User login
Clinical index predicts common postpartum mental health disorders
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
Developed by Canadian researchers, the easily implementable PMH CAREPLAN index “creates a framework for clinically actionable risk stratification that could assist patients and providers in determining an individual’s level of risk for common postpartum mental health disorders and direct them to appropriate intervention,” wrote a group led by Simone N. Vigod, MD, MSc, head of the department of psychiatry at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, in the British Journal of Psychiatry.
After giving birth, women are especially vulnerable to major depression, anxiety, PTSD, and obsessive-compulsive disorder, which have a general postpartum prevalence of 7%-20%.
Common PMH disorders are to be distinguished from the more rare but severe PMH disorders such as postpartum psychosis and bipolar disorder, the researchers stressed.
“We know there are interventions that can prevent these disorders, but these seem to work best in people who are at high risk for developing the illnesses, “ Dr. Vigod said. “So, we wanted to be able to determine the level of risk that a person might actually experience them.”
In an ideal world, she continued, physicians might be able to say to a patient: “You have a 50% chance of developing postpartum depression and anxiety, so it may be worth investing your time and resources in a course of preventive psychotherapy.” Or: “You have a 90% chance of developing these disorders, so it might be worth going back on your medications even though you are breastfeeding.” Or: “You have only a 1% chance of developing them, so probably it’s not worthwhile to go back on your medication prophylactically.”
A need for a new assessment tool, akin to the Framingham Risk Score for 10-year cardiovascular events and the FRAX scoring system for 10-year fracture risk, was evident since previous indices based largely on patient self-reporting have had moderate predictive capacity, and have not been adopted in clinical practice, Dr. Vigod and associates noted.
Split-cohort design
Using population-based health administrative data and hospital birth records from Ontario during 2012-2015, Dr. Vigod’s group created and internally validated a predictive model for common PMH disorders in a cohort of 152,362 mothers. They then converted it to a risk index after validation in an additional cohort of 75,772 mothers. The women had delivered live infants during 2012-2014.
A common PMH disorder occurred in 13,608 mothers, while 214,526 were unaffected.
Independently associated PMH variables were many: prenatal care provider, mental health diagnosis history and medications during pregnancy, psychiatric hospital admissions or ED visits, conception type and complications, and apprehension of newborn by child services. Other factors were region of maternal origin, extremes of gestational age at birth, primary maternal language, lactation intention, maternal age, and number of prenatal visits.
Based on a broad span of scores from 0 to 39, 1-year common PMH disorder risk ranged from 1.5% to 40.5%, with an overall 1-year prevalence of 6%, consistent with previous studies. That included 11,262 (5%) mothers with an anxiety or related disorder, 3,392 (1.5%) with a depressive episode, and 1,046 (0.5%) with both. The best trade-off of sensitivity/specificity for risk appeared to be at a screening threshold score of 17 or above.
Risk drivers
PMH-affected mothers were slightly younger than unaffected women (mean age, 29.9 years vs. 30.6 years), more likely to be primiparous (45.2% vs. 42%), and less likely to be recent immigrants (16.7% vs. 27.2%).
They were also more likely to have previously experienced postpartum depression (4.4% vs. 1.4%), any depression (15.3% vs. 4.4%), and any anxiety disorder (13.8% vs. 4.3%).
As to lifestyle, smoking was more common in women with PMH (15.0% vs. 10.2%), as were the use of nonprescribed substances (3% vs. 1.4%) and intimate partner violence in pregnancy (2.7% vs. 1.5%).
In addition, the affected group experienced more pregnancy complications than their unaffected peers (16% vs. 13.9%), preterm birth (8.2% vs. 6.8%), and Apgar scores below 7 at 1 or 5 minutes (10.5% vs. 7.6%).
Low income did not appear to have an impact since just over 20% in either group fell into the lowest neighborhood income quintile.
Commenting on the index but not involved in developing it, LaTasha D. Nelson, MD, an associate professor or medicine and a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, doubted the Canadian model would work as well in the more fragmented U.S. health care system, compared with Canada’s universal model with its large provincial health databases.
She also found the large number of variables and broad score range potentially problematic, especially if the risk threshold is set at less than half the maximum score at 17, at which some low-risk mothers might get screening and perhaps intervention. “Are we going to use up the resources we have for those who might not need help, or are we going to treat someone who really needs it?” she asked.
Another concern is the postpartum timing of assessment. At Dr. Nelson’s center, mothers are checked for mental health at two points during pregnancy and those with higher scores are triaged for further care.
Dr. Nelson was also puzzled by the score-lowering impact of prenatal care given by a nurse practitioner and “other” provider : –5 and –2, respectively, versus +3 for a midwife and +1 for a family doctor. “This may capture more relaxed, easy-going multiparous mothers who felt comfortable turning to an NP,” she said.
It may indeed reflect that the risk level of a person who sees those providers is overall lower, Dr. Vigod agreed. “This is one reason why we would want to see replication of these results in other jurisdictions and by other ways of diagnosis before putting it out into clinical practice.”
As to the score-lowering effect of not speaking English as the primary tongue, Dr. Nelson wondered, “is that because we’re taking better care of mothers who speak the main language and missing those who speak other languages? Are they not getting the same level of interrogation?”
It may be that individuals in these groups were less likely to access mental health care, Dr. Vigod agreed, or it might reflect the so-called healthy immigrant effect or culturally different levels of postpartum support. “It might mean that there are more people who benefit from community-level protective factors in these groups. We know that social support is an important protective factor.”
Despite her reservations about the index, Dr. Nelson said that increasing attention to the pre- and postnatal mental health of mothers is an important part of maternal care. “This is an issue that needs to be recognized.”
The next step, Dr. Vigod said, is to determine whether the index holds up in other populations. “Then, we would want to test it out to see if recommending interventions based on a certain level of risk improves outcomes. At what percentage risk would starting an antidepressant medication result in a reduced risk for postpartum depression or anxiety – 90%, 80%, 70%, or less?”
The study received funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Data were analyzed by ICES, an independent nonprofit research organization that holds population-based data. Dr. Vigod reported royalties from UpToDate for materials related to depression and pregnancy. Dr. Nelson disclosed no relevant competing interests.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY
Anti-obesity medications: Breakthroughs and limitations
Obesity is a major health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines the problem as weight that is higher than what is healthy for a given height, with quantitative definitions of overweight and obesity as body mass indices (BMIs) of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 and ≥ 30 kg/m2, respectively.1 The prevalence of obesity among adults in 2017 ̶ 2018 was reported by the CDC to be 42.4%.2 Among women, the reported prevalence of obesity was lowest among Asian individuals (17.2%) and greatest among non-Hispanic Black individuals (56.9%), with White (39.8%) and Hispanic individuals (43.7%) having rates in between.2 In a meta-analysis of prospective studies that included 4 million people who were never smokers and had no chronic disease at baseline, age- and sex-adjusted mortality rates were studied over a median of 14 years of follow-up.3 Compared with those with a BMI of 20 to 25 kg/m2, people with a BMI of 30 to 34.9 kg/m2 or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 had increased risks of death of 46% and 94%, respectively, demonstrating that obesity increases this risk.3
The increased risk of death associated with obesity is caused by obesity-related diseases that cause early mortality, including diabetes mellitus (DM), dyslipidemia, hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and venous thromboembolic events.4 Obesity is also associated with an increased risk of many cancers, including cancer of the endometrium, kidney, esophagus, stomach, colon, rectum, gallbladder, pancreas, liver, and breast.5 With regard to gynecologic disease, obesity is associated with an increased risk of fibroids and heavy menstrual bleeding.6 For pregnant patients, obesity is associated with increased risks of7:
- miscarriage and stillbirth
- preeclampsia and gestational hypertension
- gestational diabetes
- severe maternal morbidity
- postterm pregnancy
- venous thromboembolism
- endometritis.
For obese patients, weight loss can normalize blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, decrease the risk of cancer, and cure type 2 DM.8
Bariatric surgery: The gold standard treatment for reliable and sustained weight loss
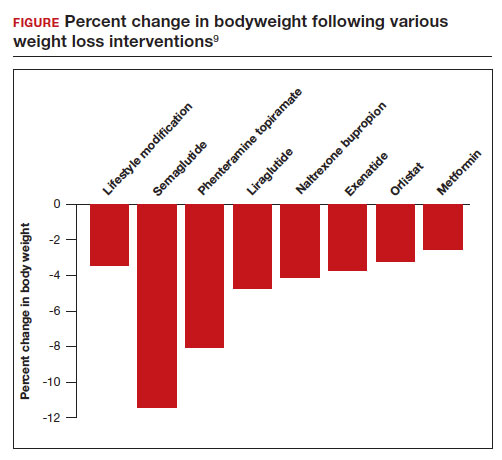
All patients with obesity should be counseled to reduce caloric intake and increase physical activity. Dietary counseling provided by a nutritionist may help reinforce advice given by a provider. However, lifestyle interventions are associated with modest weight loss (<5% of bodyweight; FIGURE
In the Swedish Obese Subjects study, involving 2,010 people, following bariatric surgery the mean decrease in bodyweight was 23% at 2 years, with a slow increase in weight thereafter, resulting in a sustained mean weight loss of 18% at 10 years.8 In this study, people in the diet and exercise control group had no change in bodyweight over 10 years of follow-up.8 Not all eligible obese patients want to undergo bariatric surgery because it is an arduous sequential process involving 6 months of intensive preoperative preparation, bariatric surgery, recovery, and intensive postoperative follow-up. The perioperative mortality rate is 0.03% to 0.2%.10 Following bariatric surgery, additional operations may be necessary for more than 10% of patients.10 With recent breakthroughs in the medication management of obesity, patients who do not want bariatric surgery can achieve reliable weight loss of greater than 10% of body weight with glucagon-like peptide -1 (GLP-1) agonists.
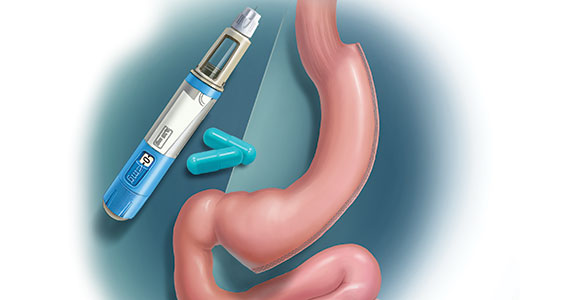
GLP-1 agonist analogues: Practice-changing breakthrough in medication treatment
GLP-1, a 30 amino acid peptide, is produced by intestinal enteroendocrine cells and neurons in the medulla and hypothalamus.11 GLP-1 reduces hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing daily food intake.12 GLP-1 also enhances the secretion of insulin, making GLP-1 agonists an effective treatment for type 2 DM. In humans and experimental animals, the administration of exogenous GLP-1 agonists decreases hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing food intake, resulting in weight loss.12 The synthetic GLP-1 agonists, liraglutide (Saxenda) and semaglutide (Wegovy) are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as anti-obesity medications.
Native GLP-1 has a short circulating half-life of approximately 2 minutes. The synthetic GLP-1 agonist medications liraglutide and semaglutide are modified to significantly increase their half-life. Liraglutide is a modified version of GLP-1 with a palmitic acid side chain and an amino acid spacer resulting in reduced degradation and a 15-hour half-life, necessitating daily administration. Semaglutide has a steric acid diacid at Lys26, a large synthetic spacer, a modification of amino acid 8 with the addition of α-aminobutyric acid and a 165-hour half-life, permitting weekly administration.13 For weight loss, liraglutide and semaglultide are administered by subcutaneous injection. Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is a novel GLP-1 agonist. It is also a gastric inhibitory peptide, is FDA approved to treat type 2 DM, and is awaiting FDA approval as a weight loss medication.Tirzepatide causes substantial weight loss, similar to the effect of semaglutide.14
Semaglutide and weight loss
Semaglutide is approved by the FDA for chronic weight management as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity in adults with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 or ≥ 27 kg/m2 in the presence of a weight-related comorbidity. It is also FDA approved to treat type 2 DM.
In a weight loss trial, 1,961 overweight and obese patients with a mean BMI of 38 kg/m2, were randomly assigned to semaglutide or placebo treatment for 68 weeks. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. The mean changes in body weight for the patients in the semaglutide and placebo treatment groups were -14.9% and -2.4%, respectively. The treatment difference was -12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], -13.4% to -11.5%; P <.001). In this study, compared with placebo, semaglutide treatment resulted in a greater decrease in waist circumference, -5.3 in versus -1.6 in.15 A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of weight loss medicines indicates that semaglutide is the most effective medication currently FDA approved for weight loss, reliably producing substantial weight loss (FIGURE).9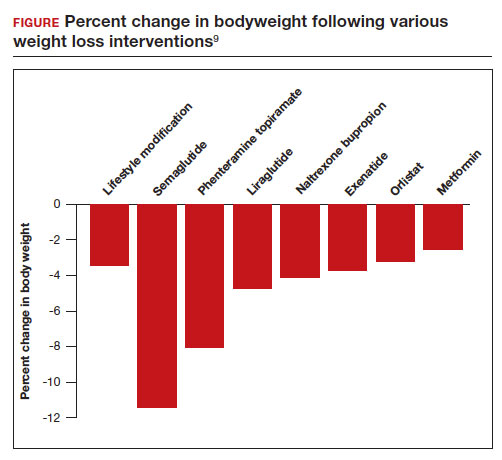
In one randomized clinical trial, investigators directly compared the efficacy of semaglutide and liraglutide in achieving weight loss. In this trial, 338 patients were assigned randomly to treatment with semaglutide 2.4 mg weekly subcutaneous injection, liraglutide 3.0 mg daily subcutaneous injection, or placebo. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity.16 After 68 weeks of treatment, the mean weight changes were -15.8%, -6.4%, and -1.9% in the semaglutide, liraglutide, and placebo groups, respectively. The difference between the semaglutide and liraglutide groups was -9.4% (95% CI, -12% to -6.8%; P <.001).16
Continue to: Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications...
Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications
For weight loss, the target dose of semaglutide is 2.4 mg once weekly subcutaneous injection achieved by sequential dose escalation. To give patients time to adjust to adverse effects caused by the medication, a standardized dose-escalation regimen is recommended. The FDA-approved escalation regimen for semaglutide treatment begins with a weekly subcutaneous dose of 0.25 mg for 4 weeks, followed by an increase in the weekly dosage every 4 weeks: 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 1.7 mg, and 2.4 mg.17 To support the dose-escalation process there are 5 unique autoinjectors that deliver the appropriate dose for the current step.
Semaglutide is contraindicated if the patient has an allergy to the medication or if there is a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer.17 In animal toxicology studies, semaglutide at clinically relevant dosing was associated with an increased risk of developing medullary thyroid cancer. Patients with a personal history of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, (medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, and primary hyperparathyroidism) should not take semaglutide. Semaglutide may cause fetal harm and the FDA recommends discontinuing semaglutide at least 2 months before pregnancy.17 According to the FDA, the safety of semaglutide during breastfeeding has not been established. In Canada, breastfeeding is a contraindication to semaglutide treatment.18
Limitations of medication treatment of obesity
There are important limitations to semaglutide treatment of obesity, including:
- weight gain after stopping treatment
- limited medical insurance supportfor an expensive medication treatment
- bothersome adverse effects.
