User login
Clinicians: Be clear about flu vaccine’s value
WASHINGTON – Flu vaccination rates remain below the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal for most of the U.S. population, but data show that a recommendation from a clinician can encourage individuals to get vaccinated and to vaccinate their children, according to a panel of experts who spoke at a press briefing sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
“Annual vaccination is our first line of defense against the flu,” William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at the briefing. The unpredictable nature of the flu makes annual vaccination even more important – and the earlier, the better, said Dr. Schaffner. “If you have seen one flu season, you have seen ... one flu season.”
In a video interview at the briefing, experts emphasized the safety and effectiveness of the flu vaccine for a range of populations, including children, pregnant women, and older adults. And they offered tips to convince patients of the importance of vaccination, as well as the need to make sure health care staff are protected.
Briefing participants included former Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Thomas A. Price, MD; Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, MS, CPNP, CIC of Children’s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota, St. Paul; Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, of the University of Maryland; and Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The clinicians interviewed had no financial conflicts to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Flu vaccination rates remain below the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal for most of the U.S. population, but data show that a recommendation from a clinician can encourage individuals to get vaccinated and to vaccinate their children, according to a panel of experts who spoke at a press briefing sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
“Annual vaccination is our first line of defense against the flu,” William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at the briefing. The unpredictable nature of the flu makes annual vaccination even more important – and the earlier, the better, said Dr. Schaffner. “If you have seen one flu season, you have seen ... one flu season.”
In a video interview at the briefing, experts emphasized the safety and effectiveness of the flu vaccine for a range of populations, including children, pregnant women, and older adults. And they offered tips to convince patients of the importance of vaccination, as well as the need to make sure health care staff are protected.
Briefing participants included former Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Thomas A. Price, MD; Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, MS, CPNP, CIC of Children’s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota, St. Paul; Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, of the University of Maryland; and Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The clinicians interviewed had no financial conflicts to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Flu vaccination rates remain below the 70% Healthy People 2020 goal for most of the U.S. population, but data show that a recommendation from a clinician can encourage individuals to get vaccinated and to vaccinate their children, according to a panel of experts who spoke at a press briefing sponsored by the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases.
“Annual vaccination is our first line of defense against the flu,” William Schaffner, MD, of Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at the briefing. The unpredictable nature of the flu makes annual vaccination even more important – and the earlier, the better, said Dr. Schaffner. “If you have seen one flu season, you have seen ... one flu season.”
In a video interview at the briefing, experts emphasized the safety and effectiveness of the flu vaccine for a range of populations, including children, pregnant women, and older adults. And they offered tips to convince patients of the importance of vaccination, as well as the need to make sure health care staff are protected.
Briefing participants included former Department of Health and Human Services Secretary Thomas A. Price, MD; Patricia A. Stinchfield, RN, MS, CPNP, CIC of Children’s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota, St. Paul; Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, of the University of Maryland; and Daniel B. Jernigan, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The clinicians interviewed had no financial conflicts to disclose.
AT A PRESS BRIEFING BY THE NATIONAL FOUNDATION FOR INFECTIOUS DISEASES
CDC: Flu vaccine recommendations broaden for pregnant women and children
, according to new recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This change from the CDC’s previous guidance that pregnant women receive a seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) was recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices after some heated debate among committee members over evidence presented to support the change in wording (MMWR. 2017 Aug 25;66[(RR-2]:1-20).
The new update gives women the ability to choose between receiving an IIV and FluBlok, a recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV) that is not egg based and can be manufactured more quickly, making it ideal in cases of pandemic or supply shortages, according to the CDC.
Although pregnant women may choose to receive a vaccination during the first trimester, the CDC warns there may be some risk involved.
“Although experience with the use of IIVs is substantial, and data from observational studies are available to support the safety of these vaccines in pregnancy, data are more limited for vaccination during the first trimester,” according to the CDC. “Moreover, there is substantially less experience with more recently licensed IIV products (e.g., quadrivalent, cell culture-based, and adjuvanted vaccines) during pregnancy in general.”
Data also are limited regarding RIVs, the CDC said, with the data used to determine safety among pregnant women “limited to reports of pregnancies occurring incidentally during clinical trials, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) reports, and pregnancy registry reports.”
Changes for children
The CDC chose to accept ACIP recommendations regarding Afluria (IIV3), expanding the age of children who can receive the vaccine from 9 years and older to 5 years and older.
Similar labeling changes were accepted for FluLaval Quadrivalent (IIV4), which had previously been given to children 3 years and older but now but will be available for children starting at 6 months of age.
New products
Recent product licensures included in the MMWR report are Afluria Quadrivalent (IIV4) and Flublok Quadrivalent (RIV4), both for persons over 18 years.
According to the CDC, Flublok Quadrivalent (an RIV) met noninferiority measures, compared with a similar IIV quadrivalent vaccine, for the A(H3H2) and B/Yamagata viruses but not for A(H1N1) or B/Victoria viruses.
Vaccine composition for 2017-2018
Approved viruses for the 2017-2018 season trivalent vaccines are an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1) pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 (H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Brisbane/60/2008–like virus (Victoria lineage), according to the MMWR. Quadrivalent vaccines will include those viruses, with the addition of an B/Phuket/3073/2013–like virus (Yamagata lineage).
The CDC continues to recommend that the quadrivalent live attenuated influenza vaccine FluMist not be used by anyone for the 2017-2018 season, a decision that was made after evidence showed poor effectiveness against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in the 2013-2014 and 2015-2016 seasons.
Vaccine updates published in this report were recommended by ACIP during meetings held in October 2016 and February and June 2017.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
, according to new recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This change from the CDC’s previous guidance that pregnant women receive a seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) was recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices after some heated debate among committee members over evidence presented to support the change in wording (MMWR. 2017 Aug 25;66[(RR-2]:1-20).
The new update gives women the ability to choose between receiving an IIV and FluBlok, a recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV) that is not egg based and can be manufactured more quickly, making it ideal in cases of pandemic or supply shortages, according to the CDC.
Although pregnant women may choose to receive a vaccination during the first trimester, the CDC warns there may be some risk involved.
“Although experience with the use of IIVs is substantial, and data from observational studies are available to support the safety of these vaccines in pregnancy, data are more limited for vaccination during the first trimester,” according to the CDC. “Moreover, there is substantially less experience with more recently licensed IIV products (e.g., quadrivalent, cell culture-based, and adjuvanted vaccines) during pregnancy in general.”
Data also are limited regarding RIVs, the CDC said, with the data used to determine safety among pregnant women “limited to reports of pregnancies occurring incidentally during clinical trials, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) reports, and pregnancy registry reports.”
Changes for children
The CDC chose to accept ACIP recommendations regarding Afluria (IIV3), expanding the age of children who can receive the vaccine from 9 years and older to 5 years and older.
Similar labeling changes were accepted for FluLaval Quadrivalent (IIV4), which had previously been given to children 3 years and older but now but will be available for children starting at 6 months of age.
New products
Recent product licensures included in the MMWR report are Afluria Quadrivalent (IIV4) and Flublok Quadrivalent (RIV4), both for persons over 18 years.
According to the CDC, Flublok Quadrivalent (an RIV) met noninferiority measures, compared with a similar IIV quadrivalent vaccine, for the A(H3H2) and B/Yamagata viruses but not for A(H1N1) or B/Victoria viruses.
Vaccine composition for 2017-2018
Approved viruses for the 2017-2018 season trivalent vaccines are an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1) pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 (H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Brisbane/60/2008–like virus (Victoria lineage), according to the MMWR. Quadrivalent vaccines will include those viruses, with the addition of an B/Phuket/3073/2013–like virus (Yamagata lineage).
The CDC continues to recommend that the quadrivalent live attenuated influenza vaccine FluMist not be used by anyone for the 2017-2018 season, a decision that was made after evidence showed poor effectiveness against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in the 2013-2014 and 2015-2016 seasons.
Vaccine updates published in this report were recommended by ACIP during meetings held in October 2016 and February and June 2017.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
, according to new recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This change from the CDC’s previous guidance that pregnant women receive a seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) was recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices after some heated debate among committee members over evidence presented to support the change in wording (MMWR. 2017 Aug 25;66[(RR-2]:1-20).
The new update gives women the ability to choose between receiving an IIV and FluBlok, a recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV) that is not egg based and can be manufactured more quickly, making it ideal in cases of pandemic or supply shortages, according to the CDC.
Although pregnant women may choose to receive a vaccination during the first trimester, the CDC warns there may be some risk involved.
“Although experience with the use of IIVs is substantial, and data from observational studies are available to support the safety of these vaccines in pregnancy, data are more limited for vaccination during the first trimester,” according to the CDC. “Moreover, there is substantially less experience with more recently licensed IIV products (e.g., quadrivalent, cell culture-based, and adjuvanted vaccines) during pregnancy in general.”
Data also are limited regarding RIVs, the CDC said, with the data used to determine safety among pregnant women “limited to reports of pregnancies occurring incidentally during clinical trials, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) reports, and pregnancy registry reports.”
Changes for children
The CDC chose to accept ACIP recommendations regarding Afluria (IIV3), expanding the age of children who can receive the vaccine from 9 years and older to 5 years and older.
Similar labeling changes were accepted for FluLaval Quadrivalent (IIV4), which had previously been given to children 3 years and older but now but will be available for children starting at 6 months of age.
New products
Recent product licensures included in the MMWR report are Afluria Quadrivalent (IIV4) and Flublok Quadrivalent (RIV4), both for persons over 18 years.
According to the CDC, Flublok Quadrivalent (an RIV) met noninferiority measures, compared with a similar IIV quadrivalent vaccine, for the A(H3H2) and B/Yamagata viruses but not for A(H1N1) or B/Victoria viruses.
Vaccine composition for 2017-2018
Approved viruses for the 2017-2018 season trivalent vaccines are an A/Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1) pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/4801/2014 (H3N2)-like virus, and a B/Brisbane/60/2008–like virus (Victoria lineage), according to the MMWR. Quadrivalent vaccines will include those viruses, with the addition of an B/Phuket/3073/2013–like virus (Yamagata lineage).
The CDC continues to recommend that the quadrivalent live attenuated influenza vaccine FluMist not be used by anyone for the 2017-2018 season, a decision that was made after evidence showed poor effectiveness against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses in the 2013-2014 and 2015-2016 seasons.
Vaccine updates published in this report were recommended by ACIP during meetings held in October 2016 and February and June 2017.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM MMWR
Inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine safe, effective in 6- to 35-month-olds
MADRID – An intramuscular inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine reduced the risk of laboratory-confirmed influenza by up to 69% in previously unvaccinated children aged 6-35 months in a large randomized trial, Stephanie Pepin, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV) is licensed by the Food and Drug Administration as Fluzone Quadrivalent for use in patients as young as 6 months of age. It contains two A- and two B-lineage influenza strains in order to address the common problem of mismatches between circulating influenza B and the single B-lineage strain included in trivalent vaccines.
The incidence of any laboratory confirmed strain of influenza illness during the period from 14 days post-vaccination to the end of flu season was 4.72% in the QIV group, compared with 9.84% in controls who received placebo, which translated to 52% efficacy. The incidence of influenza from vaccine-similar strains as determined by the Sanger sequencing method was 1.01% in children randomized to QIV, compared with 3.28% with placebo, for a 69% efficacy rate.
The QIV had a safety profile in this young population that was similar to the older licensed trivalent vaccine. The most frequently reported adverse reactions to the QIV were injection site pain, irritability, loss of appetite, abnormal crying, and malaise, each reported in 19%-25% of children after the first injection and in 14%-18% after the second. These were typically mild grade 1 or 2 reactions, which arose in the first 3 days after vaccination and resolved spontaneously 1-3 days later.
The trial was sponsored by Sanofi Pasteur and presented by a company employee.
MADRID – An intramuscular inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine reduced the risk of laboratory-confirmed influenza by up to 69% in previously unvaccinated children aged 6-35 months in a large randomized trial, Stephanie Pepin, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV) is licensed by the Food and Drug Administration as Fluzone Quadrivalent for use in patients as young as 6 months of age. It contains two A- and two B-lineage influenza strains in order to address the common problem of mismatches between circulating influenza B and the single B-lineage strain included in trivalent vaccines.
The incidence of any laboratory confirmed strain of influenza illness during the period from 14 days post-vaccination to the end of flu season was 4.72% in the QIV group, compared with 9.84% in controls who received placebo, which translated to 52% efficacy. The incidence of influenza from vaccine-similar strains as determined by the Sanger sequencing method was 1.01% in children randomized to QIV, compared with 3.28% with placebo, for a 69% efficacy rate.
The QIV had a safety profile in this young population that was similar to the older licensed trivalent vaccine. The most frequently reported adverse reactions to the QIV were injection site pain, irritability, loss of appetite, abnormal crying, and malaise, each reported in 19%-25% of children after the first injection and in 14%-18% after the second. These were typically mild grade 1 or 2 reactions, which arose in the first 3 days after vaccination and resolved spontaneously 1-3 days later.
The trial was sponsored by Sanofi Pasteur and presented by a company employee.
MADRID – An intramuscular inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine reduced the risk of laboratory-confirmed influenza by up to 69% in previously unvaccinated children aged 6-35 months in a large randomized trial, Stephanie Pepin, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
The quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV) is licensed by the Food and Drug Administration as Fluzone Quadrivalent for use in patients as young as 6 months of age. It contains two A- and two B-lineage influenza strains in order to address the common problem of mismatches between circulating influenza B and the single B-lineage strain included in trivalent vaccines.
The incidence of any laboratory confirmed strain of influenza illness during the period from 14 days post-vaccination to the end of flu season was 4.72% in the QIV group, compared with 9.84% in controls who received placebo, which translated to 52% efficacy. The incidence of influenza from vaccine-similar strains as determined by the Sanger sequencing method was 1.01% in children randomized to QIV, compared with 3.28% with placebo, for a 69% efficacy rate.
The QIV had a safety profile in this young population that was similar to the older licensed trivalent vaccine. The most frequently reported adverse reactions to the QIV were injection site pain, irritability, loss of appetite, abnormal crying, and malaise, each reported in 19%-25% of children after the first injection and in 14%-18% after the second. These were typically mild grade 1 or 2 reactions, which arose in the first 3 days after vaccination and resolved spontaneously 1-3 days later.
The trial was sponsored by Sanofi Pasteur and presented by a company employee.
AT ESPID 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The intramuscular inactivated influenza vaccine, Fluzone Quadrivalent, reduced the risk of laboratory-confirmed influenza by up to 69% in 6- to 35-month-olds.
Data source: This randomized, multinational, placebo-controlled trial included 5,806 healthy 6- to 35-month-old children.
Disclosures: The study was sponsored by Sanofi Pasteur and presented by a company employee.
Inactivated flu vaccine more effective than live version
The inactivated influenza vaccine is more effective than the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine, according to a study conducted by the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network.
After poor live vaccine performance in young children during the 2013-2014 flu season, the A(H1N1)pdm09 strain was changed. In response to earlier reports that the A(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine strain had poor thermostability, it was updated to A/Bolivia/559/2013 (an A/California/7/2009-like virus) for the 2015-2016 influenza season. Unfortunately, the changes did not increase the vaccine’s immunogenicity. At study sites in Michigan, Pennsylvania, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin, 6,879 patients aged 6 months or older who presented for acute respiratory illness with a cough of 7 or fewer days were tested for influenza. Of those, 1,309 (19%) tested positive. Vaccination histories were taken from parent interviews and electronic health records.
“Although the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine remains licensed in the United States, the [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] did not recommend this vaccine for the 2016-2017 influenza season,” the investigators wrote.
Partial funding for the research came from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jackson reported receiving a grant from Medimmune.
Read more in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017;377:534-43).
The inactivated influenza vaccine is more effective than the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine, according to a study conducted by the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network.
After poor live vaccine performance in young children during the 2013-2014 flu season, the A(H1N1)pdm09 strain was changed. In response to earlier reports that the A(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine strain had poor thermostability, it was updated to A/Bolivia/559/2013 (an A/California/7/2009-like virus) for the 2015-2016 influenza season. Unfortunately, the changes did not increase the vaccine’s immunogenicity. At study sites in Michigan, Pennsylvania, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin, 6,879 patients aged 6 months or older who presented for acute respiratory illness with a cough of 7 or fewer days were tested for influenza. Of those, 1,309 (19%) tested positive. Vaccination histories were taken from parent interviews and electronic health records.
“Although the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine remains licensed in the United States, the [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] did not recommend this vaccine for the 2016-2017 influenza season,” the investigators wrote.
Partial funding for the research came from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jackson reported receiving a grant from Medimmune.
Read more in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017;377:534-43).
The inactivated influenza vaccine is more effective than the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine, according to a study conducted by the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network.
After poor live vaccine performance in young children during the 2013-2014 flu season, the A(H1N1)pdm09 strain was changed. In response to earlier reports that the A(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine strain had poor thermostability, it was updated to A/Bolivia/559/2013 (an A/California/7/2009-like virus) for the 2015-2016 influenza season. Unfortunately, the changes did not increase the vaccine’s immunogenicity. At study sites in Michigan, Pennsylvania, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin, 6,879 patients aged 6 months or older who presented for acute respiratory illness with a cough of 7 or fewer days were tested for influenza. Of those, 1,309 (19%) tested positive. Vaccination histories were taken from parent interviews and electronic health records.
“Although the quadrivalent live attenuated vaccine remains licensed in the United States, the [Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices] did not recommend this vaccine for the 2016-2017 influenza season,” the investigators wrote.
Partial funding for the research came from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Jackson reported receiving a grant from Medimmune.
Read more in the New England Journal of Medicine (2017;377:534-43).
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Vaccine reduced risk for flu visits by 42%
Last year’s influenza vaccination reduced the overall risk for flu-related medical visits by 42%, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In an article summarizing influenza activity in the United States during October 2016–May 2017, investigators said that most of the viral strains antigenically characterized at the CDC “were similar to the reference viruses representing the recommended components for the 2016-2017 vaccine.”
The 2017-2018 influenza vaccine has been updated to include an additional influenza A (H1N1) component. This change was recommended by the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee, based on data from global influenza virologic and epidemiologic surveillance, genetic and antigenic characterization, human serology studies, antiviral susceptibility, and the availability of candidate influenza viruses (MMWR. 2017;66[25]:668-76).
Preliminary data show that, during the 2016-2017 flu season, there were 18,184 laboratory-confirmed, flu-related hospitalizations, for an overall incidence of 65 per 100,000 population, more than double that for the 2015-2017 season (31/100,000). Broken down by age groups, the rates per 100,000 population in this past season were 44 at ages 0-4 years, 17 at ages 5-17 years, 20 at ages 18-49 years, and 65 at ages 50-64 years, compared with 291 at ages 65 years and older. Finalized estimates of the number of influenza illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations averted by vaccination during the 2016-2017 season will be published in December, the investigators said.
Last year’s influenza vaccination reduced the overall risk for flu-related medical visits by 42%, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In an article summarizing influenza activity in the United States during October 2016–May 2017, investigators said that most of the viral strains antigenically characterized at the CDC “were similar to the reference viruses representing the recommended components for the 2016-2017 vaccine.”
The 2017-2018 influenza vaccine has been updated to include an additional influenza A (H1N1) component. This change was recommended by the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee, based on data from global influenza virologic and epidemiologic surveillance, genetic and antigenic characterization, human serology studies, antiviral susceptibility, and the availability of candidate influenza viruses (MMWR. 2017;66[25]:668-76).
Preliminary data show that, during the 2016-2017 flu season, there were 18,184 laboratory-confirmed, flu-related hospitalizations, for an overall incidence of 65 per 100,000 population, more than double that for the 2015-2017 season (31/100,000). Broken down by age groups, the rates per 100,000 population in this past season were 44 at ages 0-4 years, 17 at ages 5-17 years, 20 at ages 18-49 years, and 65 at ages 50-64 years, compared with 291 at ages 65 years and older. Finalized estimates of the number of influenza illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations averted by vaccination during the 2016-2017 season will be published in December, the investigators said.
Last year’s influenza vaccination reduced the overall risk for flu-related medical visits by 42%, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In an article summarizing influenza activity in the United States during October 2016–May 2017, investigators said that most of the viral strains antigenically characterized at the CDC “were similar to the reference viruses representing the recommended components for the 2016-2017 vaccine.”
The 2017-2018 influenza vaccine has been updated to include an additional influenza A (H1N1) component. This change was recommended by the Food and Drug Administration’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee, based on data from global influenza virologic and epidemiologic surveillance, genetic and antigenic characterization, human serology studies, antiviral susceptibility, and the availability of candidate influenza viruses (MMWR. 2017;66[25]:668-76).
Preliminary data show that, during the 2016-2017 flu season, there were 18,184 laboratory-confirmed, flu-related hospitalizations, for an overall incidence of 65 per 100,000 population, more than double that for the 2015-2017 season (31/100,000). Broken down by age groups, the rates per 100,000 population in this past season were 44 at ages 0-4 years, 17 at ages 5-17 years, 20 at ages 18-49 years, and 65 at ages 50-64 years, compared with 291 at ages 65 years and older. Finalized estimates of the number of influenza illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations averted by vaccination during the 2016-2017 season will be published in December, the investigators said.
FROM MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
Key clinical point: Last year’s influenza vaccination reduced the overall risk for flu-related medical visits by 42%.
Major finding: During the 2016-2017 flu season, there were 18,184 laboratory-confirmed, flu-related hospitalizations, for an overall incidence of 65 per 100,000 population.
Data source: A review of data submitted to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention regarding the 2016-2017 influenza season.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the CDC. Dr. Blanton and her associates reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ACIP approves new influenza vaccine recommendations
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) after a lengthy debate over specifics regarding recommendations for pregnant women.
The proposed recommendation that sparked the debate would change the wording of the previous recommendation for pregnant women to receive a seasonal inactivated vaccine (IIV) to “any licensed, recommended, and age-appropriate, trivalent or quadrivalent IIV or RIV [recombinant influenza vaccine] may be used.”
“I think there’s a subtle, but important difference here between making what would appear to be an affirmative statement that RIV is safe in pregnant women, versus just staying silent on it, and saying ‘we’re not saying you shouldn’t use it, but we don’t have enough data to affirmatively say it is safe,’ ” said Cindy Pellegrini, senior vice president of Public Policy and Government Affairs at the March of Dimes Foundation.
In response, members of the committee pointed out that the responsibility of determining safety lies with the Food and Drug Administration, which has already licensed the Flublok trivalent vaccine with expectations that the quadrivalent vaccine soon will follow.
While Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH, medical officer of the influenza division of the CDC, did acknowledge that there were more data on the safety of inactivated influenza vaccines, she asserted to the committee that “the general overall safety profile of Flublok in comparison to inactivated vaccines is reassuring.”
“For example, one concern that arises is reactogenicity and inflammation. [In terms of] overall reactogenicity in the studies where Flublok and inactivated vaccines have been compared, rates of the adverse and systemic reactions were similar,” Dr. Grohskopf said.
A motion was made to change the wording of the recommendation; however, the motion was not passed, and the eventual vote on the approval was conducted.
The ACIP also voted unanimously to change the safe age limit noted in influenza guidelines for use of Afluria (IIV3) from 9 years and older to 5 years and older. A footnote saying that the ACIP recommends Afluria for children 9 years and older will be removed.
This change, which mirrors the licensing Afluria has with the FDA, was based on research conducted by Seqirus that showed fever levels were the same for Afluria trivalent and quadrivalent vaccines in children 5 to 9 years old, both of which were less than historical vaccine rates.
The approved recommendations will be sent to the director of the CDC and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Once reviewed and approved, the final recommendations will be published in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. The committee members had no relevant financial disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @eaztweets
First trimester use of inactivated flu vaccine didn’t cause birth defects
, said Elyse Olshen Kharbanda, MD, of HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, and her associates.
Data from seven participating Vaccine Safety Datalink sites in six states were used to identify 52,856 women who received IIV in the first trimester of pregnancy (12% of the study total) and 373,088 not exposed to the flu vaccine in the first trimester (88%). A total of 865 women in the IIV-exposed group had an infant with 1 of the 50 selected major structural defects (1.6 per 100 live births), versus 5,730 in the unexposed group (1.5 per 100 live births).
Among the strengths of the study were the large population, which allowed the researchers to examine subgroups of major structural birth defects; their findings were consistent across all those subgroups. In addition, the investigators were able to exclude women at increased risk for major birth defects because of comorbidities such as diabetes, drug exposures, diagnosed chromosomal abnormalities, or congenital infections. Finally, the study authors were able to exclude women with potential exposure to teratogenic medications.
“Because IIV is currently recommended for all women who will be pregnant during periods of influenza circulation, these data should provide reassurance for women considering first trimester vaccination,” said Dr. Kharbanda and her associates.
Read more in the Journal of Pediatrics (2017 May 24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.039).
, said Elyse Olshen Kharbanda, MD, of HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, and her associates.
Data from seven participating Vaccine Safety Datalink sites in six states were used to identify 52,856 women who received IIV in the first trimester of pregnancy (12% of the study total) and 373,088 not exposed to the flu vaccine in the first trimester (88%). A total of 865 women in the IIV-exposed group had an infant with 1 of the 50 selected major structural defects (1.6 per 100 live births), versus 5,730 in the unexposed group (1.5 per 100 live births).
Among the strengths of the study were the large population, which allowed the researchers to examine subgroups of major structural birth defects; their findings were consistent across all those subgroups. In addition, the investigators were able to exclude women at increased risk for major birth defects because of comorbidities such as diabetes, drug exposures, diagnosed chromosomal abnormalities, or congenital infections. Finally, the study authors were able to exclude women with potential exposure to teratogenic medications.
“Because IIV is currently recommended for all women who will be pregnant during periods of influenza circulation, these data should provide reassurance for women considering first trimester vaccination,” said Dr. Kharbanda and her associates.
Read more in the Journal of Pediatrics (2017 May 24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.039).
, said Elyse Olshen Kharbanda, MD, of HealthPartners Institute, Minneapolis, and her associates.
Data from seven participating Vaccine Safety Datalink sites in six states were used to identify 52,856 women who received IIV in the first trimester of pregnancy (12% of the study total) and 373,088 not exposed to the flu vaccine in the first trimester (88%). A total of 865 women in the IIV-exposed group had an infant with 1 of the 50 selected major structural defects (1.6 per 100 live births), versus 5,730 in the unexposed group (1.5 per 100 live births).
Among the strengths of the study were the large population, which allowed the researchers to examine subgroups of major structural birth defects; their findings were consistent across all those subgroups. In addition, the investigators were able to exclude women at increased risk for major birth defects because of comorbidities such as diabetes, drug exposures, diagnosed chromosomal abnormalities, or congenital infections. Finally, the study authors were able to exclude women with potential exposure to teratogenic medications.
“Because IIV is currently recommended for all women who will be pregnant during periods of influenza circulation, these data should provide reassurance for women considering first trimester vaccination,” said Dr. Kharbanda and her associates.
Read more in the Journal of Pediatrics (2017 May 24. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.04.039).
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS
Decline in U.S. flu activity puts end of season within sight
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.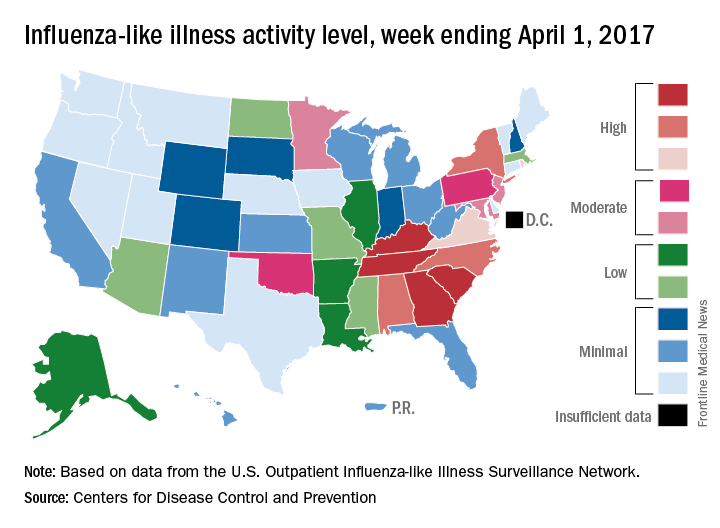
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Outpatient visits for influenza were down again in the United States during the week ending April 1, and the number of states at the highest level of flu activity dropped from seven to four, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 2.9% for the week ending April 1, compared with 3.2% the week before, the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network reported. The national baseline level is 2.2%.
There were 7 flu-related pediatric deaths reported for the week ending April 1 – six of the deaths occurred in previous weeks – which brings the total for the 2016-2017 season to 68, the CDC said. The largest share of those deaths by age group has been among 5- to 11-year-olds (36.8%), followed by those aged 12-17 years (26.5%), 6-23 months (16.2%), 2-4 years (14.7%), and 0-5 months (5.9%).
Make assessment of immunization status of older adults routine
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
ATLANTA – In the opinion of John M. Kelso, MD, assessment of immunization status in older adults should be a routine part of all visits.
“Don’t assume that your patients are getting their vaccines someplace else,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. “We should be taking advantage of the fact that these patients are in our offices.”
Inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV3)
For adults aged 65 and older, the high-dose, trivalent version of the flu vaccine (60 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain, or IIV3-HD) may be preferable to the standard dose of 15 micrograms of hemagglutinin per strain (IIV3-SD). A study of nearly 32,000 patients found that IIV3-HD induced significantly higher antibody responses and provided better protection against laboratory-confirmed influenza, compared with IIV3-SD (N Engl J Med. 2014;371:635-45). The relative efficacy of high dose vs. standard dose was 24.2%. “That means that one-quarter of all breakthrough influenza illnesses could be prevented if IIV3HD were used instead of IIV3-SD,” Dr. Kelso said.
Another approach is to use an adjuvanted influenza vaccine, which contains the standard 15 micrograms of influenza antigen but the adjuvant is MF59, a squalene-based oil-in-water emulsion. One small study of 282 patients aged 65 and older showed the adjuvanted vaccine to be more effective than the unadjuvanted vaccine (Vaccine. 2013;51:1622-8).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention does not express a preference for the high-dose or adjuvanted vaccine, but rather stresses the importance of influenza vaccination with whatever age-appropriate IIV formulation is available at the time of the patient’s visit.
The 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23)
All adults who turn 65 years of age should receive the PCV13, followed 1 year later by the PPSV23. For those who already received the PPSV23 after age 65 years of age, they should receive the PCV13 at least 1 year later. “The real bulk of hospitalizations and fatalities from invasive pneumococcal disease are happening to people over 65 year of age,” said Dr. Kelso, who is also a clinical professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at the University of California, San Diego “So there’s a real need here for vaccination.”
Tdap
This should be administered to all adolescents and adults regardless of interval since their last tetanus-diphtheria vaccine. “This includes those age 65 years of age and older in whom the vaccine has been found to be equally safe and immunogenic,” Dr. Kelso said. “This is important not only to prevent pertussis in older adults, but also to prevent them from spreading the disease to infants where it can be fatal.”
Zoster vaccine
One in three adults will develop zoster during their lifetime, he said, and one million episodes occur in the United States each year. Common complications include postherpetic neuralgia and eye involvement that can result in loss of vision. The CDC recommends routine vaccination of all immunocompetent persons over age 60 with one dose of zoster vaccine. “Persons who report a previous episode of zoster can be vaccinated but it is not indicated to treat acute zoster, to prevent persons with acute zoster from developing postherpetic neuralgia, or to treat ongoing postherpetic neuralgia,” Dr. Kelso said.
He reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS AT THE 2017 AAAAI ANNUAL MEETING
Latest weekly flu data show no decline in visits
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.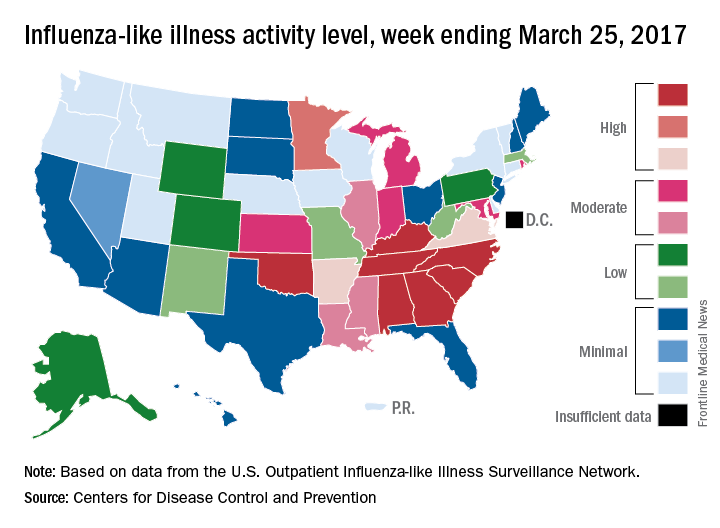
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.
Outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) held steady for the week ending March 25, but the number of states at the “high” range of activity dropped from 12 from 10 the previous week, according to the Centers for Disease Prevention and Control.
The proportion of outpatient visits for ILI was 3.2% for the second consecutive week, which halted the slowdown in activity that began the week ending Feb. 18. That 3.2% represents just under 25,000 visits for ILI of the almost 747,000 total visits reported to the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) for the week ending March 25. By age, the largest groups with ILI visits for the week were individuals aged 5-24 years (41%) and those aged 4 years and under (20%), the CDC reported.
There were six flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week ending March 25, but all occurred in earlier weeks. The total number of such deaths is now 61 for the 2016-2017 season, the CDC said.