User login
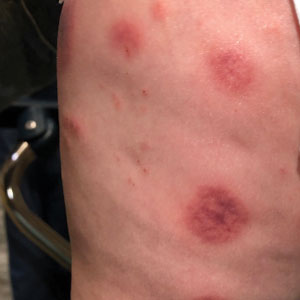
Topical gene therapy heals dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa wounds
.
In a phase 3 study of patients with DEB, “we found that repeated topical application of B-VEC [beremagene geperpavec], an HSV-1–based gene therapy, resulted in a greater likelihood of complete wound healing than the topical application of placebo at up to 6 months,” the authors wrote. The study was published in The New England Journal of Medicine. “Longer and larger trials are warranted to determine the durability of effect and risks of this approach,” the authors noted.
“The results prove that B-VEC, the first topical in vivo gene therapy to reach late-stage development, can heal DEB,” senior author M. Peter Marinkovich, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif., said in an interview.
“In the past, DEB was a very specialized disease that only a handful of dermatologists would see but could not do much to treat,” he said. “With gene therapy, many more dermatologists who may not be familiar with DEB will be able to treat these patients in their offices.” It is expected that nurses will be able to administer the treatment to patients at home, he added.
Rare, life-threatening, genetic blistering disease
DEB, a rare disease that affects one to three persons per million in the United States, is caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene that encodes the alpha-1 chain of collagen type VII (C7) protein. C7 forms the anchoring fibrils that attach the epidermis to the underlying dermal connective tissue.
COL71A mutations that lead to defective, decreased, or absent C7 can make the skin so fragile it tears with the slightest touch. This has led to patients being called “butterfly children.” Epithelial tissues blister and scar, causing esophageal and genitourinary strictures, adhesion of digits, malnutrition, anemia, infection, and bothersome itch and pain. Morbidity and mortality are high. The leading cause of death in adults is chronic wounds leading to aggressive squamous cell cancers.
The first therapy for DEB, under FDA review
B-VEC restores C7 protein by using an engineered replication-defective herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells to restore functional C7 protein fibrils that stabilize the skin structure.
On the basis of manufacturing information submitted to the FDA in December 2022, the agency extended the date for a decision on approval by 3 months, to May 19, 2023, according to a statement from Krystal Biotech, the developer of B-VEC and the sponsor of the NEJM study.
Dr. Marinkovich and his colleagues conducted the double-blind, randomized, controlled GEM-3 trial of B-VEC at three sites in the United States. The 31 study participants ranged in age from 1 to 44 years (median age, 16 years) and had genetically confirmed DEB (30 with the recessive form and 1 with the dominant form).
For each participant, a pair of wounds was chosen that were matched in size, region, and appearance. The wounds within each pair were randomly allocated to receive weekly applications of either B-VEC or placebo gel for 26 weeks.
The results of the study included the following:
- Complete healing at 6 months occurred in 67% of the wounds treated with B-VEC (including a wound in the patient with dominant DEB), vs. 22% of those who received placebo (95% confidence interval [CI], 24-68; P = .002).
- Complete healing at 3 months occurred in 71% of the wounds treated with B-VEC, vs. 20% of those who received placebo (95% CI, 29-73; P < .001).
- The mean change from baseline to week 22 in pain severity during wound-dressing changes for patients aged 6 years and older, as determined on the basis of a visual analogue scale, was –0.88 with B-VEC, vs. –0.71 with placebo (adjusted least-squares mean difference, –0.61; 95% CI, –1.10 to –0.13); similar mean changes were seen at weeks 24 and 26.
- Among all patients, 58% had at least one adverse event. Most adverse events were mild or moderate. The most common were pruritus, chills, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which were reported in three patients each (SCC cases occurred at wound sites that had not been exposed to B-VEC or placebo). Serious adverse events, which were unrelated to the treatment, occurred in three patients: diarrhea, anemia, cellulitis, and a positive blood culture related to a hemodialysis catheter.
“With the ability to treat patients with topical gene therapy, dermatology is entering a new age of treatment possibilities,” Dr. Marinkovich said in the interview.
The researchers were surprised that the redosable in vivo gene therapy worked so well, he added. In vivo gene therapy has been plagued by the occurrence of immune reactions against the viral vectors used, Dr. Marinkovich explained. But because the herpes simplex virus has evolved to evade the immune system, his team could use the viral vector every week for 6 months without inflammatory reactions.
“The immune system’s inability to fight off or get rid of the herpes simplex vector makes it bad as a disease, but as a gene therapy vector, it provides a huge advantage,” he added.
Asked to comment on the results, Christen Ebens, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, whose clinical and research interests include EB, called the results exciting for patients, families, and doctors.
“Side effects were minimal, and importantly, use of the replication-incompetent HSV vector means that the payload gene does not integrate into the patient’s DNA,” Dr. Ebens, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “B-VEC is not a lifelong cure but potentially an effective maintenance therapy requiring repeated doses,” she added.
Although the researchers found no clinically important immune reactions to B-VEC, Dr. Ebens said she would like to see results from longer studies of the treatment. “We will want to see that patients do not produce neutralizing antibodies against B-VEC or its components, as such antibodies may yield the treatment ineffective or cause significant side effects.”
In an interview, Vanessa R. Holland, MD, associate clinical professor in the division of dermatology at UCLA Health, Burbank, Calif., who was not involved in the study, said that “topical replication-defective HSV-1 is a brilliant vector to deliver the depleted collagen.” She added that “such a vehicle may significantly alter management of these disorders and improve or extend lives by minimizing potentially fatal complications.”
Paras P. Vakharia, MD, PharmD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, was surprised by the high percentage of healed wounds and wounds that remained healed over time.
In an interview, Dr. Vakharia said that he’d like to know whether patients develop antibodies against HSV and C7 with long-term treatment and whether problems will arise related to drug availability.
B-VEC for treating other conditions
Dr. Marinkovich noted that an ongoing phase 1 clinical trial, also sponsored by Krystal Biotech, is using the HSV-1 vector to deliver a different biologic (KB105) to establish dose and safety in the treatment of ichthyosis. He added that he would like to explore the use of B-VEC to treat DEB at mucosal surfaces, including inside the mouth, the eye, and the esophagus.
Authors of two editorials that accompanied the study also referred to other conditions B-VEC might treat.
This study “highlights potential future investigations,” David V. Schaffer, PhD, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, bioengineering, and molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley, wrotes in one of the editorials.
Important considerations he mentioned include the likelihood of the treatment becoming lifelong; the inability of HSV to penetrate intact skin, making B-VEC unsuitable for preventing the development of new wounds; and the inability of this treatment to treat EB lesions along the digestive tract. “This important trial builds on and extends gene-therapy successes to new targets and vectors, an advance for patients,” he added.
In the second editorial, Aimee S. Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the question of whether B-VEC’s clinical success for treating DEB can translate to other genetic diseases.
“Formulations for ophthalmic, oral-gastrointestinal, or respiratory delivery would be of great value to address the extracutaneous manifestations of epidermolysis bullosa and other genetic diseases,” she wrote.
Referring to an ongoing trial of a topical gene therapy for cystic fibrosis that is delivered by a nebulizer, Dr. Payne noted, “Ultimately, the completion of clinical trials such as this one will be required to determine whether HSV-1–mediated gene delivery can go more than skin deep.”
Earlier data and more details of the study were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in July 2022.
Dr. Marinkovich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors are employees of or have other financial relationships with Krystal Biotech, the study’s sponsor and the developer of beremagene geperpavec. Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Payne have financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Ebens, Dr. Holland, and Dr. Vakharia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In a phase 3 study of patients with DEB, “we found that repeated topical application of B-VEC [beremagene geperpavec], an HSV-1–based gene therapy, resulted in a greater likelihood of complete wound healing than the topical application of placebo at up to 6 months,” the authors wrote. The study was published in The New England Journal of Medicine. “Longer and larger trials are warranted to determine the durability of effect and risks of this approach,” the authors noted.
“The results prove that B-VEC, the first topical in vivo gene therapy to reach late-stage development, can heal DEB,” senior author M. Peter Marinkovich, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif., said in an interview.
“In the past, DEB was a very specialized disease that only a handful of dermatologists would see but could not do much to treat,” he said. “With gene therapy, many more dermatologists who may not be familiar with DEB will be able to treat these patients in their offices.” It is expected that nurses will be able to administer the treatment to patients at home, he added.
Rare, life-threatening, genetic blistering disease
DEB, a rare disease that affects one to three persons per million in the United States, is caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene that encodes the alpha-1 chain of collagen type VII (C7) protein. C7 forms the anchoring fibrils that attach the epidermis to the underlying dermal connective tissue.
COL71A mutations that lead to defective, decreased, or absent C7 can make the skin so fragile it tears with the slightest touch. This has led to patients being called “butterfly children.” Epithelial tissues blister and scar, causing esophageal and genitourinary strictures, adhesion of digits, malnutrition, anemia, infection, and bothersome itch and pain. Morbidity and mortality are high. The leading cause of death in adults is chronic wounds leading to aggressive squamous cell cancers.
The first therapy for DEB, under FDA review
B-VEC restores C7 protein by using an engineered replication-defective herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells to restore functional C7 protein fibrils that stabilize the skin structure.
On the basis of manufacturing information submitted to the FDA in December 2022, the agency extended the date for a decision on approval by 3 months, to May 19, 2023, according to a statement from Krystal Biotech, the developer of B-VEC and the sponsor of the NEJM study.
Dr. Marinkovich and his colleagues conducted the double-blind, randomized, controlled GEM-3 trial of B-VEC at three sites in the United States. The 31 study participants ranged in age from 1 to 44 years (median age, 16 years) and had genetically confirmed DEB (30 with the recessive form and 1 with the dominant form).
For each participant, a pair of wounds was chosen that were matched in size, region, and appearance. The wounds within each pair were randomly allocated to receive weekly applications of either B-VEC or placebo gel for 26 weeks.
The results of the study included the following:
- Complete healing at 6 months occurred in 67% of the wounds treated with B-VEC (including a wound in the patient with dominant DEB), vs. 22% of those who received placebo (95% confidence interval [CI], 24-68; P = .002).
- Complete healing at 3 months occurred in 71% of the wounds treated with B-VEC, vs. 20% of those who received placebo (95% CI, 29-73; P < .001).
- The mean change from baseline to week 22 in pain severity during wound-dressing changes for patients aged 6 years and older, as determined on the basis of a visual analogue scale, was –0.88 with B-VEC, vs. –0.71 with placebo (adjusted least-squares mean difference, –0.61; 95% CI, –1.10 to –0.13); similar mean changes were seen at weeks 24 and 26.
- Among all patients, 58% had at least one adverse event. Most adverse events were mild or moderate. The most common were pruritus, chills, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which were reported in three patients each (SCC cases occurred at wound sites that had not been exposed to B-VEC or placebo). Serious adverse events, which were unrelated to the treatment, occurred in three patients: diarrhea, anemia, cellulitis, and a positive blood culture related to a hemodialysis catheter.
“With the ability to treat patients with topical gene therapy, dermatology is entering a new age of treatment possibilities,” Dr. Marinkovich said in the interview.
The researchers were surprised that the redosable in vivo gene therapy worked so well, he added. In vivo gene therapy has been plagued by the occurrence of immune reactions against the viral vectors used, Dr. Marinkovich explained. But because the herpes simplex virus has evolved to evade the immune system, his team could use the viral vector every week for 6 months without inflammatory reactions.
