User login
High-Volume Burn Resuscitation Increases Neurologic Risk
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-center review of 5176 patients with burn injuries who were admitted to a verified American Burn Association center (2003-2017); 622 of them underwent head CT within 96 hours of admission, and 83 showed intracranial abnormalities.
- Of 42 patients (mean age, 49.7 years; 80.5% men) who were admitted within 24 hours of burn, 30 patients received < 200 mL/kg and 11 received > 200 mL/kg of total resuscitation fluids, with a median total body surface area (TBSA) of 20.0.
- The primary outcome assessed was the worsening of neurologic findings on imaging related to the volume of the resuscitation fluid administered; the secondary outcomes were the incidence of new or worsening intracranial abnormalities, including hemorrhage, edema, ischemia, or infarction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Neurologic findings worsened in 47.6% patients receiving < 200 mL/kg of fluid resuscitation and 85.7% of those receiving > 200 mL/kg (P =.064).
- Repeat imaging was performed in 21 (70.0%) patients receiving < 200 mL/kg and 7 (63.6%) patients receiving > 200 mL/kg of resuscitation who underwent follow-up imaging.
- The median TBSA was 16.5 in the < 200 mL/kg group and 53.2 in the > 200 mL/kg group (P <.001).
- Intracranial abnormalities were found in 31.3% patients with hemorrhage, 18.8% with worsening edema, and 43.8% with ischemia or infarction.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients who received over 200 mL/kg of resuscitation had an increased progression of intracranial abnormalities when compared with patients receiving less volume resuscitation,” the authors wrote. “Neurologic changes prompting imaging in burn patients may be undetectable, and our study further highlights the need for routine evaluation with neurologic imaging when undergoing large-volume resuscitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Connor L. Kenney, MD, Brooke Army Medical Center, San Antonio, and was published online on November 07, 2024, in the Journal of Surgical Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included a small patient sample and unclear guidelines for obtaining head CT scans, making it difficult to distinguish between trauma-related brain changes and disease progression. Additionally, the study lacked data on hypotensive episodes and long-term neurologic outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-center review of 5176 patients with burn injuries who were admitted to a verified American Burn Association center (2003-2017); 622 of them underwent head CT within 96 hours of admission, and 83 showed intracranial abnormalities.
- Of 42 patients (mean age, 49.7 years; 80.5% men) who were admitted within 24 hours of burn, 30 patients received < 200 mL/kg and 11 received > 200 mL/kg of total resuscitation fluids, with a median total body surface area (TBSA) of 20.0.
- The primary outcome assessed was the worsening of neurologic findings on imaging related to the volume of the resuscitation fluid administered; the secondary outcomes were the incidence of new or worsening intracranial abnormalities, including hemorrhage, edema, ischemia, or infarction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Neurologic findings worsened in 47.6% patients receiving < 200 mL/kg of fluid resuscitation and 85.7% of those receiving > 200 mL/kg (P =.064).
- Repeat imaging was performed in 21 (70.0%) patients receiving < 200 mL/kg and 7 (63.6%) patients receiving > 200 mL/kg of resuscitation who underwent follow-up imaging.
- The median TBSA was 16.5 in the < 200 mL/kg group and 53.2 in the > 200 mL/kg group (P <.001).
- Intracranial abnormalities were found in 31.3% patients with hemorrhage, 18.8% with worsening edema, and 43.8% with ischemia or infarction.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients who received over 200 mL/kg of resuscitation had an increased progression of intracranial abnormalities when compared with patients receiving less volume resuscitation,” the authors wrote. “Neurologic changes prompting imaging in burn patients may be undetectable, and our study further highlights the need for routine evaluation with neurologic imaging when undergoing large-volume resuscitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Connor L. Kenney, MD, Brooke Army Medical Center, San Antonio, and was published online on November 07, 2024, in the Journal of Surgical Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included a small patient sample and unclear guidelines for obtaining head CT scans, making it difficult to distinguish between trauma-related brain changes and disease progression. Additionally, the study lacked data on hypotensive episodes and long-term neurologic outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-center review of 5176 patients with burn injuries who were admitted to a verified American Burn Association center (2003-2017); 622 of them underwent head CT within 96 hours of admission, and 83 showed intracranial abnormalities.
- Of 42 patients (mean age, 49.7 years; 80.5% men) who were admitted within 24 hours of burn, 30 patients received < 200 mL/kg and 11 received > 200 mL/kg of total resuscitation fluids, with a median total body surface area (TBSA) of 20.0.
- The primary outcome assessed was the worsening of neurologic findings on imaging related to the volume of the resuscitation fluid administered; the secondary outcomes were the incidence of new or worsening intracranial abnormalities, including hemorrhage, edema, ischemia, or infarction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Neurologic findings worsened in 47.6% patients receiving < 200 mL/kg of fluid resuscitation and 85.7% of those receiving > 200 mL/kg (P =.064).
- Repeat imaging was performed in 21 (70.0%) patients receiving < 200 mL/kg and 7 (63.6%) patients receiving > 200 mL/kg of resuscitation who underwent follow-up imaging.
- The median TBSA was 16.5 in the < 200 mL/kg group and 53.2 in the > 200 mL/kg group (P <.001).
- Intracranial abnormalities were found in 31.3% patients with hemorrhage, 18.8% with worsening edema, and 43.8% with ischemia or infarction.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients who received over 200 mL/kg of resuscitation had an increased progression of intracranial abnormalities when compared with patients receiving less volume resuscitation,” the authors wrote. “Neurologic changes prompting imaging in burn patients may be undetectable, and our study further highlights the need for routine evaluation with neurologic imaging when undergoing large-volume resuscitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Connor L. Kenney, MD, Brooke Army Medical Center, San Antonio, and was published online on November 07, 2024, in the Journal of Surgical Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included a small patient sample and unclear guidelines for obtaining head CT scans, making it difficult to distinguish between trauma-related brain changes and disease progression. Additionally, the study lacked data on hypotensive episodes and long-term neurologic outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any specific funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Freezing the Pain: A New Way to Treat Rib Fractures
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Hi. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical advisor for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Joining me today to discuss a novel way to treat pain related to conditions such as rib fractures and burns is Dr. Sergey Motov, an emergency physician with expertise in pain management and research director in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York.
Also joining me is Dr. Gary Schwartz, vice chair of pain and anesthesiology at Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz is board certified in anesthesiology and interventional pain management.
Welcome, Sergey and Gary.
Sergey M. Motov, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Gary S. Schwartz, MD: Thank you, Robert.
Traditional Approaches to Pain Relief
Glatter: It’s a pleasure to have you both. Sergey, we were chatting earlier this week and you had mentioned a novel approach to treating a common condition we encounter in the emergency department — rib fractures.
As we all know, they’re very painful and can lead to pulmonary complications, including atelectasis, pneumonia due to splinting and lack of proper pain management, along with the use of incentive spirometry.
Sergey and Gary, can you describe traditional approaches to alleviating the pain associated with rib fractures? What do we typically use? Then we’ll get to some novel treatments that we’re here to discuss.
Motov: I’m going to use the emergency medicine approach to rib fractures. As you pointed out, pain relief is of utmost importance.
With the advent and acquiring of the amazing technique of interventional pain management, physicians, for the most part, are very astute about providing nerve blocks to alleviate pain, at least in immediate need. I’m talking about the relatively short term, 1-5 hours, in the emergency department.
Primarily, we focus on fascial plane blocks such as serratus anterior plane block. Traditionally, ED physicians don’t use much of the intercostal blocks. At times, we can direct the spinal block to cover the lateral aspect of the chest wall.
As part of the multimodal approach, we can use NSAIDs. If there’s a contraindication, we can use opioids. There are some data to support consideration of using topical formularies such as a lidocaine patch, but they are somewhat conflicting.
The question becomes what you’re going to send a patient home with. Again, traditional teaching is either opioids, immediate release with a short course, plus or minus NSAIDs, plus or minus acetaminophen.
The issue with rib fractures is that, while we can manage immediate and super-acute pain presentation in the ED and then discharge up to 24-72 hours, what happens afterwards is very challenging. Acute intercostal neuralgia related to traumatic rib fractures is semi-manageable, but if it’s inappropriately treated, it has a great tendency to transform into chronic intercostal neuralgia. It contributes a great deal of disability and morbidity.
Several years ago, I came across an entity called cryoneurolysis (cryo ─ cold temperature; neurolysis ─ freezing the nerve). I’m excited to be here today because Gary is the one who’s pioneering and championing this technique in our institution.
Cryoneurolysis: Mechanisms of Action and Benefits
Glatter: Gary, what do you see as the main role for this procedure at this time?
Schwartz: As Sergey alluded to, the traditional approach of opiates has side effects (ie, constipation, addiction, and tolerance). Unfortunately, many of these rib fractures occur in older patients. They come in anticoagulated, so they can’t have NSAIDs.
Sergey and his team in the ER have been pioneers in giving short-acting local anesthetic blocks that could last anywhere from 12 to 24 hours. There are long-acting local anesthetics that we can get out to 72 hours.
Unfortunately, these rib fractures and the pain associated with them, in addition to the intercostal neuralgia, could take weeks to heal. That’s where cryoneurolysis comes in. We’re all used to ice or cold temperature. For example, if your child gets an ear piercing, they put some ice on their earlobe beforehand, it numbs it up, and they don’t feel pain. It allows them to get their ears pierced without pain, but it’s short-acting.
What we have now are handheld devices with tips about as long as a pen, 3.5 inches, that allow you to go down precisely to these intercostal nerves that innervate the ribs and give a cold lesion that freezes these nerves.
The benefit of it is it’s not permanent like cryoablation, like we’ve seen for tumor necrosis, which destroys outside tissues. It’s really a small lesion, about 16 mm x 8 mm, which is enough to engulf the nerve and pretty much stun it.
It causes axonotmesis, but the epineurium, the endoneurium, and the perineurium — the inner workings of the nerve — stay intact, so it regrows. It just destroys the myelin sheath and the axon.
Glatter: You’re creating a scarring effect; is that what you’re saying? In other words, you’re doing a cold-temperature freeze and stunning the nerve. My question is, does it regrow? Is this a permanent type of injury?
Schwartz: With Wallerian degeneration, nerves do regrow after injuries.
Unfortunately, as you two probably see in the ER for big traumas, where the nerve is transected, those unfortunately do not grow back. This is considered a grade 2 lesion, so the Wallerian degeneration recurs. The nerves grow, depending on the literature you look at, about 0.5-2 mm per day.
This intervention gives us at least 3 months of relief for the patient, which is in the time frame where the rib fracture will heal, hopefully with no damage to the nerve from the fracture, and they go on living their life without having to take opiates or having to stop their anticoagulation.
Because prior to this, when I was a pain fellow, we used to put epidurals in many of these patients. The problem with that is patients can’t go home, and if they’re anticoagulated, you can’t place it because of the risk of a spinal hematoma.
Potential Use in Ventilation Weaning
Glatter: This is something we encounter daily, and certainly for those patients who have more numerous rib fractures or flail chest, this could be even more devastating, as well as for those who get intubated.
Do you see any role, in terms of ventilator weaning, in using this technique specifically in the ICU setting?
Schwartz: That’s an interesting concept. I’m not so sure about ventilator weaning, but we’ve used this in the hospital for rib fractures from traumas where patients had such severe fractures and had to go to the operating room for rib plating, and did necessitate an epidural. We’ve used this to discontinue their epidural and transition them to get the patient home.
I think that is part of the care, not only in the ER but in the hospital as well. We need to treat the patients, but we also have to have a transition plan to get them out of the hospital. Not that we don’t want to treat our patients, but we have to have a plan to get them home. I’m guessing that might be an interesting stage of research in the future if it does help with weaning from a ventilator.
Glatter: There are some studies out there suggesting that there can be some utility in terms of ventilator weaning using this technique. The ability of this to change how we manage pain is just incredible.
Sergey, do you feel that this is something that you could implement in your ED with your patients in the near future?
Motov: Definitely. I have personally been a very big proponent of it. I’m the theoreticist because I’ve covered a great deal of literature, and now having Gary and his team doing this in our institution, it’s a shame not to capitalize on it. I’m slowly moving toward figuring out the way of collaborative effort to have Gary and his team help my team and our colleagues, bring him on board, and maybe broaden the integration for pain management.
I believe, as Gary emphasized, that geriatric traumatic pain injuries are critically important due to the presence of comorbidities, potential drug interactions, and the challenges of managing these factors effectively.
There is one thing I want to bring up, and Gary, please support me on it. The procedure itself is fascinating because it provides long-term pain relief and reduces morbidity. I wouldn’t say mortality, just reduced morbidity. However, we need to be very conscious of the fact that this blockade, this ice-ball freezing of the nerve, can be detrimental to motor nerves. If your whole goal or idea of faster recovery after postoperative knee or hip replacements, or any traumatic lower- or upper-extremity surgery, includes blockade of motor nerves, it’s not going to be beneficial.
I believe the primary therapeutic application of this technology lies in targeting sensory nerves. For instance, intercostal nerves could be a focus in cases of rib fractures. Additionally, this approach shows promise for treating burns, particularly in the lower and upper extremities. Specifically, targeting nerves such as the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve or the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve could effectively neutralize pain and provide significant relief for weeks, if not months.
Based on additional predilection to what particular indications would be, maybe occipital headache with cervicalgia, occipital nerve block — it’s a sensory block — can benefit from it. Slowly but surely, there’s a slew of painful syndromes for which cryoneurolysis might have a great deal of use in the emergency department.
Cryoneurolysis for Other Pain Syndromes
Glatter: Gary, I’ll let you expand upon additional uses that you see. You did mention one on our chat earlier this week, which was postmastectomy pain syndrome with the intercostal brachial nerve. That’s a very compelling area of interest, certainly for the number of women that go through mastectomies or lumpectomies and that have axillary dissection or nerve injury.
Schwartz: Post-mastectomy is one way you could use this device and technology to attack painful syndromes, such as postmastectomy syndrome. Mastectomies are one of the most common surgeries performed in the United States, but I believe it’s a top three for post-op chronic pain, which we don’t normally think of.
There was a great study by a team in San Diego where they did intercostal brachial and intercostal nerve blocks on multiple nerves, and they decreased pain up to 3 months after the surgery and decreased opiates.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s approved for any peripheral nerve in the body. We’ve used it in our pain office for occipital neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, chronic rib pain after fractures, and surgery. Some of the most common uses are for superficial, sensory, genicular nerves, the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, the anterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous.
You could numb the skin preoperatively before a painful surgery, such as a total knee replacement — or as we like to call it, a total knee arthroplasty — to reduce opiates, improve function, and decrease length of stay. You could attack any sensory nerve.
We’ve utilized that already in our private practice. We’re trying to transition into the hospital to have everyone who gets a knee arthroplasty have this technology to decrease opiates, improve function, and recover faster.
This is quite interesting and motivating for me because when I first started, we had a femoral catheter to block the motor femoral nerve or an epidural. Patients were in the hospital for 3-5 days with the CPM [continuous passive motion] machine, which is like a medieval torture device that you might see in Mad Max — where you’re kind of moving the patient’s knee back and forth after surgery, and they were miserable, taking patient-controlled analgesia and high-dose opiates. Now, we’re freezing these nerves beforehand, doing our nerve blocks in the operating room with long-acting local anesthetic, and patients are going home the same day with minimal or even no opiates sometimes.
Implications for Patient Mobility and DVT Risk
Glatter: You’re getting up to 3 months of relief in that setting, doing it as you described?
Schwartz: Yes, up to 3 months of relief, which is huge, because most patients recovering from a knee arthroplasty, at about the 6- to 8-week mark, have improved range of motion, they have their 110° flexion, they have their extension, and they’re getting back to their normal life.
You cover the whole postoperative rehab, where patients don’t have to get recurring refills, they can participate in physical therapy. As you both know, part of the recovery process is to be able to interact with family and friends without being sleepy, angry, and in pain all day, so they can get back to their normal function.
Glatter: In terms of this procedure, would there be any increase in deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in relation to this, by chance?
Schwartz: Actually, there’s less of a risk of DVT because patients have less pain, so they can get up and move faster. Some of my surgical colleagues who have implemented this in their practice have gotten away from using the stronger anticoagulation like Xarelto (rivaroxaban) or Coumadin (warfarin), and they just give them baby aspirin postoperatively because their patients are going home the same day and walking. It’s probably safer for patients. There’s no research out there yet to show that, but we all know that the more you move and the more you’re not lying around, the lower the risk of having a DVT or a blood clot.
There are studies showing that there’s no damage to blood vessels, other than if you stick it with the needle, because the nitrogen gas in this that allows the ice ball to form does not get injected into the body. It’s all resorbed in the machine. The only thing the body sees is this ice ball, which would melt if you hit a blood vessel because we should be 98 °F and the ice ball is -88 °F. There’s no gas injected into the body either, so there’s no risk of a gas embolism.
Training and Implementation
Glatter: I was going to ask you about air emboli, and you perfectly led right into that.
In terms of training requirements, currently, what do you envision as a way we can train residents and fellows to do this? Is this currently something being considered in curriculum?
Schwartz: We are going to train our residents first. I’m training the attendings. Before you use this technology, you should have a basic understanding of ultrasound, how to use the device, the different settings, and what the risks are for each procedure you’re doing.
Let’s say, as Sergey alluded to, with an intercostal nerve block, you could have a pneumothorax. You have to be able to identify the rib, where the nerve should lie, the innermost intercostal muscle you could see on the newer ultrasounds, and where the pleura lies. People should start with just basic ultrasound training and then advance to a typical intercostal nerve block.
Once you master that, the procedure with the device is not much different than an intercostal nerve block, except you have a handheld device and the needle is just as long as a pen, 3.5 inches.
If you could do a nerve block with a spinal needle, you could do the procedure. Once people have the technical ultrasound skills, then they can advance to needle-based procedures, and once you have that training, you could use this procedure safely and efficaciously.
Glatter: Sergey, do you see this as requiring quite a bit of time and training in your program?
Motov: I mentioned earlier, before we started, that with the advent of ultrasound-guided nerve blocks, the vast majority of physicians are becoming very comfortable and fairly effective with maneuvering a needle and the ultrasound probe. The learning curve is essentially the same. The only difference is, as Gary pointed out, some of the nerves could be new to ED folks, but the technique, the understanding, the visualization, and the knowledge of anatomy are essentially the same.
As he pointed out, if you can use it with a spinal needle and local anesthetic, the procedure becomes exactly the same. It’s a slightly different drug and a different needle, and instead of local anesthetic, you’re using a gas at cold temperatures, and that’s pretty much it.
Glatter: Are there any other barriers to adoption in terms of cost, the device itself, or the companies that manufacture these handheld devices?
Schwartz: There’s always cost associated with the new device, needles, and the gas. Thankfully, they’re covered by Medicare, Medicaid, and most commercial insurances in the current framework, which I think is important. I think Congress is seeing the benefits of opiate sparing that Sergey helped lead in the ED.
At AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and Maimonides, we’re doing this intraoperatively as well. I think the government is seeing that. There was a NOPAIN Act passed in 2023 that, starting January 1, 2025, will allow certain approved companies, devices, and medications to have to be repaid by CMS, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, in the hospital setting and in the outpatient departments. In the inpatient surgical stays, we could have less opiates. I think that’s important. It is reimbursed now. Obviously, there is a cost associated.
The other benefit of this procedure and these techniques is, as Sergey alluded to, it’s done under ultrasound. The way we all learn procedures, whether it be central lines or chest tubes, is the blind technique. There is no good way to practice. In my interventional pain practice, many of our original techniques were done under fluoroscopy, and we don’t want to get extra radiation during practice.
The benefit of ultrasound and the advent of handheld ultrasound devices is that we can practice scanning and techniques on ourselves and on colleagues, without the fear of radiation. Other than the fact that we need to shower after the surgical lube is on from the scanning gel, you could practice your techniques in a safe way without harming a patient or yourself.
Future Directions in Pain Management Techniques
Glatter: Absolutely. Do you see any role for possibly stellate ganglion blocks, which are a bit riskier and have greater depth?
Schwartz: People are looking at different studies because, again, it’s a needle-based technology. We do many stellate ganglion blocks. I have not done it for this procedure yet, but that’s the next step of what I try. Under ultrasound, we could see the longus colli muscle and we could see the carotid artery. Obviously, we don’t see the ganglion per se, but anatomically, we know where it lies. You could drop a couple of lesions on there and give a theoretic prolonged sympathetic block, which might help with symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome.
I know there are some studies that have looked at stellate ganglion blocks for long-COVID symptoms. Unfortunately, it looks like we’re back in another wave right now. I think that’s the next step of the technology.
Glatter: Getting back to the emergency department, burns are something we see commonly — such painful conditions. This is something that could really provide significant relief, especially with burns that involve the chest wall, not just extremity burns.
Motov: I agree with you. Burns would be a very good indication to utilize this technique. Just listening to you and Gary, another thing that pops into my head, which may have actually some science behind it, would be any traumatic amputations done in a civilian environment or even in the military in a combat situation.
