User login
Mobile devices ‘addictive by design’: Obesity is one of many health effects
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
Wireless devices, like smart phones and tablets, appear to induce compulsive or even addictive use in many individuals, leading to adverse health consequences that are likely to be curtailed only through often difficult behavior modification, according to a pediatric endocrinologist’s take on the problem.
While the summary was based in part on the analysis of 234 published papers drawn from the medical literature, the lead author, Nidhi Gupta, MD, said the data reinforce her own clinical experience.
“As a pediatric endocrinologist, the trend in smartphone-associated health disorders, such as obesity, sleep, and behavior issues, worries me,” Dr. Gupta, director of KAP Pediatric Endocrinology, Nashville, Tenn., said at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
Based on her search of the medical literature, the available data raise concern. In one study she cited, for example, each hour per day of screen time was found to translate into a body mass index increase of 0.5 to 0.7 kg/m2 (P < .001).
With this type of progressive rise in BMI comes prediabetes, dyslipidemia, and other metabolic disorders associated with major health risks, including cardiovascular disease. And there are others. Dr. Gupta cited data suggesting screen time before bed disturbs sleep, which has its own set of health risks.
“When I say health, it includes physical health, mental health, and emotional health,” said Dr. Gupta.
In the U.S. and other countries with a growing obesity epidemic, lack of physical activity and unhealthy eating are widely considered the major culprits. Excessive screen time contributes to both.
“When we are engaged with our devices, we are often snacking subconsciously and not very mindful that we are making unhealthy choices,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem is that there is a vicious circle. Compulsive use of devices follows the same loop as other types of addictive behaviors, according to Dr. Gupta. She traced overuse of wireless devices to the dopaminergic system, which is a powerful neuroendocrine-mediated process of craving, response, and reward.
Like fat, sugar, and salt, which provoke a neuroendocrine reward signal, the chimes and buzzes of a cell phone provide their own cues for reward in the form of a dopamine surge. As a result, these become the “triggers of an irresistible and irrational urge to check our device that makes the dopamine go high in our brain,” Dr. Gupta explained.
Although the vicious cycle can be thwarted by turning off the device, Dr. Gupta characterized this as “impractical” when smartphones are so vital to daily communication. Rather, Dr. Gupta advocated a program of moderation, reserving the phone for useful tasks without succumbing to the siren song of apps that waste time.
The most conspicuous culprit is social media, which Dr. Gupta considers to be among the most Pavlovian triggers of cell phone addiction. However, she acknowledged that participation in social media has its justifications.
“I, myself, use social media for my own branding and marketing,” Dr. Gupta said.
The problem that users have is distinguishing between screen time that does and does not have value, according to Dr. Gupta. She indicated that many of those overusing their smart devices are being driven by the dopaminergic reward system, which is generally divorced from the real goals of life, such as personal satisfaction and activity that is rewarding monetarily or in other ways.
“I am not asking for these devices to be thrown out the window. I am advocating for moderation, balance, and real-life engagement,” Dr. Gupta said at the meeting, held in Atlanta and virtually.
She outlined a long list of practical suggestions, including turning off the alarms, chimes, and messages that engage the user into the vicious dopaminergic-reward system loop. She suggested mindfulness so that the user can distinguish between valuable device use and activity that is simply procrastination.
“The devices are designed to be addictive. They are designed to manipulate our brain,” she said. “Eliminate the reward. Let’s try to make our devices boring, unappealing, or enticing so that they only work as tools.”
The medical literature is filled with data that support the potential harms of excessive screen use, leading many others to make some of the same points. In 2017, Thomas N. Robinson, MD, professor of child health at Stanford (Calif.) University, reviewed data showing an association between screen media exposure and obesity in children and adolescents.
“This is an area crying out for more research,” Dr. Robinson said in an interview. The problem of screen time, sedentary behavior, and weight gain has been an issue since the television was invented, which was the point he made in his 2017 paper, but he agreed that the problem is only getting worse.
“Digital technology has become ubiquitous, touching nearly every aspect of people’s lives,” he said. Yet, as evidence grows that overuse of this technology can be harmful, it is creating a problem without a clear solution.
“There are few data about the efficacy of specific strategies to reduce harmful impacts of digital screen use,” he said.
While some of the solutions that Dr. Gupta described make sense, they are more easily described than executed. The dopaminergic reward system is strong and largely experienced subconsciously. Recruiting patients to recognize that dopaminergic rewards are not rewards in any true sense is already a challenge. Enlisting patients to take the difficult steps to avoid the behavioral cues might be even more difficult.
Dr. Gupta and Dr. Robinson report no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM ENDO 2022
Widespread rash in toddler
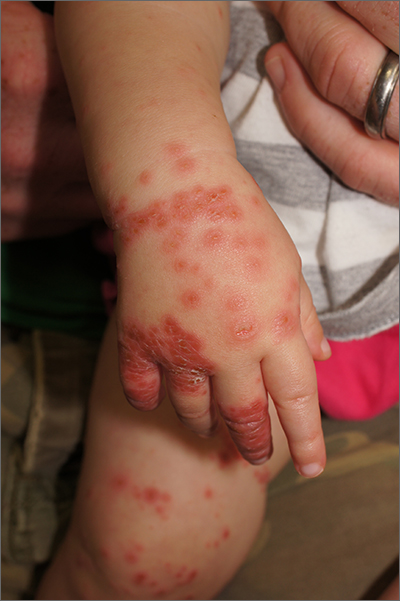
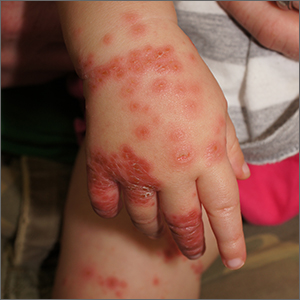
This patient was given a diagnosis of Gianotti Crosti syndrome (GCS; also called infantile acrodermatitis of childhood), which is a self-resolving (often dramatic) dermatosis triggered by a viral infection or immunization. Patients with this syndrome develop papules, vesicles, and plaques on their face, hands, feet, and extremities a week (or more) after having a viral illness or receiving an immunization. In patients with darker skin types, lesions may appear purple to brown rather than bright red to red/orange. The syndrome typically occurs in children between the ages of 1 to 4 years, but almost all patients are under the age of 15.1 Scratching and sleep disturbance are common. The condition typically resolves on its own after 3 or 4 weeks.
Globally, the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of GCS.1 Other reported triggering viruses include hepatitis A and C, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, HIV, parainfluenza viruses, parvoviruses, rubella, and COVID-19.2
Since the cause of this patient’s case of GCS was likely linked to a viral infection that produced the loose stools in a population with low-HBV risk, no further serologic testing was performed. Serologic testing may have been necessary if other infections, disease risks, or symptoms were identified. To relieve itching, topical triamcinolone 0.1% cream was prescribed for use once to twice daily on the extremities and hydrocortisone 1% cream was prescribed once to twice daily for use on the child’s face. At the 6-week follow-up visit, the lesions had resolved; light pink discoloration remained but was expected to further fade. In patients with darker skin, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may take several months to resolve.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Brandt O, Abeck D, Gianotti R, et al. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.09.033
2. Berná-Rico ED, Álvarez-Pinheiro C, Burgos-Blasco P, et al. A Gianotti-Crosti-like eruption in the setting of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e15071. Doi:10.1111/dth.15071

This patient was given a diagnosis of Gianotti Crosti syndrome (GCS; also called infantile acrodermatitis of childhood), which is a self-resolving (often dramatic) dermatosis triggered by a viral infection or immunization. Patients with this syndrome develop papules, vesicles, and plaques on their face, hands, feet, and extremities a week (or more) after having a viral illness or receiving an immunization. In patients with darker skin types, lesions may appear purple to brown rather than bright red to red/orange. The syndrome typically occurs in children between the ages of 1 to 4 years, but almost all patients are under the age of 15.1 Scratching and sleep disturbance are common. The condition typically resolves on its own after 3 or 4 weeks.
Globally, the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of GCS.1 Other reported triggering viruses include hepatitis A and C, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, HIV, parainfluenza viruses, parvoviruses, rubella, and COVID-19.2
Since the cause of this patient’s case of GCS was likely linked to a viral infection that produced the loose stools in a population with low-HBV risk, no further serologic testing was performed. Serologic testing may have been necessary if other infections, disease risks, or symptoms were identified. To relieve itching, topical triamcinolone 0.1% cream was prescribed for use once to twice daily on the extremities and hydrocortisone 1% cream was prescribed once to twice daily for use on the child’s face. At the 6-week follow-up visit, the lesions had resolved; light pink discoloration remained but was expected to further fade. In patients with darker skin, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may take several months to resolve.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).

This patient was given a diagnosis of Gianotti Crosti syndrome (GCS; also called infantile acrodermatitis of childhood), which is a self-resolving (often dramatic) dermatosis triggered by a viral infection or immunization. Patients with this syndrome develop papules, vesicles, and plaques on their face, hands, feet, and extremities a week (or more) after having a viral illness or receiving an immunization. In patients with darker skin types, lesions may appear purple to brown rather than bright red to red/orange. The syndrome typically occurs in children between the ages of 1 to 4 years, but almost all patients are under the age of 15.1 Scratching and sleep disturbance are common. The condition typically resolves on its own after 3 or 4 weeks.
Globally, the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the most common cause of GCS.1 Other reported triggering viruses include hepatitis A and C, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, enteroviruses, HIV, parainfluenza viruses, parvoviruses, rubella, and COVID-19.2
Since the cause of this patient’s case of GCS was likely linked to a viral infection that produced the loose stools in a population with low-HBV risk, no further serologic testing was performed. Serologic testing may have been necessary if other infections, disease risks, or symptoms were identified. To relieve itching, topical triamcinolone 0.1% cream was prescribed for use once to twice daily on the extremities and hydrocortisone 1% cream was prescribed once to twice daily for use on the child’s face. At the 6-week follow-up visit, the lesions had resolved; light pink discoloration remained but was expected to further fade. In patients with darker skin, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may take several months to resolve.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).
1. Brandt O, Abeck D, Gianotti R, et al. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.09.033
2. Berná-Rico ED, Álvarez-Pinheiro C, Burgos-Blasco P, et al. A Gianotti-Crosti-like eruption in the setting of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e15071. Doi:10.1111/dth.15071
1. Brandt O, Abeck D, Gianotti R, et al. Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.09.033
2. Berná-Rico ED, Álvarez-Pinheiro C, Burgos-Blasco P, et al. A Gianotti-Crosti-like eruption in the setting of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e15071. Doi:10.1111/dth.15071
No more ‘escape hatch’: Post Roe, new worries about meds linked to birth defects
As states ban or limit abortion in the wake of the demise of Roe v. Wade, physicians are turning their attention to widely-used drugs that can cause birth defects. At issue: Should these drugs still be prescribed to women of childbearing age if they don’t have the option of terminating their pregnancies?