“The immune system’s inability to fight off or get rid of the herpes simplex vector makes it bad as a disease, but as a gene therapy vector, it provides a huge advantage,” he added.
Asked to comment on the results, Christen Ebens, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, whose clinical and research interests include EB, called the results exciting for patients, families, and doctors.
“Side effects were minimal, and importantly, use of the replication-incompetent HSV vector means that the payload gene does not integrate into the patient’s DNA,” Dr. Ebens, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “B-VEC is not a lifelong cure but potentially an effective maintenance therapy requiring repeated doses,” she added.
Although the researchers found no clinically important immune reactions to B-VEC, Dr. Ebens said she would like to see results from longer studies of the treatment. “We will want to see that patients do not produce neutralizing antibodies against B-VEC or its components, as such antibodies may yield the treatment ineffective or cause significant side effects.”
In an interview, Vanessa R. Holland, MD, associate clinical professor in the division of dermatology at UCLA Health, Burbank, Calif., who was not involved in the study, said that “topical replication-defective HSV-1 is a brilliant vector to deliver the depleted collagen.” She added that “such a vehicle may significantly alter management of these disorders and improve or extend lives by minimizing potentially fatal complications.”
Paras P. Vakharia, MD, PharmD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, was surprised by the high percentage of healed wounds and wounds that remained healed over time.
In an interview, Dr. Vakharia said that he’d like to know whether patients develop antibodies against HSV and C7 with long-term treatment and whether problems will arise related to drug availability.
B-VEC for treating other conditions
Dr. Marinkovich noted that an ongoing phase 1 clinical trial, also sponsored by Krystal Biotech, is using the HSV-1 vector to deliver a different biologic (KB105) to establish dose and safety in the treatment of ichthyosis. He added that he would like to explore the use of B-VEC to treat DEB at mucosal surfaces, including inside the mouth, the eye, and the esophagus.
Authors of two editorials that accompanied the study also referred to other conditions B-VEC might treat.
This study “highlights potential future investigations,” David V. Schaffer, PhD, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, bioengineering, and molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley, wrotes in one of the editorials.
Important considerations he mentioned include the likelihood of the treatment becoming lifelong; the inability of HSV to penetrate intact skin, making B-VEC unsuitable for preventing the development of new wounds; and the inability of this treatment to treat EB lesions along the digestive tract. “This important trial builds on and extends gene-therapy successes to new targets and vectors, an advance for patients,” he added.
In the second editorial, Aimee S. Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the question of whether B-VEC’s clinical success for treating DEB can translate to other genetic diseases.
“Formulations for ophthalmic, oral-gastrointestinal, or respiratory delivery would be of great value to address the extracutaneous manifestations of epidermolysis bullosa and other genetic diseases,” she wrote.
Referring to an ongoing trial of a topical gene therapy for cystic fibrosis that is delivered by a nebulizer, Dr. Payne noted, “Ultimately, the completion of clinical trials such as this one will be required to determine whether HSV-1–mediated gene delivery can go more than skin deep.”
Earlier data and more details of the study were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in July 2022.
Dr. Marinkovich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors are employees of or have other financial relationships with Krystal Biotech, the study’s sponsor and the developer of beremagene geperpavec. Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Payne have financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Ebens, Dr. Holland, and Dr. Vakharia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
.
In a phase 3 study of patients with DEB, “we found that repeated topical application of B-VEC [beremagene geperpavec], an HSV-1–based gene therapy, resulted in a greater likelihood of complete wound healing than the topical application of placebo at up to 6 months,” the authors wrote. The study was published in The New England Journal of Medicine. “Longer and larger trials are warranted to determine the durability of effect and risks of this approach,” the authors noted.
“The results prove that B-VEC, the first topical in vivo gene therapy to reach late-stage development, can heal DEB,” senior author M. Peter Marinkovich, MD, associate professor of dermatology at Stanford University, Redwood City, Calif., said in an interview.
“In the past, DEB was a very specialized disease that only a handful of dermatologists would see but could not do much to treat,” he said. “With gene therapy, many more dermatologists who may not be familiar with DEB will be able to treat these patients in their offices.” It is expected that nurses will be able to administer the treatment to patients at home, he added.
Rare, life-threatening, genetic blistering disease
DEB, a rare disease that affects one to three persons per million in the United States, is caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene that encodes the alpha-1 chain of collagen type VII (C7) protein. C7 forms the anchoring fibrils that attach the epidermis to the underlying dermal connective tissue.
COL71A mutations that lead to defective, decreased, or absent C7 can make the skin so fragile it tears with the slightest touch. This has led to patients being called “butterfly children.” Epithelial tissues blister and scar, causing esophageal and genitourinary strictures, adhesion of digits, malnutrition, anemia, infection, and bothersome itch and pain. Morbidity and mortality are high. The leading cause of death in adults is chronic wounds leading to aggressive squamous cell cancers.
The first therapy for DEB, under FDA review
B-VEC restores C7 protein by using an engineered replication-defective herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) vector to deliver the COL7A1 gene directly to skin cells to restore functional C7 protein fibrils that stabilize the skin structure.
On the basis of manufacturing information submitted to the FDA in December 2022, the agency extended the date for a decision on approval by 3 months, to May 19, 2023, according to a statement from Krystal Biotech, the developer of B-VEC and the sponsor of the NEJM study.
Dr. Marinkovich and his colleagues conducted the double-blind, randomized, controlled GEM-3 trial of B-VEC at three sites in the United States. The 31 study participants ranged in age from 1 to 44 years (median age, 16 years) and had genetically confirmed DEB (30 with the recessive form and 1 with the dominant form).
For each participant, a pair of wounds was chosen that were matched in size, region, and appearance. The wounds within each pair were randomly allocated to receive weekly applications of either B-VEC or placebo gel for 26 weeks.
The results of the study included the following:
- Complete healing at 6 months occurred in 67% of the wounds treated with B-VEC (including a wound in the patient with dominant DEB), vs. 22% of those who received placebo (95% confidence interval [CI], 24-68; P = .002).
- Complete healing at 3 months occurred in 71% of the wounds treated with B-VEC, vs. 20% of those who received placebo (95% CI, 29-73; P < .001).
- The mean change from baseline to week 22 in pain severity during wound-dressing changes for patients aged 6 years and older, as determined on the basis of a visual analogue scale, was –0.88 with B-VEC, vs. –0.71 with placebo (adjusted least-squares mean difference, –0.61; 95% CI, –1.10 to –0.13); similar mean changes were seen at weeks 24 and 26.
- Among all patients, 58% had at least one adverse event. Most adverse events were mild or moderate. The most common were pruritus, chills, and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which were reported in three patients each (SCC cases occurred at wound sites that had not been exposed to B-VEC or placebo). Serious adverse events, which were unrelated to the treatment, occurred in three patients: diarrhea, anemia, cellulitis, and a positive blood culture related to a hemodialysis catheter.
“With the ability to treat patients with topical gene therapy, dermatology is entering a new age of treatment possibilities,” Dr. Marinkovich said in the interview.
The researchers were surprised that the redosable in vivo gene therapy worked so well, he added. In vivo gene therapy has been plagued by the occurrence of immune reactions against the viral vectors used, Dr. Marinkovich explained. But because the herpes simplex virus has evolved to evade the immune system, his team could use the viral vector every week for 6 months without inflammatory reactions.
“The immune system’s inability to fight off or get rid of the herpes simplex vector makes it bad as a disease, but as a gene therapy vector, it provides a huge advantage,” he added.
Asked to comment on the results, Christen Ebens, MD, MPH, assistant professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, whose clinical and research interests include EB, called the results exciting for patients, families, and doctors.
“Side effects were minimal, and importantly, use of the replication-incompetent HSV vector means that the payload gene does not integrate into the patient’s DNA,” Dr. Ebens, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “B-VEC is not a lifelong cure but potentially an effective maintenance therapy requiring repeated doses,” she added.
Although the researchers found no clinically important immune reactions to B-VEC, Dr. Ebens said she would like to see results from longer studies of the treatment. “We will want to see that patients do not produce neutralizing antibodies against B-VEC or its components, as such antibodies may yield the treatment ineffective or cause significant side effects.”
In an interview, Vanessa R. Holland, MD, associate clinical professor in the division of dermatology at UCLA Health, Burbank, Calif., who was not involved in the study, said that “topical replication-defective HSV-1 is a brilliant vector to deliver the depleted collagen.” She added that “such a vehicle may significantly alter management of these disorders and improve or extend lives by minimizing potentially fatal complications.”
Paras P. Vakharia, MD, PharmD, assistant professor of dermatology at Northwestern University, Chicago, who was not involved in the study, was surprised by the high percentage of healed wounds and wounds that remained healed over time.
In an interview, Dr. Vakharia said that he’d like to know whether patients develop antibodies against HSV and C7 with long-term treatment and whether problems will arise related to drug availability.
B-VEC for treating other conditions
Dr. Marinkovich noted that an ongoing phase 1 clinical trial, also sponsored by Krystal Biotech, is using the HSV-1 vector to deliver a different biologic (KB105) to establish dose and safety in the treatment of ichthyosis. He added that he would like to explore the use of B-VEC to treat DEB at mucosal surfaces, including inside the mouth, the eye, and the esophagus.
Authors of two editorials that accompanied the study also referred to other conditions B-VEC might treat.
This study “highlights potential future investigations,” David V. Schaffer, PhD, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, bioengineering, and molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley, wrotes in one of the editorials.
Important considerations he mentioned include the likelihood of the treatment becoming lifelong; the inability of HSV to penetrate intact skin, making B-VEC unsuitable for preventing the development of new wounds; and the inability of this treatment to treat EB lesions along the digestive tract. “This important trial builds on and extends gene-therapy successes to new targets and vectors, an advance for patients,” he added.
In the second editorial, Aimee S. Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, raised the question of whether B-VEC’s clinical success for treating DEB can translate to other genetic diseases.
“Formulations for ophthalmic, oral-gastrointestinal, or respiratory delivery would be of great value to address the extracutaneous manifestations of epidermolysis bullosa and other genetic diseases,” she wrote.
Referring to an ongoing trial of a topical gene therapy for cystic fibrosis that is delivered by a nebulizer, Dr. Payne noted, “Ultimately, the completion of clinical trials such as this one will be required to determine whether HSV-1–mediated gene delivery can go more than skin deep.”
Earlier data and more details of the study were presented in a poster at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology in July 2022.
Dr. Marinkovich has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors are employees of or have other financial relationships with Krystal Biotech, the study’s sponsor and the developer of beremagene geperpavec. Dr. Schaffer and Dr. Payne have financial relationships with the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Ebens, Dr. Holland, and Dr. Vakharia have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID emergency orders ending: What’s next?
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
It’s the end of an era.
The orders spanned two presidencies. The Trump administration’s Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar issued a public health emergency in January 2020. Then-President Donald Trump declared the COVID-19 pandemic a national emergency 2 months later. Both emergency declarations – which remained in effect under President Joe Biden – are set to expire May 11.
Read on for an overview of how the end of the public health emergency will trigger multiple federal policy changes.
Changes that affect everyone
- There will be cost-sharing changes for COVID-19 vaccines, testing, and certain treatments. One hundred–percent coverage for COVID testing, including free at-home tests, will expire May 11.
- Telemedicine cannot be used to prescribe controlled substances after May 11, 2023.
- Enhanced federal funding will be phased down through Dec. 31, 2023. This extends the time states must receive federally matched funds for COVID-related services and products, through the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023. Otherwise, this would have expired June 30, 2023.