Weight gain posttreatment. After stopping medication treatment of obesity, weight gain occurs in most patients. However, patients may remain below baseline weight for a long time after stopping medication therapy. In one trial of 803 patients, after 20 weeks of semaglutide treatment (16-week dose-escalation phase, followed by 4 weeks on a weekly dose of 2.4 mg), the participants were randomized to 48 additional weeks of semaglutide or placebo.19 All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. At the initial 20 weeks of treatment time point the mean weight change was -10.6%. Over the following 48 weeks, the patients treated with semaglutidehad an additional mean weight change of -7.9%, while the mean weight change for the placebo group was +6.9%.
Medical insurance coverage. A major barrier to semaglutide treatment of obesity is the medication’s cost. At the website GoodRx (https://www.goodrx.com/), the estimated price for a 1-month supply of semaglutide (Wegovy) is $1,350.20 By contrast, a 1-month supply of phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) is approximately $205. Currently, many medical insurance plans do not cover the cost of semaglutide treatment for weight loss. Patent protection for liraglutide may expire in the next few years, permitting the marketing of a lower-cost generic formulation, increasing the availability of the medication. However, as noted above, compared with liraglutide, semaglutide treatment results in much greater weight loss.
The most common adverse effects associated with semaglutide treatment are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In one randomized clinical trial involving 1,961 patients, the frequency of adverse effects reported by patients taking semaglutide incrementally above the frequency of the same adverse effect reported by patients on placebo was: nausea (27%), vomiting (18%), diarrhea (16%), constipation (14%), dyspepsia (7%), and abdominal pain (5%).15 In this study, treatment was discontinued due to adverse effects in 7% and 3% of the patients in the semaglutide and placebo groups, respectively. Experts believe that adverse effects can be minimized by increasing the dose slowly and decreasing the dose if adverse effects are bothersome to the patient.
Measuring the benefits of semaglutide weight loss
Overweight and obesity are prevalent problems with many adverse consequences, including an increased risk of death. In population studies, weight loss following bariatric surgery is associated with a substantial reduction in mortality, cancer, and heart disease compared with conventional therapy.21 Over the next few years, the effect of semaglutide-induced weight loss on the rate of cancer and heart disease should become clear. If semaglutide treatment of obesity is associated with a reduction in cancer and heart disease, it would be a truly breakthrough medication. ●
- Defining adult and overweight obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/adult-defining.html. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCH Data Brief. 2020;360. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /databriefs/db360-h.pdf. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration. Bodymass index and all-cause mortality: individual- participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet. 2016;388:776-786.
- Grover SA, Kaouache M, Rempel P, et al. Years of life lost and health life-years lost from diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the overweight and obese people: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:114-122.
- Lega IC, Lipscombe LL. Review: diabetes, obesity and cancer—pathophysiology and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:bnz014.
- Venkatesh SS, Ferreira T, Benonisdottir S, et al. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: a mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 19:e1003679.
- Catalano PM, Shankar K. Obesity and pregnancy: mechanisms of short term and longterm adverse consequences for mother and child. BMJ. 2017;356:j1.
- Sjorstrom L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial—a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219-234.
- Shi Q, Wang Y, Hao Q, et al. Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lancet. 2022;399:259-269.
- Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, et al. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:879-887.
- Brierly DI, Holt MK, Singh A, et al. Central and peripheral GLP-1 systems are involved in the control of eating behavior by linking food intake and satiety. Nat Metab. 2021;3:258-273.
- Friedrichsen M, Breitschaft A, Tadayon S, et al. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23:754-762.
- Gotfredsen CF, Molck AM, Thorup I, et al. The human GLP-1 analogs liraglutide and semaglutide: absence of histopathological effects on the pancreas in nonhuman primates. Diabetes. 2014;63:2486-2497.
- Frias JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-515.
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:989-1000.
- Rubino DM, Greenway FL, Khalid U, et al. Effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs daily liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes. JAMA. 2022;327:138-150.
- Wegovy [package insert]. Bagsvaerd, Denmark: Novo Nordisk; 2021.
- Wegovy Product Monograph. Mississauga, Ontario: Novo Nordisk Canada Inc; June 30, 2022. https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00066484.PDF
- Rubino D, Abrahamsson N, Davies M, et al. Effect of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo on weight loss maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity. JAMA. 2021;325: 1414-1425.
- GoodRx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Wiggins T, Guidozzi N, Welbourn R, et al. Association of bariatric surgery with all-cause mortality and incidence of obesity-related disease at a population level: a systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003206.
Obesity is a major health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines the problem as weight that is higher than what is healthy for a given height, with quantitative definitions of overweight and obesity as body mass indices (BMIs) of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 and ≥ 30 kg/m2, respectively.1 The prevalence of obesity among adults in 2017 ̶ 2018 was reported by the CDC to be 42.4%.2 Among women, the reported prevalence of obesity was lowest among Asian individuals (17.2%) and greatest among non-Hispanic Black individuals (56.9%), with White (39.8%) and Hispanic individuals (43.7%) having rates in between.2 In a meta-analysis of prospective studies that included 4 million people who were never smokers and had no chronic disease at baseline, age- and sex-adjusted mortality rates were studied over a median of 14 years of follow-up.3 Compared with those with a BMI of 20 to 25 kg/m2, people with a BMI of 30 to 34.9 kg/m2 or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 had increased risks of death of 46% and 94%, respectively, demonstrating that obesity increases this risk.3
The increased risk of death associated with obesity is caused by obesity-related diseases that cause early mortality, including diabetes mellitus (DM), dyslipidemia, hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and venous thromboembolic events.4 Obesity is also associated with an increased risk of many cancers, including cancer of the endometrium, kidney, esophagus, stomach, colon, rectum, gallbladder, pancreas, liver, and breast.5 With regard to gynecologic disease, obesity is associated with an increased risk of fibroids and heavy menstrual bleeding.6 For pregnant patients, obesity is associated with increased risks of7:
- miscarriage and stillbirth
- preeclampsia and gestational hypertension
- gestational diabetes
- severe maternal morbidity
- postterm pregnancy
- venous thromboembolism
- endometritis.
For obese patients, weight loss can normalize blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, decrease the risk of cancer, and cure type 2 DM.8
Bariatric surgery: The gold standard treatment for reliable and sustained weight loss
All patients with obesity should be counseled to reduce caloric intake and increase physical activity. Dietary counseling provided by a nutritionist may help reinforce advice given by a provider. However, lifestyle interventions are associated with modest weight loss (<5% of bodyweight; FIGURE
In the Swedish Obese Subjects study, involving 2,010 people, following bariatric surgery the mean decrease in bodyweight was 23% at 2 years, with a slow increase in weight thereafter, resulting in a sustained mean weight loss of 18% at 10 years.8 In this study, people in the diet and exercise control group had no change in bodyweight over 10 years of follow-up.8 Not all eligible obese patients want to undergo bariatric surgery because it is an arduous sequential process involving 6 months of intensive preoperative preparation, bariatric surgery, recovery, and intensive postoperative follow-up. The perioperative mortality rate is 0.03% to 0.2%.10 Following bariatric surgery, additional operations may be necessary for more than 10% of patients.10 With recent breakthroughs in the medication management of obesity, patients who do not want bariatric surgery can achieve reliable weight loss of greater than 10% of body weight with glucagon-like peptide -1 (GLP-1) agonists.

GLP-1 agonist analogues: Practice-changing breakthrough in medication treatment
GLP-1, a 30 amino acid peptide, is produced by intestinal enteroendocrine cells and neurons in the medulla and hypothalamus.11 GLP-1 reduces hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing daily food intake.12 GLP-1 also enhances the secretion of insulin, making GLP-1 agonists an effective treatment for type 2 DM. In humans and experimental animals, the administration of exogenous GLP-1 agonists decreases hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing food intake, resulting in weight loss.12 The synthetic GLP-1 agonists, liraglutide (Saxenda) and semaglutide (Wegovy) are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as anti-obesity medications.
Native GLP-1 has a short circulating half-life of approximately 2 minutes. The synthetic GLP-1 agonist medications liraglutide and semaglutide are modified to significantly increase their half-life. Liraglutide is a modified version of GLP-1 with a palmitic acid side chain and an amino acid spacer resulting in reduced degradation and a 15-hour half-life, necessitating daily administration. Semaglutide has a steric acid diacid at Lys26, a large synthetic spacer, a modification of amino acid 8 with the addition of α-aminobutyric acid and a 165-hour half-life, permitting weekly administration.13 For weight loss, liraglutide and semaglultide are administered by subcutaneous injection. Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is a novel GLP-1 agonist. It is also a gastric inhibitory peptide, is FDA approved to treat type 2 DM, and is awaiting FDA approval as a weight loss medication.Tirzepatide causes substantial weight loss, similar to the effect of semaglutide.14
Semaglutide and weight loss
Semaglutide is approved by the FDA for chronic weight management as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity in adults with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 or ≥ 27 kg/m2 in the presence of a weight-related comorbidity. It is also FDA approved to treat type 2 DM.
In a weight loss trial, 1,961 overweight and obese patients with a mean BMI of 38 kg/m2, were randomly assigned to semaglutide or placebo treatment for 68 weeks. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. The mean changes in body weight for the patients in the semaglutide and placebo treatment groups were -14.9% and -2.4%, respectively. The treatment difference was -12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], -13.4% to -11.5%; P <.001). In this study, compared with placebo, semaglutide treatment resulted in a greater decrease in waist circumference, -5.3 in versus -1.6 in.15 A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of weight loss medicines indicates that semaglutide is the most effective medication currently FDA approved for weight loss, reliably producing substantial weight loss (FIGURE).9
In one randomized clinical trial, investigators directly compared the efficacy of semaglutide and liraglutide in achieving weight loss. In this trial, 338 patients were assigned randomly to treatment with semaglutide 2.4 mg weekly subcutaneous injection, liraglutide 3.0 mg daily subcutaneous injection, or placebo. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity.16 After 68 weeks of treatment, the mean weight changes were -15.8%, -6.4%, and -1.9% in the semaglutide, liraglutide, and placebo groups, respectively. The difference between the semaglutide and liraglutide groups was -9.4% (95% CI, -12% to -6.8%; P <.001).16
Continue to: Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications...
Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications
For weight loss, the target dose of semaglutide is 2.4 mg once weekly subcutaneous injection achieved by sequential dose escalation. To give patients time to adjust to adverse effects caused by the medication, a standardized dose-escalation regimen is recommended. The FDA-approved escalation regimen for semaglutide treatment begins with a weekly subcutaneous dose of 0.25 mg for 4 weeks, followed by an increase in the weekly dosage every 4 weeks: 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 1.7 mg, and 2.4 mg.17 To support the dose-escalation process there are 5 unique autoinjectors that deliver the appropriate dose for the current step.
Semaglutide is contraindicated if the patient has an allergy to the medication or if there is a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer.17 In animal toxicology studies, semaglutide at clinically relevant dosing was associated with an increased risk of developing medullary thyroid cancer. Patients with a personal history of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, (medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, and primary hyperparathyroidism) should not take semaglutide. Semaglutide may cause fetal harm and the FDA recommends discontinuing semaglutide at least 2 months before pregnancy.17 According to the FDA, the safety of semaglutide during breastfeeding has not been established. In Canada, breastfeeding is a contraindication to semaglutide treatment.18
Limitations of medication treatment of obesity
There are important limitations to semaglutide treatment of obesity, including:
- weight gain after stopping treatment
- limited medical insurance supportfor an expensive medication treatment
- bothersome adverse effects.
Weight gain posttreatment. After stopping medication treatment of obesity, weight gain occurs in most patients. However, patients may remain below baseline weight for a long time after stopping medication therapy. In one trial of 803 patients, after 20 weeks of semaglutide treatment (16-week dose-escalation phase, followed by 4 weeks on a weekly dose of 2.4 mg), the participants were randomized to 48 additional weeks of semaglutide or placebo.19 All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. At the initial 20 weeks of treatment time point the mean weight change was -10.6%. Over the following 48 weeks, the patients treated with semaglutidehad an additional mean weight change of -7.9%, while the mean weight change for the placebo group was +6.9%.
Medical insurance coverage. A major barrier to semaglutide treatment of obesity is the medication’s cost. At the website GoodRx (https://www.goodrx.com/), the estimated price for a 1-month supply of semaglutide (Wegovy) is $1,350.20 By contrast, a 1-month supply of phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) is approximately $205. Currently, many medical insurance plans do not cover the cost of semaglutide treatment for weight loss. Patent protection for liraglutide may expire in the next few years, permitting the marketing of a lower-cost generic formulation, increasing the availability of the medication. However, as noted above, compared with liraglutide, semaglutide treatment results in much greater weight loss.
The most common adverse effects associated with semaglutide treatment are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In one randomized clinical trial involving 1,961 patients, the frequency of adverse effects reported by patients taking semaglutide incrementally above the frequency of the same adverse effect reported by patients on placebo was: nausea (27%), vomiting (18%), diarrhea (16%), constipation (14%), dyspepsia (7%), and abdominal pain (5%).15 In this study, treatment was discontinued due to adverse effects in 7% and 3% of the patients in the semaglutide and placebo groups, respectively. Experts believe that adverse effects can be minimized by increasing the dose slowly and decreasing the dose if adverse effects are bothersome to the patient.
Measuring the benefits of semaglutide weight loss
Overweight and obesity are prevalent problems with many adverse consequences, including an increased risk of death. In population studies, weight loss following bariatric surgery is associated with a substantial reduction in mortality, cancer, and heart disease compared with conventional therapy.21 Over the next few years, the effect of semaglutide-induced weight loss on the rate of cancer and heart disease should become clear. If semaglutide treatment of obesity is associated with a reduction in cancer and heart disease, it would be a truly breakthrough medication. ●
Obesity is a major health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines the problem as weight that is higher than what is healthy for a given height, with quantitative definitions of overweight and obesity as body mass indices (BMIs) of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 and ≥ 30 kg/m2, respectively.1 The prevalence of obesity among adults in 2017 ̶ 2018 was reported by the CDC to be 42.4%.2 Among women, the reported prevalence of obesity was lowest among Asian individuals (17.2%) and greatest among non-Hispanic Black individuals (56.9%), with White (39.8%) and Hispanic individuals (43.7%) having rates in between.2 In a meta-analysis of prospective studies that included 4 million people who were never smokers and had no chronic disease at baseline, age- and sex-adjusted mortality rates were studied over a median of 14 years of follow-up.3 Compared with those with a BMI of 20 to 25 kg/m2, people with a BMI of 30 to 34.9 kg/m2 or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 had increased risks of death of 46% and 94%, respectively, demonstrating that obesity increases this risk.3
The increased risk of death associated with obesity is caused by obesity-related diseases that cause early mortality, including diabetes mellitus (DM), dyslipidemia, hypertension, coronary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and venous thromboembolic events.4 Obesity is also associated with an increased risk of many cancers, including cancer of the endometrium, kidney, esophagus, stomach, colon, rectum, gallbladder, pancreas, liver, and breast.5 With regard to gynecologic disease, obesity is associated with an increased risk of fibroids and heavy menstrual bleeding.6 For pregnant patients, obesity is associated with increased risks of7:
- miscarriage and stillbirth
- preeclampsia and gestational hypertension
- gestational diabetes
- severe maternal morbidity
- postterm pregnancy
- venous thromboembolism
- endometritis.