A person who has either an upper or lower extremity that is partially or completely severed or amputated, and the pain — God knows how bad it is — if not properly treated, it is going to be a very long recovery. That’s, I believe, another percutaneous condition where cryoneurolysis will be very beneficial to freeze those nerves, allowing patients to recover through rehab acute care, acute phases, rehabilitation, and move on with their lives.
Glatter: In the setting of a painful distal radius fracture, a femur fracture, and things of that nature, Gary, do you see this as a modality in conjunction with emergency medicine colleagues as being something that’s going to really become an important part of our armamentarium?
Schwartz: I do think it’s going to become more important in the future, as there are more studies to show what nerves you could block with cryoneurolysis in the longer term. I think you might see people start using these for fractures, especially for fractures that are not operable at the time or if a patient needs to be optimized prior to surgery.
As Sergey alluded to, it’s optimal in burns. People have been looking for relief of stump pain or postamputation pain. There’s a big researcher in Canada who’s been looking at pain with spasticity for people with cerebral palsy and poststroke issues, where they can’t move and they have pain moving an extremity after these conditions. We’re at just the tip of the iceberg as to where people are going to use this hand-held technology in the future.
Glatter: We use long-acting nerve blocks for hip fractures already in the emergency department. Why not employ this technique, which would have longer effects and limit opiate use?
Schwartz: It might even help a certain subset of the population, at least in Brooklyn, where we have a large elderly population. I believe it’s one of the oldest boroughs in the country, and definitely in New York.
There are some people that go on to surgery just because they might be bedbound, but it’s the pain that is dictating their surgical procedure, not that they’re ever going to walk again.
It’s maybe the next step to look for. If you could block this nerve for 3 months or longer, they’re still going to be bedbound, but maybe you could avoid a surgical procedure that carries its own morbidity and mortality, which I see a big interest in in the future.
Glatter: Absolutely. The idea behind treating spasticity is very important from an occupational therapy standpoint — eating, activities of daily living — just the basics.
Getting someone’s fingers released, being able to move their legs again, and getting them out of contracture states, I think, has a huge role.
Schwartz: Not only for the patient but also for the caregivers. For many of these patients, if they’re contracted fully and the pain from the spasticity is preventing their caregivers from moving them, it’s difficult to put on a shirt, pants, and so on.
One other point I’d like to make is that it’s reproducible. It’s not one-and-done. If the pain comes back from any of these conditions, you could treat again with another cryoneurolysis treatment. The current literature to date shows that it’s just as effective time and time again. I’ve seen clinically that you can repeat this procedure, whereas some of our other procedures that we do in medicine are not as reproducible, which is important for some of these chronic conditions.
Glatter: You had mentioned reimbursement earlier. Currently, this procedure is reimbursed under Medicare, Medicaid, and third-party payers, I assume?
Schwartz: Not all, but many commercial insurers. Yes for Medicare.
Final Takeaways
Glatter: Reimbursement has to be really universal because if this is shown to be more effective and limits opiate use, then there’s no question in my mind that this is such a groundbreaking procedure.
I’ll let you both give a few pearls for our audience to summarize our discussion.
Motov: I’d say it’s somewhat long overdue that this technique and pain-relieving modality should enter the emergency department, with the auspices and the beautiful collaborative effort between emergency department folks and interventional anesthesiologists, pain management specialists, collaborative training, and a collaborative goal of improving patients’ pain throughout the entire journey during the healthcare system.
That would be my only pearl. Just reach out to your colleagues within your respective institutions who you believe have aptitude, knowledge, and expertise. Reach out, get trained, and start passing down the knowledge to your faculty, and by virtue of extension, to your fellow residents and colleagues.
Schwartz: He took the words right out of my mouth. Communication and collaboration are the two most important things. There’s a shortage of physicians in this country. We can only each do so much, so we should each utilize and implement this technology to affect and help as many patients as possible.
We can decrease the amount of opiates, help our patients, help our family members in our community live with decreased pain, improve their function, and just get back to their lives and keep pushing the envelope of what’s the next step in treatment.
Again, like we went from giving opiates for this and that’s it — maybe an epidural, maybe a 5- to 6-hour intercostal nerve block — to fascial plane blocks like Sergey said, to more advanced procedures, to now we can give months of relief.
I think the communication, the collaboration, and the camaraderie among our different specialties are important to push the envelope to help our patients.
Glatter: That’s so well put. I completely agree.
I want to thank both of you for a very lively discussion. It was very informative. Your expertise is greatly appreciated and will certainly benefit our audience. Thank you both again.
Dr. Glatter is an assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York. Dr. Motov is professor of emergency medicine and director of research in the Department of Emergency Medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Schwartz is co-owner and primary clinic director at AABP Integrative Pain Care in Brooklyn, New York. Schwartz currently serves as the co-director of AABP Integrative Pain Care and Wellness and the vice chair of pain and anesthesiology for Maimonides Medical Center. Dr. Schwartz reported conflicts of interest with Pacira Biosciences and Dorsal Health; neither Dr. Glatter nor Dr. Motov reported relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patient and Support Person Satisfaction Following a Whole Health-Informed Interdisciplinary Pain Team Meeting
Patient and Support Person Satisfaction Following a Whole Health-Informed Interdisciplinary Pain Team Meeting
Chronic pain is one of the most prevalent public health concerns in the United States, affecting > 51 million adults with about $500 billion in health care costs.1 Military veterans are among the most vulnerable subpopulations, with 65% of veterans reporting chronic pain in the last 3 months.2 Chronic pain is complex, affecting the biopsychosocial-spiritual levels of human health, and requires multimodal and comprehensive treatment approaches.3 Hence, chronic pain treatment can be best delivered via interdisciplinary teams (IDTs) that use a patient-centered approach.4,5
The Veterans Healthcare Administration (VHA) is a leader in developing and delivering interdisciplinary pain care.6,7 VHA Directive 2009-053 requires every US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center to offer an IDT for chronic pain. However, VHA and non-VHA IDT programs vary significantly.8-11 A recent systematic review found a median of 5 disciplines included on IDTs (range, 2-8), and program content often included exercise and education; only 11% of included IDTs met simultaneously with patients.11 The heterogeneity of IDT programs has made determining best practices challenging.8,11 The Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials has denoted several core measures and measurement domains that were critical for determining the success of pain management interventions, including patient satisfaction.12,13 Nevertheless, the association of IDTs with high patient satisfaction and improvement in pain measures has been documented.5,11
The VHA has worked to implement the Whole Health System into health care, which considers well-being across physical, behavioral, spiritual, and socioeconomic domains. As such, the Whole Health System involves an interpersonal, team-based approach, “anchored in trusting longitudinal relationships to promote resilience, prevent disease, and restore health.”14 It aligns with the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose. Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently endorsed this approach.15,16 Other health care systems adopting whole health tend to have higher patient satisfaction, increased access to care, and improved patient-reported outcomes.15 Within the VHA, the Whole Health System has shifted the conversation between clinicians and patients from “What is the matter with you?” to “What is important to you?” while emphasizing a proactive and personalized approach to health care.17 Rather than emphasizing passive modalities such as medications and clinician-led services (eg, interventional pain service), the Whole Health System highlights self-care.3,17 Initial research findings within the VHA have been promising.18-21 Whole health peer coaching calls appear to be an effective approach for veterans diagnosed with PTSD, and the use of whole health services is associated with a decrease in opioid use.19,22 However, there are negligible data on patient experiences after meeting with a whole health-focused pain IDT, and studies to date have focused on urban populations.23 One approach to IDT that has shown promise for other health issues involves a patient meeting simultaneously with all members of the IDT.24-27 With the integration of the Whole Health System and the VHA priorities to provide veterans with the “soonest and best care,” more data are needed on the experiences of patients and support persons with various approaches to IDT pain care.28 This study aimed to evaluate patient and support person experiences with a whole health-focused pain IDT that met simultaneously with the patient and support person during an initial evaluation. This study was approved by the institutional review board at the Salem VA Health Care System (SVAHCS) in Virginia.
Methods
The PREVAIL IDT Track is a clinical program offered at SVAHCS with a whole health-focused approach that involves patients and their support persons meeting simultaneously with a pain IDT. PREVAIL IDT Track is designed to help veterans more effectively self-manage chronic pain (Table 1).6,29 Health care practitioners (HCPs) at SVAHCS recommended that veterans with pain persisting for > 3 months participate in PREVAIL IDT Track. After meeting with an advanced practice clinician for an intake, veterans elected to participate in the PREVAIL IDT Track program and completed the initial 6 weeks of pain education. Veterans were then invited to be evaluated by the pain IDT. A team including HCPs from interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and physical therapy services met with the veteran for 60 minutes. Veterans were also invited to bring a support person to the IDT initial evaluation.
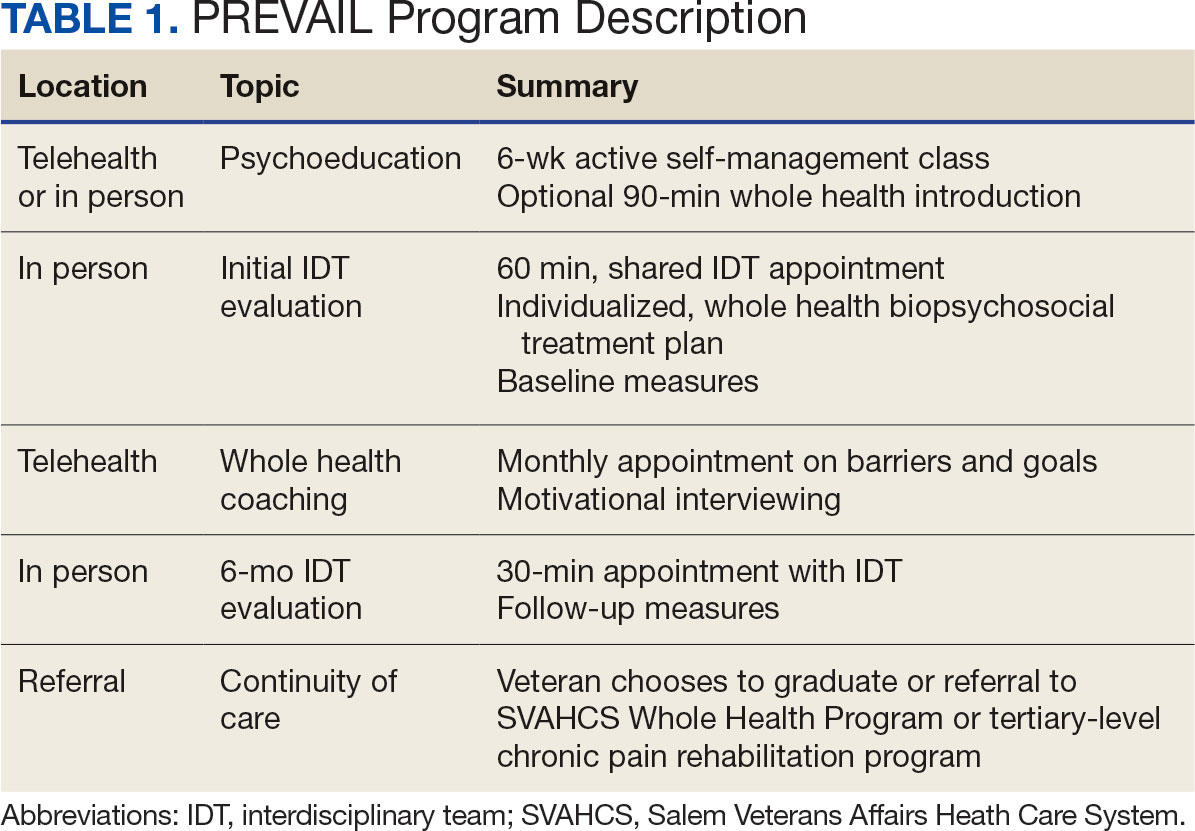
During the IDT initial evaluation, HCPs inquired about the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose (“If you were in less pain, what would you be doing more of?”) and about whole health self-care and wellness factors that may contribute to their chronic pain using the Personal Health Inventory.30,31 Veterans were then invited to select 3 whole health self-care areas to focus on during the 6-month program.3 The IDT HCPs worked with the veteran to establish the treatment plan for the first month in the areas of self-care selected by the patient and made recommendations for additional treatments. If the veteran brought a support person to the IDT initial evaluation, their feedback was elicited throughout and at the end to ensure the final treatment plan and first month’s goals were realistic. At the end of the appointment, the veteran and their support person were asked to complete a program-specific satisfaction survey. The HCPs on the team and the veteran executed the treatment plan developed during the appointment, except for medication prescribing. Recommendations for medication changes are included in clinical notes. Veterans then received 5 monthly coaching calls from a nurse navigator with training in whole health and a 6-month follow-up appointment with the IDT HCPs to discuss a plan for continuity of care.
Participant demographic information was not collected, and participants were not compensated for completing the survey. Veterans in PREVAIL IDT Track are predominantly residents of central Appalachia, White, male, unemployed, have ≥ 1 mental and physical health comorbidity, and have a history of mental health treatment.32 Veterans participating in PREVAIL IDT had a mean age of 57 years, and about 1 in 3 have opioid prescriptions.32
A program-specific 17-question satisfaction survey was developed, which included questions related to satisfaction with previous SVAHCS pain care and staff interactions. To assess the overall impression of the IDT initial evaluation, 3 yes/no questions and a 0 to 10-point scale were used. The 5 remaining open-ended questions allowed participants to give feedback about the IDT initial evaluation.
Data Analysis
A convergent mixed-methods approach was used to evaluate participant satisfaction with the initial IDT evaluation. The study team collected and analyzed quantitative and qualitative survey data and triangulated the findings.33 For quantitative responses, frequencies and means were calculated using Python. For qualitative responses, thematic data analysis was conducted by systematic coding, using inductive methods and allowing themes to emerge. Study team members performed a line-by-line analysis of responses using NVivo to identify important codes and reach a consensus. This study adhered to the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research and followed the National Institute for Health Care Excellence checklist.34,35
Results
Quantitative Responses
In 2022, 168 veterans completed the initial IDT evaluation, and 144 (85.2%) completed the satisfaction survey and were included in this study. Thirty-two support persons who attended the initial IDT evaluation and completed the survey also were included. Of the 12 quantitative questions, 4 had a 100% completion rate, while 8 had ≤ 3% missing responses. When describing care prior to participating in PREVAIL, participants indicated a mean (SD) response of 4.6 (1.4) with the health care they received at SVAHCS and 4.3 (1.4) with SVAHCS pain management services, both on 6-point scales. All but 2 participants (98.9%) reported always being treated with courtesy and respect by PREVAIL HCPs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) score of 4.0 (0.2) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents (96.6%) reported that PREVAIL HCPs always listened carefully during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 4.0 (0.3) on a 4-point scale. Similarly, 92.6% reported that PREVAIL HCPs explained things clearly during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.9 (0.3) on a 4-point scale.
All respondents agreed that PREVAIL HCPs considered veteran preferences and those of their support persons in deciding their health care needs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.7 (0.5) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents left the appointment with a good understanding of their responsibilities for chronic pain management with 99.4% (n = 169) strongly agreeing or agreeing (mean [SD] 3.6 [0.5]). A total of 135 respondents (79.4%) reported they left appointments with written information on their treatment plan. All 170 respondents reported that they would recommend PREVAIL to a friend, and 169 respondents (98.8%) felt that the initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation was a valuable use of time. Eighty-seven respondents (50.9%) rated the initial IDT evaluation as the “best clinical experience possible” with a mean (SD) score of 9.2 (1.1) on a 10-point scale (Table 2).
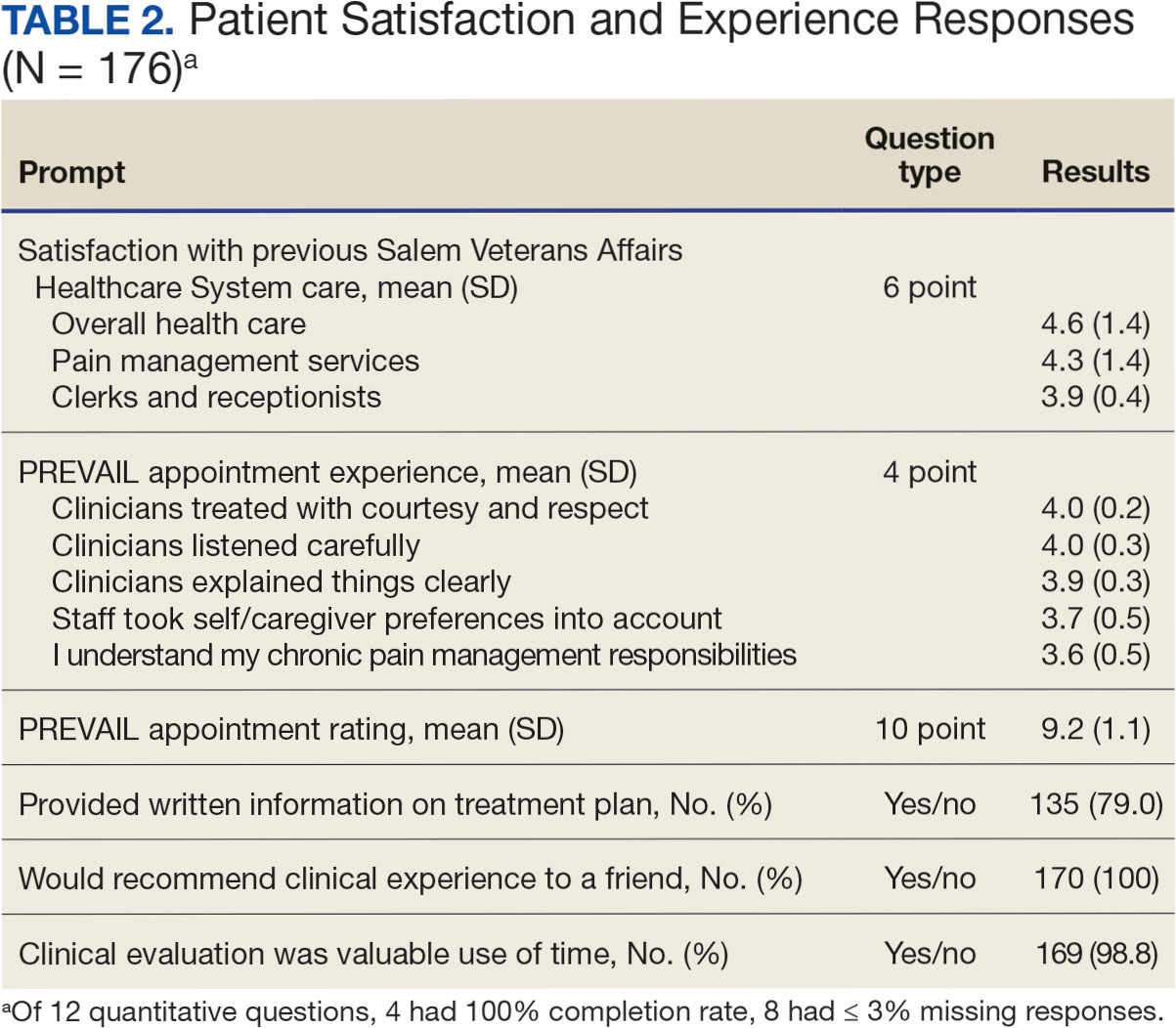
Qualitative Responses
Respondents provided complementary feedback on the program, with many participants stating that they enjoyed every aspect (eAppendix, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0503). In terms of positive aspects of the program, several themes emerged: participants appreciated meeting as an IDT, feeling cared for and listened to, learning more about their pain and ways to manage it, and specific services offered. Thirty-three of 144 respondents wanted longer appointment times. Twenty-two respondents suggested logistics improvements (eg, meeting in a larger room, having a written plan at the end, sending paperwork ahead of time, and later appointment times).
Discussion
Veterans and support persons were satisfied with the initial IDT evaluation for the PREVAIL whole health-focused pain clinical program for veterans predominantly residing in central Appalachia. These satisfaction findings are noteworthy since 20% of this same sample reported dissatisfaction with prior pain services, which could affect engagement and outcomes in pain care. In addition to high satisfaction levels, the PREVAIL IDT model may benefit veterans with limited resources. Rather than needing to attend several individual appointments, the PREVAIL IDT Track provides a 1-stop shop approach that decreases patient burden and barriers to care (eg, travel, transportation, and time) as well as health care system burden. For instance, schedulers need only to make 1 appointment for the veteran rather than several. This approach was highly acceptable to veterans served at SVAHCS and may increase the reach and impact of VHA IDT pain care.
The PREVAIL model may foster rapport with HCPs and encourage an active role in self-managing pain.36,37 Participants noted that their preferences were considered and that they had a good understanding of their responsibilities for managing their chronic pain. This patient-centered approach, emphasizing an active role for the patient, is a hallmark of the VHA Whole Health System and aligns with the overarching PREVAIL IDT Track goal to enhance self-management skills, thus improving functioning through decreased pain interference.14,38-41
Participants in PREVAIL provided substantial open-ended feedback that has contributed to the program’s improvement and may provide information into preferred components of pain IDT programs, particularly for rural veterans. When asked about their favorite component of the initial IDT evaluation, the most emergent theme was meeting simultaneously with HCPs on the IDT. This finding is significant, given that only 11% of IDTs involve direct patient interaction.
