User login
Children and COVID: Downward trend reverses with small increase in new cases
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.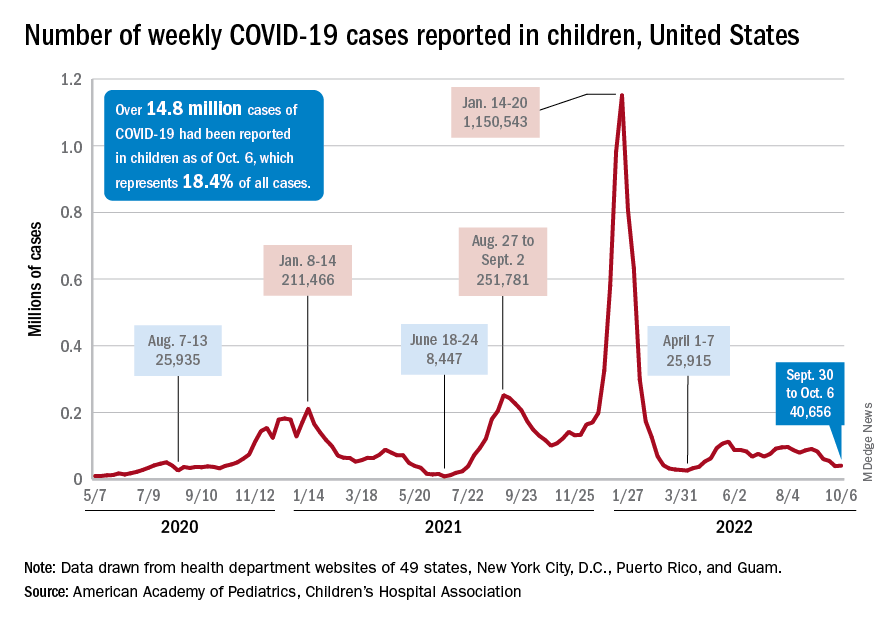
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
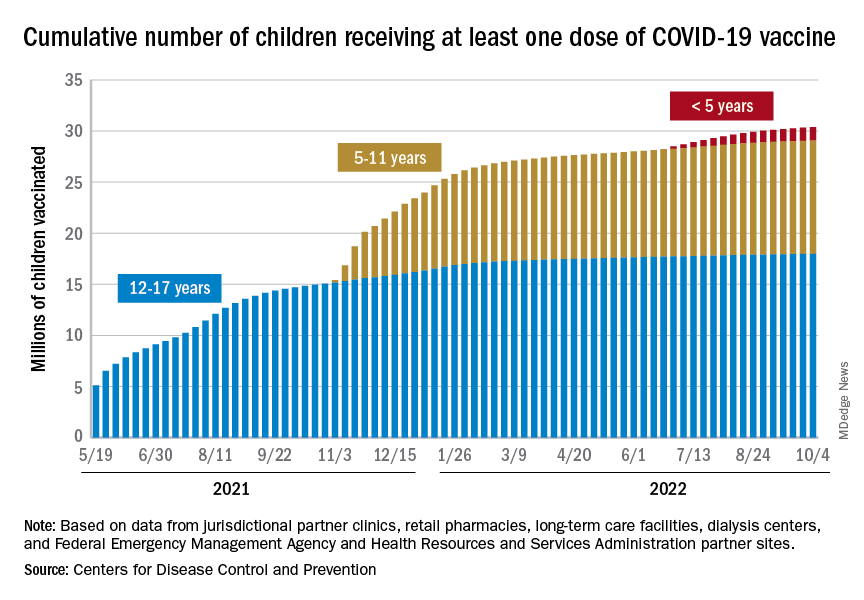
The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.

The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
A small increase in new cases brought COVID-19’s latest losing streak to an end at 4 weeks, based on data from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
The 40,656 new cases reported bring the U.S. cumulative count of child COVID-19 cases to over 14.8 million since the pandemic began, which represents 18.4% of all cases, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report based on state-level data.
The increase in new cases was not reflected in emergency department visits or hospital admissions, which both continued sustained declines that started in August. In the week from Sept. 27 to Oct. 4, the 7-day averages for ED visits with diagnosed COVID were down by 21.5% (age 0-11), 27.3% (12-15), and 18.2% (16-17), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, while the most recent 7-day average for new admissions – 127 per day for Oct. 2-8 – among children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID was down from 161 per day the previous week, a drop of over 21%.
The state-level data that are currently available (several states are no longer reporting) show Alaska (25.5%) and Vermont (25.4%) have the highest proportions of cumulative cases in children, and Florida (12.3%) and Utah (13.5%) have the lowest. Rhode Island has the highest rate of COVID-19 per 100,000 children at 40,427, while Missouri has the lowest at 14,252. The national average is 19,687 per 100,000, the AAP and CHA reported.
Taking a look at vaccination
Vaccinations were up slightly in children aged 12-17 years, as 20,000 initial doses were given during the week of Sept. 29 to Oct. 5, compared with 17,000 and 18,000 the previous 2 weeks. Initial vaccinations in younger children, however, continued declines dating back to August, the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.

The District of Columbia and Massachusetts have the most highly vaccinated groups of 12- to 17-year-olds, as 100% and 95%, respectively, have received initial doses, while Wyoming (39%) and Idaho (42%) have the lowest. D.C. (73%) and Vermont (68%) have the highest proportions of vaccinated 5- to 11-year-olds, and Alabama (17%) and Mississippi (18%) have the lowest. For children under age 5 years, those in D.C. (33%) and Vermont (26%) are the most likely to have received an initial COVID vaccination, while Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi share national-low rates of 2%, the AAP said its report, which is based on CDC data.
When all states and territories are combined, 71% of children aged 12-17 have received at least one dose of vaccine, as have 38.6% of all children 5-11 years old and 6.7% of those under age 5. Almost 61% of the nation’s 16- to 17-year-olds have been fully vaccinated, along with 31.5% of those aged 5-11 and 2.4% of children younger than 5 years, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
About 42 million children – 58% of the population under the age of 18 years – have not received any vaccine yet, the AAP noted. Meanwhile, CDC data indicate that 36 children died of COVID in the last week, with pediatric deaths now totaling 1,781 over the course of the pandemic.
Soccer player with painful toe
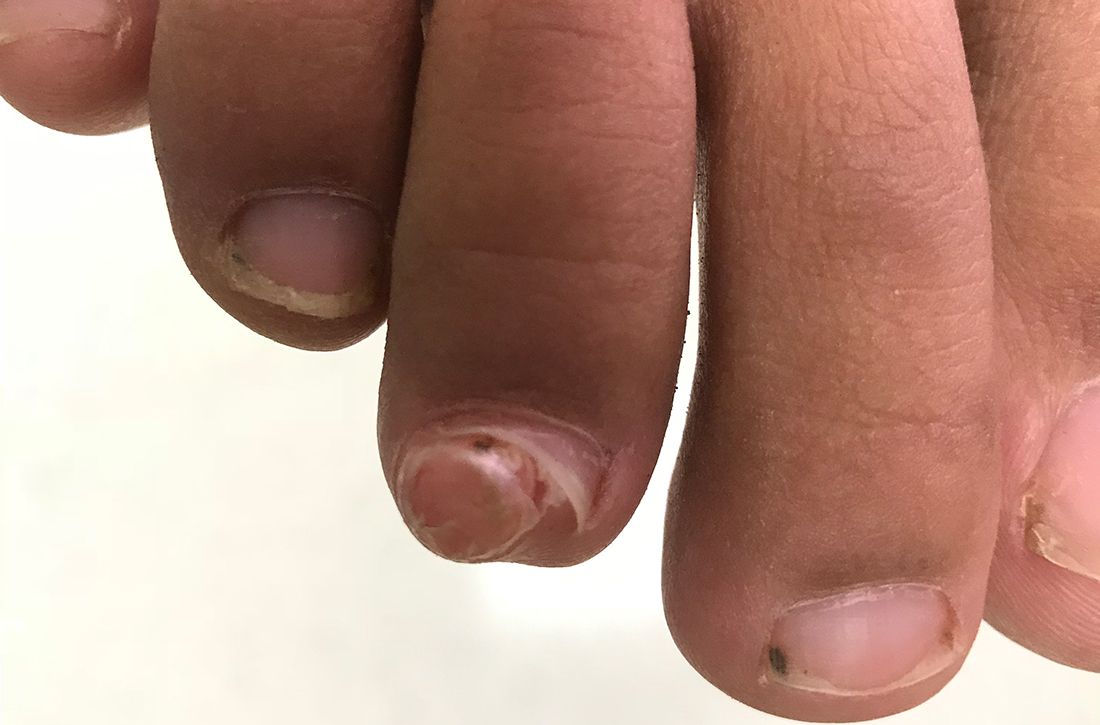
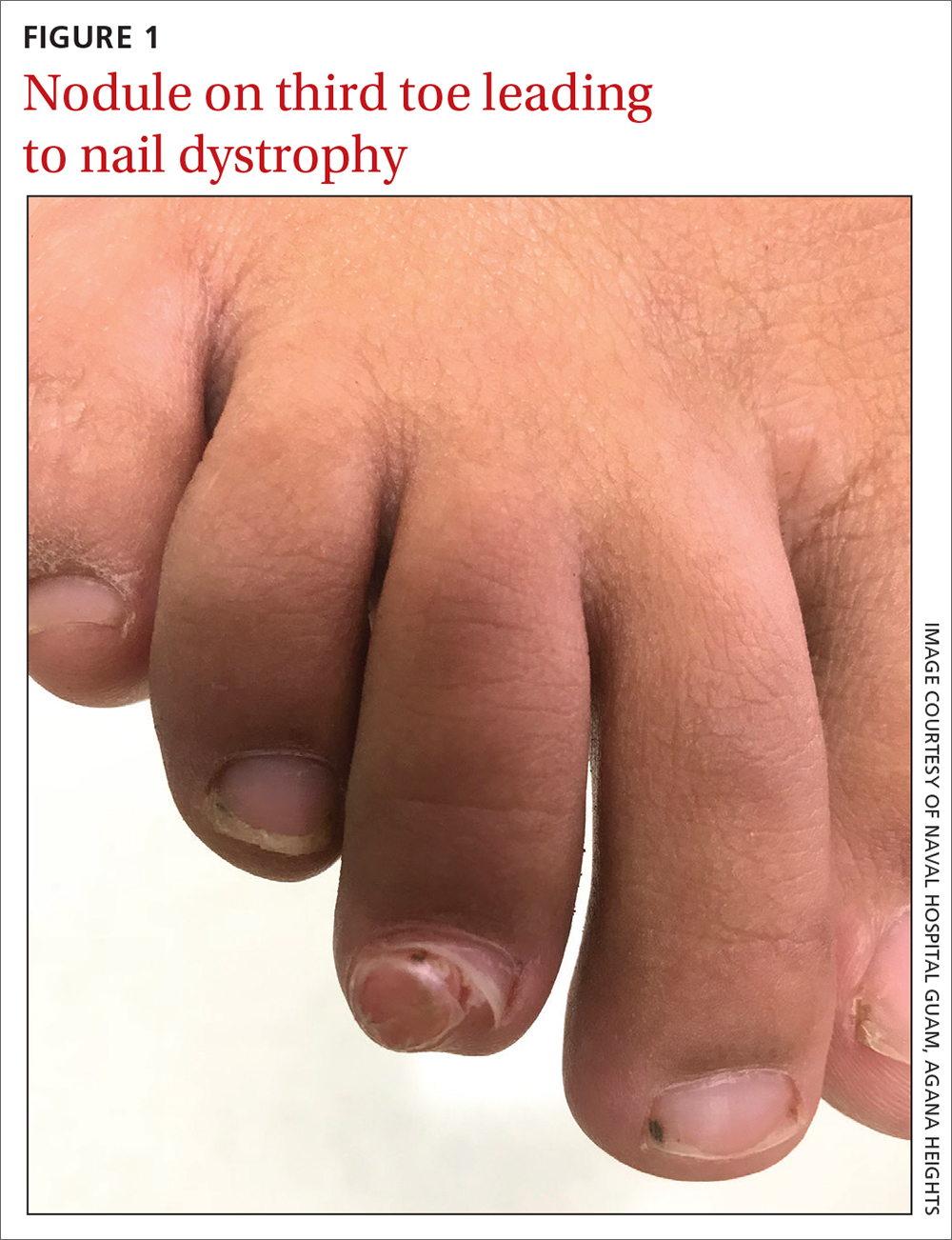
A 13-YEAR-OLD GIRL presented to the clinic with a 1-year history of a slow-growing mass on the third toe of her right foot. As a soccer player, she experienced associated pain when kicking the ball or when wearing tight-fitting shoes. The lesion was otherwise asymptomatic. She denied any overt trauma to the area and indicated that the mass had enlarged over the previous year.
