User login
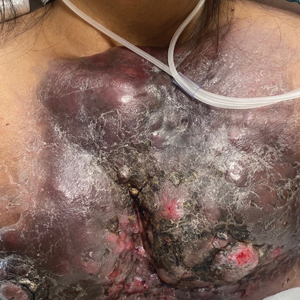
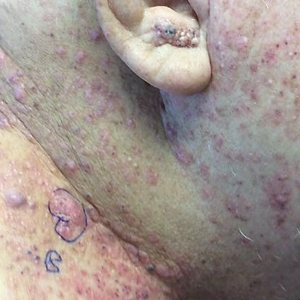
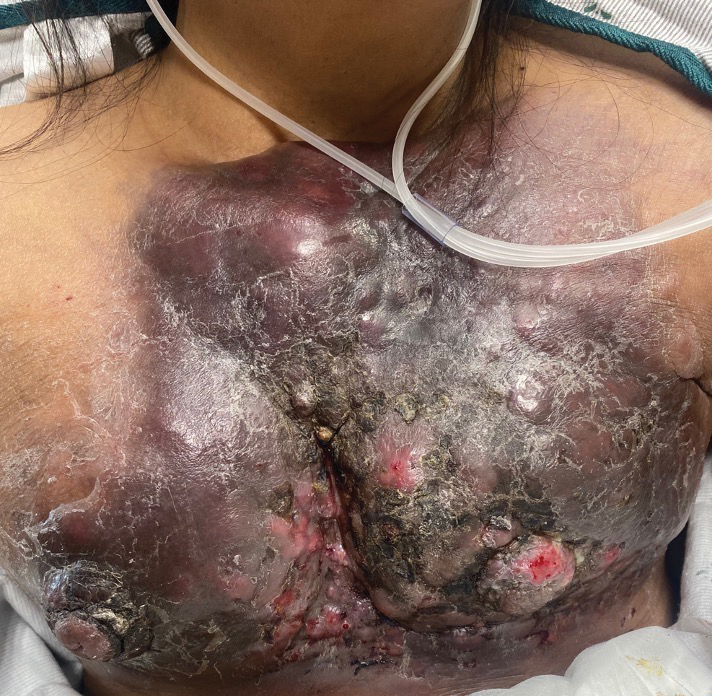
Large Indurated Plaque on the Chest With Ulceration and Necrosis
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
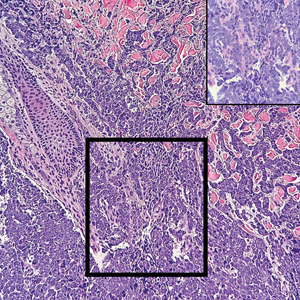
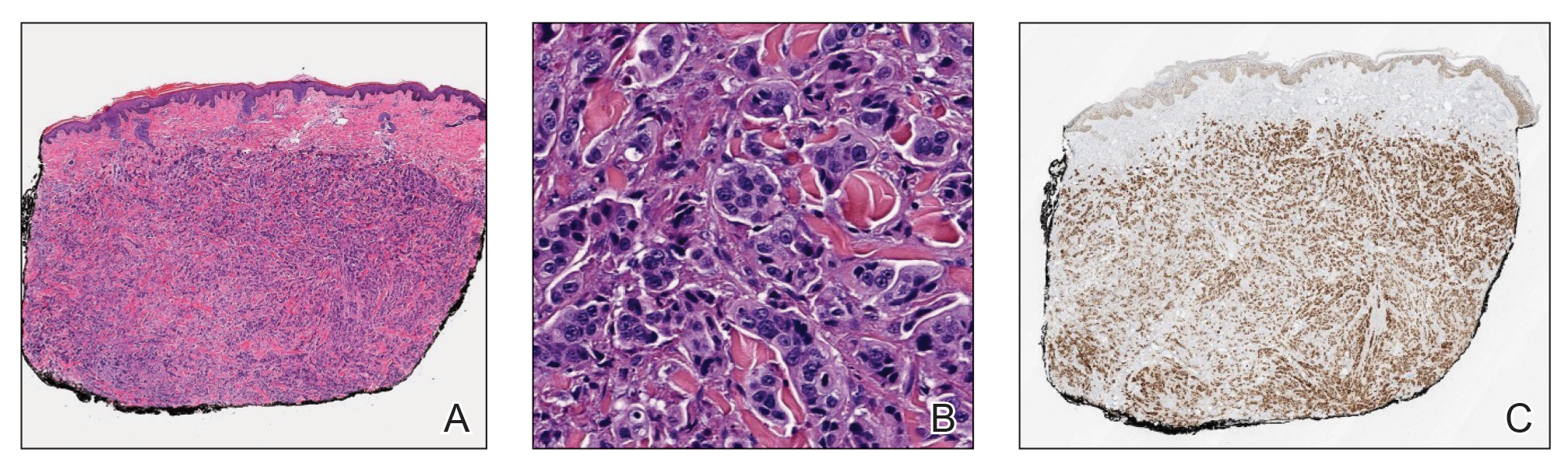
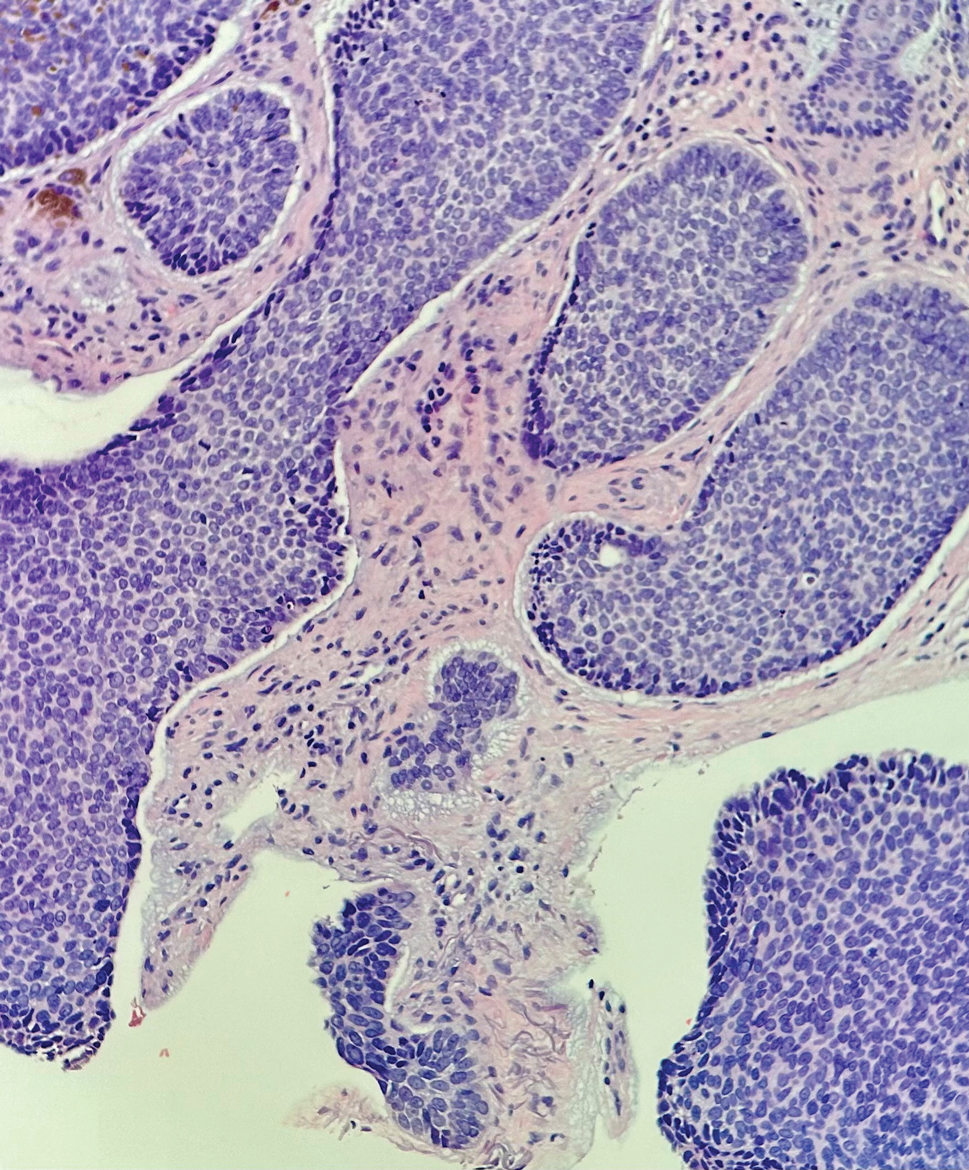
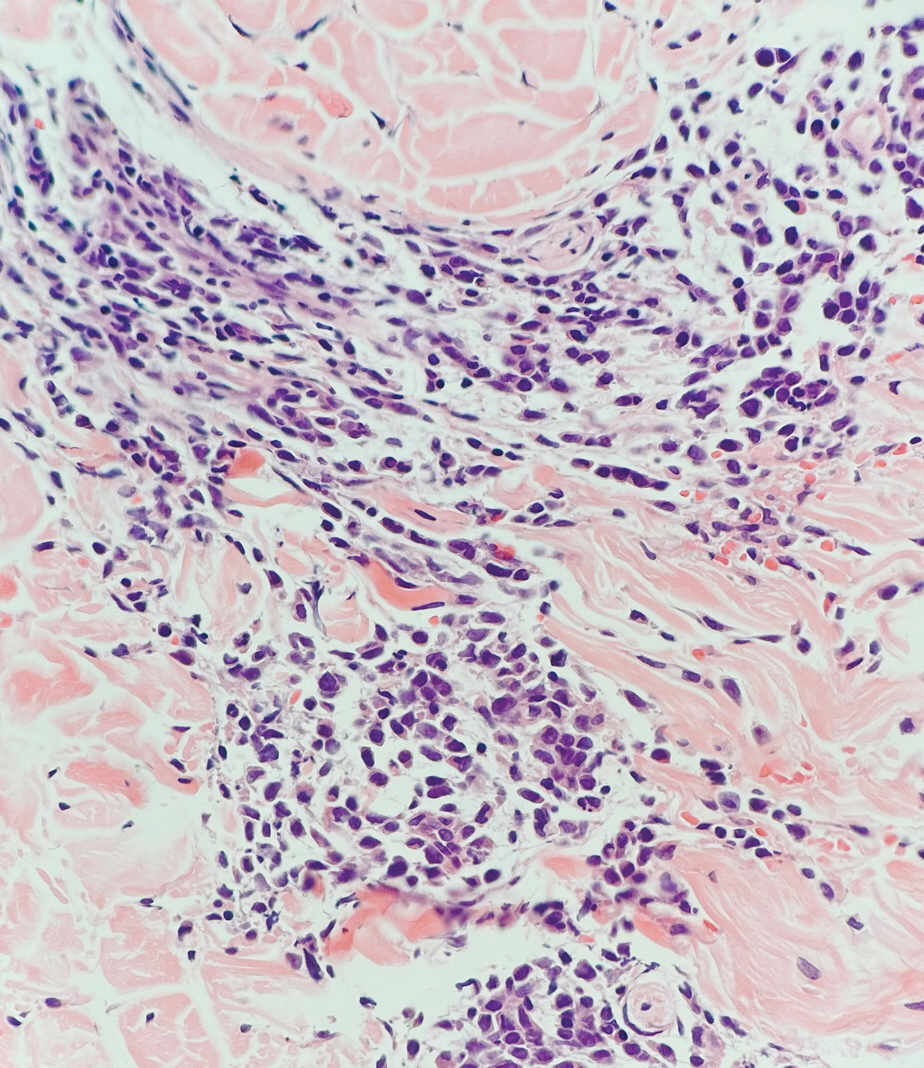
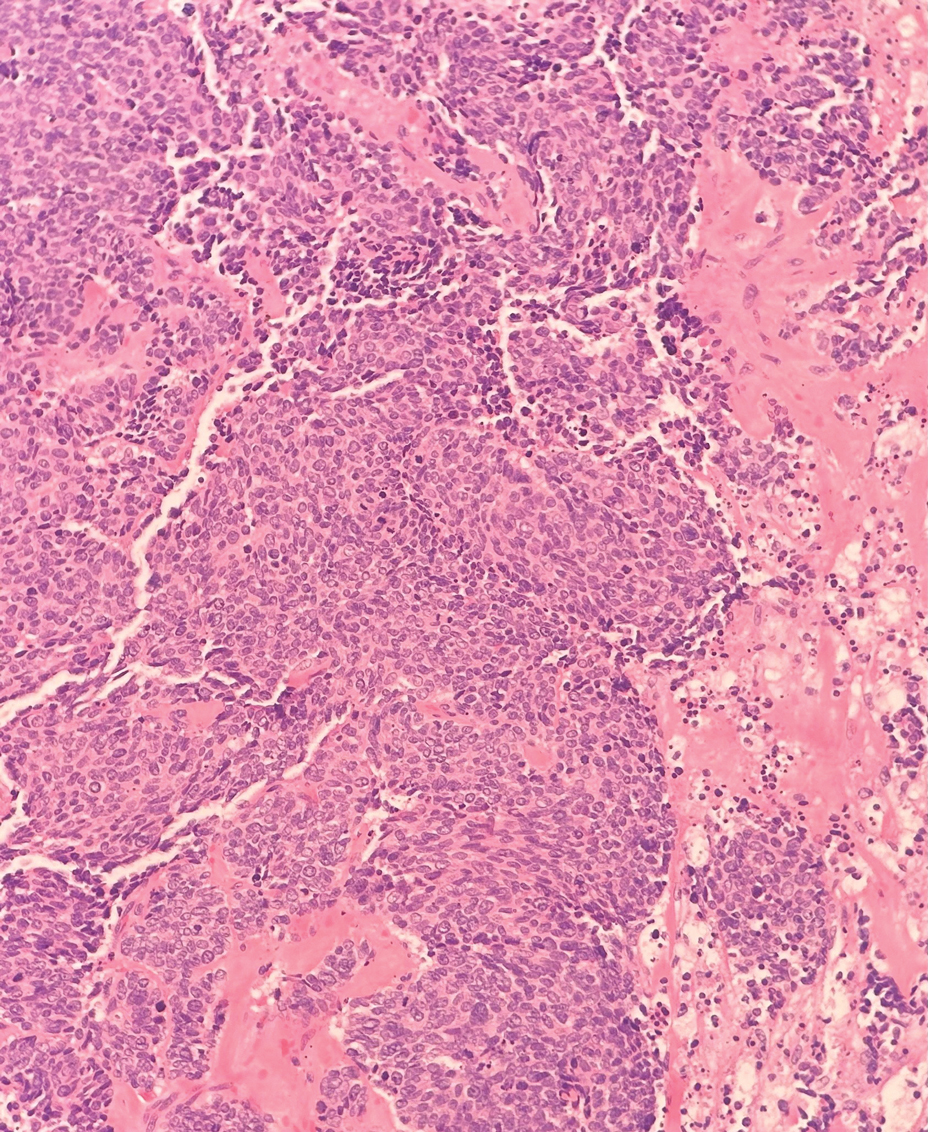
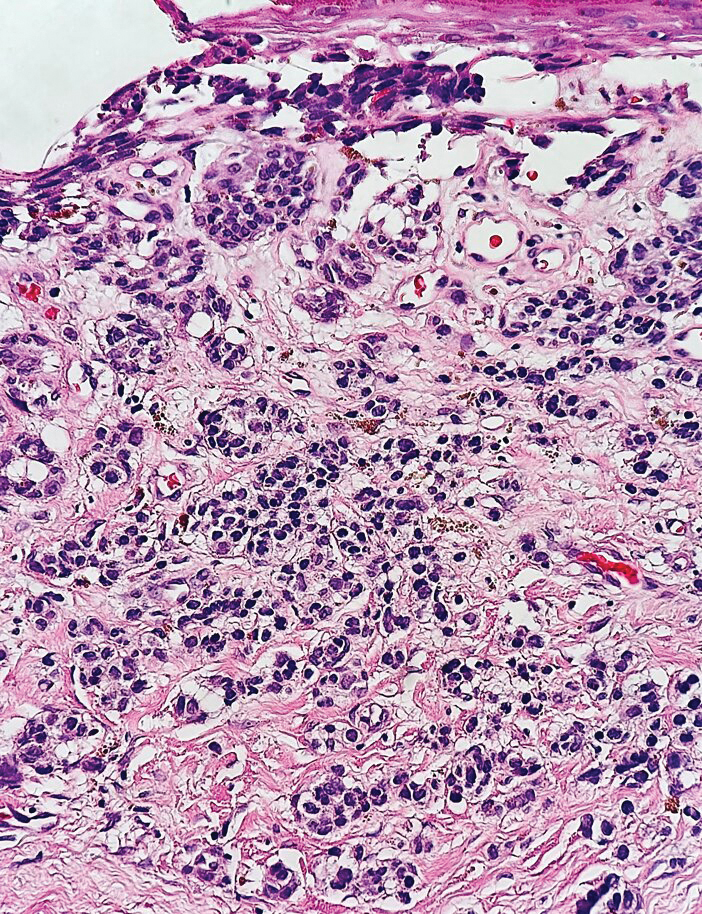
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.
Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
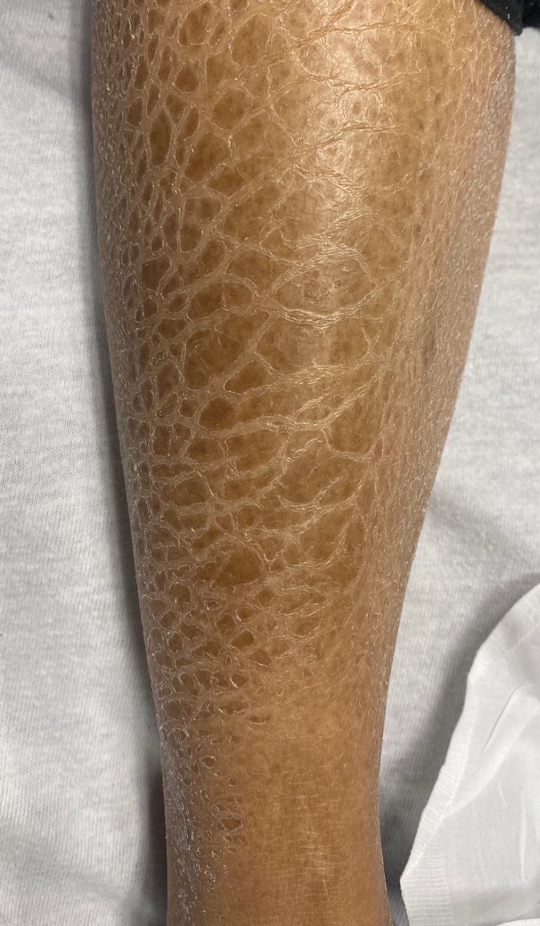
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).
Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.

Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).

Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
The Diagnosis: Carcinoma en Cuirasse
Histopathology demonstrated a cellular infiltrate filling the dermis with sparing of the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 1A). The cells were arranged in strands and cords that infiltrated between sclerotic collagen bundles. Cytomorphologically, the cells ranged from epithelioid with large vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli to cuboidal with hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and a high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (Figure 1B). Occasional mitotic figures were identified, and cells demonstrated diffuse nuclear positivity for GATA-3 (Figure 1C); 55% of the cells demonstrated estrogen receptor positivity, and immunohistochemistry of progesterone receptors was negative. These findings confirmed our patient’s diagnosis of breast carcinoma en cuirasse (CeC) as the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. Our patient was treated with intravenous chemotherapy and tamoxifen.

Histopathologic findings of morphea include thickened hyalinized collagen bundles and loss of adventitial fat.1 A diagnosis of chronic radiation dermatitis was inconsistent with our patient’s medical history and biopsy results, as pathology should reveal hyalinized collagen or stellate radiation fibroblasts.2,3 Nests of squamous epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and large vesicular nuclei were not seen, excluding squamous cell carcinoma as a possible diagnosis.4 Although sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma is characterized by infiltrating cords in sclerotic dermis, the cells were not arranged in ductlike structures 1– to 2–cell layers thick, excluding this diagnosis.5
Carcinoma en cuirasse—named for skin involvement that appears similar to the metal breastplate of a cuirassier—is a rare form of cutaneous metastasis that typically presents with extensive infiltrative plaques resulting in fibrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.6,7 Carcinoma en cuirasse most commonly metastasizes from the breast but also may represent metastases from the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, or genitourinary systems.8 In the setting of a primary breast malignancy, metastatic plaques of CeC tend to represent tumor recurrence following a mastectomy procedure; however, in rare cases CeC can present as the primary manifestation of breast cancer or as a result of untreated malignancy.6,9 In our patient, CeC was the primary manifestation of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma with additional paraneoplastic ichthyosis (Figure 2).