- Emergency use authorizations for COVID-19 treatments and vaccinations will not be affected and/or end on May 11.
Changes that affect people with private health insurance
- Many will likely see higher costs for COVID-19 tests, as free testing expires and cost-sharing begins in the coming months.
- COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters will continue to be covered until the federal government’s vaccination supply is depleted. If that happens, you will need an in-network provider.
- You will still have access to COVID-19 treatments – but that could change when the federal supply dwindles.
Changes that affect Medicare recipients
- Medicare telehealth flexibilities will be extended through Dec. 31, 2024, regardless of public health emergency status. This means people can access telehealth services from anywhere, not just rural areas; can use a smartphone for telehealth; and can access telehealth in their homes.
- Medicare cost-sharing for testing and treatments will expire May 11, except for oral antivirals.
Changes that affect Medicaid/CHIP recipients
- Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) recipients will continue to receive approved vaccinations free of charge, but testing and treatment without cost-sharing will expire during the third quarter of 2024.
- The Medicaid continuous enrollment provision will be separated from the public health emergency, and continuous enrollment will end March 31, 2023.
Changes that affect uninsured people
- The uninsured will no longer have access to 100% coverage for these products and services (free COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, and testing).
Changes that affect health care providers
- There will be changes to how much providers get paid for diagnosing people with COVID-19, ending the enhanced Inpatient Prospective Payment System reimbursement rate, as of May 11, 2023.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) potential penalty waivers will end. This allows providers to communicate with patients through telehealth on a smartphone, for example, without violating privacy laws and incurring penalties.
What the experts are saying
This news organization asked several health experts for their thoughts on ending the emergency health declarations for COVID, and what effects this could have. Many expressed concerns about the timing of the ending, saying that the move could limit access to COVID-related treatments. Others said the move was inevitable but raised concerns about federal guidance related to the decision.
Question: Do you agree with the timing of the end to the emergency order?
Answer: Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston: “A lead time to prepare and anticipate these consequences may ease the transition, compared to an abrupt declaration that ends the declaration.”
Answer: Georges C. Benjamin, MD, executive director of the American Public Health Association: “I think it’s time to do so. It has to be done in a great, thoughtful, and organized way because we’ve attached so many different things to this public health emergency. It’s going to take time for the system to adapt. [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] data collection most likely will continue. People are used to reporting now. The CDC needs to give guidance to the states so that we’re clear about what we’re reporting, what we’re not. If we did that abruptly, it would just be a mess.”
Answer: Bruce Farber, MD, chief public health and epidemiology officer at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y.: “I would have hoped to see it delayed.”
Answer: Steven Newmark, JD, chief legal officer and director of policy at the Global Healthy Living Foundation: “While we understand that an emergency cannot last forever, we hope that expanded services such as free vaccination, promotion of widespread vaccination, increased use of pharmacists to administer vaccines, telehealth availability and reimbursement, flexibility in work-from-home opportunities, and more continues. Access to equitable health care should never backtrack or be reduced.”
Q: What will the end of free COVID vaccinations and free testing mean?
A: Dr. Farber: “There will likely be a decrease in vaccinations and testing. The vaccination rates are very low to begin with, and this will likely lower it further.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “I think it will mean that fewer people will get tested and vaccinated,” which “could lead to increased transmission, although wastewater testing suggests that there is a lot of unrecognized infection already occurring.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “That is a big concern. It means that for people, particularly for people who are uninsured and underinsured, we’ve got to make sure they have access to those. There’s a lot of discussion and debate about what the cost of those tests and vaccines will be, and it looks like the companies are going to impose very steep, increasing costs.”
Q: How will this affect higher-risk populations, like people with weakened immune systems?
A: Dr. Farber: “Without monoclonals [drugs to treat COVID] and free Paxlovid,” people with weakened immune systems “may be undertreated.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “The implications of ongoing widespread virus transmission are that immunocompromised individuals may be more likely to be exposed and infected and to suffer the consequences of such infection, including severe illness. However, to a certain degree, this may already be happening. We are still seeing about 500 deaths/day, primarily in persons at highest risk of severe disease.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “People who have good insurance, can afford to get immunized, and have good relations with practitioners probably will continue to be covered. But lower-income individuals and people who really can’t afford to get tested or get immunized would likely become underimmunized and more infected.
“So even though the federal emergency declaration will go away, I’m hoping that the federal government will continue to encourage all of us to emphasize those populations at the highest risk – those with chronic disease and those who are immunocompromised.”
A: Mr. Newmark: “People who are immunocompromised by their chronic illness or the medicines they take to treat acute or chronic conditions remain at higher risk for COVID-19 and its serious complications. The administration needs to support continued development of effective treatments and updated vaccines to protect the individual and public health. We’re also concerned that increased health care services - such as vaccination or telehealth – may fall back to prepandemic levels while the burden of protection, such as masking, may fall to chronic disease patients alone, which adds to the burden of living with disease.”
Q: What effect will ending Medicaid expansion money have?
A: Dr. Benjamin: Anywhere from 16 to 20 million people are going to lose in coverage. I’m hoping that states will look at their experience over these last 2 years or so and come to the decision that there were improvements in healthier populations.
Q: Will this have any effect on how the public perceives the pandemic?
A: Dr. Farber: “It is likely to give the impression that COVID is gone, which clearly is not the case.”
A: Dr. Benjamin: “It’ll be another argument by some that the pandemic is over. People should think about this as kind of like a hurricane. A hurricane comes through and tragically tears up communities, and we have an emergency during that time. But then we have to go through a period of recovery. I’m hoping people will realize that even though the public health emergencies have gone away, that we still need to go through a period of transition ... and that means that they still need to protect themselves, get vaccinated, and wear a mask when appropriate.”
A: Dr. Atmar: “There needs to be messaging that while we are transitioning away from emergency management of COVID-19, it is still a significant public health concern.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
Autism linked to problems with cardiovascular health
People with autism are more likely to face diabetes, high cholesterol, and heart disease than those without the neurologic condition, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found that children with autism are especially likely to develop diabetes compared with their peers, and are at greater risk of hypertension, too.
While the link between autism and risk for obesity and gastrointestinal ailments is well-established, the new findings suggest that clinicians who care for these patients – particularly children – should focus on cardiometabolic health more broadly.
“Clinicians who are treating kids with autism need to pay more attention to this,” said Chanaka N. Kahathuduwa, MD, PhD, MPhil, of the department of neurology at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, in Lubbock, and a coauthor of the new study.
A pediatrician may prescribe an atypical antipsychotic medication such as risperidone to regulate the behavior of an autistic child, Dr. Kahathuduwa said, which may increase their cholesterol levels. Although this or similar drugs may be necessary in some cases, Dr. Kahathuduwa advised that clinicians explore other treatment options first.
Mining data from previously published studies
For the new analysis, Dr. Kahathuduwa and his colleagues pooled the results of 34 previously published studies, which included medical records of more than 276,000 people with autism and close to 8 million people without the condition.
Study participants were an average age of 31 years, and 47% were female. Some studies reported age ranges that enabled the researchers to differentiate between children and adults.
People with autism were 64% more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, 146% more likely to experience type 2 diabetes, and 46% more likely to have heart disease, overall, the study found. Children with autism were almost twice as likely as their peers to develop diabetes (184%) and high blood pressure (154%).
The study found associations, not causation, and does not include detailed data about medication prescribing patterns. While it would be ideal to understand why autism is linked to cardiometabolic risk, to address the link most effectively, Dr. Kahathuduwa said the causes likely are multifactorial. Medication history and genetics each play a role in a way that is hard to untangle. Even so, Dr. Kahathuduwa said he hoped the findings prompt clinicians to reevaluate how they treat their patients with autism.
“This may be an eye opener,” he said.
An editorial accompanying the study noted that people with autism may die up to 30 years earlier than people without autism, in part because of the physical health problems surfaced in the new research. They also are more likely than others to attempt suicide.
Elizabeth M. Weir, PhD, of the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge (England) and author of the editorial, argued that current health delivery models often fail autistic people by not taking their needs into account.
Dr. Weir told this news organization that making adjustments such as dimming the lights for a light-sensitive patient or allowing people with autism to bring an advocate to appointments could build rapport.
“I diagnose autism pretty much every day and I know families get so overwhelmed with all the recommendations that we give,” said Sonia Monteiro, MD, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. Still, Dr. Monteiro said clinicians should help parents of children with autism address the potential long-term cardiovascular risks – but to do so by layering in the information rather than merely adding more bullet points to an already long presentation.
“We know this information now, but finding a way to share that with families without overwhelming them even more, I think is challenging,” Dr. Monteiro said. “But it’s not something we can ignore.”
Dr. Kahathuduwa, Dr. Weir, and Dr. Monteiro report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with autism are more likely to face diabetes, high cholesterol, and heart disease than those without the neurologic condition, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found that children with autism are especially likely to develop diabetes compared with their peers, and are at greater risk of hypertension, too.
While the link between autism and risk for obesity and gastrointestinal ailments is well-established, the new findings suggest that clinicians who care for these patients – particularly children – should focus on cardiometabolic health more broadly.
“Clinicians who are treating kids with autism need to pay more attention to this,” said Chanaka N. Kahathuduwa, MD, PhD, MPhil, of the department of neurology at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, in Lubbock, and a coauthor of the new study.
A pediatrician may prescribe an atypical antipsychotic medication such as risperidone to regulate the behavior of an autistic child, Dr. Kahathuduwa said, which may increase their cholesterol levels. Although this or similar drugs may be necessary in some cases, Dr. Kahathuduwa advised that clinicians explore other treatment options first.
Mining data from previously published studies
For the new analysis, Dr. Kahathuduwa and his colleagues pooled the results of 34 previously published studies, which included medical records of more than 276,000 people with autism and close to 8 million people without the condition.
Study participants were an average age of 31 years, and 47% were female. Some studies reported age ranges that enabled the researchers to differentiate between children and adults.
People with autism were 64% more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, 146% more likely to experience type 2 diabetes, and 46% more likely to have heart disease, overall, the study found. Children with autism were almost twice as likely as their peers to develop diabetes (184%) and high blood pressure (154%).
The study found associations, not causation, and does not include detailed data about medication prescribing patterns. While it would be ideal to understand why autism is linked to cardiometabolic risk, to address the link most effectively, Dr. Kahathuduwa said the causes likely are multifactorial. Medication history and genetics each play a role in a way that is hard to untangle. Even so, Dr. Kahathuduwa said he hoped the findings prompt clinicians to reevaluate how they treat their patients with autism.
“This may be an eye opener,” he said.
An editorial accompanying the study noted that people with autism may die up to 30 years earlier than people without autism, in part because of the physical health problems surfaced in the new research. They also are more likely than others to attempt suicide.
Elizabeth M. Weir, PhD, of the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge (England) and author of the editorial, argued that current health delivery models often fail autistic people by not taking their needs into account.
Dr. Weir told this news organization that making adjustments such as dimming the lights for a light-sensitive patient or allowing people with autism to bring an advocate to appointments could build rapport.
“I diagnose autism pretty much every day and I know families get so overwhelmed with all the recommendations that we give,” said Sonia Monteiro, MD, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. Still, Dr. Monteiro said clinicians should help parents of children with autism address the potential long-term cardiovascular risks – but to do so by layering in the information rather than merely adding more bullet points to an already long presentation.
“We know this information now, but finding a way to share that with families without overwhelming them even more, I think is challenging,” Dr. Monteiro said. “But it’s not something we can ignore.”