On exam, there was a nontender 8 × 8-mm firm nodule underneath the nail with associated nail dystrophy (FIGURE 1). The toe had full mobility, sensation was intact, and capillary refill time was < 2 seconds.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Subungual exostosis
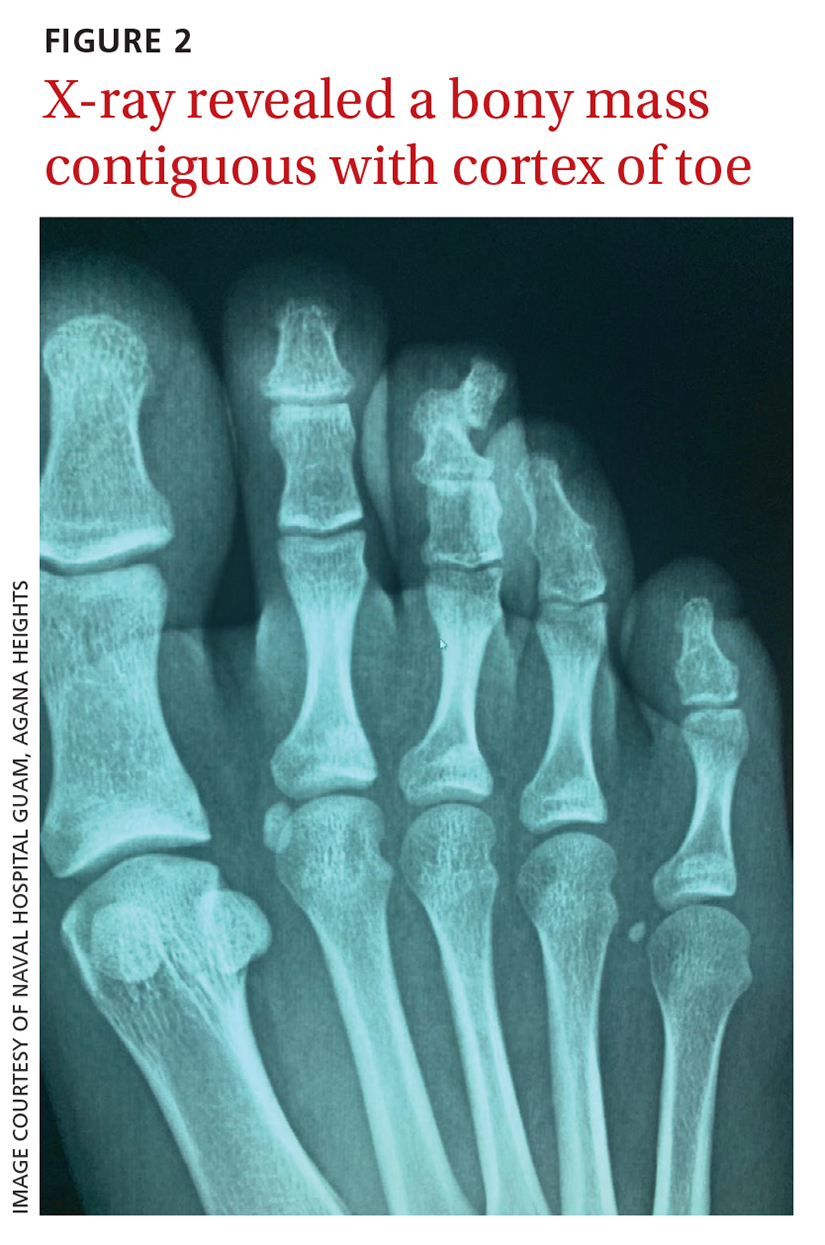
A plain radiograph of the patient’s foot showed continuity with the bony cortex and medullary space, confirming the diagnosis of subungual exostosis (FIGURE 2).1 An exostosis, or osteochondroma, is a form of benign bone tumor in which trabecular bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. When this occurs under the nail bed, it is called subungual exostosis.2 Exostosis represents 10% to 15% of all benign bone tumors, making it the most common benign bone tumor.3 Generally, the age of occurrence is 10 to 15 years.3
Repetitive trauma can be a culprit. Up to 8% of exostoses occur in the foot, with the most commonly affected area being the distal medial portion of the big toe.3,4 Repetitive trauma and infection are potential risk factors.3,4 The affected toe may be painful, but that is not always the case.4 Typically, lesions are solitary; however, multiple lesions can occur.4
Most pediatric foot lesions are benign and involve soft tissue
Benign soft-tissue masses make up the overwhelming majority of pediatric foot lesions, accounting for 61% to 87% of all foot lesions.3 Malignancies such as chondrosarcoma can occur and can be difficult to diagnose. Rapid growth, family history, size > 5 cm, heterogenous appearance on magnetic resonance imaging, and poorly defined margins are a few characteristics that should increase suspicion for possible malignancy.5
The differential diagnosis for a growth on the toe similar to the one our patient had would include pyogenic granuloma,
Pyogenic granulomas are benign vascular lesions that occur in patients of all ages. They tend to be dome-shaped and flesh-toned to violaceous red, and they are usually found on the head, neck, and extremities—especially fingers.6 They are associated with trauma and are classically tender with a propensity to bleed.6
Acral fibromyxoma is a benign, slow-growing, predominately painless, firm mass with an affinity for the great toe; the affected area includes the nail in 50% of cases.7 A radiograph may show bony erosion or scalloping due to mass effect; however, there will be no continuity with the bony matrix. (Such continuity would suggest exostosis.)
Periungual fibromas are benign soft-tissue masses, which are pink to red and firm, and emerge from underneath the nails, potentially resulting in dystrophy.8 They can bleed and cause pain, and are strongly associated with tuberous sclerosis.5
Continue to: Verruca vulgaris
Verruca vulgaris, the common wart, can also manifest in the subungual region as a firm, generally painless mass. It is the most common neoplasm of the hand and fingers.6 Tiny black dots that correspond to thrombosed capillaries are key to identifying this lesion.
Surgical excision when patient reaches maturity
The definitive treatment for subungual exostosis is surgical excision, preferably once the patient has reached skeletal maturity. Surgery at this point is associated with decreased recurrence rates.3,4 That said, excision may need to be performed sooner if the lesion is painful and leading to deformity.3
Our patient’s persistent pain prompted us to recommend surgical excision. She underwent a third digit exostectomy, which she tolerated without any issues. The patient was fitted with a postoperative shoe that she wore until her 2-week follow-up appointment, when her sutures were removed. The patient’s activity level progressed as tolerated. She regained full function and returned to playing soccer, without any pain, 3 months after her surgery.
1. Das PC, Hassan S, Kumar P. Subungual exostosis – clinical, radiological, and histological findings. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:202-203. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_104_18
2. Yousefian F, Davis B, Browning JC. Pediatric subungual exostosis. Cutis. 2021;108:256-257. doi:10.12788/cutis.0380
3. Bouchard B, Bartlett M, Donnan L. Assessment of the pediatric foot mass. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:32-41. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00397
4. DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
5. Shah SH, Callahan MJ. Ultrasound evaluation of superficial lumps and bumps of the extremities in children: a 5-year retrospective review. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43 suppl 1:S23-S40. doi: 10.1007/s00247-012-2590-0
6. Habif, Thomas P. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Mosby/Elsevier, 2016.
7. Ramya C, Nayak C, Tambe S. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:457-459. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.185734
8. Ma D, Darling T, Moss J, et al. Histologic variants of periungual fibromas in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:442-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.002
A 13-YEAR-OLD GIRL presented to the clinic with a 1-year history of a slow-growing mass on the third toe of her right foot. As a soccer player, she experienced associated pain when kicking the ball or when wearing tight-fitting shoes. The lesion was otherwise asymptomatic. She denied any overt trauma to the area and indicated that the mass had enlarged over the previous year.
On exam, there was a nontender 8 × 8-mm firm nodule underneath the nail with associated nail dystrophy (FIGURE 1). The toe had full mobility, sensation was intact, and capillary refill time was < 2 seconds.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Subungual exostosis
A plain radiograph of the patient’s foot showed continuity with the bony cortex and medullary space, confirming the diagnosis of subungual exostosis (FIGURE 2).1 An exostosis, or osteochondroma, is a form of benign bone tumor in which trabecular bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. When this occurs under the nail bed, it is called subungual exostosis.2 Exostosis represents 10% to 15% of all benign bone tumors, making it the most common benign bone tumor.3 Generally, the age of occurrence is 10 to 15 years.3

Repetitive trauma can be a culprit. Up to 8% of exostoses occur in the foot, with the most commonly affected area being the distal medial portion of the big toe.3,4 Repetitive trauma and infection are potential risk factors.3,4 The affected toe may be painful, but that is not always the case.4 Typically, lesions are solitary; however, multiple lesions can occur.4
Most pediatric foot lesions are benign and involve soft tissue
Benign soft-tissue masses make up the overwhelming majority of pediatric foot lesions, accounting for 61% to 87% of all foot lesions.3 Malignancies such as chondrosarcoma can occur and can be difficult to diagnose. Rapid growth, family history, size > 5 cm, heterogenous appearance on magnetic resonance imaging, and poorly defined margins are a few characteristics that should increase suspicion for possible malignancy.5
The differential diagnosis for a growth on the toe similar to the one our patient had would include pyogenic granuloma,
Pyogenic granulomas are benign vascular lesions that occur in patients of all ages. They tend to be dome-shaped and flesh-toned to violaceous red, and they are usually found on the head, neck, and extremities—especially fingers.6 They are associated with trauma and are classically tender with a propensity to bleed.6
Acral fibromyxoma is a benign, slow-growing, predominately painless, firm mass with an affinity for the great toe; the affected area includes the nail in 50% of cases.7 A radiograph may show bony erosion or scalloping due to mass effect; however, there will be no continuity with the bony matrix. (Such continuity would suggest exostosis.)
Periungual fibromas are benign soft-tissue masses, which are pink to red and firm, and emerge from underneath the nails, potentially resulting in dystrophy.8 They can bleed and cause pain, and are strongly associated with tuberous sclerosis.5
Continue to: Verruca vulgaris
Verruca vulgaris, the common wart, can also manifest in the subungual region as a firm, generally painless mass. It is the most common neoplasm of the hand and fingers.6 Tiny black dots that correspond to thrombosed capillaries are key to identifying this lesion.
Surgical excision when patient reaches maturity
The definitive treatment for subungual exostosis is surgical excision, preferably once the patient has reached skeletal maturity. Surgery at this point is associated with decreased recurrence rates.3,4 That said, excision may need to be performed sooner if the lesion is painful and leading to deformity.3
Our patient’s persistent pain prompted us to recommend surgical excision. She underwent a third digit exostectomy, which she tolerated without any issues. The patient was fitted with a postoperative shoe that she wore until her 2-week follow-up appointment, when her sutures were removed. The patient’s activity level progressed as tolerated. She regained full function and returned to playing soccer, without any pain, 3 months after her surgery.
A 13-YEAR-OLD GIRL presented to the clinic with a 1-year history of a slow-growing mass on the third toe of her right foot. As a soccer player, she experienced associated pain when kicking the ball or when wearing tight-fitting shoes. The lesion was otherwise asymptomatic. She denied any overt trauma to the area and indicated that the mass had enlarged over the previous year.