Carcinoma en cuirasse comprises 3% to 6% of cutaneous metastases originating from the breast.10,11 Breast cancer is the most common primary neoplasm displaying extracutaneous metastasis, comprising 70% of all cutaneous metastases in females.11 Cutaneous metastasis often indicates late stage of disease, portending a poor prognosis. In our patient, the cutaneous nodules were present for approximately 3 years prior to the diagnosis of stage IV invasive ductal cell carcinoma with metastasis to the skin and lungs. Prior to admission, she had not been diagnosed with breast cancer, thus no treatments had been administered. It is uncommon for CeC to present as the initial finding and without prior treatment of the underlying malignancy. The median length of survival after diagnosis of cutaneous metastasis from breast cancer is 13.8 months, with a 10-year survival rate of 3.1%.12
In addition to cutaneous metastasis, breast cancer also may present with paraneoplastic dermatoses such as ichthyosis.13 Ichthyosis is characterized by extreme dryness, flaking, thickening, and mild pruritus.14 It most commonly is an inherited condition, but it may be acquired due to malignancy. Acquired ichthyosis may manifest in systemic diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and hypothyroidism.15 Although acquired ichthyosis is rare, it has been reported in cases of internal malignancy, most commonly lymphoproliferative malignancies and less frequently carcinoma of the breasts, cervix, and lungs. Patients who acquire ichthyosis in association with malignancy usually present with late-stage disease.15 Our patient acquired ichthyosis 3 months prior to admission and had never experienced it previously. Although the exact mechanism for acquiring ichthyosis remains unknown, it is uncertain if ichthyosis associated with malignancy is paraneoplastic or a result of chemotherapy.14,16 In this case, the patient had not yet started chemotherapy at the time of the ichthyosis diagnosis, suggesting a paraneoplastic etiology.
Carcinoma en cuirasse and paraneoplastic ichthyosis individually are extremely rare manifestations of breast cancer. Thus, it is even rarer for these conditions to present concurrently. Treatment options for CeC include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, hormonal antagonists, and snake venom.11 Systemic chemotherapy targeting the histopathologic type of the primary tumor is the treatment of choice. Other treatment methods usually are chosen for late stages of disease progression.10 Paraneoplastic ichthyosis has been reported to show improvement with treatment of the underlying primary malignancy by surgical removal or chemotherapy.14,17 Tamoxifen less commonly is used for systemic treatment of CeC, but one case in the literature reported favorable outcomes.18
We describe 2 rare cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer occurring concomitantly: CeC and paraneoplastic ichthyosis. The combination of clinical and pathologic findings presented in this case solidified the diagnosis of metastatic invasive ductal carcinoma. We aim to improve recognition of paraneoplastic skin findings to accelerate the process of effective and efficient treatment.
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
- Walker D, Susa JS, Currimbhoy S, et al. Histopathological changes in morphea and their clinical correlates: results from the Morphea in Adults and Children Cohort V. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:1124-1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.020
- Borrelli MR, Shen AH, Lee GK, et al. Radiation-induced skin fibrosis: pathogenesis, current treatment options, and emerging therapeutics. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(4 suppl 1):S59-S64. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002098
- Boncher J, Bergfeld WF. Fluoroscopy-induced chronic radiation dermatitis: a report of two additional cases and a brief review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j .1600-0560.2011.01754.x
- Cassarino DS, Derienzo DP, Barr RJ. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: a comprehensive clinicopathologic classification. part one. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:191-206. https://doi.org/10.1111 /j.0303-6987.2006.00516_1.x
- Harvey DT, Hu J, Long JA, et al. Sclerosing sweat duct carcinoma of the lower extremity treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2016;2:284-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.05.017
- Sharma V, Kumar A. Carcinoma en cuirasse. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:2562. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm2111669
- Oliveira GM, Zachetti DB, Barros HR, et al. Breast carcinoma en cuirasse—case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:608-610. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20131926
- Alcaraz I, Cerroni L, Rütten A, et al. Cutaneous metastases from internal malignancies: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2012;34:347-393. doi:10.1097 /DAD.0b013e31823069cf
- Glazebrook AJ, Tomaszewski W. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease: report of a case, with reference to vitamin A metabolism. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1944;50:85-89. doi:10.1001 /archderm.1944.01510140008002
- Mordenti C, Concetta F, Cerroni M, et al. Cutaneous metastatic breast carcinoma: a study of 164 patients. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2000;9:143-148.
- Culver AL, Metter DM, Pippen JE Jr. Carcinoma en cuirasse. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2019;32:263-265. doi:10.1080/08998280.2018.1564966
- Schoenlaub P, Sarraux A, Grosshans E, et al. Survival after cutaneous metastasis: a study of 200 cases [in French]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2001;128:1310-1315.
- Tan AR. Cutaneous manifestations of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016;43:331-334. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2016.02.030
- Song Y, Wu Y, Fan T. Dermatosis as the initial manifestation of malignant breast tumors: retrospective analysis of 4 cases. Breast Care. 2010;5:174-176. doi:10.1159/000314265
- Polisky RB, Bronson DM. Acquired ichthyosis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the breast. Cutis. 1986;38:359-360.
- Haste AR. Acquired ichthyosis from breast cancer. Br Med J. 1967;4:96-98.
- Riesco Martínez MC, Muñoz Martín AJ, Zamberk Majlis P, et al. Acquired ichthyosis as a paraneoplastic syndrome in Hodgkin’s disease. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:552-553. doi:10.1007/s12094-009-0402-2
- Siddiqui MA, Zaman MN. Primary carcinoma en cuirasse. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:221-222. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb02455.xssss
A 47-year-old woman with no notable medical history presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath on simple exertion as well as a large lesion on the chest that had slowly increased in size over the last 3 years. The lesion was not painful or pruritic, and she had been treating it with topical emollients without substantial improvement. Physical examination revealed a large indurated plaque with areas of ulceration and necrosis spanning the mid to lateral chest. Additionally, ichthyotic brown scaling was present on the arms and legs. Upon further questioning, the patient reported that the scales on the extremities appeared in the last 3 months and were not previously noted. She had no recent routine cancer screenings, and her family history was notable for a brother with brain cancer. A punch biopsy of the chest plaque was performed.
Painful Growing Nodule on the Right Calf
The Diagnosis: Merkel Cell Carcinoma
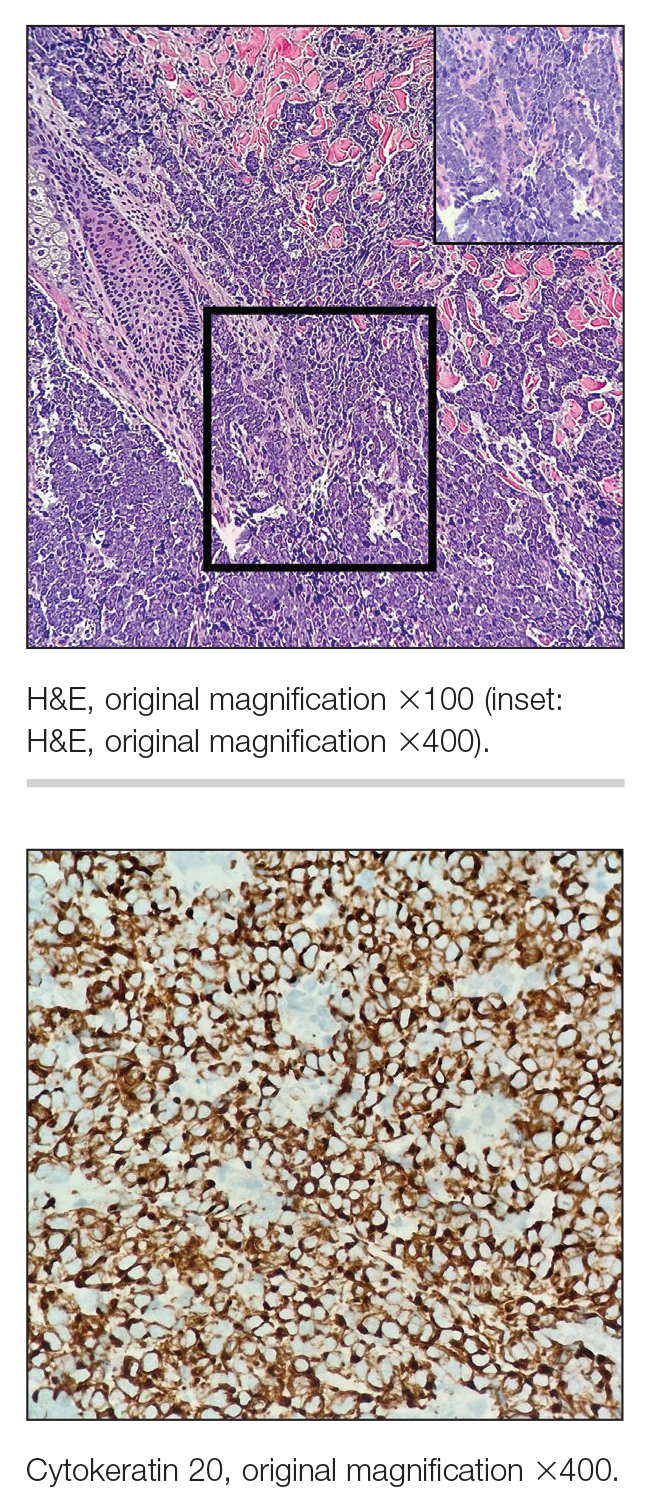
Multiple diagnoses should be considered for a small, round, blue cell neoplasm of the skin, including both primary and metastatic entities. In our patient, histopathology revealed sheets and nests of infiltrative neoplastic cells with dispersed chromatin, minimal cytoplasm, and multiple mitoses (quiz image 1).1 The lesional cells were in the dermis and superficial subcutaneous tissue but did not appear to be arising from the epidermis. Lymphovascular invasion also was evident on additional sections. Metastatic disease was identified in 3 sentinel lymph nodes from the right inguinal and right iliac regions. These features were compatible with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC).
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare malignant neuroendocrine cutaneous tumor with a worldwide incidence of 0.1 to 1.6 cases per 100,000 individuals annually.2 The typical patient is older than 75 years with fair skin and a history of extensive sun exposure. Immunocompromised individuals are predisposed and more susceptible to infection with the Merkel cell polyomavirus, which promotes oncogenesis in the majority of MCCs. Our patient’s history of combined variable immunodeficiency likely explains her presentation at a younger age.
The prognosis in patients with MCC is poor, with 5-year survival rates of 51% for local disease, 35% for nodal disease, and 14% for systemic metastases. Survival also is reduced in cases with head/ neck primary tumors and polyomavirus-negative tumors, as well as in immunocompromised patients.2 Treatment of resectable MCC consists of Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision depending on the patient’s cosmetic concerns. Radiation therapy is recommended for cases with increased risk for recurrence or positive surgical margins, as well as when additional resection is impossible. A study investigating immunotherapy with nivolumab demonstrated complete pathologic response and radiographic tumor regression in nearly half of patients when given 4 weeks prior to surgery.3
Immunohistochemistry is essential in discerning MCC from other small blue cell tumors. Most MCC cases show positive expression of neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinomaassociated protein 1. Perinuclear dotlike staining with cytokeratin (CK) 20 (quiz image 2) commonly is seen, but up to 15% of cases may be CK20 negative. Many of these CK20-negative cases also express CK7. This tumor also may stain with paired box 5 (PAX-5), CD99, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, Ber-EP4, and CD1171,4; melanoma stains (ie, human melanoma black [HMB] 45, SRYrelated HMB-box 10 [SOX-10], S-100, melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells 1 [MART-1]) should be negative. However, PAX-5 expression may be a potential pitfall given that B-cell lymphomas also would express that marker and could mimic MCC histologically. Therefore, other universal lymphoid markers such as CD45 should be ordered to rule out this entity. Even with one or a few aberrant stains, a diagnosis of MCC still can be rendered using the histomorphology and the overall staining profile.4 Of prognostic significance, p63 expression is associated with more aggressive tumors, while Bcl-2 expression is favorable, as it offers an additional targeted treatment option.5,6
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is linked to excessive sun exposure and is the most common skin cancer. Similar to MCC, it typically is mitotically active and hyperchromatic; however, lymphovascular invasion or metastasis almost never is observed in BCC, whereas approximately one-third of MCC cases have metastasized by the time of diagnosis. Additionally, BCC lacks the perinuclear dotlike staining seen with CK20.2,7 Features present in BCC that are unusual for MCC include peripheral nuclear palisading, mucin, and retraction artifact on paraffin-embedded sections (Figure 1).7
Leukemia cutis (or cutaneous infiltrates of leukemia) commonly displays a perivascular and periadnexal pattern in the dermis and subcutis. These infiltrates of neoplastic leukocytes can congregate into sheets, sometimes with an overlying Grenz zone, or form single-file infiltrates (Figure 2).1,4 The neoplastic cells can be monomorphic or atypical and commonly are susceptible to crush artifact.4 Although the immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the etiology of the underlying leukemia, broad hematologic markers such as CD43 and CD45 are helpful to discern these malignancies from MCC.4
Being neuroendocrine in origin, metastatic small cell carcinoma (Figure 3) strongly mimics MCC histologically and usually stains with synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinoma-associated protein 1. Both tumor cells typically exhibit nuclear molding and high mitotic rates. Although small cell carcinoma is more likely to stain with high-molecular-weight cytokeratins (ie, CK7), it is not uncommon for these tumors to express lowmolecular- weight cytokeratins such as CK20. Because most cases originate from the lungs, these lesions should be positive for thyroid transcription factor 1 and negative for PAX-5, whereas MCC would show the reverse for those stains.1 Ultimately, however, clinical correlation with imaging results is the single best methodology for differentiation.
Small cell melanoma, a variant of nevoid melanoma, can strongly resemble an MCC or a lymphoma. Usually located on the scalp or arising from a congenital nevus, small cell melanomas are aggressive and confer an unfavorable prognosis. Histologically, they consist of nests to sheets of atypical cells within the epidermis and dermis. These cells typically exhibit hyperchromatic nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4). Furthermore, the cells do not display maturation based on depth.8 These tumors usually are positive for HMB45, S-100, MART-1, SOX-10, and tyrosinase, all of which are extremely unlikely to stain an MCC.1
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Walsh NM, Cerroni L. Merkel cell carcinoma: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:411-421.
- Topalian SL, Bhatia S, Amin A, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab for patients with resectable Merkel cell carcinoma in the CheckMate 358 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2476-2488.
- Rapini RP. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Asioli S, Righi A, Volante M, et al. p63 expression as a new prognostic marker in Merkel cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2007;110:640-647.
- Verhaegen ME, Mangelberger D, Weick JW, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma dependence on Bcl-2 family members for survival. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2241-2250.
- Le MD, O’Steen LH, Cassarino DS. A rare case of CK20/CK7 double negative Merkel cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:208-211.
- North JP, Bastian BC, Lazar AJ. Melanoma. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin With Clinical Correlations. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
The Diagnosis: Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Multiple diagnoses should be considered for a small, round, blue cell neoplasm of the skin, including both primary and metastatic entities. In our patient, histopathology revealed sheets and nests of infiltrative neoplastic cells with dispersed chromatin, minimal cytoplasm, and multiple mitoses (quiz image 1).1 The lesional cells were in the dermis and superficial subcutaneous tissue but did not appear to be arising from the epidermis. Lymphovascular invasion also was evident on additional sections. Metastatic disease was identified in 3 sentinel lymph nodes from the right inguinal and right iliac regions. These features were compatible with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC).
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare malignant neuroendocrine cutaneous tumor with a worldwide incidence of 0.1 to 1.6 cases per 100,000 individuals annually.2 The typical patient is older than 75 years with fair skin and a history of extensive sun exposure. Immunocompromised individuals are predisposed and more susceptible to infection with the Merkel cell polyomavirus, which promotes oncogenesis in the majority of MCCs. Our patient’s history of combined variable immunodeficiency likely explains her presentation at a younger age.
The prognosis in patients with MCC is poor, with 5-year survival rates of 51% for local disease, 35% for nodal disease, and 14% for systemic metastases. Survival also is reduced in cases with head/ neck primary tumors and polyomavirus-negative tumors, as well as in immunocompromised patients.2 Treatment of resectable MCC consists of Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision depending on the patient’s cosmetic concerns. Radiation therapy is recommended for cases with increased risk for recurrence or positive surgical margins, as well as when additional resection is impossible. A study investigating immunotherapy with nivolumab demonstrated complete pathologic response and radiographic tumor regression in nearly half of patients when given 4 weeks prior to surgery.3
Immunohistochemistry is essential in discerning MCC from other small blue cell tumors. Most MCC cases show positive expression of neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinomaassociated protein 1. Perinuclear dotlike staining with cytokeratin (CK) 20 (quiz image 2) commonly is seen, but up to 15% of cases may be CK20 negative. Many of these CK20-negative cases also express CK7. This tumor also may stain with paired box 5 (PAX-5), CD99, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, Ber-EP4, and CD1171,4; melanoma stains (ie, human melanoma black [HMB] 45, SRYrelated HMB-box 10 [SOX-10], S-100, melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells 1 [MART-1]) should be negative. However, PAX-5 expression may be a potential pitfall given that B-cell lymphomas also would express that marker and could mimic MCC histologically. Therefore, other universal lymphoid markers such as CD45 should be ordered to rule out this entity. Even with one or a few aberrant stains, a diagnosis of MCC still can be rendered using the histomorphology and the overall staining profile.4 Of prognostic significance, p63 expression is associated with more aggressive tumors, while Bcl-2 expression is favorable, as it offers an additional targeted treatment option.5,6
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is linked to excessive sun exposure and is the most common skin cancer. Similar to MCC, it typically is mitotically active and hyperchromatic; however, lymphovascular invasion or metastasis almost never is observed in BCC, whereas approximately one-third of MCC cases have metastasized by the time of diagnosis. Additionally, BCC lacks the perinuclear dotlike staining seen with CK20.2,7 Features present in BCC that are unusual for MCC include peripheral nuclear palisading, mucin, and retraction artifact on paraffin-embedded sections (Figure 1).7

Leukemia cutis (or cutaneous infiltrates of leukemia) commonly displays a perivascular and periadnexal pattern in the dermis and subcutis. These infiltrates of neoplastic leukocytes can congregate into sheets, sometimes with an overlying Grenz zone, or form single-file infiltrates (Figure 2).1,4 The neoplastic cells can be monomorphic or atypical and commonly are susceptible to crush artifact.4 Although the immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the etiology of the underlying leukemia, broad hematologic markers such as CD43 and CD45 are helpful to discern these malignancies from MCC.4

Being neuroendocrine in origin, metastatic small cell carcinoma (Figure 3) strongly mimics MCC histologically and usually stains with synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinoma-associated protein 1. Both tumor cells typically exhibit nuclear molding and high mitotic rates. Although small cell carcinoma is more likely to stain with high-molecular-weight cytokeratins (ie, CK7), it is not uncommon for these tumors to express lowmolecular- weight cytokeratins such as CK20. Because most cases originate from the lungs, these lesions should be positive for thyroid transcription factor 1 and negative for PAX-5, whereas MCC would show the reverse for those stains.1 Ultimately, however, clinical correlation with imaging results is the single best methodology for differentiation.