For obese patients, weight loss can normalize blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, decrease the risk of cancer, and cure type 2 DM.8
Bariatric surgery: The gold standard treatment for reliable and sustained weight loss
All patients with obesity should be counseled to reduce caloric intake and increase physical activity. Dietary counseling provided by a nutritionist may help reinforce advice given by a provider. However, lifestyle interventions are associated with modest weight loss (<5% of bodyweight; FIGURE
In the Swedish Obese Subjects study, involving 2,010 people, following bariatric surgery the mean decrease in bodyweight was 23% at 2 years, with a slow increase in weight thereafter, resulting in a sustained mean weight loss of 18% at 10 years.8 In this study, people in the diet and exercise control group had no change in bodyweight over 10 years of follow-up.8 Not all eligible obese patients want to undergo bariatric surgery because it is an arduous sequential process involving 6 months of intensive preoperative preparation, bariatric surgery, recovery, and intensive postoperative follow-up. The perioperative mortality rate is 0.03% to 0.2%.10 Following bariatric surgery, additional operations may be necessary for more than 10% of patients.10 With recent breakthroughs in the medication management of obesity, patients who do not want bariatric surgery can achieve reliable weight loss of greater than 10% of body weight with glucagon-like peptide -1 (GLP-1) agonists.

GLP-1 agonist analogues: Practice-changing breakthrough in medication treatment
GLP-1, a 30 amino acid peptide, is produced by intestinal enteroendocrine cells and neurons in the medulla and hypothalamus.11 GLP-1 reduces hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing daily food intake.12 GLP-1 also enhances the secretion of insulin, making GLP-1 agonists an effective treatment for type 2 DM. In humans and experimental animals, the administration of exogenous GLP-1 agonists decreases hunger cravings and causes satiety, reducing food intake, resulting in weight loss.12 The synthetic GLP-1 agonists, liraglutide (Saxenda) and semaglutide (Wegovy) are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as anti-obesity medications.
Native GLP-1 has a short circulating half-life of approximately 2 minutes. The synthetic GLP-1 agonist medications liraglutide and semaglutide are modified to significantly increase their half-life. Liraglutide is a modified version of GLP-1 with a palmitic acid side chain and an amino acid spacer resulting in reduced degradation and a 15-hour half-life, necessitating daily administration. Semaglutide has a steric acid diacid at Lys26, a large synthetic spacer, a modification of amino acid 8 with the addition of α-aminobutyric acid and a 165-hour half-life, permitting weekly administration.13 For weight loss, liraglutide and semaglultide are administered by subcutaneous injection. Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) is a novel GLP-1 agonist. It is also a gastric inhibitory peptide, is FDA approved to treat type 2 DM, and is awaiting FDA approval as a weight loss medication.Tirzepatide causes substantial weight loss, similar to the effect of semaglutide.14
Semaglutide and weight loss
Semaglutide is approved by the FDA for chronic weight management as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity in adults with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 or ≥ 27 kg/m2 in the presence of a weight-related comorbidity. It is also FDA approved to treat type 2 DM.
In a weight loss trial, 1,961 overweight and obese patients with a mean BMI of 38 kg/m2, were randomly assigned to semaglutide or placebo treatment for 68 weeks. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. The mean changes in body weight for the patients in the semaglutide and placebo treatment groups were -14.9% and -2.4%, respectively. The treatment difference was -12.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], -13.4% to -11.5%; P <.001). In this study, compared with placebo, semaglutide treatment resulted in a greater decrease in waist circumference, -5.3 in versus -1.6 in.15 A network meta-analysis of the efficacy of weight loss medicines indicates that semaglutide is the most effective medication currently FDA approved for weight loss, reliably producing substantial weight loss (FIGURE).9
In one randomized clinical trial, investigators directly compared the efficacy of semaglutide and liraglutide in achieving weight loss. In this trial, 338 patients were assigned randomly to treatment with semaglutide 2.4 mg weekly subcutaneous injection, liraglutide 3.0 mg daily subcutaneous injection, or placebo. All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity.16 After 68 weeks of treatment, the mean weight changes were -15.8%, -6.4%, and -1.9% in the semaglutide, liraglutide, and placebo groups, respectively. The difference between the semaglutide and liraglutide groups was -9.4% (95% CI, -12% to -6.8%; P <.001).16
Continue to: Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications...
Semaglutide dose-escalation and contraindications
For weight loss, the target dose of semaglutide is 2.4 mg once weekly subcutaneous injection achieved by sequential dose escalation. To give patients time to adjust to adverse effects caused by the medication, a standardized dose-escalation regimen is recommended. The FDA-approved escalation regimen for semaglutide treatment begins with a weekly subcutaneous dose of 0.25 mg for 4 weeks, followed by an increase in the weekly dosage every 4 weeks: 0.5 mg, 1.0 mg, 1.7 mg, and 2.4 mg.17 To support the dose-escalation process there are 5 unique autoinjectors that deliver the appropriate dose for the current step.
Semaglutide is contraindicated if the patient has an allergy to the medication or if there is a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer.17 In animal toxicology studies, semaglutide at clinically relevant dosing was associated with an increased risk of developing medullary thyroid cancer. Patients with a personal history of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, (medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, and primary hyperparathyroidism) should not take semaglutide. Semaglutide may cause fetal harm and the FDA recommends discontinuing semaglutide at least 2 months before pregnancy.17 According to the FDA, the safety of semaglutide during breastfeeding has not been established. In Canada, breastfeeding is a contraindication to semaglutide treatment.18
Limitations of medication treatment of obesity
There are important limitations to semaglutide treatment of obesity, including:
- weight gain after stopping treatment
- limited medical insurance supportfor an expensive medication treatment
- bothersome adverse effects.
Weight gain posttreatment. After stopping medication treatment of obesity, weight gain occurs in most patients. However, patients may remain below baseline weight for a long time after stopping medication therapy. In one trial of 803 patients, after 20 weeks of semaglutide treatment (16-week dose-escalation phase, followed by 4 weeks on a weekly dose of 2.4 mg), the participants were randomized to 48 additional weeks of semaglutide or placebo.19 All the participants were following a regimen that included a calorie-reduced diet and increased physical activity. At the initial 20 weeks of treatment time point the mean weight change was -10.6%. Over the following 48 weeks, the patients treated with semaglutidehad an additional mean weight change of -7.9%, while the mean weight change for the placebo group was +6.9%.
Medical insurance coverage. A major barrier to semaglutide treatment of obesity is the medication’s cost. At the website GoodRx (https://www.goodrx.com/), the estimated price for a 1-month supply of semaglutide (Wegovy) is $1,350.20 By contrast, a 1-month supply of phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) is approximately $205. Currently, many medical insurance plans do not cover the cost of semaglutide treatment for weight loss. Patent protection for liraglutide may expire in the next few years, permitting the marketing of a lower-cost generic formulation, increasing the availability of the medication. However, as noted above, compared with liraglutide, semaglutide treatment results in much greater weight loss.
The most common adverse effects associated with semaglutide treatment are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In one randomized clinical trial involving 1,961 patients, the frequency of adverse effects reported by patients taking semaglutide incrementally above the frequency of the same adverse effect reported by patients on placebo was: nausea (27%), vomiting (18%), diarrhea (16%), constipation (14%), dyspepsia (7%), and abdominal pain (5%).15 In this study, treatment was discontinued due to adverse effects in 7% and 3% of the patients in the semaglutide and placebo groups, respectively. Experts believe that adverse effects can be minimized by increasing the dose slowly and decreasing the dose if adverse effects are bothersome to the patient.
Measuring the benefits of semaglutide weight loss
Overweight and obesity are prevalent problems with many adverse consequences, including an increased risk of death. In population studies, weight loss following bariatric surgery is associated with a substantial reduction in mortality, cancer, and heart disease compared with conventional therapy.21 Over the next few years, the effect of semaglutide-induced weight loss on the rate of cancer and heart disease should become clear. If semaglutide treatment of obesity is associated with a reduction in cancer and heart disease, it would be a truly breakthrough medication. ●
- Defining adult and overweight obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/adult-defining.html. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCH Data Brief. 2020;360. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /databriefs/db360-h.pdf. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration. Bodymass index and all-cause mortality: individual- participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet. 2016;388:776-786.
- Grover SA, Kaouache M, Rempel P, et al. Years of life lost and health life-years lost from diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the overweight and obese people: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:114-122.
- Lega IC, Lipscombe LL. Review: diabetes, obesity and cancer—pathophysiology and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:bnz014.
- Venkatesh SS, Ferreira T, Benonisdottir S, et al. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: a mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 19:e1003679.
- Catalano PM, Shankar K. Obesity and pregnancy: mechanisms of short term and longterm adverse consequences for mother and child. BMJ. 2017;356:j1.
- Sjorstrom L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial—a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219-234.
- Shi Q, Wang Y, Hao Q, et al. Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lancet. 2022;399:259-269.
- Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, et al. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:879-887.
- Brierly DI, Holt MK, Singh A, et al. Central and peripheral GLP-1 systems are involved in the control of eating behavior by linking food intake and satiety. Nat Metab. 2021;3:258-273.
- Friedrichsen M, Breitschaft A, Tadayon S, et al. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23:754-762.
- Gotfredsen CF, Molck AM, Thorup I, et al. The human GLP-1 analogs liraglutide and semaglutide: absence of histopathological effects on the pancreas in nonhuman primates. Diabetes. 2014;63:2486-2497.
- Frias JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-515.
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:989-1000.
- Rubino DM, Greenway FL, Khalid U, et al. Effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs daily liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes. JAMA. 2022;327:138-150.
- Wegovy [package insert]. Bagsvaerd, Denmark: Novo Nordisk; 2021.
- Wegovy Product Monograph. Mississauga, Ontario: Novo Nordisk Canada Inc; June 30, 2022. https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00066484.PDF
- Rubino D, Abrahamsson N, Davies M, et al. Effect of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo on weight loss maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity. JAMA. 2021;325: 1414-1425.
- GoodRx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Wiggins T, Guidozzi N, Welbourn R, et al. Association of bariatric surgery with all-cause mortality and incidence of obesity-related disease at a population level: a systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003206.
- Defining adult and overweight obesity. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/basics/adult-defining.html. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, et al. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCH Data Brief. 2020;360. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /databriefs/db360-h.pdf. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration. Bodymass index and all-cause mortality: individual- participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet. 2016;388:776-786.
- Grover SA, Kaouache M, Rempel P, et al. Years of life lost and health life-years lost from diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the overweight and obese people: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:114-122.
- Lega IC, Lipscombe LL. Review: diabetes, obesity and cancer—pathophysiology and clinical implications. Endocr Rev. 2020;41:bnz014.
- Venkatesh SS, Ferreira T, Benonisdottir S, et al. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: a mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 19:e1003679.
- Catalano PM, Shankar K. Obesity and pregnancy: mechanisms of short term and longterm adverse consequences for mother and child. BMJ. 2017;356:j1.
- Sjorstrom L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial—a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219-234.
- Shi Q, Wang Y, Hao Q, et al. Pharmacotherapy for adults with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lancet. 2022;399:259-269.
- Arterburn DE, Telem DA, Kushner RF, et al. Benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in adults: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:879-887.
- Brierly DI, Holt MK, Singh A, et al. Central and peripheral GLP-1 systems are involved in the control of eating behavior by linking food intake and satiety. Nat Metab. 2021;3:258-273.
- Friedrichsen M, Breitschaft A, Tadayon S, et al. The effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly on energy intake, appetite, control of eating and gastric emptying in adults with obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021;23:754-762.
- Gotfredsen CF, Molck AM, Thorup I, et al. The human GLP-1 analogs liraglutide and semaglutide: absence of histopathological effects on the pancreas in nonhuman primates. Diabetes. 2014;63:2486-2497.
- Frias JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:503-515.
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. Once weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:989-1000.
- Rubino DM, Greenway FL, Khalid U, et al. Effect of weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs daily liraglutide on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity without diabetes. JAMA. 2022;327:138-150.
- Wegovy [package insert]. Bagsvaerd, Denmark: Novo Nordisk; 2021.
- Wegovy Product Monograph. Mississauga, Ontario: Novo Nordisk Canada Inc; June 30, 2022. https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00066484.PDF
- Rubino D, Abrahamsson N, Davies M, et al. Effect of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo on weight loss maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity. JAMA. 2021;325: 1414-1425.
- GoodRx website. https://www.goodrx.com/. Accessed June 19, 2023.
- Wiggins T, Guidozzi N, Welbourn R, et al. Association of bariatric surgery with all-cause mortality and incidence of obesity-related disease at a population level: a systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003206.
To what extent do growth abnormalities increase the risk of stillbirth near term in pregnancies complicated by diabetes?
McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005102.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Stillbirth is defined as intrauterine demise at or beyond 20 weeks’ gestation. Pregestational DM and GDM significantly increase the risk of stillbirth. Both fetal growth restriction and macrosomia are common complications of pregnancies affected by diabetes, and they further increase the risk of stillbirth. While maternal variables such as glycemic control and medication requirement are currently used to assess the risks of expectant management and inform delivery timing, abnormal fetal growth is not.
Investigators sought to evaluate the stillbirth rates per week of expectant management during the late third trimester stratified by birth weight (as a surrogate for fetal growth) in pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM.
Details of the study
McElwee and colleagues used the US National Vital Statistics System to identify nonanomalous singleton pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM from 2014 to 2017.1 Pregnancies were stratified by birth weight and categorized as being LGA (birth weight > 90th percentile for gestational age), SGA (birth weight < 10th percentile for gestational age), or AGA. Stillbirths were identified from 34 0/7 through 39 6/7 weeks of gestation, and conditional stillbirth rates per 10,000 pregnancies were calculated for each week of gestation.
Results. Among 834,631 pregnancies complicated by PG-DM (13.1%) or GDM (86.9%), there were 3,033 stillbirths, of which 61% were in pregnancies with PG-DM. Stillbirth rates increased with advancing gestational age for both PG-DM and GDM regardless of birth weight. In pregnancies with PG-DM, fetuses that were LGA or SGA had a higher relative risk of stillbirth compared with their AGA counterparts at each gestational age. This stillbirth risk was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA. At 39 weeks, the stillbirth rate in this population was 96.9/10,000 ongoing pregnancies and was 5 times higher than pregnancies with PG-DM that were AGA. When the GDM-related AGA group was selected as the referent (as the lowest-risk comparison group), pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA had a 21-times higher relative risk of stillbirth at 37 and 38 weeks of gestation.