On exam, there was a nontender 8 × 8-mm firm nodule underneath the nail with associated nail dystrophy (FIGURE 1). The toe had full mobility, sensation was intact, and capillary refill time was < 2 seconds.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Subungual exostosis
A plain radiograph of the patient’s foot showed continuity with the bony cortex and medullary space, confirming the diagnosis of subungual exostosis (FIGURE 2).1 An exostosis, or osteochondroma, is a form of benign bone tumor in which trabecular bone overgrows its normal border in a nodular pattern. When this occurs under the nail bed, it is called subungual exostosis.2 Exostosis represents 10% to 15% of all benign bone tumors, making it the most common benign bone tumor.3 Generally, the age of occurrence is 10 to 15 years.3

Repetitive trauma can be a culprit. Up to 8% of exostoses occur in the foot, with the most commonly affected area being the distal medial portion of the big toe.3,4 Repetitive trauma and infection are potential risk factors.3,4 The affected toe may be painful, but that is not always the case.4 Typically, lesions are solitary; however, multiple lesions can occur.4
Most pediatric foot lesions are benign and involve soft tissue
Benign soft-tissue masses make up the overwhelming majority of pediatric foot lesions, accounting for 61% to 87% of all foot lesions.3 Malignancies such as chondrosarcoma can occur and can be difficult to diagnose. Rapid growth, family history, size > 5 cm, heterogenous appearance on magnetic resonance imaging, and poorly defined margins are a few characteristics that should increase suspicion for possible malignancy.5
The differential diagnosis for a growth on the toe similar to the one our patient had would include pyogenic granuloma,
Pyogenic granulomas are benign vascular lesions that occur in patients of all ages. They tend to be dome-shaped and flesh-toned to violaceous red, and they are usually found on the head, neck, and extremities—especially fingers.6 They are associated with trauma and are classically tender with a propensity to bleed.6
Acral fibromyxoma is a benign, slow-growing, predominately painless, firm mass with an affinity for the great toe; the affected area includes the nail in 50% of cases.7 A radiograph may show bony erosion or scalloping due to mass effect; however, there will be no continuity with the bony matrix. (Such continuity would suggest exostosis.)
Periungual fibromas are benign soft-tissue masses, which are pink to red and firm, and emerge from underneath the nails, potentially resulting in dystrophy.8 They can bleed and cause pain, and are strongly associated with tuberous sclerosis.5
Continue to: Verruca vulgaris
Verruca vulgaris, the common wart, can also manifest in the subungual region as a firm, generally painless mass. It is the most common neoplasm of the hand and fingers.6 Tiny black dots that correspond to thrombosed capillaries are key to identifying this lesion.
Surgical excision when patient reaches maturity
The definitive treatment for subungual exostosis is surgical excision, preferably once the patient has reached skeletal maturity. Surgery at this point is associated with decreased recurrence rates.3,4 That said, excision may need to be performed sooner if the lesion is painful and leading to deformity.3
Our patient’s persistent pain prompted us to recommend surgical excision. She underwent a third digit exostectomy, which she tolerated without any issues. The patient was fitted with a postoperative shoe that she wore until her 2-week follow-up appointment, when her sutures were removed. The patient’s activity level progressed as tolerated. She regained full function and returned to playing soccer, without any pain, 3 months after her surgery.
1. Das PC, Hassan S, Kumar P. Subungual exostosis – clinical, radiological, and histological findings. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:202-203. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_104_18
2. Yousefian F, Davis B, Browning JC. Pediatric subungual exostosis. Cutis. 2021;108:256-257. doi:10.12788/cutis.0380
3. Bouchard B, Bartlett M, Donnan L. Assessment of the pediatric foot mass. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:32-41. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00397
4. DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
5. Shah SH, Callahan MJ. Ultrasound evaluation of superficial lumps and bumps of the extremities in children: a 5-year retrospective review. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43 suppl 1:S23-S40. doi: 10.1007/s00247-012-2590-0
6. Habif, Thomas P. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Mosby/Elsevier, 2016.
7. Ramya C, Nayak C, Tambe S. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:457-459. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.185734
8. Ma D, Darling T, Moss J, et al. Histologic variants of periungual fibromas in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:442-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.002
1. Das PC, Hassan S, Kumar P. Subungual exostosis – clinical, radiological, and histological findings. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019;10:202-203. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_104_18
2. Yousefian F, Davis B, Browning JC. Pediatric subungual exostosis. Cutis. 2021;108:256-257. doi:10.12788/cutis.0380
3. Bouchard B, Bartlett M, Donnan L. Assessment of the pediatric foot mass. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:32-41. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00397
4. DaCambra MP, Gupta SK, Ferri-de-Barros F. Subungual exostosis of the toes: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1251-1259. doi: 10.1007/s11999-013-3345-4
5. Shah SH, Callahan MJ. Ultrasound evaluation of superficial lumps and bumps of the extremities in children: a 5-year retrospective review. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43 suppl 1:S23-S40. doi: 10.1007/s00247-012-2590-0
6. Habif, Thomas P. Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide to Diagnosis and Therapy. 6th ed. Mosby/Elsevier, 2016.
7. Ramya C, Nayak C, Tambe S. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:457-459. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.185734
8. Ma D, Darling T, Moss J, et al. Histologic variants of periungual fibromas in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:442-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.002
Mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 may be underestimated
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
ANAHEIM, CALIF. – The rate of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection is likely higher than the current estimate of 2%-8%, suggests a recent study using cord blood serology to determine incidence. The study was presented at the American Academy of Pediatrics National Conference.
“Cord blood screening is a potential tool to identify SARS-CoV-2 infected and/or exposed neonates who should then be followed for long-term consequences of mother-to-child transmission,” Amy Yeh, MD, an assistant professor of clinical pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, told attendees at the meeting.
Dr. Yeh and her colleagues collected cord blood from more than 500 mothers at LAC+USC Medical Center from October 2021 to April 2022 and tested them for IgG antibodies against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: nucleoprotein (N), receptor-binding domain (RBD), and spike protein (S1). Results with an IgG mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) above 700 were considered positive for IgG antibodies. A positive result for N as well as RBD or S1 indicated a natural infection while a positive result for only RBD or S1 indicated a vaccine response or past infection.
The researchers also tested a subset of the IgG positive samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against N, S1, and RBD, with an IgM MFI greater than 24 and an IgA MFI greater than 102 used as the thresholds for positive results.
Among 384 cord blood samples analyzed, 85.4% were positive for IgG against RBD, indicating that the mother had SARS-CoV-2 immunity from either a past infection or vaccination. Of these anti-RBD positive samples, 60.7% were anti-N IgG negative, suggesting that N had waned since vaccination or the past infection.
Since the other 39.3% that were anti-N IgG positive suggest a past maternal infection, the researchers assessed these 129 samples for IgM and IgA antibodies against RBD. They found that 16 of them had high levels of anti-RBD IgA and/or IgM antibodies, pointing to a rate of mother-to-child-transmission of up to 12.4%.
Sallie Permar, MD, PhD, a professor and the chair of pediatrics at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, who was not involved in the research, said most studies of placental transmission have focused on virologic testing, such as PCR. “Serologic tests for congenital infections are inherently challenged by the transfer of maternal IgG across the placenta and therefore must rely on non-IgG isotype response detection, which have inherently been more susceptible to false-positive results than IgG-based tests,” Dr. Permar said.
Also, “it is unclear if virologic testing was performed in the infants, which, if positive in the same infants for which cord blood IgM/IgA responses were identified, could further validate positive serologic findings,” added Dr. Permar, who is also pediatrician-in-chief at New York-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital.
Given these limitations, Dr. Permar reiterated that diagnostics for congenital SARS-CoV-2 continue to evolve, even if congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection currently appears rare. Dr. Permar said she agreed with Dr. Yeh that following those who do develop this infection is important.
“There have been initial reports of neurodevelopmental and other outcomes from long-term follow-up cohorts of infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 infection in utero with variable results and it should continue to be pursued using cohorts both enrolled early in the pandemic and those enrolled more recently after population-level immunity to SARS-CoV-2 was achieved,” said Dr. Permar.
Dr. Permar serves as a consultant to Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Dynavax, and Hoopika on their CMV vaccine programs and has led sponsored research programs with Moderna and Merck. Information on study funding and on disclosures for Dr. Yeh was unavailable.
AT AAP 2022
Youth killed by guns in U.S. equals classroom a day
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Preventing firearm-related injuries and deaths in children and youth “demands a public safety approach like regulation of motor vehicles,” the group said.
The organization on Oct. 8 released an updated policy statement and technical report about gun violence and children at its 2022 annual meeting in Anaheim, Calif. The reports were published in the journal Pediatrics, and the authors plan to discuss them during the conference.
“Each day, 28 U.S. children and teens – the equivalent of a high school classroom – die from gun violence, making it the No. 1 killer of youth through age 24,” the AAP said in a statement about the reports. “The national death rate is significantly higher than all other high-income countries combined, largely due to an alarming increase in suicides and homicides that do not make national headlines.”
Firearms have become the leading cause of death among children in the United States.
In 2020, guns caused 10,197 deaths of Americans younger than 24, according to the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine.
In 2015, more than 7,200 American youth were killed by firearms. That same year in 28 other high-income countries – which combined would have had a population twice that of the United States – just 685 youth were killed by firearms, according to the AAP.
Separately at the AAP conference, physicians are presenting new research about gun violence and children. And on Oct. 10, a pediatrician who was at Uvalde Memorial Hospital in Texas after the deadly school shooting in May is scheduled to address attendees. The doctor, Roy Guerrero, MD, testified on Capitol Hill to advocate for gun control after the shooting at Robb Elementary School, which killed 19 children and two adults.
“This is not a simple problem, and it cannot be fixed with a simple solution,” Lois K. Lee, MD, MPH, said in the AAP news release. Dr. Lee chairs the AAP Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention that wrote the new reports. “Pediatricians as a start can offer families guidance and education on more safely storing guns. AAP also calls for supporting legislation that, much like the common-sense requirements for obtaining a driver’s license, would improve gun ownership safety.”
Many deaths occur at home
The rate of homicide from firearms in U.S. youth, especially those aged 15-24 years, increased by 14% during the past decade, and the rate of suicide from firearms increased by 39%, according to the AAP.
Homicides account for 58% of youth firearm deaths, whereas suicides account for 37%. Another 2% of youth firearm deaths are unintentional, and 1% result from law enforcement actions, the group said.
Among children 12 years old and younger, about 85% of firearm deaths occur at home. Teen firearm deaths are about as likely to occur at home (39%) as on the street or sidewalk (38%), according to research based on 2014 data.
“School shootings represent a relatively new phenomenon over the last half-century, and the United States has the highest rate of school shootings in the world,” the AAP technical report noted. Between 1966 and 2008, according to the group, 44 such shootings occurred in the United States, or an average of about one per year. Fast forward a few years and the violence became dramatically worse: Between 2013 and 2015, officials counted 154 school shootings – or about one per week.
Still, school shootings are responsible for less than 1% of all firearm deaths among children 17 years or younger in the United States. While school shootings “receive a tremendous amount of attention,” the report stated, other child firearm deaths may be less likely to make national headlines.
“Many firearm tragedies escape public attention because they occur in a home, sometimes in a child’s own home or at a friend’s house, or their neighbor’s or grandparent’s residence,” Eric W. Fleegler, MD, MPH, Boston Children’s Hospital, a co-author of the new reports, said in a statement from AAP. “Research tells us that families tend to underestimate how children will behave when they encounter a gun and miscalculate the risks. Suicide risks are also a huge concern, especially in families where teens are struggling with their mental health.”
AAP-recommended actions include:
- Mental health screenings and safe gun storage education provided by clinicians as part of routine patient visits
- Increased funding for violence intervention programs in hospital and community settings
- Regulation of firearms like other consumer products, with national requirements that address training, licensing, insurance coverage, registration of individuals purchasing firearms, and safe storage
- The use of technology that allows only authorized users to pull the trigger
- Universal background checks that use federal databases and information from local police before all gun purchases
- Extreme risk protection order laws, or “red flag laws,” that prohibit individuals at risk for harming themselves or others from purchasing or owning a firearm
- More funding for firearm injury and prevention research.
A noticeable increase in the ED
Irma Ugalde, MD, associate professor and director of pediatric emergency medicine research at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, noticed that firearm-related injuries in children at her hospital were more common during the COVID-19 pandemic, even as pediatric emergency department visits decreased overall.
She and her colleagues studied the trends and reported their findings at the AAP meeting.
“We saw a drop in pediatric admissions overall,” Dr. Ugalde said in a statement about the study. “But what was really noticeable was that trauma was still very prevalent – in fact probably more so – and we were seeing more firearm injuries.”
The researchers found that firearm injuries in children rose from 88 cases in 2019 to 118 in 2020. The number of incidents remained elevated in 2021, with 115 cases.
In addition, the researchers found an initial increase in injuries occurring at home where the shooter was a known family member or friend, and in cases involving firearms that were not properly stored.
By comparison, pediatric ED visits overall decreased by 34.2% from 2019 to 2020, and by 11.8% from 2019 to 2021.
The increase in firearm injuries coincided with an increase in gun sales in the United States, the researchers noted.
“National and statewide initiatives to mitigate the risk of firearm-related injury and death are necessary,” Dr. Ugalde’s group said. “We recommend that health care workers remain vigilant about screening for potential risk factors and safe storage of firearms.”
