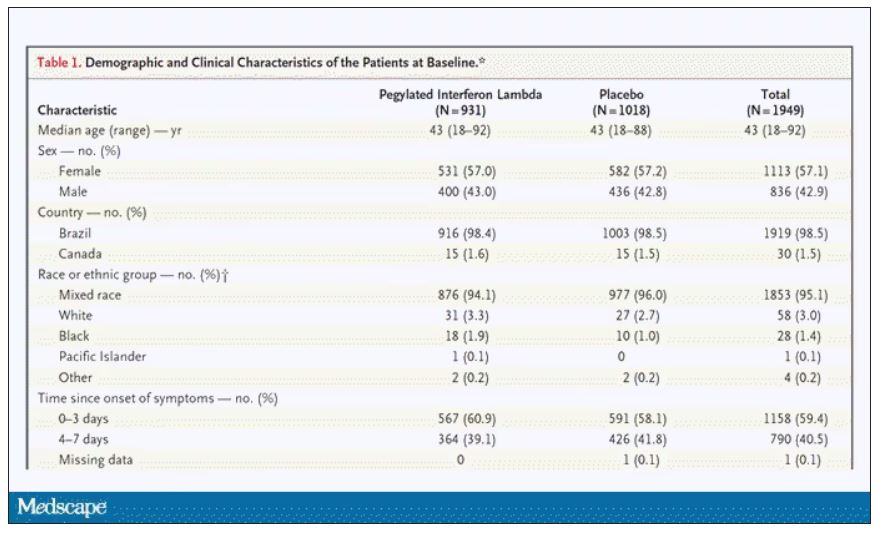
If you just want to cut to the chase, interferon worked.
The primary outcome – hospitalization or a prolonged emergency room visit for COVID – was 50% lower in the interferon group.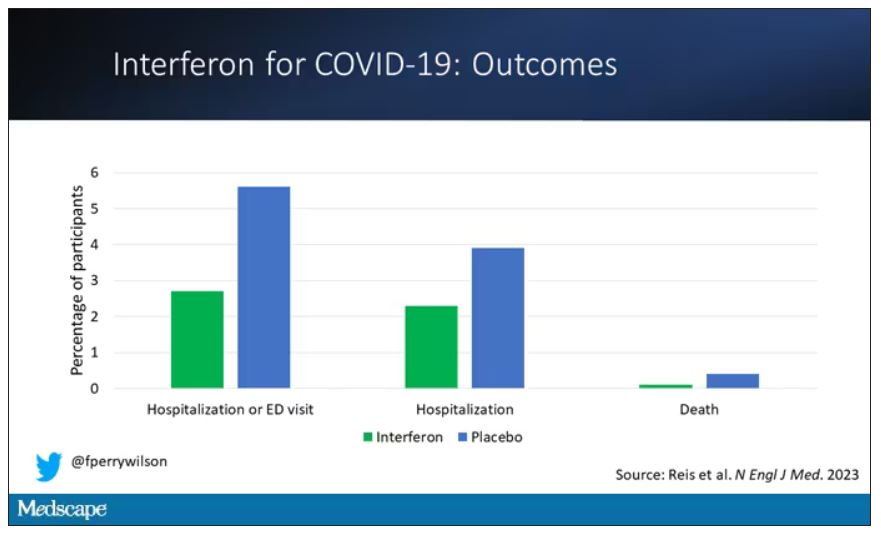
Key secondary outcomes, including death from COVID, were lower in the interferon group as well. These effects persisted across most of the subgroups I was looking out for.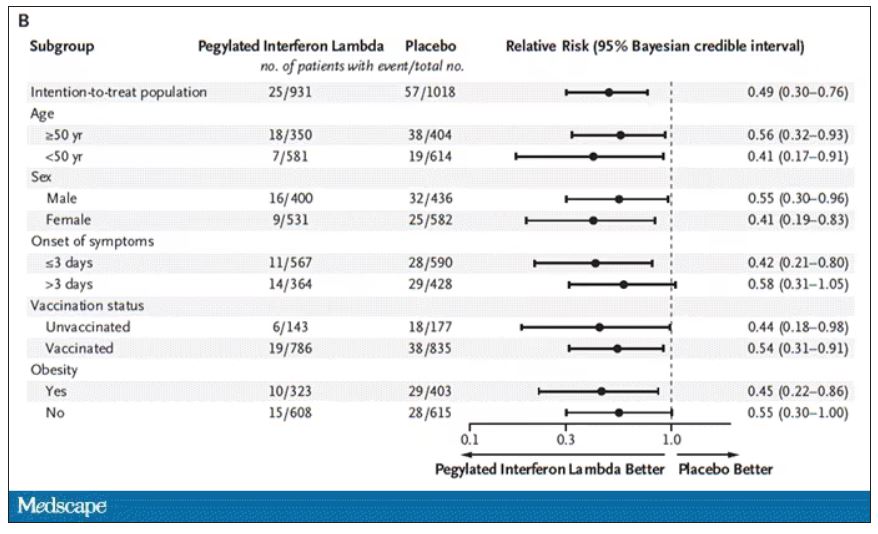
Interferon seemed to help those who were already vaccinated and those who were unvaccinated. There’s a hint that it works better within the first few days of symptoms, which isn’t surprising; we’ve seen this for many of the therapeutics, including Paxlovid. Time is of the essence. Encouragingly, the effect was a bit more pronounced among those infected with Omicron.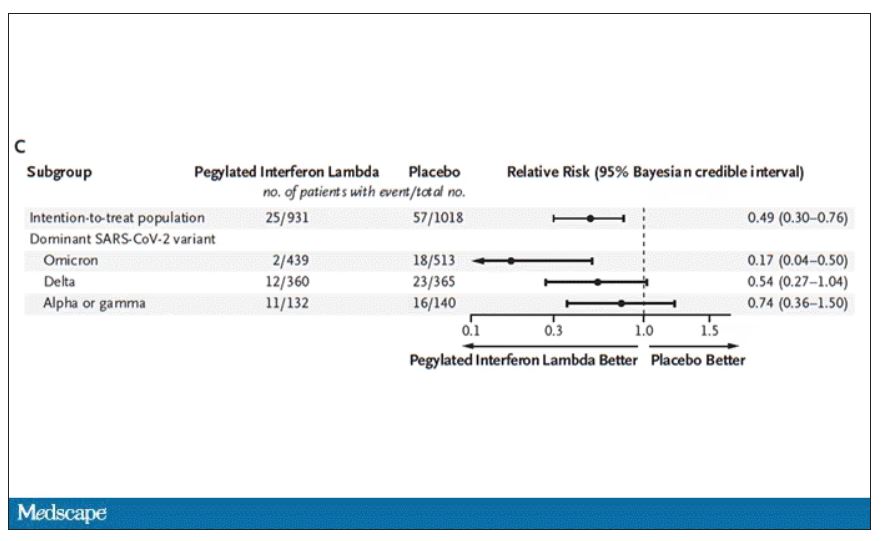
Of course, if you have any experience with interferon, you know that the side effects can be pretty rough. In the bad old days when we treated hepatitis C infection with interferon, patients would get their injections on Friday in anticipation of being essentially out of commission with flu-like symptoms through the weekend. But we don’t see much evidence of adverse events in this trial, maybe due to the greater specificity of interferon lambda.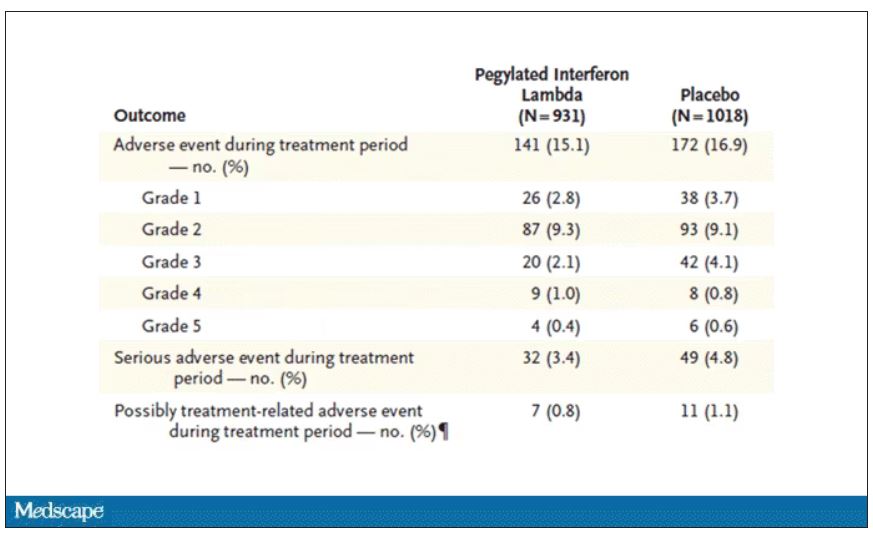
Putting it all together, the state of play for interferons in COVID may be changing. To date, the FDA has not recommended the use of interferon alfa or -beta for COVID-19, citing some data that they are ineffective or even harmful in hospitalized patients with COVID. Interferon lambda is not FDA approved and thus not even available in the United States. But the reason it has not been approved is that there has not been a large, well-conducted interferon lambda trial. Now there is. Will this study be enough to prompt an emergency use authorization? The elephant in the room, of course, is Paxlovid, which at this point has a longer safety track record and, importantly, is oral. I’d love to see a head-to-head trial. Short of that, I tend to be in favor of having more options on the table.