Study strengths and limitations
Decisions on the optimal timing of delivery seek to strike a balance between the increased neonatal morbidity with delivery before 39 weeks’ gestation and the increased risk of stillbirth with expectant management. In pregnancies complicated by diabetes, current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend consideration of maternal variables, such as medication requirement, glycemic control, and vascular sequelae, to inform decisions on delivery timing, as these factors have been postulated to influence the risk of stillbirth with pregnancy prolongation.2 These recommendations are based largely on expert opinion and retrospective data.
The question of how fetal growth abnormalities factor into this complicated decision making is also an area of low-quality evidence despite studies that demonstrate that both SGA and LGA fetuses in pregnancies complicated by diabetes are at increased risk of stillbirth.3
The large population-based study design by McElwee and colleagues allowed the investigators to examine a rare event (stillbirth) with multiple stratification levels and sufficient statistical power and to contribute to this literature.
Significant limitations, however, must be considered before generalizing these results. The data were restricted to variables available on birth and death certificates, and more granular information—such as the type of DM, level of glycemic control, frequency of antenatal testing, and stillbirth work-up—could not be assessed. Ultrasonographic estimations of fetal weight also were not included. Birth weight data were used as a proxy, although we know that these variables do not always correlate well given the limited accuracy of ultrasonography in assessing projected birth weight, particularly later in pregnancy. The authors also did not control for highly prevalent variables (for example, hypertension, obesity) that are likely associated with abnormal fetal growth and stillbirth in these populations. ●
The present study demonstrates that both SGA and LGA are significant risk factors for stillbirth in pregnancies with either PG-DM or GDM in the late preterm and early term periods, and this risk should be considered when making decisions on appropriate timing of delivery. The conditional stillbirth rate was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM with LGA fetuses, and this risk increased with each week of expectant management. This population may benefit the most from critical assessment of the risk of stillbirth with ongoing pregnancy. Notably, the quality of evidence is not sufficient to universally alter delivery timing guidelines in this population. We recommend individual assessment of each clinical scenario when making these decisions.
NIGEL MADDEN, MD; MICHELLE A. KOMINIAREK, MD, MS
- McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005102
- ACOG Committee Opinion No. 764. Medically indicated late-preterm and early-term deliveries. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e151-e155. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003083
- Starikov R, Dudley D, Reddy UM. Stillbirth in the pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2015;15:11. doi:10.1007/s11892-015-0580-y
McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005102.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Stillbirth is defined as intrauterine demise at or beyond 20 weeks’ gestation. Pregestational DM and GDM significantly increase the risk of stillbirth. Both fetal growth restriction and macrosomia are common complications of pregnancies affected by diabetes, and they further increase the risk of stillbirth. While maternal variables such as glycemic control and medication requirement are currently used to assess the risks of expectant management and inform delivery timing, abnormal fetal growth is not.
Investigators sought to evaluate the stillbirth rates per week of expectant management during the late third trimester stratified by birth weight (as a surrogate for fetal growth) in pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM.
Details of the study
McElwee and colleagues used the US National Vital Statistics System to identify nonanomalous singleton pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM from 2014 to 2017.1 Pregnancies were stratified by birth weight and categorized as being LGA (birth weight > 90th percentile for gestational age), SGA (birth weight < 10th percentile for gestational age), or AGA. Stillbirths were identified from 34 0/7 through 39 6/7 weeks of gestation, and conditional stillbirth rates per 10,000 pregnancies were calculated for each week of gestation.
Results. Among 834,631 pregnancies complicated by PG-DM (13.1%) or GDM (86.9%), there were 3,033 stillbirths, of which 61% were in pregnancies with PG-DM. Stillbirth rates increased with advancing gestational age for both PG-DM and GDM regardless of birth weight. In pregnancies with PG-DM, fetuses that were LGA or SGA had a higher relative risk of stillbirth compared with their AGA counterparts at each gestational age. This stillbirth risk was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA. At 39 weeks, the stillbirth rate in this population was 96.9/10,000 ongoing pregnancies and was 5 times higher than pregnancies with PG-DM that were AGA. When the GDM-related AGA group was selected as the referent (as the lowest-risk comparison group), pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA had a 21-times higher relative risk of stillbirth at 37 and 38 weeks of gestation.
Study strengths and limitations
Decisions on the optimal timing of delivery seek to strike a balance between the increased neonatal morbidity with delivery before 39 weeks’ gestation and the increased risk of stillbirth with expectant management. In pregnancies complicated by diabetes, current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend consideration of maternal variables, such as medication requirement, glycemic control, and vascular sequelae, to inform decisions on delivery timing, as these factors have been postulated to influence the risk of stillbirth with pregnancy prolongation.2 These recommendations are based largely on expert opinion and retrospective data.
The question of how fetal growth abnormalities factor into this complicated decision making is also an area of low-quality evidence despite studies that demonstrate that both SGA and LGA fetuses in pregnancies complicated by diabetes are at increased risk of stillbirth.3
The large population-based study design by McElwee and colleagues allowed the investigators to examine a rare event (stillbirth) with multiple stratification levels and sufficient statistical power and to contribute to this literature.
Significant limitations, however, must be considered before generalizing these results. The data were restricted to variables available on birth and death certificates, and more granular information—such as the type of DM, level of glycemic control, frequency of antenatal testing, and stillbirth work-up—could not be assessed. Ultrasonographic estimations of fetal weight also were not included. Birth weight data were used as a proxy, although we know that these variables do not always correlate well given the limited accuracy of ultrasonography in assessing projected birth weight, particularly later in pregnancy. The authors also did not control for highly prevalent variables (for example, hypertension, obesity) that are likely associated with abnormal fetal growth and stillbirth in these populations. ●
The present study demonstrates that both SGA and LGA are significant risk factors for stillbirth in pregnancies with either PG-DM or GDM in the late preterm and early term periods, and this risk should be considered when making decisions on appropriate timing of delivery. The conditional stillbirth rate was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM with LGA fetuses, and this risk increased with each week of expectant management. This population may benefit the most from critical assessment of the risk of stillbirth with ongoing pregnancy. Notably, the quality of evidence is not sufficient to universally alter delivery timing guidelines in this population. We recommend individual assessment of each clinical scenario when making these decisions.
NIGEL MADDEN, MD; MICHELLE A. KOMINIAREK, MD, MS
McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000005102.
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Stillbirth is defined as intrauterine demise at or beyond 20 weeks’ gestation. Pregestational DM and GDM significantly increase the risk of stillbirth. Both fetal growth restriction and macrosomia are common complications of pregnancies affected by diabetes, and they further increase the risk of stillbirth. While maternal variables such as glycemic control and medication requirement are currently used to assess the risks of expectant management and inform delivery timing, abnormal fetal growth is not.
Investigators sought to evaluate the stillbirth rates per week of expectant management during the late third trimester stratified by birth weight (as a surrogate for fetal growth) in pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM.
Details of the study
McElwee and colleagues used the US National Vital Statistics System to identify nonanomalous singleton pregnancies complicated by PG-DM or GDM from 2014 to 2017.1 Pregnancies were stratified by birth weight and categorized as being LGA (birth weight > 90th percentile for gestational age), SGA (birth weight < 10th percentile for gestational age), or AGA. Stillbirths were identified from 34 0/7 through 39 6/7 weeks of gestation, and conditional stillbirth rates per 10,000 pregnancies were calculated for each week of gestation.
Results. Among 834,631 pregnancies complicated by PG-DM (13.1%) or GDM (86.9%), there were 3,033 stillbirths, of which 61% were in pregnancies with PG-DM. Stillbirth rates increased with advancing gestational age for both PG-DM and GDM regardless of birth weight. In pregnancies with PG-DM, fetuses that were LGA or SGA had a higher relative risk of stillbirth compared with their AGA counterparts at each gestational age. This stillbirth risk was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA. At 39 weeks, the stillbirth rate in this population was 96.9/10,000 ongoing pregnancies and was 5 times higher than pregnancies with PG-DM that were AGA. When the GDM-related AGA group was selected as the referent (as the lowest-risk comparison group), pregnancies with PG-DM that were LGA had a 21-times higher relative risk of stillbirth at 37 and 38 weeks of gestation.
Study strengths and limitations
Decisions on the optimal timing of delivery seek to strike a balance between the increased neonatal morbidity with delivery before 39 weeks’ gestation and the increased risk of stillbirth with expectant management. In pregnancies complicated by diabetes, current guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend consideration of maternal variables, such as medication requirement, glycemic control, and vascular sequelae, to inform decisions on delivery timing, as these factors have been postulated to influence the risk of stillbirth with pregnancy prolongation.2 These recommendations are based largely on expert opinion and retrospective data.
The question of how fetal growth abnormalities factor into this complicated decision making is also an area of low-quality evidence despite studies that demonstrate that both SGA and LGA fetuses in pregnancies complicated by diabetes are at increased risk of stillbirth.3
The large population-based study design by McElwee and colleagues allowed the investigators to examine a rare event (stillbirth) with multiple stratification levels and sufficient statistical power and to contribute to this literature.
Significant limitations, however, must be considered before generalizing these results. The data were restricted to variables available on birth and death certificates, and more granular information—such as the type of DM, level of glycemic control, frequency of antenatal testing, and stillbirth work-up—could not be assessed. Ultrasonographic estimations of fetal weight also were not included. Birth weight data were used as a proxy, although we know that these variables do not always correlate well given the limited accuracy of ultrasonography in assessing projected birth weight, particularly later in pregnancy. The authors also did not control for highly prevalent variables (for example, hypertension, obesity) that are likely associated with abnormal fetal growth and stillbirth in these populations. ●
The present study demonstrates that both SGA and LGA are significant risk factors for stillbirth in pregnancies with either PG-DM or GDM in the late preterm and early term periods, and this risk should be considered when making decisions on appropriate timing of delivery. The conditional stillbirth rate was highest in pregnancies with PG-DM with LGA fetuses, and this risk increased with each week of expectant management. This population may benefit the most from critical assessment of the risk of stillbirth with ongoing pregnancy. Notably, the quality of evidence is not sufficient to universally alter delivery timing guidelines in this population. We recommend individual assessment of each clinical scenario when making these decisions.
NIGEL MADDEN, MD; MICHELLE A. KOMINIAREK, MD, MS
- McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005102
- ACOG Committee Opinion No. 764. Medically indicated late-preterm and early-term deliveries. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e151-e155. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003083
- Starikov R, Dudley D, Reddy UM. Stillbirth in the pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2015;15:11. doi:10.1007/s11892-015-0580-y
- McElwee ER, Oliver EA, McFarling K, et al. Risk of stillbirth in pregnancies complicated by diabetes, stratified by fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:801-809. doi:10.1097 /AOG.0000000000005102
- ACOG Committee Opinion No. 764. Medically indicated late-preterm and early-term deliveries. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e151-e155. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003083
- Starikov R, Dudley D, Reddy UM. Stillbirth in the pregnancy complicated by diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2015;15:11. doi:10.1007/s11892-015-0580-y
Does racial bias taint the Apgar score?
Experts say overhaul needed
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
Experts say overhaul needed
Experts say overhaul needed
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
In 1952, when Dr. Virginia Apgar developed her 10-point scale for assessing neonates’ health, the U.S. obstetrical anesthesiologst may not have foreseen it would one day become one of the commonest medical tests in the world.
Assigned even before the mother first holds her newborn, the score rapidly evaluates neonates with a score of 0-10, which leads to an algorithm of potential medical interventions. The scale evaluates heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex response, and skin coloring (typically described as blue body, pink body/blue limbs, or pink body).
“The Apgar is a very important tool used in millions of babies around the world in the very first minute after birth,” said Amos Grunebaum, MD, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y., and director of perinatal research at Northwell Lenox Hill Hospital in Manhattan.
But recently the venerable system has increasingly come under fire for colorism and racial bias, with some calling for an overhaul. That pressure is due to the 2 out of 10 points allotted to an overall “pink” skin tone, a measure that lowers the scores of non-White newborns and may expose them to unnecessary measures such as resuscitation, neonatal intensive care, and intubation.
“This is their first encounter with systemic racism,” said Dr. Grunebaum in an interview. “The score is prejudiced against Black babies because they can’t get perfect scores.”
Propagating ‘race-based medicine’
Concern about racial bias embedded in the Apgar score is not new, Dr. Grunebaum noted.
“Decades ago, when I was doing my training in Brooklyn, the nurses said that using skin color was ridiculous since Black and brown babies couldn’t be pink. And skin color looks different in different lighting. Dr. Apgar herself recognized the problem.”
Furthermore, men see color differently than women do, and some people are actually color-blind.“But nobody wanted to speak out,” Dr. Grunebaum said. “It was like the emperor’s new clothes scenario.”
In his view, embedding skin color scoring into basic data and health care decisions propagates race-based medicine. “It should not be used for White, Black, or brown babies,” he said.
Removing the skin color portion of the Apgar score – and its racial, colorist, and ethnic bias – will provide more accurate and equitable evaluation of newborn babies worldwide, Dr. Grunebaum said.
“I think there’s a pretty good argument to be made that the skin color measure should be eliminated,” agreed Sara E. Edwards, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the University of Illinois Hospital in Chicago, who has also studied Apgar and racial bias in the clinical care of Black babies.
And such clinical bias may soon be illegal in the United States thanks to a proposed new antidiscrimination provision to the Affordable Care Act regarding the use of clinical algorithms in decision-making. The proposed section, § 92.210, states that a covered entity must not discriminate against any individual on the basis of race, color, national origin, sex, age, or disability through clinical algorithms used in decision-making. Hospitals may soon have to alter clinical algorithms in response.
Dr. Grunebaum’s research in the area of clinical racism includes a large 2022 cohort study of almost 10 million mothers and more than 8 million fathers using 2016-2019 natality data from the National Center for Health Statistics, and Division of Vital Statistics. This study found that Black newborns had a less than 50% chance of having a 5-minute Apgar score of 10, compared with White newborns. White babies, both non-Hispanic and Hispanic, had the highest proportion of perfect 10s.
But can the 2-point skin tone indicator be easily replaced? According to Dr. Grunebaum, substituting indicators such as oral mucosa color or oximetry readings are not satisfactory either. “For one thing, oximetry gives different readings in Black [people],” he said.
In her group’s Apgar research, Dr. Edwards found that care providers applied variable and inaccurate scores based on neonatal race – independently of clinical factors and umbilical-cord gas values.
“In Black neonates umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores,” she said. In her view, these inaccuracies point to the existence of colorism and racial bias among health care providers.
Bias ‘creeping in’ to neonatal care
Dr. Edwards’s research was prompted by anecdotal observations that Black babies generally had lower Apgar scores and were more frequently sent to the NICU. “Admission to the NICU can have a negative effect on maternal-child bonding and contribute to PTSD in mothers,” she said.
Her group looked at Apgar scores by race for the year 2019 in an academic hospital cohort of 977 neonates, of whom 56.5% were Black, while controlling for confounding clinical factors.