Dr. Kahathuduwa, Dr. Weir, and Dr. Monteiro report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with autism are more likely to face diabetes, high cholesterol, and heart disease than those without the neurologic condition, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found that children with autism are especially likely to develop diabetes compared with their peers, and are at greater risk of hypertension, too.
While the link between autism and risk for obesity and gastrointestinal ailments is well-established, the new findings suggest that clinicians who care for these patients – particularly children – should focus on cardiometabolic health more broadly.
“Clinicians who are treating kids with autism need to pay more attention to this,” said Chanaka N. Kahathuduwa, MD, PhD, MPhil, of the department of neurology at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, in Lubbock, and a coauthor of the new study.
A pediatrician may prescribe an atypical antipsychotic medication such as risperidone to regulate the behavior of an autistic child, Dr. Kahathuduwa said, which may increase their cholesterol levels. Although this or similar drugs may be necessary in some cases, Dr. Kahathuduwa advised that clinicians explore other treatment options first.
Mining data from previously published studies
For the new analysis, Dr. Kahathuduwa and his colleagues pooled the results of 34 previously published studies, which included medical records of more than 276,000 people with autism and close to 8 million people without the condition.
Study participants were an average age of 31 years, and 47% were female. Some studies reported age ranges that enabled the researchers to differentiate between children and adults.
People with autism were 64% more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, 146% more likely to experience type 2 diabetes, and 46% more likely to have heart disease, overall, the study found. Children with autism were almost twice as likely as their peers to develop diabetes (184%) and high blood pressure (154%).
The study found associations, not causation, and does not include detailed data about medication prescribing patterns. While it would be ideal to understand why autism is linked to cardiometabolic risk, to address the link most effectively, Dr. Kahathuduwa said the causes likely are multifactorial. Medication history and genetics each play a role in a way that is hard to untangle. Even so, Dr. Kahathuduwa said he hoped the findings prompt clinicians to reevaluate how they treat their patients with autism.
“This may be an eye opener,” he said.
An editorial accompanying the study noted that people with autism may die up to 30 years earlier than people without autism, in part because of the physical health problems surfaced in the new research. They also are more likely than others to attempt suicide.
Elizabeth M. Weir, PhD, of the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge (England) and author of the editorial, argued that current health delivery models often fail autistic people by not taking their needs into account.
Dr. Weir told this news organization that making adjustments such as dimming the lights for a light-sensitive patient or allowing people with autism to bring an advocate to appointments could build rapport.
“I diagnose autism pretty much every day and I know families get so overwhelmed with all the recommendations that we give,” said Sonia Monteiro, MD, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. Still, Dr. Monteiro said clinicians should help parents of children with autism address the potential long-term cardiovascular risks – but to do so by layering in the information rather than merely adding more bullet points to an already long presentation.
“We know this information now, but finding a way to share that with families without overwhelming them even more, I think is challenging,” Dr. Monteiro said. “But it’s not something we can ignore.”
Dr. Kahathuduwa, Dr. Weir, and Dr. Monteiro report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Kid with glasses: Many children live far from pediatric eye care
More than 2,800 counties in the United States lack a practicing pediatric ophthalmologist, limiting easy access to specialized eye care, a new study found.
The review of public, online pediatric ophthalmology directories found 1,056 pediatric ophthalmologists registered. The majority of these doctors practiced in densely populated areas, leaving many poor and rural residents across the United States without a nearby doctor to visit, and with the burden of spending time and money to get care for their children.
Travel for that care may be out of reach for some, according to Hannah Walsh, a medical student at the University of Miami, who led the study published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh’s research found that the median income of families living in a county without a pediatric ophthalmologist was nearly $17,000 lower than that for families with access to such specialists (95% confidence interval, −$18,544 to −$14,389; P < .001). These families were also less likely to own a car.
“We found that counties that didn’t have access to ophthalmic care for pediatrics were already disproportionately affected by lower socioeconomic status,” she said.
Children often receive routine vision screenings through their primary care clinician, but children who fail a routine screening may need to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist for a full eye examination, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh and colleagues pulled data in March 2022 on the demographics of pediatric ophthalmologists from online directories hosted by the AAO and the American Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. Ms. Walsh cautioned that the directories might include eye doctors who are no longer practicing, or there might be specialists who had not registered for the databases.
Yasmin Bradfield, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, noted that after the study published, pediatric ophthalmologists from Vermont and New Mexico notified study authors and AAPOS that they are practicing in the states.
Dr. Bradfield, a board member of AAPOS who also heads the organization’s recruitment task force, said the organization is aware of only one state – Wyoming – without a currently practicing pediatric ophthalmologist.
But based on the March 2022 data, Ms. Walsh and her colleagues found four states – New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Vermont – did not have any pediatric ophthalmologists listed in directories for the organizations. Meanwhile, the country’s most populous states – California, New York, Florida, and Texas – had the most pediatric ophthalmologists.
For every million people, the study identified 7.7 pediatric ophthalmologists nationwide.
Julius T. Oatts, MD, the lead author of an accompanying editorial, said the findings are “valuable and sobering.” Even in San Francisco, where Dr. Oatts practices, most pediatric eye specialists have 6-month wait lists, he said.
Not fixing the shortage of children’s eye doctors could carry lifetime consequences, Dr. Oatts and his colleagues warned.
“Vision and eye health represent an important health barrier to learning in children,” Dr. Oatts and his colleagues wrote. “Lack of access to pediatric vision screening and care also contributes to the academic achievement gap and educational disparities.”
Dr. Bradfield said that disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care could leave some children at risk for losing their vision or never being able to see 20/20. Parents living in areas without a specialist may decide to instead visit an optometrist, but they are not trained to treat serious cases, such as strabismus, and only test and diagnose vision changes, according to AAPOS.
“If we don’t get to the kids in time, they can lose vision permanently, even if it’s something as simple as they just need glasses as a toddler,” Dr. Bradfield said.
Dr. Bradfield said AAPOS is recruiting new pediatric ophthalmologists by offering fellowships for medical students to attend the association’s annual conference and creating shadowing opportunities for students. The society also will release a survey of pediatric ophthalmology salaries to dispel rumors that the specialty does not have lucrative wages.
Ms. Walsh said she was interested in looking at disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care, in part, because she was surprised by how few of her classmates attending medical school were interested in the field of study.
“I hope it encourages ophthalmologists to consider pediatric ophthalmology, or to consider volunteering their time, or going to underserved areas to provide care to families that really are in need,” she said.
Coauthor Jayanth Sridhar, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Alcon, Apellis, Allergan, Dutch Ophthalmic Research Center, Genentech, OcuTerra Therapeutics, and Regeneron outside the submitted work. The other authors and the editorialists report no relevant financial relationships.
*This article was updated on 2/2/2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 2,800 counties in the United States lack a practicing pediatric ophthalmologist, limiting easy access to specialized eye care, a new study found.
The review of public, online pediatric ophthalmology directories found 1,056 pediatric ophthalmologists registered. The majority of these doctors practiced in densely populated areas, leaving many poor and rural residents across the United States without a nearby doctor to visit, and with the burden of spending time and money to get care for their children.
Travel for that care may be out of reach for some, according to Hannah Walsh, a medical student at the University of Miami, who led the study published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh’s research found that the median income of families living in a county without a pediatric ophthalmologist was nearly $17,000 lower than that for families with access to such specialists (95% confidence interval, −$18,544 to −$14,389; P < .001). These families were also less likely to own a car.
“We found that counties that didn’t have access to ophthalmic care for pediatrics were already disproportionately affected by lower socioeconomic status,” she said.
Children often receive routine vision screenings through their primary care clinician, but children who fail a routine screening may need to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist for a full eye examination, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh and colleagues pulled data in March 2022 on the demographics of pediatric ophthalmologists from online directories hosted by the AAO and the American Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. Ms. Walsh cautioned that the directories might include eye doctors who are no longer practicing, or there might be specialists who had not registered for the databases.
Yasmin Bradfield, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, noted that after the study published, pediatric ophthalmologists from Vermont and New Mexico notified study authors and AAPOS that they are practicing in the states.
Dr. Bradfield, a board member of AAPOS who also heads the organization’s recruitment task force, said the organization is aware of only one state – Wyoming – without a currently practicing pediatric ophthalmologist.
But based on the March 2022 data, Ms. Walsh and her colleagues found four states – New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Vermont – did not have any pediatric ophthalmologists listed in directories for the organizations. Meanwhile, the country’s most populous states – California, New York, Florida, and Texas – had the most pediatric ophthalmologists.
For every million people, the study identified 7.7 pediatric ophthalmologists nationwide.
Julius T. Oatts, MD, the lead author of an accompanying editorial, said the findings are “valuable and sobering.” Even in San Francisco, where Dr. Oatts practices, most pediatric eye specialists have 6-month wait lists, he said.
Not fixing the shortage of children’s eye doctors could carry lifetime consequences, Dr. Oatts and his colleagues warned.
“Vision and eye health represent an important health barrier to learning in children,” Dr. Oatts and his colleagues wrote. “Lack of access to pediatric vision screening and care also contributes to the academic achievement gap and educational disparities.”
Dr. Bradfield said that disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care could leave some children at risk for losing their vision or never being able to see 20/20. Parents living in areas without a specialist may decide to instead visit an optometrist, but they are not trained to treat serious cases, such as strabismus, and only test and diagnose vision changes, according to AAPOS.
“If we don’t get to the kids in time, they can lose vision permanently, even if it’s something as simple as they just need glasses as a toddler,” Dr. Bradfield said.
Dr. Bradfield said AAPOS is recruiting new pediatric ophthalmologists by offering fellowships for medical students to attend the association’s annual conference and creating shadowing opportunities for students. The society also will release a survey of pediatric ophthalmology salaries to dispel rumors that the specialty does not have lucrative wages.
Ms. Walsh said she was interested in looking at disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care, in part, because she was surprised by how few of her classmates attending medical school were interested in the field of study.
“I hope it encourages ophthalmologists to consider pediatric ophthalmology, or to consider volunteering their time, or going to underserved areas to provide care to families that really are in need,” she said.
Coauthor Jayanth Sridhar, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Alcon, Apellis, Allergan, Dutch Ophthalmic Research Center, Genentech, OcuTerra Therapeutics, and Regeneron outside the submitted work. The other authors and the editorialists report no relevant financial relationships.
*This article was updated on 2/2/2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 2,800 counties in the United States lack a practicing pediatric ophthalmologist, limiting easy access to specialized eye care, a new study found.
The review of public, online pediatric ophthalmology directories found 1,056 pediatric ophthalmologists registered. The majority of these doctors practiced in densely populated areas, leaving many poor and rural residents across the United States without a nearby doctor to visit, and with the burden of spending time and money to get care for their children.
Travel for that care may be out of reach for some, according to Hannah Walsh, a medical student at the University of Miami, who led the study published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh’s research found that the median income of families living in a county without a pediatric ophthalmologist was nearly $17,000 lower than that for families with access to such specialists (95% confidence interval, −$18,544 to −$14,389; P < .001). These families were also less likely to own a car.
“We found that counties that didn’t have access to ophthalmic care for pediatrics were already disproportionately affected by lower socioeconomic status,” she said.
Children often receive routine vision screenings through their primary care clinician, but children who fail a routine screening may need to visit a pediatric ophthalmologist for a full eye examination, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Ms. Walsh and colleagues pulled data in March 2022 on the demographics of pediatric ophthalmologists from online directories hosted by the AAO and the American Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. Ms. Walsh cautioned that the directories might include eye doctors who are no longer practicing, or there might be specialists who had not registered for the databases.
Yasmin Bradfield, MD, a pediatric ophthalmologist at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, noted that after the study published, pediatric ophthalmologists from Vermont and New Mexico notified study authors and AAPOS that they are practicing in the states.
Dr. Bradfield, a board member of AAPOS who also heads the organization’s recruitment task force, said the organization is aware of only one state – Wyoming – without a currently practicing pediatric ophthalmologist.
But based on the March 2022 data, Ms. Walsh and her colleagues found four states – New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Vermont – did not have any pediatric ophthalmologists listed in directories for the organizations. Meanwhile, the country’s most populous states – California, New York, Florida, and Texas – had the most pediatric ophthalmologists.
For every million people, the study identified 7.7 pediatric ophthalmologists nationwide.
Julius T. Oatts, MD, the lead author of an accompanying editorial, said the findings are “valuable and sobering.” Even in San Francisco, where Dr. Oatts practices, most pediatric eye specialists have 6-month wait lists, he said.
Not fixing the shortage of children’s eye doctors could carry lifetime consequences, Dr. Oatts and his colleagues warned.
“Vision and eye health represent an important health barrier to learning in children,” Dr. Oatts and his colleagues wrote. “Lack of access to pediatric vision screening and care also contributes to the academic achievement gap and educational disparities.”
Dr. Bradfield said that disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care could leave some children at risk for losing their vision or never being able to see 20/20. Parents living in areas without a specialist may decide to instead visit an optometrist, but they are not trained to treat serious cases, such as strabismus, and only test and diagnose vision changes, according to AAPOS.
“If we don’t get to the kids in time, they can lose vision permanently, even if it’s something as simple as they just need glasses as a toddler,” Dr. Bradfield said.
Dr. Bradfield said AAPOS is recruiting new pediatric ophthalmologists by offering fellowships for medical students to attend the association’s annual conference and creating shadowing opportunities for students. The society also will release a survey of pediatric ophthalmology salaries to dispel rumors that the specialty does not have lucrative wages.
Ms. Walsh said she was interested in looking at disparities in pediatric ophthalmology care, in part, because she was surprised by how few of her classmates attending medical school were interested in the field of study.
“I hope it encourages ophthalmologists to consider pediatric ophthalmology, or to consider volunteering their time, or going to underserved areas to provide care to families that really are in need,” she said.
Coauthor Jayanth Sridhar, MD, reported receiving personal fees from Alcon, Apellis, Allergan, Dutch Ophthalmic Research Center, Genentech, OcuTerra Therapeutics, and Regeneron outside the submitted work. The other authors and the editorialists report no relevant financial relationships.
*This article was updated on 2/2/2023.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Expert offers insights on pediatric dermatology emergencies
ORLANDO – The eruption spread away from the head and her transaminase levels were “dramatic,” in the 700s, said Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Marathe, director of the division of dermatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, reviewed this case in a presentation on pediatric dermatologic emergencies at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgery Conference, pointing out potential pitfalls and important aspects that might require swift action.
The patient was diagnosed with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Facial involvement is common in pediatric cases of DRESS, but edema of the face is less common in children than adults, Dr. Marathe said.
Antiepileptic medications are the most common cause of DRESS, followed by antibiotics – most often, vancomycin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, she said. But sometimes the trigger is not clear, she noted, recalling a vexing case she once saw in which IV contrast was eventually identified as the cause.
When DRESS is suspected, she said, lab work should be done during the acute eruption and after resolution. This should include CBC, liver function tests, creatinine, and urinalysis, and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and thyroid testing.
Treatment typically includes supportive care, unless symptoms are systemic, or if there is impending liver failure, when steroids, cyclosporine, or IVIG can be used.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): Mortality rates when these diseases overlap is 4%, Dr. Marathe said. Clues to diagnosing this other medication-induced condition include involvement of the palms and the soles of the feet; presence of the Nikolsky sign in which the top layers of the skin slip away from the lower layers when rubbed; mucosal involvement, which often precedes cutaneous involvement; and these symptoms occurring within the first 8 weeks of taking a medication, which are most commonly antibiotics and anti-epileptics.
Dr. Marathe underscored how important it is to get ophthalmology involved right away, because of the risk of vision loss. Amniotic membrane transfer to the eye at the time of diagnosis has been found to produce dramatically better outcomes, she said. The membrane has anti-inflammatory and antiscarring properties and can promote wound healing on the surface of the eye.
“I would recommend getting your ophthalmology team on board early because they have to advocate for these patients,” she said.
Corticosteroids and IVIG can improve ocular outcomes, but cyclosporine is associated with better mortality outcomes, she said. Emerging data on etanercept has also led to more use of that drug, she said.
Erythema multiforme (EM): unlike urticaria, multiforme EM can have mucosal involvement, Dr. Marathe said. Clinicians should look for three zones of color: A central duskiness, a rim of pallor, and a ring of erythema.
EM is triggered by a virus, which is usually herpes simplex virus (HSV). But she added that HSV is not always found. “So, there are certainly other triggers out there that we just haven’t identified,” she said.
If HSV is suspected, oral acyclovir is effective, she noted.
Other cases might not be as straightforward. Dr. Marathe said that during her fellowship, she saw a patient with EM that was controlled only by IVIG, so it was administered every 3 months. In that case, the trigger was never found.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): This syndrome can follow COVID-19 infection, and usually presents with 3-5 days of fever after COVID has resolved. It can include gastrointestinal, cardiorespiratory, and neurocognitive symptoms.
The skin presentation is mainly a morbilliform pattern, but clinicians might also see conjunctival involvement, mucosal involvement, and “COVID toes,” painful red or purple lesions on the toes.
Treatment is usually IVIG and systemic corticosteroids, with the treatment course depending on the severity.
MIS-C was initially thought to be Kawasaki’s disease, another autoinflammatory disorder, which is related but distinct, Dr. Marathe said.
Patients with MIS-C “are usually going to have COVID-positive antibodies,” she said. But since almost everybody may have COVID antibodies, “it’s not usually a helpful test for you now. But early on, that’s what we used as helpful indicator.”
Dr. Marathe reported no relevant financial relationships.
ORLANDO – The eruption spread away from the head and her transaminase levels were “dramatic,” in the 700s, said Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Marathe, director of the division of dermatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, reviewed this case in a presentation on pediatric dermatologic emergencies at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgery Conference, pointing out potential pitfalls and important aspects that might require swift action.
The patient was diagnosed with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Facial involvement is common in pediatric cases of DRESS, but edema of the face is less common in children than adults, Dr. Marathe said.
Antiepileptic medications are the most common cause of DRESS, followed by antibiotics – most often, vancomycin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, she said. But sometimes the trigger is not clear, she noted, recalling a vexing case she once saw in which IV contrast was eventually identified as the cause.
When DRESS is suspected, she said, lab work should be done during the acute eruption and after resolution. This should include CBC, liver function tests, creatinine, and urinalysis, and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and thyroid testing.
Treatment typically includes supportive care, unless symptoms are systemic, or if there is impending liver failure, when steroids, cyclosporine, or IVIG can be used.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): Mortality rates when these diseases overlap is 4%, Dr. Marathe said. Clues to diagnosing this other medication-induced condition include involvement of the palms and the soles of the feet; presence of the Nikolsky sign in which the top layers of the skin slip away from the lower layers when rubbed; mucosal involvement, which often precedes cutaneous involvement; and these symptoms occurring within the first 8 weeks of taking a medication, which are most commonly antibiotics and anti-epileptics.
Dr. Marathe underscored how important it is to get ophthalmology involved right away, because of the risk of vision loss. Amniotic membrane transfer to the eye at the time of diagnosis has been found to produce dramatically better outcomes, she said. The membrane has anti-inflammatory and antiscarring properties and can promote wound healing on the surface of the eye.
“I would recommend getting your ophthalmology team on board early because they have to advocate for these patients,” she said.
Corticosteroids and IVIG can improve ocular outcomes, but cyclosporine is associated with better mortality outcomes, she said. Emerging data on etanercept has also led to more use of that drug, she said.
Erythema multiforme (EM): unlike urticaria, multiforme EM can have mucosal involvement, Dr. Marathe said. Clinicians should look for three zones of color: A central duskiness, a rim of pallor, and a ring of erythema.
EM is triggered by a virus, which is usually herpes simplex virus (HSV). But she added that HSV is not always found. “So, there are certainly other triggers out there that we just haven’t identified,” she said.
If HSV is suspected, oral acyclovir is effective, she noted.
Other cases might not be as straightforward. Dr. Marathe said that during her fellowship, she saw a patient with EM that was controlled only by IVIG, so it was administered every 3 months. In that case, the trigger was never found.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): This syndrome can follow COVID-19 infection, and usually presents with 3-5 days of fever after COVID has resolved. It can include gastrointestinal, cardiorespiratory, and neurocognitive symptoms.
The skin presentation is mainly a morbilliform pattern, but clinicians might also see conjunctival involvement, mucosal involvement, and “COVID toes,” painful red or purple lesions on the toes.
Treatment is usually IVIG and systemic corticosteroids, with the treatment course depending on the severity.
MIS-C was initially thought to be Kawasaki’s disease, another autoinflammatory disorder, which is related but distinct, Dr. Marathe said.
Patients with MIS-C “are usually going to have COVID-positive antibodies,” she said. But since almost everybody may have COVID antibodies, “it’s not usually a helpful test for you now. But early on, that’s what we used as helpful indicator.”
Dr. Marathe reported no relevant financial relationships.
ORLANDO – The eruption spread away from the head and her transaminase levels were “dramatic,” in the 700s, said Kalyani S. Marathe, MD, MPH, associate professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati.
Dr. Marathe, director of the division of dermatology at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, reviewed this case in a presentation on pediatric dermatologic emergencies at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgery Conference, pointing out potential pitfalls and important aspects that might require swift action.
The patient was diagnosed with drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Facial involvement is common in pediatric cases of DRESS, but edema of the face is less common in children than adults, Dr. Marathe said.
Antiepileptic medications are the most common cause of DRESS, followed by antibiotics – most often, vancomycin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, she said. But sometimes the trigger is not clear, she noted, recalling a vexing case she once saw in which IV contrast was eventually identified as the cause.
When DRESS is suspected, she said, lab work should be done during the acute eruption and after resolution. This should include CBC, liver function tests, creatinine, and urinalysis, and human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) and thyroid testing.
Treatment typically includes supportive care, unless symptoms are systemic, or if there is impending liver failure, when steroids, cyclosporine, or IVIG can be used.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): Mortality rates when these diseases overlap is 4%, Dr. Marathe said. Clues to diagnosing this other medication-induced condition include involvement of the palms and the soles of the feet; presence of the Nikolsky sign in which the top layers of the skin slip away from the lower layers when rubbed; mucosal involvement, which often precedes cutaneous involvement; and these symptoms occurring within the first 8 weeks of taking a medication, which are most commonly antibiotics and anti-epileptics.
Dr. Marathe underscored how important it is to get ophthalmology involved right away, because of the risk of vision loss. Amniotic membrane transfer to the eye at the time of diagnosis has been found to produce dramatically better outcomes, she said. The membrane has anti-inflammatory and antiscarring properties and can promote wound healing on the surface of the eye.
“I would recommend getting your ophthalmology team on board early because they have to advocate for these patients,” she said.