Furthermore, unlike most IDTs, PREVAIL IDT includes a dietitian.11,42 IDT programs may benefit from dietitian involvement given the importance of the anti-inflammatory diet on chronic pain.43-46 Participants recommended improvements, (eg, changes to the location and timing, adding a written treatment plan at the end of the appointment, and completing paperwork prior to the appointment) many of which have been addressed. The program now uses validated measures to track progress and comprehensive assessments of pain in response to calls for measurement-based care.13,47 These process improvement suggestions may be instructive for other VA medical centers with rural populations.
Limitations
This study used a program-specific satisfaction survey with open-ended questions to allow for rich responses; however, the survey has not been validated. It also sought to minimize bias by asking participants to give completed surveys to staff members who were not HCPs on the IDT. However, participants’ responses may still have been influenced by this process. Response rate and demographics for support persons were impossible to determine. The results analyzed the responses of veterans and support persons together, which may have skewed the data. Future studies of pain IDT programs should consider analyzing responses from veterans and their support persons separately and identifying factors (eg, demographics or clinical characteristics) that influence the patients’ experiences while participating.
Conclusions
The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation at SVAHCS is associated with high-levels of satisfaction. These veterans living in rural Appalachia, similar to the 4.4 million rural US veterans, are more likely to encounter barriers to care (eg, drive time, or transportation concerns) and be prescribed opioids.48 These veterans are also at high risk of chronic physical and mental health comorbidities, drug misuse, overdose, and suicide.49,50 Providing veterans in rural communities the opportunity to attend a single appointment with a pain IDT instead of requiring several individual appointments could improve the reach of evidence-based pain care.
This model of meeting simultaneously with all HCPs on the pain IDT may connect all veterans to the most available and best care, something prioritized by the VHA.28 The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation also utilizes the Personal Health Inventory and the VHA Whole Health System Circle of Health to design patient-centered treatment plans. Integration of the Whole Health System is currently a high priority within VHA. The PREVAIL IDT Track model warrants additional efficacy research.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, Guy GP Jr. Chronic pain among adults - United States, 2019-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(15):379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Nahin RL. Severe Pain in Veterans: The effect of age and sex, and comparisons with the general population. J Pain. 2017;18(3):247-254. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.10.021
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial-spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Mackey SC, Pearl RG. Pain management: optimizing patient care through comprehensive, interdisciplinary models and continuous innovations. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):xv-xvii. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.03.011
- Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130. doi:10.1037/a0035514
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ. Chronic, noncancer pain care in the veterans administration: current trends and future directions. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):519-529. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.02.004
- Gallagher RM. Advancing the pain agenda in the veteran population. Anesthesiol Clin. 2016;34(2):357-378. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2016.01.003
- Kamper SJ, Apeldoorn AT, Chiarotto A, et al. Multidisciplinary biopsychosocial rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;350:h444. doi:10.1136/bmj.h444
- Waterschoot FPC, Dijkstra PU, Hollak N, De Vries HJ, Geertzen JHB, Reneman MF. Dose or content? Effectiveness of pain rehabilitation programs for patients with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain. 2014;155(1):179-189. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.10.006
- Scascighini L, Toma V, Dober-Spielmann S, Sprott H. Multidisciplinary treatment for chronic pain: a systematic review of interventions and outcomes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(5):670-678. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken021
- Elbers S, Wittink H, Konings S, et al. Longitudinal outcome evaluations of interdisciplinary multimodal pain Treatment programmes for patients with chronic primary musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain. 2022;26(2):310-335. doi:10.1002/ejp.1875
- Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Allen RR, et al. Core outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2003;106(3):337-345. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2003.08.001
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Farrar JT, et al. Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2005;113(1-2):9-19. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.012
- Kligler B, Hyde J, Gantt C, Bokhour B. The whole health transformation at the Veterans Health Administration: moving from “what’s the matter with you?” to “what matters to you?”. Med Care. 2022;60(5):387-391. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000001706
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee on Transforming Health Care to Create Whole Health: Strategies to Assess, Scale, and Spread the Whole Person Approach to Health, Meisnere M, SouthPaul J, Krist AH, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. National Academies Press (US); February 15, 2023.
- The time Is now for a whole-person health approach to public health. Public Health Rep. 2023;138(4):561-564. doi:10.1177/00333549231154583
- Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000000226
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the whole health system of care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Zeliadt SB, Douglas JH, Gelman H, et al. Effectiveness of a whole health model of care emphasizing complementary and integrative health on reducing opioid use among patients with chronic pain. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):1053. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-08388-2
- Reed DE 2nd, Bokhour BG, Gaj L, et al. Whole health use and interest across veterans with cooccurring chronic pain and PTSD: an examination of the 18 VA medical center flagship sites. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:21649561211065374. doi:10.1177/21649561211065374
- Etingen B, Smith BM, Zeliadt SB, et al. VHA whole health services and complementary and integrative health therapies: a gateway to evidence-based mental health treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(14):3144-3151. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08296-z
- Johnson EM, Possemato K, Khan S, Chinman M, Maisto SA. Engagement, experience, and satisfaction with peerdelivered whole health coaching for veterans with PTSD: a mixed methods process evaluation. Psychol Serv. 2021;19(2):305-316. doi:10.1037/ser0000529
- Purcell N, Zamora K, Gibson C, et al. Patient experiences with integrated pain care: a qualitative evaluation of one VA’s biopsychosocial approach to chronic pain treatment and opioid safety. Glob Adv Health Med. 2019;8:2164956119838845. doi:10.1177/2164956119838845
- Will KK, Johnson ML, Lamb G. Team-based care and patient satisfaction in the hospital setting: a systematic review. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2019;6(2):158-171. doi:10.17294/2330-0698.1695
- van Dongen JJJ, Habets IGJ, Beurskens A, van Bokhoven MA. Successful participation of patients in interprofessional team meetings: a qualitative study. Health Expect. 2017;20(4):724-733. doi:10.1111/hex.12511
- Oliver DP, Albright DL, Kruse RL, Wittenberg-Lyles E, Washington K, Demiris G. Caregiver evaluation of the ACTIVE intervention: “it was like we were sitting at the table with everyone.” Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2014;31(4):444-453. doi:10.1177/1049909113490823
- Ansmann L, Heuser C, Diekmann A, et al. Patient participation in multidisciplinary tumor conferences: how is it implemented? What is the patients’ role? What are patients’ experiences? Cancer Med. 2021;10(19):6714-6724. doi:10.1002/cam4.4213
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Updated March 20, 2023. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/priorities/index.asp
- Darnall BD, Edwards KA, Courtney RE, Ziadni MS, Simons LE, Harrison LE. Innovative treatment formats, technologies, and clinician trainings that improve access to behavioral pain treatment for youth and adults. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1223172. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1223172
- Kligler B. Whole health in the Veterans Health Administration. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:2164957X221077214.
- Howe RJ, Poulin LM, Federman DG. The personal health inventory: current use, perceived barriers, and benefits. Fed Pract. 2017;34(5):23-26. doi:10.1177/2164957X221077214
- Hicks N, Harden S, Oursler KA, Courtney RE. Determining the representativeness of participants in a whole health interdisciplinary chronic pain program (PREVAIL) in a VA medical center: who did we reach? Presented at: PAINWeek 2022; September 6-9, 2022; Las Vegas, Nevada. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00325481.2022.2116839
- Creswell JW, Creswell JD. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications; 2018.
- Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual in Health Care. 2007;19(6):349-357. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzm042
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Methods for the development of NICE public health guidance, 3rd edition. Published September 26, 2012. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg4/chapter/introduction
- Alexander JA, Hearld LR, Mittler JN, Harvey J. Patient-physician role relationships and patient activation among individuals with chronic illness. Health Serv Res. 2012;47(3 PART 1):1201-1223. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01354.x
- Fu Y, Yu G, McNichol E, Marczewski K, Closs SJ. The association between patient-professional partnerships and self-management of chronic back pain: a mixed methods study. Eur J Pain. 2018;22(7):1229-1244. doi:10.1002/ejp.1210
- Nicholas MK, Asghari A, Blyth FM, et al. Self-management intervention for chronic pain in older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Pain. 2013;154(6):824-835. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.02.009
- Nøst TH, Steinsbekk A, Bratås O, Grønning K. Twelvemonth effect of chronic pain self-management intervention delivered in an easily accessible primary healthcare service - a randomised controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1012. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3843-x
- Blyth FM, March LM, Nicholas MK, Cousins MJ. Selfmanagement of chronic pain: a population-based study. Pain. 2005;113(3):285-292. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.004
- Damush TM, Kroenke K, Bair MJ, et al. Pain self-management training increases self-efficacy, self-management behaviours and pain and depression outcomes. Eur J Pain. 2016;20(7):1070-1078. doi:10.1002/ejp.830
- Murphy JL, Palyo SA, Schmidt ZS, et al. The resurrection of interdisciplinary pain rehabilitation: outcomes across a veterans affairs collaborative. Pain Med. 2021;22(2):430- 443. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa417
- Brain K, Burrows TL, Bruggink L, et al. Diet and chronic non-cancer pain: the state of the art and future directions. J Clin Med. 2021;10(21):5203. doi:10.3390/jcm10215203
- Field R, Pourkazemi F, Turton J, Rooney K. Dietary interventions are beneficial for patients with chronic pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain Med). 2021;22(3):694-714. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa378
- Bjørklund G, Aaseth J, Do§a MD, et al. Does diet play a role in reducing nociception related to inflammation and chronic pain? Nutrition. 2019;66:153-165. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.04.007
- Kaushik AS, Strath LJ, Sorge RE. Dietary interventions for treatment of chronic pain: oxidative stress and inflammation. Pain Ther. 2020;9(2):487-498. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00200-5
- Boswell JF, Hepner KA, Lysell K, et al. The need for a measurement-based care professional practice guideline. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2023;60(1):1-16. doi:10.1037/pst0000439
- Lund BC, Ohl ME, Hadlandsmyth K, Mosher HJ. Regional and rural-urban variation in opioid prescribing in the Veterans Health Administration. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):894- 900. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz104
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- McCarthy JF, Blow FC, Ignacio R V., Ilgen MA, Austin KL, Valenstein M. Suicide among patients in the Veterans Affairs health system: rural-urban differences in rates, risks, and methods. Am J Public Health. 2012;102 Suppl 1(suppl 1):S111-S117. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300463
Chronic pain is one of the most prevalent public health concerns in the United States, affecting > 51 million adults with about $500 billion in health care costs.1 Military veterans are among the most vulnerable subpopulations, with 65% of veterans reporting chronic pain in the last 3 months.2 Chronic pain is complex, affecting the biopsychosocial-spiritual levels of human health, and requires multimodal and comprehensive treatment approaches.3 Hence, chronic pain treatment can be best delivered via interdisciplinary teams (IDTs) that use a patient-centered approach.4,5
The Veterans Healthcare Administration (VHA) is a leader in developing and delivering interdisciplinary pain care.6,7 VHA Directive 2009-053 requires every US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center to offer an IDT for chronic pain. However, VHA and non-VHA IDT programs vary significantly.8-11 A recent systematic review found a median of 5 disciplines included on IDTs (range, 2-8), and program content often included exercise and education; only 11% of included IDTs met simultaneously with patients.11 The heterogeneity of IDT programs has made determining best practices challenging.8,11 The Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials has denoted several core measures and measurement domains that were critical for determining the success of pain management interventions, including patient satisfaction.12,13 Nevertheless, the association of IDTs with high patient satisfaction and improvement in pain measures has been documented.5,11
The VHA has worked to implement the Whole Health System into health care, which considers well-being across physical, behavioral, spiritual, and socioeconomic domains. As such, the Whole Health System involves an interpersonal, team-based approach, “anchored in trusting longitudinal relationships to promote resilience, prevent disease, and restore health.”14 It aligns with the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose. Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently endorsed this approach.15,16 Other health care systems adopting whole health tend to have higher patient satisfaction, increased access to care, and improved patient-reported outcomes.15 Within the VHA, the Whole Health System has shifted the conversation between clinicians and patients from “What is the matter with you?” to “What is important to you?” while emphasizing a proactive and personalized approach to health care.17 Rather than emphasizing passive modalities such as medications and clinician-led services (eg, interventional pain service), the Whole Health System highlights self-care.3,17 Initial research findings within the VHA have been promising.18-21 Whole health peer coaching calls appear to be an effective approach for veterans diagnosed with PTSD, and the use of whole health services is associated with a decrease in opioid use.19,22 However, there are negligible data on patient experiences after meeting with a whole health-focused pain IDT, and studies to date have focused on urban populations.23 One approach to IDT that has shown promise for other health issues involves a patient meeting simultaneously with all members of the IDT.24-27 With the integration of the Whole Health System and the VHA priorities to provide veterans with the “soonest and best care,” more data are needed on the experiences of patients and support persons with various approaches to IDT pain care.28 This study aimed to evaluate patient and support person experiences with a whole health-focused pain IDT that met simultaneously with the patient and support person during an initial evaluation. This study was approved by the institutional review board at the Salem VA Health Care System (SVAHCS) in Virginia.
Methods
The PREVAIL IDT Track is a clinical program offered at SVAHCS with a whole health-focused approach that involves patients and their support persons meeting simultaneously with a pain IDT. PREVAIL IDT Track is designed to help veterans more effectively self-manage chronic pain (Table 1).6,29 Health care practitioners (HCPs) at SVAHCS recommended that veterans with pain persisting for > 3 months participate in PREVAIL IDT Track. After meeting with an advanced practice clinician for an intake, veterans elected to participate in the PREVAIL IDT Track program and completed the initial 6 weeks of pain education. Veterans were then invited to be evaluated by the pain IDT. A team including HCPs from interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and physical therapy services met with the veteran for 60 minutes. Veterans were also invited to bring a support person to the IDT initial evaluation.

During the IDT initial evaluation, HCPs inquired about the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose (“If you were in less pain, what would you be doing more of?”) and about whole health self-care and wellness factors that may contribute to their chronic pain using the Personal Health Inventory.30,31 Veterans were then invited to select 3 whole health self-care areas to focus on during the 6-month program.3 The IDT HCPs worked with the veteran to establish the treatment plan for the first month in the areas of self-care selected by the patient and made recommendations for additional treatments. If the veteran brought a support person to the IDT initial evaluation, their feedback was elicited throughout and at the end to ensure the final treatment plan and first month’s goals were realistic. At the end of the appointment, the veteran and their support person were asked to complete a program-specific satisfaction survey. The HCPs on the team and the veteran executed the treatment plan developed during the appointment, except for medication prescribing. Recommendations for medication changes are included in clinical notes. Veterans then received 5 monthly coaching calls from a nurse navigator with training in whole health and a 6-month follow-up appointment with the IDT HCPs to discuss a plan for continuity of care.
Participant demographic information was not collected, and participants were not compensated for completing the survey. Veterans in PREVAIL IDT Track are predominantly residents of central Appalachia, White, male, unemployed, have ≥ 1 mental and physical health comorbidity, and have a history of mental health treatment.32 Veterans participating in PREVAIL IDT had a mean age of 57 years, and about 1 in 3 have opioid prescriptions.32
A program-specific 17-question satisfaction survey was developed, which included questions related to satisfaction with previous SVAHCS pain care and staff interactions. To assess the overall impression of the IDT initial evaluation, 3 yes/no questions and a 0 to 10-point scale were used. The 5 remaining open-ended questions allowed participants to give feedback about the IDT initial evaluation.
Data Analysis
A convergent mixed-methods approach was used to evaluate participant satisfaction with the initial IDT evaluation. The study team collected and analyzed quantitative and qualitative survey data and triangulated the findings.33 For quantitative responses, frequencies and means were calculated using Python. For qualitative responses, thematic data analysis was conducted by systematic coding, using inductive methods and allowing themes to emerge. Study team members performed a line-by-line analysis of responses using NVivo to identify important codes and reach a consensus. This study adhered to the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research and followed the National Institute for Health Care Excellence checklist.34,35
Results
Quantitative Responses
In 2022, 168 veterans completed the initial IDT evaluation, and 144 (85.2%) completed the satisfaction survey and were included in this study. Thirty-two support persons who attended the initial IDT evaluation and completed the survey also were included. Of the 12 quantitative questions, 4 had a 100% completion rate, while 8 had ≤ 3% missing responses. When describing care prior to participating in PREVAIL, participants indicated a mean (SD) response of 4.6 (1.4) with the health care they received at SVAHCS and 4.3 (1.4) with SVAHCS pain management services, both on 6-point scales. All but 2 participants (98.9%) reported always being treated with courtesy and respect by PREVAIL HCPs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) score of 4.0 (0.2) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents (96.6%) reported that PREVAIL HCPs always listened carefully during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 4.0 (0.3) on a 4-point scale. Similarly, 92.6% reported that PREVAIL HCPs explained things clearly during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.9 (0.3) on a 4-point scale.
All respondents agreed that PREVAIL HCPs considered veteran preferences and those of their support persons in deciding their health care needs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.7 (0.5) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents left the appointment with a good understanding of their responsibilities for chronic pain management with 99.4% (n = 169) strongly agreeing or agreeing (mean [SD] 3.6 [0.5]). A total of 135 respondents (79.4%) reported they left appointments with written information on their treatment plan. All 170 respondents reported that they would recommend PREVAIL to a friend, and 169 respondents (98.8%) felt that the initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation was a valuable use of time. Eighty-seven respondents (50.9%) rated the initial IDT evaluation as the “best clinical experience possible” with a mean (SD) score of 9.2 (1.1) on a 10-point scale (Table 2).

Qualitative Responses
Respondents provided complementary feedback on the program, with many participants stating that they enjoyed every aspect (eAppendix, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0503). In terms of positive aspects of the program, several themes emerged: participants appreciated meeting as an IDT, feeling cared for and listened to, learning more about their pain and ways to manage it, and specific services offered. Thirty-three of 144 respondents wanted longer appointment times. Twenty-two respondents suggested logistics improvements (eg, meeting in a larger room, having a written plan at the end, sending paperwork ahead of time, and later appointment times).
Discussion
Veterans and support persons were satisfied with the initial IDT evaluation for the PREVAIL whole health-focused pain clinical program for veterans predominantly residing in central Appalachia. These satisfaction findings are noteworthy since 20% of this same sample reported dissatisfaction with prior pain services, which could affect engagement and outcomes in pain care. In addition to high satisfaction levels, the PREVAIL IDT model may benefit veterans with limited resources. Rather than needing to attend several individual appointments, the PREVAIL IDT Track provides a 1-stop shop approach that decreases patient burden and barriers to care (eg, travel, transportation, and time) as well as health care system burden. For instance, schedulers need only to make 1 appointment for the veteran rather than several. This approach was highly acceptable to veterans served at SVAHCS and may increase the reach and impact of VHA IDT pain care.
The PREVAIL model may foster rapport with HCPs and encourage an active role in self-managing pain.36,37 Participants noted that their preferences were considered and that they had a good understanding of their responsibilities for managing their chronic pain. This patient-centered approach, emphasizing an active role for the patient, is a hallmark of the VHA Whole Health System and aligns with the overarching PREVAIL IDT Track goal to enhance self-management skills, thus improving functioning through decreased pain interference.14,38-41
Participants in PREVAIL provided substantial open-ended feedback that has contributed to the program’s improvement and may provide information into preferred components of pain IDT programs, particularly for rural veterans. When asked about their favorite component of the initial IDT evaluation, the most emergent theme was meeting simultaneously with HCPs on the IDT. This finding is significant, given that only 11% of IDTs involve direct patient interaction.
Furthermore, unlike most IDTs, PREVAIL IDT includes a dietitian.11,42 IDT programs may benefit from dietitian involvement given the importance of the anti-inflammatory diet on chronic pain.43-46 Participants recommended improvements, (eg, changes to the location and timing, adding a written treatment plan at the end of the appointment, and completing paperwork prior to the appointment) many of which have been addressed. The program now uses validated measures to track progress and comprehensive assessments of pain in response to calls for measurement-based care.13,47 These process improvement suggestions may be instructive for other VA medical centers with rural populations.
Limitations
This study used a program-specific satisfaction survey with open-ended questions to allow for rich responses; however, the survey has not been validated. It also sought to minimize bias by asking participants to give completed surveys to staff members who were not HCPs on the IDT. However, participants’ responses may still have been influenced by this process. Response rate and demographics for support persons were impossible to determine. The results analyzed the responses of veterans and support persons together, which may have skewed the data. Future studies of pain IDT programs should consider analyzing responses from veterans and their support persons separately and identifying factors (eg, demographics or clinical characteristics) that influence the patients’ experiences while participating.
Conclusions
The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation at SVAHCS is associated with high-levels of satisfaction. These veterans living in rural Appalachia, similar to the 4.4 million rural US veterans, are more likely to encounter barriers to care (eg, drive time, or transportation concerns) and be prescribed opioids.48 These veterans are also at high risk of chronic physical and mental health comorbidities, drug misuse, overdose, and suicide.49,50 Providing veterans in rural communities the opportunity to attend a single appointment with a pain IDT instead of requiring several individual appointments could improve the reach of evidence-based pain care.