Small cell melanoma, a variant of nevoid melanoma, can strongly resemble an MCC or a lymphoma. Usually located on the scalp or arising from a congenital nevus, small cell melanomas are aggressive and confer an unfavorable prognosis. Histologically, they consist of nests to sheets of atypical cells within the epidermis and dermis. These cells typically exhibit hyperchromatic nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4). Furthermore, the cells do not display maturation based on depth.8 These tumors usually are positive for HMB45, S-100, MART-1, SOX-10, and tyrosinase, all of which are extremely unlikely to stain an MCC.1

The Diagnosis: Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Multiple diagnoses should be considered for a small, round, blue cell neoplasm of the skin, including both primary and metastatic entities. In our patient, histopathology revealed sheets and nests of infiltrative neoplastic cells with dispersed chromatin, minimal cytoplasm, and multiple mitoses (quiz image 1).1 The lesional cells were in the dermis and superficial subcutaneous tissue but did not appear to be arising from the epidermis. Lymphovascular invasion also was evident on additional sections. Metastatic disease was identified in 3 sentinel lymph nodes from the right inguinal and right iliac regions. These features were compatible with a diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC).
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare malignant neuroendocrine cutaneous tumor with a worldwide incidence of 0.1 to 1.6 cases per 100,000 individuals annually.2 The typical patient is older than 75 years with fair skin and a history of extensive sun exposure. Immunocompromised individuals are predisposed and more susceptible to infection with the Merkel cell polyomavirus, which promotes oncogenesis in the majority of MCCs. Our patient’s history of combined variable immunodeficiency likely explains her presentation at a younger age.
The prognosis in patients with MCC is poor, with 5-year survival rates of 51% for local disease, 35% for nodal disease, and 14% for systemic metastases. Survival also is reduced in cases with head/ neck primary tumors and polyomavirus-negative tumors, as well as in immunocompromised patients.2 Treatment of resectable MCC consists of Mohs micrographic surgery or wide local excision depending on the patient’s cosmetic concerns. Radiation therapy is recommended for cases with increased risk for recurrence or positive surgical margins, as well as when additional resection is impossible. A study investigating immunotherapy with nivolumab demonstrated complete pathologic response and radiographic tumor regression in nearly half of patients when given 4 weeks prior to surgery.3
Immunohistochemistry is essential in discerning MCC from other small blue cell tumors. Most MCC cases show positive expression of neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinomaassociated protein 1. Perinuclear dotlike staining with cytokeratin (CK) 20 (quiz image 2) commonly is seen, but up to 15% of cases may be CK20 negative. Many of these CK20-negative cases also express CK7. This tumor also may stain with paired box 5 (PAX-5), CD99, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, Ber-EP4, and CD1171,4; melanoma stains (ie, human melanoma black [HMB] 45, SRYrelated HMB-box 10 [SOX-10], S-100, melanoma antigen recognized by T-cells 1 [MART-1]) should be negative. However, PAX-5 expression may be a potential pitfall given that B-cell lymphomas also would express that marker and could mimic MCC histologically. Therefore, other universal lymphoid markers such as CD45 should be ordered to rule out this entity. Even with one or a few aberrant stains, a diagnosis of MCC still can be rendered using the histomorphology and the overall staining profile.4 Of prognostic significance, p63 expression is associated with more aggressive tumors, while Bcl-2 expression is favorable, as it offers an additional targeted treatment option.5,6
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is linked to excessive sun exposure and is the most common skin cancer. Similar to MCC, it typically is mitotically active and hyperchromatic; however, lymphovascular invasion or metastasis almost never is observed in BCC, whereas approximately one-third of MCC cases have metastasized by the time of diagnosis. Additionally, BCC lacks the perinuclear dotlike staining seen with CK20.2,7 Features present in BCC that are unusual for MCC include peripheral nuclear palisading, mucin, and retraction artifact on paraffin-embedded sections (Figure 1).7

Leukemia cutis (or cutaneous infiltrates of leukemia) commonly displays a perivascular and periadnexal pattern in the dermis and subcutis. These infiltrates of neoplastic leukocytes can congregate into sheets, sometimes with an overlying Grenz zone, or form single-file infiltrates (Figure 2).1,4 The neoplastic cells can be monomorphic or atypical and commonly are susceptible to crush artifact.4 Although the immunohistochemical profile varies depending on the etiology of the underlying leukemia, broad hematologic markers such as CD43 and CD45 are helpful to discern these malignancies from MCC.4

Being neuroendocrine in origin, metastatic small cell carcinoma (Figure 3) strongly mimics MCC histologically and usually stains with synaptophysin, chromogranin, and insulinoma-associated protein 1. Both tumor cells typically exhibit nuclear molding and high mitotic rates. Although small cell carcinoma is more likely to stain with high-molecular-weight cytokeratins (ie, CK7), it is not uncommon for these tumors to express lowmolecular- weight cytokeratins such as CK20. Because most cases originate from the lungs, these lesions should be positive for thyroid transcription factor 1 and negative for PAX-5, whereas MCC would show the reverse for those stains.1 Ultimately, however, clinical correlation with imaging results is the single best methodology for differentiation.

Small cell melanoma, a variant of nevoid melanoma, can strongly resemble an MCC or a lymphoma. Usually located on the scalp or arising from a congenital nevus, small cell melanomas are aggressive and confer an unfavorable prognosis. Histologically, they consist of nests to sheets of atypical cells within the epidermis and dermis. These cells typically exhibit hyperchromatic nuclei, minimal cytoplasm, and frequent mitoses (Figure 4). Furthermore, the cells do not display maturation based on depth.8 These tumors usually are positive for HMB45, S-100, MART-1, SOX-10, and tyrosinase, all of which are extremely unlikely to stain an MCC.1

- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Walsh NM, Cerroni L. Merkel cell carcinoma: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:411-421.
- Topalian SL, Bhatia S, Amin A, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab for patients with resectable Merkel cell carcinoma in the CheckMate 358 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2476-2488.
- Rapini RP. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Asioli S, Righi A, Volante M, et al. p63 expression as a new prognostic marker in Merkel cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2007;110:640-647.
- Verhaegen ME, Mangelberger D, Weick JW, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma dependence on Bcl-2 family members for survival. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2241-2250.
- Le MD, O’Steen LH, Cassarino DS. A rare case of CK20/CK7 double negative Merkel cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:208-211.
- North JP, Bastian BC, Lazar AJ. Melanoma. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin With Clinical Correlations. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
- Patterson JW, Hosler GA. Weedon’s Skin Pathology. 4th ed. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2016.
- Walsh NM, Cerroni L. Merkel cell carcinoma: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2021;48:411-421.
- Topalian SL, Bhatia S, Amin A, et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab for patients with resectable Merkel cell carcinoma in the CheckMate 358 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2476-2488.
- Rapini RP. Practical Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. Elsevier; 2021.
- Asioli S, Righi A, Volante M, et al. p63 expression as a new prognostic marker in Merkel cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2007;110:640-647.
- Verhaegen ME, Mangelberger D, Weick JW, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma dependence on Bcl-2 family members for survival. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2241-2250.
- Le MD, O’Steen LH, Cassarino DS. A rare case of CK20/CK7 double negative Merkel cell carcinoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:208-211.
- North JP, Bastian BC, Lazar AJ. Melanoma. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, et al, eds. McKee’s Pathology of the Skin With Clinical Correlations. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2020.
A 47-year-old woman with a history of combined variable immunodeficiency presented with a 2.6×2.4-cm nodule on the lateral aspect of the right calf that was first noticed 2 years prior as a smaller nodule. It increased in size and became painful to touch over the last 3 to 4 months. Following diagnostic biopsy, the nodule was removed by wide local excision and was tan-brown on gross dissection. The lesion showed dotlike perinuclear positivity with cytokeratin 20 immunostaining. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography showed no evidence of lung lesions. A complete blood cell count was within reference range.
Lower-extremity lymphedema associated with more skin cancer risk
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- In the retrospective cohort study, researchers reviewed reports at Mayo Clinic for all patients who had LE lymphedema, limiting the review to those who had an ICD code for lymphedema.
- 4,437 patients with the ICD code from 2000 to 2020 were compared with 4,437 matched controls.
- The records of patients with skin cancer diagnoses were reviewed manually to determine whether the skin cancer, its management, or both were a cause of lymphedema; cancers that caused secondary lymphedema were excluded.
- This is the first large-scale study evaluating the association between LE lymphedema and LE skin cancer.
TAKEAWAY:
- 211 patients (4.6%) in the LE lymphedema group had any ICD code for LE skin cancer, compared with 89 (2%) in the control group.
- Among those with LE lymphedema, the risk for skin cancer was 1.98 times greater compared with those without lymphedema (95% confidence interval, 1.43-2.74; P < .001). Cases included all types of skin cancer.
- Nineteen of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema had a history of immunosuppression.
- In the group of 24 patients with unilateral LE lymphedema, the lymphedematous LE was more likely to have one or more skin cancers than were the unaffected LE (87.5% vs. 33.3%; P < .05), and skin cancer was 2.65 times more likely to develop on the affected LE than in the unaffected LE (95% CI, 1.17-5.99; P = .02).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest the need for a relatively high degree of suspicion of skin cancer at sites with lymphedema,” senior author, Afsaneh Alavi, MD, professor of dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, said in a Mayo Clinic press release reporting the results.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by researchers at the Mayo Clinic and Meharry Medical College, Nashville. It was published in the November 2023 Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
LIMITATIONS:
This was a single-center retrospective study, and patients with LE lymphedema may be overdiagnosed with LE skin cancer because they have a greater number of examinations.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Alavi reports having been a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, InflaRx, Novartis, and UCB SA and an investigator for Processa Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sharps injuries are common among Mohs surgeons, survey finds
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on the incidence of sharps injuries among dermatologic surgeons is limited.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of anonymous survey responses from members of the American College of , researchers aimed to determine the incidence and types of sharps injuries among Mohs surgeons.
- The researchers used descriptive statistics for continuous and nominal variables (percentage and frequencies) to report survey data and Fisher exact or chi-square analysis of categorical variables to obtain P values.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 60 survey respondents, more than half (56.7%) were from single-specialty group practices, 26.6% were from academic practices, and fewer than half (43.3%) had been in practice for 15 or more years.
- In the past year, 56.7% of respondents experienced at least one sharps injury. Of these, 14.7% involved exposure to a blood-borne pathogen, which translated into an annual exposure risk of 7.6% for any given Mohs surgeon.
- The top two types of sharps injuries were self-inflicted suture needlestick (76.5%) and other types of self-inflicted needlestick injuries (26.5%).
- Of respondents who sustained a sharps injury, 44.1% did not report them, while 95% of all survey respondents said they had access to postexposure prophylaxis/protocols at their workplace.
- The researchers determined that the average annual rate of sharps injury was 0.87.
IN PRACTICE:
- “In best practices to prevent sharps injuries, the authors recommend that a standardized sharps handling protocol be developed and disseminated for dermatologic surgeons and their staff,” the researchers wrote.
STUDY DETAILS:
- Faezeh Talebi-Liasi, MD, and Jesse M. Lewin, MD, department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, conducted the research. The study was published in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
- The study’s cross-sectional observational design and small sample size was skewed toward single-specialty and academic practices.
DISCLOSURES:
- The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on the incidence of sharps injuries among dermatologic surgeons is limited.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of anonymous survey responses from members of the American College of , researchers aimed to determine the incidence and types of sharps injuries among Mohs surgeons.
- The researchers used descriptive statistics for continuous and nominal variables (percentage and frequencies) to report survey data and Fisher exact or chi-square analysis of categorical variables to obtain P values.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 60 survey respondents, more than half (56.7%) were from single-specialty group practices, 26.6% were from academic practices, and fewer than half (43.3%) had been in practice for 15 or more years.
- In the past year, 56.7% of respondents experienced at least one sharps injury. Of these, 14.7% involved exposure to a blood-borne pathogen, which translated into an annual exposure risk of 7.6% for any given Mohs surgeon.
- The top two types of sharps injuries were self-inflicted suture needlestick (76.5%) and other types of self-inflicted needlestick injuries (26.5%).
- Of respondents who sustained a sharps injury, 44.1% did not report them, while 95% of all survey respondents said they had access to postexposure prophylaxis/protocols at their workplace.
- The researchers determined that the average annual rate of sharps injury was 0.87.
IN PRACTICE:
- “In best practices to prevent sharps injuries, the authors recommend that a standardized sharps handling protocol be developed and disseminated for dermatologic surgeons and their staff,” the researchers wrote.
STUDY DETAILS:
- Faezeh Talebi-Liasi, MD, and Jesse M. Lewin, MD, department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, conducted the research. The study was published in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
- The study’s cross-sectional observational design and small sample size was skewed toward single-specialty and academic practices.
DISCLOSURES:
- The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data on the incidence of sharps injuries among dermatologic surgeons is limited.
- In a cross-sectional analysis of anonymous survey responses from members of the American College of , researchers aimed to determine the incidence and types of sharps injuries among Mohs surgeons.
- The researchers used descriptive statistics for continuous and nominal variables (percentage and frequencies) to report survey data and Fisher exact or chi-square analysis of categorical variables to obtain P values.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 60 survey respondents, more than half (56.7%) were from single-specialty group practices, 26.6% were from academic practices, and fewer than half (43.3%) had been in practice for 15 or more years.
- In the past year, 56.7% of respondents experienced at least one sharps injury. Of these, 14.7% involved exposure to a blood-borne pathogen, which translated into an annual exposure risk of 7.6% for any given Mohs surgeon.
- The top two types of sharps injuries were self-inflicted suture needlestick (76.5%) and other types of self-inflicted needlestick injuries (26.5%).
- Of respondents who sustained a sharps injury, 44.1% did not report them, while 95% of all survey respondents said they had access to postexposure prophylaxis/protocols at their workplace.
- The researchers determined that the average annual rate of sharps injury was 0.87.
IN PRACTICE:
- “In best practices to prevent sharps injuries, the authors recommend that a standardized sharps handling protocol be developed and disseminated for dermatologic surgeons and their staff,” the researchers wrote.
STUDY DETAILS:
- Faezeh Talebi-Liasi, MD, and Jesse M. Lewin, MD, department of dermatology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, conducted the research. The study was published in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
- The study’s cross-sectional observational design and small sample size was skewed toward single-specialty and academic practices.
DISCLOSURES:
- The authors reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Actinic keratoses may predict skin cancers in older adults
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
.
METHODOLOGY:
- AKs have been associated with a small risk for cutaneous SCC, but associations with risk for other skin cancers have not been well studied.
- AKs may be a marker of overall skin cancer risk, but guidelines for AK management lack recommendations for follow-up cancer surveillance.
- The researchers reviewed data from a random sample of 5 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries treated for AKs from 2009 through 2018 in the United States. Patients with seborrheic keratoses (SKs) were included as comparators, and patients with a history of skin cancer were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the first surgically treated skin cancer, including SCC, BCC, and melanoma.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 555,945 adults with AKs and 481,024 with SKs were included. The mean age was approximately 74.0 years. More than half were female. Most were non-Hispanic White.
- Among patients with AKs, the absolute risk for any skin cancer after the first AK was 6.3%, 18.4%, and 28.5% at 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively.
- Patients with AKs had a significantly increased relative risk for any skin cancer compared with those with SKs (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.17) and separately for keratinocyte carcinoma (aHR, 2.20), SCC (aHR, 2.63), BCC (aHR, 1.85), and melanoma (aHR, 1.67).
- Although AKs are not considered a biological precursor of melanoma or BCC, the results suggest that AKs may be clinical indicators of increased UV exposure that subsequently increases the risk for skin cancer.
IN PRACTICE:
“The present results highlight the importance of developing evidence-based guidelines for follow-up skin cancer surveillance in patients with AKs, optimally including measures of AK burden,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author on the study was Cassandra Mohr, BS, with corresponding author Mackenzie R. Wehner, MD, MPhil, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston. The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology .
LIMITATIONS:
The study population of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years or older may not be a nationally representative sample, and surveillance bias may contribute to the increased risk for skin cancer in patients with AKs. The use of both ICD and CPT codes may underestimate the number of skin cancers because of cases that were treated nonsurgically.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, and The University of Texas Rising STARS program. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AI flagged skin cancer with near-perfect accuracy, in UK study
. AI detected more than 99% of all skin cancers.
The researchers tested the AI by integrating it into a clinical diagnosis process – anticipating a future in which AI helps doctors catch skin cancer faster and triage patients.
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States; one in five 5 Americans develop skin cancer by age 70. With melanoma, the deadliest skin cancer, the 5-year survival rate is better than 99% if caught early, though only about three-quarters of melanomas are caught at this stage.
Amid rising skin cancer rates come concerns that the number of dermatologists in the workforce isn’t keeping pace. That may be why the average wait time for a dermatology appointment is trending up – in 2022, it reached 34.5 days.
The study, which was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress recently and has not yet been published, involved 6,900 patients in the United Kingdom with suspected skin cancer. The patients had been referred by their primary care physicians. The researchers took images of the suspicious areas and uploaded them to the AI software. The AI’s assessment was then shared with a dermatologist.
“Note that the diagnosis issued by the AI was not hidden from the dermatologist doing the second assessment,” said lead researcher Kashini Andrew, MBBS, a dermatologist and specialist registrar at University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust.
Dr. Andrew acknowledged that this may have influenced the dermatologist’s opinion. But that’s the vision of how doctors could use this tool.
The AI caught 59 of 59 melanomas and 189 of 190 total skin cancers (99.5%). (The one case that the AI missed was caught by the dermatologist.) It also flagged 541 of 585 precancerous lesions (92.5%). This represented a big improvement from a 2021 version of the model, which detected 86% of melanomas, 84% of all skin cancers, and 54% of precancerous lesions.
Over the 10-month period of the study, the system saved more than 1,000 face-to-face consultations, freeing dermatologists’ time to catch more cancers and serve more patients.
Limitations
The patients in the study were from “one hospital in a single region of the UK,” and the sample was not large enough to allow broad statements to be made about the use of AI in dermatology, Dr. Andrew said.
But it can open the conversation. Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Stanford (Calif.) University who has studied the pros and cons of AI in medicine, had some concerns. For one thing, doctors can gather more in-depth information during an in-person exam than AI can glean from a photo, Dr. Daneshjou noted. They can examine skin texture, gather patient history, and take photos with special lighting and magnification.
And the AI needs to get better at ruling out malignancy, Dr. Daneshjou said. In this study, the AI identified 75% of benign lesions, a decline from the earlier version. The researchers noted in the abstract that this is a potential trade-off for increased sensitivity.
“[Unnecessary] biopsies can clog up the health care system, cost money, and cause stress and scarring,” said Dr. Daneshjou. “You don’t want to increase the burden of that.”
Still, if AI software such as the kind used in the study proves just as accurate in larger, more diverse sample sizes, then it could be a powerful tool for triage, Dr. Daneshjou said. “If AI gets particularly good at finding malignancy and also ruling it out, that would be a win.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. AI detected more than 99% of all skin cancers.
The researchers tested the AI by integrating it into a clinical diagnosis process – anticipating a future in which AI helps doctors catch skin cancer faster and triage patients.
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States; one in five 5 Americans develop skin cancer by age 70. With melanoma, the deadliest skin cancer, the 5-year survival rate is better than 99% if caught early, though only about three-quarters of melanomas are caught at this stage.
Amid rising skin cancer rates come concerns that the number of dermatologists in the workforce isn’t keeping pace. That may be why the average wait time for a dermatology appointment is trending up – in 2022, it reached 34.5 days.
The study, which was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress recently and has not yet been published, involved 6,900 patients in the United Kingdom with suspected skin cancer. The patients had been referred by their primary care physicians. The researchers took images of the suspicious areas and uploaded them to the AI software. The AI’s assessment was then shared with a dermatologist.
“Note that the diagnosis issued by the AI was not hidden from the dermatologist doing the second assessment,” said lead researcher Kashini Andrew, MBBS, a dermatologist and specialist registrar at University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust.
Dr. Andrew acknowledged that this may have influenced the dermatologist’s opinion. But that’s the vision of how doctors could use this tool.
The AI caught 59 of 59 melanomas and 189 of 190 total skin cancers (99.5%). (The one case that the AI missed was caught by the dermatologist.) It also flagged 541 of 585 precancerous lesions (92.5%). This represented a big improvement from a 2021 version of the model, which detected 86% of melanomas, 84% of all skin cancers, and 54% of precancerous lesions.
Over the 10-month period of the study, the system saved more than 1,000 face-to-face consultations, freeing dermatologists’ time to catch more cancers and serve more patients.
Limitations
The patients in the study were from “one hospital in a single region of the UK,” and the sample was not large enough to allow broad statements to be made about the use of AI in dermatology, Dr. Andrew said.
But it can open the conversation. Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Stanford (Calif.) University who has studied the pros and cons of AI in medicine, had some concerns. For one thing, doctors can gather more in-depth information during an in-person exam than AI can glean from a photo, Dr. Daneshjou noted. They can examine skin texture, gather patient history, and take photos with special lighting and magnification.
And the AI needs to get better at ruling out malignancy, Dr. Daneshjou said. In this study, the AI identified 75% of benign lesions, a decline from the earlier version. The researchers noted in the abstract that this is a potential trade-off for increased sensitivity.
“[Unnecessary] biopsies can clog up the health care system, cost money, and cause stress and scarring,” said Dr. Daneshjou. “You don’t want to increase the burden of that.”
Still, if AI software such as the kind used in the study proves just as accurate in larger, more diverse sample sizes, then it could be a powerful tool for triage, Dr. Daneshjou said. “If AI gets particularly good at finding malignancy and also ruling it out, that would be a win.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
. AI detected more than 99% of all skin cancers.
The researchers tested the AI by integrating it into a clinical diagnosis process – anticipating a future in which AI helps doctors catch skin cancer faster and triage patients.
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States; one in five 5 Americans develop skin cancer by age 70. With melanoma, the deadliest skin cancer, the 5-year survival rate is better than 99% if caught early, though only about three-quarters of melanomas are caught at this stage.
Amid rising skin cancer rates come concerns that the number of dermatologists in the workforce isn’t keeping pace. That may be why the average wait time for a dermatology appointment is trending up – in 2022, it reached 34.5 days.
The study, which was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress recently and has not yet been published, involved 6,900 patients in the United Kingdom with suspected skin cancer. The patients had been referred by their primary care physicians. The researchers took images of the suspicious areas and uploaded them to the AI software. The AI’s assessment was then shared with a dermatologist.
“Note that the diagnosis issued by the AI was not hidden from the dermatologist doing the second assessment,” said lead researcher Kashini Andrew, MBBS, a dermatologist and specialist registrar at University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust.
Dr. Andrew acknowledged that this may have influenced the dermatologist’s opinion. But that’s the vision of how doctors could use this tool.
The AI caught 59 of 59 melanomas and 189 of 190 total skin cancers (99.5%). (The one case that the AI missed was caught by the dermatologist.) It also flagged 541 of 585 precancerous lesions (92.5%). This represented a big improvement from a 2021 version of the model, which detected 86% of melanomas, 84% of all skin cancers, and 54% of precancerous lesions.
Over the 10-month period of the study, the system saved more than 1,000 face-to-face consultations, freeing dermatologists’ time to catch more cancers and serve more patients.
Limitations
The patients in the study were from “one hospital in a single region of the UK,” and the sample was not large enough to allow broad statements to be made about the use of AI in dermatology, Dr. Andrew said.
But it can open the conversation. Roxana Daneshjou, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Stanford (Calif.) University who has studied the pros and cons of AI in medicine, had some concerns. For one thing, doctors can gather more in-depth information during an in-person exam than AI can glean from a photo, Dr. Daneshjou noted. They can examine skin texture, gather patient history, and take photos with special lighting and magnification.
And the AI needs to get better at ruling out malignancy, Dr. Daneshjou said. In this study, the AI identified 75% of benign lesions, a decline from the earlier version. The researchers noted in the abstract that this is a potential trade-off for increased sensitivity.
“[Unnecessary] biopsies can clog up the health care system, cost money, and cause stress and scarring,” said Dr. Daneshjou. “You don’t want to increase the burden of that.”
Still, if AI software such as the kind used in the study proves just as accurate in larger, more diverse sample sizes, then it could be a powerful tool for triage, Dr. Daneshjou said. “If AI gets particularly good at finding malignancy and also ruling it out, that would be a win.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Plaquelike Syringoma Mimicking Microcystic Adnexal Carcinoma: A Potential Histologic Pitfall
To the Editor:
Plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma is a lesser-known variant of syringoma that can appear histologically indistinguishable from the superficial portion of microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). The plaquelike variant of syringoma holds a benign clinical course, and no treatment is necessary. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is distinguished from plaquelike syringoma by an aggressive growth pattern with a high risk for local invasion and recurrence if inadequately treated. Thus, treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has been recommended as the mainstay for MAC. If superficial biopsy specimens reveal suspicion for MAC and patients are referred for MMS, careful consideration should be made to differentiate MAC and plaquelike syringoma early to prevent unnecessary morbidity.
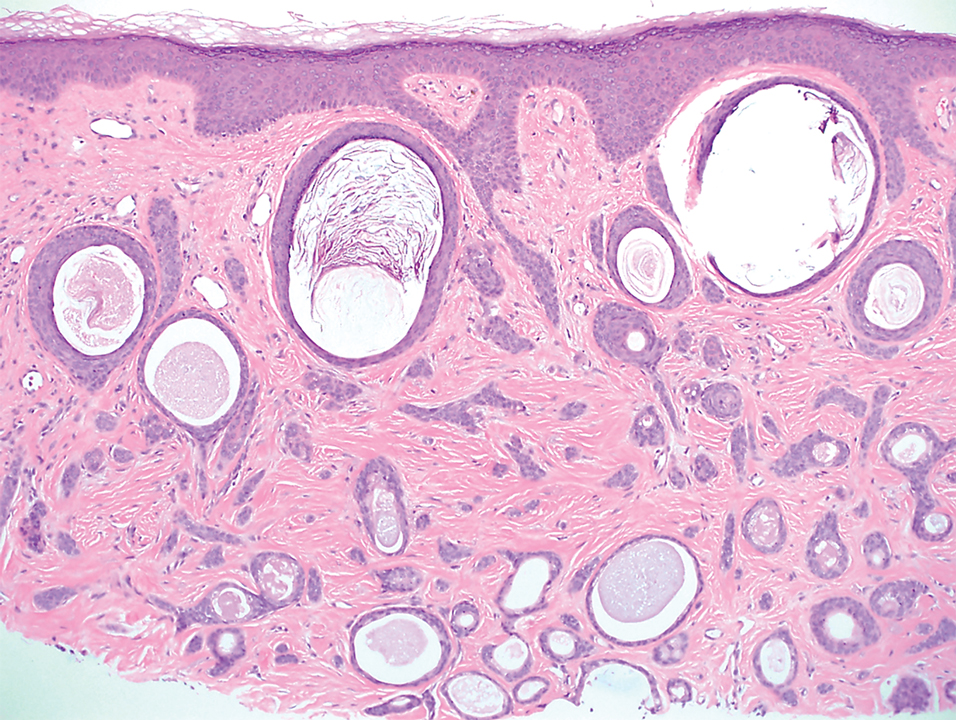
A 78-year-old woman was referred for MMS for a left forehead lesion that was diagnosed via shave biopsy as a desmoplastic and cystic adnexal neoplasm with suspicion for desmoplastic trichoepithelioma or MAC (Figure 1). Upon presentation for MMS, a well-healed, 1.0×0.9-cm scar at the biopsy site on the left forehead was observed (Figure 2A). One stage was obtained by standard MMS technique and sent for intraoperative processing (Figure 2B). Frozen section examination of the first stage demonstrated peripheral margin involvement with syringomatous change confined to the superficial and mid dermis (Figure 3). Before proceeding further, these findings were reviewed with an in-house dermatopathologist, and it was determined that no infiltrative tumor, perineural involvement, or other features to indicate malignancy were noted. A decision was made to refrain from obtaining any additional layers and to send excised Burow triangles for permanent section analysis. A primary linear closure was performed without complication, and the patient was discharged from the ambulatory surgery suite. Histopathologic examination of the Burow triangles later confirmed findings consistent with plaquelike syringoma with no evidence of malignancy (Figure 4).
Syringomas present as small flesh-colored papules in the periorbital areas. These benign neoplasms previously have been classified into 4 major clinical variants: localized, generalized, Down syndrome associated, and familial.1 The lesser-known plaquelike variant of syringoma was first described by Kikuchi et al2 in 1979. Aside from our report, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma yielded 16 cases in the literature.2-14 Of these, 6 were referred to or encountered in the MMS setting.8,9,11,12,14 Plaquelike syringoma can be solitary or multiple in presentation.6 It most commonly involves the head and neck but also can present on the trunk, arms, legs, and groin areas. The clinical size of plaquelike syringoma is variable, with the largest reported cases extending several centimeters in diameter.2,6 Similar to reported associations with conventional syringoma, the plaquelike subtype of syringoma has been reported in association with Down syndrome.13
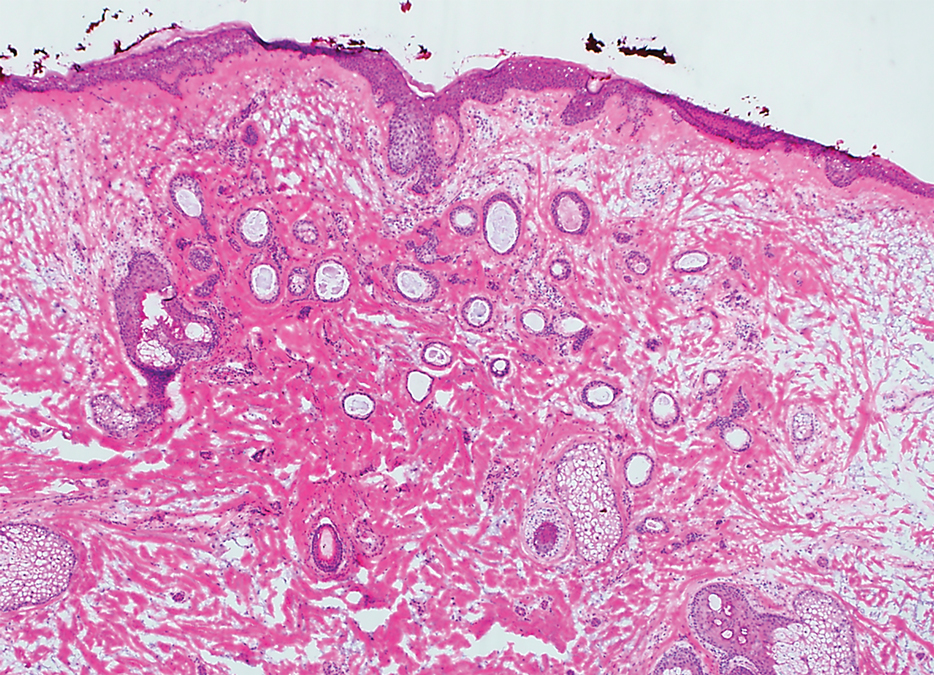
Histopathologically, plaquelike syringoma shares features with MAC as well as desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma. Plaquelike syringoma demonstrates broad proliferations of small tubules morphologically reminiscent of tadpoles confined within the dermis. Ducts typically are lined with 2 or 3 layers of small cuboidal cells. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma typically features asymmetric ductal structures lined with single cells extending from the dermis into the subcutis and even underlying muscle, cartilage, or bone.8 There are no reliable immunohistochemical stains to differentiate between these 2 entities; thus, the primary distinction lies in the depth of involvement. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is composed of narrow cords and nests of basaloid cells of follicular origin commonly admixed with small cornifying cysts appearing in the dermis.8 Colonizing Merkel cells positive for cytokeratin 20 often are present in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and not in syringoma or MAC.15 Desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma demonstrates narrow strands of basaloid cells of follicular origin appearing in the dermis. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma are each fundamentally differentiated from plaquelike syringoma in that proliferations of cords and nests are not of eccrine or apocrine origin.
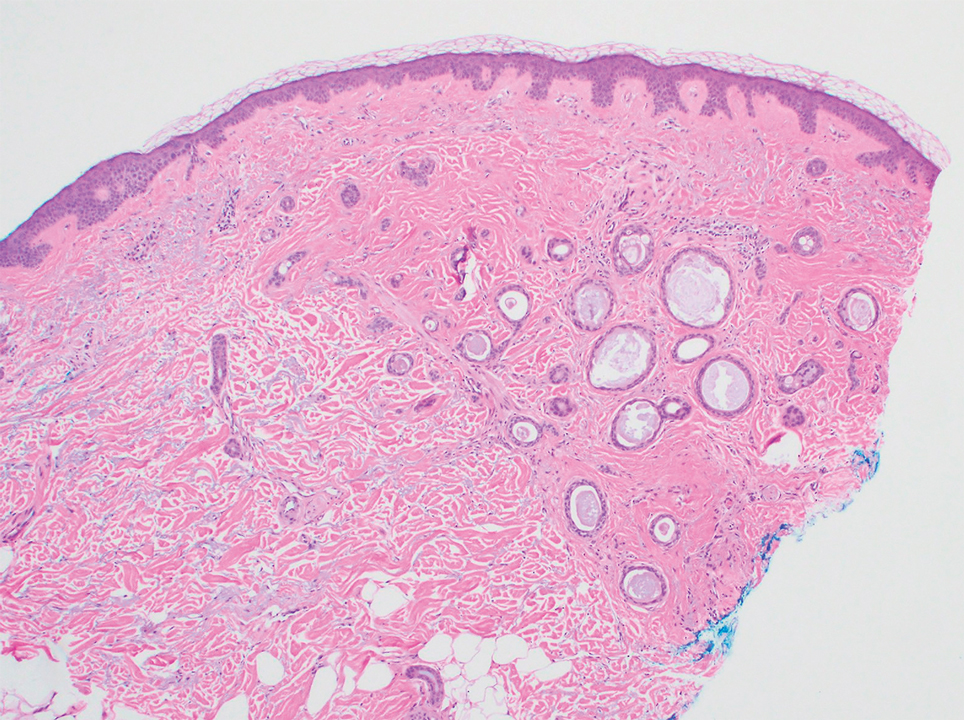
Several cases of plaquelike syringoma have been challenging to distinguish from MAC in performing MMS.8,9,11 Underlying extension of this syringoma variant can be far-reaching, extending to several centimeters in size and involving multiple cosmetic subunits.6,11,14 Inadvertent overtreatment with multiple MMS stages can be avoided with careful recognition of the differentiating histopathologic features. Syringomatous lesions commonly are encountered in MMS and may even be present at the edge of other tumor types. Plaquelike syringoma has been reported as a coexistent entity with nodular basal cell carcinoma.12 Boos et al16 similarly reported the presence of deceptive ductal proliferations along the immediate peripheral margin of MAC, which prompted multiple re-excisions. Pursuit of permanent section analysis in these cases revealed the appearance of small syringomas, and a diagnosis of benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations was made, averting further intervention.16
Our case sheds light on the threat of commission bias in dermatologic surgery, which is the tendency for action rather than inaction.17 In this context, it is important to avoid the perspective that harm to the patient can only be prevented by active intervention. Cognitive bias has been increasingly recognized as a source of medical error, and methods to mitigate bias in medical practice have been well described.17 Microcystic adnexal carcinoma and plaquelike syringoma can be hard to differentiate especially initially, as demonstrated in our case, which particularly illustrates the importance of slowing down a surgical case at the appropriate time, considering and revisiting alternative diagnoses, implementing checklists, and seeking histopathologic collaboration with colleagues when necessary. Our attempted implementation of these principles, especially early collaboration with colleagues, led to intraoperative recognition of plaquelike syringoma within the first stage of MMS.
We seek to raise the index of suspicion for plaquelike syringoma among dermatologists and dermatologic surgeons, especially when syringomatous structures are limited to the superficial dermis. We encourage familiarity with the plaquelike syringoma entity as well as careful consideration of further investigation via scouting biopsies or permanent section analysis when other characteristic features of MAC are unclear or lacking. Adequate sampling as well as collaboration with a dermatopathologist in cases of suspected syringoma can help to reduce the susceptibility to commission bias and prevent histopathologic pitfalls and unwarranted surgical morbidity.
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Dekio S, Jidoi J. Submammary syringoma—report of a case. J Dermatol. 1988;15:351-352.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Nguyen DB, Patterson JW, Wilson BB. Syringoma of the moustache area. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:337-339.
- Rongioletti F, Semino MT, Rebora A. Unilateral multiple plaque-like syringomas. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:623-625.
- Chi HI. A case of unusual syringoma: unilateral linear distribution and plaque formation. J Dermatol. 1996;23:505-506.
- Suwatee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaque-type syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Mitkov M, Balagula Y, Taube JM, et al. Plaque-like syringoma with involvement of deep reticular dermis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E206-E207.
- Schleich C, Ferringer T, Petrick M. Plaque type syringoma mimicking a microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB287.
- Yang Y, Srivastava D. Plaque-type syringoma coexisting with basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1464-1466.
- Motegi SI, Sekiguchi A, Fujiwara C, et al. Milia-like idiopathic calcinosis cutis and plaque-type syringoma in a girl with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E136-E137.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Boos MD, Elenitsas R, Seykora J, et al. Benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations adjacent to a microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a tumor mimic with significant patient implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:174-178.
- O’Sullivan ED, Schofield SJ. Cognitive bias in clinical medicine. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2018;48:225-232.
To the Editor:
Plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma is a lesser-known variant of syringoma that can appear histologically indistinguishable from the superficial portion of microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). The plaquelike variant of syringoma holds a benign clinical course, and no treatment is necessary. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is distinguished from plaquelike syringoma by an aggressive growth pattern with a high risk for local invasion and recurrence if inadequately treated. Thus, treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has been recommended as the mainstay for MAC. If superficial biopsy specimens reveal suspicion for MAC and patients are referred for MMS, careful consideration should be made to differentiate MAC and plaquelike syringoma early to prevent unnecessary morbidity.

A 78-year-old woman was referred for MMS for a left forehead lesion that was diagnosed via shave biopsy as a desmoplastic and cystic adnexal neoplasm with suspicion for desmoplastic trichoepithelioma or MAC (Figure 1). Upon presentation for MMS, a well-healed, 1.0×0.9-cm scar at the biopsy site on the left forehead was observed (Figure 2A). One stage was obtained by standard MMS technique and sent for intraoperative processing (Figure 2B). Frozen section examination of the first stage demonstrated peripheral margin involvement with syringomatous change confined to the superficial and mid dermis (Figure 3). Before proceeding further, these findings were reviewed with an in-house dermatopathologist, and it was determined that no infiltrative tumor, perineural involvement, or other features to indicate malignancy were noted. A decision was made to refrain from obtaining any additional layers and to send excised Burow triangles for permanent section analysis. A primary linear closure was performed without complication, and the patient was discharged from the ambulatory surgery suite. Histopathologic examination of the Burow triangles later confirmed findings consistent with plaquelike syringoma with no evidence of malignancy (Figure 4).

Syringomas present as small flesh-colored papules in the periorbital areas. These benign neoplasms previously have been classified into 4 major clinical variants: localized, generalized, Down syndrome associated, and familial.1 The lesser-known plaquelike variant of syringoma was first described by Kikuchi et al2 in 1979. Aside from our report, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma yielded 16 cases in the literature.2-14 Of these, 6 were referred to or encountered in the MMS setting.8,9,11,12,14 Plaquelike syringoma can be solitary or multiple in presentation.6 It most commonly involves the head and neck but also can present on the trunk, arms, legs, and groin areas. The clinical size of plaquelike syringoma is variable, with the largest reported cases extending several centimeters in diameter.2,6 Similar to reported associations with conventional syringoma, the plaquelike subtype of syringoma has been reported in association with Down syndrome.13

Histopathologically, plaquelike syringoma shares features with MAC as well as desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma. Plaquelike syringoma demonstrates broad proliferations of small tubules morphologically reminiscent of tadpoles confined within the dermis. Ducts typically are lined with 2 or 3 layers of small cuboidal cells. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma typically features asymmetric ductal structures lined with single cells extending from the dermis into the subcutis and even underlying muscle, cartilage, or bone.8 There are no reliable immunohistochemical stains to differentiate between these 2 entities; thus, the primary distinction lies in the depth of involvement. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is composed of narrow cords and nests of basaloid cells of follicular origin commonly admixed with small cornifying cysts appearing in the dermis.8 Colonizing Merkel cells positive for cytokeratin 20 often are present in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and not in syringoma or MAC.15 Desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma demonstrates narrow strands of basaloid cells of follicular origin appearing in the dermis. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma are each fundamentally differentiated from plaquelike syringoma in that proliferations of cords and nests are not of eccrine or apocrine origin.

Several cases of plaquelike syringoma have been challenging to distinguish from MAC in performing MMS.8,9,11 Underlying extension of this syringoma variant can be far-reaching, extending to several centimeters in size and involving multiple cosmetic subunits.6,11,14 Inadvertent overtreatment with multiple MMS stages can be avoided with careful recognition of the differentiating histopathologic features. Syringomatous lesions commonly are encountered in MMS and may even be present at the edge of other tumor types. Plaquelike syringoma has been reported as a coexistent entity with nodular basal cell carcinoma.12 Boos et al16 similarly reported the presence of deceptive ductal proliferations along the immediate peripheral margin of MAC, which prompted multiple re-excisions. Pursuit of permanent section analysis in these cases revealed the appearance of small syringomas, and a diagnosis of benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations was made, averting further intervention.16
Our case sheds light on the threat of commission bias in dermatologic surgery, which is the tendency for action rather than inaction.17 In this context, it is important to avoid the perspective that harm to the patient can only be prevented by active intervention. Cognitive bias has been increasingly recognized as a source of medical error, and methods to mitigate bias in medical practice have been well described.17 Microcystic adnexal carcinoma and plaquelike syringoma can be hard to differentiate especially initially, as demonstrated in our case, which particularly illustrates the importance of slowing down a surgical case at the appropriate time, considering and revisiting alternative diagnoses, implementing checklists, and seeking histopathologic collaboration with colleagues when necessary. Our attempted implementation of these principles, especially early collaboration with colleagues, led to intraoperative recognition of plaquelike syringoma within the first stage of MMS.
We seek to raise the index of suspicion for plaquelike syringoma among dermatologists and dermatologic surgeons, especially when syringomatous structures are limited to the superficial dermis. We encourage familiarity with the plaquelike syringoma entity as well as careful consideration of further investigation via scouting biopsies or permanent section analysis when other characteristic features of MAC are unclear or lacking. Adequate sampling as well as collaboration with a dermatopathologist in cases of suspected syringoma can help to reduce the susceptibility to commission bias and prevent histopathologic pitfalls and unwarranted surgical morbidity.
To the Editor:
Plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma is a lesser-known variant of syringoma that can appear histologically indistinguishable from the superficial portion of microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC). The plaquelike variant of syringoma holds a benign clinical course, and no treatment is necessary. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma is distinguished from plaquelike syringoma by an aggressive growth pattern with a high risk for local invasion and recurrence if inadequately treated. Thus, treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) has been recommended as the mainstay for MAC. If superficial biopsy specimens reveal suspicion for MAC and patients are referred for MMS, careful consideration should be made to differentiate MAC and plaquelike syringoma early to prevent unnecessary morbidity.

A 78-year-old woman was referred for MMS for a left forehead lesion that was diagnosed via shave biopsy as a desmoplastic and cystic adnexal neoplasm with suspicion for desmoplastic trichoepithelioma or MAC (Figure 1). Upon presentation for MMS, a well-healed, 1.0×0.9-cm scar at the biopsy site on the left forehead was observed (Figure 2A). One stage was obtained by standard MMS technique and sent for intraoperative processing (Figure 2B). Frozen section examination of the first stage demonstrated peripheral margin involvement with syringomatous change confined to the superficial and mid dermis (Figure 3). Before proceeding further, these findings were reviewed with an in-house dermatopathologist, and it was determined that no infiltrative tumor, perineural involvement, or other features to indicate malignancy were noted. A decision was made to refrain from obtaining any additional layers and to send excised Burow triangles for permanent section analysis. A primary linear closure was performed without complication, and the patient was discharged from the ambulatory surgery suite. Histopathologic examination of the Burow triangles later confirmed findings consistent with plaquelike syringoma with no evidence of malignancy (Figure 4).

Syringomas present as small flesh-colored papules in the periorbital areas. These benign neoplasms previously have been classified into 4 major clinical variants: localized, generalized, Down syndrome associated, and familial.1 The lesser-known plaquelike variant of syringoma was first described by Kikuchi et al2 in 1979. Aside from our report, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms plaquelike or plaque-type syringoma yielded 16 cases in the literature.2-14 Of these, 6 were referred to or encountered in the MMS setting.8,9,11,12,14 Plaquelike syringoma can be solitary or multiple in presentation.6 It most commonly involves the head and neck but also can present on the trunk, arms, legs, and groin areas. The clinical size of plaquelike syringoma is variable, with the largest reported cases extending several centimeters in diameter.2,6 Similar to reported associations with conventional syringoma, the plaquelike subtype of syringoma has been reported in association with Down syndrome.13

Histopathologically, plaquelike syringoma shares features with MAC as well as desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma. Plaquelike syringoma demonstrates broad proliferations of small tubules morphologically reminiscent of tadpoles confined within the dermis. Ducts typically are lined with 2 or 3 layers of small cuboidal cells. Microcystic adnexal carcinoma typically features asymmetric ductal structures lined with single cells extending from the dermis into the subcutis and even underlying muscle, cartilage, or bone.8 There are no reliable immunohistochemical stains to differentiate between these 2 entities; thus, the primary distinction lies in the depth of involvement. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is composed of narrow cords and nests of basaloid cells of follicular origin commonly admixed with small cornifying cysts appearing in the dermis.8 Colonizing Merkel cells positive for cytokeratin 20 often are present in desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and not in syringoma or MAC.15 Desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma demonstrates narrow strands of basaloid cells of follicular origin appearing in the dermis. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma and desmoplastic basal cell carcinoma are each fundamentally differentiated from plaquelike syringoma in that proliferations of cords and nests are not of eccrine or apocrine origin.

Several cases of plaquelike syringoma have been challenging to distinguish from MAC in performing MMS.8,9,11 Underlying extension of this syringoma variant can be far-reaching, extending to several centimeters in size and involving multiple cosmetic subunits.6,11,14 Inadvertent overtreatment with multiple MMS stages can be avoided with careful recognition of the differentiating histopathologic features. Syringomatous lesions commonly are encountered in MMS and may even be present at the edge of other tumor types. Plaquelike syringoma has been reported as a coexistent entity with nodular basal cell carcinoma.12 Boos et al16 similarly reported the presence of deceptive ductal proliferations along the immediate peripheral margin of MAC, which prompted multiple re-excisions. Pursuit of permanent section analysis in these cases revealed the appearance of small syringomas, and a diagnosis of benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations was made, averting further intervention.16
Our case sheds light on the threat of commission bias in dermatologic surgery, which is the tendency for action rather than inaction.17 In this context, it is important to avoid the perspective that harm to the patient can only be prevented by active intervention. Cognitive bias has been increasingly recognized as a source of medical error, and methods to mitigate bias in medical practice have been well described.17 Microcystic adnexal carcinoma and plaquelike syringoma can be hard to differentiate especially initially, as demonstrated in our case, which particularly illustrates the importance of slowing down a surgical case at the appropriate time, considering and revisiting alternative diagnoses, implementing checklists, and seeking histopathologic collaboration with colleagues when necessary. Our attempted implementation of these principles, especially early collaboration with colleagues, led to intraoperative recognition of plaquelike syringoma within the first stage of MMS.
We seek to raise the index of suspicion for plaquelike syringoma among dermatologists and dermatologic surgeons, especially when syringomatous structures are limited to the superficial dermis. We encourage familiarity with the plaquelike syringoma entity as well as careful consideration of further investigation via scouting biopsies or permanent section analysis when other characteristic features of MAC are unclear or lacking. Adequate sampling as well as collaboration with a dermatopathologist in cases of suspected syringoma can help to reduce the susceptibility to commission bias and prevent histopathologic pitfalls and unwarranted surgical morbidity.
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Dekio S, Jidoi J. Submammary syringoma—report of a case. J Dermatol. 1988;15:351-352.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Nguyen DB, Patterson JW, Wilson BB. Syringoma of the moustache area. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:337-339.
- Rongioletti F, Semino MT, Rebora A. Unilateral multiple plaque-like syringomas. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:623-625.
- Chi HI. A case of unusual syringoma: unilateral linear distribution and plaque formation. J Dermatol. 1996;23:505-506.
- Suwatee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaque-type syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Mitkov M, Balagula Y, Taube JM, et al. Plaque-like syringoma with involvement of deep reticular dermis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E206-E207.
- Schleich C, Ferringer T, Petrick M. Plaque type syringoma mimicking a microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB287.
- Yang Y, Srivastava D. Plaque-type syringoma coexisting with basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1464-1466.
- Motegi SI, Sekiguchi A, Fujiwara C, et al. Milia-like idiopathic calcinosis cutis and plaque-type syringoma in a girl with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E136-E137.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Boos MD, Elenitsas R, Seykora J, et al. Benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations adjacent to a microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a tumor mimic with significant patient implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:174-178.
- O’Sullivan ED, Schofield SJ. Cognitive bias in clinical medicine. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2018;48:225-232.
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Kikuchi I, Idemori M, Okazaki M. Plaque type syringoma. J Dermatol. 1979;6:329-331.
- Dekio S, Jidoi J. Submammary syringoma—report of a case. J Dermatol. 1988;15:351-352.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Nguyen DB, Patterson JW, Wilson BB. Syringoma of the moustache area. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:337-339.
- Rongioletti F, Semino MT, Rebora A. Unilateral multiple plaque-like syringomas. Br J Dermatol. 1996;135:623-625.
- Chi HI. A case of unusual syringoma: unilateral linear distribution and plaque formation. J Dermatol. 1996;23:505-506.
- Suwatee P, McClelland MC, Huiras EE, et al. Plaque-type syringoma: two cases misdiagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:570-574.
- Wallace JS, Bond JS, Seidel GD, et al. An important mimicker: plaque-type syringoma mistakenly diagnosed as microcystic adnexal carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40:810-812.
- Mitkov M, Balagula Y, Taube JM, et al. Plaque-like syringoma with involvement of deep reticular dermis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:E206-E207.
- Schleich C, Ferringer T, Petrick M. Plaque type syringoma mimicking a microcystic adnexal carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74(suppl 1):AB287.
- Yang Y, Srivastava D. Plaque-type syringoma coexisting with basal cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1464-1466.
- Motegi SI, Sekiguchi A, Fujiwara C, et al. Milia-like idiopathic calcinosis cutis and plaque-type syringoma in a girl with Down syndrome. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E136-E137.
- Clark M, Duprey C, Sutton A, et al. Plaque-type syringoma masquerading as microcystic adnexal carcinoma: review of the literature and description of a novel technique that emphasizes lesion architecture to help make the diagnosis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2019;41:E98-E101.
- Abesamis-Cubillan E, El-Shabrawi-Caelen L, LeBoit PE. Merkel cells and sclerosing epithelial neoplasms. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000;22:311-315.
- Boos MD, Elenitsas R, Seykora J, et al. Benign subclinical syringomatous proliferations adjacent to a microcystic adnexal carcinoma: a tumor mimic with significant patient implications. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:174-178.
- O’Sullivan ED, Schofield SJ. Cognitive bias in clinical medicine. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2018;48:225-232.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists should familiarize themselves with the plaquelike subtype of syringoma, which can histologically mimic the superficial portion of microcystic adnexal carcinoma (MAC).
- Careful recognition of plaquelike syringoma in the Mohs micrographic surgery setting may prevent unnecessary surgical morbidity.
- Further diagnostic investigation is warranted for superficial biopsies suggestive of MAC or when other characteristic features are lacking.
Tender Nodular Lesions in the Axilla and Vulva
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Histopathologic findings of the left axillary lesion included a diffuse infiltrate of irregular hematolymphoid cells with reniform nuclei that strongly and diffusely stained positively with CD1a and S-100 but were negative for CD138 and CD163 (Figure). Numerous eosinophils also were present. The surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate stained positively with CD45. Polymerase chain reaction of the vaginal lesion was negative for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Biopsy of the vaginal lesion revealed a mildly acanthotic epidermis and an aggregation of epithelioid cells with reniform nuclei in the papillary dermis. Positron emission tomography revealed widely disseminated disease. Sequencing of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signalregulated kinase pathway showed amplified expression of these genes but found no mutations. These results led to a diagnosis of cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) with a background of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Our patient has since initiated therapy with trametinib leading to disease improvement without known recurrence.

Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a rare disease of clonal dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) that can present in any organ.1 Most LCH diagnoses are made in pediatric patients, most often presenting in the bones, with other presentations in the skin, hypophysis, liver, lymph nodes, lungs, and spleen occurring less commonly.2 Proto-oncogene BRAF V600E mutations are a common determinant of LCH, with half of cases linked with this mutation that leads to enhanced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, though other mutations have been reported.3,4 These genetic alterations suggest LCH is neoplastic in nature; however, this is controversial, as spontaneous regression among pulmonary LCH has been observed, pointing to a reactive inflammatory process.5 Cutaneous LCH can present as a distinct papular or nodular lesion or multiple lesions with possible ulceration, but it is rare that LCH first presents on the skin.2,6 There is a substantial association of cutaneous LCH with the development of systemically disseminated LCH as well as other blood tumors, such as myelomonocytic leukemia, histiocytic sarcoma, and multiple lymphomas; this association is thought to be due to the common origin of LCH and other blood diseases in the bone marrow.6
Histopathology of LCH shows a diffuse papillary dermal infiltrate of clonal proliferation of reniform or cleaved histiocytes.5 Epidermal ulceration and epidermotropism also are common. Neoplastic cells are found admixed with variable levels of eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils, though eosinophils typically are elevated. Immunohistochemistry characteristically shows the expression of CD1a, S-100, and/or CD207, and the absence of CD163 expression.
Treatment of LCH is primarily dependent on disease dissemination status, with splenic and hepatic involvement, genetic panel results, and central nervous system risk considered in the treatment plan.5 Langerhans cell histiocytosis localized to the skin may require follow-up and monitoring, as spontaneous regression of cutaneous LCH is common. However, topical steroids or psoralen and long-wave UV radiation are potential treatments. Physicians who diagnose unifocal cutaneous LCH should have high clinical suspicion of disseminated LCH, and laboratory and radiographic evaluation may be necessary to rule out systemic disease, as more than 40% of patients with cutaneous LCH have systemic disease upon full evaluation.7 With systemic involvement, systemic chemotherapy may reduce morbidity and mortality, but clinical response should be monitored after 6 weeks of treatment, as results are variably effective. Vinblastine is the most common chemotherapy regimen, with an 84% survival rate and 51.5% event-free survival rate after 8 years.8 Targeted therapy for common genetic mutations also is possible, as vemurafenib has been used to treat patients with the BRAF V600E mutation.
Due to the variable clinical presentation of cutaneous LCH, the lesions can mimic other common skin diseases such as eczema or seborrheic dermatitis.7 However, there are limited data on LCH presenting in infiltrative skin disease. Langerhans cell histiocytosis that was misdiagnosed as HS has been reported,9-11 but LCH presenting alongside long-standing HS is rare. Although LCH often mimics infiltrative skin diseases, its simultaneous presentation with a previously confirmed diagnosis of HS was notable in our patient.
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included HS, Actinomyces infection, lymphomatoid papulosis, and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Cutaneous findings in HS include chronic acneform nodules with follicular plugging, ruptured ducts leading to epithelized sinuses, inflammation, and abscesses in the axillae or inguinal and perineal areas.11 Histopathology reveals follicular occlusion and hyperkeratinization, which cause destruction of the pilosebaceous glands. Hidradenitis suppurativa features on immunohistochemistry often are conflicting, but there consistently is co-localization of keratinocyte hyperplasia with CD3-, CD4-, CD8-, and CD68-positive staining of cells that produce tumor necrosis factor α, IL-12, IL-23, and IL-32, with CD1a staining variable.12 An infection with Actinomyces, a slow-progressing anaerobic or microaerophilic bacteria, may present in the skin with chronic suppurative inflammation on the neck, trunk, and abdomen. The classic presentation is subcutaneous nodules with localized infiltration of abscesses, fistulas, and draining sinuses.13 Morphologically, Actinomyces causes chronic granulomatous infection with 0.1- to 1-mm sulfur granules, which are seen as basophilic masses with eosinophilic terminal clubs on hematoxylin and eosin staining.14 Histopathology reveals grampositive filamentous Actinomyces bacteria that branch at the edge of the granules. Lymphomatoid papulosis, a nonaggressive T-cell lymphoma, presents as papulonodular and sometimes necrotic disseminated lesions that spontaneously can regress or can cause a higher risk for the development of more aggressive lymphomas.15 Histopathology shows consistently dense, dermal, lymphocytic infiltration. Immunohistochemistry is characterized by lymphocytes expressing CD30 of varying degrees: type A with many CD30 staining cells, type B presenting similar to mycosis fungoides with little CD30 staining, and type C with lymphocytic CD30-staining plaques. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a low-grade soft-tissue malignant tumor with extensive local infiltration characterized by asymptomatic plaques on the trunk and proximal extremities that are indurated and adhered to the skin.16 Histopathology shows extensive invasion into the adjacent tissue far from the original focus of the tumor.
- Girschikofsky M, Arico M, Castillo D, et al. Management of adult patients with Langerhans cell histiocytosis: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of Euro-Histio-Net. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:72. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-72
- Flores-Terry MA, Sanz-Trenado JL, García-Arpa M, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting in adulthood. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2019;110:167-169. doi:10.1016/j .adengl.2018.12.005
- Emile J-F, Abla O, Fraitag S, et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672-2681. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-690636
- Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
- Bohn OL, Teruya-Feldstein J, Sanchez-Sosa S. Skin biopsy diagnosis of Langerhans cell neoplasms. In: Fernando S, ed. Skin Biopsy: Diagnosis and Treatment [Internet]. InTechOpen; 2013. http://dx.doi .org/10.5772/55893
- Edelbroek JR, Vermeer MH, Jansen PM, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis first presenting in the skin in adults: frequent association with a second haematological malignancy. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1287-1294. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11169.x
- Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165: 990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
- Yag˘ ci B, Varan A, Cag˘ lar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: retrospective analysis of 217 cases in a single center. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;25:399-408. doi:10.1080/08880010802107356
- Kalen JE, Shokeen D, Mislankar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis with clinical and histologic features of hidradenitis suppurativa: brief report and review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:502-505. doi:10.1097/dad.0000000000001005
- Chertoff J, Chung J, Ataya A. Adult Langerhans cell histiocytosis masquerading as hidradenitis suppurativa. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:E34-E36. doi:10.1164/rccm.201610-2082IM
- St. Claire K, Bunney R, Ashack KA, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:223-234. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.007
- Frew JW, Hawkes JE, Krueger JG. A systematic review and critical evaluation of immunohistochemical associations in hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Research. 2019;7:1923. doi:10.12688/f1000research.17268.2
- Robati RM, Niknezhad N, Bidari-Zerehpoush F, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis along with the surgical scar on the hand [published online November 9, 2016]. Case Rep Infect Dis. doi:10.1155/2016/5943932
- Ferry T, Valour F, Karsenty J, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Res. 2014;2014:183-197. doi:10.2147/idr.s39601
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785. doi:10.1182 /blood-2004-09-3502
- Tsai Y, Lin P, Chew K, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in children and adolescents: clinical presentation, histology, treatment, and review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67:1222-1229. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2014.05.03
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Histopathologic findings of the left axillary lesion included a diffuse infiltrate of irregular hematolymphoid cells with reniform nuclei that strongly and diffusely stained positively with CD1a and S-100 but were negative for CD138 and CD163 (Figure). Numerous eosinophils also were present. The surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate stained positively with CD45. Polymerase chain reaction of the vaginal lesion was negative for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Biopsy of the vaginal lesion revealed a mildly acanthotic epidermis and an aggregation of epithelioid cells with reniform nuclei in the papillary dermis. Positron emission tomography revealed widely disseminated disease. Sequencing of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signalregulated kinase pathway showed amplified expression of these genes but found no mutations. These results led to a diagnosis of cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) with a background of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Our patient has since initiated therapy with trametinib leading to disease improvement without known recurrence.

Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a rare disease of clonal dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) that can present in any organ.1 Most LCH diagnoses are made in pediatric patients, most often presenting in the bones, with other presentations in the skin, hypophysis, liver, lymph nodes, lungs, and spleen occurring less commonly.2 Proto-oncogene BRAF V600E mutations are a common determinant of LCH, with half of cases linked with this mutation that leads to enhanced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, though other mutations have been reported.3,4 These genetic alterations suggest LCH is neoplastic in nature; however, this is controversial, as spontaneous regression among pulmonary LCH has been observed, pointing to a reactive inflammatory process.5 Cutaneous LCH can present as a distinct papular or nodular lesion or multiple lesions with possible ulceration, but it is rare that LCH first presents on the skin.2,6 There is a substantial association of cutaneous LCH with the development of systemically disseminated LCH as well as other blood tumors, such as myelomonocytic leukemia, histiocytic sarcoma, and multiple lymphomas; this association is thought to be due to the common origin of LCH and other blood diseases in the bone marrow.6
Histopathology of LCH shows a diffuse papillary dermal infiltrate of clonal proliferation of reniform or cleaved histiocytes.5 Epidermal ulceration and epidermotropism also are common. Neoplastic cells are found admixed with variable levels of eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils, though eosinophils typically are elevated. Immunohistochemistry characteristically shows the expression of CD1a, S-100, and/or CD207, and the absence of CD163 expression.
Treatment of LCH is primarily dependent on disease dissemination status, with splenic and hepatic involvement, genetic panel results, and central nervous system risk considered in the treatment plan.5 Langerhans cell histiocytosis localized to the skin may require follow-up and monitoring, as spontaneous regression of cutaneous LCH is common. However, topical steroids or psoralen and long-wave UV radiation are potential treatments. Physicians who diagnose unifocal cutaneous LCH should have high clinical suspicion of disseminated LCH, and laboratory and radiographic evaluation may be necessary to rule out systemic disease, as more than 40% of patients with cutaneous LCH have systemic disease upon full evaluation.7 With systemic involvement, systemic chemotherapy may reduce morbidity and mortality, but clinical response should be monitored after 6 weeks of treatment, as results are variably effective. Vinblastine is the most common chemotherapy regimen, with an 84% survival rate and 51.5% event-free survival rate after 8 years.8 Targeted therapy for common genetic mutations also is possible, as vemurafenib has been used to treat patients with the BRAF V600E mutation.
Due to the variable clinical presentation of cutaneous LCH, the lesions can mimic other common skin diseases such as eczema or seborrheic dermatitis.7 However, there are limited data on LCH presenting in infiltrative skin disease. Langerhans cell histiocytosis that was misdiagnosed as HS has been reported,9-11 but LCH presenting alongside long-standing HS is rare. Although LCH often mimics infiltrative skin diseases, its simultaneous presentation with a previously confirmed diagnosis of HS was notable in our patient.
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included HS, Actinomyces infection, lymphomatoid papulosis, and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Cutaneous findings in HS include chronic acneform nodules with follicular plugging, ruptured ducts leading to epithelized sinuses, inflammation, and abscesses in the axillae or inguinal and perineal areas.11 Histopathology reveals follicular occlusion and hyperkeratinization, which cause destruction of the pilosebaceous glands. Hidradenitis suppurativa features on immunohistochemistry often are conflicting, but there consistently is co-localization of keratinocyte hyperplasia with CD3-, CD4-, CD8-, and CD68-positive staining of cells that produce tumor necrosis factor α, IL-12, IL-23, and IL-32, with CD1a staining variable.12 An infection with Actinomyces, a slow-progressing anaerobic or microaerophilic bacteria, may present in the skin with chronic suppurative inflammation on the neck, trunk, and abdomen. The classic presentation is subcutaneous nodules with localized infiltration of abscesses, fistulas, and draining sinuses.13 Morphologically, Actinomyces causes chronic granulomatous infection with 0.1- to 1-mm sulfur granules, which are seen as basophilic masses with eosinophilic terminal clubs on hematoxylin and eosin staining.14 Histopathology reveals grampositive filamentous Actinomyces bacteria that branch at the edge of the granules. Lymphomatoid papulosis, a nonaggressive T-cell lymphoma, presents as papulonodular and sometimes necrotic disseminated lesions that spontaneously can regress or can cause a higher risk for the development of more aggressive lymphomas.15 Histopathology shows consistently dense, dermal, lymphocytic infiltration. Immunohistochemistry is characterized by lymphocytes expressing CD30 of varying degrees: type A with many CD30 staining cells, type B presenting similar to mycosis fungoides with little CD30 staining, and type C with lymphocytic CD30-staining plaques. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a low-grade soft-tissue malignant tumor with extensive local infiltration characterized by asymptomatic plaques on the trunk and proximal extremities that are indurated and adhered to the skin.16 Histopathology shows extensive invasion into the adjacent tissue far from the original focus of the tumor.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis
Histopathologic findings of the left axillary lesion included a diffuse infiltrate of irregular hematolymphoid cells with reniform nuclei that strongly and diffusely stained positively with CD1a and S-100 but were negative for CD138 and CD163 (Figure). Numerous eosinophils also were present. The surrounding lymphocytic infiltrate stained positively with CD45. Polymerase chain reaction of the vaginal lesion was negative for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Biopsy of the vaginal lesion revealed a mildly acanthotic epidermis and an aggregation of epithelioid cells with reniform nuclei in the papillary dermis. Positron emission tomography revealed widely disseminated disease. Sequencing of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signalregulated kinase pathway showed amplified expression of these genes but found no mutations. These results led to a diagnosis of cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) with a background of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Our patient has since initiated therapy with trametinib leading to disease improvement without known recurrence.

Langerhans cell histiocytosis is a rare disease of clonal dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) that can present in any organ.1 Most LCH diagnoses are made in pediatric patients, most often presenting in the bones, with other presentations in the skin, hypophysis, liver, lymph nodes, lungs, and spleen occurring less commonly.2 Proto-oncogene BRAF V600E mutations are a common determinant of LCH, with half of cases linked with this mutation that leads to enhanced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, though other mutations have been reported.3,4 These genetic alterations suggest LCH is neoplastic in nature; however, this is controversial, as spontaneous regression among pulmonary LCH has been observed, pointing to a reactive inflammatory process.5 Cutaneous LCH can present as a distinct papular or nodular lesion or multiple lesions with possible ulceration, but it is rare that LCH first presents on the skin.2,6 There is a substantial association of cutaneous LCH with the development of systemically disseminated LCH as well as other blood tumors, such as myelomonocytic leukemia, histiocytic sarcoma, and multiple lymphomas; this association is thought to be due to the common origin of LCH and other blood diseases in the bone marrow.6
Histopathology of LCH shows a diffuse papillary dermal infiltrate of clonal proliferation of reniform or cleaved histiocytes.5 Epidermal ulceration and epidermotropism also are common. Neoplastic cells are found admixed with variable levels of eosinophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils, though eosinophils typically are elevated. Immunohistochemistry characteristically shows the expression of CD1a, S-100, and/or CD207, and the absence of CD163 expression.
Treatment of LCH is primarily dependent on disease dissemination status, with splenic and hepatic involvement, genetic panel results, and central nervous system risk considered in the treatment plan.5 Langerhans cell histiocytosis localized to the skin may require follow-up and monitoring, as spontaneous regression of cutaneous LCH is common. However, topical steroids or psoralen and long-wave UV radiation are potential treatments. Physicians who diagnose unifocal cutaneous LCH should have high clinical suspicion of disseminated LCH, and laboratory and radiographic evaluation may be necessary to rule out systemic disease, as more than 40% of patients with cutaneous LCH have systemic disease upon full evaluation.7 With systemic involvement, systemic chemotherapy may reduce morbidity and mortality, but clinical response should be monitored after 6 weeks of treatment, as results are variably effective. Vinblastine is the most common chemotherapy regimen, with an 84% survival rate and 51.5% event-free survival rate after 8 years.8 Targeted therapy for common genetic mutations also is possible, as vemurafenib has been used to treat patients with the BRAF V600E mutation.
Due to the variable clinical presentation of cutaneous LCH, the lesions can mimic other common skin diseases such as eczema or seborrheic dermatitis.7 However, there are limited data on LCH presenting in infiltrative skin disease. Langerhans cell histiocytosis that was misdiagnosed as HS has been reported,9-11 but LCH presenting alongside long-standing HS is rare. Although LCH often mimics infiltrative skin diseases, its simultaneous presentation with a previously confirmed diagnosis of HS was notable in our patient.
In our patient, the differential diagnosis included HS, Actinomyces infection, lymphomatoid papulosis, and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Cutaneous findings in HS include chronic acneform nodules with follicular plugging, ruptured ducts leading to epithelized sinuses, inflammation, and abscesses in the axillae or inguinal and perineal areas.11 Histopathology reveals follicular occlusion and hyperkeratinization, which cause destruction of the pilosebaceous glands. Hidradenitis suppurativa features on immunohistochemistry often are conflicting, but there consistently is co-localization of keratinocyte hyperplasia with CD3-, CD4-, CD8-, and CD68-positive staining of cells that produce tumor necrosis factor α, IL-12, IL-23, and IL-32, with CD1a staining variable.12 An infection with Actinomyces, a slow-progressing anaerobic or microaerophilic bacteria, may present in the skin with chronic suppurative inflammation on the neck, trunk, and abdomen. The classic presentation is subcutaneous nodules with localized infiltration of abscesses, fistulas, and draining sinuses.13 Morphologically, Actinomyces causes chronic granulomatous infection with 0.1- to 1-mm sulfur granules, which are seen as basophilic masses with eosinophilic terminal clubs on hematoxylin and eosin staining.14 Histopathology reveals grampositive filamentous Actinomyces bacteria that branch at the edge of the granules. Lymphomatoid papulosis, a nonaggressive T-cell lymphoma, presents as papulonodular and sometimes necrotic disseminated lesions that spontaneously can regress or can cause a higher risk for the development of more aggressive lymphomas.15 Histopathology shows consistently dense, dermal, lymphocytic infiltration. Immunohistochemistry is characterized by lymphocytes expressing CD30 of varying degrees: type A with many CD30 staining cells, type B presenting similar to mycosis fungoides with little CD30 staining, and type C with lymphocytic CD30-staining plaques. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a low-grade soft-tissue malignant tumor with extensive local infiltration characterized by asymptomatic plaques on the trunk and proximal extremities that are indurated and adhered to the skin.16 Histopathology shows extensive invasion into the adjacent tissue far from the original focus of the tumor.
- Girschikofsky M, Arico M, Castillo D, et al. Management of adult patients with Langerhans cell histiocytosis: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of Euro-Histio-Net. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:72. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-72
- Flores-Terry MA, Sanz-Trenado JL, García-Arpa M, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting in adulthood. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2019;110:167-169. doi:10.1016/j .adengl.2018.12.005
- Emile J-F, Abla O, Fraitag S, et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672-2681. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-690636
- Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
- Bohn OL, Teruya-Feldstein J, Sanchez-Sosa S. Skin biopsy diagnosis of Langerhans cell neoplasms. In: Fernando S, ed. Skin Biopsy: Diagnosis and Treatment [Internet]. InTechOpen; 2013. http://dx.doi .org/10.5772/55893
- Edelbroek JR, Vermeer MH, Jansen PM, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis first presenting in the skin in adults: frequent association with a second haematological malignancy. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1287-1294. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11169.x
- Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165: 990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
- Yag˘ ci B, Varan A, Cag˘ lar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: retrospective analysis of 217 cases in a single center. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;25:399-408. doi:10.1080/08880010802107356
- Kalen JE, Shokeen D, Mislankar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis with clinical and histologic features of hidradenitis suppurativa: brief report and review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:502-505. doi:10.1097/dad.0000000000001005
- Chertoff J, Chung J, Ataya A. Adult Langerhans cell histiocytosis masquerading as hidradenitis suppurativa. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:E34-E36. doi:10.1164/rccm.201610-2082IM
- St. Claire K, Bunney R, Ashack KA, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:223-234. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.007
- Frew JW, Hawkes JE, Krueger JG. A systematic review and critical evaluation of immunohistochemical associations in hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Research. 2019;7:1923. doi:10.12688/f1000research.17268.2
- Robati RM, Niknezhad N, Bidari-Zerehpoush F, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis along with the surgical scar on the hand [published online November 9, 2016]. Case Rep Infect Dis. doi:10.1155/2016/5943932
- Ferry T, Valour F, Karsenty J, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Res. 2014;2014:183-197. doi:10.2147/idr.s39601
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785. doi:10.1182 /blood-2004-09-3502
- Tsai Y, Lin P, Chew K, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in children and adolescents: clinical presentation, histology, treatment, and review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67:1222-1229. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2014.05.03
- Girschikofsky M, Arico M, Castillo D, et al. Management of adult patients with Langerhans cell histiocytosis: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of Euro-Histio-Net. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:72. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-72
- Flores-Terry MA, Sanz-Trenado JL, García-Arpa M, et al. Cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting in adulthood. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2019;110:167-169. doi:10.1016/j .adengl.2018.12.005
- Emile J-F, Abla O, Fraitag S, et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672-2681. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-690636
- Badalian-Very G, Vergilio J-A, Degar BA, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2010;116:1919-1923. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
- Bohn OL, Teruya-Feldstein J, Sanchez-Sosa S. Skin biopsy diagnosis of Langerhans cell neoplasms. In: Fernando S, ed. Skin Biopsy: Diagnosis and Treatment [Internet]. InTechOpen; 2013. http://dx.doi .org/10.5772/55893
- Edelbroek JR, Vermeer MH, Jansen PM, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis first presenting in the skin in adults: frequent association with a second haematological malignancy. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1287-1294. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11169.x
- Simko SJ, Garmezy B, Abhyankar H, et al. Differentiating skin-limited and multisystem Langerhans cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr. 2014;165: 990-996. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.07.063
- Yag˘ ci B, Varan A, Cag˘ lar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: retrospective analysis of 217 cases in a single center. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;25:399-408. doi:10.1080/08880010802107356
- Kalen JE, Shokeen D, Mislankar M, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis with clinical and histologic features of hidradenitis suppurativa: brief report and review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:502-505. doi:10.1097/dad.0000000000001005
- Chertoff J, Chung J, Ataya A. Adult Langerhans cell histiocytosis masquerading as hidradenitis suppurativa. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:E34-E36. doi:10.1164/rccm.201610-2082IM
- St. Claire K, Bunney R, Ashack KA, et al. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a great imitator. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:223-234. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2019.10.007
- Frew JW, Hawkes JE, Krueger JG. A systematic review and critical evaluation of immunohistochemical associations in hidradenitis suppurativa. F1000Research. 2019;7:1923. doi:10.12688/f1000research.17268.2
- Robati RM, Niknezhad N, Bidari-Zerehpoush F, et al. Primary cutaneous actinomycosis along with the surgical scar on the hand [published online November 9, 2016]. Case Rep Infect Dis. doi:10.1155/2016/5943932
- Ferry T, Valour F, Karsenty J, et al. Actinomycosis: etiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and management. Infect Drug Res. 2014;2014:183-197. doi:10.2147/idr.s39601
- Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005;105:3768-3785. doi:10.1182 /blood-2004-09-3502
- Tsai Y, Lin P, Chew K, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in children and adolescents: clinical presentation, histology, treatment, and review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67:1222-1229. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2014.05.03
A 28-year-old woman presented with tender burning lesions of the left axillary and vaginal skin that had worsened over the last year. Her medical history was notable for hidradenitis suppurativa, which had been present since adolescence, as well as pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis diagnosed 7 years prior to the current presentation after a spontaneous pneumothorax that eventually led to a pulmonary transplantation 3 years prior. The patient’s Langerhans cell histiocytosis was believed to have resolved without treatment after smoking cessation. Physical examination revealed nodular inflammation and scarring with deep undermining along the left axilla as well as swelling of the mons pubis with erosive skin lesions in the surrounding vaginal area. Bilateral cervical, axillary, inguinal, supraclavicular, and femoral lymph node chains were negative for adenopathy. A shave biopsy was performed on the axillary nodule.
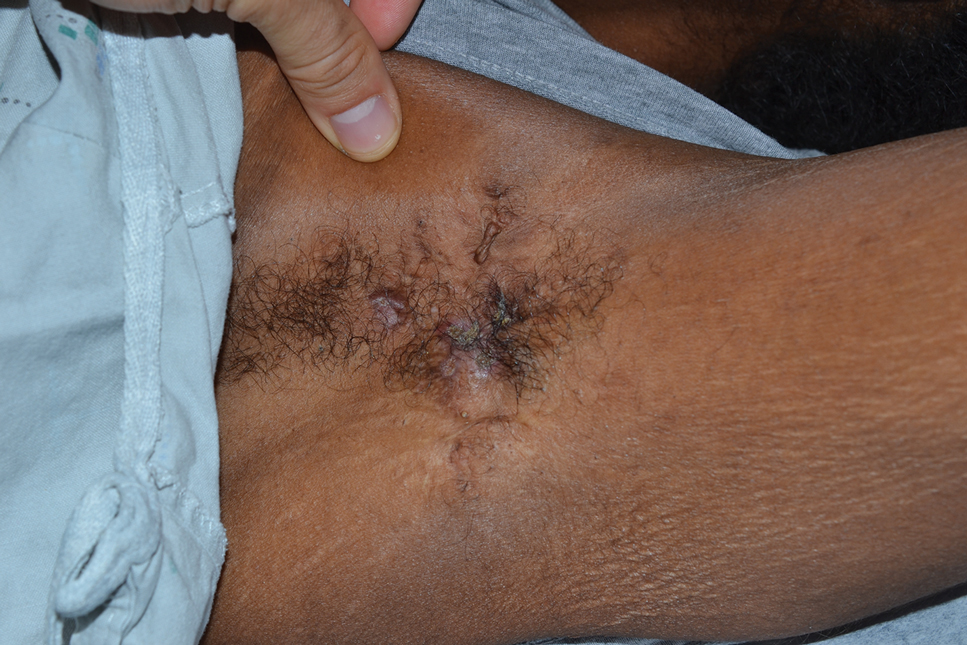
Cutaneous Presentation of Metastatic Salivary Duct Carcinoma
To the Editor:
Metastatic spread of salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) to the skin is rare. Diagnosing SDC can be challenging because the cutaneous manifestations of this disease are variable and include nodules, papules, and erysipelaslike inflammation (also known as shield sign) with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles. We describe a case of cutaneous metastatic SDC that originated from the parotid gland and presented with 2 distinct cutaneous findings: sharply demarcated erythematous plaques and focally hemorrhagic angiomatous papules.
A 60-year-old man presented with a persistent polymorphous pruritic eruption of several months’ duration involving the entire face, ears, neck, and upper chest. He had a history of unspecified adenocarcinoma of the parotid gland diagnosed 2 years prior and underwent multiple treatment cycles with several chemotherapeutic agents over the course of 18 months. Physical examination showed erythematous papules and nodules on the face and neck with slight overlying scale. Sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules were noted on the neck and chest (Figure 1). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were sampled from representative nodular areas. Histopathology showed multiple round solid-tumor nodules with central necrosis in the superficial and deep dermis that were not associated with the overlying epidermis (Figures 2A and 2B). The tumor cells appeared polygonal and contained ample eosinophilic cytoplasm. Tumor nuclei showed marked pleomorphism, and numerous atypical mitotic figures were readily identifiable (Figure 2C). There was diffuse cytoplasmic staining with cytokeratin 7 and nuclear staining with androgen receptor (Figure 2D). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of SDC metastatic to the skin.
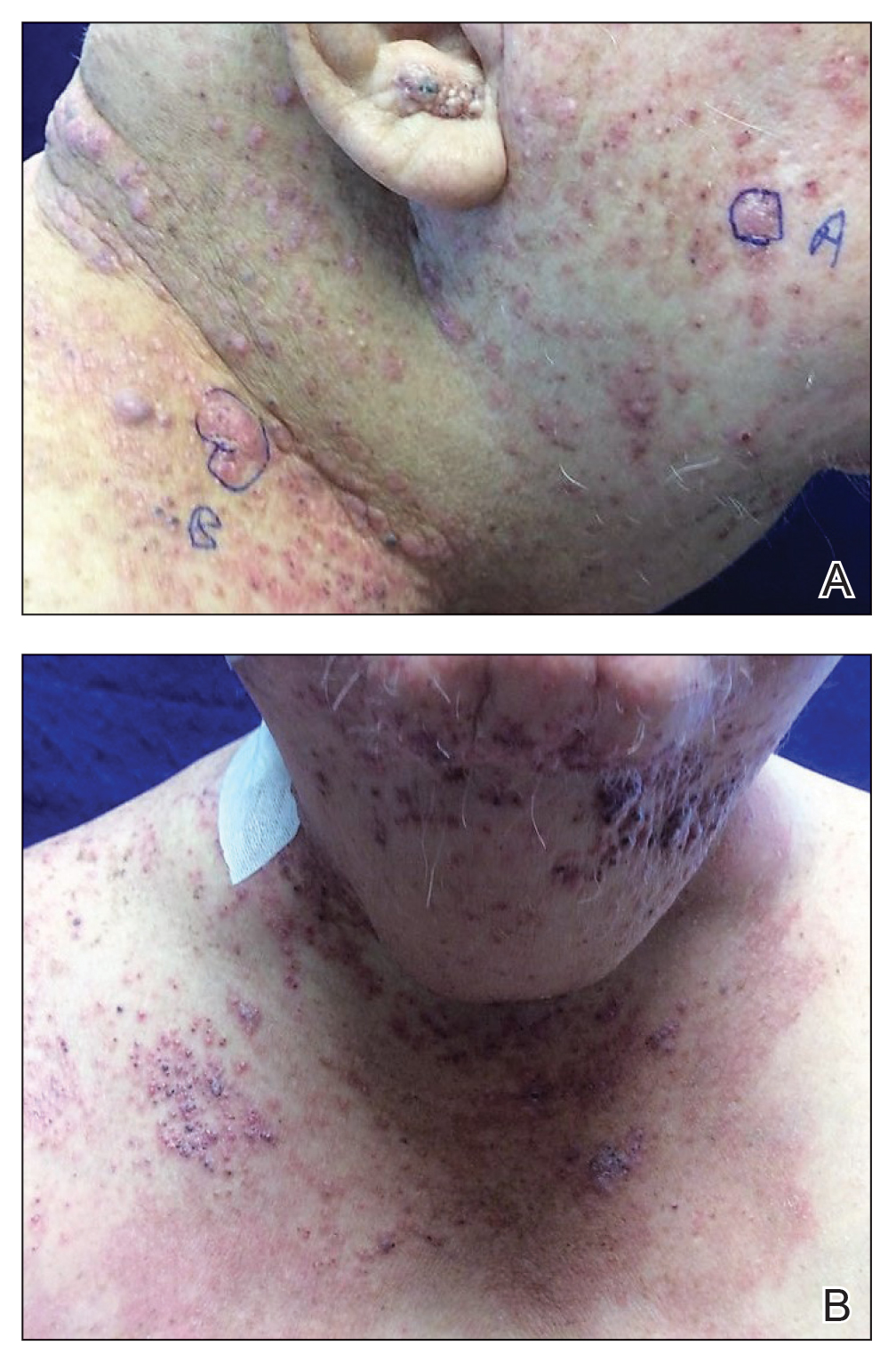
The patient underwent 8 cycles of docetaxel chemotherapy. With disease progression, the chemotherapy regimen was changed to gemcitabine and methotrexate. The patient continued to experience disease progression and died 9 months after diagnosis of skin metastases.
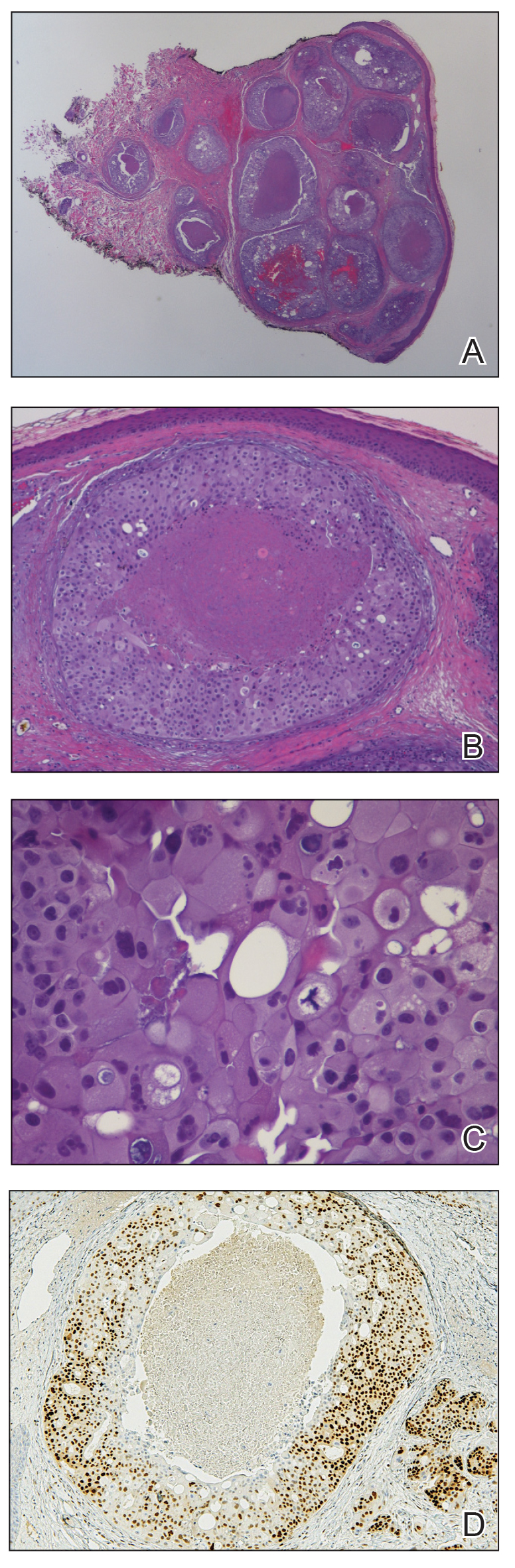
Salivary duct carcinoma is rare and is estimated to represent 1% to 3% of all salivary malignancies.1 It is a highly aggressive form of salivary gland carcinoma and is associated with a poor clinical outcome. The 3-year overall survival rate for stage I disease is 42% and only 23% for stage IV disease.2 Salivary duct carcinoma has a high rate of distant metastasis,3 but cases of cutaneous metastases are rare.3-8 Previously reported cases of SDC that metastasized to the skin originated from the parotid gland (n=6) and submandibular gland (n=1).3
The diagnosis of cutaneous metastases is challenging due to the variability of the skin manifestations. Three cases described small firm nodules in patients,3-5 while others presented with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles.6-8 Our patient presented with sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules, which further emphasizes the capricious nature of skin findings.
The morphology of SDC is strikingly similar to ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast, which can lead to diagnostic confusion. Both carcinomas may show oncocytic cells, ductal formations, and cribriform structures with central comedo necrosis. Moreover, immunohistochemical features overlap, including positive staining for cytokeratin 7 and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15. Positive immunohistochemistry with androgen receptor is consistent with SDC but also can be expressed in some cases of breast carcinoma.9,10 Therefore, the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement from metastatic SDC requires not just an evaluation of the pathologic features but careful attention to the clinical history and a thorough staging evaluation.
- D’heygere E, Meulemans J, Vander Poorten V. Salivary duct carcinoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;26:142-151.
- Gilbert MR, Sharma A, Schmitt NC, et al. A 20-year review of 75 cases of salivary duct carcinoma. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;142:489-495.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Andersen JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Tok J, Kao GF, Berberian BJ, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from a parotid adenocarcinoma. Report of a case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:303-306.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Hafiji J, Rytina E, Jani P, et al. A rare cutaneous presentation of metastatic parotid adenocarcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:E40-E42.
- Zanca A, Ferracini U, Bertazzoni MG. Telangiectatic metastasis from ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:113-114.
- Brys´ M, Wójcik M, Romanowicz-Makowska H, et al. Androgen receptor status in female breast cancer: RT-PCR and Western blot studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:85-90.
- Udager AM, Chiosea SI. Salivary duct carcinoma: an update on morphologic mimics and diagnostic use of androgen receptor immunohistochemistry. Head Neck Pathol. 2017;11:288-294.
To the Editor:
Metastatic spread of salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) to the skin is rare. Diagnosing SDC can be challenging because the cutaneous manifestations of this disease are variable and include nodules, papules, and erysipelaslike inflammation (also known as shield sign) with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles. We describe a case of cutaneous metastatic SDC that originated from the parotid gland and presented with 2 distinct cutaneous findings: sharply demarcated erythematous plaques and focally hemorrhagic angiomatous papules.
A 60-year-old man presented with a persistent polymorphous pruritic eruption of several months’ duration involving the entire face, ears, neck, and upper chest. He had a history of unspecified adenocarcinoma of the parotid gland diagnosed 2 years prior and underwent multiple treatment cycles with several chemotherapeutic agents over the course of 18 months. Physical examination showed erythematous papules and nodules on the face and neck with slight overlying scale. Sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules were noted on the neck and chest (Figure 1). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were sampled from representative nodular areas. Histopathology showed multiple round solid-tumor nodules with central necrosis in the superficial and deep dermis that were not associated with the overlying epidermis (Figures 2A and 2B). The tumor cells appeared polygonal and contained ample eosinophilic cytoplasm. Tumor nuclei showed marked pleomorphism, and numerous atypical mitotic figures were readily identifiable (Figure 2C). There was diffuse cytoplasmic staining with cytokeratin 7 and nuclear staining with androgen receptor (Figure 2D). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of SDC metastatic to the skin.

The patient underwent 8 cycles of docetaxel chemotherapy. With disease progression, the chemotherapy regimen was changed to gemcitabine and methotrexate. The patient continued to experience disease progression and died 9 months after diagnosis of skin metastases.

Salivary duct carcinoma is rare and is estimated to represent 1% to 3% of all salivary malignancies.1 It is a highly aggressive form of salivary gland carcinoma and is associated with a poor clinical outcome. The 3-year overall survival rate for stage I disease is 42% and only 23% for stage IV disease.2 Salivary duct carcinoma has a high rate of distant metastasis,3 but cases of cutaneous metastases are rare.3-8 Previously reported cases of SDC that metastasized to the skin originated from the parotid gland (n=6) and submandibular gland (n=1).3
The diagnosis of cutaneous metastases is challenging due to the variability of the skin manifestations. Three cases described small firm nodules in patients,3-5 while others presented with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles.6-8 Our patient presented with sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules, which further emphasizes the capricious nature of skin findings.
The morphology of SDC is strikingly similar to ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast, which can lead to diagnostic confusion. Both carcinomas may show oncocytic cells, ductal formations, and cribriform structures with central comedo necrosis. Moreover, immunohistochemical features overlap, including positive staining for cytokeratin 7 and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15. Positive immunohistochemistry with androgen receptor is consistent with SDC but also can be expressed in some cases of breast carcinoma.9,10 Therefore, the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement from metastatic SDC requires not just an evaluation of the pathologic features but careful attention to the clinical history and a thorough staging evaluation.
To the Editor:
Metastatic spread of salivary duct carcinoma (SDC) to the skin is rare. Diagnosing SDC can be challenging because the cutaneous manifestations of this disease are variable and include nodules, papules, and erysipelaslike inflammation (also known as shield sign) with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles. We describe a case of cutaneous metastatic SDC that originated from the parotid gland and presented with 2 distinct cutaneous findings: sharply demarcated erythematous plaques and focally hemorrhagic angiomatous papules.
A 60-year-old man presented with a persistent polymorphous pruritic eruption of several months’ duration involving the entire face, ears, neck, and upper chest. He had a history of unspecified adenocarcinoma of the parotid gland diagnosed 2 years prior and underwent multiple treatment cycles with several chemotherapeutic agents over the course of 18 months. Physical examination showed erythematous papules and nodules on the face and neck with slight overlying scale. Sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules were noted on the neck and chest (Figure 1). Two 4-mm punch biopsies were sampled from representative nodular areas. Histopathology showed multiple round solid-tumor nodules with central necrosis in the superficial and deep dermis that were not associated with the overlying epidermis (Figures 2A and 2B). The tumor cells appeared polygonal and contained ample eosinophilic cytoplasm. Tumor nuclei showed marked pleomorphism, and numerous atypical mitotic figures were readily identifiable (Figure 2C). There was diffuse cytoplasmic staining with cytokeratin 7 and nuclear staining with androgen receptor (Figure 2D). These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of SDC metastatic to the skin.

The patient underwent 8 cycles of docetaxel chemotherapy. With disease progression, the chemotherapy regimen was changed to gemcitabine and methotrexate. The patient continued to experience disease progression and died 9 months after diagnosis of skin metastases.

Salivary duct carcinoma is rare and is estimated to represent 1% to 3% of all salivary malignancies.1 It is a highly aggressive form of salivary gland carcinoma and is associated with a poor clinical outcome. The 3-year overall survival rate for stage I disease is 42% and only 23% for stage IV disease.2 Salivary duct carcinoma has a high rate of distant metastasis,3 but cases of cutaneous metastases are rare.3-8 Previously reported cases of SDC that metastasized to the skin originated from the parotid gland (n=6) and submandibular gland (n=1).3
The diagnosis of cutaneous metastases is challenging due to the variability of the skin manifestations. Three cases described small firm nodules in patients,3-5 while others presented with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles.6-8 Our patient presented with sharply demarcated, erythematous plaques studded with focally hemorrhagic, angiomatous papules, which further emphasizes the capricious nature of skin findings.
The morphology of SDC is strikingly similar to ductal adenocarcinoma of the breast, which can lead to diagnostic confusion. Both carcinomas may show oncocytic cells, ductal formations, and cribriform structures with central comedo necrosis. Moreover, immunohistochemical features overlap, including positive staining for cytokeratin 7 and gross cystic disease fluid protein 15. Positive immunohistochemistry with androgen receptor is consistent with SDC but also can be expressed in some cases of breast carcinoma.9,10 Therefore, the diagnosis of cutaneous involvement from metastatic SDC requires not just an evaluation of the pathologic features but careful attention to the clinical history and a thorough staging evaluation.
- D’heygere E, Meulemans J, Vander Poorten V. Salivary duct carcinoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;26:142-151.
- Gilbert MR, Sharma A, Schmitt NC, et al. A 20-year review of 75 cases of salivary duct carcinoma. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;142:489-495.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Andersen JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Tok J, Kao GF, Berberian BJ, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from a parotid adenocarcinoma. Report of a case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:303-306.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Hafiji J, Rytina E, Jani P, et al. A rare cutaneous presentation of metastatic parotid adenocarcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:E40-E42.
- Zanca A, Ferracini U, Bertazzoni MG. Telangiectatic metastasis from ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:113-114.
- Brys´ M, Wójcik M, Romanowicz-Makowska H, et al. Androgen receptor status in female breast cancer: RT-PCR and Western blot studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:85-90.
- Udager AM, Chiosea SI. Salivary duct carcinoma: an update on morphologic mimics and diagnostic use of androgen receptor immunohistochemistry. Head Neck Pathol. 2017;11:288-294.
- D’heygere E, Meulemans J, Vander Poorten V. Salivary duct carcinoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;26:142-151.
- Gilbert MR, Sharma A, Schmitt NC, et al. A 20-year review of 75 cases of salivary duct carcinoma. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;142:489-495.
- Chakari W, Andersen L, Andersen JL. Cutaneous metastases from salivary duct carcinoma of the submandibular gland. Case Rep Dermatol. 2017;9:254-258.
- Tok J, Kao GF, Berberian BJ, et al. Cutaneous metastasis from a parotid adenocarcinoma. Report of a case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 1995;17:303-306.
- Aygit AC, Top H, Cakir B, et al. Salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland metastasizing to the skin: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:48-50.
- Cohen PR, Prieto VG, Piha-Paul SA, et al. The “shield sign” in two men with metastatic salivary duct carcinoma to the skin: cutaneous metastases presenting as carcinoma hemorrhagiectoides. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2012;5:27-36.
- Hafiji J, Rytina E, Jani P, et al. A rare cutaneous presentation of metastatic parotid adenocarcinoma. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:E40-E42.
- Zanca A, Ferracini U, Bertazzoni MG. Telangiectatic metastasis from ductal carcinoma of the parotid gland. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;28:113-114.
- Brys´ M, Wójcik M, Romanowicz-Makowska H, et al. Androgen receptor status in female breast cancer: RT-PCR and Western blot studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:85-90.
- Udager AM, Chiosea SI. Salivary duct carcinoma: an update on morphologic mimics and diagnostic use of androgen receptor immunohistochemistry. Head Neck Pathol. 2017;11:288-294.
Practice Points
- Skin manifestations of metastatic salivary duct carcinoma can be variable, ranging from nodules to erysipelaslike inflammation (also known as shield sign) with purpuric papules and pseudovesicles.
- The specific clinical findings as well as histologic and immunohistochemical characteristics can aid in the diagnosis of this rare disease.
Endocrine Mucin-Producing Sweat Gland Carcinoma and Primary Cutaneous Mucinous Carcinoma: A Case Series
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) and
Methods
Following institutional review board approval, we conducted a retrospective, single-institution case series. We searched electronic medical records dating from 2000 to 2019 for tumors diagnosed as PCMC or extramammary Paget disease treated with MMS. We gathered demographic, clinical, pathologic, and follow-up information from the electronic medical records for each case (Tables 1 and 2). Two dermatopathologists (B.P. and B.F.K.) reviewed the hematoxylin and eosin–stained slides of each tumor as well as all available immunohistochemical stains. One of the reviewers (B.F.K.) is a board-certified dermatologist, dermatopathologist, and fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon.
Results
Demographic and Clinical Information—We identified 2 cases of EMPSGC and 3 cases of PCMC diagnosed and treated at our institution; 4 of these cases had been treated within the last 2 years. One had been treated 18 years prior; case information was limited due to planned institutional record destruction. Three of the patients were female and 2 were male. The mean age at presentation was 71 years (range, 62–87 years). None had experienced recurrence or metastases after a mean follow-up of 30 months.
Case 1—A 68-year-old woman noted a slow-growing, flesh-colored papule measuring 12×10 mm on the right lower eyelid. An excisional biopsy was completed with 2-mm clinical margins, and the defect was closed in a linear fashion. Histologic sections demonstrated EMPSGC with uninvolved margins. The patient desired no further intervention and was clinically followed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head and neck found no evidence of metastasis. She has had no recurrence after 15 months.
Case 2—A 62-year-old man presented with a 7×5-mm, flesh-colored papule on the left lower eyelid margin (Figure 1). It was previously treated conservatively as a hordeolum but was biopsied after it failed to resolve with 3-mm margins. Histopathology demonstrated an EMPSGC (Figure 2). The lesion was treated with modified MMS with permanent en face section processing and cleared after 1 stage. Computed tomography of the head and neck showed no abnormalities. He has had no recurrence after 9 months.
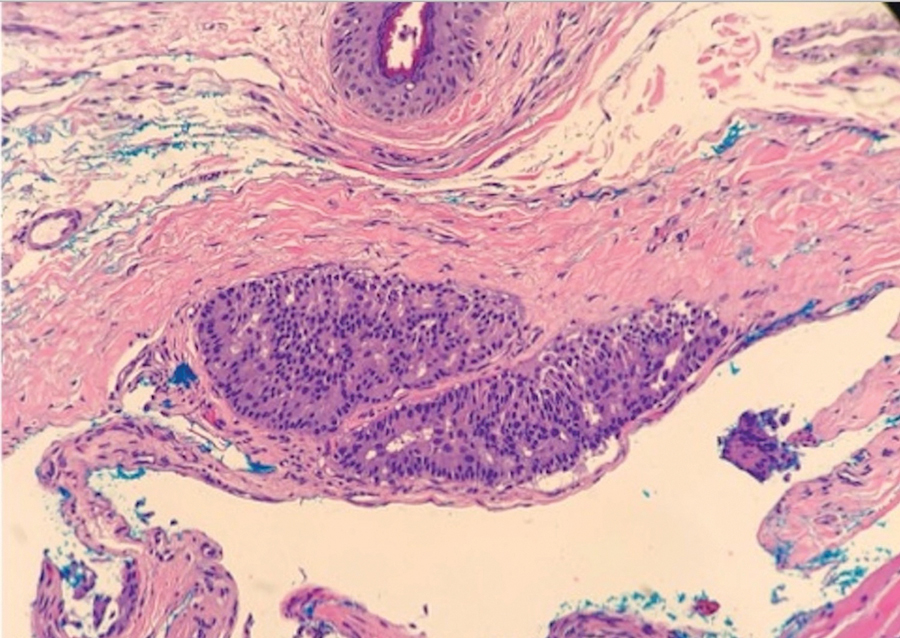
Case 3—A 72-year-old man presented with a nontender papule near the right lateral canthus. A punch biopsy demonstrated PCMC. He was treated via modified MMS with permanent en face section processing. The tumor was cleared in 1 stage. He showed no evidence of recurrence after 112 months and died of unrelated causes. The rest of his clinical information was limited because of planned institutional destruction of records.
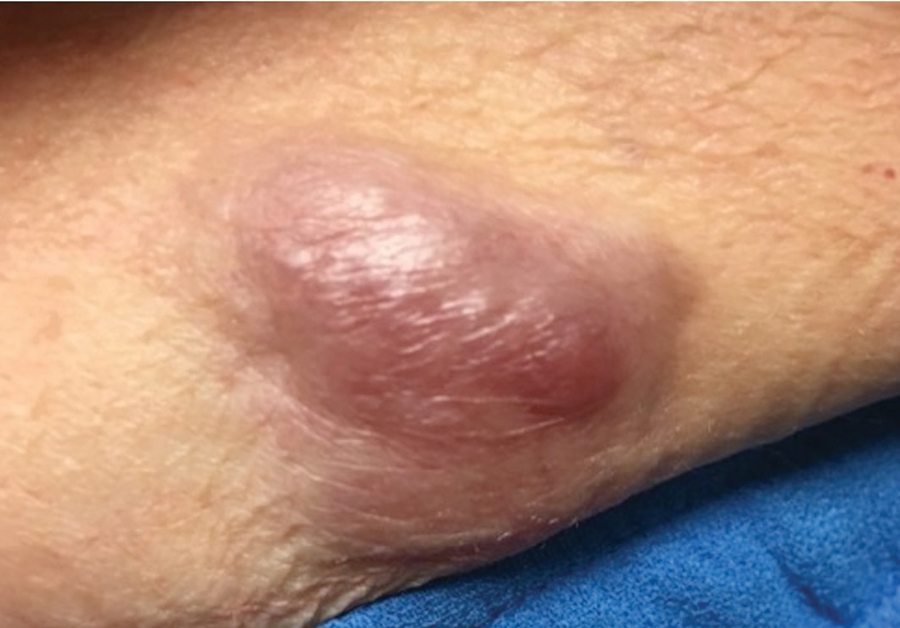
Case 4—An 87-year-old woman presented with a 25×25-mm, slow-growing mass of 12 months’ duration on the left lower abdomen (Figure 3). A biopsy demonstrated PCMC (Figure 4). Because of the size of the lesion, she underwent WLE with 20- to 30-mm margins by a general surgeon under general anesthesia. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography was unremarkable. She has remained disease free for 11 months.
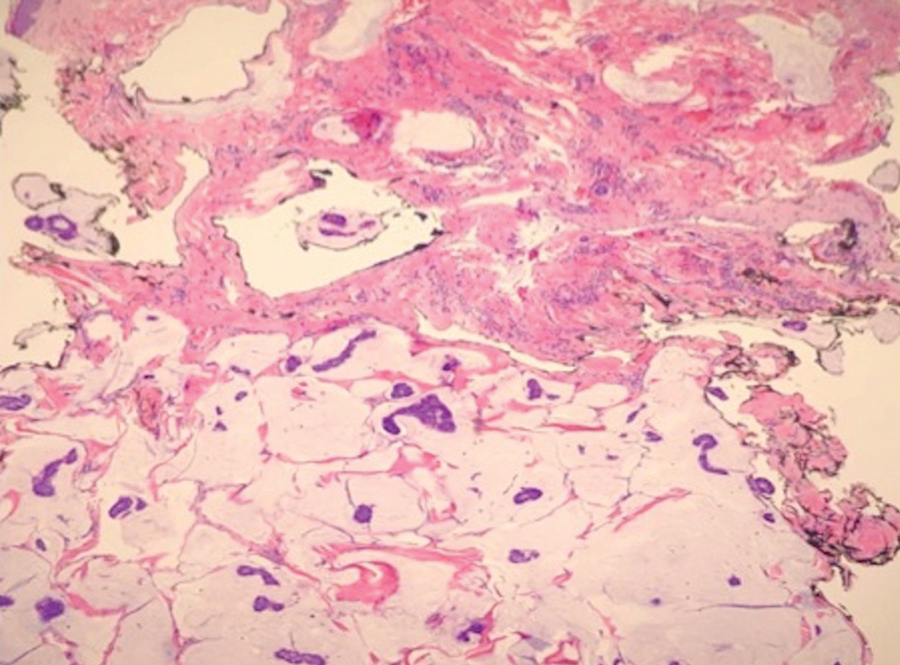
Case 5—A 66-year-old woman presented for evaluation of a posterior scalp mass measuring 23×18 mm that had grown over the last 24 months. Biopsy showed mucinous carcinoma with lymphovascular invasion consistent with PCMC (Figure 5) confirmed on multiple tissue levels and with the aid of immunohistochemistry. She was sent for an MRI of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, which demonstrated 2 enlarged postauricular lymph nodes and raised suspicion for metastatic disease vs reactive lymphadenopathy. Mohs micrographic surgery with frozen sections was performed with 1- to 3-mm margins; the final layer was sent for permanent processing and confirmed negative margins. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and lymphadenectomy of the 2 nodes present on imaging showed no evidence of metastasis. The patient had no recurrence in 1 month.
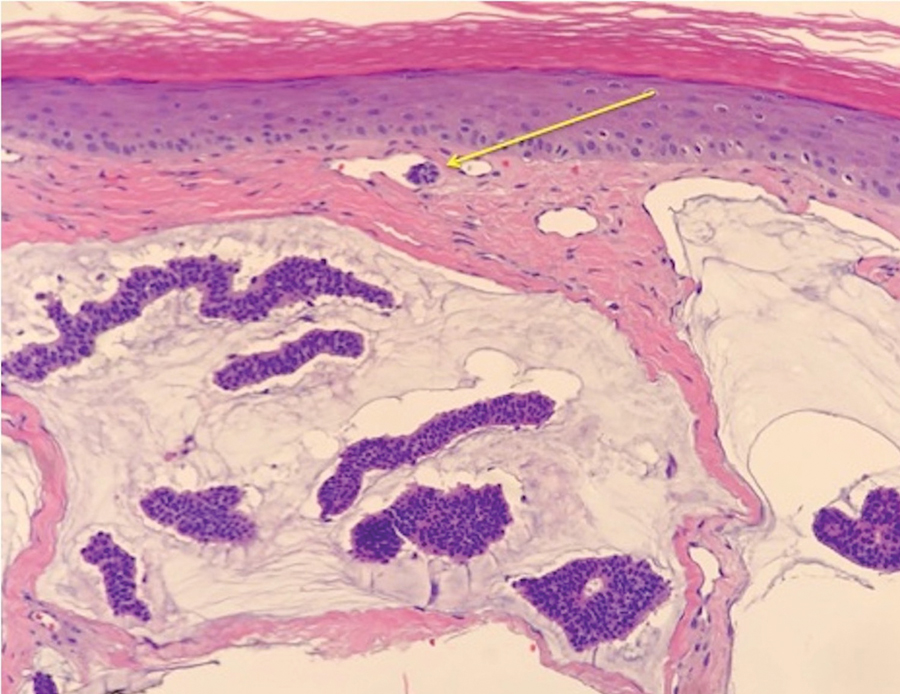
Comment
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and PCMC are sweat gland malignancies that carry low metastatic potential but are locally aggressive. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma has a strong predilection for the periorbital region, especially the lower eyelids of older women.3 Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma may arise on the eyelids, scalp, axillae, and trunk and has been reported more often in older men. These slow-growing tumors appear as nonspecific nodules.3 Lesions frequently are asymptomatic but rarely may cause pruritus and bleeding. Histologically, EMPSGC appears as solid or cystic nodules of cells with a papillary, cribriform, or pseudopapillary appearance. Intracellular or extracellular mucin as well as malignant spread of tumor cells along pre-existing ductlike structures make it difficult to histologically distinguish EMPSGC from ductal carcinoma in situ.3
A key histopathologic feature of PCMC is basophilic epithelioid cell nests in mucinous lakes.4 Rosettelike structures are seen within solid areas of the tumor. Fibrous septae separate individual collections of mucin, creating a lobulated appearance. The histopathologic differential diagnosis of EMPSGC and PCMC is broad, including basal cell carcinoma, hidradenoma, hidradenocarcinoma, apocrine adenoma, and dermal duct tumor. Positive expression of at least 1 neuroendocrine marker (ie, synaptophysin, neuron-specific enolase, chromogranin) and low-molecular cytokeratin (cytokeratin 7, CAM5.2, Ber-EP4) can aid in the diagnosis of both EMPSGC and PCMC.4 The use of p63 immunostaining is beneficial in delineating adnexal neoplasms. Adnexal tumors that stain positively with p63 are more likely to be of primary cutaneous origin, whereas lack of p63 staining usually denotes a secondary metastatic process. However, p63 staining is less reliable when distinguishing primary and metastatic mucinous neoplasms. Metastatic mucinous carcinomas often stain positive with p63, while PCMC usually stains negative despite its primary cutaneous origin, decreasing the clinical utility of p63. The tumor may be identical to metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, lung, ovary, and pancreas. Tumor islands floating in mucin are identified in both primary cutaneous and metastatic disease to the skin.3,6 Areas of tumor necrosis, notable atypia, and perineural or lymphovascular invasion are infrequently reported in EMPSGC or PCMC, though lymphatic invasion was identified in case 5 presented herein.
A metastatic workup is warranted in all cases of PCMC, including a thorough history, review of systems, breast examination, and imaging. A workup may be considered in cases of EMPSGC depending on histologic features or clinical history.
There is uncertainty regarding the optimal management of these slow-growing yet locally destructive tumors.5 The incidence of local recurrence of PCMC after WLE with narrow margins of at least 1 cm can be as high as 30% to 40%, especially on the eyelid.4 There is no consensus on surgical care for either of these tumors.5 Because of the high recurrence rate and the predilection for the eyelid and face, MMS provides an excellent alternative to WLE for tissue preservation and meticulous margin control. We advocate for the use of the Mohs technique with permanent sectioning, which may delay the repair, but reviewing tissue with permanent fixation improves the quality and accuracy of the margin evaluation because these tumors often are infiltrative and difficult to delineate under frozen section processing. Permanent en face sectioning allows the laboratory to utilize the full array of immunohistochemical stains for these tumors, providing accurate and timely results.
Limitations to our retrospective uncontrolled study include missing or incomplete data points and short follow-up time. Additionally, there was no standardization to the margins removed with MMS or WLE because of the limited available data that comment on appropriate margins.
- Held L, Ruetten A, Kutzner H, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and molecular analysis of 11 cases with emphasis on MYB immunoexpression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:674-680.
- Navrazhina K, Petukhova T, Wildman HF, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma of the scalp treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:887-889.
- Scott BL, Anyanwu CO, Vandergriff T, et al. Endocrine mucin–producing sweat gland carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1498-1500.
- Chang S, Shim SH, Joo M, et al. A case of endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma co-existing with mucinous carcinoma: a case report. Korean J Pathol. 2010;44:97-100.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Bulliard C, Murali R, Maloof A, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:812-816.
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) and