Corticosteroids and IVIG can improve ocular outcomes, but cyclosporine is associated with better mortality outcomes, she said. Emerging data on etanercept has also led to more use of that drug, she said.
Erythema multiforme (EM): unlike urticaria, multiforme EM can have mucosal involvement, Dr. Marathe said. Clinicians should look for three zones of color: A central duskiness, a rim of pallor, and a ring of erythema.
EM is triggered by a virus, which is usually herpes simplex virus (HSV). But she added that HSV is not always found. “So, there are certainly other triggers out there that we just haven’t identified,” she said.
If HSV is suspected, oral acyclovir is effective, she noted.
Other cases might not be as straightforward. Dr. Marathe said that during her fellowship, she saw a patient with EM that was controlled only by IVIG, so it was administered every 3 months. In that case, the trigger was never found.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): This syndrome can follow COVID-19 infection, and usually presents with 3-5 days of fever after COVID has resolved. It can include gastrointestinal, cardiorespiratory, and neurocognitive symptoms.
The skin presentation is mainly a morbilliform pattern, but clinicians might also see conjunctival involvement, mucosal involvement, and “COVID toes,” painful red or purple lesions on the toes.
Treatment is usually IVIG and systemic corticosteroids, with the treatment course depending on the severity.
MIS-C was initially thought to be Kawasaki’s disease, another autoinflammatory disorder, which is related but distinct, Dr. Marathe said.
Patients with MIS-C “are usually going to have COVID-positive antibodies,” she said. But since almost everybody may have COVID antibodies, “it’s not usually a helpful test for you now. But early on, that’s what we used as helpful indicator.”
Dr. Marathe reported no relevant financial relationships.
AT ODAC 2023
Hemorrhagic Lacrimation and Epistaxis: Rare Findings in Acute Hemorrhagic Edema of Infancy
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.
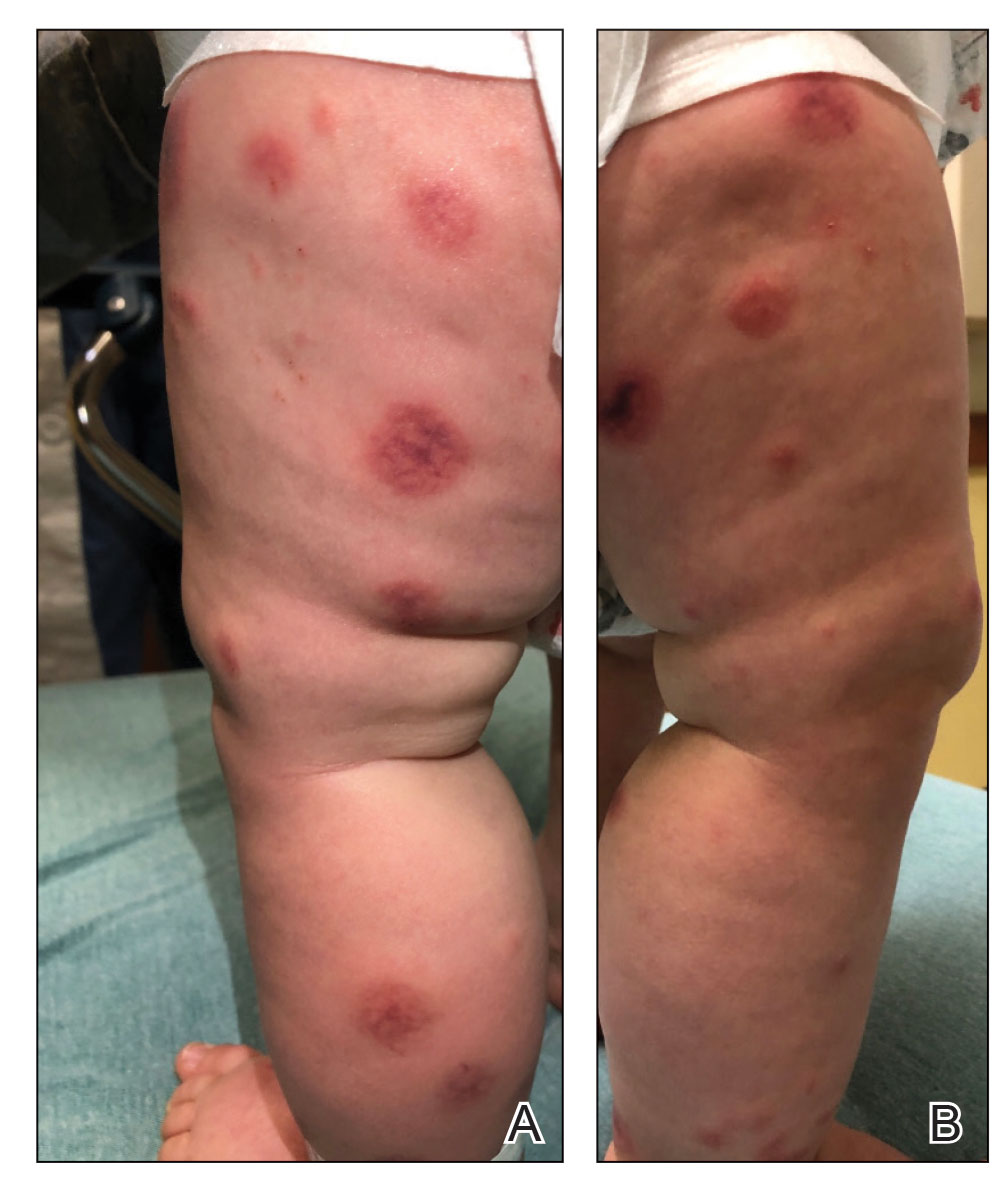
A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.
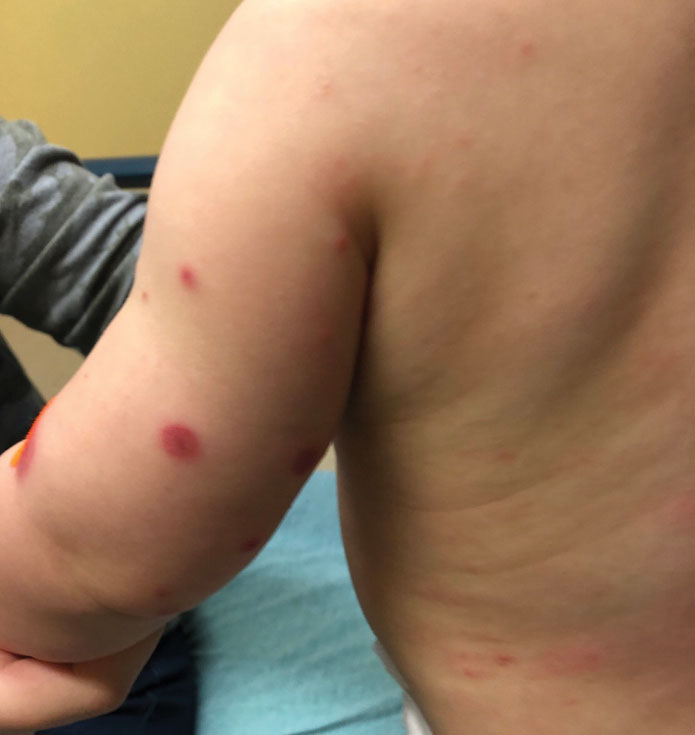
Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.

A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.

Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
To the Editor:
Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis are dramatic presentations with a narrow differential diagnosis. It rarely has been reported to present alongside the more typical features of acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI), which is a benign self-limited leukocytoclastic vasculitis most often seen in children aged 4 months to 2 years. Extracutaneous involvement rarely is seen in AHEI, though joint, gastrointestinal tract, and renal involvement have been reported.1 Most patients present with edematous, annular, or cockade purpuric vasculitic lesions classically involving the face and distal extremities with relative sparing of the trunk. We present a case of a well-appearing, 10-month-old infant boy with hemorrhagic vasculitic lesions, acral edema, and an associated episode of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis.

A 10-month-old infant boy who was otherwise healthy presented to the emergency department (ED) with an acute-onset, progressively worsening cutaneous eruption of 2 days’ duration. A thorough history revealed that the eruption initially had presented as several small, bright-red papules on the thighs. The eruption subsequently spread to involve the buttocks, legs, and arms (Figures 1 and 2). The parents also noted that the patient had experienced an episode of bloody tears and epistaxis that lasted a few minutes at the pediatrician’s office earlier that morning, a finding that prompted the urgent referral to the ED.

Dermatology was then consulted. A review of systems was notable for rhinorrhea and diarrhea during the week leading to the eruption. The patient’s parents denied fevers, decreased oral intake, or a recent course of antibiotics. The patient’s medical history was notable only for atopic dermatitis treated with emollients and occasional topical steroids. The parents denied recent travel or vaccinations. Physical examination showed an afebrile, well-appearing infant with multiple nontender, slightly edematous, circular, purpuric papules and plaques scattered on the buttocks and extremities with edema on the dorsal feet. The remainder of the patient’s workup in the ED was notable for mild elevations in C-reactive protein levels (1.4 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.2 mg/dL]) and an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (22 mm/h [reference range, 2–12 mm/h]). A complete blood cell count; liver function tests; urinalysis; and coagulation studies, including prothrombin, partial thromboplastin time, and international normalized ratio, were unremarkable. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy was diagnosed based on the clinical manifestations.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (also known as Finkelstein disease, medallionlike purpura, Seidemayer syndrome, infantile postinfectious irislike purpura and edema, and purpura en cocarde avec oedeme) is believed to result from an immune complex–related reaction, often in the setting of an upper respiratory tract infection; medications, especially antibiotics; or vaccinations. The condition previously was considered a benign form of Henoch-Schönlein purpura; however, it is now recognized as its own clinical entity. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy commonly affects children between the ages of 4 months and 2 years. The incidence peaks in the winter months, and males tend to be more affected than females.1
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Edema can develop on the hands, feet, and genitalia. Importantly, facial edema has been noted to precede skin lesions.2 Coin-shaped or targetoid hemorrhagic and purpuric lesions in a cockade or rosette pattern with scalloped margins typically begin on the distal extremities and tend to spread proximally. The lesions are variable in size but have been reported to be as large as 5 cm in diameter. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.3 Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—both present in our patient—are rare findings with AHEI. It is likely that most providers, including dermatologists, may be unfamiliar with these striking clinical findings. Although the pathophysiology of hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis has not been formally investigated, we postulate that it likely is related to the formation of immune complexes that lead to small vessel vasculitis, underpinning the characteristic findings in AHEI.4,5 This reasoning is supported by the complete resolution of symptoms corresponding with clinical clearance of the cutaneous vasculitis in 2 prior cases4,5 as well as in our patient who did not have a relapse of symptoms following cessation of the cutaneous eruption at a pediatric follow-up appointment 2 weeks later.