This model of meeting simultaneously with all HCPs on the pain IDT may connect all veterans to the most available and best care, something prioritized by the VHA.28 The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation also utilizes the Personal Health Inventory and the VHA Whole Health System Circle of Health to design patient-centered treatment plans. Integration of the Whole Health System is currently a high priority within VHA. The PREVAIL IDT Track model warrants additional efficacy research.
Chronic pain is one of the most prevalent public health concerns in the United States, affecting > 51 million adults with about $500 billion in health care costs.1 Military veterans are among the most vulnerable subpopulations, with 65% of veterans reporting chronic pain in the last 3 months.2 Chronic pain is complex, affecting the biopsychosocial-spiritual levels of human health, and requires multimodal and comprehensive treatment approaches.3 Hence, chronic pain treatment can be best delivered via interdisciplinary teams (IDTs) that use a patient-centered approach.4,5
The Veterans Healthcare Administration (VHA) is a leader in developing and delivering interdisciplinary pain care.6,7 VHA Directive 2009-053 requires every US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) medical center to offer an IDT for chronic pain. However, VHA and non-VHA IDT programs vary significantly.8-11 A recent systematic review found a median of 5 disciplines included on IDTs (range, 2-8), and program content often included exercise and education; only 11% of included IDTs met simultaneously with patients.11 The heterogeneity of IDT programs has made determining best practices challenging.8,11 The Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials has denoted several core measures and measurement domains that were critical for determining the success of pain management interventions, including patient satisfaction.12,13 Nevertheless, the association of IDTs with high patient satisfaction and improvement in pain measures has been documented.5,11
The VHA has worked to implement the Whole Health System into health care, which considers well-being across physical, behavioral, spiritual, and socioeconomic domains. As such, the Whole Health System involves an interpersonal, team-based approach, “anchored in trusting longitudinal relationships to promote resilience, prevent disease, and restore health.”14 It aligns with the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose. Surgeon General VADM Vivek H. Murthy, MD, MBA, recently endorsed this approach.15,16 Other health care systems adopting whole health tend to have higher patient satisfaction, increased access to care, and improved patient-reported outcomes.15 Within the VHA, the Whole Health System has shifted the conversation between clinicians and patients from “What is the matter with you?” to “What is important to you?” while emphasizing a proactive and personalized approach to health care.17 Rather than emphasizing passive modalities such as medications and clinician-led services (eg, interventional pain service), the Whole Health System highlights self-care.3,17 Initial research findings within the VHA have been promising.18-21 Whole health peer coaching calls appear to be an effective approach for veterans diagnosed with PTSD, and the use of whole health services is associated with a decrease in opioid use.19,22 However, there are negligible data on patient experiences after meeting with a whole health-focused pain IDT, and studies to date have focused on urban populations.23 One approach to IDT that has shown promise for other health issues involves a patient meeting simultaneously with all members of the IDT.24-27 With the integration of the Whole Health System and the VHA priorities to provide veterans with the “soonest and best care,” more data are needed on the experiences of patients and support persons with various approaches to IDT pain care.28 This study aimed to evaluate patient and support person experiences with a whole health-focused pain IDT that met simultaneously with the patient and support person during an initial evaluation. This study was approved by the institutional review board at the Salem VA Health Care System (SVAHCS) in Virginia.
Methods
The PREVAIL IDT Track is a clinical program offered at SVAHCS with a whole health-focused approach that involves patients and their support persons meeting simultaneously with a pain IDT. PREVAIL IDT Track is designed to help veterans more effectively self-manage chronic pain (Table 1).6,29 Health care practitioners (HCPs) at SVAHCS recommended that veterans with pain persisting for > 3 months participate in PREVAIL IDT Track. After meeting with an advanced practice clinician for an intake, veterans elected to participate in the PREVAIL IDT Track program and completed the initial 6 weeks of pain education. Veterans were then invited to be evaluated by the pain IDT. A team including HCPs from interventional pain, psychology, pharmacy, nutrition, and physical therapy services met with the veteran for 60 minutes. Veterans were also invited to bring a support person to the IDT initial evaluation.

During the IDT initial evaluation, HCPs inquired about the patient’s mission, aspiration, and purpose (“If you were in less pain, what would you be doing more of?”) and about whole health self-care and wellness factors that may contribute to their chronic pain using the Personal Health Inventory.30,31 Veterans were then invited to select 3 whole health self-care areas to focus on during the 6-month program.3 The IDT HCPs worked with the veteran to establish the treatment plan for the first month in the areas of self-care selected by the patient and made recommendations for additional treatments. If the veteran brought a support person to the IDT initial evaluation, their feedback was elicited throughout and at the end to ensure the final treatment plan and first month’s goals were realistic. At the end of the appointment, the veteran and their support person were asked to complete a program-specific satisfaction survey. The HCPs on the team and the veteran executed the treatment plan developed during the appointment, except for medication prescribing. Recommendations for medication changes are included in clinical notes. Veterans then received 5 monthly coaching calls from a nurse navigator with training in whole health and a 6-month follow-up appointment with the IDT HCPs to discuss a plan for continuity of care.
Participant demographic information was not collected, and participants were not compensated for completing the survey. Veterans in PREVAIL IDT Track are predominantly residents of central Appalachia, White, male, unemployed, have ≥ 1 mental and physical health comorbidity, and have a history of mental health treatment.32 Veterans participating in PREVAIL IDT had a mean age of 57 years, and about 1 in 3 have opioid prescriptions.32
A program-specific 17-question satisfaction survey was developed, which included questions related to satisfaction with previous SVAHCS pain care and staff interactions. To assess the overall impression of the IDT initial evaluation, 3 yes/no questions and a 0 to 10-point scale were used. The 5 remaining open-ended questions allowed participants to give feedback about the IDT initial evaluation.
Data Analysis
A convergent mixed-methods approach was used to evaluate participant satisfaction with the initial IDT evaluation. The study team collected and analyzed quantitative and qualitative survey data and triangulated the findings.33 For quantitative responses, frequencies and means were calculated using Python. For qualitative responses, thematic data analysis was conducted by systematic coding, using inductive methods and allowing themes to emerge. Study team members performed a line-by-line analysis of responses using NVivo to identify important codes and reach a consensus. This study adhered to the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research and followed the National Institute for Health Care Excellence checklist.34,35
Results
Quantitative Responses
In 2022, 168 veterans completed the initial IDT evaluation, and 144 (85.2%) completed the satisfaction survey and were included in this study. Thirty-two support persons who attended the initial IDT evaluation and completed the survey also were included. Of the 12 quantitative questions, 4 had a 100% completion rate, while 8 had ≤ 3% missing responses. When describing care prior to participating in PREVAIL, participants indicated a mean (SD) response of 4.6 (1.4) with the health care they received at SVAHCS and 4.3 (1.4) with SVAHCS pain management services, both on 6-point scales. All but 2 participants (98.9%) reported always being treated with courtesy and respect by PREVAIL HCPs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) score of 4.0 (0.2) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents (96.6%) reported that PREVAIL HCPs always listened carefully during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 4.0 (0.3) on a 4-point scale. Similarly, 92.6% reported that PREVAIL HCPs explained things clearly during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.9 (0.3) on a 4-point scale.
All respondents agreed that PREVAIL HCPs considered veteran preferences and those of their support persons in deciding their health care needs during the initial IDT evaluation, with a mean (SD) 3.7 (0.5) on a 4-point scale. Most respondents left the appointment with a good understanding of their responsibilities for chronic pain management with 99.4% (n = 169) strongly agreeing or agreeing (mean [SD] 3.6 [0.5]). A total of 135 respondents (79.4%) reported they left appointments with written information on their treatment plan. All 170 respondents reported that they would recommend PREVAIL to a friend, and 169 respondents (98.8%) felt that the initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation was a valuable use of time. Eighty-seven respondents (50.9%) rated the initial IDT evaluation as the “best clinical experience possible” with a mean (SD) score of 9.2 (1.1) on a 10-point scale (Table 2).

Qualitative Responses
Respondents provided complementary feedback on the program, with many participants stating that they enjoyed every aspect (eAppendix, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0503). In terms of positive aspects of the program, several themes emerged: participants appreciated meeting as an IDT, feeling cared for and listened to, learning more about their pain and ways to manage it, and specific services offered. Thirty-three of 144 respondents wanted longer appointment times. Twenty-two respondents suggested logistics improvements (eg, meeting in a larger room, having a written plan at the end, sending paperwork ahead of time, and later appointment times).
Discussion
Veterans and support persons were satisfied with the initial IDT evaluation for the PREVAIL whole health-focused pain clinical program for veterans predominantly residing in central Appalachia. These satisfaction findings are noteworthy since 20% of this same sample reported dissatisfaction with prior pain services, which could affect engagement and outcomes in pain care. In addition to high satisfaction levels, the PREVAIL IDT model may benefit veterans with limited resources. Rather than needing to attend several individual appointments, the PREVAIL IDT Track provides a 1-stop shop approach that decreases patient burden and barriers to care (eg, travel, transportation, and time) as well as health care system burden. For instance, schedulers need only to make 1 appointment for the veteran rather than several. This approach was highly acceptable to veterans served at SVAHCS and may increase the reach and impact of VHA IDT pain care.
The PREVAIL model may foster rapport with HCPs and encourage an active role in self-managing pain.36,37 Participants noted that their preferences were considered and that they had a good understanding of their responsibilities for managing their chronic pain. This patient-centered approach, emphasizing an active role for the patient, is a hallmark of the VHA Whole Health System and aligns with the overarching PREVAIL IDT Track goal to enhance self-management skills, thus improving functioning through decreased pain interference.14,38-41
Participants in PREVAIL provided substantial open-ended feedback that has contributed to the program’s improvement and may provide information into preferred components of pain IDT programs, particularly for rural veterans. When asked about their favorite component of the initial IDT evaluation, the most emergent theme was meeting simultaneously with HCPs on the IDT. This finding is significant, given that only 11% of IDTs involve direct patient interaction.
Furthermore, unlike most IDTs, PREVAIL IDT includes a dietitian.11,42 IDT programs may benefit from dietitian involvement given the importance of the anti-inflammatory diet on chronic pain.43-46 Participants recommended improvements, (eg, changes to the location and timing, adding a written treatment plan at the end of the appointment, and completing paperwork prior to the appointment) many of which have been addressed. The program now uses validated measures to track progress and comprehensive assessments of pain in response to calls for measurement-based care.13,47 These process improvement suggestions may be instructive for other VA medical centers with rural populations.
Limitations
This study used a program-specific satisfaction survey with open-ended questions to allow for rich responses; however, the survey has not been validated. It also sought to minimize bias by asking participants to give completed surveys to staff members who were not HCPs on the IDT. However, participants’ responses may still have been influenced by this process. Response rate and demographics for support persons were impossible to determine. The results analyzed the responses of veterans and support persons together, which may have skewed the data. Future studies of pain IDT programs should consider analyzing responses from veterans and their support persons separately and identifying factors (eg, demographics or clinical characteristics) that influence the patients’ experiences while participating.
Conclusions
The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation at SVAHCS is associated with high-levels of satisfaction. These veterans living in rural Appalachia, similar to the 4.4 million rural US veterans, are more likely to encounter barriers to care (eg, drive time, or transportation concerns) and be prescribed opioids.48 These veterans are also at high risk of chronic physical and mental health comorbidities, drug misuse, overdose, and suicide.49,50 Providing veterans in rural communities the opportunity to attend a single appointment with a pain IDT instead of requiring several individual appointments could improve the reach of evidence-based pain care.
This model of meeting simultaneously with all HCPs on the pain IDT may connect all veterans to the most available and best care, something prioritized by the VHA.28 The initial PREVAIL IDT evaluation also utilizes the Personal Health Inventory and the VHA Whole Health System Circle of Health to design patient-centered treatment plans. Integration of the Whole Health System is currently a high priority within VHA. The PREVAIL IDT Track model warrants additional efficacy research.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, Guy GP Jr. Chronic pain among adults - United States, 2019-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(15):379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Nahin RL. Severe Pain in Veterans: The effect of age and sex, and comparisons with the general population. J Pain. 2017;18(3):247-254. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.10.021
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial-spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Mackey SC, Pearl RG. Pain management: optimizing patient care through comprehensive, interdisciplinary models and continuous innovations. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):xv-xvii. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.03.011
- Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130. doi:10.1037/a0035514
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ. Chronic, noncancer pain care in the veterans administration: current trends and future directions. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):519-529. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.02.004
- Gallagher RM. Advancing the pain agenda in the veteran population. Anesthesiol Clin. 2016;34(2):357-378. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2016.01.003
- Kamper SJ, Apeldoorn AT, Chiarotto A, et al. Multidisciplinary biopsychosocial rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;350:h444. doi:10.1136/bmj.h444
- Waterschoot FPC, Dijkstra PU, Hollak N, De Vries HJ, Geertzen JHB, Reneman MF. Dose or content? Effectiveness of pain rehabilitation programs for patients with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain. 2014;155(1):179-189. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.10.006
- Scascighini L, Toma V, Dober-Spielmann S, Sprott H. Multidisciplinary treatment for chronic pain: a systematic review of interventions and outcomes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(5):670-678. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken021
- Elbers S, Wittink H, Konings S, et al. Longitudinal outcome evaluations of interdisciplinary multimodal pain Treatment programmes for patients with chronic primary musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain. 2022;26(2):310-335. doi:10.1002/ejp.1875
- Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Allen RR, et al. Core outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2003;106(3):337-345. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2003.08.001
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Farrar JT, et al. Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2005;113(1-2):9-19. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.012
- Kligler B, Hyde J, Gantt C, Bokhour B. The whole health transformation at the Veterans Health Administration: moving from “what’s the matter with you?” to “what matters to you?”. Med Care. 2022;60(5):387-391. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000001706
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee on Transforming Health Care to Create Whole Health: Strategies to Assess, Scale, and Spread the Whole Person Approach to Health, Meisnere M, SouthPaul J, Krist AH, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. National Academies Press (US); February 15, 2023.
- The time Is now for a whole-person health approach to public health. Public Health Rep. 2023;138(4):561-564. doi:10.1177/00333549231154583
- Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000000226
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the whole health system of care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Zeliadt SB, Douglas JH, Gelman H, et al. Effectiveness of a whole health model of care emphasizing complementary and integrative health on reducing opioid use among patients with chronic pain. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):1053. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-08388-2
- Reed DE 2nd, Bokhour BG, Gaj L, et al. Whole health use and interest across veterans with cooccurring chronic pain and PTSD: an examination of the 18 VA medical center flagship sites. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:21649561211065374. doi:10.1177/21649561211065374
- Etingen B, Smith BM, Zeliadt SB, et al. VHA whole health services and complementary and integrative health therapies: a gateway to evidence-based mental health treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(14):3144-3151. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08296-z
- Johnson EM, Possemato K, Khan S, Chinman M, Maisto SA. Engagement, experience, and satisfaction with peerdelivered whole health coaching for veterans with PTSD: a mixed methods process evaluation. Psychol Serv. 2021;19(2):305-316. doi:10.1037/ser0000529
- Purcell N, Zamora K, Gibson C, et al. Patient experiences with integrated pain care: a qualitative evaluation of one VA’s biopsychosocial approach to chronic pain treatment and opioid safety. Glob Adv Health Med. 2019;8:2164956119838845. doi:10.1177/2164956119838845
- Will KK, Johnson ML, Lamb G. Team-based care and patient satisfaction in the hospital setting: a systematic review. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2019;6(2):158-171. doi:10.17294/2330-0698.1695
- van Dongen JJJ, Habets IGJ, Beurskens A, van Bokhoven MA. Successful participation of patients in interprofessional team meetings: a qualitative study. Health Expect. 2017;20(4):724-733. doi:10.1111/hex.12511
- Oliver DP, Albright DL, Kruse RL, Wittenberg-Lyles E, Washington K, Demiris G. Caregiver evaluation of the ACTIVE intervention: “it was like we were sitting at the table with everyone.” Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2014;31(4):444-453. doi:10.1177/1049909113490823
- Ansmann L, Heuser C, Diekmann A, et al. Patient participation in multidisciplinary tumor conferences: how is it implemented? What is the patients’ role? What are patients’ experiences? Cancer Med. 2021;10(19):6714-6724. doi:10.1002/cam4.4213
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Updated March 20, 2023. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/priorities/index.asp
- Darnall BD, Edwards KA, Courtney RE, Ziadni MS, Simons LE, Harrison LE. Innovative treatment formats, technologies, and clinician trainings that improve access to behavioral pain treatment for youth and adults. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1223172. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1223172
- Kligler B. Whole health in the Veterans Health Administration. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:2164957X221077214.
- Howe RJ, Poulin LM, Federman DG. The personal health inventory: current use, perceived barriers, and benefits. Fed Pract. 2017;34(5):23-26. doi:10.1177/2164957X221077214
- Hicks N, Harden S, Oursler KA, Courtney RE. Determining the representativeness of participants in a whole health interdisciplinary chronic pain program (PREVAIL) in a VA medical center: who did we reach? Presented at: PAINWeek 2022; September 6-9, 2022; Las Vegas, Nevada. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00325481.2022.2116839
- Creswell JW, Creswell JD. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications; 2018.
- Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual in Health Care. 2007;19(6):349-357. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzm042
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Methods for the development of NICE public health guidance, 3rd edition. Published September 26, 2012. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg4/chapter/introduction
- Alexander JA, Hearld LR, Mittler JN, Harvey J. Patient-physician role relationships and patient activation among individuals with chronic illness. Health Serv Res. 2012;47(3 PART 1):1201-1223. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01354.x
- Fu Y, Yu G, McNichol E, Marczewski K, Closs SJ. The association between patient-professional partnerships and self-management of chronic back pain: a mixed methods study. Eur J Pain. 2018;22(7):1229-1244. doi:10.1002/ejp.1210
- Nicholas MK, Asghari A, Blyth FM, et al. Self-management intervention for chronic pain in older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Pain. 2013;154(6):824-835. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.02.009
- Nøst TH, Steinsbekk A, Bratås O, Grønning K. Twelvemonth effect of chronic pain self-management intervention delivered in an easily accessible primary healthcare service - a randomised controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1012. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3843-x
- Blyth FM, March LM, Nicholas MK, Cousins MJ. Selfmanagement of chronic pain: a population-based study. Pain. 2005;113(3):285-292. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.004
- Damush TM, Kroenke K, Bair MJ, et al. Pain self-management training increases self-efficacy, self-management behaviours and pain and depression outcomes. Eur J Pain. 2016;20(7):1070-1078. doi:10.1002/ejp.830
- Murphy JL, Palyo SA, Schmidt ZS, et al. The resurrection of interdisciplinary pain rehabilitation: outcomes across a veterans affairs collaborative. Pain Med. 2021;22(2):430- 443. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa417
- Brain K, Burrows TL, Bruggink L, et al. Diet and chronic non-cancer pain: the state of the art and future directions. J Clin Med. 2021;10(21):5203. doi:10.3390/jcm10215203
- Field R, Pourkazemi F, Turton J, Rooney K. Dietary interventions are beneficial for patients with chronic pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain Med). 2021;22(3):694-714. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa378
- Bjørklund G, Aaseth J, Do§a MD, et al. Does diet play a role in reducing nociception related to inflammation and chronic pain? Nutrition. 2019;66:153-165. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.04.007
- Kaushik AS, Strath LJ, Sorge RE. Dietary interventions for treatment of chronic pain: oxidative stress and inflammation. Pain Ther. 2020;9(2):487-498. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00200-5
- Boswell JF, Hepner KA, Lysell K, et al. The need for a measurement-based care professional practice guideline. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2023;60(1):1-16. doi:10.1037/pst0000439
- Lund BC, Ohl ME, Hadlandsmyth K, Mosher HJ. Regional and rural-urban variation in opioid prescribing in the Veterans Health Administration. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):894- 900. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz104
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- McCarthy JF, Blow FC, Ignacio R V., Ilgen MA, Austin KL, Valenstein M. Suicide among patients in the Veterans Affairs health system: rural-urban differences in rates, risks, and methods. Am J Public Health. 2012;102 Suppl 1(suppl 1):S111-S117. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300463
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, Guy GP Jr. Chronic pain among adults - United States, 2019-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(15):379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Nahin RL. Severe Pain in Veterans: The effect of age and sex, and comparisons with the general population. J Pain. 2017;18(3):247-254. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2016.10.021
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial-spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Mackey SC, Pearl RG. Pain management: optimizing patient care through comprehensive, interdisciplinary models and continuous innovations. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):xv-xvii. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.03.011
- Gatchel RJ, McGeary DD, McGeary CA, Lippe B. Interdisciplinary chronic pain management: past, present, and future. Am Psychol. 2014;69(2):119-130. doi:10.1037/a0035514
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ. Chronic, noncancer pain care in the veterans administration: current trends and future directions. Anesthesiol Clin. 2023;41(2):519-529. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2023.02.004
- Gallagher RM. Advancing the pain agenda in the veteran population. Anesthesiol Clin. 2016;34(2):357-378. doi:10.1016/j.anclin.2016.01.003
- Kamper SJ, Apeldoorn AT, Chiarotto A, et al. Multidisciplinary biopsychosocial rehabilitation for chronic low back pain: cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;350:h444. doi:10.1136/bmj.h444
- Waterschoot FPC, Dijkstra PU, Hollak N, De Vries HJ, Geertzen JHB, Reneman MF. Dose or content? Effectiveness of pain rehabilitation programs for patients with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain. 2014;155(1):179-189. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.10.006
- Scascighini L, Toma V, Dober-Spielmann S, Sprott H. Multidisciplinary treatment for chronic pain: a systematic review of interventions and outcomes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(5):670-678. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken021
- Elbers S, Wittink H, Konings S, et al. Longitudinal outcome evaluations of interdisciplinary multimodal pain Treatment programmes for patients with chronic primary musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain. 2022;26(2):310-335. doi:10.1002/ejp.1875
- Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Allen RR, et al. Core outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2003;106(3):337-345. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2003.08.001
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Farrar JT, et al. Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2005;113(1-2):9-19. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.09.012
- Kligler B, Hyde J, Gantt C, Bokhour B. The whole health transformation at the Veterans Health Administration: moving from “what’s the matter with you?” to “what matters to you?”. Med Care. 2022;60(5):387-391. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000001706
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Care Services; Committee on Transforming Health Care to Create Whole Health: Strategies to Assess, Scale, and Spread the Whole Person Approach to Health, Meisnere M, SouthPaul J, Krist AH, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. National Academies Press (US); February 15, 2023.