Accidental injuries
Daniel D. Guzman, MD, with Cook Children’s Health Care Center, Fort Worth, Tex., conducted a study focused on unintentional firearm injuries in children. Dr. Guzman’s group analyzed data from 204 patients younger than age 19 seen at Cook Children’s from January 2015 to June 2021.
Dr. Guzman and his colleagues examined outcomes for injuries caused by powder guns – shotguns, rifles, and handguns – and air-power guns that shoot BBs and pellets.
The researchers found that 29% of the unintentional firearm injuries occurred with powder guns and 71% with air-power weapons, often BB guns.
“It is important that all firearms, powdered and air-powered, be stored safely in a lock box or safe,” Dr. Guzman said in a statement. To that end, Cook Children’s has developed a program called Aim for Safety to teach children and parents about the dangers of unsupervised play with BB guns and pellet guns, as well as the importance of storing all firearms unloaded and in a locked safe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Preventing firearm-related injuries and deaths in children and youth “demands a public safety approach like regulation of motor vehicles,” the group said.
The organization on Oct. 8 released an updated policy statement and technical report about gun violence and children at its 2022 annual meeting in Anaheim, Calif. The reports were published in the journal Pediatrics, and the authors plan to discuss them during the conference.
“Each day, 28 U.S. children and teens – the equivalent of a high school classroom – die from gun violence, making it the No. 1 killer of youth through age 24,” the AAP said in a statement about the reports. “The national death rate is significantly higher than all other high-income countries combined, largely due to an alarming increase in suicides and homicides that do not make national headlines.”
Firearms have become the leading cause of death among children in the United States.
In 2020, guns caused 10,197 deaths of Americans younger than 24, according to the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine.
In 2015, more than 7,200 American youth were killed by firearms. That same year in 28 other high-income countries – which combined would have had a population twice that of the United States – just 685 youth were killed by firearms, according to the AAP.
Separately at the AAP conference, physicians are presenting new research about gun violence and children. And on Oct. 10, a pediatrician who was at Uvalde Memorial Hospital in Texas after the deadly school shooting in May is scheduled to address attendees. The doctor, Roy Guerrero, MD, testified on Capitol Hill to advocate for gun control after the shooting at Robb Elementary School, which killed 19 children and two adults.
“This is not a simple problem, and it cannot be fixed with a simple solution,” Lois K. Lee, MD, MPH, said in the AAP news release. Dr. Lee chairs the AAP Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention that wrote the new reports. “Pediatricians as a start can offer families guidance and education on more safely storing guns. AAP also calls for supporting legislation that, much like the common-sense requirements for obtaining a driver’s license, would improve gun ownership safety.”
Many deaths occur at home
The rate of homicide from firearms in U.S. youth, especially those aged 15-24 years, increased by 14% during the past decade, and the rate of suicide from firearms increased by 39%, according to the AAP.
Homicides account for 58% of youth firearm deaths, whereas suicides account for 37%. Another 2% of youth firearm deaths are unintentional, and 1% result from law enforcement actions, the group said.
Among children 12 years old and younger, about 85% of firearm deaths occur at home. Teen firearm deaths are about as likely to occur at home (39%) as on the street or sidewalk (38%), according to research based on 2014 data.
“School shootings represent a relatively new phenomenon over the last half-century, and the United States has the highest rate of school shootings in the world,” the AAP technical report noted. Between 1966 and 2008, according to the group, 44 such shootings occurred in the United States, or an average of about one per year. Fast forward a few years and the violence became dramatically worse: Between 2013 and 2015, officials counted 154 school shootings – or about one per week.
Still, school shootings are responsible for less than 1% of all firearm deaths among children 17 years or younger in the United States. While school shootings “receive a tremendous amount of attention,” the report stated, other child firearm deaths may be less likely to make national headlines.
“Many firearm tragedies escape public attention because they occur in a home, sometimes in a child’s own home or at a friend’s house, or their neighbor’s or grandparent’s residence,” Eric W. Fleegler, MD, MPH, Boston Children’s Hospital, a co-author of the new reports, said in a statement from AAP. “Research tells us that families tend to underestimate how children will behave when they encounter a gun and miscalculate the risks. Suicide risks are also a huge concern, especially in families where teens are struggling with their mental health.”
AAP-recommended actions include:
- Mental health screenings and safe gun storage education provided by clinicians as part of routine patient visits
- Increased funding for violence intervention programs in hospital and community settings
- Regulation of firearms like other consumer products, with national requirements that address training, licensing, insurance coverage, registration of individuals purchasing firearms, and safe storage
- The use of technology that allows only authorized users to pull the trigger
- Universal background checks that use federal databases and information from local police before all gun purchases
- Extreme risk protection order laws, or “red flag laws,” that prohibit individuals at risk for harming themselves or others from purchasing or owning a firearm
- More funding for firearm injury and prevention research.
A noticeable increase in the ED
Irma Ugalde, MD, associate professor and director of pediatric emergency medicine research at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, noticed that firearm-related injuries in children at her hospital were more common during the COVID-19 pandemic, even as pediatric emergency department visits decreased overall.
She and her colleagues studied the trends and reported their findings at the AAP meeting.
“We saw a drop in pediatric admissions overall,” Dr. Ugalde said in a statement about the study. “But what was really noticeable was that trauma was still very prevalent – in fact probably more so – and we were seeing more firearm injuries.”
The researchers found that firearm injuries in children rose from 88 cases in 2019 to 118 in 2020. The number of incidents remained elevated in 2021, with 115 cases.
In addition, the researchers found an initial increase in injuries occurring at home where the shooter was a known family member or friend, and in cases involving firearms that were not properly stored.
By comparison, pediatric ED visits overall decreased by 34.2% from 2019 to 2020, and by 11.8% from 2019 to 2021.
The increase in firearm injuries coincided with an increase in gun sales in the United States, the researchers noted.
“National and statewide initiatives to mitigate the risk of firearm-related injury and death are necessary,” Dr. Ugalde’s group said. “We recommend that health care workers remain vigilant about screening for potential risk factors and safe storage of firearms.”
Accidental injuries
Daniel D. Guzman, MD, with Cook Children’s Health Care Center, Fort Worth, Tex., conducted a study focused on unintentional firearm injuries in children. Dr. Guzman’s group analyzed data from 204 patients younger than age 19 seen at Cook Children’s from January 2015 to June 2021.
Dr. Guzman and his colleagues examined outcomes for injuries caused by powder guns – shotguns, rifles, and handguns – and air-power guns that shoot BBs and pellets.
The researchers found that 29% of the unintentional firearm injuries occurred with powder guns and 71% with air-power weapons, often BB guns.
“It is important that all firearms, powdered and air-powered, be stored safely in a lock box or safe,” Dr. Guzman said in a statement. To that end, Cook Children’s has developed a program called Aim for Safety to teach children and parents about the dangers of unsupervised play with BB guns and pellet guns, as well as the importance of storing all firearms unloaded and in a locked safe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Preventing firearm-related injuries and deaths in children and youth “demands a public safety approach like regulation of motor vehicles,” the group said.
The organization on Oct. 8 released an updated policy statement and technical report about gun violence and children at its 2022 annual meeting in Anaheim, Calif. The reports were published in the journal Pediatrics, and the authors plan to discuss them during the conference.
“Each day, 28 U.S. children and teens – the equivalent of a high school classroom – die from gun violence, making it the No. 1 killer of youth through age 24,” the AAP said in a statement about the reports. “The national death rate is significantly higher than all other high-income countries combined, largely due to an alarming increase in suicides and homicides that do not make national headlines.”
Firearms have become the leading cause of death among children in the United States.
In 2020, guns caused 10,197 deaths of Americans younger than 24, according to the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine.
In 2015, more than 7,200 American youth were killed by firearms. That same year in 28 other high-income countries – which combined would have had a population twice that of the United States – just 685 youth were killed by firearms, according to the AAP.
Separately at the AAP conference, physicians are presenting new research about gun violence and children. And on Oct. 10, a pediatrician who was at Uvalde Memorial Hospital in Texas after the deadly school shooting in May is scheduled to address attendees. The doctor, Roy Guerrero, MD, testified on Capitol Hill to advocate for gun control after the shooting at Robb Elementary School, which killed 19 children and two adults.
“This is not a simple problem, and it cannot be fixed with a simple solution,” Lois K. Lee, MD, MPH, said in the AAP news release. Dr. Lee chairs the AAP Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention that wrote the new reports. “Pediatricians as a start can offer families guidance and education on more safely storing guns. AAP also calls for supporting legislation that, much like the common-sense requirements for obtaining a driver’s license, would improve gun ownership safety.”
Many deaths occur at home
The rate of homicide from firearms in U.S. youth, especially those aged 15-24 years, increased by 14% during the past decade, and the rate of suicide from firearms increased by 39%, according to the AAP.
Homicides account for 58% of youth firearm deaths, whereas suicides account for 37%. Another 2% of youth firearm deaths are unintentional, and 1% result from law enforcement actions, the group said.
Among children 12 years old and younger, about 85% of firearm deaths occur at home. Teen firearm deaths are about as likely to occur at home (39%) as on the street or sidewalk (38%), according to research based on 2014 data.
“School shootings represent a relatively new phenomenon over the last half-century, and the United States has the highest rate of school shootings in the world,” the AAP technical report noted. Between 1966 and 2008, according to the group, 44 such shootings occurred in the United States, or an average of about one per year. Fast forward a few years and the violence became dramatically worse: Between 2013 and 2015, officials counted 154 school shootings – or about one per week.
Still, school shootings are responsible for less than 1% of all firearm deaths among children 17 years or younger in the United States. While school shootings “receive a tremendous amount of attention,” the report stated, other child firearm deaths may be less likely to make national headlines.
“Many firearm tragedies escape public attention because they occur in a home, sometimes in a child’s own home or at a friend’s house, or their neighbor’s or grandparent’s residence,” Eric W. Fleegler, MD, MPH, Boston Children’s Hospital, a co-author of the new reports, said in a statement from AAP. “Research tells us that families tend to underestimate how children will behave when they encounter a gun and miscalculate the risks. Suicide risks are also a huge concern, especially in families where teens are struggling with their mental health.”
AAP-recommended actions include:
- Mental health screenings and safe gun storage education provided by clinicians as part of routine patient visits
- Increased funding for violence intervention programs in hospital and community settings
- Regulation of firearms like other consumer products, with national requirements that address training, licensing, insurance coverage, registration of individuals purchasing firearms, and safe storage
- The use of technology that allows only authorized users to pull the trigger
- Universal background checks that use federal databases and information from local police before all gun purchases
- Extreme risk protection order laws, or “red flag laws,” that prohibit individuals at risk for harming themselves or others from purchasing or owning a firearm
- More funding for firearm injury and prevention research.
A noticeable increase in the ED
Irma Ugalde, MD, associate professor and director of pediatric emergency medicine research at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, noticed that firearm-related injuries in children at her hospital were more common during the COVID-19 pandemic, even as pediatric emergency department visits decreased overall.
She and her colleagues studied the trends and reported their findings at the AAP meeting.
“We saw a drop in pediatric admissions overall,” Dr. Ugalde said in a statement about the study. “But what was really noticeable was that trauma was still very prevalent – in fact probably more so – and we were seeing more firearm injuries.”
The researchers found that firearm injuries in children rose from 88 cases in 2019 to 118 in 2020. The number of incidents remained elevated in 2021, with 115 cases.
In addition, the researchers found an initial increase in injuries occurring at home where the shooter was a known family member or friend, and in cases involving firearms that were not properly stored.
By comparison, pediatric ED visits overall decreased by 34.2% from 2019 to 2020, and by 11.8% from 2019 to 2021.
The increase in firearm injuries coincided with an increase in gun sales in the United States, the researchers noted.
“National and statewide initiatives to mitigate the risk of firearm-related injury and death are necessary,” Dr. Ugalde’s group said. “We recommend that health care workers remain vigilant about screening for potential risk factors and safe storage of firearms.”
Accidental injuries
Daniel D. Guzman, MD, with Cook Children’s Health Care Center, Fort Worth, Tex., conducted a study focused on unintentional firearm injuries in children. Dr. Guzman’s group analyzed data from 204 patients younger than age 19 seen at Cook Children’s from January 2015 to June 2021.
Dr. Guzman and his colleagues examined outcomes for injuries caused by powder guns – shotguns, rifles, and handguns – and air-power guns that shoot BBs and pellets.
The researchers found that 29% of the unintentional firearm injuries occurred with powder guns and 71% with air-power weapons, often BB guns.
“It is important that all firearms, powdered and air-powered, be stored safely in a lock box or safe,” Dr. Guzman said in a statement. To that end, Cook Children’s has developed a program called Aim for Safety to teach children and parents about the dangers of unsupervised play with BB guns and pellet guns, as well as the importance of storing all firearms unloaded and in a locked safe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Increased body temperature triggers flares in rare autoinflammatory disorder
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
Increased core body temperature is a likely trigger of disease flares in the rare genetic autoinflammatory disorder mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), based on a study involving new mouse models.
The study also uncovered potential strategies for treating MKD, lead author Marcia A. Munoz, PhD, of the Garvan Institute of Medical Research and the University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues reported in Journal of Clinical Investigation.
“MKD encompasses a severe manifestation – mevalonic aciduria, and a milder form – a periodic fever syndrome known as hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity inversely correlates with the amount of mevalonate kinase in the body. To date, however, it’s been unclear why reduced levels of the enzyme lead to inflammation, or exactly how body temperature plays a role in this process, despite observations that disease flares can be triggered by temperature-raising activities like strenuous exercise.
“The underlying disease mechanisms in MKD have been very difficult to elucidate, because newly identified patients are usually young children (and it’s very difficult to obtain any samples of tissues or cells other than small samples of blood), and also because until now there were no laboratory models that truly mimic the human disease,” senior author Michael J. Rogers, PhD, of the Garvan Institute said in a written comment.
Dr. Rogers and colleagues addressed this gap by creating the first murine models to carry the relevant mutant allele in MVK, the gene encoding mevalonate kinase. These mice had lower levels of the enzyme, which led to increased levels of mevalonic acid and defects in protein prenylation (the addition of hydrophobic moieties), the latter of which were significantly associated with inflammation.
“The discovery that shortage of geranylgeranyl diphosphate, the substrate necessary for prenylation of over 300 substrates including small GTPases, and not the elevated mevalonic acid levels, correlated with inflammation was an important finding that ultimately provided a pathomechanism that linked the mevalonate kinase deficiency to inflammasome activation,” said Raphaela T. Goldbach-Mansky, MD, chief of the translational autoinflammatory disease studies unit at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said the new mouse models can serve as “preclinical platforms” to test the efficacy and safety of possible treatments, such as supplementing geranylgeraniol, an intermediate product in the mevalonate pathway, or blocking NLRP3, the inflammasome in question.
While both of these interventions showed efficacy in mice, it is unclear whether the same therapies will work in people, as the models may not reflect all human disease characteristics.
“It remains unclear which human features are modeled in the mouse model,” Dr. Goldbach-Mansky said, noting that humans may exhibit unique inflammasomes and disease triggers.
Dr. Rogers aims to find out. After 8 years of work that culminated in the present publication, he and his colleagues are now exploring ways of circumventing the defective enzyme to restore normal metabolism. He expects “many more years of work” to understand exactly how MKD affects the immune system and other organs, and how these processes can be mitigated.
Still, he is optimistic.
“Of the many autoinflammatory diseases that are known so far, we believe that new treatments are truly within reach to overcome MKD,” Dr. Rogers said.
The study was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, St. Vincent’s Clinic Foundation, the Allergy and Immunology Foundation of Australasia, and others. The investigators and Dr. Goldbach-Mansky declared no competing interests.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
FDA: Newborns protected by whooping cough vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a whooping cough vaccine that protects newborns under 2 months of age.
The vaccine, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, was previously approved among pregnant people for their own protection.
“Infants younger than 2 months of age are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “This is the first vaccine approved specifically for use during pregnancy to prevent a disease in young infants whose mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy.”
Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Most cases that result in hospitalizations and death are among infants within 2 months of birth.
The FDA said its decision was based on data from observational studies, which included 108 cases of pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old. According to data evaluated by the agency, the vaccine was 78% effective in preventing whooping cough.
Boostrix is administered as a single 0.5-mL dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a whooping cough vaccine that protects newborns under 2 months of age.
The vaccine, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, was previously approved among pregnant people for their own protection.
“Infants younger than 2 months of age are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “This is the first vaccine approved specifically for use during pregnancy to prevent a disease in young infants whose mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy.”
Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Most cases that result in hospitalizations and death are among infants within 2 months of birth.
The FDA said its decision was based on data from observational studies, which included 108 cases of pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old. According to data evaluated by the agency, the vaccine was 78% effective in preventing whooping cough.
Boostrix is administered as a single 0.5-mL dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved a whooping cough vaccine that protects newborns under 2 months of age.
The vaccine, manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, was previously approved among pregnant people for their own protection.
“Infants younger than 2 months of age are too young to be protected by the childhood pertussis vaccine series,” Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said in a press release. “This is the first vaccine approved specifically for use during pregnancy to prevent a disease in young infants whose mothers are vaccinated during pregnancy.”
Pertussis is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. Most cases that result in hospitalizations and death are among infants within 2 months of birth.
The FDA said its decision was based on data from observational studies, which included 108 cases of pertussis in infants younger than 2 months old. According to data evaluated by the agency, the vaccine was 78% effective in preventing whooping cough.
Boostrix is administered as a single 0.5-mL dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dupilumab study outlines benefits, safety profile in infants, preschoolers with atopic dermatitis
at 31 treatment centers in North America and Europe.
Children younger than 6 years with moderate to severe AD have few options if their symptoms are uncontrolled with topical therapies, and persistent itchiness has a negative impact on quality of life for patients and families, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, and professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote in the study, published in the Lancet.
The study was the basis of the Food and Drug Administration expanded approval of dupilumab in June 2022, to include children aged 6 months to 5 years with moderate to severe AD, whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Regulatory submission for this age group is under review by the European Medicines Agency, and by regulatory authorities in other countries, according to the manufacturers.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), which inhibits the signaling of the interleukin-4 and IL-13 pathways, was first approved in 2017 for treating adults with moderate to severe AD.
“There has not been a biologic approved before at such a young age, and for such a common disease,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “This is the drug that has revolutionized care of the most common inflammatory skin disease in children, and this is the pivotal study that brought it to market for the youngest children who suffer from the severe forms.”
The study also sets a precedent for a lower threshold for starting systemic medication in young children for treating moderate to severe disease given the absence of severe side effects and no need for lab monitoring, Dr. Paller noted. However, dupilumab will also be closely watched “for both impact on the developing immune system and the possibility that it will alter the long-term course of the eczema and the development of allergic comorbidities, such as lowering the risk of developing asthma, GI, allergy, and possibly other conditions.”
In the study, the researchers randomized 83 children aged 6 months up to 6 years to treatment with dupilumab, administered subcutaneously, and 79 to placebo every 4 weeks for 16 weeks; both groups also received topical corticosteroids. Dosage of dupilumab was based on body weight; those with a body weight of 5-15 kg received 200 mg, while those with a body weight of 15-30 kg received 300 mg. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with clear or almost clear skin at 16 weeks, defined as scores of 0 or 1 on the Investigator’s Global Assessment.
After 16 weeks, 28% of dupilumab patients met the primary endpoint versus 4% of those on placebo (P < .0001). In addition, 53% of dupilumab patients met the key secondary endpoint of a 75% improvement from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index, compared with 11% of patients on placebo (P < .0001). Treatment with dupilumab also resulted in significantly greater improvements in pruritus and skin pain, and sleep quality, as well as improved quality of life for patients and their caregivers, the authors reported.
Overall, adverse event rates were slightly lower in the dupilumab-treated patients, compared with patients on placebo (64% vs. 74%); there were no adverse events related to dupilumab that were serious or resulted in treatment discontinuation. Treatment-emergent adverse effects that were reported in 3% or more of patients and affected more of those on dupilumab than those on placebo included molluscum contagiosum (5% vs. 3%), viral gastroenteritis (4% vs. 0), rhinorrhea (5% vs. 1%), dental caries (5% vs. 0), and conjunctivitis (4% vs 0).
The rate of skin infections among the children on dupilumab was 12% vs. 24% among those on placebo.
Severe and treatment-related adverse events also were similar in both subgroups of body weight.
The findings were limited by the small number of patients younger than 2 years and the lack of study sites outside of North America and Europe, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized, double-blind design and use of background topical therapy to provide a real-world safety and efficacy assessment in a very young population.
Overcoming injection issues
The safety profile for dupilumab, which is of the highest importance, “did not surprise me at all,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “My only surprise is that the placebo injections actually led to more injection site reactions than [with] dupilumab, but numbers were quite low in both groups.” (Rates were 2% among those on dupilumab and 3% among those on placebo.)
The major barrier to the use of dupilumab in clinical practice is the requirement for injection, which, she explained, can be “unbearable for some young children, and thus becomes impossible for parents because of lack of cooperation and their intensified concern about giving the injection,” because of their child’s response.
“We like to administer the first dose in the office, allowing us to teach parents a few tricks related to proper technique,” including audio and visual distraction, tactile stimulation before and during the injection, use of topical anesthetic if helpful, “and making sure that the medication is at room temperature before administration,” she said. Cost is another potential barrier; however, even public insurance has been covering the medication, often after optimized use of topical medications has been unsuccessful.
Future research questions
As for additional research, the current study had a relatively small number of patients younger than 2 years, and more data are needed for this age group, said Dr. Paller. “We also need better understanding of the safety of dupilumab administration when live vaccines are administered. Finally, we certainly want to know what additional effects dupilumab may have beyond just the efficacy for treating eczema.”
In particular, these questions include whether dupilumab modifies the long-term course of the disease, possibly reducing the risk of persistence of disease with advancing age, or even cures the disease if started at a young age, she said. In addition, research has yet to show whether dupilumab might reduce the risk of other atopic disorders, such as asthma, food allergy, and allergic rhinitis.
“Ongoing studies and real-life experiences in the next several years will help us to answer these questions,” Dr. Paller said.
Data support safety, efficacy, quality of life
AD is associated with immense quality of life impairment, Raj Chovatiya, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. Most AD is initially diagnosed in early childhood, but previous treatment options for those with moderate to severe disease have been limited by safety concerns, which adds to the burden on infants and young children, and their parents and caregivers, said Dr. Chovatiya, who was not involved in the study.
“This phase 3 study showed that dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 mediated type 2 inflammatory signaling, provided both meaningful and statistically significant improvement in AD severity, extent of disease, and itch in patients,” he said. Dupilumab also improved children’s sleep quality and the overall quality of life in both patients and caregivers.
“These findings were quite similar to those described in older children and adults, where dupilumab is already approved for the treatment of moderate-severe AD and has demonstrated real-world safety and efficacy,” said Dr. Chovatiya. However, “the current study was limited to only a short-term analysis of 16 weeks, an ongoing open-label study should further address long-term treatment responses.”
The study was supported by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. In addition to being an investigator for Regeneron, and several other pharmaceutical companies, Dr. Paller has been a consultant with honorarium for Regeneron, Sanofi, and multiple other companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed serving as a consultant and speaker for Regeneron and Sanofi, but was not involved in the current study.
at 31 treatment centers in North America and Europe.
Children younger than 6 years with moderate to severe AD have few options if their symptoms are uncontrolled with topical therapies, and persistent itchiness has a negative impact on quality of life for patients and families, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, and professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote in the study, published in the Lancet.
The study was the basis of the Food and Drug Administration expanded approval of dupilumab in June 2022, to include children aged 6 months to 5 years with moderate to severe AD, whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Regulatory submission for this age group is under review by the European Medicines Agency, and by regulatory authorities in other countries, according to the manufacturers.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), which inhibits the signaling of the interleukin-4 and IL-13 pathways, was first approved in 2017 for treating adults with moderate to severe AD.
“There has not been a biologic approved before at such a young age, and for such a common disease,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “This is the drug that has revolutionized care of the most common inflammatory skin disease in children, and this is the pivotal study that brought it to market for the youngest children who suffer from the severe forms.”
The study also sets a precedent for a lower threshold for starting systemic medication in young children for treating moderate to severe disease given the absence of severe side effects and no need for lab monitoring, Dr. Paller noted. However, dupilumab will also be closely watched “for both impact on the developing immune system and the possibility that it will alter the long-term course of the eczema and the development of allergic comorbidities, such as lowering the risk of developing asthma, GI, allergy, and possibly other conditions.”
In the study, the researchers randomized 83 children aged 6 months up to 6 years to treatment with dupilumab, administered subcutaneously, and 79 to placebo every 4 weeks for 16 weeks; both groups also received topical corticosteroids. Dosage of dupilumab was based on body weight; those with a body weight of 5-15 kg received 200 mg, while those with a body weight of 15-30 kg received 300 mg. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with clear or almost clear skin at 16 weeks, defined as scores of 0 or 1 on the Investigator’s Global Assessment.
After 16 weeks, 28% of dupilumab patients met the primary endpoint versus 4% of those on placebo (P < .0001). In addition, 53% of dupilumab patients met the key secondary endpoint of a 75% improvement from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index, compared with 11% of patients on placebo (P < .0001). Treatment with dupilumab also resulted in significantly greater improvements in pruritus and skin pain, and sleep quality, as well as improved quality of life for patients and their caregivers, the authors reported.
Overall, adverse event rates were slightly lower in the dupilumab-treated patients, compared with patients on placebo (64% vs. 74%); there were no adverse events related to dupilumab that were serious or resulted in treatment discontinuation. Treatment-emergent adverse effects that were reported in 3% or more of patients and affected more of those on dupilumab than those on placebo included molluscum contagiosum (5% vs. 3%), viral gastroenteritis (4% vs. 0), rhinorrhea (5% vs. 1%), dental caries (5% vs. 0), and conjunctivitis (4% vs 0).
The rate of skin infections among the children on dupilumab was 12% vs. 24% among those on placebo.
Severe and treatment-related adverse events also were similar in both subgroups of body weight.
The findings were limited by the small number of patients younger than 2 years and the lack of study sites outside of North America and Europe, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized, double-blind design and use of background topical therapy to provide a real-world safety and efficacy assessment in a very young population.
Overcoming injection issues
The safety profile for dupilumab, which is of the highest importance, “did not surprise me at all,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “My only surprise is that the placebo injections actually led to more injection site reactions than [with] dupilumab, but numbers were quite low in both groups.” (Rates were 2% among those on dupilumab and 3% among those on placebo.)
The major barrier to the use of dupilumab in clinical practice is the requirement for injection, which, she explained, can be “unbearable for some young children, and thus becomes impossible for parents because of lack of cooperation and their intensified concern about giving the injection,” because of their child’s response.
“We like to administer the first dose in the office, allowing us to teach parents a few tricks related to proper technique,” including audio and visual distraction, tactile stimulation before and during the injection, use of topical anesthetic if helpful, “and making sure that the medication is at room temperature before administration,” she said. Cost is another potential barrier; however, even public insurance has been covering the medication, often after optimized use of topical medications has been unsuccessful.
Future research questions
As for additional research, the current study had a relatively small number of patients younger than 2 years, and more data are needed for this age group, said Dr. Paller. “We also need better understanding of the safety of dupilumab administration when live vaccines are administered. Finally, we certainly want to know what additional effects dupilumab may have beyond just the efficacy for treating eczema.”
In particular, these questions include whether dupilumab modifies the long-term course of the disease, possibly reducing the risk of persistence of disease with advancing age, or even cures the disease if started at a young age, she said. In addition, research has yet to show whether dupilumab might reduce the risk of other atopic disorders, such as asthma, food allergy, and allergic rhinitis.
“Ongoing studies and real-life experiences in the next several years will help us to answer these questions,” Dr. Paller said.
Data support safety, efficacy, quality of life
AD is associated with immense quality of life impairment, Raj Chovatiya, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. Most AD is initially diagnosed in early childhood, but previous treatment options for those with moderate to severe disease have been limited by safety concerns, which adds to the burden on infants and young children, and their parents and caregivers, said Dr. Chovatiya, who was not involved in the study.
“This phase 3 study showed that dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 mediated type 2 inflammatory signaling, provided both meaningful and statistically significant improvement in AD severity, extent of disease, and itch in patients,” he said. Dupilumab also improved children’s sleep quality and the overall quality of life in both patients and caregivers.
“These findings were quite similar to those described in older children and adults, where dupilumab is already approved for the treatment of moderate-severe AD and has demonstrated real-world safety and efficacy,” said Dr. Chovatiya. However, “the current study was limited to only a short-term analysis of 16 weeks, an ongoing open-label study should further address long-term treatment responses.”
The study was supported by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. In addition to being an investigator for Regeneron, and several other pharmaceutical companies, Dr. Paller has been a consultant with honorarium for Regeneron, Sanofi, and multiple other companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed serving as a consultant and speaker for Regeneron and Sanofi, but was not involved in the current study.
at 31 treatment centers in North America and Europe.
Children younger than 6 years with moderate to severe AD have few options if their symptoms are uncontrolled with topical therapies, and persistent itchiness has a negative impact on quality of life for patients and families, Amy S. Paller, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, and professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues wrote in the study, published in the Lancet.
The study was the basis of the Food and Drug Administration expanded approval of dupilumab in June 2022, to include children aged 6 months to 5 years with moderate to severe AD, whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. Regulatory submission for this age group is under review by the European Medicines Agency, and by regulatory authorities in other countries, according to the manufacturers.
Dupilumab (Dupixent), which inhibits the signaling of the interleukin-4 and IL-13 pathways, was first approved in 2017 for treating adults with moderate to severe AD.
“There has not been a biologic approved before at such a young age, and for such a common disease,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “This is the drug that has revolutionized care of the most common inflammatory skin disease in children, and this is the pivotal study that brought it to market for the youngest children who suffer from the severe forms.”
The study also sets a precedent for a lower threshold for starting systemic medication in young children for treating moderate to severe disease given the absence of severe side effects and no need for lab monitoring, Dr. Paller noted. However, dupilumab will also be closely watched “for both impact on the developing immune system and the possibility that it will alter the long-term course of the eczema and the development of allergic comorbidities, such as lowering the risk of developing asthma, GI, allergy, and possibly other conditions.”
In the study, the researchers randomized 83 children aged 6 months up to 6 years to treatment with dupilumab, administered subcutaneously, and 79 to placebo every 4 weeks for 16 weeks; both groups also received topical corticosteroids. Dosage of dupilumab was based on body weight; those with a body weight of 5-15 kg received 200 mg, while those with a body weight of 15-30 kg received 300 mg. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with clear or almost clear skin at 16 weeks, defined as scores of 0 or 1 on the Investigator’s Global Assessment.
After 16 weeks, 28% of dupilumab patients met the primary endpoint versus 4% of those on placebo (P < .0001). In addition, 53% of dupilumab patients met the key secondary endpoint of a 75% improvement from baseline in Eczema Area and Severity Index, compared with 11% of patients on placebo (P < .0001). Treatment with dupilumab also resulted in significantly greater improvements in pruritus and skin pain, and sleep quality, as well as improved quality of life for patients and their caregivers, the authors reported.
Overall, adverse event rates were slightly lower in the dupilumab-treated patients, compared with patients on placebo (64% vs. 74%); there were no adverse events related to dupilumab that were serious or resulted in treatment discontinuation. Treatment-emergent adverse effects that were reported in 3% or more of patients and affected more of those on dupilumab than those on placebo included molluscum contagiosum (5% vs. 3%), viral gastroenteritis (4% vs. 0), rhinorrhea (5% vs. 1%), dental caries (5% vs. 0), and conjunctivitis (4% vs 0).
The rate of skin infections among the children on dupilumab was 12% vs. 24% among those on placebo.
Severe and treatment-related adverse events also were similar in both subgroups of body weight.
The findings were limited by the small number of patients younger than 2 years and the lack of study sites outside of North America and Europe, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the randomized, double-blind design and use of background topical therapy to provide a real-world safety and efficacy assessment in a very young population.
Overcoming injection issues
The safety profile for dupilumab, which is of the highest importance, “did not surprise me at all,” Dr. Paller said in an interview. “My only surprise is that the placebo injections actually led to more injection site reactions than [with] dupilumab, but numbers were quite low in both groups.” (Rates were 2% among those on dupilumab and 3% among those on placebo.)
The major barrier to the use of dupilumab in clinical practice is the requirement for injection, which, she explained, can be “unbearable for some young children, and thus becomes impossible for parents because of lack of cooperation and their intensified concern about giving the injection,” because of their child’s response.
“We like to administer the first dose in the office, allowing us to teach parents a few tricks related to proper technique,” including audio and visual distraction, tactile stimulation before and during the injection, use of topical anesthetic if helpful, “and making sure that the medication is at room temperature before administration,” she said. Cost is another potential barrier; however, even public insurance has been covering the medication, often after optimized use of topical medications has been unsuccessful.
Future research questions
As for additional research, the current study had a relatively small number of patients younger than 2 years, and more data are needed for this age group, said Dr. Paller. “We also need better understanding of the safety of dupilumab administration when live vaccines are administered. Finally, we certainly want to know what additional effects dupilumab may have beyond just the efficacy for treating eczema.”
In particular, these questions include whether dupilumab modifies the long-term course of the disease, possibly reducing the risk of persistence of disease with advancing age, or even cures the disease if started at a young age, she said. In addition, research has yet to show whether dupilumab might reduce the risk of other atopic disorders, such as asthma, food allergy, and allergic rhinitis.
“Ongoing studies and real-life experiences in the next several years will help us to answer these questions,” Dr. Paller said.
Data support safety, efficacy, quality of life
AD is associated with immense quality of life impairment, Raj Chovatiya, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. Most AD is initially diagnosed in early childhood, but previous treatment options for those with moderate to severe disease have been limited by safety concerns, which adds to the burden on infants and young children, and their parents and caregivers, said Dr. Chovatiya, who was not involved in the study.
“This phase 3 study showed that dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 mediated type 2 inflammatory signaling, provided both meaningful and statistically significant improvement in AD severity, extent of disease, and itch in patients,” he said. Dupilumab also improved children’s sleep quality and the overall quality of life in both patients and caregivers.
“These findings were quite similar to those described in older children and adults, where dupilumab is already approved for the treatment of moderate-severe AD and has demonstrated real-world safety and efficacy,” said Dr. Chovatiya. However, “the current study was limited to only a short-term analysis of 16 weeks, an ongoing open-label study should further address long-term treatment responses.”
The study was supported by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. In addition to being an investigator for Regeneron, and several other pharmaceutical companies, Dr. Paller has been a consultant with honorarium for Regeneron, Sanofi, and multiple other companies. Dr. Chovatiya disclosed serving as a consultant and speaker for Regeneron and Sanofi, but was not involved in the current study.
FROM THE LANCET
Ultra-processed food intake by moms linked with childhood obesity
A mother’s consumption of ultra-processed foods appears to be related to an increased risk of overweight or obesity in her children, according to new research.
Among the 19,958 mother-child pairs studied, 12.4% of children developed obesity or overweight in the full analytic study group, and the offspring of those mothers who ate the most ultra-processed foods had a 26% higher risk of obesity/overweight (12.1 servings/day), compared with those with the lowest consumption (3.4 servings/day), report Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
This study demonstrates the possible advantages of restricting ultra-processed food consumption among women and mothers who are in their reproductive years to potentially lower the risk of childhood obesity, the investigators note.
“These data support the importance of refining dietary recommendations and the development of programs to improve nutrition for women of reproductive age to promote offspring health,” they write in their article, published in BMJ.
“As a medical and public health community, we have to understand that the period of time in which a woman is carrying a child or ... the time when she is raising her children represents a unique opportunity to potentially intervene to affect both the health of the mother and also the health of the children,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
It is important to address these trends both on an individual clinician level and on a societal level, noted Dr. Chan.
“This is a good opportunity to counsel patients about the potential linkage between their consumption of ultra-processed food for not just themselves but also their kids, and I think that added counseling and awareness may motivate individuals to think about their diets in a more favorable way,” he added.
But ultra-processed foods are affordable and convenient, and many communities are not able to easily access fresh and healthy foods, so “it is incumbent upon [clinicians] to make it a priority and to break down those social and economic barriers, which make it difficult to have healthy and less processed food,” Dr. Chan elaborated.
Assessment of maternal junk food intake during peri-pregnancy and childhood
Modern Western diets frequently include ultra-processed foods – such as packaged baked goods and snacks, fizzy drinks, and sugary cereals – which are linked to adult weight increase. The relationship between parental consumption of highly processed meals and offspring weight is, however, unclear across generations, the researchers note.
Hence, they set out to determine whether eating ultra-processed foods during peri-pregnancy and while raising children increased the risk of being overweight or having obesity among children and teens.
The study team assessed 14,553 mothers and their 19,958 children from the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS I and II) and Nurses’ Health Study II (NHS II) in the United States. Males accounted for 45% of the children in the study, and the children’s ages ranged from 7 to 17 years.