“Doctors are going to understandably be terrified that a patient may become pregnant using a teratogen that they have prescribed,” said University of Pittsburgh rheumatologist Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, who works in a state where the future of abortion rights is uncertain. “While this was a feared outcome before Roe v. Wade was overturned, abortion provided an escape hatch by which women could avoid having to continue a pregnancy and potentially raise a child with congenital anomalies. I believe that prescribing is going to become much more defensive and conservative. Some clinicians may choose not to prescribe these medications to patients who have childbearing potential, even if they don’t have much risk for pregnancy.”
Other physicians expressed similar concerns in interviews. Duke University, Durham, N.C., rheumatologist Megan E. B. Clowse, MD, MPH, fears that physicians will be wary of prescribing a variety of medications – including new ones for which there are few pregnancy data – if abortion is unavailable. “Women who receive these new or teratogenic medications will likely lose their reproductive autonomy and be forced to choose between having sexual relationships with men, obtaining procedures that make them permanently sterile, or using contraception that may cause intolerable side effects,” she said. “I am very concerned that young women with rheumatic disease will now be left with active disease resulting in joint damage and renal failure.”
Abortion is now banned in at least six states, according to The New York Times. That number may rise to 16 as more restrictions become law. Another five states aren’t expected to ban abortion soon but have implemented gestational age limits on abortion or are expected to adopt them. In another nine states, courts or lawmakers will decide whether abortion remains legal.
Only 20 states and the District of Columbia have firm abortion protections in place.
Numerous drugs are considered teratogens, which means they may cause birth defects. Thalidomide is the most infamous, but there are many more, including several used in rheumatology, dermatology, and gastroenterology. Among the most widely used teratogenic medications are the acne drugs isotretinoin and methotrexate, which are used to treat a variety of conditions, such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis.
Dr. Clowse, who helps manage an industry-supported website devoted to reproductive care for women with lupus (www.LupusPregnancy.org), noted that several drugs linked to birth defects and pregnancy loss are commonly prescribed in rheumatology.
“Methotrexate is the most common medication and has been the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis [treatment] for at least two decades,” she said. “Mycophenolate is our best medication to treat lupus nephritis, which is inflammation in the kidneys caused by lupus. This is a common complication for young women with lupus, and all of our guideline-recommended treatment regimens include a medication that causes pregnancy loss and birth defects, either mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide.”
Rheumatologists also prescribe a large number of new drugs for which there are few data about pregnancy risks. “It typically takes about two decades to have sufficient data about the safety of our medications,” she said.
Reflecting the sensitivity of the topic, Dr. Clowse made clear that her opinions don’t represent the views of her institution. She works in North Carolina, where the fate of abortion rights is uncertain, according to The New York Times.
What about alternatives? “The short answer is that some of these medications work really well and sometimes much better than the nonteratogenic alternatives,” said Dr. Birru Talabi. “I’m worried about methotrexate. It has been used to induce abortions but is primarily used in the United States as a highly effective treatment for cancer as well as a myriad of rheumatic diseases. If legislators try to restrict access to methotrexate, we may see increasing disability and even death among people who need this medication but cannot access it.”
Rheumatologists aren’t the only physicians who are worrying about the fates of their patients in a new era of abortion restrictions. Gastroenterologist Sunanda Kane, MD, MSPH, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said several teratogenic medications are used in her field to treat constipation, viral hepatitis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
“When treating women of childbearing age, there are usually alternatives. If we do prescribe a medication with a high teratogenic potential, we counsel and document that we have discussed two forms of birth control to avoid pregnancy. We usually do not prescribe a drug with teratogenic potential with the ‘out’ being an abortion if a pregnancy does occur,” she said. However, “if abortion is not even on the table as an option, we may be much less likely to prescribe these medications. This will be particularly true in patients who clearly do not have the means to travel to have an abortion in any situation.”
Abortion is expected to remain legal in Minnesota, where Dr. Kane practices, but it may be restricted or banned in nearby Wisconsin, depending on the state legislature. None of her patients have had abortions after becoming pregnant while taking the medications, she said, although she “did have a patient who because of her religious faith did not have an abortion after exposure and ended up with a stillbirth.”
The crackdown on abortion won’t just pose risks to patients who take potentially dangerous medications, physicians said. Dr. Kane said pregnancy itself is a significant risk for patients with “very active, uncontrolled gastrointestinal conditions where a pregnancy could be harmful to the mother’s health or result in offspring that are very unhealthy.” These include decompensated cirrhosis, uncontrolled Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, refractory gastroparesis, uncontrolled celiac sprue, and chronic pancreatitis, she said.
“There have been times when after shared decisionmaking, a patient with very active inflammatory bowel disease has decided to terminate the pregnancy because of her own ongoing health issues,” she said. “Not having this option will potentially lead to disastrous results.”
Dr. Clowse, the Duke University rheumatologist, echoed Dr. Kane’s concerns about women who are too sick to bear children. “The removal of abortion rights puts the lives and quality of life for women with rheumatic disease at risk. For patients with lupus and other systemic rheumatic disease, pregnancy can be medically catastrophic, leading to permanent harm and even death to the woman and her offspring. I am worried that women in these conditions will die without lifesaving pregnancy terminations, due to worries about the legal consequences for their physicians.”
The U.S. Supreme Court’s ruling that overturned Roe v. Wade has also raised the prospect that the court could ultimately allow birth control to be restricted or outlawed.
While the ruling states that “nothing in this opinion should be understood to cast doubt on precedents that do not concern abortion,” Justice Clarence Thomas wrote a concurrence in which he said that the court should reconsider a 1960s ruling that forbids the banning of contraceptives. Republicans have dismissed concerns about bans being allowed, although Democrats, including the president and vice president, starkly warn that they could happen.
“If we as providers have to be concerned that there will be an unplanned pregnancy because of the lack of access to contraception,” Dr. Kane said, “this will have significant downstream consequences to the kind of care we can provide and might just drive some providers to not give care to female patients at all given this concern.”
The physicians quoted in this article report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As states ban or limit abortion in the wake of the demise of Roe v. Wade, physicians are turning their attention to widely-used drugs that can cause birth defects. At issue: Should these drugs still be prescribed to women of childbearing age if they don’t have the option of terminating their pregnancies?
“Doctors are going to understandably be terrified that a patient may become pregnant using a teratogen that they have prescribed,” said University of Pittsburgh rheumatologist Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, who works in a state where the future of abortion rights is uncertain. “While this was a feared outcome before Roe v. Wade was overturned, abortion provided an escape hatch by which women could avoid having to continue a pregnancy and potentially raise a child with congenital anomalies. I believe that prescribing is going to become much more defensive and conservative. Some clinicians may choose not to prescribe these medications to patients who have childbearing potential, even if they don’t have much risk for pregnancy.”
Other physicians expressed similar concerns in interviews. Duke University, Durham, N.C., rheumatologist Megan E. B. Clowse, MD, MPH, fears that physicians will be wary of prescribing a variety of medications – including new ones for which there are few pregnancy data – if abortion is unavailable. “Women who receive these new or teratogenic medications will likely lose their reproductive autonomy and be forced to choose between having sexual relationships with men, obtaining procedures that make them permanently sterile, or using contraception that may cause intolerable side effects,” she said. “I am very concerned that young women with rheumatic disease will now be left with active disease resulting in joint damage and renal failure.”
Abortion is now banned in at least six states, according to The New York Times. That number may rise to 16 as more restrictions become law. Another five states aren’t expected to ban abortion soon but have implemented gestational age limits on abortion or are expected to adopt them. In another nine states, courts or lawmakers will decide whether abortion remains legal.
Only 20 states and the District of Columbia have firm abortion protections in place.
Numerous drugs are considered teratogens, which means they may cause birth defects. Thalidomide is the most infamous, but there are many more, including several used in rheumatology, dermatology, and gastroenterology. Among the most widely used teratogenic medications are the acne drugs isotretinoin and methotrexate, which are used to treat a variety of conditions, such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis.
Dr. Clowse, who helps manage an industry-supported website devoted to reproductive care for women with lupus (www.LupusPregnancy.org), noted that several drugs linked to birth defects and pregnancy loss are commonly prescribed in rheumatology.
“Methotrexate is the most common medication and has been the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis [treatment] for at least two decades,” she said. “Mycophenolate is our best medication to treat lupus nephritis, which is inflammation in the kidneys caused by lupus. This is a common complication for young women with lupus, and all of our guideline-recommended treatment regimens include a medication that causes pregnancy loss and birth defects, either mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide.”
Rheumatologists also prescribe a large number of new drugs for which there are few data about pregnancy risks. “It typically takes about two decades to have sufficient data about the safety of our medications,” she said.
Reflecting the sensitivity of the topic, Dr. Clowse made clear that her opinions don’t represent the views of her institution. She works in North Carolina, where the fate of abortion rights is uncertain, according to The New York Times.
What about alternatives? “The short answer is that some of these medications work really well and sometimes much better than the nonteratogenic alternatives,” said Dr. Birru Talabi. “I’m worried about methotrexate. It has been used to induce abortions but is primarily used in the United States as a highly effective treatment for cancer as well as a myriad of rheumatic diseases. If legislators try to restrict access to methotrexate, we may see increasing disability and even death among people who need this medication but cannot access it.”
Rheumatologists aren’t the only physicians who are worrying about the fates of their patients in a new era of abortion restrictions. Gastroenterologist Sunanda Kane, MD, MSPH, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said several teratogenic medications are used in her field to treat constipation, viral hepatitis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
“When treating women of childbearing age, there are usually alternatives. If we do prescribe a medication with a high teratogenic potential, we counsel and document that we have discussed two forms of birth control to avoid pregnancy. We usually do not prescribe a drug with teratogenic potential with the ‘out’ being an abortion if a pregnancy does occur,” she said. However, “if abortion is not even on the table as an option, we may be much less likely to prescribe these medications. This will be particularly true in patients who clearly do not have the means to travel to have an abortion in any situation.”
Abortion is expected to remain legal in Minnesota, where Dr. Kane practices, but it may be restricted or banned in nearby Wisconsin, depending on the state legislature. None of her patients have had abortions after becoming pregnant while taking the medications, she said, although she “did have a patient who because of her religious faith did not have an abortion after exposure and ended up with a stillbirth.”
The crackdown on abortion won’t just pose risks to patients who take potentially dangerous medications, physicians said. Dr. Kane said pregnancy itself is a significant risk for patients with “very active, uncontrolled gastrointestinal conditions where a pregnancy could be harmful to the mother’s health or result in offspring that are very unhealthy.” These include decompensated cirrhosis, uncontrolled Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, refractory gastroparesis, uncontrolled celiac sprue, and chronic pancreatitis, she said.