“Our anecdotal observations of how we score Black neonates were confirmed,” she said. Providers assigned Black babies significantly lower Apgar scores at 1 minute and 5 minutes (odds ratios, .63 and .64) when controlling for umbilical artery gases, gestational age, and maternal-fetal complications.
This difference was specifically associated with lower assigned color Apgar scores at 1 minute (odds ratio, .52). Moreover, full-term Black neonates were sent to neonatal intensive care at higher rates (odds ratio, 1.29) than non-Black neonates when controlling for all the above factors.
Providers applied inaccurate Apgar scores to Black neonates given that the umbilical cord gases were not in agreement with lower Apgar scores, suggesting that colorism and racial biases do exist among health care providers. “We saw bias creeping in because of subjective decisions about color,” Dr. Edwards said. But by the more objective measure of umbilical-cord gas, Black neonates did not have the abnormal values to support NICU admission. The mean umbilical artery pH was 7.259 for Black vs. 7.256 for non-Black neonates.
The solution may lie in switching to an 8 out of 8 score or looking at other indicators such as the eyes and the nail beds, she said. “Or there may be a way to score skin tone accurately when providers are appropriately trained to do so on neonates of all races, to recognize what a well-perfused skin color looks like in all babies.”
New scoring system needed
Interest in this issue continues. In 2022, a population study was conducted by Emma Gillette, MPH, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues in a cohort of almost 7 million singletons born in 2016-2017.
“We found that overall, Apgar scores were highly associated with mortality across the first year of life,” Ms. Gillette said in an interview. “But non-Hispanic Black infants were more likely to be assigned low Apgar scores compared to White infants, and the odds of death in the first year of life are not as strongly correlated with Apgar scores as in White infants.”
That finding was surprising. “Apgar scores are meant to be an indicator of newborn health and well-being and predictors of infant mortality, and therefore should not vary significantly by race or skin color,” she said. “So I think further study into the component scores of the Apgar score is warranted to try to tease out the reasons behind the differences we’re seeing.”
Ms. Gillette agreed that the skin coloring component of the variable could be inaccurate since variables related to skin color more generally are subjective and difficult to measure. What’s needed is a scoring system that performs equally well across racial groups.
In the meantime, some clinicians may be making practical accommodations. “I hate to tell you, but some people fake the skin score,” said Dr. Grunebaum. “I recently asked a doctor from Ethiopia how they handled it there, and he laughed and said they just automatically give skin color a 2. But faking it is not what you should have to do in medicine.”
Dr. Grunebaum, Dr. Edwards, and Ms. Gillette disclosed no relevant competing interests with respect to their comments.
OCD linked to adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In an observational study that followed almost 3 million pregnancies in two countries over 20 years, children of women with OCD were at increased risk for low Apgar score at 5 minutes in Sweden (adjusted risk ratio [aRR], 1.62) and British Columbia, Canada (aRR, 2.30). The risks for adverse outcomes were greater among women with OCD who were taking serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SRIs), compared with those who were not.
“To me, the most relevant things to consider are the clinical implications of these findings,” lead author Lorena Fernández de la Cruz, PhD, principal researcher at Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, told this news organization. She noted that some of the outcomes, such as preeclampsia, can be prevented or improved with collaboration among clinicians and increased monitoring.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Increased risk
OCD affects roughly 1%-3% of the population. Although it is sometimes seen as a mild psychiatric disorder, OCD entails a range of adverse outcomes, and this research suggests that the adverse outcomes extend to maternal health, Dr. Fernández de la Cruz stressed.
The researchers drew data from population registers in Sweden and British Columbia for all singleton births over a roughly 20-year period ending in 2019, with subcohorts identified by formal OCD diagnosis and exposure to SRIs within 30 days before conception. Statistical analyses were performed on a range of pregnancy, delivery, and neonatal outcomes.
In an analysis adjusted for common risk factors such as age, BMI, and smoking, Swedish women with OCD had elevated risk for several adverse outcomes, including a 40% increased risk for gestational diabetes. In British Columbia, fewer adverse pregnancy outcomes for women were associated with an OCD diagnosis.
The study, which also tracked neonatal outcomes, found that infants of mothers with OCD in both Sweden and British Columbia had higher rates of preterm birth (Sweden: aRR, 1.33; BC: aRR, 1.58), low birth weight (Sweden: aRR, 1.28; BC: aRR, 1.40), and neonatal respiratory distress (Sweden: aRR, 1.63; BC: aRR, 1.47).
These results, the authors say, show a need for more monitoring of maternal OCD and collaboration among obstetricians and psychologists. “All this evidence shows that OCD should be detected and treated so that adverse outcomes can be prevented or properly handled,” said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz.
SRI medication
SRIs are frequently used to treat OCD. The subclass of selective SRIs, which includes common antidepressants, has been associated with worsened pregnancy outcomes, but it remains unclear whether all SRIs increase pregnancy risks.
To understand the role of SRIs better in this study, the authors compared the outcomes for women taking SRIs and those who were not prescribed the medication, which is a novel aspect of the study, according to Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Women who took the medication were at greater risk for several adverse outcomes, although all women with an OCD diagnosis were at higher risk than were those without the condition. The investigators hope to continue studying the role of OCD medication during pregnancy in more detail.
The rates of SRI use varied between the two cohorts: 81% of Canadian patients took the medication, compared with 37% of Swedish patients. The disparate rates, along with other clinical practices, may have contributed to differences in outcomes for the two cohorts.
It is also important to bear in mind, however, that patients taking the medication tend to have more severe cases of OCD, said Dr. Fernández de la Cruz. Thus, the increased risk may or may not result from the medication itself. “It is important to understand that there may be other variables besides medication explaining why one group had higher risks than the other,” she said.
‘Multifactorial’ reasons
In addition to medication, other factors may play a role in the association between OCD and adverse pregnancy and neonatal outcomes, including genetics, lifestyle, and psychiatric comorbidities. The authors addressed some of these potential confounders in additional analyses, including sister and cousin comparisons in the Swedish arm of the study, which found weakened associations, compared with population wide statistics.
Commenting on the research, Benicio Frey, PhD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont., said that acknowledging these confounding factors is a strength of the study. Psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety are common among patients with OCD. Of the patients with OCD in this study, 72% and 51% had other psychiatric diagnoses in Sweden and British Columbia, respectively. About 7% of the women without OCD had one of these conditions.
However, Dr. Frey said that the effect of adjusting for psychiatric comorbidities on some outcomes should be stated more clearly. “I see a clear difference,” he said. The relative risk for gestational diabetes among the Swedish cohort, for example, drops from a 40% increased risk to 19% increased when adjusted for mood and anxiety disorders.
Regardless of the cause, the results are important and demonstrate a need to provide additional care for pregnant women with psychiatric conditions, said Dr. Frey. “The important take-home message for policymakers and health care providers is to make sure that they assess for OCD and then monitor those individuals very closely. What I would suggest as a caution is that the reasons behind it are multifactorial.”
The study was supported by the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life, and Welfare and by the Canadian Institute of Health Research. Dr. Fernández de la Cruz and Dr. Frey reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Peripartum cardiomyopathy raises risks at future pregnancy despite LV recovery
, a new study suggests.
Researchers looked at the long-term outcomes in a cohort of women who had developed PPCM and became pregnant again several years later, comparing those with LV function that had “normalized” in the interim against those with persisting LV dysfunction.
In their analysis, adverse maternal outcomes 5 years after an index pregnancy were significantly worse among those in whom LV dysfunction had persisted, compared with those with recovered LV function. The risk of relapsed PPCM persisted out to 8 years. Mortality remained high in both groups through the follow-up.
The study suggests that “women with PPCM need long-term follow-up by cardiology, as mortality does not abate over time,” Kalgi Modi, MD, Louisiana State University, Shreveport, said in an interview.
Women with a history of PPCM, she said, need “multidisciplinary and shared decision-making for family planning, because normalization of left ventricular function after index pregnancy does not guarantee a favorable outcome in the subsequent pregnancies.”
Dr. Modi is senior author on the study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The current findings are important to women with a history of PPCM who are “contemplating future pregnancy,” Afshan Hameed, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and cardiologist at the University of California, Irvine, said in an interview. The investigators suggest that “complete recovery of cardiac function after PPCM does not guarantee a favorable outcome in future pregnancy,” agreed Dr. Hameed, who was not involved in the current study. Future pregnancies must therefore “be highly discouraged or considered with caution even in patients who have recovered their cardiac function.”
To investigate the impact of PPCM on risk at subsequent pregnancies, the researchers studied 45 patients with PPCM who had gone on to have at least one more pregnancy, the first a median of 28 months later. Their mean age was 27 and 80% were Black; they were followed a median of 8 years.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy, defined as idiopathic heart failure with LV ejection fraction (LVEF) 45% or less in the last month of pregnancy through the following 5 months, was diagnosed post partum in 93.3% and antepartum in the remaining 6.7% (mean time of diagnosis, 6 weeks post partum).
The mean LVEF fell from 45.1% at the index pregnancy to 41.2% (P = .009) at subsequent pregnancies. The “recovery group” included the 30 women with LVEF recovery to 50% or higher after the index pregnancy, and the remaining 15 with persisting LV dysfunction – defined as LVEF < 50% – made up the “nonrecovery group.”
Recovery of LVEF was associated with a reduced risk of persisting LV dysfunction, the report states, at a hazard ratio of 0.08 (95% CI, 0.01-0.64; P = .02) after adjustment for hypertension, diabetes, and history of preeclampsia. But that risk went up sharply in association with illicit drug use, similarly adjusted, with an HR of 9.08 (95% CI, 1.38-59.8; P = .02).
The nonrecovery group, compared with the recovery group, experienced significantly higher rates of adverse maternal outcomes (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .04) – a composite endpoint that included relapse PPCM (33.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .01), HF (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .03), cardiogenic shock, thromboembolic events, and death – at 5 years. However, all-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups (13.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .25)
All-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups at a median of 8 years (20.0% vs. 20.0%; P = 1.00), and the difference in overall adverse maternal outcomes had gone from significant to nonsignificant (53.3% vs. 33.3%; P = .20). The difference in relapse PPCM between groups remained significant after 8 years (53.3% vs. 23.3%; P = .04)
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, a relatively small population, and lack of racial diversity, the report notes.
Indeed, most of the study’s subjects were Black, and previous studies have demonstrated a “different phenotypic presentation and outcome in African American women with PPCM, compared with non–African American women,” an accompanying editorial states.
Therefore, applicability of its findings to other populations “needs to be examined by urgently needed national prospective registries with long-term follow-up,” writes Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Moreover, the study questions “whether the reverse remodeling and improvement of [LVEF] in women with PPCM represent a true recovery.” Prior studies “have shown an impaired contractile reserve as well as abnormal myocardial strain and reduced exercise capacity and even mortality in women with PPCM after RLV,” Dr. Elkayam notes.
It’s therefore possible – as with other forms of dilated cardiomyopathy – that LVEF normalization “does not represent a true recovery but a new steady state with subclinical myocardial dysfunction that is prone to development of recurrent [LV dysfunction] and clinical deterioration in response to various triggers such as long-standing hypertension, obesity, diabetes, illicit drug use,” and, “more importantly,” subsequent pregnancies.
The study points to “the need for a close long-term follow-up of women with PPCM” and provides “a rationale for early initiation of guideline-directed medical therapy after the diagnosis of PPCM and possible continuation even after improvement of LVEF.”
No funding source was reported. Dr. Modi and coauthors, Dr. Elkayam, and Dr. Hameed declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
Researchers looked at the long-term outcomes in a cohort of women who had developed PPCM and became pregnant again several years later, comparing those with LV function that had “normalized” in the interim against those with persisting LV dysfunction.
In their analysis, adverse maternal outcomes 5 years after an index pregnancy were significantly worse among those in whom LV dysfunction had persisted, compared with those with recovered LV function. The risk of relapsed PPCM persisted out to 8 years. Mortality remained high in both groups through the follow-up.
The study suggests that “women with PPCM need long-term follow-up by cardiology, as mortality does not abate over time,” Kalgi Modi, MD, Louisiana State University, Shreveport, said in an interview.
Women with a history of PPCM, she said, need “multidisciplinary and shared decision-making for family planning, because normalization of left ventricular function after index pregnancy does not guarantee a favorable outcome in the subsequent pregnancies.”
Dr. Modi is senior author on the study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The current findings are important to women with a history of PPCM who are “contemplating future pregnancy,” Afshan Hameed, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and cardiologist at the University of California, Irvine, said in an interview. The investigators suggest that “complete recovery of cardiac function after PPCM does not guarantee a favorable outcome in future pregnancy,” agreed Dr. Hameed, who was not involved in the current study. Future pregnancies must therefore “be highly discouraged or considered with caution even in patients who have recovered their cardiac function.”
To investigate the impact of PPCM on risk at subsequent pregnancies, the researchers studied 45 patients with PPCM who had gone on to have at least one more pregnancy, the first a median of 28 months later. Their mean age was 27 and 80% were Black; they were followed a median of 8 years.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy, defined as idiopathic heart failure with LV ejection fraction (LVEF) 45% or less in the last month of pregnancy through the following 5 months, was diagnosed post partum in 93.3% and antepartum in the remaining 6.7% (mean time of diagnosis, 6 weeks post partum).
The mean LVEF fell from 45.1% at the index pregnancy to 41.2% (P = .009) at subsequent pregnancies. The “recovery group” included the 30 women with LVEF recovery to 50% or higher after the index pregnancy, and the remaining 15 with persisting LV dysfunction – defined as LVEF < 50% – made up the “nonrecovery group.”
Recovery of LVEF was associated with a reduced risk of persisting LV dysfunction, the report states, at a hazard ratio of 0.08 (95% CI, 0.01-0.64; P = .02) after adjustment for hypertension, diabetes, and history of preeclampsia. But that risk went up sharply in association with illicit drug use, similarly adjusted, with an HR of 9.08 (95% CI, 1.38-59.8; P = .02).
The nonrecovery group, compared with the recovery group, experienced significantly higher rates of adverse maternal outcomes (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .04) – a composite endpoint that included relapse PPCM (33.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .01), HF (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .03), cardiogenic shock, thromboembolic events, and death – at 5 years. However, all-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups (13.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .25)
All-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups at a median of 8 years (20.0% vs. 20.0%; P = 1.00), and the difference in overall adverse maternal outcomes had gone from significant to nonsignificant (53.3% vs. 33.3%; P = .20). The difference in relapse PPCM between groups remained significant after 8 years (53.3% vs. 23.3%; P = .04)
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, a relatively small population, and lack of racial diversity, the report notes.
Indeed, most of the study’s subjects were Black, and previous studies have demonstrated a “different phenotypic presentation and outcome in African American women with PPCM, compared with non–African American women,” an accompanying editorial states.
Therefore, applicability of its findings to other populations “needs to be examined by urgently needed national prospective registries with long-term follow-up,” writes Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Moreover, the study questions “whether the reverse remodeling and improvement of [LVEF] in women with PPCM represent a true recovery.” Prior studies “have shown an impaired contractile reserve as well as abnormal myocardial strain and reduced exercise capacity and even mortality in women with PPCM after RLV,” Dr. Elkayam notes.