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a clinical diagnosis; however, a skin biopsy can be performed to confirm the clinical suspicion and rule out more serious conditions. Histopathologic examination reveals a leukocytoclastic vasculitis involving the capillaries and postcapillary venules of the upper and mid dermis. Laboratory test results usually are nonspecific but can help distinguish AHEI from more serious diseases. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level may be slightly elevated in infants with AHEI. Urinalysis and stool guaiac tests also can be performed to evaluate for any renal or gastrointestinal involvement.6
The differential diagnosis includes IgA vasculitis, erythema multiforme, acute meningococcemia, urticarial vasculitis, Kawasaki disease, and child abuse. IgA vasculitis often presents with more systemic involvement, with abdominal pain, vomiting, hematemesis, diarrhea, and hematochezia occurring in up to 50% of patients. The cutaneous findings of erythema multiforme classically are confined to the limbs and face, and edema of the extremities typically is not seen. Patients with acute meningococcemia appear toxic with high fevers, malaise, and possible septic shock.5
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.7 Antibiotics should be given to treat concurrent bacterial infections, and antihistamines and steroids may be useful for symptomatic relief. Importantly, however, systemic corticosteroids do not appear to conclusively alter the disease course.8
Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy is a rare benign leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a striking presentation often seen following an upper respiratory tract infection or course of antibiotics. Our case demonstrates that on rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis—findings that can be quite alarming to both parents and medical providers. Nonetheless, patients and their caretakers should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
- Emerich PS, Prebianchi PA, Motta LL, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: report of three cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:1181-1184.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani H. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5:356-357.
- Krause I, Lazarov A, Rachmel A, et al. Acute haemorrhagic oedema of infancy, a benign variant of leucocytoclastic vasculitis. Acta Paediatr. 1996;85:114-117.
- Sneller H, Vega C, Zemel L, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy with associated hemorrhagic lacrimation. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2021;37:E70-E72. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000001542
- Mreish S, Al-Tatari H. Hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis in acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2016;2016:9762185. doi:10.1155/2016/9762185
- Savino F, Lupica MM, Tarasco V, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy: a troubling cutaneous presentation with a self-limiting course. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:E149-E152.
- Fiore E, Rizzi M, Ragazzi M, et al. Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children (cockade purpura and edema): a case series and systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:684-695.
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of young children: a concise narrative review. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:1507-1511.
PRACTICE POINTS
- Acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy (AHEI) is clinically characterized by a triad of large purpuric lesions, low-grade fever, and peripheral acral edema. Although joint pain, bloody diarrhea, hematuria, and proteinuria can accompany AHEI, most cases are devoid of systemic symptoms.
- It is a self-limited condition typically lasting 1 to 3 weeks and requires only supportive care.
- On rare occasions, AHEI may be accompanied by hemorrhagic lacrimation and epistaxis. Patients should be assured that the condition is self-limited and resolves without permanent sequalae.
Poor sleep quality as a teen may up MS risk in adulthood
Too little sleep or poor sleep quality during the teen years can significantly increase the risk for multiple sclerosis (MS) during adulthood, new research suggests.
In a large case-control study, individuals who slept less than 7 hours a night on average during adolescence were 40% more likely to develop MS later on. The risk was even higher for those who rated their sleep quality as bad.
On the other hand, MS was significantly less common among individuals who slept longer as teens – indicating a possible protective benefit.
While sleep duration has been associated with mortality or disease risk for other conditions, sleep quality usually has little to no effect on risk, lead investigator Torbjörn Åkerstedt, PhD, sleep researcher and professor of psychology, department of neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, told this news organization.
“I hadn’t really expected that, but those results were quite strong, even stronger than sleep duration,” Dr. Åkerstedt said.
“We don’t really know why this is happening in young age, but the most suitable explanation is that the brain in still developing quite a bit, and you’re interfering with it,” he added.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
Strong association
Other studies have tied sleep deprivation to increased risk for serious illness, but the link between sleep and MS risk isn’t as well studied.
Previous research by Dr. Åkerstedt showed that the risk for MS was higher among individuals who took part in shift work before the age of 20. However, the impact of sleep duration or quality among teens was unknown.
The current Swedish population-based case-control study included 2,075 patients with MS and 3,164 without the disorder. All participants were asked to recall how many hours on average they slept per night between the ages of 15 and 19 years and to rate their sleep quality during that time.
Results showed that individuals who slept fewer than 7 hours a night during their teen years were 40% more likely to have MS as adults (odds ratio [OR], 1.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-1.7).
Poor sleep quality increased MS risk even more (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3-1.9).
The association remained strong even after adjustment for additional sleep on weekends and breaks and excluding shift workers.
Long sleep ‘apparently good’
The researchers also conducted several sensitivity studies to rule out confounders that might bias the association, such as excluding participants who reported currently experiencing less sleep or poor sleep.
“You would expect that people who are suffering from sleep problems today would be the people who reported sleep problems during their youth,” but that didn’t happen, Dr. Åkerstedt noted.
The investigators also entered data on sleep duration and sleep quality at the same time, thinking the data would cancel each other out. However, the association remained the same.
“Quite often you see that sleep duration would eliminate the effect of sleep complaints in the prediction of disease, but here both remain significant when they are entered at the same time,” Dr. Åkerstedt said. “You get the feeling that this might mean they act together to produce results,” he added.
“One other thing that surprised me is that long sleep was apparently good,” said Dr. Åkerstedt.
The investigators have conducted several studies on sleep duration and mortality. In recent research, they found that both short sleep and long sleep predicted mortality – “and often, long sleep is a stronger predictor than short sleep,” he said.
Underestimated problem?
Commenting on the findings, Kathleen Zackowski, PhD, associate vice president of research for the National Multiple Sclerosis Society in Baltimore, noted that participants were asked to rate their own sleep quality during adolescence, a subjective report that may mean sleep quality has an even larger association with MS risk.
“That they found a result with sleep quality says to me that there probably is a bigger problem, because I don’t know if people over- or underestimate their sleep quality,” said Dr. Zackowski, who was not involved with the research.
“If we could get to that sleep quality question a little more objectively, I bet that we’d find there’s a lot more to the story,” she said.
That’s a story the researchers would like to explore, Dr. Åkerstedt reported. Designing a prospective study that more closely tracks sleeping habits during adolescence and follows individuals through adulthood could provide valuable information about how sleep quality and duration affect immune system development and MS risk, he said.
Dr. Zackowski said clinicians know that MS is not caused just by a genetic abnormality and that other environmental lifestyle factors seem to play a part.
“If we find out that sleep is one of those lifestyle factors, this is very changeable,” she added.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Brain Foundation, AFA Insurance, the European Aviation Safety Authority, the Tercentenary Fund of the Bank of Sweden, the Margaretha af Ugglas Foundation, the Swedish Foundation for MS Research, and NEURO Sweden. Dr. Åkerstadt has been supported by Tercentenary Fund of Bank of Sweden, AFA Insurance, and the European Aviation Safety Authority. Dr. Zackowski reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Too little sleep or poor sleep quality during the teen years can significantly increase the risk for multiple sclerosis (MS) during adulthood, new research suggests.
In a large case-control study, individuals who slept less than 7 hours a night on average during adolescence were 40% more likely to develop MS later on. The risk was even higher for those who rated their sleep quality as bad.
On the other hand, MS was significantly less common among individuals who slept longer as teens – indicating a possible protective benefit.
While sleep duration has been associated with mortality or disease risk for other conditions, sleep quality usually has little to no effect on risk, lead investigator Torbjörn Åkerstedt, PhD, sleep researcher and professor of psychology, department of neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, told this news organization.
“I hadn’t really expected that, but those results were quite strong, even stronger than sleep duration,” Dr. Åkerstedt said.
“We don’t really know why this is happening in young age, but the most suitable explanation is that the brain in still developing quite a bit, and you’re interfering with it,” he added.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
Strong association
Other studies have tied sleep deprivation to increased risk for serious illness, but the link between sleep and MS risk isn’t as well studied.
Previous research by Dr. Åkerstedt showed that the risk for MS was higher among individuals who took part in shift work before the age of 20. However, the impact of sleep duration or quality among teens was unknown.
The current Swedish population-based case-control study included 2,075 patients with MS and 3,164 without the disorder. All participants were asked to recall how many hours on average they slept per night between the ages of 15 and 19 years and to rate their sleep quality during that time.
Results showed that individuals who slept fewer than 7 hours a night during their teen years were 40% more likely to have MS as adults (odds ratio [OR], 1.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-1.7).
Poor sleep quality increased MS risk even more (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3-1.9).
The association remained strong even after adjustment for additional sleep on weekends and breaks and excluding shift workers.
Long sleep ‘apparently good’
The researchers also conducted several sensitivity studies to rule out confounders that might bias the association, such as excluding participants who reported currently experiencing less sleep or poor sleep.
“You would expect that people who are suffering from sleep problems today would be the people who reported sleep problems during their youth,” but that didn’t happen, Dr. Åkerstedt noted.
The investigators also entered data on sleep duration and sleep quality at the same time, thinking the data would cancel each other out. However, the association remained the same.
“Quite often you see that sleep duration would eliminate the effect of sleep complaints in the prediction of disease, but here both remain significant when they are entered at the same time,” Dr. Åkerstedt said. “You get the feeling that this might mean they act together to produce results,” he added.
“One other thing that surprised me is that long sleep was apparently good,” said Dr. Åkerstedt.
The investigators have conducted several studies on sleep duration and mortality. In recent research, they found that both short sleep and long sleep predicted mortality – “and often, long sleep is a stronger predictor than short sleep,” he said.
Underestimated problem?
Commenting on the findings, Kathleen Zackowski, PhD, associate vice president of research for the National Multiple Sclerosis Society in Baltimore, noted that participants were asked to rate their own sleep quality during adolescence, a subjective report that may mean sleep quality has an even larger association with MS risk.
“That they found a result with sleep quality says to me that there probably is a bigger problem, because I don’t know if people over- or underestimate their sleep quality,” said Dr. Zackowski, who was not involved with the research.
“If we could get to that sleep quality question a little more objectively, I bet that we’d find there’s a lot more to the story,” she said.
That’s a story the researchers would like to explore, Dr. Åkerstedt reported. Designing a prospective study that more closely tracks sleeping habits during adolescence and follows individuals through adulthood could provide valuable information about how sleep quality and duration affect immune system development and MS risk, he said.
Dr. Zackowski said clinicians know that MS is not caused just by a genetic abnormality and that other environmental lifestyle factors seem to play a part.
“If we find out that sleep is one of those lifestyle factors, this is very changeable,” she added.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Brain Foundation, AFA Insurance, the European Aviation Safety Authority, the Tercentenary Fund of the Bank of Sweden, the Margaretha af Ugglas Foundation, the Swedish Foundation for MS Research, and NEURO Sweden. Dr. Åkerstadt has been supported by Tercentenary Fund of Bank of Sweden, AFA Insurance, and the European Aviation Safety Authority. Dr. Zackowski reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Too little sleep or poor sleep quality during the teen years can significantly increase the risk for multiple sclerosis (MS) during adulthood, new research suggests.
In a large case-control study, individuals who slept less than 7 hours a night on average during adolescence were 40% more likely to develop MS later on. The risk was even higher for those who rated their sleep quality as bad.
On the other hand, MS was significantly less common among individuals who slept longer as teens – indicating a possible protective benefit.
While sleep duration has been associated with mortality or disease risk for other conditions, sleep quality usually has little to no effect on risk, lead investigator Torbjörn Åkerstedt, PhD, sleep researcher and professor of psychology, department of neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, told this news organization.
“I hadn’t really expected that, but those results were quite strong, even stronger than sleep duration,” Dr. Åkerstedt said.
“We don’t really know why this is happening in young age, but the most suitable explanation is that the brain in still developing quite a bit, and you’re interfering with it,” he added.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry.
Strong association
Other studies have tied sleep deprivation to increased risk for serious illness, but the link between sleep and MS risk isn’t as well studied.
Previous research by Dr. Åkerstedt showed that the risk for MS was higher among individuals who took part in shift work before the age of 20. However, the impact of sleep duration or quality among teens was unknown.
The current Swedish population-based case-control study included 2,075 patients with MS and 3,164 without the disorder. All participants were asked to recall how many hours on average they slept per night between the ages of 15 and 19 years and to rate their sleep quality during that time.
Results showed that individuals who slept fewer than 7 hours a night during their teen years were 40% more likely to have MS as adults (odds ratio [OR], 1.4; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.1-1.7).
Poor sleep quality increased MS risk even more (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3-1.9).
The association remained strong even after adjustment for additional sleep on weekends and breaks and excluding shift workers.
Long sleep ‘apparently good’
The researchers also conducted several sensitivity studies to rule out confounders that might bias the association, such as excluding participants who reported currently experiencing less sleep or poor sleep.
“You would expect that people who are suffering from sleep problems today would be the people who reported sleep problems during their youth,” but that didn’t happen, Dr. Åkerstedt noted.
The investigators also entered data on sleep duration and sleep quality at the same time, thinking the data would cancel each other out. However, the association remained the same.
“Quite often you see that sleep duration would eliminate the effect of sleep complaints in the prediction of disease, but here both remain significant when they are entered at the same time,” Dr. Åkerstedt said. “You get the feeling that this might mean they act together to produce results,” he added.
“One other thing that surprised me is that long sleep was apparently good,” said Dr. Åkerstedt.
The investigators have conducted several studies on sleep duration and mortality. In recent research, they found that both short sleep and long sleep predicted mortality – “and often, long sleep is a stronger predictor than short sleep,” he said.
Underestimated problem?
Commenting on the findings, Kathleen Zackowski, PhD, associate vice president of research for the National Multiple Sclerosis Society in Baltimore, noted that participants were asked to rate their own sleep quality during adolescence, a subjective report that may mean sleep quality has an even larger association with MS risk.
“That they found a result with sleep quality says to me that there probably is a bigger problem, because I don’t know if people over- or underestimate their sleep quality,” said Dr. Zackowski, who was not involved with the research.
“If we could get to that sleep quality question a little more objectively, I bet that we’d find there’s a lot more to the story,” she said.
That’s a story the researchers would like to explore, Dr. Åkerstedt reported. Designing a prospective study that more closely tracks sleeping habits during adolescence and follows individuals through adulthood could provide valuable information about how sleep quality and duration affect immune system development and MS risk, he said.
Dr. Zackowski said clinicians know that MS is not caused just by a genetic abnormality and that other environmental lifestyle factors seem to play a part.
“If we find out that sleep is one of those lifestyle factors, this is very changeable,” she added.
The study was funded by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare, the Swedish Brain Foundation, AFA Insurance, the European Aviation Safety Authority, the Tercentenary Fund of the Bank of Sweden, the Margaretha af Ugglas Foundation, the Swedish Foundation for MS Research, and NEURO Sweden. Dr. Åkerstadt has been supported by Tercentenary Fund of Bank of Sweden, AFA Insurance, and the European Aviation Safety Authority. Dr. Zackowski reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases may have doubled in early January
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”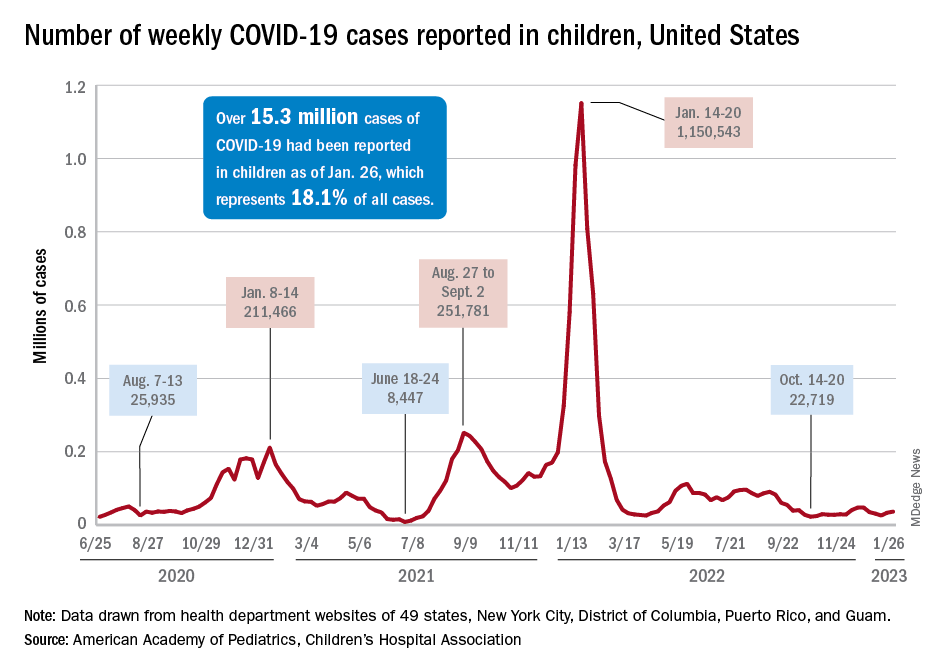
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Although new COVID-19 cases in children, as measured by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association, have remained fairly steady in recent months, data from the Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention suggest that weekly cases took a big jump in early January.
For the most recent week covered . New cases for the first 2 weeks of the year – 31,000 for the week of Dec. 30 to Jan. 5 and 26,000 during Jan. 6-12 – were consistent with the AAP/CHA assertion that “weekly reported child cases have plateaued at an average of about 32,000 cases ... over the past 4 months.”
The CDC data, however, show that new cases doubled during the week of Jan. 1-7 to over 65,000, compared with the end of December, and stayed at that level for Jan. 8-14, and since CDC figures are subject to a 6-week reporting delay, the final numbers are likely to be even higher. The composition by age changed somewhat between the 2 weeks, though, as those aged 0-4 years went from almost half of all cases in the first week down to 40% in the second, while cases rose for children aged 5-11 and 12-15, based on data from the COVID-19 response team.
Emergency department visits for January do not show a corresponding increase. ED visits among children aged 0-11 years with COVID-19, measured as a percentage of all ED visits, declined over the course of the month, as did visits for 16- and 17-year-olds, while those aged 12-15 started the month at 1.4% and were at 1.4% on Jan. 27, with a slight dip down to 1.2% in between, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker. Daily hospitalizations for children aged 0-17 also declined through mid-January and did not reflect the jump in new cases.
Meanwhile, vaccinated children are still in the minority: 57% of those under age 18 have received no COVID vaccine yet, the AAP said in a separate report. Just 7.4% of children under age 2 years had received at least one dose as of Jan. 25, as had 10.1% of those aged 2-4 years, 39.6% of 5- to 11-year-olds and 71.8% of those 12-17 years old, according to the CDC, with corresponding figures for completion of the primary series at 3.5%, 5.3%, 32.5%, and 61.5%.
Managing respiratory symptoms in the ‘tripledemic’ era
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it COVID-19, flu, or even RSV? I recently described just such a patient, an obese woman with type 2 diabetes, presenting with fever, cough, myalgia, and fatigue. I asked readers whether they agreed with my management of this patient.
Thank you for your comments as we continue to react to high rates of URIs. Your comments highlight the importance of local resources and practice habits when managing patients with URI.
It was clear that readers value testing to distinguish between infections. However, access to testing is highly variable around the world and is likely to be routinely used only in high-income countries. The Kaiser Family Foundation performed a cost analysis of testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 and found, not surprisingly, wide variability in the cost of testing. Medicare covers tests at rates of $36-$143 per test; a study of list prices for SARS-CoV-2 tests at 93 hospitals found a median cost of $148 per test. And this does not include collection or facility fees. About 20% of tests cost more than $300.
These costs are prohibitive for many health systems. However, more devices have been introduced since that analysis, and competition and evolving technology should drive down prices. Generally, multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing for multiple pathogens is less expensive than ordering two or three separate molecular tests and is more convenient for patients and practices alike.
Other reader comments focused on the challenges of getting accurate data on viral epidemiology, and there is certainly a time lag between infection trends and public health reports. This is exacerbated by underreporting of symptoms and more testing at home using antigen tests.
But please do not give up on epidemiology! If a test such as PCR is 90% sensitive for identifying infection, the yield in terms of the number of individuals infected with a particular virus should be high, and that is true when infection is in broad circulation. If 20% of a population of 1,000 has an infection and the test sensitivity is 90%, the yield of testing is 180 true cases versus 20 false positives.
However, if just 2% of the population of 1,000 has the infection in this same scenario, then only 18 true cases are identified. The effect on public health is certainly less, and a lower prevalence rate means that confounding variables, such as how long an individual might shed viral particles and the method of sample collection, have an outsized effect on results. This reduces the validity of diagnostic tests.
Even trends on a national level can provide some insight regarding whom to test. Traditionally, our practice has been to not routinely test patients for influenza or RSV from late spring to early fall unless there was a compelling reason, such as recent travel to an area where these infections were more prevalent. The loss of temporality for these infections since 2020 has altered this approach and made us pay more attention to reports from public health organizations.
I also appreciate the discussion of how to treat Agnes’s symptoms as she waits to improve, and anyone who suffers with or treats a viral URI knows that there are few interventions effective for such symptoms as cough and congestion. A systematic review of 29 randomized controlled trials of over-the-counter medications for cough yielded mixed and largely negative results.
Antihistamines alone do not seem to work, and guaifenesin was successful in only one of three trials. Combinations of different drug classes appeared to be slightly more effective.
My personal favorite for the management of acute cough is something that kids generally love: honey. In a review of 14 studies, 9 of which were limited to pediatric patients, honey was associated with significant reductions in cough frequency, cough severity, and total symptom score. However, there was a moderate risk of bias in the included research, and evidence of honey’s benefit in placebo-controlled trials was limited. Honey used in this research came in a variety of forms, so the best dosage is uncertain.
Clearly, advancements are needed. Better symptom management in viral URI will almost certainly improve productivity across the population and will probably reduce the inappropriate use of antibiotics as well. I have said for years that the scientists who can solve the Gordian knot of pediatric mucus deserve three Nobel prizes. I look forward to that golden day.
Dr. Vega is a clinical professor of family medicine at the University of California, Irvine. He reported a conflict of interest with McNeil Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Surgeon General says 13-year-olds shouldn’t be on social media
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
The U.S. Surgeon General says 13 years old is too young to begin using social media.
Most social media platforms including TikTok, Snapchat, Instagram, and Facebook allow users to create accounts if they say they are at least 13 years old.
“I, personally, based on the data I’ve seen, believe that 13 is too early. ... It’s a time where it’s really important for us to be thoughtful about what’s going into how they think about their own self-worth and their relationships, and the skewed and often distorted environment of social media often does a disservice to many of those children,” U.S. Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, told CNN.
Research has shown that teens are susceptible to cyberbullying and serious mental health impacts from social media usage and online activity during an era when the influence of the Internet has become everywhere for young people.
According to the Pew Research Center, 95% of teens age 13 and up have a smartphone, and 97% of teens say they use the Internet daily. Among 13- and 14-year-olds, 61% say they use TikTok and 51% say they use Snapchat. Older teens ages 15-17 use those social media platforms at higher rates, with 71% saying they use TikTok and 65% using Snapchat.
“If parents can band together and say you know, as a group, we’re not going to allow our kids to use social media until 16 or 17 or 18 or whatever age they choose, that’s a much more effective strategy in making sure your kids don’t get exposed to harm early,” Dr. Murthy said.
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.