- The time Is now for a whole-person health approach to public health. Public Health Rep. 2023;138(4):561-564. doi:10.1177/00333549231154583
- Krejci LP, Carter K, Gaudet T. Whole health: the vision and implementation of personalized, proactive, patient-driven health care for veterans. Med Care. 2014;52(12 Suppl 5):S5-S8. doi:10.1097/mlr.0000000000000226
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the whole health system of care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Zeliadt SB, Douglas JH, Gelman H, et al. Effectiveness of a whole health model of care emphasizing complementary and integrative health on reducing opioid use among patients with chronic pain. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):1053. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-08388-2
- Reed DE 2nd, Bokhour BG, Gaj L, et al. Whole health use and interest across veterans with cooccurring chronic pain and PTSD: an examination of the 18 VA medical center flagship sites. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:21649561211065374. doi:10.1177/21649561211065374
- Etingen B, Smith BM, Zeliadt SB, et al. VHA whole health services and complementary and integrative health therapies: a gateway to evidence-based mental health treatment. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(14):3144-3151. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08296-z
- Johnson EM, Possemato K, Khan S, Chinman M, Maisto SA. Engagement, experience, and satisfaction with peerdelivered whole health coaching for veterans with PTSD: a mixed methods process evaluation. Psychol Serv. 2021;19(2):305-316. doi:10.1037/ser0000529
- Purcell N, Zamora K, Gibson C, et al. Patient experiences with integrated pain care: a qualitative evaluation of one VA’s biopsychosocial approach to chronic pain treatment and opioid safety. Glob Adv Health Med. 2019;8:2164956119838845. doi:10.1177/2164956119838845
- Will KK, Johnson ML, Lamb G. Team-based care and patient satisfaction in the hospital setting: a systematic review. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2019;6(2):158-171. doi:10.17294/2330-0698.1695
- van Dongen JJJ, Habets IGJ, Beurskens A, van Bokhoven MA. Successful participation of patients in interprofessional team meetings: a qualitative study. Health Expect. 2017;20(4):724-733. doi:10.1111/hex.12511
- Oliver DP, Albright DL, Kruse RL, Wittenberg-Lyles E, Washington K, Demiris G. Caregiver evaluation of the ACTIVE intervention: “it was like we were sitting at the table with everyone.” Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2014;31(4):444-453. doi:10.1177/1049909113490823
- Ansmann L, Heuser C, Diekmann A, et al. Patient participation in multidisciplinary tumor conferences: how is it implemented? What is the patients’ role? What are patients’ experiences? Cancer Med. 2021;10(19):6714-6724. doi:10.1002/cam4.4213
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration. Updated March 20, 2023. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.va.gov/health/priorities/index.asp
- Darnall BD, Edwards KA, Courtney RE, Ziadni MS, Simons LE, Harrison LE. Innovative treatment formats, technologies, and clinician trainings that improve access to behavioral pain treatment for youth and adults. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1223172. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1223172
- Kligler B. Whole health in the Veterans Health Administration. Glob Adv Health Med. 2022;11:2164957X221077214.
- Howe RJ, Poulin LM, Federman DG. The personal health inventory: current use, perceived barriers, and benefits. Fed Pract. 2017;34(5):23-26. doi:10.1177/2164957X221077214
- Hicks N, Harden S, Oursler KA, Courtney RE. Determining the representativeness of participants in a whole health interdisciplinary chronic pain program (PREVAIL) in a VA medical center: who did we reach? Presented at: PAINWeek 2022; September 6-9, 2022; Las Vegas, Nevada. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00325481.2022.2116839
- Creswell JW, Creswell JD. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications; 2018.
- Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual in Health Care. 2007;19(6):349-357. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzm042
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Methods for the development of NICE public health guidance, 3rd edition. Published September 26, 2012. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg4/chapter/introduction
- Alexander JA, Hearld LR, Mittler JN, Harvey J. Patient-physician role relationships and patient activation among individuals with chronic illness. Health Serv Res. 2012;47(3 PART 1):1201-1223. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01354.x
- Fu Y, Yu G, McNichol E, Marczewski K, Closs SJ. The association between patient-professional partnerships and self-management of chronic back pain: a mixed methods study. Eur J Pain. 2018;22(7):1229-1244. doi:10.1002/ejp.1210
- Nicholas MK, Asghari A, Blyth FM, et al. Self-management intervention for chronic pain in older adults: a randomised controlled trial. Pain. 2013;154(6):824-835. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.02.009
- Nøst TH, Steinsbekk A, Bratås O, Grønning K. Twelvemonth effect of chronic pain self-management intervention delivered in an easily accessible primary healthcare service - a randomised controlled trial. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):1012. doi:10.1186/s12913-018-3843-x
- Blyth FM, March LM, Nicholas MK, Cousins MJ. Selfmanagement of chronic pain: a population-based study. Pain. 2005;113(3):285-292. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.004
- Damush TM, Kroenke K, Bair MJ, et al. Pain self-management training increases self-efficacy, self-management behaviours and pain and depression outcomes. Eur J Pain. 2016;20(7):1070-1078. doi:10.1002/ejp.830
- Murphy JL, Palyo SA, Schmidt ZS, et al. The resurrection of interdisciplinary pain rehabilitation: outcomes across a veterans affairs collaborative. Pain Med. 2021;22(2):430- 443. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa417
- Brain K, Burrows TL, Bruggink L, et al. Diet and chronic non-cancer pain: the state of the art and future directions. J Clin Med. 2021;10(21):5203. doi:10.3390/jcm10215203
- Field R, Pourkazemi F, Turton J, Rooney K. Dietary interventions are beneficial for patients with chronic pain: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain Med). 2021;22(3):694-714. doi:10.1093/pm/pnaa378
- Bjørklund G, Aaseth J, Do§a MD, et al. Does diet play a role in reducing nociception related to inflammation and chronic pain? Nutrition. 2019;66:153-165. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.04.007
- Kaushik AS, Strath LJ, Sorge RE. Dietary interventions for treatment of chronic pain: oxidative stress and inflammation. Pain Ther. 2020;9(2):487-498. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00200-5
- Boswell JF, Hepner KA, Lysell K, et al. The need for a measurement-based care professional practice guideline. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2023;60(1):1-16. doi:10.1037/pst0000439
- Lund BC, Ohl ME, Hadlandsmyth K, Mosher HJ. Regional and rural-urban variation in opioid prescribing in the Veterans Health Administration. Mil Med. 2019;184(11-12):894- 900. doi:10.1093/milmed/usz104
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans. Updated May 14, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp
- McCarthy JF, Blow FC, Ignacio R V., Ilgen MA, Austin KL, Valenstein M. Suicide among patients in the Veterans Affairs health system: rural-urban differences in rates, risks, and methods. Am J Public Health. 2012;102 Suppl 1(suppl 1):S111-S117. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300463
Patient and Support Person Satisfaction Following a Whole Health-Informed Interdisciplinary Pain Team Meeting
Patient and Support Person Satisfaction Following a Whole Health-Informed Interdisciplinary Pain Team Meeting
Drugs Targeting Osteoarthritis Pain: What’s in Development?
WASHINGTON — Investigational treatments aimed specifically at reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis (OA) are moving forward in parallel with disease-modifying approaches.
“We still have very few treatments for the pain of osteoarthritis…It worries me that people think the only way forward is structure modification. I think while we’re waiting for some drugs to be structure modifying, we still need more pain relief. About 70% of people can’t tolerate or shouldn’t be on a [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug], and that leaves a large number of people with pain,” Philip Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, Chair of Musculoskeletal Medicine at the University of Leeds in England, said in an interview.
At the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, Conaghan, who is also honorary consultant rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, presented new data for two novel approaches, both targeting peripheral nociceptive pain signaling.
In a late-breaking poster, he presented phase 2 trial data on RTX-GRT7039 (resiniferatoxin [RTX]), an agonist of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 that is a driver of OA pain. The trial investigated the efficacy and safety of a single intra-articular injection of RTX-GRT7039 in people with knee OA.
And separately, in a late-breaking oral abstract session, Conaghan presented phase 2 trial safety and efficacy data for another investigational agent called LEVI-04, a first-in-class neurotrophin receptor fusion protein (p75NTR-Fc) that supplements the endogenous protein and provides analgesia via inhibition of NT-3 activity.
“I think both have potential to provide good pain relief, through slightly different mechanisms,” Conaghan said in an interview.
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview: “I think the results are really exciting terms of the ability to control pain to a significant degree in patients with osteoarthritis.”
However, Gardner also said, “The molecules can be very expensive ... so who do we give them to? Will insurance companies pay for this simply for OA pain? They improve function ... so clearly, [they] will be a boon to treating osteoarthritis, but do we give them to people with only more advanced forms of osteoarthritis or earlier on?”
Moreover, Gardner said, “One of my concerns about treating osteoarthritis is I don’t want to do too good of a job treating pain in somebody who has a biomechanically abnormal joint. ... You’ve got a knee that’s worn out some of the cartilage, and now you feel like you can go out and play soccer again. That’s not a good thing. That joint will wear out very quickly, even though it doesn’t feel pain.”
Another OA expert, Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, said in an interview, “I think we don’t focus nearly enough on pain, and that’s [partly] because the [Food and Drug Administration] has defined endpoints for knee OA trials that are radiographic. ... Patients do not care what their joint space narrowing is. They care what their pain is. And joint space changes and pain do not correlate in knee OA. ... About 20% or 30% of patients who have completely normal x-rays have a lot of pain…I hope that we’ll have some new OA pain therapeutics in the future because that’s what patients actually care about.”
But Jeffries noted that it will be very important to ensure that these agents don’t produce significant side effects, as had been seen previously in several large industry-sponsored trials of drugs targeting nerve growth factors.
“The big concern that we have in the field ... is that the nerve growth factor antibody trials were all stopped because there was a low but persistent risk of rapidly progressive OA in a small percent of patients. I think one of the questions in the field is whether targeting other things having to do with OA pain is going to result in similar bad outcomes. I think the answer is probably not, but that’s one thing that people do worry about, and they never really figured out why the [rapidly progressive OA] was happening.”
‘Potential to Provide Meaningful and Sustained Analgesia’
The phase 2 trial of RTX-GRT7039, funded by manufacturer Grünenthal, enrolled 40 patients with a baseline visual analog pain score (VAS) of > 40 mm on motion for average joint pain in the target knee over the past 2 days with or without analgesic medication and Kellgren-Lawrence grades 2-4.
They were randomized to receive a single intra-articular injection of 2 mg or 4 mg RTX-GRT7039 within 1 minute after receiving 5 mL ropivacaine (0.5%) or 4 mg or 8 mg RTX-GRT7039 administered 15 minutes after 5 mL ropivacaine pretreatment, or equivalent placebo treatments plus ropivacaine.
Plasma samples were collected for up to 2 hours, and VAS pain scores were collected for up to 3 hours post injection.
Reductions in VAS scores from baseline in the treated knee were seen in all RTX treatment groups as early as day 8 post injection and were maintained up to 6 months, while no reductions in VAS pain on motion scores were seen in the placebo group.
At 3 months, the absolute baseline-adjusted reductions in VAS scores were similar for RTX 2 mg (–39.75), RTX 4 mg (–40.20), and RTX 8 mg (–30.25), while the reduction in the placebo group was just –8.50. At 6 months, the mean absolute reduction in VAS score was numerically greater in the RTX 2-mg (–46.49), RTX 4-mg (–43.40), and RTX 8-mg (–38.60) groups vs the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute after receiving ropivacaine (–22.00).
At both 3 and 6 months, a higher proportion of patients receiving any dose of RTX-GRT7039 achieved ≥ 50% and ≥ 70% reduction in pain on motion, compared with those who received placebo. All RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups reported a greater improvement in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) total score than the placebo group at both 3 and 6 months.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the RTX groups (85.7%-90.9%) and placebo (85.7%) and slightly lower in the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute of receiving ropivacaine (60.0%).
There was a trend toward greater procedural/injection site pain in the RTX treatment groups, compared with placebo, most commonly arthralgia (37.5%), headache (17.5%), and back pain (10%). This tended to peak around 0.5 hours post injection and resolve by 1.5-3.0 hours.
No treatment-related serious adverse events occurred, and no treatment-emergent adverse events led to discontinuation or death.
“This early-phase trial indicates that RTX-GRT7039 has the potential to provide meaningful and sustained analgesia for patients with knee OA pain,” Conaghan and colleagues wrote in their poster.
The drug is now being evaluated in three phase 3 trials (NCT05248386, NCT05449132, and NCT05377489).
LEVI-04: Modulation of NT-3 Appears to Work Safely
LEVI-04 was evaluated in a phase 2, 20-week, 13-center (Europe and Hong Kong) randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 518 people with knee OA who had WOMAC pain subscale scores ≥ 20, mean average daily pain numeric rating scale score of 4-9, and radiographic Kellgren-Lawrence grade ≥ 2.
They were randomized to a total of five infusions of placebo or 0.3 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, or 2 mg/kg LEVI-04 from baseline through week 16, with safety follow-up to week 30.
The primary endpoint, change in WOMAC pain from baseline to weeks 5 and 17, was met for all three doses. At 17 weeks, those were –2.79, –2.89, and –3.08 for 0.3 mg, 1.0 mg, and 2 mg, respectively, vs –2.28 for placebo (all P < .05).
Secondary endpoints, including WOMAC physical function, WOMAC stiffness, and Patient Global Assessment, and > 50% pain responders, were also all met at weeks 5 and 17. More than 50% of the LEVI-04–treated patients reported ≥ 50% reduction in pain, and > 25% reported ≥ 75% reduction at weeks 5 and 17.
“So, this modulation of NT-3 is working,” Conaghan commented.
There were no increased incidences of severe adverse events, treatment-emergent adverse events, or joint pathologies, including rapidly progressive OA, compared with placebo.
There were more paresthesias reported with the active drug, 2-4 vs 1 with placebo. “That says to me that the drug is working and that it’s having an effect on peripheral nerves, but luckily these were all mild or moderate and didn’t lead to any study withdrawal or discontinuation,” Conaghan said.
Phase 3 trials are in the planning stages, he noted.
Other Approaches to Treating OA Pain
Other approaches to treating OA pain have included methotrexate, for which Conaghan was also a coauthor on one paper that came out earlier in 2024. “This presumably works by treating inflammation, but it’s not clear if that is within-joint inflammation or systemic inflammation,” he said in an interview.
Another approach, using the weight loss drug semaglutide, was presented in April 2024 at the 2024 World Congress on Osteoarthritis annual meeting and published in October 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine
The trial involving RTX-GRT7039 was funded by Grünenthal, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. The trial involving LEVI-04 was funded by Levicept, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. Conaghan is a consultant and/or speaker for Eli Lilly, Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals, Formation Bio, Galapagos, Genascence, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Kolon TissueGene, Levicept, Medipost, Moebius, Novartis, Pacira, Sandoz, Stryker Corporation, and Takeda. Gardner and Jeffries had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Investigational treatments aimed specifically at reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis (OA) are moving forward in parallel with disease-modifying approaches.
“We still have very few treatments for the pain of osteoarthritis…It worries me that people think the only way forward is structure modification. I think while we’re waiting for some drugs to be structure modifying, we still need more pain relief. About 70% of people can’t tolerate or shouldn’t be on a [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug], and that leaves a large number of people with pain,” Philip Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, Chair of Musculoskeletal Medicine at the University of Leeds in England, said in an interview.
At the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, Conaghan, who is also honorary consultant rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, presented new data for two novel approaches, both targeting peripheral nociceptive pain signaling.
In a late-breaking poster, he presented phase 2 trial data on RTX-GRT7039 (resiniferatoxin [RTX]), an agonist of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 that is a driver of OA pain. The trial investigated the efficacy and safety of a single intra-articular injection of RTX-GRT7039 in people with knee OA.
And separately, in a late-breaking oral abstract session, Conaghan presented phase 2 trial safety and efficacy data for another investigational agent called LEVI-04, a first-in-class neurotrophin receptor fusion protein (p75NTR-Fc) that supplements the endogenous protein and provides analgesia via inhibition of NT-3 activity.
“I think both have potential to provide good pain relief, through slightly different mechanisms,” Conaghan said in an interview.
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview: “I think the results are really exciting terms of the ability to control pain to a significant degree in patients with osteoarthritis.”
However, Gardner also said, “The molecules can be very expensive ... so who do we give them to? Will insurance companies pay for this simply for OA pain? They improve function ... so clearly, [they] will be a boon to treating osteoarthritis, but do we give them to people with only more advanced forms of osteoarthritis or earlier on?”
Moreover, Gardner said, “One of my concerns about treating osteoarthritis is I don’t want to do too good of a job treating pain in somebody who has a biomechanically abnormal joint. ... You’ve got a knee that’s worn out some of the cartilage, and now you feel like you can go out and play soccer again. That’s not a good thing. That joint will wear out very quickly, even though it doesn’t feel pain.”
Another OA expert, Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, said in an interview, “I think we don’t focus nearly enough on pain, and that’s [partly] because the [Food and Drug Administration] has defined endpoints for knee OA trials that are radiographic. ... Patients do not care what their joint space narrowing is. They care what their pain is. And joint space changes and pain do not correlate in knee OA. ... About 20% or 30% of patients who have completely normal x-rays have a lot of pain…I hope that we’ll have some new OA pain therapeutics in the future because that’s what patients actually care about.”
But Jeffries noted that it will be very important to ensure that these agents don’t produce significant side effects, as had been seen previously in several large industry-sponsored trials of drugs targeting nerve growth factors.
“The big concern that we have in the field ... is that the nerve growth factor antibody trials were all stopped because there was a low but persistent risk of rapidly progressive OA in a small percent of patients. I think one of the questions in the field is whether targeting other things having to do with OA pain is going to result in similar bad outcomes. I think the answer is probably not, but that’s one thing that people do worry about, and they never really figured out why the [rapidly progressive OA] was happening.”
‘Potential to Provide Meaningful and Sustained Analgesia’
The phase 2 trial of RTX-GRT7039, funded by manufacturer Grünenthal, enrolled 40 patients with a baseline visual analog pain score (VAS) of > 40 mm on motion for average joint pain in the target knee over the past 2 days with or without analgesic medication and Kellgren-Lawrence grades 2-4.
They were randomized to receive a single intra-articular injection of 2 mg or 4 mg RTX-GRT7039 within 1 minute after receiving 5 mL ropivacaine (0.5%) or 4 mg or 8 mg RTX-GRT7039 administered 15 minutes after 5 mL ropivacaine pretreatment, or equivalent placebo treatments plus ropivacaine.
Plasma samples were collected for up to 2 hours, and VAS pain scores were collected for up to 3 hours post injection.
Reductions in VAS scores from baseline in the treated knee were seen in all RTX treatment groups as early as day 8 post injection and were maintained up to 6 months, while no reductions in VAS pain on motion scores were seen in the placebo group.
At 3 months, the absolute baseline-adjusted reductions in VAS scores were similar for RTX 2 mg (–39.75), RTX 4 mg (–40.20), and RTX 8 mg (–30.25), while the reduction in the placebo group was just –8.50. At 6 months, the mean absolute reduction in VAS score was numerically greater in the RTX 2-mg (–46.49), RTX 4-mg (–43.40), and RTX 8-mg (–38.60) groups vs the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute after receiving ropivacaine (–22.00).
At both 3 and 6 months, a higher proportion of patients receiving any dose of RTX-GRT7039 achieved ≥ 50% and ≥ 70% reduction in pain on motion, compared with those who received placebo. All RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups reported a greater improvement in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) total score than the placebo group at both 3 and 6 months.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the RTX groups (85.7%-90.9%) and placebo (85.7%) and slightly lower in the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute of receiving ropivacaine (60.0%).
There was a trend toward greater procedural/injection site pain in the RTX treatment groups, compared with placebo, most commonly arthralgia (37.5%), headache (17.5%), and back pain (10%). This tended to peak around 0.5 hours post injection and resolve by 1.5-3.0 hours.
No treatment-related serious adverse events occurred, and no treatment-emergent adverse events led to discontinuation or death.
“This early-phase trial indicates that RTX-GRT7039 has the potential to provide meaningful and sustained analgesia for patients with knee OA pain,” Conaghan and colleagues wrote in their poster.
The drug is now being evaluated in three phase 3 trials (NCT05248386, NCT05449132, and NCT05377489).
LEVI-04: Modulation of NT-3 Appears to Work Safely
LEVI-04 was evaluated in a phase 2, 20-week, 13-center (Europe and Hong Kong) randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 518 people with knee OA who had WOMAC pain subscale scores ≥ 20, mean average daily pain numeric rating scale score of 4-9, and radiographic Kellgren-Lawrence grade ≥ 2.
They were randomized to a total of five infusions of placebo or 0.3 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, or 2 mg/kg LEVI-04 from baseline through week 16, with safety follow-up to week 30.
The primary endpoint, change in WOMAC pain from baseline to weeks 5 and 17, was met for all three doses. At 17 weeks, those were –2.79, –2.89, and –3.08 for 0.3 mg, 1.0 mg, and 2 mg, respectively, vs –2.28 for placebo (all P < .05).
Secondary endpoints, including WOMAC physical function, WOMAC stiffness, and Patient Global Assessment, and > 50% pain responders, were also all met at weeks 5 and 17. More than 50% of the LEVI-04–treated patients reported ≥ 50% reduction in pain, and > 25% reported ≥ 75% reduction at weeks 5 and 17.
“So, this modulation of NT-3 is working,” Conaghan commented.
There were no increased incidences of severe adverse events, treatment-emergent adverse events, or joint pathologies, including rapidly progressive OA, compared with placebo.
There were more paresthesias reported with the active drug, 2-4 vs 1 with placebo. “That says to me that the drug is working and that it’s having an effect on peripheral nerves, but luckily these were all mild or moderate and didn’t lead to any study withdrawal or discontinuation,” Conaghan said.
Phase 3 trials are in the planning stages, he noted.
Other Approaches to Treating OA Pain
Other approaches to treating OA pain have included methotrexate, for which Conaghan was also a coauthor on one paper that came out earlier in 2024. “This presumably works by treating inflammation, but it’s not clear if that is within-joint inflammation or systemic inflammation,” he said in an interview.
Another approach, using the weight loss drug semaglutide, was presented in April 2024 at the 2024 World Congress on Osteoarthritis annual meeting and published in October 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine
The trial involving RTX-GRT7039 was funded by Grünenthal, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. The trial involving LEVI-04 was funded by Levicept, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. Conaghan is a consultant and/or speaker for Eli Lilly, Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals, Formation Bio, Galapagos, Genascence, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Kolon TissueGene, Levicept, Medipost, Moebius, Novartis, Pacira, Sandoz, Stryker Corporation, and Takeda. Gardner and Jeffries had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Investigational treatments aimed specifically at reducing pain in knee osteoarthritis (OA) are moving forward in parallel with disease-modifying approaches.
“We still have very few treatments for the pain of osteoarthritis…It worries me that people think the only way forward is structure modification. I think while we’re waiting for some drugs to be structure modifying, we still need more pain relief. About 70% of people can’t tolerate or shouldn’t be on a [nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug], and that leaves a large number of people with pain,” Philip Conaghan, MBBS, PhD, Chair of Musculoskeletal Medicine at the University of Leeds in England, said in an interview.
At the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, Conaghan, who is also honorary consultant rheumatologist for the Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust, presented new data for two novel approaches, both targeting peripheral nociceptive pain signaling.
In a late-breaking poster, he presented phase 2 trial data on RTX-GRT7039 (resiniferatoxin [RTX]), an agonist of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 that is a driver of OA pain. The trial investigated the efficacy and safety of a single intra-articular injection of RTX-GRT7039 in people with knee OA.
And separately, in a late-breaking oral abstract session, Conaghan presented phase 2 trial safety and efficacy data for another investigational agent called LEVI-04, a first-in-class neurotrophin receptor fusion protein (p75NTR-Fc) that supplements the endogenous protein and provides analgesia via inhibition of NT-3 activity.
“I think both have potential to provide good pain relief, through slightly different mechanisms,” Conaghan said in an interview.
Asked to comment, session moderator Gregory C. Gardner, MD, emeritus professor in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview: “I think the results are really exciting terms of the ability to control pain to a significant degree in patients with osteoarthritis.”
However, Gardner also said, “The molecules can be very expensive ... so who do we give them to? Will insurance companies pay for this simply for OA pain? They improve function ... so clearly, [they] will be a boon to treating osteoarthritis, but do we give them to people with only more advanced forms of osteoarthritis or earlier on?”
Moreover, Gardner said, “One of my concerns about treating osteoarthritis is I don’t want to do too good of a job treating pain in somebody who has a biomechanically abnormal joint. ... You’ve got a knee that’s worn out some of the cartilage, and now you feel like you can go out and play soccer again. That’s not a good thing. That joint will wear out very quickly, even though it doesn’t feel pain.”
Another OA expert, Matlock Jeffries, MD, director of the Arthritis Research Unit at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, Oklahoma City, said in an interview, “I think we don’t focus nearly enough on pain, and that’s [partly] because the [Food and Drug Administration] has defined endpoints for knee OA trials that are radiographic. ... Patients do not care what their joint space narrowing is. They care what their pain is. And joint space changes and pain do not correlate in knee OA. ... About 20% or 30% of patients who have completely normal x-rays have a lot of pain…I hope that we’ll have some new OA pain therapeutics in the future because that’s what patients actually care about.”
But Jeffries noted that it will be very important to ensure that these agents don’t produce significant side effects, as had been seen previously in several large industry-sponsored trials of drugs targeting nerve growth factors.
“The big concern that we have in the field ... is that the nerve growth factor antibody trials were all stopped because there was a low but persistent risk of rapidly progressive OA in a small percent of patients. I think one of the questions in the field is whether targeting other things having to do with OA pain is going to result in similar bad outcomes. I think the answer is probably not, but that’s one thing that people do worry about, and they never really figured out why the [rapidly progressive OA] was happening.”
‘Potential to Provide Meaningful and Sustained Analgesia’
The phase 2 trial of RTX-GRT7039, funded by manufacturer Grünenthal, enrolled 40 patients with a baseline visual analog pain score (VAS) of > 40 mm on motion for average joint pain in the target knee over the past 2 days with or without analgesic medication and Kellgren-Lawrence grades 2-4.
They were randomized to receive a single intra-articular injection of 2 mg or 4 mg RTX-GRT7039 within 1 minute after receiving 5 mL ropivacaine (0.5%) or 4 mg or 8 mg RTX-GRT7039 administered 15 minutes after 5 mL ropivacaine pretreatment, or equivalent placebo treatments plus ropivacaine.
Plasma samples were collected for up to 2 hours, and VAS pain scores were collected for up to 3 hours post injection.
Reductions in VAS scores from baseline in the treated knee were seen in all RTX treatment groups as early as day 8 post injection and were maintained up to 6 months, while no reductions in VAS pain on motion scores were seen in the placebo group.
At 3 months, the absolute baseline-adjusted reductions in VAS scores were similar for RTX 2 mg (–39.75), RTX 4 mg (–40.20), and RTX 8 mg (–30.25), while the reduction in the placebo group was just –8.50. At 6 months, the mean absolute reduction in VAS score was numerically greater in the RTX 2-mg (–46.49), RTX 4-mg (–43.40), and RTX 8-mg (–38.60) groups vs the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute after receiving ropivacaine (–22.00).
At both 3 and 6 months, a higher proportion of patients receiving any dose of RTX-GRT7039 achieved ≥ 50% and ≥ 70% reduction in pain on motion, compared with those who received placebo. All RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups reported a greater improvement in Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) total score than the placebo group at both 3 and 6 months.
Rates of treatment-emergent adverse events were similar between the RTX groups (85.7%-90.9%) and placebo (85.7%) and slightly lower in the group that received RTX 4 mg within 1 minute of receiving ropivacaine (60.0%).
There was a trend toward greater procedural/injection site pain in the RTX treatment groups, compared with placebo, most commonly arthralgia (37.5%), headache (17.5%), and back pain (10%). This tended to peak around 0.5 hours post injection and resolve by 1.5-3.0 hours.
No treatment-related serious adverse events occurred, and no treatment-emergent adverse events led to discontinuation or death.
“This early-phase trial indicates that RTX-GRT7039 has the potential to provide meaningful and sustained analgesia for patients with knee OA pain,” Conaghan and colleagues wrote in their poster.
The drug is now being evaluated in three phase 3 trials (NCT05248386, NCT05449132, and NCT05377489).
LEVI-04: Modulation of NT-3 Appears to Work Safely
LEVI-04 was evaluated in a phase 2, 20-week, 13-center (Europe and Hong Kong) randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 518 people with knee OA who had WOMAC pain subscale scores ≥ 20, mean average daily pain numeric rating scale score of 4-9, and radiographic Kellgren-Lawrence grade ≥ 2.
They were randomized to a total of five infusions of placebo or 0.3 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, or 2 mg/kg LEVI-04 from baseline through week 16, with safety follow-up to week 30.
The primary endpoint, change in WOMAC pain from baseline to weeks 5 and 17, was met for all three doses. At 17 weeks, those were –2.79, –2.89, and –3.08 for 0.3 mg, 1.0 mg, and 2 mg, respectively, vs –2.28 for placebo (all P < .05).
Secondary endpoints, including WOMAC physical function, WOMAC stiffness, and Patient Global Assessment, and > 50% pain responders, were also all met at weeks 5 and 17. More than 50% of the LEVI-04–treated patients reported ≥ 50% reduction in pain, and > 25% reported ≥ 75% reduction at weeks 5 and 17.
“So, this modulation of NT-3 is working,” Conaghan commented.
There were no increased incidences of severe adverse events, treatment-emergent adverse events, or joint pathologies, including rapidly progressive OA, compared with placebo.
There were more paresthesias reported with the active drug, 2-4 vs 1 with placebo. “That says to me that the drug is working and that it’s having an effect on peripheral nerves, but luckily these were all mild or moderate and didn’t lead to any study withdrawal or discontinuation,” Conaghan said.
Phase 3 trials are in the planning stages, he noted.
Other Approaches to Treating OA Pain
Other approaches to treating OA pain have included methotrexate, for which Conaghan was also a coauthor on one paper that came out earlier in 2024. “This presumably works by treating inflammation, but it’s not clear if that is within-joint inflammation or systemic inflammation,” he said in an interview.
Another approach, using the weight loss drug semaglutide, was presented in April 2024 at the 2024 World Congress on Osteoarthritis annual meeting and published in October 2024 in The New England Journal of Medicine
The trial involving RTX-GRT7039 was funded by Grünenthal, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. The trial involving LEVI-04 was funded by Levicept, and some study coauthors are employees of the company. Conaghan is a consultant and/or speaker for Eli Lilly, Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals, Formation Bio, Galapagos, Genascence, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Kolon TissueGene, Levicept, Medipost, Moebius, Novartis, Pacira, Sandoz, Stryker Corporation, and Takeda. Gardner and Jeffries had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Is 1-Week Radiotherapy Safe for Breast Cancer?
TOPLINE:
Most patients also reported that the reduced treatment time was a major benefit of the 1-week radiotherapy schedule.
METHODOLOGY:
- In March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, international and national guidelines recommended adopting a 1-week ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy schedule for patients with node-negative breast cancer. Subsequently, a phase 3 trial demonstrated that a 1-week regimen of 26 Gy in five fractions led to similar breast cancer outcomes compared with a standard moderately hypofractionated regimen.
- In this study, researchers wanted to assess real world toxicities following ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy and enrolled 135 consecutive patients who received 1-week ultrahypofractionated adjuvant radiation of 26 Gy in five fractions from March to August 2020 at three centers in Ireland, with 33 patients (25%) receiving a sequential boost.
- Researchers recorded patient-reported outcomes on breast pain, swelling, firmness, and hypersensitivity at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months. Virtual consultations without video occurred at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and video consultations were offered at 1 year for a physician-led breast evaluation.
- Researchers assessed patient perspectives on this new schedule and telehealth workflows using questionnaires.
- Overall, 90% of patients completed the 1-year assessment plus another assessment. The primary endpoint was the worst toxicity reported at each time point.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 76% of patients reported no or mild toxicities at 3 and 6 months, and 82% reported no or mild toxicities 12 months.
- At 1 year, 20 patients (17%) reported moderate toxicity, most commonly breast pain, and only two patients (2%) reported marked toxicities, including breast firmness and skin changes.
- Researchers found no difference in toxicities between patients who received only 26 Gy in five fractions and those who received an additional sequential boost.
- Most patients reported reduced treatment time (78.6%) and infection control (59%) as major benefits of the 1-week radiotherapy regimen. Patients also reported high satisfaction with the use of telehealth, with 97.3% feeling well-informed about their diagnosis, 88% feeling well-informed about treatment side effects, and 94% feeling supported by the medical team. However, only 27% agreed to video consultations for breast inspections at 1 year.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ultrahypofractionated whole breast radiotherapy leads to acceptable late toxicity rates at 1 year even when followed by a hypofractionated tumour bed boost,” the authors wrote. “Patient satisfaction with ultrahypofractionated treatment and virtual consultations without video was high.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jill Nicholson, MBBS, MRCP, FFFRRCSI, St Luke’s Radiation Oncology Network, St. Luke’s Hospital, Dublin, Ireland, was published online in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The short follow-up period might not capture all late toxicities. Variability in patient-reported outcomes could affect consistency. The range in boost received (four to eight fractions) could have influenced patients’ experiences.
DISCLOSURES:
Nicholson received funding from the St. Luke’s Institute of Cancer Research, Dublin, Ireland. No other relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Most patients also reported that the reduced treatment time was a major benefit of the 1-week radiotherapy schedule.
METHODOLOGY:
- In March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, international and national guidelines recommended adopting a 1-week ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy schedule for patients with node-negative breast cancer. Subsequently, a phase 3 trial demonstrated that a 1-week regimen of 26 Gy in five fractions led to similar breast cancer outcomes compared with a standard moderately hypofractionated regimen.
- In this study, researchers wanted to assess real world toxicities following ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy and enrolled 135 consecutive patients who received 1-week ultrahypofractionated adjuvant radiation of 26 Gy in five fractions from March to August 2020 at three centers in Ireland, with 33 patients (25%) receiving a sequential boost.
- Researchers recorded patient-reported outcomes on breast pain, swelling, firmness, and hypersensitivity at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months. Virtual consultations without video occurred at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and video consultations were offered at 1 year for a physician-led breast evaluation.
- Researchers assessed patient perspectives on this new schedule and telehealth workflows using questionnaires.
- Overall, 90% of patients completed the 1-year assessment plus another assessment. The primary endpoint was the worst toxicity reported at each time point.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 76% of patients reported no or mild toxicities at 3 and 6 months, and 82% reported no or mild toxicities 12 months.
- At 1 year, 20 patients (17%) reported moderate toxicity, most commonly breast pain, and only two patients (2%) reported marked toxicities, including breast firmness and skin changes.
- Researchers found no difference in toxicities between patients who received only 26 Gy in five fractions and those who received an additional sequential boost.
- Most patients reported reduced treatment time (78.6%) and infection control (59%) as major benefits of the 1-week radiotherapy regimen. Patients also reported high satisfaction with the use of telehealth, with 97.3% feeling well-informed about their diagnosis, 88% feeling well-informed about treatment side effects, and 94% feeling supported by the medical team. However, only 27% agreed to video consultations for breast inspections at 1 year.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ultrahypofractionated whole breast radiotherapy leads to acceptable late toxicity rates at 1 year even when followed by a hypofractionated tumour bed boost,” the authors wrote. “Patient satisfaction with ultrahypofractionated treatment and virtual consultations without video was high.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jill Nicholson, MBBS, MRCP, FFFRRCSI, St Luke’s Radiation Oncology Network, St. Luke’s Hospital, Dublin, Ireland, was published online in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The short follow-up period might not capture all late toxicities. Variability in patient-reported outcomes could affect consistency. The range in boost received (four to eight fractions) could have influenced patients’ experiences.
DISCLOSURES:
Nicholson received funding from the St. Luke’s Institute of Cancer Research, Dublin, Ireland. No other relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Most patients also reported that the reduced treatment time was a major benefit of the 1-week radiotherapy schedule.
METHODOLOGY:
- In March 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, international and national guidelines recommended adopting a 1-week ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy schedule for patients with node-negative breast cancer. Subsequently, a phase 3 trial demonstrated that a 1-week regimen of 26 Gy in five fractions led to similar breast cancer outcomes compared with a standard moderately hypofractionated regimen.
- In this study, researchers wanted to assess real world toxicities following ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy and enrolled 135 consecutive patients who received 1-week ultrahypofractionated adjuvant radiation of 26 Gy in five fractions from March to August 2020 at three centers in Ireland, with 33 patients (25%) receiving a sequential boost.
- Researchers recorded patient-reported outcomes on breast pain, swelling, firmness, and hypersensitivity at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months. Virtual consultations without video occurred at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and video consultations were offered at 1 year for a physician-led breast evaluation.
- Researchers assessed patient perspectives on this new schedule and telehealth workflows using questionnaires.
- Overall, 90% of patients completed the 1-year assessment plus another assessment. The primary endpoint was the worst toxicity reported at each time point.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 76% of patients reported no or mild toxicities at 3 and 6 months, and 82% reported no or mild toxicities 12 months.
- At 1 year, 20 patients (17%) reported moderate toxicity, most commonly breast pain, and only two patients (2%) reported marked toxicities, including breast firmness and skin changes.
- Researchers found no difference in toxicities between patients who received only 26 Gy in five fractions and those who received an additional sequential boost.
- Most patients reported reduced treatment time (78.6%) and infection control (59%) as major benefits of the 1-week radiotherapy regimen. Patients also reported high satisfaction with the use of telehealth, with 97.3% feeling well-informed about their diagnosis, 88% feeling well-informed about treatment side effects, and 94% feeling supported by the medical team. However, only 27% agreed to video consultations for breast inspections at 1 year.
IN PRACTICE:
“Ultrahypofractionated whole breast radiotherapy leads to acceptable late toxicity rates at 1 year even when followed by a hypofractionated tumour bed boost,” the authors wrote. “Patient satisfaction with ultrahypofractionated treatment and virtual consultations without video was high.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Jill Nicholson, MBBS, MRCP, FFFRRCSI, St Luke’s Radiation Oncology Network, St. Luke’s Hospital, Dublin, Ireland, was published online in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
The short follow-up period might not capture all late toxicities. Variability in patient-reported outcomes could affect consistency. The range in boost received (four to eight fractions) could have influenced patients’ experiences.
DISCLOSURES:
Nicholson received funding from the St. Luke’s Institute of Cancer Research, Dublin, Ireland. No other relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Data: The Most Promising Treatments for Long COVID
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID is a symptom-driven disease, meaning that with no cure, physicians primarily treat the symptoms their patients are experiencing. But as 2024 winds down, researchers have begun to pinpoint a number of treatments that are bringing relief to the 17 million Americans diagnosed with long COVID.
Here’s a current look at what research has identified as some of the most promising treatments.
Low-Dose Naltrexone
Some research suggests that low-dose naltrexone may be helpful for patients suffering from brain fog, pain, sleep issues, and fatigue, said Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, a global expert on long COVID and chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs St Louis Health Care System in Missouri.
Low-dose naltrexone is an anti-inflammatory agent currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of alcohol and opioid dependence.
“We don’t know the mechanism for how the medication works, and for that matter, we don’t really understand what causes brain fog. But perhaps its anti-inflammatory properties seem to help, and for some patients, low-dose naltrexone has been helpful,” said Al-Aly.
A March 2024 study found that both fatigue and pain were improved in patients taking low-dose naltrexone. In another study, published in the June 2024 issue of Frontiers in Medicine, researchers found that low-dose naltrexone was associated with improvement of several clinical symptoms related to long COVID such as fatigue, poor sleep quality, brain fog, post-exertional malaise, and headache.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Antidepressants
In 2023, University of Pennsylvania researchers uncovered a link between long COVID and lower levels of serotonin in the body. This helped point to the potential treatment of using SSRIs to treat the condition.
For patients who have overlapping psychiatric issues that go along with brain fog, SSRIs prescribed to treat depression and other mental health conditions, as well as the antidepressant Wellbutrin, have been shown effective at dealing with concentration issues, brain fog, and depression, said Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Long COVID Program at UCLA Health.
A study published in the November 2023 issue of the journal Scientific Reports found that SSRIs led to a “considerable reduction of symptoms,” especially brain fog, fatigue, sensory overload, and overall improved functioning. Low-dose Abilify, which contains aripiprazole, an antipsychotic medication, has also been found to be effective for cognitive issues caused by long COVID.
“Abilify is traditionally used for the treatment of schizophrenia or other psychotic disorders, but in a low-dose format, there is some data to suggest that it can also be anti-inflammatory and helpful for cognitive issues like brain fog,” said Viswanathan.
Modafinil
Modafinil, a medication previously used for managing narcolepsy, has also been shown effective for the treatment of fatigue and neurocognitive deficits caused by long COVID, said Viswanathan, adding that it’s another medication that she’s found useful for a number of her patients.
It’s thought that these cognitive symptoms are caused by an inflammatory cytokine release that leads to excessive stimulation of neurotransmitters in the body. According to a June 2024 article in the American Journal of Psychiatry, “Modafinil can therapeutically act on these pathways, which possibly contributed to the symptomatic improvement.” But the medication has not been studied widely in patients with long COVID and has been shown to have interactions with other medications.
Metformin
Some research has shown that metformin, a well-known diabetes medication, reduces instances of long COVID when taken during the illness’s acute phase. It seems to boost metabolic function in patients.
“It makes sense that it would work because it seems to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body,” said Grace McComsey, MD, who leads one of the 15 nationwide long COVID centers funded by the federal RECOVER (Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery) Initiative in Cleveland, Ohio. McComsey added that it may reduce the viral persistence that causes some forms of long COVID.
A study published in the October 2023 issue of the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases found that metformin seemed to reduce instances of long COVID in patients who took it after being diagnosed with acute COVID. It seems less effective in patients who already have long COVID.
Antihistamines
Other data suggest that some patients with long COVID showed improvement after taking antihistamines. Research has shown that long COVID symptoms improved in 29% of patients with long COVID.
While researchers aren’t sure why antihistamines work to quell long COVID, the thought is that, when mast cells, a white blood cell that’s part of the immune system, shed granules and cause an inflammatory reaction, they release a lot of histamines. Antihistamine medications like famotidine block histamine receptors in the body, improving symptoms like brain fog, difficulty breathing, and elevated heart rate in patients.
“For some patients, these can be a lifesaver,” said David Putrino, the Nash Family Director of the Cohen Center for Recovery from Complex Chronic Illness and a national leader in the treatment of long COVID.
Putrino cautions patients toward taking these and other medications haphazardly without fully understanding that all treatments have risks, especially if they’re taking a number of them.
“Often patients are told that there’s no risk to trying something, but physicians should be counseling their patients and reminding them that there is a risk that includes medication sensitivities and medication interactions,” said Putrino.
The good news is that doctors have begun to identify some treatments that seem to be working in their patients, but we still don’t have the large-scale clinical trials to identify which treatments will work for certain patients and why.
There’s still so much we don’t know, and for physicians on the front lines of treating long COVID, it’s still largely a guessing game. “This is a constellation of symptoms; it’s not just one thing,” said Al-Aly. And while a treatment might be wildly effective for one patient, it might be ineffective or worse, problematic, for another.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Spinal Cord Stimulation Promising for Chronic Back, Leg Pain
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapies for chronic back and/or leg pain is superior to conventional medical management (CMM) for reduced pain intensity and functional disability, new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a systematic review and network meta-analysis of 13 randomized clinical trials that compared conventional and novel SCS therapies with CMM.
- More than 1500 adults with chronic back and/or leg pain and no past history of receiving SCS therapies were included.
- Novel therapies included high frequency, burst, differential target multiplexed, and closed-loop SCS; conventional therapies included tonic SCS wave forms.
- Study outcomes included pain intensity in the back and in the leg, proportion of patients achieving at least 50% pain reduction in the back and in the leg, quality of life as measured by the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index, and functional disability on the Oswestry Disability Index.
- The analysis included data from multiple follow-up points at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months, with 6-month data being those from the longest mutually reported timepoint across all outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both conventional and novel SCS therapies demonstrated superior efficacy vs CMM in pain reduction, but the novel SCS therapies were more likely to provide ≥ 50% reduction in back pain (odds ratio, 8.76; 95% credible interval [CrI], 3.84-22.31).
- Both SCS therapies showed a significant reduction in pain intensity, with novel SCS providing the greatest mean difference (MD) for back pain (–2.34; 95% CrI, –2.96 to –1.73) and lower leg pain (MD, –4.01; 95% CrI, –5.31 to –2.75).
- Quality of life improved with both types of SCS therapies, with novel SCS therapies yielding the highest MD (0.17; 95% CrI, 0.13-0.21) in EQ-5D index score.
- Conventional SCS showed greater improvement in functionality vs CMM, yielding the lowest MD (–7.10; 95% CrI, –10.91 to –3.36) in Oswestry Disability Index score.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that SCS was associated with improved pain and QOL [quality of life] and reduced disability, compared with CMM, after 6 months of follow-up. These findings highlight the potential of SCS therapies as an effective and valuable option in chronic pain management,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Frank J.P.M. Huygen, PhD, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of randomized clinical trials with long-term follow-up data restricted the inclusion of extended outcome assessments. Most included studies showed a high risk for bias. Safety estimates could not be evaluated as adverse events were only reported as procedure-related outcomes, which are not applicable for CMM. Additionally, the network meta-analytical approach, which combined evidence from studies with varying patient eligibility criteria, may have introduced bias because of between-study heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Medtronic. Huygen reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Saluda, and Grunenthal outside the submitted work. The four other authors reported receiving funding from Medtronic.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapies for chronic back and/or leg pain is superior to conventional medical management (CMM) for reduced pain intensity and functional disability, new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a systematic review and network meta-analysis of 13 randomized clinical trials that compared conventional and novel SCS therapies with CMM.
- More than 1500 adults with chronic back and/or leg pain and no past history of receiving SCS therapies were included.
- Novel therapies included high frequency, burst, differential target multiplexed, and closed-loop SCS; conventional therapies included tonic SCS wave forms.
- Study outcomes included pain intensity in the back and in the leg, proportion of patients achieving at least 50% pain reduction in the back and in the leg, quality of life as measured by the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index, and functional disability on the Oswestry Disability Index.
- The analysis included data from multiple follow-up points at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months, with 6-month data being those from the longest mutually reported timepoint across all outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both conventional and novel SCS therapies demonstrated superior efficacy vs CMM in pain reduction, but the novel SCS therapies were more likely to provide ≥ 50% reduction in back pain (odds ratio, 8.76; 95% credible interval [CrI], 3.84-22.31).
- Both SCS therapies showed a significant reduction in pain intensity, with novel SCS providing the greatest mean difference (MD) for back pain (–2.34; 95% CrI, –2.96 to –1.73) and lower leg pain (MD, –4.01; 95% CrI, –5.31 to –2.75).
- Quality of life improved with both types of SCS therapies, with novel SCS therapies yielding the highest MD (0.17; 95% CrI, 0.13-0.21) in EQ-5D index score.
- Conventional SCS showed greater improvement in functionality vs CMM, yielding the lowest MD (–7.10; 95% CrI, –10.91 to –3.36) in Oswestry Disability Index score.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that SCS was associated with improved pain and QOL [quality of life] and reduced disability, compared with CMM, after 6 months of follow-up. These findings highlight the potential of SCS therapies as an effective and valuable option in chronic pain management,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Frank J.P.M. Huygen, PhD, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of randomized clinical trials with long-term follow-up data restricted the inclusion of extended outcome assessments. Most included studies showed a high risk for bias. Safety estimates could not be evaluated as adverse events were only reported as procedure-related outcomes, which are not applicable for CMM. Additionally, the network meta-analytical approach, which combined evidence from studies with varying patient eligibility criteria, may have introduced bias because of between-study heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Medtronic. Huygen reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Saluda, and Grunenthal outside the submitted work. The four other authors reported receiving funding from Medtronic.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapies for chronic back and/or leg pain is superior to conventional medical management (CMM) for reduced pain intensity and functional disability, new research suggests.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers performed a systematic review and network meta-analysis of 13 randomized clinical trials that compared conventional and novel SCS therapies with CMM.
- More than 1500 adults with chronic back and/or leg pain and no past history of receiving SCS therapies were included.
- Novel therapies included high frequency, burst, differential target multiplexed, and closed-loop SCS; conventional therapies included tonic SCS wave forms.
- Study outcomes included pain intensity in the back and in the leg, proportion of patients achieving at least 50% pain reduction in the back and in the leg, quality of life as measured by the EuroQol-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D) index, and functional disability on the Oswestry Disability Index.
- The analysis included data from multiple follow-up points at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months, with 6-month data being those from the longest mutually reported timepoint across all outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Both conventional and novel SCS therapies demonstrated superior efficacy vs CMM in pain reduction, but the novel SCS therapies were more likely to provide ≥ 50% reduction in back pain (odds ratio, 8.76; 95% credible interval [CrI], 3.84-22.31).
- Both SCS therapies showed a significant reduction in pain intensity, with novel SCS providing the greatest mean difference (MD) for back pain (–2.34; 95% CrI, –2.96 to –1.73) and lower leg pain (MD, –4.01; 95% CrI, –5.31 to –2.75).
- Quality of life improved with both types of SCS therapies, with novel SCS therapies yielding the highest MD (0.17; 95% CrI, 0.13-0.21) in EQ-5D index score.
- Conventional SCS showed greater improvement in functionality vs CMM, yielding the lowest MD (–7.10; 95% CrI, –10.91 to –3.36) in Oswestry Disability Index score.
IN PRACTICE:
“We found that SCS was associated with improved pain and QOL [quality of life] and reduced disability, compared with CMM, after 6 months of follow-up. These findings highlight the potential of SCS therapies as an effective and valuable option in chronic pain management,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Frank J.P.M. Huygen, PhD, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The lack of randomized clinical trials with long-term follow-up data restricted the inclusion of extended outcome assessments. Most included studies showed a high risk for bias. Safety estimates could not be evaluated as adverse events were only reported as procedure-related outcomes, which are not applicable for CMM. Additionally, the network meta-analytical approach, which combined evidence from studies with varying patient eligibility criteria, may have introduced bias because of between-study heterogeneity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Medtronic. Huygen reported receiving personal fees from Abbott, Saluda, and Grunenthal outside the submitted work. The four other authors reported receiving funding from Medtronic.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Deprescribe Low-Value Meds to Reduce Polypharmacy Harms
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VANCOUVER, BRITISH COLUMBIA — While polypharmacy is inevitable for patients with multiple chronic diseases, not all medications improve patient-oriented outcomes, members of the Patients, Experience, Evidence, Research (PEER) team, a group of Canadian primary care professionals who develop evidence-based guidelines, told attendees at the Family Medicine Forum (FMF) 2024.
In a thought-provoking presentation called “Axe the Rx: Deprescribing Chronic Medications with PEER,” the panelists gave examples of medications that may be safely stopped or tapered, particularly for older adults “whose pill bag is heavier than their lunch bag.”
Curbing Cardiovascular Drugs
The 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults call for reaching an LDL-C < 1.8 mmol/L in secondary cardiovascular prevention by potentially adding on medical therapies such as proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors or ezetimibe or both if that target is not reached with the maximal dosage of a statin.
But family physicians do not need to follow this guidance for their patients who have had a myocardial infarction, said Ontario family physician Jennifer Young, MD, a physician advisor in the Canadian College of Family Physicians’ Knowledge Experts and Tools Program.
Treating to below 1.8 mmol/L “means lab testing for the patients,” Young told this news organization. “It means increasing doses [of a statin] to try and get to that level.” If the patient is already on the highest dose of a statin, it means adding other medications that lower cholesterol.
“If that was translating into better outcomes like [preventing] death and another heart attack, then all of that extra effort would be worth it,” said Young. “But we don’t have evidence that it actually does have a benefit for outcomes like death and repeated heart attacks,” compared with putting them on a high dose of a potent statin.
Tapering Opioids
Before placing patients on an opioid taper, clinicians should first assess them for opioid use disorder (OUD), said Jessica Kirkwood, MD, assistant professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada. She suggested using the Prescription Opioid Misuse Index questionnaire to do so.
Clinicians should be much more careful in initiating a taper with patients with OUD, said Kirkwood. They must ensure that these patients are motivated to discontinue their opioids. “We’re losing 21 Canadians a day to the opioid crisis. We all know that cutting someone off their opioids and potentially having them seek opioids elsewhere through illicit means can be fatal.”
In addition, clinicians should spend more time counseling patients with OUD than those without, Kirkwood continued. They must explain to these patients how they are being tapered (eg, the intervals and doses) and highlight the benefits of a taper, such as reduced constipation. Opioid agonist therapy (such as methadone or buprenorphine) can be considered in these patients.
Some research has pointed to the importance of patient motivation as a factor in the success of opioid tapers, noted Kirkwood.
Deprescribing Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine receptor agonists, too, often can be deprescribed. These drugs should not be prescribed to promote sleep on a long-term basis. Yet clinicians commonly encounter patients who have been taking them for more than a year, said pharmacist Betsy Thomas, assistant adjunct professor of family medicine at the University of Alberta.
The medications “are usually fairly effective for the first couple of weeks to about a month, and then the benefits start to decrease, and we start to see more harms,” she said.
Some of the harms that have been associated with continued use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists include delayed reaction time and impaired cognition, which can affect the ability to drive, the risk for falls, and the risk for hip fractures, she noted. Some research suggests that these drugs are not an option for treating insomnia in patients aged 65 years or older.
Clinicians should encourage tapering the use of benzodiazepine receptor agonists to minimize dependence and transition patients to nonpharmacologic approaches such as cognitive behavioral therapy to manage insomnia, she said. A recent study demonstrated the efficacy of the intervention, and Thomas suggested that family physicians visit the mysleepwell.ca website for more information.
Young, Kirkwood, and Thomas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FMF 2024
Vaping Linked to Higher Risk of Blurred Vision & Eye Pain
TOPLINE:
Adults who use electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes/vapes) had more than double the risk for developing uveitis than nonusers, with elevated risks persisting for up to 4 years after initial use. This increased risk was observed across all age groups and affected both men and women as well as various ethnic groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used the TriNetX global database, which contains data from over 100 million patients across the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, to examine the risk for developing uveitis among e-cigarette users.
- 419,325 e-cigarette users over the age of 18 years (mean age, 51.41 years; 48.65% women) were included, based on diagnosis codes for vaping and unspecified nicotine dependence.
- The e-cigarette users were propensity score–matched to non-e-cigarette-users.
- People were excluded if they had comorbid conditions that might have influenced the risk for uveitis.
- The primary outcome measure was the first-time encounter diagnosis of uveitis using diagnosis codes for iridocyclitis, unspecified choroidal inflammation, posterior cyclitis, choroidal degeneration, retinal vasculitis, and pan-uveitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- E-cigarette users had a significantly higher risk for developing uveitis than nonusers (hazard ratio [HR], 2.53; 95% CI, 2.33-2.76 ), for iridocyclitis (HR, 2.59), unspecified chorioretinal inflammation (HR, 2.34), and retinal vasculitis (HR, 1.95).
- This increased risk for uveitis was observed across all age groups, affecting all genders and patients from Asian, Black or African American, and White ethnic backgrounds.
- The risk for uveitis increased as early as within 7 days after smoking an e-cigarettes (HR, 6.35) and was present even at 4 years (HR, 2.58) after initial use.
- A higher risk for uveitis was observed among individuals with a history of both e-cigarette and traditional cigarette use than among those who used traditional cigarettes only (HR, 1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study has real-world implications as clinicians caring for patients with e-cigarette history should be aware of the potentially increased risk of new-onset uveitis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alan Y. Hsu, MD, from the Department of Ophthalmology at China Medical University Hospital in Taichung, Taiwan, and was published online on November 12, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study limited the determination of direct causality between e-cigarette use and the risk for uveitis. The study lacked information on the duration and quantity of e-cigarette exposure, which may have impacted the findings. Moreover, researchers could not isolate the effect of secondhand exposure to vaping or traditional cigarettes.
DISCLOSURES:
Study authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults who use electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes/vapes) had more than double the risk for developing uveitis than nonusers, with elevated risks persisting for up to 4 years after initial use. This increased risk was observed across all age groups and affected both men and women as well as various ethnic groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used the TriNetX global database, which contains data from over 100 million patients across the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, to examine the risk for developing uveitis among e-cigarette users.
- 419,325 e-cigarette users over the age of 18 years (mean age, 51.41 years; 48.65% women) were included, based on diagnosis codes for vaping and unspecified nicotine dependence.
- The e-cigarette users were propensity score–matched to non-e-cigarette-users.
- People were excluded if they had comorbid conditions that might have influenced the risk for uveitis.
- The primary outcome measure was the first-time encounter diagnosis of uveitis using diagnosis codes for iridocyclitis, unspecified choroidal inflammation, posterior cyclitis, choroidal degeneration, retinal vasculitis, and pan-uveitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- E-cigarette users had a significantly higher risk for developing uveitis than nonusers (hazard ratio [HR], 2.53; 95% CI, 2.33-2.76 ), for iridocyclitis (HR, 2.59), unspecified chorioretinal inflammation (HR, 2.34), and retinal vasculitis (HR, 1.95).
- This increased risk for uveitis was observed across all age groups, affecting all genders and patients from Asian, Black or African American, and White ethnic backgrounds.
- The risk for uveitis increased as early as within 7 days after smoking an e-cigarettes (HR, 6.35) and was present even at 4 years (HR, 2.58) after initial use.
- A higher risk for uveitis was observed among individuals with a history of both e-cigarette and traditional cigarette use than among those who used traditional cigarettes only (HR, 1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study has real-world implications as clinicians caring for patients with e-cigarette history should be aware of the potentially increased risk of new-onset uveitis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alan Y. Hsu, MD, from the Department of Ophthalmology at China Medical University Hospital in Taichung, Taiwan, and was published online on November 12, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study limited the determination of direct causality between e-cigarette use and the risk for uveitis. The study lacked information on the duration and quantity of e-cigarette exposure, which may have impacted the findings. Moreover, researchers could not isolate the effect of secondhand exposure to vaping or traditional cigarettes.
DISCLOSURES:
Study authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults who use electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes/vapes) had more than double the risk for developing uveitis than nonusers, with elevated risks persisting for up to 4 years after initial use. This increased risk was observed across all age groups and affected both men and women as well as various ethnic groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used the TriNetX global database, which contains data from over 100 million patients across the United States, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, to examine the risk for developing uveitis among e-cigarette users.
- 419,325 e-cigarette users over the age of 18 years (mean age, 51.41 years; 48.65% women) were included, based on diagnosis codes for vaping and unspecified nicotine dependence.
- The e-cigarette users were propensity score–matched to non-e-cigarette-users.
- People were excluded if they had comorbid conditions that might have influenced the risk for uveitis.
- The primary outcome measure was the first-time encounter diagnosis of uveitis using diagnosis codes for iridocyclitis, unspecified choroidal inflammation, posterior cyclitis, choroidal degeneration, retinal vasculitis, and pan-uveitis.
TAKEAWAY:
- E-cigarette users had a significantly higher risk for developing uveitis than nonusers (hazard ratio [HR], 2.53; 95% CI, 2.33-2.76 ), for iridocyclitis (HR, 2.59), unspecified chorioretinal inflammation (HR, 2.34), and retinal vasculitis (HR, 1.95).
- This increased risk for uveitis was observed across all age groups, affecting all genders and patients from Asian, Black or African American, and White ethnic backgrounds.
- The risk for uveitis increased as early as within 7 days after smoking an e-cigarettes (HR, 6.35) and was present even at 4 years (HR, 2.58) after initial use.
- A higher risk for uveitis was observed among individuals with a history of both e-cigarette and traditional cigarette use than among those who used traditional cigarettes only (HR, 1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“This study has real-world implications as clinicians caring for patients with e-cigarette history should be aware of the potentially increased risk of new-onset uveitis,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Alan Y. Hsu, MD, from the Department of Ophthalmology at China Medical University Hospital in Taichung, Taiwan, and was published online on November 12, 2024, in Ophthalmology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study limited the determination of direct causality between e-cigarette use and the risk for uveitis. The study lacked information on the duration and quantity of e-cigarette exposure, which may have impacted the findings. Moreover, researchers could not isolate the effect of secondhand exposure to vaping or traditional cigarettes.
DISCLOSURES:
Study authors reported no relevant financial disclosures.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Shoulder Pain Pointers for Primary Care
The causes of shoulder pain may be as common as a traumatic injury or as rare as a systemic inflammatory condition, according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The combination of joints, tendons, and muscles that make up the shoulder can present diagnostic and clinical challenges, but several experts shared their tips for management.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Rotator cuff tendinopathy/tendinitis and subacromial bursitis are typically the most common causes of shoulder pain presenting to a primary care provider, said Jason Kolfenbach, MD, a rheumatologist at UC Health, Denver, Colorado, in an interview. “Other causes of shoulder pain may include acromioclavicular osteoarthritis, biceps tendinitis (often a secondary process in the setting of rotator cuff disease), and true glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis,” he said.
Experts estimate that as much as 80% of shoulder pain involves the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint, rather than true arthritis, said Kolfenbach, who was a co-author of a Medscape slideshow on evaluating shoulder pain. In the slideshow, the authors noted that proper evaluation is needed for successful pain management. Some patients may do well with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), rest, ice, and physical therapy, but more serious conditions may require steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or surgery.