The NHS II is a continuing investigation following the lifestyle and health choices of over 100,000 female registered nurses in the United States in 1989, while the GUTS I involved about 17,000 children of the nurses in the NHS II. Participants in GUTS I filled out an initial lifestyle and health survey and were evaluated annually between 1997 and 2001 and every 2 years thereafter.
Roughly 11,000 children from the NHS II were included in the GUTS II. The children were further evaluated in 2006, 2008, and 2011, as well as every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed until the children reached 18 years of age or experienced obesity and overweight onset. A subcohort consisted of 2,925 mother-child pairs with data on peri-pregnancy eating patterns.
Maternal intake of ultra-processed foods while raising children was linked with obesity or overweight in children. Moreover, compared with the lowest consumption cohort (3.4 servings/day), there was a 26% greater risk for the greatest maternal ultra-processed food intake cohort (12.1 servings/day) after adjusting for child’s sedentary time, ultra-processed food intake, physical activity, and established maternal risk factors.
Even though rates were elevated, ultra-processed food intake during pregnancy was not significantly linked to a higher risk of obesity or overweight in children (P for trend = .07).
Sex, birth weight, age, gestational age, or maternal body weight had no effect on these correlations either.
The study’s limitations include the fact that some of the children in the pairs were lost during follow-up; there may have been data misreporting, as the weight and diet measures were provided via self-reported questionnaires; and potential residual confounding given the observational study design, the researchers note.
Other limitations include that the mothers involved in the study came from similar socioeconomic backgrounds, had similar personal and familial educational statuses, and were primarily White, which limits the generalizability of these data to other ethnic groups, the authors add.
“Further studies are warranted to investigate specific biological mechanisms and socioeconomic determinants underlying the observed associations between maternal ultra-processed food intake and offspring overweight and obesity,” the researchers conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A mother’s consumption of ultra-processed foods appears to be related to an increased risk of overweight or obesity in her children, according to new research.
Among the 19,958 mother-child pairs studied, 12.4% of children developed obesity or overweight in the full analytic study group, and the offspring of those mothers who ate the most ultra-processed foods had a 26% higher risk of obesity/overweight (12.1 servings/day), compared with those with the lowest consumption (3.4 servings/day), report Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
This study demonstrates the possible advantages of restricting ultra-processed food consumption among women and mothers who are in their reproductive years to potentially lower the risk of childhood obesity, the investigators note.
“These data support the importance of refining dietary recommendations and the development of programs to improve nutrition for women of reproductive age to promote offspring health,” they write in their article, published in BMJ.
“As a medical and public health community, we have to understand that the period of time in which a woman is carrying a child or ... the time when she is raising her children represents a unique opportunity to potentially intervene to affect both the health of the mother and also the health of the children,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
It is important to address these trends both on an individual clinician level and on a societal level, noted Dr. Chan.
“This is a good opportunity to counsel patients about the potential linkage between their consumption of ultra-processed food for not just themselves but also their kids, and I think that added counseling and awareness may motivate individuals to think about their diets in a more favorable way,” he added.
But ultra-processed foods are affordable and convenient, and many communities are not able to easily access fresh and healthy foods, so “it is incumbent upon [clinicians] to make it a priority and to break down those social and economic barriers, which make it difficult to have healthy and less processed food,” Dr. Chan elaborated.
Assessment of maternal junk food intake during peri-pregnancy and childhood
Modern Western diets frequently include ultra-processed foods – such as packaged baked goods and snacks, fizzy drinks, and sugary cereals – which are linked to adult weight increase. The relationship between parental consumption of highly processed meals and offspring weight is, however, unclear across generations, the researchers note.
Hence, they set out to determine whether eating ultra-processed foods during peri-pregnancy and while raising children increased the risk of being overweight or having obesity among children and teens.
The study team assessed 14,553 mothers and their 19,958 children from the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS I and II) and Nurses’ Health Study II (NHS II) in the United States. Males accounted for 45% of the children in the study, and the children’s ages ranged from 7 to 17 years.
The NHS II is a continuing investigation following the lifestyle and health choices of over 100,000 female registered nurses in the United States in 1989, while the GUTS I involved about 17,000 children of the nurses in the NHS II. Participants in GUTS I filled out an initial lifestyle and health survey and were evaluated annually between 1997 and 2001 and every 2 years thereafter.
Roughly 11,000 children from the NHS II were included in the GUTS II. The children were further evaluated in 2006, 2008, and 2011, as well as every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed until the children reached 18 years of age or experienced obesity and overweight onset. A subcohort consisted of 2,925 mother-child pairs with data on peri-pregnancy eating patterns.
Maternal intake of ultra-processed foods while raising children was linked with obesity or overweight in children. Moreover, compared with the lowest consumption cohort (3.4 servings/day), there was a 26% greater risk for the greatest maternal ultra-processed food intake cohort (12.1 servings/day) after adjusting for child’s sedentary time, ultra-processed food intake, physical activity, and established maternal risk factors.
Even though rates were elevated, ultra-processed food intake during pregnancy was not significantly linked to a higher risk of obesity or overweight in children (P for trend = .07).
Sex, birth weight, age, gestational age, or maternal body weight had no effect on these correlations either.
The study’s limitations include the fact that some of the children in the pairs were lost during follow-up; there may have been data misreporting, as the weight and diet measures were provided via self-reported questionnaires; and potential residual confounding given the observational study design, the researchers note.
Other limitations include that the mothers involved in the study came from similar socioeconomic backgrounds, had similar personal and familial educational statuses, and were primarily White, which limits the generalizability of these data to other ethnic groups, the authors add.
“Further studies are warranted to investigate specific biological mechanisms and socioeconomic determinants underlying the observed associations between maternal ultra-processed food intake and offspring overweight and obesity,” the researchers conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A mother’s consumption of ultra-processed foods appears to be related to an increased risk of overweight or obesity in her children, according to new research.
Among the 19,958 mother-child pairs studied, 12.4% of children developed obesity or overweight in the full analytic study group, and the offspring of those mothers who ate the most ultra-processed foods had a 26% higher risk of obesity/overweight (12.1 servings/day), compared with those with the lowest consumption (3.4 servings/day), report Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues.
This study demonstrates the possible advantages of restricting ultra-processed food consumption among women and mothers who are in their reproductive years to potentially lower the risk of childhood obesity, the investigators note.
“These data support the importance of refining dietary recommendations and the development of programs to improve nutrition for women of reproductive age to promote offspring health,” they write in their article, published in BMJ.
“As a medical and public health community, we have to understand that the period of time in which a woman is carrying a child or ... the time when she is raising her children represents a unique opportunity to potentially intervene to affect both the health of the mother and also the health of the children,” Dr. Chan said in an interview.
It is important to address these trends both on an individual clinician level and on a societal level, noted Dr. Chan.
“This is a good opportunity to counsel patients about the potential linkage between their consumption of ultra-processed food for not just themselves but also their kids, and I think that added counseling and awareness may motivate individuals to think about their diets in a more favorable way,” he added.
But ultra-processed foods are affordable and convenient, and many communities are not able to easily access fresh and healthy foods, so “it is incumbent upon [clinicians] to make it a priority and to break down those social and economic barriers, which make it difficult to have healthy and less processed food,” Dr. Chan elaborated.
Assessment of maternal junk food intake during peri-pregnancy and childhood
Modern Western diets frequently include ultra-processed foods – such as packaged baked goods and snacks, fizzy drinks, and sugary cereals – which are linked to adult weight increase. The relationship between parental consumption of highly processed meals and offspring weight is, however, unclear across generations, the researchers note.
Hence, they set out to determine whether eating ultra-processed foods during peri-pregnancy and while raising children increased the risk of being overweight or having obesity among children and teens.
The study team assessed 14,553 mothers and their 19,958 children from the Growing Up Today Study (GUTS I and II) and Nurses’ Health Study II (NHS II) in the United States. Males accounted for 45% of the children in the study, and the children’s ages ranged from 7 to 17 years.
The NHS II is a continuing investigation following the lifestyle and health choices of over 100,000 female registered nurses in the United States in 1989, while the GUTS I involved about 17,000 children of the nurses in the NHS II. Participants in GUTS I filled out an initial lifestyle and health survey and were evaluated annually between 1997 and 2001 and every 2 years thereafter.
Roughly 11,000 children from the NHS II were included in the GUTS II. The children were further evaluated in 2006, 2008, and 2011, as well as every 2 years thereafter.
Participants were followed until the children reached 18 years of age or experienced obesity and overweight onset. A subcohort consisted of 2,925 mother-child pairs with data on peri-pregnancy eating patterns.
Maternal intake of ultra-processed foods while raising children was linked with obesity or overweight in children. Moreover, compared with the lowest consumption cohort (3.4 servings/day), there was a 26% greater risk for the greatest maternal ultra-processed food intake cohort (12.1 servings/day) after adjusting for child’s sedentary time, ultra-processed food intake, physical activity, and established maternal risk factors.
Even though rates were elevated, ultra-processed food intake during pregnancy was not significantly linked to a higher risk of obesity or overweight in children (P for trend = .07).
Sex, birth weight, age, gestational age, or maternal body weight had no effect on these correlations either.
The study’s limitations include the fact that some of the children in the pairs were lost during follow-up; there may have been data misreporting, as the weight and diet measures were provided via self-reported questionnaires; and potential residual confounding given the observational study design, the researchers note.
Other limitations include that the mothers involved in the study came from similar socioeconomic backgrounds, had similar personal and familial educational statuses, and were primarily White, which limits the generalizability of these data to other ethnic groups, the authors add.
“Further studies are warranted to investigate specific biological mechanisms and socioeconomic determinants underlying the observed associations between maternal ultra-processed food intake and offspring overweight and obesity,” the researchers conclude.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: Weekly cases dropped by 57% in September
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.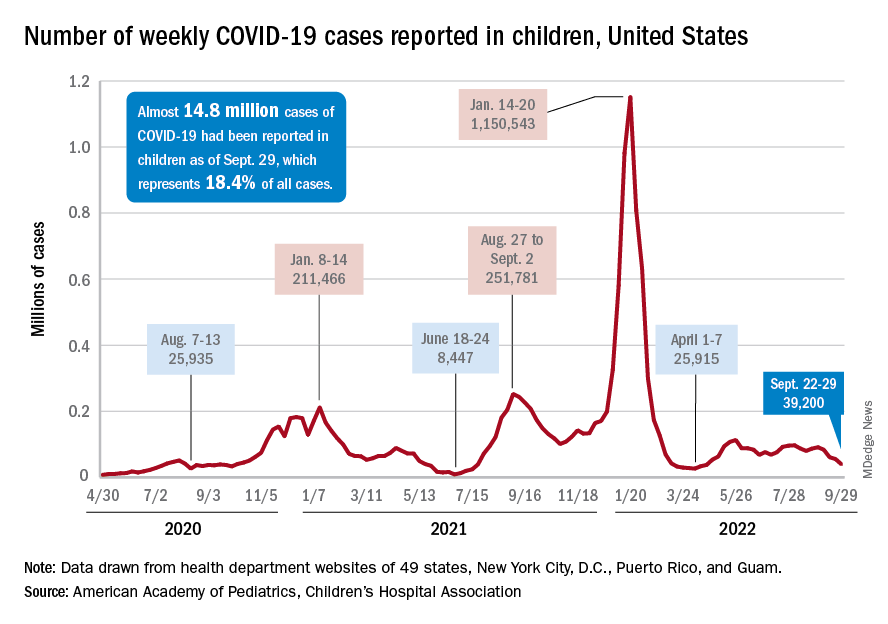
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.
The last full week of September brought a 4th straight week of declines in the number of new COVID-19 cases reported among children, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
, with the month of September bringing a decline of about 57% in reported cases for the 45 states and territories that are still releasing pediatric COVID data on their health department websites, the AAP and CHA said in their joint weekly report.
New cases dropped in all four regions after the Northeast and West had seen increases the previous week, and the distribution of cases for the latest week was fairly even, with the Midwest and Northeast right around 10,000, the South slightly over 10,000, and the West under 10,000 by about the same amount. At the state level, the largest increases – around 1.5% – over the last 2 weeks occurred in Kentucky and Nevada, the AAP/CHA data show.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children was almost 14.8 million as of Sept. 29, with children representing 18.4% of all cases since the pandemic began, the AAP and CHA said. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is able to use a uniform age range of 0-17 years, puts total cases at 15.2 million and the proportion of child cases at 17.4%. Total deaths in children from COVID as of Oct. 3 were 1,745, the CDC reported.
New vaccinations, in the meantime, are being added in numbers only slightly higher than new cases. Initial COVID vaccinations for the week of Sept. 22-28 were about 44,000 for children under 5 years of age (down from 51,000 the week before), 24,000 for children aged 5-11 years (down from 28,000), and 17,000 for those aged 12-17 (down from 18,000), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination report.
To look at it another way, the total proportion of children under 5 years of age who had received at least one dose of COVID vaccine as of Sept. 28 was 6.5%, compared with 6.4% on Sept. 21, while the corresponding rates for children aged 5-11 and 12-17 were unchanged at 38.5% and 70.9%. The 12- to 17-year-olds, in fact, have been stuck at 70.9% since Sept. 13, according to data from the CDC.
In a recent study published in Vaccine, investigators attributed the discrepancies between age groups at least partly to the acceptance of misinformation about vaccine safety in general and the COVID-19 vaccines in particular.
“All of the misconceptions we studied focused in one way or another on the safety of vaccination, and that explains why people’s misbeliefs about vaccinating kids are so highly related to their concerns about vaccines in general. Unfortunately, those concerns weigh even more heavily when adults consider vaccinating children,” lead author Dan Romer, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a written statement.
Childhood peanut allergy linked with other legume allergies
, a retrospective study reports.
“Among children allergic to peanut, at least two-thirds were sensitized to one other legume, and legume allergy was diagnosed in one-quarter of the sensitized patients,” senior study author Amandine Divaret-Chauveau, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nancy in Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy, France, and colleagues reported in Pediatric Allergy and Immunology.
People worldwide are eating more legumes these days, the authors noted. High in protein, low in unsaturated fats, with low production costs, legumes are important components of increasingly vegetarian, healthy, sustainable diets.
Food allergens are the most common childhood triggers of allergic reactions. Among children in France, legumes cause 14.6% of food-related anaphylactic reactions, with peanut as the main allergen, they added.
Dr. Divaret-Chauveau and colleagues assessed the prevalence and relevance of sensitization to legumes among all children and adolescents aged 1-17 years who had peanut allergy and had been admitted to one academic pediatric allergy department over roughly 3 years, beginning in early 2017. For the 195 study participants, peanut allergy had been confirmed, and they had been documented to have consumed or to have sensitization to at least one nonpeanut legume; 69.7% were boys.
The researchers analyzed data on consumption history, skin-prick tests, specific immunoglobulin E status, prior allergic reactions, and oral food challenges for each legume. They found the following:
Among the 195 children with peanut allergy, 98.4% had at least one other atopic disease.
Of the 195 children with peanut allergy, 122 (63.9%) were sensitized to at least one other legume. Of these 122 children, 66.3% were sensitized to fenugreek, 42.2% to lentil, 39.9% to soy, and 34.2% to lupin.
Allergy to one or more legumes was confirmed for 27.9% of the 122 sensitized children, including 4.9% who had multiple legume allergies. Lentil, lupin, and pea were the main allergens.
Of the 118 children also having a nonlegume food allergy, the main food allergens were egg (57.6%), cow’s milk (33.0%), cashew (39.0%), pistachio (23.7%), and hazelnut (30.5%).
50% of allergic reactions to nonpeanut legumes were severe, often showing as asthma. Atopic comorbidities, including asthma, in most participants may have contributed to the severity of allergic reactions, the authors noted.
Allergy awareness needs to grow with plant-based diets
“The high prevalence of legume sensitization reported in our study highlights the need to explore legume consumption in children with PA [peanut allergy], and the need to investigate sensitization in the absence of consumption,” they added.
Jodi A. Shroba, MSN, APRN, CPNP, coordinator for the Food Allergy Program at Children’s Mercy Kansas City (Mo.), said in an interview that few data are available in the literature regarding allergies to legumes other than peanut.
“It was interesting that these authors found such a high legume sensitization in their peanut-allergic patients,” Dr. Shroba, who was not involved in the study, said by email. “As more people are starting to eat plant-based diets, it is important that we better understand their allergenicity and cross-reactivity so we can better help guide patient management and education.”
Deborah Albright, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh, agreed.
“As plant-based protein consumption broadens worldwide, awareness of the potential for cross-reactivity and co-allergy amongst legumes will become increasingly important,” she said in a comment.
“However, positive allergy tests do not reliably correlate with true food allergy; therefore, the diagnosis of legume co-allergy should be confirmed by the individual patient’s history, a formal food challenge, or both,” advised Dr. Albright. She was not involved in the study.
“Cross-sensitization to other legumes in patients with a single legume allergy is common; however, true clinical reactivity is often not present,” she added. “Also, legume allergy test sensitization rates and objective reactivity on food challenge can vary by region, depending on diet and pollen aeroallergen exposure.
“Systematic exploration of tolerance versus co-allergy to other legumes should be considered in patients allergic to peanut or other legumes,” Dr. Albright said.
The authors recommend further research and registry data collection of legume anaphylaxis.
Details regarding funding for the study were not provided. The authors, Dr. Shroba, and Dr. Albright report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a retrospective study reports.
“Among children allergic to peanut, at least two-thirds were sensitized to one other legume, and legume allergy was diagnosed in one-quarter of the sensitized patients,” senior study author Amandine Divaret-Chauveau, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nancy in Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy, France, and colleagues reported in Pediatric Allergy and Immunology.
People worldwide are eating more legumes these days, the authors noted. High in protein, low in unsaturated fats, with low production costs, legumes are important components of increasingly vegetarian, healthy, sustainable diets.
Food allergens are the most common childhood triggers of allergic reactions. Among children in France, legumes cause 14.6% of food-related anaphylactic reactions, with peanut as the main allergen, they added.
Dr. Divaret-Chauveau and colleagues assessed the prevalence and relevance of sensitization to legumes among all children and adolescents aged 1-17 years who had peanut allergy and had been admitted to one academic pediatric allergy department over roughly 3 years, beginning in early 2017. For the 195 study participants, peanut allergy had been confirmed, and they had been documented to have consumed or to have sensitization to at least one nonpeanut legume; 69.7% were boys.
The researchers analyzed data on consumption history, skin-prick tests, specific immunoglobulin E status, prior allergic reactions, and oral food challenges for each legume. They found the following:
Among the 195 children with peanut allergy, 98.4% had at least one other atopic disease.
Of the 195 children with peanut allergy, 122 (63.9%) were sensitized to at least one other legume. Of these 122 children, 66.3% were sensitized to fenugreek, 42.2% to lentil, 39.9% to soy, and 34.2% to lupin.
Allergy to one or more legumes was confirmed for 27.9% of the 122 sensitized children, including 4.9% who had multiple legume allergies. Lentil, lupin, and pea were the main allergens.
Of the 118 children also having a nonlegume food allergy, the main food allergens were egg (57.6%), cow’s milk (33.0%), cashew (39.0%), pistachio (23.7%), and hazelnut (30.5%).
50% of allergic reactions to nonpeanut legumes were severe, often showing as asthma. Atopic comorbidities, including asthma, in most participants may have contributed to the severity of allergic reactions, the authors noted.
Allergy awareness needs to grow with plant-based diets
“The high prevalence of legume sensitization reported in our study highlights the need to explore legume consumption in children with PA [peanut allergy], and the need to investigate sensitization in the absence of consumption,” they added.
Jodi A. Shroba, MSN, APRN, CPNP, coordinator for the Food Allergy Program at Children’s Mercy Kansas City (Mo.), said in an interview that few data are available in the literature regarding allergies to legumes other than peanut.
“It was interesting that these authors found such a high legume sensitization in their peanut-allergic patients,” Dr. Shroba, who was not involved in the study, said by email. “As more people are starting to eat plant-based diets, it is important that we better understand their allergenicity and cross-reactivity so we can better help guide patient management and education.”
Deborah Albright, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh, agreed.
“As plant-based protein consumption broadens worldwide, awareness of the potential for cross-reactivity and co-allergy amongst legumes will become increasingly important,” she said in a comment.
“However, positive allergy tests do not reliably correlate with true food allergy; therefore, the diagnosis of legume co-allergy should be confirmed by the individual patient’s history, a formal food challenge, or both,” advised Dr. Albright. She was not involved in the study.
“Cross-sensitization to other legumes in patients with a single legume allergy is common; however, true clinical reactivity is often not present,” she added. “Also, legume allergy test sensitization rates and objective reactivity on food challenge can vary by region, depending on diet and pollen aeroallergen exposure.
“Systematic exploration of tolerance versus co-allergy to other legumes should be considered in patients allergic to peanut or other legumes,” Dr. Albright said.
The authors recommend further research and registry data collection of legume anaphylaxis.
Details regarding funding for the study were not provided. The authors, Dr. Shroba, and Dr. Albright report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a retrospective study reports.
“Among children allergic to peanut, at least two-thirds were sensitized to one other legume, and legume allergy was diagnosed in one-quarter of the sensitized patients,” senior study author Amandine Divaret-Chauveau, MD, of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nancy in Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy, France, and colleagues reported in Pediatric Allergy and Immunology.
People worldwide are eating more legumes these days, the authors noted. High in protein, low in unsaturated fats, with low production costs, legumes are important components of increasingly vegetarian, healthy, sustainable diets.
Food allergens are the most common childhood triggers of allergic reactions. Among children in France, legumes cause 14.6% of food-related anaphylactic reactions, with peanut as the main allergen, they added.
Dr. Divaret-Chauveau and colleagues assessed the prevalence and relevance of sensitization to legumes among all children and adolescents aged 1-17 years who had peanut allergy and had been admitted to one academic pediatric allergy department over roughly 3 years, beginning in early 2017. For the 195 study participants, peanut allergy had been confirmed, and they had been documented to have consumed or to have sensitization to at least one nonpeanut legume; 69.7% were boys.
The researchers analyzed data on consumption history, skin-prick tests, specific immunoglobulin E status, prior allergic reactions, and oral food challenges for each legume. They found the following:
Among the 195 children with peanut allergy, 98.4% had at least one other atopic disease.
Of the 195 children with peanut allergy, 122 (63.9%) were sensitized to at least one other legume. Of these 122 children, 66.3% were sensitized to fenugreek, 42.2% to lentil, 39.9% to soy, and 34.2% to lupin.
Allergy to one or more legumes was confirmed for 27.9% of the 122 sensitized children, including 4.9% who had multiple legume allergies. Lentil, lupin, and pea were the main allergens.
Of the 118 children also having a nonlegume food allergy, the main food allergens were egg (57.6%), cow’s milk (33.0%), cashew (39.0%), pistachio (23.7%), and hazelnut (30.5%).
50% of allergic reactions to nonpeanut legumes were severe, often showing as asthma. Atopic comorbidities, including asthma, in most participants may have contributed to the severity of allergic reactions, the authors noted.
Allergy awareness needs to grow with plant-based diets
“The high prevalence of legume sensitization reported in our study highlights the need to explore legume consumption in children with PA [peanut allergy], and the need to investigate sensitization in the absence of consumption,” they added.
Jodi A. Shroba, MSN, APRN, CPNP, coordinator for the Food Allergy Program at Children’s Mercy Kansas City (Mo.), said in an interview that few data are available in the literature regarding allergies to legumes other than peanut.
“It was interesting that these authors found such a high legume sensitization in their peanut-allergic patients,” Dr. Shroba, who was not involved in the study, said by email. “As more people are starting to eat plant-based diets, it is important that we better understand their allergenicity and cross-reactivity so we can better help guide patient management and education.”
Deborah Albright, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Pittsburgh, agreed.
“As plant-based protein consumption broadens worldwide, awareness of the potential for cross-reactivity and co-allergy amongst legumes will become increasingly important,” she said in a comment.
“However, positive allergy tests do not reliably correlate with true food allergy; therefore, the diagnosis of legume co-allergy should be confirmed by the individual patient’s history, a formal food challenge, or both,” advised Dr. Albright. She was not involved in the study.
“Cross-sensitization to other legumes in patients with a single legume allergy is common; however, true clinical reactivity is often not present,” she added. “Also, legume allergy test sensitization rates and objective reactivity on food challenge can vary by region, depending on diet and pollen aeroallergen exposure.
“Systematic exploration of tolerance versus co-allergy to other legumes should be considered in patients allergic to peanut or other legumes,” Dr. Albright said.
The authors recommend further research and registry data collection of legume anaphylaxis.
Details regarding funding for the study were not provided. The authors, Dr. Shroba, and Dr. Albright report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PEDIATRIC ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY