User login
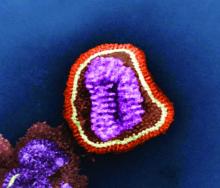
Majority of influenza-related deaths among hospitalized patients occur after discharge
SAN DIEGO – Over half of hospitalized, influenza-related deaths occurred within 30 days of discharge, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
As physicians and pharmaceutical companies attempt to measure the burden of seasonal influenza, discharged patients are currently not considered as much as they should be, according to investigators.
Among 968 deceased patients studied, 444 (46%) died in hospital, while 524 (54%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Investigators conducted a retrospective study of 15,562 patients hospitalized for influenza-related cases between 2014 and 2015, as recorded in Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations Surveillance (FluSurv-NET), a database of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The majority of the studied patients were women (55%) and the majority were white.
Those who died were more likely to have been admitted to the hospital immediately after influenza onset, with 26% of those who died after discharge and 22% of those who died in hospital having been admitted the same day. In contrast, 13% of those who lived past 30 days were admitted immediately after onset.
A total of 46% of those who died after hospitalization had a length of stay longer than 1 week, compared to 15% of those who lived.
Among patients who died after discharge, 356 (68%) died within 2 weeks of discharge, with the highest number of deaths occurring within the first few days, according to presenter Craig McGowan of the Influenza Division of the CDC in Atlanta.
Age also seemed to be a possible mortality predictor, according to Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators. “Those who died were more likely to be elderly, and those who died after discharge were even more likely to be 85 [years or older] than those who died during their influenza-related hospitalizations,” said Mr. McGowan, who added that patients aged 85 years and older made up more than half of those who died after discharge.
Patients who died in hospital were significantly more likely to have influenza listed as a cause of death. Overall, influenza-related and non–influenza-related respiratory issues were the two most common causes of death listed on death certificates of patients who died during hospitalization or within 14 days of discharge, while cardiovascular or other symptoms were listed for those who died between 15 and 30 days after discharge.
Admission and discharge locations among patients who did not die were almost 80% from a private residence to a private residence, while observations of those who died revealed a different pattern. “Those individuals who died after discharge were almost evenly split between admission from a nursing home or a private residence,” Mr. McGowan said. “Those who were admitted from the nursing home were almost exclusively discharged to either hospice care or back to a nursing home.”
Mr. McGowan noted rehospitalization to be a significant factor among those who died, with 34% of deaths occurring back in the hospital after initial discharge.
Influenza testing of studied patients was given at clinicians’ discretion, which may make the sample not generalizable to the overall influenza population, and the investigators included only bivariate associations, which means there were likely confounding effects that could not be accounted for.
Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators plan to expand their research by determining underlying causes of death in these patients, to create more accurate estimates of influenza-associated mortality.
Mr. McGowan reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McGowan, C., et al., ID Week 2017, Abstract 951.
SAN DIEGO – Over half of hospitalized, influenza-related deaths occurred within 30 days of discharge, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
As physicians and pharmaceutical companies attempt to measure the burden of seasonal influenza, discharged patients are currently not considered as much as they should be, according to investigators.
Among 968 deceased patients studied, 444 (46%) died in hospital, while 524 (54%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Investigators conducted a retrospective study of 15,562 patients hospitalized for influenza-related cases between 2014 and 2015, as recorded in Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations Surveillance (FluSurv-NET), a database of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The majority of the studied patients were women (55%) and the majority were white.
Those who died were more likely to have been admitted to the hospital immediately after influenza onset, with 26% of those who died after discharge and 22% of those who died in hospital having been admitted the same day. In contrast, 13% of those who lived past 30 days were admitted immediately after onset.
A total of 46% of those who died after hospitalization had a length of stay longer than 1 week, compared to 15% of those who lived.
Among patients who died after discharge, 356 (68%) died within 2 weeks of discharge, with the highest number of deaths occurring within the first few days, according to presenter Craig McGowan of the Influenza Division of the CDC in Atlanta.
Age also seemed to be a possible mortality predictor, according to Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators. “Those who died were more likely to be elderly, and those who died after discharge were even more likely to be 85 [years or older] than those who died during their influenza-related hospitalizations,” said Mr. McGowan, who added that patients aged 85 years and older made up more than half of those who died after discharge.
Patients who died in hospital were significantly more likely to have influenza listed as a cause of death. Overall, influenza-related and non–influenza-related respiratory issues were the two most common causes of death listed on death certificates of patients who died during hospitalization or within 14 days of discharge, while cardiovascular or other symptoms were listed for those who died between 15 and 30 days after discharge.
Admission and discharge locations among patients who did not die were almost 80% from a private residence to a private residence, while observations of those who died revealed a different pattern. “Those individuals who died after discharge were almost evenly split between admission from a nursing home or a private residence,” Mr. McGowan said. “Those who were admitted from the nursing home were almost exclusively discharged to either hospice care or back to a nursing home.”
Mr. McGowan noted rehospitalization to be a significant factor among those who died, with 34% of deaths occurring back in the hospital after initial discharge.
Influenza testing of studied patients was given at clinicians’ discretion, which may make the sample not generalizable to the overall influenza population, and the investigators included only bivariate associations, which means there were likely confounding effects that could not be accounted for.
Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators plan to expand their research by determining underlying causes of death in these patients, to create more accurate estimates of influenza-associated mortality.
Mr. McGowan reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McGowan, C., et al., ID Week 2017, Abstract 951.
SAN DIEGO – Over half of hospitalized, influenza-related deaths occurred within 30 days of discharge, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
As physicians and pharmaceutical companies attempt to measure the burden of seasonal influenza, discharged patients are currently not considered as much as they should be, according to investigators.
Among 968 deceased patients studied, 444 (46%) died in hospital, while 524 (54%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Investigators conducted a retrospective study of 15,562 patients hospitalized for influenza-related cases between 2014 and 2015, as recorded in Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations Surveillance (FluSurv-NET), a database of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The majority of the studied patients were women (55%) and the majority were white.
Those who died were more likely to have been admitted to the hospital immediately after influenza onset, with 26% of those who died after discharge and 22% of those who died in hospital having been admitted the same day. In contrast, 13% of those who lived past 30 days were admitted immediately after onset.
A total of 46% of those who died after hospitalization had a length of stay longer than 1 week, compared to 15% of those who lived.
Among patients who died after discharge, 356 (68%) died within 2 weeks of discharge, with the highest number of deaths occurring within the first few days, according to presenter Craig McGowan of the Influenza Division of the CDC in Atlanta.
Age also seemed to be a possible mortality predictor, according to Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators. “Those who died were more likely to be elderly, and those who died after discharge were even more likely to be 85 [years or older] than those who died during their influenza-related hospitalizations,” said Mr. McGowan, who added that patients aged 85 years and older made up more than half of those who died after discharge.
Patients who died in hospital were significantly more likely to have influenza listed as a cause of death. Overall, influenza-related and non–influenza-related respiratory issues were the two most common causes of death listed on death certificates of patients who died during hospitalization or within 14 days of discharge, while cardiovascular or other symptoms were listed for those who died between 15 and 30 days after discharge.
Admission and discharge locations among patients who did not die were almost 80% from a private residence to a private residence, while observations of those who died revealed a different pattern. “Those individuals who died after discharge were almost evenly split between admission from a nursing home or a private residence,” Mr. McGowan said. “Those who were admitted from the nursing home were almost exclusively discharged to either hospice care or back to a nursing home.”
Mr. McGowan noted rehospitalization to be a significant factor among those who died, with 34% of deaths occurring back in the hospital after initial discharge.
Influenza testing of studied patients was given at clinicians’ discretion, which may make the sample not generalizable to the overall influenza population, and the investigators included only bivariate associations, which means there were likely confounding effects that could not be accounted for.
Mr. McGowan and his fellow investigators plan to expand their research by determining underlying causes of death in these patients, to create more accurate estimates of influenza-associated mortality.
Mr. McGowan reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McGowan, C., et al., ID Week 2017, Abstract 951.
AT IDWEEK 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among patients who died with confirmed influenza, 46% died in hospital, while 54% died within 30 days of discharge.
Data source: Retrospective study of 15,562 influenza patients hospitalized or within 30 days of discharge between 2014 and 2015, recorded in Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations Surveillance (FluSurv-NET).
Disclosures: Mr. McGowen reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Inpatient antiviral treatment reduces ICU admissions among influenza patients
SAN DIEGO – Administering inpatient antiviral influenza treatment may reduce admissions to the ICU among adults hospitalized with flu, according to a study presented at ID Week 2017, an infectious diseases meeting.
While interventions did not directly affect flu-related deaths, lower ICU admission rates could reduce morbidity as well as ease the financial burden felt during the influenza season.
Investigators retrospectively studied 4,679 influenza patients admitted to Canadian Immunization Research Network Serious Outcomes Surveillance (SOS) Network hospitals during 2011-2014. Of the 54% of patients given inpatient antiviral treatment, the risk of being admitted to the ICU was reduced by 90% (odds ratio, 0.10;95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.13; P less than .001).
Antiviral treatment was not protective against death outcomes in patients with either influenza A or influenza B (OR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.7-1.2; P =.454).
The median age of patients was 70 years, with a majority older than 75 years(41%); the majority presented with one or more comorbidities (89%), and had influenza A (72%).
Researchers found that, of the 4,679 patients studied, 798 (16%) were admitted to the ICU, 511 (11%) required mechanical ventilation, and the average length of hospital stay was 11 days.
Of those studied, 444 (9%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Researchers also found that only 38% of those studied had received the current seasonal vaccine upon admittance. However, these numbers may be skewed from the general population, because patients who have not taken the vaccine are more likely to be hospitalized.
Along with the results of antivirals on hospitalized patients, researchers wanted to uncover how the effectiveness of inpatient vaccine administration would vary based on treatment timing, said presenter Zach Shaffelburg of the Canadian Center for Vaccinology, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS.
Even when administered 4.28 days after symptom onset, antiviral treatments in patients proved to be associated with significant reductions in ICU admissions and the need for mechanical ventilation.
The investigators concluded that antivirals show a strong association with positive effects on serious, influenza-related outcomes in hospitalized patients and, while therapy remained effective with later treatment start, patients would benefit the most from initiation as soon as possible.
Currently, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Canadian Immunization Research Network (CIRN) have guidelines instructing best practice for inpatient antiviral treatment, however the number of hospitalized patients given treatment has declined in Canada since 2009, according to Mr. Shaffelburg.
The reason more patients were not receiving inpatient antiviral treatment may be related to studies of different populations that failed to show significant impact, Mr. Shaffelburg suggested during a question and answer session following the presentation: “I think a lot of that comes from outpatient studies that involve patients who are younger and quite healthy [who received] antivirals, and it showed a very minimal impact,” Mr. Shaffelburg said. “So a lot of people saw that study and thought, ‘What’s that point of giving it if it’s not going to make an impact?’ ”
Mr. Shaffelburg and his colleagues are planning to continue their study of inpatient antiviral treatment, focusing more on the effectiveness of treatment in relation to time administered after onset.
Mr. Shaffelburg reported having no disclosures. The study was funded by the CIRN SOS network, Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and a partnership with GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals. Some of the investigators were GSK employees or received grant funding from the company.
SOURCE: Shaffelburg Z et al. IDWeek 2017 Abstract 890.
SAN DIEGO – Administering inpatient antiviral influenza treatment may reduce admissions to the ICU among adults hospitalized with flu, according to a study presented at ID Week 2017, an infectious diseases meeting.
While interventions did not directly affect flu-related deaths, lower ICU admission rates could reduce morbidity as well as ease the financial burden felt during the influenza season.
Investigators retrospectively studied 4,679 influenza patients admitted to Canadian Immunization Research Network Serious Outcomes Surveillance (SOS) Network hospitals during 2011-2014. Of the 54% of patients given inpatient antiviral treatment, the risk of being admitted to the ICU was reduced by 90% (odds ratio, 0.10;95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.13; P less than .001).
Antiviral treatment was not protective against death outcomes in patients with either influenza A or influenza B (OR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.7-1.2; P =.454).
The median age of patients was 70 years, with a majority older than 75 years(41%); the majority presented with one or more comorbidities (89%), and had influenza A (72%).
Researchers found that, of the 4,679 patients studied, 798 (16%) were admitted to the ICU, 511 (11%) required mechanical ventilation, and the average length of hospital stay was 11 days.
Of those studied, 444 (9%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Researchers also found that only 38% of those studied had received the current seasonal vaccine upon admittance. However, these numbers may be skewed from the general population, because patients who have not taken the vaccine are more likely to be hospitalized.
Along with the results of antivirals on hospitalized patients, researchers wanted to uncover how the effectiveness of inpatient vaccine administration would vary based on treatment timing, said presenter Zach Shaffelburg of the Canadian Center for Vaccinology, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS.
Even when administered 4.28 days after symptom onset, antiviral treatments in patients proved to be associated with significant reductions in ICU admissions and the need for mechanical ventilation.
The investigators concluded that antivirals show a strong association with positive effects on serious, influenza-related outcomes in hospitalized patients and, while therapy remained effective with later treatment start, patients would benefit the most from initiation as soon as possible.
Currently, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Canadian Immunization Research Network (CIRN) have guidelines instructing best practice for inpatient antiviral treatment, however the number of hospitalized patients given treatment has declined in Canada since 2009, according to Mr. Shaffelburg.
The reason more patients were not receiving inpatient antiviral treatment may be related to studies of different populations that failed to show significant impact, Mr. Shaffelburg suggested during a question and answer session following the presentation: “I think a lot of that comes from outpatient studies that involve patients who are younger and quite healthy [who received] antivirals, and it showed a very minimal impact,” Mr. Shaffelburg said. “So a lot of people saw that study and thought, ‘What’s that point of giving it if it’s not going to make an impact?’ ”
Mr. Shaffelburg and his colleagues are planning to continue their study of inpatient antiviral treatment, focusing more on the effectiveness of treatment in relation to time administered after onset.
Mr. Shaffelburg reported having no disclosures. The study was funded by the CIRN SOS network, Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and a partnership with GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals. Some of the investigators were GSK employees or received grant funding from the company.
SOURCE: Shaffelburg Z et al. IDWeek 2017 Abstract 890.
SAN DIEGO – Administering inpatient antiviral influenza treatment may reduce admissions to the ICU among adults hospitalized with flu, according to a study presented at ID Week 2017, an infectious diseases meeting.
While interventions did not directly affect flu-related deaths, lower ICU admission rates could reduce morbidity as well as ease the financial burden felt during the influenza season.
Investigators retrospectively studied 4,679 influenza patients admitted to Canadian Immunization Research Network Serious Outcomes Surveillance (SOS) Network hospitals during 2011-2014. Of the 54% of patients given inpatient antiviral treatment, the risk of being admitted to the ICU was reduced by 90% (odds ratio, 0.10;95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.13; P less than .001).
Antiviral treatment was not protective against death outcomes in patients with either influenza A or influenza B (OR, 0.9; 95% CI, 0.7-1.2; P =.454).
The median age of patients was 70 years, with a majority older than 75 years(41%); the majority presented with one or more comorbidities (89%), and had influenza A (72%).
Researchers found that, of the 4,679 patients studied, 798 (16%) were admitted to the ICU, 511 (11%) required mechanical ventilation, and the average length of hospital stay was 11 days.
Of those studied, 444 (9%) died within 30 days of discharge.
Researchers also found that only 38% of those studied had received the current seasonal vaccine upon admittance. However, these numbers may be skewed from the general population, because patients who have not taken the vaccine are more likely to be hospitalized.
Along with the results of antivirals on hospitalized patients, researchers wanted to uncover how the effectiveness of inpatient vaccine administration would vary based on treatment timing, said presenter Zach Shaffelburg of the Canadian Center for Vaccinology, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS.
Even when administered 4.28 days after symptom onset, antiviral treatments in patients proved to be associated with significant reductions in ICU admissions and the need for mechanical ventilation.
The investigators concluded that antivirals show a strong association with positive effects on serious, influenza-related outcomes in hospitalized patients and, while therapy remained effective with later treatment start, patients would benefit the most from initiation as soon as possible.
Currently, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Canadian Immunization Research Network (CIRN) have guidelines instructing best practice for inpatient antiviral treatment, however the number of hospitalized patients given treatment has declined in Canada since 2009, according to Mr. Shaffelburg.
The reason more patients were not receiving inpatient antiviral treatment may be related to studies of different populations that failed to show significant impact, Mr. Shaffelburg suggested during a question and answer session following the presentation: “I think a lot of that comes from outpatient studies that involve patients who are younger and quite healthy [who received] antivirals, and it showed a very minimal impact,” Mr. Shaffelburg said. “So a lot of people saw that study and thought, ‘What’s that point of giving it if it’s not going to make an impact?’ ”
Mr. Shaffelburg and his colleagues are planning to continue their study of inpatient antiviral treatment, focusing more on the effectiveness of treatment in relation to time administered after onset.
Mr. Shaffelburg reported having no disclosures. The study was funded by the CIRN SOS network, Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and a partnership with GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals. Some of the investigators were GSK employees or received grant funding from the company.
SOURCE: Shaffelburg Z et al. IDWeek 2017 Abstract 890.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Patients who received antiviral treatment were significantly less likely to go to the ICU or need mechanical ventilation (OR, 0.10; 95% CI, 0.08-0.13; P less than .001).
Study details: Study of 4,679 hospitalized influenza patients admitted to the Canadian Immunization Research Network Serious Outcomes Surveillance (CIRN SOS) network hospitals between 2011 to 2014.
Disclosures: Mr. Shaffelburg reported having no disclosures. The study was funded by the CIRN SOS network, Canadian Institutes for Health Research, and a partnership with GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals. Some of the investigators were GSK employees or received grant funding from the company.
Source: Shaffelburg Z et al. IDWeek 2017 Abstract 890.
Expanded hospital testing improves respiratory pathogen detection
SAN DIEGO – Systematic testing of acute respiratory illness patients can increase the likelihood of finding relevant pathogens, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Currently, hospitals conduct either nonroutine assessments or rely heavily on clinical laboratory testing among severe acute respiratory illness patients, which can lead to missing clinically key viruses.
Systematic testing expands on tests ordered and carried out at hospitals, expanding on them by testing for influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human metapneumovirus, rhinovirus and enterovirus, adenovirus, coronavirus, and parainfluenza viruses 1-4. To test the efficacy of systematic testing, investigators studied 2,216 severe acute respiratory illness patients hospitalized in one of three hospitals in Minnesota during September 2015-August 2016. Patients were predominantly younger than 5 years old (57%) and had one or more chronic medical condition (63%).
Detection of at least one virus increased from 1,062 patients (48%) to 1,600 patients (72%) when comparing clinically ordered tests against expanded, systematic RT-PCR testing conducted through the Minnesota Health Department (MDH).
By patient age, viral detection increased by 27%, 24%, 18%, and 21% for patients aged younger than 5 years, 5-17 years, 18-64 years, and 65 years and older, respectively. Except for influenza viruses and RSV, the proportions of viruses identified, regardless of age, were all lower in hospital testing, compared with MDH testing.
“RSV targeting was almost systematic among children less than 5 years, but [accounted for] only 28% of RSV detection,” said Dr. Steffen in her presentation. “A smaller proportion of other respiratory viruses, including the human metapneumovirus, were detected at the hospital, and this was especially true for adults.”
Patients with rhinovirus and enterovirus saw a difference between hospital and expanded testing, increasing from a little over 300 patients detected, to nearly 800 patients.
“Patients admitted to the ICU were less likely to have a pathogen detection than those not admitted to the ICU, and those with one or more chronic medical condition had lower viral detection than those without,” Dr. Steffens said. “While testing at MDH did increase the percent of patients in each category, trends remained consistent and significant.”
Since testing information was only collected for patients with positive test results at the hospital, investigators were not able to compare testing practices between patients with and without viruses. This study may also have underrepresented pathogens detected through means other than the hospital laboratory, like rapid tests in emergency departments. The study was also limited by the short time frame of only 1 year.
The presenters reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Steffens A et al. Abstract 885.
SAN DIEGO – Systematic testing of acute respiratory illness patients can increase the likelihood of finding relevant pathogens, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Currently, hospitals conduct either nonroutine assessments or rely heavily on clinical laboratory testing among severe acute respiratory illness patients, which can lead to missing clinically key viruses.
Systematic testing expands on tests ordered and carried out at hospitals, expanding on them by testing for influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human metapneumovirus, rhinovirus and enterovirus, adenovirus, coronavirus, and parainfluenza viruses 1-4. To test the efficacy of systematic testing, investigators studied 2,216 severe acute respiratory illness patients hospitalized in one of three hospitals in Minnesota during September 2015-August 2016. Patients were predominantly younger than 5 years old (57%) and had one or more chronic medical condition (63%).
Detection of at least one virus increased from 1,062 patients (48%) to 1,600 patients (72%) when comparing clinically ordered tests against expanded, systematic RT-PCR testing conducted through the Minnesota Health Department (MDH).
By patient age, viral detection increased by 27%, 24%, 18%, and 21% for patients aged younger than 5 years, 5-17 years, 18-64 years, and 65 years and older, respectively. Except for influenza viruses and RSV, the proportions of viruses identified, regardless of age, were all lower in hospital testing, compared with MDH testing.
“RSV targeting was almost systematic among children less than 5 years, but [accounted for] only 28% of RSV detection,” said Dr. Steffen in her presentation. “A smaller proportion of other respiratory viruses, including the human metapneumovirus, were detected at the hospital, and this was especially true for adults.”
Patients with rhinovirus and enterovirus saw a difference between hospital and expanded testing, increasing from a little over 300 patients detected, to nearly 800 patients.
“Patients admitted to the ICU were less likely to have a pathogen detection than those not admitted to the ICU, and those with one or more chronic medical condition had lower viral detection than those without,” Dr. Steffens said. “While testing at MDH did increase the percent of patients in each category, trends remained consistent and significant.”
Since testing information was only collected for patients with positive test results at the hospital, investigators were not able to compare testing practices between patients with and without viruses. This study may also have underrepresented pathogens detected through means other than the hospital laboratory, like rapid tests in emergency departments. The study was also limited by the short time frame of only 1 year.
The presenters reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Steffens A et al. Abstract 885.
SAN DIEGO – Systematic testing of acute respiratory illness patients can increase the likelihood of finding relevant pathogens, according to a study presented at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
Currently, hospitals conduct either nonroutine assessments or rely heavily on clinical laboratory testing among severe acute respiratory illness patients, which can lead to missing clinically key viruses.
Systematic testing expands on tests ordered and carried out at hospitals, expanding on them by testing for influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human metapneumovirus, rhinovirus and enterovirus, adenovirus, coronavirus, and parainfluenza viruses 1-4. To test the efficacy of systematic testing, investigators studied 2,216 severe acute respiratory illness patients hospitalized in one of three hospitals in Minnesota during September 2015-August 2016. Patients were predominantly younger than 5 years old (57%) and had one or more chronic medical condition (63%).
Detection of at least one virus increased from 1,062 patients (48%) to 1,600 patients (72%) when comparing clinically ordered tests against expanded, systematic RT-PCR testing conducted through the Minnesota Health Department (MDH).
By patient age, viral detection increased by 27%, 24%, 18%, and 21% for patients aged younger than 5 years, 5-17 years, 18-64 years, and 65 years and older, respectively. Except for influenza viruses and RSV, the proportions of viruses identified, regardless of age, were all lower in hospital testing, compared with MDH testing.
“RSV targeting was almost systematic among children less than 5 years, but [accounted for] only 28% of RSV detection,” said Dr. Steffen in her presentation. “A smaller proportion of other respiratory viruses, including the human metapneumovirus, were detected at the hospital, and this was especially true for adults.”
Patients with rhinovirus and enterovirus saw a difference between hospital and expanded testing, increasing from a little over 300 patients detected, to nearly 800 patients.
“Patients admitted to the ICU were less likely to have a pathogen detection than those not admitted to the ICU, and those with one or more chronic medical condition had lower viral detection than those without,” Dr. Steffens said. “While testing at MDH did increase the percent of patients in each category, trends remained consistent and significant.”
Since testing information was only collected for patients with positive test results at the hospital, investigators were not able to compare testing practices between patients with and without viruses. This study may also have underrepresented pathogens detected through means other than the hospital laboratory, like rapid tests in emergency departments. The study was also limited by the short time frame of only 1 year.
The presenters reported no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Steffens A et al. Abstract 885.
REPORTING FROM ID WEEK 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Among 2,216 patients studied, 1,600 (72%) were found to have at least one respiratory virus through expanded testing, compared with 1,062 (48%) patients tested through clincian-directed testing.
Study details: 2,351 severe acute respiratory illness patients hospitalized in one of three hospitals in Minnesota.
Disclosures: The presenter reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Steffens A et al. Abstract 885.
Chinese school-based flu vaccination program reduced outbreaks
, said Yang Pan, PhD, of the Institute for Infectious Disease and Endemic Disease Control, Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control, and associates.
School-based trivalent inactivated influenza vaccination programs generally occurred Oct. 15-Nov. 30 each year since 2007, with greater than 50% vaccination coverage. In an 11-year retrospective study of school outbreaks of influenza in elementary, middle, and high schools in the Beijing area during Sept. 1, 2006-March 31, 2017, there were 286 febrile outbreaks in schools, involving 6,863 children.
During the 11 years, a mismatch between circulating strains and vaccine strains was identified in two influenza seasons, such as “the A(H3N2) 3C.1 (vaccine strain)-A(H3N2) 3C.3a (circulating strains) mismatch in 2014-2015, the B(Yamagata) Clade 2 (vaccine strain)-B(Yamagata) Clade 3 (circulating strain) mismatch in the 2014-2015 influenza season, and B(Yamagata) (vaccine strain)-B(Victoria) (circulating strains) mismatch in 2015-2016,” they reported.
A combination of high flu vaccine coverage because of school-based vaccinations and a good vaccine match reduced influenza outbreaks in schools by 89% (odds ratio, 0.111), Dr. Pan and associates concluded.
“The school-based influenza vaccination program has been in operation for nearly 10 years in the Beijing area, is unique in China, and is one of the few school-based influenza programs in the world,” the researchers explained. “These data can inform and improve vaccination policy locally and nationally.”
Read more in Vaccine (2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.096).
, said Yang Pan, PhD, of the Institute for Infectious Disease and Endemic Disease Control, Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control, and associates.
School-based trivalent inactivated influenza vaccination programs generally occurred Oct. 15-Nov. 30 each year since 2007, with greater than 50% vaccination coverage. In an 11-year retrospective study of school outbreaks of influenza in elementary, middle, and high schools in the Beijing area during Sept. 1, 2006-March 31, 2017, there were 286 febrile outbreaks in schools, involving 6,863 children.
During the 11 years, a mismatch between circulating strains and vaccine strains was identified in two influenza seasons, such as “the A(H3N2) 3C.1 (vaccine strain)-A(H3N2) 3C.3a (circulating strains) mismatch in 2014-2015, the B(Yamagata) Clade 2 (vaccine strain)-B(Yamagata) Clade 3 (circulating strain) mismatch in the 2014-2015 influenza season, and B(Yamagata) (vaccine strain)-B(Victoria) (circulating strains) mismatch in 2015-2016,” they reported.
A combination of high flu vaccine coverage because of school-based vaccinations and a good vaccine match reduced influenza outbreaks in schools by 89% (odds ratio, 0.111), Dr. Pan and associates concluded.
“The school-based influenza vaccination program has been in operation for nearly 10 years in the Beijing area, is unique in China, and is one of the few school-based influenza programs in the world,” the researchers explained. “These data can inform and improve vaccination policy locally and nationally.”
Read more in Vaccine (2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.096).
, said Yang Pan, PhD, of the Institute for Infectious Disease and Endemic Disease Control, Beijing Center for Disease Prevention and Control, and associates.
School-based trivalent inactivated influenza vaccination programs generally occurred Oct. 15-Nov. 30 each year since 2007, with greater than 50% vaccination coverage. In an 11-year retrospective study of school outbreaks of influenza in elementary, middle, and high schools in the Beijing area during Sept. 1, 2006-March 31, 2017, there were 286 febrile outbreaks in schools, involving 6,863 children.
During the 11 years, a mismatch between circulating strains and vaccine strains was identified in two influenza seasons, such as “the A(H3N2) 3C.1 (vaccine strain)-A(H3N2) 3C.3a (circulating strains) mismatch in 2014-2015, the B(Yamagata) Clade 2 (vaccine strain)-B(Yamagata) Clade 3 (circulating strain) mismatch in the 2014-2015 influenza season, and B(Yamagata) (vaccine strain)-B(Victoria) (circulating strains) mismatch in 2015-2016,” they reported.
A combination of high flu vaccine coverage because of school-based vaccinations and a good vaccine match reduced influenza outbreaks in schools by 89% (odds ratio, 0.111), Dr. Pan and associates concluded.
“The school-based influenza vaccination program has been in operation for nearly 10 years in the Beijing area, is unique in China, and is one of the few school-based influenza programs in the world,” the researchers explained. “These data can inform and improve vaccination policy locally and nationally.”
Read more in Vaccine (2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.096).
FROM VACCINE
Public health hazard: Bring your flu to work day
Slightly more than 41% of health care personnel who had the flu during the 2014-2015 influenza season went to work while they were ill, according to an annual survey.
Physicians, however, were well above this average, with 63% reporting they had worked with an influenza-like illness (ILI); they were not quite as far above average as pharmacists, though, who had a 67% rate of “presenteeism” – the highest among all of the health care occupations included in the survey, said Sophia Chiu, MD, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, and her associates.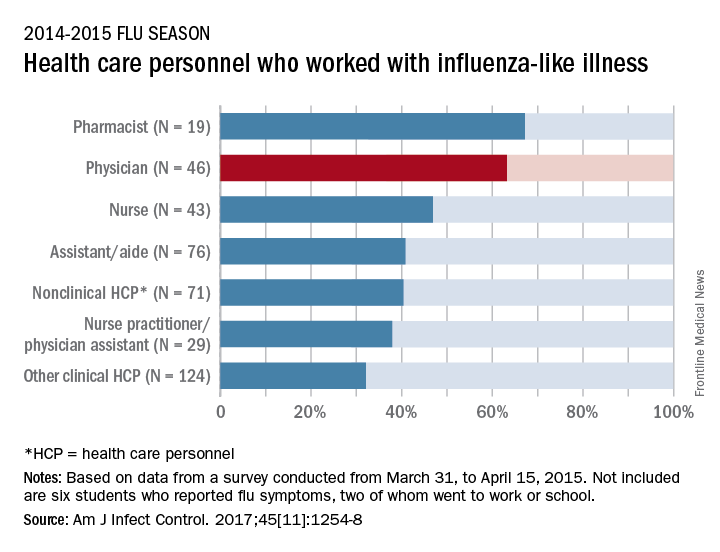
“The statistics are alarming. At least one earlier study has shown that patients who are exposed to a health care worker who is sick are five times more likely to get a health care–associated infection,” Dr. Chiu said in a separate written statement.
For the study, ILI was defined as “fever (without a specified temperature cutoff) and sore throat or cough.” The “nonclinical personnel” category included managers, food service workers, and janitors, while the “other clinical personnel” category included technicians and technologists. The annual Internet panel survey was conducted from March 31, 2015, to April 15, 2015, and 414 of its 1,914 respondents self-reported having an ILI, of whom 183 said that they worked during their illness, Dr. Chiu and her associates said.
The investigators are all CDC employees. The respondents were recruited from Internet panels operated by Survey Sampling International through a contract with Abt Associates.
Slightly more than 41% of health care personnel who had the flu during the 2014-2015 influenza season went to work while they were ill, according to an annual survey.
Physicians, however, were well above this average, with 63% reporting they had worked with an influenza-like illness (ILI); they were not quite as far above average as pharmacists, though, who had a 67% rate of “presenteeism” – the highest among all of the health care occupations included in the survey, said Sophia Chiu, MD, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, and her associates.
“The statistics are alarming. At least one earlier study has shown that patients who are exposed to a health care worker who is sick are five times more likely to get a health care–associated infection,” Dr. Chiu said in a separate written statement.
For the study, ILI was defined as “fever (without a specified temperature cutoff) and sore throat or cough.” The “nonclinical personnel” category included managers, food service workers, and janitors, while the “other clinical personnel” category included technicians and technologists. The annual Internet panel survey was conducted from March 31, 2015, to April 15, 2015, and 414 of its 1,914 respondents self-reported having an ILI, of whom 183 said that they worked during their illness, Dr. Chiu and her associates said.
The investigators are all CDC employees. The respondents were recruited from Internet panels operated by Survey Sampling International through a contract with Abt Associates.
Slightly more than 41% of health care personnel who had the flu during the 2014-2015 influenza season went to work while they were ill, according to an annual survey.
Physicians, however, were well above this average, with 63% reporting they had worked with an influenza-like illness (ILI); they were not quite as far above average as pharmacists, though, who had a 67% rate of “presenteeism” – the highest among all of the health care occupations included in the survey, said Sophia Chiu, MD, MPH, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, and her associates.
“The statistics are alarming. At least one earlier study has shown that patients who are exposed to a health care worker who is sick are five times more likely to get a health care–associated infection,” Dr. Chiu said in a separate written statement.
For the study, ILI was defined as “fever (without a specified temperature cutoff) and sore throat or cough.” The “nonclinical personnel” category included managers, food service workers, and janitors, while the “other clinical personnel” category included technicians and technologists. The annual Internet panel survey was conducted from March 31, 2015, to April 15, 2015, and 414 of its 1,914 respondents self-reported having an ILI, of whom 183 said that they worked during their illness, Dr. Chiu and her associates said.
The investigators are all CDC employees. The respondents were recruited from Internet panels operated by Survey Sampling International through a contract with Abt Associates.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF INFECTION CONTROL
In-hospital outcomes are better for vaccinated H1N1 patients
TORONTO – Patients who received an influenza vaccination but still required hospitalization for H1N1 influenza had better outcomes, compared with unvaccinated patients, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In the hospital, vaccinated patients had significantly lower rates of acute kidney injury (6% vs. 35%; P = .038) and were more likely to be satisfactorily managed with noninvasive mechanical ventilation (41% vs. 6%; P = .004).
Dr. Chandak and her colleagues studied 72 cases of seasonal influenza requiring hospitalization from September 2015 to April 2016 at Berkshire Medical Center, a 300-bed teaching hospital in western Massachusetts. Based on rapid polymerase chain reaction testing, 51 of these patients were positive for H1N1, of which 38 had received a seasonal flu vaccine.
H1N1 patients who had received vaccination were significantly older (70.4 years vs. 59.6 years; P = .016) and were more often smokers (76% vs. 38%; P = .017), compared with patients who were unvaccinated.
The finding that the unvaccinated patients were younger and still had poorer outcomes, “emphasizes the need for widespread vaccination,” Dr. Chandak said.
There were several parameters that trended in favor of vaccination, but did not reach statistical significance due to the relatively small sample size, Dr. Chandak said. These included a trend towards more ICU admission in the unvaccinated, compared with vaccinated patients (21% and 12%, respectively; P = .699), a longer ICU stay (1.7 days and 0.2 days; P = .144), more multiorgan dysfunction syndrome (12% and 6%; P = .654), and more acute respiratory distress syndrome (6% and 0%; P = .547). Vasopressors were needed in a similar proportion of patients (12% of both groups).
During the 2009-2010 flu season, H1N1 was the cause of about 61 million cases of influenza in the United States, 274,000 hospitalizations, and 12,470 deaths, Dr. Chandak reported.
Since the 2010-2011 influenza season, the trivalent influenza vaccine has included antigen from the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. This has prevented between 700,000 and 1.5 million cases of H1N1, up to 10,000 hospitalizations, and as many as 500 deaths, according to surveillance data (Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19[3]:439-48).
The viral subtype made a strong reappearance in the 2015-2016 flu season when it was again the predominant viral subtype of the season, according to the CDC. Most studies have looked at the effectiveness of the vaccine, but have not studied critical care outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients, Dr. Chandak noted.
Dr. Chandak reported having no financial disclosures.
Daniel Ouellette, MD, FCCP, comments: “I never take the flu vaccine,” my patient stated, following my suggestion that she be inoculated. “It makes me sick.”
I reflected on the cases of influenza patients that I took care of the previous year in the ICU: the 50-year-old man with no comorbidities who died in respiratory failure; the 32-year-old pregnant woman who survived a 3-month hospitalization during which she was treated with ECMO and suffered irreversible kidney failure. “I take it every year,” I told her.
While the influenza vaccine may not prevent all cases of influenza, those who develop influenza may have an attenuated illness. Data from Chandak and colleagues affirm improved outcomes in patients who receive the vaccine and still develop influenza.
Daniel Ouellette, MD, FCCP, comments: “I never take the flu vaccine,” my patient stated, following my suggestion that she be inoculated. “It makes me sick.”
I reflected on the cases of influenza patients that I took care of the previous year in the ICU: the 50-year-old man with no comorbidities who died in respiratory failure; the 32-year-old pregnant woman who survived a 3-month hospitalization during which she was treated with ECMO and suffered irreversible kidney failure. “I take it every year,” I told her.
While the influenza vaccine may not prevent all cases of influenza, those who develop influenza may have an attenuated illness. Data from Chandak and colleagues affirm improved outcomes in patients who receive the vaccine and still develop influenza.
Daniel Ouellette, MD, FCCP, comments: “I never take the flu vaccine,” my patient stated, following my suggestion that she be inoculated. “It makes me sick.”
I reflected on the cases of influenza patients that I took care of the previous year in the ICU: the 50-year-old man with no comorbidities who died in respiratory failure; the 32-year-old pregnant woman who survived a 3-month hospitalization during which she was treated with ECMO and suffered irreversible kidney failure. “I take it every year,” I told her.
While the influenza vaccine may not prevent all cases of influenza, those who develop influenza may have an attenuated illness. Data from Chandak and colleagues affirm improved outcomes in patients who receive the vaccine and still develop influenza.
TORONTO – Patients who received an influenza vaccination but still required hospitalization for H1N1 influenza had better outcomes, compared with unvaccinated patients, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In the hospital, vaccinated patients had significantly lower rates of acute kidney injury (6% vs. 35%; P = .038) and were more likely to be satisfactorily managed with noninvasive mechanical ventilation (41% vs. 6%; P = .004).
Dr. Chandak and her colleagues studied 72 cases of seasonal influenza requiring hospitalization from September 2015 to April 2016 at Berkshire Medical Center, a 300-bed teaching hospital in western Massachusetts. Based on rapid polymerase chain reaction testing, 51 of these patients were positive for H1N1, of which 38 had received a seasonal flu vaccine.
H1N1 patients who had received vaccination were significantly older (70.4 years vs. 59.6 years; P = .016) and were more often smokers (76% vs. 38%; P = .017), compared with patients who were unvaccinated.
The finding that the unvaccinated patients were younger and still had poorer outcomes, “emphasizes the need for widespread vaccination,” Dr. Chandak said.
There were several parameters that trended in favor of vaccination, but did not reach statistical significance due to the relatively small sample size, Dr. Chandak said. These included a trend towards more ICU admission in the unvaccinated, compared with vaccinated patients (21% and 12%, respectively; P = .699), a longer ICU stay (1.7 days and 0.2 days; P = .144), more multiorgan dysfunction syndrome (12% and 6%; P = .654), and more acute respiratory distress syndrome (6% and 0%; P = .547). Vasopressors were needed in a similar proportion of patients (12% of both groups).
During the 2009-2010 flu season, H1N1 was the cause of about 61 million cases of influenza in the United States, 274,000 hospitalizations, and 12,470 deaths, Dr. Chandak reported.
Since the 2010-2011 influenza season, the trivalent influenza vaccine has included antigen from the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. This has prevented between 700,000 and 1.5 million cases of H1N1, up to 10,000 hospitalizations, and as many as 500 deaths, according to surveillance data (Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19[3]:439-48).
The viral subtype made a strong reappearance in the 2015-2016 flu season when it was again the predominant viral subtype of the season, according to the CDC. Most studies have looked at the effectiveness of the vaccine, but have not studied critical care outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients, Dr. Chandak noted.
Dr. Chandak reported having no financial disclosures.
TORONTO – Patients who received an influenza vaccination but still required hospitalization for H1N1 influenza had better outcomes, compared with unvaccinated patients, according to findings from a retrospective study.
In the hospital, vaccinated patients had significantly lower rates of acute kidney injury (6% vs. 35%; P = .038) and were more likely to be satisfactorily managed with noninvasive mechanical ventilation (41% vs. 6%; P = .004).
Dr. Chandak and her colleagues studied 72 cases of seasonal influenza requiring hospitalization from September 2015 to April 2016 at Berkshire Medical Center, a 300-bed teaching hospital in western Massachusetts. Based on rapid polymerase chain reaction testing, 51 of these patients were positive for H1N1, of which 38 had received a seasonal flu vaccine.
H1N1 patients who had received vaccination were significantly older (70.4 years vs. 59.6 years; P = .016) and were more often smokers (76% vs. 38%; P = .017), compared with patients who were unvaccinated.
The finding that the unvaccinated patients were younger and still had poorer outcomes, “emphasizes the need for widespread vaccination,” Dr. Chandak said.
There were several parameters that trended in favor of vaccination, but did not reach statistical significance due to the relatively small sample size, Dr. Chandak said. These included a trend towards more ICU admission in the unvaccinated, compared with vaccinated patients (21% and 12%, respectively; P = .699), a longer ICU stay (1.7 days and 0.2 days; P = .144), more multiorgan dysfunction syndrome (12% and 6%; P = .654), and more acute respiratory distress syndrome (6% and 0%; P = .547). Vasopressors were needed in a similar proportion of patients (12% of both groups).
During the 2009-2010 flu season, H1N1 was the cause of about 61 million cases of influenza in the United States, 274,000 hospitalizations, and 12,470 deaths, Dr. Chandak reported.
Since the 2010-2011 influenza season, the trivalent influenza vaccine has included antigen from the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza A virus. This has prevented between 700,000 and 1.5 million cases of H1N1, up to 10,000 hospitalizations, and as many as 500 deaths, according to surveillance data (Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19[3]:439-48).
The viral subtype made a strong reappearance in the 2015-2016 flu season when it was again the predominant viral subtype of the season, according to the CDC. Most studies have looked at the effectiveness of the vaccine, but have not studied critical care outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated patients, Dr. Chandak noted.
Dr. Chandak reported having no financial disclosures.
AT CHEST 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Unvaccinated patients had a significantly higher risk of acute kidney injury (35% vs. 6%; P = .038) and were less likely to be managed with noninvasive mechanical ventilation (6% vs. 41%; P = .004).
Data source: Retrospective analysis including 72 reported influenza cases, 51 (71%) testing positive for H1N1.
Disclosures: Dr. Chandak reported having no financial disclosures.
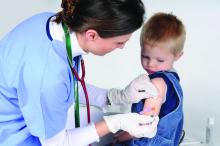
Nearly 80% of health care personnel stepped up for flu shots
Nearly four out of five health care personnel in the United States received a flu vaccination during the 2016-2017 flu season, but a majority of those working in long-term care settings were not vaccinated, based on data from an Internet survey of more than 2,000 individuals that was conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A total of 78.6% of the survey’s respondents said they’d been vaccinated during the 2016-2017 season. Vaccination coverage for health care personnel overall has remained in the 77%-79% range in recent years, but that represents an increase from 64% in 2010-2011.
“As in previous seasons, the highest coverage was among HCP whose workplace had vaccination requirements,” noted Carla L. Black, PhD, of the CDC, and colleagues (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1009-15). The researchers reviewed data collected from an Internet panel survey of 2,438 health care personnel between March 28, 2017, and April 19, 2017.
Physicians boasted the highest vaccination coverage in 2016-2017 (96%), followed by pharmacists (94%), nurses (93%), nurse practitioners and physician assistants (92%), other clinical providers (80%), nonclinical health care providers (74%), and aides and assistants (69%).
Flu vaccination rates were highest among HCPs working in a hospital setting (92%); 94% of survey respondents in hospitals reported either having a vaccination requirement at work or being provided at least 1 day of on-site vaccination.
Vaccination rates were lowest among health care personnel in long-term care settings (68%), where only 26% reported a workplace vaccination requirement. However, vaccination rates in long-term care rose to 90% when employers required vaccination.
The report’s findings were limited by several factors, including the use of a volunteer sample, the reliance on self-reports, and the potential differences between Internet survey results and population-based estimates of flu vaccination.
However, “in the absence of vaccination requirements, the findings in this study support the recommendations found in the Guide to Community Preventive Services, which include active promotion of on-site vaccination at no cost or low cost to increase influenza vaccination coverage among HCPs,” the researchers said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly four out of five health care personnel in the United States received a flu vaccination during the 2016-2017 flu season, but a majority of those working in long-term care settings were not vaccinated, based on data from an Internet survey of more than 2,000 individuals that was conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A total of 78.6% of the survey’s respondents said they’d been vaccinated during the 2016-2017 season. Vaccination coverage for health care personnel overall has remained in the 77%-79% range in recent years, but that represents an increase from 64% in 2010-2011.
“As in previous seasons, the highest coverage was among HCP whose workplace had vaccination requirements,” noted Carla L. Black, PhD, of the CDC, and colleagues (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1009-15). The researchers reviewed data collected from an Internet panel survey of 2,438 health care personnel between March 28, 2017, and April 19, 2017.
Physicians boasted the highest vaccination coverage in 2016-2017 (96%), followed by pharmacists (94%), nurses (93%), nurse practitioners and physician assistants (92%), other clinical providers (80%), nonclinical health care providers (74%), and aides and assistants (69%).
Flu vaccination rates were highest among HCPs working in a hospital setting (92%); 94% of survey respondents in hospitals reported either having a vaccination requirement at work or being provided at least 1 day of on-site vaccination.
Vaccination rates were lowest among health care personnel in long-term care settings (68%), where only 26% reported a workplace vaccination requirement. However, vaccination rates in long-term care rose to 90% when employers required vaccination.
The report’s findings were limited by several factors, including the use of a volunteer sample, the reliance on self-reports, and the potential differences between Internet survey results and population-based estimates of flu vaccination.
However, “in the absence of vaccination requirements, the findings in this study support the recommendations found in the Guide to Community Preventive Services, which include active promotion of on-site vaccination at no cost or low cost to increase influenza vaccination coverage among HCPs,” the researchers said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly four out of five health care personnel in the United States received a flu vaccination during the 2016-2017 flu season, but a majority of those working in long-term care settings were not vaccinated, based on data from an Internet survey of more than 2,000 individuals that was conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
A total of 78.6% of the survey’s respondents said they’d been vaccinated during the 2016-2017 season. Vaccination coverage for health care personnel overall has remained in the 77%-79% range in recent years, but that represents an increase from 64% in 2010-2011.
“As in previous seasons, the highest coverage was among HCP whose workplace had vaccination requirements,” noted Carla L. Black, PhD, of the CDC, and colleagues (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1009-15). The researchers reviewed data collected from an Internet panel survey of 2,438 health care personnel between March 28, 2017, and April 19, 2017.
Physicians boasted the highest vaccination coverage in 2016-2017 (96%), followed by pharmacists (94%), nurses (93%), nurse practitioners and physician assistants (92%), other clinical providers (80%), nonclinical health care providers (74%), and aides and assistants (69%).
Flu vaccination rates were highest among HCPs working in a hospital setting (92%); 94% of survey respondents in hospitals reported either having a vaccination requirement at work or being provided at least 1 day of on-site vaccination.
Vaccination rates were lowest among health care personnel in long-term care settings (68%), where only 26% reported a workplace vaccination requirement. However, vaccination rates in long-term care rose to 90% when employers required vaccination.
The report’s findings were limited by several factors, including the use of a volunteer sample, the reliance on self-reports, and the potential differences between Internet survey results and population-based estimates of flu vaccination.
However, “in the absence of vaccination requirements, the findings in this study support the recommendations found in the Guide to Community Preventive Services, which include active promotion of on-site vaccination at no cost or low cost to increase influenza vaccination coverage among HCPs,” the researchers said.
The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM MMWR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Overall flu vaccination coverage among U.S. health care personnel was 78.6% in the 2016-2017 season
Data source: The data come from an Internet survey of 2,438 health care personnel.
Disclosures: The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Not recommending LAIV didn’t reduce flu vaccination in Oregon children
Oregon researchers studying the effect of not recommending intranasal live attenuated influenza vaccines (LAIV) in favor of injected influenza vaccines (IIV) for the 2016-2017 flu season found that the change in recommendation had a minimal impact on overall flu vaccination rates, but that patients who had been given injected flu vaccine previously were slightly more likely to return for it the following season.
Steve G. Robison, MPH, of the Immunization Program of the Oregon Health Authority in Salem, led the study to monitor the effects of the new recommendation in Oregon, where he and his coauthors noted that there is “a substantial vaccine-hesitant population” (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct 6. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0516).
They considered data from the state’s immunization registry, simply counting seasonal immunization rates from 2012 to 2017. As a second assessment, they compared children who had previously received LAIV between Aug. 1 and Dec. 31, 2015, and children who received IIV during the same period, to see which cohort was more likely to return for flu vaccination the following season.
“Overall, 53.1% of children in the study with previous LAIV and 56.4% with a previous IIV returned for an IIV during the 2016-2017 season,” they reported. Those rates showed that the cohort with past injected vaccine was only 1.05 times more likely to return than the cohort with past nasal spray vaccine (95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.06). The investigators also concluded that overall rates have undergone “minimal changes” in the past 5 years, and the effect of the committee’s recommendation additionally was considered to be minimal.
Mr. Robison and his associates said they had no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded in part by the CDC’s grants to Oregon statefor immunization surveillance.
Oregon researchers studying the effect of not recommending intranasal live attenuated influenza vaccines (LAIV) in favor of injected influenza vaccines (IIV) for the 2016-2017 flu season found that the change in recommendation had a minimal impact on overall flu vaccination rates, but that patients who had been given injected flu vaccine previously were slightly more likely to return for it the following season.
Steve G. Robison, MPH, of the Immunization Program of the Oregon Health Authority in Salem, led the study to monitor the effects of the new recommendation in Oregon, where he and his coauthors noted that there is “a substantial vaccine-hesitant population” (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct 6. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0516).
They considered data from the state’s immunization registry, simply counting seasonal immunization rates from 2012 to 2017. As a second assessment, they compared children who had previously received LAIV between Aug. 1 and Dec. 31, 2015, and children who received IIV during the same period, to see which cohort was more likely to return for flu vaccination the following season.
“Overall, 53.1% of children in the study with previous LAIV and 56.4% with a previous IIV returned for an IIV during the 2016-2017 season,” they reported. Those rates showed that the cohort with past injected vaccine was only 1.05 times more likely to return than the cohort with past nasal spray vaccine (95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.06). The investigators also concluded that overall rates have undergone “minimal changes” in the past 5 years, and the effect of the committee’s recommendation additionally was considered to be minimal.
Mr. Robison and his associates said they had no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded in part by the CDC’s grants to Oregon statefor immunization surveillance.
Oregon researchers studying the effect of not recommending intranasal live attenuated influenza vaccines (LAIV) in favor of injected influenza vaccines (IIV) for the 2016-2017 flu season found that the change in recommendation had a minimal impact on overall flu vaccination rates, but that patients who had been given injected flu vaccine previously were slightly more likely to return for it the following season.
Steve G. Robison, MPH, of the Immunization Program of the Oregon Health Authority in Salem, led the study to monitor the effects of the new recommendation in Oregon, where he and his coauthors noted that there is “a substantial vaccine-hesitant population” (Pediatrics. 2017 Oct 6. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-0516).
They considered data from the state’s immunization registry, simply counting seasonal immunization rates from 2012 to 2017. As a second assessment, they compared children who had previously received LAIV between Aug. 1 and Dec. 31, 2015, and children who received IIV during the same period, to see which cohort was more likely to return for flu vaccination the following season.
“Overall, 53.1% of children in the study with previous LAIV and 56.4% with a previous IIV returned for an IIV during the 2016-2017 season,” they reported. Those rates showed that the cohort with past injected vaccine was only 1.05 times more likely to return than the cohort with past nasal spray vaccine (95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.06). The investigators also concluded that overall rates have undergone “minimal changes” in the past 5 years, and the effect of the committee’s recommendation additionally was considered to be minimal.
Mr. Robison and his associates said they had no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded in part by the CDC’s grants to Oregon statefor immunization surveillance.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: 53.1% of children in the study with previous LAIV and 56.4% with a previous IIV returned for an IIV during the 2016-2017 season.
Data source: Data from Oregon’s immunization registry.
Disclosures: Mr. Robison and his associates said they had no relevant financial disclosures. The study was funded in part by the CDC’s grants to Oregon state for immunization surveillance.
Just over half of pregnant women got flu vaccine in 2016-2017
Influenza vaccination among pregnant women during the 2016-2017 flu season was slightly higher than during the 2015-2016 season, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
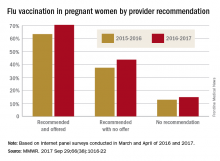
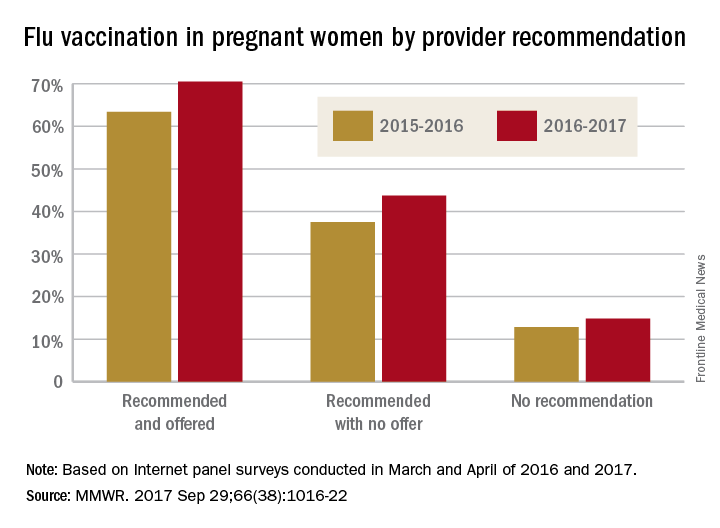
Overall coverage for 2016-2017 was 53.6% among pregnant women, compared with 49.9% in 2015-2016, continuing the overall rise seen over the last several flu seasons. Among pregnant women who received a recommendation from a health care provider and were offered vaccination, coverage was 70.5% in 2016-2017, while coverage was 43.7% among women who received a recommendation but no offer and 14.8% among those who did not receive a recommendation, the CDC reported (MMWR. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1016-22).
Among other subgroups, coverage by age for the 2016-2017 flu season was 41.7% for those aged 18-24 years, 58.4% for those aged 25-34 years, and 58.5% for those 35-49 years old. There also was considerable variation by race/ethnicity, with coverage at 61.2% for Hispanics, 55.4% for whites, 42.3% for blacks, and 51.7% for others. Coverage for the subgroups corresponded with the rates at which vaccination was recommended: Younger women were less likely than older women to receive a recommendation, and Hispanic and white women more likely to receive recommendations than did blacks and other races/ethnicities, the CDC said.
The 2017 data include 1,893 responses to an Internet panel survey conducted from March 28 to April 7, 2017. The analysis of the 2016 panel survey, which was conducted from March 29 to April 7, 2016, included responses from 1,692 women.
Influenza vaccination among pregnant women during the 2016-2017 flu season was slightly higher than during the 2015-2016 season, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Overall coverage for 2016-2017 was 53.6% among pregnant women, compared with 49.9% in 2015-2016, continuing the overall rise seen over the last several flu seasons. Among pregnant women who received a recommendation from a health care provider and were offered vaccination, coverage was 70.5% in 2016-2017, while coverage was 43.7% among women who received a recommendation but no offer and 14.8% among those who did not receive a recommendation, the CDC reported (MMWR. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1016-22).
Among other subgroups, coverage by age for the 2016-2017 flu season was 41.7% for those aged 18-24 years, 58.4% for those aged 25-34 years, and 58.5% for those 35-49 years old. There also was considerable variation by race/ethnicity, with coverage at 61.2% for Hispanics, 55.4% for whites, 42.3% for blacks, and 51.7% for others. Coverage for the subgroups corresponded with the rates at which vaccination was recommended: Younger women were less likely than older women to receive a recommendation, and Hispanic and white women more likely to receive recommendations than did blacks and other races/ethnicities, the CDC said.
The 2017 data include 1,893 responses to an Internet panel survey conducted from March 28 to April 7, 2017. The analysis of the 2016 panel survey, which was conducted from March 29 to April 7, 2016, included responses from 1,692 women.
Influenza vaccination among pregnant women during the 2016-2017 flu season was slightly higher than during the 2015-2016 season, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Overall coverage for 2016-2017 was 53.6% among pregnant women, compared with 49.9% in 2015-2016, continuing the overall rise seen over the last several flu seasons. Among pregnant women who received a recommendation from a health care provider and were offered vaccination, coverage was 70.5% in 2016-2017, while coverage was 43.7% among women who received a recommendation but no offer and 14.8% among those who did not receive a recommendation, the CDC reported (MMWR. 2017 Sep 29;66[38]:1016-22).
Among other subgroups, coverage by age for the 2016-2017 flu season was 41.7% for those aged 18-24 years, 58.4% for those aged 25-34 years, and 58.5% for those 35-49 years old. There also was considerable variation by race/ethnicity, with coverage at 61.2% for Hispanics, 55.4% for whites, 42.3% for blacks, and 51.7% for others. Coverage for the subgroups corresponded with the rates at which vaccination was recommended: Younger women were less likely than older women to receive a recommendation, and Hispanic and white women more likely to receive recommendations than did blacks and other races/ethnicities, the CDC said.
The 2017 data include 1,893 responses to an Internet panel survey conducted from March 28 to April 7, 2017. The analysis of the 2016 panel survey, which was conducted from March 29 to April 7, 2016, included responses from 1,692 women.
FROM MMWR
Insist on flu vaccination for all, say experts
sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
Some good news about the flu – vaccination rates increased slightly last year, compared with the previous year among all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Experts continue to recommend annual influenza vaccination for all persons aged 6 months and older, but they emphasize the need to identify those at risk of not getting vaccinated and develop strategies to increase vaccination coverage.
“Vaccines are among the greatest public health achievements of modern times, but they are only as useful as we as a society take advantage of them,” Secretary of Health & Human Services Thomas E. Price, MD, said at the briefing.
Overall flu vaccination in the United States was 47% for the 2016-2017 season, compared with 46% during the 2015-2016 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Price emphasized that vaccination is only part of a successful flu prevention strategy. Stay home when you are sick to help avoid spreading germs to others and take antiviral drugs if a doctor prescribes them to help reduce and avoid complications from flu, he said.
Children aged 6-23 months were the only population subgroup to meet the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal last year, with a rate of 73%, said Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, CPNP, senior director of infection prevention and control at Children’s Hospital Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“Our goal is to increase coverage for children of all ages,” she said. But it’s not just about the kids themselves, she emphasized.
“If your child gets the flu, they expose babies, grandparents, pregnant women. We need to vaccinate children to protect the public at large,” she said. In addition, health care professionals must be clear about recommending vaccination. The research shows that a specific recommendation often makes the difference for vaccinating families.
Pregnant women are among those who can and should safely be vaccinated, Ms. Stinchfield emphasized. Flu vaccination among pregnant women was 54% in 2016-2017, similar to the past three flu seasons, and approximately two-thirds (67%) of pregnant women in 2016-2017 reported that a health care provider recommended and offered flu vaccination, according to CDC data.
Older adults also are important targets for flu vaccination, noted Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, director of the Center for Vaccine Development at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Last year, approximately 65% of U.S. adults aged 65 years and older were vaccinated, which was the largest subgroup of adults aged 18 years and older, she said. Older adults may be caring for frail spouses or infant grandchildren, so protecting others should be a motivating factor in continuing to encourage vaccination in this age group, she noted.
The flu vaccine supply is plentiful going into the start of the 2016-2017 flu season, with an estimated 166 million doses available in several formulations, said Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, director of the CDC’s Influenza Division.
Options for vaccination include the standard vaccine, a cell-based vaccine, and a recombinant vaccine. In addition, an adjuvanted vaccine and a high-dose vaccine are available specifically for adults aged 65 years and older; these vaccines are designed to provoke a stronger immune response, Dr. Jernigan said.
However, the briefing participants agreed that the best strategy is to get vaccinated as soon as possible, rather than postponing vaccination in order to secure a particular vaccine type.
Clinicians should not underestimate the power of leading by example when it comes to flu vaccination, Dr. Schaffner noted. Support from the highest levels of administration is important to help overcome barriers to vaccination coverage for health care workers by making vaccination easy and accessible, he said.
The overall influenza vaccination coverage estimate among health care providers was 79% for the 2016-2017 season, similar to the 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 seasons, but representing a 15% increase since 2010-2011. Vaccination coverage was highest among health care personnel whose workplaces required it.
Complete data on 2016-2017 vaccination coverage in health care workers and in pregnant women were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on Sept. 29.
The CDC’s complete flu vaccination recommendations are available online.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
Some good news about the flu – vaccination rates increased slightly last year, compared with the previous year among all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Experts continue to recommend annual influenza vaccination for all persons aged 6 months and older, but they emphasize the need to identify those at risk of not getting vaccinated and develop strategies to increase vaccination coverage.
“Vaccines are among the greatest public health achievements of modern times, but they are only as useful as we as a society take advantage of them,” Secretary of Health & Human Services Thomas E. Price, MD, said at the briefing.
Overall flu vaccination in the United States was 47% for the 2016-2017 season, compared with 46% during the 2015-2016 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Price emphasized that vaccination is only part of a successful flu prevention strategy. Stay home when you are sick to help avoid spreading germs to others and take antiviral drugs if a doctor prescribes them to help reduce and avoid complications from flu, he said.
Children aged 6-23 months were the only population subgroup to meet the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal last year, with a rate of 73%, said Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, CPNP, senior director of infection prevention and control at Children’s Hospital Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“Our goal is to increase coverage for children of all ages,” she said. But it’s not just about the kids themselves, she emphasized.
“If your child gets the flu, they expose babies, grandparents, pregnant women. We need to vaccinate children to protect the public at large,” she said. In addition, health care professionals must be clear about recommending vaccination. The research shows that a specific recommendation often makes the difference for vaccinating families.
Pregnant women are among those who can and should safely be vaccinated, Ms. Stinchfield emphasized. Flu vaccination among pregnant women was 54% in 2016-2017, similar to the past three flu seasons, and approximately two-thirds (67%) of pregnant women in 2016-2017 reported that a health care provider recommended and offered flu vaccination, according to CDC data.
Older adults also are important targets for flu vaccination, noted Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, director of the Center for Vaccine Development at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Last year, approximately 65% of U.S. adults aged 65 years and older were vaccinated, which was the largest subgroup of adults aged 18 years and older, she said. Older adults may be caring for frail spouses or infant grandchildren, so protecting others should be a motivating factor in continuing to encourage vaccination in this age group, she noted.
The flu vaccine supply is plentiful going into the start of the 2016-2017 flu season, with an estimated 166 million doses available in several formulations, said Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, director of the CDC’s Influenza Division.
Options for vaccination include the standard vaccine, a cell-based vaccine, and a recombinant vaccine. In addition, an adjuvanted vaccine and a high-dose vaccine are available specifically for adults aged 65 years and older; these vaccines are designed to provoke a stronger immune response, Dr. Jernigan said.
However, the briefing participants agreed that the best strategy is to get vaccinated as soon as possible, rather than postponing vaccination in order to secure a particular vaccine type.
Clinicians should not underestimate the power of leading by example when it comes to flu vaccination, Dr. Schaffner noted. Support from the highest levels of administration is important to help overcome barriers to vaccination coverage for health care workers by making vaccination easy and accessible, he said.
The overall influenza vaccination coverage estimate among health care providers was 79% for the 2016-2017 season, similar to the 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 seasons, but representing a 15% increase since 2010-2011. Vaccination coverage was highest among health care personnel whose workplaces required it.
Complete data on 2016-2017 vaccination coverage in health care workers and in pregnant women were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on Sept. 29.
The CDC’s complete flu vaccination recommendations are available online.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
Some good news about the flu – vaccination rates increased slightly last year, compared with the previous year among all individuals aged 6 months and older without contraindications, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Experts continue to recommend annual influenza vaccination for all persons aged 6 months and older, but they emphasize the need to identify those at risk of not getting vaccinated and develop strategies to increase vaccination coverage.
“Vaccines are among the greatest public health achievements of modern times, but they are only as useful as we as a society take advantage of them,” Secretary of Health & Human Services Thomas E. Price, MD, said at the briefing.
Overall flu vaccination in the United States was 47% for the 2016-2017 season, compared with 46% during the 2015-2016 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Price emphasized that vaccination is only part of a successful flu prevention strategy. Stay home when you are sick to help avoid spreading germs to others and take antiviral drugs if a doctor prescribes them to help reduce and avoid complications from flu, he said.
Children aged 6-23 months were the only population subgroup to meet the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal last year, with a rate of 73%, said Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, CPNP, senior director of infection prevention and control at Children’s Hospital Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“Our goal is to increase coverage for children of all ages,” she said. But it’s not just about the kids themselves, she emphasized.
“If your child gets the flu, they expose babies, grandparents, pregnant women. We need to vaccinate children to protect the public at large,” she said. In addition, health care professionals must be clear about recommending vaccination. The research shows that a specific recommendation often makes the difference for vaccinating families.
Pregnant women are among those who can and should safely be vaccinated, Ms. Stinchfield emphasized. Flu vaccination among pregnant women was 54% in 2016-2017, similar to the past three flu seasons, and approximately two-thirds (67%) of pregnant women in 2016-2017 reported that a health care provider recommended and offered flu vaccination, according to CDC data.
Older adults also are important targets for flu vaccination, noted Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, director of the Center for Vaccine Development at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. Last year, approximately 65% of U.S. adults aged 65 years and older were vaccinated, which was the largest subgroup of adults aged 18 years and older, she said. Older adults may be caring for frail spouses or infant grandchildren, so protecting others should be a motivating factor in continuing to encourage vaccination in this age group, she noted.
The flu vaccine supply is plentiful going into the start of the 2016-2017 flu season, with an estimated 166 million doses available in several formulations, said Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, director of the CDC’s Influenza Division.
Options for vaccination include the standard vaccine, a cell-based vaccine, and a recombinant vaccine. In addition, an adjuvanted vaccine and a high-dose vaccine are available specifically for adults aged 65 years and older; these vaccines are designed to provoke a stronger immune response, Dr. Jernigan said.
However, the briefing participants agreed that the best strategy is to get vaccinated as soon as possible, rather than postponing vaccination in order to secure a particular vaccine type.
Clinicians should not underestimate the power of leading by example when it comes to flu vaccination, Dr. Schaffner noted. Support from the highest levels of administration is important to help overcome barriers to vaccination coverage for health care workers by making vaccination easy and accessible, he said.
The overall influenza vaccination coverage estimate among health care providers was 79% for the 2016-2017 season, similar to the 2014-2015 and 2015-2016 seasons, but representing a 15% increase since 2010-2011. Vaccination coverage was highest among health care personnel whose workplaces required it.
Complete data on 2016-2017 vaccination coverage in health care workers and in pregnant women were published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on Sept. 29.
The CDC’s complete flu vaccination recommendations are available online.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.