If a patient’s joint pain with active range of motion is relieved when an examiner supports the affected limb (passive range of motion), the cause is more likely related to muscles, tendons, or ligaments, Kolfenbach said.
Primary care providers may not be familiar with examination maneuvers to diagnose shoulder pain, although they are often tasked with evaluating and managing these patients, said Kolfenbach.
Education focused on practical aspects of these maneuvers may help improve primary care confidence in utilizing them and lead to more appropriate ordering of imaging testing and better pain management plans for patients, he said.
However, “If there is concern for a true intra-articular process, plain radiographs are recommended to determine if there is loss of cartilage space and/or other anatomic drivers of pain,” he noted. “Even in conditions of documented intra-articular arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, weakness, and atrophy of the surrounding musculature can contribute to joint disability and pain,” he said. For these patients, referral to physical therapy for periarticular strengthening can provide pain relief, he added.
Pinning Down the Pain Point
The many different structures within the shoulder that can cause pain make diagnosis a challenge, Nicole Angelo, DO, MS, a physiatrist at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City, said in an interview.
Potential sources of pain include the joint of the shoulder itself, the structures within it (labrum, capsule, and ligaments), and the surrounding rotator cuff muscles and tendons, she said. Patients also may experience overlapping pain referred from the neck (cervical spine) related to nerve irritation (cervical radiculopathy) or arthritis, she noted.
“A patient’s history, including mechanism and acuity of injury, as well as exam, specifically weakness in certain movements,” can help determine whether advanced imaging and surgical intervention may be required,” Angelo told this news organization.
Frozen shoulder is the most missed diagnosis of shoulder pain in primary care, Brian Feeley, MD, chief of sports medicine and shoulder surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, can mimic many other conditions including rotator cuff problems, shoulder arthritis, and biceps problems, Feeley said. “When people have a loss of active and passive range of motion and no evidence of arthritis on x-rays, their diagnosis is most likely frozen shoulder,” he said.
Another challenge for primary care providers is identifying the severity of rotator cuff problems, Feeley said. “I like to think of rotator cuff problems along a spectrum — impingement is inflammation above the rotator cuff and suggests an imbalance between rotator cuff strength and deltoid strength,” said Feeley. “Partial thickness tears are often normal age-related problems but can be a source of pain,” he added.
However, full-thickness tears encompass a range of problems, from very small asymptomatic holes in the rotator cuff to massive tears that require shoulder replacement, Feeley explained. “Tendinopathy, or changes in the collagen organization in the tendon of the rotator cuff, sounds problematic, but most often is either incidental or part of aging,” he added.
When Shoulder Pain Isn’t Caused by the Shoulder
Primary care patients presenting with shoulder pain may in fact have a neck or spine problem instead, Feeley told this news organization. “Pain that is in the shoulder blade area or down the arm and into the fingers is usually coming from the neck/cervical spine,” he said.
In some cases, shoulder pain stems from the joints below the shoulder, including the elbow, because of arthritis, tennis elbow (lateral epicondylopathy), or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylopathy), said Angelo. “Conditions of the elbow and neck can also affect shoulder mechanics or cause someone to use the joint more or less frequently,” she said. The interconnections between the neck and joints of the upper extremity, including referral patterns, complicate the diagnosis of shoulder pain; therefore, careful history-taking and examination of joints both above and below the shoulder are essential, she added.
Conservative Care
Shoulder problems often can be managed conservatively with therapeutic exercise focused on maintaining range of motion of the shoulder and strengthening the musculature around the shoulder, Angelo said. “Often, working with a physical therapist to address the mechanics of how the shoulder is moving and how the muscles are firing can help decrease pain and help patients meet their functional goals,” said Angelo. “Injections into the joint, the bursa adjacent to the rotator cuff, and, at times, into the tendons themselves can also be beneficial in relieving pain and improving function,” she said.
In some cases, a short, consistent course of anti-inflammatory medications can be part of a conservative strategy for the management of shoulder pain, Angelo noted.
“Utilizing these medications on an as-needed basis can also help patients improve their ability to sleep, perform their daily activities, and participate in physical therapy,” she said. A course of physical therapy that promotes maintaining shoulder range of motion, strengthening of the rotator cuff musculature, and working on the mechanics between the scapula and humerus is a good first step for most shoulder conditions, Angelo told this news organization.
“If there is concern due to recent trauma, significant weakness, or new/persistent numbness, referral to a specialist should be considered,” she said. If conservative measures including analgesics and exercise have failed to improve shoulder pain, advanced imaging and further interventional treatment may be necessary, Angelo added.
Most shoulder problems can and should be managed nonoperatively, Feeley said. Surgery should be reserved for patients whose shoulder pain has not improved with nonoperative care in most situations, he said. “It is often surprising for patients to hear, but most things in the shoulder actually get better without surgery, and changes on MRI are often normal for age,” Feeley noted. For example, more than 80% of individuals older than 50 will show signs of a labral tear or arthritis in the acromioclavicular joint, he said. “These are incidental findings that don’t need treatment,” he added.
More research is needed to develop more medications to manage pain for all musculoskeletal conditions, including shoulder pain, said Feeley. “But for now, for patients with shoulder pain, I tend to recommend a combination of Tylenol and an NSAID to improve inflammation and reduce pain, and a guided [physical] therapy program at home or in person. The combination of both usually will be successful,” he said.
Postsurgical Shoulder Pain
“For patients who have shoulder surgery, the techniques to manage pain around surgery have improved tremendously over the last decade, particularly with multimodal pain management and nerve blocks,” Feeley told this news organization. These advances have tremendously reduced the need for narcotics for pain management beyond the first 72 hours after surgery, he said. “I strongly recommend patients and primary care doctors to stop all narcotics as soon as possible after shoulder surgery, since they are not nearly as effective for management of pain after the first few days, and they should never be used as a sleep aid,” he emphasized.
Managing pain during recovery from shoulder surgery also involves about 6 weeks in a sling to protect the repair, followed by 6 weeks of active motion but no strengthening, then 3 months of strengthening exercises, he said.
Shoulder pain resources for patients: https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_shoulder-pain-causes.asp
Feeley’s 10-minute video on shoulder examination and pain assessment at the UCSF 14th Annual Primary Care Sports Medicine Conference, 2019: Video on the Essential Shoulder Exam
Kolfenbach disclosed receiving royalties from Elsevier for being the editor of Rheumatology Secrets and Wolters Kluwer for authoring several articles on UpToDate. Feeley and Angelo had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The causes of shoulder pain may be as common as a traumatic injury or as rare as a systemic inflammatory condition, according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The combination of joints, tendons, and muscles that make up the shoulder can present diagnostic and clinical challenges, but several experts shared their tips for management.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Rotator cuff tendinopathy/tendinitis and subacromial bursitis are typically the most common causes of shoulder pain presenting to a primary care provider, said Jason Kolfenbach, MD, a rheumatologist at UC Health, Denver, Colorado, in an interview. “Other causes of shoulder pain may include acromioclavicular osteoarthritis, biceps tendinitis (often a secondary process in the setting of rotator cuff disease), and true glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis,” he said.
Experts estimate that as much as 80% of shoulder pain involves the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint, rather than true arthritis, said Kolfenbach, who was a co-author of a Medscape slideshow on evaluating shoulder pain. In the slideshow, the authors noted that proper evaluation is needed for successful pain management. Some patients may do well with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), rest, ice, and physical therapy, but more serious conditions may require steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or surgery.
If a patient’s joint pain with active range of motion is relieved when an examiner supports the affected limb (passive range of motion), the cause is more likely related to muscles, tendons, or ligaments, Kolfenbach said.
Primary care providers may not be familiar with examination maneuvers to diagnose shoulder pain, although they are often tasked with evaluating and managing these patients, said Kolfenbach.
Education focused on practical aspects of these maneuvers may help improve primary care confidence in utilizing them and lead to more appropriate ordering of imaging testing and better pain management plans for patients, he said.
However, “If there is concern for a true intra-articular process, plain radiographs are recommended to determine if there is loss of cartilage space and/or other anatomic drivers of pain,” he noted. “Even in conditions of documented intra-articular arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, weakness, and atrophy of the surrounding musculature can contribute to joint disability and pain,” he said. For these patients, referral to physical therapy for periarticular strengthening can provide pain relief, he added.
Pinning Down the Pain Point
The many different structures within the shoulder that can cause pain make diagnosis a challenge, Nicole Angelo, DO, MS, a physiatrist at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City, said in an interview.
Potential sources of pain include the joint of the shoulder itself, the structures within it (labrum, capsule, and ligaments), and the surrounding rotator cuff muscles and tendons, she said. Patients also may experience overlapping pain referred from the neck (cervical spine) related to nerve irritation (cervical radiculopathy) or arthritis, she noted.
“A patient’s history, including mechanism and acuity of injury, as well as exam, specifically weakness in certain movements,” can help determine whether advanced imaging and surgical intervention may be required,” Angelo told this news organization.
Frozen shoulder is the most missed diagnosis of shoulder pain in primary care, Brian Feeley, MD, chief of sports medicine and shoulder surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, can mimic many other conditions including rotator cuff problems, shoulder arthritis, and biceps problems, Feeley said. “When people have a loss of active and passive range of motion and no evidence of arthritis on x-rays, their diagnosis is most likely frozen shoulder,” he said.
Another challenge for primary care providers is identifying the severity of rotator cuff problems, Feeley said. “I like to think of rotator cuff problems along a spectrum — impingement is inflammation above the rotator cuff and suggests an imbalance between rotator cuff strength and deltoid strength,” said Feeley. “Partial thickness tears are often normal age-related problems but can be a source of pain,” he added.
However, full-thickness tears encompass a range of problems, from very small asymptomatic holes in the rotator cuff to massive tears that require shoulder replacement, Feeley explained. “Tendinopathy, or changes in the collagen organization in the tendon of the rotator cuff, sounds problematic, but most often is either incidental or part of aging,” he added.
When Shoulder Pain Isn’t Caused by the Shoulder
Primary care patients presenting with shoulder pain may in fact have a neck or spine problem instead, Feeley told this news organization. “Pain that is in the shoulder blade area or down the arm and into the fingers is usually coming from the neck/cervical spine,” he said.
In some cases, shoulder pain stems from the joints below the shoulder, including the elbow, because of arthritis, tennis elbow (lateral epicondylopathy), or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylopathy), said Angelo. “Conditions of the elbow and neck can also affect shoulder mechanics or cause someone to use the joint more or less frequently,” she said. The interconnections between the neck and joints of the upper extremity, including referral patterns, complicate the diagnosis of shoulder pain; therefore, careful history-taking and examination of joints both above and below the shoulder are essential, she added.
Conservative Care
Shoulder problems often can be managed conservatively with therapeutic exercise focused on maintaining range of motion of the shoulder and strengthening the musculature around the shoulder, Angelo said. “Often, working with a physical therapist to address the mechanics of how the shoulder is moving and how the muscles are firing can help decrease pain and help patients meet their functional goals,” said Angelo. “Injections into the joint, the bursa adjacent to the rotator cuff, and, at times, into the tendons themselves can also be beneficial in relieving pain and improving function,” she said.
In some cases, a short, consistent course of anti-inflammatory medications can be part of a conservative strategy for the management of shoulder pain, Angelo noted.
“Utilizing these medications on an as-needed basis can also help patients improve their ability to sleep, perform their daily activities, and participate in physical therapy,” she said. A course of physical therapy that promotes maintaining shoulder range of motion, strengthening of the rotator cuff musculature, and working on the mechanics between the scapula and humerus is a good first step for most shoulder conditions, Angelo told this news organization.
“If there is concern due to recent trauma, significant weakness, or new/persistent numbness, referral to a specialist should be considered,” she said. If conservative measures including analgesics and exercise have failed to improve shoulder pain, advanced imaging and further interventional treatment may be necessary, Angelo added.
Most shoulder problems can and should be managed nonoperatively, Feeley said. Surgery should be reserved for patients whose shoulder pain has not improved with nonoperative care in most situations, he said. “It is often surprising for patients to hear, but most things in the shoulder actually get better without surgery, and changes on MRI are often normal for age,” Feeley noted. For example, more than 80% of individuals older than 50 will show signs of a labral tear or arthritis in the acromioclavicular joint, he said. “These are incidental findings that don’t need treatment,” he added.
More research is needed to develop more medications to manage pain for all musculoskeletal conditions, including shoulder pain, said Feeley. “But for now, for patients with shoulder pain, I tend to recommend a combination of Tylenol and an NSAID to improve inflammation and reduce pain, and a guided [physical] therapy program at home or in person. The combination of both usually will be successful,” he said.
Postsurgical Shoulder Pain
“For patients who have shoulder surgery, the techniques to manage pain around surgery have improved tremendously over the last decade, particularly with multimodal pain management and nerve blocks,” Feeley told this news organization. These advances have tremendously reduced the need for narcotics for pain management beyond the first 72 hours after surgery, he said. “I strongly recommend patients and primary care doctors to stop all narcotics as soon as possible after shoulder surgery, since they are not nearly as effective for management of pain after the first few days, and they should never be used as a sleep aid,” he emphasized.
Managing pain during recovery from shoulder surgery also involves about 6 weeks in a sling to protect the repair, followed by 6 weeks of active motion but no strengthening, then 3 months of strengthening exercises, he said.
Shoulder pain resources for patients: https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_shoulder-pain-causes.asp
Feeley’s 10-minute video on shoulder examination and pain assessment at the UCSF 14th Annual Primary Care Sports Medicine Conference, 2019: Video on the Essential Shoulder Exam
Kolfenbach disclosed receiving royalties from Elsevier for being the editor of Rheumatology Secrets and Wolters Kluwer for authoring several articles on UpToDate. Feeley and Angelo had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The causes of shoulder pain may be as common as a traumatic injury or as rare as a systemic inflammatory condition, according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. The combination of joints, tendons, and muscles that make up the shoulder can present diagnostic and clinical challenges, but several experts shared their tips for management.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Rotator cuff tendinopathy/tendinitis and subacromial bursitis are typically the most common causes of shoulder pain presenting to a primary care provider, said Jason Kolfenbach, MD, a rheumatologist at UC Health, Denver, Colorado, in an interview. “Other causes of shoulder pain may include acromioclavicular osteoarthritis, biceps tendinitis (often a secondary process in the setting of rotator cuff disease), and true glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis,” he said.
Experts estimate that as much as 80% of shoulder pain involves the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the joint, rather than true arthritis, said Kolfenbach, who was a co-author of a Medscape slideshow on evaluating shoulder pain. In the slideshow, the authors noted that proper evaluation is needed for successful pain management. Some patients may do well with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), rest, ice, and physical therapy, but more serious conditions may require steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, or surgery.
If a patient’s joint pain with active range of motion is relieved when an examiner supports the affected limb (passive range of motion), the cause is more likely related to muscles, tendons, or ligaments, Kolfenbach said.
Primary care providers may not be familiar with examination maneuvers to diagnose shoulder pain, although they are often tasked with evaluating and managing these patients, said Kolfenbach.
Education focused on practical aspects of these maneuvers may help improve primary care confidence in utilizing them and lead to more appropriate ordering of imaging testing and better pain management plans for patients, he said.
However, “If there is concern for a true intra-articular process, plain radiographs are recommended to determine if there is loss of cartilage space and/or other anatomic drivers of pain,” he noted. “Even in conditions of documented intra-articular arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, weakness, and atrophy of the surrounding musculature can contribute to joint disability and pain,” he said. For these patients, referral to physical therapy for periarticular strengthening can provide pain relief, he added.
Pinning Down the Pain Point
The many different structures within the shoulder that can cause pain make diagnosis a challenge, Nicole Angelo, DO, MS, a physiatrist at the Hospital for Special Surgery, New York City, said in an interview.
Potential sources of pain include the joint of the shoulder itself, the structures within it (labrum, capsule, and ligaments), and the surrounding rotator cuff muscles and tendons, she said. Patients also may experience overlapping pain referred from the neck (cervical spine) related to nerve irritation (cervical radiculopathy) or arthritis, she noted.
“A patient’s history, including mechanism and acuity of injury, as well as exam, specifically weakness in certain movements,” can help determine whether advanced imaging and surgical intervention may be required,” Angelo told this news organization.
Frozen shoulder is the most missed diagnosis of shoulder pain in primary care, Brian Feeley, MD, chief of sports medicine and shoulder surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), said in an interview.
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, can mimic many other conditions including rotator cuff problems, shoulder arthritis, and biceps problems, Feeley said. “When people have a loss of active and passive range of motion and no evidence of arthritis on x-rays, their diagnosis is most likely frozen shoulder,” he said.
Another challenge for primary care providers is identifying the severity of rotator cuff problems, Feeley said. “I like to think of rotator cuff problems along a spectrum — impingement is inflammation above the rotator cuff and suggests an imbalance between rotator cuff strength and deltoid strength,” said Feeley. “Partial thickness tears are often normal age-related problems but can be a source of pain,” he added.
However, full-thickness tears encompass a range of problems, from very small asymptomatic holes in the rotator cuff to massive tears that require shoulder replacement, Feeley explained. “Tendinopathy, or changes in the collagen organization in the tendon of the rotator cuff, sounds problematic, but most often is either incidental or part of aging,” he added.
When Shoulder Pain Isn’t Caused by the Shoulder
Primary care patients presenting with shoulder pain may in fact have a neck or spine problem instead, Feeley told this news organization. “Pain that is in the shoulder blade area or down the arm and into the fingers is usually coming from the neck/cervical spine,” he said.
In some cases, shoulder pain stems from the joints below the shoulder, including the elbow, because of arthritis, tennis elbow (lateral epicondylopathy), or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylopathy), said Angelo. “Conditions of the elbow and neck can also affect shoulder mechanics or cause someone to use the joint more or less frequently,” she said. The interconnections between the neck and joints of the upper extremity, including referral patterns, complicate the diagnosis of shoulder pain; therefore, careful history-taking and examination of joints both above and below the shoulder are essential, she added.
Conservative Care
Shoulder problems often can be managed conservatively with therapeutic exercise focused on maintaining range of motion of the shoulder and strengthening the musculature around the shoulder, Angelo said. “Often, working with a physical therapist to address the mechanics of how the shoulder is moving and how the muscles are firing can help decrease pain and help patients meet their functional goals,” said Angelo. “Injections into the joint, the bursa adjacent to the rotator cuff, and, at times, into the tendons themselves can also be beneficial in relieving pain and improving function,” she said.
In some cases, a short, consistent course of anti-inflammatory medications can be part of a conservative strategy for the management of shoulder pain, Angelo noted.
“Utilizing these medications on an as-needed basis can also help patients improve their ability to sleep, perform their daily activities, and participate in physical therapy,” she said. A course of physical therapy that promotes maintaining shoulder range of motion, strengthening of the rotator cuff musculature, and working on the mechanics between the scapula and humerus is a good first step for most shoulder conditions, Angelo told this news organization.
“If there is concern due to recent trauma, significant weakness, or new/persistent numbness, referral to a specialist should be considered,” she said. If conservative measures including analgesics and exercise have failed to improve shoulder pain, advanced imaging and further interventional treatment may be necessary, Angelo added.
Most shoulder problems can and should be managed nonoperatively, Feeley said. Surgery should be reserved for patients whose shoulder pain has not improved with nonoperative care in most situations, he said. “It is often surprising for patients to hear, but most things in the shoulder actually get better without surgery, and changes on MRI are often normal for age,” Feeley noted. For example, more than 80% of individuals older than 50 will show signs of a labral tear or arthritis in the acromioclavicular joint, he said. “These are incidental findings that don’t need treatment,” he added.
More research is needed to develop more medications to manage pain for all musculoskeletal conditions, including shoulder pain, said Feeley. “But for now, for patients with shoulder pain, I tend to recommend a combination of Tylenol and an NSAID to improve inflammation and reduce pain, and a guided [physical] therapy program at home or in person. The combination of both usually will be successful,” he said.
Postsurgical Shoulder Pain
“For patients who have shoulder surgery, the techniques to manage pain around surgery have improved tremendously over the last decade, particularly with multimodal pain management and nerve blocks,” Feeley told this news organization. These advances have tremendously reduced the need for narcotics for pain management beyond the first 72 hours after surgery, he said. “I strongly recommend patients and primary care doctors to stop all narcotics as soon as possible after shoulder surgery, since they are not nearly as effective for management of pain after the first few days, and they should never be used as a sleep aid,” he emphasized.
Managing pain during recovery from shoulder surgery also involves about 6 weeks in a sling to protect the repair, followed by 6 weeks of active motion but no strengthening, then 3 months of strengthening exercises, he said.
Shoulder pain resources for patients: https://www.hss.edu/condition-list_shoulder-pain-causes.asp
Feeley’s 10-minute video on shoulder examination and pain assessment at the UCSF 14th Annual Primary Care Sports Medicine Conference, 2019: Video on the Essential Shoulder Exam
Kolfenbach disclosed receiving royalties from Elsevier for being the editor of Rheumatology Secrets and Wolters Kluwer for authoring several articles on UpToDate. Feeley and Angelo had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.