Methods
Following institutional review board approval, we conducted a retrospective, single-institution case series. We searched electronic medical records dating from 2000 to 2019 for tumors diagnosed as PCMC or extramammary Paget disease treated with MMS. We gathered demographic, clinical, pathologic, and follow-up information from the electronic medical records for each case (Tables 1 and 2). Two dermatopathologists (B.P. and B.F.K.) reviewed the hematoxylin and eosin–stained slides of each tumor as well as all available immunohistochemical stains. One of the reviewers (B.F.K.) is a board-certified dermatologist, dermatopathologist, and fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon.

Results
Demographic and Clinical Information—We identified 2 cases of EMPSGC and 3 cases of PCMC diagnosed and treated at our institution; 4 of these cases had been treated within the last 2 years. One had been treated 18 years prior; case information was limited due to planned institutional record destruction. Three of the patients were female and 2 were male. The mean age at presentation was 71 years (range, 62–87 years). None had experienced recurrence or metastases after a mean follow-up of 30 months.
Case 1—A 68-year-old woman noted a slow-growing, flesh-colored papule measuring 12×10 mm on the right lower eyelid. An excisional biopsy was completed with 2-mm clinical margins, and the defect was closed in a linear fashion. Histologic sections demonstrated EMPSGC with uninvolved margins. The patient desired no further intervention and was clinically followed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head and neck found no evidence of metastasis. She has had no recurrence after 15 months.

Case 2—A 62-year-old man presented with a 7×5-mm, flesh-colored papule on the left lower eyelid margin (Figure 1). It was previously treated conservatively as a hordeolum but was biopsied after it failed to resolve with 3-mm margins. Histopathology demonstrated an EMPSGC (Figure 2). The lesion was treated with modified MMS with permanent en face section processing and cleared after 1 stage. Computed tomography of the head and neck showed no abnormalities. He has had no recurrence after 9 months.

Case 3—A 72-year-old man presented with a nontender papule near the right lateral canthus. A punch biopsy demonstrated PCMC. He was treated via modified MMS with permanent en face section processing. The tumor was cleared in 1 stage. He showed no evidence of recurrence after 112 months and died of unrelated causes. The rest of his clinical information was limited because of planned institutional destruction of records.

Case 4—An 87-year-old woman presented with a 25×25-mm, slow-growing mass of 12 months’ duration on the left lower abdomen (Figure 3). A biopsy demonstrated PCMC (Figure 4). Because of the size of the lesion, she underwent WLE with 20- to 30-mm margins by a general surgeon under general anesthesia. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography was unremarkable. She has remained disease free for 11 months.

Case 5—A 66-year-old woman presented for evaluation of a posterior scalp mass measuring 23×18 mm that had grown over the last 24 months. Biopsy showed mucinous carcinoma with lymphovascular invasion consistent with PCMC (Figure 5) confirmed on multiple tissue levels and with the aid of immunohistochemistry. She was sent for an MRI of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, which demonstrated 2 enlarged postauricular lymph nodes and raised suspicion for metastatic disease vs reactive lymphadenopathy. Mohs micrographic surgery with frozen sections was performed with 1- to 3-mm margins; the final layer was sent for permanent processing and confirmed negative margins. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and lymphadenectomy of the 2 nodes present on imaging showed no evidence of metastasis. The patient had no recurrence in 1 month.

Comment
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and PCMC are sweat gland malignancies that carry low metastatic potential but are locally aggressive. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma has a strong predilection for the periorbital region, especially the lower eyelids of older women.3 Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma may arise on the eyelids, scalp, axillae, and trunk and has been reported more often in older men. These slow-growing tumors appear as nonspecific nodules.3 Lesions frequently are asymptomatic but rarely may cause pruritus and bleeding. Histologically, EMPSGC appears as solid or cystic nodules of cells with a papillary, cribriform, or pseudopapillary appearance. Intracellular or extracellular mucin as well as malignant spread of tumor cells along pre-existing ductlike structures make it difficult to histologically distinguish EMPSGC from ductal carcinoma in situ.3
A key histopathologic feature of PCMC is basophilic epithelioid cell nests in mucinous lakes.4 Rosettelike structures are seen within solid areas of the tumor. Fibrous septae separate individual collections of mucin, creating a lobulated appearance. The histopathologic differential diagnosis of EMPSGC and PCMC is broad, including basal cell carcinoma, hidradenoma, hidradenocarcinoma, apocrine adenoma, and dermal duct tumor. Positive expression of at least 1 neuroendocrine marker (ie, synaptophysin, neuron-specific enolase, chromogranin) and low-molecular cytokeratin (cytokeratin 7, CAM5.2, Ber-EP4) can aid in the diagnosis of both EMPSGC and PCMC.4 The use of p63 immunostaining is beneficial in delineating adnexal neoplasms. Adnexal tumors that stain positively with p63 are more likely to be of primary cutaneous origin, whereas lack of p63 staining usually denotes a secondary metastatic process. However, p63 staining is less reliable when distinguishing primary and metastatic mucinous neoplasms. Metastatic mucinous carcinomas often stain positive with p63, while PCMC usually stains negative despite its primary cutaneous origin, decreasing the clinical utility of p63. The tumor may be identical to metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, lung, ovary, and pancreas. Tumor islands floating in mucin are identified in both primary cutaneous and metastatic disease to the skin.3,6 Areas of tumor necrosis, notable atypia, and perineural or lymphovascular invasion are infrequently reported in EMPSGC or PCMC, though lymphatic invasion was identified in case 5 presented herein.
A metastatic workup is warranted in all cases of PCMC, including a thorough history, review of systems, breast examination, and imaging. A workup may be considered in cases of EMPSGC depending on histologic features or clinical history.
There is uncertainty regarding the optimal management of these slow-growing yet locally destructive tumors.5 The incidence of local recurrence of PCMC after WLE with narrow margins of at least 1 cm can be as high as 30% to 40%, especially on the eyelid.4 There is no consensus on surgical care for either of these tumors.5 Because of the high recurrence rate and the predilection for the eyelid and face, MMS provides an excellent alternative to WLE for tissue preservation and meticulous margin control. We advocate for the use of the Mohs technique with permanent sectioning, which may delay the repair, but reviewing tissue with permanent fixation improves the quality and accuracy of the margin evaluation because these tumors often are infiltrative and difficult to delineate under frozen section processing. Permanent en face sectioning allows the laboratory to utilize the full array of immunohistochemical stains for these tumors, providing accurate and timely results.
Limitations to our retrospective uncontrolled study include missing or incomplete data points and short follow-up time. Additionally, there was no standardization to the margins removed with MMS or WLE because of the limited available data that comment on appropriate margins.
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma (EMPSGC) and

Methods
Following institutional review board approval, we conducted a retrospective, single-institution case series. We searched electronic medical records dating from 2000 to 2019 for tumors diagnosed as PCMC or extramammary Paget disease treated with MMS. We gathered demographic, clinical, pathologic, and follow-up information from the electronic medical records for each case (Tables 1 and 2). Two dermatopathologists (B.P. and B.F.K.) reviewed the hematoxylin and eosin–stained slides of each tumor as well as all available immunohistochemical stains. One of the reviewers (B.F.K.) is a board-certified dermatologist, dermatopathologist, and fellowship-trained Mohs surgeon.

Results
Demographic and Clinical Information—We identified 2 cases of EMPSGC and 3 cases of PCMC diagnosed and treated at our institution; 4 of these cases had been treated within the last 2 years. One had been treated 18 years prior; case information was limited due to planned institutional record destruction. Three of the patients were female and 2 were male. The mean age at presentation was 71 years (range, 62–87 years). None had experienced recurrence or metastases after a mean follow-up of 30 months.
Case 1—A 68-year-old woman noted a slow-growing, flesh-colored papule measuring 12×10 mm on the right lower eyelid. An excisional biopsy was completed with 2-mm clinical margins, and the defect was closed in a linear fashion. Histologic sections demonstrated EMPSGC with uninvolved margins. The patient desired no further intervention and was clinically followed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head and neck found no evidence of metastasis. She has had no recurrence after 15 months.

Case 2—A 62-year-old man presented with a 7×5-mm, flesh-colored papule on the left lower eyelid margin (Figure 1). It was previously treated conservatively as a hordeolum but was biopsied after it failed to resolve with 3-mm margins. Histopathology demonstrated an EMPSGC (Figure 2). The lesion was treated with modified MMS with permanent en face section processing and cleared after 1 stage. Computed tomography of the head and neck showed no abnormalities. He has had no recurrence after 9 months.

Case 3—A 72-year-old man presented with a nontender papule near the right lateral canthus. A punch biopsy demonstrated PCMC. He was treated via modified MMS with permanent en face section processing. The tumor was cleared in 1 stage. He showed no evidence of recurrence after 112 months and died of unrelated causes. The rest of his clinical information was limited because of planned institutional destruction of records.

Case 4—An 87-year-old woman presented with a 25×25-mm, slow-growing mass of 12 months’ duration on the left lower abdomen (Figure 3). A biopsy demonstrated PCMC (Figure 4). Because of the size of the lesion, she underwent WLE with 20- to 30-mm margins by a general surgeon under general anesthesia. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography was unremarkable. She has remained disease free for 11 months.

Case 5—A 66-year-old woman presented for evaluation of a posterior scalp mass measuring 23×18 mm that had grown over the last 24 months. Biopsy showed mucinous carcinoma with lymphovascular invasion consistent with PCMC (Figure 5) confirmed on multiple tissue levels and with the aid of immunohistochemistry. She was sent for an MRI of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, which demonstrated 2 enlarged postauricular lymph nodes and raised suspicion for metastatic disease vs reactive lymphadenopathy. Mohs micrographic surgery with frozen sections was performed with 1- to 3-mm margins; the final layer was sent for permanent processing and confirmed negative margins. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and lymphadenectomy of the 2 nodes present on imaging showed no evidence of metastasis. The patient had no recurrence in 1 month.

Comment
Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and PCMC are sweat gland malignancies that carry low metastatic potential but are locally aggressive. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma has a strong predilection for the periorbital region, especially the lower eyelids of older women.3 Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma may arise on the eyelids, scalp, axillae, and trunk and has been reported more often in older men. These slow-growing tumors appear as nonspecific nodules.3 Lesions frequently are asymptomatic but rarely may cause pruritus and bleeding. Histologically, EMPSGC appears as solid or cystic nodules of cells with a papillary, cribriform, or pseudopapillary appearance. Intracellular or extracellular mucin as well as malignant spread of tumor cells along pre-existing ductlike structures make it difficult to histologically distinguish EMPSGC from ductal carcinoma in situ.3
A key histopathologic feature of PCMC is basophilic epithelioid cell nests in mucinous lakes.4 Rosettelike structures are seen within solid areas of the tumor. Fibrous septae separate individual collections of mucin, creating a lobulated appearance. The histopathologic differential diagnosis of EMPSGC and PCMC is broad, including basal cell carcinoma, hidradenoma, hidradenocarcinoma, apocrine adenoma, and dermal duct tumor. Positive expression of at least 1 neuroendocrine marker (ie, synaptophysin, neuron-specific enolase, chromogranin) and low-molecular cytokeratin (cytokeratin 7, CAM5.2, Ber-EP4) can aid in the diagnosis of both EMPSGC and PCMC.4 The use of p63 immunostaining is beneficial in delineating adnexal neoplasms. Adnexal tumors that stain positively with p63 are more likely to be of primary cutaneous origin, whereas lack of p63 staining usually denotes a secondary metastatic process. However, p63 staining is less reliable when distinguishing primary and metastatic mucinous neoplasms. Metastatic mucinous carcinomas often stain positive with p63, while PCMC usually stains negative despite its primary cutaneous origin, decreasing the clinical utility of p63. The tumor may be identical to metastatic mucinous adenocarcinoma of the breast, gastrointestinal tract, lung, ovary, and pancreas. Tumor islands floating in mucin are identified in both primary cutaneous and metastatic disease to the skin.3,6 Areas of tumor necrosis, notable atypia, and perineural or lymphovascular invasion are infrequently reported in EMPSGC or PCMC, though lymphatic invasion was identified in case 5 presented herein.
A metastatic workup is warranted in all cases of PCMC, including a thorough history, review of systems, breast examination, and imaging. A workup may be considered in cases of EMPSGC depending on histologic features or clinical history.
There is uncertainty regarding the optimal management of these slow-growing yet locally destructive tumors.5 The incidence of local recurrence of PCMC after WLE with narrow margins of at least 1 cm can be as high as 30% to 40%, especially on the eyelid.4 There is no consensus on surgical care for either of these tumors.5 Because of the high recurrence rate and the predilection for the eyelid and face, MMS provides an excellent alternative to WLE for tissue preservation and meticulous margin control. We advocate for the use of the Mohs technique with permanent sectioning, which may delay the repair, but reviewing tissue with permanent fixation improves the quality and accuracy of the margin evaluation because these tumors often are infiltrative and difficult to delineate under frozen section processing. Permanent en face sectioning allows the laboratory to utilize the full array of immunohistochemical stains for these tumors, providing accurate and timely results.
Limitations to our retrospective uncontrolled study include missing or incomplete data points and short follow-up time. Additionally, there was no standardization to the margins removed with MMS or WLE because of the limited available data that comment on appropriate margins.
- Held L, Ruetten A, Kutzner H, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and molecular analysis of 11 cases with emphasis on MYB immunoexpression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:674-680.
- Navrazhina K, Petukhova T, Wildman HF, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma of the scalp treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:887-889.
- Scott BL, Anyanwu CO, Vandergriff T, et al. Endocrine mucin–producing sweat gland carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1498-1500.
- Chang S, Shim SH, Joo M, et al. A case of endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma co-existing with mucinous carcinoma: a case report. Korean J Pathol. 2010;44:97-100.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Bulliard C, Murali R, Maloof A, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:812-816.
- Held L, Ruetten A, Kutzner H, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and molecular analysis of 11 cases with emphasis on MYB immunoexpression. J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:674-680.
- Navrazhina K, Petukhova T, Wildman HF, et al. Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma of the scalp treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:887-889.
- Scott BL, Anyanwu CO, Vandergriff T, et al. Endocrine mucin–producing sweat gland carcinoma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2017;43:1498-1500.
- Chang S, Shim SH, Joo M, et al. A case of endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma co-existing with mucinous carcinoma: a case report. Korean J Pathol. 2010;44:97-100.
- Kamalpour L, Brindise RT, Nodzenski M, et al. Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes after surgery. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150:380-384.
- Bulliard C, Murali R, Maloof A, et al. Endocrine mucin‐producing sweat gland carcinoma: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:812-816.
Practice Points
- Endocrine mucin-producing sweat gland carcinoma and primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma are rare low-grade neoplasms thought to arise from apocrine glands that are morphologically and immunohistochemically analogous to ductal carcinoma in situ and mucinous carcinoma of the breast, respectively.
- Management involves a metastatic workup and either wide local excision with margins greater than 5 mm or Mohs micrographic surgery in anatomically sensitive areas.