Dr. Perry Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.

At this point, with the monoclonals found to be essentially useless, we are left with remdesivir with its modest efficacy and Paxlovid, which, for some reason, people don’t seem to be taking.
Part of the reason the monoclonals have failed lately is because of their specificity; they are homogeneous antibodies targeted toward a very specific epitope that may change from variant to variant. We need a broader therapeutic, one that has activity across all variants — maybe even one that has activity against all viruses? We’ve got one. Interferon.
The first mention of interferon as a potential COVID therapy was at the very start of the pandemic, so I’m sort of surprised that the first large, randomized trial is only being reported now in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Before we dig into the results, let’s talk mechanism. This is a trial of interferon-lambda, also known as interleukin-29.
The lambda interferons were only discovered in 2003. They differ from the more familiar interferons only in their cellular receptors; the downstream effects seem quite similar. As opposed to the cellular receptors for interferon alfa, which are widely expressed, the receptors for lambda are restricted to epithelial tissues. This makes it a good choice as a COVID treatment, since the virus also preferentially targets those epithelial cells.
In this study, 1,951 participants from Brazil and Canada, but mostly Brazil, with new COVID infections who were not yet hospitalized were randomized to receive 180 mcg of interferon lambda or placebo.
This was a relatively current COVID trial, as you can see from the participant characteristics. The majority had been vaccinated, and nearly half of the infections were during the Omicron phase of the pandemic.
If you just want to cut to the chase, interferon worked.
The primary outcome – hospitalization or a prolonged emergency room visit for COVID – was 50% lower in the interferon group.
Key secondary outcomes, including death from COVID, were lower in the interferon group as well. These effects persisted across most of the subgroups I was looking out for.
Interferon seemed to help those who were already vaccinated and those who were unvaccinated. There’s a hint that it works better within the first few days of symptoms, which isn’t surprising; we’ve seen this for many of the therapeutics, including Paxlovid. Time is of the essence. Encouragingly, the effect was a bit more pronounced among those infected with Omicron.
Of course, if you have any experience with interferon, you know that the side effects can be pretty rough. In the bad old days when we treated hepatitis C infection with interferon, patients would get their injections on Friday in anticipation of being essentially out of commission with flu-like symptoms through the weekend. But we don’t see much evidence of adverse events in this trial, maybe due to the greater specificity of interferon lambda.
Putting it all together, the state of play for interferons in COVID may be changing. To date, the FDA has not recommended the use of interferon alfa or -beta for COVID-19, citing some data that they are ineffective or even harmful in hospitalized patients with COVID. Interferon lambda is not FDA approved and thus not even available in the United States. But the reason it has not been approved is that there has not been a large, well-conducted interferon lambda trial. Now there is. Will this study be enough to prompt an emergency use authorization? The elephant in the room, of course, is Paxlovid, which at this point has a longer safety track record and, importantly, is oral. I’d love to see a head-to-head trial. Short of that, I tend to be in favor of having more options on the table.
Dr. Perry Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.

At this point, with the monoclonals found to be essentially useless, we are left with remdesivir with its modest efficacy and Paxlovid, which, for some reason, people don’t seem to be taking.
Part of the reason the monoclonals have failed lately is because of their specificity; they are homogeneous antibodies targeted toward a very specific epitope that may change from variant to variant. We need a broader therapeutic, one that has activity across all variants — maybe even one that has activity against all viruses? We’ve got one. Interferon.
The first mention of interferon as a potential COVID therapy was at the very start of the pandemic, so I’m sort of surprised that the first large, randomized trial is only being reported now in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Before we dig into the results, let’s talk mechanism. This is a trial of interferon-lambda, also known as interleukin-29.
The lambda interferons were only discovered in 2003. They differ from the more familiar interferons only in their cellular receptors; the downstream effects seem quite similar. As opposed to the cellular receptors for interferon alfa, which are widely expressed, the receptors for lambda are restricted to epithelial tissues. This makes it a good choice as a COVID treatment, since the virus also preferentially targets those epithelial cells.
In this study, 1,951 participants from Brazil and Canada, but mostly Brazil, with new COVID infections who were not yet hospitalized were randomized to receive 180 mcg of interferon lambda or placebo.
This was a relatively current COVID trial, as you can see from the participant characteristics. The majority had been vaccinated, and nearly half of the infections were during the Omicron phase of the pandemic.
If you just want to cut to the chase, interferon worked.
The primary outcome – hospitalization or a prolonged emergency room visit for COVID – was 50% lower in the interferon group.
Key secondary outcomes, including death from COVID, were lower in the interferon group as well. These effects persisted across most of the subgroups I was looking out for.
Interferon seemed to help those who were already vaccinated and those who were unvaccinated. There’s a hint that it works better within the first few days of symptoms, which isn’t surprising; we’ve seen this for many of the therapeutics, including Paxlovid. Time is of the essence. Encouragingly, the effect was a bit more pronounced among those infected with Omicron.
Of course, if you have any experience with interferon, you know that the side effects can be pretty rough. In the bad old days when we treated hepatitis C infection with interferon, patients would get their injections on Friday in anticipation of being essentially out of commission with flu-like symptoms through the weekend. But we don’t see much evidence of adverse events in this trial, maybe due to the greater specificity of interferon lambda.
Putting it all together, the state of play for interferons in COVID may be changing. To date, the FDA has not recommended the use of interferon alfa or -beta for COVID-19, citing some data that they are ineffective or even harmful in hospitalized patients with COVID. Interferon lambda is not FDA approved and thus not even available in the United States. But the reason it has not been approved is that there has not been a large, well-conducted interferon lambda trial. Now there is. Will this study be enough to prompt an emergency use authorization? The elephant in the room, of course, is Paxlovid, which at this point has a longer safety track record and, importantly, is oral. I’d love to see a head-to-head trial. Short of that, I tend to be in favor of having more options on the table.
Dr. Perry Wilson is associate professor, department of medicine, and director, Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Maternal COVID-19 vaccine curbs infant infection
a new study shows.
Previous research has confirmed that COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies following maternal vaccination or maternal COVID-19 infection are present in umbilical cord blood, breast milk, and infant serum specimens, wrote Sarah C.J. Jorgensen, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues in their article published in The BMJ.
In the study, the researchers identified maternal and newborn pairs using administrative databases from Canada. The study population included 8,809 infants aged younger than 6 months who were born between May 7, 2021, and March 31, 2022, and who underwent testing for COVID-19 between May 7, 2021, and September 5, 2022.
Maternal vaccination with the primary COVID-19 mRNA monovalent vaccine series was defined as two vaccine doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of the doses after the conception date.
Maternal vaccination with the primary series plus one booster was defined as three doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of these doses after the conception date.
The primary outcome was the presence of delta or omicron COVID-19 infection or hospital admission of the infants.
The study population included 99 COVID-19 cases with the delta variant (with 4,365 controls) and 1,501 cases with the omicron variant (with 4,847 controls).
Overall, the vaccine effectiveness of maternal doses was 95% against delta infection and 45% against omicron.
The effectiveness against hospital admission in cases of delta and omicron variants were 97% and 53%, respectively.
The effectiveness of three doses was 73% against omicron infant infection and 80% against omicron-related infant hospitalization. Data were not available for the effectiveness of three doses against the delta variant.
The effectiveness of two doses of vaccine against infant omicron infection was highest when mothers received the second dose during the third trimester of pregnancy, compared with during the first trimester or second trimester (53% vs. 47% and 53% vs. 37%, respectively).
Vaccine effectiveness with two doses against infant infection from omicron was highest in the first 8 weeks of life (57%), then decreased to 40% among infants after 16 weeks of age.
Although the study was not designed to assess the mechanism of action of the impact of maternal vaccination on infants, the current study results were consistent with other recent studies showing a reduction in infections and hospitalizations among infants whose mothers received COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential unmeasured confounders not available in databases, such as whether infants were breastfed, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on home test results and the inability to assess the waning impact of the vaccine effectiveness against the delta variant because of the small number of delta cases, they said. However, the results suggest that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy was moderately to highly effective for protection against omicron and delta infection and infection-related hospitalization – especially during the first 8 weeks of life.
Effectiveness is encouraging, but updates are needed
The effectiveness of maternal vaccination to prevent COVID-19 infection and related hospitalizations in infants is promising, especially since those younger than 6 months have no other source of vaccine protection against COVID-19 infection, wrote Dana Danino, MD, of Soroka University Medical Center, Israel, and Ilan Youngster, MD, of Shamir Medical Center, Israel, in an accompanying editorial also published in The BMJ.
They also noted that maternal vaccination during pregnancy is an established method of protecting infants from infections such as influenza and pertussis.
Data from previous studies show that most infants whose mothers were vaccinated against COVID-19 during pregnancy retained maternal antibodies at 6 months, “but evidence for protection against neonatal COVID-19 infection has been deficient,” they said.
The current study findings support the value of vaccination during pregnancy, and the findings were strengthened by the large study population, the editorialists wrote. However, whether the same effectiveness holds for other COVID-19 strains such as BQ.1, BQ.1.1, BF.7, XBB, and XBB.1 remains unknown, they said.
Other areas in need of exploration include the optimal timing of vaccination during pregnancy, the protective effects of a bivalent mRNA vaccine (vs. the primary monovalent vaccine in the current study), and the potential benefits of additional boosters, they added.
“Although Jorgenson and colleagues’ study reinforces the value of maternal vaccination against COVID-19 during pregnancy, more studies are needed to better inform vaccination recommendations in an evolving landscape of new SARS-CoV-2 strains and novel vaccines,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-term Care; the study also received funding from the Canadian Immunization Research Network and the Public Health Agency of Canada. Dr. Jorgensen and the editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This article was updated on 3/2/2023.
a new study shows.
Previous research has confirmed that COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies following maternal vaccination or maternal COVID-19 infection are present in umbilical cord blood, breast milk, and infant serum specimens, wrote Sarah C.J. Jorgensen, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues in their article published in The BMJ.
In the study, the researchers identified maternal and newborn pairs using administrative databases from Canada. The study population included 8,809 infants aged younger than 6 months who were born between May 7, 2021, and March 31, 2022, and who underwent testing for COVID-19 between May 7, 2021, and September 5, 2022.
Maternal vaccination with the primary COVID-19 mRNA monovalent vaccine series was defined as two vaccine doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of the doses after the conception date.
Maternal vaccination with the primary series plus one booster was defined as three doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of these doses after the conception date.
The primary outcome was the presence of delta or omicron COVID-19 infection or hospital admission of the infants.
The study population included 99 COVID-19 cases with the delta variant (with 4,365 controls) and 1,501 cases with the omicron variant (with 4,847 controls).
Overall, the vaccine effectiveness of maternal doses was 95% against delta infection and 45% against omicron.
The effectiveness against hospital admission in cases of delta and omicron variants were 97% and 53%, respectively.
The effectiveness of three doses was 73% against omicron infant infection and 80% against omicron-related infant hospitalization. Data were not available for the effectiveness of three doses against the delta variant.
The effectiveness of two doses of vaccine against infant omicron infection was highest when mothers received the second dose during the third trimester of pregnancy, compared with during the first trimester or second trimester (53% vs. 47% and 53% vs. 37%, respectively).
Vaccine effectiveness with two doses against infant infection from omicron was highest in the first 8 weeks of life (57%), then decreased to 40% among infants after 16 weeks of age.
Although the study was not designed to assess the mechanism of action of the impact of maternal vaccination on infants, the current study results were consistent with other recent studies showing a reduction in infections and hospitalizations among infants whose mothers received COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential unmeasured confounders not available in databases, such as whether infants were breastfed, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on home test results and the inability to assess the waning impact of the vaccine effectiveness against the delta variant because of the small number of delta cases, they said. However, the results suggest that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy was moderately to highly effective for protection against omicron and delta infection and infection-related hospitalization – especially during the first 8 weeks of life.
Effectiveness is encouraging, but updates are needed
The effectiveness of maternal vaccination to prevent COVID-19 infection and related hospitalizations in infants is promising, especially since those younger than 6 months have no other source of vaccine protection against COVID-19 infection, wrote Dana Danino, MD, of Soroka University Medical Center, Israel, and Ilan Youngster, MD, of Shamir Medical Center, Israel, in an accompanying editorial also published in The BMJ.
They also noted that maternal vaccination during pregnancy is an established method of protecting infants from infections such as influenza and pertussis.
Data from previous studies show that most infants whose mothers were vaccinated against COVID-19 during pregnancy retained maternal antibodies at 6 months, “but evidence for protection against neonatal COVID-19 infection has been deficient,” they said.
The current study findings support the value of vaccination during pregnancy, and the findings were strengthened by the large study population, the editorialists wrote. However, whether the same effectiveness holds for other COVID-19 strains such as BQ.1, BQ.1.1, BF.7, XBB, and XBB.1 remains unknown, they said.
Other areas in need of exploration include the optimal timing of vaccination during pregnancy, the protective effects of a bivalent mRNA vaccine (vs. the primary monovalent vaccine in the current study), and the potential benefits of additional boosters, they added.
“Although Jorgenson and colleagues’ study reinforces the value of maternal vaccination against COVID-19 during pregnancy, more studies are needed to better inform vaccination recommendations in an evolving landscape of new SARS-CoV-2 strains and novel vaccines,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-term Care; the study also received funding from the Canadian Immunization Research Network and the Public Health Agency of Canada. Dr. Jorgensen and the editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This article was updated on 3/2/2023.
a new study shows.
Previous research has confirmed that COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies following maternal vaccination or maternal COVID-19 infection are present in umbilical cord blood, breast milk, and infant serum specimens, wrote Sarah C.J. Jorgensen, PharmD, MPH, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues in their article published in The BMJ.
In the study, the researchers identified maternal and newborn pairs using administrative databases from Canada. The study population included 8,809 infants aged younger than 6 months who were born between May 7, 2021, and March 31, 2022, and who underwent testing for COVID-19 between May 7, 2021, and September 5, 2022.
Maternal vaccination with the primary COVID-19 mRNA monovalent vaccine series was defined as two vaccine doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of the doses after the conception date.
Maternal vaccination with the primary series plus one booster was defined as three doses administered up to 14 days before delivery, with at least one of these doses after the conception date.
The primary outcome was the presence of delta or omicron COVID-19 infection or hospital admission of the infants.
The study population included 99 COVID-19 cases with the delta variant (with 4,365 controls) and 1,501 cases with the omicron variant (with 4,847 controls).
Overall, the vaccine effectiveness of maternal doses was 95% against delta infection and 45% against omicron.
The effectiveness against hospital admission in cases of delta and omicron variants were 97% and 53%, respectively.
The effectiveness of three doses was 73% against omicron infant infection and 80% against omicron-related infant hospitalization. Data were not available for the effectiveness of three doses against the delta variant.
The effectiveness of two doses of vaccine against infant omicron infection was highest when mothers received the second dose during the third trimester of pregnancy, compared with during the first trimester or second trimester (53% vs. 47% and 53% vs. 37%, respectively).
Vaccine effectiveness with two doses against infant infection from omicron was highest in the first 8 weeks of life (57%), then decreased to 40% among infants after 16 weeks of age.
Although the study was not designed to assess the mechanism of action of the impact of maternal vaccination on infants, the current study results were consistent with other recent studies showing a reduction in infections and hospitalizations among infants whose mothers received COVID-19 vaccines during pregnancy, the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential unmeasured confounders not available in databases, such as whether infants were breastfed, the researchers noted. Other limitations included a lack of data on home test results and the inability to assess the waning impact of the vaccine effectiveness against the delta variant because of the small number of delta cases, they said. However, the results suggest that the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy was moderately to highly effective for protection against omicron and delta infection and infection-related hospitalization – especially during the first 8 weeks of life.
Effectiveness is encouraging, but updates are needed
The effectiveness of maternal vaccination to prevent COVID-19 infection and related hospitalizations in infants is promising, especially since those younger than 6 months have no other source of vaccine protection against COVID-19 infection, wrote Dana Danino, MD, of Soroka University Medical Center, Israel, and Ilan Youngster, MD, of Shamir Medical Center, Israel, in an accompanying editorial also published in The BMJ.
They also noted that maternal vaccination during pregnancy is an established method of protecting infants from infections such as influenza and pertussis.
Data from previous studies show that most infants whose mothers were vaccinated against COVID-19 during pregnancy retained maternal antibodies at 6 months, “but evidence for protection against neonatal COVID-19 infection has been deficient,” they said.
The current study findings support the value of vaccination during pregnancy, and the findings were strengthened by the large study population, the editorialists wrote. However, whether the same effectiveness holds for other COVID-19 strains such as BQ.1, BQ.1.1, BF.7, XBB, and XBB.1 remains unknown, they said.
Other areas in need of exploration include the optimal timing of vaccination during pregnancy, the protective effects of a bivalent mRNA vaccine (vs. the primary monovalent vaccine in the current study), and the potential benefits of additional boosters, they added.
“Although Jorgenson and colleagues’ study reinforces the value of maternal vaccination against COVID-19 during pregnancy, more studies are needed to better inform vaccination recommendations in an evolving landscape of new SARS-CoV-2 strains and novel vaccines,” the editorialists concluded.
The study was supported by ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Long-term Care; the study also received funding from the Canadian Immunization Research Network and the Public Health Agency of Canada. Dr. Jorgensen and the editorialists had no financial conflicts to disclose.
*This article was updated on 3/2/2023.
FROM THE BMJ
Acute cardiac events common during COVID hospitalization
particularly among those with underlying heart disease, and are associated with more severe disease outcomes, a new study suggests.
“We expected to see acute cardiac events occurring among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 but were surprised by how frequently they occurred,” Rebecca C. Woodruff, PhD, MPH, of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, told this news organization.
Overall, she said, “about 1 in 10 adults experienced an acute cardiac event – including heart attacks and acute heart failure – while hospitalized with COVID-19, and this included people with no preexisting heart disease.”
However, she added, “about a quarter of those with underlying heart disease had an acute cardiac event. These patients tended to experience more severe disease outcomes relative to patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who did not experience an acute cardiac event.”
The findings might be relevant to hospitalizations for other viral diseases, “though we can’t say for sure,” she noted. “This study was modeled off a previous study conducted before the COVID-19 pandemic among adults hospitalized with influenza. About 11.7% of [those] adults experienced an acute cardiac event, which was a similar percentage as what we found among patients hospitalized with COVID-19.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Underlying cardiac disease key
Dr. Woodruff and colleagues analyzed medical records on a probability sample of 8,460 adults hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection identified from 99 U.S. counties in 14 U.S. states (about 10% of the United States population) from January to November 2021.
Among participants, 11.4% had an acute cardiac event during their hospitalization. The median age was 69 years; 56.5% were men; 48.7%, non-Hispanic White; 33.6%, non-Hispanic Black; 7.4%, Hispanic; and 7.1%, non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander.
As indicated, the prevalence was higher among those with underlying cardiac disease (23.4%), compared with those without (6.2%).
Acute ischemic heart disease (5.5%) and acute heart failure (5.4%) were the most prevalent events; 0.3% of participants had acute myocarditis or pericarditis.
Risk factors varied, depending on underlying cardiac disease status. Those who experienced one or more acute cardiac events had a greater risk for intensive care unit admission (adjusted risk ratio,1.9) and in-hospital death (aRR, 1.7) versus those who did not.
In multivariable analyses, the risk of experiencing acute heart failure was significantly greater among men (aRR, 1.5) and among those with a history of congestive heart failure (aRR, 13.5), atrial fibrillation (aRR, 1.6) or hypertension (aRR,1.3).
Among patients who experienced one or more acute cardiac events, 39.2% required an intensive care unit stay for a median of 5 days. Approximately 22.4% required invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and 21.1% died while hospitalized.
“Persons at greater risk for experiencing acute cardiac events during COVID-19–associated hospitalizations might benefit from more intensive clinical evaluation and monitoring during hospitalization,” the authors conclude.
The team currently is taking a closer look at acute myocarditis among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Woodruff said. Preliminary results were presented at the 2022 annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and a paper is forthcoming.
Contemporary data needed
James A. de Lemos, MD, co-chair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry Steering Committee and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said the findings mirror his team’s clinical experience in 2020 and 2021 and echo what was seen in the AHA COVID registry: that is, a 0.3% rate of myocarditis.
“The major caveat is that [the findings] may not be generalizable to contemporary COVID infection, both due to changing viral variants and higher levels of immunity in the population,” he said.
“Rates of COVID hospitalization are markedly lower with the current dominant variants, and we would expect the cardiac risk to be lower as well. I would like to see more contemporary data with current variants, particularly focused on higher risk patients with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. de Lemos added.
In a related editorial, George A. Mensa, MD, of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues suggest that the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on human health remains “incompletely examined.”
“The impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular mortality, in particular, appears to have varied widely, with no large increases seen in a number of the most developed countries but marked increases in hypertensive heart disease mortality seen in the United States in 2021,” they conclude. “The potential contribution of COVID-19 to these deaths, either directly or indirectly, remains to be determined.”
No commercial funding or relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
particularly among those with underlying heart disease, and are associated with more severe disease outcomes, a new study suggests.
“We expected to see acute cardiac events occurring among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 but were surprised by how frequently they occurred,” Rebecca C. Woodruff, PhD, MPH, of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, told this news organization.
Overall, she said, “about 1 in 10 adults experienced an acute cardiac event – including heart attacks and acute heart failure – while hospitalized with COVID-19, and this included people with no preexisting heart disease.”
However, she added, “about a quarter of those with underlying heart disease had an acute cardiac event. These patients tended to experience more severe disease outcomes relative to patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who did not experience an acute cardiac event.”
The findings might be relevant to hospitalizations for other viral diseases, “though we can’t say for sure,” she noted. “This study was modeled off a previous study conducted before the COVID-19 pandemic among adults hospitalized with influenza. About 11.7% of [those] adults experienced an acute cardiac event, which was a similar percentage as what we found among patients hospitalized with COVID-19.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Underlying cardiac disease key
Dr. Woodruff and colleagues analyzed medical records on a probability sample of 8,460 adults hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection identified from 99 U.S. counties in 14 U.S. states (about 10% of the United States population) from January to November 2021.
Among participants, 11.4% had an acute cardiac event during their hospitalization. The median age was 69 years; 56.5% were men; 48.7%, non-Hispanic White; 33.6%, non-Hispanic Black; 7.4%, Hispanic; and 7.1%, non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander.
As indicated, the prevalence was higher among those with underlying cardiac disease (23.4%), compared with those without (6.2%).
Acute ischemic heart disease (5.5%) and acute heart failure (5.4%) were the most prevalent events; 0.3% of participants had acute myocarditis or pericarditis.
Risk factors varied, depending on underlying cardiac disease status. Those who experienced one or more acute cardiac events had a greater risk for intensive care unit admission (adjusted risk ratio,1.9) and in-hospital death (aRR, 1.7) versus those who did not.
In multivariable analyses, the risk of experiencing acute heart failure was significantly greater among men (aRR, 1.5) and among those with a history of congestive heart failure (aRR, 13.5), atrial fibrillation (aRR, 1.6) or hypertension (aRR,1.3).
Among patients who experienced one or more acute cardiac events, 39.2% required an intensive care unit stay for a median of 5 days. Approximately 22.4% required invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and 21.1% died while hospitalized.
“Persons at greater risk for experiencing acute cardiac events during COVID-19–associated hospitalizations might benefit from more intensive clinical evaluation and monitoring during hospitalization,” the authors conclude.
The team currently is taking a closer look at acute myocarditis among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Woodruff said. Preliminary results were presented at the 2022 annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and a paper is forthcoming.
Contemporary data needed
James A. de Lemos, MD, co-chair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry Steering Committee and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said the findings mirror his team’s clinical experience in 2020 and 2021 and echo what was seen in the AHA COVID registry: that is, a 0.3% rate of myocarditis.
“The major caveat is that [the findings] may not be generalizable to contemporary COVID infection, both due to changing viral variants and higher levels of immunity in the population,” he said.
“Rates of COVID hospitalization are markedly lower with the current dominant variants, and we would expect the cardiac risk to be lower as well. I would like to see more contemporary data with current variants, particularly focused on higher risk patients with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. de Lemos added.
In a related editorial, George A. Mensa, MD, of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues suggest that the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on human health remains “incompletely examined.”
“The impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular mortality, in particular, appears to have varied widely, with no large increases seen in a number of the most developed countries but marked increases in hypertensive heart disease mortality seen in the United States in 2021,” they conclude. “The potential contribution of COVID-19 to these deaths, either directly or indirectly, remains to be determined.”
No commercial funding or relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
particularly among those with underlying heart disease, and are associated with more severe disease outcomes, a new study suggests.
“We expected to see acute cardiac events occurring among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 but were surprised by how frequently they occurred,” Rebecca C. Woodruff, PhD, MPH, of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, told this news organization.
Overall, she said, “about 1 in 10 adults experienced an acute cardiac event – including heart attacks and acute heart failure – while hospitalized with COVID-19, and this included people with no preexisting heart disease.”
However, she added, “about a quarter of those with underlying heart disease had an acute cardiac event. These patients tended to experience more severe disease outcomes relative to patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who did not experience an acute cardiac event.”
The findings might be relevant to hospitalizations for other viral diseases, “though we can’t say for sure,” she noted. “This study was modeled off a previous study conducted before the COVID-19 pandemic among adults hospitalized with influenza. About 11.7% of [those] adults experienced an acute cardiac event, which was a similar percentage as what we found among patients hospitalized with COVID-19.”
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Underlying cardiac disease key
Dr. Woodruff and colleagues analyzed medical records on a probability sample of 8,460 adults hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection identified from 99 U.S. counties in 14 U.S. states (about 10% of the United States population) from January to November 2021.
Among participants, 11.4% had an acute cardiac event during their hospitalization. The median age was 69 years; 56.5% were men; 48.7%, non-Hispanic White; 33.6%, non-Hispanic Black; 7.4%, Hispanic; and 7.1%, non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander.
As indicated, the prevalence was higher among those with underlying cardiac disease (23.4%), compared with those without (6.2%).
Acute ischemic heart disease (5.5%) and acute heart failure (5.4%) were the most prevalent events; 0.3% of participants had acute myocarditis or pericarditis.
Risk factors varied, depending on underlying cardiac disease status. Those who experienced one or more acute cardiac events had a greater risk for intensive care unit admission (adjusted risk ratio,1.9) and in-hospital death (aRR, 1.7) versus those who did not.
In multivariable analyses, the risk of experiencing acute heart failure was significantly greater among men (aRR, 1.5) and among those with a history of congestive heart failure (aRR, 13.5), atrial fibrillation (aRR, 1.6) or hypertension (aRR,1.3).
Among patients who experienced one or more acute cardiac events, 39.2% required an intensive care unit stay for a median of 5 days. Approximately 22.4% required invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and 21.1% died while hospitalized.
“Persons at greater risk for experiencing acute cardiac events during COVID-19–associated hospitalizations might benefit from more intensive clinical evaluation and monitoring during hospitalization,” the authors conclude.
The team currently is taking a closer look at acute myocarditis among patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Dr. Woodruff said. Preliminary results were presented at the 2022 annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association and a paper is forthcoming.
Contemporary data needed
James A. de Lemos, MD, co-chair of the American Heart Association’s COVID-19 CVD Registry Steering Committee and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said the findings mirror his team’s clinical experience in 2020 and 2021 and echo what was seen in the AHA COVID registry: that is, a 0.3% rate of myocarditis.
“The major caveat is that [the findings] may not be generalizable to contemporary COVID infection, both due to changing viral variants and higher levels of immunity in the population,” he said.
“Rates of COVID hospitalization are markedly lower with the current dominant variants, and we would expect the cardiac risk to be lower as well. I would like to see more contemporary data with current variants, particularly focused on higher risk patients with cardiovascular disease,” Dr. de Lemos added.
In a related editorial, George A. Mensa, MD, of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in Bethesda, Md., and colleagues suggest that the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on human health remains “incompletely examined.”
“The impact of COVID-19 on cardiovascular mortality, in particular, appears to have varied widely, with no large increases seen in a number of the most developed countries but marked increases in hypertensive heart disease mortality seen in the United States in 2021,” they conclude. “The potential contribution of COVID-19 to these deaths, either directly or indirectly, remains to be determined.”
No commercial funding or relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
A technicality could keep RSV shots from kids in need
which has put an estimated 90,000 U.S. infants and small children in the hospital since the start of October.
But only one of the shots is designed to be given to babies, and a glitch in congressional language may make it difficult to allow children from low-income families to get it as readily as the well insured.
Since 1994, routine vaccination has been a childhood entitlement under the Vaccines for Children program, through which the federal government buys millions of vaccines and provides them free through pediatricians and clinics to children who are uninsured, underinsured, or on Medicaid – more than half of all American kids.
The 1993 law creating the program didn’t specifically include antibody shots, which were used only as rare emergency therapy at the time the bill was written.
But the first medication of its kind likely to be available to babies, called nirsevimab (it was approved in Europe in December, and Food and Drug Administration approval is expected in the summer of 2023), is not a vaccine but rather a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes RSV in the bloodstream.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is certain to recommend giving the antibody to infants, said Kelly Moore, MD, president of the advocacy group Immunize.org. The CDC is currently assessing whether nirsevimab would be eligible for the Vaccines for Children program, agency spokesperson Kristen Nordlund told KHN.
Failing to do so would “consign thousands upon thousands of infants to hospitalization and serious illness for semantic reasons despite existence of an immunization that functionally performs just like a seasonal vaccine,” Dr. Moore said.
Officials from Sanofi, which is producing the nirsevimab injection along with AstraZeneca, declined to state a price but said the range would be similar to that of a pediatric vaccine course. The CDC pays about $650 for the most expensive routine vaccine, the four shots against pneumococcal infection. In other words, FDA approval would make nirsevimab a blockbuster drug worth billions annually if it’s given to a large share of the 3.7 million or so children born in the U.S. each year.
Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline are making traditional vaccines against RSV and expect FDA approval later in 2023. Pfizer’s shot initially would be given to pregnant women – to shield their babies from the disease – while GSK’s would be given to the elderly.
Vaccines designed for infants are in the pipeline, but some experts are still nervous about them. A 1966 RSV vaccine trial failed spectacularly, killing two toddlers, and immunologists aren’t totally in agreement over the cause, said Barney Graham, MD, PhD, the retired National Institutes of Health scientist whose studies of the episode contributed to successful COVID-19 and RSV vaccines.
After 2 years of COVID lockdowns and masking slowed its transmission, RSV exploded across the United States in 2023, swamping pediatric intensive care units.
Sanofi and AstraZeneca hope to have nirsevimab approved by the FDA, recommended by the CDC, and deployed nationwide by fall to prevent future RSV epidemics.
Their product is designed to be provided before a baby’s first winter RSV season. In clinical trials, the antibodies provided up to 5 months of protection. Most children wouldn’t need a second dose because the virus is not a mortal danger to healthy kids over a year old, said Jon Heinrichs, a senior member of Sanofi’s vaccines division.
If the antibody treatment is not accepted for the Vaccines for Children program, that will limit access to the shot for the uninsured and those on Medicaid, the majority of whom represent racial or ethnic minorities, Dr. Moore said. The drugmakers would have to negotiate with each state’s Medicaid program to get it on their formularies.
Excluding the shot from Vaccines for Children “would only worsen existing health disparities,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chair of the infectious diseases committee of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
RSV affects babies of all social classes but tends to hit poor, crowded households hardest, said Dr. Graham. “Family history of asthma or allergy makes it worse,” he said, and premature babies are also at higher risk.
While 2%-3% of U.S. infants are hospitalized with RSV each year, only a few hundred don’t survive. But as many as 10,000 people 65 and older perish because of an infection every year, and a little-discussed legal change will make RSV and other vaccines more available to this group.
A section of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act that went into effect Jan. 1 ends out-of-pocket payments for all vaccines by Medicare patients – including RSV vaccines, if they are licensed for this group.
Before, “if you hadn’t met your deductible, it could be very expensive,” said Leonard Friedland, MD, vice president for scientific affairs and public health in GSK’s vaccines division, which also makes shingles and combination tetanus-diphtheria-whooping cough boosters covered by the new law. “It’s a tremendously important advance.”
Of course, high levels of vaccine hesitancy are likely to blunt uptake of the shots regardless of who pays, said Jennifer Reich, a sociologist at the University of Colorado who studies vaccination attitudes.
New types of shots, like the Sanofi-AstraZeneca antibodies, often alarm parents, and Pfizer’s shot for pregnant women is likely to push fear buttons as well, she said.
Public health officials “don’t seem very savvy about how to get ahead” of claims that vaccines undermine fertility or otherwise harm people, said Ms. Reich.
On the other hand, this winter’s RSV epidemic will be persuasive to many parents, said Heidi Larson, leader of the Vaccine Confidence Project and a professor of anthropology at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“It’s a scary thing to have your kid hospitalized with RSV,” she said.
While unfortunate, “the high number of children who died or were admitted to the ICU in the past season with RSV – in some ways that’s helpful,” said Laura Riley, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Specialists in her field haven’t really started talking about how to communicate with women about the vaccine, said Dr. Riley, who chairs the immunization group at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Everyone’s been waiting to see if it gets approved,” she said. “The education has to start soon, but it’s hard to roll out education before you roll out the shot.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
which has put an estimated 90,000 U.S. infants and small children in the hospital since the start of October.
But only one of the shots is designed to be given to babies, and a glitch in congressional language may make it difficult to allow children from low-income families to get it as readily as the well insured.
Since 1994, routine vaccination has been a childhood entitlement under the Vaccines for Children program, through which the federal government buys millions of vaccines and provides them free through pediatricians and clinics to children who are uninsured, underinsured, or on Medicaid – more than half of all American kids.
The 1993 law creating the program didn’t specifically include antibody shots, which were used only as rare emergency therapy at the time the bill was written.
But the first medication of its kind likely to be available to babies, called nirsevimab (it was approved in Europe in December, and Food and Drug Administration approval is expected in the summer of 2023), is not a vaccine but rather a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes RSV in the bloodstream.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is certain to recommend giving the antibody to infants, said Kelly Moore, MD, president of the advocacy group Immunize.org. The CDC is currently assessing whether nirsevimab would be eligible for the Vaccines for Children program, agency spokesperson Kristen Nordlund told KHN.
Failing to do so would “consign thousands upon thousands of infants to hospitalization and serious illness for semantic reasons despite existence of an immunization that functionally performs just like a seasonal vaccine,” Dr. Moore said.
Officials from Sanofi, which is producing the nirsevimab injection along with AstraZeneca, declined to state a price but said the range would be similar to that of a pediatric vaccine course. The CDC pays about $650 for the most expensive routine vaccine, the four shots against pneumococcal infection. In other words, FDA approval would make nirsevimab a blockbuster drug worth billions annually if it’s given to a large share of the 3.7 million or so children born in the U.S. each year.
Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline are making traditional vaccines against RSV and expect FDA approval later in 2023. Pfizer’s shot initially would be given to pregnant women – to shield their babies from the disease – while GSK’s would be given to the elderly.
Vaccines designed for infants are in the pipeline, but some experts are still nervous about them. A 1966 RSV vaccine trial failed spectacularly, killing two toddlers, and immunologists aren’t totally in agreement over the cause, said Barney Graham, MD, PhD, the retired National Institutes of Health scientist whose studies of the episode contributed to successful COVID-19 and RSV vaccines.
After 2 years of COVID lockdowns and masking slowed its transmission, RSV exploded across the United States in 2023, swamping pediatric intensive care units.
Sanofi and AstraZeneca hope to have nirsevimab approved by the FDA, recommended by the CDC, and deployed nationwide by fall to prevent future RSV epidemics.
Their product is designed to be provided before a baby’s first winter RSV season. In clinical trials, the antibodies provided up to 5 months of protection. Most children wouldn’t need a second dose because the virus is not a mortal danger to healthy kids over a year old, said Jon Heinrichs, a senior member of Sanofi’s vaccines division.
If the antibody treatment is not accepted for the Vaccines for Children program, that will limit access to the shot for the uninsured and those on Medicaid, the majority of whom represent racial or ethnic minorities, Dr. Moore said. The drugmakers would have to negotiate with each state’s Medicaid program to get it on their formularies.
Excluding the shot from Vaccines for Children “would only worsen existing health disparities,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chair of the infectious diseases committee of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
RSV affects babies of all social classes but tends to hit poor, crowded households hardest, said Dr. Graham. “Family history of asthma or allergy makes it worse,” he said, and premature babies are also at higher risk.
While 2%-3% of U.S. infants are hospitalized with RSV each year, only a few hundred don’t survive. But as many as 10,000 people 65 and older perish because of an infection every year, and a little-discussed legal change will make RSV and other vaccines more available to this group.
A section of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act that went into effect Jan. 1 ends out-of-pocket payments for all vaccines by Medicare patients – including RSV vaccines, if they are licensed for this group.
Before, “if you hadn’t met your deductible, it could be very expensive,” said Leonard Friedland, MD, vice president for scientific affairs and public health in GSK’s vaccines division, which also makes shingles and combination tetanus-diphtheria-whooping cough boosters covered by the new law. “It’s a tremendously important advance.”
Of course, high levels of vaccine hesitancy are likely to blunt uptake of the shots regardless of who pays, said Jennifer Reich, a sociologist at the University of Colorado who studies vaccination attitudes.
New types of shots, like the Sanofi-AstraZeneca antibodies, often alarm parents, and Pfizer’s shot for pregnant women is likely to push fear buttons as well, she said.
Public health officials “don’t seem very savvy about how to get ahead” of claims that vaccines undermine fertility or otherwise harm people, said Ms. Reich.
On the other hand, this winter’s RSV epidemic will be persuasive to many parents, said Heidi Larson, leader of the Vaccine Confidence Project and a professor of anthropology at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“It’s a scary thing to have your kid hospitalized with RSV,” she said.
While unfortunate, “the high number of children who died or were admitted to the ICU in the past season with RSV – in some ways that’s helpful,” said Laura Riley, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Specialists in her field haven’t really started talking about how to communicate with women about the vaccine, said Dr. Riley, who chairs the immunization group at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Everyone’s been waiting to see if it gets approved,” she said. “The education has to start soon, but it’s hard to roll out education before you roll out the shot.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
which has put an estimated 90,000 U.S. infants and small children in the hospital since the start of October.
But only one of the shots is designed to be given to babies, and a glitch in congressional language may make it difficult to allow children from low-income families to get it as readily as the well insured.
Since 1994, routine vaccination has been a childhood entitlement under the Vaccines for Children program, through which the federal government buys millions of vaccines and provides them free through pediatricians and clinics to children who are uninsured, underinsured, or on Medicaid – more than half of all American kids.
The 1993 law creating the program didn’t specifically include antibody shots, which were used only as rare emergency therapy at the time the bill was written.
But the first medication of its kind likely to be available to babies, called nirsevimab (it was approved in Europe in December, and Food and Drug Administration approval is expected in the summer of 2023), is not a vaccine but rather a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes RSV in the bloodstream.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is certain to recommend giving the antibody to infants, said Kelly Moore, MD, president of the advocacy group Immunize.org. The CDC is currently assessing whether nirsevimab would be eligible for the Vaccines for Children program, agency spokesperson Kristen Nordlund told KHN.
Failing to do so would “consign thousands upon thousands of infants to hospitalization and serious illness for semantic reasons despite existence of an immunization that functionally performs just like a seasonal vaccine,” Dr. Moore said.
Officials from Sanofi, which is producing the nirsevimab injection along with AstraZeneca, declined to state a price but said the range would be similar to that of a pediatric vaccine course. The CDC pays about $650 for the most expensive routine vaccine, the four shots against pneumococcal infection. In other words, FDA approval would make nirsevimab a blockbuster drug worth billions annually if it’s given to a large share of the 3.7 million or so children born in the U.S. each year.
Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline are making traditional vaccines against RSV and expect FDA approval later in 2023. Pfizer’s shot initially would be given to pregnant women – to shield their babies from the disease – while GSK’s would be given to the elderly.
Vaccines designed for infants are in the pipeline, but some experts are still nervous about them. A 1966 RSV vaccine trial failed spectacularly, killing two toddlers, and immunologists aren’t totally in agreement over the cause, said Barney Graham, MD, PhD, the retired National Institutes of Health scientist whose studies of the episode contributed to successful COVID-19 and RSV vaccines.
After 2 years of COVID lockdowns and masking slowed its transmission, RSV exploded across the United States in 2023, swamping pediatric intensive care units.
Sanofi and AstraZeneca hope to have nirsevimab approved by the FDA, recommended by the CDC, and deployed nationwide by fall to prevent future RSV epidemics.
Their product is designed to be provided before a baby’s first winter RSV season. In clinical trials, the antibodies provided up to 5 months of protection. Most children wouldn’t need a second dose because the virus is not a mortal danger to healthy kids over a year old, said Jon Heinrichs, a senior member of Sanofi’s vaccines division.
If the antibody treatment is not accepted for the Vaccines for Children program, that will limit access to the shot for the uninsured and those on Medicaid, the majority of whom represent racial or ethnic minorities, Dr. Moore said. The drugmakers would have to negotiate with each state’s Medicaid program to get it on their formularies.
Excluding the shot from Vaccines for Children “would only worsen existing health disparities,” said Sean O’Leary, MD, a professor of pediatrics at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and chair of the infectious diseases committee of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
RSV affects babies of all social classes but tends to hit poor, crowded households hardest, said Dr. Graham. “Family history of asthma or allergy makes it worse,” he said, and premature babies are also at higher risk.
While 2%-3% of U.S. infants are hospitalized with RSV each year, only a few hundred don’t survive. But as many as 10,000 people 65 and older perish because of an infection every year, and a little-discussed legal change will make RSV and other vaccines more available to this group.
A section of the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act that went into effect Jan. 1 ends out-of-pocket payments for all vaccines by Medicare patients – including RSV vaccines, if they are licensed for this group.
Before, “if you hadn’t met your deductible, it could be very expensive,” said Leonard Friedland, MD, vice president for scientific affairs and public health in GSK’s vaccines division, which also makes shingles and combination tetanus-diphtheria-whooping cough boosters covered by the new law. “It’s a tremendously important advance.”
Of course, high levels of vaccine hesitancy are likely to blunt uptake of the shots regardless of who pays, said Jennifer Reich, a sociologist at the University of Colorado who studies vaccination attitudes.
New types of shots, like the Sanofi-AstraZeneca antibodies, often alarm parents, and Pfizer’s shot for pregnant women is likely to push fear buttons as well, she said.
Public health officials “don’t seem very savvy about how to get ahead” of claims that vaccines undermine fertility or otherwise harm people, said Ms. Reich.
On the other hand, this winter’s RSV epidemic will be persuasive to many parents, said Heidi Larson, leader of the Vaccine Confidence Project and a professor of anthropology at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
“It’s a scary thing to have your kid hospitalized with RSV,” she said.
While unfortunate, “the high number of children who died or were admitted to the ICU in the past season with RSV – in some ways that’s helpful,” said Laura Riley, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Specialists in her field haven’t really started talking about how to communicate with women about the vaccine, said Dr. Riley, who chairs the immunization group at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
“Everyone’s been waiting to see if it gets approved,” she said. “The education has to start soon, but it’s hard to roll out education before you roll out the shot.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
COVID emergency orders ending: What’s next?
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Washington medical board charges doctor with spreading COVID misinformation
Doctors and professional organizations are standing guard, hoping to protect patients from any harm that results from mistruths spread by colleagues.
Case in point: Several physicians and the American Board of Pathology filed complaints with Washington and Idaho medical boards alleging that Ryan Cole, MD, a board-certified pathologist who practices in Boise, Idaho, but who also holds a license in Washington, has spread antivaccine and pro-ivermectin statements on social media. Dr. Cole is one of the founders of America’s Frontline Doctors, a right-wing political organization. Dr. Cole did not respond to a request for comment.
Gary W. Procop, MD, CEO, American Board of Pathology, told this news organization that “as physicians and board-certified pathologists, we have a public trust, and we must be accountable to patients, society, and the profession. Misinformation can cause real harm to patients, which may include death. Misinformation diverts patients away from lifesaving vaccination and other preventive measures, promotes viral transmission, and recommends ineffective therapies that may be toxic instead of evidence-based medical care.”
Cavalcade of complaints
Several doctors also chimed in with formal complaints alleging that Cole is spreading unreliable information, according to a report from KTVB News. For example, a Boise doctor wrote in his complaint that Dr. Cole is “a major purveyor of misinformation” and called it “amazing” that the physician was continuing to publicly support debunked information about COVID-19 more than a year into the pandemic. The doctor also stated, “Cole is a health menace, abusing his status as a physician to mislead the public.”
As a result of such complaints, the Washington medical board has charged Cole with COVID-19–related violations. It is unclear whether or not the Idaho medical board will sanction the doctor. At least 12 medical boards have sanctioned doctors for similar violations since the start of the pandemic.
The statement of charges from the Washington medical board contends that since March 2021, Dr. Cole has made numerous misleading statements regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines, the use of ivermectin to treat COVID-19, and the effectiveness of masks.
In addition, the statement alleges that Dr. Cole treated several COVID-19 patients via telemedicine. During these sessions, he prescribed ivermectin, an antiparasite drug that has not been found to have any effectiveness in treating, curing, or preventing COVID-19. One of the patients died after receiving this treatment, according to the complaint.
Citing a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Procop pointed out that use of ivermectin, which is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID-19, is particularly troubling.
“There is a concern whenever an ineffective treatment is prescribed when more effective and scientifically proven therapies are available. Therapeutics have potential side effects, and toxicities have been associated with the use of ivermectin,” Dr. Procop said. “The benefits of therapy should always outweigh the risks of treatment.”
If the Washington medical board finds that Dr. Cole has engaged in unprofessional conduct, possible sanctions include revocation or suspension of his license. Washington state law also provides for a range of other possible sanctions, including restriction or limitation of his practice, requiring that he complete a specific program of remedial education or treatment, monitoring of his practice, censure or reprimand, probation, a fine of up to $5,000 for each violation, or refunding fees that his practice has billed to and collected from patients. Dr. Cole had until January 30 to respond to the medical board’s statement.
“The American Board of Pathology supports the actions of the Washington State Medical Board regarding their inquiries into any physician that holds license in their state who makes false and misleading medical claims, or provides medical care beyond their scope of practice, as indicated by their training,” Dr. Procop said.
Law in limbo
While medical boards are seeking to sanction professionals who spread falsehoods, the pause button has been hit on the California law that allows regulators to punish doctors for spreading false information about COVID-19 vaccinations and treatments.
The law went into effect Jan. 1 but was temporarily halted when U.S. District Judge William B. Shubb of the Eastern District of California granted a preliminary injunction against the law on Jan. 25, according to a report in the Sacramento Bee.
Mr. Shubb said the measure’s definition of “misinformation” was “unconstitutionally vague” under the due process clause of the 14th Amendment. He also criticized the law’s definition of “misinformation” as being “grammatically incoherent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors and professional organizations are standing guard, hoping to protect patients from any harm that results from mistruths spread by colleagues.
Case in point: Several physicians and the American Board of Pathology filed complaints with Washington and Idaho medical boards alleging that Ryan Cole, MD, a board-certified pathologist who practices in Boise, Idaho, but who also holds a license in Washington, has spread antivaccine and pro-ivermectin statements on social media. Dr. Cole is one of the founders of America’s Frontline Doctors, a right-wing political organization. Dr. Cole did not respond to a request for comment.
Gary W. Procop, MD, CEO, American Board of Pathology, told this news organization that “as physicians and board-certified pathologists, we have a public trust, and we must be accountable to patients, society, and the profession. Misinformation can cause real harm to patients, which may include death. Misinformation diverts patients away from lifesaving vaccination and other preventive measures, promotes viral transmission, and recommends ineffective therapies that may be toxic instead of evidence-based medical care.”
Cavalcade of complaints
Several doctors also chimed in with formal complaints alleging that Cole is spreading unreliable information, according to a report from KTVB News. For example, a Boise doctor wrote in his complaint that Dr. Cole is “a major purveyor of misinformation” and called it “amazing” that the physician was continuing to publicly support debunked information about COVID-19 more than a year into the pandemic. The doctor also stated, “Cole is a health menace, abusing his status as a physician to mislead the public.”
As a result of such complaints, the Washington medical board has charged Cole with COVID-19–related violations. It is unclear whether or not the Idaho medical board will sanction the doctor. At least 12 medical boards have sanctioned doctors for similar violations since the start of the pandemic.
The statement of charges from the Washington medical board contends that since March 2021, Dr. Cole has made numerous misleading statements regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines, the use of ivermectin to treat COVID-19, and the effectiveness of masks.
In addition, the statement alleges that Dr. Cole treated several COVID-19 patients via telemedicine. During these sessions, he prescribed ivermectin, an antiparasite drug that has not been found to have any effectiveness in treating, curing, or preventing COVID-19. One of the patients died after receiving this treatment, according to the complaint.
Citing a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Procop pointed out that use of ivermectin, which is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID-19, is particularly troubling.
“There is a concern whenever an ineffective treatment is prescribed when more effective and scientifically proven therapies are available. Therapeutics have potential side effects, and toxicities have been associated with the use of ivermectin,” Dr. Procop said. “The benefits of therapy should always outweigh the risks of treatment.”
If the Washington medical board finds that Dr. Cole has engaged in unprofessional conduct, possible sanctions include revocation or suspension of his license. Washington state law also provides for a range of other possible sanctions, including restriction or limitation of his practice, requiring that he complete a specific program of remedial education or treatment, monitoring of his practice, censure or reprimand, probation, a fine of up to $5,000 for each violation, or refunding fees that his practice has billed to and collected from patients. Dr. Cole had until January 30 to respond to the medical board’s statement.
“The American Board of Pathology supports the actions of the Washington State Medical Board regarding their inquiries into any physician that holds license in their state who makes false and misleading medical claims, or provides medical care beyond their scope of practice, as indicated by their training,” Dr. Procop said.
Law in limbo
While medical boards are seeking to sanction professionals who spread falsehoods, the pause button has been hit on the California law that allows regulators to punish doctors for spreading false information about COVID-19 vaccinations and treatments.
The law went into effect Jan. 1 but was temporarily halted when U.S. District Judge William B. Shubb of the Eastern District of California granted a preliminary injunction against the law on Jan. 25, according to a report in the Sacramento Bee.
Mr. Shubb said the measure’s definition of “misinformation” was “unconstitutionally vague” under the due process clause of the 14th Amendment. He also criticized the law’s definition of “misinformation” as being “grammatically incoherent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doctors and professional organizations are standing guard, hoping to protect patients from any harm that results from mistruths spread by colleagues.
Case in point: Several physicians and the American Board of Pathology filed complaints with Washington and Idaho medical boards alleging that Ryan Cole, MD, a board-certified pathologist who practices in Boise, Idaho, but who also holds a license in Washington, has spread antivaccine and pro-ivermectin statements on social media. Dr. Cole is one of the founders of America’s Frontline Doctors, a right-wing political organization. Dr. Cole did not respond to a request for comment.
Gary W. Procop, MD, CEO, American Board of Pathology, told this news organization that “as physicians and board-certified pathologists, we have a public trust, and we must be accountable to patients, society, and the profession. Misinformation can cause real harm to patients, which may include death. Misinformation diverts patients away from lifesaving vaccination and other preventive measures, promotes viral transmission, and recommends ineffective therapies that may be toxic instead of evidence-based medical care.”
Cavalcade of complaints
Several doctors also chimed in with formal complaints alleging that Cole is spreading unreliable information, according to a report from KTVB News. For example, a Boise doctor wrote in his complaint that Dr. Cole is “a major purveyor of misinformation” and called it “amazing” that the physician was continuing to publicly support debunked information about COVID-19 more than a year into the pandemic. The doctor also stated, “Cole is a health menace, abusing his status as a physician to mislead the public.”
As a result of such complaints, the Washington medical board has charged Cole with COVID-19–related violations. It is unclear whether or not the Idaho medical board will sanction the doctor. At least 12 medical boards have sanctioned doctors for similar violations since the start of the pandemic.
The statement of charges from the Washington medical board contends that since March 2021, Dr. Cole has made numerous misleading statements regarding the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines, the use of ivermectin to treat COVID-19, and the effectiveness of masks.
In addition, the statement alleges that Dr. Cole treated several COVID-19 patients via telemedicine. During these sessions, he prescribed ivermectin, an antiparasite drug that has not been found to have any effectiveness in treating, curing, or preventing COVID-19. One of the patients died after receiving this treatment, according to the complaint.
Citing a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, Dr. Procop pointed out that use of ivermectin, which is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat COVID-19, is particularly troubling.
“There is a concern whenever an ineffective treatment is prescribed when more effective and scientifically proven therapies are available. Therapeutics have potential side effects, and toxicities have been associated with the use of ivermectin,” Dr. Procop said. “The benefits of therapy should always outweigh the risks of treatment.”
If the Washington medical board finds that Dr. Cole has engaged in unprofessional conduct, possible sanctions include revocation or suspension of his license. Washington state law also provides for a range of other possible sanctions, including restriction or limitation of his practice, requiring that he complete a specific program of remedial education or treatment, monitoring of his practice, censure or reprimand, probation, a fine of up to $5,000 for each violation, or refunding fees that his practice has billed to and collected from patients. Dr. Cole had until January 30 to respond to the medical board’s statement.
“The American Board of Pathology supports the actions of the Washington State Medical Board regarding their inquiries into any physician that holds license in their state who makes false and misleading medical claims, or provides medical care beyond their scope of practice, as indicated by their training,” Dr. Procop said.
Law in limbo
While medical boards are seeking to sanction professionals who spread falsehoods, the pause button has been hit on the California law that allows regulators to punish doctors for spreading false information about COVID-19 vaccinations and treatments.
The law went into effect Jan. 1 but was temporarily halted when U.S. District Judge William B. Shubb of the Eastern District of California granted a preliminary injunction against the law on Jan. 25, according to a report in the Sacramento Bee.
Mr. Shubb said the measure’s definition of “misinformation” was “unconstitutionally vague” under the due process clause of the 14th Amendment. He also criticized the law’s definition of “misinformation” as being “grammatically incoherent.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Managing respiratory symptoms in the ‘tripledemic’ era
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID affecting more than one-third of college students, faculty
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
With a median age of 23 years, the study is unique for evaluating mostly healthy, young adults and for its rare look at long COVID in a university community.
The more symptoms during a bout with COVID, the greater the risk for long COVID, the researchers found. That lines up with previous studies. Also, the more vaccinations and booster shots against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID, the lower the long COVID risk.
Women were more likely than men to be affected. Current or prior smoking, seeking medical care for COVID, and receiving antibody treatment also were linked to higher chances for developing long COVID.
Lead author Megan Landry, DrPH, MPH, and colleagues were already assessing students, staff, and faculty at George Washington University, Washington, who tested positive for COVID. Then they started seeing symptoms that lasted 28 days or more after their 10-day isolation period.
“We were starting to recognize that individuals ... were still having symptoms longer than the typical isolation period,” said Dr. Landry. So they developed a questionnaire to figure out the how long these symptoms last and how many people are affected by them.
The list of potential symptoms was long and included trouble thinking, fatigue, loss of smell or taste, shortness of breath, and more.
The study was published online in Emerging Infectious Diseases. Results are based on records and responses from 1,388 students, faculty, and staff from July 2021 to March 2022.
People had a median of four long COVID symptoms, about 63% were women, and 56% were non-Hispanic White. About three-quarters were students and the remainder were faculty and staff.
The finding that 36% of people with a history of COVID reported long COVID symptoms did not surprise Dr. Landry.
“Based on the literature that’s currently out there, it ranges from a 10% to an 80% prevalence of long COVID,” she said. “We kind of figured that we would fall somewhere in there.”
In contrast, that figure seemed high to Eric Topol, MD.
“That’s really high,” said Dr. Topol, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif. He added most studies estimate that about 10% of people with a history of acute infection develop long COVID.
Even at 10%, which could be an underestimate, that’s a lot of affected people globally.
“At least 65 million individuals around the world have long COVID, based on a conservative estimated incidence of 10% of infected people and more than 651 million documented COVID-19 cases worldwide; the number is likely much higher due to many undocumented cases,” Dr. Topol and colleagues wrote in a long COVID review article published in Nature Reviews Microbiology.
About 30% of study participants were fully vaccinated with an initial vaccine series, 42% had received a booster dose, and 29% were not fully vaccinated at the time of their first positive test for COVID. Those who were not fully vaccinated were significantly more likely to report symptoms of long COVID.
“I know a lot of people wish they could put COVID on the back burner or brush it under the rug, but COVID is still a real thing. We need to continue supporting vaccines and boosters and make sure people are up to date. Not only for COVID, but for flu as well,” Dr. Topol said
Research continues
“Long COVID is still evolving and we continue to learn more about it every day,” Landry said. “It’s just so new and there are still a lot of unknowns. That’s why it’s important to get this information out.”
People with long COVID often have a hard time with occupational, educational, social, or personal activities, compared with before COVID, with effects that can last for more than 6 months, the authors noted.
“I think across the board, universities in general need to consider the possibility of folks on their campuses are having symptoms of long COVID,” Dr. Landry said.
Moving forward, Dr. Landry and colleagues would like to continue investigating long COVID. For example, in the current study, they did not ask about severity of symptoms or how the symptoms affected daily functioning.
“I would like to continue this and dive deeper into how disruptive their symptoms of long COVID are to their everyday studying, teaching, or their activities to keeping a university running,” Dr. Landry said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES