User login
New skin papules
A 49-year-old woman with a history of end-stage renal disease, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes, and congestive heart failure visited the hospital for an acute heart failure exacerbation secondary to missed dialysis appointments. On admission, her provider noted that she had tender, pruritic lesions on the extensor surface of her arms. She said they had appeared 2 to 3 months after she started dialysis. She had attempted to control the pain and pruritus with over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone and oral diphenhydramine but nothing provided relief. She was recommended for follow-up at the hospital for further examination and biopsy of one of her lesions.
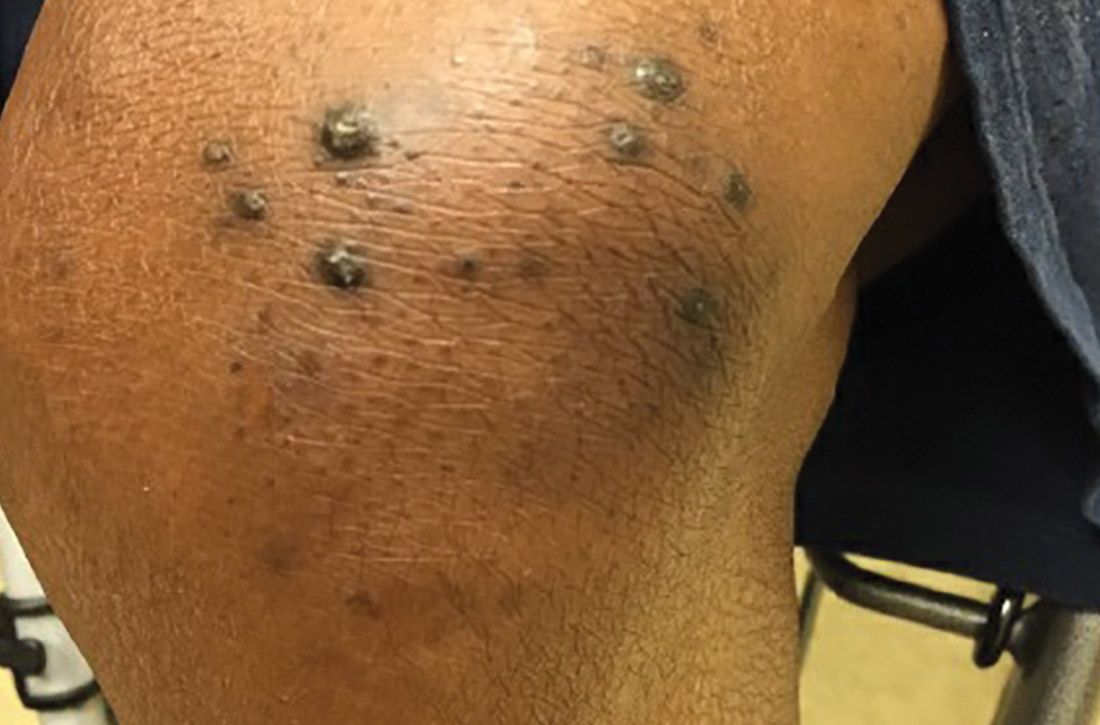
At this follow-up visit, the patient noted that the lesions had spread to her left knee. Multiple firm discrete papules and nodules, with central hyperkeratotic plugs, were noted along the extensor surfaces of her forearms, left extensor knee, and around her ankles (FIGURES 1A and 1B). Some of the lesions were tender. Examination of the rest of her skin was normal. A punch biopsy was obtained.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Kyrle disease
The patient’s end-stage renal disease and type 2 diabetes—along with findings from the physical examination—led us to suspect Kyrle disease. The punch biopsy, as well as the characteristic keratotic plugs (FIGURE 2) within epidermal invagination that was bordered by hyperkeratotic epidermis, confirmed the diagnosis.

Kyrle disease (also known as hyperkeratosis follicularis et follicularis in cutem penetrans) is a rare skin condition. It is 1 of 4 skin conditions that are classified as perforating skin disorders; the other 3 are elastosis perforans serpiginosa, reactive perforating collagenosis, and perforating folliculitis (TABLE1,2).3 Perforating skin disorders share the common characteristic of transepidermal elimination of material from the upper dermis.4 These disorders are typically classified based on the nature of the eliminated material and the type of epidermal disruption.5

There are 2 forms of Kyrle disease: an inherited form often seen in childhood that is not associated with systemic disease and an acquired form that occurs in adulthood, most commonly among women ages 35 to 70 years who have systemic disease.3,4,6 The acquired form of Kyrle disease is associated with diabetes and renal failure, but there is a lack of data on its pathogenesis.7,8
Characteristic findings include discrete pruritic, dry papules and nodules with central keratotic plugs that are occasionally tender. These can manifest over the extensor surface of the extremities, trunk, face, and scalp.4,7,9 Lesions most commonly manifest on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities.
Other conditions that feature pruritic lesions
In addition to the other perforating skin disorders described in the TABLE,1,2 the differential for Kyrle disease includes the following:
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a skin disorder in which the manifestation of extremely pruritic nodules leads to vigorous scratching and secondary infections. These lesions typically have a grouped and symmetrically distributed appearance. They often appear on extensor surfaces of upper and lower extremities.10 PN has no known etiology, but like Kyrle disease, is associated with renal failure. Biopsy can help to distinguish PN from Kyrle disease.
Continue to: Hypertrophic lichen planus
Hypertrophic lichen planus is a pruritic skin disorder characterized by the “6 Ps”: planar, purple, polygonal, pruritic, papules, and plaques. These lesions can mimic the early stages of Kyrle disease.11 However, in the later stages of Kyrle disease, discrete papules with hyperkeratotic plugs develop, whereas large plaques will be seen with lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is an extremely common, yet benign, disorder in which hair follicles become keratinized.12 KP can feature rough papules that are often described as “goosebumps” or having a sandpaper–like appearance. These papules often affect the upper arms. KP usually manifests in adolescents or young adults and tends to improve with age.12 The lesions are typically smaller than those seen in Kyrle disease and are asymptomatic. In addition, KP is not associated with systemic disease.
Target symptoms and any underlying conditions
In patients who have an acquired form of the disease, symptoms may improve by
For patients whose Kyrle disease is inherited or whose underlying condition is not easily treated, there are a number of treatment options to consider. First-line treatment includes topical keratolytics (salicylic acid and urea), topical retinoids, and ultraviolet light therapy.5,7 Systemic retinoids, topical steroids, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, CO2 laser surgery, and surgical excision have also been used with some success.7,14 Oral histamines and emollients also may help to relieve the pruritus. Lesions often recur upon discontinuation of therapy.
Our patient was referred to Dermatology for ultraviolet light therapy. She was also treated with topical 12% ammonium lactate twice daily. Within a few months, she reported improvement of her symptoms.
1. Rapini R. Perforating disorders. Plastic Surgery Key. Published April 22, 2017. Accessed February 18, 2021. https://plasticsurgerykey.com/perforating-disorders/
2. Patterson JW. The perforating disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10:561-581
3. Azad K, Hajirnis K, Sawant S, et al. Kyrle’s disease. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:378-379.
4. Arora K, Hajirnis KA, Sawant S, et al. Perforating disorders of the skin. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2013;56:355-358.
5. Ataseven A, Ozturk P, Kucukosmanoglu I, et al. Kyrle’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014: bcr2013009905.
6. Cunningham SR, Walsh M, Matthews R. Kyrle’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16(pt 1):117-123.
7. Nair PA, Jivani NB, Diwan NG. Kyrle’s disease in a patient of diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure on dialysis. J Family Med Prim Care. 2015;4:284-286.
8. Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT 3rd, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
9. Kolla PK, Desai M, Pathapati RM, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in patients with chronic kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:679619.
10. Lee MR, Shumack S. Prurigo nodularis: a review. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:211-220.
11. Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
12. Thomas M, Khopkar US. Keratosis pilaris revisited: is it more than just a follicular keratosis? Int J Trichology. 2012;4:255-258.
13. Chang P, Fernández V. Acquired perforating disease: report of nine cases. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:874-876.
14. Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729.
A 49-year-old woman with a history of end-stage renal disease, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes, and congestive heart failure visited the hospital for an acute heart failure exacerbation secondary to missed dialysis appointments. On admission, her provider noted that she had tender, pruritic lesions on the extensor surface of her arms. She said they had appeared 2 to 3 months after she started dialysis. She had attempted to control the pain and pruritus with over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone and oral diphenhydramine but nothing provided relief. She was recommended for follow-up at the hospital for further examination and biopsy of one of her lesions.
At this follow-up visit, the patient noted that the lesions had spread to her left knee. Multiple firm discrete papules and nodules, with central hyperkeratotic plugs, were noted along the extensor surfaces of her forearms, left extensor knee, and around her ankles (FIGURES 1A and 1B). Some of the lesions were tender. Examination of the rest of her skin was normal. A punch biopsy was obtained.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Kyrle disease
The patient’s end-stage renal disease and type 2 diabetes—along with findings from the physical examination—led us to suspect Kyrle disease. The punch biopsy, as well as the characteristic keratotic plugs (FIGURE 2) within epidermal invagination that was bordered by hyperkeratotic epidermis, confirmed the diagnosis.

Kyrle disease (also known as hyperkeratosis follicularis et follicularis in cutem penetrans) is a rare skin condition. It is 1 of 4 skin conditions that are classified as perforating skin disorders; the other 3 are elastosis perforans serpiginosa, reactive perforating collagenosis, and perforating folliculitis (TABLE1,2).3 Perforating skin disorders share the common characteristic of transepidermal elimination of material from the upper dermis.4 These disorders are typically classified based on the nature of the eliminated material and the type of epidermal disruption.5

There are 2 forms of Kyrle disease: an inherited form often seen in childhood that is not associated with systemic disease and an acquired form that occurs in adulthood, most commonly among women ages 35 to 70 years who have systemic disease.3,4,6 The acquired form of Kyrle disease is associated with diabetes and renal failure, but there is a lack of data on its pathogenesis.7,8
Characteristic findings include discrete pruritic, dry papules and nodules with central keratotic plugs that are occasionally tender. These can manifest over the extensor surface of the extremities, trunk, face, and scalp.4,7,9 Lesions most commonly manifest on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities.
Other conditions that feature pruritic lesions
In addition to the other perforating skin disorders described in the TABLE,1,2 the differential for Kyrle disease includes the following:
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a skin disorder in which the manifestation of extremely pruritic nodules leads to vigorous scratching and secondary infections. These lesions typically have a grouped and symmetrically distributed appearance. They often appear on extensor surfaces of upper and lower extremities.10 PN has no known etiology, but like Kyrle disease, is associated with renal failure. Biopsy can help to distinguish PN from Kyrle disease.
Continue to: Hypertrophic lichen planus
Hypertrophic lichen planus is a pruritic skin disorder characterized by the “6 Ps”: planar, purple, polygonal, pruritic, papules, and plaques. These lesions can mimic the early stages of Kyrle disease.11 However, in the later stages of Kyrle disease, discrete papules with hyperkeratotic plugs develop, whereas large plaques will be seen with lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is an extremely common, yet benign, disorder in which hair follicles become keratinized.12 KP can feature rough papules that are often described as “goosebumps” or having a sandpaper–like appearance. These papules often affect the upper arms. KP usually manifests in adolescents or young adults and tends to improve with age.12 The lesions are typically smaller than those seen in Kyrle disease and are asymptomatic. In addition, KP is not associated with systemic disease.
Target symptoms and any underlying conditions
In patients who have an acquired form of the disease, symptoms may improve by
For patients whose Kyrle disease is inherited or whose underlying condition is not easily treated, there are a number of treatment options to consider. First-line treatment includes topical keratolytics (salicylic acid and urea), topical retinoids, and ultraviolet light therapy.5,7 Systemic retinoids, topical steroids, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, CO2 laser surgery, and surgical excision have also been used with some success.7,14 Oral histamines and emollients also may help to relieve the pruritus. Lesions often recur upon discontinuation of therapy.
Our patient was referred to Dermatology for ultraviolet light therapy. She was also treated with topical 12% ammonium lactate twice daily. Within a few months, she reported improvement of her symptoms.
A 49-year-old woman with a history of end-stage renal disease, uncontrolled type 2 diabetes, and congestive heart failure visited the hospital for an acute heart failure exacerbation secondary to missed dialysis appointments. On admission, her provider noted that she had tender, pruritic lesions on the extensor surface of her arms. She said they had appeared 2 to 3 months after she started dialysis. She had attempted to control the pain and pruritus with over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone and oral diphenhydramine but nothing provided relief. She was recommended for follow-up at the hospital for further examination and biopsy of one of her lesions.
At this follow-up visit, the patient noted that the lesions had spread to her left knee. Multiple firm discrete papules and nodules, with central hyperkeratotic plugs, were noted along the extensor surfaces of her forearms, left extensor knee, and around her ankles (FIGURES 1A and 1B). Some of the lesions were tender. Examination of the rest of her skin was normal. A punch biopsy was obtained.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Kyrle disease
The patient’s end-stage renal disease and type 2 diabetes—along with findings from the physical examination—led us to suspect Kyrle disease. The punch biopsy, as well as the characteristic keratotic plugs (FIGURE 2) within epidermal invagination that was bordered by hyperkeratotic epidermis, confirmed the diagnosis.

Kyrle disease (also known as hyperkeratosis follicularis et follicularis in cutem penetrans) is a rare skin condition. It is 1 of 4 skin conditions that are classified as perforating skin disorders; the other 3 are elastosis perforans serpiginosa, reactive perforating collagenosis, and perforating folliculitis (TABLE1,2).3 Perforating skin disorders share the common characteristic of transepidermal elimination of material from the upper dermis.4 These disorders are typically classified based on the nature of the eliminated material and the type of epidermal disruption.5

There are 2 forms of Kyrle disease: an inherited form often seen in childhood that is not associated with systemic disease and an acquired form that occurs in adulthood, most commonly among women ages 35 to 70 years who have systemic disease.3,4,6 The acquired form of Kyrle disease is associated with diabetes and renal failure, but there is a lack of data on its pathogenesis.7,8
Characteristic findings include discrete pruritic, dry papules and nodules with central keratotic plugs that are occasionally tender. These can manifest over the extensor surface of the extremities, trunk, face, and scalp.4,7,9 Lesions most commonly manifest on the extensor surfaces of the lower extremities.
Other conditions that feature pruritic lesions
In addition to the other perforating skin disorders described in the TABLE,1,2 the differential for Kyrle disease includes the following:
Prurigo nodularis (PN) is a skin disorder in which the manifestation of extremely pruritic nodules leads to vigorous scratching and secondary infections. These lesions typically have a grouped and symmetrically distributed appearance. They often appear on extensor surfaces of upper and lower extremities.10 PN has no known etiology, but like Kyrle disease, is associated with renal failure. Biopsy can help to distinguish PN from Kyrle disease.
Continue to: Hypertrophic lichen planus
Hypertrophic lichen planus is a pruritic skin disorder characterized by the “6 Ps”: planar, purple, polygonal, pruritic, papules, and plaques. These lesions can mimic the early stages of Kyrle disease.11 However, in the later stages of Kyrle disease, discrete papules with hyperkeratotic plugs develop, whereas large plaques will be seen with lichen planus.
Keratosis pilaris (KP) is an extremely common, yet benign, disorder in which hair follicles become keratinized.12 KP can feature rough papules that are often described as “goosebumps” or having a sandpaper–like appearance. These papules often affect the upper arms. KP usually manifests in adolescents or young adults and tends to improve with age.12 The lesions are typically smaller than those seen in Kyrle disease and are asymptomatic. In addition, KP is not associated with systemic disease.
Target symptoms and any underlying conditions
In patients who have an acquired form of the disease, symptoms may improve by
For patients whose Kyrle disease is inherited or whose underlying condition is not easily treated, there are a number of treatment options to consider. First-line treatment includes topical keratolytics (salicylic acid and urea), topical retinoids, and ultraviolet light therapy.5,7 Systemic retinoids, topical steroids, cryotherapy, electrosurgery, CO2 laser surgery, and surgical excision have also been used with some success.7,14 Oral histamines and emollients also may help to relieve the pruritus. Lesions often recur upon discontinuation of therapy.
Our patient was referred to Dermatology for ultraviolet light therapy. She was also treated with topical 12% ammonium lactate twice daily. Within a few months, she reported improvement of her symptoms.
1. Rapini R. Perforating disorders. Plastic Surgery Key. Published April 22, 2017. Accessed February 18, 2021. https://plasticsurgerykey.com/perforating-disorders/
2. Patterson JW. The perforating disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10:561-581
3. Azad K, Hajirnis K, Sawant S, et al. Kyrle’s disease. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:378-379.
4. Arora K, Hajirnis KA, Sawant S, et al. Perforating disorders of the skin. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2013;56:355-358.
5. Ataseven A, Ozturk P, Kucukosmanoglu I, et al. Kyrle’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014: bcr2013009905.
6. Cunningham SR, Walsh M, Matthews R. Kyrle’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16(pt 1):117-123.
7. Nair PA, Jivani NB, Diwan NG. Kyrle’s disease in a patient of diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure on dialysis. J Family Med Prim Care. 2015;4:284-286.
8. Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT 3rd, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
9. Kolla PK, Desai M, Pathapati RM, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in patients with chronic kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:679619.
10. Lee MR, Shumack S. Prurigo nodularis: a review. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:211-220.
11. Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
12. Thomas M, Khopkar US. Keratosis pilaris revisited: is it more than just a follicular keratosis? Int J Trichology. 2012;4:255-258.
13. Chang P, Fernández V. Acquired perforating disease: report of nine cases. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:874-876.
14. Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729.
1. Rapini R. Perforating disorders. Plastic Surgery Key. Published April 22, 2017. Accessed February 18, 2021. https://plasticsurgerykey.com/perforating-disorders/
2. Patterson JW. The perforating disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10:561-581
3. Azad K, Hajirnis K, Sawant S, et al. Kyrle’s disease. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2013;4:378-379.
4. Arora K, Hajirnis KA, Sawant S, et al. Perforating disorders of the skin. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2013;56:355-358.
5. Ataseven A, Ozturk P, Kucukosmanoglu I, et al. Kyrle’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014: bcr2013009905.
6. Cunningham SR, Walsh M, Matthews R. Kyrle’s disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16(pt 1):117-123.
7. Nair PA, Jivani NB, Diwan NG. Kyrle’s disease in a patient of diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure on dialysis. J Family Med Prim Care. 2015;4:284-286.
8. Hurwitz RM, Melton ME, Creech FT 3rd, et al. Perforating folliculitis in association with hemodialysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 1982;4:101-108.
9. Kolla PK, Desai M, Pathapati RM, et al. Cutaneous manifestations in patients with chronic kidney disease on maintenance hemodialysis. ISRN Dermatol. 2012;2012:679619.
10. Lee MR, Shumack S. Prurigo nodularis: a review. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:211-220.
11. Usatine RP, Tinitigan M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:53-60.
12. Thomas M, Khopkar US. Keratosis pilaris revisited: is it more than just a follicular keratosis? Int J Trichology. 2012;4:255-258.
13. Chang P, Fernández V. Acquired perforating disease: report of nine cases. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:874-876.
14. Wagner G, Sachse MM. Acquired reactive perforating dermatosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:723-729.
FDA approves voclosporin for lupus nephritis
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved voclosporin (Lupkynis) for the treatment of lupus nephritis, according to a Jan. 22 press release from manufacturer Aurinia Pharmaceuticals.
Lupkynis is a calcineurin-inhibitor immunosuppressant, and is the first oral medication to show effectiveness in lupus nephritis, according to the company. The drug is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active lupus nephritis in combination with a background immunosuppressive therapy regimen, according to the drug label, which also has a boxed warning describing the increased risk of infections and malignancies, including lymphoma.
The approval of voclosporin was based on data from two studies, the AURORA phase 3 study and the AURA-LV phase 2 study. The studies included 533 adults with lupus nephritis who were randomized to 23.7 mg or placebo of voclosporin twice daily in the form of oral capsules, or placebo capsules, in addition to standard of care (mycophenolate mofetil plus low-dose glucocorticoids).
In the AURORA phase 3 study of 357 patients, close to twice as many patients in the treatment group showed a complete renal response, compared with the placebo group after 1 year (40.8% vs. 22.5%). In addition, patients treated with voclosporin more quickly achieved a significant reduction in urine protein to creatinine ratio, compared with the placebo patients (169 days vs. 372 days).
Severe adverse events were similar between the groups, including the most common complication of infection (10.1% and 11.2% for voclosporin and control groups, respectively). Other adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of the study participants included a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, hypertension, diarrhea, headache, anemia, cough, urinary tract infection, upper abdominal pain, dyspepsia, alopecia, renal impairment, abdominal pain, mouth ulceration, fatigue, tremor, acute kidney injury, and decreased appetite, according to the company press release.
Full clinical trial information for the AURORA study is available here.
Severe renal arteriosclerosis may indicate cardiovascular risk in lupus nephritis
Severe renal arteriosclerosis was associated with a ninefold increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with lupus nephritis, based on data from an observational study of 189 individuals.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) has traditionally been thought to be a late complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but this has been challenged in recent population-based studies of patients with SLE and lupus nephritis (LN) that indicated an early and increased risk of ASCVD at the time of diagnosis. However, it is unclear which early risk factors may predispose patients to ASCVD, Shivani Garg, MD, of the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Arthritis Care & Research.
In patients with IgA nephropathy and renal transplantation, previous studies have shown that severe renal arteriosclerosis (r-ASCL) based on kidney biopsies at the time of diagnosis predicts ASCVD, but “a few studies including LN biopsies failed to report a similar association between the presence of severe r-ASCL and ASCVD occurrence,” possibly because of underreporting of r-ASCL. Dr. Garg and colleagues also noted the problem of underreporting of r-ASCL in their own previous study of its prevalence in LN patients at the time of diagnosis.
To get a more detailed view of how r-ASCL may be linked to early occurrence of ASCVD in LN patients, Dr. Garg and coauthors identified 189 consecutive patients with incident LN who underwent diagnostic biopsies between 1994 and 2017. The median age of the patients was 25 years, 78% were women, and 73% were white. The researchers developed a composite score for r-ASCL severity based on reported and overread biopsies.
Overall, 31% of the patients had any reported r-ASCL, and 7% had moderate-severe r-ASCL. After incorporating systematically reexamined r-ASCL grades, the prevalence of any and moderate-severe r-ASCL increased to 39% and 12%, respectively.
Based on their composite of reported and overread r-ASCL grade, severe r-ASCL in diagnostic LN biopsies was associated with a ninefold increased risk of ASCVD.
The researchers identified 22 incident ASCVD events over an 11-year follow-up for an overall 12% incidence of ASCVD in LN. ASCVD was defined as ischemic heart disease (including myocardial infarction, coronary artery revascularization, abnormal stress test, abnormal angiogram, and events documented by a cardiologist); stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA); and peripheral vascular disease. Incident ASCVD was defined as the first ASCVD event between 1 and 10 years after LN diagnosis.
The most common ASCVD events were stroke or TIA (12 patients), events related to ischemic heart disease (7 patients), and events related to peripheral vascular disease (3 patients).
Lack of statin use
The researchers also hypothesized that the presence of gaps in statin use among eligible LN patients would be present in their study population. “Among the 20 patients with incident ASCVD events after LN diagnosis in our cohort, none was on statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis,” the researchers said, noting that current guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (now known as the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) recommend initiating statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis in all patients who have hyperlipidemia and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage ≥3. “Further, 11 patients (55%) met high-risk criteria (hyperlipidemia and CKD stage ≥3) to implement statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis, yet only one patient (9%) was initiated on statin therapy.” In addition, patients with stage 3 or higher CKD were more likely to develop ASCVD than patients without stage 3 or higher CKD, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the majority white study population, the ability to overread only 25% of the biopsies, and the lack of data on the potential role of chronic lesions in ASCVD, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a validated LN cohort, and the data provide “the basis to establish severe composite r-ASCL as a predictor of ASCVD events using a larger sample size in different cohorts,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Severe renal arteriosclerosis was associated with a ninefold increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with lupus nephritis, based on data from an observational study of 189 individuals.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) has traditionally been thought to be a late complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but this has been challenged in recent population-based studies of patients with SLE and lupus nephritis (LN) that indicated an early and increased risk of ASCVD at the time of diagnosis. However, it is unclear which early risk factors may predispose patients to ASCVD, Shivani Garg, MD, of the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Arthritis Care & Research.
In patients with IgA nephropathy and renal transplantation, previous studies have shown that severe renal arteriosclerosis (r-ASCL) based on kidney biopsies at the time of diagnosis predicts ASCVD, but “a few studies including LN biopsies failed to report a similar association between the presence of severe r-ASCL and ASCVD occurrence,” possibly because of underreporting of r-ASCL. Dr. Garg and colleagues also noted the problem of underreporting of r-ASCL in their own previous study of its prevalence in LN patients at the time of diagnosis.
To get a more detailed view of how r-ASCL may be linked to early occurrence of ASCVD in LN patients, Dr. Garg and coauthors identified 189 consecutive patients with incident LN who underwent diagnostic biopsies between 1994 and 2017. The median age of the patients was 25 years, 78% were women, and 73% were white. The researchers developed a composite score for r-ASCL severity based on reported and overread biopsies.
Overall, 31% of the patients had any reported r-ASCL, and 7% had moderate-severe r-ASCL. After incorporating systematically reexamined r-ASCL grades, the prevalence of any and moderate-severe r-ASCL increased to 39% and 12%, respectively.
Based on their composite of reported and overread r-ASCL grade, severe r-ASCL in diagnostic LN biopsies was associated with a ninefold increased risk of ASCVD.
The researchers identified 22 incident ASCVD events over an 11-year follow-up for an overall 12% incidence of ASCVD in LN. ASCVD was defined as ischemic heart disease (including myocardial infarction, coronary artery revascularization, abnormal stress test, abnormal angiogram, and events documented by a cardiologist); stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA); and peripheral vascular disease. Incident ASCVD was defined as the first ASCVD event between 1 and 10 years after LN diagnosis.
The most common ASCVD events were stroke or TIA (12 patients), events related to ischemic heart disease (7 patients), and events related to peripheral vascular disease (3 patients).
Lack of statin use
The researchers also hypothesized that the presence of gaps in statin use among eligible LN patients would be present in their study population. “Among the 20 patients with incident ASCVD events after LN diagnosis in our cohort, none was on statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis,” the researchers said, noting that current guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (now known as the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) recommend initiating statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis in all patients who have hyperlipidemia and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage ≥3. “Further, 11 patients (55%) met high-risk criteria (hyperlipidemia and CKD stage ≥3) to implement statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis, yet only one patient (9%) was initiated on statin therapy.” In addition, patients with stage 3 or higher CKD were more likely to develop ASCVD than patients without stage 3 or higher CKD, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the majority white study population, the ability to overread only 25% of the biopsies, and the lack of data on the potential role of chronic lesions in ASCVD, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a validated LN cohort, and the data provide “the basis to establish severe composite r-ASCL as a predictor of ASCVD events using a larger sample size in different cohorts,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Severe renal arteriosclerosis was associated with a ninefold increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with lupus nephritis, based on data from an observational study of 189 individuals.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) has traditionally been thought to be a late complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but this has been challenged in recent population-based studies of patients with SLE and lupus nephritis (LN) that indicated an early and increased risk of ASCVD at the time of diagnosis. However, it is unclear which early risk factors may predispose patients to ASCVD, Shivani Garg, MD, of the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues wrote in a study published in Arthritis Care & Research.
In patients with IgA nephropathy and renal transplantation, previous studies have shown that severe renal arteriosclerosis (r-ASCL) based on kidney biopsies at the time of diagnosis predicts ASCVD, but “a few studies including LN biopsies failed to report a similar association between the presence of severe r-ASCL and ASCVD occurrence,” possibly because of underreporting of r-ASCL. Dr. Garg and colleagues also noted the problem of underreporting of r-ASCL in their own previous study of its prevalence in LN patients at the time of diagnosis.
To get a more detailed view of how r-ASCL may be linked to early occurrence of ASCVD in LN patients, Dr. Garg and coauthors identified 189 consecutive patients with incident LN who underwent diagnostic biopsies between 1994 and 2017. The median age of the patients was 25 years, 78% were women, and 73% were white. The researchers developed a composite score for r-ASCL severity based on reported and overread biopsies.
Overall, 31% of the patients had any reported r-ASCL, and 7% had moderate-severe r-ASCL. After incorporating systematically reexamined r-ASCL grades, the prevalence of any and moderate-severe r-ASCL increased to 39% and 12%, respectively.
Based on their composite of reported and overread r-ASCL grade, severe r-ASCL in diagnostic LN biopsies was associated with a ninefold increased risk of ASCVD.
The researchers identified 22 incident ASCVD events over an 11-year follow-up for an overall 12% incidence of ASCVD in LN. ASCVD was defined as ischemic heart disease (including myocardial infarction, coronary artery revascularization, abnormal stress test, abnormal angiogram, and events documented by a cardiologist); stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA); and peripheral vascular disease. Incident ASCVD was defined as the first ASCVD event between 1 and 10 years after LN diagnosis.
The most common ASCVD events were stroke or TIA (12 patients), events related to ischemic heart disease (7 patients), and events related to peripheral vascular disease (3 patients).
Lack of statin use
The researchers also hypothesized that the presence of gaps in statin use among eligible LN patients would be present in their study population. “Among the 20 patients with incident ASCVD events after LN diagnosis in our cohort, none was on statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis,” the researchers said, noting that current guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism (now known as the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology) recommend initiating statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis in all patients who have hyperlipidemia and chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage ≥3. “Further, 11 patients (55%) met high-risk criteria (hyperlipidemia and CKD stage ≥3) to implement statin therapy at the time of LN diagnosis, yet only one patient (9%) was initiated on statin therapy.” In addition, patients with stage 3 or higher CKD were more likely to develop ASCVD than patients without stage 3 or higher CKD, they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the majority white study population, the ability to overread only 25% of the biopsies, and the lack of data on the potential role of chronic lesions in ASCVD, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the use of a validated LN cohort, and the data provide “the basis to establish severe composite r-ASCL as a predictor of ASCVD events using a larger sample size in different cohorts,” they said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Tactics to prevent or slow progression of CKD in patients with diabetes
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant comorbidity of diabetes mellitus. The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) of the National Kidney Foundation defines CKD as the presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for ≥ 3 months. CKD caused by diabetes is called diabetic kidney disease (DKD), which is 1 of 3 principal microvascular complications of diabetes. DKD can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring kidney replacement therapy, and is the leading cause of CKD and ESRD in the United States.1-3 Studies have also shown that, particularly in patients with diabetes, CKD considerably increases the risk of cardiovascular events, which often occur prior to ESRD.1,4
This article provides the latest recommendations for evaluating and managing DKD to help you prevent or slow its progression.
Defining and categorizing diabetic kidney disease
CKD is defined as persistently elevated excretion of urinary albumin (albuminuria) and decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), or as the presence of signs of progressive kidney damage.5,6 DKD, also known as diabetic nephropathy, is CKD attributed to long-term diabetes. A patient’s eGFR is the established basis for assignment to a stage (1, 2, 3a, 3b, 4, or 5) of CKD (TABLE 17) and, along with the category of albuminuria (A1, A2, or A3), can indicate prognosis.
Taking its toll in diabetes
As many as 40% of patients with diabetes develop DKD.8-10 Most studies of DKD have been conducted in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), because the time of clinical onset is typically known.
Type 1 diabetes. DKD usually occurs 10 to 15 years, or later, after the onset of diabetes.6 As many as 30% of people with T1D have albuminuria approximately 15 years after onset of diabetes; almost one-half of those develop DKD.5,11 After approximately 22.5 years without albuminuria, patients with T1D have approximately a 1% annual risk of DKD.12
Type 2 diabetes (T2D). DKD is often present at diagnosis, likely due to a delay in diagnosis and briefer clinical exposure, compared to T1D. Albuminuria has been reported in as many as 40% of patients with T2D approximately 10 years after onset of diabetes.12,13
Multiple risk factors with no standout “predictor”
Genetic susceptibility, ethnicity, glycemic control, smoking, blood pressure (BP), and the eGFR have been identified as risk factors for renal involvement in diabetes; obesity, oral contraceptives, and age can also contribute. Although each risk factor increases the risk of DKD, no single factor is adequately predictive. Moderately increased albuminuria, the earliest sign of DKD, is associated with progressive nephropathy.12
Continue to: How great is the risk?
How great is the risk? From disease onset to proteinuria and from proteinuria to ESRD, the risk of DKD in T1D and T2D is similar. With appropriate treatment, albuminuria can regress, and the risk of ESRD can be < 20% at 10 years in T1D.12 As in T1D, good glycemic control might result in regression of albuminuria in T2D.14
For unknown reasons, the degree of albuminuria can exist independent of the progression of DKD. Factors responsible for a progressive decline in eGFR in DKD without albuminuria are unknown.12,15
Patient evaluation with an eye toward comorbidities
A comprehensive initial medical evaluation for DKD includes a review of microvascular complications; visits to specialists; lifestyle and behavior patterns (eg, diet, sleep, substance use, and social support); and medication adherence, adverse drug effects, and alternative medicines. Although DKD is often a clinical diagnosis, it can be ruled in by persistent albuminuria or decreased eGFR, or both, in established diabetes or diabetic retinopathy when other causes are unlikely (see “Recommended DKD screening protocol,” below).
Screening for mental health conditions and barriers to self-management is also key.6
Comorbidities, of course, can complicate disease management in patients with diabetes.16-20 Providers and patients therefore need to be aware of potential diabetic comorbidities. For example, DKD and even moderately increased albuminuria significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).12 Other possible comorbidities include (but are not limited to) nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, fracture, hearing impairment, cancer (eg, liver, pancreas, endometrium, colon, rectum, breast, and bladder), pancreatitis, hypogonadism, obstructive sleep apnea, periodontal disease, anxiety, depression, and eating disorders.6
Continue to: Recommended DKD screening protocol
Recommended DKD screening protocol
In all cases of T2D, in cases of T1D of ≥ 5 years’ duration, and in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension, perform annual screening for albuminuria, an elevated creatinine level, and a decline in eGFR.
To confirm the diagnosis of DKD, at least 2 of 3 urine specimens must demonstrate an elevated urinary albumin:creatinine ratio (UACR) over a 3- to 6-month period.21 Apart from renal damage, exercise within 24 hours before specimen collection, infection, fever, congestive heart failure, hyperglycemia, menstruation, and hypertension can elevate the UACR.6
Levels of the UACR are established as follows22:
- Normal UACR is defined as < 30 milligrams of albumin per gram of creatinine (expressed as “mg/g”).
- Increased urinary albumin excretion is defined as ≥ 30 mg/g.
- Moderately increased albuminuria, a predictor of potential nephropathy, is the excretion of 30 to 300 mg/g.
- Severely increased albuminuria is excretion > 300 mg/g; it is often followed by a gradual decline in eGFR that, without treatment, eventually leads to ESRD.
The rate of decline in eGFR once albuminuria is severely increased is equivalent in T1D and T2D.12 Without intervention, the time from severely increased albuminuria to ESRD in T1D and T2D averages approximately 6 or 7 years.
Clinical features
DKD is typically a clinical diagnosis seen in patients with longstanding diabetes, albuminuria, retinopathy, or a reduced eGFR in the absence of another primary cause of kidney damage. In patients with T1D and DKD, signs of retinopathy and neuropathy are almost always present at diagnosis, unless a diagnosis is made early in the course of diabetes.12 Therefore, the presence of retinopathy suggests that diabetes is the likely cause of CKD.
Continue to: The presence of microvascular disease...
The presence of microvascular disease in patients with T2D and DKD is less predictable.12 In T2D patients who do not have retinopathy, consider causes of CKD other than DKD. Features suggesting that the cause of CKD is an underlying condition other than diabetes are rapidly increasing albuminuria or decreasing eGFR; urinary sediment comprising red blood cells or white blood cells; and nephrotic syndrome.6
As the prevalence of diabetes increases, it has become more common to diagnose DKD by eGFR without albuminuria—underscoring the importance of routine monitoring of eGFR in patients with diabetes.6
Sources of expert guidance. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation23 is preferred for calculating eGFR from serum creatinine: An eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 is considered abnormal.3,12 At these rates, the prevalence of complications related to CKD rises and screening for complications becomes necessary.
A more comprehensive classification of the stages of CKD, incorporating albuminuria and progression of CKD, has been recommended by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO).7 Because eGFR and excretion of albumin vary, abnormal test results need to be verified over time to stage the degree of CKD.3,12 Kidney damage often manifests as albuminuria, but also as hematuria, other types of abnormal urinary sediment, radiographic abnormalities, and other abnormal presentations.
Management
Nutritional factors
Excessive protein intake has been shown to increase albuminuria, worsen renal function, and increase CVD mortality in DKD.24-26 Therefore, daily dietary protein intake of 0.8 g/kg body weight is recommended for patients who are not on dialysis.3 Patients on dialysis might require higher protein intake to preserve muscle mass caused by protein-energy wasting, which is common in dialysis patients.6
Continue to: Low sodium intake
Low sodium intake in CKD patients has been shown to decrease BP and thus slow the progression of renal disease and lower the risk of CVD. The recommended dietary sodium intake in CKD patients is 1500-3000 mg/d.3
Low potassium intake. Hyperkalemia is a serious complication of CKD. A low-potassium diet is recommended in ESRD patients who have a potassium level > 5.5 mEq/L.6
Blood pressure
Preventing and treating hypertension is critical to slowing the progression of CKD and reducing cardiovascular risk. BP should be measured at every clinic visit. Aside from lifestyle changes, medication might be needed to reach target BP.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a BP goal of ≤ 140/90 mm Hg for hypertensive patients with diabetes, although they do state that a lower BP target (≤ 130/80 mm Hg) might be more appropriate for patients with DKD.27
The American College of Cardiology recommends that hypertensive patients with CKD have a BP target of ≤ 130/80 mm Hg.28
Continue to: ACE inhibitors and ARBs
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have renoprotective benefits. These agents are recommended as first-line medications for patients with diabetes, hypertension, and an eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and a UACR > 300 mg/g.29-31 Evidence also supports their use when the UACR is 30 to 299 mg/g.
Studies have shown that, in patients with DKD, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can slow the progression of renal disease.29,30,32 There is no difference between ACE inhibitors and ARBs in their effectiveness for preventing progression of DKD.6 There is no added benefit in combining an ACE inhibitor and an ARB33; notably, combination ACE inhibitor and ARB therapy can increase the risk of adverse events, such as hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury, especially in patients with DKD.33
There is no evidence for starting an ACE inhibitor or ARB to prevent CKD in patients with diabetes who are not hypertensive.5
ACE inhibitors and ARBs should be used with caution in women of childbearing age, who should use a reliable form of contraception if taking one of these drugs.
Diuretics. Thiazide-type and loop diuretics might potentiate the positive effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs. KDOQI guidelines recommend that, in patients who require a second agent to control BP, a diuretic should be considered in combination with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.20 A loop diuretic is preferred if the eGFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Continue to: Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers
Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers (CCBs), such as diltiazem and verapamil, have been shown to be more effective then dihydrophyridine CCBs, such as amlodipine and nifedipine, in slowing the progression of renal disease because of their antiproteinuric effects. However, the antiproteinuric effects of nondihydropyridine CCBs are not as strong as those of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and these drugs do not appear to potentiate the effects of an ACE inhibitor or ARB when used in combination.20
Nondihydropyridine CCBs might be a reasonable alternative in patients who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in combination with an ACE inhibitor or ARB have been demonstrated to reduce albuminuria in short-term studies.34,35
Glycemic levels
Studies conducted in patients with T1D, and others in patients with T2D, have shown that tight glycemic control can delay the onset and slow the progression of albuminuria and a decline in the eGFR.10,36-39 The target glycated hemoglobin (A1C) should be < 7% to prevent or slow progression of DKD.40 However, patients with DKD have an increased risk of hypoglycemic events and increased mortality with more intensive glycemic control.40,41 Given those findings, some patients with DKD and significant comorbidities, ESRD, or limited life expectancy might need to have an A1C target set at 8%.6,42
Adjustments to antidiabetes medications in DKD
In patients with stages 3 to 5 DKD, several common antidiabetic medications might need to be adjusted or discontinued because they decrease creatinine clearance.
Continue to: First-generation sulfonylureas
First-generation sulfonylureas should be avoided in DKD. Glipizide and gliclazide are preferred among second-generation sulfonylureas because they do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia in DKD patients, although patients taking these medications still require close monitoring of their blood glucose level.20
Metformin. In 2016, recommendations changed for the use of metformin in patients with DKD: The eGFR, not the serum creatinine level, should guide treatment.43 Metformin can be used safely in patients with (1) an eGFR of < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and (2) an eGFR of 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with close monitoring. Metformin should not be initiated if the eGFR is < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.43
Antidiabetes medications with direct effect on the kidney
Several antidiabetes medications have a direct effect on the kidney apart from their effect on the blood glucose level.
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to reduce albuminuria and slow the decrease of eGFR independent of glycemic control. In addition, SGLT2 inhibitors have also been shown to have cardiovascular benefits in patients with DKD.44,45
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have been shown to delay and decrease the progression of DKD.46-48 Also, similar to what is seen with SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 agonists have demonstrable cardiovascular benefit in patients with DKD.46,48
Continue to: Dyslipidemia and DKD
Dyslipidemia and DKD
Because the risk of CVD is increased in patients with DKD, addressing other modifiable risk factors, including dyslipidemia, is recommended in these patients. Patients with diabetes and stages 1 to 4 DKD should be treated with a high-intensity statin or a combination of a statin and ezetimibe.49,50
If a patient is taking a statin and starting dialysis, it’s important to discuss with him or her whether to continue the statin, based on perceived benefits and risks. It is not recommended that statins be initiated in patients on dialysis unless there is a specific cardiovascular indication for doing so. Risk reduction with a statin has been shown to be significantly less in dialysis patients than in patients who are not being treated with dialysis.49
Complications of CKD
Anemia is a common complication of CKD. KDIGO recommends measuring the hemoglobin concentration annually in DKD stage 3 patients without anemia; at least every 6 months in stage 4 patients; and at least every 3 months in stage 5. DKD patients with anemia should have additional laboratory testing: the absolute reticulocyte count, serum ferritin, serum transferrin saturation, vitamin B12, and folate.51
Mineral and bone disorder should be screened for in patients with DKD. TABLE 252 outlines when clinical laboratory tests should be ordered to assess for mineral bone disease.
When to refer to a nephrologist
Refer patients with stage 4 or 5 CKD (eGFR, ≤ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) to a nephrologist for discussion of kidney replacement therapy.6 Patients with stage 3a CKD and severely increased albuminuria or with stage 3b CKD and moderately or severely increased albuminuria should also be referred to a nephrologist for intervention to delay disease progression.
Continue to: Identifying the need for early referral...
Identifying the need for early referral to a nephrologist has been shown to reduce the cost, and improve the quality, of care.53 Other indications for earlier referral include uncertainty about the etiology of renal disease, persistent or severe albuminuria, persistent hematuria, a rapid decline in eGFR, and acute kidney injury. Additionally, referral at an earlier stage of DKD might be needed to assist with complications associated with DKD, such as anemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, mineral and bone disorder, resistant hypertension, fluid overload, and electrolyte disturbances.6
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Colleen Colbert, PhD, and Iqbal Ahmad, PhD, for their review and critique of the manuscript of this article. They also thank Christopher Babiuch, MD, for his guidance in the preparation of the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Faraz Ahmad, MD, MPH, Care Point East Family Medicine, 543 Taylor Avenue, 2nd floor, Columbus, OH 43203; faraz. [email protected].
1. Radbill B, Murphy B, LeRoith D. Rationale and strategies for early detection and management of diabetic kidney disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:1373-1381.
2. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71(3 suppl 1):A7.
3. Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:510-533.
4. Fox CS, Matsushita K, Woodward M, et al; . Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;380:1662-1673.
5. Orchard TJ, Dorman JS, Maser RE, et al. Prevalence of complications in IDDM by sex and duration. Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study II. Diabetes. 1990;39:1116-1124.
6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(suppl 1):S1-S159. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/Supplement_1
7. National Kidney Foundation. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1-150. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf
8. Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. 2016;316:602-610.
9. de Boer IH, Rue TC, Hall YN, et al. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2011;305:2532-2539.
10. de Boer IH; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Kidney disease and related findings in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:24-30.
11. Stanton RC. Clinical challenges in diagnosis and management of diabetic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(2 suppl 2):S3-S21.
12. Mottl AK, Tuttle KR. Diabetic kidney disease: Pathogenesis and epidemiology. UpToDate. Updated August 19, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/diabetic-kidney-disease-pathogenesis-and-epidemiology
13. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 2 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated November 3, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-2-diabetes-mellitus
14. Bandak G, Sang Y, Gasparini A, et al. Hyperkalemia after initiating renin-angiotensin system blockade: the Stockholm Creatinine Measurements (SCREAM) Project. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e005428.
15. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(3 suppl 1):A7-A8.
16. Nilsson E, Gasparini A, Ärnlöv J, et al. Incidence and determinants of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in a large healthcare system. Int J Cardiol. 2017;245:277-284.
17. de Boer IH, Gao X, Cleary PA, et al; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Research Group. Albuminuria changes and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 1 diabetes: The DCCT/EDIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1969-1977.
18. Sumida K, Molnar MZ, Potukuchi PK, et al. Changes in albuminuria and subsequent risk of incident kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12:1941-1949.
19. Borch-Johnsen K, Wenzel H, Viberti GC, et al. Is screening and intervention for microalbuminuria worthwhile in patient with insulin dependent diabetes? BMJ. 1993;306:1722-1725.
20. KDOQI. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(2 suppl 2):S12-154.
21. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 1 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated December 3, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-1-diabetes-mellitus
22. Delanaye P, Glassock RJ, Pottel H, et al. An age-calibrated definition of chronic kidney disease: rationale and benefits. Clin Biochem Rev. 2016;37:17-26.
23. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, et al; , A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:604-612.
24. Wrone EM, Carnethon MR, Palaniappan L, et al; . Association of dietary protein intake and microalbuminuria in healthy adults: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:580-587.
25. Knight EL, Stampfer MJ, Hankinson SE, et al. The impact of protein intake on renal function decline in women with normal renal function or mild renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:460-467.
26. Bernstein AM, Sun Q, Hu FB, et al. Major dietary protein sources and risk of coronary heart disease in women. Circulation. 2010;122:876-883.
27. de Boer, IH, Bangalore S, Benetos A, et al. Diabetes and hypertension: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1273-1284.
28. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:e127-e248.
29. Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al; Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861-869.
30. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, et al. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456-1462.
31. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355;253-259.
32. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, et al; . Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851-860.
33. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, et al; . Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892-1903.
34. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, et al; . Effect of finerenone on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314:884-894.
35. Filippatos G, Anker SD, M, et al. Randomized controlled study of finerenone vs. eplerenone in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2105-2114.
36. The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560-2572.
37. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, et al; . Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376:419-430.
38. Zoungas S, Chalmers J, Neal B, et al; . Follow-up of blood-pressure lowering and glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1392-1406.
39. Zoungas S, Arima H, Gerstein HC, et al; . Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:431-437.
40. Miller ME, Bonds DE, Gerstein HC, et al; . The effects of baseline characteristics, glycaemia treatment approach, and glycated haemoglobin concentration on the risk of severe hypoglycaemia: post hoc epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ. 2010;340;b5444.
41. Papademetriou V, Lovato L, Doumas M, et al; . Chronic kidney disease and intensive glycemic control increase cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2015;87:649-659.
42. National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:850-886.
43. Imam TH. Changes in metformin use in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10:301-304.
44. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al; Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323-334.
45. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al; . Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644-657.
46. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:311-322.
47. Mann JFE, DD, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:839-848.
48. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al; . Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834-1844.
49. Wanner C, Tonelli M; Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Lipid Guideline Development Work Group Members. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for lipid management in CKD: summary of recommendation statements and clinical approach to the patient. Kidney Int. 2014;85:1303-1309.
50. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e1082-e1143.
51. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:279-335. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.sciencedirect.com/journal/kidney-international-supplements/vol/2/issue/4
52. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. Evaluation and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). 2010. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.kidney.org/sites/default/files/02-10-390B_LBA_KDOQI_BoneGuide.pdf
53. Smart MA, Dieberg G, Ladhani M, et al. Early referral to specialist nephrology services for preventing the progression to end-stage kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(6):CD007333.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant comorbidity of diabetes mellitus. The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) of the National Kidney Foundation defines CKD as the presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for ≥ 3 months. CKD caused by diabetes is called diabetic kidney disease (DKD), which is 1 of 3 principal microvascular complications of diabetes. DKD can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring kidney replacement therapy, and is the leading cause of CKD and ESRD in the United States.1-3 Studies have also shown that, particularly in patients with diabetes, CKD considerably increases the risk of cardiovascular events, which often occur prior to ESRD.1,4
This article provides the latest recommendations for evaluating and managing DKD to help you prevent or slow its progression.
Defining and categorizing diabetic kidney disease
CKD is defined as persistently elevated excretion of urinary albumin (albuminuria) and decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), or as the presence of signs of progressive kidney damage.5,6 DKD, also known as diabetic nephropathy, is CKD attributed to long-term diabetes. A patient’s eGFR is the established basis for assignment to a stage (1, 2, 3a, 3b, 4, or 5) of CKD (TABLE 17) and, along with the category of albuminuria (A1, A2, or A3), can indicate prognosis.

Taking its toll in diabetes
As many as 40% of patients with diabetes develop DKD.8-10 Most studies of DKD have been conducted in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), because the time of clinical onset is typically known.
Type 1 diabetes. DKD usually occurs 10 to 15 years, or later, after the onset of diabetes.6 As many as 30% of people with T1D have albuminuria approximately 15 years after onset of diabetes; almost one-half of those develop DKD.5,11 After approximately 22.5 years without albuminuria, patients with T1D have approximately a 1% annual risk of DKD.12
Type 2 diabetes (T2D). DKD is often present at diagnosis, likely due to a delay in diagnosis and briefer clinical exposure, compared to T1D. Albuminuria has been reported in as many as 40% of patients with T2D approximately 10 years after onset of diabetes.12,13
Multiple risk factors with no standout “predictor”
Genetic susceptibility, ethnicity, glycemic control, smoking, blood pressure (BP), and the eGFR have been identified as risk factors for renal involvement in diabetes; obesity, oral contraceptives, and age can also contribute. Although each risk factor increases the risk of DKD, no single factor is adequately predictive. Moderately increased albuminuria, the earliest sign of DKD, is associated with progressive nephropathy.12
Continue to: How great is the risk?
How great is the risk? From disease onset to proteinuria and from proteinuria to ESRD, the risk of DKD in T1D and T2D is similar. With appropriate treatment, albuminuria can regress, and the risk of ESRD can be < 20% at 10 years in T1D.12 As in T1D, good glycemic control might result in regression of albuminuria in T2D.14
For unknown reasons, the degree of albuminuria can exist independent of the progression of DKD. Factors responsible for a progressive decline in eGFR in DKD without albuminuria are unknown.12,15
Patient evaluation with an eye toward comorbidities
A comprehensive initial medical evaluation for DKD includes a review of microvascular complications; visits to specialists; lifestyle and behavior patterns (eg, diet, sleep, substance use, and social support); and medication adherence, adverse drug effects, and alternative medicines. Although DKD is often a clinical diagnosis, it can be ruled in by persistent albuminuria or decreased eGFR, or both, in established diabetes or diabetic retinopathy when other causes are unlikely (see “Recommended DKD screening protocol,” below).
Screening for mental health conditions and barriers to self-management is also key.6
Comorbidities, of course, can complicate disease management in patients with diabetes.16-20 Providers and patients therefore need to be aware of potential diabetic comorbidities. For example, DKD and even moderately increased albuminuria significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).12 Other possible comorbidities include (but are not limited to) nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, fracture, hearing impairment, cancer (eg, liver, pancreas, endometrium, colon, rectum, breast, and bladder), pancreatitis, hypogonadism, obstructive sleep apnea, periodontal disease, anxiety, depression, and eating disorders.6
Continue to: Recommended DKD screening protocol
Recommended DKD screening protocol
In all cases of T2D, in cases of T1D of ≥ 5 years’ duration, and in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension, perform annual screening for albuminuria, an elevated creatinine level, and a decline in eGFR.
To confirm the diagnosis of DKD, at least 2 of 3 urine specimens must demonstrate an elevated urinary albumin:creatinine ratio (UACR) over a 3- to 6-month period.21 Apart from renal damage, exercise within 24 hours before specimen collection, infection, fever, congestive heart failure, hyperglycemia, menstruation, and hypertension can elevate the UACR.6
Levels of the UACR are established as follows22:
- Normal UACR is defined as < 30 milligrams of albumin per gram of creatinine (expressed as “mg/g”).
- Increased urinary albumin excretion is defined as ≥ 30 mg/g.
- Moderately increased albuminuria, a predictor of potential nephropathy, is the excretion of 30 to 300 mg/g.
- Severely increased albuminuria is excretion > 300 mg/g; it is often followed by a gradual decline in eGFR that, without treatment, eventually leads to ESRD.
The rate of decline in eGFR once albuminuria is severely increased is equivalent in T1D and T2D.12 Without intervention, the time from severely increased albuminuria to ESRD in T1D and T2D averages approximately 6 or 7 years.
Clinical features
DKD is typically a clinical diagnosis seen in patients with longstanding diabetes, albuminuria, retinopathy, or a reduced eGFR in the absence of another primary cause of kidney damage. In patients with T1D and DKD, signs of retinopathy and neuropathy are almost always present at diagnosis, unless a diagnosis is made early in the course of diabetes.12 Therefore, the presence of retinopathy suggests that diabetes is the likely cause of CKD.
Continue to: The presence of microvascular disease...
The presence of microvascular disease in patients with T2D and DKD is less predictable.12 In T2D patients who do not have retinopathy, consider causes of CKD other than DKD. Features suggesting that the cause of CKD is an underlying condition other than diabetes are rapidly increasing albuminuria or decreasing eGFR; urinary sediment comprising red blood cells or white blood cells; and nephrotic syndrome.6
As the prevalence of diabetes increases, it has become more common to diagnose DKD by eGFR without albuminuria—underscoring the importance of routine monitoring of eGFR in patients with diabetes.6
Sources of expert guidance. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation23 is preferred for calculating eGFR from serum creatinine: An eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 is considered abnormal.3,12 At these rates, the prevalence of complications related to CKD rises and screening for complications becomes necessary.
A more comprehensive classification of the stages of CKD, incorporating albuminuria and progression of CKD, has been recommended by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO).7 Because eGFR and excretion of albumin vary, abnormal test results need to be verified over time to stage the degree of CKD.3,12 Kidney damage often manifests as albuminuria, but also as hematuria, other types of abnormal urinary sediment, radiographic abnormalities, and other abnormal presentations.
Management
Nutritional factors
Excessive protein intake has been shown to increase albuminuria, worsen renal function, and increase CVD mortality in DKD.24-26 Therefore, daily dietary protein intake of 0.8 g/kg body weight is recommended for patients who are not on dialysis.3 Patients on dialysis might require higher protein intake to preserve muscle mass caused by protein-energy wasting, which is common in dialysis patients.6
Continue to: Low sodium intake
Low sodium intake in CKD patients has been shown to decrease BP and thus slow the progression of renal disease and lower the risk of CVD. The recommended dietary sodium intake in CKD patients is 1500-3000 mg/d.3
Low potassium intake. Hyperkalemia is a serious complication of CKD. A low-potassium diet is recommended in ESRD patients who have a potassium level > 5.5 mEq/L.6
Blood pressure
Preventing and treating hypertension is critical to slowing the progression of CKD and reducing cardiovascular risk. BP should be measured at every clinic visit. Aside from lifestyle changes, medication might be needed to reach target BP.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a BP goal of ≤ 140/90 mm Hg for hypertensive patients with diabetes, although they do state that a lower BP target (≤ 130/80 mm Hg) might be more appropriate for patients with DKD.27
The American College of Cardiology recommends that hypertensive patients with CKD have a BP target of ≤ 130/80 mm Hg.28
Continue to: ACE inhibitors and ARBs
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have renoprotective benefits. These agents are recommended as first-line medications for patients with diabetes, hypertension, and an eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and a UACR > 300 mg/g.29-31 Evidence also supports their use when the UACR is 30 to 299 mg/g.
Studies have shown that, in patients with DKD, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can slow the progression of renal disease.29,30,32 There is no difference between ACE inhibitors and ARBs in their effectiveness for preventing progression of DKD.6 There is no added benefit in combining an ACE inhibitor and an ARB33; notably, combination ACE inhibitor and ARB therapy can increase the risk of adverse events, such as hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury, especially in patients with DKD.33
There is no evidence for starting an ACE inhibitor or ARB to prevent CKD in patients with diabetes who are not hypertensive.5
ACE inhibitors and ARBs should be used with caution in women of childbearing age, who should use a reliable form of contraception if taking one of these drugs.
Diuretics. Thiazide-type and loop diuretics might potentiate the positive effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs. KDOQI guidelines recommend that, in patients who require a second agent to control BP, a diuretic should be considered in combination with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.20 A loop diuretic is preferred if the eGFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Continue to: Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers
Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers (CCBs), such as diltiazem and verapamil, have been shown to be more effective then dihydrophyridine CCBs, such as amlodipine and nifedipine, in slowing the progression of renal disease because of their antiproteinuric effects. However, the antiproteinuric effects of nondihydropyridine CCBs are not as strong as those of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and these drugs do not appear to potentiate the effects of an ACE inhibitor or ARB when used in combination.20
Nondihydropyridine CCBs might be a reasonable alternative in patients who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in combination with an ACE inhibitor or ARB have been demonstrated to reduce albuminuria in short-term studies.34,35
Glycemic levels
Studies conducted in patients with T1D, and others in patients with T2D, have shown that tight glycemic control can delay the onset and slow the progression of albuminuria and a decline in the eGFR.10,36-39 The target glycated hemoglobin (A1C) should be < 7% to prevent or slow progression of DKD.40 However, patients with DKD have an increased risk of hypoglycemic events and increased mortality with more intensive glycemic control.40,41 Given those findings, some patients with DKD and significant comorbidities, ESRD, or limited life expectancy might need to have an A1C target set at 8%.6,42
Adjustments to antidiabetes medications in DKD
In patients with stages 3 to 5 DKD, several common antidiabetic medications might need to be adjusted or discontinued because they decrease creatinine clearance.
Continue to: First-generation sulfonylureas
First-generation sulfonylureas should be avoided in DKD. Glipizide and gliclazide are preferred among second-generation sulfonylureas because they do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia in DKD patients, although patients taking these medications still require close monitoring of their blood glucose level.20
Metformin. In 2016, recommendations changed for the use of metformin in patients with DKD: The eGFR, not the serum creatinine level, should guide treatment.43 Metformin can be used safely in patients with (1) an eGFR of < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and (2) an eGFR of 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with close monitoring. Metformin should not be initiated if the eGFR is < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.43
Antidiabetes medications with direct effect on the kidney
Several antidiabetes medications have a direct effect on the kidney apart from their effect on the blood glucose level.
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to reduce albuminuria and slow the decrease of eGFR independent of glycemic control. In addition, SGLT2 inhibitors have also been shown to have cardiovascular benefits in patients with DKD.44,45
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have been shown to delay and decrease the progression of DKD.46-48 Also, similar to what is seen with SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 agonists have demonstrable cardiovascular benefit in patients with DKD.46,48
Continue to: Dyslipidemia and DKD
Dyslipidemia and DKD
Because the risk of CVD is increased in patients with DKD, addressing other modifiable risk factors, including dyslipidemia, is recommended in these patients. Patients with diabetes and stages 1 to 4 DKD should be treated with a high-intensity statin or a combination of a statin and ezetimibe.49,50
If a patient is taking a statin and starting dialysis, it’s important to discuss with him or her whether to continue the statin, based on perceived benefits and risks. It is not recommended that statins be initiated in patients on dialysis unless there is a specific cardiovascular indication for doing so. Risk reduction with a statin has been shown to be significantly less in dialysis patients than in patients who are not being treated with dialysis.49
Complications of CKD
Anemia is a common complication of CKD. KDIGO recommends measuring the hemoglobin concentration annually in DKD stage 3 patients without anemia; at least every 6 months in stage 4 patients; and at least every 3 months in stage 5. DKD patients with anemia should have additional laboratory testing: the absolute reticulocyte count, serum ferritin, serum transferrin saturation, vitamin B12, and folate.51
Mineral and bone disorder should be screened for in patients with DKD. TABLE 252 outlines when clinical laboratory tests should be ordered to assess for mineral bone disease.

When to refer to a nephrologist
Refer patients with stage 4 or 5 CKD (eGFR, ≤ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) to a nephrologist for discussion of kidney replacement therapy.6 Patients with stage 3a CKD and severely increased albuminuria or with stage 3b CKD and moderately or severely increased albuminuria should also be referred to a nephrologist for intervention to delay disease progression.
Continue to: Identifying the need for early referral...
Identifying the need for early referral to a nephrologist has been shown to reduce the cost, and improve the quality, of care.53 Other indications for earlier referral include uncertainty about the etiology of renal disease, persistent or severe albuminuria, persistent hematuria, a rapid decline in eGFR, and acute kidney injury. Additionally, referral at an earlier stage of DKD might be needed to assist with complications associated with DKD, such as anemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, mineral and bone disorder, resistant hypertension, fluid overload, and electrolyte disturbances.6
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Colleen Colbert, PhD, and Iqbal Ahmad, PhD, for their review and critique of the manuscript of this article. They also thank Christopher Babiuch, MD, for his guidance in the preparation of the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Faraz Ahmad, MD, MPH, Care Point East Family Medicine, 543 Taylor Avenue, 2nd floor, Columbus, OH 43203; faraz. [email protected].
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant comorbidity of diabetes mellitus. The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) of the National Kidney Foundation defines CKD as the presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for ≥ 3 months. CKD caused by diabetes is called diabetic kidney disease (DKD), which is 1 of 3 principal microvascular complications of diabetes. DKD can progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), requiring kidney replacement therapy, and is the leading cause of CKD and ESRD in the United States.1-3 Studies have also shown that, particularly in patients with diabetes, CKD considerably increases the risk of cardiovascular events, which often occur prior to ESRD.1,4
This article provides the latest recommendations for evaluating and managing DKD to help you prevent or slow its progression.
Defining and categorizing diabetic kidney disease
CKD is defined as persistently elevated excretion of urinary albumin (albuminuria) and decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), or as the presence of signs of progressive kidney damage.5,6 DKD, also known as diabetic nephropathy, is CKD attributed to long-term diabetes. A patient’s eGFR is the established basis for assignment to a stage (1, 2, 3a, 3b, 4, or 5) of CKD (TABLE 17) and, along with the category of albuminuria (A1, A2, or A3), can indicate prognosis.

Taking its toll in diabetes
As many as 40% of patients with diabetes develop DKD.8-10 Most studies of DKD have been conducted in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), because the time of clinical onset is typically known.
Type 1 diabetes. DKD usually occurs 10 to 15 years, or later, after the onset of diabetes.6 As many as 30% of people with T1D have albuminuria approximately 15 years after onset of diabetes; almost one-half of those develop DKD.5,11 After approximately 22.5 years without albuminuria, patients with T1D have approximately a 1% annual risk of DKD.12
Type 2 diabetes (T2D). DKD is often present at diagnosis, likely due to a delay in diagnosis and briefer clinical exposure, compared to T1D. Albuminuria has been reported in as many as 40% of patients with T2D approximately 10 years after onset of diabetes.12,13
Multiple risk factors with no standout “predictor”
Genetic susceptibility, ethnicity, glycemic control, smoking, blood pressure (BP), and the eGFR have been identified as risk factors for renal involvement in diabetes; obesity, oral contraceptives, and age can also contribute. Although each risk factor increases the risk of DKD, no single factor is adequately predictive. Moderately increased albuminuria, the earliest sign of DKD, is associated with progressive nephropathy.12
Continue to: How great is the risk?
How great is the risk? From disease onset to proteinuria and from proteinuria to ESRD, the risk of DKD in T1D and T2D is similar. With appropriate treatment, albuminuria can regress, and the risk of ESRD can be < 20% at 10 years in T1D.12 As in T1D, good glycemic control might result in regression of albuminuria in T2D.14
For unknown reasons, the degree of albuminuria can exist independent of the progression of DKD. Factors responsible for a progressive decline in eGFR in DKD without albuminuria are unknown.12,15
Patient evaluation with an eye toward comorbidities
A comprehensive initial medical evaluation for DKD includes a review of microvascular complications; visits to specialists; lifestyle and behavior patterns (eg, diet, sleep, substance use, and social support); and medication adherence, adverse drug effects, and alternative medicines. Although DKD is often a clinical diagnosis, it can be ruled in by persistent albuminuria or decreased eGFR, or both, in established diabetes or diabetic retinopathy when other causes are unlikely (see “Recommended DKD screening protocol,” below).
Screening for mental health conditions and barriers to self-management is also key.6
Comorbidities, of course, can complicate disease management in patients with diabetes.16-20 Providers and patients therefore need to be aware of potential diabetic comorbidities. For example, DKD and even moderately increased albuminuria significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).12 Other possible comorbidities include (but are not limited to) nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, fracture, hearing impairment, cancer (eg, liver, pancreas, endometrium, colon, rectum, breast, and bladder), pancreatitis, hypogonadism, obstructive sleep apnea, periodontal disease, anxiety, depression, and eating disorders.6
Continue to: Recommended DKD screening protocol
Recommended DKD screening protocol
In all cases of T2D, in cases of T1D of ≥ 5 years’ duration, and in patients with diabetes and comorbid hypertension, perform annual screening for albuminuria, an elevated creatinine level, and a decline in eGFR.
To confirm the diagnosis of DKD, at least 2 of 3 urine specimens must demonstrate an elevated urinary albumin:creatinine ratio (UACR) over a 3- to 6-month period.21 Apart from renal damage, exercise within 24 hours before specimen collection, infection, fever, congestive heart failure, hyperglycemia, menstruation, and hypertension can elevate the UACR.6
Levels of the UACR are established as follows22:
- Normal UACR is defined as < 30 milligrams of albumin per gram of creatinine (expressed as “mg/g”).
- Increased urinary albumin excretion is defined as ≥ 30 mg/g.
- Moderately increased albuminuria, a predictor of potential nephropathy, is the excretion of 30 to 300 mg/g.
- Severely increased albuminuria is excretion > 300 mg/g; it is often followed by a gradual decline in eGFR that, without treatment, eventually leads to ESRD.
The rate of decline in eGFR once albuminuria is severely increased is equivalent in T1D and T2D.12 Without intervention, the time from severely increased albuminuria to ESRD in T1D and T2D averages approximately 6 or 7 years.
Clinical features
DKD is typically a clinical diagnosis seen in patients with longstanding diabetes, albuminuria, retinopathy, or a reduced eGFR in the absence of another primary cause of kidney damage. In patients with T1D and DKD, signs of retinopathy and neuropathy are almost always present at diagnosis, unless a diagnosis is made early in the course of diabetes.12 Therefore, the presence of retinopathy suggests that diabetes is the likely cause of CKD.
Continue to: The presence of microvascular disease...
The presence of microvascular disease in patients with T2D and DKD is less predictable.12 In T2D patients who do not have retinopathy, consider causes of CKD other than DKD. Features suggesting that the cause of CKD is an underlying condition other than diabetes are rapidly increasing albuminuria or decreasing eGFR; urinary sediment comprising red blood cells or white blood cells; and nephrotic syndrome.6
As the prevalence of diabetes increases, it has become more common to diagnose DKD by eGFR without albuminuria—underscoring the importance of routine monitoring of eGFR in patients with diabetes.6
Sources of expert guidance. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation23 is preferred for calculating eGFR from serum creatinine: An eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 is considered abnormal.3,12 At these rates, the prevalence of complications related to CKD rises and screening for complications becomes necessary.
A more comprehensive classification of the stages of CKD, incorporating albuminuria and progression of CKD, has been recommended by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO).7 Because eGFR and excretion of albumin vary, abnormal test results need to be verified over time to stage the degree of CKD.3,12 Kidney damage often manifests as albuminuria, but also as hematuria, other types of abnormal urinary sediment, radiographic abnormalities, and other abnormal presentations.
Management
Nutritional factors
Excessive protein intake has been shown to increase albuminuria, worsen renal function, and increase CVD mortality in DKD.24-26 Therefore, daily dietary protein intake of 0.8 g/kg body weight is recommended for patients who are not on dialysis.3 Patients on dialysis might require higher protein intake to preserve muscle mass caused by protein-energy wasting, which is common in dialysis patients.6
Continue to: Low sodium intake
Low sodium intake in CKD patients has been shown to decrease BP and thus slow the progression of renal disease and lower the risk of CVD. The recommended dietary sodium intake in CKD patients is 1500-3000 mg/d.3
Low potassium intake. Hyperkalemia is a serious complication of CKD. A low-potassium diet is recommended in ESRD patients who have a potassium level > 5.5 mEq/L.6
Blood pressure
Preventing and treating hypertension is critical to slowing the progression of CKD and reducing cardiovascular risk. BP should be measured at every clinic visit. Aside from lifestyle changes, medication might be needed to reach target BP.
The American Diabetes Association recommends a BP goal of ≤ 140/90 mm Hg for hypertensive patients with diabetes, although they do state that a lower BP target (≤ 130/80 mm Hg) might be more appropriate for patients with DKD.27
The American College of Cardiology recommends that hypertensive patients with CKD have a BP target of ≤ 130/80 mm Hg.28
Continue to: ACE inhibitors and ARBs
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have renoprotective benefits. These agents are recommended as first-line medications for patients with diabetes, hypertension, and an eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and a UACR > 300 mg/g.29-31 Evidence also supports their use when the UACR is 30 to 299 mg/g.
Studies have shown that, in patients with DKD, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can slow the progression of renal disease.29,30,32 There is no difference between ACE inhibitors and ARBs in their effectiveness for preventing progression of DKD.6 There is no added benefit in combining an ACE inhibitor and an ARB33; notably, combination ACE inhibitor and ARB therapy can increase the risk of adverse events, such as hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury, especially in patients with DKD.33
There is no evidence for starting an ACE inhibitor or ARB to prevent CKD in patients with diabetes who are not hypertensive.5
ACE inhibitors and ARBs should be used with caution in women of childbearing age, who should use a reliable form of contraception if taking one of these drugs.
Diuretics. Thiazide-type and loop diuretics might potentiate the positive effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs. KDOQI guidelines recommend that, in patients who require a second agent to control BP, a diuretic should be considered in combination with an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.20 A loop diuretic is preferred if the eGFR is < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Continue to: Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers
Nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blockers (CCBs), such as diltiazem and verapamil, have been shown to be more effective then dihydrophyridine CCBs, such as amlodipine and nifedipine, in slowing the progression of renal disease because of their antiproteinuric effects. However, the antiproteinuric effects of nondihydropyridine CCBs are not as strong as those of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and these drugs do not appear to potentiate the effects of an ACE inhibitor or ARB when used in combination.20
Nondihydropyridine CCBs might be a reasonable alternative in patients who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor or an ARB.
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in combination with an ACE inhibitor or ARB have been demonstrated to reduce albuminuria in short-term studies.34,35
Glycemic levels
Studies conducted in patients with T1D, and others in patients with T2D, have shown that tight glycemic control can delay the onset and slow the progression of albuminuria and a decline in the eGFR.10,36-39 The target glycated hemoglobin (A1C) should be < 7% to prevent or slow progression of DKD.40 However, patients with DKD have an increased risk of hypoglycemic events and increased mortality with more intensive glycemic control.40,41 Given those findings, some patients with DKD and significant comorbidities, ESRD, or limited life expectancy might need to have an A1C target set at 8%.6,42
Adjustments to antidiabetes medications in DKD
In patients with stages 3 to 5 DKD, several common antidiabetic medications might need to be adjusted or discontinued because they decrease creatinine clearance.
Continue to: First-generation sulfonylureas
First-generation sulfonylureas should be avoided in DKD. Glipizide and gliclazide are preferred among second-generation sulfonylureas because they do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia in DKD patients, although patients taking these medications still require close monitoring of their blood glucose level.20
Metformin. In 2016, recommendations changed for the use of metformin in patients with DKD: The eGFR, not the serum creatinine level, should guide treatment.43 Metformin can be used safely in patients with (1) an eGFR of < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and (2) an eGFR of 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with close monitoring. Metformin should not be initiated if the eGFR is < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2.43
Antidiabetes medications with direct effect on the kidney
Several antidiabetes medications have a direct effect on the kidney apart from their effect on the blood glucose level.
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to reduce albuminuria and slow the decrease of eGFR independent of glycemic control. In addition, SGLT2 inhibitors have also been shown to have cardiovascular benefits in patients with DKD.44,45
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have been shown to delay and decrease the progression of DKD.46-48 Also, similar to what is seen with SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 agonists have demonstrable cardiovascular benefit in patients with DKD.46,48
Continue to: Dyslipidemia and DKD
Dyslipidemia and DKD
Because the risk of CVD is increased in patients with DKD, addressing other modifiable risk factors, including dyslipidemia, is recommended in these patients. Patients with diabetes and stages 1 to 4 DKD should be treated with a high-intensity statin or a combination of a statin and ezetimibe.49,50
If a patient is taking a statin and starting dialysis, it’s important to discuss with him or her whether to continue the statin, based on perceived benefits and risks. It is not recommended that statins be initiated in patients on dialysis unless there is a specific cardiovascular indication for doing so. Risk reduction with a statin has been shown to be significantly less in dialysis patients than in patients who are not being treated with dialysis.49
Complications of CKD
Anemia is a common complication of CKD. KDIGO recommends measuring the hemoglobin concentration annually in DKD stage 3 patients without anemia; at least every 6 months in stage 4 patients; and at least every 3 months in stage 5. DKD patients with anemia should have additional laboratory testing: the absolute reticulocyte count, serum ferritin, serum transferrin saturation, vitamin B12, and folate.51
Mineral and bone disorder should be screened for in patients with DKD. TABLE 252 outlines when clinical laboratory tests should be ordered to assess for mineral bone disease.

When to refer to a nephrologist
Refer patients with stage 4 or 5 CKD (eGFR, ≤ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) to a nephrologist for discussion of kidney replacement therapy.6 Patients with stage 3a CKD and severely increased albuminuria or with stage 3b CKD and moderately or severely increased albuminuria should also be referred to a nephrologist for intervention to delay disease progression.
Continue to: Identifying the need for early referral...
Identifying the need for early referral to a nephrologist has been shown to reduce the cost, and improve the quality, of care.53 Other indications for earlier referral include uncertainty about the etiology of renal disease, persistent or severe albuminuria, persistent hematuria, a rapid decline in eGFR, and acute kidney injury. Additionally, referral at an earlier stage of DKD might be needed to assist with complications associated with DKD, such as anemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, mineral and bone disorder, resistant hypertension, fluid overload, and electrolyte disturbances.6
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank Colleen Colbert, PhD, and Iqbal Ahmad, PhD, for their review and critique of the manuscript of this article. They also thank Christopher Babiuch, MD, for his guidance in the preparation of the manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Faraz Ahmad, MD, MPH, Care Point East Family Medicine, 543 Taylor Avenue, 2nd floor, Columbus, OH 43203; faraz. [email protected].
1. Radbill B, Murphy B, LeRoith D. Rationale and strategies for early detection and management of diabetic kidney disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:1373-1381.
2. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71(3 suppl 1):A7.
3. Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:510-533.
4. Fox CS, Matsushita K, Woodward M, et al; . Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;380:1662-1673.
5. Orchard TJ, Dorman JS, Maser RE, et al. Prevalence of complications in IDDM by sex and duration. Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study II. Diabetes. 1990;39:1116-1124.
6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(suppl 1):S1-S159. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/Supplement_1
7. National Kidney Foundation. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1-150. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf
8. Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. 2016;316:602-610.
9. de Boer IH, Rue TC, Hall YN, et al. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2011;305:2532-2539.
10. de Boer IH; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Kidney disease and related findings in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:24-30.
11. Stanton RC. Clinical challenges in diagnosis and management of diabetic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(2 suppl 2):S3-S21.
12. Mottl AK, Tuttle KR. Diabetic kidney disease: Pathogenesis and epidemiology. UpToDate. Updated August 19, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/diabetic-kidney-disease-pathogenesis-and-epidemiology
13. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 2 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated November 3, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-2-diabetes-mellitus
14. Bandak G, Sang Y, Gasparini A, et al. Hyperkalemia after initiating renin-angiotensin system blockade: the Stockholm Creatinine Measurements (SCREAM) Project. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e005428.
15. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(3 suppl 1):A7-A8.
16. Nilsson E, Gasparini A, Ärnlöv J, et al. Incidence and determinants of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in a large healthcare system. Int J Cardiol. 2017;245:277-284.
17. de Boer IH, Gao X, Cleary PA, et al; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Research Group. Albuminuria changes and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 1 diabetes: The DCCT/EDIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1969-1977.
18. Sumida K, Molnar MZ, Potukuchi PK, et al. Changes in albuminuria and subsequent risk of incident kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12:1941-1949.
19. Borch-Johnsen K, Wenzel H, Viberti GC, et al. Is screening and intervention for microalbuminuria worthwhile in patient with insulin dependent diabetes? BMJ. 1993;306:1722-1725.
20. KDOQI. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(2 suppl 2):S12-154.
21. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 1 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated December 3, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-1-diabetes-mellitus
22. Delanaye P, Glassock RJ, Pottel H, et al. An age-calibrated definition of chronic kidney disease: rationale and benefits. Clin Biochem Rev. 2016;37:17-26.
23. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, et al; , A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:604-612.
24. Wrone EM, Carnethon MR, Palaniappan L, et al; . Association of dietary protein intake and microalbuminuria in healthy adults: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:580-587.
25. Knight EL, Stampfer MJ, Hankinson SE, et al. The impact of protein intake on renal function decline in women with normal renal function or mild renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:460-467.
26. Bernstein AM, Sun Q, Hu FB, et al. Major dietary protein sources and risk of coronary heart disease in women. Circulation. 2010;122:876-883.
27. de Boer, IH, Bangalore S, Benetos A, et al. Diabetes and hypertension: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1273-1284.
28. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:e127-e248.
29. Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al; Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861-869.
30. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, et al. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456-1462.
31. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355;253-259.
32. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, et al; . Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851-860.
33. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, et al; . Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892-1903.
34. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, et al; . Effect of finerenone on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314:884-894.
35. Filippatos G, Anker SD, M, et al. Randomized controlled study of finerenone vs. eplerenone in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2105-2114.
36. The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560-2572.
37. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, et al; . Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376:419-430.
38. Zoungas S, Chalmers J, Neal B, et al; . Follow-up of blood-pressure lowering and glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1392-1406.
39. Zoungas S, Arima H, Gerstein HC, et al; . Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:431-437.
40. Miller ME, Bonds DE, Gerstein HC, et al; . The effects of baseline characteristics, glycaemia treatment approach, and glycated haemoglobin concentration on the risk of severe hypoglycaemia: post hoc epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ. 2010;340;b5444.
41. Papademetriou V, Lovato L, Doumas M, et al; . Chronic kidney disease and intensive glycemic control increase cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2015;87:649-659.
42. National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:850-886.
43. Imam TH. Changes in metformin use in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10:301-304.
44. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al; Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323-334.
45. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al; . Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644-657.
46. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:311-322.
47. Mann JFE, DD, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:839-848.
48. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al; . Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834-1844.
49. Wanner C, Tonelli M; Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Lipid Guideline Development Work Group Members. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for lipid management in CKD: summary of recommendation statements and clinical approach to the patient. Kidney Int. 2014;85:1303-1309.
50. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e1082-e1143.
51. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:279-335. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.sciencedirect.com/journal/kidney-international-supplements/vol/2/issue/4
52. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. Evaluation and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). 2010. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.kidney.org/sites/default/files/02-10-390B_LBA_KDOQI_BoneGuide.pdf
53. Smart MA, Dieberg G, Ladhani M, et al. Early referral to specialist nephrology services for preventing the progression to end-stage kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(6):CD007333.
1. Radbill B, Murphy B, LeRoith D. Rationale and strategies for early detection and management of diabetic kidney disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:1373-1381.
2. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71(3 suppl 1):A7.
3. Tuttle KR, Bakris GL, Bilous RW, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: a report from an ADA Consensus Conference. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64:510-533.
4. Fox CS, Matsushita K, Woodward M, et al; . Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without diabetes: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;380:1662-1673.
5. Orchard TJ, Dorman JS, Maser RE, et al. Prevalence of complications in IDDM by sex and duration. Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study II. Diabetes. 1990;39:1116-1124.
6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(suppl 1):S1-S159. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/Supplement_1
7. National Kidney Foundation. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1-150. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf
8. Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. 2016;316:602-610.
9. de Boer IH, Rue TC, Hall YN, et al. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2011;305:2532-2539.
10. de Boer IH; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Kidney disease and related findings in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:24-30.
11. Stanton RC. Clinical challenges in diagnosis and management of diabetic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(2 suppl 2):S3-S21.
12. Mottl AK, Tuttle KR. Diabetic kidney disease: Pathogenesis and epidemiology. UpToDate. Updated August 19, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.uptodate.com/contents/diabetic-kidney-disease-pathogenesis-and-epidemiology
13. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 2 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated November 3, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-2-diabetes-mellitus
14. Bandak G, Sang Y, Gasparini A, et al. Hyperkalemia after initiating renin-angiotensin system blockade: the Stockholm Creatinine Measurements (SCREAM) Project. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e005428.
15. Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. US Renal Data System 2016 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017;69(3 suppl 1):A7-A8.
16. Nilsson E, Gasparini A, Ärnlöv J, et al. Incidence and determinants of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in a large healthcare system. Int J Cardiol. 2017;245:277-284.
17. de Boer IH, Gao X, Cleary PA, et al; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Research Group. Albuminuria changes and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 1 diabetes: The DCCT/EDIC study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1969-1977.
18. Sumida K, Molnar MZ, Potukuchi PK, et al. Changes in albuminuria and subsequent risk of incident kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12:1941-1949.
19. Borch-Johnsen K, Wenzel H, Viberti GC, et al. Is screening and intervention for microalbuminuria worthwhile in patient with insulin dependent diabetes? BMJ. 1993;306:1722-1725.
20. KDOQI. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(2 suppl 2):S12-154.
21. Bakris GL. Moderately increased albuminuria (microalbuminuria) in type 1 diabetes mellitus. UpToDate. Updated December 3, 2019. Accessed January 5, 2021. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/moderately-increased-albuminuria-microalbuminuria-in-type-1-diabetes-mellitus
22. Delanaye P, Glassock RJ, Pottel H, et al. An age-calibrated definition of chronic kidney disease: rationale and benefits. Clin Biochem Rev. 2016;37:17-26.
23. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, et al; , A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:604-612.
24. Wrone EM, Carnethon MR, Palaniappan L, et al; . Association of dietary protein intake and microalbuminuria in healthy adults: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41:580-587.
25. Knight EL, Stampfer MJ, Hankinson SE, et al. The impact of protein intake on renal function decline in women with normal renal function or mild renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:460-467.
26. Bernstein AM, Sun Q, Hu FB, et al. Major dietary protein sources and risk of coronary heart disease in women. Circulation. 2010;122:876-883.
27. de Boer, IH, Bangalore S, Benetos A, et al. Diabetes and hypertension: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40:1273-1284.
28. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71:e127-e248.
29. Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al; Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861-869.
30. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, et al. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1456-1462.
31. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000;355;253-259.
32. Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, et al; . Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851-860.
33. Fried LF, Emanuele N, Zhang JH, et al; . Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892-1903.
34. Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, et al; . Effect of finerenone on albuminuria in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;314:884-894.
35. Filippatos G, Anker SD, M, et al. Randomized controlled study of finerenone vs. eplerenone in patients with worsening chronic heart failure and diabetes mellitus and/or chronic kidney disease. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2105-2114.
36. The ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2560-2572.
37. Ismail-Beigi F, Craven T, Banerji MA, et al; . Effect of intensive treatment of hyperglycaemia on microvascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an analysis of the ACCORD randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376:419-430.
38. Zoungas S, Chalmers J, Neal B, et al; . Follow-up of blood-pressure lowering and glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1392-1406.
39. Zoungas S, Arima H, Gerstein HC, et al; . Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:431-437.
40. Miller ME, Bonds DE, Gerstein HC, et al; . The effects of baseline characteristics, glycaemia treatment approach, and glycated haemoglobin concentration on the risk of severe hypoglycaemia: post hoc epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ. 2010;340;b5444.
41. Papademetriou V, Lovato L, Doumas M, et al; . Chronic kidney disease and intensive glycemic control increase cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2015;87:649-659.
42. National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:850-886.
43. Imam TH. Changes in metformin use in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. 2017;10:301-304.
44. Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al; Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323-334.
45. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al; . Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644-657.
46. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:311-322.
47. Mann JFE, DD, Brown-Frandsen K, et al; . Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:839-848.
48. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al; . Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834-1844.
49. Wanner C, Tonelli M; Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Lipid Guideline Development Work Group Members. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for lipid management in CKD: summary of recommendation statements and clinical approach to the patient. Kidney Int. 2014;85:1303-1309.
50. Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline on the management of blood cholesterol. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139:e1082-e1143.
51. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:279-335. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.sciencedirect.com/journal/kidney-international-supplements/vol/2/issue/4
52. National Kidney Foundation KDOQI. Evaluation and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). 2010. Accessed January 5, 2021. www.kidney.org/sites/default/files/02-10-390B_LBA_KDOQI_BoneGuide.pdf
53. Smart MA, Dieberg G, Ladhani M, et al. Early referral to specialist nephrology services for preventing the progression to end-stage kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(6):CD007333.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
› Screen patients with diabetes annually for diabetic kidney disease with measurement of urinary albumin and the estimated glomerular filtration rate. B
› Optimize blood glucose and blood pressure control in patients with diabetes to prevent or delay progression to diabetic kidney disease. A
› Treat hypertensive patients with diabetes and stages 1 to 4 chronic kidney disease with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II-receptor blocker as a first-line antihypertensive, absent contraindications. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
Further warning on SGLT2 inhibitor use and DKA risk in COVID-19
a new case series suggests.
Five patients with type 2 diabetes who were taking SGLT2 inhibitors presented in DKA despite having glucose levels below 300 mg/dL. The report was published online last month in AACE Clinical Case Reports by Rebecca J. Vitale, MD, and colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“A cluster of euglycemic DKA cases at our hospital during the first wave of the pandemic suggests that patients with diabetes taking SGLT2 inhibitors may be at enhanced risk for euDKA when they contract COVID-19,” senior author Naomi D.L. Fisher, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Fisher, an endocrinologist, added: “This complication is preventable with the simple measure of holding the drug. We are hopeful that widespread patient and physician education will prevent future cases of euDKA as COVID-19 infections continue to surge.”
These cases underscore recommendations published early in the COVID-19 pandemic by an international panel, she noted.
“Patients who are acutely ill with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, or who are experiencing loss of appetite with reduced food and fluid intake, should be advised to hold their SGLT2 inhibitor. This medication should not be resumed until patients are feeling better and eating and drinking normally.”
On the other hand, “If patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 infection are otherwise well, and are eating and drinking normally, there is no evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors need to be stopped. These patients should monitor [themselves] closely for worsening symptoms, especially resulting in poor hydration and nutrition, which would be reason to discontinue their medication.”
Pay special attention to the elderly, those with complications
However, special consideration should be given to elderly patients and those with medical conditions known to increase the likelihood of severe infection, like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Dr. Fisher added.
The SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs causes significant urinary glucose excretion, and they are also diuretics. A decrease in available glucose and volume depletion are probably both important contributors to euDKA, she explained.
With COVID-19 infection the euDKA risk is compounded by several mechanisms. Most cases of euDKA are associated with an underlying state of starvation that can be triggered by vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and poor oral intake.
In addition – although not yet known for certain – SARS-CoV-2 may also be toxic to pancreatic beta cells and thus reduce insulin secretion. The maladaptive inflammatory response seen with COVID-19 may also contribute, she said.
The patients in the current case series were three men and two women seen between March and May 2020. They ranged in age from 52 to 79 years.
None had a prior history of DKA or any known diabetes complications. In all of them, antihyperglycemic medications, including SGLT2 inhibitors, were stopped on hospital admission. The patients were initially treated with intravenous insulin, and then subcutaneous insulin after the DKA diagnosis.
Three of the patients were discharged to rehabilitation facilities on hospital days 28-47 and one (age 53 years) was discharged home on day 11. The other patient also had hypertension and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new case series suggests.
Five patients with type 2 diabetes who were taking SGLT2 inhibitors presented in DKA despite having glucose levels below 300 mg/dL. The report was published online last month in AACE Clinical Case Reports by Rebecca J. Vitale, MD, and colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“A cluster of euglycemic DKA cases at our hospital during the first wave of the pandemic suggests that patients with diabetes taking SGLT2 inhibitors may be at enhanced risk for euDKA when they contract COVID-19,” senior author Naomi D.L. Fisher, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Fisher, an endocrinologist, added: “This complication is preventable with the simple measure of holding the drug. We are hopeful that widespread patient and physician education will prevent future cases of euDKA as COVID-19 infections continue to surge.”
These cases underscore recommendations published early in the COVID-19 pandemic by an international panel, she noted.
“Patients who are acutely ill with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, or who are experiencing loss of appetite with reduced food and fluid intake, should be advised to hold their SGLT2 inhibitor. This medication should not be resumed until patients are feeling better and eating and drinking normally.”
On the other hand, “If patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 infection are otherwise well, and are eating and drinking normally, there is no evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors need to be stopped. These patients should monitor [themselves] closely for worsening symptoms, especially resulting in poor hydration and nutrition, which would be reason to discontinue their medication.”
Pay special attention to the elderly, those with complications
However, special consideration should be given to elderly patients and those with medical conditions known to increase the likelihood of severe infection, like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Dr. Fisher added.
The SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs causes significant urinary glucose excretion, and they are also diuretics. A decrease in available glucose and volume depletion are probably both important contributors to euDKA, she explained.
With COVID-19 infection the euDKA risk is compounded by several mechanisms. Most cases of euDKA are associated with an underlying state of starvation that can be triggered by vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and poor oral intake.
In addition – although not yet known for certain – SARS-CoV-2 may also be toxic to pancreatic beta cells and thus reduce insulin secretion. The maladaptive inflammatory response seen with COVID-19 may also contribute, she said.
The patients in the current case series were three men and two women seen between March and May 2020. They ranged in age from 52 to 79 years.
None had a prior history of DKA or any known diabetes complications. In all of them, antihyperglycemic medications, including SGLT2 inhibitors, were stopped on hospital admission. The patients were initially treated with intravenous insulin, and then subcutaneous insulin after the DKA diagnosis.
Three of the patients were discharged to rehabilitation facilities on hospital days 28-47 and one (age 53 years) was discharged home on day 11. The other patient also had hypertension and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
a new case series suggests.
Five patients with type 2 diabetes who were taking SGLT2 inhibitors presented in DKA despite having glucose levels below 300 mg/dL. The report was published online last month in AACE Clinical Case Reports by Rebecca J. Vitale, MD, and colleagues at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“A cluster of euglycemic DKA cases at our hospital during the first wave of the pandemic suggests that patients with diabetes taking SGLT2 inhibitors may be at enhanced risk for euDKA when they contract COVID-19,” senior author Naomi D.L. Fisher, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Fisher, an endocrinologist, added: “This complication is preventable with the simple measure of holding the drug. We are hopeful that widespread patient and physician education will prevent future cases of euDKA as COVID-19 infections continue to surge.”
These cases underscore recommendations published early in the COVID-19 pandemic by an international panel, she noted.
“Patients who are acutely ill with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea, or who are experiencing loss of appetite with reduced food and fluid intake, should be advised to hold their SGLT2 inhibitor. This medication should not be resumed until patients are feeling better and eating and drinking normally.”
On the other hand, “If patients with asymptomatic or mild COVID-19 infection are otherwise well, and are eating and drinking normally, there is no evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors need to be stopped. These patients should monitor [themselves] closely for worsening symptoms, especially resulting in poor hydration and nutrition, which would be reason to discontinue their medication.”
Pay special attention to the elderly, those with complications
However, special consideration should be given to elderly patients and those with medical conditions known to increase the likelihood of severe infection, like heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Dr. Fisher added.
The SGLT2 inhibitor class of drugs causes significant urinary glucose excretion, and they are also diuretics. A decrease in available glucose and volume depletion are probably both important contributors to euDKA, she explained.
With COVID-19 infection the euDKA risk is compounded by several mechanisms. Most cases of euDKA are associated with an underlying state of starvation that can be triggered by vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and poor oral intake.
In addition – although not yet known for certain – SARS-CoV-2 may also be toxic to pancreatic beta cells and thus reduce insulin secretion. The maladaptive inflammatory response seen with COVID-19 may also contribute, she said.
The patients in the current case series were three men and two women seen between March and May 2020. They ranged in age from 52 to 79 years.
None had a prior history of DKA or any known diabetes complications. In all of them, antihyperglycemic medications, including SGLT2 inhibitors, were stopped on hospital admission. The patients were initially treated with intravenous insulin, and then subcutaneous insulin after the DKA diagnosis.
Three of the patients were discharged to rehabilitation facilities on hospital days 28-47 and one (age 53 years) was discharged home on day 11. The other patient also had hypertension and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DOACs show safety benefit in early stages of CKD
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is both a prothrombotic state and a condition with an elevated bleeding risk that increases in a linear fashion as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decreases. These features of the disease along with the exclusion of patients with CKD from most anticoagulation trials have resulted in uncertainty about overall risks and benefits of anticoagulant use in this population.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Variable across included trials.
Synopsis: Forty-five randomized, controlled trials of anticoagulation covering a broad range of anticoagulants, doses, indications, and methodologies were included in this meta-analysis, representing 34,082 patients with CKD or end-stage kidney disease.
The most compelling data were seen in the management of atrial fibrillation in early-stage CKD (five studies representing 11,332 patients) in which high-dose DOACs were associated with a lower risk for stroke or systemic embolism (risk ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.92), hemorrhagic stroke (RR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.30-0.76), and all-cause death (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.78-0.99). Overall stroke reduction was primarily hemorrhagic, and DOACs were equivalent to vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) for ischemic stroke risk.
The analysis also suggests that, in CKD, DOACs may reduce major bleeding when compared with VKAs across a variety of indications, though that finding was not statistically significant.
Efficacy of DOACs, compared with VKAs, in treatment of venous thromboembolism was uncertain, and patients with end-stage kidney disease and advanced CKD (creatinine clearance, less than 25 mL/min) were excluded from all trials comparing DOACs with VKAs, with limited overall data in these populations.
Bottom line: For patients with atrial fibrillation and early-stage CKD, direct oral anticoagulants show a promising risk-benefit profile when compared with vitamin K antagonists. Very few data are available on the safety and efficacy of anticoagulants in patients with advanced CKD and end-stage kidney disease.
Citation: Ha JT et al. Benefits and harms of oral anticoagulant therapy in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 6;171(3):181-9.
Dr. Herrle is a hospitalist at Maine Medical Center in Portland and at Stephens Memorial Hospital in Norway, Maine.
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is both a prothrombotic state and a condition with an elevated bleeding risk that increases in a linear fashion as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decreases. These features of the disease along with the exclusion of patients with CKD from most anticoagulation trials have resulted in uncertainty about overall risks and benefits of anticoagulant use in this population.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Variable across included trials.
Synopsis: Forty-five randomized, controlled trials of anticoagulation covering a broad range of anticoagulants, doses, indications, and methodologies were included in this meta-analysis, representing 34,082 patients with CKD or end-stage kidney disease.
The most compelling data were seen in the management of atrial fibrillation in early-stage CKD (five studies representing 11,332 patients) in which high-dose DOACs were associated with a lower risk for stroke or systemic embolism (risk ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.92), hemorrhagic stroke (RR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.30-0.76), and all-cause death (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.78-0.99). Overall stroke reduction was primarily hemorrhagic, and DOACs were equivalent to vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) for ischemic stroke risk.
The analysis also suggests that, in CKD, DOACs may reduce major bleeding when compared with VKAs across a variety of indications, though that finding was not statistically significant.
Efficacy of DOACs, compared with VKAs, in treatment of venous thromboembolism was uncertain, and patients with end-stage kidney disease and advanced CKD (creatinine clearance, less than 25 mL/min) were excluded from all trials comparing DOACs with VKAs, with limited overall data in these populations.
Bottom line: For patients with atrial fibrillation and early-stage CKD, direct oral anticoagulants show a promising risk-benefit profile when compared with vitamin K antagonists. Very few data are available on the safety and efficacy of anticoagulants in patients with advanced CKD and end-stage kidney disease.
Citation: Ha JT et al. Benefits and harms of oral anticoagulant therapy in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 6;171(3):181-9.
Dr. Herrle is a hospitalist at Maine Medical Center in Portland and at Stephens Memorial Hospital in Norway, Maine.
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is both a prothrombotic state and a condition with an elevated bleeding risk that increases in a linear fashion as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decreases. These features of the disease along with the exclusion of patients with CKD from most anticoagulation trials have resulted in uncertainty about overall risks and benefits of anticoagulant use in this population.
Study design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: Variable across included trials.
Synopsis: Forty-five randomized, controlled trials of anticoagulation covering a broad range of anticoagulants, doses, indications, and methodologies were included in this meta-analysis, representing 34,082 patients with CKD or end-stage kidney disease.
The most compelling data were seen in the management of atrial fibrillation in early-stage CKD (five studies representing 11,332 patients) in which high-dose DOACs were associated with a lower risk for stroke or systemic embolism (risk ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.92), hemorrhagic stroke (RR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.30-0.76), and all-cause death (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.78-0.99). Overall stroke reduction was primarily hemorrhagic, and DOACs were equivalent to vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) for ischemic stroke risk.
The analysis also suggests that, in CKD, DOACs may reduce major bleeding when compared with VKAs across a variety of indications, though that finding was not statistically significant.
Efficacy of DOACs, compared with VKAs, in treatment of venous thromboembolism was uncertain, and patients with end-stage kidney disease and advanced CKD (creatinine clearance, less than 25 mL/min) were excluded from all trials comparing DOACs with VKAs, with limited overall data in these populations.
Bottom line: For patients with atrial fibrillation and early-stage CKD, direct oral anticoagulants show a promising risk-benefit profile when compared with vitamin K antagonists. Very few data are available on the safety and efficacy of anticoagulants in patients with advanced CKD and end-stage kidney disease.
Citation: Ha JT et al. Benefits and harms of oral anticoagulant therapy in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Aug 6;171(3):181-9.
Dr. Herrle is a hospitalist at Maine Medical Center in Portland and at Stephens Memorial Hospital in Norway, Maine.
New findings add to questions about existence of gouty nephropathy
Is gouty nephropathy real? It’s a question that has been posed often in rheumatology over the last several decades.
A new study found 36% of patients with untreated gout at a medical center in Vietnam have diffuse hyperechoic renal medulla as seen on ultrasound, which could indicate the presence of microcrystalline nephropathy. However, the results, published in Kidney International, may raise more questions than answers about the existence of gouty nephropathy and its relation to chronic kidney disease (CKD).
In their study, Thomas Bardin, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Lariboisière Hospital in Paris and colleagues evaluated 502 consecutive patients from Vien Gut Medical Center in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, using B-mode renal ultrasound. The patients were mostly men with a median age of 46 years, body mass index of 25 kg/m2, estimated disease duration of 4 years, and uricemia of 423.2 micromol/L (7.11 mg/dL). Patients had a median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 78 mL/min per 1.73 m2. There was a history of hypertension in 112 patients (22.3%), type 2 diabetes in 58 patients (11.5%), renal lithiasis in 28 patients (5.6%), and coronary heart disease in 5 patients (1%).
While 39% of patients had previously used allopurinol for “a generally short period,” patients were not on urate-lowering therapy at the time of the study. Clinical tophi were present in 279 patients (55.6%), urate arthropathies in 154 patients (30.7%), and 43 patients (10.4%) used steroids daily.
B-mode renal ultrasound showed 181 patients (36%; 95% confidence interval, 32%-40%) had “hyperechoic pattern of Malpighi pyramids compared with the adjacent cortex,” which was “associated with twinkling artifacts” visible on color Doppler ultrasound. There was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and patient age, disease duration, use of steroids, clinical tophi, and urate arthropathy (P less than .0001 for all). A significant association was also seen between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and decreased eGFR (P < .0001), proteinuria (P = .0006), leukocyturia (P = .0008), hypertension (P = .0008), hyperuricemia (P = .002), and coronary heart disease (P = .006).
In a multivariate analysis, there was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and clinical tophi (odds ratio, 7.27; 95% CI, 3.68–15.19; P < .0001), urate arthropathy (OR, 3.46; 95% CI, 1.99–6.09; P < .0001), estimated gout duration (OR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.55–2.96; P < .0001), double contour thickness (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.06–1.97; P < .02), and eGFR (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.09–0.89; P < .034).
“The finding was observed mainly in tophaceous gout, which involved a large proportion of our patients who had received very little treatment with urate-lowering drugs and was associated with moderately impaired renal function and urinary features compatible with tubulointerstitial nephritis,” Dr. Bardin and colleagues wrote in the study. The researchers also found “similar features” in 4 of 10 French patients at the Paris Necker Hospital in Paris, and noted that similar findings have been reported in Japan and Korea, which they said may mean hyperechoic medulla “is not unique to Vietnamese patients.”
Relation to CKD still unclear
In a related editorial, Federica Piani, MD, and Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the division of renal diseases and hypertension at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained that gout was considered by some clinicians to be a cause of CKD in a time before urate-lowering therapies, because as many as 25% of patients with gout went on to experience kidney failure and about half experienced lower kidney function.
The association between gout and CKD was thought to be attributable to “frequent deposition of urate crystals in the tubular lumens and interstitium in the outer medulla of these patients,” but the concept was later challenged because “the crystals were generally found focally and did not readily explain the kidney damage.”
But even as interest in rheumatology moved away from the concept of gouty nephropathy to how serum uric acid impacts CKD, “the possibility that urate crystal deposition in the kidney could also be contributing to the kidney injury was never ruled out,” according to Dr. Piani and Dr. Johnson.
Kidney biopsies can sometimes miss urate crystals because the crystals dissolve if alcohol fixation is not used and because the biopsy site is often in the renal cortex, the authors noted. Recent research has identified that dual-energy CT scans can distinguish between calcium deposits and urate crystals better than ultrasound, and previous research from Thomas Bardin, MD, and colleagues in two patients noted a correlation between dual-energy CT scan findings of urate crystals and hyperechoic medulla findings on renal ultrasound.
The results by Dr. Bardin and associates, they said, “have reawakened the entity of urate microcrystalline nephropathy as a possible cause of CKD.”
Robert Terkeltaub, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of Rheumatology at the San Diego VA Medical Center, said in an interview that he also believes the findings by Dr. Bardin and associates are real. He cited a study by Isabelle Ayoub, MD, and colleagues in Clinical Nephrology from 2016 that evaluated kidney biopsies in Germany and found medullary tophi were more likely to be present in patients with CKD than without.
“Chronic gouty nephropathy did not disappear. It still exists,” said Dr. Terkeltaub, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Bardin and colleagues.
The prospect that, if “you look hard enough, you’re going to see urate crystals and a pattern that’s attributed in the renal medulla” in patients with untreated gout is “very provocative, and interesting, and clinically relevant, and merits more investigation,” noted Dr. Terkeltaub, who is also president of the Gout, Hyperuricemia and Crystal-Associated Disease Network.
If verified, the results have important implications for patients with gout and its relationship to CKD, Dr. Terkeltaub said, but they raise “more questions than answers.
“I think it’s a really good wake-up call to start looking, doing good detective work here, and looking especially in people who have gout as opposed to just people with chronic kidney disease,” he said.
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Johnson, who coauthored an accompanying editorial, reported having equity in XORTX Therapeutics, serving as a consultant for Horizon Pharma, and having equity in Colorado Research Partners LLC. Dr. Terkeltaub reported receiving a research grant from AstraZeneca in the field of hyperuricemia and consultancies with AstraZeneca, Horizon, Sobi, Selecta Biosciences.
Is gouty nephropathy real? It’s a question that has been posed often in rheumatology over the last several decades.
A new study found 36% of patients with untreated gout at a medical center in Vietnam have diffuse hyperechoic renal medulla as seen on ultrasound, which could indicate the presence of microcrystalline nephropathy. However, the results, published in Kidney International, may raise more questions than answers about the existence of gouty nephropathy and its relation to chronic kidney disease (CKD).
In their study, Thomas Bardin, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Lariboisière Hospital in Paris and colleagues evaluated 502 consecutive patients from Vien Gut Medical Center in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, using B-mode renal ultrasound. The patients were mostly men with a median age of 46 years, body mass index of 25 kg/m2, estimated disease duration of 4 years, and uricemia of 423.2 micromol/L (7.11 mg/dL). Patients had a median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 78 mL/min per 1.73 m2. There was a history of hypertension in 112 patients (22.3%), type 2 diabetes in 58 patients (11.5%), renal lithiasis in 28 patients (5.6%), and coronary heart disease in 5 patients (1%).
While 39% of patients had previously used allopurinol for “a generally short period,” patients were not on urate-lowering therapy at the time of the study. Clinical tophi were present in 279 patients (55.6%), urate arthropathies in 154 patients (30.7%), and 43 patients (10.4%) used steroids daily.
B-mode renal ultrasound showed 181 patients (36%; 95% confidence interval, 32%-40%) had “hyperechoic pattern of Malpighi pyramids compared with the adjacent cortex,” which was “associated with twinkling artifacts” visible on color Doppler ultrasound. There was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and patient age, disease duration, use of steroids, clinical tophi, and urate arthropathy (P less than .0001 for all). A significant association was also seen between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and decreased eGFR (P < .0001), proteinuria (P = .0006), leukocyturia (P = .0008), hypertension (P = .0008), hyperuricemia (P = .002), and coronary heart disease (P = .006).
In a multivariate analysis, there was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and clinical tophi (odds ratio, 7.27; 95% CI, 3.68–15.19; P < .0001), urate arthropathy (OR, 3.46; 95% CI, 1.99–6.09; P < .0001), estimated gout duration (OR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.55–2.96; P < .0001), double contour thickness (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.06–1.97; P < .02), and eGFR (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.09–0.89; P < .034).
“The finding was observed mainly in tophaceous gout, which involved a large proportion of our patients who had received very little treatment with urate-lowering drugs and was associated with moderately impaired renal function and urinary features compatible with tubulointerstitial nephritis,” Dr. Bardin and colleagues wrote in the study. The researchers also found “similar features” in 4 of 10 French patients at the Paris Necker Hospital in Paris, and noted that similar findings have been reported in Japan and Korea, which they said may mean hyperechoic medulla “is not unique to Vietnamese patients.”
Relation to CKD still unclear
In a related editorial, Federica Piani, MD, and Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the division of renal diseases and hypertension at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained that gout was considered by some clinicians to be a cause of CKD in a time before urate-lowering therapies, because as many as 25% of patients with gout went on to experience kidney failure and about half experienced lower kidney function.
The association between gout and CKD was thought to be attributable to “frequent deposition of urate crystals in the tubular lumens and interstitium in the outer medulla of these patients,” but the concept was later challenged because “the crystals were generally found focally and did not readily explain the kidney damage.”
But even as interest in rheumatology moved away from the concept of gouty nephropathy to how serum uric acid impacts CKD, “the possibility that urate crystal deposition in the kidney could also be contributing to the kidney injury was never ruled out,” according to Dr. Piani and Dr. Johnson.
Kidney biopsies can sometimes miss urate crystals because the crystals dissolve if alcohol fixation is not used and because the biopsy site is often in the renal cortex, the authors noted. Recent research has identified that dual-energy CT scans can distinguish between calcium deposits and urate crystals better than ultrasound, and previous research from Thomas Bardin, MD, and colleagues in two patients noted a correlation between dual-energy CT scan findings of urate crystals and hyperechoic medulla findings on renal ultrasound.
The results by Dr. Bardin and associates, they said, “have reawakened the entity of urate microcrystalline nephropathy as a possible cause of CKD.”
Robert Terkeltaub, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of Rheumatology at the San Diego VA Medical Center, said in an interview that he also believes the findings by Dr. Bardin and associates are real. He cited a study by Isabelle Ayoub, MD, and colleagues in Clinical Nephrology from 2016 that evaluated kidney biopsies in Germany and found medullary tophi were more likely to be present in patients with CKD than without.
“Chronic gouty nephropathy did not disappear. It still exists,” said Dr. Terkeltaub, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Bardin and colleagues.
The prospect that, if “you look hard enough, you’re going to see urate crystals and a pattern that’s attributed in the renal medulla” in patients with untreated gout is “very provocative, and interesting, and clinically relevant, and merits more investigation,” noted Dr. Terkeltaub, who is also president of the Gout, Hyperuricemia and Crystal-Associated Disease Network.
If verified, the results have important implications for patients with gout and its relationship to CKD, Dr. Terkeltaub said, but they raise “more questions than answers.
“I think it’s a really good wake-up call to start looking, doing good detective work here, and looking especially in people who have gout as opposed to just people with chronic kidney disease,” he said.
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Johnson, who coauthored an accompanying editorial, reported having equity in XORTX Therapeutics, serving as a consultant for Horizon Pharma, and having equity in Colorado Research Partners LLC. Dr. Terkeltaub reported receiving a research grant from AstraZeneca in the field of hyperuricemia and consultancies with AstraZeneca, Horizon, Sobi, Selecta Biosciences.
Is gouty nephropathy real? It’s a question that has been posed often in rheumatology over the last several decades.
A new study found 36% of patients with untreated gout at a medical center in Vietnam have diffuse hyperechoic renal medulla as seen on ultrasound, which could indicate the presence of microcrystalline nephropathy. However, the results, published in Kidney International, may raise more questions than answers about the existence of gouty nephropathy and its relation to chronic kidney disease (CKD).
In their study, Thomas Bardin, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Lariboisière Hospital in Paris and colleagues evaluated 502 consecutive patients from Vien Gut Medical Center in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, using B-mode renal ultrasound. The patients were mostly men with a median age of 46 years, body mass index of 25 kg/m2, estimated disease duration of 4 years, and uricemia of 423.2 micromol/L (7.11 mg/dL). Patients had a median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 78 mL/min per 1.73 m2. There was a history of hypertension in 112 patients (22.3%), type 2 diabetes in 58 patients (11.5%), renal lithiasis in 28 patients (5.6%), and coronary heart disease in 5 patients (1%).
While 39% of patients had previously used allopurinol for “a generally short period,” patients were not on urate-lowering therapy at the time of the study. Clinical tophi were present in 279 patients (55.6%), urate arthropathies in 154 patients (30.7%), and 43 patients (10.4%) used steroids daily.
B-mode renal ultrasound showed 181 patients (36%; 95% confidence interval, 32%-40%) had “hyperechoic pattern of Malpighi pyramids compared with the adjacent cortex,” which was “associated with twinkling artifacts” visible on color Doppler ultrasound. There was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and patient age, disease duration, use of steroids, clinical tophi, and urate arthropathy (P less than .0001 for all). A significant association was also seen between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and decreased eGFR (P < .0001), proteinuria (P = .0006), leukocyturia (P = .0008), hypertension (P = .0008), hyperuricemia (P = .002), and coronary heart disease (P = .006).
In a multivariate analysis, there was a significant association between renal medulla hyperechogenicity and clinical tophi (odds ratio, 7.27; 95% CI, 3.68–15.19; P < .0001), urate arthropathy (OR, 3.46; 95% CI, 1.99–6.09; P < .0001), estimated gout duration (OR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.55–2.96; P < .0001), double contour thickness (OR, 1.45; 95% CI, 1.06–1.97; P < .02), and eGFR (OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.09–0.89; P < .034).
“The finding was observed mainly in tophaceous gout, which involved a large proportion of our patients who had received very little treatment with urate-lowering drugs and was associated with moderately impaired renal function and urinary features compatible with tubulointerstitial nephritis,” Dr. Bardin and colleagues wrote in the study. The researchers also found “similar features” in 4 of 10 French patients at the Paris Necker Hospital in Paris, and noted that similar findings have been reported in Japan and Korea, which they said may mean hyperechoic medulla “is not unique to Vietnamese patients.”
Relation to CKD still unclear
In a related editorial, Federica Piani, MD, and Richard J. Johnson, MD, of the division of renal diseases and hypertension at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, explained that gout was considered by some clinicians to be a cause of CKD in a time before urate-lowering therapies, because as many as 25% of patients with gout went on to experience kidney failure and about half experienced lower kidney function.
The association between gout and CKD was thought to be attributable to “frequent deposition of urate crystals in the tubular lumens and interstitium in the outer medulla of these patients,” but the concept was later challenged because “the crystals were generally found focally and did not readily explain the kidney damage.”
But even as interest in rheumatology moved away from the concept of gouty nephropathy to how serum uric acid impacts CKD, “the possibility that urate crystal deposition in the kidney could also be contributing to the kidney injury was never ruled out,” according to Dr. Piani and Dr. Johnson.
Kidney biopsies can sometimes miss urate crystals because the crystals dissolve if alcohol fixation is not used and because the biopsy site is often in the renal cortex, the authors noted. Recent research has identified that dual-energy CT scans can distinguish between calcium deposits and urate crystals better than ultrasound, and previous research from Thomas Bardin, MD, and colleagues in two patients noted a correlation between dual-energy CT scan findings of urate crystals and hyperechoic medulla findings on renal ultrasound.
The results by Dr. Bardin and associates, they said, “have reawakened the entity of urate microcrystalline nephropathy as a possible cause of CKD.”
Robert Terkeltaub, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego, and section chief of Rheumatology at the San Diego VA Medical Center, said in an interview that he also believes the findings by Dr. Bardin and associates are real. He cited a study by Isabelle Ayoub, MD, and colleagues in Clinical Nephrology from 2016 that evaluated kidney biopsies in Germany and found medullary tophi were more likely to be present in patients with CKD than without.
“Chronic gouty nephropathy did not disappear. It still exists,” said Dr. Terkeltaub, who was not involved in the study by Dr. Bardin and colleagues.
The prospect that, if “you look hard enough, you’re going to see urate crystals and a pattern that’s attributed in the renal medulla” in patients with untreated gout is “very provocative, and interesting, and clinically relevant, and merits more investigation,” noted Dr. Terkeltaub, who is also president of the Gout, Hyperuricemia and Crystal-Associated Disease Network.
If verified, the results have important implications for patients with gout and its relationship to CKD, Dr. Terkeltaub said, but they raise “more questions than answers.
“I think it’s a really good wake-up call to start looking, doing good detective work here, and looking especially in people who have gout as opposed to just people with chronic kidney disease,” he said.
The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Johnson, who coauthored an accompanying editorial, reported having equity in XORTX Therapeutics, serving as a consultant for Horizon Pharma, and having equity in Colorado Research Partners LLC. Dr. Terkeltaub reported receiving a research grant from AstraZeneca in the field of hyperuricemia and consultancies with AstraZeneca, Horizon, Sobi, Selecta Biosciences.
FROM KIDNEY INTERNATIONAL
FDA expands belimumab indication to adults with lupus nephritis
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for belimumab (Benlysta) to adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Roughly 40% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develop lupus nephritis (LN), which causes inflammation in the kidneys and can lead to end-stage kidney disease.
“Benlysta is the first medicine approved to treat systemic lupus and adults with active lupus nephritis, an important treatment advance for patients with this incurable autoimmune disease,” Hal Barron, MD, GlaxoSmithKline’s chief scientific officer and president of research and development, said in a company news release.
Belimumab IV infusion was first approved in the United States in March 2011 for adults with SLE. The FDA approved belimumab IV infusion for use in children as young as age 5 years with SLE in 2019.
Both the IV and subcutaneous formulations are now indicated in the United States for adults with SLE and LN.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor that is thought to decrease the amount of abnormal B cells; the latter are thought to play a role in lupus.
The expanded indication for belimumab for patients with LN is based on findings from the BLISS-LN phase 3 trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in September.
“Neutralizing B-cell activating factor and down-regulating autoreactive B-cell function in kidneys” represents a “compelling therapeutic approach to lupus nephritis,” the lead investigator of BLISS-LN, Richard Furie, MD, told the online annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases meeting recently.
“In the 4 decades I have been caring for people with lupus, we have not been able to achieve remission in more than just one-third of patients with lupus nephritis, and despite all of our efforts, 10%-30% of patients with lupus kidney disease still progress to end-stage kidney disease,” Dr. Furie, who is chief of the division of rheumatology at Northwell Health, notes in the GSK statement.
“The data from the BLISS-LN study show that Benlysta added to standard therapy not only increased response rates over 2 years, but it also prevented worsening of kidney disease in patients with active lupus nephritis, compared to standard therapy alone,” he added.
BLISS-LN study: Belimumab effect seen mostly in those on MMF
BLISS-LN enrolled 448 adults with biopsy-confirmed active LN. Half were randomly allocated to receive IV belimumab (10 mg/kg) plus standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil for induction and maintenance or cyclophosphamide for induction followed by azathioprine for maintenance, with steroids) and half to receive placebo plus standard therapy.
At 2 years, significantly more patients in the belimumab group than in the placebo group had a primary efficacy renal response (43% vs. 32%; odds ratio, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.0- 2.3; P = .03).
This primary endpoint was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of ≤0.7, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the value before the renal flare or ≥60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 of body surface area, without use of rescue therapy.
The risk for a renal-related event or death was also significantly lower among patients who received belimumab than among those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .001). The safety profile of belimumab was consistent with that observed in prior studies.
But in a commentary that accompanied the publication of BLISS-LN, editorialists noted that “most of the treatment effect was seen in patients who had received mycophenolate mofetil. No benefit was present in the subgroup of patients who received cyclophosphamide-azathioprine.”
In addition, induction treatment was not randomly assigned, editorialists Michael Ward, MD, MPH, and Maria Tektonidou, MD, PhD, noted.
“If patients with more severe nephritis were preferentially treated with cyclophosphamide, a likely inclination among most physicians, the trial may be telling us that belimumab enhances responses only among less severely affected patients,” observed Dr. Ward, who is with the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Tektonidou, of the National and Kopodistrian University, in Athens.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for belimumab (Benlysta) to adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Roughly 40% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develop lupus nephritis (LN), which causes inflammation in the kidneys and can lead to end-stage kidney disease.
“Benlysta is the first medicine approved to treat systemic lupus and adults with active lupus nephritis, an important treatment advance for patients with this incurable autoimmune disease,” Hal Barron, MD, GlaxoSmithKline’s chief scientific officer and president of research and development, said in a company news release.
Belimumab IV infusion was first approved in the United States in March 2011 for adults with SLE. The FDA approved belimumab IV infusion for use in children as young as age 5 years with SLE in 2019.
Both the IV and subcutaneous formulations are now indicated in the United States for adults with SLE and LN.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor that is thought to decrease the amount of abnormal B cells; the latter are thought to play a role in lupus.
The expanded indication for belimumab for patients with LN is based on findings from the BLISS-LN phase 3 trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in September.
“Neutralizing B-cell activating factor and down-regulating autoreactive B-cell function in kidneys” represents a “compelling therapeutic approach to lupus nephritis,” the lead investigator of BLISS-LN, Richard Furie, MD, told the online annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases meeting recently.
“In the 4 decades I have been caring for people with lupus, we have not been able to achieve remission in more than just one-third of patients with lupus nephritis, and despite all of our efforts, 10%-30% of patients with lupus kidney disease still progress to end-stage kidney disease,” Dr. Furie, who is chief of the division of rheumatology at Northwell Health, notes in the GSK statement.
“The data from the BLISS-LN study show that Benlysta added to standard therapy not only increased response rates over 2 years, but it also prevented worsening of kidney disease in patients with active lupus nephritis, compared to standard therapy alone,” he added.
BLISS-LN study: Belimumab effect seen mostly in those on MMF
BLISS-LN enrolled 448 adults with biopsy-confirmed active LN. Half were randomly allocated to receive IV belimumab (10 mg/kg) plus standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil for induction and maintenance or cyclophosphamide for induction followed by azathioprine for maintenance, with steroids) and half to receive placebo plus standard therapy.
At 2 years, significantly more patients in the belimumab group than in the placebo group had a primary efficacy renal response (43% vs. 32%; odds ratio, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.0- 2.3; P = .03).
This primary endpoint was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of ≤0.7, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the value before the renal flare or ≥60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 of body surface area, without use of rescue therapy.
The risk for a renal-related event or death was also significantly lower among patients who received belimumab than among those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .001). The safety profile of belimumab was consistent with that observed in prior studies.
But in a commentary that accompanied the publication of BLISS-LN, editorialists noted that “most of the treatment effect was seen in patients who had received mycophenolate mofetil. No benefit was present in the subgroup of patients who received cyclophosphamide-azathioprine.”
In addition, induction treatment was not randomly assigned, editorialists Michael Ward, MD, MPH, and Maria Tektonidou, MD, PhD, noted.
“If patients with more severe nephritis were preferentially treated with cyclophosphamide, a likely inclination among most physicians, the trial may be telling us that belimumab enhances responses only among less severely affected patients,” observed Dr. Ward, who is with the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Tektonidou, of the National and Kopodistrian University, in Athens.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for belimumab (Benlysta) to adults with active lupus nephritis who are receiving standard therapy.
Roughly 40% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) develop lupus nephritis (LN), which causes inflammation in the kidneys and can lead to end-stage kidney disease.
“Benlysta is the first medicine approved to treat systemic lupus and adults with active lupus nephritis, an important treatment advance for patients with this incurable autoimmune disease,” Hal Barron, MD, GlaxoSmithKline’s chief scientific officer and president of research and development, said in a company news release.
Belimumab IV infusion was first approved in the United States in March 2011 for adults with SLE. The FDA approved belimumab IV infusion for use in children as young as age 5 years with SLE in 2019.
Both the IV and subcutaneous formulations are now indicated in the United States for adults with SLE and LN.
Belimumab is a B-lymphocyte stimulator protein inhibitor that is thought to decrease the amount of abnormal B cells; the latter are thought to play a role in lupus.
The expanded indication for belimumab for patients with LN is based on findings from the BLISS-LN phase 3 trial, published in The New England Journal of Medicine in September.
“Neutralizing B-cell activating factor and down-regulating autoreactive B-cell function in kidneys” represents a “compelling therapeutic approach to lupus nephritis,” the lead investigator of BLISS-LN, Richard Furie, MD, told the online annual Perspectives in Rheumatic Diseases meeting recently.
“In the 4 decades I have been caring for people with lupus, we have not been able to achieve remission in more than just one-third of patients with lupus nephritis, and despite all of our efforts, 10%-30% of patients with lupus kidney disease still progress to end-stage kidney disease,” Dr. Furie, who is chief of the division of rheumatology at Northwell Health, notes in the GSK statement.
“The data from the BLISS-LN study show that Benlysta added to standard therapy not only increased response rates over 2 years, but it also prevented worsening of kidney disease in patients with active lupus nephritis, compared to standard therapy alone,” he added.
BLISS-LN study: Belimumab effect seen mostly in those on MMF
BLISS-LN enrolled 448 adults with biopsy-confirmed active LN. Half were randomly allocated to receive IV belimumab (10 mg/kg) plus standard therapy (mycophenolate mofetil for induction and maintenance or cyclophosphamide for induction followed by azathioprine for maintenance, with steroids) and half to receive placebo plus standard therapy.
At 2 years, significantly more patients in the belimumab group than in the placebo group had a primary efficacy renal response (43% vs. 32%; odds ratio, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.0- 2.3; P = .03).
This primary endpoint was defined as a ratio of urinary protein to creatinine of ≤0.7, an estimated glomerular filtration rate that was no worse than 20% below the value before the renal flare or ≥60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 of body surface area, without use of rescue therapy.
The risk for a renal-related event or death was also significantly lower among patients who received belimumab than among those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.51; P = .001). The safety profile of belimumab was consistent with that observed in prior studies.
But in a commentary that accompanied the publication of BLISS-LN, editorialists noted that “most of the treatment effect was seen in patients who had received mycophenolate mofetil. No benefit was present in the subgroup of patients who received cyclophosphamide-azathioprine.”
In addition, induction treatment was not randomly assigned, editorialists Michael Ward, MD, MPH, and Maria Tektonidou, MD, PhD, noted.
“If patients with more severe nephritis were preferentially treated with cyclophosphamide, a likely inclination among most physicians, the trial may be telling us that belimumab enhances responses only among less severely affected patients,” observed Dr. Ward, who is with the National Institutes of Health, and Dr. Tektonidou, of the National and Kopodistrian University, in Athens.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ADA 2021 standards address financial hardship in diabetes
For 2021, the American Diabetes Association offers new guidance on assessing patients’ financial and social barriers to care, especially given the COVID-19 pandemic, individualizing treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes, and use of diabetes technology.
As it does every year, the annual update incorporates new clinical information that has become available since the last guideline, with occasional revisions during the year as needed. “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2021,” was published online as a supplement to Diabetes Care.
The new standards advise that patients be assessed for food and housing insecurity, social support, and “cost-related medication nonadherence,” and those found to have difficulty referred to appropriate community resources.
“Clinicians need to be sensitive to the fact that patients may have very good reasons for not taking their medication, [as in] if they can’t afford it,” ADA chief science & medical officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Gabbay noted that “a heightened awareness” of social determinants of health is weaved throughout the 2021 standards because of the pandemic, with information on the topic derived from a July 2020 joint consensus statement in Diabetes Care, endorsed by a number of other societies, as well as a November publication also in Diabetes Care.
“We made several recommendations that speak to social determinants of health, placing an emphasis on engaging in conversations around this subject and screening for related issues such as food insecurity that weren’t there previously,” he said.
“Screening tools are suggested. It helped us to have an in-depth scientific review of the literature to know the prevalence of this in people with diabetes. ... Having the science to put it in was a key step,” Dr. Gabbay noted.
Consider kidney, heart disease in type 2 treatment individualization
Recent data from trials such as CREDENCE and DAPA-HF, among others, have been added to inform the choice of pharmacologic treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes with comorbid diabetic kidney disease and chronic heart failure.
“ADA has been advocating individualization of treatment based on comorbidities for a while, but we’ve taken more steps in that direction. Beyond lifestyle for all individuals with type 2 diabetes, clinicians want to think early on about which comorbidities patients have and then think about the appropriate treatment based on that,” Dr. Gabbay said.
And for the third year in a row, the section on cardiovascular disease and risk management has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology.
“All the things in that section are very much aligned with ACC and that’s been a great partnership,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Now, ADA is in discussions with other professional societies representing relevant specialties to create further such unified messages.
“What we all want to avoid is having multiple different guidelines. We want to speak with one voice and find common ground as much as possible. … It makes it much easier for clinicians to know what to do. That’s the goal of all this,” he noted.
Diabetes technology: The rise of CGM during pandemic and beyond
New information about continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been added to the diabetes technology section. Use of CGM is now recommended for anyone with diabetes who takes multiple daily injections or uses an insulin pump, regardless of age or diabetes type. The document provides expanded advice on use of time in range data for glycemic monitoring, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic when remote monitoring is preferable.
Insurers are increasingly covering CGM for patients on insulin, but it’s far from universal. While the ultimate goal is to ensure access to CGM for everyone with diabetes, those treated with multiple daily insulin doses are the priority for now.
“Our hope is that as there’s greater evidence there will be more movement towards coverage. There are still so many people for whom it’s quite clear they would benefit because they’re on insulin but don’t have access to it. That’s an important area that ADA is advocating for, and it’s reflected in the standards of care,” Dr. Gabbay said.
In another technology-related revision, the term “blinded” CGM has been replaced with “professional CGM,” because clinic-based use of the devices can be “blinded” to the patient or monitored in real-time by both the patient and clinician. Also, a new recommendation has been added to address skin reactions associated with diabetes technology use.
Information about use of CGM in hospital settings during the COVID-19 pandemic has also been added in the technology section.
The COVID-19 pandemic comes up again in the section on vaccines.
“We mention that people with diabetes should be considered high priority [for COVID-19 vaccines], and that’s something that ADA is strongly advocating for because 40% of COVID-19 deaths have been in people with diabetes,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Dr. Gabbay reported being on the advisory boards of Onduo, Health Reveal, Vida Health, Lark, and Form Health.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
For 2021, the American Diabetes Association offers new guidance on assessing patients’ financial and social barriers to care, especially given the COVID-19 pandemic, individualizing treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes, and use of diabetes technology.
As it does every year, the annual update incorporates new clinical information that has become available since the last guideline, with occasional revisions during the year as needed. “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2021,” was published online as a supplement to Diabetes Care.
The new standards advise that patients be assessed for food and housing insecurity, social support, and “cost-related medication nonadherence,” and those found to have difficulty referred to appropriate community resources.
“Clinicians need to be sensitive to the fact that patients may have very good reasons for not taking their medication, [as in] if they can’t afford it,” ADA chief science & medical officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Gabbay noted that “a heightened awareness” of social determinants of health is weaved throughout the 2021 standards because of the pandemic, with information on the topic derived from a July 2020 joint consensus statement in Diabetes Care, endorsed by a number of other societies, as well as a November publication also in Diabetes Care.
“We made several recommendations that speak to social determinants of health, placing an emphasis on engaging in conversations around this subject and screening for related issues such as food insecurity that weren’t there previously,” he said.
“Screening tools are suggested. It helped us to have an in-depth scientific review of the literature to know the prevalence of this in people with diabetes. ... Having the science to put it in was a key step,” Dr. Gabbay noted.
Consider kidney, heart disease in type 2 treatment individualization
Recent data from trials such as CREDENCE and DAPA-HF, among others, have been added to inform the choice of pharmacologic treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes with comorbid diabetic kidney disease and chronic heart failure.
“ADA has been advocating individualization of treatment based on comorbidities for a while, but we’ve taken more steps in that direction. Beyond lifestyle for all individuals with type 2 diabetes, clinicians want to think early on about which comorbidities patients have and then think about the appropriate treatment based on that,” Dr. Gabbay said.
And for the third year in a row, the section on cardiovascular disease and risk management has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology.
“All the things in that section are very much aligned with ACC and that’s been a great partnership,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Now, ADA is in discussions with other professional societies representing relevant specialties to create further such unified messages.
“What we all want to avoid is having multiple different guidelines. We want to speak with one voice and find common ground as much as possible. … It makes it much easier for clinicians to know what to do. That’s the goal of all this,” he noted.
Diabetes technology: The rise of CGM during pandemic and beyond
New information about continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been added to the diabetes technology section. Use of CGM is now recommended for anyone with diabetes who takes multiple daily injections or uses an insulin pump, regardless of age or diabetes type. The document provides expanded advice on use of time in range data for glycemic monitoring, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic when remote monitoring is preferable.
Insurers are increasingly covering CGM for patients on insulin, but it’s far from universal. While the ultimate goal is to ensure access to CGM for everyone with diabetes, those treated with multiple daily insulin doses are the priority for now.
“Our hope is that as there’s greater evidence there will be more movement towards coverage. There are still so many people for whom it’s quite clear they would benefit because they’re on insulin but don’t have access to it. That’s an important area that ADA is advocating for, and it’s reflected in the standards of care,” Dr. Gabbay said.
In another technology-related revision, the term “blinded” CGM has been replaced with “professional CGM,” because clinic-based use of the devices can be “blinded” to the patient or monitored in real-time by both the patient and clinician. Also, a new recommendation has been added to address skin reactions associated with diabetes technology use.
Information about use of CGM in hospital settings during the COVID-19 pandemic has also been added in the technology section.
The COVID-19 pandemic comes up again in the section on vaccines.
“We mention that people with diabetes should be considered high priority [for COVID-19 vaccines], and that’s something that ADA is strongly advocating for because 40% of COVID-19 deaths have been in people with diabetes,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Dr. Gabbay reported being on the advisory boards of Onduo, Health Reveal, Vida Health, Lark, and Form Health.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
For 2021, the American Diabetes Association offers new guidance on assessing patients’ financial and social barriers to care, especially given the COVID-19 pandemic, individualizing treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes, and use of diabetes technology.
As it does every year, the annual update incorporates new clinical information that has become available since the last guideline, with occasional revisions during the year as needed. “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2021,” was published online as a supplement to Diabetes Care.
The new standards advise that patients be assessed for food and housing insecurity, social support, and “cost-related medication nonadherence,” and those found to have difficulty referred to appropriate community resources.
“Clinicians need to be sensitive to the fact that patients may have very good reasons for not taking their medication, [as in] if they can’t afford it,” ADA chief science & medical officer Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Dr. Gabbay noted that “a heightened awareness” of social determinants of health is weaved throughout the 2021 standards because of the pandemic, with information on the topic derived from a July 2020 joint consensus statement in Diabetes Care, endorsed by a number of other societies, as well as a November publication also in Diabetes Care.
“We made several recommendations that speak to social determinants of health, placing an emphasis on engaging in conversations around this subject and screening for related issues such as food insecurity that weren’t there previously,” he said.
“Screening tools are suggested. It helped us to have an in-depth scientific review of the literature to know the prevalence of this in people with diabetes. ... Having the science to put it in was a key step,” Dr. Gabbay noted.
Consider kidney, heart disease in type 2 treatment individualization
Recent data from trials such as CREDENCE and DAPA-HF, among others, have been added to inform the choice of pharmacologic treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes with comorbid diabetic kidney disease and chronic heart failure.
“ADA has been advocating individualization of treatment based on comorbidities for a while, but we’ve taken more steps in that direction. Beyond lifestyle for all individuals with type 2 diabetes, clinicians want to think early on about which comorbidities patients have and then think about the appropriate treatment based on that,” Dr. Gabbay said.
And for the third year in a row, the section on cardiovascular disease and risk management has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology.
“All the things in that section are very much aligned with ACC and that’s been a great partnership,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Now, ADA is in discussions with other professional societies representing relevant specialties to create further such unified messages.
“What we all want to avoid is having multiple different guidelines. We want to speak with one voice and find common ground as much as possible. … It makes it much easier for clinicians to know what to do. That’s the goal of all this,” he noted.
Diabetes technology: The rise of CGM during pandemic and beyond
New information about continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been added to the diabetes technology section. Use of CGM is now recommended for anyone with diabetes who takes multiple daily injections or uses an insulin pump, regardless of age or diabetes type. The document provides expanded advice on use of time in range data for glycemic monitoring, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic when remote monitoring is preferable.
Insurers are increasingly covering CGM for patients on insulin, but it’s far from universal. While the ultimate goal is to ensure access to CGM for everyone with diabetes, those treated with multiple daily insulin doses are the priority for now.
“Our hope is that as there’s greater evidence there will be more movement towards coverage. There are still so many people for whom it’s quite clear they would benefit because they’re on insulin but don’t have access to it. That’s an important area that ADA is advocating for, and it’s reflected in the standards of care,” Dr. Gabbay said.
In another technology-related revision, the term “blinded” CGM has been replaced with “professional CGM,” because clinic-based use of the devices can be “blinded” to the patient or monitored in real-time by both the patient and clinician. Also, a new recommendation has been added to address skin reactions associated with diabetes technology use.
Information about use of CGM in hospital settings during the COVID-19 pandemic has also been added in the technology section.
The COVID-19 pandemic comes up again in the section on vaccines.
“We mention that people with diabetes should be considered high priority [for COVID-19 vaccines], and that’s something that ADA is strongly advocating for because 40% of COVID-19 deaths have been in people with diabetes,” Dr. Gabbay said.
Dr. Gabbay reported being on the advisory boards of Onduo, Health Reveal, Vida Health, Lark, and Form Health.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
How to refine your approach to peripheral arterial disease
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD), the progressive disorder that results in ischemia to distal vascular territories as a result of atherosclerosis, spans a wide range of presentations, from minimally symptomatic disease to limb ischemia secondary to acute or chronic occlusion.
The prevalence of PAD is variable, due to differing diagnostic criteria used in studies, but PAD appears to affect 1 in every 22 people older than age 40.1 However, since PAD incidence increases with age, it is increasing in prevalence as the US population ages.1-3
PAD is associated with increased hospitalizations and decreased quality of life.4 Patients with PAD have an estimated 30% 5-year risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from a vascular cause.3
Screening. Although PAD is underdiagnosed and appears to be undertreated,3 population-based screening for PAD in asymptomatic patients is not recommended. A Cochrane review found no studies evaluating the benefit of asymptomatic population-based screening.5 Similarly, in 2018, the USPSTF performed a comprehensive review and found no studies to support routine screening and determined there was insufficient evidence to recommend it.6,7
Risk factors and associated comorbidities
PAD risk factors, like the ones detailed below, have a potentiating effect. The presence of 2 risk factors doubles PAD risk, while 3 or more risk factors increase PAD risk by a factor of 10.1
Increasing age is the greatest single risk factor for PAD.1,2,8,9 Researchers using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) found that the prevalence of PAD increased from 1.4% in individuals ages 40 to 49 years to almost 17% in those age 70 or older.1
Demographic characteristics. Most studies demonstrate a higher risk for PAD in men.1-3,10 African-American patients have more than twice the risk for PAD, compared with Whites, even after adjustment for the increased prevalence of associated diseases such as hypertension and diabetes in this population.1-3,10
Continue to: Genetics...
Genetics. A study performed by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute suggested that genetic correlations between twins were more important than environmental factors in the development of PAD.11
Smoking. Most population studies show smoking to be the greatest modifiable risk factor for PAD. An analysis of the NHANES data yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 4.1 for current smokers and of 1.8 for former smokers.1 Risk increases linearly with cumulative years of smoking.1,2,9,10
Diabetes is another significant modifiable risk factor, increasing PAD risk by 2.5 times.2 Diabetes is also associated with increases in functional limitation from claudication, risk for acute coronary syndrome, and progression to amputation.1
Hypertension nearly doubles the risk for PAD, and poor control further increases this risk.2,9,10
Chronic kidney disease (CKD). Patients with CKD have a progressively higher prevalence of PAD with worsening renal function.1 There is also an association between CKD and increased morbidity, revascularization failure, and increased mortality.1
Two additional risk factors that are less well understood are dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation. There is conflicting data regarding the role of individual components of cholesterol and their effect on PAD, although lipoprotein (a) has been shown to be an independent risk factor for both the development and progression of PAD.12 Similarly, chronic inflammation has been shown to play a role in the initiation and progression of the disease, although the role of inflammatory markers in evaluation and treatment is unclear and assessment for these purposes is not currently recommended.12,13
Continue to: Diagnosis...
Diagnosis
Clinical presentation
Lower extremity pain is the hallmark symptom of PAD, but presentation varies. The classic presentation is claudication, pain within a defined muscle group that occurs with exertion and is relieved by rest. Claudication is most common in the calf but also occurs in the buttock/thigh and the foot.
However, most patients with PAD present with pain that does not fit the definition of claudication. Patients with comorbidities, physical inactivity, and neuropathy are more likely to present with atypical pain.14 These patients may demonstrate critical or acute limb ischemia, characterized by pain at rest and most often localized to the forefoot and toes. Patients with critical limb ischemia may also present with nonhealing wounds/ulcers or gangrene.15
Physical exam findings can support the diagnosis of PAD, but none are reliable enough to rule the diagnosis in or out. Findings suggestive of PAD include cool skin, presence of a bruit (iliac, femoral, or popliteal), and palpable pulse abnormality. Multiple abnormal physical exam findings increase the likelihood of PAD, while the absence of a bruit or palpable pulse abnormality makes PAD less likely.16 In patients with PAD, an associated wound/ulcer is most often distal in the foot and usually appears dry.17
The differential diagnosis for intermittent leg pain is broad and includes neurologic, musculoskeletal, and venous etiologies. Table 118 lists some common alternate diagnoses for patients presenting with leg pain or claudication.
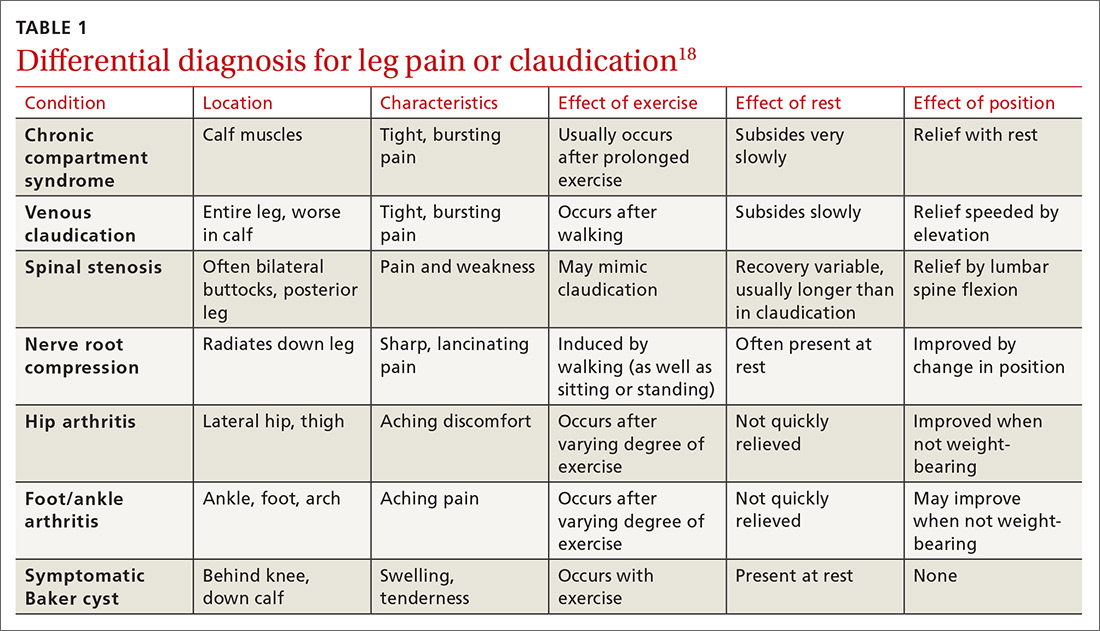
Continue to: Diagnostic testing...
Diagnostic testing
An ankle-brachial index (ABI) test should be performed in patients with history or physical exam findings suggestive of PAD. A resting ABI is performed with the patient in the supine position, with measurement of systolic blood pressure in both arms and ankles using a Doppler ultrasound device. Table 213 outlines ABI scoring and interpretation.
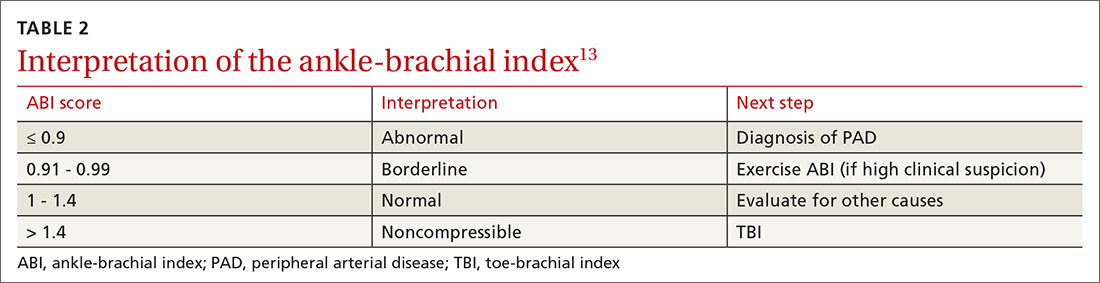
An ABI > 1.4 is an invalid measurement, indicating that the arteries are too calcified to be compressed. These highly elevated ABI measurements are common in patients with diabetes and/or advanced CKD. In these patients, a toe-brachial index (TBI) test should be performed, because the digital arteries are almost always compressible.13
Patients with symptomatic PAD who are under consideration for revascularization may benefit from radiologic imaging of the lower extremities with duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography to determine the anatomic location and severity of stenosis.13
Management of PAD
Lifestyle interventions
For patients with PAD, lifestyle modifications are an essential—but challenging—component of disease management.
Continue to: Smoking cessation...
Smoking cessation. As with other atherosclerotic diseases, PAD progression is strongly correlated with smoking. A trial involving 204 active smokers with PAD showed that 5-year mortality and amputation rates dropped by more than half in those who quit smoking within a year, with numbers needed to treat (NNT) of 6 for mortality and 5 for amputation.19 Because of this dramatic effect, American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines encourage providers to address smoking at every visit and use cessation programs and medication to increase quit rates.13
Exercise may be the most important intervention for PAD. A 2017 Cochrane review found that supervised, structured exercise programs increase pain-free and maximal walking distances by at least 20% and also improve physical and mental quality of life.20 In a trial involving 111 patients with aortoiliac PAD, supervised exercise plus medical care led to greater functional improvement than either revascularization plus medical care or medical care alone.21 In a 2018 Cochrane review, neither revascularization or revascularization added to supervised exercise were better than supervised exercise alone.22 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend supervised exercise programs for claudication prior to considering revascularization.13TABLE 313 outlines the components of a structured exercise program.

Unfortunately, the benefit of these programs has been difficult to reproduce without supervision. Another 2018 Cochrane review demonstrated significant improvement with supervised exercise and no clear improvement in patients given home exercise or advice to walk.23 A recent study examined the effect of having patients use a wearable fitness tracker for home exercise and demonstrated no benefit over usual care.24
Diet. There is some evidence that dietary interventions can prevent and possibly improve PAD. A large randomized controlled trial showed that a Mediterranean diet lowered rates of PAD over 1 year compared to a low-fat diet, with an NNT of 336 if supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil and 448 if supplemented with nuts.25 A small trial of 25 patients who consumed non-soy legumes daily for 8 weeks showed average ABI improvement of 6%, although there was no control group.26
Medical therapy to address peripheral and cardiovascular events
Standard medical therapy for coronary artery disease (CAD) is recommended for patients with PAD to reduce cardiovascular and limb events. For example, treatment of hypertension reduces cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, and studies verify that lowering blood pressure does not worsen claudication or limb perfusion.
13TABLE 413,27-30 outlines the options for medical therapy.
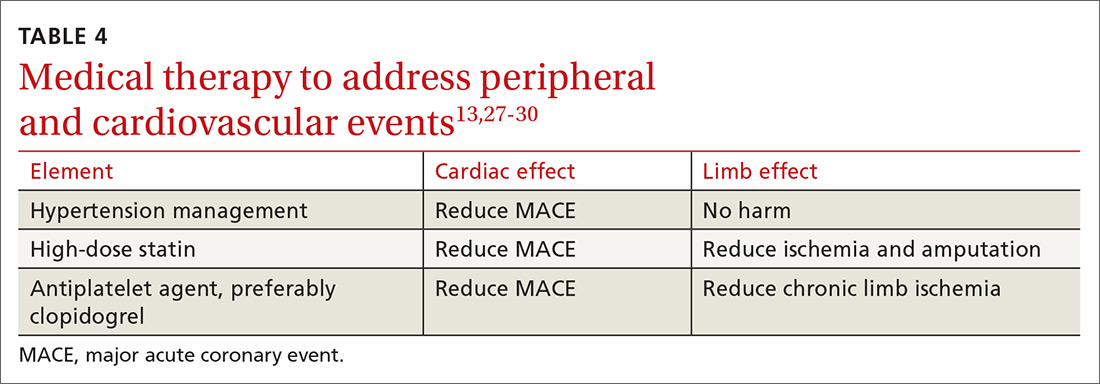
Continue to: Statins...
Statins reduce cardiovascular events in PAD patients. A large study demonstrated that 40 mg of simvastatin has an NNT of 21 to prevent a coronary or cerebrovascular event in PAD, similar to the NNT of 23 seen in treatment of CAD.27 Statins also reduce adverse limb outcomes. A registry of atherosclerosis patients showed that statins have an NNT of 56 to prevent amputation in PAD and an NNT of 28 to prevent worsening claudication, critical limb ischemia, revascularization, or amputation.28
Antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin or clopidogrel is recommended for symptomatic patients and for asymptomatic patients with an ABI ≤ 0.9.13 A Cochrane review demonstrated significantly reduced mortality with nonaspirin antiplatelet agents vs aspirin (NNT = 94) without increase in major bleeding.29 Only British guidelines specifically recommend clopidogrel over aspirin.31
Dual antiplatelet therapy has not shown consistent benefits over aspirin alone. ACC/AHA guidelines state that dual antiplatelet therapy is not well established for PAD but may be reasonable after revascularization.13
Voraxapar is a novel antiplatelet agent that targets the thrombin-binding receptor on platelets. However, trials show no significant coronary benefit, and slight reductions in acute limb ischemia are offset by increases in major bleeding.13
For patients receiving medical therapy, ongoing evaluation and treatment should be based on claudication symptoms and clinical assessment.
Medical therapy for claudication
Several medications have been proposed for symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication. Cilostazol is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with the best risk-benefit ratio. A Cochrane review showed improvements in maximal and pain-free walking distances compared to placebo and improvements in quality of life with cilostazol 100 mg taken twice daily.32 Adverse effects included headache, dizziness, palpitations, and diarrhea.29
Continue to: Pentoxifylline...
Pentoxifylline is another phosphodiesterase inhibitor with less evidence of improvement, higher adverse effect rates, and more frequent dosing. It is not recommended for treatment of intermittent claudication.13,33
Supplements. Padma 28, a Tibetan herbal formulation, appears to improve maximal walking distance with adverse effect rates similar to placebo.34 Other supplements, including vitamin E, ginkgo biloba, and omega-3 fatty acids, have no evidence of benefit.35-37
When revascularizationis needed
Patients who develop limb ischemia or lifestyle-limiting claudication despite conservative therapy are candidates for revascularization. Endovascular techniques include angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, and precise medication delivery. Surgical approaches mainly consist of thrombectomy and bypass grafting. For intermittent claudication despite conservative care, ACC/AHA guidelines state endovascular procedures are appropriate for aortoiliac disease and reasonable for femoropopliteal disease, but unproven for infrapopliteal disease.13
Acute limb ischemia is an emergency requiring immediate intervention. Two trials revealed identical overall and amputation-free survival rates for percutaneous thrombolysis and surgical thrombectomy.38,39 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend anticoagulation with heparin followed by the revascularization technique that will most rapidly restore arterial flow.13
For chronic limb ischemia, a large trial showed angioplasty had lower initial morbidity, length of hospitalization, and cost than surgical repair. However, surgical mortality was lower after 2 years.40 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend either surgery or endovascular procedures and propose initial endovascular treatment followed by surgery if needed.13 After revascularization, the patient should be followed periodically with a clinical evaluation and ABI measurement with further consideration for routine duplex ultrasound surveillance.13
Outcomes
Patients with PAD have variable outcomes. About 70% to 80% of patients with this diagnosis will have a stable disease process with no worsening of symptoms, 10% to 20% will experience worsening symptoms over time, 5% to 10% will require revascularization within 5 years of diagnosis, and 1% to 5% will progress to critical limb ischemia, which has a 5-year amputation rate of 1% to 4%.2 Patients who require amputation have poor outcomes: Within 2 years, 30% are dead and 15% have had further amputations.18
In addition to the morbidity and mortality from its own progression, PAD is an important predictor of CAD and is associated with a significant elevation in morbidity and mortality from CAD. One small but well-designed prospective cohort study found that patients with PAD had a more than 6-fold increased risk of death from CAD than did patients without PAD.41
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Francesca Cimino, MD, FAAFP, for her help in reviewing this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Dustin K. Smith, DO, 2080 Child Street, Jacksonville, FL 32214; [email protected]
1. Eraso LH, Fukaya E, Mohler ER 3rd, et al. Peripheral arterial disease, prevalence and cumulative risk factor profile analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21:704-711.
2. Pasternak RC, Criqui MH, Benjamin EJ, et al; American Heart Association. Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Conference: Writing Group I: epidemiology. Circulation. 2004;109:2605-2612.
3. Hirsch AT, Criqui MH, Treat-Jacobson D, et al. Peripheral arterial disease detection, awareness, and treatment in primary care. JAMA. 2001;286:1317-1324.
4. Olin JW, Sealove BA. Peripheral artery disease: current insight into the disease and its diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:678-692.
5. Andras A, Ferkert B. Screening for peripheral arterial disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(4):CD010835.
6. Guirguis-Blake JM, Evans CV, Redmond N, et al. Screening for peripheral artery disease using ankle-brachial index: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;320:184-196.
7. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for peripheral artery disease and cardiovascular disease risk assessment with ankle-brachial index: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;230:177-183.
8. American Heart Association Writing Group 2. Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Symposium II: screening for atherosclerotic vascular diseases: should nationwide programs be instituted? Circulation. 2008;118:2830-2836.
9. Berger JS, Hochman J, Lobach I, et al. Modifiable risk factor burden and the prevalence of peripheral artery disease in different vascular territories. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58:673-681.
10. Joosten MM, Pai JK, Bertoia ML, et al. Associations between conventional cardiovascular risk factors and risk of peripheral artery disease in men. JAMA. 2012;308:1660-1667.
11. Carmelli D, Fabsitz RR, Swan GE, et al. Contribution of genetic and environmental influences to ankle-brachial blood pressure index in the NHLBI Twin Study. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:452-458.
12. Aboyans V, Criqui MH, Denenberg JO, et al. Risk factors for progression of peripheral arterial disease in large and small vessels. Circulation. 2006;113:2623-2629.
13. Gerald-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e726-e779.
14. McDermott MM, Greenland P, Liu K, et al. Leg symptoms in peripheral arterial disease: associated clinical characteristics and functional impairment. JAMA. 2001;286:1599-1606.
15. Cranley JJ. Ischemic rest pain. Arch Surg. 1969;98:187-188.
16. Khan NA, Rahim SA, Anand SS, et al. Does the clinical examination predict lower extremity peripheral arterial disease? JAMA. 2006;295:536-546.
17. Wennberg PW. Approach to the patient with peripheral arterial disease. Circulation. 2013;128:2241-2250.
18. Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, et al. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). Eur J Vas Endovasc Surg. 2007;33:S1-S75.
19. Armstrong EJ, Wu J, Singh GD, et al. Smoking cessation is associated with decreased mortality and improved amputation-free survival among patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1565-1571.
20. Lane R, Harwood A, Watson L, et al. Exercise for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;(12):CD000990.
21. Murphy TP, Cutlip DE, Regensteiner JG, et al; CLEVER Study Investigators. Supervised exercise versus primary stenting for claudication resulting from aortoiliac peripheral artery disease: six-month outcomes from the claudication: exercise versus endoluminal revascularization (CLEVER) study. Circulation. 2012;125:130-139.
22. Fakhry F, Fokkenrood HJP, Pronk S, et al. Endovascular revascularization versus conservative management for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(3):CD010512.
23. Hageman D, Fokkenrood HJ, Gommans LN, et al. Supervised exercise therapy versus home-based exercise therapy versus walking advice for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(4):CD005263.
24. McDermott MM, Spring B, Berger JS, et al. Effect of a home-based exercise intervention of wearable technology and telephone coaching on walking performance in peripheral artery disease: the HONOR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;319:1665-1676.
25. Ruiz-Canela M, Estruch R, Corella D, et al. Association of Mediterranean diet with peripheral artery disease: the PREDIMED randomized trial. JAMA. 2014;311:415-417.
26. Zahradka P, Wright B, Weighell W, et al. Daily non-soy legume consumption reverses vascular impairment due to peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2013;230:310-314.
27. Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. Randomized trial of the effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on peripheral vascular and other major vascular outcomes in 20536 people with peripheral arterial disease and other high-risk conditions. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:645-655.
28. Kumbhani DJ, Steg G, Cannon CP, et al. Statin therapy and long-term adverse limb outcomes in patients with peripheral artery disease: insights from the REACH registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2864-2872.
29. Wong PF, Chong LY, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Antiplatelet agents for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(11):CD001272.
30. Critical Leg Ischaemia Prevention Study (CLIPS) Group, Catalano M, Born G, Peto R. Prevention of serious vascular events by aspirin amongst patients with peripheral arterial disease: randomized, double-blind trial. J Intern Med. 2007;261:276-284.
31. Morley RL, Sharma A, Horsch AD, et al. Peripheral artery disease. BMJ. 2018;360:j5842.
32. Bedenis R, Stewart M, Cleanthis M, et al. Cilostazol for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(10):CD003748.