“There have been times when after shared decisionmaking, a patient with very active inflammatory bowel disease has decided to terminate the pregnancy because of her own ongoing health issues,” she said. “Not having this option will potentially lead to disastrous results.”
Dr. Clowse, the Duke University rheumatologist, echoed Dr. Kane’s concerns about women who are too sick to bear children. “The removal of abortion rights puts the lives and quality of life for women with rheumatic disease at risk. For patients with lupus and other systemic rheumatic disease, pregnancy can be medically catastrophic, leading to permanent harm and even death to the woman and her offspring. I am worried that women in these conditions will die without lifesaving pregnancy terminations, due to worries about the legal consequences for their physicians.”
The U.S. Supreme Court’s ruling that overturned Roe v. Wade has also raised the prospect that the court could ultimately allow birth control to be restricted or outlawed.
While the ruling states that “nothing in this opinion should be understood to cast doubt on precedents that do not concern abortion,” Justice Clarence Thomas wrote a concurrence in which he said that the court should reconsider a 1960s ruling that forbids the banning of contraceptives. Republicans have dismissed concerns about bans being allowed, although Democrats, including the president and vice president, starkly warn that they could happen.
“If we as providers have to be concerned that there will be an unplanned pregnancy because of the lack of access to contraception,” Dr. Kane said, “this will have significant downstream consequences to the kind of care we can provide and might just drive some providers to not give care to female patients at all given this concern.”
The physicians quoted in this article report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As states ban or limit abortion in the wake of the demise of Roe v. Wade, physicians are turning their attention to widely-used drugs that can cause birth defects. At issue: Should these drugs still be prescribed to women of childbearing age if they don’t have the option of terminating their pregnancies?
“Doctors are going to understandably be terrified that a patient may become pregnant using a teratogen that they have prescribed,” said University of Pittsburgh rheumatologist Mehret Birru Talabi, MD, PhD, who works in a state where the future of abortion rights is uncertain. “While this was a feared outcome before Roe v. Wade was overturned, abortion provided an escape hatch by which women could avoid having to continue a pregnancy and potentially raise a child with congenital anomalies. I believe that prescribing is going to become much more defensive and conservative. Some clinicians may choose not to prescribe these medications to patients who have childbearing potential, even if they don’t have much risk for pregnancy.”
Other physicians expressed similar concerns in interviews. Duke University, Durham, N.C., rheumatologist Megan E. B. Clowse, MD, MPH, fears that physicians will be wary of prescribing a variety of medications – including new ones for which there are few pregnancy data – if abortion is unavailable. “Women who receive these new or teratogenic medications will likely lose their reproductive autonomy and be forced to choose between having sexual relationships with men, obtaining procedures that make them permanently sterile, or using contraception that may cause intolerable side effects,” she said. “I am very concerned that young women with rheumatic disease will now be left with active disease resulting in joint damage and renal failure.”
Abortion is now banned in at least six states, according to The New York Times. That number may rise to 16 as more restrictions become law. Another five states aren’t expected to ban abortion soon but have implemented gestational age limits on abortion or are expected to adopt them. In another nine states, courts or lawmakers will decide whether abortion remains legal.
Only 20 states and the District of Columbia have firm abortion protections in place.
Numerous drugs are considered teratogens, which means they may cause birth defects. Thalidomide is the most infamous, but there are many more, including several used in rheumatology, dermatology, and gastroenterology. Among the most widely used teratogenic medications are the acne drugs isotretinoin and methotrexate, which are used to treat a variety of conditions, such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis.
Dr. Clowse, who helps manage an industry-supported website devoted to reproductive care for women with lupus (www.LupusPregnancy.org), noted that several drugs linked to birth defects and pregnancy loss are commonly prescribed in rheumatology.
“Methotrexate is the most common medication and has been the cornerstone of rheumatoid arthritis [treatment] for at least two decades,” she said. “Mycophenolate is our best medication to treat lupus nephritis, which is inflammation in the kidneys caused by lupus. This is a common complication for young women with lupus, and all of our guideline-recommended treatment regimens include a medication that causes pregnancy loss and birth defects, either mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide.”
Rheumatologists also prescribe a large number of new drugs for which there are few data about pregnancy risks. “It typically takes about two decades to have sufficient data about the safety of our medications,” she said.
Reflecting the sensitivity of the topic, Dr. Clowse made clear that her opinions don’t represent the views of her institution. She works in North Carolina, where the fate of abortion rights is uncertain, according to The New York Times.
What about alternatives? “The short answer is that some of these medications work really well and sometimes much better than the nonteratogenic alternatives,” said Dr. Birru Talabi. “I’m worried about methotrexate. It has been used to induce abortions but is primarily used in the United States as a highly effective treatment for cancer as well as a myriad of rheumatic diseases. If legislators try to restrict access to methotrexate, we may see increasing disability and even death among people who need this medication but cannot access it.”
Rheumatologists aren’t the only physicians who are worrying about the fates of their patients in a new era of abortion restrictions. Gastroenterologist Sunanda Kane, MD, MSPH, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said several teratogenic medications are used in her field to treat constipation, viral hepatitis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
“When treating women of childbearing age, there are usually alternatives. If we do prescribe a medication with a high teratogenic potential, we counsel and document that we have discussed two forms of birth control to avoid pregnancy. We usually do not prescribe a drug with teratogenic potential with the ‘out’ being an abortion if a pregnancy does occur,” she said. However, “if abortion is not even on the table as an option, we may be much less likely to prescribe these medications. This will be particularly true in patients who clearly do not have the means to travel to have an abortion in any situation.”
Abortion is expected to remain legal in Minnesota, where Dr. Kane practices, but it may be restricted or banned in nearby Wisconsin, depending on the state legislature. None of her patients have had abortions after becoming pregnant while taking the medications, she said, although she “did have a patient who because of her religious faith did not have an abortion after exposure and ended up with a stillbirth.”
The crackdown on abortion won’t just pose risks to patients who take potentially dangerous medications, physicians said. Dr. Kane said pregnancy itself is a significant risk for patients with “very active, uncontrolled gastrointestinal conditions where a pregnancy could be harmful to the mother’s health or result in offspring that are very unhealthy.” These include decompensated cirrhosis, uncontrolled Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, refractory gastroparesis, uncontrolled celiac sprue, and chronic pancreatitis, she said.
“There have been times when after shared decisionmaking, a patient with very active inflammatory bowel disease has decided to terminate the pregnancy because of her own ongoing health issues,” she said. “Not having this option will potentially lead to disastrous results.”
Dr. Clowse, the Duke University rheumatologist, echoed Dr. Kane’s concerns about women who are too sick to bear children. “The removal of abortion rights puts the lives and quality of life for women with rheumatic disease at risk. For patients with lupus and other systemic rheumatic disease, pregnancy can be medically catastrophic, leading to permanent harm and even death to the woman and her offspring. I am worried that women in these conditions will die without lifesaving pregnancy terminations, due to worries about the legal consequences for their physicians.”
The U.S. Supreme Court’s ruling that overturned Roe v. Wade has also raised the prospect that the court could ultimately allow birth control to be restricted or outlawed.
While the ruling states that “nothing in this opinion should be understood to cast doubt on precedents that do not concern abortion,” Justice Clarence Thomas wrote a concurrence in which he said that the court should reconsider a 1960s ruling that forbids the banning of contraceptives. Republicans have dismissed concerns about bans being allowed, although Democrats, including the president and vice president, starkly warn that they could happen.
“If we as providers have to be concerned that there will be an unplanned pregnancy because of the lack of access to contraception,” Dr. Kane said, “this will have significant downstream consequences to the kind of care we can provide and might just drive some providers to not give care to female patients at all given this concern.”
The physicians quoted in this article report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sugar highs and royal meltdowns
I can dimly recall watching Queen Elizabeth’s coronation on a very small black and white television screen. Even in monochrome it was a riveting event. Recently, the Queen celebrated her Platinum Jubilee, marking her 70-year reign. Apparently it was a multiday event with all the trappings, floating above an undercurrent of scandal and intrigue. I had better things to do than I did as a 7-year-old entranced by the novelty of a neighbor’s television set.
But, it turns out that I had missed the opportunity to see live and in color a royal meltdown starring the Queen’s great-grandson, 4-year-old Prince Louis. Not to worry. It remains on video archives for our education and pleasure ad infinitum. His performance was no more dramatic than what you have seen numerous times in the checkout line of the grocery store. However, this meltdown was on the world stage in the front row of the royal box and performed in various venues on each day of a 4-day event.
As long as you weren’t his parents, Kate Middleton and Prince William, the meltdown had its moments of hilarity. Louis made full use of his youthful and plastic face, creating a wide variety of taunts and responses to his mother’s praiseworthy and understated attempts at regaining control. Of course, the British press and every armchair parent with a Twitter account had a field day contributing their explanations and advice.
For example, here’s the headline on an international news website that caught my eye: “Royal reveals why Prince Louis was so ‘mischievous’ during the Jubilee”. In the article, a fellow royal and former rugby star who was sitting directly behind the little Prince during one of his performances chalked up the 4-year-old’s behavior to a “sugar high” resulting from the ample supply of sweets available behind the royal box.
Nowhere in the article is there a question of whether the “sugar high” is a science-based phenomenon. In fact, the reporter assumes we all know it exists and writes that “parents across the globe can probably [read: definitely] relate.”
I’m curious: How do you respond when a parent in the office explains the child’s behavior as the result of a “sugar high”? Or when you’re at a cookout and someone makes a comment that makes it obvious that they believe that “sugar highs” are real? Do you immediately pause the conversation and launch into a short but tasteful observation that you know of no scientific studies that sugar can cause a high? Or, figuring that in the face of an overwhelming burden of old wives’ tales it’s not worth mounting a rebuttal, do you pretend you didn’t hear the comment?
Or am I completely off base because your experience has left you convinced that despite the lack of supporting studies the “sugar high” phenomenon exists? Maybe you even include it on your list of explanations and remedies for pediatric misbehaviors. I am ready to listen, but it will take some heavy lifting to convince me.
I suspect your response to offhand comments about “sugar highs” is similar to mine. It depends on the situation. If I think there are obvious and correctable causes for the child’s misbehavior such as sleep deprivation or a mismatch between parental expectation and the child’s tolerance for a stimulating environment I will include in my parenting advice the comment, “Sugar highs probably don’t exist.”
On the other hand, if I’m tired and think my observation will fall on deaf ears I let the conversation drift. I worry that my silence will be interpreted as a confirmation of an old wives’ tale. What I really don’t want to do is perpetuate a myth that may prevent some children from getting the care they need.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I can dimly recall watching Queen Elizabeth’s coronation on a very small black and white television screen. Even in monochrome it was a riveting event. Recently, the Queen celebrated her Platinum Jubilee, marking her 70-year reign. Apparently it was a multiday event with all the trappings, floating above an undercurrent of scandal and intrigue. I had better things to do than I did as a 7-year-old entranced by the novelty of a neighbor’s television set.
But, it turns out that I had missed the opportunity to see live and in color a royal meltdown starring the Queen’s great-grandson, 4-year-old Prince Louis. Not to worry. It remains on video archives for our education and pleasure ad infinitum. His performance was no more dramatic than what you have seen numerous times in the checkout line of the grocery store. However, this meltdown was on the world stage in the front row of the royal box and performed in various venues on each day of a 4-day event.
As long as you weren’t his parents, Kate Middleton and Prince William, the meltdown had its moments of hilarity. Louis made full use of his youthful and plastic face, creating a wide variety of taunts and responses to his mother’s praiseworthy and understated attempts at regaining control. Of course, the British press and every armchair parent with a Twitter account had a field day contributing their explanations and advice.
For example, here’s the headline on an international news website that caught my eye: “Royal reveals why Prince Louis was so ‘mischievous’ during the Jubilee”. In the article, a fellow royal and former rugby star who was sitting directly behind the little Prince during one of his performances chalked up the 4-year-old’s behavior to a “sugar high” resulting from the ample supply of sweets available behind the royal box.
Nowhere in the article is there a question of whether the “sugar high” is a science-based phenomenon. In fact, the reporter assumes we all know it exists and writes that “parents across the globe can probably [read: definitely] relate.”
I’m curious: How do you respond when a parent in the office explains the child’s behavior as the result of a “sugar high”? Or when you’re at a cookout and someone makes a comment that makes it obvious that they believe that “sugar highs” are real? Do you immediately pause the conversation and launch into a short but tasteful observation that you know of no scientific studies that sugar can cause a high? Or, figuring that in the face of an overwhelming burden of old wives’ tales it’s not worth mounting a rebuttal, do you pretend you didn’t hear the comment?
Or am I completely off base because your experience has left you convinced that despite the lack of supporting studies the “sugar high” phenomenon exists? Maybe you even include it on your list of explanations and remedies for pediatric misbehaviors. I am ready to listen, but it will take some heavy lifting to convince me.
I suspect your response to offhand comments about “sugar highs” is similar to mine. It depends on the situation. If I think there are obvious and correctable causes for the child’s misbehavior such as sleep deprivation or a mismatch between parental expectation and the child’s tolerance for a stimulating environment I will include in my parenting advice the comment, “Sugar highs probably don’t exist.”
On the other hand, if I’m tired and think my observation will fall on deaf ears I let the conversation drift. I worry that my silence will be interpreted as a confirmation of an old wives’ tale. What I really don’t want to do is perpetuate a myth that may prevent some children from getting the care they need.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
I can dimly recall watching Queen Elizabeth’s coronation on a very small black and white television screen. Even in monochrome it was a riveting event. Recently, the Queen celebrated her Platinum Jubilee, marking her 70-year reign. Apparently it was a multiday event with all the trappings, floating above an undercurrent of scandal and intrigue. I had better things to do than I did as a 7-year-old entranced by the novelty of a neighbor’s television set.
But, it turns out that I had missed the opportunity to see live and in color a royal meltdown starring the Queen’s great-grandson, 4-year-old Prince Louis. Not to worry. It remains on video archives for our education and pleasure ad infinitum. His performance was no more dramatic than what you have seen numerous times in the checkout line of the grocery store. However, this meltdown was on the world stage in the front row of the royal box and performed in various venues on each day of a 4-day event.
As long as you weren’t his parents, Kate Middleton and Prince William, the meltdown had its moments of hilarity. Louis made full use of his youthful and plastic face, creating a wide variety of taunts and responses to his mother’s praiseworthy and understated attempts at regaining control. Of course, the British press and every armchair parent with a Twitter account had a field day contributing their explanations and advice.
For example, here’s the headline on an international news website that caught my eye: “Royal reveals why Prince Louis was so ‘mischievous’ during the Jubilee”. In the article, a fellow royal and former rugby star who was sitting directly behind the little Prince during one of his performances chalked up the 4-year-old’s behavior to a “sugar high” resulting from the ample supply of sweets available behind the royal box.
Nowhere in the article is there a question of whether the “sugar high” is a science-based phenomenon. In fact, the reporter assumes we all know it exists and writes that “parents across the globe can probably [read: definitely] relate.”
I’m curious: How do you respond when a parent in the office explains the child’s behavior as the result of a “sugar high”? Or when you’re at a cookout and someone makes a comment that makes it obvious that they believe that “sugar highs” are real? Do you immediately pause the conversation and launch into a short but tasteful observation that you know of no scientific studies that sugar can cause a high? Or, figuring that in the face of an overwhelming burden of old wives’ tales it’s not worth mounting a rebuttal, do you pretend you didn’t hear the comment?
Or am I completely off base because your experience has left you convinced that despite the lack of supporting studies the “sugar high” phenomenon exists? Maybe you even include it on your list of explanations and remedies for pediatric misbehaviors. I am ready to listen, but it will take some heavy lifting to convince me.
I suspect your response to offhand comments about “sugar highs” is similar to mine. It depends on the situation. If I think there are obvious and correctable causes for the child’s misbehavior such as sleep deprivation or a mismatch between parental expectation and the child’s tolerance for a stimulating environment I will include in my parenting advice the comment, “Sugar highs probably don’t exist.”
On the other hand, if I’m tired and think my observation will fall on deaf ears I let the conversation drift. I worry that my silence will be interpreted as a confirmation of an old wives’ tale. What I really don’t want to do is perpetuate a myth that may prevent some children from getting the care they need.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Acute hepatitis cases in children show declining trend; adenovirus, COVID-19 remain key leads
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONDON – Case numbers of acute hepatitis in children show “a declining trajectory,” and COVID-19 and adenovirus remain the most likely, but as yet unproven, causative agents, said experts in an update at the annual International Liver Congress sponsored by the European Association for the Study of the Liver.
Philippa Easterbrook, MD, medical expert at the World Health Organization Global HIV, Hepatitis, and STI Programme, shared the latest case numbers and working hypotheses of possible causative agents in the outbreak of acute hepatitis among children in Europe and beyond.
Global data across the five WHO regions show there were 244 cases in the past month, bringing the total to 894 probable cases reported since October 2021 from 33 countries.
“It’s important to remember that this includes new cases, as well as retrospectively identified cases,” Dr.Easterbrook said. “Over half (52%) are from the European region, while 262 cases (30% of the global total) are from the United Kingdom.”
Data from Europe and the United States show a declining trajectory of reports of new cases. “This is a positive development,” she said.
The second highest reporting region is the Americas, she said, with 368 cases total, 290 cases of which come from the United States, accounting for 35% of the global total.
“Together the United Kingdom and the United States make up 65% of the global total,” she said.
Dr. Easterbrook added that 17 of the 33 reporting countries had more than five cases. Most cases (75%) are in young children under 5 years of age.
Serious cases are relatively few, but 44 (5%) children have required liver transplantation. Data from the European region show that 30% have required intensive care at some point during their hospitalization. There have been 18 (2%) reported deaths.
Possible post-COVID phenomenon, adenovirus most commonly reported
Dr. Easterbrook acknowledged the emerging hypothesis of a post-COVID phenomenon.
“Is this a variant of the rare but recognized multisystem inflammatory syndrome condition in children that’s been reported, often 1-2 months after COVID, causing widespread organ damage?” But she pointed out that the reported COVID cases with hepatitis “don’t seem to fit these features.”
Adenovirus remains the most commonly detected virus in acute hepatitis in children, found in 53% of cases overall, she said. The adenovirus detection rate is higher in the United Kingdom, at 68%.
“There are quite high rates of detection, but they’re not in all cases. There does seem to be a high rate of detection in the younger age groups and in those who are developing severe disease, so perhaps there is some link to severity,” Dr. Easterbrook said.
The working hypotheses continue to favor adenovirus together with past or current SARS-CoV-2 infection, as proposed early in the outbreak, she said. “These either work independently or work together as cofactors in some way to result in hepatitis. And there has been some clear progress on this. WHO is bringing together the data from different countries on some of these working hypotheses.”
Dr. Easterbrook highlighted the importance of procuring global data, especially given that two countries are reporting the majority of cases and in high numbers. “It’s a mixed picture with different rates of adenovirus detection and of COVID,” she said. “We need good-quality data collected in a standardized way.” WHO is requesting that countries provide these data.
She also highlighted the need for good in-depth studies, citing the UK Health Security Agency as an example of this. “There’s only a few countries that have the capacity or the patient numbers to look at this in detail, for example, the U.K. and the UKHSA.”
She noted that the UKHSA had laid out a comprehensive, systematic set of further investigations. For example, a case-control study is trying to establish whether there is a difference in the rate of adenovirus detection in children with hepatitis compared with other hospitalized children at the same time. “This aims to really tease out whether adenovirus is a cause or just a bystander,” she said.
She added that there were also genetic studies investigating whether genes were predisposing some children to develop a more severe form of disease. Other studies are evaluating the immune response of the patients.
Dr. Easterbrook added that the WHO will soon launch a global survey asking whether the reports of acute hepatitis are greater than the expected background rate for cases of hepatitis of unknown etiology.
Acute hepatitis is not new, but high caseload is
Also speaking at the ILC special briefing was Maria Buti, MD, PhD, policy and public health chair for the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and chief of the internal medicine and hepatology department at Hospital General Universitari Valle Hebron in Barcelona.
Dr. Buti drew attention to the fact that severe acute hepatitis of unknown etiology in children is not new.
“We have cases of acute hepatitis that even needed liver transplantation some years ago, and every year in our clinics we see these type of patients,” Dr. Buti remarked. What is really new, she added, is the amount of cases, particularly in the United Kingdom.
Dr. Easterbrook and Dr. Buti have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ILC 2022
Anorexia linked to notable shrinkage of key brain structures
, a new brain imaging study shows.
The reductions of cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and cortical surface area were “very pronounced in acutely underweight anorexia,” Stefan Ehrlich, MD, PhD, head of the Eating Disorder Treatment and Research Center, Technical University, Dresden, Germany, told this news organization.
Yet even a “partial weight gain brings some normalization of these shrinkages. From this it can be deduced that a fast/early normalization of weight is also very important for brain health,” said Dr. Ehrlich.
The study was published online in Biological Psychiatry.
‘A wake-up call’
Researchers with the international ENIGMA Eating Disorders Working Group analyzed T1-weighted structural magnetic resonance imaging scans for nearly 2,000 people with AN (including those in recovery) and healthy controls across 22 sites worldwide.
In the AN sample, reductions in cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and, to a lesser extent, cortical surface area, were “sizable (Cohen’s d up to 0.95), widespread, and co-localized with hub regions,” they report.
These reductions were two and four times larger than the abnormalities in brain size and shape seen in patients with other mental illnesses, the researchers note.
Noting the harmful impact of anorexia-related undernutrition on the brain, these deficits were associated with lower body mass index in the AN sample and were less severe in partially weight-restored patients – implying that, with appropriate early treatment and support, the brain might be able to repair itself, the investigators note.
“This really is a wake-up call, showing the need for early interventions for people with eating disorders,” Paul Thompson, PhD, author and lead scientist for the ENIGMA Consortium, said in a news release.
“The international scale of this work is extraordinary. Scientists from 22 centers worldwide pooled their brain scans to create the most detailed picture to date of how anorexia affects the brain,” Dr. Thompson added.
“The brain changes in anorexia were more severe than in other any psychiatric condition we have studied. Effects of treatments and interventions can now be evaluated, using these new brain maps as a reference,” he noted.
Immediate clinical implications
Reached for comment, Allison Eliscu, MD, chief of the division of adolescent medicine, department of pediatrics, at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, said the findings have immediate implications for clinical care.
“When we talk to our patients and the parents, a lot of them focus on things that they can see, such as the way they look. It adds a lot to the conversation to be able to say: You’re obviously not seeing these changes in the brain, but they’re happening and could be potentially long term if you don’t start weight restoring, or if you weight restore and then continue to drop again,” Dr. Eliscu said in an interview.
The findings, she said, really do highlight what anorexia can do to the brain.
“Adolescents need to know, anorexia can absolutely decrease the size of your brain in different areas; you’re not just losing weight in your belly and your thighs, you’re losing weight in the brain as well and that’s really concerning,” said Dr. Eliscu.
The study had no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Eliscu report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new brain imaging study shows.
The reductions of cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and cortical surface area were “very pronounced in acutely underweight anorexia,” Stefan Ehrlich, MD, PhD, head of the Eating Disorder Treatment and Research Center, Technical University, Dresden, Germany, told this news organization.
Yet even a “partial weight gain brings some normalization of these shrinkages. From this it can be deduced that a fast/early normalization of weight is also very important for brain health,” said Dr. Ehrlich.
The study was published online in Biological Psychiatry.
‘A wake-up call’
Researchers with the international ENIGMA Eating Disorders Working Group analyzed T1-weighted structural magnetic resonance imaging scans for nearly 2,000 people with AN (including those in recovery) and healthy controls across 22 sites worldwide.
In the AN sample, reductions in cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and, to a lesser extent, cortical surface area, were “sizable (Cohen’s d up to 0.95), widespread, and co-localized with hub regions,” they report.
These reductions were two and four times larger than the abnormalities in brain size and shape seen in patients with other mental illnesses, the researchers note.
Noting the harmful impact of anorexia-related undernutrition on the brain, these deficits were associated with lower body mass index in the AN sample and were less severe in partially weight-restored patients – implying that, with appropriate early treatment and support, the brain might be able to repair itself, the investigators note.
“This really is a wake-up call, showing the need for early interventions for people with eating disorders,” Paul Thompson, PhD, author and lead scientist for the ENIGMA Consortium, said in a news release.
“The international scale of this work is extraordinary. Scientists from 22 centers worldwide pooled their brain scans to create the most detailed picture to date of how anorexia affects the brain,” Dr. Thompson added.
“The brain changes in anorexia were more severe than in other any psychiatric condition we have studied. Effects of treatments and interventions can now be evaluated, using these new brain maps as a reference,” he noted.
Immediate clinical implications
Reached for comment, Allison Eliscu, MD, chief of the division of adolescent medicine, department of pediatrics, at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, said the findings have immediate implications for clinical care.
“When we talk to our patients and the parents, a lot of them focus on things that they can see, such as the way they look. It adds a lot to the conversation to be able to say: You’re obviously not seeing these changes in the brain, but they’re happening and could be potentially long term if you don’t start weight restoring, or if you weight restore and then continue to drop again,” Dr. Eliscu said in an interview.
The findings, she said, really do highlight what anorexia can do to the brain.
“Adolescents need to know, anorexia can absolutely decrease the size of your brain in different areas; you’re not just losing weight in your belly and your thighs, you’re losing weight in the brain as well and that’s really concerning,” said Dr. Eliscu.
The study had no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Eliscu report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new brain imaging study shows.
The reductions of cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and cortical surface area were “very pronounced in acutely underweight anorexia,” Stefan Ehrlich, MD, PhD, head of the Eating Disorder Treatment and Research Center, Technical University, Dresden, Germany, told this news organization.
Yet even a “partial weight gain brings some normalization of these shrinkages. From this it can be deduced that a fast/early normalization of weight is also very important for brain health,” said Dr. Ehrlich.
The study was published online in Biological Psychiatry.
‘A wake-up call’
Researchers with the international ENIGMA Eating Disorders Working Group analyzed T1-weighted structural magnetic resonance imaging scans for nearly 2,000 people with AN (including those in recovery) and healthy controls across 22 sites worldwide.
In the AN sample, reductions in cortical thickness, subcortical volumes, and, to a lesser extent, cortical surface area, were “sizable (Cohen’s d up to 0.95), widespread, and co-localized with hub regions,” they report.
These reductions were two and four times larger than the abnormalities in brain size and shape seen in patients with other mental illnesses, the researchers note.
Noting the harmful impact of anorexia-related undernutrition on the brain, these deficits were associated with lower body mass index in the AN sample and were less severe in partially weight-restored patients – implying that, with appropriate early treatment and support, the brain might be able to repair itself, the investigators note.
“This really is a wake-up call, showing the need for early interventions for people with eating disorders,” Paul Thompson, PhD, author and lead scientist for the ENIGMA Consortium, said in a news release.
“The international scale of this work is extraordinary. Scientists from 22 centers worldwide pooled their brain scans to create the most detailed picture to date of how anorexia affects the brain,” Dr. Thompson added.
“The brain changes in anorexia were more severe than in other any psychiatric condition we have studied. Effects of treatments and interventions can now be evaluated, using these new brain maps as a reference,” he noted.
Immediate clinical implications
Reached for comment, Allison Eliscu, MD, chief of the division of adolescent medicine, department of pediatrics, at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University, said the findings have immediate implications for clinical care.
“When we talk to our patients and the parents, a lot of them focus on things that they can see, such as the way they look. It adds a lot to the conversation to be able to say: You’re obviously not seeing these changes in the brain, but they’re happening and could be potentially long term if you don’t start weight restoring, or if you weight restore and then continue to drop again,” Dr. Eliscu said in an interview.
The findings, she said, really do highlight what anorexia can do to the brain.
“Adolescents need to know, anorexia can absolutely decrease the size of your brain in different areas; you’re not just losing weight in your belly and your thighs, you’re losing weight in the brain as well and that’s really concerning,” said Dr. Eliscu.
The study had no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Eliscu report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY
School shootings rose to highest number in 20 years, data shows
School shootings from 2020 to 2021 climbed to the highest point in 2 decades, according to a new report from the National Center for Education Statistics and the Bureau of Justice Statistics.
There were 93 shootings with casualties at public and private K-12 schools across the United States from 2020 to 2021, as compared with 23 in the 2000-2001 school year. The latest number included 43 incidents with deaths.
The annual report, which examines crime and safety in schools and colleges, also found a rise in cyberbullying and verbal abuse or disrespect of teachers during the past decade.
“While the lasting impact of these crime and safety issues cannot be measured in statistics alone, these data are valuable to the efforts of our policymakers, school officials and community members to identify and implement preventive and responsive measures,” Peggy Carr, PhD, the commissioner for the National Center for Education Statistics, said in a statement.
The report used a broad definition of shootings, which included instances when guns were fired or flashed on school property, as well as when a bullet hit school grounds for any reason and shootings that happened on school property during remote instruction throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
More than 311,000 children at 331 schools have gone through gun violence since the shooting at Columbine High School in 1999, according to The Washington Post.
“The increase in shootings in schools is likely a consequence of an overall increase in gun violence and not specific to schools,” Dewey Cornell, PhD, a professor of education at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, told the newspaper.
“However, most schools will never have a shooting, and their main problems will be fighting and bullying,” he said.
Between 2009 and 2020, the rate of nonfatal criminal victimization, including theft and violent crimes, decreased for ages 12-18, the report found. The rate fell from 51 victimizations per 1,000 students to 11. A major portion of the decline happened during the first year of the pandemic.
Lower percentages of public schools reported certain issues from 2019 to 2020 than from 2009 to 2010, the report found. For instance, 15% of schools reported student bullying at least once a week, as compared with 23% a decade ago. Student sexual harassment of other students dropped from 3% to 2%, and student harassment of other students based on sexual orientation or gender identity dropped from 3% to 2%.
At the same time, teachers faced more hardships, the report found. Schools reporting verbal abuse of teachers at least once a week rose to 10% in the 2019-2020 school year, as compared with 5% in the 2009-2010 school year. Schools reporting acts of disrespect for teachers climbed from 9% to 15%.
The percentage of schools that reported cyberbullying at least once a week doubled during the decade, rising from 8% in 2009-2010 to 16% in 2019-2020, the report found. The prominence of social media has likely added to that increase, the Post reported.
What’s more, about 55% of public schools offered mental health assessments in 2019-2020, and 42% offered mental health treatment services, the report found. The low rates could be linked to not having enough funding or access to licensed professionals, the newspaper reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
School shootings from 2020 to 2021 climbed to the highest point in 2 decades, according to a new report from the National Center for Education Statistics and the Bureau of Justice Statistics.
There were 93 shootings with casualties at public and private K-12 schools across the United States from 2020 to 2021, as compared with 23 in the 2000-2001 school year. The latest number included 43 incidents with deaths.
The annual report, which examines crime and safety in schools and colleges, also found a rise in cyberbullying and verbal abuse or disrespect of teachers during the past decade.
“While the lasting impact of these crime and safety issues cannot be measured in statistics alone, these data are valuable to the efforts of our policymakers, school officials and community members to identify and implement preventive and responsive measures,” Peggy Carr, PhD, the commissioner for the National Center for Education Statistics, said in a statement.
The report used a broad definition of shootings, which included instances when guns were fired or flashed on school property, as well as when a bullet hit school grounds for any reason and shootings that happened on school property during remote instruction throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
More than 311,000 children at 331 schools have gone through gun violence since the shooting at Columbine High School in 1999, according to The Washington Post.