It’s therefore possible – as with other forms of dilated cardiomyopathy – that LVEF normalization “does not represent a true recovery but a new steady state with subclinical myocardial dysfunction that is prone to development of recurrent [LV dysfunction] and clinical deterioration in response to various triggers such as long-standing hypertension, obesity, diabetes, illicit drug use,” and, “more importantly,” subsequent pregnancies.
The study points to “the need for a close long-term follow-up of women with PPCM” and provides “a rationale for early initiation of guideline-directed medical therapy after the diagnosis of PPCM and possible continuation even after improvement of LVEF.”
No funding source was reported. Dr. Modi and coauthors, Dr. Elkayam, and Dr. Hameed declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
Researchers looked at the long-term outcomes in a cohort of women who had developed PPCM and became pregnant again several years later, comparing those with LV function that had “normalized” in the interim against those with persisting LV dysfunction.
In their analysis, adverse maternal outcomes 5 years after an index pregnancy were significantly worse among those in whom LV dysfunction had persisted, compared with those with recovered LV function. The risk of relapsed PPCM persisted out to 8 years. Mortality remained high in both groups through the follow-up.
The study suggests that “women with PPCM need long-term follow-up by cardiology, as mortality does not abate over time,” Kalgi Modi, MD, Louisiana State University, Shreveport, said in an interview.
Women with a history of PPCM, she said, need “multidisciplinary and shared decision-making for family planning, because normalization of left ventricular function after index pregnancy does not guarantee a favorable outcome in the subsequent pregnancies.”
Dr. Modi is senior author on the study published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The current findings are important to women with a history of PPCM who are “contemplating future pregnancy,” Afshan Hameed, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist and cardiologist at the University of California, Irvine, said in an interview. The investigators suggest that “complete recovery of cardiac function after PPCM does not guarantee a favorable outcome in future pregnancy,” agreed Dr. Hameed, who was not involved in the current study. Future pregnancies must therefore “be highly discouraged or considered with caution even in patients who have recovered their cardiac function.”
To investigate the impact of PPCM on risk at subsequent pregnancies, the researchers studied 45 patients with PPCM who had gone on to have at least one more pregnancy, the first a median of 28 months later. Their mean age was 27 and 80% were Black; they were followed a median of 8 years.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy, defined as idiopathic heart failure with LV ejection fraction (LVEF) 45% or less in the last month of pregnancy through the following 5 months, was diagnosed post partum in 93.3% and antepartum in the remaining 6.7% (mean time of diagnosis, 6 weeks post partum).
The mean LVEF fell from 45.1% at the index pregnancy to 41.2% (P = .009) at subsequent pregnancies. The “recovery group” included the 30 women with LVEF recovery to 50% or higher after the index pregnancy, and the remaining 15 with persisting LV dysfunction – defined as LVEF < 50% – made up the “nonrecovery group.”
Recovery of LVEF was associated with a reduced risk of persisting LV dysfunction, the report states, at a hazard ratio of 0.08 (95% CI, 0.01-0.64; P = .02) after adjustment for hypertension, diabetes, and history of preeclampsia. But that risk went up sharply in association with illicit drug use, similarly adjusted, with an HR of 9.08 (95% CI, 1.38-59.8; P = .02).
The nonrecovery group, compared with the recovery group, experienced significantly higher rates of adverse maternal outcomes (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .04) – a composite endpoint that included relapse PPCM (33.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .01), HF (53.3% vs. 20.0%; P = .03), cardiogenic shock, thromboembolic events, and death – at 5 years. However, all-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups (13.3% vs. 3.3%; P = .25)
All-cause mortality was nonsignificantly different between the two groups at a median of 8 years (20.0% vs. 20.0%; P = 1.00), and the difference in overall adverse maternal outcomes had gone from significant to nonsignificant (53.3% vs. 33.3%; P = .20). The difference in relapse PPCM between groups remained significant after 8 years (53.3% vs. 23.3%; P = .04)
The study is limited by its retrospective nature, a relatively small population, and lack of racial diversity, the report notes.
Indeed, most of the study’s subjects were Black, and previous studies have demonstrated a “different phenotypic presentation and outcome in African American women with PPCM, compared with non–African American women,” an accompanying editorial states.
Therefore, applicability of its findings to other populations “needs to be examined by urgently needed national prospective registries with long-term follow-up,” writes Uri Elkayam, MD, University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
Moreover, the study questions “whether the reverse remodeling and improvement of [LVEF] in women with PPCM represent a true recovery.” Prior studies “have shown an impaired contractile reserve as well as abnormal myocardial strain and reduced exercise capacity and even mortality in women with PPCM after RLV,” Dr. Elkayam notes.
It’s therefore possible – as with other forms of dilated cardiomyopathy – that LVEF normalization “does not represent a true recovery but a new steady state with subclinical myocardial dysfunction that is prone to development of recurrent [LV dysfunction] and clinical deterioration in response to various triggers such as long-standing hypertension, obesity, diabetes, illicit drug use,” and, “more importantly,” subsequent pregnancies.
The study points to “the need for a close long-term follow-up of women with PPCM” and provides “a rationale for early initiation of guideline-directed medical therapy after the diagnosis of PPCM and possible continuation even after improvement of LVEF.”
No funding source was reported. Dr. Modi and coauthors, Dr. Elkayam, and Dr. Hameed declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
‘Artificial pancreas’ for all type 1 diabetes pregnancies?
In the largest randomized controlled trial of an automated insulin delivery (AID) system (hybrid closed-loop) versus standard insulin delivery in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, the automated CamAPS FX system prevailed.
Helen R. Murphy, MD, presented these topline findings from the Automated Insulin Delivery Amongst Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (AiDAPT) trial during an e-poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The “hybrid closed-loop significantly improved maternal glucose and should be offered to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” concluded Dr. Murphy, professor of medicine at the University of East Anglia and a clinician at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital in the United Kingdom.
CamAPS FX is the only AID system approved in Europe and the United Kingdom for type 1 diabetes from age 1 and during pregnancy. The hybrid closed-loop system is not available in the United States but other systems are available and sometimes used off label in pregnancy. Such systems are sometimes known colloquially as an “artificial pancreas.”
The researchers said their findings provide evidence for the UK National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) to recommend that all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered the CamAPS FX system.
Asked by an audience member about type 2 diabetes in pregnancy, Dr. Murphy said: “I don’t think we can necessarily extend these data to women with type 2 diabetes. We just don’t have enough data on glucose profiles in type 2 to train an algorithm yet.”
However, the data provide support for earlier use of closed-loop therapy in type 1 diabetes, she said. “The ideal time to start closed-loop is not necessarily between 8 and 12 weeks. Half of all pregnancies are unplanned,” she noted, “so start [AID] as early as possible [in patients with type 1 diabetes].”
Two experts weigh in
Whether pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered hybrid closed-loop therapy “depends,” said Anne L. Peters, MD, who was not involved with the research.
“It is all about being able to set [blood glucose] targets,” according to Dr. Peters, director of the University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes in Los Angeles.
“If a woman is on an AID system – except for DIY loop – I have them stop the automation and adjust manually,” she said in an email. “My [patients] do amazingly well in pregnancy – most can get their A1cs below 6%,” she noted. “But if someone can’t do that and their A1cs are higher, automation can help.
“It is always about individualizing care,” said Dr. Peters. “The one thing that helps the most is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). And I do have patients who remain on [insulin] injections throughout pregnancy.”
And Sarit Polsky, MD, MPH, who was also not involved with the current study, agrees that “AID with CamAPS, which has an option to customize the glucose target in the pregnancy-specific range, appears to be safe and effective in pregnancy and should be offered” to patients in Europe and the United Kingdom.
“Whether other AID systems should be recommended in pregnancy is still unclear, said Dr. Polsky, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
“Around 48% of [global] pregnancies are unplanned,” Dr. Polsky said in an interview. “Many women do indeed become pregnant while using AID systems and many opt to continue use of these systems.
“Off-label use of these products can be beneficial in pregnancy in select cases, but the systems generally need the use of assistive techniques, which we previously published, to help get glucose levels to pregnancy-specific targets,” she noted in an email.
Study rationale, method, and findings
Pregnant women with diabetes are advised to aim for very tight glucose targets throughout pregnancy and avoid hyperglycemia, to reduce risk of preterm delivery, neonatal weight > 90th percentile, and neonatal morbidity, according to Dr. Murphy and colleagues.
“However, despite increased use of [CGM], continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII), and improved insulin analogs, achieving and maintaining the recommended glucose targets remains challenging for most pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” they wrote in their abstract.
Researchers randomized 124 women who had type 1 diabetes for at least 12 months, were at < 13 weeks’ to 6 days’ gestation, and had an A1c of 6.5% to < 10% who were taking intensive standard insulin therapy at nine antenatal clinics in the United Kingdom. Half of the women were using CSII and half were receiving multiple daily injections of insulin.
As explained in the published study protocol, the women were randomized to continue their standard insulin delivery or switch to a closed-loop system consisting of the study insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS), a CGM transmitter, and an app (CamAPS FX) on an Android smartphone that communicates wirelessly with the insulin pump and CGM transmitter.
Participants in both groups used the same CGM system and received support for insulin dose adjustment from their antenatal clinical care team.
They were a mean age of 31 years, had a mean A1c of 7.7%, and had had type 1 diabetes for 17 years on average. Their body mass index varied; 37% had normal weight, 27% had overweight, and 26% had obesity.
A significantly higher percentage of women in the AID group than in the control group had blood glucose in target range more than 70% of the time (46% vs. 10%; P < .001).
Compared with women in the control group, those in the AID group had larger reductions in hyperglycemia (–11%; P < .001), higher overnight time-in-range (13%; P < .001), and lower A1c (–0.34%; P < .001), without additional insulin, weight gain, or hypoglycemia.
The effect was consistent across clinical sites and maternal age and A1c categories.
Ongoing studies, off-label use
Hybrid closed-loop systems “including Tandem Control IQ, the Omnipod 5, and the Medtronic 780G give insulin continuously on the basis of values obtained from a sensor,” Dr. Peters explained in a recent commentary. “These aren’t fully closed-loop systems because the individual still has to interact with the system and give doses for meals, and then adjust doses for exercise.”
There are currently three studies using commercially available AID systems without pregnancy-specific glucose targets, in type 1 diabetes pregnancies, Dr. Polsky noted.
The Pregnancy Intervention With a Closed-Loop System (PICLS) trial used the Medtronic 670G system in pregnancy and was conducted in the United States. The Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (CRISTAL) study is using the Medtronic 780G system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Belgium and the Netherlands. And the Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Type 1 Diabetes Pregnancies (CIRCUIT) study is using the Tandem Control IQ system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Canada, she explained.
“The decision to continue to use or to initiate (off-label) use of any of these systems in pregnancy should be individualized, and pregnant individuals should make these decisions by working with an experienced endocrine/diabetes team,” Dr. Polsky stressed.
“The hope is that the results of these exciting trials will show safe and effective use of these systems throughout gestation with improvements in glucose control and quality of life,” she concluded.
The study was funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research, JDRF, and Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation. Dr. Murphy has reported being on the advisory panel for Medtronic and receiving research support from Dexcom. Dr. Peters disclosed that she served as a consultant for Blue Circle Health, Vertex, and Abbott Diabetes Care, received a research grant from Abbott Diabetes Care, and received stock options from Teladoc and Omada Health. Dr. Polsky has disclosed that she is a contributing writer for diaTribe, was on a medical advisory board for Medtronic MiniMed, has received research funding from DexCom, Eli Lilly, JDRF, Leona & Harry Helmsley Charitable Trust, NIDDK, and Sanofi, and has received research support from Diasome Pharmaceuticals, LabStyle Innovation, Lexicon, Medtronic MiniMed, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest randomized controlled trial of an automated insulin delivery (AID) system (hybrid closed-loop) versus standard insulin delivery in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, the automated CamAPS FX system prevailed.
Helen R. Murphy, MD, presented these topline findings from the Automated Insulin Delivery Amongst Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (AiDAPT) trial during an e-poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The “hybrid closed-loop significantly improved maternal glucose and should be offered to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” concluded Dr. Murphy, professor of medicine at the University of East Anglia and a clinician at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital in the United Kingdom.
CamAPS FX is the only AID system approved in Europe and the United Kingdom for type 1 diabetes from age 1 and during pregnancy. The hybrid closed-loop system is not available in the United States but other systems are available and sometimes used off label in pregnancy. Such systems are sometimes known colloquially as an “artificial pancreas.”
The researchers said their findings provide evidence for the UK National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) to recommend that all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered the CamAPS FX system.
Asked by an audience member about type 2 diabetes in pregnancy, Dr. Murphy said: “I don’t think we can necessarily extend these data to women with type 2 diabetes. We just don’t have enough data on glucose profiles in type 2 to train an algorithm yet.”
However, the data provide support for earlier use of closed-loop therapy in type 1 diabetes, she said. “The ideal time to start closed-loop is not necessarily between 8 and 12 weeks. Half of all pregnancies are unplanned,” she noted, “so start [AID] as early as possible [in patients with type 1 diabetes].”
Two experts weigh in
Whether pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered hybrid closed-loop therapy “depends,” said Anne L. Peters, MD, who was not involved with the research.
“It is all about being able to set [blood glucose] targets,” according to Dr. Peters, director of the University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes in Los Angeles.
“If a woman is on an AID system – except for DIY loop – I have them stop the automation and adjust manually,” she said in an email. “My [patients] do amazingly well in pregnancy – most can get their A1cs below 6%,” she noted. “But if someone can’t do that and their A1cs are higher, automation can help.
“It is always about individualizing care,” said Dr. Peters. “The one thing that helps the most is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). And I do have patients who remain on [insulin] injections throughout pregnancy.”
And Sarit Polsky, MD, MPH, who was also not involved with the current study, agrees that “AID with CamAPS, which has an option to customize the glucose target in the pregnancy-specific range, appears to be safe and effective in pregnancy and should be offered” to patients in Europe and the United Kingdom.
“Whether other AID systems should be recommended in pregnancy is still unclear, said Dr. Polsky, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
“Around 48% of [global] pregnancies are unplanned,” Dr. Polsky said in an interview. “Many women do indeed become pregnant while using AID systems and many opt to continue use of these systems.
“Off-label use of these products can be beneficial in pregnancy in select cases, but the systems generally need the use of assistive techniques, which we previously published, to help get glucose levels to pregnancy-specific targets,” she noted in an email.
Study rationale, method, and findings
Pregnant women with diabetes are advised to aim for very tight glucose targets throughout pregnancy and avoid hyperglycemia, to reduce risk of preterm delivery, neonatal weight > 90th percentile, and neonatal morbidity, according to Dr. Murphy and colleagues.
“However, despite increased use of [CGM], continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII), and improved insulin analogs, achieving and maintaining the recommended glucose targets remains challenging for most pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” they wrote in their abstract.