33. Salhiyyah K, Forster R, Senanayake E, et al. Pentoxifylline for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(9):CD005262.
34. Stewart M, Morling JR, Maxwell H. Padma 28 for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(3):CD007371.
35. Kleijnen J, Mackerras D. Vitamin E for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1998;(1):CD000987.
36. Nicolai SPA, Kruidenior LM, Bendermacher BLW, et al. Ginkgo biloba for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(6):CD006888.
37. Campbell A, Price J, Hiatt WR. Omega-3 fatty acids for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD003833.
38. American Surgical Association, New York Surgical Society, Philadelphia Academy of Surgery, Southern Surgical Association (US), Central Surgical Association. Results of a prospective randomized trial evaluating surgery versus thrombolysis for ischemia of the lower extremity: the STILE trial. Ann Surg. 1994;220:251-268.
39. Ouriel K, Veith FJ, Sasahara AA.
40. Bradbury AW, Ruckley CV, Fowkes FGR, et al. Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:1925-1934.
41. Criqui MH, Langer RD, Fronek A, et al. Mortality over a period of 10 years in patients with peripheral arterial disease. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:381-386.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD), the progressive disorder that results in ischemia to distal vascular territories as a result of atherosclerosis, spans a wide range of presentations, from minimally symptomatic disease to limb ischemia secondary to acute or chronic occlusion.
The prevalence of PAD is variable, due to differing diagnostic criteria used in studies, but PAD appears to affect 1 in every 22 people older than age 40.1 However, since PAD incidence increases with age, it is increasing in prevalence as the US population ages.1-3
PAD is associated with increased hospitalizations and decreased quality of life.4 Patients with PAD have an estimated 30% 5-year risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from a vascular cause.3
Screening. Although PAD is underdiagnosed and appears to be undertreated,3 population-based screening for PAD in asymptomatic patients is not recommended. A Cochrane review found no studies evaluating the benefit of asymptomatic population-based screening.5 Similarly, in 2018, the USPSTF performed a comprehensive review and found no studies to support routine screening and determined there was insufficient evidence to recommend it.6,7
Risk factors and associated comorbidities
PAD risk factors, like the ones detailed below, have a potentiating effect. The presence of 2 risk factors doubles PAD risk, while 3 or more risk factors increase PAD risk by a factor of 10.1
Increasing age is the greatest single risk factor for PAD.1,2,8,9 Researchers using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) found that the prevalence of PAD increased from 1.4% in individuals ages 40 to 49 years to almost 17% in those age 70 or older.1

Demographic characteristics. Most studies demonstrate a higher risk for PAD in men.1-3,10 African-American patients have more than twice the risk for PAD, compared with Whites, even after adjustment for the increased prevalence of associated diseases such as hypertension and diabetes in this population.1-3,10
Continue to: Genetics...
Genetics. A study performed by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute suggested that genetic correlations between twins were more important than environmental factors in the development of PAD.11
Smoking. Most population studies show smoking to be the greatest modifiable risk factor for PAD. An analysis of the NHANES data yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 4.1 for current smokers and of 1.8 for former smokers.1 Risk increases linearly with cumulative years of smoking.1,2,9,10
Diabetes is another significant modifiable risk factor, increasing PAD risk by 2.5 times.2 Diabetes is also associated with increases in functional limitation from claudication, risk for acute coronary syndrome, and progression to amputation.1
Hypertension nearly doubles the risk for PAD, and poor control further increases this risk.2,9,10
Chronic kidney disease (CKD). Patients with CKD have a progressively higher prevalence of PAD with worsening renal function.1 There is also an association between CKD and increased morbidity, revascularization failure, and increased mortality.1
Two additional risk factors that are less well understood are dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation. There is conflicting data regarding the role of individual components of cholesterol and their effect on PAD, although lipoprotein (a) has been shown to be an independent risk factor for both the development and progression of PAD.12 Similarly, chronic inflammation has been shown to play a role in the initiation and progression of the disease, although the role of inflammatory markers in evaluation and treatment is unclear and assessment for these purposes is not currently recommended.12,13
Continue to: Diagnosis...
Diagnosis
Clinical presentation
Lower extremity pain is the hallmark symptom of PAD, but presentation varies. The classic presentation is claudication, pain within a defined muscle group that occurs with exertion and is relieved by rest. Claudication is most common in the calf but also occurs in the buttock/thigh and the foot.
However, most patients with PAD present with pain that does not fit the definition of claudication. Patients with comorbidities, physical inactivity, and neuropathy are more likely to present with atypical pain.14 These patients may demonstrate critical or acute limb ischemia, characterized by pain at rest and most often localized to the forefoot and toes. Patients with critical limb ischemia may also present with nonhealing wounds/ulcers or gangrene.15
Physical exam findings can support the diagnosis of PAD, but none are reliable enough to rule the diagnosis in or out. Findings suggestive of PAD include cool skin, presence of a bruit (iliac, femoral, or popliteal), and palpable pulse abnormality. Multiple abnormal physical exam findings increase the likelihood of PAD, while the absence of a bruit or palpable pulse abnormality makes PAD less likely.16 In patients with PAD, an associated wound/ulcer is most often distal in the foot and usually appears dry.17
The differential diagnosis for intermittent leg pain is broad and includes neurologic, musculoskeletal, and venous etiologies. Table 118 lists some common alternate diagnoses for patients presenting with leg pain or claudication.

Continue to: Diagnostic testing...
Diagnostic testing
An ankle-brachial index (ABI) test should be performed in patients with history or physical exam findings suggestive of PAD. A resting ABI is performed with the patient in the supine position, with measurement of systolic blood pressure in both arms and ankles using a Doppler ultrasound device. Table 213 outlines ABI scoring and interpretation.

An ABI > 1.4 is an invalid measurement, indicating that the arteries are too calcified to be compressed. These highly elevated ABI measurements are common in patients with diabetes and/or advanced CKD. In these patients, a toe-brachial index (TBI) test should be performed, because the digital arteries are almost always compressible.13
Patients with symptomatic PAD who are under consideration for revascularization may benefit from radiologic imaging of the lower extremities with duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography to determine the anatomic location and severity of stenosis.13
Management of PAD
Lifestyle interventions
For patients with PAD, lifestyle modifications are an essential—but challenging—component of disease management.
Continue to: Smoking cessation...
Smoking cessation. As with other atherosclerotic diseases, PAD progression is strongly correlated with smoking. A trial involving 204 active smokers with PAD showed that 5-year mortality and amputation rates dropped by more than half in those who quit smoking within a year, with numbers needed to treat (NNT) of 6 for mortality and 5 for amputation.19 Because of this dramatic effect, American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines encourage providers to address smoking at every visit and use cessation programs and medication to increase quit rates.13
Exercise may be the most important intervention for PAD. A 2017 Cochrane review found that supervised, structured exercise programs increase pain-free and maximal walking distances by at least 20% and also improve physical and mental quality of life.20 In a trial involving 111 patients with aortoiliac PAD, supervised exercise plus medical care led to greater functional improvement than either revascularization plus medical care or medical care alone.21 In a 2018 Cochrane review, neither revascularization or revascularization added to supervised exercise were better than supervised exercise alone.22 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend supervised exercise programs for claudication prior to considering revascularization.13TABLE 313 outlines the components of a structured exercise program.

Unfortunately, the benefit of these programs has been difficult to reproduce without supervision. Another 2018 Cochrane review demonstrated significant improvement with supervised exercise and no clear improvement in patients given home exercise or advice to walk.23 A recent study examined the effect of having patients use a wearable fitness tracker for home exercise and demonstrated no benefit over usual care.24
Diet. There is some evidence that dietary interventions can prevent and possibly improve PAD. A large randomized controlled trial showed that a Mediterranean diet lowered rates of PAD over 1 year compared to a low-fat diet, with an NNT of 336 if supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil and 448 if supplemented with nuts.25 A small trial of 25 patients who consumed non-soy legumes daily for 8 weeks showed average ABI improvement of 6%, although there was no control group.26
Medical therapy to address peripheral and cardiovascular events
Standard medical therapy for coronary artery disease (CAD) is recommended for patients with PAD to reduce cardiovascular and limb events. For example, treatment of hypertension reduces cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, and studies verify that lowering blood pressure does not worsen claudication or limb perfusion.
13TABLE 413,27-30 outlines the options for medical therapy.

Continue to: Statins...
Statins reduce cardiovascular events in PAD patients. A large study demonstrated that 40 mg of simvastatin has an NNT of 21 to prevent a coronary or cerebrovascular event in PAD, similar to the NNT of 23 seen in treatment of CAD.27 Statins also reduce adverse limb outcomes. A registry of atherosclerosis patients showed that statins have an NNT of 56 to prevent amputation in PAD and an NNT of 28 to prevent worsening claudication, critical limb ischemia, revascularization, or amputation.28
Antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin or clopidogrel is recommended for symptomatic patients and for asymptomatic patients with an ABI ≤ 0.9.13 A Cochrane review demonstrated significantly reduced mortality with nonaspirin antiplatelet agents vs aspirin (NNT = 94) without increase in major bleeding.29 Only British guidelines specifically recommend clopidogrel over aspirin.31
Dual antiplatelet therapy has not shown consistent benefits over aspirin alone. ACC/AHA guidelines state that dual antiplatelet therapy is not well established for PAD but may be reasonable after revascularization.13
Voraxapar is a novel antiplatelet agent that targets the thrombin-binding receptor on platelets. However, trials show no significant coronary benefit, and slight reductions in acute limb ischemia are offset by increases in major bleeding.13
For patients receiving medical therapy, ongoing evaluation and treatment should be based on claudication symptoms and clinical assessment.
Medical therapy for claudication
Several medications have been proposed for symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication. Cilostazol is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with the best risk-benefit ratio. A Cochrane review showed improvements in maximal and pain-free walking distances compared to placebo and improvements in quality of life with cilostazol 100 mg taken twice daily.32 Adverse effects included headache, dizziness, palpitations, and diarrhea.29
Continue to: Pentoxifylline...
Pentoxifylline is another phosphodiesterase inhibitor with less evidence of improvement, higher adverse effect rates, and more frequent dosing. It is not recommended for treatment of intermittent claudication.13,33
Supplements. Padma 28, a Tibetan herbal formulation, appears to improve maximal walking distance with adverse effect rates similar to placebo.34 Other supplements, including vitamin E, ginkgo biloba, and omega-3 fatty acids, have no evidence of benefit.35-37
When revascularizationis needed
Patients who develop limb ischemia or lifestyle-limiting claudication despite conservative therapy are candidates for revascularization. Endovascular techniques include angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, and precise medication delivery. Surgical approaches mainly consist of thrombectomy and bypass grafting. For intermittent claudication despite conservative care, ACC/AHA guidelines state endovascular procedures are appropriate for aortoiliac disease and reasonable for femoropopliteal disease, but unproven for infrapopliteal disease.13
Acute limb ischemia is an emergency requiring immediate intervention. Two trials revealed identical overall and amputation-free survival rates for percutaneous thrombolysis and surgical thrombectomy.38,39 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend anticoagulation with heparin followed by the revascularization technique that will most rapidly restore arterial flow.13
For chronic limb ischemia, a large trial showed angioplasty had lower initial morbidity, length of hospitalization, and cost than surgical repair. However, surgical mortality was lower after 2 years.40 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend either surgery or endovascular procedures and propose initial endovascular treatment followed by surgery if needed.13 After revascularization, the patient should be followed periodically with a clinical evaluation and ABI measurement with further consideration for routine duplex ultrasound surveillance.13
Outcomes
Patients with PAD have variable outcomes. About 70% to 80% of patients with this diagnosis will have a stable disease process with no worsening of symptoms, 10% to 20% will experience worsening symptoms over time, 5% to 10% will require revascularization within 5 years of diagnosis, and 1% to 5% will progress to critical limb ischemia, which has a 5-year amputation rate of 1% to 4%.2 Patients who require amputation have poor outcomes: Within 2 years, 30% are dead and 15% have had further amputations.18
In addition to the morbidity and mortality from its own progression, PAD is an important predictor of CAD and is associated with a significant elevation in morbidity and mortality from CAD. One small but well-designed prospective cohort study found that patients with PAD had a more than 6-fold increased risk of death from CAD than did patients without PAD.41
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Francesca Cimino, MD, FAAFP, for her help in reviewing this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Dustin K. Smith, DO, 2080 Child Street, Jacksonville, FL 32214; [email protected]
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD), the progressive disorder that results in ischemia to distal vascular territories as a result of atherosclerosis, spans a wide range of presentations, from minimally symptomatic disease to limb ischemia secondary to acute or chronic occlusion.
The prevalence of PAD is variable, due to differing diagnostic criteria used in studies, but PAD appears to affect 1 in every 22 people older than age 40.1 However, since PAD incidence increases with age, it is increasing in prevalence as the US population ages.1-3
PAD is associated with increased hospitalizations and decreased quality of life.4 Patients with PAD have an estimated 30% 5-year risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from a vascular cause.3
Screening. Although PAD is underdiagnosed and appears to be undertreated,3 population-based screening for PAD in asymptomatic patients is not recommended. A Cochrane review found no studies evaluating the benefit of asymptomatic population-based screening.5 Similarly, in 2018, the USPSTF performed a comprehensive review and found no studies to support routine screening and determined there was insufficient evidence to recommend it.6,7
Risk factors and associated comorbidities
PAD risk factors, like the ones detailed below, have a potentiating effect. The presence of 2 risk factors doubles PAD risk, while 3 or more risk factors increase PAD risk by a factor of 10.1
Increasing age is the greatest single risk factor for PAD.1,2,8,9 Researchers using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) found that the prevalence of PAD increased from 1.4% in individuals ages 40 to 49 years to almost 17% in those age 70 or older.1

Demographic characteristics. Most studies demonstrate a higher risk for PAD in men.1-3,10 African-American patients have more than twice the risk for PAD, compared with Whites, even after adjustment for the increased prevalence of associated diseases such as hypertension and diabetes in this population.1-3,10
Continue to: Genetics...
Genetics. A study performed by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute suggested that genetic correlations between twins were more important than environmental factors in the development of PAD.11
Smoking. Most population studies show smoking to be the greatest modifiable risk factor for PAD. An analysis of the NHANES data yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 4.1 for current smokers and of 1.8 for former smokers.1 Risk increases linearly with cumulative years of smoking.1,2,9,10
Diabetes is another significant modifiable risk factor, increasing PAD risk by 2.5 times.2 Diabetes is also associated with increases in functional limitation from claudication, risk for acute coronary syndrome, and progression to amputation.1
Hypertension nearly doubles the risk for PAD, and poor control further increases this risk.2,9,10
Chronic kidney disease (CKD). Patients with CKD have a progressively higher prevalence of PAD with worsening renal function.1 There is also an association between CKD and increased morbidity, revascularization failure, and increased mortality.1
Two additional risk factors that are less well understood are dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation. There is conflicting data regarding the role of individual components of cholesterol and their effect on PAD, although lipoprotein (a) has been shown to be an independent risk factor for both the development and progression of PAD.12 Similarly, chronic inflammation has been shown to play a role in the initiation and progression of the disease, although the role of inflammatory markers in evaluation and treatment is unclear and assessment for these purposes is not currently recommended.12,13
Continue to: Diagnosis...
Diagnosis
Clinical presentation
Lower extremity pain is the hallmark symptom of PAD, but presentation varies. The classic presentation is claudication, pain within a defined muscle group that occurs with exertion and is relieved by rest. Claudication is most common in the calf but also occurs in the buttock/thigh and the foot.
However, most patients with PAD present with pain that does not fit the definition of claudication. Patients with comorbidities, physical inactivity, and neuropathy are more likely to present with atypical pain.14 These patients may demonstrate critical or acute limb ischemia, characterized by pain at rest and most often localized to the forefoot and toes. Patients with critical limb ischemia may also present with nonhealing wounds/ulcers or gangrene.15
Physical exam findings can support the diagnosis of PAD, but none are reliable enough to rule the diagnosis in or out. Findings suggestive of PAD include cool skin, presence of a bruit (iliac, femoral, or popliteal), and palpable pulse abnormality. Multiple abnormal physical exam findings increase the likelihood of PAD, while the absence of a bruit or palpable pulse abnormality makes PAD less likely.16 In patients with PAD, an associated wound/ulcer is most often distal in the foot and usually appears dry.17
The differential diagnosis for intermittent leg pain is broad and includes neurologic, musculoskeletal, and venous etiologies. Table 118 lists some common alternate diagnoses for patients presenting with leg pain or claudication.

Continue to: Diagnostic testing...
Diagnostic testing
An ankle-brachial index (ABI) test should be performed in patients with history or physical exam findings suggestive of PAD. A resting ABI is performed with the patient in the supine position, with measurement of systolic blood pressure in both arms and ankles using a Doppler ultrasound device. Table 213 outlines ABI scoring and interpretation.

An ABI > 1.4 is an invalid measurement, indicating that the arteries are too calcified to be compressed. These highly elevated ABI measurements are common in patients with diabetes and/or advanced CKD. In these patients, a toe-brachial index (TBI) test should be performed, because the digital arteries are almost always compressible.13
Patients with symptomatic PAD who are under consideration for revascularization may benefit from radiologic imaging of the lower extremities with duplex ultrasound, computed tomography angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography to determine the anatomic location and severity of stenosis.13
Management of PAD
Lifestyle interventions
For patients with PAD, lifestyle modifications are an essential—but challenging—component of disease management.
Continue to: Smoking cessation...
Smoking cessation. As with other atherosclerotic diseases, PAD progression is strongly correlated with smoking. A trial involving 204 active smokers with PAD showed that 5-year mortality and amputation rates dropped by more than half in those who quit smoking within a year, with numbers needed to treat (NNT) of 6 for mortality and 5 for amputation.19 Because of this dramatic effect, American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines encourage providers to address smoking at every visit and use cessation programs and medication to increase quit rates.13
Exercise may be the most important intervention for PAD. A 2017 Cochrane review found that supervised, structured exercise programs increase pain-free and maximal walking distances by at least 20% and also improve physical and mental quality of life.20 In a trial involving 111 patients with aortoiliac PAD, supervised exercise plus medical care led to greater functional improvement than either revascularization plus medical care or medical care alone.21 In a 2018 Cochrane review, neither revascularization or revascularization added to supervised exercise were better than supervised exercise alone.22 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend supervised exercise programs for claudication prior to considering revascularization.13TABLE 313 outlines the components of a structured exercise program.

Unfortunately, the benefit of these programs has been difficult to reproduce without supervision. Another 2018 Cochrane review demonstrated significant improvement with supervised exercise and no clear improvement in patients given home exercise or advice to walk.23 A recent study examined the effect of having patients use a wearable fitness tracker for home exercise and demonstrated no benefit over usual care.24
Diet. There is some evidence that dietary interventions can prevent and possibly improve PAD. A large randomized controlled trial showed that a Mediterranean diet lowered rates of PAD over 1 year compared to a low-fat diet, with an NNT of 336 if supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil and 448 if supplemented with nuts.25 A small trial of 25 patients who consumed non-soy legumes daily for 8 weeks showed average ABI improvement of 6%, although there was no control group.26
Medical therapy to address peripheral and cardiovascular events
Standard medical therapy for coronary artery disease (CAD) is recommended for patients with PAD to reduce cardiovascular and limb events. For example, treatment of hypertension reduces cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, and studies verify that lowering blood pressure does not worsen claudication or limb perfusion.
13TABLE 413,27-30 outlines the options for medical therapy.

Continue to: Statins...
Statins reduce cardiovascular events in PAD patients. A large study demonstrated that 40 mg of simvastatin has an NNT of 21 to prevent a coronary or cerebrovascular event in PAD, similar to the NNT of 23 seen in treatment of CAD.27 Statins also reduce adverse limb outcomes. A registry of atherosclerosis patients showed that statins have an NNT of 56 to prevent amputation in PAD and an NNT of 28 to prevent worsening claudication, critical limb ischemia, revascularization, or amputation.28
Antiplatelet therapy with low-dose aspirin or clopidogrel is recommended for symptomatic patients and for asymptomatic patients with an ABI ≤ 0.9.13 A Cochrane review demonstrated significantly reduced mortality with nonaspirin antiplatelet agents vs aspirin (NNT = 94) without increase in major bleeding.29 Only British guidelines specifically recommend clopidogrel over aspirin.31
Dual antiplatelet therapy has not shown consistent benefits over aspirin alone. ACC/AHA guidelines state that dual antiplatelet therapy is not well established for PAD but may be reasonable after revascularization.13
Voraxapar is a novel antiplatelet agent that targets the thrombin-binding receptor on platelets. However, trials show no significant coronary benefit, and slight reductions in acute limb ischemia are offset by increases in major bleeding.13
For patients receiving medical therapy, ongoing evaluation and treatment should be based on claudication symptoms and clinical assessment.
Medical therapy for claudication
Several medications have been proposed for symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication. Cilostazol is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with the best risk-benefit ratio. A Cochrane review showed improvements in maximal and pain-free walking distances compared to placebo and improvements in quality of life with cilostazol 100 mg taken twice daily.32 Adverse effects included headache, dizziness, palpitations, and diarrhea.29
Continue to: Pentoxifylline...
Pentoxifylline is another phosphodiesterase inhibitor with less evidence of improvement, higher adverse effect rates, and more frequent dosing. It is not recommended for treatment of intermittent claudication.13,33
Supplements. Padma 28, a Tibetan herbal formulation, appears to improve maximal walking distance with adverse effect rates similar to placebo.34 Other supplements, including vitamin E, ginkgo biloba, and omega-3 fatty acids, have no evidence of benefit.35-37
When revascularizationis needed
Patients who develop limb ischemia or lifestyle-limiting claudication despite conservative therapy are candidates for revascularization. Endovascular techniques include angioplasty, stenting, atherectomy, and precise medication delivery. Surgical approaches mainly consist of thrombectomy and bypass grafting. For intermittent claudication despite conservative care, ACC/AHA guidelines state endovascular procedures are appropriate for aortoiliac disease and reasonable for femoropopliteal disease, but unproven for infrapopliteal disease.13
Acute limb ischemia is an emergency requiring immediate intervention. Two trials revealed identical overall and amputation-free survival rates for percutaneous thrombolysis and surgical thrombectomy.38,39 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend anticoagulation with heparin followed by the revascularization technique that will most rapidly restore arterial flow.13
For chronic limb ischemia, a large trial showed angioplasty had lower initial morbidity, length of hospitalization, and cost than surgical repair. However, surgical mortality was lower after 2 years.40 ACC/AHA guidelines recommend either surgery or endovascular procedures and propose initial endovascular treatment followed by surgery if needed.13 After revascularization, the patient should be followed periodically with a clinical evaluation and ABI measurement with further consideration for routine duplex ultrasound surveillance.13
Outcomes
Patients with PAD have variable outcomes. About 70% to 80% of patients with this diagnosis will have a stable disease process with no worsening of symptoms, 10% to 20% will experience worsening symptoms over time, 5% to 10% will require revascularization within 5 years of diagnosis, and 1% to 5% will progress to critical limb ischemia, which has a 5-year amputation rate of 1% to 4%.2 Patients who require amputation have poor outcomes: Within 2 years, 30% are dead and 15% have had further amputations.18
In addition to the morbidity and mortality from its own progression, PAD is an important predictor of CAD and is associated with a significant elevation in morbidity and mortality from CAD. One small but well-designed prospective cohort study found that patients with PAD had a more than 6-fold increased risk of death from CAD than did patients without PAD.41
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Francesca Cimino, MD, FAAFP, for her help in reviewing this manuscript.
CORRESPONDENCE
Dustin K. Smith, DO, 2080 Child Street, Jacksonville, FL 32214; [email protected]
1. Eraso LH, Fukaya E, Mohler ER 3rd, et al. Peripheral arterial disease, prevalence and cumulative risk factor profile analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21:704-711.
2. Pasternak RC, Criqui MH, Benjamin EJ, et al; American Heart Association. Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Conference: Writing Group I: epidemiology. Circulation. 2004;109:2605-2612.
3. Hirsch AT, Criqui MH, Treat-Jacobson D, et al. Peripheral arterial disease detection, awareness, and treatment in primary care. JAMA. 2001;286:1317-1324.
4. Olin JW, Sealove BA. Peripheral artery disease: current insight into the disease and its diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:678-692.
5. Andras A, Ferkert B. Screening for peripheral arterial disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(4):CD010835.
6. Guirguis-Blake JM, Evans CV, Redmond N, et al. Screening for peripheral artery disease using ankle-brachial index: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;320:184-196.
7. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for peripheral artery disease and cardiovascular disease risk assessment with ankle-brachial index: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;230:177-183.
8. American Heart Association Writing Group 2. Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Symposium II: screening for atherosclerotic vascular diseases: should nationwide programs be instituted? Circulation. 2008;118:2830-2836.
9. Berger JS, Hochman J, Lobach I, et al. Modifiable risk factor burden and the prevalence of peripheral artery disease in different vascular territories. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58:673-681.
10. Joosten MM, Pai JK, Bertoia ML, et al. Associations between conventional cardiovascular risk factors and risk of peripheral artery disease in men. JAMA. 2012;308:1660-1667.
11. Carmelli D, Fabsitz RR, Swan GE, et al. Contribution of genetic and environmental influences to ankle-brachial blood pressure index in the NHLBI Twin Study. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:452-458.
12. Aboyans V, Criqui MH, Denenberg JO, et al. Risk factors for progression of peripheral arterial disease in large and small vessels. Circulation. 2006;113:2623-2629.
13. Gerald-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e726-e779.
14. McDermott MM, Greenland P, Liu K, et al. Leg symptoms in peripheral arterial disease: associated clinical characteristics and functional impairment. JAMA. 2001;286:1599-1606.
15. Cranley JJ. Ischemic rest pain. Arch Surg. 1969;98:187-188.
16. Khan NA, Rahim SA, Anand SS, et al. Does the clinical examination predict lower extremity peripheral arterial disease? JAMA. 2006;295:536-546.
17. Wennberg PW. Approach to the patient with peripheral arterial disease. Circulation. 2013;128:2241-2250.
18. Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, et al. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). Eur J Vas Endovasc Surg. 2007;33:S1-S75.
19. Armstrong EJ, Wu J, Singh GD, et al. Smoking cessation is associated with decreased mortality and improved amputation-free survival among patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1565-1571.
20. Lane R, Harwood A, Watson L, et al. Exercise for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;(12):CD000990.
21. Murphy TP, Cutlip DE, Regensteiner JG, et al; CLEVER Study Investigators. Supervised exercise versus primary stenting for claudication resulting from aortoiliac peripheral artery disease: six-month outcomes from the claudication: exercise versus endoluminal revascularization (CLEVER) study. Circulation. 2012;125:130-139.
22. Fakhry F, Fokkenrood HJP, Pronk S, et al. Endovascular revascularization versus conservative management for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(3):CD010512.
23. Hageman D, Fokkenrood HJ, Gommans LN, et al. Supervised exercise therapy versus home-based exercise therapy versus walking advice for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(4):CD005263.
24. McDermott MM, Spring B, Berger JS, et al. Effect of a home-based exercise intervention of wearable technology and telephone coaching on walking performance in peripheral artery disease: the HONOR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;319:1665-1676.
25. Ruiz-Canela M, Estruch R, Corella D, et al. Association of Mediterranean diet with peripheral artery disease: the PREDIMED randomized trial. JAMA. 2014;311:415-417.
26. Zahradka P, Wright B, Weighell W, et al. Daily non-soy legume consumption reverses vascular impairment due to peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2013;230:310-314.
27. Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. Randomized trial of the effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on peripheral vascular and other major vascular outcomes in 20536 people with peripheral arterial disease and other high-risk conditions. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:645-655.
28. Kumbhani DJ, Steg G, Cannon CP, et al. Statin therapy and long-term adverse limb outcomes in patients with peripheral artery disease: insights from the REACH registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2864-2872.
29. Wong PF, Chong LY, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Antiplatelet agents for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(11):CD001272.
30. Critical Leg Ischaemia Prevention Study (CLIPS) Group, Catalano M, Born G, Peto R. Prevention of serious vascular events by aspirin amongst patients with peripheral arterial disease: randomized, double-blind trial. J Intern Med. 2007;261:276-284.
31. Morley RL, Sharma A, Horsch AD, et al. Peripheral artery disease. BMJ. 2018;360:j5842.
32. Bedenis R, Stewart M, Cleanthis M, et al. Cilostazol for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(10):CD003748.

33. Salhiyyah K, Forster R, Senanayake E, et al. Pentoxifylline for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(9):CD005262.
34. Stewart M, Morling JR, Maxwell H. Padma 28 for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(3):CD007371.
35. Kleijnen J, Mackerras D. Vitamin E for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1998;(1):CD000987.
36. Nicolai SPA, Kruidenior LM, Bendermacher BLW, et al. Ginkgo biloba for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(6):CD006888.
37. Campbell A, Price J, Hiatt WR. Omega-3 fatty acids for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD003833.
38. American Surgical Association, New York Surgical Society, Philadelphia Academy of Surgery, Southern Surgical Association (US), Central Surgical Association. Results of a prospective randomized trial evaluating surgery versus thrombolysis for ischemia of the lower extremity: the STILE trial. Ann Surg. 1994;220:251-268.
39. Ouriel K, Veith FJ, Sasahara AA.
40. Bradbury AW, Ruckley CV, Fowkes FGR, et al. Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:1925-1934.
41. Criqui MH, Langer RD, Fronek A, et al. Mortality over a period of 10 years in patients with peripheral arterial disease. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:381-386.
1. Eraso LH, Fukaya E, Mohler ER 3rd, et al. Peripheral arterial disease, prevalence and cumulative risk factor profile analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21:704-711.
2. Pasternak RC, Criqui MH, Benjamin EJ, et al; American Heart Association. Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Conference: Writing Group I: epidemiology. Circulation. 2004;109:2605-2612.
3. Hirsch AT, Criqui MH, Treat-Jacobson D, et al. Peripheral arterial disease detection, awareness, and treatment in primary care. JAMA. 2001;286:1317-1324.
4. Olin JW, Sealove BA. Peripheral artery disease: current insight into the disease and its diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85:678-692.
5. Andras A, Ferkert B. Screening for peripheral arterial disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(4):CD010835.
6. Guirguis-Blake JM, Evans CV, Redmond N, et al. Screening for peripheral artery disease using ankle-brachial index: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018;320:184-196.
7. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for peripheral artery disease and cardiovascular disease risk assessment with ankle-brachial index: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;230:177-183.
8. American Heart Association Writing Group 2. Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Symposium II: screening for atherosclerotic vascular diseases: should nationwide programs be instituted? Circulation. 2008;118:2830-2836.
9. Berger JS, Hochman J, Lobach I, et al. Modifiable risk factor burden and the prevalence of peripheral artery disease in different vascular territories. J Vasc Surg. 2013;58:673-681.
10. Joosten MM, Pai JK, Bertoia ML, et al. Associations between conventional cardiovascular risk factors and risk of peripheral artery disease in men. JAMA. 2012;308:1660-1667.
11. Carmelli D, Fabsitz RR, Swan GE, et al. Contribution of genetic and environmental influences to ankle-brachial blood pressure index in the NHLBI Twin Study. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:452-458.
12. Aboyans V, Criqui MH, Denenberg JO, et al. Risk factors for progression of peripheral arterial disease in large and small vessels. Circulation. 2006;113:2623-2629.
13. Gerald-Herman MD, Gornik HL, Barrett C, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC guideline on the management of patients with lower extremity peripheral artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2017;135:e726-e779.
14. McDermott MM, Greenland P, Liu K, et al. Leg symptoms in peripheral arterial disease: associated clinical characteristics and functional impairment. JAMA. 2001;286:1599-1606.
15. Cranley JJ. Ischemic rest pain. Arch Surg. 1969;98:187-188.
16. Khan NA, Rahim SA, Anand SS, et al. Does the clinical examination predict lower extremity peripheral arterial disease? JAMA. 2006;295:536-546.
17. Wennberg PW. Approach to the patient with peripheral arterial disease. Circulation. 2013;128:2241-2250.
18. Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, et al. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). Eur J Vas Endovasc Surg. 2007;33:S1-S75.
19. Armstrong EJ, Wu J, Singh GD, et al. Smoking cessation is associated with decreased mortality and improved amputation-free survival among patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1565-1571.
20. Lane R, Harwood A, Watson L, et al. Exercise for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;(12):CD000990.
21. Murphy TP, Cutlip DE, Regensteiner JG, et al; CLEVER Study Investigators. Supervised exercise versus primary stenting for claudication resulting from aortoiliac peripheral artery disease: six-month outcomes from the claudication: exercise versus endoluminal revascularization (CLEVER) study. Circulation. 2012;125:130-139.
22. Fakhry F, Fokkenrood HJP, Pronk S, et al. Endovascular revascularization versus conservative management for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(3):CD010512.
23. Hageman D, Fokkenrood HJ, Gommans LN, et al. Supervised exercise therapy versus home-based exercise therapy versus walking advice for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(4):CD005263.
24. McDermott MM, Spring B, Berger JS, et al. Effect of a home-based exercise intervention of wearable technology and telephone coaching on walking performance in peripheral artery disease: the HONOR randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;319:1665-1676.
25. Ruiz-Canela M, Estruch R, Corella D, et al. Association of Mediterranean diet with peripheral artery disease: the PREDIMED randomized trial. JAMA. 2014;311:415-417.
26. Zahradka P, Wright B, Weighell W, et al. Daily non-soy legume consumption reverses vascular impairment due to peripheral artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2013;230:310-314.
27. Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. Randomized trial of the effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on peripheral vascular and other major vascular outcomes in 20536 people with peripheral arterial disease and other high-risk conditions. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:645-655.
28. Kumbhani DJ, Steg G, Cannon CP, et al. Statin therapy and long-term adverse limb outcomes in patients with peripheral artery disease: insights from the REACH registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2864-2872.
29. Wong PF, Chong LY, Mikhailidis DP, et al. Antiplatelet agents for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(11):CD001272.
30. Critical Leg Ischaemia Prevention Study (CLIPS) Group, Catalano M, Born G, Peto R. Prevention of serious vascular events by aspirin amongst patients with peripheral arterial disease: randomized, double-blind trial. J Intern Med. 2007;261:276-284.
31. Morley RL, Sharma A, Horsch AD, et al. Peripheral artery disease. BMJ. 2018;360:j5842.
32. Bedenis R, Stewart M, Cleanthis M, et al. Cilostazol for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(10):CD003748.

33. Salhiyyah K, Forster R, Senanayake E, et al. Pentoxifylline for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(9):CD005262.
34. Stewart M, Morling JR, Maxwell H. Padma 28 for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(3):CD007371.
35. Kleijnen J, Mackerras D. Vitamin E for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1998;(1):CD000987.
36. Nicolai SPA, Kruidenior LM, Bendermacher BLW, et al. Ginkgo biloba for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(6):CD006888.
37. Campbell A, Price J, Hiatt WR. Omega-3 fatty acids for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(7):CD003833.
38. American Surgical Association, New York Surgical Society, Philadelphia Academy of Surgery, Southern Surgical Association (US), Central Surgical Association. Results of a prospective randomized trial evaluating surgery versus thrombolysis for ischemia of the lower extremity: the STILE trial. Ann Surg. 1994;220:251-268.
39. Ouriel K, Veith FJ, Sasahara AA.
40. Bradbury AW, Ruckley CV, Fowkes FGR, et al. Bypass versus angioplasty in severe ischaemia of the leg (BASIL): multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;366:1925-1934.
41. Criqui MH, Langer RD, Fronek A, et al. Mortality over a period of 10 years in patients with peripheral arterial disease. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:381-386.
PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS
❯ Use the ankle-brachial index for diagnosis in patients with history/physical exam findings suggestive of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). A
❯ Strongly encourage smoking cessation in patients with PAD as doing so reduces 5-year mortality and amputation rates. B
❯ Use structured exercise programs for patients with intermittent claudication prior to consideration of revascularization; doing so offers similar benefit and lower risks. A
❯ Recommend revascularization for patients who have limb ischemia or lifestyle-limiting claudication despite medical and exercise therapy. B
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series