“The increase in shootings in schools is likely a consequence of an overall increase in gun violence and not specific to schools,” Dewey Cornell, PhD, a professor of education at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, told the newspaper.
“However, most schools will never have a shooting, and their main problems will be fighting and bullying,” he said.
Between 2009 and 2020, the rate of nonfatal criminal victimization, including theft and violent crimes, decreased for ages 12-18, the report found. The rate fell from 51 victimizations per 1,000 students to 11. A major portion of the decline happened during the first year of the pandemic.
Lower percentages of public schools reported certain issues from 2019 to 2020 than from 2009 to 2010, the report found. For instance, 15% of schools reported student bullying at least once a week, as compared with 23% a decade ago. Student sexual harassment of other students dropped from 3% to 2%, and student harassment of other students based on sexual orientation or gender identity dropped from 3% to 2%.
At the same time, teachers faced more hardships, the report found. Schools reporting verbal abuse of teachers at least once a week rose to 10% in the 2019-2020 school year, as compared with 5% in the 2009-2010 school year. Schools reporting acts of disrespect for teachers climbed from 9% to 15%.
The percentage of schools that reported cyberbullying at least once a week doubled during the decade, rising from 8% in 2009-2010 to 16% in 2019-2020, the report found. The prominence of social media has likely added to that increase, the Post reported.
What’s more, about 55% of public schools offered mental health assessments in 2019-2020, and 42% offered mental health treatment services, the report found. The low rates could be linked to not having enough funding or access to licensed professionals, the newspaper reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
School shootings from 2020 to 2021 climbed to the highest point in 2 decades, according to a new report from the National Center for Education Statistics and the Bureau of Justice Statistics.
There were 93 shootings with casualties at public and private K-12 schools across the United States from 2020 to 2021, as compared with 23 in the 2000-2001 school year. The latest number included 43 incidents with deaths.
The annual report, which examines crime and safety in schools and colleges, also found a rise in cyberbullying and verbal abuse or disrespect of teachers during the past decade.
“While the lasting impact of these crime and safety issues cannot be measured in statistics alone, these data are valuable to the efforts of our policymakers, school officials and community members to identify and implement preventive and responsive measures,” Peggy Carr, PhD, the commissioner for the National Center for Education Statistics, said in a statement.
The report used a broad definition of shootings, which included instances when guns were fired or flashed on school property, as well as when a bullet hit school grounds for any reason and shootings that happened on school property during remote instruction throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
More than 311,000 children at 331 schools have gone through gun violence since the shooting at Columbine High School in 1999, according to The Washington Post.
“The increase in shootings in schools is likely a consequence of an overall increase in gun violence and not specific to schools,” Dewey Cornell, PhD, a professor of education at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, told the newspaper.
“However, most schools will never have a shooting, and their main problems will be fighting and bullying,” he said.
Between 2009 and 2020, the rate of nonfatal criminal victimization, including theft and violent crimes, decreased for ages 12-18, the report found. The rate fell from 51 victimizations per 1,000 students to 11. A major portion of the decline happened during the first year of the pandemic.
Lower percentages of public schools reported certain issues from 2019 to 2020 than from 2009 to 2010, the report found. For instance, 15% of schools reported student bullying at least once a week, as compared with 23% a decade ago. Student sexual harassment of other students dropped from 3% to 2%, and student harassment of other students based on sexual orientation or gender identity dropped from 3% to 2%.
At the same time, teachers faced more hardships, the report found. Schools reporting verbal abuse of teachers at least once a week rose to 10% in the 2019-2020 school year, as compared with 5% in the 2009-2010 school year. Schools reporting acts of disrespect for teachers climbed from 9% to 15%.
The percentage of schools that reported cyberbullying at least once a week doubled during the decade, rising from 8% in 2009-2010 to 16% in 2019-2020, the report found. The prominence of social media has likely added to that increase, the Post reported.
What’s more, about 55% of public schools offered mental health assessments in 2019-2020, and 42% offered mental health treatment services, the report found. The low rates could be linked to not having enough funding or access to licensed professionals, the newspaper reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Pandemic stress tied to increased headache burden in teens
Contrary to previous research findings, the stress of the COVID-19 pandemic has been linked to an increased headache burden in teens.
Investigators found factors contributing to headache for preteens and teens during the pandemic included increased screen time for online learning, depression, anxiety, female sex, and weight gain.
“The stressors and pressures of the pandemic may have eventually taken their toll,” lead author Ayşe Nur Özdağ Acarli, MD, Ermenek State Hospital, department of neurology, Karaman, Turkey, told this news organization.
“Limiting screen time and providing more psychosocial supports would help lessen the burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on adolescents with headache.”
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2022.
Most common neurological problem in kids
Headache is the most common neurological problem in children and adolescents. Potential factors contributing to headache in this population include lack of sleep and physical activity, mental health problems, and socioeconomic conditions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a “striking” impact on every aspect of life for young people, said Dr. Acarli.
Some studies reported an improvement in headache prevalence among adolescents during COVID-19, which was attributed to less school-related stress. However, said Dr. Acarli in her personal clinical experience, young patients suffered more frequent and severe headaches during the pandemic.
She noted previous research examining the impact of the pandemic on headache in youth was conducted only in the early days of the pandemic and examined shorter-term effects. Research examining the long-term effects of the pandemic on headache in this patient population has been “lacking,” she said.
The study included 851 participants aged 10-18 years (mean age 14.9 years and 62% female) who were seen at a neurology or pediatric outpatient clinic from August-December 2021. The study excluded subjects with neurological problems, intellectual deficits, autism spectrum disorder, and epilepsy.
Participants completed detailed questionnaires providing data on demographics, exposure to COVID-19, and electronics, as well as information on depressive symptoms as assessed by the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and anxiety symptoms using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and COVID-related anxiety.
“We used two distinct scales for anxiety: one for generalized anxiety and the other for COVID-related anxiety,” said Dr. Acarli.
Of the total study population, 756 (89%) reported headaches. This headache prevalence in children and adolescents is like that found in other studies.
Dr. Acarli noted several differences in the headache group versus the non-headache group. The female/male ratio was 2:1 versus 1:1, the mean age was 15.0 versus 14.4, and depression and generalized anxiety scores were significantly higher. There was no significant difference in COVID-19 history in those with and without headache.
Researchers categorized those with headache into four groups: worsening headaches (27%), improved headaches (3%), new onset headaches (10%), and stable headaches (61%).
Compared with the other groups, the worsened headache group included significantly more females and older individuals with more severe and frequent headaches. This group also had more participants reporting at least 15 headache attacks a month and using painkillers at least once a month.
The study showed headache severity was significantly increased with age, headache duration, depression, generalized anxiety (all P < .001), and COVID-19 anxiety (P < .01). Headache frequency, measured as attacks per month, was significantly increased with age, depression, and generalized anxiety (all P < .001).
Worsening headache outcomes during the pandemic were associated with longer exposure to computer screens (odds ratio, 1.7; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-2.3; P < .01), lack of suitable conditions for online learning (OR, 2.6; 95% CI, 1.8-3.8; P < .001), depression (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.8; P < .001); and COVID-19 anxiety (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.3-8.0; P < .01). Other contributing factors included school exams, living in a city, female sex, and weight gain.
There may be a link between COVID-related headaches and anxiety or depression, but it’s unclear what’s causing what. “We don’t know which is the chicken and which is the egg,” said Dr. Acarli.
Headache triggers
Commenting for this news organization, Raquel Gil-Gouveia, MD, PhD, head of the neurology department, Hospital da Luz, Lisbon, Portugal, who co-chaired the session where the research was presented, said the information collected for the study was “extensive.”
Some results were expected, including the fact that patients with headaches were more anxious and depressed, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
“Anxiety and depression are frequent comorbidities of headache and can act as a triggering factor for headache attacks but can also be a consequence of intense or chronic pain,” she said.
She agreed the new results differ from those of studies carried out during the first pandemic lockdown, which showed an improvement in headache, but noted online learning was not fully implemented at that time, “so it was much like being on vacation.”
In addition to isolation, anxiety, and prolonged screen exposure, the lack of peer contact and fewer sports and leisure activities may also have contributed to worsening headaches during the COVID lockdown, but these were not explored in this study, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
The study was supported by the Global Migraine and Pain Society. The investigators and Dr. Gil-Gouveia report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contrary to previous research findings, the stress of the COVID-19 pandemic has been linked to an increased headache burden in teens.
Investigators found factors contributing to headache for preteens and teens during the pandemic included increased screen time for online learning, depression, anxiety, female sex, and weight gain.
“The stressors and pressures of the pandemic may have eventually taken their toll,” lead author Ayşe Nur Özdağ Acarli, MD, Ermenek State Hospital, department of neurology, Karaman, Turkey, told this news organization.
“Limiting screen time and providing more psychosocial supports would help lessen the burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on adolescents with headache.”
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2022.
Most common neurological problem in kids
Headache is the most common neurological problem in children and adolescents. Potential factors contributing to headache in this population include lack of sleep and physical activity, mental health problems, and socioeconomic conditions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a “striking” impact on every aspect of life for young people, said Dr. Acarli.
Some studies reported an improvement in headache prevalence among adolescents during COVID-19, which was attributed to less school-related stress. However, said Dr. Acarli in her personal clinical experience, young patients suffered more frequent and severe headaches during the pandemic.
She noted previous research examining the impact of the pandemic on headache in youth was conducted only in the early days of the pandemic and examined shorter-term effects. Research examining the long-term effects of the pandemic on headache in this patient population has been “lacking,” she said.
The study included 851 participants aged 10-18 years (mean age 14.9 years and 62% female) who were seen at a neurology or pediatric outpatient clinic from August-December 2021. The study excluded subjects with neurological problems, intellectual deficits, autism spectrum disorder, and epilepsy.
Participants completed detailed questionnaires providing data on demographics, exposure to COVID-19, and electronics, as well as information on depressive symptoms as assessed by the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and anxiety symptoms using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and COVID-related anxiety.
“We used two distinct scales for anxiety: one for generalized anxiety and the other for COVID-related anxiety,” said Dr. Acarli.
Of the total study population, 756 (89%) reported headaches. This headache prevalence in children and adolescents is like that found in other studies.
Dr. Acarli noted several differences in the headache group versus the non-headache group. The female/male ratio was 2:1 versus 1:1, the mean age was 15.0 versus 14.4, and depression and generalized anxiety scores were significantly higher. There was no significant difference in COVID-19 history in those with and without headache.
Researchers categorized those with headache into four groups: worsening headaches (27%), improved headaches (3%), new onset headaches (10%), and stable headaches (61%).
Compared with the other groups, the worsened headache group included significantly more females and older individuals with more severe and frequent headaches. This group also had more participants reporting at least 15 headache attacks a month and using painkillers at least once a month.
The study showed headache severity was significantly increased with age, headache duration, depression, generalized anxiety (all P < .001), and COVID-19 anxiety (P < .01). Headache frequency, measured as attacks per month, was significantly increased with age, depression, and generalized anxiety (all P < .001).
Worsening headache outcomes during the pandemic were associated with longer exposure to computer screens (odds ratio, 1.7; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-2.3; P < .01), lack of suitable conditions for online learning (OR, 2.6; 95% CI, 1.8-3.8; P < .001), depression (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.8; P < .001); and COVID-19 anxiety (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.3-8.0; P < .01). Other contributing factors included school exams, living in a city, female sex, and weight gain.
There may be a link between COVID-related headaches and anxiety or depression, but it’s unclear what’s causing what. “We don’t know which is the chicken and which is the egg,” said Dr. Acarli.
Headache triggers
Commenting for this news organization, Raquel Gil-Gouveia, MD, PhD, head of the neurology department, Hospital da Luz, Lisbon, Portugal, who co-chaired the session where the research was presented, said the information collected for the study was “extensive.”
Some results were expected, including the fact that patients with headaches were more anxious and depressed, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
“Anxiety and depression are frequent comorbidities of headache and can act as a triggering factor for headache attacks but can also be a consequence of intense or chronic pain,” she said.
She agreed the new results differ from those of studies carried out during the first pandemic lockdown, which showed an improvement in headache, but noted online learning was not fully implemented at that time, “so it was much like being on vacation.”
In addition to isolation, anxiety, and prolonged screen exposure, the lack of peer contact and fewer sports and leisure activities may also have contributed to worsening headaches during the COVID lockdown, but these were not explored in this study, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
The study was supported by the Global Migraine and Pain Society. The investigators and Dr. Gil-Gouveia report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contrary to previous research findings, the stress of the COVID-19 pandemic has been linked to an increased headache burden in teens.
Investigators found factors contributing to headache for preteens and teens during the pandemic included increased screen time for online learning, depression, anxiety, female sex, and weight gain.
“The stressors and pressures of the pandemic may have eventually taken their toll,” lead author Ayşe Nur Özdağ Acarli, MD, Ermenek State Hospital, department of neurology, Karaman, Turkey, told this news organization.
“Limiting screen time and providing more psychosocial supports would help lessen the burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on adolescents with headache.”
The findings were presented at the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN) 2022.
Most common neurological problem in kids
Headache is the most common neurological problem in children and adolescents. Potential factors contributing to headache in this population include lack of sleep and physical activity, mental health problems, and socioeconomic conditions.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a “striking” impact on every aspect of life for young people, said Dr. Acarli.
Some studies reported an improvement in headache prevalence among adolescents during COVID-19, which was attributed to less school-related stress. However, said Dr. Acarli in her personal clinical experience, young patients suffered more frequent and severe headaches during the pandemic.
She noted previous research examining the impact of the pandemic on headache in youth was conducted only in the early days of the pandemic and examined shorter-term effects. Research examining the long-term effects of the pandemic on headache in this patient population has been “lacking,” she said.
The study included 851 participants aged 10-18 years (mean age 14.9 years and 62% female) who were seen at a neurology or pediatric outpatient clinic from August-December 2021. The study excluded subjects with neurological problems, intellectual deficits, autism spectrum disorder, and epilepsy.
Participants completed detailed questionnaires providing data on demographics, exposure to COVID-19, and electronics, as well as information on depressive symptoms as assessed by the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and anxiety symptoms using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 and COVID-related anxiety.
“We used two distinct scales for anxiety: one for generalized anxiety and the other for COVID-related anxiety,” said Dr. Acarli.
Of the total study population, 756 (89%) reported headaches. This headache prevalence in children and adolescents is like that found in other studies.
Dr. Acarli noted several differences in the headache group versus the non-headache group. The female/male ratio was 2:1 versus 1:1, the mean age was 15.0 versus 14.4, and depression and generalized anxiety scores were significantly higher. There was no significant difference in COVID-19 history in those with and without headache.
Researchers categorized those with headache into four groups: worsening headaches (27%), improved headaches (3%), new onset headaches (10%), and stable headaches (61%).
Compared with the other groups, the worsened headache group included significantly more females and older individuals with more severe and frequent headaches. This group also had more participants reporting at least 15 headache attacks a month and using painkillers at least once a month.
The study showed headache severity was significantly increased with age, headache duration, depression, generalized anxiety (all P < .001), and COVID-19 anxiety (P < .01). Headache frequency, measured as attacks per month, was significantly increased with age, depression, and generalized anxiety (all P < .001).
Worsening headache outcomes during the pandemic were associated with longer exposure to computer screens (odds ratio, 1.7; 95% confidence interval, 1.2-2.3; P < .01), lack of suitable conditions for online learning (OR, 2.6; 95% CI, 1.8-3.8; P < .001), depression (OR, 2.0; 95% CI, 1.4-2.8; P < .001); and COVID-19 anxiety (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.3-8.0; P < .01). Other contributing factors included school exams, living in a city, female sex, and weight gain.
There may be a link between COVID-related headaches and anxiety or depression, but it’s unclear what’s causing what. “We don’t know which is the chicken and which is the egg,” said Dr. Acarli.
Headache triggers
Commenting for this news organization, Raquel Gil-Gouveia, MD, PhD, head of the neurology department, Hospital da Luz, Lisbon, Portugal, who co-chaired the session where the research was presented, said the information collected for the study was “extensive.”
Some results were expected, including the fact that patients with headaches were more anxious and depressed, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
“Anxiety and depression are frequent comorbidities of headache and can act as a triggering factor for headache attacks but can also be a consequence of intense or chronic pain,” she said.
She agreed the new results differ from those of studies carried out during the first pandemic lockdown, which showed an improvement in headache, but noted online learning was not fully implemented at that time, “so it was much like being on vacation.”
In addition to isolation, anxiety, and prolonged screen exposure, the lack of peer contact and fewer sports and leisure activities may also have contributed to worsening headaches during the COVID lockdown, but these were not explored in this study, said Dr. Gil-Gouveia.
The study was supported by the Global Migraine and Pain Society. The investigators and Dr. Gil-Gouveia report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EAN 2022
Study finds higher risk of skin cancer after childhood organ transplant
A large study showing an increased risk of keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in children who receive a solid-organ transplant highlights the need for early education about risk reduction and more research to determine optimal timing for screening, say an investigator and two dermatologists with expertise in transplant-related skin issues.
The increased incidence of KC in pediatric transplant recipients is “really high, so we definitely know there’s risk there,” just as there is for adult recipients of solid-organ transplants, said Cathryn Sibbald, MD, MSc, a dermatologist at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and coauthor of a research letter published in June in JAMA Dermatology.
For their study, Dr. Sibbald and her coinvestigators turned to the Ontario Health Insurance plan database, which covers health care for Canadian citizens and qualified residents in the province. They identified 951 patients younger than the age of 18 who received a solid-organ transplant between 1991 and 2004 at an Ontario hospital
They then used a validated health insurance claims–based algorithm to identify diagnoses of KC for the transplant recipients and for more than 5 million age-matched controls. KC, including squamous and basal cell carcinoma, is the most prevalent skin cancer for people who have had a solid-organ transplant.
Fifteen posttransplant KCs (10 patients, 1.1%) were reported a mean of 13.1 years after transplant, with none reported in the first 4 years. The mean age at transplant was 7.8 years, and the mean age at KC diagnosis was 25.2 years. Kidney transplants were the most common (42.1% of transplantations). Most of the transplants recipients (eight patients) who developed KC had kidney transplantation, and most of them had functional graft at the time of KC diagnosis.
Researchers found an increased incidence of KC compared with that of the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 9.09; 95% confidence interval, 5.48-15.08). And the risk for KC increased with time since transplant, with adjusted hazard ratios for KC of 3.63 (95% CI, 0.51-25.77) for 1-5 years, 5.14 (95% CI, 1.28-20.55) for 5-10 years, and 4.80 (95% CI, 2.29-10.08) for 10 years or more, compared with the control population.
Several years ago, another research team performed a similar population-based cohort study of adult transplant recipients in Ontario and found a 6.6-times increased risk of KC in transplant recipients compared with the general population.
Sun protection and skin cancer screening
In commenting on the study, Sarah Arron, MD, PhD, a San Francisco Bay area dermatologist and immediate past president of the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative (www.itscc.org), said she feels “reassured” that young transplant patients tend not to develop the skin cancer until young adulthood.
A ”large study like this is important because the overall rate of KC is low in this age group,” she noted.
The findings “suggest that we can focus our efforts on prevention during childhood, with sun protection and skin cancer education,” she said. “Then, as these children move into adulthood, we can begin screening with skin examinations. Of course, [any child] with a skin lesion or mole that concerns their parents or transplant team should be referred to dermatology for evaluation.”
Pediatric transplant recipients and their parents are most interested in learning about skin cancer prevention either before or immediately after transplantation, according to a survey by other researchers.
Intervention studies needed
The increased risk of KC probably stems largely from immunosuppression, said Dr. Sibbald in an interview. “We know [this is the case] in the older population, and it’s likely true in the younger population as well that it’s one of the primary drivers,” she said.
More research to extensively analyze risk factors should come next, she said. This includes “the granularity of what [immunosuppressants and other] medications are received, and at what dose and for what periods of time, so we can calculate cumulative exposure and its relation to risk,” she said.
Kristin Bibee, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said she’d like to see further studies “evaluate appropriate interventions, like sun-protective behavior in childhood and adolescence or immunosuppression modulation, to prevent malignancy development.”
The optimal time and intensity of screening for young transplant recipients must still be determined, both Dr. Bibee and Dr. Arron said. Patients deemed through further research to be at higher risk may need earlier and/or more intensive surveillance.
The role of race in skin cancer risk in this population is “one question the study leaves open,” said Dr. Arron. U.S. studies have shown that among adult transplant recipients White patients are “at highest risk for the ultraviolet-associated melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma, followed by Asian and Latino patients. African Americans have had the lowest risk, but some still developed skin cancer after transplant,” she said.
Prior studies of cancer in pediatric transplant recipients have reported primarily on internal malignant neoplasms, with limited data on KC, Dr. Sibbald and coauthors wrote. It is possible the incidence of KS is underestimated in the new study because of “undiagnosed or unreported KCs,” they noted.
The new study was funded by a grant from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and a Hospital for Sick Children grant. In disclosures, Dr. Sibbald reported to JAMA Dermatology receiving grants from the alliance and from Paediatric Consultants Partnership during the conduct of the study. Dr. Arron and Dr. Bibee both said they have no disclosures relevant to the study and its content.
A large study showing an increased risk of keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in children who receive a solid-organ transplant highlights the need for early education about risk reduction and more research to determine optimal timing for screening, say an investigator and two dermatologists with expertise in transplant-related skin issues.
The increased incidence of KC in pediatric transplant recipients is “really high, so we definitely know there’s risk there,” just as there is for adult recipients of solid-organ transplants, said Cathryn Sibbald, MD, MSc, a dermatologist at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and coauthor of a research letter published in June in JAMA Dermatology.
For their study, Dr. Sibbald and her coinvestigators turned to the Ontario Health Insurance plan database, which covers health care for Canadian citizens and qualified residents in the province. They identified 951 patients younger than the age of 18 who received a solid-organ transplant between 1991 and 2004 at an Ontario hospital
They then used a validated health insurance claims–based algorithm to identify diagnoses of KC for the transplant recipients and for more than 5 million age-matched controls. KC, including squamous and basal cell carcinoma, is the most prevalent skin cancer for people who have had a solid-organ transplant.
Fifteen posttransplant KCs (10 patients, 1.1%) were reported a mean of 13.1 years after transplant, with none reported in the first 4 years. The mean age at transplant was 7.8 years, and the mean age at KC diagnosis was 25.2 years. Kidney transplants were the most common (42.1% of transplantations). Most of the transplants recipients (eight patients) who developed KC had kidney transplantation, and most of them had functional graft at the time of KC diagnosis.
Researchers found an increased incidence of KC compared with that of the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 9.09; 95% confidence interval, 5.48-15.08). And the risk for KC increased with time since transplant, with adjusted hazard ratios for KC of 3.63 (95% CI, 0.51-25.77) for 1-5 years, 5.14 (95% CI, 1.28-20.55) for 5-10 years, and 4.80 (95% CI, 2.29-10.08) for 10 years or more, compared with the control population.
Several years ago, another research team performed a similar population-based cohort study of adult transplant recipients in Ontario and found a 6.6-times increased risk of KC in transplant recipients compared with the general population.
Sun protection and skin cancer screening
In commenting on the study, Sarah Arron, MD, PhD, a San Francisco Bay area dermatologist and immediate past president of the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative (www.itscc.org), said she feels “reassured” that young transplant patients tend not to develop the skin cancer until young adulthood.
A ”large study like this is important because the overall rate of KC is low in this age group,” she noted.
The findings “suggest that we can focus our efforts on prevention during childhood, with sun protection and skin cancer education,” she said. “Then, as these children move into adulthood, we can begin screening with skin examinations. Of course, [any child] with a skin lesion or mole that concerns their parents or transplant team should be referred to dermatology for evaluation.”
Pediatric transplant recipients and their parents are most interested in learning about skin cancer prevention either before or immediately after transplantation, according to a survey by other researchers.
Intervention studies needed
The increased risk of KC probably stems largely from immunosuppression, said Dr. Sibbald in an interview. “We know [this is the case] in the older population, and it’s likely true in the younger population as well that it’s one of the primary drivers,” she said.
More research to extensively analyze risk factors should come next, she said. This includes “the granularity of what [immunosuppressants and other] medications are received, and at what dose and for what periods of time, so we can calculate cumulative exposure and its relation to risk,” she said.
Kristin Bibee, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said she’d like to see further studies “evaluate appropriate interventions, like sun-protective behavior in childhood and adolescence or immunosuppression modulation, to prevent malignancy development.”
The optimal time and intensity of screening for young transplant recipients must still be determined, both Dr. Bibee and Dr. Arron said. Patients deemed through further research to be at higher risk may need earlier and/or more intensive surveillance.
The role of race in skin cancer risk in this population is “one question the study leaves open,” said Dr. Arron. U.S. studies have shown that among adult transplant recipients White patients are “at highest risk for the ultraviolet-associated melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma, followed by Asian and Latino patients. African Americans have had the lowest risk, but some still developed skin cancer after transplant,” she said.
Prior studies of cancer in pediatric transplant recipients have reported primarily on internal malignant neoplasms, with limited data on KC, Dr. Sibbald and coauthors wrote. It is possible the incidence of KS is underestimated in the new study because of “undiagnosed or unreported KCs,” they noted.
The new study was funded by a grant from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and a Hospital for Sick Children grant. In disclosures, Dr. Sibbald reported to JAMA Dermatology receiving grants from the alliance and from Paediatric Consultants Partnership during the conduct of the study. Dr. Arron and Dr. Bibee both said they have no disclosures relevant to the study and its content.
A large study showing an increased risk of keratinocyte carcinoma (KC) in children who receive a solid-organ transplant highlights the need for early education about risk reduction and more research to determine optimal timing for screening, say an investigator and two dermatologists with expertise in transplant-related skin issues.
The increased incidence of KC in pediatric transplant recipients is “really high, so we definitely know there’s risk there,” just as there is for adult recipients of solid-organ transplants, said Cathryn Sibbald, MD, MSc, a dermatologist at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto and coauthor of a research letter published in June in JAMA Dermatology.
For their study, Dr. Sibbald and her coinvestigators turned to the Ontario Health Insurance plan database, which covers health care for Canadian citizens and qualified residents in the province. They identified 951 patients younger than the age of 18 who received a solid-organ transplant between 1991 and 2004 at an Ontario hospital
They then used a validated health insurance claims–based algorithm to identify diagnoses of KC for the transplant recipients and for more than 5 million age-matched controls. KC, including squamous and basal cell carcinoma, is the most prevalent skin cancer for people who have had a solid-organ transplant.
Fifteen posttransplant KCs (10 patients, 1.1%) were reported a mean of 13.1 years after transplant, with none reported in the first 4 years. The mean age at transplant was 7.8 years, and the mean age at KC diagnosis was 25.2 years. Kidney transplants were the most common (42.1% of transplantations). Most of the transplants recipients (eight patients) who developed KC had kidney transplantation, and most of them had functional graft at the time of KC diagnosis.
Researchers found an increased incidence of KC compared with that of the general population (standardized incidence ratio, 9.09; 95% confidence interval, 5.48-15.08). And the risk for KC increased with time since transplant, with adjusted hazard ratios for KC of 3.63 (95% CI, 0.51-25.77) for 1-5 years, 5.14 (95% CI, 1.28-20.55) for 5-10 years, and 4.80 (95% CI, 2.29-10.08) for 10 years or more, compared with the control population.
Several years ago, another research team performed a similar population-based cohort study of adult transplant recipients in Ontario and found a 6.6-times increased risk of KC in transplant recipients compared with the general population.
Sun protection and skin cancer screening
In commenting on the study, Sarah Arron, MD, PhD, a San Francisco Bay area dermatologist and immediate past president of the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative (www.itscc.org), said she feels “reassured” that young transplant patients tend not to develop the skin cancer until young adulthood.
A ”large study like this is important because the overall rate of KC is low in this age group,” she noted.
The findings “suggest that we can focus our efforts on prevention during childhood, with sun protection and skin cancer education,” she said. “Then, as these children move into adulthood, we can begin screening with skin examinations. Of course, [any child] with a skin lesion or mole that concerns their parents or transplant team should be referred to dermatology for evaluation.”
Pediatric transplant recipients and their parents are most interested in learning about skin cancer prevention either before or immediately after transplantation, according to a survey by other researchers.
Intervention studies needed
The increased risk of KC probably stems largely from immunosuppression, said Dr. Sibbald in an interview. “We know [this is the case] in the older population, and it’s likely true in the younger population as well that it’s one of the primary drivers,” she said.
More research to extensively analyze risk factors should come next, she said. This includes “the granularity of what [immunosuppressants and other] medications are received, and at what dose and for what periods of time, so we can calculate cumulative exposure and its relation to risk,” she said.
Kristin Bibee, MD, PhD, assistant professor of dermatology at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, said she’d like to see further studies “evaluate appropriate interventions, like sun-protective behavior in childhood and adolescence or immunosuppression modulation, to prevent malignancy development.”
The optimal time and intensity of screening for young transplant recipients must still be determined, both Dr. Bibee and Dr. Arron said. Patients deemed through further research to be at higher risk may need earlier and/or more intensive surveillance.
The role of race in skin cancer risk in this population is “one question the study leaves open,” said Dr. Arron. U.S. studies have shown that among adult transplant recipients White patients are “at highest risk for the ultraviolet-associated melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma, followed by Asian and Latino patients. African Americans have had the lowest risk, but some still developed skin cancer after transplant,” she said.
Prior studies of cancer in pediatric transplant recipients have reported primarily on internal malignant neoplasms, with limited data on KC, Dr. Sibbald and coauthors wrote. It is possible the incidence of KS is underestimated in the new study because of “undiagnosed or unreported KCs,” they noted.
The new study was funded by a grant from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance and a Hospital for Sick Children grant. In disclosures, Dr. Sibbald reported to JAMA Dermatology receiving grants from the alliance and from Paediatric Consultants Partnership during the conduct of the study. Dr. Arron and Dr. Bibee both said they have no disclosures relevant to the study and its content.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Children and COVID: Vaccination off to slow start for the newly eligible
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
New cases of COVID-19 continue to drop among children, but the vaccination effort in those under age 5 years began with something less than a bang.
In the first 2 days after their respective approvals, almost 99,000 children aged 5-11 years and over 675,000 children aged 12-15 were vaccinated, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Children aged 0-4 years represent almost 6% of the overall population, compared with 8.7% for the 5- to 11-year-olds and 5.1% for those aged 12-15.
The recent decline in new cases over the past 4 weeks and the substantial decline since the Omicron surge could be a factor in the lack of response, but it is worth noting that the almost 68,000 new child cases reported in the past week, June 17-23, are “far higher than 1 year ago, June 24, 2021, when 8,400 child cases were reported,” the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association said in their weekly COVID report.
That total for June 17-23 was 19% lower than the previous week and down by 40% since new cases hit a spring peak of 112,000 in late May. Regionally, new cases were down in the Midwest, the South, and the West, the AAP/CHA report showed, but the Northeast saw a small increase, which could be a signal of things to come for the summer.
The decline in new cases, however, has not been accompanied by decreases in hospitalizations or emergency department visits. New admissions of children aged 0-17 with confirmed COVID were at 0.31 per 100,000 population on June 24 after reaching that level on June 15, so no drop-off has occurred yet but there are signs of leveling off, based on CDC data.
The ED visit rates have been fairly steady through June, although COVID-related visits were up to 3.4% of all ED visits on June 22 for children aged 0-11 years, after being below 3% for the first 2 weeks of the month. The rate for children aged 12-15 has been between 1.6% and 1.9% for the past 3 weeks and the rate for 16- and 17-year-olds has been hovering between 1.7% and 2.2% for most of June, after going as high as 2.7% in late May, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.