Researchers randomized 124 women who had type 1 diabetes for at least 12 months, were at < 13 weeks’ to 6 days’ gestation, and had an A1c of 6.5% to < 10% who were taking intensive standard insulin therapy at nine antenatal clinics in the United Kingdom. Half of the women were using CSII and half were receiving multiple daily injections of insulin.
As explained in the published study protocol, the women were randomized to continue their standard insulin delivery or switch to a closed-loop system consisting of the study insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS), a CGM transmitter, and an app (CamAPS FX) on an Android smartphone that communicates wirelessly with the insulin pump and CGM transmitter.
Participants in both groups used the same CGM system and received support for insulin dose adjustment from their antenatal clinical care team.
They were a mean age of 31 years, had a mean A1c of 7.7%, and had had type 1 diabetes for 17 years on average. Their body mass index varied; 37% had normal weight, 27% had overweight, and 26% had obesity.
A significantly higher percentage of women in the AID group than in the control group had blood glucose in target range more than 70% of the time (46% vs. 10%; P < .001).
Compared with women in the control group, those in the AID group had larger reductions in hyperglycemia (–11%; P < .001), higher overnight time-in-range (13%; P < .001), and lower A1c (–0.34%; P < .001), without additional insulin, weight gain, or hypoglycemia.
The effect was consistent across clinical sites and maternal age and A1c categories.
Ongoing studies, off-label use
Hybrid closed-loop systems “including Tandem Control IQ, the Omnipod 5, and the Medtronic 780G give insulin continuously on the basis of values obtained from a sensor,” Dr. Peters explained in a recent commentary. “These aren’t fully closed-loop systems because the individual still has to interact with the system and give doses for meals, and then adjust doses for exercise.”
There are currently three studies using commercially available AID systems without pregnancy-specific glucose targets, in type 1 diabetes pregnancies, Dr. Polsky noted.
The Pregnancy Intervention With a Closed-Loop System (PICLS) trial used the Medtronic 670G system in pregnancy and was conducted in the United States. The Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (CRISTAL) study is using the Medtronic 780G system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Belgium and the Netherlands. And the Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Type 1 Diabetes Pregnancies (CIRCUIT) study is using the Tandem Control IQ system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Canada, she explained.
“The decision to continue to use or to initiate (off-label) use of any of these systems in pregnancy should be individualized, and pregnant individuals should make these decisions by working with an experienced endocrine/diabetes team,” Dr. Polsky stressed.
“The hope is that the results of these exciting trials will show safe and effective use of these systems throughout gestation with improvements in glucose control and quality of life,” she concluded.
The study was funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research, JDRF, and Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation. Dr. Murphy has reported being on the advisory panel for Medtronic and receiving research support from Dexcom. Dr. Peters disclosed that she served as a consultant for Blue Circle Health, Vertex, and Abbott Diabetes Care, received a research grant from Abbott Diabetes Care, and received stock options from Teladoc and Omada Health. Dr. Polsky has disclosed that she is a contributing writer for diaTribe, was on a medical advisory board for Medtronic MiniMed, has received research funding from DexCom, Eli Lilly, JDRF, Leona & Harry Helmsley Charitable Trust, NIDDK, and Sanofi, and has received research support from Diasome Pharmaceuticals, LabStyle Innovation, Lexicon, Medtronic MiniMed, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the largest randomized controlled trial of an automated insulin delivery (AID) system (hybrid closed-loop) versus standard insulin delivery in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes, the automated CamAPS FX system prevailed.
Helen R. Murphy, MD, presented these topline findings from the Automated Insulin Delivery Amongst Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (AiDAPT) trial during an e-poster session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
The “hybrid closed-loop significantly improved maternal glucose and should be offered to all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” concluded Dr. Murphy, professor of medicine at the University of East Anglia and a clinician at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital in the United Kingdom.
CamAPS FX is the only AID system approved in Europe and the United Kingdom for type 1 diabetes from age 1 and during pregnancy. The hybrid closed-loop system is not available in the United States but other systems are available and sometimes used off label in pregnancy. Such systems are sometimes known colloquially as an “artificial pancreas.”
The researchers said their findings provide evidence for the UK National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE) to recommend that all pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered the CamAPS FX system.
Asked by an audience member about type 2 diabetes in pregnancy, Dr. Murphy said: “I don’t think we can necessarily extend these data to women with type 2 diabetes. We just don’t have enough data on glucose profiles in type 2 to train an algorithm yet.”
However, the data provide support for earlier use of closed-loop therapy in type 1 diabetes, she said. “The ideal time to start closed-loop is not necessarily between 8 and 12 weeks. Half of all pregnancies are unplanned,” she noted, “so start [AID] as early as possible [in patients with type 1 diabetes].”
Two experts weigh in
Whether pregnant women with type 1 diabetes should be offered hybrid closed-loop therapy “depends,” said Anne L. Peters, MD, who was not involved with the research.
“It is all about being able to set [blood glucose] targets,” according to Dr. Peters, director of the University of Southern California Westside Center for Diabetes in Los Angeles.
“If a woman is on an AID system – except for DIY loop – I have them stop the automation and adjust manually,” she said in an email. “My [patients] do amazingly well in pregnancy – most can get their A1cs below 6%,” she noted. “But if someone can’t do that and their A1cs are higher, automation can help.
“It is always about individualizing care,” said Dr. Peters. “The one thing that helps the most is continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). And I do have patients who remain on [insulin] injections throughout pregnancy.”
And Sarit Polsky, MD, MPH, who was also not involved with the current study, agrees that “AID with CamAPS, which has an option to customize the glucose target in the pregnancy-specific range, appears to be safe and effective in pregnancy and should be offered” to patients in Europe and the United Kingdom.
“Whether other AID systems should be recommended in pregnancy is still unclear, said Dr. Polsky, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
“Around 48% of [global] pregnancies are unplanned,” Dr. Polsky said in an interview. “Many women do indeed become pregnant while using AID systems and many opt to continue use of these systems.
“Off-label use of these products can be beneficial in pregnancy in select cases, but the systems generally need the use of assistive techniques, which we previously published, to help get glucose levels to pregnancy-specific targets,” she noted in an email.
Study rationale, method, and findings
Pregnant women with diabetes are advised to aim for very tight glucose targets throughout pregnancy and avoid hyperglycemia, to reduce risk of preterm delivery, neonatal weight > 90th percentile, and neonatal morbidity, according to Dr. Murphy and colleagues.
“However, despite increased use of [CGM], continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII), and improved insulin analogs, achieving and maintaining the recommended glucose targets remains challenging for most pregnant women with type 1 diabetes,” they wrote in their abstract.
Researchers randomized 124 women who had type 1 diabetes for at least 12 months, were at < 13 weeks’ to 6 days’ gestation, and had an A1c of 6.5% to < 10% who were taking intensive standard insulin therapy at nine antenatal clinics in the United Kingdom. Half of the women were using CSII and half were receiving multiple daily injections of insulin.
As explained in the published study protocol, the women were randomized to continue their standard insulin delivery or switch to a closed-loop system consisting of the study insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS), a CGM transmitter, and an app (CamAPS FX) on an Android smartphone that communicates wirelessly with the insulin pump and CGM transmitter.
Participants in both groups used the same CGM system and received support for insulin dose adjustment from their antenatal clinical care team.
They were a mean age of 31 years, had a mean A1c of 7.7%, and had had type 1 diabetes for 17 years on average. Their body mass index varied; 37% had normal weight, 27% had overweight, and 26% had obesity.
A significantly higher percentage of women in the AID group than in the control group had blood glucose in target range more than 70% of the time (46% vs. 10%; P < .001).
Compared with women in the control group, those in the AID group had larger reductions in hyperglycemia (–11%; P < .001), higher overnight time-in-range (13%; P < .001), and lower A1c (–0.34%; P < .001), without additional insulin, weight gain, or hypoglycemia.
The effect was consistent across clinical sites and maternal age and A1c categories.
Ongoing studies, off-label use
Hybrid closed-loop systems “including Tandem Control IQ, the Omnipod 5, and the Medtronic 780G give insulin continuously on the basis of values obtained from a sensor,” Dr. Peters explained in a recent commentary. “These aren’t fully closed-loop systems because the individual still has to interact with the system and give doses for meals, and then adjust doses for exercise.”
There are currently three studies using commercially available AID systems without pregnancy-specific glucose targets, in type 1 diabetes pregnancies, Dr. Polsky noted.
The Pregnancy Intervention With a Closed-Loop System (PICLS) trial used the Medtronic 670G system in pregnancy and was conducted in the United States. The Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Pregnant Women With Type 1 Diabetes (CRISTAL) study is using the Medtronic 780G system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Belgium and the Netherlands. And the Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery in Type 1 Diabetes Pregnancies (CIRCUIT) study is using the Tandem Control IQ system in pregnancy and is being conducted in Canada, she explained.
“The decision to continue to use or to initiate (off-label) use of any of these systems in pregnancy should be individualized, and pregnant individuals should make these decisions by working with an experienced endocrine/diabetes team,” Dr. Polsky stressed.
“The hope is that the results of these exciting trials will show safe and effective use of these systems throughout gestation with improvements in glucose control and quality of life,” she concluded.
The study was funded by the UK National Institute for Health Research, JDRF, and Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation. Dr. Murphy has reported being on the advisory panel for Medtronic and receiving research support from Dexcom. Dr. Peters disclosed that she served as a consultant for Blue Circle Health, Vertex, and Abbott Diabetes Care, received a research grant from Abbott Diabetes Care, and received stock options from Teladoc and Omada Health. Dr. Polsky has disclosed that she is a contributing writer for diaTribe, was on a medical advisory board for Medtronic MiniMed, has received research funding from DexCom, Eli Lilly, JDRF, Leona & Harry Helmsley Charitable Trust, NIDDK, and Sanofi, and has received research support from Diasome Pharmaceuticals, LabStyle Innovation, Lexicon, Medtronic MiniMed, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2023
Vaginal microbiota transfer may affect neurodevelopment in cesarean infants
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous studies have shown that gut microbiota in infancy could affect neurodevelopment, and infants delivered by cesarean are not exposed to potentially helpful microbes acquired by infants during vaginal delivery, wrote Lepeng Zhou, MD, of Southern Medical University, Guangdong, China, and colleagues.
“Infants delivered by C-section start life with very different bacteria than those born vaginally,” corresponding author Jose Clemente, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Because this is the first time the newborn is exposed to microbes, we and others have hypothesized for some time that this ‘first encounter’ might be significant to shape the development of the baby,” he said.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to change the microbiome of C-section–delivered infants using an intervention that makes their microbiome more similar to that of a vaginally-delivered infant,” Dr. Clemente told this news organization. “In this study just published, we show that this procedure not only changes the microbiome of C-section infants, but it also modifies a health outcome (in this case, neurodevelopment). This is highly significant because it opens the way to reduce the risk that C-section infants have for certain conditions through a very simple microbial intervention,” he said.
‘Significantly higher’ ASQ-3 scores
In the current study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, the researchers examined the impact of vaginal microbiota transfer (VMT) on the neurodevelopment of cesarean-delivered infants. They randomized 35 women scheduled for cesarean delivery with a single infant to VMT and 41 to a control intervention of saline gauze for their infants immediately after delivery.
The primary outcome of infant neurodevelopment was assessed using the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (ASQ-3) score at 6 months. The researchers also collected fecal samples and assessed safety outcomes for the infants at 3, 7, 30, and 42 days after birth. The final analysis comprised 32 infants in the VMT group and 36 in the control group. The mean age of the mothers was 32 years; the mean gestational age of the infants was 39 weeks, but the difference was significant and slightly less in the VMT group compared with the controls (38.38 weeks vs. 39.13 weeks, P = .007). A group of 33 vaginally-delivered infants (VD) underwent ASQ-3 testing to serve as a reference group.
At 6 months, ASQ-3 scores were significantly higher (10.09%, P = .014) with VMT compared with controls, and the difference remained significant after adjustment for multiple factors including gestational age.
ASQ-3 total scores at 6 months were not significantly different between the VMT group and the VD reference group (mean difference of 8.84 VMT to VD, P = .346); scores between these groups also were similar at 3 months (mean difference of –1.48 VMT to VD, P = .900) and no significant differences appeared in ASQ-3 subdomains between these groups at either time period.
An examination of gut metabolites in stool showed significant differences in fecal metabolites and metabolic function, signs of gut microbiota maturation, the researchers noted.
“Interestingly, all the genera and metabolites that exhibited positive correlations with neurodevelopmental scores were upregulated in the VMT group, whereas the only negative correlation of Klebsiella was downregulated, indicating that VMT may impact neurodevelopment through the modulation of specific gut microbial genera and metabolites,” the researchers wrote.
No serious adverse events occurred in either group during the study period. Nine adverse events were reported; 4 in the VMT group and 5 in the control group. The most common AEs were mild skin disorders, including papules, pustules, and erythema.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential for transfer not only of vaginal microbiota, but also vaginal metabolites, mycobiome, and virome, which blurs the potential mechanism of VMT, the researchers noted. Other limitations were the relatively short study period, small sample size, and cervical HPV screening within the past 5 years, not during pregnancy, they wrote.
However, the results suggest that VMT is safe, and may help improve the fecal microbiome in cesarean-delivered infants, and the long-term effects merit further studies in larger populations, they concluded.
Limitations and outlook
Dr. Clemente said in an interview that the researchers were “hopeful that the study would demonstrate a health benefit, as it does with some limitations.” The current study findings confirm some previous results showing that modification of the microbiomes of C-section infants is possible through a transfer of maternal vaginal microbes, he said.
“There is also an important aspect that was confirmed here: The lack of serious adverse events associated with the procedure, and the fact that transferring vaginal microbes did not increase the risk of adverse events compared to the control group or to vaginally-delivered infants. This is fundamental to establish that using rigorous exclusion criteria we can perform this procedure safely for infants and mothers,” he added.
“We are at very early stages yet to talk about clinical implications,” said Dr. Clemente. “This is one of the first studies to demonstrate a benefit to the transfer of microbes from mothers to infants, and as such it opens the way for future trials that confirm these findings. The clinical application is still in the future, but this is an important first step towards that goal.”
Interest in restoring gut microbiota to potentially benefit infants persists, but a recent study published in Frontiers and Cellular and Infection Microbiology contradicted the potential association between maternal vaginal microbiome and an infant’s gut microbiome based on an analysis of infant stool.
“There are many reasons why different studies might reach different conclusions: The experimental procedures, the analytical methods, the cohort under study,” Dr. Clemente said when asked to comment on the Frontiers study. “Further studies are needed to establish whether this procedure is equally effective under all conditions and whether health benefits are generalizable or specific to particular populations.”
Several research gaps remain, Dr. Clemente said. “First, neurodevelopment was measured through a questionnaire that captures various aspects such as communication, motor skills, or problem solving. While this is a standard way to establish that an infant is in the correct neurodevelopmental pathway, it is not a ‘hard’ measure of cellular or biochemical processes being impacted by the intervention. Some of our results suggest that there is a change in the metabolome of this infants, particularly an enrichment in GABA, a neurotransmitter, but the exact mechanisms by which the intervention is resulting in a health benefit still remains to be explored,” he said.
“We have an ongoing study here at Mount Sinai to test whether this microbial intervention can be effective in lowering the risk of developing food allergies in newborns who are at high risk, so that is another important future question: What other conditions could benefit from this approach,” said Dr. Clemente.
A third research goal, he added, is “determining what microbes precisely are responsible for the health benefits; this study uses a full microbial community to colonize infants. We show that this is effective and, importantly, that there were no significant adverse events in the treated infants,” he noted. “However, identifying what specific microbes are beneficial would further lower the risk of any potential side effects, while facilitating the development of drugs based on defined microbial consortia,” he said.
Safety and efficacy support further studies
“It is widely accepted that the gut microbiome of neonates varies based on mode of delivery,” Anna K. Knight, PhD, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview.
“C-sections have been associated with increased risk of asthma and metabolic disease, and have been associated with differences in the development of the immune system,” said Dr. Knight, who was not involved in the study. “There have been small pilot studies examining the use of vaginal microbiome transplants to shift the gut microbiome of neonates born by C-section to be more like the gut microbiome of neonates born via vaginal delivery, but the safety and efficacy of this treatment has not been well established. This study examines both, while also evaluating potential changes in the metabolome and neurodevelopmental trajectories.”
The current study confirmed the impact of the neonatal gut microbe on neurodevelopmental outcomes during a sensitive period, said Dr. Knight. “The fact that these differences persisted at 6 months suggests that even if the microbiome composition between vaginally-delivered and preterm infants converged at 1-2 years old, there may be lasting impacts of mode of delivery,” she said.
“The results of this study suggest that vaginal microbiome transplant may be a safe and effective way to mitigate the negative impacts of C-section delivery on the neonatal gut microbiome, and may be protective for neurodevelopment,” she added.
Regarding the Frontiers in Medicine study, Dr. Knight noted that it examined a very different population, with Zhou and colleagues focusing on Chinese infants, while Dos Santos and colleagues focused on Canadian infants.
“There was also a substantial difference in sample size between the two studies, with Dos Santos and colleagues examining > 500 more infants,” she said. “Additionally, the two studies differed in the sequencing technology used, sample collection methods, and antibiotic exposure, which can all impact microbiome study results.”
Since the current study showed efficacy and safety of VMT in a small clinical trial, larger trials with more diverse participants are needed to further examine the impact of VMT, said Dr. Knight. “The risks of vaginal microbiome transplant in mothers with infections should also be considered, and the mechanisms by which the neonatal gut microbiome impacts neurodevelopment need further investigation,” she said.
The study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Canadian Institute of Health Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Clinical Research Startup Program of Southern Medical University, China, and the Top Talent Program of Foshan Women and Children Hospital, China. The researchers and Dr. Knight had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CELL HOST & MICROBE
Malpractice lawsuits over denied abortion care may be on the horizon
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Some experts predict those providers could soon face a new legal threat: medical malpractice lawsuits alleging they harmed patients by failing to provide timely, necessary abortion care.
“We will absolutely see medical malpractice cases emerge,” said Diana Nordlund, an emergency physician in Grand Rapids, Mich., and former malpractice defense attorney, who chairs the Medical-Legal Committee of the American College of Emergency Physicians. When physicians decide not to provide treatments widely accepted as the standard of care because of these new laws, “that’s perceived as substandard care and there is increased civil liability.”
To some physicians and malpractice attorneys, the question is when – not if – a pregnant patient will die from lack of care and set the stage for a big-dollar wrongful death claim. Abortion rights supporters said such a case could pressure doctors and hospitals to provide appropriate abortion care, counterbalancing their fears of running afoul of state abortion bans, many of which call for criminal prosecution and revocation of medical licenses as punishment for violations.
“If we want to encourage proper care, there has to be some sort of counter-risk to physicians and hospitals for refusing to provide care that should be legal,” said Greer Donley, an associate professor at the University of Pittsburgh school of law who studies the impact of abortion bans. “But most rational people would be more afraid of going to jail.”
Some supporters of abortion bans said they would welcome malpractice lawsuits. Providers are refusing to use the exceptions in some state laws that allow them to perform abortions to save a patient’s life or health, they said.
“It could help achieve our goal if it clarifies that the law did not contradict standard medical practice,” said John Seago, president of Texas Right to Life, referring to the state’s abortion ban.
A new KFF poll found that 59% of ob.gyns. practicing in states with gestational limits on abortion, and 61% of those in states with bans, are somewhat or very concerned about their legal risk when making decisions about the necessity of an abortion.
Some attorneys are exploring lawsuits on behalf of women who they said have been harmed by a state abortion ban. An attorney for Mylissa Farmer, a Missouri woman who was refused an abortion at two hospitals in August after her water broke about 18 weeks into her pregnancy, said she may sue for malpractice. Missouri’s abortion ban, which took effect last year, makes an exception for medical emergencies.
The federal government recently found that the two hospitals violated a federal emergency care law in denying Ms. Farmer an abortion, which experts said could strengthen a malpractice claim. One of the hospitals, Freeman Health System in Joplin, Mo., did not respond to a request for comment. The other, the University of Kansas Health System in Kansas City, said the care provided “was reviewed by the hospital and found to be in accordance with hospital policy,” according to a spokesperson, Jill Chadwick.
Ms. Farmer “experienced permanent physical and emotional damage,” said Michelle Banker, one of her lawyers at the National Women’s Law Center, who added that Ms. Farmer and her attorneys are “considering all our legal options.”
News reports and medical studies show that some women with pregnancy complications have suffered serious health consequences when doctors and hospitals did not provide once-routine abortion care.
Last month, researchers released a study identifying dozens of cases in 14 states in which physicians said deficiencies in care due to abortion restrictions led to preventable complications and hospitalizations, with some patients nearly dying.
“The patients were sent home and told to come back when they had signs of infection,” said Daniel Grossman, an ob.gyn. at the University of California, San Francisco, who led the study. “Many developed serious infections. And it’s clear many of these cases were very emotionally traumatic.”
He said though the researchers did not track patient outcomes, the lack of timely abortion care in such cases could result in severe health harms including loss of fertility, stroke, or heart attack.
“It’s just a matter of time before there will be a death that comes to light,” Dr. Grossman said.
Still, considering the conflict for doctors between medical ethics and personal risk, some stakeholders said patients may be reluctant to sue doctors and juries may balk at finding them liable.
“It’s a terrible position that providers are being put into, and I don’t think juries will blame the doctor unless it’s a super clear case,” said Morgan Murphy, a malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Missouri.
She said her firm will not pursue malpractice cases based on abortion denials except in “pretty extreme” situations, such as when a patient dies. “Unless a mother is on her deathbed, it’s pretty hard to fault a provider who thinks if they provide treatment they’re going to be criminally liable or will lose their medical license.”
Another hurdle for malpractice cases is that state abortion bans could undermine the argument that abortion is the legal “standard of care,” meaning that it is a widely accepted and prescribed treatment for pregnancy complications such as miscarriage and for fatal fetal abnormalities.
“I absolutely see a breach of the standard of care in these cases,” said Maria A. Phillis, an ob.gyn. and former lawyer in Cleveland. “But if someone goes to trial in a malpractice case, it will come down to a battle of medical experts about whether it’s no longer the standard of care, and the jury would have to decide.”
An additional justification for physicians not to provide abortions is that medical liability insurers generally do not cover damages from criminal acts, which “puts the finger on the scales even more to not do anything,” Dr. Phillis said.
Stuart Grossman, a prominent malpractice plaintiff’s attorney in Florida, said he would be eager to take an abortion-denial case in which the woman suffered serious health or emotional injuries.
Unlike other states with abortion bans, Florida does not cap damage amounts for pain and suffering in malpractice cases, making it more financially viable to sue there.
Mr. Grossman cited the case of Deborah Dorbert, a Florida woman who reportedly was denied an abortion despite being told by her physicians at 24 weeks of pregnancy that her fetus, with no kidneys and underdeveloped lungs, had a fatal condition called Potter syndrome.
Her doctors and the hospital refused to end the pregnancy even though the state’s abortion ban has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. Months later, her baby died in his parents’ arms shortly after birth.
“You can see how she’s been devastated mentally,” Mr. Grossman said. “She has a wrongful death case that I’d take in a minute.” He said the couple could file a malpractice suit for Ms. Dorbert’s physical and emotional damages and a separate malpractice and wrongful death suit for the couple’s suffering over the infant’s death.
Failing to counsel patients about their options and connect them with providers willing to terminate a pregnancy is also possible grounds for a malpractice suit, attorneys said. Katie Watson, an associate professor at Northwestern University, Chicago’s school of medicine who has studied state abortion bans, said counseling and referral are not prohibited under these laws and that physicians have an ethical obligation to offer those services.
“I think breaching the obligation for counseling would make a strong malpractice lawsuit,” she said.
Nancy Davis said she received no counseling or referral assistance last July after her doctors at Woman’s Hospital in Baton Rouge, La., told her 10 weeks into her pregnancy that her fetus would not survive because it was missing the top of its skull, a fatal condition called acrania. She said they recommended that she terminate the pregnancy and she agreed.
Ms. Davis said her doctors then told her a hospital executive had denied permission for the procedure because of Louisiana’s abortion ban, even though the law has an exception for fatal fetal abnormalities. A hospital spokesperson declined to comment.
Ms. Davis, who has three children, contacted Planned Parenthood of Greater New York, which arranged for child care and a flight to New York. She had an abortion performed there in September.
“The whole situation has been mentally and physically draining, and my family and I are receiving counseling,” Ms. Davis said. “I’m still very angry at the hospital and the doctors. I feel like I’m owed compensation for the trauma and the heartbreak.”
She sought the counsel of Benjamin Crump, a prominent attorney known for pursuing high-profile cases like wrongful death lawsuits on behalf of the families of Trayvon Martin and George Floyd.
But Mr. Crump said that after studying Ms. Davis’ legal options, he decided a judge would likely dismiss a malpractice suit and that Ms. Davis could end up paying the defendants’ legal fees and costs.
“The doctor’s lawyers will say, ‘You can’t expect my client to break the law and go to prison for up to 25 years,’ ” Mr. Crump said. “Unless you change the law, there is no option for her to receive compensation.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Updates on pregnancy outcomes in transgender men
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.
Despite increased societal gains, transgender individuals are still a medically and socially underserved group. The historic rise of antitransgender legislation and the overturning of Roe v. Wade, further compound existing health care disparities, particularly in the realm of contraception and pregnancy. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives are typically first-line providers when discussing family planning and fertility options for all patients assigned female at birth. Unfortunately,
Only individuals who are assigned female at birth and have a uterus are capable of pregnancy. This can include both cisgender women and nonbinary/transgender men. However, societal and medical institutions are struggling with this shift in perspective from a traditionally gendered role to a more inclusive one. Obstetrician-gynecologists and midwives can serve to bridge this gap between these patients and societal misconceptions surrounding transgender men who desire and experience pregnancy.
Providers need to remember that many transmasculine individuals will still retain their uterus and are therefore capable of getting pregnant. While testosterone causes amenorrhea, if patients are engaging in penile-vaginal intercourse, conception is still possible. If a patient does not desire pregnancy, all contraceptive options available for cisgender women, which also include combined oral contraceptives, should be offered.
For patients seeking to become pregnant, testosterone must be discontinued. Testosterone is teratogenic; it can cause abnormal urogenital development in the female fetus and should be avoided even prior to conception.1,2 The timing of testosterone discontinuation is debatable. There are no well-established guidelines dictating how early pregnancy can be attempted after cessation of testosterone, but typically if menses has resumed, the teratogenic effects of testosterone are less likely.
For amenorrheic patients on testosterone, menses will occur, on average, 3-6 months after testosterone is stopped. Of note, the longer that testosterone has been suspended, the greater the likelihood of achieving pregnancy.3 In a study by Light et al., 72% of patients conceived within 6 months of attempting pregnancy, 80% resumed menses within 6 months of stopping testosterone, and 20% of individuals conceived while they were amenorrheic from testosterone.4
Psychosocial support is an essential part of pregnancy care in transgender men. For some patients, pregnancy can worsen gender dysphoria, whereas others are empowered by the experience. Insurance companies may also deny obstetric care services to transgender males who have already changed their gender marker from female to male on insurance policies.
Whether transmasculine individuals are at higher risk for pregnancy complications is largely unknown, although emerging research in this field has yielded interesting results. While testosterone can cause vaginal atrophy, it does not seem to increase a patient’s risk of vaginal lacerations or their ability to have a successful vaginal delivery. For transgender men with significant discomfort around their genitalia, an elective cesarean section may be appropriate.5
More recently, Stroumsa et al. conducted an analysis of all deliveries at a Michigan institution from 2014 to 2018. Patients with male gender at the time of delivery or with the diagnostic code of gender dysphoria were identified as transgender.6 The primary outcome of this study was severe parental morbidity (such as amniotic fluid embolism, acute myocardial infarction, eclampsia, etc.), with secondary outcomes investigating rates of cesarean delivery and preterm birth.
During this time period, the researchers identified 256 transgender patients and 1.3 million cisgender patients in their Medicaid database and 1,651 transgender patients and 1.5 million cisgender patients in the commercial database who had experienced a delivery.6 Compared with cisgender patients, transgender patients in the Medicaid database were younger, less likely to be white, and more likely to have a chronic condition.6 Compared with cisgender patients in the commercial database, transgender patients experienced higher rates of anxiety and depression.6 Both transgender and cisgender patients had similar rates of severe parental morbidity. Ironically, rates of cesarean delivery were lower, compared with cisgender patients, in both the Medicaid and commercial databases, with no differences observed between rates of preterm birth.6
While more research is needed on pregnancy in transgender men, this analysis is not only one of the largest to date, but it also challenges many misconceptions providers have regarding pregnancy outcomes. Even though transmasculine patients may require additional medical interventions to achieve pregnancy, such as assisted reproductive technology, or increased psychosocial support during the process, these initial studies are reassuring. Based on current evidence, these patients are not at greater risk for perinatal complications than their cisgender counterparts.
Despite these encouraging findings, there are still several challenges faced by transgender men when it comes to getting pregnant. For instance, they may have difficulty accessing fertility services because of financial constraints or experience a lack of awareness or prejudice from providers; they might also be subject to discrimination or stigma within health care settings. As front-line providers for obstetrical care, we must lead the way towards improving the care for pregnant transmasculine individuals.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa.
References
1. Light A et al. Family planning and contraception use in transgender men. Contraception. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.06.006.
2. Krempasky C et al. Contraception across the transmasculine spectrum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.07.043.
3. Obedin-Maliver J, De Haan G. “Gynecologic care for transgender patients” in Ferrando C, ed., Comprehensive Care of the Transgender Patient. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2019. 131-51.
4. Light AD et al. Transgender men who experienced pregnancy after female-to-male gender transitioning. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Dec. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000540.
5. Brandt JS et al. Transgender men, pregnancy, and the “new” advanced paternal age: A review of the literature. Maturitas. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.07.004.
6. Stroumsa D et al. Pregnancy outcomes in a U.S. cohort of transgender people. JAMA. 2023 Jun 6. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.7688.